Proton beam therapy for a patient with large rhabdomyosarcoma of the body trunk
|
|
|
- Joel Rodger Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Takizawa et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2015) 41:90 DOI /s ITALIAN JOURNAL OF PEDIATRICS CASE REPORT Proton beam therapy for a patient with large rhabdomyosarcoma of the body trunk Daichi Takizawa 1,4*, Yoshiko Oshiro 1,2, Masashi Mizumoto 1,4, Hiroko Fukushima 3, Takashi Fukushima 3 and Hideyuki Sakurai 1,4 Open Access Abstract Background: We present the clinical course of a pediatric patient with large rhabdomyosarcoma of the body trunk who received proton beam therapy (PBT). Case presentation: A 1-year-old girl was diagnosed with stage IV alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma in A large tumor was located in the central diaphragm and had infiltrated the liver and pericardium with peritoneal dissemination. Chemotherapy was immediately started with six courses of vincristine, actinomycin-d and cyclophosphamide (VAC) firstly, and secondly followed by 2 courses of ifosfamide, carboplatin and etoposide (ICE), but a large tumor of 15 cm in size remained. The tumor was inoperable because of its location, and photon radiotherapy could not be performed due to limited liver tolerance. The patient was referred to our hospital and received PBT at a dose of 54 GyE in 30 fractions in June The tumor quickly responded and 95 % of volume reduction was achieved at the end of PBT. However, marginal recurrence in the caudal part of the irradiated field, where we reduced the proton dose because of the presence of the intestine, was detected in August The recurrent tumor size was less than 1 cm. Chemotherapy with VAC followed by topotecan and carboplatin (TC) was again tried, but the tumor size was stable. Repeated PBT was not possible because of limited intestinal tolerance; therefore, intraoperative radiotherapy was conducted with 20 Gy of electron beams in April The tumor was subsequently well controlled, but secondary myelodysplastic syndrome developed and the patient died of hemophagocytic syndrome after umbilical cord blood transplantation in May Conclusion: PBT was performed safely and effectively for a 1-year-old girl with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma with liver and cardiac invasion that was resistant to surgery and chemotherapy. This case illustrates that PBT can be useful in cases that are difficult to treat with conventional radiotherapy. Keywords: Particle therapy, Proton therapy, Pediatric, Rhabdomyosarcoma, Respiratory gating Background Radiotherapy plays an important role in treatment of rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), with a dose of Gy typically required, and hyperfractionation (1.1-Gy twice daily fractions) or standard fractionation (1.8-Gy daily fractions) is used for definitive treatment [1]. The risk of morbidity radiation-related should be carefully considered depending on the volume and the dose delivered in the * Correspondence: dtakizawa@pmrc.tsukuba.ac.jp 1 Departments of Radiation Oncology1 and Child Health3, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan 4 Proton Medical Research Center, University of Tsukuba, Tennoudai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan Full list of author information is available at the end of the article pediatric patients. We experienced a pediatric patient with an unresectable large alveolar RMS with liver invasion. Photon radiotherapy was considered as the first treatment choice, but was not administered because of the lack of tolerance of the liver. Proton beam therapy (PBT) was chosen in this case, since PBT is a particle radiotherapy with excellent dose localization because of the sharp and narrow Bragg peak [2, 3]. Here, we present the clinical course of the patient after treatment with PBT Takizawa et al. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
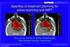
2 Takizawa et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2015) 41:90 Page 2 of 5 Case presentation A girl aged 1 year and 6 months initially presented with an abdominal mass with a maximum diameter of over 15 cm. The mass was located in the central diaphragm and was infiltrating the liver and pericardium with peritoneal dissemination. Ascites cytology showed class V in Papanicolaou s classification. The patient was diagnosed as alveolar RMS IRS Stage 4, postoperative group IV, and classified in the high risk group. Chemotherapy was started, but the tumor did not shrink sufficiently: with disease progression after the first 2 courses of VAC every 3 weeks, including vincristine (VCR) + actinomycin-d (Act-D) + cyclophosphamide (CPA); and partial response (PR) after 2 courses of ICE, including ifosfamide (IFM) + carboplatin (CBDCA) + etoposide (VP-16). Surgical resection was not possible for broad tumor s invasion of the surrounding diaphragm and radical photon radiotherapy could not be performed because the liver could not tolerate the definitive treatment dose. Palliative care was initially recommended from local pediatric oncologists, but subsequently the patient and her family visited our hospital to receive PBT, which was started in June 2009 at age 1 year and 11 months. Peritoneal dissemination disappeared after the chemotherapy, but the tumor was still located in the central diaphragm with infiltration of the liver and pericardium, and the maximum diameter was still over 8 cm at the point (Fig. 1). One month after the last chemotherapy (ICE), a PBT dose of 54 GyE in 30 fractions was applied over a course of 58 days. The relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of the PBT was assumed to be 1.1. We used the passive scattering method for PBT [4]. During PBT, the patient was sedated with anesthesia and immobilized in a body cast. We used a laser displacement sensor (LDS: KEYENCE LB-300) that was the prototype of AZ-733. Respiratory gating in the expiratory phase was used. A respiratory waveform is obtained using a laser range finder that monitors movement of the abdominal surface, and a gating signal is developed. The phase shifts between the respiratory waveform and the 3D tumor motion are principally in the range 0.0 to 0.3 s, regardless of the organ being measured in the system [18]. The gating signal is applied to the accelerator, and the accelerator is triggered within 0.1 s and delivers proton beams. The CTV encompassed the gross tumor volume with a 5- to 10-mm margin in all directions. An additional 5-mm margin was included on the caudal axes to compensate for uncertainty due to respiration-induced hepatic movements. An additional margin of 10 mm was added to cover the entire CTV by enlarging the multileaf collimator and adjusting the range shifter. Proton beams from 155 to 250 MeV generated through a linear accelerator and synchrotron were spread out and shaped with ridge filters, double-scattering sheets, multicollimators, and a custom-made bolus to ensure that the beams conformed to the treatment planning data. The tumor shrunk during PBT, and the treatment field was reduced to fit the tumor size and to keep the intestinal dose within the 50Gy tolerance level [11] (Fig. 2). The tumor showed a good PR ( 95 % of the tumor volume) after PBT and the acute toxicity was only Grade 1 radiation hepatitis and dermatitis. After PBT, high dose chemotherapy with VP-16 + CPA + pirarubicine (THP-ADR) + cisplatin (CDDP) + VCR, IFM + VP-16 + Act-D + VCR, and irinotecan (CPT-11) + VCR was continued. The tumor was well controlled for 1 year with regular follow-up MR or CT scans performed every 3 months, but then recurred at the edge of the irradiation field where the irradiation dose was reduced due to the proximity to the intestine (Fig. 3). The chemotherapy regimen was changed to low dose VAC, but the tumor volume remained stable. Repeated radiotherapy was considered, but could not be administered due to intestinal tolerance. Therefore, tumor excision with intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT) using an electron beam of 20 Gy was conducted in May 2011, at age 3 years and 10 months. After IORT, the tumor was well controlled and a CT image showed only radiation hepatitis without a tumor (Fig. 4). However, the patient developed secondary myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) in December 2011, and died of hemophagocytic syndrome after umbilical cord blood transplantation in May Fig. 1 CT images after 6 courses of VAC and 2 courses of ICE, just before the start of PBT
