Soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas also show some malignant features: A clinicopathological study of a 15-year database
|
|
|
- Philippa Phelps
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi: /medoral Soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas also show some malignant features: A clinicopathological study of a 15-year database Zitong Lin 1, Guowen Sun 2, Tiemei Wang 1, Qingang Hu 2, Fei Chen 3, Shanhui Wen 1 1 Department of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University, Zhong Yang Road 30, Nanjing, China 2 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University, Zhong Yang Road 30, Nanjing, China 3 Department of Dentomaxillofacial Pathology, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University, Zhong Yang Road 30, Nanjing, China Correspondence: Department of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Medical School Nanjing University, Zhong Yang Road 30 Nanjing, China tiemeiwang106@163.com Received: 11/07/2014 Accepted: 16/10/2014 Lin Z, Sun G, Wang T, Hu Q, Chen F, Wen S. Soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas also show some malignant features: A clinicopathological study of a 15-year database. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal May 1;20 (3):e Article Number: Medicina Oral S. L. C.I.F. B pissn eissn: medicina@medicinaoral.com Indexed in: Science Citation Index Expanded Journal Citation Reports Index Medicus, MEDLINE, PubMed Scopus, Embase and Emcare Indice Médico Español Abstract Background: To investigate the clinicopathological features of six cases of soft tissue recurrent ameloblastoma and explore the role of increased aggressive biological behavior in the recurrences and treatment of this type of ameloblastomas. Material and Methods: In this study, we retrospectively reviewed recurrent ameloblastomas during a 15-year period; six cases were diagnosed as soft tissue recurrent ameloblastoma. The clinical, radiographic, cytological and immunohistochemical records of these six cases were investigated and analyzed. Results: All the six soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas occurred after radical bone resection, and were located in the adjacent soft tissues around the osteotomy regions. In Case 4, the patient developed pulmonary metastasis, extensive skull-base infiltration and cytological malignancy after multiple recurrences and malignant transformation was diagnosed. In the other five cases, although there were no cytological signs are sufficient to justify an ameloblastoma as malignant, some malignant features were observed. In Case 1, the tumor showed moderate atypical hyperplasia and the Ki-67 staining percentage was 40% positive, which are strongly suggestive of potential malignance. In Case 5, the patient developed a second soft tissue recurrence in the parapharyngeal region and later died of tumor-related complications. All the remaining three patients showed cytology atypia of varying degrees and high expression of PCNA or Ki-67, which confirmed active cell proliferation. Conclusions: Increased aggressiveness is an important factor of soft tissue recurrence. An intraoperative rapid pathological examination and more radical treatment are suggested for these cases. Key words: Ameloblastoma, soft tissue recurrence, aggressive biological behaviour. e365
2 Introduction Ameloblastoma is the most common epithelial odontogenic tumor, and it accounts for 10% of all tumors that arise in the mandible and maxilla (1). Ameloblastoma is generally considered to be a benign lesion with locally invasive behavior and a tendency to reoccur after inadequate treatment (2-4). The risk of recurrence is reported to be significantly reduced by radical treatment compared to conservative surgical treatment (5,6). However, there are some reports of soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas after radical treatment too. Olaitan retrospectively reviewed 26 cases of recurrent ameloblastoma within a 15-year period, and reported that four intraosseous ameloblastomas recurred in the soft tissues of the head and neck (3). Adebayo et al. described a case of soft issue recurrence in the chin 21 years after radical resection of an ameloblastoma of the mandible (7). Recurrence ameloblastoma due to inadequate treatment is often emphasized in literatures; however, the mechanism of recurrence could be quite complex due to their highly variable biological behaviors. Ameloblastoma recurrence has been suggested to be correlated to both the type of surgical treatment and increased aggressive biological behavior (8). Ameloblastomas constitute a group of heterogeneous lesions that exhibit rather variable biological behaviors ranging from cystic expansion to aggressive solid mass formation and even malignant transformation (1). Furthermore, ameloblastomas occasionally demonstrate clinical course characteristic of malignancies and may be associated with significant morbidity and sometimes death (9). The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified ameloblastomas into the following variants: solid/multicystic ameloblastoma, unicystic ameloblastoma, desmoplastic ameloblastoma and peripheral ameloblastoma, as well as malignant counterparts such as malignant ameloblastoma and ameloblastic carcinoma (10). Moreover, there are atypical ameloblastomas that showed cytology atypia but could not be classified as malignant ameloblastoma or ameloblastic carcinoma (11). In this study, we retrospectively reviewed recurrent ameloblastomas during a 15-year period ( ), six soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas were diagnosed of 25 recurrent ameloblastomas. The soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas which occurred after radical bone resection and located in the adjacent soft tissues and without involvement of the residual jaw, showed clincopathologcial features which were not quite consistent with intraossous recurrent ameloblastomas. The role of increased aggressive biological behavior in the recurrences and treatment are discussed in this paper. Material and Methods We retrospectively reviewed the clinical data of ameloblastoma patients admitted to our hospital who underwent resection and had histopathologically confirmed recurrent ameloblastoma during Of the 25 recurrent ameloblastomas, six cases were diagnosed as soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas based on their clinical, radiographic and histological presentations. Of these six cases, three cases had multiple recurrences: Case 4 showed six recurrences during ; cases 5, two recurrences during the period of study, and Case 6, had recurrences in 1992 and 1996 respectively. The following clinical data of the six recurrent cases were recorded for the six soft tissue recurrence cases: sex, age at presentation of recurrence, site of recurrence, time interval between primary operation and recurrence, number of recurrences, types of surgery and follow-up reviews. Histopathological sections of the primary and recurrent lesions were collected and evaluated for the histopathologic type and presence of cytology atypia. The histopathologic classifications included follicular, plexiform, acanthomatous, granular, basal cell type, and keratoameloblastoma (4,12). The cytological atypic features included hypercellularity, pleomorphism, hyperchromatic nuclei, and presence of mitotic figures (13). Immunohistochemical examination for the quantitative expression of Ki-67 or semi-quantitative expression (-, + or ++) of antigen proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) was conducted in all the six recurrent cases (14,15). All patients gave their written informed consent. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University. Results The clinical and pathological data of the six intraosseous ameloblastomas with soft tissue recurrence are shown in table 1. - Basal clinical data for recurrences Four men and two women with soft tissue recurrent ameloblastoma were investigated in this study. The mean age at presentation of recurrence was 52.5 years (range, years). The average time interval between the primary operation and recurrence was 22.3 years (range, 7-40 years). With the exception of Case 4, the time interval between the primary operation and the recurrences was 10 years in the remaining five cases. - Type of primary surgery In Case 4, enucleation and curettage were performed for the primary maxillary ameloblastoma; further, radical bone resection (partial maxillectomy) was performed for the first recurrence 2 years later. In the other five cases, radical bone resection was performed for all the primary lesions: hemimandibulectomy in three cases, segmental resection in one case and resection of the lesion with the dentoalveolar segment and preservation e366
3 Table 1. Clinical, pathological and immunohistochemical findings of six soft tissue recurrent ameloblastoma cases. Case No *5 6 Gender M F M M M F Age (years) Time interval (years) No. of recurrences Primary treatments Site of recurrence L M (osteotom y region) L SM Pathological classification Follicular Plexiform Follicular Basal cell Follicular Follicular Cytological features HC,HN, PM, HC, HN, HC, HN, HC, HN, HC,HN, HC, HN MF MF MF MF MF Ki-67 40% 32% / / / / PCNA / / Primary treatments in this study are divided into five types: 1: Curettage and enucleation, 2: Resection of the lesion with the dentoalveolar segment and preservation of the lower border; 3: Segmental resection; 4: Hemimandibulectomy and hemimaxillectomy 5: Osseous reconstruction. Site of recurrence: L: Left; R: Right; M: Molar region; SM: Submandibular region. Cytological features: HC: Hypercellularity; HN: Hyperchromatic nuclei; PM: Pleomorphism; MF: Mitotic figures. Case 4 had multiple recurrences and in the table was the fifth recurrence. *Case 5 had two soft tissue recurrences, but the patient refused further treatment for the second recurrence. The table provides information about the first recurrence. L M R SM R SM L M of the lower border in one case. In two cases, osseous reconstruction was performed for the defects. - Location of the recurrent tumors In three cases, the recurrent tumors were located in the submandibular region on the same side of the primary lesion; in one case, it was located in the soft tissue of the osteotomy region; and in two cases, the tumors recurred in the gingival tissue of the molar regions. - Follow-up review In all six cases, extensive tumor excision was performed for the recurrent tumors to prevent further recurrences. The follow-up time was 2-10 years, and in four cases, there were no additional recurrences after that. However, in Case 4, the patient developed pulmonary metastasis and extensive skull-base infiltration after multiple recurrences and died in 2013; in Case 5, the patient developed a second soft tissue recurrence in the parapharyngeal region, but he refused further treatment and died not long after that due to complications caused by the tumor. - Radiographic features In all the six cases, all the primary lesions showed extensive bone destruction involving the cortical plate. With regard to the soft tissue recurrences, all the bone margins were totally intact and without signs of bone recurrence. - Histopathological features Of the six cases, four were of the follicular type; one was plexiform type and one, basal cell type. All the six patients presented with cytology atypia of varying degrees for both the primary lesions and recurrent lesions (13). In Case 4, the primary lesion showed hypercellularity and the fifth recurrent tumor demonstrated increased cytological malignancy with hypercellularity, hyperchromatic nuclei, cellular and nuclear pleomorphism, increased mitotic figures, and focal areas of necrosis. In the other five cases, there were no significant signs indicating malignant transformation (ameloblastic carcinoma ex-ameloblastoma). In Case 1 and Case 2, the percentage of Ki-67-positive cells was 40% and 32% respectively. The other four cases were positive for PCNA (+ in two cases, and ++ in two cases). - Case Reports - Case 1 The patient was 22 years old at the time of the initial diagnosis of ameloblastoma in Resection of the lesion with dentoalveolar segment and preservation of the lower border was performed. Eighteen years later, the patient developed an intraoral swelling in the right mandibular body. CT revealed a soft tissue mass in the osteotomy region with an intact bone defect (Fig. 1A and 1B). Thereafter, extensive resection of the tumor and lower border of the jaw and transplantation of the ribs and fibula were performed. The final histological classification was recurrent follicular ameloblastoma. The patient has been followed up continuously with no evidence of recurrence. In the case of the recurrent tumor, moderate atypia was detected but it was not enough to justify an ameloblastic carcinoma. Moreover, the Ki- 67 staining percentage was 40% which confirmed active cell proliferation (Fig. 1C and 1D). Further, retrospective evaluation of the histopathological sections of primary lesion also showed cytology atypia including e367
4 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal May 1;20 (3):e Fig. 1. Radiographic, histological and immunohistochemical findings in Case 1. A: Panoramic radiograph showing a rectangular resection in the dentoalveolar side of the right mandible. B: Spiral CT image showing a soft tissue mass in the bone defect region (star). C: Pathological specimen of the recurrence showing moderate cellular atypia: hypercellularity, hyperchromatic nuclei, pleomorphism and mitotic figures (arrow). (hematoxylin and eosin staining; original magnification, 400). D: Strong positive staining of the nuclei is seen in the tumor cells (Ki-67, arrow; 100). E: Histopathological appearance of the primary lesion revealed hypercellularity, hyperchromatic nuclei and pleomorphism (hematoxylin and eosin staining; original magnification, 200). recurrent tumors and the patient has been followed up with no evidence of recurrence. The histopathological classification was follicular ameloblastoma and cytology atypia was found for the primary lesions and two times of recurrent lesions. - Case 4 The patient was referred to our hospital and underwent total enucleation and curettage for maxillary ameloblastoma in 1999 (Fig. 2A). Histological examination showed a follicular ameloblastoma with slight cytology atypia. In 2001, the patient developed his first recurrence and a partial maxillectomy was performed. Following this, the patient had two more soft tissue recurrences in 2002 and 2004, and radical resection was performed on both occasions. All three recurrent tumors were treated at another hospital. In 2006, the patient was admitted to our hospital again with a soft tissue recurrence in the right pterygomaxillary fossa (Fig. 2B) and extensive tumor excision was performed. In 2007, the patient presented once again with recurrent ameloblastoma