MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA WITH MONTELUKAST
|
|
|
- Ann Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA WITH MONTELUKAST Nipun Shrestha and Hongzhu Lu * Department of Pediatrics, Clinical Medical College, Yangtze University. Jingzhou, Hubei, P.R.China. ABSTRACT Respiratory tract disorder is a very common problem faced by pediatric population, asthma being one of the most common chronic disorders in young children. Many preschool children regularly wheeze, especially during common cold infection and cold seasons. Some children wheeze after a simple exercise or some after the introduction of medication like aspirin or after introduction to allergens. An anti-inflammatory therapy, consisting mainly of inhaled corticosteroids (ICs) has been the main treatment of asthma since the beginning and it still remains the first line therapy in asthma management. Since Leukotriene (LTs) are chemical mediators of airway inflammation in asthma, Leukotriene receptor antagonist (LTRAs) can be a potent anti-inflammatory drugs in the long term treatment of asthma. There are different LRTA medicines, but mainly Montelukast can be used in pediatric population, that can decrease the airway inflammation and provide bronchoprotection. The safety profile, oral administration as single daily dose and better compliance is the highlight of this drug. In this review, we describe the advances on the use of montelukast in the treatment of asthma. Keywords: montelukast; asthma; children 24
2 INTRODUCTION Asthma is a very common childhood disorder. It is a chronic inflammatory condition of airways resulting in bronchospasm and episodic obstruction. Its characteristic feature is bronchial hyperresponsiveness to stimuli and causes bronchoconstriction, predominantly by their action on effector cells such as smooth muscle. Indirect stimuli such as exercise, cold air and hyperosmolar aerosol such as mannitol and hypertonic saline provoke bronchospasm through the release of mediator from inflammatory cells. Many symptomatic children looses their symptoms after the age of 5 to 6 yr but there are many for whom it still remains the burden and also for the family. The medical treatment of asthma began more than 50 yrs ago and till date the mainstay of treatment still remains the same as before and it is inhaled corticosteroids and B2-agonists bronchodilators. The treatment mainly focuses on reducing airway inflammation by minimizing proinflammatory environmental exposures using daily medication. Inhaled corticosteroids are the most effective treatment of asthma and it has long been used as the first line therapy. However, there are some groups of population of asthma that are resistant to inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) and large group of patients remains symptomatic despite treatment and need other medication as monotherapy or add on therapy. Montelukast is a leukotriene receptor antagonist that has been shown to be effective as monotherapy or as an add-on therapy for the treatments of asthma, in those whose symptoms are not well controlled with ICS therapy. Leukotriene modifiers (LTRs): Leukotrienes are chemical mediators of asthmatic airway inflammation. They are formed from arachidonic acid, which are derived from the action of phospholipase A2 and they are releaseded by eosinophils, mast cells, neutrophils, lymphocytes, macrophages, and basophils. Arachiodonic acid is metabolized by two major pathways, the cyclooxygenase pathway (forming prostaglandins and thromboxanes) and the 5-lipoxygenase pathway (producing leukotrienes). The cysteinyl leukotrienes LTC4 and LTE4, are found to play very important role in the pathophysiology of asthma. The leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs) selectively block the binding of cysteinyl leukotrienes to the CysLT1 receptor. This receptor was found to be the receptor through which most of their actions are mediated like bronchospasm, mucus hypersecretion and eosinophil migration and increased vascular permeability (1). Consequently, the LTRAs inhibit bronchconstriction. Moreover, LTRAs prevent many types of provoked asthmatic responses, including allergen-induced, exercise- and cold-air-hyperventilation-induced, and aspirin- induced asthma. Three drugs of this class are in use at present zafirlukast, pranlukast, and montelukast.. Only montelukast has been extensively studied in children and proven to be safe and effective in children. Pediatric studies on montelukast found that it is well tolerated. The majority of the reported adverse effects were mild. In clinical trials the incidence of these adverse effects was not higher than with placebo. 25
3 Montelukast as a Management of childhood asthma: For the past few decades, we have been using inhaled corticosteroids and B2-agonists bronchodilators for the treatment or management of asthma. No new therapy has been introduced or developed and we are still bound to use the same old protocols to control it. Inhaled corticosteroids and B2- agonists bronchodilators remains the first and second lines of therapies for past few decades. Certain groups of population of asthma sufferers are becoming resistant to these drugs. The side effect of continuous use of these drugs still remains a big concern, particularly with the high doses. And also, some patients finds it hard to use the inhalation route of administration of drugs and ensuring adequate and correct dosing is a concern. In such cases, montelukast overcomes ICS and B2-agonists as it has an advantage of oral administration, once daily dosing protocol and has properties of bronchodilation. Such propertites of montelukast makes it a new drug of interest in the treatment of asthma. Montelukast improves symptoms, rescue medication use and pulmonary function, and reduced the rate of exacerbation and the level of blood eosinophils, in mild-to moderate asthmatics, as proven by many clinical trials. Several randomized trials have been performed in the treatment of asthma comparing montelukast with placebo. Comparing montelukast with placebo, the result showed that the drug helps the patients suffering from mild to moderate symptoms and helps improve day time asthma symptoms like cough, wheeze, difficulty in breathing and activity limitation. At the same time, the overnight asthma symptoms, the duration suffering days, the need of increasing dosing of ICS and B2agonist were also decreased. The laboratory investions suggested that there is a marked improvement in the peripheral blood eosinophil, forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) in the montelukast population(2). A study after conducting a randomized controlled trail, concluded that montelukast provides clinical significance in controlling asthma symptoms and helps improve morning FEV1 (3)(4). A randomized controlled trial with montelukast 5 mg for 4 week concluded that the medicine helps in suppressing sputum eosinophilic cationic protein, sputum eosiniphilic count and fractional exhaled nitric oxide and improves asthma symptoms(5). Another randomized controlled trails with children of 6 to 14 yrs with montelukast for 8 weeks concluded the similar improvements in asthma symptoms and improvement in FEV1(6). Similar improvement and reduced exacerbation was seen after a randomized controlled trail performed with children of 2 to 5 yr with montelukast for longer duration of time (7). A study conducted among preschool children revealed that 4 weeks treatment with montelukast resulted in a decrease in bronchial hyperreactivity compared with placebo (8). Another randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial was performed among 689 patients (228 placebo group and 461 montelukast group). Overall, approximately 60% of patients were boys and approximately 60% were white. Patients were relatively evenly divided by age: 21%, 24%, 30%, 26