3 Takizawa et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2015) 41:90 Page 3 of 5 Fig. 2 The tumor shrunk during PBT and the treatment field was reduced to fit the tumor size. The white line was clinical target volume. The surrounding low dosing area (arrows) showed acute radiation hepatitis Discussion The incidence of soft tissue sarcomas in children and adolescents younger than 20 years of age is 11.0 per million, representing 7.4 % of cancer cases for this age group [5]. Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common soft tissue sarcoma in children aged 0 14 years, representing nearly 50 % of soft tissue sarcomas for this age range, with an incidence rate of 4.6 per million. There are two major types of rhabdomyosarcoma: the embryonal one which occur in 75 % of the cases and alveolar [6]. The incidence of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma is higher among children aged 0 4 years, while the alveolar subtype incidence is similar throughout childhood [5]. The embryonal type has a better prognosis than the alveolar type [7]. The standard therapy for pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma is multiagent chemotherapy and local therapy of surgery with or without radiotherapy. Only 15 % of patients with completely resected embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma have a good outcome without radiotherapy, and thus radiotherapy is used in most cases. The radiotherapy dose mainly depends on the amount of residual disease, if any, after primary surgical resection, with doses increased from 36 to 50.4 Gy as the risk increases [8 10]. In our case, the tumor widely involved the liver, and this prevented definitive radiotherapy because of the low tolerance of radiation doses of 30, 35, and 50 Gy for the total, two-thirds, and one-third of the liver, respectively [11]. For comparison, we planned intensitymodulated radiation therapy (IMRT) using the same conditions as those used for PBT. In the IMRT plan, the Fig. 3 These images were contrast enhanced CT image a and PET-CT image b, at 1 year after PBT. In figure a, local recurrence of the tumor is enhanced at the edge of irradiation, and FDG accumulated same place
4 Takizawa et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2015) 41:90 Page 4 of 5 Fig. 4 The tumor was well controlled on CT images at 2 months after IORT liver volume irradiated with 20 Gy (V20) was 60 % at a treatment dose of 54 Gy, compared to 34 % in PBT. PBT reduced low dose area and was expected [Fig. 5]. The total liver volume was 500 cc and the remnant volume was only 200 cc, which made it difficult to administer photon radiotherapy in the present case. Surgery was also not possible for broad tumor s invasion of the surrounding diaphragm and chemotherapy alone was ineffective. Palliative irradiation was also recommended, but survival was estimated to be less than one year with palliative therapy. Proton beams have a Bragg peak in which the dose rapidly falls off at the end of the beam range at a depth within the patient. For this reason PBT can deliver a high dose to the limited volume of a liver tumor while non-cancerous liver tissue is only exposed to very low doses. PBT also allows preservation of a larger volume of normal liver tissue compared to photon radiotherapy. Based on these advantages, we have treated many patients with liver malignancies [12 14]. Therefore, we thought that PBT was reasonable and might be effective in the present case, even though we had not previously used this approach for pediatric RMS widely located in the liver. Several reports have described the advantages of PBT compared to photon radiotherapy, including IMRT. Cotter et al. found that proton beams can reduce the dose to normal organs adjacent to the tumor, such as the bladder, testis and bones, compared to IMRT in radiotherapy for bladder or prostate rhabdomyosarcoma [15]. In spot-scan PBT for pediatric malignant soft tissue tumor including rhabdomyosarcoma, Timmerman et al. found high tolerability of PBT and suggested that IMRT requires a wider field compared to PBT; therefore, PBT results in lower doses to the volume around the target and the secondary cancer risk is decreased [16]. In a phase II study comparing PBT and IMRT, Ladra et al. reported favorable disease control and dose distribution [17]. The tumor recurrence 1 year after PBT in our case may have been due to field shrinkage to reduce the dose to the gastrointestinal tract after 41.4 GyE. In adults, a dose of about 50 GyE may be acceptable, but radiation sensitivity is higher in pediatric patients and may have been further enhanced by concurrent chemotherapy in the present case. For these reasons, we reduced the small bowel dose after administration of 41.4 GyE. The recurrence was well controlled by IORT. Unfortunately, the patient died of a regimen-related toxicity of unrelated cord blood transplantation during treatment for secondary MDS. However, PBT seemed to be effective with a good tolerance to the radiation treatment and with few acute side effects (G1 hepatitis), and potentially beneficial with IORT to improve the local control. In conclusion, we suggest that PBT could be a valide and safe alternative technique to be considered for pediatric patients with RMS who cannot receive definitive photon radiotherapy. Fig. 5 These graphs showed DVHs of PBT and IMRT for OARs of heart (a), total-lung (b), and liver (c). PBT reduced low-dose area compared with IMRT
5 Takizawa et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2015) 41:90 Page 5 of 5 Conclusion In this case, PBT was performed safely and effectively with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma with liver and cardiac invasion that was unable to be removed with surgery and was resistant to chemotherapy. We supposed that side effect and tumor s local control turned worse, if we used conventional radiotherapy not PBT. This case illustrates that PBT can be useful in cases that are difficult to treat with conventional radiotherapy. Consent Written informed consent was obtained from the patient s legal guardians for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal. Competing interest None to declare. Authors contributions DT made the figure and drafted the manuscript, YO made PBT plan for treatment and drafted the manuscript, MM participated in the sequence alignment and drafted the manuscript, HF participated in general care and every sedation during the radiation therapy, TF participated in general care and every sedation during the radiation therapy, HS participated in coordination and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Acknowledgments This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) ( ); Challenging Exploratory Research ( ), Young Scientists (B) ( ); and Scientific Research (C) ( ) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan. We wish to thank the members of the Tsukuba Critical Path Research and Education Integrated Leading Center (CREIL) at the University of Tsukuba for their critical advice in conducting the study and data management during the study period. This work was presented at a conference of the International Society of Pediatric Oncology 2013, Hong Kong (Pediatric Blood Cancer. 2013;60(S3):93.). Author details 1 Departments of Radiation Oncology1 and Child Health3, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan. 2 Department of Radiation Oncology, Tsukuba Medical Center Hospital, Ibaraki, Japan. 3 Departments of Child Health, University of Tsukuba and Proton Medical Research Center, Ibaraki, Japan. 4 Proton Medical Research Center, University of Tsukuba, Tennoudai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan. 5. Ries LAG, Smith MA, Gurney JG, Linet M, Tamra T, Young JL, Bunin GR (eds). Cancer Incidence and Survival among Children and Adolescents: United States SEER Program , National Cancer Institute, SEER Program. NIH Pub. No Bethesda, MD; McDowell HP. Update on childhood rhabdomyosarcoma. Arch Dis Child. 2003;88: Breneman JC, Lyden E, Pappo AS, Link MP, Anderson JR, Parham DM, et al. Prognostic factors and clinical outcomes in children and adolescents with metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma study IV. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21: Crist WM, Anderson JR, Meza JL, Fryer C, Raney RB, Ruymann FB, et al. Intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma study-iv: results for patients with nonmetastatic disease. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19: Wolden SL, Anderson JR, Crist WM, Breneman JC, Wharam Jr MD, Wiener ES, et al. Indications for radiotherapy and chemotherapy after complete resection in rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma studies I to III. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17: Regine WF, Fontanesi J, Kumar P, Ayers D, Bowman LC, Pappo AS, et al. Local tumor control in rhabdomyosarcoma following low-dose irradiation: Comparison of group II and select group III patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;31: Emami B, Lyman J, Brown A, Coia L, Goitein M, Munzenrider JE, et al. Tolerance of normal tissue to therapeutic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991;21: Kanemoto A, Mizumoto M, Okumura T, Takahashi H, Hashimoto T, Oshiro Y, et al. Dose-volume histogram analysis for risk factors of radiation-induced rib fracture after hypofractionated proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2013;52: Mizumoto M, Okumura T, Hashimoto T, Fukuda K, Oshiro Y, Fukumitsu N, et al. Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparison of three treatment protocols. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81: Mizumoto M, Oshiro Y, Ayuzawa K, Miyamoto T, Okumura T, Fukushima T, et al. Preparation of pediatric patients for treatment with proton beam therapy. Radiother Oncol. 2015;114: Cotter SE, Herrup DA, Friedmann A, Macdonald SM, Pieretti RV, Robinson G, et al. Proton radiotherapy for pediatric bladder/prostate rhabdomyosarcoma: clinical outcomes and dosimetry compared to intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81: Timmermann B, Schuck A, Niggli F, Weiss M, Lomax AJ, Pedroni E, et al. Spot-scanning proton therapy for malignant soft tissue tumors in childhood: First experiences at the Paul Scherrer Institute. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67: Ladra MM, Szymonifka JD, Mahajan A, Friedmann AM, Yong Yeap B, Goebel CP, et al. Preliminary results of a phase II trial of proton radiotherapy for pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32: Tsunashima Y, Sakae T, Shioyama Y, Kagei K, Terunuma T, Akihiro N, et al. Correlation between the respiratory waveform measured using a respiratory sensor and 3D tumor motion in gated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;60(3): Received: 2 July 2015 Accepted: 8 November 2015 References 1. Donaldson SS, Meza J, Breneman JC, Crist WM, Laurie F, Qualman SJ, et al. Results from the IRS-IV randomized trial of hyperfractionated radiotherapy in children with rhabdomyosarcoma-a report from the IRSG. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51: Oshiro Y, Okumura T, Mizumoto M, Fukushima T, Ishikawa H, Hashimoto T, et al. Proton beam therapy for unresectable hepatoblastoma in children: survival in one case. Acta Oncol. 2013;52: Mizumoto M, Tokuuye K, Sugahara S, Nakayama H, Fukumitsu N, Ohara K. Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma adjacent to the porta hepatis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71: Kanemoto A, Hirayama R, Moritake T, Furusawa Y, Sun L, Sakae T, et al. RBE and OER within the spread-out Bragg peak for proton beam therapy: in vitro study at the Proton Medical Research Center at the University of Tsukuba. J Radiat Res. 2014;55: Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Proton and heavy ion radiotherapy: Effect of LET
 Proton and heavy ion radiotherapy: Effect of LET As a low LET particle traverses a DNA molecule, ionizations are far apart and double strand breaks are rare With high LET particles, ionizations are closer
Proton and heavy ion radiotherapy: Effect of LET As a low LET particle traverses a DNA molecule, ionizations are far apart and double strand breaks are rare With high LET particles, ionizations are closer
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a common cause
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Results of Proton Beam Therapy without Concurrent Chemotherapy for Patients with Unresectable Stage III Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Yoshiko Oshiro, MD,* Masashi Mizumoto, MD,* Toshiyuki
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Results of Proton Beam Therapy without Concurrent Chemotherapy for Patients with Unresectable Stage III Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Yoshiko Oshiro, MD,* Masashi Mizumoto, MD,* Toshiyuki
A comparative study of dose distribution of PBT, 3D-CRT and IMRT for pediatric brain tumors
 Takizawa et al. Radiation Oncology (2017) 12:40 DOI 10.1186/s13014-017-0775-2 RESEARCH A comparative study of dose distribution of PBT, 3D-CRT and IMRT for pediatric brain tumors Daichi Takizawa 1*, Masashi
Takizawa et al. Radiation Oncology (2017) 12:40 DOI 10.1186/s13014-017-0775-2 RESEARCH A comparative study of dose distribution of PBT, 3D-CRT and IMRT for pediatric brain tumors Daichi Takizawa 1*, Masashi
Effective local and systemic therapy is necessary for the cure of Ewing tumor Most chemotherapy regimens are a combination of cyclophosphamide,
 Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
Radiotherapy for liver cancer
 Received: 7 November 2015 Accepted: 10 March 2016 DOI: 10.1002/jgf2.19 REVIEW ARTICLE Radiotherapy for liver cancer Nobuyoshi Fukumitsu MD Toshiyuki Okumura MD Hideyuki Sakurai MD Proton Medical Research
Received: 7 November 2015 Accepted: 10 March 2016 DOI: 10.1002/jgf2.19 REVIEW ARTICLE Radiotherapy for liver cancer Nobuyoshi Fukumitsu MD Toshiyuki Okumura MD Hideyuki Sakurai MD Proton Medical Research
State of the Art Radiotherapy for Pediatric Tumors. Suzanne L. Wolden, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
 State of the Art Radiotherapy for Pediatric Tumors Suzanne L. Wolden, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Introduction Progress and success in pediatric oncology Examples of low-tech and high-tech
State of the Art Radiotherapy for Pediatric Tumors Suzanne L. Wolden, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Introduction Progress and success in pediatric oncology Examples of low-tech and high-tech
11/28/2018. Proton Therapy for Liver Cancer: Who, Why, and How. Disclosures. Michael Chuong, MD. None
 Proton Therapy for Liver Cancer: Who, Why, and How Michael Chuong, MD Disclosures None 1 Rationale for proton therapy Hepatic toxicity Biliary toxicity GI toxicity Potentially significant benefit especially
Proton Therapy for Liver Cancer: Who, Why, and How Michael Chuong, MD Disclosures None 1 Rationale for proton therapy Hepatic toxicity Biliary toxicity GI toxicity Potentially significant benefit especially
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a heterogeneous
 Survival rate of children with rhabdomyosarcoma and prognostic factors Khadijeh Arjmandi Rafsanjani, Parvaneh Vossough, Ali Bashardoust, Mohammad Faranoush Tehran, Iran 36 Background: Rhabdomyosarcoma
Survival rate of children with rhabdomyosarcoma and prognostic factors Khadijeh Arjmandi Rafsanjani, Parvaneh Vossough, Ali Bashardoust, Mohammad Faranoush Tehran, Iran 36 Background: Rhabdomyosarcoma
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 Douglas et al. BMC Cancer 2012, 12:425 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma Sarah Douglas 1, Steven E Schild 2 and Dirk
Douglas et al. BMC Cancer 2012, 12:425 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma Sarah Douglas 1, Steven E Schild 2 and Dirk
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: , 2015
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: 201-205, 2015 Proton beam therapy for locally advanced and unresectable (T4bN0M0) squamous cell carcinoma of the ethmoid sinus: A report of seven cases and a literature review TAKASHI
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: 201-205, 2015 Proton beam therapy for locally advanced and unresectable (T4bN0M0) squamous cell carcinoma of the ethmoid sinus: A report of seven cases and a literature review TAKASHI
Sarcoma and Radiation Therapy. Gabrielle M Kane MB BCh EdD FRCPC Muir Professorship in Radiation Oncology University of Washington
