Session outline. Introduction to psychoses. Assessment of psychoses. Management of psychoses. Follow-up. Review.
|
|
|
- Leo Armstrong
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Psychoses 1
2 Session outline Introduction to psychoses. Assessment of psychoses. Management of psychoses. Follow-up. Review. 2
3 Activity 1: Person s story Present the person s story of what it feels like to live with psychoses. First thoughts. 3
4 What do local people believe? What are the local names for people with psychoses? How are individuals with psychoses treated in the local community? How are their family treated? Where can the individual and their family seek help? 4
5 Symptoms 5
6 Symptoms of psychosis Disturbed perceptions: Hallucinations Altered perception, i.e. hearing voices, seeing or feeling things that are not there. Disturbed thinking: Delusions: False belief that the person is sure is true, i.e. person believes family are poisoning her. Or person believes he is royalty. Or person may believe his family are aliens in disguise. Disturbed behaviours and emotions: Disturbances of behaviour: social withdrawal, agitation, disorganized behaviour, inactivity or hyperactivity, selfneglect, loss of interest and motivation. Disturbances of emotions: marked apathy, poor speech, one word answers, slowed speech, thoughts may be disorganized and hard to follow, disconnect between reported emotion and facial expressions or body language. 6
7 Symptoms of bipolar disorder Disturbed mood: Person has episodes where they are manic and other episodes where they are depressed Characteristically recovery between the episodes is complete. Manic episode: Increased activity levels, elevation of mood (potentially very happy and very agitated). They may talk very rapidly, have lots of different ideas and increased levels of self-worth and selfimportance. They may have hallucinations and delusions, i.e. hear voices and/or believe that they are powerful, that their ideas can change the world. Engage in risk taking behaviours (gambling, spending money, promiscuity etc.). 7
8 Natural history of psychosis First onset typically between age 15 and 29 years. There are three possible clinical courses: o The person recovers completely or partially with some symptoms. o The person recovers but has a future episode (relapse). o Symptoms continue for a longer period. 8
9 Natural history of bipolar disorder First onset typically between the ages of years. The pattern of mood swings can vary widely between people: o Some will have a couple of bipolar episodes in their life time and stay stable in between. o Others will have many episodes. o Some will only experience manic episodes. o Some will experience more depressed episodes than manic episodes. 9
10 Impact of psychoses Impact on the individual: Break up of relationships Negative and at times scary experience of symptoms. Loss of employment, studies, opportunities. Financial consequences. Stigma and rejection by community. Impact on the family: Medical costs. Time and energy looking after the person (carer burden). Emotional distress. 10
11 Impact of psychoses Impact on society: Loss of workforce. Costly medical interventions and (unnecessarily) lengthy hospitalizations. Human rights violations: People with psychoses maybe chained and confined. They may be beaten as punishment or treatment. They may receive treatments that are ineffective and dangerous due to misunderstanding the causes of psychoses. 11
12 Human rights violations Asdila is a young woman who hears voices. As she was wandering on the street and talking out loud, the police arrested her. She had not committed any offence but while in custody she was told that she would be transferred to a psychiatric hospital. In the hospital she was forced to take high doses of psychotropic drugs which made her extremely unwell. She was bullied and attacked by staff and other male patients. She has no way to challenge her detention. 12
13 Discussion What stigma and discrimination do people with psychoses face in your community? What can you do to reduce the stigma? 13
14 What you can do to decrease stigma, discrimination and human rights violations Treat people with respect and dignity. Avoid making assumptions, e.g. The person is dangerous or the person lacks capacity. Do not assume that the person is unable to make choices or decisions concerning treatment. Involve the person in the development of their treatment plan. Avoid involuntary admission and treatment, seclusions and restraints and other coercive practices. Treat psychoses at the non-specialist level which is less stigmatizing, more acceptable and accessible for people. 14
15 What you can do to decrease stigma, discrimination and human rights violations Provide accurate and supportive information to the person concerned and their family: o About psychoses as well as treatment and recovery options. o Dispel myths about psychoses. o Raise awareness on the rights of people with mental disorders including psychoses. Raise awareness among other health professionals and colleagues, family members and the wider community in order to dispel the stigma, myths and misconceptions about psychoses. Involve people with mental disabilities and their carers in any awareness raising activities. Empower them to speak for themselves. 15
16 Global impact of psychoses Affects 21 million people globally (more common among men 12 million than women 9 million). Has an early onset in many (15 29 years old). People with psychoses are two and a half times more likely to die early than the general population, due to physical illness such as cardiovascular, metabolic and infectious diseases. 16
17 Why it is important to treat in non-specialized health settings Psychoses is treatable. Medicines and psychosocial interventions are effective at treating psychoses. People with psychoses can be cared for outside of hospitals in non-specialized health settings and the community. Engaging the family and community in the care of people with psychoses is important. 17
18 Activity 2: Exploring the symptoms of psychoses 1. Identify whether the person is experiencing a hallucination or delusions? Explain your decisions. 2. Identify how the hallucination or delusion impact on the person s life? Explain your decisions. 18
19 19
20 Factors influencing communication The person s thoughts might be disorganized and unclear. The person might be sharing unusual beliefs. The person might refuse to speak. The person might avoid any eye contact. The person may not feel that they need medical care. Often the family will report the issue, not the person. Now we will discuss how these issues affect your interaction with the person. 20
21 Establish communication and build trust Treat the person with respect and dignity. Try to understand the person s perspective. Introduce your questions in a respectful way. Do not rush; it may take several sessions to build trust. Do not challenge false beliefs or mock the person. Ask how the person s life has been affected. Advocate on the person's behalf. 21
22 Activity 3: Video demonstration: Assessment Show the mhgap-ig psychoses assessment video. tpy5nbfmijy&index=4&list=plu4ies koli8gicaendwesq6-yagxhes5v 22
23 23
24 Delirium An organic brain syndrome characterized by acute onset of: Confusion (person appears confused, struggles to understand surroundings). Difficulty in focusing, shifting or maintaining attention. Changes in feeling (sensations and perceptions). Changes in level of consciousness or awareness. Disturbance in orientation to time, place and sometimes person. Disorganized thinking speech does not make sense. Changes in mood anger, agitation, anxiety, irritability, anxiety to apathy and depression. 24
25 Management of delirium If you think that a person has delirium: Try to identify and manage underlying cause. Assess for dehydration and give fluid. Ensure that the person is safe and comfortable. Continue to reassess and monitor the person after initiating management. Refer the person to a specialist (e.g. neurologist, psychiatrist, or internal medicine specialist). 25
26 26
27 Managing concurrent MNS conditions and psychoses Psychoses can occur with: Depressive episodes people can experience hallucinations and delusions when depressed. Post-partum psychosis in the days and weeks after giving birth women can experience changes in mood (including mania and depression). They can experience hallucinations and delusions and significant confusion in their thinking and behaviour. Substance use disorders intoxication due to substance use can produce significant disturbances in mood and changes in levels of consciousness, confusions and erratic behaviour. Withdrawal from substances can also cause confusion, erratic behaviour, changes in consciousness and perception. Dementia people living with dementia can report experiencing changes in perceptions (hallucinations and delusions). 27
