A to Z of Desmoid Tumors
|
|
|
- Lorin Hardy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
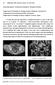
1 Special rticle Pictorial Essay Shinagare et al. Imaging of Desmoid Tumors Special rticle Pictorial Essay Downloaded from by on 11/27/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved tul. Shinagare 1 Nikhil H. Ramaiya 1 Jyothi P. Jagannathan 1 Katherine M. Krajewski 1 ngela. Giardino 1 James E. utrynski 2 Chandrajit P. Raut 3 Shinagare, Ramaiya NH, Jagannathan JP, et al. Keywords: complications, deep fibromatosis, desmoid tumors, extraabdominal desmoids, treatment-related changes DOI: /JR Received February 10, 2011; accepted after revision May 3, Department of Imaging, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and Department of Radiology, righam and Women s Hospital, 450 rookline ve, oston, M ddress correspondence to.. Shinagare (ashinagare@partners.org). 2 Department of Medical Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, oston, M. 3 Department of Surgery, righam and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, oston, M. WE This is a Web exclusive article. JR 2011; 197:W1008 W X/11/1976 W1008 merican Roentgen Ray Society to Z of Desmoid Tumors OJECTIVE. The purpose of this article is to illustrate the common locations of desmoid tumors (deep fibromatosis), complications of intra- and extraabdominal desmoids, and treatment-related changes in their imaging appearance. CONCLUSION. Desmoids are locally aggressive fibrous tumors with a tendency to recur. Desmoids can be intraabdominal, in the abdominal wall, or extraabdominal. Complications, such as compression or invasion of adjacent structures, and abscess formation can occur. Treatment options include observation, local treatment (surgery, radiotherapy), or systemic therapy (conventional chemotherapy, molecular targeted agents). D esmoid tumors, also called deep or aggressive fibromatosis, are uncommon mesenchymal neoplasms with a fibrotic bandlike consistency [1]. These are locally aggressive tumors without potential for distant metastases. Local recurrence and adjacent organ involvement are important causes of morbidity and mortality. The incidence of desmoid tumors in the general population is 2 4 cases per million per year, with a slight female preponderance and peak incidence in the third and fourth decades [2]. These tumors are more aggressive in younger patients, with recurrence rates up to 87% [3]. Desmoids present as a firm mass, particularly when extraabdominal. The firm consistency can make penetration of tumor difficult during imaging-guided biopsy [4]. Desmoids have spiculated infiltrative margins and are typically adherent to adjacent structures. Microscopically, they consist of poorly defined fascicles of uniform spindle cells and fibroblasts in dense collagen stroma. Mitotic activity is low, and necrosis is rare [2, 4]. This article will summarize the features of desmoids that radiologists should be aware of, specifically the common locations, complications, and treatment-related changes. Risk Factors The association of abdominal and extraabdominal desmoids with familial adenomatous polyposis (FP) (Fig. 1) and Gardner syndrome (Fig. 2) is well established [5]. Trauma, prior surgery, pregnancy (Fig. 3), and oral contraceptive use are other risk factors [1, 6]. Estrogen has been implicated as a growth factor for desmoids [1]. Location Desmoid tumors can be intraabdominal (Figs. 1 3), within the abdominal wall (Fig. 4), or extraabdominal (Figs. 5 10). In various studies, 28 69% of desmoids were intraabdominal (mesenteric or pelvic) or abdominal wall, and the remaining were extraabdominal [7]. Desmoids associated with FP and Gardner syndrome are typically intraabdominal, usually located in the smallbowel mesentery (Figs. 1 3). Pregnancy-associated desmoids tend to arise within the rectus abdominis or internal oblique muscles [1] (Fig. 4). Extraabdominal desmoids are intimately associated with muscle and fascia, with the most common locations being the shoulder and upper extremity (33%) (Figs. 5 and 6), gluteal region and lower extremity (30%) (Figs. 7 and 8), chest wall or back (17%) (Fig. 9), and head and neck (10%) [1, 2, 4]. Isolated cases of breast desmoids have been reported [8] (Fig. 10). Multiple desmoid tumors are seen in 15% of cases [1]. Imaging Features lthough use of radiography, bone scintigraphy, and ultrasound for imaging of desmoid tumors has been described, in practice, the imaging of desmoids relies mainly on CT and MRI. On ultrasound, desmoid tumors appear W1008 JR:197, December 2011
2 Imaging of Desmoid Tumors Downloaded from by on 11/27/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved as hypoechoic soft tissue masses with variable vascularity [4] (Fig. 11). CT shows a softtissue mass of variable attenuation and enhancement [4] (Figs. 2 4 and 10). Margins may be indistinct because of infiltration of adjacent structures. Heterogeneous attenuation may be seen because of necrosis or degeneration (Figs. 3 and 4). MRI, with its excellent soft-tissue contrast, is best suited for optimum evaluation of extraabdominal desmoids because it allows accurate depiction of their relationship with adjacent structures [4]. Desmoids may have heterogeneous signal and inhomogeneous enhancement because of variable distribution of spindle cells, collagen, and myxoid matrix (Figs. 7 9). On T2-weighted and proton density images, signal intensity is usually intermediate, between skeletal muscles and subcutaneous fat (Figs. 5 9), at times with the presence of hypointense bands corresponding to collagen bundles [9]. Over time, they become more hypointense because of increasing collagen deposition and decreasing cellularity (Fig. 7), whereas recurrent or actively growing desmoids tend to have a higher T2 signal, probably because of higher cellularity (Fig. 7) [10]. On 18 F-FDG-PET/ CT, the median maximum standardized uptake value of desmoid tumors has been reported to be 4.1 (range, ) [11]. The differential diagnosis of desmoid tumors includes other neoplasms, such as lymphoma, pleomorphic sarcoma, fibrosarcoma, and giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath [1]. lthough the imaging appearance may be suggestive, histopathologic confirmation must be obtained in all cases before definitive treatment. Complications Complications of desmoid tumors result from their locally aggressive nature, leading to compression and invasion of adjacent structures. Intraabdominal desmoids, especially those associated with FP or Gardner syndrome, are more infiltrative and may cause intestinal (Fig. 12) or ureteral obstruction or encase the mesenteric vessels [2, 12] (Fig. 2). Non-FP-associated desmoids, in our experience, have smooth margins and are less likely to be infiltrative (Fig. 13). Pelvic