 Sarcoma and Radiation Therapy Gabrielle M Kane MB BCh EdD FRCPC Muir Professorship in Radiation Oncology University of Washington Objective: Helping you make informed decisions Introduction Process Radiation
Sarcoma and Radiation Therapy Gabrielle M Kane MB BCh EdD FRCPC Muir Professorship in Radiation Oncology University of Washington Objective: Helping you make informed decisions Introduction Process Radiation
RMS, RMS. (rhabdomyosarcoma,rms) (Intergroup RMS Study Group,IRSG) ( European Pediatric soft tissue sarcomas study group,epssg)
 724 2017 10 55 10 Chin J Pediatr, October 2017, Vol.55, No.10 ( CCCG-RMS-2016) (rhabdomyosarcoma,rms), 6.5% [1-3], RMS,, (Intergroup RMS Study Group,IRSG) ( European Pediatric soft tissue sarcomas study
724 2017 10 55 10 Chin J Pediatr, October 2017, Vol.55, No.10 ( CCCG-RMS-2016) (rhabdomyosarcoma,rms), 6.5% [1-3], RMS,, (Intergroup RMS Study Group,IRSG) ( European Pediatric soft tissue sarcomas study
Status of H 1 and C 12
 Status of H 1 and C 12 Herman Suit No Conflict of Interest 1 Goal of a New Treatment Modality Tumor Control Probability or No in Complication Rate 2 Truism No Advantage to: any Patient for any Radiation
Status of H 1 and C 12 Herman Suit No Conflict of Interest 1 Goal of a New Treatment Modality Tumor Control Probability or No in Complication Rate 2 Truism No Advantage to: any Patient for any Radiation
Present status and future of Proton beam therapy
 Present status and future of Proton beam therapy Description At present, the types of proven treatment for cancer are surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. Depending on the characteristics of cancer
Present status and future of Proton beam therapy Description At present, the types of proven treatment for cancer are surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. Depending on the characteristics of cancer
Kavita V. Dharmarajan, MD, MSc, 1 * Leonard H. Wexler, MD, 2 and Suzanne L. Wolden, MD 1 INTRODUCTION. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2013;60:
 Pediatr Blood Cancer 2013;60:242 247 Concurrent Radiation With Irinotecan and Carboplatin in Intermediate- and High-Risk Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report on Toxicity and Efficacy From a Prospective Pilot Phase
Pediatr Blood Cancer 2013;60:242 247 Concurrent Radiation With Irinotecan and Carboplatin in Intermediate- and High-Risk Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report on Toxicity and Efficacy From a Prospective Pilot Phase
Proton Beam Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Li Jiamin, MD Wanjie Proton Therapy Center
 Proton Beam Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Li Jiamin, MD Wanjie Proton Therapy Center 1 1 Hepatocelluar carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide It is the eighth most common neoplasm
Proton Beam Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Li Jiamin, MD Wanjie Proton Therapy Center 1 1 Hepatocelluar carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide It is the eighth most common neoplasm
Specifics of treatment planning for active scanning and IMPT
 Specifics of treatment planning for active scanning and IMPT SFUD IMPT Tony Lomax, Centre for Proton Radiotherapy, Paul Scherrer Institute, Switzerland Treatment planning for scanning 1. Single Field,
Specifics of treatment planning for active scanning and IMPT SFUD IMPT Tony Lomax, Centre for Proton Radiotherapy, Paul Scherrer Institute, Switzerland Treatment planning for scanning 1. Single Field,
IJC International Journal of Cancer
 IJC International Journal of Cancer Delayed primary excision with subsequent modification of radiotherapy dose for intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Children s Oncology Group Soft Tissue
IJC International Journal of Cancer Delayed primary excision with subsequent modification of radiotherapy dose for intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Children s Oncology Group Soft Tissue
Designed-seamless irradiation technique for extended whole mediastinal proton-beam irradiation for esophageal cancer
 Okonogi et al. Radiation Oncology 2012, 7:173 RESEARCH Open Access Designed-seamless irradiation technique for extended whole mediastinal proton-beam irradiation for esophageal cancer Noriyuki Okonogi
Okonogi et al. Radiation Oncology 2012, 7:173 RESEARCH Open Access Designed-seamless irradiation technique for extended whole mediastinal proton-beam irradiation for esophageal cancer Noriyuki Okonogi
Specification of Tumor Dose. Prescription dose. Purpose
 Specification of Tumor Dose George Starkschall, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Physics U.T. M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Prescription dose What do we mean by a dose prescription of 63 Gy? Isocenter dose
Specification of Tumor Dose George Starkschall, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Physics U.T. M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Prescription dose What do we mean by a dose prescription of 63 Gy? Isocenter dose
Bone HDR brachytherapy in a patient with recurrent Ewing s sarcoma of the acetabulum: Alternative to aggressive surgery
 Bone HDR brachytherapy in a patient with recurrent Ewing s sarcoma of the acetabulum: Alternative to aggressive surgery Rafael Martínez-Monge 1,* Agata Pérez-Ochoa 1, Mikel San Julián 2, Dámaso Aquerreta
Bone HDR brachytherapy in a patient with recurrent Ewing s sarcoma of the acetabulum: Alternative to aggressive surgery Rafael Martínez-Monge 1,* Agata Pérez-Ochoa 1, Mikel San Julián 2, Dámaso Aquerreta
NCCN GUIDELINES ON PROTON THERAPY (AS OF 4/23/18) BONE (Version , 03/28/18)
 BONE (Version 2.2018, 03/28/18) NCCN GUIDELINES ON PROTON THERAPY (AS OF 4/23/18) Radiation Therapy Specialized techniques such as intensity-modulated RT (IMRT); particle beam RT with protons, carbon ions,
BONE (Version 2.2018, 03/28/18) NCCN GUIDELINES ON PROTON THERAPY (AS OF 4/23/18) Radiation Therapy Specialized techniques such as intensity-modulated RT (IMRT); particle beam RT with protons, carbon ions,
Where are we with radiotherapy for biliary tract cancers?
 Where are we with radiotherapy for biliary tract cancers? Professor Maria A. Hawkins Associate Professor in Clinical Oncology MRC Group Leader/Honorary Consultant Clinical Oncologist CRUK MRC Oxford Institute
Where are we with radiotherapy for biliary tract cancers? Professor Maria A. Hawkins Associate Professor in Clinical Oncology MRC Group Leader/Honorary Consultant Clinical Oncologist CRUK MRC Oxford Institute
The Physics of Oesophageal Cancer Radiotherapy
 The Physics of Oesophageal Cancer Radiotherapy Dr. Philip Wai Radiotherapy Physics Royal Marsden Hospital 1 Contents Brief clinical introduction Imaging and Target definition Dose prescription & patient
The Physics of Oesophageal Cancer Radiotherapy Dr. Philip Wai Radiotherapy Physics Royal Marsden Hospital 1 Contents Brief clinical introduction Imaging and Target definition Dose prescription & patient
Treatment Planning (Protons vs. Photons)
 Treatment Planning Treatment Planning (Protons vs. Photons) Acquisition of imaging data Delineation of regions of interest Selection of beam directions Dose calculation Optimization of the plan Hounsfield
Treatment Planning Treatment Planning (Protons vs. Photons) Acquisition of imaging data Delineation of regions of interest Selection of beam directions Dose calculation Optimization of the plan Hounsfield
INTRAOPERATIVE RADIATION THERAPY FOR RETROPERITONEAL SARCOMA
 INTRAOPERATIVE RADIATION THERAPY FOR RETROPERITONEAL SARCOMA ISIORT 2014 Ivy A Petersen, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN NOTHING TO DISCLOSE SOFT TISSUE SARCOMAS 2014 Estimated cases in the USA 12,020 diagnosed
INTRAOPERATIVE RADIATION THERAPY FOR RETROPERITONEAL SARCOMA ISIORT 2014 Ivy A Petersen, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN NOTHING TO DISCLOSE SOFT TISSUE SARCOMAS 2014 Estimated cases in the USA 12,020 diagnosed
Proton Treatment. Keith Brown, Ph.D., CHP. Associate Director, Radiation Safety University of Pennsylvania
 Proton Treatment Keith Brown, Ph.D., CHP Associate Director, Radiation Safety University of Pennsylvania Proton Dose vs. Depth Wilson,. R.R. Radiological use of fast protons. Radiology 47:487-491, 1946.
Proton Treatment Keith Brown, Ph.D., CHP Associate Director, Radiation Safety University of Pennsylvania Proton Dose vs. Depth Wilson,. R.R. Radiological use of fast protons. Radiology 47:487-491, 1946.
