Proton Radiation Therapy for Osteosarcomas, Chondrogenic Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas
|
|
|
- Simon Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proton Radiation Therapy for Osteosarcomas, Chondrogenic Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas Eugen B. Hug Center for Proton Radiation Therapy Paul Scherrer Institute
2 Histologies Osteogenic Tumors Osteogenic Sarcoma (Ewing Sarcoma) Chondrogenic Tumors Chordomas Chondrosarcomas Soft Tissue Sarcomas STS (Rhabdomyosarcoma)
3 Is there a place for Proton/Particle Radiotherapy in the treatment of Sarcomas? = Is there still a need to improve outcome for a subgroup of Sarcoma patients? Is it desirable to reduce side effects and improve functional outcome?
4 RT for UNRESECTED Soft Tissue Sarcoma (Kepka, Delaney et al., MGH, IJROBP, 2005) 112 patients with STS RTx between Gross disease (unresected or unresectable) RT Dose: median 64 Gy ( 21 % > 70 Gy, max Gy) (included 4/112 pts. with Proton-RT F/U: median 139 months (max. 365 months) Location: 43% extremities, 26% retroperitoneal, 24 % H&N, 7% trunk Tumor size: median 8 cm (max. 30 cm)
5 Kepka, Delaney et al., MGH, IJROBP, 2005 cont. Prognosticators for LC multivariate analysis: Size RT-Dose AJCC Stage P=0.0022
6 Kepka, Delaney et al., MGH, IJROBP, 2005 cont. Grade 3-4 Complications: 18/112 9/18: wound healing delay or skin necrosis 9/18 fibrosis, bone necrosis, ureteral and sigmoid stenosis, SM Type of complication WHD requiring amputation WHD coupled with massive tissues necrosis requiring amputation WHD requiring amputation WHD requiring major surgery WHD requiring major surgery WHD requiring major surgery WHD requiring major surgery Skin necrosis and cellulites after minor injury requiring skin graft Skin necrosis requiring skin graft Severe neuropathy Severe neuropathy Severe fibrosis, limb strength leaving useless leg Severe fibrosis, limb strength leaving useless leg Bone necrosis and bone fracture Ureteral stenosis requiring surgery Ureteral stenosis requiring surgery Sigmoid stenosis requiring surgery Radiation induced malignancy 8% < 68 Gy dose > 26 % Radiation dose (details on techniques) 76 Gy (1.2 Gy per fraction, b.i.d) 75 Gy (1.8 Gy per fraction, b.i.d) 64 Gy (2 Gy per fraction) 66 Gy (2 Gy per fraction) 75 Gy (60 Gy with 2 Gy per fraction) 76 Gy (2 Gy per fraction, b.i.d) 68 Gy (1.8 Gy per fraction) 70 Gy (2 Gy per fraction) 68 Gy (2 Gy per fraction) 66 Gy (2 Gy per fraction) 75 Gy (1.8 Gy per fraction, b.i.d) 68 Gy (2 Gy per fraction) 70 Gy (50 Gy at 2 Gy and 20 Gy IORT) 65 Gy (2 Gy per fraction) 68.5 Gy (2 Gy per fraction) 56 Gy (2 Gy per fraction) 68.5 Gy (2 Gy per fraction) 66.5 Gy (1.8 Gy per fraction)
7 Mundt, Weichselbaum et al., U Chicago, IJROBP 1995 RT for extremity sarcomas Livi et al, U Florence, Am J Surg 2006 S + postop RT for extremity sarcomas 23 / 213 pts. With Severe Late Complications > 66 Gy < 66 Gy Bone fracture 7 O Fibrosis 5 0 Per. Neuropathy 3 0 Wound complic. 5 3
8 Opportunity for Protons: Tumor subgroups with unsatisfactory local control: Tumor size Anatomic site Status of tumor resection Reduction of Adverse Events Improvement of functional outcome Local control translates into survival
9 Histologies Osteogenic Tumors Chondrogenic Tumors Soft Tissue Sarcomas Indications and Sites presently treated with Protons Published Data
10 Indications and Sites presently treated with Protons Skull Base Paraspinal / Neck /Trunk / Pelvis (Extremities) Published Data Retrospective review Prospective data gathering Phase I-II studies (obviously)) no Level I evidence (Phase III randomized trial)
11 There is a paucity of proton- literature specifically on Osteosarcoma and Soft Tissue Sarcomas Essentially one has to anticipate Osteo- and STS outcomes data from extrapolating data from Chordomas and Chondrosarcomas
12 Histologies Osteogenic Tumors Osteogenic Sarcoma (Ewing Sarcoma) Chondrogenic Tumors Chordomas Chondrosarcomas Soft Tissue Sarcomas STS Rhabdomyosarcoma
13 MGH update: Radiotherapy for Local Control of Osteosarcoma Delaney, Park et al., IJROBP 61(2), 2005 Retrospective reivew of 41 patients RT Location: H&Skull Base 17 pts., extremity 8, spine 8, pelvis 7, trunk 1 Chemo-Tx: 85% 23 patients (56%) combined photons/protons (H&Skull Base, Spine) 66% primary, 24% recurrent, 10% metastatic disease Dose: Gy (median 66 Gy),
14 Delaney, Park et al., IJROBP 61(2), 2005 Local control: 68 % at 5-years Local control: Axial versus Extremity versus H&N location P= n. s.
15 Delaney, Park et al., IJROBP 61(2), 2005 Local control: Total and subtotal resection: 78% versus Biopsy only: 40% P=0.01 Dose-response? LC: 54 % <55 Gy > 71% (P= n.s.) NO subgroup analysis protons/photons versus photons
16 Initial MGH / HCL report, 1995, IJROBP 31(3) 47 patients tx with combined photons/protons 3 groups: Chordomas/Chondrosarc. (20 pts.), Osteogenic Sarc.. (15 pts.), GCT, Osteo-and chondroblastomas (12 pts.) Dose: mean 73.9 Gy (Gr.I), 69.8 Gy (Gr.II( Gr.II), 61.8 Gy (Gr. III) ( Gy (RBE)) F/U: mean: 3.2 years, min. 1/2 year, max yrs.)
17 E. Hug et al. IJROBP 31(3), 1995
18 E. Hug et al. IJROBP 31(3), patients with osteogenic sarcoma of the axial skeleton LC and OS after combined photon/proton RT 60 % LC
19 Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcoma (Phase II: 9901 Fixed dose: 70.4 or 73.6 GyE/16fr/6wks 1.0 Local Control.8.6 Carbon Ions Survival Probability.4 n= Time (months) Courtesy of H. Tsujii
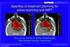
20 Osteosarcoma of the Pelvic Bone before carbon ion RT after carbon ion RT Phase I/II Studie, Chiba, Japan
21 Histologies Osteogenic Tumors Osteogenic Sarcoma (Ewing Sarcoma) Chondrogenic Tumors Chordomas Chondrosarcomas Soft Tissue Sarcomas STS Rhabdomyosarcoma
22 Proton-Radiotherapy for Chordomas and Chondrosarcomas: Practiced since 1973 Published data: MGH, LBL; Loma Linda, PSI, Orsay Skull base and paraspinal location approx patients treated with protons thus far
23 Proton Radiation Therapy for Skull Base Chordomas and Chondrosarcomas: Published Results: Massachusetts General Hospital Loma Linda Univ. Med Center Paul Scherrer Institute Centre de Protontherapie d Orsay
24 Courtesy: John Munzenrider, MGH/HCL
25 World wide largest experience: Mass. General Hospital (since 1974) Courtesy: John Munzenrider, MGH/HCL
26 Long term tumor control: MGH data Courtesy: John Munzenrider, MGH/HCL
27 Chordomas: Prognostic Factors female Courtesy: John Munzenrider, MGH/HCL
28 Chondrosarcoma vs. Chordoma; PRT- Results CPT Proton RadiationTherapy (PRT) for Chondrosarcomas and Chordomas of the Skull Base. Hug, Laredo, Slater, Devries et al. J Neurosurg. 91: , 1999 Tumor size at PRT and Local Control Percent p = 0.03 < 25ml GTV 25ml GTV Months CH_EH/dV99
29 Chondrosarcoma vs. Chordoma; PRT- Results CPT Proton RadiationTherapy (PRT) for Chondrosarcomas and Chordomas of the Skull Base. Hug, Laredo, Slater, Devries et al. J Neurosurg. 91: , 1999 Local Control Overall Survival 100 No Brainstem involvement 100 Percent p = 0.04 Brainstem involvement p = Months CH_EH/dV99
30 Prognostic factors: Proton-Radiotherapy for CHORDOMAS of the Skull Base and Axial Skeleton +++ Tumor Size (++) Skull Base versus Spine + Primary versus recurrent disease (+) Chondroid versus Non-Chondroid Pathology ++ Gender (+) Age (+) Pediatric versus Adult +++ Ability versus Inability to deliver dose: Optimal/suboptimal Dose Distribution by involvement or abutment of critical structures +++ Radiation Dose
31 Skull Base Chordomas and Chondrosarcomas at PSI: 5-year outcome* of spot scanning based PT To be presented by Dr. Ares Mean follow-up time: > 3 years Local Control for Chordomas: > 75% Local control for Chondrosarcomas: > 90 % High Grade Toxicity: < 7% * Ares, Lomax, Hug, Goitein in preparation
32 Chordomas of the Base of Skull 5-year local control rates (%) Photons Romero 1993 Zorlu 2000 Debus 2000 Protons Munzenrider 1999 Ares 2007 Hug 1999 C-Ions Schulz-Ertner Dose [ Gy (RBE)]
33 Chordomas and Chondrosarcomas of the Base of Skull Small Chordomas Photons 5-year Local Control rates(%) Chondrosarcomas Romero 1993 Zorlu 2000 Debus 2000 Protons Munzenrider 1999 Ares 2007 Hug 1999 C-Ions Schulz-Ertner Dose [ Gy (RBE)]
34 Neoplasms of the Skull Base: The present state of Tx for Chordomas and Chondrosarcomas The majority of Chondrosarcomas of the skull base are of low grade histology. Long-term outcome data suggest possible CURE for the majority of patients following subtotal surgical resection and high-dose radiation therapy (protons) to approx Gy. Gross total resection should not be pursued if increased surgical risks (the last 5 % = 90% risk ) This represents a dramatic improvement of prognosis in a disease considered universally fatal 20 years ago
35 RT for Skull Base Chordomas GOAL: Develop a risk-classification low - intermediate - high to correlate with recommendations for adjuvant Tx, i.e. treatment algorithm:,, observation - aggressive Tx - palliative Tx
36 Long-term Side Effects of Skull Base Irradiation The risks of severe side effects following high dose,precision RT depend on several variables: Tumor size, tumor compression of normal brain, critical structure involvement, dose to normal tissues, number of prior surgeries, general medical risk factors (diabetes, HTN, smoking,), KPS Low-risk group: < 5% High-risk group: > 10 % -?? * * RT as last modality after multiple failures