desmoids can infiltrate the urinary bladder (Fig. 14) or may cause hydrosalpinx (Fig. 12). Extraabdominal desmoids may encase and compress adjacent structures, including vessels or nerves. Chest wall desmoids can invade the pleura (Fig. 5). Desmoids rarely undergo abscess formation (Fig. 12), which may require surgical intervention or percutaneous drainage. Large desmoid tumors may undergo mucoid or cystic degeneration. Treatment Options multidisciplinary approach tailored to the individual patient is required for optimum management of desmoids. Stable asymptomatic desmoids can be observed [13] (Fig. 15). Treatment is necessary for symptomatic desmoids, especially those with mass effect on critical structures. Treatment choice is dictated by anatomic considerations. If feasible, surgical resection with a wide margin is the conventional treatment of choice for symptomatic desmoids [2]. However, recurrence is common (19 77%) (Fig. 7) and more frequent with extraabdominal desmoids (30 50%) than intraabdominal desmoids (15 30%) [1, 4]. Often, resection is not possible because of close association with vital structures, in which cases, systemic therapy with or without surgical excision should be considered [2] (Fig. 2). This is more commonly seen with FP- or Gardner-associated mesenteric desmoids, which are often unresectable or lead to significant morbidity, including perioperative hemorrhage, short-bowel syndrome, intestinal ischemia, obstruction, or fistula formation [12]. Therefore, conservative management has been recommended in such cases whenever possible, using analgesia and minimally invasive therapy as needed [12]. Recently, there has been an increasing shift toward conservative management of desmoids [12, 13]. Nonsurgical treatment options include radiation and systemic therapy. Radiation has been reported to be comparable to surgery and is also useful as an adjuvant treatment to reduce the risk of local recurrence [14] (Fig. 16). Systemic treatment options include cytotoxic agents, such as anthracyclines (Fig. 2); molecular targeted agents, such as imatinib; interferon; and antiestrogen hormonal therapy, such as tamoxifen [2, 11, 7]. mong systemic agents, a higher radiologic response rate has been reported with anthracyclines and antiestrogen treatment [7]. In some cases, after treatment, the size of the desmoid tumors may remain unchanged, but there may be a decrease in signal intensity and enhancement of the desmoids (Fig. 8). Role of Imaging in Desmoid Tumors Initial imaging in desmoids is usually performed to determine the extent, local mass effects, and potential resectability. Desmoids being observed or managed nonoperatively should undergo periodic imaging assessment, especially if intraabdominal. MRI may have prognostic value because higher T2 signal is reportedly associated with more rapid growth [15]. Given the potential for recurrence, regular clinical and possible imaging follow-up have been recommended after therapy, initially every 3 6 months [12, 16]. Patients undergoing chemoradiation undergo 6- to 12-week imaging follow-up. Desmoids being observed are initially followed-up with imaging at a 3- to 6-month interval. The imaging interval is then adjusted depending on the rate of growth and presence of symptoms. t our institution, MRI is usually preferred for pre- and postoperative evaluation of patients undergoing surgery, and whenever possible, we prefer the use of gadolinium for better delineation of the extent of desmoids. Conclusion Desmoid tumors are a challenging clinical condition with locally aggressive behavior and a strong tendency for recurrence. lthough the imaging appearance may be suggestive, histopathologic confirmation is necessary before treatment. Management options include observation, surgical resection, radiotherapy, conventional chemotherapy, hormonal agents, and newer molecular targeted agents. multidisciplinary approach tailored to the individual patient is usually needed, depending on the location, local effects, and clinical course. References 1. Dinauer P, rixey CJ, Moncur JT, Fanburg- Smith JC, Murphey MD. Pathologic and MR imaging features of benign fibrous soft-tissue tumors in adults. RadioGraphics 2007; 27: Shields CJ, Winter DC, Kirwan WO, Redmond HP. Desmoid tumours. Eur J Surg Oncol 2001; 27: Romero J, Kim EE, Kim CG, Chung WK, Isiklar I. Different biologic features of desmoid tumors in adult and juvenile patients: MR demonstration. J Comput ssist Tomogr 1995; 19: Murphey MD, Ruble CM, Tyszko SM, Zbojniewicz M, Potter K, Miettinen M. From the archives of the FIP: musculoskeletal fibromatoses radiologic-pathologic correlation. RadioGraphics 2009; 29: Lindor NM, Greene MH. The concise handbook of family cancer syndromes: Mayo Familial Cancer Program. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998; 90: Häyry P, Reitamo JJ, Tötterman S, Hopfner-Hallikainen D, Sivula. The desmoid tumor. II. JR:197, December 2011 W1009
3 Shinagare et al. Downloaded from by on 11/27/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig year-old woman with familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome. T2-weighted MR image in coronal plane shows large mesenteric mass (arrow) that was proven to be desmoid tumor on histopathology. Fig year-old woman with pregnancyassociated mesenteric desmoid. Mass, which presented during second trimester of pregnancy, was initially thought to be of ovarian origin. During exploration at time of cesarean delivery, mass was found to be of mesenteric origin and unresectable because it was adherent to superior mesenteric vessels. It was biopsied, and histopathology showed it to be desmoid. xial image from contrast-enhanced CT performed postpartum shows large mesenteric mass (arrowheads) that is intimately associated with mesenteric vessels (arrow). nalysis of factors possibly contributing to the etiology and growth behavior. m J Clin Pathol 1982; 77: de Camargo VP, Keohan ML, D damo DR, et al. Clinical outcomes of systemic therapy for patients with deep fibromatosis (desmoid tumor). Cancer 2010; 116: Okamoto K, Kurihara Y, Imamura K, et al. Desmoid tumor of the breast: the role of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy for a benign breast lesion mimicking a malignancy. reast J 2008; 14: Kransdorf MJ, Jelinek JS, Moser RP, et al. Magnetic resonance appearance of fibromatosis: a report of 14 cases and review of the literature. Skeletal Radiol 1990; 19: Vandevenne JE, De Schepper M, De euckeleer L, et al. New concepts in understanding evolution of desmoid tumors: MR imaging of 30 lesions. Eur Radiol 1997; 7: Kasper, Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss, Strauss LG, Hohenberger P. Positron emission tomography in patients with aggressive fibromatosis/desmoid tumours undergoing therapy with imatinib. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010; 37: Sturt NJ, Clark SK. Current ideas in desmoid tumours. Fam Cancer 2006; 5: ; discussion, Fiore M, Rimareix F, Mariani L, et al. Desmoidtype fibromatosis: a front-line conservative ap- proach to select patients for surgical treatment. nn Surg Oncol 2009; 16: Nuyttens JJ, Rust PF, Thomas CR, Turrisi T. Surgery versus radiation therapy for patients with aggressive fibromatosis or desmoid tumors: a comparative review of 22 articles. Cancer 2000; 88: Healy JC, Reznek RH, Clark SK, Phillips RK, rmstrong P. MR appearances of desmoid tumors in familial adenomatous polyposis. JR 1997; 169: National Comprehensive Cancer Network Website. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. f_guidelines.asp. ccessed November 26, 2010 Fig year-old man with Gardner syndrome and large mesenteric desmoid., Coronal contrast-enhanced CT image shows large homogeneous mesenteric desmoid tumor (thick arrow). Note infiltrative margins of mass (curved arrow). Desmoid is intimately associated with mesenteric artery (thin arrow). On axial images (not shown), mesenteric vessels could be seen branching within mass. Close association with mesenteric vessels made surgical resection difficult. Hence, patient was treated with doxorubicin., xial contrast-enhanced CT image after 3 months of treatment with doxorubicin shows marked decrease in size of desmoid (thick arrow). Mesenteric vessels can be seen separate from mass (thin arrow). Desmoid was then successfully resected. W1010 JR:197, December 2011
4 Imaging of Desmoid Tumors Fig year-old woman with Gardner syndrome with abdominal wall and mesenteric desmoids. xial contrast-enhanced CT image shows large somewhat low-attenuation desmoid arising within right rectus muscle (straight arrow) and another smaller mesenteric desmoid (arrowhead). Ill-defined soft tissue is also noted surrounding mesenteric vessels (curved arrow). Downloaded from by on 11/27/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig year-old woman with large mass in left shoulder region., T1-weighted MR image in coronal plane shows large homogeneous mass in left shoulder region (arrows) that is isointense to skeletal muscle. This was proven to be desmoid on histopathology., T2-weighted fat-suppressed MR image in coronal plane shows intermediate signal of desmoid (straight arrows). Note nodular protrusion from mass medially toward pleura (curved arrow), raising concern for pleural invasion. C, T1-weighted fat-suppressed gadolinium-enhanced MR image in axial plane shows homogeneously enhancing mass (straight arrows) and better delineates pleural invasion (curved arrow). Fig year-old woman with desmoid tumor of left arm., Proton density MR image in axial plane shows mass involving left deltoid muscle (straight arrows). Note that signal intensity of mass is between low signal of preserved deltoid muscle (curved arrow) and high signal of subcutaneous fat (black dot)., T1-weighted fat-suppressed gadolinium-enhanced MR image in coronal plane shows moderate homogeneous enhancement of mass (straight arrows). Note subcutaneous stranding, and overlying skin thickening and retraction (curved arrow), which may represent reactive changes or extension of desmoid tumor. C JR:197, December 2011 W1011
5 Shinagare et al. Downloaded from by on 11/27/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig year-old man with left gluteal desmoid tumor., T2-weighted MR image in axial plane shows mass deep in relation to gluteus maximus muscle (thick arrows) that is iso- to hypointense to muscle. Note hypointense areas within mass (thin arrow). Patient underwent resection of this desmoid., MRI was performed 4 years after surgical resection. Proton density image in axial plane shows heterogeneous recurrent mass with predominantly intermediate signal intensity (arrows). Note atrophy of overlying gluteus maximus muscle (arrowhead). Fig year-old woman with thigh desmoid., T1-weighted fat-suppressed gadolinium-enhanced MR image in coronal plane shows heterogeneous mass in left thigh (arrowheads) with heterogeneous enhancement in its superior portion., Coronal T1-weighted fat-suppressed gadoliniumenhanced image from follow-up MRI performed after 9 months of doxorubicin treatment shows minimal decrease in size of desmoid (arrowheads); however, moderate decrease in degree of enhancement is noted, indicating response to treatment. lso note decreased signal intensity of desmoid, which indicates treatment response as well. This patient also had calf desmoid (not shown) that showed similar posttreatment changes. Fig year-old man with posterior chest wall desmoid., xial proton density MR image shows infiltrative heterogeneous mass in posterior chest wall that has superficial moderate signal component (arrow) and deeper linear low-signal component (arrowhead)., xial T1-weighted fat-suppressed gadoliniumenhanced MR image shows heterogeneous enhancement. Superficial component that had moderate T2-signal intensity shows higher enhancement (arrow), and deeper T2-hypointense component shows less enhancement (arrowhead). W1012 JR:197, December 2011
6 Imaging of Desmoid Tumors Downloaded from by on 11/27/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig year-old woman with desmoid tumor of right rectus sheath. Ultrasound image in transverse plane shows heterogeneous hypoechoic mass (arrowheads) showing low-grade vascularity on color Doppler imaging (square). Fig year-old woman with resected right breast cancer who has breast desmoid. Note bilateral breast implants (arrowheads)., Contrast-enhanced CT image in coronal plane shows low-attenuation mass in right breast (arrow), causing mass effect on inferior surface of right breast implant. Note tail of mass insinuating between costal cartilages (curved arrow)., Coronal T1-weighted fat-suppressed gadoliniumenhanced subtracted MR image shows enhancing mass (arrow). reast implant is again noted (arrowhead). Fig year-old woman with Gardner syndrome and intraabdominal desmoid tumor, with history of multiple episodes of acute abdominal pain and vomiting., Coronal image from contrast-enhanced CT obtained during episode of acute abdominal pain and vomiting shows mildly enhancing low-attenuation mass in left hemiabdomen (arrow), causing intestinal obstruction. Note multiple dilated small-bowel loops (arrowheads)., Patient later presented with fever and abdominal pain. xial contrast-enhanced CT image shows large pelvic desmoid with central low-attenuation necrotic area (straight arrow). lso note tiny air specks within desmoid (curved arrow) suggestive of abscess formation, which was later confirmed at surgery where desmoid and few adherent bowel loops were resected. Note mildly dilated small-bowel loop (arrowhead). C, xial contrast-enhanced CT image through pelvis shows elongated low-attenuation structure with incomplete septation seen in left hemipelvis (arrows), which was proven to be hydrosalpinx caused by pelvic desmoid. Desmoid tumor is not visible on this image. C JR:197, December 2011 W1013