in the right submandibular region (Fig. 2C). And a thoracic CT examination indicated pulmonary metastasis (Fig. hypercellularity, hyperchromatic nuclei and pleomorphism (Fig. 1E). - Case 2 The female patient was 30 years old at the time of the initial diagnosis of ameloblastoma, and hemimandibulectomy was performed in Thirty years later, the patient developed a swelling in the submandibular region. CT revealed a soft tissue mass with a totally intact bone defect. Extensive resection of the tumor was performed, and the histological diagnosis was recurrent ameloblastoma. The Ki-67 staining percentage was 32% positive for the recurrent ameloblastoma. Retrospective evaluation of the histopathological sections of both the primary and recurrent lesion showed plexiform ameloblastoma with cytology atypia including hypercellularity, hyperchromatic nuclei and mitotic figures. - Case 3 The patient was 30 years old at the time of the initial diagnosis of ameloblastoma in In 1992 and 2006, the patient had soft tissue recurrences located in the buccal mucosa and mandibular retromolar pad respectively. Extensive resections were performed for the e368
5 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal May 1;20 (3):e Fig. 2. Radiographic and histological findings in Case 4. A: Panoramic radiograph from February 1999 showing a well-defined multilocular radiolucent shadow located from the second premolar to the maxillary tuberosity (arrow); B: Scan from 2006 showing an irregular soft-tissue density mass in the right pterygomaxillary fossa (star). C: Spiral CT images taken in 2007 showing soft tissue recurrences (star) behind the right submandibular gland. D: The specimen from 2007 depicting a region of cytology atypia with mitotic figures (arrows) and hyperchromatic nuclei (hematoxylin and eosin staining; original magnification, 400). E: Thoracic CT images showing multiple nodules in both lung fields (arrows). F: Spiral CT images taken in 2008 showing erosion of the right petrosal apex of the temporal bone and the cranial base surface of the sphenoid bone with a diffuse boundary (arrow). was performed, and histological examination confirmed soft tissue recurrent ameloblastoma (follicular). Cytology atypia was confirmed for both the primary and recurrent lesions, based on the observed hypercellularity, hyperchromatic nuclei and mitotic figures (Fig. 3C, 3D). One year later, the patient developed a second recurrence in the parapharyngeal region (Fig. 3E), but he refused further treatment and died not long after that. - Case 6 The patient was 36 years old at the time of the initial diagnosis of ameloblastoma in 1989; hemimandibulectomy and osseous reconstruction were performed. Twelve years later, the patient developed a soft tissue recurrence in the mandibular third molar region. The final histological classification was recurrent follicular ameloblastoma. Similar with the other cases, retrospective cytological evaluation of the histopathological sections for the primary and recurrent lesion showed cytology atypia including hypercellularity and hyperchromatic nuclei. 2D). Extended tumor excision from the submandibular space was performed. Histological examination of the submandibular tumor specimen demonstrated cytological malignancy with hypercellularity, hyperchromatic nuclei, cellular and nuclear pleomorphism, and increased mitotic figures (Fig. 2E). In 2008, the patient had the sixth recurrence that manifested as numbness of the right face. Craniofacial CT revealed infiltration of the skull-base, including the petrous bone (Fig. 2F). The patient did not undergo further treatment and died in Based on the entire aggressive clinic course and cytological progression, malignant transformation was diagnosed. - Case 5 The patient was 33 years old at the time of the initial diagnosis in 1982 and hemimandibulectomy was performed for the primary lesion (Fig. 3A). Twenty-four years later, the patient developed a painful swelling in the right submandibular region with significant aggravation in a short time. Extra-oral examination revealed adhesion of a mass to the skin in the submandibular region. A panoramic radiograph revealed that the bone margin was completely intact (Fig. 3B). Extensive tumor resection Discussion According to the present classification of ameloblastoma, the benign ameloblastomas are divided into e369
6 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal May 1;20 (3):e Fig. 3. Radiographic and histological findings in Case 4. A: Lateral mandible radiograph from 1978 showing a multilocular radiolucent shadow spreading from the mandibular body to the ramus. B: Soft tissue recurrence in the submandibular region in 2002; the panoramic radiograph shows an intact bone margin of the mandible. C: Spiral CT scan from 2003 showing a second soft tissue recurrence in the right pterygomaxillary fossa (star). D and E: Histopathological appearance of the tumor in 1978 and 2002 depicting regions of cellular atypia with hypercellularity, hyperchromatic and nuclei mitotic figures (arrows) (hematoxylin and eosin staining; original magnification, 400). 1) solid/multicystic, 2) extra-osseous/peripheral, 3) desmoplastic, and 4) unicystic ameloblastoma. The solid/multicystic ameloblastomas are more aggressive than other types because they carry a high risk of local recurrences after inadequate treatment (1,4). Malignant ameloblastic lesions are divided into malignant (metastasizing) ameloblastoma and ameloblastic carcinoma. Malignant ameloblastoma describe an ameloblastoma with distant metastasis, and both primary and metastatic tumors retain a benign histological appearance. Ameloblastic carcinomas are tumors that combined morphologic features of ameloblastoma and carcinoma, regardless of the presence or absence of metastasis (13). However, ameloblastomas are on a complex spectrum of a single disease, there are atypical subtypes which presenting anaplastic features not sufficient to justify an ameloblastoma as malignant, but it carries increased aggressive biological behavior. In this study, some malignant features were observed for these cases at varied degrees. In case 4, pulmonary metastasis, extensive skull base infiltration and increased cellular atypia were found after multiple recurrences, and malignant transformation was diagnosed. However, in the other five cases, although there were no significant signs indicating ameloblastic carcinoma in both the primary and recurrent tumors, varying degrees of cellular atypia including hypercellularity, hyperchromatic nuclei, pleomorphism, and mitotic figures were observed (13). High expression of Ki-67 or PCNA was also found, which confirmed active cell proliferation (14,15). In Case 1, moderate atypical hyperplasia and 40% positive staining for Ki-67 were observed, which is strongly suggestive of potential malignance (11,12,14). In Case 5, the patient developed a second recurrence in the parapharyngeal region and died of tumor-related complications. In all the remaining three cases, the tumors showed cytology atypia and high expression of PCNA or Ki-67, which confirmed active cell proliferation. Ameloblastoma recurrence has been suggested to be correlated to both the histological features and the type of surgical treatment (8). It is known that ameloblastomas may recur from tumor tissue remaining in the residual stump of the jaw, from adjacent soft tissues, or from intraoperative contamination (16). However, in the present cases, tumors remaining in the stump of the jaw are less likely to recur because of the intact bone e370
