Effect of Inhaled Corticosteroids on Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness in Patients with Mild Asthma
|
|
|
- Damian Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2 3 ai.r. 259 Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology (1995) 13 : Effect of Inhaled Corticosteroids on Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness in Patients with Mild Asthma Somkiat Wongtim, Somkld Mogmued, Pradit Chareonlap and Sakchai Umthongkul Bronchial hyperresponsiveness (BHR) is defined as a condition in which there is an increased tendency of airways to develop exaggerated bronchoconstriction response to many stimuli such as respiratory tract infection, cold air, cigarette smoke, chemical and pharmacolo gical agents. l BHR is important in the pathogensis of bronchial asthma. It is a consequence of airway inflam mation. 2 The role of airway inflammation is so well established that it is incorporated into the definition of the disease and is an important target of therapy.3 The mechanisms of air way inflammation, in both IgE-de pendent and IgE-independent mechanisms, involve the release of various inflammatory mediators and cytokines such as prostaglandin metabolites, interleukins, granulocytemacrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF), intercellular adhesion molecule-l (ICAM-I) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-l (VCAM-I).4,5 The net result is the 'ruitment of inflammatory cells in,. especially eosinophils. 6 7 'e' eosinophil major basic. P) and various cellular ese inflammatory medial. y, products of these / SUMMARY We studied the effect of Inhaled budesonlde on bronchial hyperresponslveness (BHA) In twenty mild asthmatic patialts. The study was conducted as a randomized, double- blind, placebo- controlled study. Before entering the study, the patients perfonned methacholine Inhalation challenge (M IC) using a reservoir method to assess BHR. Then, they were randomly allocated to receive budesonide turbuhaler (2 JlGIdose) or placebo turbuhaler two inhalations, twice dally for eight weeks. During the study, each patient recorded dally asthma score and dally number of puffs of 2 agonist and they were assessed at weeks 4 and 8. At the end of the treatment, MIC was repeated again. Patients receiving budesonida showed a significant improvement In airway responsiveness compared with those receiving placebo (p <.5). They also showed a significant Improvement In asthma severity score and a significant decrease In agonist bronchodilator use. This study also suggested that inhaied corticosteroids may be the primary treatment in patients, even with mild asthmatic and well-controlled symptoms. tors cause airway epithelial damage and shedding, goblet cell hyperpla sia, basement membrane changes, vascular leakage, and smooth muscle contraction. 8 9 Inflammatory pro cesses contribute to increased bronchial reactivity through a direct effect on smooth muscle, by increasing airway wall thickness or via activation of the axon reflex. 1.1 I Such inflammation has been found to exist even in patients with mild disease. 12 In a previous study, we found that Thai patients with mild asthma still had BHR to methacholine challenge at a mean concentration of 4 mg/mt 13 Corticosteroids have to be effective in treatment of asthma by suppression of the inflammatory response, resulting in improvement of BHR.l4 Budesonide, an inhaled corticosteroid, has been used for many years in treatment of asthma. 15 Several studies have found that budesonide was effective in both short-term and long-term treat- From the Department of Internal Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok 133, Thailand. Correspondence: Somkiat Wongtim, Department of Internal Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok 133, Thailand.
2 82 CORTICOSTEROIDS IN ASTHMA PATIENTS ment of asthma and reduction of BHR In those studies, budesonide administered by a pressurised, metered-dose inhaler (MOl) with a spacer was used. At present there are several delivery systems using inhaler devices. 19 Budesonide turbuhaler, another type of delivery system, is claimed to be better than MOl because it has no propellent and it achieves greater drug deposition in the lung. Since there was no such study in Thailand, we investigated the effect of budesonide turbuhaler in Thai subjects. The purpose of this study was to investigate the change of BHR in patients with mild asthma after 8 weeks of treatment with inhaled budesonide turbuhaler using the methacholine inhalation challenge (MIC) method. PATIENTS AND METHODS Subjects Twenty subjects with mild bronchial asthma were enrolled in the study. They were selected from out -patients of the Chest and Allergy Clinic, Chulalongkorn Hospital. They were diagnosed as having bronchial asthma with the presence of coughing or wheezing in the past three years; their baseline spirometry showed a decrease of FEVII FVC of less than 77, with an improvement in FEV 1 greater than 157 