This tutorial presentation is prepared by. Mohammad Ehsanul Karim
|
|
|
- Garry Lang
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STATA: The Red tutorial
2 STATA: The Red tutorial This tutorial presentation is prepared by Mohammad Ehsanul Karim
3 STATA: The Red tutorial This tutorial presentation is prepared by Mohammad Ehsanul Karim
4 Contents Linear Regression Analysis 1. Introduction to Linear Regression 2. Tests for Normality of Residuals 3. Tests for Heteroscedasticity 4. Tests for Multicollinearity 5. Tests for Autocorrelation 6. Detecting Unusual and Influential Data 7. Tests for Model Specification
5 1. Introduction to Linear Regression
6 Linear Regression The command regress is used to perform linear regressions. The first variable after the regress command is always the dependent variable ( left-hand-side variable), and the list of the independent variables that we chose to include in the estimation model follows ( right-hand-side variables).
7 Linear Regression. clear. use hs1, clear. regress write read female
8 Linear Regression. clear. use hs1, clear. regress write read female Source SS df MS Number of obs = F( 2, 197) = Model Prob > F = Residual R-squared = Adj R-squared = Total Root MSE = write Coef. Std. Err. t P> t [95% Conf. Interval] read female _cons
9 Linear Regression. clear. use hs1, clear. regress write read female Source SS df MS Number of obs = F( 2, 197) = Model Prob > F = Residual R-squared = Adj R-squared = Total Root MSE = write Coef. Std. Err. t P> t [95% Conf. Interval] read female _cons
10 2. Tests for Normality of Residuals
11 Tests for Normality of Residuals We use the predict command with the resid option to generate residuals and we name the residuals r.. predict r, resid
12 Tests for Normality of Residuals Shapiro-Wilk W test for Normality For verifying that the residuals are normally distributed, which is a very important assumption for regression, we use Shapiro-Wilk W test for normal data
13 Tests for Normality of Residuals Shapiro-Wilk W test for Normality For verifying that the residuals are normally distributed, which is a very important assumption for regression, we use Shapiro-Wilk W test for normal data. swilk r
14 Tests for Normality of Residuals Shapiro-Wilk W test for Normality For verifying that the residuals are normally distributed, which is a very important assumption for regression, we use Shapiro-Wilk W test for normal data. swilk r Shapiro-Wilk W test for normal data Variable Obs W V z Prob>z r
15 Tests for Normality of Residuals In verifying that the residuals are normally distributed, which is a very important assumption for regression, the kdensity command with the normal option displays a density graph of the residuals with an normal distribution superimposed on the graph.
16 Tests for Normality of Residuals. kdensity r, normal
17 Tests for Normality of Residuals. kdensity r, normal
18 Tests for Normality of Residuals The pnorm command produces a normal probability plot and it is another method of testing whether the residuals from the regression are normally distributed.
19 Tests for Normality of Residuals. pnorm r
20 Tests for Normality of Residuals. pnorm r
21 Tests for Normality of Residuals The qnorm command produces a normal quantile plot. It is yet another method for testing if the residuals are normally distributed.
22 Tests for Normality of Residuals. qnorm r
23 Tests for Normality of Residuals. qnorm r
24 Tests for Normality of Residuals Summary of Tests for Normality of Residuals swilk performs the Shapiro-Wilk W test for normality. kdensity produces kernel density plot with normal distribution overlayed. pnorm graphs a standardized normal probability (P-P) plot. qnorm plots the quantiles of varname against the quantiles of a normal distribution.
25 3. Tests for Heteroscedasticity
26 Tests for Heteroscedasticity One of the basic assumptions for the ordinary least squares regression is the homogeneity of variance of the residuals. There are graphical and non-graphical methods for detecting heteroscedasticity.
27 Tests for Heteroscedasticity Cook-Weisberg test for heteroskedasticity
28 Tests for Heteroscedasticity Cook-Weisberg test for heteroskedasticity. hettest Cook-Weisberg test for heteroskedasticity using fitted values of write Ho: Constant variance chi2(1) = 5.79 Prob > chi2 =
29 Tests for Heteroscedasticity we use the rvfplot command with the yline(0) option to put a reference line at y=0.
30 Tests for Heteroscedasticity we use the rvfplot command with the yline(0) option to put a reference line at y=0.. rvfplot, yline(0)
31 Tests for Heteroscedasticity we use the rvfplot command with the yline(0) option to put a reference line at y=0.. rvfplot, yline(0)
32 Tests for Heteroscedasticity Summary of Tests for Heteroscedasticity hettest performs Cook and Weisberg test rvfplot graphs residual-versus-fitted plot.
33 4. Tests for Multicollinearity
34 Tests for Multicollinearity Multicollinearity is a concern for multiple regression, not for its existence, but for its degree. For severe degree of multicollinearity, the regression model estimates of the coefficients become unstable and the standard errors for the coefficients can get wildly inflated.
35 Tests for Multicollinearity We can use the vif command after the regression to check for multicollinearity. vif stands for variance inflation factor.
36 Tests for Multicollinearity We can use the vif command after the regression to check for multicollinearity. vif stands for variance inflation factor.. vif Variable VIF 1/VIF female read Mean VIF 1.00
37 Tests for Multicollinearity We can use the vif command after the regression to check for multicollinearity. vif stands for variance inflation factor.. vif Variable VIF 1/VIF female read Mean VIF 1.00 A variable whose VIF values are greater than 10 may merit further investigation. Tolerance= 1/VIF, is used to check on the degree of collinearity. A tolerance value lower than 0.1 is comparable to a VIF of 10.
38 Tests for Multicollinearity Summary of Tests for Multicollinearity vif calculates the variance inflation factor for the independent variables in the linear model.
39 5. Tests for Autocorrelation
40 Tests for Autocorrelation. tsset id time variable: id, 1 to 200. dwstat Durbin-Watson d-statistic( 3, 200) =
41 6. Detecting Unusual and Influential Data
42 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data Outliers: In linear regression, an outlier is an observation with large residual. In other words, it is an observation whose dependent-variable value is unusual given its values on the predictor variables. An outlier may indicate a sample peculiarity or may indicate a data entry error or other problem. Leverage: An observation with an extreme value on a predictor variable is called a point with high leverage. Leverage is a measure of how far an independent variable deviates from its mean. These leverage points can have an effect on the estimate of regression coefficients. Influence: An observation is said to be influential if removing the observation substantially changes the estimate of coefficients. Influence can be thought of as the product of leverage and outlierness.
43 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data Here we summarize the general rules of thumb we use for these measures to identify observations worthy of further investigation (where k is the number of predictors and n is the number of observations). Measure Value leverage >(2k+2)/n abs(rstu) > 2 Cook's D > 4/n abs(dfits) > 2*sqrt(k/n) abs(dfbeta) > 2/sqrt(n)
44 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data We use the predict command with the rstudent option to generate studentized residuals and we name the residuals r. Studentized residuals are a type of standardized residual that can be used to identify outliers.