7 and recurrences occurring in the soft tissues around the osteotomy region. Moreover, although en-bloc bone resections had been performed before the soft tissue recurrences in all the cases, intraoperative contamination cannot be ignored; therefore, intraoperative contamination could have been a cause of tumor recurrence in the present cases. Nonetheless, it seems that residual tumor in adjacent soft tissue was the main cause of recurrence in the cases investigated in the present study. The soft tissue recurrent tumors in our study were aggressive, and the pre-surgical radiograph of the primary lesion showed destruction of the cortical plate and possible infiltration into the adjacent soft tissues. However, the high level of aggressiveness of the lesions was not noted at the time of surgery, and only radical bone resection was performed in all cases. Thus, from the present findings, it can be speculated that insufficient resection of adjacent soft tissue in the primary treatments and presence of residual tumor tissue in the adjacent soft tissues are the most likely causes of recurrence; this is in agreement with the observation of other published studies (17,18). Considering the highly aggressive nature of these atypical ameloblastomas, firstly, a preoperative radiographic evaluation of whether the tumor involves the cortical plate is required, as destruction of the cortical plate suggests possible infiltration into the adjacent soft tissues. Secondly, a frozen rapid pathological examination during the surgery is suggested for these ameloblastomas cases; if cytological atypia indicative of aggressiveness is observed, more radical treatment including clearance of at least one more layer of tissue around such lesions should be performed (18). Moreover, for soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas, a more radical treatment with enough safe margins is important to avoid secondary recurrences. Therefore, pathological examination of the resection edge is necessary for confirming the resection boundary in these cases. It has also been reported that 50 80% of ameloblastoma recurrences are diagnosed within the first 5 years (2-4). However, in this study, late recurrence was found in five patients for whom the time interval between the primary operation and recurrence was 10 years; in agreement with this, late recurrences have been reported in some recent studies (7). Eckardt reported that the rate of cumulative relapses was 17% after 5 years and 19% after 10 years (6). Therefore, a long-term follow-up beyond 5 years is required, especially in cases where the tumors are of an aggressive nature. Conclusions In this clinical retrospective study of recurrent ameloblastomas during a 15-year database ( ), it was noted that soft tissue recurrence following radical bone resection also showed some malignant features. An intraoperative rapid pathological examination and more radical treatment are suggested for these cases of aggressive tumors. References 1. Mendenhall WM, Werning JW, Fernandes R, Malyapa RS, Mendenhall NP. Ameloblastoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2007;30: Reichart PA, Philipsen HP, Sonner S. Ameloblastoma: biological profile of 3677 cases. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol. 1995;31B: Olaitan AA, Arole G, Adekeye EO. Recurrent ameloblastoma of the jaws. A follow-up study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998;27: Kim SG, Jang HS. Ameloblastoma: a clinical, radiographic, and histopathologic analysis of 71 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001;91: Migaldi M, Sartori G, Rossi G, Cittadini A, Sgambato A. Tumor cell proliferation and microsatellite alterations in human ameloblastoma. Oral Oncol. 2008;44: Eckardt AM, Kokemüller H, Flemming P, Schultze A. Recurrent ameloblastoma following osseous reconstruction--a review of twenty years. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2009;37: Adebayo ET, Fomete B, Adekeye EO. Delayed soft tissue recurrence after treatment of ameloblastoma in a black African: case report and review of the literature. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2011;39: Hertog D, Schulten EA, Leemans CR, Winters HA, Van der Waal I. Management of recurrent ameloblastoma of the jaws; a 40-year single institution experience. Oral Oncol. 2011;47: Okada H, Davies JE, Yamamoto H. Malignant ameloblastoma: a case study and review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999;57: González-González R, Molina-Frechero N, Damian-Matsumura P, Bologna-Molina R. Molecular markers of cell adhesion in ameloblastomas. An update. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2014;19:e8- e Slater LJ. Odontogenic malignancies. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2004;16: Hertog D, Bloemena E, Aartman IH, van-der-waal I. Histopathology of ameloblastoma of the jaws; some critical observations based on a 40 years single institution experience. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012;17:e Dhir K, Sciubba J, Tufano RP. Ameloblastic carcinoma of the maxilla. Oral Oncol. 2003;39: Bologna-Molina R, Mosqueda-Taylor A, Molina-Frechero N, Mori-Estevez AD, Sánchez-Acuña G. Comparison of the value of PCNA and Ki-67 as markers of cell proliferation in ameloblastic tumors. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2013;18:e Kim J, Yook JI. Immunohistochemical study on proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in ameloblastomas. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol. 1994;30B: Martins WD, Fávaro DM. Recurrence of an ameloblastoma in an autogenous iliac bone graft. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004;98: Xavier SP, Faria AC, de Mello Filho FV, Silva ER, de Santana Santos T. Recurrence of ameloblastoma in soft tissue. J Craniofac Surg. 2013;24: Rauso R, Tartaro G, Gherardini G, Puglia F, Santagata M, Colella G. Recurrence of ameloblastoma in temporal area: primary treatment influences recurrence rate. J Craniofac Surg. 2010;21: Funding This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, No.:BK Co-corresponding authors: Tiemei Wang and Qingang Hu are equally contributed to this work. Conflict of interest None of the authors have any other conflict of interest. e371
Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 478-482 CASE REPORT Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report Zhi-Yu Zhu Zhi-Gang Chu 1 Yu Chen Wei-Ping
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 478-482 CASE REPORT Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report Zhi-Yu Zhu Zhi-Gang Chu 1 Yu Chen Wei-Ping
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
Ameloblastomas: Clinicopathological features from 70 cases diagnosed in a single Oral Pathology service in an 8-year period
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19802 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19802 Ameloblastomas: Clinicopathological features from 70 cases
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19802 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19802 Ameloblastomas: Clinicopathological features from 70 cases
Rong Yang 1*, Zheqi Liu 1*, Sandhya Gokavarapu 2, Canbang Peng 1, Wei Cao 1, Tong Ji 1. Original Article. Abstract
 Original Article Recurrence and cancerization of ameloblastoma: multivariate analysis of 87 recurrent craniofacial ameloblastoma to assess risk factors associated with early recurrence and secondary ameloblastic