Sacral Chordoma: The Loma Linda University Radiation Medicine Experience. Kevin Yiee MD, MPH Resident Physician
 Sacral Chordoma: The Loma Linda University Radiation Medicine Experience Kevin Yiee MD, MPH Resident Physician What is a chordoma? 1 st chordoma discovered in clivus by Virchow and Luschka 1856 Rare tumor
Sacral Chordoma: The Loma Linda University Radiation Medicine Experience Kevin Yiee MD, MPH Resident Physician What is a chordoma? 1 st chordoma discovered in clivus by Virchow and Luschka 1856 Rare tumor
肺癌放射治療新進展 Recent Advance in Radiation Oncology in Lung Cancer 許峰銘成佳憲國立台灣大學醫學院附設醫院腫瘤醫學部
 肺癌放射治療新進展 Recent Advance in Radiation Oncology in Lung Cancer 許峰銘成佳憲國立台灣大學醫學院附設醫院腫瘤醫學部 Outline Current status of radiation oncology in lung cancer Focused on stage III non-small cell lung cancer Radiation
肺癌放射治療新進展 Recent Advance in Radiation Oncology in Lung Cancer 許峰銘成佳憲國立台灣大學醫學院附設醫院腫瘤醫學部 Outline Current status of radiation oncology in lung cancer Focused on stage III non-small cell lung cancer Radiation
Toramatsu et al. Radiation Oncology 2013, 8:48
 Toramatsu et al. Radiation Oncology 2013, 8:48 RESEARCH Open Access What is the appropriate size criterion for proton radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma? A dosimetric comparison of spot-scanning
Toramatsu et al. Radiation Oncology 2013, 8:48 RESEARCH Open Access What is the appropriate size criterion for proton radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma? A dosimetric comparison of spot-scanning
The treatment of soft tissue tumours (STS)
 Soft Tissue Sarcoma Current Management Meriel Jenney, Ken Brown The treatment of soft tissue tumours (STS) in children and adolescents is complex. The commonest STS occurring in childhood is rhabdomyosarcoma
Soft Tissue Sarcoma Current Management Meriel Jenney, Ken Brown The treatment of soft tissue tumours (STS) in children and adolescents is complex. The commonest STS occurring in childhood is rhabdomyosarcoma
Spinal Cord Doses in Palliative Lung Radiotherapy Schedules
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 8, No., June: -, 00 Spinal Cord Doses in Palliative Lung Radiotherapy Schedules HODA AL-BOOZ, FRCR FFRRCSI M.D.* and CAROL PARTON, Ph.D.** The Departments
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 8, No., June: -, 00 Spinal Cord Doses in Palliative Lung Radiotherapy Schedules HODA AL-BOOZ, FRCR FFRRCSI M.D.* and CAROL PARTON, Ph.D.** The Departments
Hampton University Proton Therapy Institute
 Hampton University Proton Therapy Institute Brief introduction to proton therapy technology, its advances and Hampton University Proton Therapy Institute Vahagn Nazaryan, Ph.D. Executive Director, HUPTI
Hampton University Proton Therapy Institute Brief introduction to proton therapy technology, its advances and Hampton University Proton Therapy Institute Vahagn Nazaryan, Ph.D. Executive Director, HUPTI
Clinical Education A comprehensive and specific training program. carry out effective treatments from day one
 Proton Therapy Clinical Education A comprehensive and specific training program carry out effective treatments from day one Forewarned is forearmed Although over 100,000 patients have been treated in proton
Proton Therapy Clinical Education A comprehensive and specific training program carry out effective treatments from day one Forewarned is forearmed Although over 100,000 patients have been treated in proton
State-of-the-art proton therapy: The physicist s perspective
 State-of-the-art proton therapy: Tony Lomax, Centre for Proton Radiotherapy, Paul Scherrer Institute, Switzerland Overview of presentation 1. State-of-the-art proton delivery 2. Current challenges 3. New
State-of-the-art proton therapy: Tony Lomax, Centre for Proton Radiotherapy, Paul Scherrer Institute, Switzerland Overview of presentation 1. State-of-the-art proton delivery 2. Current challenges 3. New
Proton beam therapy with concurrent chemotherapy for glioblastoma multiforme: comparison of nimustine hydrochloride and temozolomide
 J Neurooncol DOI 1.17/s11-1-2228-4 CLINIcAL STUDY Proton beam therapy with concurrent chemotherapy for glioblastoma multiforme: comparison of nimustine hydrochloride and temozolomide Masashi Mizumoto 1
J Neurooncol DOI 1.17/s11-1-2228-4 CLINIcAL STUDY Proton beam therapy with concurrent chemotherapy for glioblastoma multiforme: comparison of nimustine hydrochloride and temozolomide Masashi Mizumoto 1
Protocol of Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer
 107 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Indications for Post-Mastectomy Radiotherapy (1) Axillary lymph node 4 positive (2) Axillary lymph node 1-3 positive:
107 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Indications for Post-Mastectomy Radiotherapy (1) Axillary lymph node 4 positive (2) Axillary lymph node 1-3 positive:
Proton therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
 Review Article Proton therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma Ted C. Ling, Joseph I. Kang, David A. Bush, Jerry D. Slater, Gary Y. Yang Department of Radiation Medicine, Loma Linda University Medical Center,
Review Article Proton therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma Ted C. Ling, Joseph I. Kang, David A. Bush, Jerry D. Slater, Gary Y. Yang Department of Radiation Medicine, Loma Linda University Medical Center,
Radiation qualities in carbon-ion radiotherapy at NIRS/HIMAC
 Radiation qualities in carbon-ion radiotherapy at NIRS/ Shunsuke YONAI Radiological Protection Section Research Center for Charged Particle Therapy National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS) E-mail:
Radiation qualities in carbon-ion radiotherapy at NIRS/ Shunsuke YONAI Radiological Protection Section Research Center for Charged Particle Therapy National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS) E-mail:
Does serum CA125 have clinical value for follow-up monitoring of postoperative patients with epithelial ovarian cancer? Results of a 12-year study
 Guo and Peng Journal of Ovarian Research (2017) 10:14 DOI 10.1186/s13048-017-0310-y RESEARCH Does serum CA125 have clinical value for follow-up monitoring of postoperative patients with epithelial ovarian
Guo and Peng Journal of Ovarian Research (2017) 10:14 DOI 10.1186/s13048-017-0310-y RESEARCH Does serum CA125 have clinical value for follow-up monitoring of postoperative patients with epithelial ovarian
Dose escalation for NSCLC using conformal RT: 3D and IMRT. Hasan Murshed
 Dose escalation for NSCLC using conformal RT: 3D and IMRT. Hasan Murshed Take home message Preliminary data shows CRT technique in NSCLC allows dose escalation to an unprecedented level maintaining cancer
Dose escalation for NSCLC using conformal RT: 3D and IMRT. Hasan Murshed Take home message Preliminary data shows CRT technique in NSCLC allows dose escalation to an unprecedented level maintaining cancer
Stereotactic radiotherapy
 Stereotactic radiotherapy Influence of patient positioning and fixation on treatment planning - clinical results Frank Zimmermann Institut für Radioonkologie Universitätsspital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH
Stereotactic radiotherapy Influence of patient positioning and fixation on treatment planning - clinical results Frank Zimmermann Institut für Radioonkologie Universitätsspital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH
Radiotherapy What are our options and what is on the horizon. Dr Kevin So Specialist Radiation Oncologist Epworth Radiation Oncology
 Radiotherapy What are our options and what is on the horizon Dr Kevin So Specialist Radiation Oncologist Epworth Radiation Oncology Outline Advances in radiotherapy technique Oligo - disease Advancements
Radiotherapy What are our options and what is on the horizon Dr Kevin So Specialist Radiation Oncologist Epworth Radiation Oncology Outline Advances in radiotherapy technique Oligo - disease Advancements
Proton Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Clinical Overview. Brian Winey, Ph.D. Physicist, MGH Assistant Professor, HMS
 Proton Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Clinical Overview Brian Winey, Ph.D. Physicist, MGH Assistant Professor, HMS Acknowledgements Radiation Oncologists and Physicists at various institutions (MGH, MDACC,
Proton Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Clinical Overview Brian Winey, Ph.D. Physicist, MGH Assistant Professor, HMS Acknowledgements Radiation Oncologists and Physicists at various institutions (MGH, MDACC,
Treatment outcome of rhabdomyosarcoma in Hong Kong Chinese children
 Title Treatment outcome of rhabdomyosarcoma in Hong Kong Chinese children Author(s) Yuan, XJ; Chan, GCF; Chan, SK; Shek, TWH; Kwong, DLW; Wei, WI; Ha, SY; Chiang, AKS Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal,
Title Treatment outcome of rhabdomyosarcoma in Hong Kong Chinese children Author(s) Yuan, XJ; Chan, GCF; Chan, SK; Shek, TWH; Kwong, DLW; Wei, WI; Ha, SY; Chiang, AKS Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal,
Proton therapy for prostate cancer
 Proton therapy for prostate cancer Shafak Aluwini Radiation oncologist UMCG Protons versus photons Superior beam properties 200 180 Advantage of protons 160 Photons 140 120 100 Spread out Bragg Peak 80
Proton therapy for prostate cancer Shafak Aluwini Radiation oncologist UMCG Protons versus photons Superior beam properties 200 180 Advantage of protons 160 Photons 140 120 100 Spread out Bragg Peak 80
Lymph Node Management in Patients With Paratesticular Rhabdomyosarcoma
 Original Article Lymph Node Management in Patients With Paratesticular Rhabdomyosarcoma A Population-Based Analysis Nguyen D. Dang, MD 1 ; Phuong-Thanh Dang, BS 2 ; Jason Samuelian, DO 1 ; and Arnold C.