after inhalation of bronchodilator. All patients had been followed up in the clinics for many years. They were classified as having mild asthma, according to National Institutes of Health (NIH) guidelines,2 which defined this condition as having few clinical symptoms (exacerbation of cough and wheezing no more than 1-2 timeslweek, nocturnal attack no more than 1-2 times/month) and minimal or no evidence of airway obstruction on spirometry. Most of the patients used long-acting theophylline once or twice daily, and inhaled a /32 agonist bronchodilator as needed. None used systemic corticosteroids, ketotifen or disodium chromoglycate within the three months before entering the study. At the time of study entry, MIC was performed. Then each patient was randomly allocated to receive budesonide turbuhaler 2 /lgl dose or placebo turbuhaler, 2 inhalations twice daily for 8 weeks. Each patient was given a diary card to record: (a) symptom scores with scale -3 ( = no symptoms, I = mild symptoms easily tolerated, 2 moderate symptoms causing interference with daily activity, and 3 = severe symptoms causing inability to work), (b) daily numbers of puffs of 2 agonist MOl taken. Patients came for check up at weeks 4 and 8. At the 8th week, MIC was repeated again by the same method. Procedure MIC was performed at 9. by using the procedure as previously described.13 Briefly, stock solutions of methacholine in a citrate buffer were prepared under sterile conditions for each concentration; (diluent),.5, 1,5, 1, and 25 mg/ml. Six milliliters of the solution were filled in an atomized nebulizer part of the equipment (Provocation test I, Pari-Starnberg, Germany). It has been determined that about.4 ml of the solution is necessary to produce 1 litres of methacholine aerosol to fill the reservoir bag. Before methacholine inhalation, baseline spirometry was performed with subjects standing using the Autospiror Oiscom-21 (Chest Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). At least three satisfactory and two reproducible spirometric maneuvers were required according to A TS recommendation. 21 The largest FEV I value from acceptable maneuver was used for the baseline FEV 1. Then each subject inhaled diluent aerosol from the reservoir bag via slow inspiratory vital capacity maneuver until the bag was empty. Three minutes after the inhalation, spirometry was repeated. The largest FEV I from an acceptable maneuver was used as the post-diluent control value. After that, subjects inhaled an increasing concentration of the methacholine aerosol (.5, I, 5, 1, and 25 mglml, respectively) from the reservoir bag. Spirometry was performed in a similar manner after inhalation of each concentration of methacholine, the largest FEV I from an acceptable maneuver being selected for analysis. The test was terminated if there was more than 27 decline from the control value of FEV I after any inhalation. At the end of the test, the subjects who had a decline of FEV I more than 157 was given one nebule of fenoterol and ipratropium bromide solution via nebulizer and spirometry was repeated 1 minutes later. Subjects were informed about the possible late phase reaction which could occur 6-8 hours after the test and they were discharged from the unit after their FEV I had returned to within 17 of their baseline values. Data analysis Subjects were categorized as having BHR (positive test) if they showed more than 27 decrease in FEV 1 (PC2) from baseline after inhalation of diluent or any concentration of methacholine up to and including 25 mg/ml.22 Data were analyzed by computer using Excel 5.. 'Results were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SO). For comparisons of the mean value, the I-test was used. A p value of less than '.5 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS The results of the study are presented in Table 1 and Figs. and 3. The mean values ± r deviation for age, sex, h 7oFVC, FEVI, 7FEV I: the first PC2 were not
3 WONGTIM, ET AL. 83 Table 1. Age (years) Sex (F/M) Height (cm) FVC(I) % FVC/FVCpredicted FEV1 (I) % FEV 1 /FVC 1 st PC2 (mg/ml) 2 nd PC2 (mg/ml) Subject characteristics in the study. Budesonide Placebo p-value 33.2 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ±8.6 5/ ± ± ± ± ± ± ±(j.8 <.5 different between the two groups. No patient withdrew during the study. Although these patients had mild symptoms and were well-controlled at the time of enrollment, the patients who used budesonide still showed a significant improvement in asthma severity by asthma score, compared with those receiving placebo (p <.5) as shown in Fig. I. None of these patients had acute exacerbation during the study. There was also significant reduction in the amount of inhaled bronchodi '" Ṣ ri:j. c... ri:j (\I E.c "!il < Budesonide -Placebo 4 8 Weeks Fig. 1. Effect of budesonide on asthma severity scores.,-...:.: t: 3 I:: = '-' Ṣ. =- 2.! 1 ].c.. =.. == Budesonide -Placebo Weeks Fig. 2. Effect of budesonide on bronchodilator use.
