Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma A Report of 45 Cases of a Kidney Tumor of Low Malignant Potential
|
|
|
- Corey Sharleen Horton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomic Pathology / MULTILOCULAR CYSTIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma A Report of 45 Cases of a Kidney Tumor of Low Malignant Potential Sueli Suzigan, MD, 1 Antonio López-Beltrán, MD, PhD, 2 Rodolfo Montironi, MD, FRCPath, 3 Ricardo Drut, MD, 4 Ana Romero, MD, 2 Tomayoshi Hayashi, MD, 5 Ana L.C. Gentili, MD, 6 Paulo S.P. Fonseca, MD, 7 Ines detorres, MD, 8 Athanase Billis, MD, 9 Lucia C. Japp, MD, 10 Enrico Bollito, MD, 11 Ferran Algaba, MD, 12 and Maria J. Requena-Tapias, MD 13 Key Words: Cystic renal cell carcinoma; Multilocular cystic carcinoma; Clear cell renal cell carcinoma; Low-grade cystic carcinoma Abstract The 2004 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of kidney tumors recognizes multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma (MCRCC) as a rare variant of clear cell renal cell carcinoma with a good prognosis. Available information on its clinical significance is limited. The study cohort included 45 MCRCC cases classified according to 2004 WHO criteria obtained through a multi-institutional international search. Most patients had unilateral MCRCC with no side predominance that was found incidentally; 62% were men, but women had tumors at an earlier age (P =.385). MCRCC occurred slightly more often in men than in women (1.7:1). At diagnosis, 82% of patients had stage T1 and 16%, stage T2; 1 patient had stage T3. The Fuhrman grade was 1 (62%) or 2 (38%), with smaller tumors ( 4 cm) most likely Fuhrman grade 1 (P =.911). All 45 patients were alive with no evidence of disease at mean follow-up of 66.1 months, confirming an extremely good prognosis after surgery and a 5-year disease-specific survival rate of 100%. To rename this tumor as multilocular cystic renal cell neoplasm of low malignant potential might help urologists approach the patients conservatively. Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma (MCRCC), also known as multilocular clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and multicystic clear cell carcinoma, is a rare cystic tumor of the kidney with an excellent outcome. 1-7 Diagnostic criteria for MCRCC were defined by the 2004 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of kidney tumors based on previous reports and the suggestions of Eble and Bonsib. 1,8 The true incidence is unknown because no strict criteria were defined previously. Some reports suggest that cystic renal cell carcinomas (crcc, a category including MCRCC, unilocular cystic RCC, RCC with extensive cystic necrosis, and cystic RCC characterized by a unilocular cyst with one or a few isolated mural tumor nodules) might represent 3% to 14% of RCC Studies have focused on unilocular and multilocular crcc with variable proportions of a solid clear cell component but usually with no more than 25% and no evidence of tumor necrosis. 2-6 Although each of these studies reported that patients with crcc had a better prognosis than patients with solid clear cell RCC, some concern persists about the true clinical significance of the diagnosis of MCRCC in a given patient and its malignant potential. 9 This is in part because of the lack of reports on large series of cases defined according to the more restrictive 2004 WHO criteria. MCRCC is considered a distinct subtype of clear cell RCC in the 2004 WHO classification based on the characteristic gross features with a multilocular cystic appearance and a variegated, yellowish solid component limited to small areas with no expansive nodules or necrosis. 1,18-27 Histologic examination reveals cysts lined by occasionally flattened cuboidal clear cells and septa that contain aggregates of epithelial cells with clear cytoplasm; tumors usually are Fuhrman grade 1. 1 Because there is little difference between nuclear grades 1 and Downloaded from Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125:
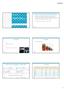