28 28
29 29
30 Case scenario A 22-year-old woman is brought to the clinic by her parents. They are concerned about her bizarre behaviour and strange speech. They explain the young woman keeps getting very agitated and angry and states that she wishes to escape from a terrible monster taking the shape of her father. Today she violently attacked her father. 30
31 Case scenario continued Her father has multiple cuts and bruises on his face and body from where he was attacked. The young woman is obviously still agitated and restless. She cannot stay still and keeps trying to get away from her father. She is shouting at him to go away get out leave me. What can you do to manage the situation? 31
32 32
33 33
34 How to ask about hallucinations and delusions? Symptoms Person Family Hallucinations Delusions e.g. Do you hear voices or see things that no one else can? e.g. Do you believe that someone is planning to hurt you? Do you feel that you are under surveillance? e.g. Do you see the person talking to someone else when alone? As if the person is talking to someone? e.g. Did the person share any ideas that you found strange and unlikely to be true? 34
35 Activity 4: Role play: Assessment - A man who is well known to you is homeless and lives under the tree opposite your practice. He has been seen talking to himself and laughing to himself, is unkempt and ungroomed. - Assess him according to the psychoses assessment algorithm on page 35 mhgap- IG. 35
36 36
37 Reducing stress and strengthening social support Promoting daily activities Ensuring safety in the community and mobility community support Pharmacology Psychoeducation 37
38 38
39 Activity 5 Video demonstration: Managing psychoses How did the health-care provider explain the treatment options? Were the risks and benefits of medication explained? Were the benefits of psychosocial interventions explained? 4&list=PLU4ieskOli8GicaEnDweSQ6- yagxhes5v&index=5 39
40 40
41 Activity 6: Psychoeducation Group 1: Key messages in psychoeducation for psychosis. Group 2: Key messages in psychoeducation for bipolar disorder. 41
42 Activity 7: Promoting functioning in daily living activities Promoting functioning in daily living activities is a crucial step in their journey to recovery. It will: Help a person cope with and manage their symptoms. Reconnect the person with their community. Empower the person to take back some control of their life. Give the person the opportunity to learn and/or earn an income so they can live independently in the future. Give the person hope that they will recover and have a better future. 42
43 Initiating antipsychotic medication Are antipsychotics better started early or late? Early! For prompt control of psychotic symptoms, health-care providers should begin antipsychotic medication immediately after assessment. The sooner the better. 43
44 Initiating antipsychotic medication Is it better to start with a low dose or a high dose? Low! Start with a low dose within the therapeutic range and increase slowly to the lowest effective dose in order to reduce the risk of side-effects. Start low, go slow. 44
45 Initiating antipsychotic medication Which route is preferable? oral intramuscular. Oral! Consider intramuscular treatment only if oral treatment is not feasible. Do not prescribe long-term injections (depot) for control of acute psychotic symptoms. 45
46 Initiating antipsychotic medication How many antipsychotic medications should we prescribe at a time? one more than one. One! Try the first medication at an optimum dose for at least four to six weeks before considering it ineffective. 46
47 47
48 48
49 Case scenario Yosef is 21 years old has been brought to you by his mother. His mother says that recently Yosef "is not the same." He is no longer studying and prefers to stay home doing nothing. You notice that Yosef is wearing summer clothes although it is cold and raining. He looks like he has not washed for weeks. When you talk to him, Yosef avoids eye contact. He gazes at the ceiling as if looking at someone. He mumbles and gestures as if he is talking to someone. He does not want to see his friends, he seems disconnected from his family and has no energy. He is refusing to eat food in the home as he believes his mother is trying to poison him. You assess Yosef and decide to start him on antispyshchotic medication to see if that improves his symptoms. 49
50 Antipsychotic medications What are the starting doses for haloperidol, chlorpromazine and riseperdione? What are the effective doses? What are the side-effects for each drug? 50
51 Case scenario Maria is a 35-year-old woman. She is married and has two children (10 and 8 years old). For the last five years she has held a management level position in a local bank and has been enjoying her career. In the last two months she has been experiencing changes in her mood. She has been arguing with people at work and her family at home. She is getting frustrated as she does not feel people are listening to her or understanding her. Her speech is very fast and confusing as she is having so many ideas at the same time. She is spending a lot of money and that is causing arguments with her husband. She is active all the time and is not sleeping well. After a thorough assessment you decide she is experiencing a manic episode. 51
52 Mood stabilizers What are the starting doses for lithium, sodium valproate and carbamazepine? When should you not use lithium? What are the effective doses? What are the side-effects of each drug? 52
53 Review and adherence What should you do if Yosef complains of muscle rigidity and stiffness, and you notice that he has involuntary repetitive lip smacking? What could you do if a person who has started to take risperidone complains that they feel it is not doing anything to help them? How would you help someone who stopped taking sodium valproate because they were gaining too much weight and felt uncomfortable? 53
54 Case scenario A 28-year-old woman called Fatima gave birth to her second child two weeks ago. Her husband explains that she is not sleeping at all and she is struggling to feed the baby. She believes that her baby is in danger but she does not know how to protect it. Sometimes she thinks it would be better if she and the baby were both dead. On one occasion the husband has stopped her from being violent towards the baby. 54
55 55
56 56
57 57
58 58
59 59
60 Activity 8: Role play: Follow-up Follow-up with a person with psychosis. Focus on reassessment of the symptoms. Assessment of side-effects of medication. Assessment of psychosocial interventions specifically strengthening social support, reducing stress and life skills. 60
61 Review MCQs 61
Module: Psychoses. Overview. Learning objectives PSY. Key messages
 Module: Psychoses Overview Learning objectives Promote respect and dignity for people with psychoses. Name common presentations of psychoses. Name assessment principles of psychoses. Name management principles
Module: Psychoses Overview Learning objectives Promote respect and dignity for people with psychoses. Name common presentations of psychoses. Name assessment principles of psychoses. Name management principles
Session outline. Introduction to dementia Assessment of dementia Management of dementia Follow-up Review
 Dementia 1 Session outline Introduction to dementia Assessment of dementia Management of dementia Follow-up Review 2 Activity 1: Person s story Present a person s story of what it feels like to live with
Dementia 1 Session outline Introduction to dementia Assessment of dementia Management of dementia Follow-up Review 2 Activity 1: Person s story Present a person s story of what it feels like to live with
Session outline. Introduction to depression Assessment of depression Management of depression Follow-up Review
 Depression 1 Session outline Introduction to depression Assessment of depression Management of depression Follow-up Review 2 Activity 1: Person s story followed by group discussion Present the first person
Depression 1 Session outline Introduction to depression Assessment of depression Management of depression Follow-up Review 2 Activity 1: Person s story followed by group discussion Present the first person
Other significant mental health complaints
 Other significant mental health complaints 2 Session outline Introduction to other significant mental health complaints Assessment of other significant mental health complaints Management of other significant
Other significant mental health complaints 2 Session outline Introduction to other significant mental health complaints Assessment of other significant mental health complaints Management of other significant
Schizophrenia. This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available.