4 84 CORTICOSTEROIDS IN ASTHMA PATIENTS U I:l "'; $ Pre Post Pre Post Budesonide Fig. 3. lators used by the budesonide group compared with those receiving placebo (p <.5) as seen in Fig. 2. Patients receiving budesonide had an increase of PC2 corresponding to.6 doubling concentration of methacholine from the baseline to the end of treatment. In the placebo group, the increase was.4 doubling concentration which was significantly different from the budesonide group (p <.5) as shown in Fig. 3. DISCUSSION Placebo Airway responsivenest to methacholine. The mechanism of action of corticosteroids in asthma is related to their anti-inflammatory effects. They interfere with arachidonic acid metabolism and the synthesis of leukotrienes and prostaglandins, reduce microvascular leakage, inhibit cytokine production and secretion, prevent directed migration and activation of inflammatory cells, and increase responsiveness of beta receptors of the airway smooth muscle. Corticosteroids have shown to reduce epithelial damage and improve cellular morphology, reduce vascular leakage, reduce the numbers and activation of inflammatory cells, and inhibit the release of preformed and newly formed mediators from inflammatory cells which are related to the improvement in signs and symptoms of asthma as well as the improvement of BHR The improvement of BHR by corticosteroids depended on dose and duration of the treatment. Kraan et al. 16 found an increase in PD2 to histamine of +.4 doublingdose (DD) after 2 weeks of treatment with loo J,lg budesonide MOl twice daily, and a further increase to +.8 DD after 8 weeks. Vethenen et al. 26 studied inhaled budesonide MOl 8 J,lg twice a day for 6 weeks in 4 asthmatic patients. They found that there was a significant increase in PD2 to DD of histamine. Juniper et al. 17 evaluated the effect of longterm treatment with inhaled budesonide MOl 4 J,lg daily for 1 year on BHR in 32 stable adult asthma. The patients receiving budesonide showed a fourfold mean improvement in BHR. The largest improvement occurred during the first 3 months. The improvement in BH R was also accompanied by significant improvement in asthma symptoms, the need for bronchodilator use and the number of asthmatic exacerbation. They concluded that regular and prolonged use of inhaled corticosteroid could produce marked improvement in BHR, sometimes with full resolution and clinical improvement. Moreover. they also demonstrated that, when inhaled corticosteroids were reduced after prolonged treatment, improvements in BHR could be maintained for at least 3 months before deterioration in symptoms, spirometry and increased airway responsiveness again. 27 Kivity et al. 28 used budesonide MOl 4 p.g twice daily for 8 weeks in 2 patients with mild to moderate asthma. They found that the treatment caused a moderate increase in spirometry which was significantly different from the placebo group. The BHR was also increased 1.8 DD but it was not statistically significant different when compared with the.8 DD of the placebo group. Our study showed that mild asthmatic patients receiving inhaled budesonide turbuhaler 4 J,lg twice daily delivered a significant decrease in (32 agonist bronchodilator use with significant symptom control. In fact, even though these patients had been considered to be in good control initially, it appeared that there was still further clinical improvement when they regularly used inhaled budesonide turbuhaler. Although the improvement in the second PC2 in the budesonide group was only +.6 doubling concentration, it was statistically increased when compared with the +.4 of the placebo group (p <.5). We do not understand the reasons why the improvement of
5 WONGTIM, ET AL 85 BHR in our study was so small when compared with those reports in the literature. It may be a technical error in turbuhaler usage resulting in lesser amount of drug deposition in the lower airway or it may be that budesonide turbuhaler was not as effective as budesonide MOL In a further study we would compare the effectiveness of the turbuhaler and the MOL In conclusion, our study demonstrated that mild asthmatic patients receiving inhaled budesonide turbuhaler showed a significant improvement in asthma severity, decreased 112 agonist use and reduced BHR, compared with those receiving placebo. However, the improvement of BHR was not so much, this needs to be clarified in a further study. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This study was financially supported by Chao Praya Mahaisawan Fund under the Research Project to the Department of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University. The authors would like to thank the Astra Thailand who supported the Pulmicort turbuhaler and placebo turbuhaler. REFERENCES I. Boushey HA, Holtzman MJ, Sheller JR, Nadel JA. Bronchial hyperreactivity. Am Rev Respir Dis 198; 121 : Snapper JR. Inflammation and airway function: the asthma syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 199; 141 : Barnes PJ. A new approach to the treatment of asthma. N Eng J Med 1989; 321 : Busse WW, Calhoun WF, Sedgwick JD. Mechanism of airway inflammation in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 1993; 147 : S National Institute of Health. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention, January National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (publication number ). 6. Gleich GJ. The eosinophil and bronchial asthma: current understanding. J Allergy CUn Immunol 199; 85 : Corrigan CJ, Kay AB. The roles of inflammatory cells in the pathogenesis of asthma and COPD. Am Rev Respir Dis 1991; 143: Laitinen LA, Heino M, Laitinen A, Kava T, Haahtela T. Damage of the epithelium and bronchial reactivity in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 1985; 131 : Jeffery PK, Wardlaw AJ, Nelson FC, Collins JV, Kay AB. Bronchial biopsy in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 1989; 14 : Barnes P J. New concepts in the pathogenesis of bronchial hyperresponsiveness and asthma. J J\lIergy Clin Immunol 1989; 83 : II. Barnes PJ, Baraniuk IN, Belvisi MG. Neuropeptides in the respiratory tract. Am Rev Respir Dis 1991; 144 : Beasley R, Roche WR, Roberts JA, Holgate ST. Cellular events in the bronchi in mild asthma and after bronchial provocation. Am Rev Respir Dis 1989; 139: Wongtim S, Mogmued S, Chareonlap P, Phanuphak P. Standardization of methacholine inhalation challenge by a reservoir method. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 1994; 12: Szelfler SJ. Glucocorticoid therapy for asthma. J Allergy Clin ImmunoI 1991; 88 : IS. Barnes PJ. Budesonide: clinical experience in asthma and rhinitis. Adis Press International Limited, Manchester Kraan J, Koeter GH, Mark TW, Sluiter HJ, de Vries K. Change of bronchial hyperreactivity induced by 4 weeks of treatment with antiasthmatic drugs in patients with allergic asthma : a com parison between budesonide and tufbutaline. J Allergy Clin Immunol1985; 76: Juniper EF, Kline PA, Vanzieleghem MA. Ramsdale EH, O'Byrne PM, Hargreave FE. Effect of long-term treatment with an inhaled corticosteroid (budesonide) on airway hyperresponsiveness and clinical asthma in nonsteroid-dependent asthmatics. Am Rev Respir Dis 199; 142 : Haahtela T, Jarvinen M, Kava T, et al. Comparison of a 2 agonist, turbutaline, with an inhaled corticosteroid, budesonide, in newly detected asthma. N Eng J Med 1991; 325 : Summer W. Elston R. Tharpe L. Nelson S. Haponik EF. Aerosol bronchodilator delivery method. Arch Intern Med 1989; 149: National Institutes of Health. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma, August National Heart, Lung. and Blood Institute (publication ). 21. American Thoracic Society. Standardization of spirometry 1987 update. Am Rev Respir Dis 1987; 136 : Tashkin DP, Altose MD, Bleeker ER, er al. The lung health study: airway responsiveness to inhaled methacholine in smokers with mild to moderate airflow limitation. Am Rev Respir Dis 1992; 145 : Barnes PJ. Effects of corticosteroids on airway hyperesponsiveness. Am Rev Respir Dis 199; 141 : S7-S Schleimer RP. Effects of glucocorticoids on inflammatory cells relevant to their therapeutic applications in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 199; 141 : S59-S Laitinen LA. Laitinen A,Haahtela T. A comparative study of effects of an inhaled corticosteroid. budesonide. and a 1)2-agonist, turbutaline, on airway inflammation in newly diagnosed asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1992; 9 : Vathenen AS. Knox AJ, Wisneiski A, Tattersfeild AE. Time course of change in bronchial reactivity with an inhaled corticosteroid (budesonide) in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 1991; 143: Juniper EF, Kline PA, Venzieleghem MA, Hargreave FE. Reduction of budesonide after a year of increased used: a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether improvements in airway responsiveness and clinical asthma are maintained. J Allergy Clin lmmunol 1991; 87 : Kivity S, Fireman E, Greif J, Schwarz Y. Topilsky M. Effect of budesonide on bronchial hyper responsiveness and pulmonary function in patients with mild to moderate asthma. Ann Allergy 1994; 72 :
Impact of Asthma in the U.S. per Year. Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Risk Factors for Asthma. Childhood Asthma Costs of Asthma
 American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma
 Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Does ketotifen have a steroid-sparing effect in childhood asthma?
 Eur Respir J, 1997; 1: 65 7 DOI: 1.1183/931936.97.1165 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1997 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Does ketotifen have a steroid-sparing
Eur Respir J, 1997; 1: 65 7 DOI: 1.1183/931936.97.1165 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1997 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Does ketotifen have a steroid-sparing
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Performing a Methacholine Challenge Test
 powder for solution, for inhalation Performing a Methacholine Challenge Test Provocholine is a registered trademark of Methapharm Inc. Copyright Methapharm Inc. 2016. All rights reserved. Healthcare professionals
powder for solution, for inhalation Performing a Methacholine Challenge Test Provocholine is a registered trademark of Methapharm Inc. Copyright Methapharm Inc. 2016. All rights reserved. Healthcare professionals
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Effect of 1 year daily treatment with 400 µg budesonide (Pulmicort Turbuhaler ) in newly diagnosed asthmatics
 Eur Respir J 1997; 10: 2210 2215 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.97.10102210 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1997 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Effect of 1 year daily
Eur Respir J 1997; 10: 2210 2215 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.97.10102210 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1997 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Effect of 1 year daily
DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES:
 TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): Α A REVIEW
 Volume 23, Issue 3 December 2007 BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): A REVIEW Donna L. Smith, Pharm. D. Candidate More than 22 million people in the United States have asthma according to the Centers
Volume 23, Issue 3 December 2007 BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): A REVIEW Donna L. Smith, Pharm. D. Candidate More than 22 million people in the United States have asthma according to the Centers
Comparison of the Effect of Short Course of Oral Prednisone in Patients with Acute Asthma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 7 Number 1 Comparison of the Effect of Short Course of Oral Prednisone in Patients with Acute Asthma E Razi, G Moosavi Citation E Razi, G Moosavi.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 7 Number 1 Comparison of the Effect of Short Course of Oral Prednisone in Patients with Acute Asthma E Razi, G Moosavi Citation E Razi, G Moosavi.
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic adults A long-term correlation study
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2005; 9: 125-131 Bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic adults A long-term correlation study R. CARBONE, F. LUPPI *, A. MONSELISE **, G. BOTTINO
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2005; 9: 125-131 Bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic adults A long-term correlation study R. CARBONE, F. LUPPI *, A. MONSELISE **, G. BOTTINO
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Mechanisms of action of bronchial provocation testing
 Mechanisms of action of bronchial provocation testing TSANZ / ANZSRS Masterclass: April 3rd, 2016 13:00 13:30 John D. Brannan PhD Scientific Director - Dept. Respiratory & Sleep Medicine John Hunter Hospital,
Mechanisms of action of bronchial provocation testing TSANZ / ANZSRS Masterclass: April 3rd, 2016 13:00 13:30 John D. Brannan PhD Scientific Director - Dept. Respiratory & Sleep Medicine John Hunter Hospital,
Immunology of Asthma. Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph. Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline! Consensus characteristics! Allergens:role in asthma! Immune/inflammatory basis! Genetic basis!
Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline! Consensus characteristics! Allergens:role in asthma! Immune/inflammatory basis! Genetic basis!
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Asthma Update A/Prof. John Abisheganaden. Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Outline FEF Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications?
 Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications. Potential Conflict Of Interest. Objectives. Rationale: Why Test?
 Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Effect of inhaled budesonide therapy on lung function in schoolchildren born preterm
 RESPIRATORY MEDICINE (2001) 95, 565 570 doi:10.1053/rmed.2001.1104, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Effect of inhaled budesonide therapy on lung function in schoolchildren born preterm
RESPIRATORY MEDICINE (2001) 95, 565 570 doi:10.1053/rmed.2001.1104, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Effect of inhaled budesonide therapy on lung function in schoolchildren born preterm
Clinical Issues Research Implemented April 2010 Asthma Major Recommendations Goals of asthma: - 1) reduction of impairment freedom from symptoms,
 Asthma Major Recommendations Goals of : - 1) reduction of impairment freedom from symptoms, such as cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, and disturbed sleep minimal need (< 2 times per week) of short
Asthma Major Recommendations Goals of : - 1) reduction of impairment freedom from symptoms, such as cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, and disturbed sleep minimal need (< 2 times per week) of short
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse
 Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse study Soren Pedersen, MD, PhD, and Ove Ramsgaard Hansen, MD Kolding, Denmark Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate
Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse study Soren Pedersen, MD, PhD, and Ove Ramsgaard Hansen, MD Kolding, Denmark Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack. Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus
 Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Viral-Induced Asthma:
 Viral-Induced : Sorting through the Studies Malcolm R. Sears, MB, FRACP, FRCPC Presented at the Respirology Update Continuing Education Program, January 2005 Viral-associated wheezing is common and not
Viral-Induced : Sorting through the Studies Malcolm R. Sears, MB, FRACP, FRCPC Presented at the Respirology Update Continuing Education Program, January 2005 Viral-associated wheezing is common and not
Peak Expiratory Flow Variability Adjusted by Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second is a Good Index for Airway Responsiveness in Asthmatics
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Peak Expiratory Flow Variability Adjusted by Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second is a Good Index for Airway Responsiveness in Asthmatics Kazuto Matsunaga, Masae Kanda, Atsushi Hayata,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Peak Expiratory Flow Variability Adjusted by Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second is a Good Index for Airway Responsiveness in Asthmatics Kazuto Matsunaga, Masae Kanda, Atsushi Hayata,
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Starting with a Higher Dose of Inhaled Corticosteroids in Primary Care Asthma Treatment
 Starting with a Higher Dose of Inhaled Corticosteroids in Primary Care Asthma Treatment THYS van der MOLEN, BETTY MEYBOOM-DE JONG, HELMA H. MULDER, and DIRKJE S. POSTMA Department of General Practice,
Starting with a Higher Dose of Inhaled Corticosteroids in Primary Care Asthma Treatment THYS van der MOLEN, BETTY MEYBOOM-DE JONG, HELMA H. MULDER, and DIRKJE S. POSTMA Department of General Practice,
Defining COPD. Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist
 Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
cough threshold in smokers with chronic
 372 Department of Pulmonology B Auffarth D S Postma Th W van der Mark G H Koeter Department of Allergy J G R de Monchy University Hospital, 9713 EZ, Groningen, The Netherlands Astra BV, PO Box 1, 2280
372 Department of Pulmonology B Auffarth D S Postma Th W van der Mark G H Koeter Department of Allergy J G R de Monchy University Hospital, 9713 EZ, Groningen, The Netherlands Astra BV, PO Box 1, 2280
The Role of the Methacholine Inhalation Challenge in Adult Patients Presenting with Chronic Cough
 IASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (997) 5: 9-4 The Role of the Methacholine Inhalation Challenge in Adult Patients Presenting with Chronic Cough Somkiat Wongtim, Somkid Mogmeud, Sakchai
IASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (997) 5: 9-4 The Role of the Methacholine Inhalation Challenge in Adult Patients Presenting with Chronic Cough Somkiat Wongtim, Somkid Mogmeud, Sakchai
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists
 Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management
 Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management Learning Objectives After participating in this educational activity, participants should be better able to: 1. Choose the optimal
Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management Learning Objectives After participating in this educational activity, participants should be better able to: 1. Choose the optimal
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II
 Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Inhaled glucocorticoids (GCs) have revolutionized
 Factors Influencing the Responsiveness to Inhaled Glucocorticoids of Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Asthma* An-Soo Jang, MD; June-Hyuk Lee, MD; Sung Woo Park, MD; Young Mok Lee, MD; Soo Taek Uh, MD;
Factors Influencing the Responsiveness to Inhaled Glucocorticoids of Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Asthma* An-Soo Jang, MD; June-Hyuk Lee, MD; Sung Woo Park, MD; Young Mok Lee, MD; Soo Taek Uh, MD;
