Spirometry Clinical Guideline V2.0. May 2018
|
|
|
- Penelope Whitehead
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spirometry Clinical Guideline V2.0 May 2018 Spirometry Clinical Guideline V2.0 1
2 Summary REFERRAL FOR SPIROMETRY QUALITY ASSURED SPIROMETRY PERFORMED BY TECHNICIAN TRAINED AND ASSESSED AS COMPETENT SPIROMETRY HARD COPY FILED IN MEDICAL NOTES SPIROMETRY INTERPRETED BY COMPETENT INTERPRETER PATIENT REVIEWED WITH DIAGNOSIS OR TREATMENT PLAN Page 2 of 20
3 Table of Contents 1. Introduction Purpose of this Policy/Procedure Scope Definitions / Glossary Ownership and Responsibilities... 5 The Respiratory Nurse Specialists are responsible for: Role of the Managers Role of Individual Staff Standards and Practice Dissemination and Implementation Monitoring compliance and effectiveness Updating and Review Equality and Diversity Appendix 1. Governance Information Appendix 2. Initial Equality Impact Assessment Form Page 3 of 20
4 1. Introduction 1.1 Spirometry is the recommended objective test performed to identify abnormalities in lung volumes and air flow. It is used in conjunction with physical assessment, history taking, blood tests and x-rays, to exclude or confirm particular types of lung disease, enabling timely diagnosis and treatment. 1.2 To be valid, spirometry that is used for diagnosis must be quality- assured and should only be performed by people who have been trained and assessed to ARTP or equivalent standards by recognised training bodies in the performance and interpretation of spirometry. Without this overall quality assurance, the accuracy of the diagnosis cannot be relied upon. 1.3 Spirometry is the standardised measurement of a forced expiration [and sometimes inspiration] into a calibrated measuring device called a spirometer. Spirometers are usually flow-measuring devices that use a variety of physical techniques [turbine, pneumotachograph, ultrasonic] to measure flow and then calculate volume with respect to time. 1.4 This version supersedes any previous versions of this document. 2. Purpose of this Policy/Procedure 2.1 This guideline shows how high quality diagnostic spirometry should be delivered. 2.2 It provides a clear outline covering operator competency, calibration and cleaning, preparation of the patient, operation of the equipment, interpretation of results and quality assurance. 3. Scope 3.1 This guideline applies to technicians performing spirometry and those interpreting spirometry. This includes nurses, physiologists, doctors and physiotherapists. 3.2 This will be implemented by the Respiratory Nurse Specialists. 3.3 This will be audited by the Respiratory Nurse Specialists. 4. Definitions / Glossary ARTP Association for Respiratory Technology and Physiology. BTS British Thoracic Society FEV1 Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second. The volume of air that can be forcefully expelled from the lungs within 1 second. FVC Forced Vital Capacity. The volume of air that can be forcefully expelled from the lungs, following fullest inspiration. LLN Lower Limit of Normal SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network SD Standard Deviation VC Vital Capacity. The volume of air that can be expelled from the lungs slowly, following deepest inspiration. Page 4 of 20
5 5. Ownership and Responsibilities The Respiratory Nurse Specialists are responsible for: Ensuring the guideline is suitable for purpose and is reviewed as required and at least every 3 years. Ensuring the guideline is disseminated to relevant healthcare professionals Ensuring training is arranged for healthcare professionals 5.1. Role of the Managers Line managers are responsible for: Ensuring that all staff are aware of and adhere to this guideline within their clinical areas Ensure staff are released for training, including up-dates when required 5.2. Role of Individual Staff All staff members are responsible for: Ensuring their individual practice reflects this guideline Ensuring they have been assessed as competent 6. Standards and Practice 6.1. Calibration Calibration of spirometry test equipment should be performed using a 3 litre syringe following the manufacturer s recommended procedures. For the device to be within calibration limits it must read +/- 3% of true. Calibration should be verified prior to every clinic / session or after every 10 th patient [whichever comes first]. A calibration log should be maintained Calibration standard Use an annually certificated calibration 3 litre syringe. Document calibration results consistently, including a simple log of any problems as they arise. Document all repairs and computer software updates related to each spirometer. The same member of staff should perform a biological control on a weekly basis, the results of which should be logged Performing Spirometry Step 1: Before day of test, decide what type of spirometry is required: Baseline spirometry to investigate lung function where diagnosis hasn t been established. Post-bronchodilator spirometry to investigate a diagnosis of obstructive conditions where baseline spirometry shows an obstructive pattern, or to monitor clinical progress in diagnosed COPD and asthma. Reversibility testing to hep differentiate between asthma and COPD. This is rarely required and differentiation is usually based on clinical features. Page 5 of 20
6 Step 2: Pre-test advice to patient [will depend on purpose of spirometry] Baseline spirometry - to establish diagnosis [if obstructive pattern proceed to post bronchodilator test.] Before test stop - short-acting bronchodilators for 4 hours long acting beta 2 agonist bronchodilators for 8 hours long acting anticholinergic bronchodilators for 36 hours but continue inhaled and oral steroids Monitoring existing conditions [perform post bronchodilator test] Before test, continue all usual inhaled therapy Reversibility testing Perform baseline test then post bronchodilator test. Before test stop short acting bronchodilators for 4 hours long acting beta 2 agonist bronchodilators for 8 hours long acting anticholinergic bronchodilators for 36 hours but continue inhaled steroids and oral steroids For all types of spirometry, ask the patient to avoid: smoking for at least 24 hours before test eating a large meal before the test vigorous exercise before the test wearing tight clothing 6.4. On day of test: Ask the patient to bring all their existing inhalers to the appointment Check for any contra-indications Check there is a prescription or a Patient Group Directive in place for reversibility testing Step 1 Assess the patient for contra-indications to spirometry Absolute recent surgery, within 6 weeks; including ophthalmic, thoracic, abdominal or neurosurgery [may cause serious consequences if aggravated by forced expiration] current pneumothorax [may cause serious consequences if aggravated by forced expiration] active infection such as AFB positive TB, until treated for 2 weeks. Page 6 of 20
7 Relative undiagnosed chest symptoms such as haemoptysis unstable vascular status, such as recent [within 1 month] myocardial infarction, uncontrolled hypertension, pulmonary embolism, history of haemorrhagic event [stroke] if the patient is too unwell to perform forced expiration communication problems, such as learning disability or confusion Step 2 Measure the patient s height without shoes [or arm span if unable to measure height] Weigh patient [provides useful information to the healthcare interpreting the results if they do not meet the patient in person] Age Ethnicity Enter these values into the spirometer as per manufacturer s instructions Step 3 Explain and demonstrate the procedure to the patient, ensuring they understand what is required of them and why it s important to perform each manoeuvre as best they can. You will need to explain the differences between the two different blows performed Vital Capacity (VC) and Forced Vital Capacity (FVC). Some patients may need to perform both, several times. Inform the patient of any possible side-effects they may experience, such as light-headedness Step 4 Prepare patient and equipment to perform baseline VC Standard for VC Seat patient comfortably in a chair with arms Wash your hands Attach a bacterial / viral filter to handset Apply a nose-clip Instruct patient to take their fullest breath in, [maximal inspiration] place lips around the mouth-piece before blowing out long and slow They must ensure the mouthpiece is not obstructed by lips or tongue Ensure there are no leaks from the mouthpiece Remove false teeth if loose A minimum of 3 acceptable VC manoeuvres must be obtained A repeatability criteria is met when there is no more than 100ml ideally and certainly no more than 150ml between Page 7 of 20
8 each blow. Some spirometers will inform the user when this has been achieved Verbally encourage patient to exhale as long as possible This will usually be achieved within 4 VC manoeuvres If patient unable to achieve the quality criteria, record why this has not been possible Step 5 Prepare the patient and the equipment to perform a baseline FVC Standard for FVC Seat patient comfortably in a chair with arms [A nose-clip is not essential ] Wash your hands Attach a bacterial / viral filter to handset Instruct patient to take their fullest breath in, [maximal inspiration] place lips around the mouthpiece before blowing out as hard and fast as possible, for as long as possible They must ensure the mouthpiece is not obstructed by lips or tongue Ensure there are no leaks from the mouthpiece Remove false teeth if loose Verbally encourage patient to exhale for as long as possible Observe each FVC manoeuvre to identify slow starts, early stops or variability in flow Ensure patient exhales fully and that this is demonstrated on the graph, showing a time / volume plateau A minimum of 3 acceptable FVC manoeuvres must be obtained Repeatability criteria is met when there is no more than 100ml ideally and certainly no more than 150ml between each blow. Some spirometers will inform the user when this has been achieved. Do not attempt more than 8 FVC manoeuvres in one session If patient unable to achieve the quality criteria, record why this has not been possible and arrange another appointment if appropriate Step 6 Record baseline spirometry results in electronic or paper template, using the largest FEV1 and VC or FVC to determine the FEV1 / VC or FEV1 / FVC ratio Step 7 Post bronchodilator testing. Page 8 of 20