Original Article Recurrence and cancerization of ameloblastoma: multivariate analysis of 87 recurrent craniofacial ameloblastoma to assess risk factors associated with early recurrence and secondary ameloblastic
MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
The Epidemiology, treatment, and complication of ameloblastoma in East-Indonesia: 6 years retrospective study
 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 8 Jan ; ():e54-8. Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:.47/medoral.85 http://dx.doi.org/doi:.47/medoral.85 The Epidemiology, treatment,
Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 8 Jan ; ():e54-8. Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:.47/medoral.85 http://dx.doi.org/doi:.47/medoral.85 The Epidemiology, treatment,
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 18/May 05, 2014 Page 4859
 CYSTIC DEGENERATION IN FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA: A CASE REPORT Neeraj Kumar 1, Niharika Rathore 2, Hemant Shakya 3, Anshuman Jamdade 4, Puneet Chitlangia 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Neeraj Kumar, Niharika
CYSTIC DEGENERATION IN FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA: A CASE REPORT Neeraj Kumar 1, Niharika Rathore 2, Hemant Shakya 3, Anshuman Jamdade 4, Puneet Chitlangia 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Neeraj Kumar, Niharika
Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Case Report A Conservative Approach to a Peripheral Ameloblastoma
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 8254571, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8254571 Case Report A Conservative Approach to a Peripheral Ameloblastoma Rocco Borrello, 1 Elia Bettio,
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 8254571, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8254571 Case Report A Conservative Approach to a Peripheral Ameloblastoma Rocco Borrello, 1 Elia Bettio,
Recurrent odontogenic ghost cell carcinoma (OGCC) at a reconstructed fibular flap: A case report with immunohistochemical findings
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/medoral.17207 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17207 at a reconstructed fibular flap: A case report with immunohistochemical
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/medoral.17207 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17207 at a reconstructed fibular flap: A case report with immunohistochemical
Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma
 Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma Rajesh B Dhirawani, Sumit Asrani, Anshalika Agrawal, Sauvik Singha* and Kshitij Aggarwal Department
Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma Rajesh B Dhirawani, Sumit Asrani, Anshalika Agrawal, Sauvik Singha* and Kshitij Aggarwal Department
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Ameloblastic Carcinoma of the Mandible: a Rare Case Report
 IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
Upper lip malignant neoplasms. A study of 59 cases
 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 212 May 1;17 (3):e371-6. Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:1.4317/medoral.1751 http://dx.doi.org/doi:1.4317/medoral.1751 Upper
Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 212 May 1;17 (3):e371-6. Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:1.4317/medoral.1751 http://dx.doi.org/doi:1.4317/medoral.1751 Upper
Management of Unicystic Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year Old Female: Report of a Case
 Article ID: WMC002613 2046-1690 Management of Unicystic Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year Old Female: Report of a Case Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial
Article ID: WMC002613 2046-1690 Management of Unicystic Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year Old Female: Report of a Case Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial
Low-grade spindle-cell ameloblastic carcinoma: report of an unusual case with immunohistochemical findings and review of the literature
 JINDAL et al. C A S E R E P O R T Low-grade spindle-cell ameloblastic carcinoma: report of an unusual case with immunohistochemical findings and review of the literature C. Jindal m d s,* S. Palaskar m
JINDAL et al. C A S E R E P O R T Low-grade spindle-cell ameloblastic carcinoma: report of an unusual case with immunohistochemical findings and review of the literature C. Jindal m d s,* S. Palaskar m
Case Report Acanthomatous Ameloblastoma treated with Hemimandibulectomy
 Case Report Acanthomatous Ameloblastoma treated with Hemimandibulectomy Shobha Bijjargi, Ashwini Rani S.R, Jaishankar HP, Shashidara R 1, Veerendra Patil 2 Departments of Oral Medicine &Radiology, 1 Oral
Case Report Acanthomatous Ameloblastoma treated with Hemimandibulectomy Shobha Bijjargi, Ashwini Rani S.R, Jaishankar HP, Shashidara R 1, Veerendra Patil 2 Departments of Oral Medicine &Radiology, 1 Oral
Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report
 Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, MIDSR,
Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, MIDSR,
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
Glandular odontogenic cyst associated with ameloblastoma: Case report and review of the literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
SURGICAL'MANAGEMENT'OF' PLEXIFORM'AMELOBLASTOMA:'A' CASE'REPORT'
 HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
AMELOBLASTIC CARCINOMA OF
 AMELOBLASTIC CARCINOMA OF MANDIBLE- A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature Mubeen K (1), Shakya HK (2), Jigna VR (3) (1) MDS, Professor and Head of Department, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology,
AMELOBLASTIC CARCINOMA OF MANDIBLE- A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature Mubeen K (1), Shakya HK (2), Jigna VR (3) (1) MDS, Professor and Head of Department, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology,
Ameoblastic carcinoma of mandible - A rare case report with review of literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case report doi:10.4317/jced.2.e100 Ameoblastic carcinoma of mandible - A rare case report with review of literature K Mubeen 1, Hemant Kumar
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case report doi:10.4317/jced.2.e100 Ameoblastic carcinoma of mandible - A rare case report with review of literature K Mubeen 1, Hemant Kumar
Reconstruction of large mandibular defects
 Immediate Reconstruction of a Large Mandibular Defect of Locally Invasive Benign Lesions (A New Method) Gholamreza Shirani, OMFS, DDS, MS,* Mahnaz Arshad, DDS, 1 Farnoush Mohammadi, OMFS, DDS, MS* Tehran,
Immediate Reconstruction of a Large Mandibular Defect of Locally Invasive Benign Lesions (A New Method) Gholamreza Shirani, OMFS, DDS, MS,* Mahnaz Arshad, DDS, 1 Farnoush Mohammadi, OMFS, DDS, MS* Tehran,
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH e-issn - 2348-2184 Print ISSN - 2348-2176 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajbpr SOLID AND MULTICYSTIC FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA - A CASE
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH e-issn - 2348-2184 Print ISSN - 2348-2176 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajbpr SOLID AND MULTICYSTIC FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA - A CASE
Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case Report?