45 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data We use the predict command with the rstudent option to generate studentized residuals and we name the residuals r. Studentized residuals are a type of standardized residual that can be used to identify outliers.. predict r, rstudent
46 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data. stem r Stem-and-leaf plot for r (Studentized residuals) r rounded to nearest multiple of.01 plot in units of.01-2** 50,42-2** 26,21-2** 18-1** 92,85,84,83-1** 75,72,69,61,61,60-1** 50,48,46,46,42-1** 33,32,22,20,20,20-1** 17,16,13,12,10,01-0** 97,97,96,96,93,93,92,92,90,89,89,89,86,86,84,82,82,80,80-0** 74,74,71,70,67-0** 59,59,58,53,49,49,47,42,42,40-0** 35,35,33,31,31,31,30,28,28,28,28,27,25,23,23,22-0** 19,17,16,16,16,16,14,13,13,09,09,07,04,03,03,02 0** 00,02,02,04,04,04,04,07,09,11,14,16,16,19 0** 21,23,23,24,24,26,28,29,30,33,33,35,35 0** 40,44,44,51,51,54,54,54,54,56,56,57,57,57 0** 61,63,64,64,64,64,64,66,70,70,71,73,73,73,74,78 0** 88,88,89,93,94,94,97,98,99 1** 01,06,06,08,08,13,13,13,13,15,19 1** 23,29,32,36,36,37,37,39 1** 42,43,44,48,51,52,53,55 1** 60,68,73,73,75,77 1** 80,84 2** 16
47 Detecting Unusual and. stem r. sort r. list r in 1/10 r Influential Data
48 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data. stem r. sort r. list r in 1/10 r list r in -10/l r
49 Detecting Unusual and. stem r. sort r. list r in 1/10 r Influential Data. We should pay attention to. list r in -10/lstudentized r residuals that exceed +2 or , and get even more concerned about residuals that exceed or -2.5 and even yet more concerned about residuals that exceed +3 or -3.
50 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data. We should pay attention to studentized residuals that exceed +2 or - 2, and get even more concerned about residuals that exceed +2.5 or -2.5 and even yet more concerned about residuals that exceed +3 or -3.
51 Detecting Unusual and. list r if r<-2 r>2 r Influential Data. We should pay attention to studentized residuals that exceed +2 or - 2, and get even more concerned about residuals that exceed +2.5 or -2.5 and even yet more concerned about residuals that exceed +3 or -3.
52 Detecting Unusual and. list r if r<-2 r>2 r list r if r<-2.5 r>2.5 Influential Data r We should pay attention to studentized residuals that exceed +2 or - 2, and get even more concerned about residuals that exceed +2.5 or -2.5 and even yet more concerned about residuals that exceed +3 or -3.
53 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data To get Leverage points, we use the predict command with the leverage option and we name them lev.
54 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data To get Leverage points, we use the predict command with the leverage option and we name them lev.. predict lev, leverage
55 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data Cook's D and DFITS measures both combine information on the residual and leverage. Cook's D and DFITS are very similar except that they scale differently but they give us similar answers.
56 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data Cook's D and DFITS measures both combine information on the residual and leverage. Cook's D and DFITS are very similar except that they scale differently but they give us similar answers.. predict d, cooksd
57 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data Cook's D and DFITS measures both combine information on the residual and leverage. Cook's D and DFITS are very similar except that they scale differently but they give us similar answers.. predict d, cooksd. list female read d if d>4/_n female read d 13. male male female male
58 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data Cook's D and DFITS measures both combine information on the residual and leverage. Cook's D and DFITS are very similar except that they scale differently but they give us similar answers.. predict dfit, dfits. list dfit if abs(dfit)>2*sqrt(3/51)
59 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data Cook's D and DFITS measures both combine information on the residual and leverage. Cook's D and DFITS are very similar except that they scale differently but they give us similar answers.. predict dfit, dfits. list dfit if abs(dfit)>2*sqrt(3/51) The above measures are general measures of influence.
60 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data We can also consider more specific measures of influence that assess how each coefficient is changed by deleting the observation. This measure is called DFBETA and is created for each of the predictors.
61 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data We can also consider more specific measures of influence that assess how each coefficient is changed by deleting the observation. This measure is called DFBETA and is created for each of the predictors. Apparently this is more computational intensive than summary statistics such as Cook's D.
62 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data We can also consider more specific measures of influence that assess how each coefficient is changed by deleting the observation. This measure is called DFBETA and is created for each of the predictors. In Stata, the dfbeta command will produce the DFBETAs for each of the predictors.
63 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data We can also consider more specific measures of influence that assess how each coefficient is changed by deleting the observation. This measure is called DFBETA and is created for each of the predictors. In Stata, the dfbeta command will produce the DFBETAs for each of the predictors.. dfbeta DFread: DFbeta(read) DFfemale: DFbeta(female)
64 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data We can also consider more specific measures of influence that assess how each coefficient is changed by deleting the observation. This measure is called DFBETA and is created for each of the predictors.. list DFread DFfemale in 1/5 DFread DFfemale
65 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data There are also several graphs that can be used to search for unusual and influential observations. The avplot command graphs an addedvariable plot.
66 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data avplot command not only works for the variables in the model, it also works for variables that are not in the model, which is why it is called added-variable plot. We can do an avplot on variable grade.
67 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data. avplot grade
68 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data. avplot grade Added-Variable plot
69 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data rvpplot is another convenience command which produces a plot of the residual versus a specified predictor and it is also used after regress or anova.
70 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data. rvpplot read
71 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data. rvpplot read
72 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data lvr2plot stands for leverage versus residual squared plot.
73 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data. lvr2plot
74 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data. lvr2plot
75 Detecting Unusual and Influential Data Summary of Detecting Unusual and Influential Data predict create predicted values, residuals, and measures of influence. dfbeta DFBETAs for all the independent variables avplot graphs an added-variable plot lvr2plot graphs a leverage-versus-squaredresidual plot. rvpplot graphs a residual-versus-predictor plot. rvfplot graphs residual-versus-fitted plot.
76 7. Tests for Model Specification
77 Tests for Model Specification A model specification error can occur when one or more relevant variables are omitted from the model or one or more irrelevant variables are included in the model.
78 Tests for Model Specification There are several methods to detect specification errors. The linktest command performs a model specification link test for single-equation models.
79 Tests for Model Specification. Linktest Source SS df MS Number of obs = F( 2, 197) = Model Prob > F = Residual R-squared = Adj R-squared = Total Root MSE = write Coef. Std. Err. t P> t [95% Conf. Interval] _hat _hatsq _cons
80 Tests for Model Specification The ovtest command performs performs a regression specification error test (RESET) for omitted variables.
81 Tests for Model Specification The ovtest command performs performs a regression specification error test (RESET) for omitted variables.. ovtest
82 Tests for Model Specification The ovtest command performs performs a regression specification error test (RESET) for omitted variables.. ovtest Ramsey RESET test using powers of the fitted values of write Ho: model has no omitted variables F(3, 194) = 1.95 Prob > F =
83 Tests for Model Specification Summary of Tests for Model Specification linktest performs a link test for model specification. ovtest performs regression specification error test (RESET) for omitted variables.
84 STATA: The Red tutorial
Notes for laboratory session 2
 Notes for laboratory session 2 Preliminaries Consider the ordinary least-squares (OLS) regression of alcohol (alcohol) and plasma retinol (retplasm). We do this with STATA as follows:. reg retplasm alcohol
Notes for laboratory session 2 Preliminaries Consider the ordinary least-squares (OLS) regression of alcohol (alcohol) and plasma retinol (retplasm). We do this with STATA as follows:. reg retplasm alcohol
Multiple Regression Analysis
 Multiple Regression Analysis Basic Concept: Extend the simple regression model to include additional explanatory variables: Y = β 0 + β1x1 + β2x2 +... + βp-1xp + ε p = (number of independent variables
Multiple Regression Analysis Basic Concept: Extend the simple regression model to include additional explanatory variables: Y = β 0 + β1x1 + β2x2 +... + βp-1xp + ε p = (number of independent variables
Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
 Revised July 2018 Multiple Linear Regression Analysis This set of notes shows how to use Stata in multiple regression analysis. It assumes that you have set Stata up on your computer (see the Getting Started
Revised July 2018 Multiple Linear Regression Analysis This set of notes shows how to use Stata in multiple regression analysis. It assumes that you have set Stata up on your computer (see the Getting Started
Introduction to regression
 Introduction to regression Regression describes how one variable (response) depends on another variable (explanatory variable). Response variable: variable of interest, measures the outcome of a study
Introduction to regression Regression describes how one variable (response) depends on another variable (explanatory variable). Response variable: variable of interest, measures the outcome of a study
Sociology 63993, Exam1 February 12, 2015 Richard Williams, University of Notre Dame,
 Sociology 63993, Exam1 February 12, 2015 Richard Williams, University of Notre Dame, http://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ I. True-False. (20 points) Indicate whether the following statements are true or false.