 This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available. What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a severe mental health condition. However,
This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available. What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a severe mental health condition. However,
Emergency Care 3/9/15. Multimedia Directory. Topics. Emergency Care for Behavioral and. Psychiatric Emergencies CHAPTER
 Emergency Care THIRTEENTH EDITION CHAPTER 23 Behavioral and Psychiatric Emergencies and Suicide Multimedia Directory Slide 42 Applications of Mechanical Restraints Video Topics Behavioral and Psychiatric
Emergency Care THIRTEENTH EDITION CHAPTER 23 Behavioral and Psychiatric Emergencies and Suicide Multimedia Directory Slide 42 Applications of Mechanical Restraints Video Topics Behavioral and Psychiatric
A-Z of Mental Health Problems
 Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Module: Dementia. Overview. Learning objectives. Key messages DEM
 Module: Dementia Overview Learning objectives Promote respect and dignity for people with dementia. Know common presentations of dementia. Know the assessment principles of dementia. Know the management
Module: Dementia Overview Learning objectives Promote respect and dignity for people with dementia. Know common presentations of dementia. Know the assessment principles of dementia. Know the management
Why does someone develop bipolar disorder?
 Bipolar Disorder Do you go through intense moods? Do you feel very happy and energized some days, and very sad and depressed on other days? Do these moods last for a week or more? Do your mood changes
Bipolar Disorder Do you go through intense moods? Do you feel very happy and energized some days, and very sad and depressed on other days? Do these moods last for a week or more? Do your mood changes
Session outline. Introduction to self-harm/suicide. Assessment of self-harm/suicide. Management of self-harm/suicide. Follow-up.
 Self-harm/suicide 1 Session outline Introduction to self-harm/suicide. Assessment of self-harm/suicide. Management of self-harm/suicide. Follow-up. Activity 1: Person stories Present the person stories
Self-harm/suicide 1 Session outline Introduction to self-harm/suicide. Assessment of self-harm/suicide. Management of self-harm/suicide. Follow-up. Activity 1: Person stories Present the person stories
Practitioner Guidelines for Enhanced IMR for COD Handout #2: Practical Facts About Mental Illness
 Chapter II Practitioner Guidelines for Enhanced IMR for COD Handout #2: Practical Facts About Mental Illness There are four handouts to choose from, depending on the client and his or her diagnosis: 2A:
Chapter II Practitioner Guidelines for Enhanced IMR for COD Handout #2: Practical Facts About Mental Illness There are four handouts to choose from, depending on the client and his or her diagnosis: 2A:
Positive language Style guidelines. Positive language. An Alzheimer s Society guide to talking about dementia. April 2018 alzheimers.org.
 Positive language Style guidelines 1 Positive language An Alzheimer s Society guide to talking about dementia April 2018 alzheimers.org.uk 2 What is positive language and why is it important? There are
Positive language Style guidelines 1 Positive language An Alzheimer s Society guide to talking about dementia April 2018 alzheimers.org.uk 2 What is positive language and why is it important? There are
Module: Self-harm/suicide
 Module: Self-harm/suicide Overview Learning objectives Promote respect and dignity for people with self-harm/suicide. Know the common presentations of self-harm/suicide. Know the principles of assessment
Module: Self-harm/suicide Overview Learning objectives Promote respect and dignity for people with self-harm/suicide. Know the common presentations of self-harm/suicide. Know the principles of assessment
The treatment of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents
 DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION The treatment of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents The paragraphs in the draft are numbered for the purposes of consultation. The final version will not contain
DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION The treatment of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents The paragraphs in the draft are numbered for the purposes of consultation. The final version will not contain
Mood Disorders. Moderate depression that will go away without therapy. Restlessness, inability to concentrate, and rapid speech. Dysthymic Disorder
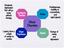 Moderate depression that will go away without therapy Dysthymic Disorder Mania Restlessness, inability to concentrate, and rapid speech Mood Disorders Lasting from a couple of weeks to months Major Depression
Moderate depression that will go away without therapy Dysthymic Disorder Mania Restlessness, inability to concentrate, and rapid speech Mood Disorders Lasting from a couple of weeks to months Major Depression
Delirium. Delirium is characterized by an acute onset (hours or days) and fluctuating course of deterioration in mental functioning.