2 Suzigan et al / MULTILOCULAR CYSTIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 in conventional clear cell RCC in terms of outcome, we found a reasonable expansion of the criteria to include lowgrade tumors (Fuhrman grade 1 or 2). An important issue is the differential diagnosis of MCRCC, which in adults includes multicystic kidney, segmental cystic disease, cystic nephroma, and other crccs, including cystic necrosis in RCC (pseudocystic necrotic carcinoma). 9,17,28-32 The difficulties of differential diagnosis might be responsible as a confounding factor for the variable outcome observed in some series in which other crccs are incorporated into the analysis in addition to true MCRCC; therefore, some controversy exists in the literature concerning its malignant potential. Likewise, the recent finding of VHL gene mutations in MCRCC supports its classification as a type of clear cell RCC. 32 This article reports the clinical and pathologic findings in a series of 45 cases of MCRCC diagnosed according to the 2004 WHO criteria to better define their clinical significance. Materials and Methods For this retrospective, observational study, the sample series was obtained through an international and multi-institutional search including centers from Brazil, Argentina, Japan, Spain, and Italy. Surgical pathology files of the participating institutions were reviewed from January 1987 to December 2004, and cases of MCRCC that met the inclusion criteria were obtained; this included meeting the 2004 WHO 1 diagnostic criteria Table 1 and available follow-up data. Clinical and demographic information obtained through the hospital records included clinical manifestations, treatment, and follow-up. Gross features were recorded in each case from pathology reports and photographs of the gross specimens. Pathologic evaluation consisted of reassessing all original histologic material by at least 3 dedicated pathologists (S.S., A.L.B., and I.T.) blinded to the clinical outcomes of the patients. Nuclear grade was determined according to the Fuhrman system, and tumor stage was assessed according to Table 1 Main Pathologic Features of Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma According to the 2004 World Health Organization Classification of Kidney Tumors 1 Gross features Multilocular cystic appearance and encapsulated Yellowish solid component limited to small areas No expansive nodules Tumor necrosis absent Microscopic features Cysts lined by cuboidal clear cells or flattened epithelium Septa containing aggregates of epithelial cells with clear cytoplasm Low Fuhrman grade the 2002 revision of the TNM system. 33 Tumor size was measured according to the longest diameter. Radiologic and operative surgical information and pathology reports were used to assess the extent of disease. The end point of the study was disease-specific survival determined from the date of nephrectomy to the date of last follow-up. In addition to descriptive statistics, bivariate and multivariate analysis was undertaken using contingency table methods and tested for significance by using the Fisher exact test and χ 2 analysis. All statistical analysis was performed using SPSS for Windows software (SPSS, Chicago, IL). A P value of.05 or less was considered indicative of a statistically significant difference. All were 2-sided tests. Results Table 2 shows the clinical and pathologic variables of the 45 cases that met gross and microscopic criteria for MCRCC Image 1. 1 The mean age at diagnosis was 54.3 years (range, years). There were 28 men (62%) with a mean age of 56.3 years (range, years), and 17 (38%) women (mean age, 51.1 years; range, years); 50% of the patients were 52 years old or younger Figure 1. MCRCC occurred slightly more often in men than in women (1.7:1), and it was found incidentally during evaluation for an unrelated condition in 51% of the cases. All cases except 1 were unilateral at diagnosis, and in 22 patients (49%), the tumor was in the left kidney (P =.794). Two patients had multifocal tumors and 1 patient had bilateral MCRCC. Tumor size was similar in men and women (mean, 4.9 cm; range, 1-14 cm), but the tumors occurred at a somewhat earlier age in women (P =.385; Figure 1). In 25 patients (56%), the tumors were smaller than 4 cm (Figure 1). A total of 28 cases (women, 11 [65%]; men, 17 [61%]) were Fuhrman grade 1, and 17 (women, 6 [35%]; men, 11 [39%]) were Fuhrman grade 2 (P =.173). Of the tumors smaller than 4 cm, 68% were Fuhrman grade 1 (Figure 1; P =.911). Of the 45 patients, 24 (53%) had stage T1a, 13 (29%) had stage T1b, 7 (16%) had stage T2, and 1 (2%) had stage T3a disease (renal sinus fat involvement) (P =.186); smaller tumors ( 4 cm) were most likely Fuhrman grade 1 (P =.911). None of the patients had Fuhrman grade 3 or 4, stage T4, renal vein neoplastic thrombus, or metastatic disease at diagnosis; all cases were N0 M0. All patients were alive with no evidence of recurrent disease at a mean follow-up of 66.1 months (range, 1 month to 17.9 years; Figure 1). The Fuhrman grade and TNM stage were unrelated to clinical variables included in the analysis (tumor size, age at diagnosis, sex, side of tumor location, and TNM stage; P >.05). Table 2 shows a comparison of the main findings in our case series with those in other series reported in the literature. 218 Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125: Downloaded 218 from