37 CPT Optic neuropathy and temporal lobe toxicity 1.5 yrs. 2.0 yrs.
38 Dose limitations for OAR at PSI OAR Brainstem surface Brainstem center Optic Chiasm Optic Nerves Dmax 64 CGE 53 CGE 60 CGE 60 CGE
39 Extracranial Chordomas of the Axial Skeleton treated with spot scanning Proton Therapy at PSI: Hans Peter Rutz et al.
40 Extracranial chordomas of the Axial Skeleton treated with spot scanning Proton Therapy at PSI: (Rutz et al.) Update of the initial publication (Rutz HP et al. IJROBP 67(2):512; 2007). Updated manuscript in progress. N = 40 Tx: Location:
41 Chordomas of the Axial Skeleton at PSI: Surgical Stabilization - Reconstruction (plates, screws, cage, rods etc.) in 21 / 40 patients. 19 / 40 patients without inserted instrumentation IMPT part of treatment plan since 2004 Median total dose: 72 Gy (RBE) (range: Gy (RBE)) Follow-up period: Minimum: Median: Maximum: 2 years (24 months) 43 months 91 months
42 Chordomas of the Axial Skeleton at PSI: 5-year outcomes data Local control 13 / 40 patients with local failure % Local control [all] Months
43 Chordomas of the Axial Skeleton at PSI: 5-year outcomes data Impact of Surgical Stabilization Reconstruction (SS-R) on Local control no SS-R No SS-R: only 1 LF in 19 pts. 0.7 Local control with SS-R P= Months Implant Non Implant With SS-R: 12 LF in 21 pts. or 12 / 13 Local Failures
44 Extracranial chordoma CT artifacts for surgical implants for stabilization / fusion on spinal axis tumors Clinical factors: Negative selection of patients with more advanced tumor i.e. larger and more complex tumor presentation requiring more extensive surgery? Treatment planning issues: (Difficulties defining Targets?) Difficulties in dose calculation? Difficulties in range calculations? Similar experience for passive scattering technique?
45 Proton RT for Sacral Chordomas: MGH results Park et al., MGH, IJROBP 65(5), patients, treated photons and/or protons 16 primary chordomas, 11 recurrent Combined S + RT = 21 patients Mean dose 71 Gy(E) for primary Mean dose 77 Gy (E) for recurrent chordoma RT alone: 6 patients 60, 62, Gy photons and Gy photons/protons
46 Park et al., MGH, IJROBP 65(5), 2006 Local Control following S + RT (21 pts.): Primary >>> Recurrent Description Time Local control % Disease free survival % Overall survival % 14 primary chordomas treated by 5 years 90.9 ± ± ± 6.9 surgery & radiation 10 years 90.9 ± ± ± recurrent chordomas treated 5 years 57.1 ± ± ± 19.3 by surgery & radiation 10 years 19.1 ± ± ± 22.2
47 Park et al., MGH, IJROBP 65(5), 2006 Local Control following RT alone (6 pts.): Photons only: 60 Gy LFailure 62 Gy LFailure Mixed photons / protons: 77, 74, 77 Gy (E) Local control 73 Gy (E) LFailure
48 Histologies Osteogenic Tumors Osteogenic Sarcoma Ewing Sarcoma Chondrogenic Tumors Chordomas Chondrosarcomas Soft Tissue Sarcomas STS Rhabdomyosarcoma
49 Proton Photon planning comparison for Soft Tissue Sarcomas
50 Planning Comparison for STS:: Photon IMRT versus Proton IMPT Weber, Delaney et al., PSI + MGH, IJROBP 2004 Step 1: Planning assumptions: 77.4 Gy (RBE) to CTV with identical OAR constraints. Calculate target covergae and DVH s for normal tissues Step 2: Attempt dose escalation with protons leaving OAR constraints unchanged
51 Weber, Delaney et al., PSI + MGH, IJROBP 2004 cont. IMRT IMPT
52 Weber, Delaney et al., PSI + MGH, IJROBP 2004 cont. Integral Normal Tissue dose consistently reduced by IMPT (factor ) Inhomogeneity coefficients and Conformity Indices were not significantly different The optimization IMPT algorithm was used to increase the total dose to the target by 10% and 20%, within the maximal OAR dose constraints. Dose escalation could be achieved in all patients, at the 20% (92.9 CGE) dose escalation level, regardless of tumor size, location, and geometry.
53 The Integral Dose Differential Comparative dose distributions for 9-field photon intensitymodulated photon (IMXT) and 3-field intensity-modulated protonradiation (IMPT) treatment plans for a patient with pelvic Ewing s sarcoma. IMXT IMPT (Courtesy of A.R. Smith and A.J. Lomax, in Delaney, Cancer Control, 2005) IMXT - IMPT
54 Proton Therapy for Adult Patients with STS: the PSI experience (Weber et al., IJROBP 2007) 13 patients with STS tx with protons (6) or mixed protons/photons (7) Gross tumor: 9 / 13. R1 resection: 4 / 13 Location: H&N, Skull Base, Paraspinal. Pelvis, Trunk, Reroperitoneal (2 pts), Shoulder (2pts.) Primary: 9 (69%), recurrent: 4 pts. Dose: median 69.4 Gy (RBE) ( Gy (RBE)) F/U: minimum 1 year, 12 pts. > 2 years, median for surviving patients: 48 months.
55 Weber et al., IJROBP 2007 cont. Tumor histology: liposarcoma (n = 3), peripheral nerve sheet tumor (PNST, n = 3), leiomyosarcoma (n = 2), desmoid tumors (n = 2), angiosarcoma (n = 1), spindle cell sarcoma (n = 1), and malignant hemoangioperiocytoma (n = 1) Treatment plan for (A) retroperitoneal, (B) head and neck, and (C) paravertebral sarcoma. Sparing of the kidney (A), spinal cord (A, C), and brainstem (B).
