A review of the current guidelines for allergic rhinitis and asthma
|
|
|
- Shannon Peters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A review of the current guidelines for allergic rhinitis and asthma Robert F. Lemanske, Jr., MD Madison, Wis. Allergic rhinitis and asthma are common chronic respiratory tract disorders. These disorders generate a significant burden to the patient, the patient s family, and to society because of lost productivity, impaired quality of life, healthcare costs, and even loss of life. To improve the management of asthma, guidelines have been developed to aid clinicians in proper diagnosis and treatment. 1, 2 Although these guidelines can serve as a basis for determining how to treat patients with these disorders, the best therapy regimens are those that are individualized to meet the specific needs of the patient. ALLERGIC RHINITIS Rhinitis is a heterogeneous disorder that is triggered by a number of factors 3 and is generally classified as atopic, idiopathic, nonallergic, or infectious. Other types include occupational, hormonal, and drug-induced rhinitis. The two main categories of allergic rhinitis are seasonal and perennial. Allergic rhinitis is characterized by the temporal relationship of symptoms to allergen exposure. 3 Allergens can include pollens, animal dander, dust mites, and mold spores, among others. Allergic rhinitis may be associated with coexisting diseases, such as viral and bacterial upper respiratory tract infections or structural abnormalities primarily related to nasal polyps. To be considered an important clinical phenomenon, two or more symptoms of allergic rhinitis must be experienced for more than 1 hour on most days. 4 Symptoms can include nasal discharge, blockage, and sneezing, itching, or both. 3 Chronic allergic rhinitis can lead to loss of smell or other complications. Allergic rhinitis is initiated by sensitization when an airborne antigen contacts the nasal mucosa epithelium. 5 In response to the allergen, mature B cells produce specific immunoglobulin E antibodies that bind to receptors on mast cells and basophils. Reexposure to the allergen causes the mast cells and eosinophils to release inflammatory mediators, leading to the immediate or early phase of an allergic reaction. Patients may also experience a late- or delayed-phase response characterized by a continued influx of eosinophils, basophils, neutrophils, and mononuclear cells in nasal tissues. From the University of Wisconsin Hospital. Reprint requests: Robert F. Lemanske, Jr., MD, Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics, University of Wisconsin Hospital, 600 Highland Ave. H4/432, Madison, WI J Allergy Clin Immunol 1998;101:S Copyright 1998 by Mosby, Inc /98 $ /0/86486 Diagnosis of allergic rhinitis The diagnosis of allergic rhinitis requires a careful patient history and physical examination. Nasal smears for microscopic examination of nasal secretions, allergy testing, and sinus radiography also may yield important information about the patient s condition. Allergy testing by a board-certified allergist is generally indicated for the patient with significant recurrent symptoms and common complications (e.g., sinusitis, asthma). A skin test can confirm the presence of immunoglobulin E antibody, and the radioallergosorbent test for immunoglobulin E antibodies can also provide useful information. Treatment of allergic rhinitis The main treatment for allergic rhinitis is allergen avoidance to reduce or eliminate exposure. Pharmacologic therapy may be used and is directed at the inflammatory process. If allergen avoidance and pharmacologic therapy are ineffective, immunotherapy can be considered. Allergen avoidance should be based on the specific allergens to which the patient is sensitive. 4 Patients with pollen sensitivity should monitor pollen forecasts, avoid high-pollen areas, and stay inside the house with windows and doors closed when the pollen count is high. In addition, these patients should use high-efficiency particulate filters in cars and should consider wearing glasses when outside of the house. For those who are sensitive to dust mites, control should focus initially on the bed, because patients may spend 7 to 10 hours a day at that site. Allergen-impermeable mattress, duvet, and pillow covers should be used. The mattress, pillows, and the base of the bed should be vacuumed weekly. In addition, carpeting in the bedroom may need to be removed. Pharmacologic therapies for allergic rhinitis include decongestants, antihistamines, intranasal cromolyn, and topical nasal corticosteroids. 4 For patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis, therapy choices are made based on the degree of symptoms. Patients with mild disease or with occasional symptoms can benefit from a rapid-onset, oral, nonsedating H 1 antihistamine when they are symptomatic. If there is a substantial ocular component to the patient s symptomatology, a topical antihistamine or sodium cromoglycate can be applied to the eyes, nose, or both. For patients with moderate disease and prominent nasal symptoms, a topical nasal steroid can be used daily beginning early in the allergy season, in addition to a second-generation nonsedating antihistamine. In pa- S392