3 Anatomic Pathology / ORIGINAL ARTICLE Table 2 Main Clinical and Pathologic Findings in Recent Series of MCRCC * Fuhrman Grade (%) Stage (%) Mean Right-Sided Incidental NED at Age Male Tumors Presentation Mean Follow- Study (y) (%) (%) (%) T1 T2 T3 Size (cm) up (%) Corica et al, (n = 24) Nassir et al, (n = 12) Murad et al, (n = 6) Brinker et al, (n = 7) Present study, 2005 (n = 45) MCRCC, multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma; NED, no evidence of disease. * None of the reported cases in these series had Fuhrman grade 4, stage T4, renal vein thrombus, or metastatic disease at diagnosis. Corica et al 3 and Nassir et al 5 included cases with less than 25% solid growth as their criteria for MCRCC; Murad et al 26 accepted cases with less than 10% solid growth. Brinker et al 30 and the present series followed more strict criteria as recommended by the 2004 World Health Organization classification of kidney tumors, accepting cases with no grossly visible expansive nodules (see the text). A B C D Image 1 (Case 32) A, Gross presentation in a case of multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma. B and C, Histologic examination revealed thin septa lined up by cuboidal clear cells (B) with small groups of cells forming solid areas in the septum (C) (B and C, H&E, 200). D, Tumor cells show low Fuhrman grade (H&E, 400). Downloaded from Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125:
4 Suzigan et al / MULTILOCULAR CYSTIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA A B No. of Cases No. of Cases C Men Women Age (y) <4 >4 to 7 >7 Tumor Size (cm) F1 F2 No. of Cases Follow-up (y) Figure 1 Age vs sex (A), follow-up (B), and Fuhrman grade vs tumor size (C) in 45 cases of multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma. Discussion MCRCC is considered a distinct subtype of clear cell RCC in the 2004 WHO classification based on the characteristic gross and microscopic features. 1 No tumor with these features has ever recurred or metastasized. 1,13 Therefore, the use of these somewhat more restrictive criteria should be adopted in daily practice. Low Fuhrman grade and stage are characteristic features of MCRCC, with only rare cases considered to be stage T3, 3 as seen in our series including 1 stage T3 case and other reported series such that by Corica et al 3 that included 12.5% of cases in stage T3. In their series, 92% of patients had no evidence of disease at a mean follow-up of 77.6 months (Table 2), in contrast with our series, in which 100% of patients were alive without evidence of disease at a mean follow-up of 66.1 months. This minor finding of aggressiveness in the report by Corica et al 3 might be related to the criteria for accepting cases in their study because cases of MCRCC with up to 25% solid nodules were included. This criterion was modified in the 2004 WHO classification, and solid expansive nodules are no longer accepted for the diagnosis of MCRCC. 1 In fact, a recent series of 12 cases of MCRCC by Nassir et al 5 showed patients with no evidence of disease at a mean follow-up of 42.5 months, confirming our results on the excellent prognosis of MCRCC with no solid component. A notable difference between MCRCC and conventional RCC is the absence of nodal or metastatic spread at diagnosis in MCRCC. 9,14,17,31 According to most authors, it seems that in general, crcc has a better outcome than noncystic conventional RCC. 15,31 Evidence supporting this includes that crcc in general is of low Fuhrman grade and stage at diagnosis and the mean tumor size is less than 5 cm, compared with 7.4 cm in the recent study by Han et al. 31 Because at diagnosis crccs tend to be smaller tumors and have a lower T stage and nuclear grade, these lesions may be more amenable to nephron-sparing surgery. 