56 Weber et al., IJROBP 2007 cont. Local control: 10 / 13 pts. Local control 3-year actuarial LC: 74% Late adverse events: 2 pts. 1 cataract Late adverse events 1 Grade 3 temporal lobe necrosis
57 Proton Radiotherapy for STS in Children
58 Proton Radiotherapy for pediatric STS treated at PSI (Timmermann et al., PSI, IJROBP, 2007) 16 children with STS (including 12 with RMS or RMSlike histology) 14/16 children with chemotherapy Age: median 3.7 years ( years). 9 children requiring anesthesia Tumor volume: 52 cc 1225 cc Location: H&N, Skull Base, Paraspinal, Pelvis Proton RT Dose: median 50 Gy (RBE) ( Gy (RBE) doses according to CWS2002, MMT-95, COG- D9803 in 14 pts. F/U: median 18.6 months ( months)
59 Timmermann et al., PSI, IJROBP 2007 cont. Outcome (very preliminary) Local control Local control: 12/16 = 75% at 2 years 2/12 Failures in RMS- Group Overall Survival 2/4 in Non-RMS Group (after 50.4, 50 GY(RBE)) Late toxicity: F/U too short
60 2 principal Concepts for applying Proton RT in relation to Photon-RT Pediatric Clinical Trials Concept 1 Enrollement in photon trials or Tx according to photon trial study board recommendations dose and volume regimen identical to photon concepts Advantage: Proton-RT emdedded in multi-institutional concepts. Matched-case comparability of outcomes data with photons Disadvantage: no increase in tumor control probability from protons by applying Tx-prescriptions similar to photons
61 2 principal Concepts for applying Proton RT in relation to Photon-RT Pediatric Clinical Trials Concept 2 High risk STS (mainly Non-RMS STS with gross residual) Apply high doses based on peds. skull base chordoma data Low risk STS (mainly RMS STS ) Enrollement in photon trial Example: COG / IRS RMS dose and volume regimen High dose proton-rt: Gy(RBE) Enrollement in photon trials only if high doses permissible Normal tissue sparing advantage, but no expectation for increased tumor control
62 Example Concept 2: Proton Radiation Therapy in the management of pediatric base of skull tumors (Hug et al., MGH+LLUMC, IJROBP, 2002) 29 children with mesenchymal tumors tx with protons or mixed protons/photons Age: median 12 years (1-19 years). Gross tumor: 28/29 patients (97%) Tumor histology grouped in malignant versus benign Dose for malignant histologies according to adult experience F/U: mean 40 months (13-92 months)
63 Hug et al., MGH + LLUMC, IJROBP 2002 cont. No. of Patients TOTAL 29 Malignant Histology 20 Chordoma 10 Chondrosarcoma 3 Epithelioid Sarcoma 1 Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma 1 Myxoid Sarcoma 1 Rhabdomyosarcoma 4 Benign Histology 9 Giant Cell Tumor 6 Median dose: 70 CGE ( ) Median dose: 60.4 CGE ( ) Angiofibroma 2 Chondroblastoma 1
64 Example: 13 y.o. M with Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma CTV: 50.4 Gy (RBE) GTV: 66.6 Gy (RBE) 20 pts. with Malignant Histology 5-yr LC: 72% 5-Yr OS: 56% 9 pts. Benign Histology LC: 8/9, OS 100% Severe late effects: 2 pts. (motor weakness, sensory deficit)
65 Proton/Particle - Radiotherapy for Sarcomas: There is a need for improving local controle by RT for high-risk, unresected/resectable sarcomas
66 Potential and Future Increasing Local Control by dose escalation: Residual disease or unresectable disease Disease at high risk for failure Decreasing Late Adverse Events by reduction of Integral dose: Improving functional outcome by reducing normal tissue dose Reducing risks of Secondary malignancy
67 Proton Radiotherapy for STS: possible trial designs Scenario 1: Proton- versus Photon - Radiotherapy for STS. A Phase III Trial using moderately high dose levels Scenario 2: High dose RT for high-risk STS using stereotactic precision-modality radiotherapy. A Phase II trial open for QAapproved equipment Scenario 3: Dose-escalation study using proton radiotherapy for unresectable STS
68 Proton Radiotherapy for STS: possible trial designs Scenario 1: Proton- versus EB-Photon Radiotherapy for.sarcoma. A Phase III Trial using moderately high dose levels Scenario 2: High dose RT for high risk Sarcoma using stereotactic precisionmodality radiotherapy. A Phase II trial open for QA-approved equipment Scenario 3: Dose-escalation study using proton radiotherapy for unresectable..s
69 THANK YOU
Proton Radiation Therapy for Osteosarcomas, Chondrogenic Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas
 Proton Radiation Therapy for Osteosarcomas, Chondrogenic Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas Eugen B. Hug Center for Proton Radiation Therapy Paul Scherrer Institute Is there a place for Proton/Particle Radiotherapy
Proton Radiation Therapy for Osteosarcomas, Chondrogenic Tumors and Soft Tissue Sarcomas Eugen B. Hug Center for Proton Radiation Therapy Paul Scherrer Institute Is there a place for Proton/Particle Radiotherapy
Proton-Radiotherapy for Tumors of the Skull Base: Indications, Advantages, Limitations
 Proton-Radiotherapy for Tumors of the Skull Base: Indications, Advantages, Limitations Eugen B. Hug, MD Director, Center for Proton-Radiotherapy, Paul Scherrer Institut, Villigen and Chair of Proton-Radiotherapy.
Proton-Radiotherapy for Tumors of the Skull Base: Indications, Advantages, Limitations Eugen B. Hug, MD Director, Center for Proton-Radiotherapy, Paul Scherrer Institut, Villigen and Chair of Proton-Radiotherapy.
Effectiveness and Safety of Spot Scanning Proton Radiation Therapy for Skull Base Tumors: First Long Term Report of the PSI Experience
 Effectiveness and Safety of Spot Scanning Proton Radiation Therapy for Skull Base Tumors: First Long Term Report of the PSI Experience Carmen Ares, Antony J Lomax, Eugen B Hug, Alessandra Bolsi, Beate
Effectiveness and Safety of Spot Scanning Proton Radiation Therapy for Skull Base Tumors: First Long Term Report of the PSI Experience Carmen Ares, Antony J Lomax, Eugen B Hug, Alessandra Bolsi, Beate
Proton Therapy for tumors of the skull base - RESULTS. Eugen B. Hug, MD Medical Director, ProCure Proton Therapy Centers, NY
 Proton Therapy for tumors of the skull base - RESULTS Eugen B. Hug, MD Medical Director, ProCure Proton Therapy Centers, NY Petroclival Chondrosarcoma: 68 72 Gy(RBE) at 1.8 or 2.0 Gy(RBE) GTV: 70.2 Gy(RBE)
Proton Therapy for tumors of the skull base - RESULTS Eugen B. Hug, MD Medical Director, ProCure Proton Therapy Centers, NY Petroclival Chondrosarcoma: 68 72 Gy(RBE) at 1.8 or 2.0 Gy(RBE) GTV: 70.2 Gy(RBE)
Proton Radiotherapy for Skull Base and Para-spinal Tumors
 Proton Radiotherapy for Skull Base and Para-spinal Tumors Carmen Ares Primary tumors Tumors of the Skull Base - Chordomas, Chondrosarcomas Secondary infiltration or involvement by intracranial tumors -
Proton Radiotherapy for Skull Base and Para-spinal Tumors Carmen Ares Primary tumors Tumors of the Skull Base - Chordomas, Chondrosarcomas Secondary infiltration or involvement by intracranial tumors -
Particle Therapy for Tumors of the Skull Base. Eugen B. Hug, MD Medical Director, ProCure Proton Therapy Centers, NY
 Particle Therapy for Tumors of the Skull Base Eugen B. Hug, MD Medical Director, ProCure Proton Therapy Centers, NY Particle Radiation Therapy for Tumors of the Skull Base Primary skull base tumors: Chordoma,
Particle Therapy for Tumors of the Skull Base Eugen B. Hug, MD Medical Director, ProCure Proton Therapy Centers, NY Particle Radiation Therapy for Tumors of the Skull Base Primary skull base tumors: Chordoma,
Carbon Ion Radiotherapy for Skull Base and Paracervical Chordomas
 Carbon Ion Radiotherapy for Skull Base and Paracervical Chordomas Azusa Hasegawa, Jun-etsu Mizoe and Hirohiko Tsujii Research Center Hospital for Charged Particle Therapy National Institute of Radiological
Carbon Ion Radiotherapy for Skull Base and Paracervical Chordomas Azusa Hasegawa, Jun-etsu Mizoe and Hirohiko Tsujii Research Center Hospital for Charged Particle Therapy National Institute of Radiological
Sacral Chordoma: The Loma Linda University Radiation Medicine Experience. Kevin Yiee MD, MPH Resident Physician
 Sacral Chordoma: The Loma Linda University Radiation Medicine Experience Kevin Yiee MD, MPH Resident Physician What is a chordoma? 1 st chordoma discovered in clivus by Virchow and Luschka 1856 Rare tumor
Sacral Chordoma: The Loma Linda University Radiation Medicine Experience Kevin Yiee MD, MPH Resident Physician What is a chordoma? 1 st chordoma discovered in clivus by Virchow and Luschka 1856 Rare tumor
Proton- Radiotherapy: Overview of Clinical Indications
 Proton- Radiotherapy: Overview of Clinical Indications Eugen B. Hug (with emphasis on indications treated at PSI For comprehensive clinical reviews: ESTRO or PTCOG seminars) HUG 11/07 Complication Free
Proton- Radiotherapy: Overview of Clinical Indications Eugen B. Hug (with emphasis on indications treated at PSI For comprehensive clinical reviews: ESTRO or PTCOG seminars) HUG 11/07 Complication Free
Particle Radiation Therapy: CurrentStatus Indications -Results
 Particle Radiation Therapy: CurrentStatus Indications -Results Eugen B. Hug Center for Proton Therapy Paul Scherrer Institute and University of Zürich Switzerland Particle Radiation Therapy: Selection
Particle Radiation Therapy: CurrentStatus Indications -Results Eugen B. Hug Center for Proton Therapy Paul Scherrer Institute and University of Zürich Switzerland Particle Radiation Therapy: Selection
NCCN GUIDELINES ON PROTON THERAPY (AS OF 4/23/18) BONE (Version , 03/28/18)
 BONE (Version 2.2018, 03/28/18) NCCN GUIDELINES ON PROTON THERAPY (AS OF 4/23/18) Radiation Therapy Specialized techniques such as intensity-modulated RT (IMRT); particle beam RT with protons, carbon ions,
BONE (Version 2.2018, 03/28/18) NCCN GUIDELINES ON PROTON THERAPY (AS OF 4/23/18) Radiation Therapy Specialized techniques such as intensity-modulated RT (IMRT); particle beam RT with protons, carbon ions,
Protons for Head and Neck Cancer. William M Mendenhall, M.D.