2 J ALLERGY CLIN IMMUNOL VOLUME 101, NUMBER 2, PART 2 Lemanske S393 tients with prominent eye symptoms, sodium cromoglycate or other topical antiallergic medications can be used, and an ophthalmologic evaluation may be recommended to determine if administration of topical corticosteroids to the eye would be beneficial or if there is a risk for increasing intraocular pressure. For patients with perennial allergic rhinitis, topical nasal steroids should be used if the patients are undergoing long-term exposure. Disease flares can be treated with oral, nonsedating H 1 antihistamines with or without oral decongestants. (For more information on pharmacologic therapies, see Pharmacologic Management of Allergic Rhinitis by Gary S. Rachelefsky, MD, in this issue.) If allergen avoidance and pharmacotherapy are ineffective, referral to a specialist should be considered for further investigation, including examination of the nose, allergy tests, additional pharmacotherapy (e.g., systemic steroids for crisis situations), and consideration of immunotherapy. 4 Immunotherapy involves the subcutaneous injection of incremental doses of allergenic substances. 3, 5 Patients who are to receive immunotherapy should have a history of allergic rhinitis for at least two seasons or 6 months and should have positive skin tests that correlate with their symptomatic histories. If immunotherapy is indicated, it is crucial that clinicians talk candidly with patients about potential adverse events, including death. 6 In all cases, immunotherapy should be prescribed by an allergist and administered under the supervision of a physician who is trained to assess and treat anaphylaxis. Immunotherapy is contraindicated in patients taking oral or topical -blockers, patients who are pregnant (although immunotherapy can be safely continued during pregnancy if it was initiated before pregnancy), or patients with uncontrolled asthma. ASTHMA Asthma is recognized as a serious global health problem. In addition, the incidence of asthma is increasing, 7-9 and this trend probably reflects both a true increase and the tendency of clinicians to label all wheezing episodes as asthma. Although family history is a risk factor for the development of asthma, environmental factors are important in the onset and persistence of this disorder In 1991, guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma were released by the Expert Panel for the National Asthma Education Program. 1 In addition, guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma have been developed by the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). 2 These international guidelines provide direction for the diagnosis and management of patients with asthma. Because the revision of the National Asthma Education Program guidelines was ongoing at the time of this writing, the GINA guidelines are described below. Diagnosis of asthma Epidemiologic studies suggest that asthma is underdiagnosed. 13 This may reflect the nonspecific nature of asthma symptoms or the fact that patients tend to tolerate these intermittent symptoms. Unfortunately, establishing an accurate diagnosis is essential for determining appropriate treatment. For example, a clinician may diagnose bronchitis rather than asthma and subsequently treat inappropriately and ineffectively with successive courses of antibiotics and cough medications. 14 Information regarding the patient s history is critical for the diagnosis of asthma. 3 Symptoms reported by the patient may include episodic breathlessness, wheezing, chest tightness, and cough that worsen at night and in the early hours of the morning. The patient may have a history of recurrent exacerbations that are provoked by allergens, irritants, exercise, or infectious agents. A useful clinical marker of asthma is the relief of symptoms subsequent to bronchodilator and anti-inflammatory treatments. Seasonal variability of symptoms and a positive family history of asthma and atopic disease are suggestive evidence for diagnosis. Measurements of lung function are important parameters for appraising the characteristics of the patient s asthma. 3 Two methods that are commonly used for assessing airflow limitation are FEV 1, the related forced vital capacity, and the PEF. These measurements rely on the relationship between airflow limitation and airway luminal size (airway caliber) and the elastic properties of the alveoli. 2 It should be noted that although measurements of airway responsiveness may be used to diagnose asthma, other disorders such as rhinitis, cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease may invoke similar results. Treatment of asthma The GINA guidelines were designed with a stepwise approach to the long-term management of asthma. 2 The goal of treatment is to control asthma such that the patient has minimal or no chronic symptoms (including nocturnal symptoms), minimal episodes, no emergency visits, minimal need for rescue 2 -agonist therapy, no activity limitations (including exercise), PEF circadian variation less than 20%, near normal PEF, and minimal or no adverse effects from medication. In short, the disorder should be put into remission. The GINA guidelines categorize asthma into four different steps: step 1 is intermittent; step 2 is mild persistent; step 3 is moderate persistent; and step 4 is severe persistent (Fig. 1). 2 This design permits the concept of stepping up or stepping down therapy. For example, therapy may need to be stepped up in response to seasonal fluctuations in disease activity, particularly in children with regard to upper respiratory tract infection or allergen exposure. In addition, the GINA guidelines use specific terminology designed to provide meaning to the patient regarding therapy actions such that bronchodilator therapies are termed relievers and anti-inflammatory therapies are termed controllers. The clinical features of step 1, or intermittent asthma, include symptoms less than once per week, brief exacerbations, nighttime asthma symptoms less than two