2,31 This seems to be particularly agreeable in MCRCC, which seems to be the end of the spectrum of crccs composed exclusively of cysts and showing an excellent outcome. In these cases, the clear cell component is limited to small aggregates within the septa. All cases in our series and most reported cases of MCRCC were N0 M0 at diagnosis, further suggesting a tumor of low malignant potential. 1-7,17,31 A number of reasons might help explain the improved outcome for predominantly crcc: (1) Compared with solid RCC these MCRCCs contain fewer malignant cells, which seem to be proliferating at a slower rate, as shown in our cases by the observed very low mitotic rate. (2) The majority of these tumors are Fuhrman grade 1 or 2, a finding that carries a better prognosis by itself. To our knowledge, our study reports the largest series of MCRCCs in the English literature that incorporated the recent 2004 WHO diagnostic criteria. 220 Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125: Downloaded 220 from
5 Anatomic Pathology / ORIGINAL ARTICLE Although somewhat limited by the relatively small number of patients and short follow-up, it allows confirmation that the 5- year disease-related survival is excellent for patients with MCRCC. Our results indicate that MCRCC is an important subtype of crcc that can be cured by surgical resection. 1 Of our patients, 100% had no evidence of disease at a mean of about 66.1 months after surgery. Patient outcome was not affected adversely by large tumor size or advanced stage that was observed occasionally in our cases. Thus, patients with MCRCC might benefit from nephron-sparing surgery. Owing to the limited available follow-up in our series and in other reported series, it remains to be proven whether the excellent 5- year outcome observed in MCRCC persists in a longer followup period. It is our belief that MCRCC should be renamed and reclassified to indicate the most probably benign nature of this tumor. Multilocular cystic renal cell neoplasm of low malignant potential seems to be an appropriate term for this lesion. From the 1 Laborclin Laboratory, São José do Rio Prêto, Brazil; 2 Unit of Anatomic Pathology, Cordoba University Medical School and Reina Sofia University Hospital, Cordoba, Spain; 3 Institute of Pathological Anatomy and Histopathology, Polytechnic University of the Marche Region, Ancona, Italy; 4 Pathology Service, Sor María Ludovica Children s Hospital, La Plata, Argentina; 5 Department of Pathology, Nagasaki University Hospital, Nagasaki, Japan; 6 Lins Laboratory of Histopathology and Cytopathology, Lins, Brazil; 7 Anápolis Center for Anatomic Pathology and Cytopathology, Anápolis, Brazil; 8 Pathology Service, Val d Hebron University Hospital, Barcelona, Spain; 9 Department of Pathology, Unicamp, Campinas, Brazil; 10 Department of Pathology, Sarah Hospital, Brasília, Brazil; 11 Department of Pathology, San Luigi Gonzaga Hospital, Turin, Italy; 12 Department of Pathology, Puigvert Foundation and Department of Morphology, Autonomous University, Barcelona, Spain; and 13 Urology Service, Reina Sofia University Hospital, Cordoba, Spain. Supported by grant FIS 03/0952 from the Ministry of Health, Madrid, Spain. Presented in part at the Sixth Latin American Virtual Congress of Anatomic Pathology, Burgos, Spain, March 1, Address correspondence to Dr López-Beltrán: Unit of Anatomical Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Avda. Menendez Pidal s/n, E-14004, Cordoba. Spain. None of the 45 cases of MCRCC reported in this article have been published in the English literature. References 1. Eble JN. Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma. In: Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, et al, eds. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs. Lyon, France: IARC Press; World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. 2. Bloom TL, Gray-Sears CL, Williams TR, et al. Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma with osseous metaplasia in a 25- year-old woman. Urology. 2003;61: Corica FA, Iczkowski KA, Cheng L, et al. Cystic renal cell carcinoma is cured by resection: a study of 24 cases with longterm followup. J Urol. 1999;161: Murphy WM, Grignon DJ, Perlman EJ. Tumors of the Kidney, Bladder, and Related Urinary Structures. Washington, DC: American Registry of Pathology; 2004: AFIP Atlas of Tumor Pathology; Fourth Series, Fascicle Nassir A, Jollimore J, Gupta R, et al. Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma: a series of 12 cases and review of the literature. Urology. 