 Protons for Head and Neck Cancer William M Mendenhall, M.D. Protons for Head and Neck Cancer Potential Advantages: Reduce late complications via more conformal dose distributions Likely to be the major
Protons for Head and Neck Cancer William M Mendenhall, M.D. Protons for Head and Neck Cancer Potential Advantages: Reduce late complications via more conformal dose distributions Likely to be the major
Status of H 1 and C 12
 Status of H 1 and C 12 Herman Suit No Conflict of Interest 1 Goal of a New Treatment Modality Tumor Control Probability or No in Complication Rate 2 Truism No Advantage to: any Patient for any Radiation
Status of H 1 and C 12 Herman Suit No Conflict of Interest 1 Goal of a New Treatment Modality Tumor Control Probability or No in Complication Rate 2 Truism No Advantage to: any Patient for any Radiation
Clinical Results of Carbon Ion Radiotherapy: The Heidelberg Experience
 Clinical Results of Carbon Ion Radiotherapy: The Heidelberg Experience Stephanie E. Combs, MD Department of Radiation Oncology University of Heidelberg, Germany Carbon ion RT at GSI Active beam delivery
Clinical Results of Carbon Ion Radiotherapy: The Heidelberg Experience Stephanie E. Combs, MD Department of Radiation Oncology University of Heidelberg, Germany Carbon ion RT at GSI Active beam delivery
25 Years of Proton Radiation Therapy at PSI an Overview
 25 Years of Proton Radiation Therapy at PSI an Overview Gudrun Goitein for the Team of the Center for Proton Therapy Center for Proton Therapy Paul Scherrer Institut (www.psi.ch) 5232 Villigen PSI Switzerland
25 Years of Proton Radiation Therapy at PSI an Overview Gudrun Goitein for the Team of the Center for Proton Therapy Center for Proton Therapy Paul Scherrer Institut (www.psi.ch) 5232 Villigen PSI Switzerland
Proton- Radiotherapy:
 Proton- Radiotherapy: Future of Medical Indications and Treatment Concepts Eugen B. Hug and Ralf A. Schneider HUG 11/07 The emerging role of Proton Radiotherapy in the framework of modern Photon-RT 2000
Proton- Radiotherapy: Future of Medical Indications and Treatment Concepts Eugen B. Hug and Ralf A. Schneider HUG 11/07 The emerging role of Proton Radiotherapy in the framework of modern Photon-RT 2000
What s new in bone and soft tissue sarcoma Treatment and Guidelines 2012? Rob Grimer
 What s new in bone and soft tissue sarcoma Treatment and Guidelines 2012? Rob Grimer ESMO conference 2012 Top Oncologists in world (~ 400) Lots of sarcoma basic science key messages: 40% of STS diagnoses
What s new in bone and soft tissue sarcoma Treatment and Guidelines 2012? Rob Grimer ESMO conference 2012 Top Oncologists in world (~ 400) Lots of sarcoma basic science key messages: 40% of STS diagnoses
-Proton Beam Therapy in Paediatric Radiation Oncology -
 -Proton Beam Therapy in Paediatric Radiation Oncology - Beate Timmermann, M.D. West German Proton Therapy Centre Essen Germany Preview Survival Toxicity Why protons? (theoretically) Experiences so far
-Proton Beam Therapy in Paediatric Radiation Oncology - Beate Timmermann, M.D. West German Proton Therapy Centre Essen Germany Preview Survival Toxicity Why protons? (theoretically) Experiences so far
PEDIATRIC ORBITAL TUMORS RADIOTHERAPY PLANNING
 PEDIATRIC ORBITAL TUMORS RADIOTHERAPY PLANNING ANATOMY ANATOMY CONT ANATOMY CONT. ANATOMY CONT. EYE OF A CHILD Normal tissue tolerance doses (in conventional #) TD 5/5 TD 50/5 Endpoint Gy Gy Optic nerve
PEDIATRIC ORBITAL TUMORS RADIOTHERAPY PLANNING ANATOMY ANATOMY CONT ANATOMY CONT. ANATOMY CONT. EYE OF A CHILD Normal tissue tolerance doses (in conventional #) TD 5/5 TD 50/5 Endpoint Gy Gy Optic nerve
Radiation Therapy for Soft Tissue Sarcomas
 Radiation Therapy for Soft Tissue Sarcomas Alexander R. Gottschalk, MD, PhD Assistant Professor, Radiation Oncology University of California, San Francisco 1/25/08 NCI: limb salvage vs. amputation 43 patients
Radiation Therapy for Soft Tissue Sarcomas Alexander R. Gottschalk, MD, PhD Assistant Professor, Radiation Oncology University of California, San Francisco 1/25/08 NCI: limb salvage vs. amputation 43 patients
Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck. Kevin Harrington
 Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck Kevin Harrington Overview Classification and incidence of sarcomas Clinical presentation Challenges to treatment Management approaches Prognostic factors Radiation-induced
Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck Kevin Harrington Overview Classification and incidence of sarcomas Clinical presentation Challenges to treatment Management approaches Prognostic factors Radiation-induced
Future Directions in Prostate Cancer: The Case for Protons. John J. Coen, MD Helen & Harry Gray Cancer Center
 Future Directions in Prostate Cancer: The Case for Protons John J. Coen, MD Helen & Harry Gray Cancer Center November 14, 2012 Protons and prostate cancer Early proton experience at the MGH The case for
Future Directions in Prostate Cancer: The Case for Protons John J. Coen, MD Helen & Harry Gray Cancer Center November 14, 2012 Protons and prostate cancer Early proton experience at the MGH The case for
Specifics of treatment planning for active scanning and IMPT
 Specifics of treatment planning for active scanning and IMPT SFUD IMPT Tony Lomax, Centre for Proton Radiotherapy, Paul Scherrer Institute, Switzerland Treatment planning for scanning 1. Single Field,
Specifics of treatment planning for active scanning and IMPT SFUD IMPT Tony Lomax, Centre for Proton Radiotherapy, Paul Scherrer Institute, Switzerland Treatment planning for scanning 1. Single Field,
Clinical Report for Wanjie Proton Therapy Center. Li Jiamin, MD Wanjie Proton Therapy Center
 Clinical Report for Wanjie Proton Therapy Center Li Jiamin, MD Wanjie Proton Therapy Center General Information Wanjie Proton Therapy Center was founded in June 2001 The first patient was treated in Dec.
Clinical Report for Wanjie Proton Therapy Center Li Jiamin, MD Wanjie Proton Therapy Center General Information Wanjie Proton Therapy Center was founded in June 2001 The first patient was treated in Dec.