3 S394 Lemanske J ALLERGY CLIN IMMUNOL FEBRUARY 1998 FIG. 1. Long-term management of asthma: a stepwise approach. From Global Initiative for Asthma. National Institutes of Health; NHLBI Publication No times per month, asymptomatic and normal lung function between exacerbations, and PEF or FEV 1 at least 80% of predicted with variability less than 20%. 2 The recommended therapy regimen for this group of patients is an intermittent reliever medication (i.e., short-acting inhaled 2 -agonist) taken as needed. The intensity of this treatment will reflect the severity of the exacerbation. In addition, a prophylactic reliever, such as an inhaled 2 -agonist or cromolyn, before exercise or exposure may be beneficial. For patients at step 2, or mild persistent, symptoms occur more than one time per week but less than one time per day. 2 Exacerbations may affect activity and sleep, and nighttime asthma symptoms occur more than two times per month. The PEF or FEV 1 is greater than 80% of predicted, and the variability is between 20% and 30%. In addition to a quick reliever medication (i.e., inhaled 2 -agonist), these patients benefit from one daily controller medication, such as an inhaled corticosteroid, cromoglycate, nedocromil, or sustained-release theophylline. The clinical features of step 3, or moderate persistent, include daily symptoms, exacerbations that affect activity and sleep, nighttime asthma symptoms that occur more than once per week, daily use of a short-acting inhaled 2 -agonist, and PEF or FEV 1 between 60% and 80% of predicted with variability greater than 30%. 2 These patients should receive a daily controller medication of inhaled corticosteroid and a long-acting bronchodilator (i.e., long-acting inhaled 2 -agonist, sustained-release theophylline, long-acting oral 2 -agonist), particularly for nighttime symptoms. The reliever medication should be a short-acting inhaled 2 -agonist. For severe persistent asthmatics, or patients at step 4, symptoms are continuous with frequent exacerbations. 2 Patients experience frequent nighttime asthma symptoms, physical activities are limited by symptoms, and PEF or FEV 1 is less than or equal to 60% of predicted with variability more than 30%. The daily controller medication should be high doses of inhaled corticosteroid, a long-acting bronchodilator, and at times longterm, alternate-day oral corticosteroids. The quick reliever is a short-acting 2 -agonist. Management of exacerbations of asthma Exacerbations of asthma do occur, and several steps need to be taken to manage these events (Fig. 2). 2 First, the severity of the episode must be determined by measuring the PEF and assessing clinical features. Initial treatment should consist of a short-acting inhaled 2 - agonist that can be given up to three times per hour either by a power-driven nebulizer or a metered-dose inhaler with holding chamber. After this initial treatment, the patient s response should be assessed and defined as either good, intermediate, or poor to determine the next steps that can range from continuing 2 -agonist therapy to immediate transportation to the hospital emergency department. If the patient does need hospital-based care, history and physical examination are the first steps. 2 Initial treatment should include a short-acting inhaled 2 - agonist, usually by nebulization, given every 20 minutes for 1 hour. Oxygen is provided to achieve greater than 90% saturation. Systemic corticosteroids are used if there is no immediate response, if the patient recently took oral steroids, or if the episode is severe. The patient is subsequently reassessed, and a specific treatment regimen is selected depending on whether the patient
4 J ALLERGY CLIN IMMUNOL VOLUME 101, NUMBER 2, PART 2 Lemanske S395 FIG. 2. Management of exacerbation of asthma: home treatment. Patients at high risk of asthma-related death should contact a clinician promptly after initial treatment. Additional therapy may be required. From Global Initiative for Asthma. National Institutes of Health; NHLBI Publication No experienced a moderate or severe episode. Patients who respond to the treatment regimen can be discharged, but patients who have an incomplete response within 1 to 2 hours should be admitted to the hospital or kept in the emergency room, and those who have a poor response within 1 hour should be admitted to intensive care. CONCLUSIONS Guidelines have been developed that are useful for determining the appropriate treatment regimens for patients with allergic rhinitis or asthma. These guidelines provide information regarding how to evaluate and treat these patients with chronic therapy and how to
5 S396 Lemanske J ALLERGY CLIN IMMUNOL FEBRUARY 1998 manage acute exacerbations. Nevertheless, bear in mind that the best therapy regimens for these patients are individualized to maximize both efficacy and tolerability. REFERENCES 1. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. National Asthma Education Program. Expert Panel Report. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1991;88: Global Initiative for Asthma. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: NHLBI/WHO Workshop report. Bethesda, Md: National Institutes of Health; NHBLI Publication No Greenberger PA. Use of immunotherapy for allergic disorders: diagnostic considerations and indications. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 1992;12: International Rhinitis Management Working Group. International consensus report on the diagnosis and management of rhinitis. Eur J Allergy Clin Immunol 1994;19(suppl): Creticos PS. Immunotherapy with allergens. JAMA 1992;268: Stewart GE II, Lockey RF. Systemic reactions from allergen immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1992;90: Aberg N. Asthma and allergic rhinitis in Swedish conscripts. Clin Exp Allergy 1989;19: Burney PG, Chinn S, Rona RJ. Has the prevalence of asthma increased in children? Evidence from the National Study of Health and Growth Br Med J 1990;300: Burr ML. Is asthma increasing? J Epidemiol Community Health 1987;41: Sears MR, Herbison GP, Holdaway MD, Hewitt CJ, Flannery EM, Silva PA. The relative risks of sensitivity to grass pollen, house dust mite and cat dander in the development of childhood asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 1989;19: Martinez FD, Antognoni G, Macri F, Bonci E, Midulla F, DeCastro G, et al. Parental smoking enhances bronchial responsiveness in nine-year-old children. Am Rev Respir Dis 1988;138: Murray AB, Morrison BJ. It is children with atopic dermatitis who develop asthma more frequently if the mother smokes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1990;86: Burney PGJ. Current questions in the epidemiology of asthma. In: Holgate ST, Austen KF, Lichtenstein LM, Kay AB, editors. Asthma: physiology, immunopharmacology, and treatment. London, England: Academic Press, Inc.; p Wilson NM. Wheezy bronchitis revisited. Arch Dis Child 1989;64:
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes. Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy
 Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
In 2002, it was reported that 72 of 1000
 REPORTS Aligning Patient Care and Asthma Treatment Guidelines Eric Cannon, PharmD Abstract This article describes how the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Guidelines for the Diagnosis and
REPORTS Aligning Patient Care and Asthma Treatment Guidelines Eric Cannon, PharmD Abstract This article describes how the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Guidelines for the Diagnosis and
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes
 Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Asthma in the Athlete
 Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016
 Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Pathology of Asthma Epidemiology
 Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Does rhinitis. lead to asthma? Does sneezing lead to wheezing? What allergic patients should know about the link between allergic rhinitis and asthma
 Does rhinitis lead to asthma? Does sneezing lead to wheezing? What allergic patients should know about the link between allergic rhinitis and asthma For a better management of allergies in Europe Allergy
Does rhinitis lead to asthma? Does sneezing lead to wheezing? What allergic patients should know about the link between allergic rhinitis and asthma For a better management of allergies in Europe Allergy
Asthma in Pediatric Patients. DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP. Disclosures. None
 Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Derriford Hospital. Peninsula Medical School
 Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis iti What is the Connection? Hisham Khalil Consultant ENT Surgeon Clinical Senior Lecturer, PMS Clinical Sub-Dean GP Evening 25 June 2008 Plymouth Derriford Hospital Peninsula
Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis iti What is the Connection? Hisham Khalil Consultant ENT Surgeon Clinical Senior Lecturer, PMS Clinical Sub-Dean GP Evening 25 June 2008 Plymouth Derriford Hospital Peninsula
TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Inclusion Criterion Exclusion Criterion RECOMMENDATIONS
 TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Inclusion Criterion Exclusion Criterion RECOMMENDATIONS Recommendation PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING (SPIROMETRY) Conditional: The Expert Panel that spirometry measurements FEV1,
TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Inclusion Criterion Exclusion Criterion RECOMMENDATIONS Recommendation PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING (SPIROMETRY) Conditional: The Expert Panel that spirometry measurements FEV1,
HealthPartners Care Coordination Clinical Care Planning and Resource Guide ASTHMA
 The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007
 Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007 TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Inclusion Criterion Exclusion Criterion RECOMMENDATIONS Selecting Initial Therapy
Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007 TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Inclusion Criterion Exclusion Criterion RECOMMENDATIONS Selecting Initial Therapy
Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis (Hay Fever)
 Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis (Hay Fever) Link to prescribing guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ear-nose-and-oropharynx Clinical Presentation Link to CKS NICE guidance: https://cks.nice.org.uk/allergicrhinitis
Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis (Hay Fever) Link to prescribing guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ear-nose-and-oropharynx Clinical Presentation Link to CKS NICE guidance: https://cks.nice.org.uk/allergicrhinitis
SCREENING AND PREVENTION
 These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
1. ASTHMA 1. Eve A. Kerr, MD, MPH and Kenneth A. Clark, MD, MPH
 1. ASTHMA 1 Eve A. Kerr, MD, MPH and Kenneth A. Clark, MD, MPH The general approach to developing quality indicators for asthma diagnosis and treatment was based on Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management
1. ASTHMA 1 Eve A. Kerr, MD, MPH and Kenneth A. Clark, MD, MPH The general approach to developing quality indicators for asthma diagnosis and treatment was based on Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management
(pedi) Patient Name: date of birth:
 (pedi) Patient Name: date of birth:_ Date: I am being seen on: a) self referral _ b) physician referral from Dr. Please share the main reasons for your office visit today (check all those that apply):
(pedi) Patient Name: date of birth:_ Date: I am being seen on: a) self referral _ b) physician referral from Dr. Please share the main reasons for your office visit today (check all those that apply):
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Glossary of Asthma Terms
 HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
ALLERGIC RHINITIS Eve Kerr, M.D., M.P.H.