Original Article Lymph Node Management in Patients With Paratesticular Rhabdomyosarcoma A Population-Based Analysis Nguyen D. Dang, MD 1 ; Phuong-Thanh Dang, BS 2 ; Jason Samuelian, DO 1 ; and Arnold C.
REVISITING ICRU VOLUME DEFINITIONS. Eduardo Rosenblatt Vienna, Austria
 REVISITING ICRU VOLUME DEFINITIONS Eduardo Rosenblatt Vienna, Austria Objective: To introduce target volumes and organ at risk concepts as defined by ICRU. 3D-CRT is the standard There was a need for a
REVISITING ICRU VOLUME DEFINITIONS Eduardo Rosenblatt Vienna, Austria Objective: To introduce target volumes and organ at risk concepts as defined by ICRU. 3D-CRT is the standard There was a need for a
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Quality ID #156 (NQF 0382): Oncology: Radiation Dose Limits to Normal Tissues National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety
 Quality ID #156 (NQF 0382): Oncology: Radiation Dose Limits to Normal Tissues National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION:
Quality ID #156 (NQF 0382): Oncology: Radiation Dose Limits to Normal Tissues National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION:
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Proton Beam Therapy for Cancer of the Prostate
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Proton Beam Therapy for Cancer of the Prostate Reference: NHS England B01X09 First published: March 2016 Prepared by NHS England Specialised Services Clinical
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Proton Beam Therapy for Cancer of the Prostate Reference: NHS England B01X09 First published: March 2016 Prepared by NHS England Specialised Services Clinical
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
Proton Radiation Therapy for Osteosarcomas, Chondrogenic Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas
 Proton Radiation Therapy for Osteosarcomas, Chondrogenic Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas Eugen B. Hug Center for Proton Radiation Therapy Paul Scherrer Institute Is there a place for Proton/Particle Radiotherapy
Proton Radiation Therapy for Osteosarcomas, Chondrogenic Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas Eugen B. Hug Center for Proton Radiation Therapy Paul Scherrer Institute Is there a place for Proton/Particle Radiotherapy
A TREATMENT PLANNING STUDY COMPARING VMAT WITH 3D CONFORMAL RADIOTHERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER USING PINNACLE PLANNING SYSTEM *
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 66, No. 2, P. 394 400, 2014 A TREATMENT PLANNING STUDY COMPARING VMAT WITH 3D CONFORMAL RADIOTHERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER USING PINNACLE PLANNING SYSTEM * D. ADAM 1,2,
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 66, No. 2, P. 394 400, 2014 A TREATMENT PLANNING STUDY COMPARING VMAT WITH 3D CONFORMAL RADIOTHERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER USING PINNACLE PLANNING SYSTEM * D. ADAM 1,2,
PEDIATRIC ORBITAL TUMORS RADIOTHERAPY PLANNING
 PEDIATRIC ORBITAL TUMORS RADIOTHERAPY PLANNING ANATOMY ANATOMY CONT ANATOMY CONT. ANATOMY CONT. EYE OF A CHILD Normal tissue tolerance doses (in conventional #) TD 5/5 TD 50/5 Endpoint Gy Gy Optic nerve
PEDIATRIC ORBITAL TUMORS RADIOTHERAPY PLANNING ANATOMY ANATOMY CONT ANATOMY CONT. ANATOMY CONT. EYE OF A CHILD Normal tissue tolerance doses (in conventional #) TD 5/5 TD 50/5 Endpoint Gy Gy Optic nerve
The role of chemoradiotherapy in GE junction and gastric cancer. Karin Haustermans
 The role of chemoradiotherapy in GE junction and gastric cancer Karin Haustermans Overview Postoperative chemoradiotherapy Preoperative chemoradiotherapy Palliative radiation Technical aspects Overview
The role of chemoradiotherapy in GE junction and gastric cancer Karin Haustermans Overview Postoperative chemoradiotherapy Preoperative chemoradiotherapy Palliative radiation Technical aspects Overview
Radiotherapy Planning (Contouring Lung Cancer for Radiotherapy dose prescription) Dr Raj K Shrimali
 Radiotherapy Planning (Contouring Lung Cancer for Radiotherapy dose prescription) Dr Raj K Shrimali Let us keep this simple and stick to some basic rules Patient positioning Must be reproducible Must be
Radiotherapy Planning (Contouring Lung Cancer for Radiotherapy dose prescription) Dr Raj K Shrimali Let us keep this simple and stick to some basic rules Patient positioning Must be reproducible Must be
First, how does radiation work?
 Hello, I am Prajnan Das, Faculty Member in the Department of Radiation Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. We are going to talk today about some of the basic principles regarding
Hello, I am Prajnan Das, Faculty Member in the Department of Radiation Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. We are going to talk today about some of the basic principles regarding
PTCOG 46. Educational Workshop Session IV. Head & Neck CLINICAL. J. Mizoe (NIRS, Japan)
 PTCOG 46 Educational Workshop Session IV CLINICAL Head & Neck J. Mizoe (NIRS, Japan) Photon X-Ray γ-ray Fast Neutron Non-Charged Radiation Electron Proton Helium Light Ion Heavy Particle Carbon Neon Argon
PTCOG 46 Educational Workshop Session IV CLINICAL Head & Neck J. Mizoe (NIRS, Japan) Photon X-Ray γ-ray Fast Neutron Non-Charged Radiation Electron Proton Helium Light Ion Heavy Particle Carbon Neon Argon
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of the Chest File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_the_chest
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of the Chest File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_the_chest
Advances in external beam radiotherapy
 International Conference on Modern Radiotherapy: Advances and Challenges in Radiation Protection of Patients Advances in external beam radiotherapy New techniques, new benefits and new risks Michael Brada
International Conference on Modern Radiotherapy: Advances and Challenges in Radiation Protection of Patients Advances in external beam radiotherapy New techniques, new benefits and new risks Michael Brada
Measure #156 (NQF 0382): Oncology: Radiation Dose Limits to Normal Tissues National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety
 Measure #156 (NQF 0382): Oncology: Radiation Dose Limits to Normal Tissues National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION: Percentage
Measure #156 (NQF 0382): Oncology: Radiation Dose Limits to Normal Tissues National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION: Percentage
Dosimetric Analysis of 3DCRT or IMRT with Vaginal-cuff Brachytherapy (VCB) for Gynaecological Cancer
 Dosimetric Analysis of 3DCRT or IMRT with Vaginal-cuff Brachytherapy (VCB) for Gynaecological Cancer Tan Chek Wee 15 06 2016 National University Cancer Institute, Singapore Clinical Care Education Research
Dosimetric Analysis of 3DCRT or IMRT with Vaginal-cuff Brachytherapy (VCB) for Gynaecological Cancer Tan Chek Wee 15 06 2016 National University Cancer Institute, Singapore Clinical Care Education Research
Clinical Report for Wanjie Proton Therapy Center. Li Jiamin, MD Wanjie Proton Therapy Center
 Clinical Report for Wanjie Proton Therapy Center Li Jiamin, MD Wanjie Proton Therapy Center General Information Wanjie Proton Therapy Center was founded in June 2001 The first patient was treated in Dec.
Clinical Report for Wanjie Proton Therapy Center Li Jiamin, MD Wanjie Proton Therapy Center General Information Wanjie Proton Therapy Center was founded in June 2001 The first patient was treated in Dec.
Radiation Therapy 2013 The Role of Protons. Bob Gaston, D.O.