9 This should be performed if baseline spirometry reveals an obstructive picture, if reversibility testing is required to differentiate between asthma and COPD; and for chronic disease monitoring. The standard Administer bronchodilator [usually 4 x 100mcg salbutamol as single puffs via a spacer or 2.5mg via nebuliser] Perform spirometry after 15 minutes Step 8 Record post-bronchodilator spirometry results in electronic format or paper template, using the largest of the postbronchodilator FEV1 and largest VC or FVC, to determine the FEV1 / VC ratio. Attach to patient s healthcare records. The standard In primary care the VC should always be measured and recorded as well as the FVC. The ratio should be calculated using whichever is the higher of the VC measurements, the baseline VC or FVC Both the flow volume / volume and time / volume graphs must be documented in patient s healthcare records Spirometry reporting across healthcare communities should be in a uniform manner Step 9 Infection prevention: The standard Wash your hands before start of procedure Dispose of waste in line with the Trust waste management procedure. The single use bacterial / viral filter should be disposed of in a clinical waste bin. Wash your hands. Follow the manufacturer s guidelines on cleaning the outside of the equipment after each use. Wash your hands Follow the manufacturer s guidelines on thorough weekly cleaning where certain elements are taken apart, washed, disinfected and dried, before placing together again. [see below] Step 10 Arrange interpretation of the spirometry results by a competent interpreter [see below] Step 11 Ensure the patient has a follow-up appointment to discuss the results and arrange on-going management. Page 9 of 20
10 6.5. Interpreting spirometry results: The interpreter must be trained and assessed to ARTP or equivalent standards, in the interpretation of spirometry Step 1 Select the best value for clinical use The standard Obtain 3 technically acceptable results from a maximum of 8 efforts Repeatability criteria are met when there is no more than 100mls ideally [or 150mls in the occasional highly variable patient] between each blow Highest FEV1, VC and FVC from 3 efforts, meeting repeatability criteria or within 5% of each other whichever is smaller [below 1 litre] or higher [above 1 litre] The highest FEV1, VC or FVC can come from any one of the efforts [they don t have to come from the same blow] Step 2 Reference values for clinical use. See section below on Reference Values from 16 th May 2018 Predicted values and normal ranges can be obtained from reference tables and are calculated from: Patient s height in metres, age in years and sex to calculate the mean predicted values for FEV1, VC and FVC The actual best measurement and the mean predicted value is used to calculate the % predicted value The lower limit of normal [LLN] or range is calculated from the mean predicted value and the residual deviation from the mean predicted value and the residual standard deviation the standardised residual [RD] or Z-score is calculated. Z-score value below 1.64 signifies a 95% chance of the value being outside the normal reference range and is therefore abnormal] Step 3 Reporting spirometry results Standard Adherence to criteria for preparation and performance should be reported. The results should be reported with graphs of volume / time and flow / volume and a clear table of results showing FEV1, VC and FVC Results should show Patient s actual values Mean predicted values % predicted value [LLN or range] Abnormal values should be highlighted Standard Residual or Z-score Page 10 of 20
11 Reference Values As from 16th May 2018 Historically, predicted values and normal ranges have been derived from the ECSC reference values. However, in 2012, the Global Lung Initiative [GLI] published multi-ethnic reference values for spirometry, for the 3 95 years age range. The Trust will start using these reference values from 16th May 2018 once the Full Lung Function machine in the Respiratory Physiology laboratory has been replaced, which will be set to use the GLI reference values. If you are using a Vitalograph digital spirometer, such as the Alpha Touch model or similar, please set your reference values to the GLI setting on 16 th May If you are manually calculating reference values, use this link: excel-individual-calculator.html You will notice that the percentage of predicted measurements are lower than the old reference values, but are much more accurate and up-to-date. Remember to look at the actual patient measurements [as well as the percentages] Step 4 Storing and communicating results. Procedures for data storage should ensure: Store spirometers which contain patient details in a safe place [treat them as you would medical notes] Heat sensitive paper traces should be photocopied or scanned as they can fade with time Good quality reports with minimum patient details to comply with information governance procedures Facility to share results between primary care and secondary care Step 5 Interpretation of spirometry It is important not to interpret the spirometry results in isolation. Diagnosis should always be based on the history, examination and airflow. If results show an obstructive picture, severity should be graded as per NICE 2010 If the pattern is obstructive, grading of severity as per NICE 2010 / GOLD Any comment on the quality of the measurements Summary statement answering the original question asked by the referrer Suggestions on further tests, urgent treatments or referral to a specialist Page 11 of 20
12 6.6. Spirometry results can show the following patterns: Normal Obstructive Restrictive Mixed Obstructive abnormalities: The presence of airway obstruction is suggested by a reduced FEV1 / FVC ratio. The expiratory flow volume curve will appear concave. Some organisations have tried to simplify this with a fixed cut-off point of 0.7 however, since the FEV1 / FVC ratio is dependent on age, height and sex, this leads to over-diagnosis of obstruction in elderly patients and to under-diagnosis in young patients. Therefore the presence of obstructive lung disease should be based on an FEV1 / FVC ratio below the LLN Restrictive abnormalities: This is characterised by a normal or increased FEV1 / FVC ratio and a low FEV1 and low FVC. The flow volume curve will appear convex. The most common cause of a restrictive picture is poor technique [premature termination of the FVC manoeuvre or failure to perform maximum inhalation] Mixed abnormalities: This is characterised when a true restrictive ventilatory defect occurs concurrently with airway obstruction. Both FVC and FEV1 / FVC ratio are below their LLN. This diagnosis cannot be made on the basis of spirometry alone and may require referral to the pulmonary function laboratory to measure total lung capacity and gas transfer Severity of lung function impairment Generally, severity of lung function impairment is based on FEV1 % predicted Severity of Airway Obstruction in COPD [based on post-broncho-dilator FEV1] FEV1 as a percentage of the predicted / reference value in patients with FEV1 / FVC <0.7 Degree of severity Stage NICE 2010 / Gold 2017 FEV1 % predicted Mild I > 80 Moderate II Severe III Very severe IV < 30 Page 12 of 20
13 Reversibility interpretation: Use this calculation to work out percentage changes between baseline spirometry and 15 minutes post bronchodilator: post FEV1 pre FEV1 X 100% = pre FEV1 Some digital spirometers will calculate this for you. BTS / SIGN Asthma guideline September 2016 Increase in FEV1 > 12% + 200ml = reversible Increase in FEV1 > 400ml = strongly suggests asthma Quality assurance of diagnostic spirometry To be of clinical value, diagnostic spirometry must be performed to a high standard. Providers of this service need to provide assurance that every spirometry test meets the required standards. To demonstrate quality assurance, providers should: Ensure equipment and processes meet the standards in this guide. Ensure that all staff performing spirometry are trained and assessed to ARTP or equivalent standards. They should receive regular up-dating and demonstrate competence. Ensure that all staff responsible for interpreting spirometry are trained and assessed to ARTP or equivalent standards and that they receive regular up-dating and demonstrate competence. Conduct quality control checks at least weekly to ensure reliability and reproducibility of results. These should use physical checks [with a calibration syringe done daily] and biological controls using one member of staff with healthy lungs [see below] Maintain a log of:- Calibration and verification records Biological controls 6.7. Biological Control Data: Select biological controls that are fit and healthy aged years, with no respiratory symptoms, no lung disease and not in the 3 rd trimester of pregnancy. Establish normal range and variation of FEV1, FVC and VC for the biological control by obtaining 20 measurements over 10 sessions on different days. Obtain the mean SD for each index and plot these on a graph with the mean value and +/- 1SD and +/- 2SD On subsequent measurements, obtain the FEV1, FVC and VC for the control. Page 13 of 20