 Delirium Delirium is characterized by an acute onset (hours or days) and fluctuating course of deterioration in mental functioning. DELIRIUM IS A MEDICAL EMERGENCY! Delirium: Hallmark Features Inattention-
Delirium Delirium is characterized by an acute onset (hours or days) and fluctuating course of deterioration in mental functioning. DELIRIUM IS A MEDICAL EMERGENCY! Delirium: Hallmark Features Inattention-
Some Common Mental Disorders in Young People Module 3B
 Some Common Mental Disorders in Young People Module 3B MENTAL ILLNESS AND TEENS About 70% of all mental illnesses can be diagnosed before 25 years of age When they start, most mental illnesses are mild
Some Common Mental Disorders in Young People Module 3B MENTAL ILLNESS AND TEENS About 70% of all mental illnesses can be diagnosed before 25 years of age When they start, most mental illnesses are mild
Health Point: Mood Disorders
 Health Point: Mood Disorders A mood disorder is one type of mental health condition. Mental health conditions affect your brain and can change the way you feel, think, or behave. Mood disorders mainly
Health Point: Mood Disorders A mood disorder is one type of mental health condition. Mental health conditions affect your brain and can change the way you feel, think, or behave. Mood disorders mainly
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Baby Blues and More DRAFT. Knowing About This in Advance Can Help
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Recognizing and coping with postpartum mood disorders Some women have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. It helps to know about these
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Recognizing and coping with postpartum mood disorders Some women have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. It helps to know about these
Suicide Prevention Carroll County Public Schools
 Suicide Prevention Carroll County Public Schools 2012-13 The Facts Statistics 3 rd leading cause of death for adolescents (15-24 yrs. old) 6 th leading cause of death for children (5-14 yrs. old) 11 th
Suicide Prevention Carroll County Public Schools 2012-13 The Facts Statistics 3 rd leading cause of death for adolescents (15-24 yrs. old) 6 th leading cause of death for children (5-14 yrs. old) 11 th
ASAM Criteria, Third Edition Matrix for Matching Adult Severity and Level of Function with Type and Intensity of Service
 1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 0 1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 1 1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 2 The patient
1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 0 1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 1 1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 2 The patient
DEPRESSION. There are a couple of kinds, or forms. The most common are major depression and dysthymic disorder.
 DEPRESSION OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class, you will be able to: 1.list and describe several kinds of depression, 2.discuss the signs of depression, and 3.relate the treatment of depression. INTRODUCTION
DEPRESSION OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class, you will be able to: 1.list and describe several kinds of depression, 2.discuss the signs of depression, and 3.relate the treatment of depression. INTRODUCTION
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 25.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13, 36 37 25.2 Recognize behaviors that are abnormal in a given context. Slide 13 25.3 Discuss
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 25.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13, 36 37 25.2 Recognize behaviors that are abnormal in a given context. Slide 13 25.3 Discuss
The cancer of mental illness
 The cancer of mental illness KWL Chart and Hearing Voices Simulations De-brief on activity What is schizophrenia? Recognition of Schizophrenia Symptoms Anderson Cooper Simulation Diagnosis and Treatment
The cancer of mental illness KWL Chart and Hearing Voices Simulations De-brief on activity What is schizophrenia? Recognition of Schizophrenia Symptoms Anderson Cooper Simulation Diagnosis and Treatment
keep track of other information like warning discuss with your doctor, and numbers of signs for relapse, things you want to
 Helping you set your brain free from psychosis. www.heretohelp.bc.ca This book was written by Sophia Kelly and the BC Schizophrenia Society, for the BC Partners for Mental Health and Addictions Information.
Helping you set your brain free from psychosis. www.heretohelp.bc.ca This book was written by Sophia Kelly and the BC Schizophrenia Society, for the BC Partners for Mental Health and Addictions Information.
Schizophrenia: core interventions in the treatment and management of schizophrenia
 Schizophrenia: core interventions in the treatment and management of schizophrenia A guide for people with schizophrenia, their advocates and carers, and the public Information for the public (2 nd consultation)
Schizophrenia: core interventions in the treatment and management of schizophrenia A guide for people with schizophrenia, their advocates and carers, and the public Information for the public (2 nd consultation)
Understanding Perinatal Mood Disorders (PMD)
 Understanding Perinatal Mood Disorders (PMD) Postpartum Depression and Beyond Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital 25 North Winfield Road Winfield, Illinois 60190 630.933.1600 Northwestern Medicine
Understanding Perinatal Mood Disorders (PMD) Postpartum Depression and Beyond Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital 25 North Winfield Road Winfield, Illinois 60190 630.933.1600 Northwestern Medicine
It s Mental Health Week!
 It s Mental Health Week! This year, the Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) presents Mental Health Week from May 5 th to May 11 th. CMHA is launching a Be Mind Full initiative asking Canadians if
It s Mental Health Week! This year, the Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) presents Mental Health Week from May 5 th to May 11 th. CMHA is launching a Be Mind Full initiative asking Canadians if
HELPING A PERSON WITH SCHIZOPHRENIA
 HELPING A PERSON WITH SCHIZOPHRENIA OVERCOMING CHALLENGES WHILE TAKING CARE OF YOURSELF The love and support of family plays an important role in schizophrenia treatment and recovery. If someone close
HELPING A PERSON WITH SCHIZOPHRENIA OVERCOMING CHALLENGES WHILE TAKING CARE OF YOURSELF The love and support of family plays an important role in schizophrenia treatment and recovery. If someone close
Understanding Depression
 Understanding Depression What causes Depression? Family History Having family members who have depression may increase a person s risk Deficiencies of certain chemicals in the brain may lead to depression
Understanding Depression What causes Depression? Family History Having family members who have depression may increase a person s risk Deficiencies of certain chemicals in the brain may lead to depression
This information explains the advice about supporting people with dementia and their carers that is set out in NICE SCIE clinical guideline 42.
 Supporting people with dementia and their carers Information for the public Published: 1 November 2006 nice.org.uk About this information NICEclinicalguidelinesadvisetheNHSoncaringforpeoplewithspe cificconditionsordiseasesandthetreatmentstheyshouldreceive.
Supporting people with dementia and their carers Information for the public Published: 1 November 2006 nice.org.uk About this information NICEclinicalguidelinesadvisetheNHSoncaringforpeoplewithspe cificconditionsordiseasesandthetreatmentstheyshouldreceive.
Dr Steve Moss BSc MSc Phd, Consultant Research Psychologist attached to the Estia Centre, Guys Hospital, London.
 INFORMATION SHEET Psychiatric disorders in people with learning disability Dr Steve Moss BSc MSc Phd, Consultant Research Psychologist attached to the Estia Centre, Guys Hospital, London. In the whole
INFORMATION SHEET Psychiatric disorders in people with learning disability Dr Steve Moss BSc MSc Phd, Consultant Research Psychologist attached to the Estia Centre, Guys Hospital, London. In the whole
L;ve L;fe; Your story is not over yet.