 - 63-3. ALLERGIC RHINITIS Eve Kerr, M.D., M.P.H. We conducted a MEDLINE search of review articles on rhinitis between the years of 1990-1995 and selected articles pertaining to allergic rhinitis. We also
- 63-3. ALLERGIC RHINITIS Eve Kerr, M.D., M.P.H. We conducted a MEDLINE search of review articles on rhinitis between the years of 1990-1995 and selected articles pertaining to allergic rhinitis. We also
Systems Pharmacology Respiratory Pharmacology. Lecture series : General outline
 Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
An Update on Allergic Rhinitis. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Department of Paediatrics University of Cape Town Red Cross Hospital
 An Update on Allergic Rhinitis Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Department of Paediatrics University of Cape Town Red Cross Hospital Allergic Rhinitis Common condition with increasing prevalence
An Update on Allergic Rhinitis Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Department of Paediatrics University of Cape Town Red Cross Hospital Allergic Rhinitis Common condition with increasing prevalence
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP?
 THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION
 ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY. This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma.
 ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma. April 21, Spring Managed Care Forum
 Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma April 21, 2016 2016 Spring Managed Care Forum David M. Mannino, M.D. Professor Department of Preventive Medicine and Environmental Health University
Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma April 21, 2016 2016 Spring Managed Care Forum David M. Mannino, M.D. Professor Department of Preventive Medicine and Environmental Health University
Asthma. Guide to Good Health. Healthy Living Guide
 Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: xolair_omalizumab 9/2003 11/2017 11/2018 11/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Asthma is a chronic
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: xolair_omalizumab 9/2003 11/2017 11/2018 11/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Asthma is a chronic
Why does the body develop allergies?
 Allergies & Hay Fever Millions of Americans suffer from nasal allergies, commonly known as hay fever. Often fragrant flowers are blamed for the uncomfortable symptoms, yet they are rarely the cause; their
Allergies & Hay Fever Millions of Americans suffer from nasal allergies, commonly known as hay fever. Often fragrant flowers are blamed for the uncomfortable symptoms, yet they are rarely the cause; their
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
National Asthma Educator Certification Board Detailed Content Outline
 I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
Asthma. The prevalence of asthma has been increasing worldwide, but why this is happening is not known.
 Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Phototherapy in Allergic Rhinitis
 Phototherapy in Allergic Rhinitis Rhinology Chair KSU KAUH Ibrahim AlAwadh 18\1\2017 MBBS, SB & KSUF Resident, ORL-H&N Background: Endonasal phototherapy can relieve the symptoms of allergic rhinitis
Phototherapy in Allergic Rhinitis Rhinology Chair KSU KAUH Ibrahim AlAwadh 18\1\2017 MBBS, SB & KSUF Resident, ORL-H&N Background: Endonasal phototherapy can relieve the symptoms of allergic rhinitis
MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER
 MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER 16 year old female with h/o moderate persistent asthma presents to the ED after 6 hours of difficulty breathing, cough, and wheezing
MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER 16 year old female with h/o moderate persistent asthma presents to the ED after 6 hours of difficulty breathing, cough, and wheezing
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction
 Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief.
 Sinus Sinus Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief. So what is sinusitis? Although many individuals interpret
Sinus Sinus Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief. So what is sinusitis? Although many individuals interpret
Seasonal Allergic Rhinoconjunctivitis
 Seasonal Allergic Rhinoconjunctivitis Allergic rhinoconjunctivitis is a common condition. Most patients can achieve good symptom control through allergen avoidance and pharmacotherapy with non-sedating
Seasonal Allergic Rhinoconjunctivitis Allergic rhinoconjunctivitis is a common condition. Most patients can achieve good symptom control through allergen avoidance and pharmacotherapy with non-sedating
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Asthma By Mayo Clinic staff
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
Allergies and Asthma 5/21/2013. Objectives. Allergic Rhinitis (AR): Risk Factor for ASTHMA. Rhinitis and Asthma
 Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control
 Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Omalizumab (Xolair ) ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September Indication
 ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ
 Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Pediatric and Adult. Disclosure. Asthma. Learning Objectives. EPR-3: What s Changed? Asthma: Pediatric and Adult
 Asthma: Pediatric and Adult Americo D. Fraboni, MD, FAAFP Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Family Practice & Community Health University of Minnesota Medical School Minneapolis, Minnesota Disclosure
Asthma: Pediatric and Adult Americo D. Fraboni, MD, FAAFP Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Family Practice & Community Health University of Minnesota Medical School Minneapolis, Minnesota Disclosure
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016?
 Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016? GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention GINA: A Brief History Established in 1993 Collaboration between NHLBI and WHO Multiple
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016? GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention GINA: A Brief History Established in 1993 Collaboration between NHLBI and WHO Multiple
Asthma. Permafold Topics. What You Need To Know
 1. What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways to narrow. Airflow is limited due to inflammation in the airways. Asthma What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What Is Asthma?
1. What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways to narrow. Airflow is limited due to inflammation in the airways. Asthma What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What Is Asthma?
ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN BASKET OF CARE SUBCOMMITTEE Report to: Minnesota Department of Health. June 22, 2009
 This document is made available electronically by the Minnesota Legislative Reference Library as part of an ongoing digital archiving project. http://www.leg.state.mn.us/lrl/lrl.asp ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN
This document is made available electronically by the Minnesota Legislative Reference Library as part of an ongoing digital archiving project. http://www.leg.state.mn.us/lrl/lrl.asp ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN
MANAGING ASTHMA. Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
Childhood Asthma. The pathophysiology of asthma is an interplay. CME Case Study. Case Study. By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC
 CME Case Study Childhood Asthma By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC Case Study A two-year-old child presents to your office with a cough, which has been present for three weeks. It is worse at nighttime
CME Case Study Childhood Asthma By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC Case Study A two-year-old child presents to your office with a cough, which has been present for three weeks. It is worse at nighttime
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
The burden of asthma on the US Healthcare system and for the State of Texas is enormous. The causes of asthma are multifactorial and well known.
 The burden of asthma on the US Healthcare system and for the State of Texas is enormous. The causes of asthma are multifactorial and well known. There are also indications that rural counties have a higher
The burden of asthma on the US Healthcare system and for the State of Texas is enormous. The causes of asthma are multifactorial and well known. There are also indications that rural counties have a higher
LivingWith Asthma. A Guide to Understanding Asthma...
 A Guide to Understanding... LivingWith Understanding Diagnosing Treating Frequently Asked Questions [2] A Guide to Understanding... Understanding What Is? (AZ-muh) is a chronic disease that affects your
A Guide to Understanding... LivingWith Understanding Diagnosing Treating Frequently Asked Questions [2] A Guide to Understanding... Understanding What Is? (AZ-muh) is a chronic disease that affects your
Impact of Asthma in the U.S. per Year. Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Risk Factors for Asthma. Childhood Asthma Costs of Asthma
 American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management
 Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management Learning Objectives After participating in this educational activity, participants should be better able to: 1. Choose the optimal
Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management Learning Objectives After participating in this educational activity, participants should be better able to: 1. Choose the optimal
Respiratory Health L O O K, F E E L A N D L I V E B E T T E R
 LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BET TER Respiratory health: hay-fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay-fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body s immune system
LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BET TER Respiratory health: hay-fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay-fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body s immune system
Breathe Easy. Living with Asthma
 Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma
 Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Public Dissemination
 1. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 18 3 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
1. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 18 3 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss?
 ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment. John R. Holcomb, M.D.
 Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Coverage Criteria: Express Scripts, Inc. monograph dated 03/03/2010
 BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Xolair (omalizumab) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP HMO/PPO/CDHP: Rx
BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Xolair (omalizumab) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP HMO/PPO/CDHP: Rx
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
Ear, Nose & Throat (ENT) - Head & Neck Surgery. Allergic Rhinitis (Sinus)
 Ear, Nose & Throat (ENT) - Head & Neck Surgery Allergic Rhinitis (Sinus) The Department of Ear, Nose & Throat (ENT) - Head & Neck Surgery provides a wide range of surgical services for adult patients with
Ear, Nose & Throat (ENT) - Head & Neck Surgery Allergic Rhinitis (Sinus) The Department of Ear, Nose & Throat (ENT) - Head & Neck Surgery provides a wide range of surgical services for adult patients with
PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS COPD CT MRI IG PID Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Computed tomography
PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS COPD CT MRI IG PID Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Computed tomography
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergic Rhinitis. Dr. Sasan Dabiri. Otorhinolaryngologist Head & Neck Surgeon January 2011 Imam Hospital complex - Tehran
 In the name of God Dr. Sasan Dabiri Otorhinolaryngologist Head & Neck Surgeon January 2011 Imam Hospital complex - Tehran Rhinitis Allergic Rhinitis Infectious Rhinitis Nonallergic Rhinitis Neoplastic
In the name of God Dr. Sasan Dabiri Otorhinolaryngologist Head & Neck Surgeon January 2011 Imam Hospital complex - Tehran Rhinitis Allergic Rhinitis Infectious Rhinitis Nonallergic Rhinitis Neoplastic
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE
 CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE ALLERGIC RHINITIS (JOINT HOMERTON / ELIC PATHWAY) 1. Classification (See ARIA guidelines for full details) Allergic rhinitis is common and affects >20% of
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE ALLERGIC RHINITIS (JOINT HOMERTON / ELIC PATHWAY) 1. Classification (See ARIA guidelines for full details) Allergic rhinitis is common and affects >20% of
Bronchial asthma. E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics. Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013
 Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Work Group on the Algorithm for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma: a Practice Parameter update:
 Página 1 de 10 MD Consult information may not be reproduced, retransmitted, stored, distributed, disseminated, sold, published, broadcast or circulated in any medium to anyone, including but not limited
Página 1 de 10 MD Consult information may not be reproduced, retransmitted, stored, distributed, disseminated, sold, published, broadcast or circulated in any medium to anyone, including but not limited
Ailléirge Péidiatraiceach. Pediatric Allergy 3/9/2018. Disclosures & Conflicts Of Interest
 Ailléirge Péidiatraiceach Michael Zacharisen, M.D. Allergy/Immunology Pediatric Allergy Michael Zacharisen, M.D. Allergy/Immunology Disclosures & Conflicts Of Interest Green Bay Packer fan I drive a Jeep
Ailléirge Péidiatraiceach Michael Zacharisen, M.D. Allergy/Immunology Pediatric Allergy Michael Zacharisen, M.D. Allergy/Immunology Disclosures & Conflicts Of Interest Green Bay Packer fan I drive a Jeep
Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes:
 Dr. W. Wijnant Paediatric Pulmonology Steve Biko Academic Hospital Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes: Viral wheezer Multiple trigger wheezer Transient wheezer Persistent early
Dr. W. Wijnant Paediatric Pulmonology Steve Biko Academic Hospital Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes: Viral wheezer Multiple trigger wheezer Transient wheezer Persistent early
Hayfever. Allergic reaction. Prognosis
 Hayfever Hay fever is a type of allergic rhinitis caused by pollen or spores. Allergic rhinitis is a condition where an allergen (something that causes an allergic reaction) makes the inside of your nose
Hayfever Hay fever is a type of allergic rhinitis caused by pollen or spores. Allergic rhinitis is a condition where an allergen (something that causes an allergic reaction) makes the inside of your nose
INVESTIGATIONS & PROCEDURES IN PULMONOLOGY. Immunotherapy in Asthma Dr. Zia Hashim
 INVESTIGATIONS & PROCEDURES IN PULMONOLOGY Immunotherapy in Asthma Dr. Zia Hashim Definition Involves Administration of gradually increasing quantities of specific allergens to patients with IgE-mediated
INVESTIGATIONS & PROCEDURES IN PULMONOLOGY Immunotherapy in Asthma Dr. Zia Hashim Definition Involves Administration of gradually increasing quantities of specific allergens to patients with IgE-mediated
ASTHMA CONTROL. Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms.
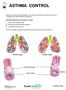 ASTHMA CONTROL Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms. Asthma changes the lung airways in 3 ways: 1. Lining of the airways
ASTHMA CONTROL Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms. Asthma changes the lung airways in 3 ways: 1. Lining of the airways
What are Allergy shots / SCIT?
 Allergy diagnosis must be made accurately with correct history and tests including the skin prick test and the blood test like immunocap / Phadiatop study. This once made will help decide the dose and
Allergy diagnosis must be made accurately with correct history and tests including the skin prick test and the blood test like immunocap / Phadiatop study. This once made will help decide the dose and
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Case Study. Allergic Rhinitis 5/18/2015
 John A. Fling, M.D. Professor Allergy/Immunology University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, Texas Case Study 38 year old male with a history of nasal congestion, clear nasal discharge
John A. Fling, M.D. Professor Allergy/Immunology University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, Texas Case Study 38 year old male with a history of nasal congestion, clear nasal discharge
Sensitivity to Sorghum Vulgare (Jowar) Pollens in Allergic Bronchial Asthma and Effect of Allergen Specific Immunotherapy
 Indian J Allergy Asthma Immunol 2002; 16(1) : 41-45 Sensitivity to Sorghum Vulgare (Jowar) Pollens in Allergic Bronchial Asthma and Effect of Allergen Specific Immunotherapy Sanjay S. Pawar Shriratna Intensive
Indian J Allergy Asthma Immunol 2002; 16(1) : 41-45 Sensitivity to Sorghum Vulgare (Jowar) Pollens in Allergic Bronchial Asthma and Effect of Allergen Specific Immunotherapy Sanjay S. Pawar Shriratna Intensive
The Role of Allergy Testing to Achieve Personalized Treatment Goals for Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Some Facts About Asthma
 Some Facts About Asthma Contents What is asthma? Diagnosing asthma Asthma symptoms Asthma triggers Thanks What is asthma?? Asthma is a chronic lung-disease that inflames and narrows the airways (tubes
Some Facts About Asthma Contents What is asthma? Diagnosing asthma Asthma symptoms Asthma triggers Thanks What is asthma?? Asthma is a chronic lung-disease that inflames and narrows the airways (tubes
WILLIAM B. COBB, M.D. KEITH MATHENY, M.D. EWEN TSENG, M.D. KENNY CARTER, M.D.