14 Plot out the new data to ensure that values are within 1SD of the mean. If so, testing patients can proceed. If data are between 1SD and 2SD, an error has been highlighted. Recalibrate spirometer and check circuit. Repeat data biological control data. If error remains, withdraw equipment from use and send to Medical Physics Department for assessment. Spirometer may need to be returned to the manufacturer Cleaning and disinfection of equipment: Follow manufacture s guidance Re: Alpha touch 6000 model After each use Wipe outside casing with detergent wipes or 70% alcohol wipes ensuring screen does not come into contact with alcohol wipes A new bacterial / viral filter to be used with each patient Weekly The complete Fleisch flowhead should be disassembled and cleaned. The flowhead body should be wiped with 70% alcohol wipes. The remaining parts of the Fleisch element should be swilled vigorously in warm soapy water and rinsed. All parts of the flowhead, except the flowhead body, should be disinfected in a solution of actichlor, 1 tablet per 1litre water strength, for 15 minutes. Rinse with distilled water. [distilled water can be purchased from Unit 4 under Cow and Gate sterilised water, ingredients = demineralised water, in 90 ml bottles. You ll require 5 x 90ml bottles to rinse the parts thoroughly]. Leave to dry thoroughly, [at least over - night] before re-assembling. Check all parts for wear or damage [details for obtaining replacement parts can be found in the User Training Manual.] 7. Dissemination and Implementation The guideline will be found in the RCHT documents library and disseminated at the Respiratory Governance meetings. This guideline will replace Clinical Guideline in Spirometry version 1. The guideline will be implemented by provision of training supplied by the Respiratory Nurse Specialists. Training needs and practice changes will be discussed at ward meetings where spirometry is performed. Support will be provided in small group sessions during the Mash Up Monday nurse training sessions. Theoretical knowledge of the guideline will be enhanced in the form of the up-dated Spirometry Self-Directed Learning Pack. Page 14 of 20
15 8. Monitoring compliance and effectiveness Element to be monitored Lead Tool Frequency Reporting arrangements Acting on recommendations and Lead(s) Change in practice and lessons to be shared The whole guideline will be monitored The Respiratory Nurse specialists will lead the process [Ruth Holding and Julie Jephson Audit, in the form of direct observation, portfolio of evidence and questioning Monitoring will be completed 3 yearly Audit reports will be presented at the Respiratory Governance meetings, to the Governance Lead and other healthcare professionals. It is the Lead s responsibility to read and interrogate the report to identify discrepancies in the system and act on them. The Governance Lead will undertake subsequent recommendations and action planning following consultation with the Respiratory Nurse Specialists within 2 months of receiving audit report. Practice changes will be shared during Governance meetings, ward meetings and during training sessions / up-dates. Required changes to practice will be identified and actioned within 3 months. Ruth Holding and Julie Jephson will take each change forward in the form of practical training sessions. 9. Updating and Review The guideline will be reviewed in 3 years or sooner if any major revisions are required. 10. Equality and Diversity This document complies with the Royal Cornwall Hospitals NHS Trust service Equality and Diversity statement which can be found in the 'Equality, Diversity & Human Rights Policy' or the Equality and Diversity website Royal Cornwall Hospitals NHS Trust is committed to a Policy of Equal Opportunities in employment. The aim of this policy is to ensure that no job applicant or employee receives less favourable treatment because of their race, colour, nationality, ethnic or national origin, or on the grounds of their age, gender, gender reassignment, marital status, domestic circumstances, disability, HIV status, sexual orientation, religion, belief, political affiliation or trade union membership, social or employment status or is disadvantaged by conditions or requirements which are not justified by the job to be done. This policy concerns all aspects of employment for existing staff and potential employees Equality Impact Assessment The Initial Equality Impact Assessment Screening Form is at Appendix 2. Page 15 of 20
16 Appendix 1. Governance Information Document Title Spirometry Clinical Guideline v2.0 Date Issued/Approved: Date Valid From: Date Valid To: Directorate / Department responsible (author/owner): Ruth Holding Respiratory Clinical Nurse Specialist Contact details: Brief summary of contents Suggested Keywords: Target Audience Executive Director responsible for Policy: A guideline to show health professionals how high quality diagnostic spirometry can be delivered. Spirometry, lung function, pulmonary disease, breathing test, pulmonary function, ARTP, COPD RCHT CPFT KCCG Medical director Date revised: This document replaces (exact title of previous version): Approval route (names of committees)/consultation: Clinical Guideline for Spirometry V1.0 Respiratory Department and Governance Lead Divisional Manager confirming approval processes Margaret Dalziel Name and Post Title of additional signatories Name and Signature of Divisional/Directorate Governance Lead confirming approval by specialty and divisional management meetings {Original Copy Signed} Name: Tim Mumford Signature of Executive Director giving approval Publication Location (refer to Policy on Policies Approvals and Ratification): {Original Copy Signed} Internet & Intranet Page 16 of 20 Intranet Only
17 Document Library Folder/Sub Folder Links to key external standards Related Documents: Training Need Identified? Clinical/Respiratory Association for Respiratory Technology and Physiology. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network 2016 British Thoracic Society. Asthma guideline. Yes, the Respiratory Nurse Specialists will need to provide training and assessments. The Learning and Development department have been informed of the training needs Version Control Table Date Version No V1.0 Initial issue Summary of Changes Changes Made by (Name and Job Title) Ruth Holding Respiratory Nurse Specialist V2.0 Up-dated guideline, up-dated IEIA form and up-dated Governance Information form Ruth Holding Respiratory Nurse Specialist All or part of this document can be released under the Freedom of Information Act 2000 This document is to be retained for 10 years from the date of expiry. This document is only valid on the day of printing Controlled Document This document has been created following the Royal Cornwall Hospitals NHS Trust Policy on Document Production. It should not be altered in any way without the express permission of the author or their Line Manager. Page 17 of 20
18 Appendix 2. Initial Equality Impact Assessment Form Name of the strategy / policy /proposal / service function to be assessed Spirometry Clinical Guideline V2.0 Directorate and service area: Is this a new or existing Policy? Medical Directorate / Respiratory Existing policy Name of individual completing assessment: Telephone: Ruth Holding Policy Aim* This guideline shows how high quality diagnostic spirometry can be delivered. It provides a clear outline covering operator competency, calibration and cleaning, preparation of the patients, operation of the equipment, interpretation of the results and quality assurance. Who is the strategy / policy / proposal / service function aimed at? This guideline is aimed at nurses, respiratory physiologists, physiotherapists, doctors 2. Policy Objectives* To ensure spirometry is performed to a quality assured standard 3. Policy intended Outcomes* 4. *How will you measure the outcome? 5. Who is intended to benefit from the policy? 6a Who did you consult with b). Please identify the groups who have been consulted about this procedure. What was the outcome of the consultation? All operators will be trained and assessed as being competent at performing spirometry, [to provide reliable results to support diagnosis and treatment] Audit Patients requiring respiratory investigations Workforce Patients Local groups External organisations Other Please record specific names of groups Respiratory consultants, Respiratory nurses, Respiratory Physiologist, Respiratory and Cardiology ward managers and manager of Cardiac Investigation Unit have received a copy of this guideline and have had the chance to contribute and provide feedback. This guideline will be discussed at the Respiratory Governance meeting 7. The Impact Please complete the following table. If you are unsure/don t know if there is a negative impact you need to repeat the consultation step. Are there concerns that the policy could have differential impact on: Equality Strands: Yes No Unsure Rationale for Assessment / Existing Evidence Age X Page 18 of 20
19 Sex (male, female, trans-gender / gender reassignment) Race / Ethnic communities /groups Disability - Learning disability, physical impairment, sensory impairment, mental health conditions and some long term health conditions. Religion / other beliefs Marriage and Civil partnership Pregnancy and maternity X X X X X X Sexual X Orientation, Bisexual, Gay, heterosexual, Lesbian You will need to continue to a full Equality Impact Assessment if the following have been highlighted: You have ticked Yes in any column above and No consultation or evidence of there being consultation- this excludes any policies which have been identified as not requiring consultation. or Major this relates to service redesign or development 8. Please indicate if a full equality analysis is recommended. Yes No X 9. If you are not recommending a Full Impact assessment please explain why. Signature of policy developer / lead manager / director Ruth Holding Date of completion and submission Names and signatures of members carrying out the Screening Assessment 1. Ruth Holding 2. Human Rights, Equality & Inclusion Lead Keep one copy and send a copy to the Human Rights, Equality and Inclusion Lead Page 19 of 20
20 c/o Royal Cornwall Hospitals NHS Trust, Human Resources Department, Knowledge Spa, Truro, Cornwall, TR1 3HD This EIA will not be uploaded to the Trust website without the signature of the Human Rights, Equality & Inclusion Lead. A summary of the results will be published on the Trust s web site. Signed Ruth Holding Date Page 20 of 20
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF NEBULISED PENTAMIDINE Summary. 1.