7 Shinagare et al. Downloaded from by on 11/27/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig year-old woman with small mesenteric desmoid tumor., xial contrast-enhanced CT image shows small mesenteric mass (straight arrow) closely associated with mesenteric vessels (curved arrow). In view of small asymptomatic desmoid and its proximity to mesenteric vessels, this was observed without any treatment., xial image from follow-up contrast-enhanced CT performed after 2 years shows no significant change in size of mesenteric desmoid (arrow). Fig year-old woman with recurrent desmoid in right lung apex after initial surgical resection., Coronal contrast-enhanced CT image shows soft-tissue mass in right lung apex (arrow). Note postoperative changes in right upper chest wall (arrowheads)., Patient received radiation and cycles of doxorubicin. Coronal image from follow-up contrastenhanced CT shows markedly decreased size of desmoid (straight arrow), and postradiation changes in right lung apex (curved arrow). Fig year-old man with nonfamilial adenomatous polyposis associated mesenteric desmoid tumor. xial contrast-enhanced CT image shows large homogeneous low-attenuation mesenteric desmoid (arrow). Note well-defined margins of mass. Compare with infiltrative margin of Gardner syndrome associated desmoid in Figure 9. Fig year-old man with familial adenomatous polyposis associated desmoid tumor. Coronal contrast-enhanced CT image shows infiltrative mass in pelvis with invasion of urinary bladder wall (arrows) and involvement of multiple small-bowel loops (arrowheads). Patient underwent cystectomy because of severe urinary complaints. W1014 JR:197, December 2011
Case Report Desmoid Tumor of the Popliteal Fossa during Pregnancy
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2015, Article ID 262654, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/262654 Case Report Desmoid Tumor of the Popliteal Fossa during Pregnancy Wolfram Weschenfelder, Robert Lindner,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2015, Article ID 262654, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/262654 Case Report Desmoid Tumor of the Popliteal Fossa during Pregnancy Wolfram Weschenfelder, Robert Lindner,
Multidisciplinary management of retroperitoneal sarcomas
 Multidisciplinary management of retroperitoneal sarcomas Eric K. Nakakura, MD UCSF Department of Surgery UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center San Francisco, CA 7 th Annual Clinical Cancer Update North Lake
Multidisciplinary management of retroperitoneal sarcomas Eric K. Nakakura, MD UCSF Department of Surgery UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center San Francisco, CA 7 th Annual Clinical Cancer Update North Lake
MRI and Biologic Behavior of Desmoid Tumors in Children
 MRI of Desmoid s Pediatric Imaging Original Research M. Beth McCarville 1,2 Fredric A. Hoffer 1,2 C. Scott Adelman 1 Joseph D. Khoury 3 Chenghong Li 4 Stephen X. Skapek 5,6 McCarville MB, Hoffer FA, Adelman
MRI of Desmoid s Pediatric Imaging Original Research M. Beth McCarville 1,2 Fredric A. Hoffer 1,2 C. Scott Adelman 1 Joseph D. Khoury 3 Chenghong Li 4 Stephen X. Skapek 5,6 McCarville MB, Hoffer FA, Adelman
Brief History. Identification : Past History : HTN without regular treatment.
 Brief History Identification : Name : 陳 x - Admission : 94/10/06 Gender : male Age : 75 y/o Chief Complaint : Urinary difficulty for months. Past History : HTN without regular treatment. Brief History
Brief History Identification : Name : 陳 x - Admission : 94/10/06 Gender : male Age : 75 y/o Chief Complaint : Urinary difficulty for months. Past History : HTN without regular treatment. Brief History
Synovial Sarcoma: Imaging Features of Common and Uncommon Primary Sites, Metastatic Patterns, and Treatment Response
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay akri et al. Synovial Sarcoma Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay mit akri 1,2 tul. Shinagare 1 Katherine M. Krajewski 1 Stephanie. Howard 1 Jyothi P. Jagannathan
Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay akri et al. Synovial Sarcoma Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay mit akri 1,2 tul. Shinagare 1 Katherine M. Krajewski 1 Stephanie. Howard 1 Jyothi P. Jagannathan
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis
 Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: MRI, Ultrasound, and Mammographic Appearances
 Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Eiada et al. Imaging Papillary Lesions of the reast Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.194 on 01/27/18 from IP address 37.44.198.194.
Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Eiada et al. Imaging Papillary Lesions of the reast Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.194 on 01/27/18 from IP address 37.44.198.194.
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling
 Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
Nodular Fasciitis of the Face Diagnosed by US-Guided Core Needle Biopsy: A Case Report 1
 Nodular Fasciitis of the Face Diagnosed by US-Guided ore Needle iopsy: ase Report 1 Sang Kwon Lee, M.D., Sun Young Kwon, M.D. 2 We report here on a case of nodular fasciitis (NF) that was diagnosed by
Nodular Fasciitis of the Face Diagnosed by US-Guided ore Needle iopsy: ase Report 1 Sang Kwon Lee, M.D., Sun Young Kwon, M.D. 2 We report here on a case of nodular fasciitis (NF) that was diagnosed by
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 46/Sep 22, 2014 Page 11296
 CT SPECTRUM OF GIANT RETROPERITONEAL LIPOSARCOMAS WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION Shashikumar M. R 1, Rajendra Kumar N. L 2, C. P. Nanjaraj 3, Nishanth R. K 4, Vishwanath Joshi 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
CT SPECTRUM OF GIANT RETROPERITONEAL LIPOSARCOMAS WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION Shashikumar M. R 1, Rajendra Kumar N. L 2, C. P. Nanjaraj 3, Nishanth R. K 4, Vishwanath Joshi 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Interpectoral Venous Angioma Presenting as a Breast Mass
 Case Report Interpectoral Venous ngioma Presenting as a reast Mass Dae Jung Kim, MD, Eun Ju Son, MD, Soon Won Hong, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Jin Young Kwak, MD, Ki Keun Oh, MD, Joon Jeong, MD C hest wall
Case Report Interpectoral Venous ngioma Presenting as a reast Mass Dae Jung Kim, MD, Eun Ju Son, MD, Soon Won Hong, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Jin Young Kwak, MD, Ki Keun Oh, MD, Joon Jeong, MD C hest wall
CASE REPORT PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE.
 PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Elastofibroma dorsi: 8 case reports and a literature review
 DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0102-7 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Elastofibroma dorsi: 8 case reports and a literature review F. Muratori M. Esposito F. Rosa F. Liuzza N. Magarelli B. Rossi H.M. Folath F. Pacelli G. Maccauro
DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0102-7 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Elastofibroma dorsi: 8 case reports and a literature review F. Muratori M. Esposito F. Rosa F. Liuzza N. Magarelli B. Rossi H.M. Folath F. Pacelli G. Maccauro
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
Peritoneal Sarcomatosis Versus Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: Imaging Findings at MDCT
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Oei et al. MDCT of Peritoneal Sarcomatosis and Carcinomatosis Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.60 on 01/12/18
Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Oei et al. MDCT of Peritoneal Sarcomatosis and Carcinomatosis Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.60 on 01/12/18
Calcifying Aponeurotic Fibroma of the Knee: a Case Report with Radiographic and MRI Finding
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:259-263 Calcifying Aponeurotic Fibroma of the Knee: a Case Report with Radiographic and MRI Finding Seung Hyun Lee 1,2, In Sook Lee 1,2, You Seon Song 1,2,
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:259-263 Calcifying Aponeurotic Fibroma of the Knee: a Case Report with Radiographic and MRI Finding Seung Hyun Lee 1,2, In Sook Lee 1,2, You Seon Song 1,2,
MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 5 Number 2 MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System C Costelloe, A Yasko, W Murphy, R Kumar, V Lewis, P Lin, R Stafford,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 5 Number 2 MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System C Costelloe, A Yasko, W Murphy, R Kumar, V Lewis, P Lin, R Stafford,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Imaging of Liposarcoma: Classification, Patterns of Tumor Recurrence, and Response to Treatment
 Special Article Pictorial Essay O Regan et al. Imaging of Liposarcoma Special Article Pictorial Essay Kevin N. O Regan 1 Jyothi Jagannathan Katherine Krajewski Katherine Zukotynski Frederico Souza Andrew
Special Article Pictorial Essay O Regan et al. Imaging of Liposarcoma Special Article Pictorial Essay Kevin N. O Regan 1 Jyothi Jagannathan Katherine Krajewski Katherine Zukotynski Frederico Souza Andrew
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay
 rown et al. MRI of the Female Pelvis Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.41 on 12/17/17 from IP address 37.44.202.41. Copyright RRS. For personal use only;
rown et al. MRI of the Female Pelvis Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.41 on 12/17/17 from IP address 37.44.202.41. Copyright RRS. For personal use only;
Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma
 49 Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma Loredana Miglietta a Maria Angela Parodi b Luciano Canobbio b Luca Anselmi c a Medical
49 Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma Loredana Miglietta a Maria Angela Parodi b Luciano Canobbio b Luca Anselmi c a Medical
A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen
 May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Primary Breast Liposarcoma
 Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
DTRF Annual Patient Meeting September 22, Breelyn A. Wilky, MD. Assistant Professor, Sarcoma Program
 DTRF Annual Patient Meeting September 22, 2018 Breelyn A. Wilky, MD Assistant Professor, Sarcoma Program 1 2 1. I have a desmoid tumor. Do I have cancer? Do I have sarcoma? Tumor vs. cancer Growth of abnormal,
DTRF Annual Patient Meeting September 22, 2018 Breelyn A. Wilky, MD Assistant Professor, Sarcoma Program 1 2 1. I have a desmoid tumor. Do I have cancer? Do I have sarcoma? Tumor vs. cancer Growth of abnormal,
Multitechnique Imaging Findings of Prolene Plug Hernia Repair
 Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Cronin et al. Imaging of Prolene Plug Hernia Repair Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Carmel G. Cronin 1 Mukesh G. Harisinghani Onofrio Catalano Michael. lake
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Cronin et al. Imaging of Prolene Plug Hernia Repair Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Carmel G. Cronin 1 Mukesh G. Harisinghani Onofrio Catalano Michael. lake
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
Imaging Features of Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis in Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Patients
 Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Ti et al. Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis in CPD Patients Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Joanna P. Ti 1 li l-radi 2 Peter J. Conlon 2 Michael J. Lee 1 Martina
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Ti et al. Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis in CPD Patients Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Joanna P. Ti 1 li l-radi 2 Peter J. Conlon 2 Michael J. Lee 1 Martina
Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee joint- A Case Report and Review of Literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.5 March. (2018), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.5 March. (2018), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee
3/27/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
CT of the Abdominal Wall
 1207 CT of the Abdominal Wall PhilipGoodma& 2 and Bharat Raval1 CT is an excellent method for evaluating the abdominal wall. Various abnormalities including hernia, hematoma, abscess, tumor, and neuromuscular
1207 CT of the Abdominal Wall PhilipGoodma& 2 and Bharat Raval1 CT is an excellent method for evaluating the abdominal wall. Various abnormalities including hernia, hematoma, abscess, tumor, and neuromuscular
Takayuki Ohguri 1 Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masanori Hisaoka 2 Hideyuki Watanabe 1 Katsumi Nakamura 1 Hiroshi Hashimoto 2 Toshitaka Nakamura 3 Hajime Nakata 1
 Takayuki Ohguri 1 Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masanori Hisaoka 2 Hideyuki Watanabe 1 Katsumi Nakamura 1 Hiroshi Hashimoto 2 Toshitaka Nakamura 3 Hajime Nakata 1 Received July 1, 2002; accepted after revision November
Takayuki Ohguri 1 Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masanori Hisaoka 2 Hideyuki Watanabe 1 Katsumi Nakamura 1 Hiroshi Hashimoto 2 Toshitaka Nakamura 3 Hajime Nakata 1 Received July 1, 2002; accepted after revision November
Images In Gastroenterology
 Images In Gastroenterology Thong-Ngam D, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2005 Vol. 6 No. 2 May - Aug. 2005 105 Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Pornpim Fuangtharnthip, M.D. Narumol Hargroove, M.D.
Images In Gastroenterology Thong-Ngam D, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2005 Vol. 6 No. 2 May - Aug. 2005 105 Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Pornpim Fuangtharnthip, M.D. Narumol Hargroove, M.D.