4 and 23% were aged 2, 3, 4, and 5 years, respectively. For about 77% of patients had history of asthma symptoms that had first developed during the first 3 years of their life. During the placebo baseline period, patients had asthma symptoms on 6.1 days/week and used B2-agonist on 6.0 days/week. There were no clinically important demographic differences between the 2 treatment groups. Seventy-one patients (26 from placebo group and 45 from montelukast group) did not complete the study. In the placebo group, 12 patients were withdrawn because of protocol deviations, 7 stopped treatment because of adverse effects, 4 withdrew consent, 2 were lost to follow-up, and 1 stopped treatment because of an elevated alkaline phosphatase value. In the monte-lukast group, 12 were withdrawn because of protocol deviations, 16 patients stopped treatment because of adverse effects, 8 withdrew consent, 7 were lost to follow-up, and 1 each discontinued because of lack of efficacy and an error by the study center. A total of 12 and 17 patients in placebo and montelukast groups, respectively, were excluded from 1 or more efficacy analyses because they lacked baseline or treatment period data. Over 12 weeks of treatment, the percentage of days with daytime asthma symptoms was significantly lower and the percentage of days without asthma was significantly higher in the montelukast group compared with the placebo group. Moreover, the improvements for the montelukast group in overall daytime asthma symptom scores and in individual symptoms scores for cough, wheeze, trouble breathing, and activity limitations were significantly greater than those for the placebo group. Furthermore, the percentage of days on which B2-agonist was used and percentage of patients requiring oral corticosteroid rescue were significantly lower in the montelukast group (9). Another 8-week trial of 336 children 6 to 14 years old with intermittent or persistent asthma was conducted which found that 5 mg of montelukast nightly increased mean morning FEV1 significantly more than placebo (approximately 8% vs 4%) (10). In the group, Short-acting B2-agonist use decreased by 0.57 puffs daily among montelukast-treated children and increased by 0.22 puffs daily among placebo-treated children. Another trial studied patients with mild to moderate asthma and made a conclusion that montelukast administration was associated with dose-related improvements in asthma control end points. Improvements were seen in FEV1 and peak expiratory flow rate and in daytime symptom scores, use of as-needed inhaled B2-agonists, and asthma-specific quality of life (11). A study reported that montelukast permitted a 47% reduction in inhaled corticosteroid dosage compared with a 30% reduction with placebo in a group of asthma patients previously well controlled on inhaled corticosteroids (12). Many studies compared montelukast with corticosteroids. Those studies mainly focuses on specific outcome like pulmonary function, symptoms and rate of exacervations and the majority of studies have confirmed the greater efficacy of low dose ICS against montelukast (13)(14). Because of this reason, many institutional guidelines state that ICS are more effective than LTRAs as monotherapy for asthma management. And, montelukast becomes the latter choice. But the majority of the these studies were done in cases with 27
5 patients who had frequent symptoms and poor pulmonary function and thus ICS was expected to be more effective than montelukast. Montelukast was still more effective than placebo when the selected patients had mild asthma(15). At doses equivalent to 500 mg daily of beclomethasone, LTRAs were less effective than ICS on symptoms, pulmonary function and sputum eosinophils (16)(17). However, in a study of 534 patients with mild asthma well controlled by low-dose ICS, when replacing it with montelukast, was found to have good asthma control in over 75% of cases after 6 weeks, with an increase in compliance to treatment (18). Some trials concluded that Mild-to-moderate chronic asthmatic patients treated with LTRAs were 60% more likely to experience an asthma exacerbation requiring oral steroids than those treated with ICSs (19)(20). But in most this trials the daily dose of ICSs was 400 mg of beclomethasone or equivalent. After 6 weeks of treatment, the patients using ICSs showed more improvement in clinical symptoms and FEV1. The use of montelukast as a mono therapy in asthma remain a doubt and the patients using montelukast is more likely to suffer an exacerbation requiring systemic steroids (20). On the other hand there aren t enough researches to conclude the advantage of ICSs over montelukast and further studies need to be done. A study evaluated the efficacy of montelukast versus budesonide, mostly in preschool age group with mild persistent asthma, and found no differences between the two groups as far as drug tolerability, time to first additional anti-asthma medications and time to first severe exacerbation over a 52 weeks-study period (21). Other RCT also assessed the efficacy of montelukast or fluticasone given as monotherapy versus placebo for three months and many such studies have concluded that both drugs decreased asthma-like symptoms and improved the daily symptoms score, even though fluticasone appeared more effective than placebo. Some studies showed that montelukast added to the usual treatment with ICS reduced the risk of worsening asthma symptoms and unscheduled physician visits during the annual September asthma epidemic. Some studies even showed children treated with montelukast and fluticasone as monotherapy, showed that both drugs decrease rescue medications use and hospital visits. In particular, in children aged 2 to 5 years, montelukast was associated to less emergency visits compared to subjects aged 6 to 14 years. The findings suggest that montelukast could be beneficial to preschool and school going children suffering from asthma. There are limited studies that compares the advantage of montelukast over long acting beta agonist (LABA) or vise versa. One study found that FeNO levels were significantly higher after salmeterol add on treatment compared with both placebo and montelukast (22). Other trial concluded that montelukast as an add-on therapy with ICSs provide equivalent result compared to salmeterol (23). The study conducted among children has revealed that add on therapy with montelukast plus low-dose budesonide was more effective than the addition of LABA or doubling the dose budesonide for controlling FeNO in asthmatic children (24). Histamine and cysteinyl leukotrienese are the inflammatory mediators that are released during exercise. Evaporation of water on the airway surface, during exerceise, is the stimulus for their release (25). 28