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF NEBULISED PENTAMIDINE Summary. 1. Patient requires nebulised Pentamidine Ensure equipment listed is available Ensure HEPA filtered room in Haematology Clinic
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF NEBULISED PENTAMIDINE Summary. 1. Patient requires nebulised Pentamidine Ensure equipment listed is available Ensure HEPA filtered room in Haematology Clinic
Blood Glucose and Hyperglycaemia Management in Hospital for Adults with Diabetes Clinical Guideline V2.0. March 2018
 Blood Glucose and Hyperglycaemia Management in Hospital for Adults with Diabetes Clinical Guideline V2.0 March 2018 Page 1 of 8 Summary flow chart for monitoring of blood glucose if >11mmol/L For Adults
Blood Glucose and Hyperglycaemia Management in Hospital for Adults with Diabetes Clinical Guideline V2.0 March 2018 Page 1 of 8 Summary flow chart for monitoring of blood glucose if >11mmol/L For Adults
28 th September Author Jeremy Gilbert Bariatric Nurse Specialist
 POLICY FOR SELF ADMINISTRATION OF CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE BY COMPETENT PATIENTS COMING IN FOR METABOLIC AND OBESITY SURGERY (BARIATRIC SURGERY) TO PENDENNIS WARD 28 th September 2014 Author
POLICY FOR SELF ADMINISTRATION OF CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE BY COMPETENT PATIENTS COMING IN FOR METABOLIC AND OBESITY SURGERY (BARIATRIC SURGERY) TO PENDENNIS WARD 28 th September 2014 Author
SALBUTAMOL INHALER PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION CHILD HEALTH 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 SALBUTAMOL INHALER PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION CHILD HEALTH 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This Patient Group Direction (PGD) applies to all nursing and clinical staff in the Child Health Department
SALBUTAMOL INHALER PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION CHILD HEALTH 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This Patient Group Direction (PGD) applies to all nursing and clinical staff in the Child Health Department
Clinical Guideline for Intravenous Opioids for Adults in Recovery Areas The Recovery Protocol
 Clinical Guideline for Intravenous Opioids for Adults in Recovery Areas The Recovery Protocol 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. To Provide safe and efficient administration of Opioids in Recovery.
Clinical Guideline for Intravenous Opioids for Adults in Recovery Areas The Recovery Protocol 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. To Provide safe and efficient administration of Opioids in Recovery.
Spirometry in primary care
 Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT S OESOPHAGUS Summary.
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT S OESOPHAGUS Summary. Page 1 of 12 Recurrent LGD at any point- discuss at MDT And consider RFA Patients with LGD should have a repeat endoscopy in 6 months.
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT S OESOPHAGUS Summary. Page 1 of 12 Recurrent LGD at any point- discuss at MDT And consider RFA Patients with LGD should have a repeat endoscopy in 6 months.
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF PYLORIC STENOSIS IN CHILDREN CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0
 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF PYLORIC STENOSIS IN CHILDREN CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline This guideline is relevant to all medical and nursing staff caring for children with Pyloric
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF PYLORIC STENOSIS IN CHILDREN CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline This guideline is relevant to all medical and nursing staff caring for children with Pyloric
School Hearing Screening Policy
 School Hearing Screening Policy V2.1 1st August 2017 Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this Policy... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. Definitions / Glossary... 3 5. Ownership and Responsibilities...
School Hearing Screening Policy V2.1 1st August 2017 Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this Policy... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. Definitions / Glossary... 3 5. Ownership and Responsibilities...
METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0
 METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 Page 1 of 10 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline To provide guidance on the prevention of metabolic bone disease in the neonate. All
METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 Page 1 of 10 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline To provide guidance on the prevention of metabolic bone disease in the neonate. All
SPIROMETRY. Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: Copyright CARE Medical ltd
 SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual can
SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual can
1.1. This guideline applies to medical, nursing and pharmacy staff in the safe and appropriate prescription and administration of acamprosate.
 SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR ACAMPROSATE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical, nursing and pharmacy staff in the safe and appropriate prescription and administration of
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR ACAMPROSATE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical, nursing and pharmacy staff in the safe and appropriate prescription and administration of
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF MESNA WITH IFOSFAMIDE AND CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE Summary.