Sociology 63993, Exam1 February 12, 2015 Richard Williams, University of Notre Dame, http://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ I. True-False. (20 points) Indicate whether the following statements are true or false.
CHILD HEALTH AND DEVELOPMENT STUDY
 CHILD HEALTH AND DEVELOPMENT STUDY 9. Diagnostics In this section various diagnostic tools will be used to evaluate the adequacy of the regression model with the five independent variables developed in
CHILD HEALTH AND DEVELOPMENT STUDY 9. Diagnostics In this section various diagnostic tools will be used to evaluate the adequacy of the regression model with the five independent variables developed in
Age (continuous) Gender (0=Male, 1=Female) SES (1=Low, 2=Medium, 3=High) Prior Victimization (0= Not Victimized, 1=Victimized)
 Criminal Justice Doctoral Comprehensive Exam Statistics August 2016 There are two questions on this exam. Be sure to answer both questions in the 3 and half hours to complete this exam. Read the instructions
Criminal Justice Doctoral Comprehensive Exam Statistics August 2016 There are two questions on this exam. Be sure to answer both questions in the 3 and half hours to complete this exam. Read the instructions
Final Exam - section 2. Thursday, December hours, 30 minutes
 Econometrics, ECON312 San Francisco State University Michael Bar Fall 2011 Final Exam - section 2 Thursday, December 15 2 hours, 30 minutes Name: Instructions 1. This is closed book, closed notes exam.
Econometrics, ECON312 San Francisco State University Michael Bar Fall 2011 Final Exam - section 2 Thursday, December 15 2 hours, 30 minutes Name: Instructions 1. This is closed book, closed notes exam.
WELCOME! Lecture 11 Thommy Perlinger
 Quantitative Methods II WELCOME! Lecture 11 Thommy Perlinger Regression based on violated assumptions If any of the assumptions are violated, potential inaccuracies may be present in the estimated regression
Quantitative Methods II WELCOME! Lecture 11 Thommy Perlinger Regression based on violated assumptions If any of the assumptions are violated, potential inaccuracies may be present in the estimated regression
Business Research Methods. Introduction to Data Analysis
 Business Research Methods Introduction to Data Analysis Data Analysis Process STAGES OF DATA ANALYSIS EDITING CODING DATA ENTRY ERROR CHECKING AND VERIFICATION DATA ANALYSIS Introduction Preparation of
Business Research Methods Introduction to Data Analysis Data Analysis Process STAGES OF DATA ANALYSIS EDITING CODING DATA ENTRY ERROR CHECKING AND VERIFICATION DATA ANALYSIS Introduction Preparation of
Name: emergency please discuss this with the exam proctor. 6. Vanderbilt s academic honor code applies.
 Name: Biostatistics 1 st year Comprehensive Examination: Applied in-class exam May 28 th, 2015: 9am to 1pm Instructions: 1. There are seven questions and 12 pages. 2. Read each question carefully. Answer
Name: Biostatistics 1 st year Comprehensive Examination: Applied in-class exam May 28 th, 2015: 9am to 1pm Instructions: 1. There are seven questions and 12 pages. 2. Read each question carefully. Answer
MODEL I: DRINK REGRESSED ON GPA & MALE, WITHOUT CENTERING
 Interpreting Interaction Effects; Interaction Effects and Centering Richard Williams, University of Notre Dame, https://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Last revised February 20, 2015 Models with interaction effects
Interpreting Interaction Effects; Interaction Effects and Centering Richard Williams, University of Notre Dame, https://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Last revised February 20, 2015 Models with interaction effects
5 To Invest or not to Invest? That is the Question.
 5 To Invest or not to Invest? That is the Question. Before starting this lab, you should be familiar with these terms: response y (or dependent) and explanatory x (or independent) variables; slope and
5 To Invest or not to Invest? That is the Question. Before starting this lab, you should be familiar with these terms: response y (or dependent) and explanatory x (or independent) variables; slope and
Stat 13, Lab 11-12, Correlation and Regression Analysis
 Stat 13, Lab 11-12, Correlation and Regression Analysis Part I: Before Class Objective: This lab will give you practice exploring the relationship between two variables by using correlation, linear regression
Stat 13, Lab 11-12, Correlation and Regression Analysis Part I: Before Class Objective: This lab will give you practice exploring the relationship between two variables by using correlation, linear regression
MULTIPLE REGRESSION OF CPS DATA
 MULTIPLE REGRESSION OF CPS DATA A further inspection of the relationship between hourly wages and education level can show whether other factors, such as gender and work experience, influence wages. Linear
MULTIPLE REGRESSION OF CPS DATA A further inspection of the relationship between hourly wages and education level can show whether other factors, such as gender and work experience, influence wages. Linear
M15_BERE8380_12_SE_C15.6.qxd 2/21/11 8:21 PM Page Influence Analysis 1
 M15_BERE8380_12_SE_C15.6.qxd 2/21/11 8:21 PM Page 1 15.6 Influence Analysis FIGURE 15.16 Minitab worksheet containing computed values for the Studentized deleted residuals, the hat matrix elements, and
M15_BERE8380_12_SE_C15.6.qxd 2/21/11 8:21 PM Page 1 15.6 Influence Analysis FIGURE 15.16 Minitab worksheet containing computed values for the Studentized deleted residuals, the hat matrix elements, and
ANOVA. Thomas Elliott. January 29, 2013
 ANOVA Thomas Elliott January 29, 2013 ANOVA stands for analysis of variance and is one of the basic statistical tests we can use to find relationships between two or more variables. ANOVA compares the
ANOVA Thomas Elliott January 29, 2013 ANOVA stands for analysis of variance and is one of the basic statistical tests we can use to find relationships between two or more variables. ANOVA compares the
Preliminary Report on Simple Statistical Tests (t-tests and bivariate correlations)
 Preliminary Report on Simple Statistical Tests (t-tests and bivariate correlations) After receiving my comments on the preliminary reports of your datasets, the next step for the groups is to complete
Preliminary Report on Simple Statistical Tests (t-tests and bivariate correlations) After receiving my comments on the preliminary reports of your datasets, the next step for the groups is to complete
Daniel Boduszek University of Huddersfield
 Daniel Boduszek University of Huddersfield d.boduszek@hud.ac.uk Introduction to Multiple Regression (MR) Types of MR Assumptions of MR SPSS procedure of MR Example based on prison data Interpretation of
Daniel Boduszek University of Huddersfield d.boduszek@hud.ac.uk Introduction to Multiple Regression (MR) Types of MR Assumptions of MR SPSS procedure of MR Example based on prison data Interpretation of
An Introduction to Modern Econometrics Using Stata
 An Introduction to Modern Econometrics Using Stata CHRISTOPHER F. BAUM Department of Economics Boston College A Stata Press Publication StataCorp LP College Station, Texas Contents Illustrations Preface
An Introduction to Modern Econometrics Using Stata CHRISTOPHER F. BAUM Department of Economics Boston College A Stata Press Publication StataCorp LP College Station, Texas Contents Illustrations Preface
Multiple Regression Using SPSS/PASW