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
The concept of unicystic ameloblastoma (UA) was
 Publication Treatment of Giant Unicystic Ameloblastoma Suction Drainage and Secondary Curettage: a Case Report Bing LIU 1, Wen Feng ZHANG 1, Xin Ming CHEN 2, Zhi Jun SUN 3, Mohd Jamal Alsharif 1, Yi Fang
Publication Treatment of Giant Unicystic Ameloblastoma Suction Drainage and Secondary Curettage: a Case Report Bing LIU 1, Wen Feng ZHANG 1, Xin Ming CHEN 2, Zhi Jun SUN 3, Mohd Jamal Alsharif 1, Yi Fang
Clinical, radiological and therapeutic features of keratocystic odontogenic tumours: a study over a decade
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.51408 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51408 Clinical, radiological and therapeutic features of keratocystic odontogenic
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.51408 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51408 Clinical, radiological and therapeutic features of keratocystic odontogenic
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Recurrence rate of odontogenic keratocyst treated by enucleation and peripheral ostectomy: Retrospective case series with up to 12 years of follow-up
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.22366 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.22366 treated by enucleation and peripheral ostectomy: Retrospective
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.22366 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.22366 treated by enucleation and peripheral ostectomy: Retrospective
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
Original Article Mandible ameloblastoma with lung metastasis: a rare case report
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(6):6793-6799 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0008818 Original Article Mandible ameloblastoma with lung metastasis: a rare case report Rui-Na Yang 1*, Xin-Shuai Wang 1*,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(6):6793-6799 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0008818 Original Article Mandible ameloblastoma with lung metastasis: a rare case report Rui-Na Yang 1*, Xin-Shuai Wang 1*,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/31632 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mensink, Gertjan Title: Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy by the splitter-separator
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/31632 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mensink, Gertjan Title: Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy by the splitter-separator
Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
 (2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
(2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Odontogenic tumours: A review of 266 cases
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.50949 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.50949 Odontogenic tumours: A review of 266 cases Ahmed O. Lawal 1, Akinyele
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.50949 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.50949 Odontogenic tumours: A review of 266 cases Ahmed O. Lawal 1, Akinyele
Disclosures. Parathyroid Pathology. Objectives. The normal parathyroid 11/10/2012
 Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Mandibular Metastasis in Patients of Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: A Rare Entity; Report of Two Cases Channabasappa
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Mandibular Metastasis in Patients of Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: A Rare Entity; Report of Two Cases Channabasappa
Primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma of the maxilla possibly arising from an infected residual cyst: A case report
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 131-135, 2015 Primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma of the maxilla possibly arising from an infected residual cyst: A case report SHINTARO SUKEGAWA 1, HIDENOBU MATSUZAKI 2, NAOKI
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 131-135, 2015 Primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma of the maxilla possibly arising from an infected residual cyst: A case report SHINTARO SUKEGAWA 1, HIDENOBU MATSUZAKI 2, NAOKI
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know?