6 Exhaled breath condensate Cys-LT values are shown to be higher in asthmatic children with EIB (exercise induced bronchospasm) and correlate with the dicrease in FEV1 after exercise (26). LTRAs decreases exhaled LTE4 in atopic children with asthma(27). Accordingly, montelukast was found to be effective in controlling asthma symptoms after exercise in children. It is approved for the prevention of EIB from 2 years of age(28). Clinical datas have shown that once-daily treatment with montelukast (5 or 10 mg tablet) can offer protection against EIB within 3 days for some patient. The cysteinyl leukotrienes are the leading mediators of the reaction that occurs in persons with aspirin-sensitive asthma after exposure to aspirin(29). LTRs resulted in almost complete inhibition of aspirininduced bronchoconstriction as well as symptoms of the skin and gastrointestinal tract (30). For this reason LTRs are the treatment of choice for these patients (31)(32). Few studies also support the fact that montelukast effectively reduces acute asthma episodes if started before the viral season, when the exacerbation rate is higher. A study done with asthmatic children who were aged 2 5 years showed that the response of administration of 5 mg/day of montelukast for two days protects against cold air-induced bronchial hyperreactivity(33). Similar finding was later confirmed in such patients who showed a significant decrease in methacoline-induced bronchial reactivity after a four weeks treatment with montelukast (34). In atopic children with asthma, monotherapy with montelukast for 28 days showed effectiveness for reducing airway resistance and bronchial inflammation(35), and for improving lung function and symptoms score(36). An Australian RCT conducted in children having mild intermittent asthma and the study showed that a short course of montelukast, introduced early at the first signs of an asthma episode, resulted in a significant reduction in acute health care resource utilization, symptoms, time off from school, and parental time off from work (37). Another study showed that a 1-year course of montelukast in children with virus-induced asthma significantly reduces asthma exacerbations and the use of rescue medications. This study remains one of the few RCTs (random controlled trials) in preschool children with mild intermittent asthma that proves that prolonged treatment with montelukast reduces the consumption of ICS at 39.8% (38) Obesity is also considered as a risk factor for asthma. It also plays an important role in poor asthma control through different mechanisms (39). Such obese patients often faces airway inflammation, though to a low degree and their symptoms are poorly controlled by ICS. A study suggests that in such cases, montelukast may be more effective than ICS. (40). Adverse effect of montelukast: A variety of studies shows that montelukast is well tolerated by children and adults. There are few 29
7 reported adverse effects but they are generally mild and includes headache, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, pharyngitis and ear infection. Over dose of montelukast may be associated with thirst, mydriasis and somnolence (41).Since the beginning of the use of montelukast, several case reports on the occurrence of a Churg_Strauss syndrome (CSS) have been reported. This is thought to be due to reduced steroid dosage but not related to montelukast. In addition, the fact that CSS has developed not only with montelukast, but also with zafirlukast and pranlukast, suggests that the syndrome may be related to the effect of antileukotriene drugs on leukotriene receptors. In clinical trials the incidence of these adverse effects was not higher than with placebo (42). No dose adjustment with montelukast is necessary for patients with renal and mildmoderate hepatic dysfunction. It crosses the placenta and is excreted in breast milk. Montelukast should not be prescribed to pregnant and lactating women, due to lack of controlled trials. CONCLUSION The current evidence indicates that first-line monotherapy with montelukast is still controversial and generally not used in asthma sufferers, with perhaps the exclusion of those who have aspirin-intolerant asthma and exercise-induced asthma and asthma in obese children. It has shown good effect in some cases of mild asthma but its use as monotherapy in severe form still remains to be studied. The adddition of montelukast in patients whose symptoms remain uncontrolled by ICSs could provide equivalent clinical control to salmeterol. It has shown a very good outcome as an add-on therapy. Montelukast reduces shortacting B2 stimulant requirements in patients with chronic asthma and allows the dose of inhaled steroids to be reduced. Montelukast may be valuable in those asthmatic patients who find it difficult to use inhaled medications. Oral montelukast (4-mg chewable tablet) administered once daily is generally well tolerated without clinically important adverse effects in preschool children. Additionally, montelukast improved multiple exploratory efficacy end points, which is consistent with clinically important improvements in the treatment of asthma. Moreover, the results of these studies are consistent with and confirm results seen in studies pediatric patients above 6 yrs. Many studies demonstrated its safety in pediatric population above 2 yrs of age. Its safety and efficacy in young pediatric population( less than 2 yr) still need to be studied further. REFERENCES 1. Drazen JM, Israel E, O Byrrne PM. Treatment of asthma with drugs modifying the leukotriene pathway. N Engl J Med, 1999, 340: Bisgaard H, Loland L, Anhoj J. Nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatic children is reduced by the leukotriene receptor antagonist montelukast. AM J RESPIR CRIT CARE MED, 1999, 160: Knorr B, Larson P, Nguyen HH et al. Montelukast dose selection in 6- to 14-year-olds: comparison of single dose pharmacokinetics in children and adults. J Clin Pharmacol,1999, 39:
8 4. Knorr B, Nguyen HH, Kearns GL et al. Montelukast dose selection in children ages 2 to 5 years: comparison of population pharmacokinetics between children and adults. JClin Pharmacol, 2001, 41: Strauch E, Moske O, Thoma S et al. A randomized controlled trial on the effect of montelukast on sputum eosinophils cationic protein in children with corticosteroid-dependent asthma. Pediatr Res, 2003, 54 : Becker A, Swern A, Tozzi CA, Yu Q, Reiss T, Knorr B. Montelukast in asthmatic patients 6 years-14 years old with an FEV1 > 75%. Curr Med Res Opin, 2004, 20: Bisgaard H, Zielen S, Garcia-Garcia ML et al. Montelukast reduces asthma exacerbations in 2- to 5-yearold children with intermittent asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2005, 171 : Hakim F, Vilzoni D, Adler A, Livnat G, Tal A, Bentur L: The effect of montelukast on bronchial hyperreactivity in preschool children, 2007, 13: Barbara Knorr, Luis M Franchi, Hans Bisgaard, Jan Hendrik Vermeulen, Peter Lesouef, Nancy Santanello, Theresa M Michele, Theodore F Reiss, HA H Nguyen, Donna L Bratton. Montelukast, a Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist, for the treatment of Persistent Asthma in children aged 2-5 years. Pediatrics 2001, 108;e Knorr B, Matz J, Bernstein JA, Nguyen H, Seidenberg BC, Reiss TF, et al. Montelukast for chronic asthma in 6 to 14 year old children. JAMA, 1998; 279: Knorr B, Matz J, Bernstein JA, Nguyen H, Seidenberg BC, Reiss TF, et al. Montelukast for chronic asthma in 6 to 14 year old children. JAMA, 1998; 279: Lofdahl CG, Reiss TF, Leff AJ, Isreal E,Noonan JM, Finn AF, et al. Randomized,placebo-controlled trial of effect of aleukotriene receptor antagonist, montelukast,on tapering inhaled corticosteroidsin asthmatic patients. BMJ, 1999; 319: Busse, W., Raphael, G., Galant, S., Kalberg, C., Goode-Sellers, S., Srebro, S. et al. Low-dose fluticasone propionate compared with montelukast for first-line treatment of persistent asthma: A randomized clinical trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2001, 107: 461_ Malmstrom, K., Rodriguez-Gomez, G., Guerra, J.,Villaran, C., Pin eiro, A., Wei, L.X. et al. Oral montelukast, inhaled beclomethasone, and placebo for chronic asthma. Ann Intern Med, 1999, 130: 487_ Barnes, N., Wei, L.X., Reiss, T.F., Leff, J.A., Shingo, S., Yu, C. et al. Analysis of montelukast in mild persistent 31