 MultipleRegressionUsingSPSS/PASW The following sections have been adapted from Field (2009) Chapter 7. These sections have been edited down considerablyandisuggest(especiallyifyou reconfused)thatyoureadthischapterinitsentirety.youwillalsoneed
MultipleRegressionUsingSPSS/PASW The following sections have been adapted from Field (2009) Chapter 7. These sections have been edited down considerablyandisuggest(especiallyifyou reconfused)thatyoureadthischapterinitsentirety.youwillalsoneed
CLASSICAL AND. MODERN REGRESSION WITH APPLICATIONS
 - CLASSICAL AND. MODERN REGRESSION WITH APPLICATIONS SECOND EDITION Raymond H. Myers Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State university 1 ~l~~l~l~~~~~~~l!~ ~~~~~l~/ll~~ Donated by Duxbury o Thomson Learning,,
- CLASSICAL AND. MODERN REGRESSION WITH APPLICATIONS SECOND EDITION Raymond H. Myers Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State university 1 ~l~~l~l~~~~~~~l!~ ~~~~~l~/ll~~ Donated by Duxbury o Thomson Learning,,
List of Figures. List of Tables. Preface to the Second Edition. Preface to the First Edition
 List of Figures List of Tables Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xv xxv xxix xxxi 1 What Is R? 1 1.1 Introduction to R................................ 1 1.2 Downloading and Installing
List of Figures List of Tables Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xv xxv xxix xxxi 1 What Is R? 1 1.1 Introduction to R................................ 1 1.2 Downloading and Installing
CHAPTER TWO REGRESSION
 CHAPTER TWO REGRESSION 2.0 Introduction The second chapter, Regression analysis is an extension of correlation. The aim of the discussion of exercises is to enhance students capability to assess the effect
CHAPTER TWO REGRESSION 2.0 Introduction The second chapter, Regression analysis is an extension of correlation. The aim of the discussion of exercises is to enhance students capability to assess the effect
Biology 345: Biometry Fall 2005 SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY Lab Exercise 5 Residuals and multiple regression Introduction
 Biology 345: Biometry Fall 2005 SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY Lab Exercise 5 Residuals and multiple regression Introduction In this exercise, we will gain experience assessing scatterplots in regression and
Biology 345: Biometry Fall 2005 SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY Lab Exercise 5 Residuals and multiple regression Introduction In this exercise, we will gain experience assessing scatterplots in regression and
APPENDIX D REFERENCE AND PREDICTIVE VALUES FOR PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATE (PEFR)
 APPENDIX D REFERENCE AND PREDICTIVE VALUES FOR PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATE (PEFR) Lung function is related to physical characteristics such as age and height. In order to assess the Peak Expiratory Flow
APPENDIX D REFERENCE AND PREDICTIVE VALUES FOR PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATE (PEFR) Lung function is related to physical characteristics such as age and height. In order to assess the Peak Expiratory Flow
2. Scientific question: Determine whether there is a difference between boys and girls with respect to the distance and its change over time.
 LDA lab Feb, 11 th, 2002 1 1. Objective:analyzing dental data using ordinary least square (OLS) and Generalized Least Square(GLS) in STATA. 2. Scientific question: Determine whether there is a difference
LDA lab Feb, 11 th, 2002 1 1. Objective:analyzing dental data using ordinary least square (OLS) and Generalized Least Square(GLS) in STATA. 2. Scientific question: Determine whether there is a difference
1.4 - Linear Regression and MS Excel
 1.4 - Linear Regression and MS Excel Regression is an analytic technique for determining the relationship between a dependent variable and an independent variable. When the two variables have a linear
1.4 - Linear Regression and MS Excel Regression is an analytic technique for determining the relationship between a dependent variable and an independent variable. When the two variables have a linear
Understandable Statistics
 Understandable Statistics correlated to the Advanced Placement Program Course Description for Statistics Prepared for Alabama CC2 6/2003 2003 Understandable Statistics 2003 correlated to the Advanced Placement
Understandable Statistics correlated to the Advanced Placement Program Course Description for Statistics Prepared for Alabama CC2 6/2003 2003 Understandable Statistics 2003 correlated to the Advanced Placement
4. STATA output of the analysis
 Biostatistics(1.55) 1. Objective: analyzing epileptic seizures data using GEE marginal model in STATA.. Scientific question: Determine whether the treatment reduces the rate of epileptic seizures. 3. Dataset:
Biostatistics(1.55) 1. Objective: analyzing epileptic seizures data using GEE marginal model in STATA.. Scientific question: Determine whether the treatment reduces the rate of epileptic seizures. 3. Dataset:
Dr. Kelly Bradley Final Exam Summer {2 points} Name
 {2 points} Name You MUST work alone no tutors; no help from classmates. Email me or see me with questions. You will receive a score of 0 if this rule is violated. This exam is being scored out of 00 points.
{2 points} Name You MUST work alone no tutors; no help from classmates. Email me or see me with questions. You will receive a score of 0 if this rule is violated. This exam is being scored out of 00 points.
Small Group Presentations
 Admin Assignment 1 due next Tuesday at 3pm in the Psychology course centre. Matrix Quiz during the first hour of next lecture. Assignment 2 due 13 May at 10am. I will upload and distribute these at the
Admin Assignment 1 due next Tuesday at 3pm in the Psychology course centre. Matrix Quiz during the first hour of next lecture. Assignment 2 due 13 May at 10am. I will upload and distribute these at the
Effects of Nutrients on Shrimp Growth
 Data Set 5: Effects of Nutrients on Shrimp Growth Statistical setting This Handout is an example of extreme collinearity of the independent variables, and of the methods used for diagnosing this problem.
Data Set 5: Effects of Nutrients on Shrimp Growth Statistical setting This Handout is an example of extreme collinearity of the independent variables, and of the methods used for diagnosing this problem.
6. Unusual and Influential Data
 Sociology 740 John ox Lecture Notes 6. Unusual and Influential Data Copyright 2014 by John ox Unusual and Influential Data 1 1. Introduction I Linear statistical models make strong assumptions about the
Sociology 740 John ox Lecture Notes 6. Unusual and Influential Data Copyright 2014 by John ox Unusual and Influential Data 1 1. Introduction I Linear statistical models make strong assumptions about the
Modeling unobserved heterogeneity in Stata
 Modeling unobserved heterogeneity in Stata Rafal Raciborski StataCorp LLC November 27, 2017 Rafal Raciborski (StataCorp) Modeling unobserved heterogeneity November 27, 2017 1 / 59 Plan of the talk Concepts
Modeling unobserved heterogeneity in Stata Rafal Raciborski StataCorp LLC November 27, 2017 Rafal Raciborski (StataCorp) Modeling unobserved heterogeneity November 27, 2017 1 / 59 Plan of the talk Concepts
Problem 1) Match the terms to their definitions. Every term is used exactly once. (In the real midterm, there are fewer terms).