Proton radiation therapy for chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base
 J Neurosurg 91:432 439, 1999 Proton radiation therapy for chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base EUGEN B. HUG, M.D., LILIA N. LOREDO, M.D., JERRY D. SLATER, M.D., ALEXANDER DEVRIES, M.D., ROGER
J Neurosurg 91:432 439, 1999 Proton radiation therapy for chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base EUGEN B. HUG, M.D., LILIA N. LOREDO, M.D., JERRY D. SLATER, M.D., ALEXANDER DEVRIES, M.D., ROGER
Clinical Concept and History of Protons. Relevance and Limitations of Conformality. Gudrun Goitein
 Clinical Concept and History of Protons Relevance and Limitations of Conformality Gudrun Goitein PSI Winter School January 2010 Bad Zurzach and PSI, Villigen Switzerland P + Who came first: The Clinical
Clinical Concept and History of Protons Relevance and Limitations of Conformality Gudrun Goitein PSI Winter School January 2010 Bad Zurzach and PSI, Villigen Switzerland P + Who came first: The Clinical
Multidisciplinary management of retroperitoneal sarcomas
 Multidisciplinary management of retroperitoneal sarcomas Eric K. Nakakura, MD UCSF Department of Surgery UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center San Francisco, CA 7 th Annual Clinical Cancer Update North Lake
Multidisciplinary management of retroperitoneal sarcomas Eric K. Nakakura, MD UCSF Department of Surgery UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center San Francisco, CA 7 th Annual Clinical Cancer Update North Lake
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablative therapy, nonsurgical, for pulmonary metastases of soft tissue sarcoma, 279 280 Adipocytic tumors, atypical lipomatous tumor vs. well-differentiated
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablative therapy, nonsurgical, for pulmonary metastases of soft tissue sarcoma, 279 280 Adipocytic tumors, atypical lipomatous tumor vs. well-differentiated
PTCOG 46. Educational Workshop Session IV. Head & Neck CLINICAL. J. Mizoe (NIRS, Japan)
 PTCOG 46 Educational Workshop Session IV CLINICAL Head & Neck J. Mizoe (NIRS, Japan) Photon X-Ray γ-ray Fast Neutron Non-Charged Radiation Electron Proton Helium Light Ion Heavy Particle Carbon Neon Argon
PTCOG 46 Educational Workshop Session IV CLINICAL Head & Neck J. Mizoe (NIRS, Japan) Photon X-Ray γ-ray Fast Neutron Non-Charged Radiation Electron Proton Helium Light Ion Heavy Particle Carbon Neon Argon
HEAVY PARTICLE THERAPY
 HEAVY PARTICLE THERAPY DR. G.V. GIRI KIDWAI MEMORIAL INSTITUTE OF ONCOLOGY ICRO 2012 BHATINDA HEAVY PARTICLES USED IN A EFFORT TO IMPROVE TUMOR CONTROL, THAT DO NOT RESPOND TO PHOTONS OR ELECTRONS BETTER
HEAVY PARTICLE THERAPY DR. G.V. GIRI KIDWAI MEMORIAL INSTITUTE OF ONCOLOGY ICRO 2012 BHATINDA HEAVY PARTICLES USED IN A EFFORT TO IMPROVE TUMOR CONTROL, THAT DO NOT RESPOND TO PHOTONS OR ELECTRONS BETTER
Treatment Planning for Skull Base Tumors PTCOG 52, June 2013
 Treatment Planning for Skull Base Tumors PTCOG 52, June 2013 Judy Adams CMD Hanne Kooy Ph.D, Norbert Liebsch MD Department of Radiation Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Chordomas and Chondrosarcomas
Treatment Planning for Skull Base Tumors PTCOG 52, June 2013 Judy Adams CMD Hanne Kooy Ph.D, Norbert Liebsch MD Department of Radiation Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Chordomas and Chondrosarcomas
Collection of Recorded Radiotherapy Seminars
 IAEA Human Health Campus Collection of Recorded Radiotherapy Seminars http://humanhealth.iaea.org The Role of Radiosurgery in the Treatment of Gliomas Luis Souhami, MD Professor Department of Radiation
IAEA Human Health Campus Collection of Recorded Radiotherapy Seminars http://humanhealth.iaea.org The Role of Radiosurgery in the Treatment of Gliomas Luis Souhami, MD Professor Department of Radiation
Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Presley Regional Trauma Center Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee
 Soft Tissue Sarcoma Presley Regional Trauma Center Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Soft Tissue Sarcoma Collective term for an unusual and diverse
Soft Tissue Sarcoma Presley Regional Trauma Center Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Soft Tissue Sarcoma Collective term for an unusual and diverse
Proton Therapy for Ependymoma and Craniopharyngioma at the University of Florida: Lessons Learned About Efficacy and Toxicity
 Proton Therapy for Ependymoma and Craniopharyngioma at the University of Florida: Lessons Learned About Efficacy and Toxicity Danny Indelicato, MD Mendenhall Chair of Pediatric Radiotherapy University
Proton Therapy for Ependymoma and Craniopharyngioma at the University of Florida: Lessons Learned About Efficacy and Toxicity Danny Indelicato, MD Mendenhall Chair of Pediatric Radiotherapy University
Case Conference: SBRT for spinal metastases D A N I E L S I M P S O N M D 3 / 2 7 / 1 2
 Case Conference: SBRT for spinal metastases D A N I E L S I M P S O N M D 3 / 2 7 / 1 2 Case 79 yo M with hx of T3N0 colon cancer diagnosed in 2008 metastatic liver disease s/p liver segmentectomy 2009
Case Conference: SBRT for spinal metastases D A N I E L S I M P S O N M D 3 / 2 7 / 1 2 Case 79 yo M with hx of T3N0 colon cancer diagnosed in 2008 metastatic liver disease s/p liver segmentectomy 2009
Role of protons, heavy ions and BNCT in brain tumors
 Role of protons, heavy ions and BNCT in brain tumors Prof G K Rath Head, NCI (AIIMS-2) Chief, Dr. BRA IRCH, Professor Radiation Oncology All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi 1 Overview of
Role of protons, heavy ions and BNCT in brain tumors Prof G K Rath Head, NCI (AIIMS-2) Chief, Dr. BRA IRCH, Professor Radiation Oncology All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi 1 Overview of
INTRAOPERATIVE RADIATION THERAPY FOR RETROPERITONEAL SARCOMA
 INTRAOPERATIVE RADIATION THERAPY FOR RETROPERITONEAL SARCOMA ISIORT 2014 Ivy A Petersen, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN NOTHING TO DISCLOSE SOFT TISSUE SARCOMAS 2014 Estimated cases in the USA 12,020 diagnosed
INTRAOPERATIVE RADIATION THERAPY FOR RETROPERITONEAL SARCOMA ISIORT 2014 Ivy A Petersen, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN NOTHING TO DISCLOSE SOFT TISSUE SARCOMAS 2014 Estimated cases in the USA 12,020 diagnosed
Disclosures. Proton therapy advantages. Why are comparing therapies difficult? Proton Therapy for Low Risk Prostate Cancer
 Proton Therapy for Low Risk Prostate Cancer Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures This presentation will not discuss off-label or investigational treatments Andrew K. Lee, MD, MPH Associate Professor
Proton Therapy for Low Risk Prostate Cancer Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures This presentation will not discuss off-label or investigational treatments Andrew K. Lee, MD, MPH Associate Professor
Summary Talk of the Workshop
 Medical experience History of IBT 1954 1975 1976 1977 1982 1987 1992 Pituitary 1st He pt Treatment 1st C, Ne pt Eye treatment Phase-1 He Phase I-II Ne Phase I-II Ne & He 1st Comp Tx Plan 3D planning LBNL
Medical experience History of IBT 1954 1975 1976 1977 1982 1987 1992 Pituitary 1st He pt Treatment 1st C, Ne pt Eye treatment Phase-1 He Phase I-II Ne Phase I-II Ne & He 1st Comp Tx Plan 3D planning LBNL
Feasibility of Proton Beam Therapy for Chordoma and Chondrosarcoma of the Skull Base
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Feasibility of Proton Beam Therapy for Chordoma and Chondrosarcoma of the Skull Base Hiroshi Fuji, M.D., Ph.D., 1 Yoko Nakasu, M.D., Ph.D., 2 Yuji Ishida, M.D., Ph.D., 3 Satoshi Horiguchi,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Feasibility of Proton Beam Therapy for Chordoma and Chondrosarcoma of the Skull Base Hiroshi Fuji, M.D., Ph.D., 1 Yoko Nakasu, M.D., Ph.D., 2 Yuji Ishida, M.D., Ph.D., 3 Satoshi Horiguchi,
4/25/2018. Proton Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer: The Future is Now. Disclosures. Overview. Physical limitations of photons
 Proton Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer: The Future is Now Michael Chuong, MD Radiation Oncologist Disclosures None Overview Physical limitations of photons Dosimetric/clinical proton data for HNC Proton
Proton Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer: The Future is Now Michael Chuong, MD Radiation Oncologist Disclosures None Overview Physical limitations of photons Dosimetric/clinical proton data for HNC Proton
State of the Art Radiotherapy for Pediatric Tumors. Suzanne L. Wolden, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
 State of the Art Radiotherapy for Pediatric Tumors Suzanne L. Wolden, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Introduction Progress and success in pediatric oncology Examples of low-tech and high-tech
State of the Art Radiotherapy for Pediatric Tumors Suzanne L. Wolden, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Introduction Progress and success in pediatric oncology Examples of low-tech and high-tech
DOES RADIOTHERAPY TECHNIQUE / DOSE / FRACTIONATION REALLY MATTER? YES
 DOES RADIOTHERAPY TECHNIQUE / DOSE / FRACTIONATION REALLY MATTER? YES Marco Krengli Radiotherapy, Department of Translational Medicine, University of Piemonte Orientale A. Avogadro THE STANDARD OF CARE
DOES RADIOTHERAPY TECHNIQUE / DOSE / FRACTIONATION REALLY MATTER? YES Marco Krengli Radiotherapy, Department of Translational Medicine, University of Piemonte Orientale A. Avogadro THE STANDARD OF CARE
Particle Therapy for CNS Tumors Anita Mahajan MD MD Anderson Cancer Center PTCOG, Shanghai June 10, 2014
 Particle Therapy for CNS Tumors Anita Mahajan MD MD Anderson Cancer Center PTCOG, Shanghai June 10, 2014 TCP/NTCP (%) The Potential for Protons in the CNS 10 0 Increase Tumor Control Increase TCP increased
Particle Therapy for CNS Tumors Anita Mahajan MD MD Anderson Cancer Center PTCOG, Shanghai June 10, 2014 TCP/NTCP (%) The Potential for Protons in the CNS 10 0 Increase Tumor Control Increase TCP increased
Effective local and systemic therapy is necessary for the cure of Ewing tumor Most chemotherapy regimens are a combination of cyclophosphamide,
 Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
Radiation Technology, Hyogo Ion Beam Medical Center, Tatsuno, Hyogo, JAPAN
 Analysis of Visual Loss Due to Radiation- Induced Optic Neuropathy After Particle Therapy for Head and Neck and Skull Base Tumors Adjacent to Optic Nerves Y. Demizu 1, M. Murakami 1, D. Miyawaki 1, Y.