9 asthmatic patients with near-normal lung. Respir Med, 2001; 95(5): Bacci, E., Di Franco, A., Dente, F.L., Bartoli, M.L., Cianchetti, S., Vagaggini, B. et al. Short-term effects of oral zafirlukast on sputum eosinophilia in mild asthmatics: Comparison with inhaled corticosteroids, Jayaram I, Pizzichini E, Lemie`re C, Man S.F, Cartier A, Hargreave F.E. et al. Steroid naive eosinophilic asthma: Anti-inflammatory effects of fluticasone and montelukast. Thorax, 2005; 60: McIvor, R.A., Kaplan, A., Koch, C. and Sampalis, J.S. Montelukast as an aternative to low-dose inhaled corticosteroids in to management of mild asthma (the SIMPLE trial): An open-label effectiveness trial. Can Respir J, 2009 May-Jun;16 Suppl A:11A-21A 19. Ducharme FM, Di Salvio F. Antileukotriene agents compared to inhaled corticosteroids in the management of recurrent and/or chronic asthma in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2014(1): CD Ng D, Salvio F, Hicks G. Antileukotriene agents compared to inhaled corticosteroids in the management of recurrent and/or chronic asthma in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2012, (5):CD Szefler SJ, Martin RJ. Lessons learned from variation in response to therapy in clinical trials. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2010; 125: Buchvald F, Bisgaard H. Comparisons of the complementary effect on exhaled nitric oxide of salmeterol vs montelukast in asthmatic children taking regular inhaled budesonide.ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2003, 91: Bjermer L, Bisgaard H, Bousquet J, et al. Montelukast or salmeterol combined with an inhaled steroid in adult asthma: design and rationale of a randomized, double-blind comparative study (the IMPACT Investigation of Montelukast as a Partner Agent for Complementary Therapy-trial). Resp Med, 2000, 94: Miraglia DGM, Piacentini GL, Caposso M, et al. Formoterol, montelukast, and budesonide in asthmatic children: Effect on lung function and exhaled nitric oxide. Respir Med, 2007, 101: Stelmach I, Korzeniewska A, Smejda K, et al. Effect of montelukast on lung function and clinical symptoms in patients with cystic fi brosis. Pneumonol Alergol Pol, 2004, 72: Carraro S, Corradi M, Zanconato S, et al. Exhaled breath condensate cysteinyl leukotrienes are increased in children with exercise-induced bronchoconstriction.j Allergy Clin Immunol, 2005, 115:
10 27. Montuschi P, Mondino C, Koch P, et al. Effects of a leukotriene receptorantagonist on exhaled leukotriene E4 and prostanoids in childrenwith asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2006, 118: Pajaron-Fernandez M, Garcia-Rubia S, Sanchez-Solis M, et al. Montelukast administered in the morning or evening to prevent exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children.pediatr Pulmonol, 2006, 41: O Byrne PM, Israel E, Drazen JM. Antileukotrienes in the treatment of asthma Ann Intern Med, 127: Israel E, Fischer AR, Rosenberg MA. The pivotal role of 5-lipoxygenase products in the reaction of aspirinsensitive asthmatics to aspirin. Am Rev Respir Dis, 1993, 148: Wenzel SE. Antileukotriene drugs in the management of asthma. JAMA, 1998, 280: Mehta, NP. Montelukast in childhood asthma. Indian Pediatr 2000, 37: Bisgaard H, Nielsen KG: Bronchoprotection with a leukotriene receptor antagonist in asthmatic preschool children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2000, 162: Hakim F, Vilzoni D, Adler A, Livnat G, Tal A, Bentur L: The effect of montelukast on bronchial hyperreactivity in preschool children. Chest, 2007, 13: Straub DA, Minocchieri S, Moeller A, Hamacher J, Wildhaber JH: The effect of montelukast on exhaled nitric oxide and lung function in asthmatic children 2 to 5 years old. Chest, 2005, 127: Straub DA, Moeller A, Minocchieri S, Hamacher J, Sennhauser FH, Hall GL, Wildhaber JH: The effect of montelukast on lung function and exhalednitric oxide in infants with early childhood asthma. Eur Respir J,2005, 25: Robertson CF, Price D, Henry R, Mellis C, Glasgow N, Fitzgerald D, Lee AJ, Turner J, Sant M: Short-course montelukast for intermittent asthma inchildren: a randomised controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2007, 175: Bisgaard H, Zielen S, Garcia-Garcia ML, Johnston SL, Gilles L, Menten J, TozziCA, Polos P: Montelukast reduces asthma exacerbations in 2- to 5-yearoldchildren with intermittent asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2005, 171: Lugogo, N.L., Kraft, M. and Dixon, A.E. Does obesity produce a distinct asthma phenotype?, J Appl. Physiol,2010, 108: 729_ Peters-Golden M, Swern A, Bird S.S, Hustad C.M, Grant E. and Edelman J.M. Influence of body mass index 33
11 on the response to asthma controller agents. Eur Respir J, 2006, 27: Barbara Knorr, Luis M Franchi, Hans Bisgaard, Jan Hendrik, Vermeulen, Peter LeSouef, Nancy Santanello, Theresa M Michele, Theodore F Reiss. Ha H nguyen, Donna L Bratton. Montelukast, a Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist, for the Treatment of Persistent Asthma in Children Aged 2 to 5 Years. Pediatrics, 2001, 108; e R Solans, J A Bosch, A Selva, R Orriols, M Vilardell. Montelukast and Churg-Strauss syndrome. Thorax 2002, 57:
Montelukast: its role in the treatment of childhood asthma
 REVIEW Montelukast: its role in the treatment of childhood asthma Koray Harmanci Department of Allergy, Ministry of Health, Ankara Diskapi Children s Diseases Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
REVIEW Montelukast: its role in the treatment of childhood asthma Koray Harmanci Department of Allergy, Ministry of Health, Ankara Diskapi Children s Diseases Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier
 Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier Department of Pediatrics, Division of Allergy and Pulmonary Medicine, Washington
Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier Department of Pediatrics, Division of Allergy and Pulmonary Medicine, Washington
Pathophysiology of the cysteinyl leukotrienes and effects of leukotriene receptor antagonists in asthma
 Allergy 2001: 56: Suppl. 66: 7 11 Printed in UK. All rights reserved Copyright # Munksgaard 2001 ALLERGY ISSN 0108-1675 Pathophysiology of the cysteinyl leukotrienes and effects of leukotriene receptor
Allergy 2001: 56: Suppl. 66: 7 11 Printed in UK. All rights reserved Copyright # Munksgaard 2001 ALLERGY ISSN 0108-1675 Pathophysiology of the cysteinyl leukotrienes and effects of leukotriene receptor
Efficacy and Safety of Montelukast as Monotherapy in Children with Mild Persistent Asthma. Gautam Ghosh, Arun Kumar Manglik and Subhasis Roy
 Efficacy and Safety of Montelukast as Monotherapy in Children with Mild Persistent Asthma Gautam Ghosh, Arun Kumar Manglik and Subhasis Roy From the Shree Jain Hospital & Research Center, Howrah 711 102
Efficacy and Safety of Montelukast as Monotherapy in Children with Mild Persistent Asthma Gautam Ghosh, Arun Kumar Manglik and Subhasis Roy From the Shree Jain Hospital & Research Center, Howrah 711 102
Montelukast vs. Inhaled Low-Dose Budesonide as Monotherapy in the Treatment of Mild Persistent Asthma: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial
 Montelukast vs. Inhaled Low-Dose Budesonide as Monotherapy in the Treatment of Mild Persistent Asthma: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial by Vikram Kumar, a P. Ramesh, a Rakesh Lodha, a R. M. Pandey,
Montelukast vs. Inhaled Low-Dose Budesonide as Monotherapy in the Treatment of Mild Persistent Asthma: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial by Vikram Kumar, a P. Ramesh, a Rakesh Lodha, a R. M. Pandey,
Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits
 B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
Role of Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists in the Treatment of Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction: A Review
 Review Article Role of Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists in the Treatment of Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction: A Review George S. Philteos, MD, FRCP(C); Beth E. Davis, BSc; Donald W. Cockcroft, MD,
Review Article Role of Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists in the Treatment of Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction: A Review George S. Philteos, MD, FRCP(C); Beth E. Davis, BSc; Donald W. Cockcroft, MD,
Monocast Description Indications