2002;60: Bielsa O, Lloreta J, Gelabert-Mas A. Cystic renal cell carcinoma: pathological features, survival and implications for treatment. J Urol. 1998;82: Koga S, Nishikido M, Hayashy T, et al. Outcome of surgery in cystic renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 2000;56: Eble JN, Bonsib SM. Extensively cystic renal neoplasms: cystic nephroma, cystic partially differentiated nephroblastoma, multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma and cystic hamartoma of renal pelvis. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1998;15: Truong LD, Choi YJ, Shen SS, et al. Renal cystic neoplasms and renal neoplasms associated with cystic renal disease: pathogenetic and molecular links. Adv Anat Pathol. 2003;10: Kim JC, Kim KH, Lee JW. CT and US findings of multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma. Korean J Radiol. 2000;1: Tosaka A, Yoshida K, Kobayashi N, et al. A report of two cases of multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma: review of 51 cases reported and the results of a prognostic survey [in Japanese]. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1992;38: Agrons GA, Wagner BJ, Davidson AJ, et al. Multilocular cystic renal tumor in children: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 1995;15: Lopez-Beltran A, Scarpelli M, Montironi R WHO classification of the renal tumours of the adults. Eur Urol. In press. 14. Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C. Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1982;6: Bostwick DG, Eble JN. Diagnosis and classification of renal cell carcinoma. Urol Clin North Am. 1999;26: Suzigan S, Müller MEA, Lima WS, et al. Brazilian primary renal tumors: clinical and pathological review of 137 cases with emphasis on renal cortical epithelial neoplasms. Available at 2001; COMUNICACION-E/002/index.htm. Accessed March 1, Sakurai M, Sugimura Y, Satani H, et al. Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma: a report of two cases [in Japanese]. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1993;39: Desligneres S. Clear cell unilocular and multilocular cystic renal tumors and in situ clear cell intratubular carcinoma. J Urol. 1993;99: Geller E, Smergel EM, Lowry PA. Renal neoplasms of childhood. Radiol Clin North Am. 1997;35: Castillo OA, Boyle ET Jr, Kramer SA. Multilocular cysts of kidney: a study of 29 patients and review of literature. Urology. 1991;37: Levy P, Helenon O, Merran S, et al. Cystic tumors of the kidney in adults: radio-histopathologic correlations. J Radiol. 1999;80: Taxy JB, Fray F, Marshall FF. Multilocular renal cysts in adults: possible relationship to renal adenocarcinoma. Arch Path Lab Med. 1983;107: Downloaded from Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125:
6 Suzigan et al / MULTILOCULAR CYSTIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 23. Takeuchi T, Tanaka T, Tokuyama H, et al. Multilocular cystic renal adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature. J Surg Oncol. 1984;25: Laperriere J, Filion R, Houde M, et al. Renal cell carcinoma presenting as multilocular cystic mass. Urology. 1986;28: Sherman ME, Silverman ML, Balogh K, et al. Multilocular renal cyst: a hamartoma with potential for neoplastic transformation? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987;111: Murad T, Komaiko W, Oyasu R, et al. Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1991;95: Koga S, Yamasaki A, Nishikido M, et al. Multiloculated renal cell carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol. 1991;23: Yamamoto H, Maruyama T, Kuwae H, et al. Bilateral multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma: a case report [in Japanese]. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1996;42: Ooi GC, Sagar G, Lynch D, et al. Cystic renal cell carcinoma: radiological features and clinico-pathological correlation. Clin Radiol. 1996;51: Brinker DA, Amin MB, De Peralta-Venturina M, et al. Extensively necrotic cystic renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24: Han K, Janzen NK, McWhorter VC, et al. Cystic renal cell carcinoma: biology and clinical behavior. Urol Oncol. 2004;22: Grignon DJ, Bismar TA, Bianco F, et al. VHL gene mutations in multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma: evidence in support of its classification as a type of clear cell renal cell carcinoma [abstract]. Mod Pathol. 2004;17(suppl 1):154A. 33. Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, et al (American Joint Committee on Cancer). AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 6th ed. New York, NY: Springer; Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125: Downloaded 222 from