 L;ve L;fe; Your story is not over yet. Suicide is not as rare as some think. Who is more at risk? In the U.S., suicide rates are highest during the spring. Suicide is the 3rd leading cause of death for
L;ve L;fe; Your story is not over yet. Suicide is not as rare as some think. Who is more at risk? In the U.S., suicide rates are highest during the spring. Suicide is the 3rd leading cause of death for
Crisis Management. Crisis Management Goals. Emotionally Disturbed Persons 10/29/2009
 Crisis Management Crisis Management Goals try to ensure safety for yourself, other officers, subjects, and other citizens establish and maintain control resolve the situation positively when appropriate,
Crisis Management Crisis Management Goals try to ensure safety for yourself, other officers, subjects, and other citizens establish and maintain control resolve the situation positively when appropriate,
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Baby Blues and More. Postpartum mood disorders DRAFT. Emotional Changes After Giving Birth
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Postpartum mood disorders Some new mothers have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. This chapter gives ideas for things you can do to
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Postpartum mood disorders Some new mothers have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. This chapter gives ideas for things you can do to
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Presented by Bevan Gibson Southern IL Professional Development Center -Part of the Illinois Community College Board Service Center Network
 Bipolar Disorder: What It Means to You and Your Classroom Presented by Bevan Gibson Southern IL Professional Development Center -Part of the Illinois Community College Board Service Center Network Introduction
Bipolar Disorder: What It Means to You and Your Classroom Presented by Bevan Gibson Southern IL Professional Development Center -Part of the Illinois Community College Board Service Center Network Introduction
What is Schizophrenia?
 What is Schizophrenia? What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a mental illness which affects one person in every hundred. Schizophrenia interferes with the mental functioning of a person and, in the long
What is Schizophrenia? What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a mental illness which affects one person in every hundred. Schizophrenia interferes with the mental functioning of a person and, in the long
Delirium Information for patients and relatives. Delirium is common Delirium is treatable Relatives can stay to help us
 Delirium Information for patients and relatives Delirium is common Delirium is treatable Relatives can stay to help us What is delirium? Delirium is caused by a disturbance of brain function. It is used
Delirium Information for patients and relatives Delirium is common Delirium is treatable Relatives can stay to help us What is delirium? Delirium is caused by a disturbance of brain function. It is used
Managing conversations around mental health. Blue Light Programme mind.org.uk/bluelight
 Managing conversations around mental health Blue Light Programme 1 Managing conversations around mental health Managing conversations about mental wellbeing Find a quiet place with an informal atmosphere,
Managing conversations around mental health Blue Light Programme 1 Managing conversations around mental health Managing conversations about mental wellbeing Find a quiet place with an informal atmosphere,
Handout 3: Mood Disorders
 Handout 3: Mood Disorders Mood disorders are called affective (emotional) disorders. There are two categories of mood disorders: Depressive Disorders Bipolar Affective Disorders Depressive Disorders Minor
Handout 3: Mood Disorders Mood disorders are called affective (emotional) disorders. There are two categories of mood disorders: Depressive Disorders Bipolar Affective Disorders Depressive Disorders Minor
Pharmacists as a vital part of the mental health of the nation
 Pharmacists as a vital part of the mental health of the nation P H I L I P P I N E S P H A R M A C Y A S S O C I A T I O N C O N V E N T I O N A P R I L 2 5, 2 0 1 5 B A C O L O D T R U D I H I L T O N
Pharmacists as a vital part of the mental health of the nation P H I L I P P I N E S P H A R M A C Y A S S O C I A T I O N C O N V E N T I O N A P R I L 2 5, 2 0 1 5 B A C O L O D T R U D I H I L T O N
The Psychiatric Liaison Team for Older Adults
 The Psychiatric Liaison Team for Older Adults A guide to delirium, depression and dementia for patients and carers South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust Page The Liaison Team We are a mental health
The Psychiatric Liaison Team for Older Adults A guide to delirium, depression and dementia for patients and carers South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust Page The Liaison Team We are a mental health
ALZHEIMER S DISEASE, DEMENTIA & DEPRESSION
 ALZHEIMER S DISEASE, DEMENTIA & DEPRESSION Daily Activities/Tasks As Alzheimer's disease and dementia progresses, activities like dressing, bathing, eating, and toileting may become harder to manage. Each
ALZHEIMER S DISEASE, DEMENTIA & DEPRESSION Daily Activities/Tasks As Alzheimer's disease and dementia progresses, activities like dressing, bathing, eating, and toileting may become harder to manage. Each
Treatment Options for Bipolar Disorder Contents
 Keeping Your Balance Treatment Options for Bipolar Disorder Contents Medication Treatment for Bipolar Disorder 2 Page Medication Record 5 Psychosocial Treatments for Bipolar Disorder 6 Module Summary 8
Keeping Your Balance Treatment Options for Bipolar Disorder Contents Medication Treatment for Bipolar Disorder 2 Page Medication Record 5 Psychosocial Treatments for Bipolar Disorder 6 Module Summary 8
Depression: what you should know
 Depression: what you should know If you think you, or someone you know, might be suffering from depression, read on. What is depression? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness and
Depression: what you should know If you think you, or someone you know, might be suffering from depression, read on. What is depression? Depression is an illness characterized by persistent sadness and
Early Warning Signs of Psychotic Disorders and the Importance of Early Intervention
 Early Warning Signs of Psychotic Disorders and the Importance of Early Intervention Margaret Migliorati, MA, LPCC The University of New Mexico mmigliorati@salud.unm.edu Mental Health As a Public Health
Early Warning Signs of Psychotic Disorders and the Importance of Early Intervention Margaret Migliorati, MA, LPCC The University of New Mexico mmigliorati@salud.unm.edu Mental Health As a Public Health
Discussion Guide. Tell me about the person: What are they wearing? How old are they? What are they doing? How do the media portray it?