 Monocast Tablet Description The active ingredient of Monocast tablet is Montelukast Sodium INN. Montelukast is a selective and orally active leukotriene receptor antagonist that inhibits the cysteinyl
Monocast Tablet Description The active ingredient of Monocast tablet is Montelukast Sodium INN. Montelukast is a selective and orally active leukotriene receptor antagonist that inhibits the cysteinyl
Leukotriene receptor antagonists in the management of childhood asthma
 Information Paper paper for health Health professionals Professionals LTRAs for childhood asthma Leukotriene receptor antagonists in the management of childhood asthma Key points Introduction This information
Information Paper paper for health Health professionals Professionals LTRAs for childhood asthma Leukotriene receptor antagonists in the management of childhood asthma Key points Introduction This information
Viral-Induced Asthma:
 Viral-Induced : Sorting through the Studies Malcolm R. Sears, MB, FRACP, FRCPC Presented at the Respirology Update Continuing Education Program, January 2005 Viral-associated wheezing is common and not
Viral-Induced : Sorting through the Studies Malcolm R. Sears, MB, FRACP, FRCPC Presented at the Respirology Update Continuing Education Program, January 2005 Viral-associated wheezing is common and not
ALLERGIC RHINITIS AND ASTHMA :
 ALLERGIC RHINITIS AND ASTHMA : from the Link to Emerging Therapies Allergic rhinitis and asthma are both chronic heterogeneous disorders, with an overlapping epidemiology of prevalence, health care costs
ALLERGIC RHINITIS AND ASTHMA : from the Link to Emerging Therapies Allergic rhinitis and asthma are both chronic heterogeneous disorders, with an overlapping epidemiology of prevalence, health care costs
Impact of Asthma in the U.S. per Year. Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Risk Factors for Asthma. Childhood Asthma Costs of Asthma
 American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
Historically, the structural and
 46 supplement to Journal of the association of physicians of india march 2014 VOL. 62 Montelukast - Place in Therapy Agam C Vora * Historically, the structural and functional differences within the respiratory
46 supplement to Journal of the association of physicians of india march 2014 VOL. 62 Montelukast - Place in Therapy Agam C Vora * Historically, the structural and functional differences within the respiratory
Clinical efficacy of montelukast in anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma and allergic rhinitis
 Clinical efficacy of montelukast in anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma and allergic rhinitis Kim Hyun Hee, MD, PhD. Dept. of Pediatrics The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine Achieving
Clinical efficacy of montelukast in anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma and allergic rhinitis Kim Hyun Hee, MD, PhD. Dept. of Pediatrics The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine Achieving
Clinical trial efficacy: What does it really tell you?
 Clinical trial efficacy: What does it really tell you? Joseph Spahn, MD Denver, Colo The primary goal of most clinical trials is an evaluation of the efficacy of the drug being evaluated. Therefore, it
Clinical trial efficacy: What does it really tell you? Joseph Spahn, MD Denver, Colo The primary goal of most clinical trials is an evaluation of the efficacy of the drug being evaluated. Therefore, it
Lack of tolerance to the protective effect of montelukast in exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children
 Eur Respir J 2006; 28: 291 295 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00020606 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Lack of tolerance to the protective effect of montelukast in exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children
Eur Respir J 2006; 28: 291 295 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00020606 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Lack of tolerance to the protective effect of montelukast in exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children
Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations. Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa
 Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa Asthma exacerbations Predicting exacerbation recognising
Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa Asthma exacerbations Predicting exacerbation recognising
Q: Should patients with mild asthma
 1-MINUTE CONSULT CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider prescribing inhaled corticosteroids to their patients who have mild persistent asthma brief answers to specific clinical questions
1-MINUTE CONSULT CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider prescribing inhaled corticosteroids to their patients who have mild persistent asthma brief answers to specific clinical questions
Title: Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist (LTRA) for Asthma. Date: April 12, 2007
 Title: Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist (LTRA) for Asthma Date: April 12, 2007 Context and policy issues: Asthma is a chronic airways condition with symptoms varying from person to person and episode to
Title: Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist (LTRA) for Asthma Date: April 12, 2007 Context and policy issues: Asthma is a chronic airways condition with symptoms varying from person to person and episode to
Omalizumab (Xolair ) ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September Indication
 ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
Montelukast in the treatment of asthma and beyond
 For reprint orders, please contact reprints@expert-reviews.com Montelukast in the treatment of asthma and beyond Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 5(6), 639 658 (2009) Zuzana Diamant, Eva Mantzouranis and Leif
For reprint orders, please contact reprints@expert-reviews.com Montelukast in the treatment of asthma and beyond Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 5(6), 639 658 (2009) Zuzana Diamant, Eva Mantzouranis and Leif
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Distinction and Overlap. Allergy Dpt, 2 nd Pediatric Clinic, University of Athens
 Asthma Phenotypes: Distinction and Overlap Nikos Papadopoulos Allergy Dpt, 2 nd Pediatric Clinic, University of Athens Asthma as a syndrome From the Iliad to ADAM 33 and back again Bronchoconstriction,
Asthma Phenotypes: Distinction and Overlap Nikos Papadopoulos Allergy Dpt, 2 nd Pediatric Clinic, University of Athens Asthma as a syndrome From the Iliad to ADAM 33 and back again Bronchoconstriction,
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma
 Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Evidence-based recommendations or Show me the patients selected and I will tell you the results
 Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, S17 S21 Evidence-based recommendations or Show me the patients selected and I will tell you the results Leif Bjermer Department of Respiratory Medicine & Allergology, 221
Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, S17 S21 Evidence-based recommendations or Show me the patients selected and I will tell you the results Leif Bjermer Department of Respiratory Medicine & Allergology, 221
NG80. Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80)
 Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) NG80 NICE has checked the use of its content in this product and the sponsor has had no influence on the content of this booklet. NICE
Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) NG80 NICE has checked the use of its content in this product and the sponsor has had no influence on the content of this booklet. NICE
The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications
 The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Objectives Define Asthma.