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF MESNA WITH IFOSFAMIDE AND CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE Summary. Yes Is patient prescribed ifosfamide or cyclophosphamide >1g/m 2? Chemotherapy prescription on Aria should
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF MESNA WITH IFOSFAMIDE AND CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE Summary. Yes Is patient prescribed ifosfamide or cyclophosphamide >1g/m 2? Chemotherapy prescription on Aria should
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR BUCCAL MIDAZOLAM FOR THE TREATMENT OF PROLONGED SEIZURES IN CHILDREN
 SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR BUCCAL MIDAZOLAM FOR THE TREATMENT OF PROLONGED SEIZURES IN CHILDREN 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical, nursing and pharmacy staff in the
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR BUCCAL MIDAZOLAM FOR THE TREATMENT OF PROLONGED SEIZURES IN CHILDREN 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical, nursing and pharmacy staff in the
BETTER SPIROMETRY. Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: Copyright CARE Medical ltd
 BETTER SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual
BETTER SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual
Named Responsible Officer Approved By Date. Clinical Services Manager Clinical Procedures Group July 2010
 PROCEDURE FOR THE USE OF SPIROMETRY IN WIRRAL INTERMEDIATE CARDIAC CLINICS (WICC) Issue History October 2006 July 2010 Issue Version Two Purpose of issue/description of change To assist WICC practitioners
PROCEDURE FOR THE USE OF SPIROMETRY IN WIRRAL INTERMEDIATE CARDIAC CLINICS (WICC) Issue History October 2006 July 2010 Issue Version Two Purpose of issue/description of change To assist WICC practitioners
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS IN ADULT CANCER PATIENTS (this guideline excludes haematology patients)
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS IN ADULT CANCER PATIENTS (this guideline excludes haematology patients) 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Systemic cancer treatments and immunological
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS IN ADULT CANCER PATIENTS (this guideline excludes haematology patients) 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Systemic cancer treatments and immunological
PRESEPTAL AND ORBITAL CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN- CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0
 PRESEPTAL AND ORBITAL CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN- CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 Page 1 of 8 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical and nursing staff caring for a child with Preseptal
PRESEPTAL AND ORBITAL CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN- CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 Page 1 of 8 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical and nursing staff caring for a child with Preseptal
MANAGEMENT OF THE BLADDER IN THE POSTOPERATIVE PERIOD FOLLOWING UNCOMPLICATED GYNAECOLOGICAL SURGERY CLINICAL GUIDELINES
 MANAGEMENT OF THE BLADDER IN THE POSTOPERATIVE PERIOD FOLLOWING UNCOMPLICATED GYNAECOLOGICAL SURGERY CLINICAL GUIDELINES 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline All clinical staff working in the Division of women,
MANAGEMENT OF THE BLADDER IN THE POSTOPERATIVE PERIOD FOLLOWING UNCOMPLICATED GYNAECOLOGICAL SURGERY CLINICAL GUIDELINES 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline All clinical staff working in the Division of women,
Fasting for Adults (including Young Adults Age 16+ years) who require Anaesthesia or Intravenous Sedation Clinical Guideline V5.0
 Fasting for Adults (including Young Adults Age 16+ years) who require Anaesthesia or Intravenous Sedation November 2018 Summary. Fasting for Adults (including Young Adults Age 16+ years) who require Anaesthesia
Fasting for Adults (including Young Adults Age 16+ years) who require Anaesthesia or Intravenous Sedation November 2018 Summary. Fasting for Adults (including Young Adults Age 16+ years) who require Anaesthesia
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN UNDER SIXTEEN YEARS OF AGE V3.0
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ANAPHYLAIS IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN UNDER SITEEN YEARS OF AGE V3.0 Page 1 of 16 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. The purpose of this guideline is to provide
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ANAPHYLAIS IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN UNDER SITEEN YEARS OF AGE V3.0 Page 1 of 16 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. The purpose of this guideline is to provide
Start. What is the serum phosphate concentration? Moderate Hypophosphataemia mmol/l. Replace using oral. phosphate. (See section 3.
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPOPHOSPHATAEMIA IN ADULTS Summary. Key: General Notes GP/SWASFT ED/MAU/SRU/Acute GP/Amb-Care In-patient wards Start What is the serum concentration? Mild Hypophosphataemia
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPOPHOSPHATAEMIA IN ADULTS Summary. Key: General Notes GP/SWASFT ED/MAU/SRU/Acute GP/Amb-Care In-patient wards Start What is the serum concentration? Mild Hypophosphataemia
HYPOSPADIAS NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE. 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline. 2. The Guidance
 HYPOSPADIAS NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to all staff managing the initial care of infants born with hypospadias. It includes assessment and
HYPOSPADIAS NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to all staff managing the initial care of infants born with hypospadias. It includes assessment and
How to Perform Spirometry
 Purpose How to Perform Spirometry This guideline provides recommendations regarding best practice to support high quality spirometry practice for KINNECT Pre-Employment Medicals. Scope This guideline provides
Purpose How to Perform Spirometry This guideline provides recommendations regarding best practice to support high quality spirometry practice for KINNECT Pre-Employment Medicals. Scope This guideline provides
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPOKALAEMIA
 POLICY UNDER REVIEW Please note that this policy is under review. It does, however, remain current Trust policy subject to any recent legislative changes, national policy instruction (NHS or Department
POLICY UNDER REVIEW Please note that this policy is under review. It does, however, remain current Trust policy subject to any recent legislative changes, national policy instruction (NHS or Department
Captopril and Enalapril (Ace Inhibitor) Therapy Clinical Guideline V1.0
 Captopril and Enalapril (Ace Inhibitor) Therapy Clinical Guideline V1.0 November 2018 Summary Prescribing, monitoring and administration of Captopril and Enalapril FOR STAFF PATIENTS Medical and Nursing
Captopril and Enalapril (Ace Inhibitor) Therapy Clinical Guideline V1.0 November 2018 Summary Prescribing, monitoring and administration of Captopril and Enalapril FOR STAFF PATIENTS Medical and Nursing
UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY. A. Definition of Spirometry
 UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY A. Definition of Spirometry Spirometry is a medical screening test that measures various aspects of breathing and lung function. It is performed by using a spirometer,
UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY A. Definition of Spirometry Spirometry is a medical screening test that measures various aspects of breathing and lung function. It is performed by using a spirometer,
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF GALLSTONES PATHOLOGY IN ADULTS
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF GALLSTONES PATHOLOGY IN ADULTS 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline This guideline is for the management of gallstones pathology in adults. It has been benchmarked against
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF GALLSTONES PATHOLOGY IN ADULTS 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline This guideline is for the management of gallstones pathology in adults. It has been benchmarked against
GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS AND SUBSEQUENT MANAGEMENT OF CONFIRMED GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS (GDM) AND SELECTIVE SCREENING - CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS AND SUBSEQUENT MANAGEMENT OF CONFIRMED GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS (GDM) AND SELECTIVE SCREENING - CLINICAL GUIDELINE V 1.5 2017 Screening - Clinical Guideline Page 1 of
GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS AND SUBSEQUENT MANAGEMENT OF CONFIRMED GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS (GDM) AND SELECTIVE SCREENING - CLINICAL GUIDELINE V 1.5 2017 Screening - Clinical Guideline Page 1 of
Clinical guideline for the introduction of Sacubitril Valsartan in primary and secondary care in Cornwall
 Clinical guideline for the introduction of Sacubitril Valsartan in primary and secondary care in Cornwall Page 1 of 15 Summary Patient clinically assessed and reviewed by a Consultant Cardiologist, Cardiology
Clinical guideline for the introduction of Sacubitril Valsartan in primary and secondary care in Cornwall Page 1 of 15 Summary Patient clinically assessed and reviewed by a Consultant Cardiologist, Cardiology
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY FOR ADULTS IN HOSPITAL 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY FOR ADULTS IN HOSPITAL 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline contains recommendations about general principles for managing intravenous (IV)
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY FOR ADULTS IN HOSPITAL 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline contains recommendations about general principles for managing intravenous (IV)
Spirometry: FEVER DISEASE DIABETES HOW RELIABLE IS THIS? 9/2/2010 BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools
 SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
Patient assessment - spirometry
 Patient assessment - spirometry STEP 1 Learning objectives This module will provide you with an understanding of spirometry and the role it plays in aiding the diagnosis of lung diseases, particularly
Patient assessment - spirometry STEP 1 Learning objectives This module will provide you with an understanding of spirometry and the role it plays in aiding the diagnosis of lung diseases, particularly
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR MODAFINIL 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline. 2. The Guidance
 SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR MODAFINIL 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical, nursing and pharmacy staff in the safe and appropriate prescription and administration of modafinil.
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR MODAFINIL 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical, nursing and pharmacy staff in the safe and appropriate prescription and administration of modafinil.
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR RIFAXIMIN FOR PREVENTING EPISODES OF OVERT HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY IN ADULT PATIENTS 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR RIFAXIMIN FOR PREVENTING EPISODES OF OVERT HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY IN ADULT PATIENTS 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical, nursing and pharmacy
SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR RIFAXIMIN FOR PREVENTING EPISODES OF OVERT HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY IN ADULT PATIENTS 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline applies to medical, nursing and pharmacy
2.0 Scope: This document is to be used by the DCS staff when collecting participants spirometry measurements using the TruFlow Easy-On Spirometer.