MRI XR, CT, NM. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # 2. Date accepted: 15 March 2013
 Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
MDCT signs differentiating retroperitoneal and intraperitoneal lesions- diagnostic pearls
 MDCT signs differentiating retroperitoneal and intraperitoneal lesions- diagnostic pearls Poster No.: C-0987 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. V. Bhargavi, R. Avantsa, P. Kala; Bangalore/IN
MDCT signs differentiating retroperitoneal and intraperitoneal lesions- diagnostic pearls Poster No.: C-0987 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. V. Bhargavi, R. Avantsa, P. Kala; Bangalore/IN
Spectrum of MRI Findings of Synovial Sarcoma
 Spectrum of MRI Findings of Synovial Sarcoma Poster No.: C-1523 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. A. Molina, J. Llauger Rosselló, J. Palmer Sancho, G. M. 1 1 2 1 3 1 1 Santandreu,
Spectrum of MRI Findings of Synovial Sarcoma Poster No.: C-1523 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. A. Molina, J. Llauger Rosselló, J. Palmer Sancho, G. M. 1 1 2 1 3 1 1 Santandreu,
Intra-abdominal Mesenteric fibromatosis : CT findings, patterns and differential diagnosis. Our experience.
 Intra-abdominal Mesenteric fibromatosis : CT findings, patterns and differential diagnosis. Our experience. Poster No.: C-1120 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Carbone, F. R. Setola,
Intra-abdominal Mesenteric fibromatosis : CT findings, patterns and differential diagnosis. Our experience. Poster No.: C-1120 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Carbone, F. R. Setola,
Intramuscular Myxoma: Characteristic MR Imaging Features
 Laura W. ancroft 1 Mark J. Kransdorf 1 David M. Menke 2 Mary I. O Connor 3 William C. Foster 4 Received September 17, 2001; accepted after revision October 30, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic,
Laura W. ancroft 1 Mark J. Kransdorf 1 David M. Menke 2 Mary I. O Connor 3 William C. Foster 4 Received September 17, 2001; accepted after revision October 30, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic,
PET IMAGING (POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPY) FACT SHEET
 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Using T2-Weighted Sequences to More Accurately Characterize Breast Masses Seen on MRI
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Westra et al. MRI of reast Masses Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.58 on 12/28/17 from IP address 46.3.195.58.
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Westra et al. MRI of reast Masses Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.58 on 12/28/17 from IP address 46.3.195.58.
The Imaging Features of Desmoid Tumors: the Usefulness of Diffusion Weighted Imaging to Differentiate between Desmoid and Malignant Soft Tissue Tumors
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:162-170 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.3.162 The Imaging Features of Desmoid Tumors: the Usefulness of Diffusion Weighted Imaging to Differentiate between
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:162-170 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.3.162 The Imaging Features of Desmoid Tumors: the Usefulness of Diffusion Weighted Imaging to Differentiate between
Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck. Kevin Harrington
 Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck Kevin Harrington Overview Classification and incidence of sarcomas Clinical presentation Challenges to treatment Management approaches Prognostic factors Radiation-induced
Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck Kevin Harrington Overview Classification and incidence of sarcomas Clinical presentation Challenges to treatment Management approaches Prognostic factors Radiation-induced
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 EXTRA SKELETAL MESENCHYMAL CHONDROSARCOMA :A CASE REPORT Rajaraman R Subbiah S Navin Naushad Kilpaulk Medical College Abstract:
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 EXTRA SKELETAL MESENCHYMAL CHONDROSARCOMA :A CASE REPORT Rajaraman R Subbiah S Navin Naushad Kilpaulk Medical College Abstract:
Index. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) 465 469 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adjuvant therapy, preoperative for gastric cancer, staging and, 339 B Breast cancer, metabolic
Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) 465 469 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adjuvant therapy, preoperative for gastric cancer, staging and, 339 B Breast cancer, metabolic
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
The radiologic workup of a palpable breast mass
 Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging
 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy 85 Chapter 5 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging Neurological symptoms and signs of brachial plexopathy may develop in patients who have had radiation
Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy 85 Chapter 5 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging Neurological symptoms and signs of brachial plexopathy may develop in patients who have had radiation
Dr Sneha Shah Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai.
 Dr Sneha Shah Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai. Topics covered Lymphomas including Burkitts Pediatric solid tumors (non CNS) Musculoskeletal Ewings & osteosarcoma. Neuroblastomas Nasopharyngeal carcinomas
Dr Sneha Shah Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai. Topics covered Lymphomas including Burkitts Pediatric solid tumors (non CNS) Musculoskeletal Ewings & osteosarcoma. Neuroblastomas Nasopharyngeal carcinomas
Case Fibrothecoma of the ovary
 Case 10646 Fibrothecoma of the ovary Elisa Melo Abreu, Teresa Margarida Cunha Section: Genital (Female) Imaging Published: 2015, Jan. 2 Patient: 70 year(s), female Authors' Institution Department of Radiology,
Case 10646 Fibrothecoma of the ovary Elisa Melo Abreu, Teresa Margarida Cunha Section: Genital (Female) Imaging Published: 2015, Jan. 2 Patient: 70 year(s), female Authors' Institution Department of Radiology,
Update on RECIST and Staging of Common Pediatric Tumors Ethan A. Smith, MD
 Update on RECIST and Staging of Common Pediatric Tumors Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures No relevant
Update on RECIST and Staging of Common Pediatric Tumors Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures No relevant
Case Report Desmoid Tumour of the Brachial Plexus
 Volume 2013, Article ID 575982, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/575982 Case Report Desmoid Tumour of the Brachial Plexus Orege Juliette, 1 Koech Florentius, 2 Ndiangui Francis, 3 Benson Ndegwa Macharia,
Volume 2013, Article ID 575982, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/575982 Case Report Desmoid Tumour of the Brachial Plexus Orege Juliette, 1 Koech Florentius, 2 Ndiangui Francis, 3 Benson Ndegwa Macharia,
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
X-ray Corner. Imaging of The Peritoneum and Mesentery. Pantongrag-Brown L. Case 1. A 47-year-old woman presenting with abdominal distension.