 Discussion Guide If you do not have AV access, you can use this discussion guide instead of the PowerPoint Presentation. For a more complete, scripted discussion guide please use the talking points provided
Discussion Guide If you do not have AV access, you can use this discussion guide instead of the PowerPoint Presentation. For a more complete, scripted discussion guide please use the talking points provided
Changes to your behaviour
 Life after stroke Changes to your behaviour Together we can conquer stroke Because there is so much to deal with after a stroke, it s normal for your behaviour to change in some way. In this booklet we
Life after stroke Changes to your behaviour Together we can conquer stroke Because there is so much to deal with after a stroke, it s normal for your behaviour to change in some way. In this booklet we
Delirium. Information for patients, relatives and carers. Nursing and Patient Experience. Royal Surrey County Hospital. Patient information leaflet
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Delirium Information for patients, relatives and carers Nursing and Patient Experience What is delirium? Delirium is a word
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Delirium Information for patients, relatives and carers Nursing and Patient Experience What is delirium? Delirium is a word
Elements for a Public Summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental disorder often characterized by abnormal social behaviour and failure to recognize what
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental disorder often characterized by abnormal social behaviour and failure to recognize what
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental illness with a number of symptoms, including confused or unclear thinking and speech,
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental illness with a number of symptoms, including confused or unclear thinking and speech,
Delirium: Information for Patients and Families
 health information Delirium: Information for Patients and Families 605837 Alberta Health Services, (2016/11) Resources Delirium in the Older Person Family Guide: search delirium at viha.ca Go to myhealth.alberta.ca
health information Delirium: Information for Patients and Families 605837 Alberta Health Services, (2016/11) Resources Delirium in the Older Person Family Guide: search delirium at viha.ca Go to myhealth.alberta.ca
Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES
 Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES Communication Think of a situation where you missed out on an opportunity because of lack of communication. What communication skills in particular could have
Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES Communication Think of a situation where you missed out on an opportunity because of lack of communication. What communication skills in particular could have
HealthyPlace s Introductory Guide to Bipolar Disorder. By Natasha Tracy
 HealthyPlace s Introductory Guide to Bipolar Disorder By Natasha Tracy 1 Index Introduction Chapter One Bipolar Disorder Basics Chapter Two Bipolar Disorder Diagnosis Chapter Three Treatment of Bipolar
HealthyPlace s Introductory Guide to Bipolar Disorder By Natasha Tracy 1 Index Introduction Chapter One Bipolar Disorder Basics Chapter Two Bipolar Disorder Diagnosis Chapter Three Treatment of Bipolar
The Mental Health of People with Prader- Willi Syndrome with Specific Focus on Mood Disorders and Psychotic Illness
 The Mental Health of People with Prader- Willi Syndrome with Specific Focus on Mood Disorders and Psychotic Illness By Tony Holland B.Sc., M.B.B.S., M.R.C.P., M.Phil., F.R.C.Psych., Emeritus Professor
The Mental Health of People with Prader- Willi Syndrome with Specific Focus on Mood Disorders and Psychotic Illness By Tony Holland B.Sc., M.B.B.S., M.R.C.P., M.Phil., F.R.C.Psych., Emeritus Professor
A NEW MOTHER S. emotions. Your guide to understanding maternal mental health
 A NEW MOTHER S emotions Your guide to understanding maternal mental health It is not your fault It is treatable Understanding Maternal Mental Health Life with a new baby is not always easy and the adjustment
A NEW MOTHER S emotions Your guide to understanding maternal mental health It is not your fault It is treatable Understanding Maternal Mental Health Life with a new baby is not always easy and the adjustment
CHILD / ADOLESCENT HISTORY
 CHILD / ADOLESCENT HISTORY PERSON FILLING OUT THIS FORM DATE PATIENT NAME: DATE OF BIRTH AGE APPOINTMENT DATE: HOME TELEPHONE: MOTHER NAME: _ OCCUPATION WK TEL FATHER NAME: OCCUPATION _ WK TEL YOU ARE
CHILD / ADOLESCENT HISTORY PERSON FILLING OUT THIS FORM DATE PATIENT NAME: DATE OF BIRTH AGE APPOINTMENT DATE: HOME TELEPHONE: MOTHER NAME: _ OCCUPATION WK TEL FATHER NAME: OCCUPATION _ WK TEL YOU ARE
suicide Part of the Plainer Language Series
 Part of the Plainer Language Series www.heretohelp.bc.ca What is? Suicide means ending your own life. It is sometimes a way for people to escape pain or suffering. When someone ends their own life, we
Part of the Plainer Language Series www.heretohelp.bc.ca What is? Suicide means ending your own life. It is sometimes a way for people to escape pain or suffering. When someone ends their own life, we
Understanding Bipolar Disorder
 A Resource for Consumers Understanding Bipolar disorder is a brain disorder that affects people s moods. People with bipolar disorder have moods and feelings that are more extreme than normal ups and downs.
A Resource for Consumers Understanding Bipolar disorder is a brain disorder that affects people s moods. People with bipolar disorder have moods and feelings that are more extreme than normal ups and downs.
Depressive, Bipolar and Related Disorders
 Depressive, Bipolar and Related Disorders Robert Kelly, MD Assistant Professor of Psychiatry Weill Cornell Medical College White Plains, New York Lecture available at www.robertkelly.us Financial Conflicts
Depressive, Bipolar and Related Disorders Robert Kelly, MD Assistant Professor of Psychiatry Weill Cornell Medical College White Plains, New York Lecture available at www.robertkelly.us Financial Conflicts
NCMH National Centre for Mental Health Schizophrenia Information for individuals, partners and families
 www.ncmh.info NCMH National Centre for Mental Health Schizophrenia Information for individuals, partners and families What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is an illness that affects thinking, feelings
www.ncmh.info NCMH National Centre for Mental Health Schizophrenia Information for individuals, partners and families What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is an illness that affects thinking, feelings
Warning Signs of Mental Illness in Children/Adolescents. Beth Confer, MA, LPC Director, Community Relations Clarity Child Guidance Center
 Warning Signs of Mental Illness in Children/Adolescents Beth Confer, MA, LPC Director, Community Relations Clarity Child Guidance Center Identify At least 5 warning signs of mental illness in children
Warning Signs of Mental Illness in Children/Adolescents Beth Confer, MA, LPC Director, Community Relations Clarity Child Guidance Center Identify At least 5 warning signs of mental illness in children
Early Intervention in Psychosis Program (EIP)
 Early Intervention in Psychosis Program (EIP) UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: What the Early Intervention in Psychosis Program is How it helps members of the Chinese
Early Intervention in Psychosis Program (EIP) UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: What the Early Intervention in Psychosis Program is How it helps members of the Chinese
Bipolar Disorder in Children and Teens
 Bipolar Disorder in Children and Teens Does your child go through intense mood changes? Does your child have extreme behavior changes? Does your child get much more excited and active than other kids his
Bipolar Disorder in Children and Teens Does your child go through intense mood changes? Does your child have extreme behavior changes? Does your child get much more excited and active than other kids his