 Title: Spirometry Version Date: 2017-MAR-21 Document Effective Date: 2017-MAY-15 Number: Data Collection Site (DCS) Version: 2.3 Number of Pages: SOP_DCS_0012 6 1.0 Purpose: The purpose of this document
Title: Spirometry Version Date: 2017-MAR-21 Document Effective Date: 2017-MAY-15 Number: Data Collection Site (DCS) Version: 2.3 Number of Pages: SOP_DCS_0012 6 1.0 Purpose: The purpose of this document
Procedure for Subcutaneous Injection of Insulin or GLP1 Analogue in Adults Using a Pen Device V2.0
 Procedure for Subcutaneous Injection of Insulin or GLP1 Analogue in Adults Using a Pen Device V2.0 11 October 2017 Table of Contents 1. Introduction.. 3 2. Purpose of this Policy/Procedure. 3 3. Scope
Procedure for Subcutaneous Injection of Insulin or GLP1 Analogue in Adults Using a Pen Device V2.0 11 October 2017 Table of Contents 1. Introduction.. 3 2. Purpose of this Policy/Procedure. 3 3. Scope
Spirometry: Introduction
 Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HIGH BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS AND SICK DAYS FOR INSULIN PUMP USERS UNDER THE PAEDIATRIC DIABETES SERVICE. V4.
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HIGH BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS AND SICK DAYS FOR INSULIN PUMP USERS UNDER THE PAEDIATRIC DIABETES SERVICE. V4.1 Page 1 of 11 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. The
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HIGH BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS AND SICK DAYS FOR INSULIN PUMP USERS UNDER THE PAEDIATRIC DIABETES SERVICE. V4.1 Page 1 of 11 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. The
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR NEONATAL BCG VACCINATION V3.0
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR NEONATAL BCG VACCINATION V3.0 Page 1 of 11 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Tuberculosis is a notifiable disease in the UK and although incidence is low it remains a Public
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR NEONATAL BCG VACCINATION V3.0 Page 1 of 11 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Tuberculosis is a notifiable disease in the UK and although incidence is low it remains a Public
Breathing and pulmonary function
 EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
SPIROMETRY TECHNIQUE. Jim Reid New Zealand
 Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements
 Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Hypoglycaemia in Adults with Diabetes Clinical Guideline V5.0. March 2018
 March 2018 Page 1 of 11 Adult with Diabetes and blood glucose < 4 mmol/l Treatment as per Guideline: Nursing / Clinical Staff Patient reviewed as per guideline guidance notes: Nursing / Clinical Staff
March 2018 Page 1 of 11 Adult with Diabetes and blood glucose < 4 mmol/l Treatment as per Guideline: Nursing / Clinical Staff Patient reviewed as per guideline guidance notes: Nursing / Clinical Staff
2.0 Scope: This document is to be used by the DCS staff when collecting participants spirometry measurements using the TruFlow Easy-On Spirometer.
 Title: Spirometry Version Date: 2014-AUG-20 Effective Date: 2014-OCT-15 Data Collection Site (DCS) Version: 2.2 Document Number: Number of Pages: SOP_DCS_0012 7 1.0 Purpose: The purpose of this document
Title: Spirometry Version Date: 2014-AUG-20 Effective Date: 2014-OCT-15 Data Collection Site (DCS) Version: 2.2 Document Number: Number of Pages: SOP_DCS_0012 7 1.0 Purpose: The purpose of this document
Patient Controlled Analgesia/Intravenous Opiate Infusion in Child Health Clinical Guideline V4.0 October 2018
 Patient Controlled Analgesia/Intravenous Opiate Infusion in Child Health Clinical Guideline V4.0 October 2018 Page 1 of 12 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline Guideline for children with a Patient Controlled
Patient Controlled Analgesia/Intravenous Opiate Infusion in Child Health Clinical Guideline V4.0 October 2018 Page 1 of 12 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline Guideline for children with a Patient Controlled
MANAGEMENT OF NEONATAL HYPOTENSION CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 MANAGEMENT OF NEONATAL HYPOTENSION CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. To provide guidance on the assessment and management of infants with hypotension. All involved will benefit from
MANAGEMENT OF NEONATAL HYPOTENSION CLINICAL GUIDELINE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. To provide guidance on the assessment and management of infants with hypotension. All involved will benefit from
File: Spirometry-Vimeo 720p-MP3 for Audio Podcasting.mp3 Duration: 0:07:09 Date: 05/02/2014 START AUDIO
 BMJ LEARNING VIDEO TRANSCRIPT File: Spirometry-Vimeo 720p-MP3 for Audio Podcasting.mp3 Duration: 0:07:09 Date: 05/02/2014 START AUDIO Dr Kevin Gruffyd-Jones: Spirometry is important in several ways. Firstly,
BMJ LEARNING VIDEO TRANSCRIPT File: Spirometry-Vimeo 720p-MP3 for Audio Podcasting.mp3 Duration: 0:07:09 Date: 05/02/2014 START AUDIO Dr Kevin Gruffyd-Jones: Spirometry is important in several ways. Firstly,
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR USE OF A PATIENT CONTROLLED ANALGESIA OR INTRAVENOUS OPIATE INFUSION IN CHILD HEALTH. 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR USE OF A PATIENT CONTROLLED ANALGESIA OR INTRAVENOUS OPIATE INFUSION IN CHILD HEALTH. 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline Guideline for children with a Patient Controlled Analgesia
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR USE OF A PATIENT CONTROLLED ANALGESIA OR INTRAVENOUS OPIATE INFUSION IN CHILD HEALTH. 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline Guideline for children with a Patient Controlled Analgesia
SPIROMETRY. Performance and Interpretation for Healthcare Professionals. Faculty of Respiratory Physiology IICMS. Version 1 April 2015
 SPIROMETRY Performance and Interpretation for Healthcare Professionals Faculty of Respiratory Physiology IICMS Version 1 April 2015 Authors: Maria Mc Neill & Geraldine Nolan www.iars.ie Contents Page Background
SPIROMETRY Performance and Interpretation for Healthcare Professionals Faculty of Respiratory Physiology IICMS Version 1 April 2015 Authors: Maria Mc Neill & Geraldine Nolan www.iars.ie Contents Page Background
CLINICAL PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE REMOVAL OF FEMORAL ARTERIAL SHEATHS USING A DIGITAL APPROACH 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 POLICY UNDER REVIEW Please note that this policy is under review. It does, however, remain current Trust policy subject to any recent legislative changes, national policy instruction (NHS or Department
POLICY UNDER REVIEW Please note that this policy is under review. It does, however, remain current Trust policy subject to any recent legislative changes, national policy instruction (NHS or Department
Content Indica c tion Lung v olumes e & Lung Indica c tions i n c paci c ties
 Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Community COPD Service Protocol
 Community COPD Service Protocol Acknowledgements This protocol is based on the following documents: 1. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults
Community COPD Service Protocol Acknowledgements This protocol is based on the following documents: 1. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults
Suspected Pulmonary embolus Ambulatory Pathway. Document Title. Date Issued/Approved: Date Valid From: 11/11/17. Date Valid To: 11/05/18
 POLICY UNDER REVIEW Please note that this policy is under review. It does, however, remain current Trust policy subject to any recent legislative changes, national policy instruction (NHS or Department
POLICY UNDER REVIEW Please note that this policy is under review. It does, however, remain current Trust policy subject to any recent legislative changes, national policy instruction (NHS or Department
behaviour are out of scope of the present review.