Analysis of Visual Loss Due to Radiation- Induced Optic Neuropathy After Particle Therapy for Head and Neck and Skull Base Tumors Adjacent to Optic Nerves Y. Demizu 1, M. Murakami 1, D. Miyawaki 1, Y.
Potential benefits of intensity-modulated proton therapy in head and neck cancer van de Water, Tara Arpana
 University of Groningen Potential benefits of intensity-modulated proton therapy in head and neck cancer van de Water, Tara Arpana IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen Potential benefits of intensity-modulated proton therapy in head and neck cancer van de Water, Tara Arpana IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
Clinical considerations of RBE in proton therapy
 Clinical considerations of RBE in proton therapy H. Paganetti PhD Professor, Harvard Medical School Director of Physics Research, Massachusetts General Hospital, Radiation Oncology Why do we need the RBE
Clinical considerations of RBE in proton therapy H. Paganetti PhD Professor, Harvard Medical School Director of Physics Research, Massachusetts General Hospital, Radiation Oncology Why do we need the RBE
Current Status and Future Medical Perspectives at MedAustron. U. Mock EBG MedAustron GmbH
 Current Status and Future Medical Perspectives at MedAustron U. Mock EBG MedAustron GmbH Cancer treatment facility Ion beam therapy with protons and carbon ions Research facility Medical physics Radiobiology
Current Status and Future Medical Perspectives at MedAustron U. Mock EBG MedAustron GmbH Cancer treatment facility Ion beam therapy with protons and carbon ions Research facility Medical physics Radiobiology
What s New in Radiotherapy For STS of The Extremity? Kaled M. Alektiar, MD, FASTRO Dept of Rad Onc Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
 What s New in Radiotherapy For STS of The Extremity? Kaled M. Alektiar, MD, FASTRO Dept of Rad Onc Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Topics Predictive tools for risk assessment Reassessment of dose/volume
What s New in Radiotherapy For STS of The Extremity? Kaled M. Alektiar, MD, FASTRO Dept of Rad Onc Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Topics Predictive tools for risk assessment Reassessment of dose/volume
8/3/2016. Clinical Significance of RBE Variations in Proton Therapy. Why RBE (relative biological effectiveness)?
 8//06 Clinical Significance of Variations in Proton Therapy H. Paganetti PhD Professor, Harvard Medical School Director of Physics Research, Massachusetts General Hospital, Radiation Oncology Introduction
8//06 Clinical Significance of Variations in Proton Therapy H. Paganetti PhD Professor, Harvard Medical School Director of Physics Research, Massachusetts General Hospital, Radiation Oncology Introduction
IMPT with Carbon Ions
 IMPT with Carbon Ions PTCOG 48, Heidelberg, 28.09.-03.10.2009 Malte Ellerbrock Medical Physics Expert Heidelberg Ion-Beam Therapy Center HIT Betriebs GmbH am Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg http://www.hit-centrum.de
IMPT with Carbon Ions PTCOG 48, Heidelberg, 28.09.-03.10.2009 Malte Ellerbrock Medical Physics Expert Heidelberg Ion-Beam Therapy Center HIT Betriebs GmbH am Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg http://www.hit-centrum.de
State-of-the-art proton therapy: The physicist s perspective
 State-of-the-art proton therapy: Tony Lomax, Centre for Proton Radiotherapy, Paul Scherrer Institute, Switzerland Overview of presentation 1. State-of-the-art proton delivery 2. Current challenges 3. New
State-of-the-art proton therapy: Tony Lomax, Centre for Proton Radiotherapy, Paul Scherrer Institute, Switzerland Overview of presentation 1. State-of-the-art proton delivery 2. Current challenges 3. New
Radiotherapy Considerations in Extremity Sarcoma
 Radiotherapy Considerations in Extremity Sarcoma Peter Chung Department of Radiation Oncology Princess Margaret Hospital University of Toronto Role of RT in STS Local tumour eradication while allowing
Radiotherapy Considerations in Extremity Sarcoma Peter Chung Department of Radiation Oncology Princess Margaret Hospital University of Toronto Role of RT in STS Local tumour eradication while allowing
Sarcoma and Radiation Therapy. Gabrielle M Kane MB BCh EdD FRCPC Muir Professorship in Radiation Oncology University of Washington
 Sarcoma and Radiation Therapy Gabrielle M Kane MB BCh EdD FRCPC Muir Professorship in Radiation Oncology University of Washington Objective: Helping you make informed decisions Introduction Process Radiation
Sarcoma and Radiation Therapy Gabrielle M Kane MB BCh EdD FRCPC Muir Professorship in Radiation Oncology University of Washington Objective: Helping you make informed decisions Introduction Process Radiation
Treatment Planning (Protons vs. Photons)
 Treatment Planning Treatment Planning (Protons vs. Photons) Acquisition of imaging data Delineation of regions of interest Selection of beam directions Dose calculation Optimization of the plan Hounsfield
Treatment Planning Treatment Planning (Protons vs. Photons) Acquisition of imaging data Delineation of regions of interest Selection of beam directions Dose calculation Optimization of the plan Hounsfield
11/28/2018. Proton Therapy for Liver Cancer: Who, Why, and How. Disclosures. Michael Chuong, MD. None
 Proton Therapy for Liver Cancer: Who, Why, and How Michael Chuong, MD Disclosures None 1 Rationale for proton therapy Hepatic toxicity Biliary toxicity GI toxicity Potentially significant benefit especially
Proton Therapy for Liver Cancer: Who, Why, and How Michael Chuong, MD Disclosures None 1 Rationale for proton therapy Hepatic toxicity Biliary toxicity GI toxicity Potentially significant benefit especially
The Physics of Oesophageal Cancer Radiotherapy
 The Physics of Oesophageal Cancer Radiotherapy Dr. Philip Wai Radiotherapy Physics Royal Marsden Hospital 1 Contents Brief clinical introduction Imaging and Target definition Dose prescription & patient
The Physics of Oesophageal Cancer Radiotherapy Dr. Philip Wai Radiotherapy Physics Royal Marsden Hospital 1 Contents Brief clinical introduction Imaging and Target definition Dose prescription & patient
Proton and heavy ion radiotherapy: Effect of LET
 Proton and heavy ion radiotherapy: Effect of LET As a low LET particle traverses a DNA molecule, ionizations are far apart and double strand breaks are rare With high LET particles, ionizations are closer
Proton and heavy ion radiotherapy: Effect of LET As a low LET particle traverses a DNA molecule, ionizations are far apart and double strand breaks are rare With high LET particles, ionizations are closer
The role of Radiation Oncologist: Hi-tech treatments for liver metastases
 The role of Radiation Oncologist: Hi-tech treatments for liver metastases Icro Meattini, MD Radiotherapy-Oncology Unit AOU Careggi Hospital Florence University, Italy Liver Metastases - Background The
The role of Radiation Oncologist: Hi-tech treatments for liver metastases Icro Meattini, MD Radiotherapy-Oncology Unit AOU Careggi Hospital Florence University, Italy Liver Metastases - Background The
UPDATE ON RADIOTHERAPY
 1 Miriam Kleiter UPDATE ON RADIOTHERAPY Department for Companion Animals and Horses, Plattform Radiooncology and Nuclear Medicine, University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna Introduction Radiotherapy has
1 Miriam Kleiter UPDATE ON RADIOTHERAPY Department for Companion Animals and Horses, Plattform Radiooncology and Nuclear Medicine, University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna Introduction Radiotherapy has
Potential benefits of intensity-modulated proton therapy in head and neck cancer van de Water, Tara Arpana
 University of Groningen Potential benefits of intensity-modulated proton therapy in head and neck cancer van de Water, Tara Arpana IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen Potential benefits of intensity-modulated proton therapy in head and neck cancer van de Water, Tara Arpana IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
Disclosures. The Challenges Facing Proton Beam Therapy and Opportunities. Minesh P Mehta, MBChB, FASTRO
 Minesh P Mehta, MBChB, FASTRO The Challenges Facing Proton Beam Therapy and Opportunities Disclosures Consultant: Varian, IBA, Agenus, Remedy, Insys DSMB: Monteris Current as of October 2016 1 The Challenges
Minesh P Mehta, MBChB, FASTRO The Challenges Facing Proton Beam Therapy and Opportunities Disclosures Consultant: Varian, IBA, Agenus, Remedy, Insys DSMB: Monteris Current as of October 2016 1 The Challenges
14. Background. Sarcoma. Resectable extremity soft tissue sarcomas
 96 14. Sarcoma Background Radiotherapy is widely used as an adjunct to surgery in the management of soft tissue sarcomas as the risk of failure in the surgical bed can be high. For bone sarcomas, radiotherapy