The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Objectives Define Asthma.
Tips on managing asthma in children
 Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Meeting the Challenges of Asthma
 Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Meeting the Challenge of Asthma SPEAKER Christopher Fanta, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher Fanta, MD: No financial
Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Meeting the Challenge of Asthma SPEAKER Christopher Fanta, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher Fanta, MD: No financial
The FDA Critical Path Initiative
 The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN. Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department
 TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department Literature review current through: Feb 2013. This topic last updated: Aug 14, 2012 INTRODUCTION Wheezing
TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department Literature review current through: Feb 2013. This topic last updated: Aug 14, 2012 INTRODUCTION Wheezing
Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention
 Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Approximately 22 million Americans, including 6 million children, have asthma. It is one of the most prevalent
Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Approximately 22 million Americans, including 6 million children, have asthma. It is one of the most prevalent
Antileukotrienes and asthma: Alternative or adjunct to inhaled steroids?
 CURRENT DRUG THERAPY MANI S. KAVURU, MD Director, Pulmonary Function Laboratory, Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Cleveland Clinic REVATHI SUBRAMONY, RPH Staff Pharmacist, Metrohealth
CURRENT DRUG THERAPY MANI S. KAVURU, MD Director, Pulmonary Function Laboratory, Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Cleveland Clinic REVATHI SUBRAMONY, RPH Staff Pharmacist, Metrohealth
Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies
 Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies Stanley J. Szefler, MD Helen Wohlberg and Herman Lambert Chair in Pharmacokinetics, Head, Pediatric
Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies Stanley J. Szefler, MD Helen Wohlberg and Herman Lambert Chair in Pharmacokinetics, Head, Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Safety and Tolerability of Montelukast in Placebo-Controlled Pediatric Studies and Their Open-Label Extensions
 44:568 579 (2009) Safety and Tolerability of Montelukast in -Controlled Pediatric Studies and Their Open-Label Extensions Hans Bisgaard, MD, DMSci, 1 * David Skoner, MD, 2 Maria L. Boza, MD, 3 Carol A.
44:568 579 (2009) Safety and Tolerability of Montelukast in -Controlled Pediatric Studies and Their Open-Label Extensions Hans Bisgaard, MD, DMSci, 1 * David Skoner, MD, 2 Maria L. Boza, MD, 3 Carol A.
Mechanisms of action of bronchial provocation testing
 Mechanisms of action of bronchial provocation testing TSANZ / ANZSRS Masterclass: April 3rd, 2016 13:00 13:30 John D. Brannan PhD Scientific Director - Dept. Respiratory & Sleep Medicine John Hunter Hospital,
Mechanisms of action of bronchial provocation testing TSANZ / ANZSRS Masterclass: April 3rd, 2016 13:00 13:30 John D. Brannan PhD Scientific Director - Dept. Respiratory & Sleep Medicine John Hunter Hospital,
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Asthma Update A/Prof. John Abisheganaden. Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma in Pediatric Patients. DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP. Disclosures. None
 Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Asthma Upate 2018: What s New Since the 2007 Asthma Guidelines of NAEPP?
 10:50-11:50am Asthma Update 2018: What s New Since the 2007 National Asthma Guidelines? SPEAKER Christopher H. Fanta, MD Disclosures The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher
10:50-11:50am Asthma Update 2018: What s New Since the 2007 National Asthma Guidelines? SPEAKER Christopher H. Fanta, MD Disclosures The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher
Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care
 Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care Leonard B. Bacharier, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Clinical Director, Division of Allergy, Immunology, & Pulmonary Medicine
Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care Leonard B. Bacharier, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Clinical Director, Division of Allergy, Immunology, & Pulmonary Medicine
Composition: Each tablet contain. Levocetirizine. Each 5ml contains. Montelukast. Pharmacokinetic properties:
 Composition: Each tablet contain Montelukast Levocetirizine 10mg 5mg Each 5ml contains Montelukast Levocetirizine 4mg 2.5mg Pharmacokinetic properties: Peak plasma concentrations of montelukast are achieved
Composition: Each tablet contain Montelukast Levocetirizine 10mg 5mg Each 5ml contains Montelukast Levocetirizine 4mg 2.5mg Pharmacokinetic properties: Peak plasma concentrations of montelukast are achieved
#1 cause of school absenteeism in children 13 million missed days annually
 Asthma Update 2013 Jennifer W. McCallister, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Disclosures None 2 Objectives Review burden
Asthma Update 2013 Jennifer W. McCallister, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Disclosures None 2 Objectives Review burden
Available online at
 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org 285 Tapering Dose of Inhaled Budesonide in Subjects with Mild-to-Moderate Persistent Asthma Treated with Montelukast: A 16-Week Single-Blind Randomized Study Graziano
Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org 285 Tapering Dose of Inhaled Budesonide in Subjects with Mild-to-Moderate Persistent Asthma Treated with Montelukast: A 16-Week Single-Blind Randomized Study Graziano
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium montelukast 10mg tablets (Singulair ) No. (185/05) Merck, Sharp & Dohme Ltd (MSD) New indication: for asthmatic patients in whom montelukast is indicated in asthma, montelukast
Scottish Medicines Consortium montelukast 10mg tablets (Singulair ) No. (185/05) Merck, Sharp & Dohme Ltd (MSD) New indication: for asthmatic patients in whom montelukast is indicated in asthma, montelukast
Personalized medicine in childhood asthma. Dr Mariëlle Pijnenburg, Erasmus MC Sophia, Rotterdam, NL
 Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as submitted by the author.
Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as submitted by the author.
The recent guidelines from the
 ...PRESENTATIONS... Adjunctive Therapy for Asthma: Treatment Options Robert A. Nathan, MD Abstract The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute guidelines on the diagnosis and management of asthma recommend
...PRESENTATIONS... Adjunctive Therapy for Asthma: Treatment Options Robert A. Nathan, MD Abstract The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute guidelines on the diagnosis and management of asthma recommend
Bronchial asthma. MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL
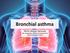 Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management?
 Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management? Ting Fan LEUNG, MBChB, MD, FRCPCH, FAAAAI Professor and Chairman Department of Paediatrics The Chinese University of Hong Kong Asthma and Allergy by
Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management? Ting Fan LEUNG, MBChB, MD, FRCPCH, FAAAAI Professor and Chairman Department of Paediatrics The Chinese University of Hong Kong Asthma and Allergy by
Preschool Wheeze. AC Jeevarathnum 04/03/16. Paediatric Pulmonologist Steve Biko Academic Hospital
 Preschool Wheeze AC Jeevarathnum Paediatric Pulmonologist Steve Biko Academic Hospital MBBCh FcPaed(SA) MMED Dip Allergy(SA) Cert Pulm(Paed)(SA) European Respiratory Diploma 04/03/16 Overview Introduction
Preschool Wheeze AC Jeevarathnum Paediatric Pulmonologist Steve Biko Academic Hospital MBBCh FcPaed(SA) MMED Dip Allergy(SA) Cert Pulm(Paed)(SA) European Respiratory Diploma 04/03/16 Overview Introduction
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Asthma phenotypes: the intriguing selective intervention with Montelukast
 Marcello and Carlo Asthma Research and Practice (2016) 2:11 DOI 10.1186/s40733-016-0026-6 REVIEW Asthma phenotypes: the intriguing selective intervention with Montelukast Cottini Marcello 1* and Lombardi
Marcello and Carlo Asthma Research and Practice (2016) 2:11 DOI 10.1186/s40733-016-0026-6 REVIEW Asthma phenotypes: the intriguing selective intervention with Montelukast Cottini Marcello 1* and Lombardi
Identifying and managing the infant and toddler at risk for asthma
 Clinical pearls Identifying and managing the infant and toddler at risk for asthma Theresa W. Guilbert, MD Madison, Wis Key words: Infants, children, asthma, wheezing, inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene
Clinical pearls Identifying and managing the infant and toddler at risk for asthma Theresa W. Guilbert, MD Madison, Wis Key words: Infants, children, asthma, wheezing, inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene
Outcome, classification and management of wheezing in preschool children Paul L.P. Brand
 Outcome, classification and management of wheezing in preschool children Paul L.P. Brand Princess Amalia Children s Clinic Isala klinieken, Zwolle the Netherlands p.l.p.brand@isala.nl Valle de la Luna,
Outcome, classification and management of wheezing in preschool children Paul L.P. Brand Princess Amalia Children s Clinic Isala klinieken, Zwolle the Netherlands p.l.p.brand@isala.nl Valle de la Luna,
Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit)
 Line of Business: All Lines of Business Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit) This policy has been developed through review
Line of Business: All Lines of Business Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit) This policy has been developed through review
Is reslizumab effective in improving quality of life and asthma control in adolescent and adult patients with poorly controlled eosinophilic asthma?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
COPD and Asthma: Similarities and differences Prof. Peter Barnes
 and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ
 Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Drug Use Criteria: Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
 Texas Vendor Drug Program Drug Use Criteria: Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists Publication History Developed February 2007. Revised March 2016; June 2014; October 2012; November 2010; October 2010; September
Texas Vendor Drug Program Drug Use Criteria: Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists Publication History Developed February 2007. Revised March 2016; June 2014; October 2012; November 2010; October 2010; September
Evolution of asthma from childhood. Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT
 Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
EIB in adults and children
 Onset and duration of protection against exercise-induced bronchoconstriction by a single oral dose of montelukast David S. Pearlman, MD*; Janet van Adelsberg, MD ; George Philip, MD ; Stephen A. Tilles,
Onset and duration of protection against exercise-induced bronchoconstriction by a single oral dose of montelukast David S. Pearlman, MD*; Janet van Adelsberg, MD ; George Philip, MD ; Stephen A. Tilles,
Additive effect of cysteinyl leukotriene or thromboxane modifiers to inhaled corticosteroids in asthmatic patients
 Allergology International (2004) 53: 211 217 Review Article Additive effect of cysteinyl leukotriene or thromboxane modifiers to inhaled corticosteroids in asthmatic patients Shigeharu Myou, 1 Masaki Fujimura
Allergology International (2004) 53: 211 217 Review Article Additive effect of cysteinyl leukotriene or thromboxane modifiers to inhaled corticosteroids in asthmatic patients Shigeharu Myou, 1 Masaki Fujimura
Management of wheeze in pre-school children. Prof Colin Robertson, Respiratory Medicine, Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne
 Management of wheeze in pre-school children Prof Colin Robertson, Respiratory Medicine, Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne General Practitioner encounters for asthma Asthma in Australia, 2003 Emergency
Management of wheeze in pre-school children Prof Colin Robertson, Respiratory Medicine, Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne General Practitioner encounters for asthma Asthma in Australia, 2003 Emergency
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack. Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus
 Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
12/18/2017. Disclosures. Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences
 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 2 Issue 3 July - Sep Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2013 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 23 th May 2013 Revised: 24 th Jun 2013 Accepted:
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 2 Issue 3 July - Sep Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2013 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 23 th May 2013 Revised: 24 th Jun 2013 Accepted:
The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma
 The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Objectives Know how the diagnosis of asthma
The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Objectives Know how the diagnosis of asthma
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Montelukast adult (10-mg film-coated tablet) and pediatric (5-mg chewable tablet) dose selections
 Montelukast adult (10-mg film-coated tablet) and pediatric (5-mg chewable tablet) dose selections Barbara Knorr, MD, a Sherry Holland, PhD, b J. Douglas Rogers, PhD, c Ha H. Nguyen, PhD, d and Theodore
Montelukast adult (10-mg film-coated tablet) and pediatric (5-mg chewable tablet) dose selections Barbara Knorr, MD, a Sherry Holland, PhD, b J. Douglas Rogers, PhD, c Ha H. Nguyen, PhD, d and Theodore
MODERATE PERSISTENT ASTHMA IN CHILDREN; COMPARISON OF INHALED BECLOMETHASONE WITH ORAL MONTELUKAST IN THE MANAGEMENT
 The Professional Medical Journal www.theprofesional.com ORIGINAL PROF-2495 MODERATE PERSISTENT ASTHMA IN CHILDREN; COMPARISON OF INHALED BECLOMETHASONE WITH ORAL MONTELUKAST IN THE MANAGEMENT 1 2 3 Dr.
The Professional Medical Journal www.theprofesional.com ORIGINAL PROF-2495 MODERATE PERSISTENT ASTHMA IN CHILDREN; COMPARISON OF INHALED BECLOMETHASONE WITH ORAL MONTELUKAST IN THE MANAGEMENT 1 2 3 Dr.