 Problem 1) Match the terms to their definitions. Every term is used exactly once. (In the real midterm, there are fewer terms). 1. Bayesian Information Criterion 2. Cross-Validation 3. Robust 4. Imputation
Problem 1) Match the terms to their definitions. Every term is used exactly once. (In the real midterm, there are fewer terms). 1. Bayesian Information Criterion 2. Cross-Validation 3. Robust 4. Imputation
Linear Regression in SAS
 1 Suppose we wish to examine factors that predict patient s hemoglobin levels. Simulated data for six patients is used throughout this tutorial. data hgb_data; input id age race $ bmi hgb; cards; 21 25
1 Suppose we wish to examine factors that predict patient s hemoglobin levels. Simulated data for six patients is used throughout this tutorial. data hgb_data; input id age race $ bmi hgb; cards; 21 25
Validity, Reliability and Classical Assumptions
 , Reliability and Classical Assumptions Presented by Mahendra AN Sources: www-psych.stanford.edu/~bigopp/.ppt http://ets.mnsu.edu/darbok/ethn402-502/reliability.ppt http://5martconsultingbandung.blogspot.com/2011/01/uji-asumsi-klasik.html
, Reliability and Classical Assumptions Presented by Mahendra AN Sources: www-psych.stanford.edu/~bigopp/.ppt http://ets.mnsu.edu/darbok/ethn402-502/reliability.ppt http://5martconsultingbandung.blogspot.com/2011/01/uji-asumsi-klasik.html
RESPONSE SURFACE MODELING AND OPTIMIZATION TO ELUCIDATE THE DIFFERENTIAL EFFECTS OF DEMOGRAPHIC CHARACTERISTICS ON HIV PREVALENCE IN SOUTH AFRICA
 RESPONSE SURFACE MODELING AND OPTIMIZATION TO ELUCIDATE THE DIFFERENTIAL EFFECTS OF DEMOGRAPHIC CHARACTERISTICS ON HIV PREVALENCE IN SOUTH AFRICA W. Sibanda 1* and P. Pretorius 2 1 DST/NWU Pre-clinical
RESPONSE SURFACE MODELING AND OPTIMIZATION TO ELUCIDATE THE DIFFERENTIAL EFFECTS OF DEMOGRAPHIC CHARACTERISTICS ON HIV PREVALENCE IN SOUTH AFRICA W. Sibanda 1* and P. Pretorius 2 1 DST/NWU Pre-clinical
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables.
 bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
Psych 5741/5751: Data Analysis University of Boulder Gary McClelland & Charles Judd. Exam #2, Spring 1992
 Exam #2, Spring 1992 Question 1 A group of researchers from a neurobehavioral institute are interested in the relationships that have been found between the amount of cerebral blood flow (CB FLOW) to the
Exam #2, Spring 1992 Question 1 A group of researchers from a neurobehavioral institute are interested in the relationships that have been found between the amount of cerebral blood flow (CB FLOW) to the
isc ove ring i Statistics sing SPSS
 isc ove ring i Statistics sing SPSS S E C O N D! E D I T I O N (and sex, drugs and rock V roll) A N D Y F I E L D Publications London o Thousand Oaks New Delhi CONTENTS Preface How To Use This Book Acknowledgements
isc ove ring i Statistics sing SPSS S E C O N D! E D I T I O N (and sex, drugs and rock V roll) A N D Y F I E L D Publications London o Thousand Oaks New Delhi CONTENTS Preface How To Use This Book Acknowledgements
Chapter 10: Moderation, mediation and more regression
 Chapter 10: Moderation, mediation and more regression Smart Alex s Solutions Task 1 McNulty et al. (2008) found a relationship between a person s Attractiveness and how much Support they give their partner
Chapter 10: Moderation, mediation and more regression Smart Alex s Solutions Task 1 McNulty et al. (2008) found a relationship between a person s Attractiveness and how much Support they give their partner
Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data
 Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data Area Principle Bar Chart Boxplot Conditional Distribution Dotplot Empirical Rule Five Number Summary Frequency Distribution Frequency Polygon Histogram Interquartile
Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data Area Principle Bar Chart Boxplot Conditional Distribution Dotplot Empirical Rule Five Number Summary Frequency Distribution Frequency Polygon Histogram Interquartile
Least likely observations in regression models for categorical outcomes
 The Stata Journal (2002) 2, Number 3, pp. 296 300 Least likely observations in regression models for categorical outcomes Jeremy Freese University of Wisconsin Madison Abstract. This article presents a
The Stata Journal (2002) 2, Number 3, pp. 296 300 Least likely observations in regression models for categorical outcomes Jeremy Freese University of Wisconsin Madison Abstract. This article presents a
Simple Linear Regression
 Simple Linear Regression Assoc. Prof Dr Sarimah Abdullah Unit of Biostatistics & Research Methodology School of Medical Sciences, Health Campus Universiti Sains Malaysia Regression Regression analysis
Simple Linear Regression Assoc. Prof Dr Sarimah Abdullah Unit of Biostatistics & Research Methodology School of Medical Sciences, Health Campus Universiti Sains Malaysia Regression Regression analysis
TEACHING REGRESSION WITH SIMULATION. John H. Walker. Statistics Department California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo, CA 93407, U.S.A.
 Proceedings of the 004 Winter Simulation Conference R G Ingalls, M D Rossetti, J S Smith, and B A Peters, eds TEACHING REGRESSION WITH SIMULATION John H Walker Statistics Department California Polytechnic
Proceedings of the 004 Winter Simulation Conference R G Ingalls, M D Rossetti, J S Smith, and B A Peters, eds TEACHING REGRESSION WITH SIMULATION John H Walker Statistics Department California Polytechnic
Study Guide #2: MULTIPLE REGRESSION in education
 Study Guide #2: MULTIPLE REGRESSION in education What is Multiple Regression? When using Multiple Regression in education, researchers use the term independent variables to identify those variables that
Study Guide #2: MULTIPLE REGRESSION in education What is Multiple Regression? When using Multiple Regression in education, researchers use the term independent variables to identify those variables that
1. Objective: analyzing CD4 counts data using GEE marginal model and random effects model. Demonstrate the analysis using SAS and STATA.
 LDA lab Feb, 6 th, 2002 1 1. Objective: analyzing CD4 counts data using GEE marginal model and random effects model. Demonstrate the analysis using SAS and STATA. 2. Scientific question: estimate the average
LDA lab Feb, 6 th, 2002 1 1. Objective: analyzing CD4 counts data using GEE marginal model and random effects model. Demonstrate the analysis using SAS and STATA. 2. Scientific question: estimate the average
Staff Papers Series. Department of Agricultural and Applied Economics
 Staff Paper P89-19 June 1989 Staff Papers Series CHOICE OF REGRESSION METHOD FOR DETRENDING TIME SERIES DATA WITH NONNORMAL ERRORS by Scott M. Swinton and Robert P. King Department of Agricultural and
Staff Paper P89-19 June 1989 Staff Papers Series CHOICE OF REGRESSION METHOD FOR DETRENDING TIME SERIES DATA WITH NONNORMAL ERRORS by Scott M. Swinton and Robert P. King Department of Agricultural and
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY DATA AND PROBLEM
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Every morning, almost half of Americans start the day with a bowl of cereal, but choosing the right healthy breakfast is not always easy. Consumer Reports is therefore calculated by an
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Every morning, almost half of Americans start the day with a bowl of cereal, but choosing the right healthy breakfast is not always easy. Consumer Reports is therefore calculated by an
NEUROBLASTOMA DATA -- TWO GROUPS -- QUANTITATIVE MEASURES 38 15:37 Saturday, January 25, 2003
 NEUROBLASTOMA DATA -- TWO GROUPS -- QUANTITATIVE MEASURES 38 15:37 Saturday, January 25, 2003 Obs GROUP I DOPA LNDOPA 1 neurblst 1 48.000 1.68124 2 neurblst 1 133.000 2.12385 3 neurblst 1 34.000 1.53148
NEUROBLASTOMA DATA -- TWO GROUPS -- QUANTITATIVE MEASURES 38 15:37 Saturday, January 25, 2003 Obs GROUP I DOPA LNDOPA 1 neurblst 1 48.000 1.68124 2 neurblst 1 133.000 2.12385 3 neurblst 1 34.000 1.53148
Exercise Verify that the term on the left of the equation showing the decomposition of "total" deviation in a two-factor experiment.