96 14. Sarcoma Background Radiotherapy is widely used as an adjunct to surgery in the management of soft tissue sarcomas as the risk of failure in the surgical bed can be high. For bone sarcomas, radiotherapy
Advances in radiation oncology in the management of soft tissue sarcoma 放疗于治疗肉瘤的最新发展
 Advances in radiation oncology in the management of soft tissue sarcoma 放疗于治疗肉瘤的最新发展 Brian O Sullivan Bartley-Smith / Wharton Chair Professor, Department of Radiation Oncology The Princess Margaret / University
Advances in radiation oncology in the management of soft tissue sarcoma 放疗于治疗肉瘤的最新发展 Brian O Sullivan Bartley-Smith / Wharton Chair Professor, Department of Radiation Oncology The Princess Margaret / University
Protontherapy in paediatric skull base and cervical canal chordomas. Long term outcome
 Protontherapy in paediatric skull base and cervical canal chordomas. Long term outcome Jean-Louis Habrand, MD François Baclesse Cancer Center- Caen University, Institut Curie-Proton Therapy Center (ICPO),
Protontherapy in paediatric skull base and cervical canal chordomas. Long term outcome Jean-Louis Habrand, MD François Baclesse Cancer Center- Caen University, Institut Curie-Proton Therapy Center (ICPO),
Dose escalation for NSCLC using conformal RT: 3D and IMRT. Hasan Murshed
 Dose escalation for NSCLC using conformal RT: 3D and IMRT. Hasan Murshed Take home message Preliminary data shows CRT technique in NSCLC allows dose escalation to an unprecedented level maintaining cancer
Dose escalation for NSCLC using conformal RT: 3D and IMRT. Hasan Murshed Take home message Preliminary data shows CRT technique in NSCLC allows dose escalation to an unprecedented level maintaining cancer
Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiotherapy for Neoplastic Conditions
 Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiotherapy for Neoplastic Conditions Policy Number: 8.01.10 Last Review: 11/2017 Origination: 11/2006 Next Review: 11/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of
Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiotherapy for Neoplastic Conditions Policy Number: 8.01.10 Last Review: 11/2017 Origination: 11/2006 Next Review: 11/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of
Case Report Carbon Ion Beam Radiotherapy for Sinonasal Malignant Tumors Invading Skull Base
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology, Article ID 241856, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/241856 Case Report Carbon Ion Beam Radiotherapy for Sinonasal Malignant Tumors Invading Skull Base Nobuo Ohta,
Case Reports in Otolaryngology, Article ID 241856, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/241856 Case Report Carbon Ion Beam Radiotherapy for Sinonasal Malignant Tumors Invading Skull Base Nobuo Ohta,
RESEARCH INFORMATION AWARENESS SUPPORT PRIMARY BONE CANCER CHONDROSARCOMA. Visit bcrt.org.uk for more information
 RESEARCH INFORMATION AWARENESS SUPPORT PRIMARY BONE CANCER CHONDROSARCOMA Visit bcrt.org.uk for more information CONTENTS What is it? Who does it affect? Symptoms Types of Chondrosarcoma Cause and Risk
RESEARCH INFORMATION AWARENESS SUPPORT PRIMARY BONE CANCER CHONDROSARCOMA Visit bcrt.org.uk for more information CONTENTS What is it? Who does it affect? Symptoms Types of Chondrosarcoma Cause and Risk
Advances in external beam radiotherapy
 International Conference on Modern Radiotherapy: Advances and Challenges in Radiation Protection of Patients Advances in external beam radiotherapy New techniques, new benefits and new risks Michael Brada
International Conference on Modern Radiotherapy: Advances and Challenges in Radiation Protection of Patients Advances in external beam radiotherapy New techniques, new benefits and new risks Michael Brada
IMRT - the physician s eye-view. Cinzia Iotti Department of Radiation Oncology S.Maria Nuova Hospital Reggio Emilia
 IMRT - the physician s eye-view Cinzia Iotti Department of Radiation Oncology S.Maria Nuova Hospital Reggio Emilia The goals of cancer therapy Local control Survival Functional status Quality of life Causes
IMRT - the physician s eye-view Cinzia Iotti Department of Radiation Oncology S.Maria Nuova Hospital Reggio Emilia The goals of cancer therapy Local control Survival Functional status Quality of life Causes
ProtonTherapy: A ballistic that will benefit patients? Pr. Xavier Geets MIRO Lab, IREC UCL Radiotherapy Dept. CUSL, Belgium
 ProtonTherapy: A ballistic that will benefit patients? Pr. Xavier Geets MIRO Lab, IREC UCL Radiotherapy Dept. CUSL, Belgium Proton Therapy, a swissknife The balistic advantage of protons P PHOTON THERAPY
ProtonTherapy: A ballistic that will benefit patients? Pr. Xavier Geets MIRO Lab, IREC UCL Radiotherapy Dept. CUSL, Belgium Proton Therapy, a swissknife The balistic advantage of protons P PHOTON THERAPY
Proton Therapy in Neurosurgery: A Historical Review and Future Perspective Based on Currently Available New Generation Systems
 Review Article Proton Therapy in Neurosurgery: A Historical Review and Future Perspective Based on Currently Available New Generation Systems Parisa Azimi 1, Amir Movafeghi 2 1 Functional Neurosurgery
Review Article Proton Therapy in Neurosurgery: A Historical Review and Future Perspective Based on Currently Available New Generation Systems Parisa Azimi 1, Amir Movafeghi 2 1 Functional Neurosurgery
Pediatrics -Proton Beam Therapy in Children -
 Pediatrics -Proton Beam Therapy in Children - Beate Timmermann, M.D. West German Proton Therapy Centre Essen Germany Preview Survival Toxicity Why protons? (theoretically) Experiences so far (clinically)
Pediatrics -Proton Beam Therapy in Children - Beate Timmermann, M.D. West German Proton Therapy Centre Essen Germany Preview Survival Toxicity Why protons? (theoretically) Experiences so far (clinically)
Proton Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Clinical Overview. Brian Winey, Ph.D. Physicist, MGH Assistant Professor, HMS
 Proton Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Clinical Overview Brian Winey, Ph.D. Physicist, MGH Assistant Professor, HMS Acknowledgements Radiation Oncologists and Physicists at various institutions (MGH, MDACC,
Proton Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Clinical Overview Brian Winey, Ph.D. Physicist, MGH Assistant Professor, HMS Acknowledgements Radiation Oncologists and Physicists at various institutions (MGH, MDACC,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: charged_particle_radiotherapy 3/12/96 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Charged-particle
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: charged_particle_radiotherapy 3/12/96 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Charged-particle
Radiation Therapy for Liver Malignancies
 Outline Radiation Therapy for Liver Malignancies Albert J. Chang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Radiation Oncology, UCSF March 23, 2014 Rationale for developing liver directed therapies Liver directed therapies
Outline Radiation Therapy for Liver Malignancies Albert J. Chang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Radiation Oncology, UCSF March 23, 2014 Rationale for developing liver directed therapies Liver directed therapies
Soft Tissue Sarcomas: Questions and Answers
 Soft Tissue Sarcomas: Questions and Answers 1. What is soft tissue? The term soft tissue refers to tissues that connect, support, or surround other structures and organs of the body. Soft tissue includes
Soft Tissue Sarcomas: Questions and Answers 1. What is soft tissue? The term soft tissue refers to tissues that connect, support, or surround other structures and organs of the body. Soft tissue includes
ES-SCLC Joint Case Conference. Anthony Paravati Adam Yock
 ES-SCLC Joint Case Conference Anthony Paravati Adam Yock Case 57 yo woman with 35 pack year smoking history presented with persistent cough and rash Chest x-ray showed a large left upper lobe/left hilar
ES-SCLC Joint Case Conference Anthony Paravati Adam Yock Case 57 yo woman with 35 pack year smoking history presented with persistent cough and rash Chest x-ray showed a large left upper lobe/left hilar
Printed by Maria Chen on 3/11/2012 5:46:52 AM. For personal use only. Not approved for distribution. Copyright 2012 National Comprehensive Cancer
 , Table of Contents NCCN Categories of Evidence and Consensus Category 1: Based upon high-level evidence, there is uniform NCCN consensus that the intervention is appropriate. Category 2A: Based upon lower-level
, Table of Contents NCCN Categories of Evidence and Consensus Category 1: Based upon high-level evidence, there is uniform NCCN consensus that the intervention is appropriate. Category 2A: Based upon lower-level
Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiation Therapy