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Indian journals.com DOI: /j ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Vol. 2, No. 1, February 2014, pp- 75-79 Indian journals.com DOI: 10.5958/j.2347-6206.2.1.015 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma: Report of a Rare Case with Review of Literature Siva Kumar Pendyala 1
Vol. 2, No. 1, February 2014, pp- 75-79 Indian journals.com DOI: 10.5958/j.2347-6206.2.1.015 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma: Report of a Rare Case with Review of Literature Siva Kumar Pendyala 1
CASE year old male with a PET avid nodule in the left adrenal gland
 CASE 1 55 year old male with a PET avid nodule in the left adrenal gland Case 1 Adrenal gland parenchyma partly replaced by a spindle cell tumour with mild nuclear pleomorphism Atypical mitoses present
CASE 1 55 year old male with a PET avid nodule in the left adrenal gland Case 1 Adrenal gland parenchyma partly replaced by a spindle cell tumour with mild nuclear pleomorphism Atypical mitoses present
Acanthomatous Ameloblastoma- A Case Report
 Acanthomatous Ameloblastoma- A Case Report Geeta Singh 1, Rashmi Agarwal 2, Vimlesh Kumar 3, Deepak Passi 4 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, King George Dental University,
Acanthomatous Ameloblastoma- A Case Report Geeta Singh 1, Rashmi Agarwal 2, Vimlesh Kumar 3, Deepak Passi 4 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, King George Dental University,
T been frequently reported as arising centrally
 CENTRAL SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS OF JAWS I. K. DHAWAN, MS, FACS,* S. BHARGAVA, MD,~ N. C. NAYAK, AND R. K. GUPTA, MS" MD,~ Nine cases of central salivary gland tumors of the jaws were seen during the period
CENTRAL SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS OF JAWS I. K. DHAWAN, MS, FACS,* S. BHARGAVA, MD,~ N. C. NAYAK, AND R. K. GUPTA, MS" MD,~ Nine cases of central salivary gland tumors of the jaws were seen during the period
Unicystic Ameloblastoma: Implant- supported Reconstruction and Long-Term Follow-up
 OLGU RAPORU (Case Report) Hacettepe Dişhekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi Cilt: 31, Sayı: 2, Sayfa: 49-53, 2007 Unicystic Ameloblastoma: Implant- supported Reconstruction and Long-Term Follow-up Unikistik Ameloblastoma:
OLGU RAPORU (Case Report) Hacettepe Dişhekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi Cilt: 31, Sayı: 2, Sayfa: 49-53, 2007 Unicystic Ameloblastoma: Implant- supported Reconstruction and Long-Term Follow-up Unikistik Ameloblastoma:
Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma mimicking a cystic lesion: a case of misdiagnosis
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.4.199 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma mimicking a cystic lesion: a case of misdiagnosis Minkyu Kim 1, Eunae Cho 2,
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.4.199 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma mimicking a cystic lesion: a case of misdiagnosis Minkyu Kim 1, Eunae Cho 2,
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors
 The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
PhD, Associates lecturers in Oral Surgery, Faculty of Dentistry, Complutense University of Madrid, Madrid, Spain
 UNICYSTIC AMELOBLASTOMA: REHABILITATION WITH CHIN GRAFT HARVESTED AND IMPLANT-SUPPORTED FIXED PROSTHESIS J. SANZ-ALONSO 1, N. MARTÍNEZ-RODRÍGUEZ 2, M. MARTÍN-ARES 3, C. BARONA-DORADO 1, J. CORTÉS BRETÓN-BRINKMANN
UNICYSTIC AMELOBLASTOMA: REHABILITATION WITH CHIN GRAFT HARVESTED AND IMPLANT-SUPPORTED FIXED PROSTHESIS J. SANZ-ALONSO 1, N. MARTÍNEZ-RODRÍGUEZ 2, M. MARTÍN-ARES 3, C. BARONA-DORADO 1, J. CORTÉS BRETÓN-BRINKMANN
Key words: Third molar, Impacted tooth, Tooth Eruption, Molar, Mandible, Unerupted Tooth.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
Maxillary Verrucous Carcinoma Coincident With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Colon Adenocarcinoma
 Int Surg 2012;97:270 274 Case Report Maxillary Verrucous Carcinoma Coincident With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Colon Adenocarcinoma Hatsumi Yano Kato 1, Hiroaki Ishibashi 1, Yoshiki Nariai 1, Katsumi
Int Surg 2012;97:270 274 Case Report Maxillary Verrucous Carcinoma Coincident With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Colon Adenocarcinoma Hatsumi Yano Kato 1, Hiroaki Ishibashi 1, Yoshiki Nariai 1, Katsumi
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE. Jonathan I. Epstein
 INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
Myoepithelial Carcinoma: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Review article: Myoepithelial Carcinoma: A Rare Case Report with Review Dr. Shilpa Parikh 1, *Dr. Bhavik Mavani 2, Dr. Jigna Shah 3,Dr.Sheetal Sharma 4 1 Professor, Dept of Oral Medicine & Radiology, Govt.
Review article: Myoepithelial Carcinoma: A Rare Case Report with Review Dr. Shilpa Parikh 1, *Dr. Bhavik Mavani 2, Dr. Jigna Shah 3,Dr.Sheetal Sharma 4 1 Professor, Dept of Oral Medicine & Radiology, Govt.
Case Report RESECTION OF AMELOBLASTOMA FOLLOWED BY RECONSTRUCTION WITH NONVASCULARISED ILIAC BONE GRAFT A CASE REPORT
 Case Report FOLLOWED BY RECONSTRUCTION WITH NONVASCULARISED ILIAC BONE GRAFT A CASE REPORT Tariq Javed 1, Waqar Jeelani 2, Qurat ul Ain 1 1 Senior Registrar, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,
Case Report FOLLOWED BY RECONSTRUCTION WITH NONVASCULARISED ILIAC BONE GRAFT A CASE REPORT Tariq Javed 1, Waqar Jeelani 2, Qurat ul Ain 1 1 Senior Registrar, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,
Case Report Mandibular Ameloblastoma in an Elderly Patient: A Case Report
 Volume 2013, Article ID 145282, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/145282 Case Report andibular Ameloblastoma in an Elderly Patient: A Case Report Kokoro Nagata, Kasumi Shimizu, Chu Sato, Hiroshi orita,
Volume 2013, Article ID 145282, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/145282 Case Report andibular Ameloblastoma in an Elderly Patient: A Case Report Kokoro Nagata, Kasumi Shimizu, Chu Sato, Hiroshi orita,
Granular cell Ameloblastoma of the mandible A rare case report with brief review of literature
 Case Report Granular cell Ameloblastoma of the mandible A rare case report with brief review of literature Vandana Reddy 1, Vishal Bansal 2, Vijay Wadhwan 3, Arvind Venkatesh 4 1. Reader, Oral & Maxillofacial
Case Report Granular cell Ameloblastoma of the mandible A rare case report with brief review of literature Vandana Reddy 1, Vishal Bansal 2, Vijay Wadhwan 3, Arvind Venkatesh 4 1. Reader, Oral & Maxillofacial
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
The use of pedicled buccal fat pad combined with sequestrectomy in bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the maxilla
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.17422 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17422 The use of pedicled buccal fat pad combined with sequestrectomy in bisphosphonate-related
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.17422 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17422 The use of pedicled buccal fat pad combined with sequestrectomy in bisphosphonate-related
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms
 My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms Douglas R. Gnepp Warren Alpert Medical School at Brown University Rhode Island Hospital Pathology Department Providence RI Asked to present
My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms Douglas R. Gnepp Warren Alpert Medical School at Brown University Rhode Island Hospital Pathology Department Providence RI Asked to present
Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience
 wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1
 Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Solitary Plasmacytoma of Mandible: A rare case report Singh A 1, Singh V 2, Sharma N 3
 Case Report Solitary Plasmacytoma of Mandible: A rare case report Singh A 1, Singh V 2, Sharma N 3 1 Dr. Anurag Singh Consultant Sir Ganga Ram Hospital Delhi, India 2 Dr. Vishal Singh Professor, Oral &
Case Report Solitary Plasmacytoma of Mandible: A rare case report Singh A 1, Singh V 2, Sharma N 3 1 Dr. Anurag Singh Consultant Sir Ganga Ram Hospital Delhi, India 2 Dr. Vishal Singh Professor, Oral &
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours
 Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR )
 ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report
 Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A.
 BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A. Anvar Ali 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, Rehana Tippoo, P. Viswanathan,
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A. Anvar Ali 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, Rehana Tippoo, P. Viswanathan,
Recurrent adamantinoma of the tibia and lymph node metastasis
 Case Report Recurrent adamantinoma of the tibia and lymph node metastasis Sunil B Gudaganatti, Meena N Jadhav, Rashmi K Patil, Shreekant K Kittur Department of Pathology, Belgaum Institute of Medical Sciences,
Case Report Recurrent adamantinoma of the tibia and lymph node metastasis Sunil B Gudaganatti, Meena N Jadhav, Rashmi K Patil, Shreekant K Kittur Department of Pathology, Belgaum Institute of Medical Sciences,
Squamous odontogenic tumor: with recurrence and 12 years of follow-up
 SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOR 51 RELATO DE CASO Squamous odontogenic tumor: with recurrence and 12 years of follow-up Tumor odontogênico escamoso: com recidiva e doze anos de acompanhamento Márcia Gaiger
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOR 51 RELATO DE CASO Squamous odontogenic tumor: with recurrence and 12 years of follow-up Tumor odontogênico escamoso: com recidiva e doze anos de acompanhamento Márcia Gaiger
Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth or a need. Case report and Extensive review of literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 12, Issue 2 (Nov.- Dec. 2013), PP 26-31 Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 12, Issue 2 (Nov.- Dec. 2013), PP 26-31 Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies. No Disclosures or Conflicts of Interest. Anatomy 10/4/2013
 Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL. Primary Intraosseous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Incidental Finding
 MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL Primary Intraosseous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Incidental Finding Yew CC 1, Abd Ghani N 1, Jamal Din SKK 2, Najar Din MY 3 1 Dental Officer, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL Primary Intraosseous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Incidental Finding Yew CC 1, Abd Ghani N 1, Jamal Din SKK 2, Najar Din MY 3 1 Dental Officer, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report. A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 13 Number 1 Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi Citation A Narwal,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 13 Number 1 Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi Citation A Narwal,
Epithelial Myoepithelial Carcinoma- A Rare Case Report Shruthi H 1, Sumona P 2
 Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 11 No. 02 April 12 Case Report Epithelial Myoepithelial Carcinoma- A Rare Case Report Shruthi H 1, Sumona P 2 Abstract: Background: Salivary gland tumors occupy
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 11 No. 02 April 12 Case Report Epithelial Myoepithelial Carcinoma- A Rare Case Report Shruthi H 1, Sumona P 2 Abstract: Background: Salivary gland tumors occupy
Update in Salivary Gland Pathology. Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016
 Update in Salivary Gland Pathology Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016 Objectives Review the different appearances of a selection of salivary gland tumor types Establish
Update in Salivary Gland Pathology Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016 Objectives Review the different appearances of a selection of salivary gland tumor types Establish
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
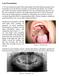 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Morphological Variants of Ameloblastoma and Their Mimickers
 20 Jan 2012 Vol 5 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Review Morphological Variants of Ameloblastoma and Their Mimickers Khaled Shaikhi, BDS; 1 Mirdza Neiders, DDS, MS; 1 Frank Chen, MD,
20 Jan 2012 Vol 5 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Review Morphological Variants of Ameloblastoma and Their Mimickers Khaled Shaikhi, BDS; 1 Mirdza Neiders, DDS, MS; 1 Frank Chen, MD,
Case Report Recurrent multifocal eosinophilic granuloma of the mandible and maxilla: a case report and literature review
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(10):20367-20371 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0026782 Case Report Recurrent multifocal eosinophilic granuloma of the mandible and maxilla: a case report and literature review
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(10):20367-20371 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0026782 Case Report Recurrent multifocal eosinophilic granuloma of the mandible and maxilla: a case report and literature review
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor: Case series of 14 with wide range of clinical presentation
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.54216 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.54216 : Case series of 14 with wide range of clinical presentation Fatima
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.54216 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.54216 : Case series of 14 with wide range of clinical presentation Fatima
JOURNAL TAOMFR Mandiblular Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
 Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
R. Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia: Evaluation.
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia:
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia:
Characteristics of bony changes and tooth displacement in the mandibular cystic lesion involving the impacted third molar
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.55/jkaoms.04.40.5.5 pissn 34-550 eissn 34-5930 Characteristics of bony changes and tooth displacement in the mandibular cystic lesion involving the impacted third molar
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.55/jkaoms.04.40.5.5 pissn 34-550 eissn 34-5930 Characteristics of bony changes and tooth displacement in the mandibular cystic lesion involving the impacted third molar
Disclosures. Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone. Outline. The osteoclast. Giant cell rich tumors 5/21/11
 Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance
 & 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
& 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
Carcinoma ex Pleomorphic Adenoma on Right Parotid Gland: A Case Report. School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University
 Korean Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology 2017;41(4):189-194 ISSN:1225-1577(Print); 2384-0900(Online) Available online at http://journal.kaomp.org https://doi.org/10.17779/kaomp.2017.41.4.006
Korean Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology 2017;41(4):189-194 ISSN:1225-1577(Print); 2384-0900(Online) Available online at http://journal.kaomp.org https://doi.org/10.17779/kaomp.2017.41.4.006