 Exercise 2.2.1 Verify that the term on the left of the equation showing the decomposition of "total" deviation in a two-factor experiment y ijk y = ( y i y ) + ( y j y ) + [( y ij y ) ( y i y ) ( y j y
Exercise 2.2.1 Verify that the term on the left of the equation showing the decomposition of "total" deviation in a two-factor experiment y ijk y = ( y i y ) + ( y j y ) + [( y ij y ) ( y i y ) ( y j y
Answer Key to Problem Set #1
 Answer Key to Problem Set #1 Two notes: q#4e: Please disregard q#5e: The frequency tables of the total CESD scales of 94, 96 and 98 in question 5e should sum up to 328 observation not 924 (the student
Answer Key to Problem Set #1 Two notes: q#4e: Please disregard q#5e: The frequency tables of the total CESD scales of 94, 96 and 98 in question 5e should sum up to 328 observation not 924 (the student
11/18/2013. Correlational Research. Correlational Designs. Why Use a Correlational Design? CORRELATIONAL RESEARCH STUDIES
 Correlational Research Correlational Designs Correlational research is used to describe the relationship between two or more naturally occurring variables. Is age related to political conservativism? Are
Correlational Research Correlational Designs Correlational research is used to describe the relationship between two or more naturally occurring variables. Is age related to political conservativism? Are
11/24/2017. Do not imply a cause-and-effect relationship
 Correlational research is used to describe the relationship between two or more naturally occurring variables. Is age related to political conservativism? Are highly extraverted people less afraid of rejection
Correlational research is used to describe the relationship between two or more naturally occurring variables. Is age related to political conservativism? Are highly extraverted people less afraid of rejection
Question 1(25= )
 MSG500 Final 20-0-2 Examiner: Rebecka Jörnsten, 060-49949 Remember: To pass this course you also have to hand in a final project to the examiner. Open book, open notes but no calculators or computers allowed.
MSG500 Final 20-0-2 Examiner: Rebecka Jörnsten, 060-49949 Remember: To pass this course you also have to hand in a final project to the examiner. Open book, open notes but no calculators or computers allowed.
Item-Total Statistics
 64 Reliability Case Processing Summary N % Cases Valid 46 00.0 Excluded a 0.0 46 00.0 a. Listwise deletion based on all variables in the procedure. Reliability Statistics Cronbach's Alpha N of Items.869
64 Reliability Case Processing Summary N % Cases Valid 46 00.0 Excluded a 0.0 46 00.0 a. Listwise deletion based on all variables in the procedure. Reliability Statistics Cronbach's Alpha N of Items.869
Answer all three questions. All questions carry equal marks.
 UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN TRINITY COLLEGE Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science School of Computer Science and Statistics Postgraduate Diploma in Statistics Trinity Term 2 Introduction to Regression
UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN TRINITY COLLEGE Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science School of Computer Science and Statistics Postgraduate Diploma in Statistics Trinity Term 2 Introduction to Regression
ECON Introductory Econometrics Seminar 7
 ECON4150 - Introductory Econometrics Seminar 7 Stock and Watson EE11.2 April 28, 2015 Stock and Watson EE11.2 ECON4150 - Introductory Econometrics Seminar 7 April 28, 2015 1 / 25 E. 11.2 b clear set more
ECON4150 - Introductory Econometrics Seminar 7 Stock and Watson EE11.2 April 28, 2015 Stock and Watson EE11.2 ECON4150 - Introductory Econometrics Seminar 7 April 28, 2015 1 / 25 E. 11.2 b clear set more
Modern Regression Methods
 Modern Regression Methods Second Edition THOMAS P. RYAN Acworth, Georgia WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. PUBLICATION Contents Preface 1. Introduction 1.1 Simple Linear Regression Model, 3 1.2 Uses of Regression
Modern Regression Methods Second Edition THOMAS P. RYAN Acworth, Georgia WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. PUBLICATION Contents Preface 1. Introduction 1.1 Simple Linear Regression Model, 3 1.2 Uses of Regression
THE UNIVERSITY OF SUSSEX. BSc Second Year Examination DISCOVERING STATISTICS SAMPLE PAPER INSTRUCTIONS
 C8552 THE UNIVERSITY OF SUSSEX BSc Second Year Examination DISCOVERING STATISTICS SAMPLE PAPER INSTRUCTIONS Do not, under any circumstances, remove the question paper, used or unused, from the examination
C8552 THE UNIVERSITY OF SUSSEX BSc Second Year Examination DISCOVERING STATISTICS SAMPLE PAPER INSTRUCTIONS Do not, under any circumstances, remove the question paper, used or unused, from the examination
Doctors Fees in Ireland Following the Change in Reimbursement: Did They Jump?
 The Economic and Social Review, Vol. 38, No. 2, Summer/Autumn, 2007, pp. 259 274 Doctors Fees in Ireland Following the Change in Reimbursement: Did They Jump? DAVID MADDEN University College Dublin Abstract:
The Economic and Social Review, Vol. 38, No. 2, Summer/Autumn, 2007, pp. 259 274 Doctors Fees in Ireland Following the Change in Reimbursement: Did They Jump? DAVID MADDEN University College Dublin Abstract:
Chapter 11: Advanced Remedial Measures. Weighted Least Squares (WLS)
 Chapter : Advanced Remedial Measures Weighted Least Squares (WLS) When the error variance appears nonconstant, a transformation (of Y and/or X) is a quick remedy. But it may not solve the problem, or it
Chapter : Advanced Remedial Measures Weighted Least Squares (WLS) When the error variance appears nonconstant, a transformation (of Y and/or X) is a quick remedy. But it may not solve the problem, or it
Seid M. Zekavat, Loyola Marymount University
 THE INVESTIGATION OF SUICIDE USING SAS" SOFTWARE PROCEDURES: A SAS" / ETS APPROACH Seid M. Zekavat, Loyola Marymount University INTRODUCTION A careful look at the suicide data suggests a possible link
THE INVESTIGATION OF SUICIDE USING SAS" SOFTWARE PROCEDURES: A SAS" / ETS APPROACH Seid M. Zekavat, Loyola Marymount University INTRODUCTION A careful look at the suicide data suggests a possible link
Midterm STAT-UB.0003 Regression and Forecasting Models. I will not lie, cheat or steal to gain an academic advantage, or tolerate those who do.