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Case Presentation. Gordon Callender M.D. Surgical Resident
 Case Presentation Gordon Callender M.D. Surgical Resident Retroperitoneal Sarcomas Sarcomas Heterogeneous group of rare tumors that arise predominantly from the embryonic mesoderm. Expected incidence for
Case Presentation Gordon Callender M.D. Surgical Resident Retroperitoneal Sarcomas Sarcomas Heterogeneous group of rare tumors that arise predominantly from the embryonic mesoderm. Expected incidence for
Treatment Planning Evaluation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) for Craniospinal Irradiation (CSI)
 Treatment Planning Evaluation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) for Craniospinal Irradiation (CSI) Tagreed AL-ALAWI Medical Physicist King Abdullah Medical City- Jeddah Aim 1. Simplify and standardize
Treatment Planning Evaluation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) for Craniospinal Irradiation (CSI) Tagreed AL-ALAWI Medical Physicist King Abdullah Medical City- Jeddah Aim 1. Simplify and standardize
Insights into Thymic Epithelial Tumors: Radiation Therapy
 Insights into Thymic Epithelial Tumors: Radiation Therapy Charles R. Thomas, MD Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiation Medicine Professor, Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Medical
Insights into Thymic Epithelial Tumors: Radiation Therapy Charles R. Thomas, MD Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiation Medicine Professor, Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Medical
Particle Radiation Therapy Using Proton and Heavier Ion Beams Daniela Schulz-Ertner and Hirohiko Tsujii
 VOLUME 25 NUMBER 8 MARCH 10 2007 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY R E V I E W A R T I C L E Particle Radiation Therapy Using Proton and Heavier Ion Beams Daniela Schulz-Ertner and Hirohiko Tsujii From the
VOLUME 25 NUMBER 8 MARCH 10 2007 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY R E V I E W A R T I C L E Particle Radiation Therapy Using Proton and Heavier Ion Beams Daniela Schulz-Ertner and Hirohiko Tsujii From the
JAMES EWING, Endothelial origin. 14 yr Girl
 JAMES EWING, 1921 Endothelial origin 14 yr Girl SPECTRUM OF ESFT NEURAL DIFFERENTIATION Least Well EWING S SARCOMA ATYPICAL EWING S SARCOMA PNET Peripheral Neuroepithelioma ASKIN TUMOR (thoraco-pulmonary)
JAMES EWING, 1921 Endothelial origin 14 yr Girl SPECTRUM OF ESFT NEURAL DIFFERENTIATION Least Well EWING S SARCOMA ATYPICAL EWING S SARCOMA PNET Peripheral Neuroepithelioma ASKIN TUMOR (thoraco-pulmonary)
Radiation Therapy 2013 The Role of Protons. Bob Gaston, D.O.
 Radiation Therapy 2013 The Role of Protons Bob Gaston, D.O. Disclosures Oklahoma ProCure Treatment Center Radiation Medicine Associates Goal of Radiation Therapy Increase the Therapeutic Ratio Therapeutic
Radiation Therapy 2013 The Role of Protons Bob Gaston, D.O. Disclosures Oklahoma ProCure Treatment Center Radiation Medicine Associates Goal of Radiation Therapy Increase the Therapeutic Ratio Therapeutic
Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiotherapy for Neoplastic Conditions
 Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiotherapy for Neoplastic Conditions Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.005 07/01/2009 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST
Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiotherapy for Neoplastic Conditions Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.005 07/01/2009 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST
3/27/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
TOMOTERAPIA in Italia: Esperienze a confronto
 TOMOTERAPIA in Italia: Esperienze a confronto BARD 20 novembre 2010 L esperienza di Reggio Emilia Testa collo Alessandro Muraglia Reasons for the use of tomotherapy: - Complex tumor geometry and proximity
TOMOTERAPIA in Italia: Esperienze a confronto BARD 20 novembre 2010 L esperienza di Reggio Emilia Testa collo Alessandro Muraglia Reasons for the use of tomotherapy: - Complex tumor geometry and proximity
Radiotherapy and tumours in veterinary practice: part one
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Radiotherapy and tumours in veterinary practice: part one Author : Aleksandra Marcinowska, Jane Dobson Categories : Companion
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Radiotherapy and tumours in veterinary practice: part one Author : Aleksandra Marcinowska, Jane Dobson Categories : Companion
The Evolution of SBRT and Hypofractionation in Thoracic Radiation Oncology
 The Evolution of SBRT and Hypofractionation in Thoracic Radiation Oncology (specifically, lung cancer) 2/10/18 Jeffrey Kittel, MD Radiation Oncology, Aurora St. Luke s Medical Center Outline The history
The Evolution of SBRT and Hypofractionation in Thoracic Radiation Oncology (specifically, lung cancer) 2/10/18 Jeffrey Kittel, MD Radiation Oncology, Aurora St. Luke s Medical Center Outline The history
IAEA Pediatric Radiation Oncology Training Dr Laskar Version 1 June SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA (Non Rhabdomyosarcoma)
 SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA (Non Rhabdomyosarcoma) Soft Tissue structures Fat, Muscles, Fibrous tissue, Blood vessels, Supporting cells of peripheral nervous system Soft Tissue Sarcomas:- embryologically arise
SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA (Non Rhabdomyosarcoma) Soft Tissue structures Fat, Muscles, Fibrous tissue, Blood vessels, Supporting cells of peripheral nervous system Soft Tissue Sarcomas:- embryologically arise
Musculoskeletal Sarcomas
 Musculoskeletal Sarcomas Robert C. Orth, M.D., Ph.D. Edward B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Page 0 xxx00.#####.ppt 9/23/2012 9:01:18 AM No disclosures Page 1 xxx00.#####.ppt
Musculoskeletal Sarcomas Robert C. Orth, M.D., Ph.D. Edward B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Page 0 xxx00.#####.ppt 9/23/2012 9:01:18 AM No disclosures Page 1 xxx00.#####.ppt
Page 1. Helical (Spiral) Tomotherapy. UW Helical Tomotherapy Unit. Helical (Spiral) Tomotherapy. MVCT of an Anesthetized Dog with a Sinus Tumor
 Helical (Spiral) Tomotherapy Novel Clinical Applications of IMRT Linac Ring Gantry CT Detector X-Ray Fan Beam Binary Multileaf Collimator Binary MLC Leaves James S Welsh, MS, MD Department of Human Oncology
Helical (Spiral) Tomotherapy Novel Clinical Applications of IMRT Linac Ring Gantry CT Detector X-Ray Fan Beam Binary Multileaf Collimator Binary MLC Leaves James S Welsh, MS, MD Department of Human Oncology
Andrew K. Lee, MD, MPH Associate Professor Department tof fradiation Oncology M.D. Anderson Cancer Center
 Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer Andrew K. Lee, MD, MPH Associate Professor Department tof fradiation Oncology M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Seungtaek Choi, MD Assistant Professor Department tof fradiation
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer Andrew K. Lee, MD, MPH Associate Professor Department tof fradiation Oncology M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Seungtaek Choi, MD Assistant Professor Department tof fradiation
Tecniche Radioterapiche U. Ricardi
 Tecniche Radioterapiche U. Ricardi UNIVERSITA DEGLI STUDI DI TORINO Should we always rely on stage? T4N0M0 Stage IIIB T2N3M0 Early stage NSCLC The treatment of choice for early-stage NSCLC is anatomic
Tecniche Radioterapiche U. Ricardi UNIVERSITA DEGLI STUDI DI TORINO Should we always rely on stage? T4N0M0 Stage IIIB T2N3M0 Early stage NSCLC The treatment of choice for early-stage NSCLC is anatomic
La chemioterapia neoadiuvante nei sarcomi: novità e attuali indicazioni Lorenzo D Ambrosio, MD PhD Divisione di Oncologia Medica Istituto di Candiolo
 La chemioterapia neoadiuvante nei sarcomi: novità e attuali indicazioni Lorenzo D Ambrosio, MD PhD Divisione di Oncologia Medica Istituto di Candiolo Fondazione del Piemonte per l Oncologia. IRCCS 12 CONGRESSO
La chemioterapia neoadiuvante nei sarcomi: novità e attuali indicazioni Lorenzo D Ambrosio, MD PhD Divisione di Oncologia Medica Istituto di Candiolo Fondazione del Piemonte per l Oncologia. IRCCS 12 CONGRESSO
Associated Terms: Osteosarcoma, Bone Cancer, Limb Salvage, Appendicular Osteosarcoma, Pathologic Fracture, Chondrosarcoma
 1 of 9 9/29/2014 8:25 PM Associated Terms: Osteosarcoma, Bone Cancer, Limb Salvage, Appendicular Osteosarcoma, Pathologic Fracture, Chondrosarcoma The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who
1 of 9 9/29/2014 8:25 PM Associated Terms: Osteosarcoma, Bone Cancer, Limb Salvage, Appendicular Osteosarcoma, Pathologic Fracture, Chondrosarcoma The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who