 Radiation Therapy 2013 The Role of Protons Bob Gaston, D.O. Disclosures Oklahoma ProCure Treatment Center Radiation Medicine Associates Goal of Radiation Therapy Increase the Therapeutic Ratio Therapeutic
Radiation Therapy 2013 The Role of Protons Bob Gaston, D.O. Disclosures Oklahoma ProCure Treatment Center Radiation Medicine Associates Goal of Radiation Therapy Increase the Therapeutic Ratio Therapeutic
THE EFFECTIVE OF BRAIN CANCER AND XAY BETWEEN THEORY AND IMPLEMENTATION. Mustafa Rashid Issa
 THE EFFECTIVE OF BRAIN CANCER AND XAY BETWEEN THEORY AND IMPLEMENTATION Mustafa Rashid Issa ABSTRACT: Illustrate malignant tumors that form either in the brain or in the nerves originating in the brain.
THE EFFECTIVE OF BRAIN CANCER AND XAY BETWEEN THEORY AND IMPLEMENTATION Mustafa Rashid Issa ABSTRACT: Illustrate malignant tumors that form either in the brain or in the nerves originating in the brain.
IMRT - the physician s eye-view. Cinzia Iotti Department of Radiation Oncology S.Maria Nuova Hospital Reggio Emilia
 IMRT - the physician s eye-view Cinzia Iotti Department of Radiation Oncology S.Maria Nuova Hospital Reggio Emilia The goals of cancer therapy Local control Survival Functional status Quality of life Causes
IMRT - the physician s eye-view Cinzia Iotti Department of Radiation Oncology S.Maria Nuova Hospital Reggio Emilia The goals of cancer therapy Local control Survival Functional status Quality of life Causes
8/1/2016. Motion Management for Proton Lung SBRT. Outline. Protons and motion. Protons and Motion. Proton lung SBRT Future directions
 Motion Management for Proton Lung SBRT AAPM 2016 Outline Protons and Motion Dosimetric effects Remedies and mitigation techniques Proton lung SBRT Future directions Protons and motion Dosimetric perturbation
Motion Management for Proton Lung SBRT AAPM 2016 Outline Protons and Motion Dosimetric effects Remedies and mitigation techniques Proton lung SBRT Future directions Protons and motion Dosimetric perturbation
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of Head and Neck File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_head_and_neck
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of Head and Neck File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_head_and_neck
Conventional (2D) Versus Conformal (3D) Techniques in Radiotherapy for Malignant Pediatric Tumors: Dosimetric Perspectives
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 2,. 3, December: 39-34, 29 Conventional (2D) Versus Conformal (3D) Techniques in Radiotherapy for Malignant Pediatric Tumors: Dosimetric Perspectives NESREEN
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 2,. 3, December: 39-34, 29 Conventional (2D) Versus Conformal (3D) Techniques in Radiotherapy for Malignant Pediatric Tumors: Dosimetric Perspectives NESREEN
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.006 03/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 03/01/2015 Section: Radiology
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.006 03/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 03/01/2015 Section: Radiology
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: charged_particle_radiotherapy 3/12/96 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Charged-particle
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: charged_particle_radiotherapy 3/12/96 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Charged-particle
ENDPOINTS IN ONCOLOGY- HOW LONG WILL A CANCER PATIENT SURVIVE? DR GUNJAN BAIJAL CONSULTANT RADIATION ONCOLOGY MANIPAL GOA
 ENDPOINTS IN ONCOLOGY- HOW LONG WILL A CANCER PATIENT SURVIVE? DR GUNJAN BAIJAL CONSULTANT RADIATION ONCOLOGY MANIPAL GOA Why so much of cancer today? Times have changed HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE CANCER as
ENDPOINTS IN ONCOLOGY- HOW LONG WILL A CANCER PATIENT SURVIVE? DR GUNJAN BAIJAL CONSULTANT RADIATION ONCOLOGY MANIPAL GOA Why so much of cancer today? Times have changed HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE CANCER as
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.006 03/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 06/24/2011 Section: Radiology Place(s) of
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.006 03/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 06/24/2011 Section: Radiology Place(s) of
Radiation Therapy for Soft Tissue Sarcomas
 Radiation Therapy for Soft Tissue Sarcomas Alexander R. Gottschalk, MD, PhD Assistant Professor, Radiation Oncology University of California, San Francisco 1/25/08 NCI: limb salvage vs. amputation 43 patients
Radiation Therapy for Soft Tissue Sarcomas Alexander R. Gottschalk, MD, PhD Assistant Professor, Radiation Oncology University of California, San Francisco 1/25/08 NCI: limb salvage vs. amputation 43 patients
Cancer Treatment by Charged Particles - Carbon Ion Radiotherapy -
 Cancer Treatment by Charged Particles - Carbon Ion Radiotherapy - Takeshi Murakami Research Center of Charged Particle Therapy National Institute of Radiological Sciences 2012.11.21 1. Introduction to
Cancer Treatment by Charged Particles - Carbon Ion Radiotherapy - Takeshi Murakami Research Center of Charged Particle Therapy National Institute of Radiological Sciences 2012.11.21 1. Introduction to
Original Articles. The World Health Organization Classification of Skeletal Muscle Tumors in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma
 Original Articles The World Health Organization Classification of Skeletal Muscle Tumors in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma A Report From the Children s Oncology Group Erin R. Rudzinski, MD; James R. Anderson,
Original Articles The World Health Organization Classification of Skeletal Muscle Tumors in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma A Report From the Children s Oncology Group Erin R. Rudzinski, MD; James R. Anderson,
CT findings in patients with Cabazitaxel induced pelvic pain and haematuria: a case series
 Malalagama et al. Cancer Imaging (2017) 17:17 DOI 10.1186/s40644-017-0119-3 CASE SERIES CT findings in patients with Cabazitaxel induced pelvic pain and haematuria: a case series Geethal N. Malalagama
Malalagama et al. Cancer Imaging (2017) 17:17 DOI 10.1186/s40644-017-0119-3 CASE SERIES CT findings in patients with Cabazitaxel induced pelvic pain and haematuria: a case series Geethal N. Malalagama
Proton Radiation Therapy for Osteosarcomas, Chondrogenic Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas
 Proton Radiation Therapy for Osteosarcomas, Chondrogenic Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas Eugen B. Hug Center for Proton Radiation Therapy Paul Scherrer Institute Histologies Osteogenic Tumors Osteogenic
Proton Radiation Therapy for Osteosarcomas, Chondrogenic Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas Eugen B. Hug Center for Proton Radiation Therapy Paul Scherrer Institute Histologies Osteogenic Tumors Osteogenic
and Strength of Recommendations
 ASTRO with ASCO Qualifying Statements in Bold Italics s patients with T1-2, N0 non-small cell lung cancer who are medically operable? 1A: Patients with stage I NSCLC should be evaluated by a thoracic surgeon,
ASTRO with ASCO Qualifying Statements in Bold Italics s patients with T1-2, N0 non-small cell lung cancer who are medically operable? 1A: Patients with stage I NSCLC should be evaluated by a thoracic surgeon,
Protocol of Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer
 106 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Indication of definitive radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy (1) Resectable, but medically unfit, or high
106 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Indication of definitive radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy (1) Resectable, but medically unfit, or high
Demands and Perspectives of Hadron Therapy
 Demands and Perspectives of Hadron Therapy Alexander Lin, M.D. Assistant Professor University of Pennsylvania Direction of Operations Roberts Proton Therapy Center Disclosures Teva Pharmaceuticals: Advisory
Demands and Perspectives of Hadron Therapy Alexander Lin, M.D. Assistant Professor University of Pennsylvania Direction of Operations Roberts Proton Therapy Center Disclosures Teva Pharmaceuticals: Advisory
Dosimetry of conformal dynamic arc radiotherapy and intensity modulated radiotherapy in unresectable cholangiocarcinoma