MULTILOCULAR CYSTIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA
 MULTILOCULAR CYSTIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Khalaf M. Al-Jader, MD* ABSTRACT Objective: Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma appears to be uncommon subtype of renal cell carcinoma with characteristic
MULTILOCULAR CYSTIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Khalaf M. Al-Jader, MD* ABSTRACT Objective: Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma appears to be uncommon subtype of renal cell carcinoma with characteristic
CT and US Findings of Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma
 CT and US Findings of Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma Jong Chul Kim, MD 1 Kie Hwan Kim, MD 2 Jun Woo Lee, MD 3 Index words: Kidney neoplasms, CT Kidney neoplasms, US Korean J Radiol 2000;1:104-109
CT and US Findings of Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma Jong Chul Kim, MD 1 Kie Hwan Kim, MD 2 Jun Woo Lee, MD 3 Index words: Kidney neoplasms, CT Kidney neoplasms, US Korean J Radiol 2000;1:104-109
CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. CYSTIC NEPHROMA
 Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association
 218 Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association Min Su Cheong a Dong Hun Koo a In-Sung Kim a Kyung Chul Moon b Ja Hyeon Ku a
218 Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association Min Su Cheong a Dong Hun Koo a In-Sung Kim a Kyung Chul Moon b Ja Hyeon Ku a
The diagnostic criteria of multilocular renal cysts
 Case Report 772 Multilocular Renal Cysts with Renal Cell Carcinoma: Report of Four Cases Chia-Hsi Chen, MD; Cheng-Keng Chuang, MD, PhD; Chun-Te Wu, MD; Kwai-Fong Ng 1, MD; Shuen-Kuei Liao 2, PhD According
Case Report 772 Multilocular Renal Cysts with Renal Cell Carcinoma: Report of Four Cases Chia-Hsi Chen, MD; Cheng-Keng Chuang, MD, PhD; Chun-Te Wu, MD; Kwai-Fong Ng 1, MD; Shuen-Kuei Liao 2, PhD According
CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (135)
 Medical Education Singapore Med J 2011; 52(5) : 384 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (135) Pojchamarnwiputh S, Muttarak M, Sriplakich S H 1a 1b 1c 1d Fig. 1 (a) Axial unenhanced; (b & c) delayed
Medical Education Singapore Med J 2011; 52(5) : 384 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (135) Pojchamarnwiputh S, Muttarak M, Sriplakich S H 1a 1b 1c 1d Fig. 1 (a) Axial unenhanced; (b & c) delayed
Spectrum of Incidental Renal Masses Detected at Autopsy
 9bhoc02 4th proof Spectrum of Incidental Renal Masses Detected at Autopsy Vinaya B Shah*, Madhavi S Deokar** Abstract The incidence of benign renal tumours is less, especially when compared to renal cell
9bhoc02 4th proof Spectrum of Incidental Renal Masses Detected at Autopsy Vinaya B Shah*, Madhavi S Deokar** Abstract The incidence of benign renal tumours is less, especially when compared to renal cell
Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma, Multilocular or Cystic Necrosis
 J Med Sci 004;4(5):63-70 http://jms.ndmctsgh.edu.tw/40563.pdf Copyright 004 JMS Shih-Ming Ou, et al. Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma, Multilocular or Cystic Necrosis Shih-Ming Ou, Shang-Sen Lee, En Meng, Jong-Shiaw
J Med Sci 004;4(5):63-70 http://jms.ndmctsgh.edu.tw/40563.pdf Copyright 004 JMS Shih-Ming Ou, et al. Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma, Multilocular or Cystic Necrosis Shih-Ming Ou, Shang-Sen Lee, En Meng, Jong-Shiaw
Cystic renal cell carcinoma: a report of 67 cases including 4 cases with concurrent renal cell carcinoma
 Chen et al. BMC Urology 2014, 14:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cystic renal cell carcinoma: a report of 67 cases including 4 cases with concurrent renal cell carcinoma Shanwen Chen 1, Baiye Jin 1,3*,
Chen et al. BMC Urology 2014, 14:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cystic renal cell carcinoma: a report of 67 cases including 4 cases with concurrent renal cell carcinoma Shanwen Chen 1, Baiye Jin 1,3*,
BRAZILIAN PRIMARY RENAL TUMORS: CLINICAL AND PATHOLOGICAL REVIEW OF 137 CASES WITH EMPHASIS ON RENAL CORTICAL EPITHELIAL NEOPLASMS.