The transition to parenthood, mood changes, postnatal depression and post traumatic stress disorder
 The transition to parenthood, mood changes, postnatal depression and post traumatic stress disorder A Parent Information Leaflet Contents The transition to parenthood 3 What are the Baby Blues? 3 What
The transition to parenthood, mood changes, postnatal depression and post traumatic stress disorder A Parent Information Leaflet Contents The transition to parenthood 3 What are the Baby Blues? 3 What
Self-Injury. What is it? How do I get help? Adapted from Signs of Self-Injury Program
 Self-Injury What is it? How do I get help? Adapted from Signs of Self-Injury Program Why are we doing this? *Prevention of self-injury-it s happening so why ignore it? *Statistics show high prevalence
Self-Injury What is it? How do I get help? Adapted from Signs of Self-Injury Program Why are we doing this? *Prevention of self-injury-it s happening so why ignore it? *Statistics show high prevalence
Cluster 1 Common Mental Health Problems (mild)
 Cluster 1 Common Mental Health Problems (mild) You have recently sought help for the first time. You have experienced depression and/or anxiety. This may cause distraction or minor disruption to you as
Cluster 1 Common Mental Health Problems (mild) You have recently sought help for the first time. You have experienced depression and/or anxiety. This may cause distraction or minor disruption to you as
Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC
 Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC What is a first episode of psychosis? The word psychosis is used to describe
Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC What is a first episode of psychosis? The word psychosis is used to describe
Dementia Training Session for Carers. By Dr Rahul Tomar Consultant Psychiatrist
 Dementia Training Session for Carers By Dr Rahul Tomar Consultant Psychiatrist Dementia in the UK: Facts & Figures National Dementia strategy launched in 2009 800,000 people living with dementia (2012)
Dementia Training Session for Carers By Dr Rahul Tomar Consultant Psychiatrist Dementia in the UK: Facts & Figures National Dementia strategy launched in 2009 800,000 people living with dementia (2012)
Do not write below this line DSM IV Code: Primary Secondary. Clinical Information
 New Client Registration Today s date Name Age Sex Address Social security # Date of birth Home phone May I call you at this number? y / n Leave a message? y / n Other numbers at which I can call you Can
New Client Registration Today s date Name Age Sex Address Social security # Date of birth Home phone May I call you at this number? y / n Leave a message? y / n Other numbers at which I can call you Can
Mental Health Strategy. Easy Read
 Mental Health Strategy Easy Read Mental Health Strategy Easy Read The Scottish Government, Edinburgh 2012 Crown copyright 2012 You may re-use this information (excluding logos and images) free of charge
Mental Health Strategy Easy Read Mental Health Strategy Easy Read The Scottish Government, Edinburgh 2012 Crown copyright 2012 You may re-use this information (excluding logos and images) free of charge
Agenda TOWARDS HOPE AND HEALING: A MENTAL HEALTH AWARENESS EVENT 11/3/2018. Mental Health First Aid. Intro to Mental Health First Aid
 TOWARDS HOPE AND HEALING: A MENTAL HEALTH AWARENESS EVENT November 3, 2018 Presented by: Amanda Gentz Agenda Intro to Mental Health First Aid About Mental Health Myths and Facts Types of Mental Health
TOWARDS HOPE AND HEALING: A MENTAL HEALTH AWARENESS EVENT November 3, 2018 Presented by: Amanda Gentz Agenda Intro to Mental Health First Aid About Mental Health Myths and Facts Types of Mental Health
Depression and Bipolar Disorder
 The Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) is a nation-wide, charitable organization that promotes the mental health of all and supports the resilience and recovery of people experiencing mental illness.
The Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) is a nation-wide, charitable organization that promotes the mental health of all and supports the resilience and recovery of people experiencing mental illness.
ADHD clinic for adults Feedback on services for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
 ADHD clinic for adults Feedback on services for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder Healthwatch Islington Healthwatch Islington is an independent organisation led by volunteers from the local community.
ADHD clinic for adults Feedback on services for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder Healthwatch Islington Healthwatch Islington is an independent organisation led by volunteers from the local community.
maintaining gains and relapse prevention
 maintaining gains and relapse prevention Tips for preventing a future increase in symptoms 3 If you do experience an increase in symptoms 8 What to do if you become pregnant again 9 2013 BC Reproductive
maintaining gains and relapse prevention Tips for preventing a future increase in symptoms 3 If you do experience an increase in symptoms 8 What to do if you become pregnant again 9 2013 BC Reproductive
Understanding Schizophrenia Relapse
 Framing Schizophrenia A Guide for Caregivers Understanding Schizophrenia Relapse Caregivers can play an important role in helping their loved one who has schizophrenia 2016 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development
Framing Schizophrenia A Guide for Caregivers Understanding Schizophrenia Relapse Caregivers can play an important role in helping their loved one who has schizophrenia 2016 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development
THE PSYCHIATRIC PATIENT JENNIFER NOCE REGIONAL CLINICAL EDUCATION MANAGER CCEMPT/FP-C/CCP-C
 THE PSYCHIATRIC PATIENT JENNIFER NOCE REGIONAL CLINICAL EDUCATION MANAGER CCEMPT/FP-C/CCP-C Objectives The student will be able to recognize behaviors that pose a risk Assess and manage basic principles
THE PSYCHIATRIC PATIENT JENNIFER NOCE REGIONAL CLINICAL EDUCATION MANAGER CCEMPT/FP-C/CCP-C Objectives The student will be able to recognize behaviors that pose a risk Assess and manage basic principles
The Recovery Journey after a PICU admission
 The Recovery Journey after a PICU admission A guide for families Introduction This booklet has been written for parents and young people who have experienced a Paediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) admission.
The Recovery Journey after a PICU admission A guide for families Introduction This booklet has been written for parents and young people who have experienced a Paediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) admission.
Delirium in Palliative care. Presentation to Volunteers 2016 David Falk
 Delirium in Palliative care Presentation to Volunteers 2016 David Falk Delirium What is delirium? Case Study - Delirium 60+ year old PQ presents to hospice very somnolent. She was admitted with her adult
Delirium in Palliative care Presentation to Volunteers 2016 David Falk Delirium What is delirium? Case Study - Delirium 60+ year old PQ presents to hospice very somnolent. She was admitted with her adult
Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY
 Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY Accrued deficits: The delays or lack of development in emotional, social, academic, or behavioral skills that a child
Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY Accrued deficits: The delays or lack of development in emotional, social, academic, or behavioral skills that a child
Mental Health Information For Teens, Fifth Edition
 Teen Health Series Mental Health Information For Teens, Fifth Edition Health Tips About Mental Wellness And Mental Illness Including Facts About Recognizing And Treating Mood, Anxiety, Personality, Psychotic,
Teen Health Series Mental Health Information For Teens, Fifth Edition Health Tips About Mental Wellness And Mental Illness Including Facts About Recognizing And Treating Mood, Anxiety, Personality, Psychotic,
ECI WEBINAR SERIES: PRACTICAL STRATEGIES FOR WORKING WITH CHILDREN WITH AUTISM. Kathleen McConnell Fad, Ph.D.