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 1 February 2010; 131-139 Technical report Dosimetry of conformal dynamic arc radiotherapy and intensity modulated radiotherapy in unresectable cholangiocarcinoma Thanarpan
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 1 February 2010; 131-139 Technical report Dosimetry of conformal dynamic arc radiotherapy and intensity modulated radiotherapy in unresectable cholangiocarcinoma Thanarpan
Pediatric electron intraoperative radiotherapy: results and innovations
 Pediatric electron intraoperative radiotherapy: results and innovations Felipe A. Calvo ESTRO Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañon Madrid, Spain 2017 IOeRT in pediatric cancer: results and innovations
Pediatric electron intraoperative radiotherapy: results and innovations Felipe A. Calvo ESTRO Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañon Madrid, Spain 2017 IOeRT in pediatric cancer: results and innovations
A prospective feasibility study of respiratory-gated proton beam therapy for liver tumors
 A prospective feasibility study of respiratory-gated proton beam therapy for liver tumors The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
A prospective feasibility study of respiratory-gated proton beam therapy for liver tumors The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Clinical results of proton beam therapy for advanced neuroblastoma
 Oshiro et al. Radiation Oncology 2013, 8:142 RESEARCH Clinical results of proton beam therapy for advanced neuroblastoma Open Access Yoshiko Oshiro 1, Masashi Mizumoto 1, Toshiyuki Okumura 1, Shinji Sugahara
Oshiro et al. Radiation Oncology 2013, 8:142 RESEARCH Clinical results of proton beam therapy for advanced neuroblastoma Open Access Yoshiko Oshiro 1, Masashi Mizumoto 1, Toshiyuki Okumura 1, Shinji Sugahara
THORACIC MALIGNANCIES
 THORACIC MALIGNANCIES Summary for Malignant Malignancies. Lung Ca 1 Lung Cancer Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnostic Evaluation for Non-Small Lung Cancer 1. History and Physical examination. 2. CBCDE,
THORACIC MALIGNANCIES Summary for Malignant Malignancies. Lung Ca 1 Lung Cancer Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnostic Evaluation for Non-Small Lung Cancer 1. History and Physical examination. 2. CBCDE,
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy and Radiofrequency Ablation 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery
 Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy and Radiofrequency Ablation 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery Matthew Hartwig, M.D. Duke Cancer Institute Case Presentation I: Patient ER 74 y/o male with A1A
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy and Radiofrequency Ablation 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery Matthew Hartwig, M.D. Duke Cancer Institute Case Presentation I: Patient ER 74 y/o male with A1A
Image Guided Stereotactic Radiotherapy of the Lung
 Image Guided Stereotactic Radiotherapy of the Lung Jamie Marie Harris, MS DABR Avera McKennan Radiation Oncology September 25, 2015 Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy - Clinical Dose/Fractionation - Normal
Image Guided Stereotactic Radiotherapy of the Lung Jamie Marie Harris, MS DABR Avera McKennan Radiation Oncology September 25, 2015 Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy - Clinical Dose/Fractionation - Normal
Martin Stuschke 1,2*, Andreas Kaiser 1,2, Jehad Abu Jawad 1, Christoph Pöttgen 1, Sabine Levegrün 1 and Jonathan Farr 2,3
 Stuschke et al. Radiation Oncology 2013, 8:145 SHORT REPORT Open Access Multi-scenario based robust intensity-modulated proton therapy (IMPT) plans can account for set-up errors more effectively in terms
Stuschke et al. Radiation Oncology 2013, 8:145 SHORT REPORT Open Access Multi-scenario based robust intensity-modulated proton therapy (IMPT) plans can account for set-up errors more effectively in terms
Chapters from Clinical Oncology
 Chapters from Clinical Oncology Lecture notes University of Szeged Faculty of Medicine Department of Oncotherapy 2012. 1 RADIOTHERAPY Technical aspects Dr. Elemér Szil Introduction There are three possibilities
Chapters from Clinical Oncology Lecture notes University of Szeged Faculty of Medicine Department of Oncotherapy 2012. 1 RADIOTHERAPY Technical aspects Dr. Elemér Szil Introduction There are three possibilities
Carbon Ion Radiotherapy for Skull Base and Paracervical Chordomas
 Carbon Ion Radiotherapy for Skull Base and Paracervical Chordomas Azusa Hasegawa, Jun-etsu Mizoe and Hirohiko Tsujii Research Center Hospital for Charged Particle Therapy National Institute of Radiological
Carbon Ion Radiotherapy for Skull Base and Paracervical Chordomas Azusa Hasegawa, Jun-etsu Mizoe and Hirohiko Tsujii Research Center Hospital for Charged Particle Therapy National Institute of Radiological
Medical Dosimetry Graduate Certificate Program IU Graduate School & The Department of Radiation Oncology IU Simon Cancer Center
 Medical Dosimetry Graduate Certificate Program IU Graduate School & The Department of Radiation Oncology IU Simon Cancer Center All students accepted into the Medical Dosimetry Graduate Certificate Program
Medical Dosimetry Graduate Certificate Program IU Graduate School & The Department of Radiation Oncology IU Simon Cancer Center All students accepted into the Medical Dosimetry Graduate Certificate Program
Head and Neck Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Treatment Head and neck cancer overview The way a particular head and neck cancer behaves depends on the site in which it arises (the primary site). For example,
Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Treatment Head and neck cancer overview The way a particular head and neck cancer behaves depends on the site in which it arises (the primary site). For example,
TomoTherapy. Michelle Roach CNC Radiation Oncology Liverpool Hospital CNSA. May 2016
 TomoTherapy Michelle Roach CNC Radiation Oncology Liverpool Hospital CNSA May 2016 TomoTherapy The Facts Greek Tomo = slice Advanced form of IMRT 3D computerised tomography (CT) imaging immediately prior
TomoTherapy Michelle Roach CNC Radiation Oncology Liverpool Hospital CNSA May 2016 TomoTherapy The Facts Greek Tomo = slice Advanced form of IMRT 3D computerised tomography (CT) imaging immediately prior
Protocol of Radiotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer
 107 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Limited stage: AJCC (8th edition) stage I-III (T any, N any, M0) that can be safely treated with definitive RT
107 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Limited stage: AJCC (8th edition) stage I-III (T any, N any, M0) that can be safely treated with definitive RT
Concept for quantifying the dose from image guided radiotherapy
 Schneider et al. Radiation Oncology (2015) 10:188 DOI 10.1186/s13014-015-0492-7 RESEARCH Open Access Concept for quantifying the dose from image guided radiotherapy Uwe Schneider 1,2*, Roger Hälg 1,2 and
Schneider et al. Radiation Oncology (2015) 10:188 DOI 10.1186/s13014-015-0492-7 RESEARCH Open Access Concept for quantifying the dose from image guided radiotherapy Uwe Schneider 1,2*, Roger Hälg 1,2 and
ISSN: (Print) (Online) Journal homepage:
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Brachytherapy Technique for Abdominal Wall Metastases of Colorectal Cancer: Ultrasound-
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Brachytherapy Technique for Abdominal Wall Metastases of Colorectal Cancer: Ultrasound-
Application of Implanted Markers in Proton Therapy. Course Outline. McLaren Proton Therapy Center Karmanos Cancer Institute McLaren - Flint
 Application of Implanted Markers in Proton Therapy Sung Yong Park, Ph.D. McLaren Proton Therapy Center Karmanos Cancer Institute McLaren - Flint AAPM 2016, SAM Therapy Educational Course, 2016.08.04. Course
Application of Implanted Markers in Proton Therapy Sung Yong Park, Ph.D. McLaren Proton Therapy Center Karmanos Cancer Institute McLaren - Flint AAPM 2016, SAM Therapy Educational Course, 2016.08.04. Course
Chapter 8 Adenocarcinoma
 Page 80 Chapter 8 Adenocarcinoma Overview In Japan, the proportion of squamous cell carcinoma among all cervical cancers has been declining every year. In a recent survey, non-squamous cell carcinoma accounted
Page 80 Chapter 8 Adenocarcinoma Overview In Japan, the proportion of squamous cell carcinoma among all cervical cancers has been declining every year. In a recent survey, non-squamous cell carcinoma accounted