 explained about the test, a trial may be done before recording the results. The maneuver consists initially of normal tidal breathing. The subject then inhales to maximally fill the lungs. This is followed
explained about the test, a trial may be done before recording the results. The maneuver consists initially of normal tidal breathing. The subject then inhales to maximally fill the lungs. This is followed
Getting Spirometry Right It Matters! Performance, Quality Assessment, and Interpretation. Susan Blonshine RRT, RPFT, AE-C, FAARC
 Getting Spirometry Right It Matters! Performance, Quality Assessment, and Interpretation Susan Blonshine RRT, RPFT, AE-C, FAARC Objectives Sample Title Recognize acceptable spirometry that meets the start
Getting Spirometry Right It Matters! Performance, Quality Assessment, and Interpretation Susan Blonshine RRT, RPFT, AE-C, FAARC Objectives Sample Title Recognize acceptable spirometry that meets the start
Developed By Name Signature Date
 Patient Group Direction 2155 version 2.0 Administration / Supply of Inhaled Salbutamol in Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust Date of Introduction:
Patient Group Direction 2155 version 2.0 Administration / Supply of Inhaled Salbutamol in Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust Date of Introduction:
S P I R O M E T R Y. Objectives. Objectives 3/12/2018
 S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
Care and Use of Nebulisers
 For further information visit: www.nhsdirect.nhs.uk www.lhch.nhs.uk www.dipex.org If you require a copy of this leaflet in any other format or language please contact us quoting the leaflet code and the
For further information visit: www.nhsdirect.nhs.uk www.lhch.nhs.uk www.dipex.org If you require a copy of this leaflet in any other format or language please contact us quoting the leaflet code and the
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. Pre-filled Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA) syringes
 The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Pre-filled Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA) syringes Version.: 2.2 Effective From: 1 June 2016 Expiry Date: 1 June 2019 Date Ratified: 20 April
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Pre-filled Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA) syringes Version.: 2.2 Effective From: 1 June 2016 Expiry Date: 1 June 2019 Date Ratified: 20 April
Prevention and Treatment of Mucositis in Children and Young People with Cancer Clinical Guideline V3.1 December 2018
 Prevention and Treatment of Mucositis in Children and Young People with Cancer Clinical Guideline V3.1 December 2018 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline This guideline applies to all medical and nursing staff
Prevention and Treatment of Mucositis in Children and Young People with Cancer Clinical Guideline V3.1 December 2018 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline This guideline applies to all medical and nursing staff
INITIATING A COPD CLINIC: PROTOCOL & ASSESSMENT
 COPD Resource Pack Section 2A INITIATING A COPD CLINIC: PROTOCOL & ASSESSMENT In this section: 1. Initiating a COPD Clinic 2. Equipment for a COPD Clinic 3. Primary Care Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
COPD Resource Pack Section 2A INITIATING A COPD CLINIC: PROTOCOL & ASSESSMENT In this section: 1. Initiating a COPD Clinic 2. Equipment for a COPD Clinic 3. Primary Care Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Spirometry Training Courses. Spirometry for. Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand. June Developed in partnership with
 Standards for Spirometry Training Courses Companion Document to Standards for the Delivery of Spirometry for Coal Mine Workers Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand June 2017 Developed in partnership
Standards for Spirometry Training Courses Companion Document to Standards for the Delivery of Spirometry for Coal Mine Workers Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand June 2017 Developed in partnership
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING. By: Gh. Pouryaghoub. MD Center for Research on Occupational Diseases (CROD) Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS)
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING By: Gh. Pouryaghoub. MD Center for Research on Occupational Diseases (CROD) Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS) PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS CATEGORIES Spirometry Lung volumes
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING By: Gh. Pouryaghoub. MD Center for Research on Occupational Diseases (CROD) Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS) PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS CATEGORIES Spirometry Lung volumes
S P I R O M E T R Y. Objectives. Objectives 2/5/2019
 S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
Procedure/ Care Plan for Domiciliary Care Workers/ Support Workers - Assisting a Service User to use an Inhaler (Adult)
 Procedure/ Care Plan for Domiciliary Care Workers/ Support Workers - Assisting a Service User to use an Inhaler (Adult) CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Medicines Management Specific Title: Procedure: Assisting
Procedure/ Care Plan for Domiciliary Care Workers/ Support Workers - Assisting a Service User to use an Inhaler (Adult) CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Medicines Management Specific Title: Procedure: Assisting
Spirometric protocol
 Spirometric protocol Spirometry is the most common of the Pulmonary Function Test, that measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled.
Spirometric protocol Spirometry is the most common of the Pulmonary Function Test, that measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled.
Office Based Spirometry
 Osteopathic Family Physician (2014)1, 14-18 Scott Klosterman, DO; Woodson Crenshaw, OMS4 Spartanburg Regional Family Medicine Residency Program; Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine - Virginia Campus
Osteopathic Family Physician (2014)1, 14-18 Scott Klosterman, DO; Woodson Crenshaw, OMS4 Spartanburg Regional Family Medicine Residency Program; Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine - Virginia Campus
Understanding the Basics of Spirometry It s not just about yelling blow
 Understanding the Basics of Spirometry It s not just about yelling blow Carl D. Mottram, RRT RPFT FAARC Technical Director - Pulmonary Function Labs and Rehabilitation Associate Professor of Medicine -
Understanding the Basics of Spirometry It s not just about yelling blow Carl D. Mottram, RRT RPFT FAARC Technical Director - Pulmonary Function Labs and Rehabilitation Associate Professor of Medicine -
Lung Function Tests. General information and instructions for patients, relatives and carers. Caring with pride
 Lung Function Tests General information and instructions for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Cardio-Respiratory Department The York Hospital Wigginton Road, York, YO31
Lung Function Tests General information and instructions for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Cardio-Respiratory Department The York Hospital Wigginton Road, York, YO31
P01. Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) P01 Guideline for Peak flow recording
 Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Guideline for Peak flow recording Caroline Youle,
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Guideline for Peak flow recording Caroline Youle,
Purpose Of This Guide
 AOHC Session 5 April 9, Speaker Disclosures Spirometry Testing in Occupational Health Programs Best Practices for Healthcare Professionals Mary C. Townsend, Dr.P.H M.C. Townsend Associates, LLC Adjunct
AOHC Session 5 April 9, Speaker Disclosures Spirometry Testing in Occupational Health Programs Best Practices for Healthcare Professionals Mary C. Townsend, Dr.P.H M.C. Townsend Associates, LLC Adjunct
#7 - Respiratory System
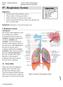 #7 - Respiratory System Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Perform spirometry to measure lung volumes Define and understand the lung volumes and
#7 - Respiratory System Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Perform spirometry to measure lung volumes Define and understand the lung volumes and
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 DRAFT NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the management of adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in primary
DRAFT NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the management of adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in primary
Cough Assist. Information for patients, families and carers Therapy Services
 Cough Assist Information for patients, families and carers Therapy Services PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST page 2 of 16 Table of contents Why do I need a Cough
Cough Assist Information for patients, families and carers Therapy Services PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST page 2 of 16 Table of contents Why do I need a Cough
National COPD Audit Programme
 National COPD Audit Programme Planning for every breath National Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Audit Programme: Primary care audit (Wales) 2015 17 Data analysis and methodology Section 2:
National COPD Audit Programme Planning for every breath National Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Audit Programme: Primary care audit (Wales) 2015 17 Data analysis and methodology Section 2:
Lung function testing
 ACTIVITY BRIEF Lung function testing The science at work Common respiratory complaints include asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Peak flow meters and spirometers can be used by health
ACTIVITY BRIEF Lung function testing The science at work Common respiratory complaints include asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Peak flow meters and spirometers can be used by health
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the management of adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in primary and secondary
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the management of adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in primary and secondary
Analysis of Lung Function
 Computer 21 Spirometry is a valuable tool for analyzing the flow rate of air passing into and out of the lungs. Flow rates vary over the course of a respiratory cycle (a single inspiration followed by
Computer 21 Spirometry is a valuable tool for analyzing the flow rate of air passing into and out of the lungs. Flow rates vary over the course of a respiratory cycle (a single inspiration followed by
Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy
 Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy Purpose Date Version August 2016 7 To ensure that Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust complies with all relevant legislation with regard to the use of ionising
Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy Purpose Date Version August 2016 7 To ensure that Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust complies with all relevant legislation with regard to the use of ionising
Developed By Name Signature Date
 Patient Group Direction 2156 version 2.0 Administration of Ipratropium 250mcg/ml Nebuliser Solution in Acute Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Date of
Patient Group Direction 2156 version 2.0 Administration of Ipratropium 250mcg/ml Nebuliser Solution in Acute Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Date of
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests
 6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
DIAGNOSTIC ACCREDITATION PROGRAM. Spirometry Quality Control Plan
 DIAGNOSTIC ACCREDITATION PROGRAM Spirometry Quality Control Plan Table of Contents Introduction...1 Spirometry Definitions and Requirements...2 Spirometry Requirements... 2...4 Daily Quality Control (see
DIAGNOSTIC ACCREDITATION PROGRAM Spirometry Quality Control Plan Table of Contents Introduction...1 Spirometry Definitions and Requirements...2 Spirometry Requirements... 2...4 Daily Quality Control (see
SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES Issue History Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To ensure vaccines are stored in accordance with manufacturers
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES Issue History Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To ensure vaccines are stored in accordance with manufacturers
This leaflet can be made available in other formats including large print, CD and Braille and in languages other than English, upon request.