 ECI WEBINAR SERIES: PRACTICAL STRATEGIES FOR WORKING WITH CHILDREN WITH AUTISM Kathleen McConnell Fad, Ph.D. PART 1: ESTABLISHING RELATIONSHIPS WITH FAMILIES AND BECOMING AN EFFECTIVE COACH Let s start
ECI WEBINAR SERIES: PRACTICAL STRATEGIES FOR WORKING WITH CHILDREN WITH AUTISM Kathleen McConnell Fad, Ph.D. PART 1: ESTABLISHING RELATIONSHIPS WITH FAMILIES AND BECOMING AN EFFECTIVE COACH Let s start
MODULE III Challenging Behaviors
 Mental Health Ombudsman Training Manual Advocacy and the Adult Home Resident MODULE III Challenging Behaviors S WEHRY 2004 Objectives: Part One Describe principles of communication Describe behavior as
Mental Health Ombudsman Training Manual Advocacy and the Adult Home Resident MODULE III Challenging Behaviors S WEHRY 2004 Objectives: Part One Describe principles of communication Describe behavior as
Crisis Intervention Team (CIT) Training
 Crisis Intervention Team (CIT) Training Student Guide Bipolar Disorder Created by: Nils Rosenbaum Matthew Tinney Lawrence Saavedra Bipolar Disorder What is bipolar disorder? Bipolar disorder is a brain
Crisis Intervention Team (CIT) Training Student Guide Bipolar Disorder Created by: Nils Rosenbaum Matthew Tinney Lawrence Saavedra Bipolar Disorder What is bipolar disorder? Bipolar disorder is a brain
CASE 5 - Toy & Klamen CASE FILES: Psychiatry
 CASE 5 - Toy & Klamen CASE FILES: Psychiatry A 14-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after being found in the basement of his home by his parents during the middle of a school day. The
CASE 5 - Toy & Klamen CASE FILES: Psychiatry A 14-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after being found in the basement of his home by his parents during the middle of a school day. The
Cognitive Changes Workshop Outcomes
 HO 4.1 Cognitive Changes Workshop Outcomes At the end of this session, participants should be able to: define Neuropsychology and the role of the Neuropsychologist (optional) recognise normal difficulties
HO 4.1 Cognitive Changes Workshop Outcomes At the end of this session, participants should be able to: define Neuropsychology and the role of the Neuropsychologist (optional) recognise normal difficulties
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust. Your guide to understanding Delirium. Issued by Department of Medicine
 Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Your guide to understanding Delirium Issued by Department of Medicine Purpose of this leaflet This leaflet is for patients and carers and aims to give you information
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Your guide to understanding Delirium Issued by Department of Medicine Purpose of this leaflet This leaflet is for patients and carers and aims to give you information
SECTION 1. Children and Adolescents with Depressive Disorder: Summary of Findings. from the Literature and Clinical Consultation in Ontario
 SECTION 1 Children and Adolescents with Depressive Disorder: Summary of Findings from the Literature and Clinical Consultation in Ontario Children's Mental Health Ontario Children and Adolescents with
SECTION 1 Children and Adolescents with Depressive Disorder: Summary of Findings from the Literature and Clinical Consultation in Ontario Children's Mental Health Ontario Children and Adolescents with
Schizophrenia. Introduction. Overview and Facts
 Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
Conducting Groups. March 2015
 Conducting Groups March 2015 Agenda Advantages of groups Members of the group Group leader Role of the leader, maximize participation, & use effective communication skills Group participants The forceful,
Conducting Groups March 2015 Agenda Advantages of groups Members of the group Group leader Role of the leader, maximize participation, & use effective communication skills Group participants The forceful,
SECTION 8 SURVIVOR HEALING MAINE COALITION AGAINST SEXUAL ASSAULT
 SECTION 8 SURVIVOR HEALING MAINE COALITION AGAINST SEXUAL ASSAULT SECTION 8: SURVIVOR HEALING SURVIVOR HEALING INTRODUCTION Healing from any type of sexual violence is a personal journey and will vary
SECTION 8 SURVIVOR HEALING MAINE COALITION AGAINST SEXUAL ASSAULT SECTION 8: SURVIVOR HEALING SURVIVOR HEALING INTRODUCTION Healing from any type of sexual violence is a personal journey and will vary
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Substance and Alcohol Related Disorders. Substance use Disorder Alcoholism Gambling Disorder
 Substance and Alcohol Related Disorders Substance use Disorder Alcoholism Gambling Disorder What is a Substance Use Disorder? According to the DSM-5, a substance use disorder describes a problematic pattern
Substance and Alcohol Related Disorders Substance use Disorder Alcoholism Gambling Disorder What is a Substance Use Disorder? According to the DSM-5, a substance use disorder describes a problematic pattern
Hallucinations and Delusions
 PBO 930022142 NPO 049-191 Hallucinations and Delusions Some people with dementia may experience hallucinations or delusions. A delusion is a false idea or misinterpretation of a situation e.g. that a family
PBO 930022142 NPO 049-191 Hallucinations and Delusions Some people with dementia may experience hallucinations or delusions. A delusion is a false idea or misinterpretation of a situation e.g. that a family
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Baby Blues and More. Knowing About This in Advance Can Help
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Recognizing and coping with postpartum mood disorders Some women have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. It helps to know about these
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Baby Blues and More Recognizing and coping with postpartum mood disorders Some women have baby blues or more serious postpartum mood disorders. It helps to know about these
Dealing with Depression Feature Article July 2008
 Dealing with Depression Feature Article July 2008 Marjorie and Ann were housemates for about three years. Everyone thought that they did not like each other very much. Direct support staff said that they
Dealing with Depression Feature Article July 2008 Marjorie and Ann were housemates for about three years. Everyone thought that they did not like each other very much. Direct support staff said that they
Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects
 Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects a person s thoughts, feelings and behaviours. Whilst it is serious, schizophrenia is both treatable and manageable, and we
Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects a person s thoughts, feelings and behaviours. Whilst it is serious, schizophrenia is both treatable and manageable, and we
Postnatal anxiety and depression
 What Dads and Mums need to know Postnatal anxiety and depression What Dads and Mums need to know 1 Postnatal anxiety and depression Feelings and emotions after birth Having a baby can be an exciting time,
What Dads and Mums need to know Postnatal anxiety and depression What Dads and Mums need to know 1 Postnatal anxiety and depression Feelings and emotions after birth Having a baby can be an exciting time,