 X-ray Corner Pantongrag-Brown L THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2016 Vol. 17 No. 3 Sep. - Dec. 2016 187 Pantongrag-Brown L Modern imaging modalities commonly used in peritoneum and mesentery include ultrasound (US),
X-ray Corner Pantongrag-Brown L THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2016 Vol. 17 No. 3 Sep. - Dec. 2016 187 Pantongrag-Brown L Modern imaging modalities commonly used in peritoneum and mesentery include ultrasound (US),
Educational: Desmoid Tumors
 17 th March 2011, Berlin Systemic Therapy and PET Imaging Bernd Kasper University of Heidelberg Mannheim University Medical Center ITM - Interdisciplinary Tumor Center Mannheim Sarcoma Unit German Interdisciplinary
17 th March 2011, Berlin Systemic Therapy and PET Imaging Bernd Kasper University of Heidelberg Mannheim University Medical Center ITM - Interdisciplinary Tumor Center Mannheim Sarcoma Unit German Interdisciplinary
Index. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 14 (2005) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Surg Oncol Clin N Am 14 (2005) 433 439 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominosacral resection, of recurrent rectal cancer, 202 215 Ablative techniques, image-guided,
Surg Oncol Clin N Am 14 (2005) 433 439 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominosacral resection, of recurrent rectal cancer, 202 215 Ablative techniques, image-guided,
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation
 246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
Understanding desmoid-type fibromatosis
 Understanding desmoid-type fibromatosis Sarcoma UK Support Line 0808 801 0401 supportline@ The bone & soft tissue cancer charity About this booklet This booklet is for anyone who has been diagnosed with
Understanding desmoid-type fibromatosis Sarcoma UK Support Line 0808 801 0401 supportline@ The bone & soft tissue cancer charity About this booklet This booklet is for anyone who has been diagnosed with
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research hun et al. MRI of Skeletal Muscle Lymphoma Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research hang Woo hun 1 Won-Hee Jee 1 Hye Jung Park 1 Yeo Joo Kim 1 Jeong-Mi Park 1
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research hun et al. MRI of Skeletal Muscle Lymphoma Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research hang Woo hun 1 Won-Hee Jee 1 Hye Jung Park 1 Yeo Joo Kim 1 Jeong-Mi Park 1
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
Pre-operative assessment of patients for cytoreduction and HIPEC
 Pre-operative assessment of patients for cytoreduction and HIPEC Washington Hospital Center Washington, DC, USA Ovarian Cancer Surgery New Strategies Bergamo, Italy May 5, 2011 Background Cytoreductive
Pre-operative assessment of patients for cytoreduction and HIPEC Washington Hospital Center Washington, DC, USA Ovarian Cancer Surgery New Strategies Bergamo, Italy May 5, 2011 Background Cytoreductive
* I have no disclosures or any
 Howard Rosenthal, M.D. Associate Professor of Orthopedic Surgery University of Kansas Sarcoma Center I have no disclosures or any conflicts related to the content of this presentation. Objectives 1. Describe
Howard Rosenthal, M.D. Associate Professor of Orthopedic Surgery University of Kansas Sarcoma Center I have no disclosures or any conflicts related to the content of this presentation. Objectives 1. Describe
Contents. Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology. Ultrasound Nodule Characteristics
 Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Extraosseous Ewing s Sarcoma Presented as a Rectal Subepithelial Tumor: Radiological and Pathological Features
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:51-55 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.1.51 Extraosseous Ewing s Sarcoma Presented as a Rectal Subepithelial Tumor: Radiological and Pathological Features
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:51-55 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.1.51 Extraosseous Ewing s Sarcoma Presented as a Rectal Subepithelial Tumor: Radiological and Pathological Features
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) Amir Reza Radmard, MD Assistant Professor Shariati hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences
 Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) Amir Reza Radmard, MD Assistant Professor Shariati hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences Describe the typical imaging findings of GIST at initial
Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) Amir Reza Radmard, MD Assistant Professor Shariati hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences Describe the typical imaging findings of GIST at initial
Clinical indications for positron emission tomography
 Clinical indications for positron emission tomography Oncology applications Brain and spinal cord Parotid Suspected tumour recurrence when anatomical imaging is difficult or equivocal and management will
Clinical indications for positron emission tomography Oncology applications Brain and spinal cord Parotid Suspected tumour recurrence when anatomical imaging is difficult or equivocal and management will
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV
 DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C.
 Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses. Case #1
 University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
Accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and extension of pelvic endometriosis
 Accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and extension of pelvic endometriosis A.Salem, Kh. Fakhfakh, S. Mehiri, Y. Ben Brahim, F. Ben Amara, H. Rajhi, R. Hamza,
Accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and extension of pelvic endometriosis A.Salem, Kh. Fakhfakh, S. Mehiri, Y. Ben Brahim, F. Ben Amara, H. Rajhi, R. Hamza,
is time consuming and expensive. An intra-operative assessment is not going to be helpful if there is no more tissue that can be taken to improve the
 My name is Barry Feig. I am a Professor of Surgical Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas. I am going to talk to you today about the role for surgery in the treatment
My name is Barry Feig. I am a Professor of Surgical Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas. I am going to talk to you today about the role for surgery in the treatment
Advanced Pelvic Malignancy: Defining Resectability Be Aggressive. Lloyd A. Mack September 19, 2015
 Advanced Pelvic Malignancy: Defining Resectability Be Aggressive Lloyd A. Mack September 19, 2015 CONFLICT OF INTEREST DECLARATION I have no conflicts of interest Advanced Pelvic Malignancies Locally Advanced
Advanced Pelvic Malignancy: Defining Resectability Be Aggressive Lloyd A. Mack September 19, 2015 CONFLICT OF INTEREST DECLARATION I have no conflicts of interest Advanced Pelvic Malignancies Locally Advanced
Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh
 Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.2.138 Malignant Granular Cell Tumor of the Abdominal Wall Mimicking Desmoid Tumor: A Case Report with CT Imaging Findings
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.2.138 Malignant Granular Cell Tumor of the Abdominal Wall Mimicking Desmoid Tumor: A Case Report with CT Imaging Findings
RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION
 RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION ELIZABETH DAVID M D FRCPC VASCULAR A ND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCIENCES CENTRE GIST GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMORS Stromal or mesenchymal neoplasms affecting
RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION ELIZABETH DAVID M D FRCPC VASCULAR A ND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCIENCES CENTRE GIST GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMORS Stromal or mesenchymal neoplasms affecting
FDG-PET value in deep endometriosis
 Gynecol Surg (2011) 8:305 309 DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0652-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE FDG-PET value in deep endometriosis A. Setubal & S. Maia & C. Lowenthal & Z. Sidiropoulou Received: 3 December 2010 / Accepted:
Gynecol Surg (2011) 8:305 309 DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0652-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE FDG-PET value in deep endometriosis A. Setubal & S. Maia & C. Lowenthal & Z. Sidiropoulou Received: 3 December 2010 / Accepted:
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Nodular Fasciitis Characteristic Imaging Features on Sonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Nodular Fasciitis Characteristic Imaging Features on Sonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Anthony Khuu, MD, Corrie M. Yablon, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Alero Inyang, MD, David R.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Nodular Fasciitis Characteristic Imaging Features on Sonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Anthony Khuu, MD, Corrie M. Yablon, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Alero Inyang, MD, David R.