 WILLIAM B. COBB, M.D. KEITH MATHENY, M.D. EWEN TSENG, M.D. KENNY CARTER, M.D. INSTRUCTIONS FOR ALLERGY SKIN TESTING FOR SUBLINGUAL DROPS TREATMENT SKIN TESTING 1. Discontinue all antihistamines, oral or
WILLIAM B. COBB, M.D. KEITH MATHENY, M.D. EWEN TSENG, M.D. KENNY CARTER, M.D. INSTRUCTIONS FOR ALLERGY SKIN TESTING FOR SUBLINGUAL DROPS TREATMENT SKIN TESTING 1. Discontinue all antihistamines, oral or
CME/CE POSTTEST CME/CE QUESTIONS
 CME/CE POSTTEST CME/CE QUESTIONS Controlling Asthma Severity: Identifying Unmet Needs and Optimizing Therapeutic Options There are no fees for participating in and receiving continuing medical education
CME/CE POSTTEST CME/CE QUESTIONS Controlling Asthma Severity: Identifying Unmet Needs and Optimizing Therapeutic Options There are no fees for participating in and receiving continuing medical education
Get Healthy Stay Healthy
 Asthma Management WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma causes swelling and inflammation in the breathing passages that lead to your lungs. When asthma flares up, the airways tighten and become narrower. This keeps the
Asthma Management WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma causes swelling and inflammation in the breathing passages that lead to your lungs. When asthma flares up, the airways tighten and become narrower. This keeps the
Allergen and Environment in Severe Asthma
 Allergen and Environment in Severe Asthma Hye-Ryun Kang MD., PhD. Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital Role of Allergen in Asthma Pathogenesis Early response of allergen
Allergen and Environment in Severe Asthma Hye-Ryun Kang MD., PhD. Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital Role of Allergen in Asthma Pathogenesis Early response of allergen
Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies
 Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies Timothy Craig, DO Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Distinguished Educator Penn State University Hershey Medical Center Objectives 1. Learn the Asthma
Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies Timothy Craig, DO Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Distinguished Educator Penn State University Hershey Medical Center Objectives 1. Learn the Asthma
I have no perceived conflicts of interest or commercial relationships to disclose.
 ASTHMA BASICS Michelle Dickens RN FNP-C AE-C Nurse Practitioner/Certified Asthma Educator Ferrell Duncan Allergy/Asthma/Immunology Coordinator, CoxHealth Asthma Center DISCLOSURES I have no perceived conflicts
ASTHMA BASICS Michelle Dickens RN FNP-C AE-C Nurse Practitioner/Certified Asthma Educator Ferrell Duncan Allergy/Asthma/Immunology Coordinator, CoxHealth Asthma Center DISCLOSURES I have no perceived conflicts
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition
 Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 13 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma, Chronic Bronchitis, and Emphysema Multimedia Directory Slide 7 Slide 12 Slide 60 COPD Video Passive
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 13 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma, Chronic Bronchitis, and Emphysema Multimedia Directory Slide 7 Slide 12 Slide 60 COPD Video Passive
LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BETTER. Respiratory Health
 LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BETTER Respiratory Health Respiratory health: hay fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body
LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BETTER Respiratory Health Respiratory health: hay fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body
Breathe Easy ACTIVITIES. A Family Guide to Living with Asthma F O R T H E K ! I D S
 Breathe Easy A Family Guide to Living with Asthma ACTIVITIES FUN & EDUCATIONAL F O R T H E K! I D S What Is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the lungs. It s a chronic (long-term) condition that affects the
Breathe Easy A Family Guide to Living with Asthma ACTIVITIES FUN & EDUCATIONAL F O R T H E K! I D S What Is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the lungs. It s a chronic (long-term) condition that affects the
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA
 Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