Asthma. Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital. Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence,
 Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Implications on therapy. Prof. of Medicine and Allergy Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University
 Implications on therapy Dr. Hisham Tarraf MD,FRCP(Edinb.) Prof. of Medicine and Allergy Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University Need for better understanding Global health problem Impact on quality of life
Implications on therapy Dr. Hisham Tarraf MD,FRCP(Edinb.) Prof. of Medicine and Allergy Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University Need for better understanding Global health problem Impact on quality of life
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016
 Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System
 Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Effect of disease duration on dose response of inhaled budesonide in asthma
 Respiratory Medicine (2008) 102, 1065 1072 Effect of disease duration on dose response of inhaled budesonide in asthma Olof Selroos a,b, a Mjölbolsta Hospital, Karis, Finland b SEMECO AB, Skogsvägen 5,
Respiratory Medicine (2008) 102, 1065 1072 Effect of disease duration on dose response of inhaled budesonide in asthma Olof Selroos a,b, a Mjölbolsta Hospital, Karis, Finland b SEMECO AB, Skogsvägen 5,
Salmeterol, a new long acting inhaled,f2 adrenoceptor agonist: comparison with salbutamol in adult asthmatic patients
 Thorax 1988;43:674-678 Salmeterol, a new long acting inhaled,f2 adrenoceptor agonist: comparison with salbutamol in adult asthmatic patients ANDERS ULLMAN, NILS SVEDMYR From the Department of Clinical
Thorax 1988;43:674-678 Salmeterol, a new long acting inhaled,f2 adrenoceptor agonist: comparison with salbutamol in adult asthmatic patients ANDERS ULLMAN, NILS SVEDMYR From the Department of Clinical
responsiveness in asthmatic patients and smokers
 63 Department of Pulmonology B Auffarth D S Postma G H Koeter Th W van der Mark Department of Allergology J G R de Monchy University Hospital, 973 EZ Groningen, The Netherlands Reprint requests to: Professor
63 Department of Pulmonology B Auffarth D S Postma G H Koeter Th W van der Mark Department of Allergology J G R de Monchy University Hospital, 973 EZ Groningen, The Netherlands Reprint requests to: Professor
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Phenotypes of asthma; implications for treatment. Medical Grand Rounds Feb 2018 Jim Martin MD DSc
 Phenotypes of asthma; implications for treatment Medical Grand Rounds Feb 2018 Jim Martin MD DSc No conflicts to declare Objectives To understand the varied clinical forms of asthma To understand the pathobiologic
Phenotypes of asthma; implications for treatment Medical Grand Rounds Feb 2018 Jim Martin MD DSc No conflicts to declare Objectives To understand the varied clinical forms of asthma To understand the pathobiologic
Update on Pulmonary Diseases. Jeffrey Lessar, MD
 Update on Pulmonary Diseases Jeffrey Lessar, MD 1 No disclosures to make No conflicts 2 Goals Update on key changes in Pulmonary Therapy 3 Spirometry Spirometry FEV1- forced expiratory Volume in 1 Sec
Update on Pulmonary Diseases Jeffrey Lessar, MD 1 No disclosures to make No conflicts 2 Goals Update on key changes in Pulmonary Therapy 3 Spirometry Spirometry FEV1- forced expiratory Volume in 1 Sec
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring
 Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Time course of action of two inhaled corticosteroids, fluticasone propionate and budesonide
 ASTHMA Time course of action of two inhaled corticosteroids, fluticasone propionate and budesonide K Phillips, J Oborne, S Lewis, T W Harrison, A E Tattersfield... See end of article for authors affiliations...
ASTHMA Time course of action of two inhaled corticosteroids, fluticasone propionate and budesonide K Phillips, J Oborne, S Lewis, T W Harrison, A E Tattersfield... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits
 B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
(Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management
 Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
NON-SPECIFIC BRONCHIAL HYPERESPONSIVENESS. J. Sastre. Allergy Service
 NON-SPECIFIC BRONCHIAL HYPERESPONSIVENESS J. Sastre. Allergy Service Asthma: definition Asthma is a syndrome defined on basis of three main aspects: 1- Symptoms due to variable and reversible airway obstruction
NON-SPECIFIC BRONCHIAL HYPERESPONSIVENESS J. Sastre. Allergy Service Asthma: definition Asthma is a syndrome defined on basis of three main aspects: 1- Symptoms due to variable and reversible airway obstruction
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Definition and Pathology CHAPTER 1. John Rees
 CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
Systems Pharmacology Respiratory Pharmacology. Lecture series : General outline
 Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Add on therapy in asthma. Local experience in context J Paul Dilworth, Nicola Marks, Lauren Geddes
 Add on therapy in asthma Local experience in context J Paul Dilworth, Nicola Marks, Lauren Geddes Programme Omalizumab Evidence and assessment Local Experience Dysfunctional breathing The other effective
Add on therapy in asthma Local experience in context J Paul Dilworth, Nicola Marks, Lauren Geddes Programme Omalizumab Evidence and assessment Local Experience Dysfunctional breathing The other effective
GETTING STARTED WITH MANNITOL CHALLENGE TESTING. Rick Ballard, RRT, RPFT Applications/Education Specialist MGC Diagnostics
 GETTING STARTED WITH MANNITOL CHALLENGE TESTING Rick Ballard, RRT, RPFT Applications/Education Specialist MGC Diagnostics OBJECTIVES Indications for provocation testing Identify candidates for testing
GETTING STARTED WITH MANNITOL CHALLENGE TESTING Rick Ballard, RRT, RPFT Applications/Education Specialist MGC Diagnostics OBJECTIVES Indications for provocation testing Identify candidates for testing
Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide.
 Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide. By: DR MOHD SHAMSUL AMRI Supervisor: Associate Professor Dr
Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide. By: DR MOHD SHAMSUL AMRI Supervisor: Associate Professor Dr
Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma?
 Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 458 462 Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma? Haim S. Bibi a,, David Feigenbaum a, Mariana Hessen
Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 458 462 Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma? Haim S. Bibi a,, David Feigenbaum a, Mariana Hessen
Full Length Original Research Paper
 Copyright 2013 By IYPF All rights reserved Open Access Contents Int. J. Drug Dev. & Res. October - December 2013 Vol. 5 Issue 4 ISSN 0975-9344 www.ijddr.in Effect of Budesonide by metered dose inhaler
Copyright 2013 By IYPF All rights reserved Open Access Contents Int. J. Drug Dev. & Res. October - December 2013 Vol. 5 Issue 4 ISSN 0975-9344 www.ijddr.in Effect of Budesonide by metered dose inhaler
History & Development
 RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria. Defining Asthma: Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness
 Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria Atopy 34% Recent wheeze 20% Asthma 11% AHR 19% n = 807 From: Woolcock, AJ. Asthma in Textbook of Respiratory Medicine, 2nd ed. Murray, Nadel, eds.(saunders:philadelphia)
Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria Atopy 34% Recent wheeze 20% Asthma 11% AHR 19% n = 807 From: Woolcock, AJ. Asthma in Textbook of Respiratory Medicine, 2nd ed. Murray, Nadel, eds.(saunders:philadelphia)
Increased Leukotriene E 4 in the Exhaled Breath Condensate of Children With Mild Asthma*
 CHEST Original Research Increased Leukotriene E 4 in the Exhaled Breath Condensate of Children With Mild Asthma* Atsushi Shibata, MD; Toshio Katsunuma, MD, PhD; Morimitsu Tomikawa, MD; Aiko Tan, MD; Keisuke
CHEST Original Research Increased Leukotriene E 4 in the Exhaled Breath Condensate of Children With Mild Asthma* Atsushi Shibata, MD; Toshio Katsunuma, MD, PhD; Morimitsu Tomikawa, MD; Aiko Tan, MD; Keisuke
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 120 No 1267 ISSN 1175 8716 Is Salamol less effective than Ventolin? A randomised, blinded, crossover study in New Zealand Catherina L Chang, Manisha Cooray, Graham Mills,
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 120 No 1267 ISSN 1175 8716 Is Salamol less effective than Ventolin? A randomised, blinded, crossover study in New Zealand Catherina L Chang, Manisha Cooray, Graham Mills,
Asthma: Chronic Management. Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015
 Asthma: Chronic Management Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015 Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Evidence-based Implementation
Asthma: Chronic Management Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015 Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Evidence-based Implementation
Benzalkonium Chloride Induced Bronchoconstriction in Patients with Stable Bronchial Asthma
 The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine : 22:244-248, 2007 Benzalkonium Chloride Induced Bronchoconstriction in Patients with Stable Bronchial Asthma Byoung Hoon Lee, M.D. and Sang-Hoon Kim, M.D. Department
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine : 22:244-248, 2007 Benzalkonium Chloride Induced Bronchoconstriction in Patients with Stable Bronchial Asthma Byoung Hoon Lee, M.D. and Sang-Hoon Kim, M.D. Department
Content Indica c tion Lung v olumes e & Lung Indica c tions i n c paci c ties
 Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Clinical trial efficacy: What does it really tell you?
 Clinical trial efficacy: What does it really tell you? Joseph Spahn, MD Denver, Colo The primary goal of most clinical trials is an evaluation of the efficacy of the drug being evaluated. Therefore, it
Clinical trial efficacy: What does it really tell you? Joseph Spahn, MD Denver, Colo The primary goal of most clinical trials is an evaluation of the efficacy of the drug being evaluated. Therefore, it
Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies
 Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies Stanley J. Szefler, MD Helen Wohlberg and Herman Lambert Chair in Pharmacokinetics, Head, Pediatric
Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies Stanley J. Szefler, MD Helen Wohlberg and Herman Lambert Chair in Pharmacokinetics, Head, Pediatric
MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C
 MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C Explain the importance of objective measures in the management of asthma Explain the different types of objective measures used in the management
MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C Explain the importance of objective measures in the management of asthma Explain the different types of objective measures used in the management
Borg scores before and after challenge with adenosine 5'-monophosphate and methacholine in subjects with COPD and asthma
 Eur Respir J 2000; 16: 486±490 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2000 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Borg scores before and after challenge with adenosine 5'-monophosphate
Eur Respir J 2000; 16: 486±490 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2000 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Borg scores before and after challenge with adenosine 5'-monophosphate
**This form MUST accompany a TUE Application for a Beta-2 Agonist if submitted to USADA**
 **This form MUST accompany a TUE Application for a Beta-2 Agonist if submitted to USADA** PHYSICIAN- You must select one of the Objective Tests in the Table below and report the result. Please take note
**This form MUST accompany a TUE Application for a Beta-2 Agonist if submitted to USADA** PHYSICIAN- You must select one of the Objective Tests in the Table below and report the result. Please take note
Q: Should patients with mild asthma
 1-MINUTE CONSULT CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider prescribing inhaled corticosteroids to their patients who have mild persistent asthma brief answers to specific clinical questions
1-MINUTE CONSULT CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider prescribing inhaled corticosteroids to their patients who have mild persistent asthma brief answers to specific clinical questions
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION
 ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
Low- and high-dose fluticasone propionate in asthma; effects during and after treatment
 Eur Respir J 2000; 15: 11±18 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2000 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Low- and high-dose fluticasone propionate in asthma; effects
Eur Respir J 2000; 15: 11±18 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2000 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Low- and high-dose fluticasone propionate in asthma; effects
Bronchial asthma. MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL
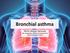 Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
The FDA Critical Path Initiative
 The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment. John R. Holcomb, M.D.
 Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
TUE PHYSICIAN GUIDELINES Medical Information to Support the Decisions of TUE Committees Asthma ASTHMA
 1. Medical Condition ASTHMA is a syndrome of the respiratory airways manifested by recurrent episodic symptoms. It is associated with variable airway obstruction that is reversible either spontaneously
1. Medical Condition ASTHMA is a syndrome of the respiratory airways manifested by recurrent episodic symptoms. It is associated with variable airway obstruction that is reversible either spontaneously
12/18/2017. Disclosures. Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University
 Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
Preschool Asthma What you need to know in 10 minutes
 Preschool Asthma What you need to know in 10 minutes Alan Kaplan MD CCFP(EM) FCFP Family Physician Airways Group of Canada Respiratory Medicine section CFPC Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Alan Kaplan
Preschool Asthma What you need to know in 10 minutes Alan Kaplan MD CCFP(EM) FCFP Family Physician Airways Group of Canada Respiratory Medicine section CFPC Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Alan Kaplan
Asthma. Don Hayes, Jr., MD, FAAP, FACP
 Asthma Don Hayes, Jr., MD, FAAP, FACP Director, University of Kentucky Asthma Center Kentucky Children s Hospital & Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Internal Medicine University of Kentucky College
Asthma Don Hayes, Jr., MD, FAAP, FACP Director, University of Kentucky Asthma Center Kentucky Children s Hospital & Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Internal Medicine University of Kentucky College
2/12/2015. ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang. Asthma General Information. Asthma General Information
 ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
Effects of Terbutaline and Budesonide on Sputum Cells and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness In Asthma
 Effects of Terbutaline and Budesonide on Sputum Cells and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness In Asthma RUTH E. ALDRIDGE, ROBERT J. HANCOX, D. ROBIN TAYLOR, JAN O. COWAN, MARTI C. WINN, CHRIS M. FRAMPTON, and
Effects of Terbutaline and Budesonide on Sputum Cells and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness In Asthma RUTH E. ALDRIDGE, ROBERT J. HANCOX, D. ROBIN TAYLOR, JAN O. COWAN, MARTI C. WINN, CHRIS M. FRAMPTON, and
Asthma in Day to Day Practice
 Asthma in Day to Day Practice VIJAY.K.VANAM Financial relationships: Disclosures Employed at Mercy Medical Center, Mason City. Nonfinancial relationships: I receive no financial gain from any pharmaceutical
Asthma in Day to Day Practice VIJAY.K.VANAM Financial relationships: Disclosures Employed at Mercy Medical Center, Mason City. Nonfinancial relationships: I receive no financial gain from any pharmaceutical
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction
 Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Is reslizumab effective in improving quality of life and asthma control in adolescent and adult patients with poorly controlled eosinophilic asthma?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
James P. Kemp, MD; Margaret C. Minkwitz, PhD; Catherine M. Bonuccelli, MD; and Marshelle S. Warren, MD
 Therapeutic Effect of Zafirlukast as Monotherapy in Steroid-Naive Patients With Severe Persistent Asthma* James P. Kemp, MD; Margaret C. Minkwitz, PhD; Catherine M. Bonuccelli, MD; and Marshelle S. Warren,
Therapeutic Effect of Zafirlukast as Monotherapy in Steroid-Naive Patients With Severe Persistent Asthma* James P. Kemp, MD; Margaret C. Minkwitz, PhD; Catherine M. Bonuccelli, MD; and Marshelle S. Warren,
Methacholine versus Mannitol Challenge in the Evaluation of Asthma Clinical applications of methacholine and mannitol challenges
 Methacholine versus Mannitol Challenge in the Evaluation of Asthma Clinical applications of methacholine and mannitol challenges AAAAI San Antonio Tx February 2013 Catherine Lemière MD, MSc Hôpital du
Methacholine versus Mannitol Challenge in the Evaluation of Asthma Clinical applications of methacholine and mannitol challenges AAAAI San Antonio Tx February 2013 Catherine Lemière MD, MSc Hôpital du
Respiratory Health L O O K, F E E L A N D L I V E B E T T E R
 LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BET TER Respiratory health: hay-fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay-fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body s immune system
LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BET TER Respiratory health: hay-fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay-fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body s immune system