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma
 Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers?
 Disclosures: Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers? Stanley Fineman, MD Past-President, American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Adjunct Associate
Disclosures: Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers? Stanley Fineman, MD Past-President, American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Adjunct Associate
International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn eissn
 COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
Alberta Childhood Asthma Pathway for Primary Care
 Asthma Diagnosis Box 1 Diagnosis: Based on symptom pattern, careful and thorough history of symptoms (wheeze, cough, night waking and activity limitations), and assessment of family history of asthma and
Asthma Diagnosis Box 1 Diagnosis: Based on symptom pattern, careful and thorough history of symptoms (wheeze, cough, night waking and activity limitations), and assessment of family history of asthma and
Alternative agents for anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma
 Alternative agents for anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma Stanley J. Szefler, MD, a,b and Harold S. Nelson, MD, c Denver, Colo Recent guidelines for the management of asthma have emphasized the role
Alternative agents for anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma Stanley J. Szefler, MD, a,b and Harold S. Nelson, MD, c Denver, Colo Recent guidelines for the management of asthma have emphasized the role
Cynthia S. Kelly, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Division Director Allergy Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters
 Cynthia S. Kelly, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Division Director Allergy Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Disclosures Speakers bureau of Novartis and Genentech
Cynthia S. Kelly, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Division Director Allergy Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Disclosures Speakers bureau of Novartis and Genentech
Treating asthma: is there a place for leukotriene receptor antagonists?
 Respiratory Medicine (2005) 99, 655 662 Treating asthma: is there a place for leukotriene receptor antagonists? Zuzana Diamant a,, Thys van der Molen b,c a Centre for Human Drug Research, Zernikedreef
Respiratory Medicine (2005) 99, 655 662 Treating asthma: is there a place for leukotriene receptor antagonists? Zuzana Diamant a,, Thys van der Molen b,c a Centre for Human Drug Research, Zernikedreef
Increased Leukotriene E 4 in the Exhaled Breath Condensate of Children With Mild Asthma*
 CHEST Original Research Increased Leukotriene E 4 in the Exhaled Breath Condensate of Children With Mild Asthma* Atsushi Shibata, MD; Toshio Katsunuma, MD, PhD; Morimitsu Tomikawa, MD; Aiko Tan, MD; Keisuke
CHEST Original Research Increased Leukotriene E 4 in the Exhaled Breath Condensate of Children With Mild Asthma* Atsushi Shibata, MD; Toshio Katsunuma, MD, PhD; Morimitsu Tomikawa, MD; Aiko Tan, MD; Keisuke
The natural history of asthma and early intervention
 The natural history of asthma and early intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Denver, Colo The understanding of the natural history of asthma has changed significantly during the last 4 decades, with the
The natural history of asthma and early intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Denver, Colo The understanding of the natural history of asthma has changed significantly during the last 4 decades, with the
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Pediatric Asthma: Pharmacotherapy. Joseph Spahn, MD Children s Hospital Colorado & University of Colorado Medical School Aurora, Colorado
 Pediatric Asthma: Pharmacotherapy Joseph Spahn, MD Children s Hospital Colorado & University of Colorado Medical School Aurora, Colorado Pediatric Asthma: Pharmacotherapy Disclosures/Conflicts of Interest:
Pediatric Asthma: Pharmacotherapy Joseph Spahn, MD Children s Hospital Colorado & University of Colorado Medical School Aurora, Colorado Pediatric Asthma: Pharmacotherapy Disclosures/Conflicts of Interest:
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control
 Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
James P. Kemp, MD; Margaret C. Minkwitz, PhD; Catherine M. Bonuccelli, MD; and Marshelle S. Warren, MD
 Therapeutic Effect of Zafirlukast as Monotherapy in Steroid-Naive Patients With Severe Persistent Asthma* James P. Kemp, MD; Margaret C. Minkwitz, PhD; Catherine M. Bonuccelli, MD; and Marshelle S. Warren,
Therapeutic Effect of Zafirlukast as Monotherapy in Steroid-Naive Patients With Severe Persistent Asthma* James P. Kemp, MD; Margaret C. Minkwitz, PhD; Catherine M. Bonuccelli, MD; and Marshelle S. Warren,
Distribution of therapeutic response in asthma control between oral montelukast and inhaled beclomethasone
 Eur Respir J 2003; 21: 123 128 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.03.00028803 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2003 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Distribution of therapeutic
Eur Respir J 2003; 21: 123 128 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.03.00028803 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2003 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Distribution of therapeutic
Dual-controller therapy, or combinations REVIEW DUAL-CONTROLLER REGIMENS I: DATA FROM RANDOMIZED, CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIALS.
 DUAL-CONTROLLER REGIMENS I: DATA FROM RANDOMIZED, CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIALS Samy Suissa, PhD ABSTRACT Dual-controller therapy, or combinations of 2 or more pharmacotherapies with complementary mechanisms
DUAL-CONTROLLER REGIMENS I: DATA FROM RANDOMIZED, CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIALS Samy Suissa, PhD ABSTRACT Dual-controller therapy, or combinations of 2 or more pharmacotherapies with complementary mechanisms
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes. Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy
 Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
7/7/2015. Somboon Chansakulporn, MD. History of variable respiratory symptoms. 1. Documented excessive variability in PFT ( 1 test)
 Definition of Asthma GINA 2010: Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways Airway hyper-responsiveness Recurrent wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, coughing Variable, reversible airflow obstruction
Definition of Asthma GINA 2010: Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways Airway hyper-responsiveness Recurrent wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, coughing Variable, reversible airflow obstruction
SYNOPSIS THIS IS A PRINTED COPY OF AN ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT. PLEASE CHECK ITS VALIDITY BEFORE USE.
 Drug product: Drug substance(s): Document No.: Edition No.: 1 Study code: Accolate Zafirlukast (ZD9188) 9188IL/0138 Date: 02 May 2007 SYNOPSIS A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, -controlled, Parallel
Drug product: Drug substance(s): Document No.: Edition No.: 1 Study code: Accolate Zafirlukast (ZD9188) 9188IL/0138 Date: 02 May 2007 SYNOPSIS A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, -controlled, Parallel
Dr Christopher Worsnop
 Dr Christopher Worsnop Respiratory & Sleep Physician Austin Hospital, Melbourne Supported by: Top Tips in Modern Asthma Management Dr Christopher Worsnop Rotorua GPCME Meeting June 2013 Speaker declaration
Dr Christopher Worsnop Respiratory & Sleep Physician Austin Hospital, Melbourne Supported by: Top Tips in Modern Asthma Management Dr Christopher Worsnop Rotorua GPCME Meeting June 2013 Speaker declaration
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes
 Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
(Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management
 Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