Bone HDR brachytherapy in a patient with recurrent Ewing s sarcoma of the acetabulum: Alternative to aggressive surgery
 Bone HDR brachytherapy in a patient with recurrent Ewing s sarcoma of the acetabulum: Alternative to aggressive surgery Rafael Martínez-Monge 1,* Agata Pérez-Ochoa 1, Mikel San Julián 2, Dámaso Aquerreta
Bone HDR brachytherapy in a patient with recurrent Ewing s sarcoma of the acetabulum: Alternative to aggressive surgery Rafael Martínez-Monge 1,* Agata Pérez-Ochoa 1, Mikel San Julián 2, Dámaso Aquerreta
Soft Tissue Tumour & Sarcoma Imaging Guidelines 2012
 Soft Tissue Tumour & Sarcoma Imaging Guidelines 2012 Version Control This is a controlled document please destroy all previous versions on receipt of a new version. Date Approved: March 2011 reissued April
Soft Tissue Tumour & Sarcoma Imaging Guidelines 2012 Version Control This is a controlled document please destroy all previous versions on receipt of a new version. Date Approved: March 2011 reissued April
Myxoid soft tissue tumor in the loin
 J1 Myxoid soft tissue tumor in the loin Atsuji Matsuyama 1, Masamichi Nakayama 2, Masanori Hisaoka 1 1 Department of Pathology & Oncology, School of Medicine, University of Occupational & Environmental
J1 Myxoid soft tissue tumor in the loin Atsuji Matsuyama 1, Masamichi Nakayama 2, Masanori Hisaoka 1 1 Department of Pathology & Oncology, School of Medicine, University of Occupational & Environmental
Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa
 Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa Poster No.: P-0040 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. YESILDAG, S. Keskin, H. Kalkan, S. Kucuksen, U. Kerimoglu; Konya/TR
Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa Poster No.: P-0040 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. YESILDAG, S. Keskin, H. Kalkan, S. Kucuksen, U. Kerimoglu; Konya/TR
Review Article Imaging Features of Superficial and Deep Fibromatoses in the Adult Population
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Sarcoma Volume 2012, Article ID 215810, 17 pages doi:10.1155/2012/215810 Review Article Imaging Features of Superficial and Deep Fibromatoses in the Adult Population Eric
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Sarcoma Volume 2012, Article ID 215810, 17 pages doi:10.1155/2012/215810 Review Article Imaging Features of Superficial and Deep Fibromatoses in the Adult Population Eric
Giant-cell tumor of the tendon sheath: when must we suspect it?
 Giant-cell tumor of the tendon sheath: when must we suspect it? Poster No.: C-0538 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Santos Montón, J. M. Alonso Sánchez, D. C. Cuellar, P. A. Chaparro
Giant-cell tumor of the tendon sheath: when must we suspect it? Poster No.: C-0538 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Santos Montón, J. M. Alonso Sánchez, D. C. Cuellar, P. A. Chaparro
A case of giant benign localized fibrous tumor of the pleura
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.30 / No. 4/2000 A case of giant benign localized fibrous tumor of the pleura ALİ KEMAL UZUNLAR 1, MEHMET YALDIZ 1, İBRAHİM H. ÖZERCAN 2, FAHRİ YILMAZ 1, AKIN E. BALCI 3 1
Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.30 / No. 4/2000 A case of giant benign localized fibrous tumor of the pleura ALİ KEMAL UZUNLAR 1, MEHMET YALDIZ 1, İBRAHİM H. ÖZERCAN 2, FAHRİ YILMAZ 1, AKIN E. BALCI 3 1
Effective local and systemic therapy is necessary for the cure of Ewing tumor Most chemotherapy regimens are a combination of cyclophosphamide,
 Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University
 objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of Primary Ovarian Leiomyosarcoma: a Case Report and Review of the Literature
 May, 2017 2017; Vol1; Issue4 http://iamresearcher.online Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of Primary Ovarian Leiomyosarcoma: a Case Report and Review of the Literature Lama M AlMudaimeegh Department of
May, 2017 2017; Vol1; Issue4 http://iamresearcher.online Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of Primary Ovarian Leiomyosarcoma: a Case Report and Review of the Literature Lama M AlMudaimeegh Department of
Utility of FDG PET/CT in the Assessment of Myeloid Sarcoma
 Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Pictorial Essay Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Pictorial Essay Elaine Yuen Phin Lee 1 Marina-Portia nthony 1 nskar Yu-Hung Leung 2 Florence Loong 3 Pek-Lan
Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Pictorial Essay Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Pictorial Essay Elaine Yuen Phin Lee 1 Marina-Portia nthony 1 nskar Yu-Hung Leung 2 Florence Loong 3 Pek-Lan
Case Report Monophasic Synovial Sarcoma of Prostatic Fascia: Case Report and Literature Review
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2015, Article ID 419180, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/419180 Case Report Monophasic Synovial Sarcoma of Prostatic Fascia: Case Report and Literature Review Lucio
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2015, Article ID 419180, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/419180 Case Report Monophasic Synovial Sarcoma of Prostatic Fascia: Case Report and Literature Review Lucio
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: Available online at: Case Study
 International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
Original Report. Nontraumatic Avulsions of the Pelvis. Liem T. Bui-Mansfield 1 3 Felix S. Chew 2 Leon Lenchik 2 Mitch J. Kline 4 Carol A.
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 05/12/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Liem T. ui-mansfield 1 3 Felix S. hew 2 Leon Lenchik
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 05/12/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Liem T. ui-mansfield 1 3 Felix S. hew 2 Leon Lenchik