 Midterm STAT-UB.0003 Regression and Forecasting Models The exam is closed book and notes, with the following exception: you are allowed to bring one letter-sized page of notes into the exam (front and
Midterm STAT-UB.0003 Regression and Forecasting Models The exam is closed book and notes, with the following exception: you are allowed to bring one letter-sized page of notes into the exam (front and
STAT445 Midterm Project1
 STAT445 Midterm Project1 Executive Summary This report works on the dataset of Part of This Nutritious Breakfast! In this dataset, 77 different breakfast cereals were collected. The dataset also explores
STAT445 Midterm Project1 Executive Summary This report works on the dataset of Part of This Nutritious Breakfast! In this dataset, 77 different breakfast cereals were collected. The dataset also explores
Data Analysis for Project. Tutorial
 Data Analysis for Project Tutorial Research Model Topic 2 Remanufactured Products Environmental Concern Attitude towards Recycling H2 (+) H1 (+) Subjective Norm Perceived Moral Obligation Convenience Perceived
Data Analysis for Project Tutorial Research Model Topic 2 Remanufactured Products Environmental Concern Attitude towards Recycling H2 (+) H1 (+) Subjective Norm Perceived Moral Obligation Convenience Perceived
Statistics Assignment 11 - Solutions
 Statistics 44.3 Assignment 11 - Solutions 1. Samples were taken of individuals with each blood type to see if the average white blood cell count differed among types. Eleven individuals in each group were
Statistics 44.3 Assignment 11 - Solutions 1. Samples were taken of individuals with each blood type to see if the average white blood cell count differed among types. Eleven individuals in each group were
Regression Analysis II
 Regression Analysis II Lee D. Walker University of South Carolina e-mail: walker23@gwm.sc.edu COURSE OVERVIEW This course focuses on the theory, practice, and application of linear regression. As Agresti
Regression Analysis II Lee D. Walker University of South Carolina e-mail: walker23@gwm.sc.edu COURSE OVERVIEW This course focuses on the theory, practice, and application of linear regression. As Agresti
m 11 m.1 > m 12 m.2 risk for smokers risk for nonsmokers
 SOCY5061 RELATIVE RISKS, RELATIVE ODDS, LOGISTIC REGRESSION RELATIVE RISKS: Suppose we are interested in the association between lung cancer and smoking. Consider the following table for the whole population:
SOCY5061 RELATIVE RISKS, RELATIVE ODDS, LOGISTIC REGRESSION RELATIVE RISKS: Suppose we are interested in the association between lung cancer and smoking. Consider the following table for the whole population:
Sample Exam Paper Answer Guide
 Sample Exam Paper Answer Guide Notes This handout provides perfect answers to the sample exam paper. I would not expect you to be able to produce such perfect answers in an exam. So, use this document
Sample Exam Paper Answer Guide Notes This handout provides perfect answers to the sample exam paper. I would not expect you to be able to produce such perfect answers in an exam. So, use this document
The Stata Journal. Editor Nicholas J. Cox Geography Department Durham University South Road Durham City DH1 3LE UK
 The Stata Journal Editor H. Joseph Newton Department of Statistics Texas A & M University College Station, Texas 77843 979-845-3142; FAX 979-845-3144 jnewton@stata-journal.com Associate Editors Christopher
The Stata Journal Editor H. Joseph Newton Department of Statistics Texas A & M University College Station, Texas 77843 979-845-3142; FAX 979-845-3144 jnewton@stata-journal.com Associate Editors Christopher
Choosing a Significance Test. Student Resource Sheet
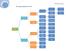 Choosing a Significance Test Student Resource Sheet Choosing Your Test Choosing an appropriate type of significance test is a very important consideration in analyzing data. If an inappropriate test is
Choosing a Significance Test Student Resource Sheet Choosing Your Test Choosing an appropriate type of significance test is a very important consideration in analyzing data. If an inappropriate test is
Correlation and Regression
 Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Books/Book Chapters School of Management 2012-10 Correlation and Regression Donal O'Brien Dublin Institute of Technology, donal.obrien@dit.ie Pamela Sharkey Scott
Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Books/Book Chapters School of Management 2012-10 Correlation and Regression Donal O'Brien Dublin Institute of Technology, donal.obrien@dit.ie Pamela Sharkey Scott
Online Appendix. According to a recent survey, most economists expect the economic downturn in the United
 Online Appendix Part I: Text of Experimental Manipulations and Other Survey Items a. Macroeconomic Anxiety Prime According to a recent survey, most economists expect the economic downturn in the United
Online Appendix Part I: Text of Experimental Manipulations and Other Survey Items a. Macroeconomic Anxiety Prime According to a recent survey, most economists expect the economic downturn in the United
STA 3024 Spring 2013 EXAM 3 Test Form Code A UF ID #
 STA 3024 Spring 2013 Name EXAM 3 Test Form Code A UF ID # Instructions: This exam contains 34 Multiple Choice questions. Each question is worth 3 points, for a total of 102 points (there are TWO bonus
STA 3024 Spring 2013 Name EXAM 3 Test Form Code A UF ID # Instructions: This exam contains 34 Multiple Choice questions. Each question is worth 3 points, for a total of 102 points (there are TWO bonus
Subject index. A about this book downloading programs...4 errata...19 example datasets... 4, 19
 Subject index A about this book downloading programs...4 errata...19 example datasets... 4, 19 GSS dataset...16 17 online resources...19 overview...13 18 Read me first...3 user-written programs... 4, 5
Subject index A about this book downloading programs...4 errata...19 example datasets... 4, 19 GSS dataset...16 17 online resources...19 overview...13 18 Read me first...3 user-written programs... 4, 5
Sociology Exam 3 Answer Key [Draft] May 9, 201 3
![Sociology Exam 3 Answer Key [Draft] May 9, 201 3 Sociology Exam 3 Answer Key [Draft] May 9, 201 3](/thumbs/96/127470588.jpg) Sociology 63993 Exam 3 Answer Key [Draft] May 9, 201 3 I. True-False. (20 points) Indicate whether the following statements are true or false. If false, briefly explain why. 1. Bivariate regressions are
Sociology 63993 Exam 3 Answer Key [Draft] May 9, 201 3 I. True-False. (20 points) Indicate whether the following statements are true or false. If false, briefly explain why. 1. Bivariate regressions are
HZAU MULTIVARIATE HOMEWORK #2 MULTIPLE AND STEPWISE LINEAR REGRESSION
 HZAU MULTIVARIATE HOMEWORK #2 MULTIPLE AND STEPWISE LINEAR REGRESSION Using the malt quality dataset on the class s Web page: 1. Determine the simple linear correlation of extract with the remaining variables.
HZAU MULTIVARIATE HOMEWORK #2 MULTIPLE AND STEPWISE LINEAR REGRESSION Using the malt quality dataset on the class s Web page: 1. Determine the simple linear correlation of extract with the remaining variables.
Introduction of Empirical Analysis using Stata: For Beginners
 WBS seminar ('17/12/23) 1 Introduction of Empirical Analysis using Stata: For Beginners Lecturer: Tohru Yoshioka-Kobayashi Project Research Associate Department of Technology Management for innovation
WBS seminar ('17/12/23) 1 Introduction of Empirical Analysis using Stata: For Beginners Lecturer: Tohru Yoshioka-Kobayashi Project Research Associate Department of Technology Management for innovation
Use the above variables and any you might need to construct to specify the MODEL A/C comparisons you would use to ask the following questions.