 Information for patients and parents This leaflet can be made available in other formats including large print, CD and Braille and in languages other than English, upon request. You have been given this
Information for patients and parents This leaflet can be made available in other formats including large print, CD and Braille and in languages other than English, upon request. You have been given this
No Smoking Policy. No Smoking Policy
 No Smoking Policy Document Status Version: V4.0 Approved DOCUMENT CHANGE HISTORY Initiated by Date Author HR Version Date Comments (i.e. viewed, or reviewed, amended approved by person or committee) V1.1
No Smoking Policy Document Status Version: V4.0 Approved DOCUMENT CHANGE HISTORY Initiated by Date Author HR Version Date Comments (i.e. viewed, or reviewed, amended approved by person or committee) V1.1
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR AN EPIDURAL INFUSION IN CHILD HEALTH 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR AN EPIDURAL INFUSION IN CHILD HEALTH 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. The purpose of this guideline is to provide guidance on caring for children who are receiving epidural
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR AN EPIDURAL INFUSION IN CHILD HEALTH 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. The purpose of this guideline is to provide guidance on caring for children who are receiving epidural
Coexistence of confirmed obstruction in spirometry and restriction in body plethysmography, e.g.: COPD + pulmonary fibrosis
 Volumes: IRV inspiratory reserve volume Vt tidal volume ERV expiratory reserve volume RV residual volume Marcin Grabicki Department of Pulmonology, Allergology and Respiratory Oncology Poznań University
Volumes: IRV inspiratory reserve volume Vt tidal volume ERV expiratory reserve volume RV residual volume Marcin Grabicki Department of Pulmonology, Allergology and Respiratory Oncology Poznań University
Spirometry Technique Maximizing Effort, Comprehension & Coordination
 Spirometry Technique Maximizing Effort, Comprehension & Coordination Carl Mottram, RRT RPFT FAARC Director - Pulmonary Function Labs & Rehabilitation Associate Professor of Medicine - Mayo Clinic College
Spirometry Technique Maximizing Effort, Comprehension & Coordination Carl Mottram, RRT RPFT FAARC Director - Pulmonary Function Labs & Rehabilitation Associate Professor of Medicine - Mayo Clinic College
Vitalograph Alpha Spirometer
 Product Catalogue Vitalograph Alpha Spirometer Dedicated all-in-one desktop unit Simple to use Rapid and low cost testing Clear and bright color screen Accurate Fleisch pneumotachograph Measures VC, FVC,
Product Catalogue Vitalograph Alpha Spirometer Dedicated all-in-one desktop unit Simple to use Rapid and low cost testing Clear and bright color screen Accurate Fleisch pneumotachograph Measures VC, FVC,
Physiology lab (RS) First : Spirometry. ** Objectives :-
 Physiology lab (RS) ** Objectives :- 1. Spirometry in general. 2. Spirogram (volumes and capacities). 3. The importance of vital capacity in diagnosis. 4. Flow volume loop. 5. Miss Arwa s part (the practical
Physiology lab (RS) ** Objectives :- 1. Spirometry in general. 2. Spirogram (volumes and capacities). 3. The importance of vital capacity in diagnosis. 4. Flow volume loop. 5. Miss Arwa s part (the practical
Care Bundle. Adult patients with COPD
 Care Bundle Adult patients with COPD Version 2 July 2014 What is a care bundle? A care bundle is a set of interventions that, when used together, significantly improve patient outcomes. The measures chosen
Care Bundle Adult patients with COPD Version 2 July 2014 What is a care bundle? A care bundle is a set of interventions that, when used together, significantly improve patient outcomes. The measures chosen
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE USE OF PHENYTOIN IN EPILEPSY
 This applies to adult patients only CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE USE OF PHENYTOIN IN EPILEPSY Key: General Notes ED/MAU/SRU/Acute GP/Amb-Care GP/SWASFT In-patient wards Start Yes Patient already taking phenytoin?
This applies to adult patients only CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR THE USE OF PHENYTOIN IN EPILEPSY Key: General Notes ED/MAU/SRU/Acute GP/Amb-Care GP/SWASFT In-patient wards Start Yes Patient already taking phenytoin?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Great Yarmouth and Waveney Clinical Commissioning Group HealthEast Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Information and Advice for Patients
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Great Yarmouth and Waveney Clinical Commissioning Group HealthEast Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Information and Advice for Patients
Lung Function Unit Patient Information Leaflet
 Routine Lung Function Tests Lung Function Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This booklet aims to provide general information before your visit on the routine lung function tests carried out
Routine Lung Function Tests Lung Function Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This booklet aims to provide general information before your visit on the routine lung function tests carried out
Bronchial Provocation Testing Using Mannitol
 Patient Information Leaflet Bronchial Provocation Testing Using Mannitol Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Cardio-Respiratory Department The York Hospital,
Patient Information Leaflet Bronchial Provocation Testing Using Mannitol Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Cardio-Respiratory Department The York Hospital,
NO SMOKING POLICY. Organisational
 NO SMOKING POLICY Policy Title State previous title where relevant. State if Policy New or Revised Policy Strand Org, HR, Clinical, H&S, Infection Control, Finance For clinical policies only - state index
NO SMOKING POLICY Policy Title State previous title where relevant. State if Policy New or Revised Policy Strand Org, HR, Clinical, H&S, Infection Control, Finance For clinical policies only - state index
Pulmonary Function Tests. Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist
 Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
IT and Information Acceptable Use Policy
 BMI IMpol04 Information Management IT and Information Acceptable Use Policy This is a controlled document and whilst this document may be printed, the electronic version posted on the intranet/shared drive
BMI IMpol04 Information Management IT and Information Acceptable Use Policy This is a controlled document and whilst this document may be printed, the electronic version posted on the intranet/shared drive
NEBULISERS AND NEBULISED MEDICATION. A Guide for the use of nebulisers and nebulised medication in the community setting
 NEBULISERS AND NEBULISED MEDICATION A Guide for the use of nebulisers and nebulised medication in the community setting Aim This guide has been developed from the generic guidance circulated in April 2014.
NEBULISERS AND NEBULISED MEDICATION A Guide for the use of nebulisers and nebulised medication in the community setting Aim This guide has been developed from the generic guidance circulated in April 2014.