 Fall, 2002 Grad Stats Final Exam There are four questions on this exam, A through D, and each question has multiple sub-questions. Unless otherwise indicated, each sub-question is worth 3 points. Question
Fall, 2002 Grad Stats Final Exam There are four questions on this exam, A through D, and each question has multiple sub-questions. Unless otherwise indicated, each sub-question is worth 3 points. Question
Bangor University Laboratory Exercise 1, June 2008
 Laboratory Exercise, June 2008 Classroom Exercise A forest land owner measures the outside bark diameters at.30 m above ground (called diameter at breast height or dbh) and total tree height from ground
Laboratory Exercise, June 2008 Classroom Exercise A forest land owner measures the outside bark diameters at.30 m above ground (called diameter at breast height or dbh) and total tree height from ground
ANOVA in SPSS (Practical)
 ANOVA in SPSS (Practical) Analysis of Variance practical In this practical we will investigate how we model the influence of a categorical predictor on a continuous response. Centre for Multilevel Modelling
ANOVA in SPSS (Practical) Analysis of Variance practical In this practical we will investigate how we model the influence of a categorical predictor on a continuous response. Centre for Multilevel Modelling
SPSS output for 420 midterm study
 Ψ Psy Midterm Part In lab (5 points total) Your professor decides that he wants to find out how much impact amount of study time has on the first midterm. He randomly assigns students to study for hours,
Ψ Psy Midterm Part In lab (5 points total) Your professor decides that he wants to find out how much impact amount of study time has on the first midterm. He randomly assigns students to study for hours,
Regression Output: Table 5 (Random Effects OLS) Random-effects GLS regression Number of obs = 1806 Group variable (i): subject Number of groups = 70
 Regression Output: Table 5 (Random Effects OLS) Random-effects GLS regression Number of obs = 1806 R-sq: within = 0.1498 Obs per group: min = 18 between = 0.0205 avg = 25.8 overall = 0.0935 max = 28 Random
Regression Output: Table 5 (Random Effects OLS) Random-effects GLS regression Number of obs = 1806 R-sq: within = 0.1498 Obs per group: min = 18 between = 0.0205 avg = 25.8 overall = 0.0935 max = 28 Random
Cross-over trials. Martin Bland. Cross-over trials. Cross-over trials. Professor of Health Statistics University of York
 Cross-over trials Martin Bland Professor of Health Statistics University of York http://martinbland.co.uk Cross-over trials Use the participant as their own control. Each participant gets more than one
Cross-over trials Martin Bland Professor of Health Statistics University of York http://martinbland.co.uk Cross-over trials Use the participant as their own control. Each participant gets more than one
Research Methods in Forest Sciences: Learning Diary. Yoko Lu December Research process
 Research Methods in Forest Sciences: Learning Diary Yoko Lu 285122 9 December 2016 1. Research process It is important to pursue and apply knowledge and understand the world under both natural and social
Research Methods in Forest Sciences: Learning Diary Yoko Lu 285122 9 December 2016 1. Research process It is important to pursue and apply knowledge and understand the world under both natural and social
Bambang Subroto, Rosidi, Bambang Purnomosidhi Departement of Accounting, Faculty of Economics and Business, Brawijaya University
 GEDER DIFFERECES O THE IFLUECE OF ETHICAL JUDGMET AD MORAL REASOIG TOWARD BUDGET SLACK BEHAVIOR I PUBLIC SECTOR Syamsuri Rahim Doctoral Program of Accounting, Faculty of Economics and Business, Brawijaya
GEDER DIFFERECES O THE IFLUECE OF ETHICAL JUDGMET AD MORAL REASOIG TOWARD BUDGET SLACK BEHAVIOR I PUBLIC SECTOR Syamsuri Rahim Doctoral Program of Accounting, Faculty of Economics and Business, Brawijaya
In many cardiovascular experiments and observational studies,
 Statistical Primer for Cardiovascular Research Multiple Linear Regression Accounting for Multiple Simultaneous Determinants of a Continuous Dependent Variable Bryan K. Slinker, DVM, PhD; Stanton A. Glantz,
Statistical Primer for Cardiovascular Research Multiple Linear Regression Accounting for Multiple Simultaneous Determinants of a Continuous Dependent Variable Bryan K. Slinker, DVM, PhD; Stanton A. Glantz,
Multiple Bivariate Gaussian Plotting and Checking
 Multiple Bivariate Gaussian Plotting and Checking Jared L. Deutsch and Clayton V. Deutsch The geostatistical modeling of continuous variables relies heavily on the multivariate Gaussian distribution. It
Multiple Bivariate Gaussian Plotting and Checking Jared L. Deutsch and Clayton V. Deutsch The geostatistical modeling of continuous variables relies heavily on the multivariate Gaussian distribution. It
MMI 409 Spring 2009 Final Examination Gordon Bleil. 1. Is there a difference in depression as a function of group and drug?
 MMI 409 Spring 2009 Final Examination Gordon Bleil Table of Contents Research Scenario and General Assumptions Questions for Dataset (Questions are hyperlinked to detailed answers) 1. Is there a difference
MMI 409 Spring 2009 Final Examination Gordon Bleil Table of Contents Research Scenario and General Assumptions Questions for Dataset (Questions are hyperlinked to detailed answers) 1. Is there a difference
CRITERIA FOR USE. A GRAPHICAL EXPLANATION OF BI-VARIATE (2 VARIABLE) REGRESSION ANALYSISSys
 Multiple Regression Analysis 1 CRITERIA FOR USE Multiple regression analysis is used to test the effects of n independent (predictor) variables on a single dependent (criterion) variable. Regression tests
Multiple Regression Analysis 1 CRITERIA FOR USE Multiple regression analysis is used to test the effects of n independent (predictor) variables on a single dependent (criterion) variable. Regression tests
Data Analysis in Practice-Based Research. Stephen Zyzanski, PhD Department of Family Medicine Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine
 Data Analysis in Practice-Based Research Stephen Zyzanski, PhD Department of Family Medicine Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine Multilevel Data Statistical analyses that fail to recognize
Data Analysis in Practice-Based Research Stephen Zyzanski, PhD Department of Family Medicine Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine Multilevel Data Statistical analyses that fail to recognize
EPS 625 INTERMEDIATE STATISTICS TWO-WAY ANOVA IN-CLASS EXAMPLE (FLEXIBILITY)
 EPS 625 INTERMEDIATE STATISTICS TO-AY ANOVA IN-CLASS EXAMPLE (FLEXIBILITY) A researcher conducts a study to evaluate the effects of the length of an exercise program on the flexibility of female and male
EPS 625 INTERMEDIATE STATISTICS TO-AY ANOVA IN-CLASS EXAMPLE (FLEXIBILITY) A researcher conducts a study to evaluate the effects of the length of an exercise program on the flexibility of female and male
Overview of Lecture. Survey Methods & Design in Psychology. Correlational statistics vs tests of differences between groups
 Survey Methods & Design in Psychology Lecture 10 ANOVA (2007) Lecturer: James Neill Overview of Lecture Testing mean differences ANOVA models Interactions Follow-up tests Effect sizes Parametric Tests
Survey Methods & Design in Psychology Lecture 10 ANOVA (2007) Lecturer: James Neill Overview of Lecture Testing mean differences ANOVA models Interactions Follow-up tests Effect sizes Parametric Tests
Multivariate dose-response meta-analysis: an update on glst
 Multivariate dose-response meta-analysis: an update on glst Nicola Orsini Unit of Biostatistics Unit of Nutritional Epidemiology Institute of Environmental Medicine Karolinska Institutet http://www.imm.ki.se/biostatistics/
Multivariate dose-response meta-analysis: an update on glst Nicola Orsini Unit of Biostatistics Unit of Nutritional Epidemiology Institute of Environmental Medicine Karolinska Institutet http://www.imm.ki.se/biostatistics/
Data Analysis with SPSS
 Data Analysis with SPSS A First Course in Applied Statistics Fourth Edition Stephen Sweet Ithaca College Karen Grace-Martin The Analysis Factor Allyn & Bacon Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco
Data Analysis with SPSS A First Course in Applied Statistics Fourth Edition Stephen Sweet Ithaca College Karen Grace-Martin The Analysis Factor Allyn & Bacon Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco
Demystifying causal inference in randomised trials. Lecture 3: Introduction to mediation and mediation analysis using instrumental variables
 Demystifying causal inference in randomised trials Lecture 3: Introduction to mediation and mediation analysis using instrumental variables ISCB 2016 Graham Dunn and Richard Emsley Centre for Biostatistics,
Demystifying causal inference in randomised trials Lecture 3: Introduction to mediation and mediation analysis using instrumental variables ISCB 2016 Graham Dunn and Richard Emsley Centre for Biostatistics,
What you should know before you collect data. BAE 815 (Fall 2017) Dr. Zifei Liu
 What you should know before you collect data BAE 815 (Fall 2017) Dr. Zifei Liu Zifeiliu@ksu.edu Types and levels of study Descriptive statistics Inferential statistics How to choose a statistical test
What you should know before you collect data BAE 815 (Fall 2017) Dr. Zifei Liu Zifeiliu@ksu.edu Types and levels of study Descriptive statistics Inferential statistics How to choose a statistical test