 IV CONGRESO VIRTUAL HISPANO AMERICANO DE ANATOMÍA PATOLÓGICA Abstract CONTENIDO PDF Comentarios Título Resumen Introducción Material Resultados Discusión Correspondencia Referencias Imágenes BRAZILIAN
IV CONGRESO VIRTUAL HISPANO AMERICANO DE ANATOMÍA PATOLÓGICA Abstract CONTENIDO PDF Comentarios Título Resumen Introducción Material Resultados Discusión Correspondencia Referencias Imágenes BRAZILIAN
I mportant prognostic factors in renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
 39 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic relevance of extensive necrosis in renal cell carcinoma V Foria, T Surendra, D N Poller... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr D N Poller,
39 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic relevance of extensive necrosis in renal cell carcinoma V Foria, T Surendra, D N Poller... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr D N Poller,
Cystic Renal Cell Carcinomas: Do They Grow, Metastasize, or Recur?
 Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Jhaveri et al. Growth Patterns of Cystic Renal Cell Carcinomas Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Kartik Jhaveri 1 Priya Gupta 1 Azadeh Elmi 2 Lior Flor 1 Hadas
Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Jhaveri et al. Growth Patterns of Cystic Renal Cell Carcinomas Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Kartik Jhaveri 1 Priya Gupta 1 Azadeh Elmi 2 Lior Flor 1 Hadas
Diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumor biopsy May 10 th 2018
 Diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumor biopsy May 10 th 2018 Dr. Tzahi Neuman Dep.Of Pathology Hadassah Medical Center Jerusalem, Israel, (tneuman@hadassah.org.il) Disclosure: 1 no conflicts of
Diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumor biopsy May 10 th 2018 Dr. Tzahi Neuman Dep.Of Pathology Hadassah Medical Center Jerusalem, Israel, (tneuman@hadassah.org.il) Disclosure: 1 no conflicts of
Various hereditary, acquired and neoplastic conditions can lead to cyst formation in the kidney.
 Dr. Fatima AlAl-Hashimi Hashimi,, MD, FRCPath Salmaniya Medical Complex, Bahrain Various hereditary, acquired and neoplastic conditions can lead to cyst formation in the kidney. The most frequently encountered
Dr. Fatima AlAl-Hashimi Hashimi,, MD, FRCPath Salmaniya Medical Complex, Bahrain Various hereditary, acquired and neoplastic conditions can lead to cyst formation in the kidney. The most frequently encountered
2004 World Health Organization Classification of the Noninvasive Urothelial Neoplasms: Inherent Problems and Clinical Reflections
 european urology supplements 8 (2009) 453 457 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com 2004 World Health Organization Classification of the Noninvasive Urothelial Neoplasms:
european urology supplements 8 (2009) 453 457 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com 2004 World Health Organization Classification of the Noninvasive Urothelial Neoplasms:
Bilateral Renal Angiomyolipomas with Invasion of the Renal Vein: A Case Report
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2008) 8, 145 148 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2008.29 Bilateral Renal Angiomyolipomas with Invasion of the Renal Vein: A Case Report C. Blick, N. Ravindranath,
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2008) 8, 145 148 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2008.29 Bilateral Renal Angiomyolipomas with Invasion of the Renal Vein: A Case Report C. Blick, N. Ravindranath,
Are Prostate Carcinoma Clinical Stages T1c and T2 Similar?
 Clinical Urology Are Clinical Stages T1c and T2 Similar? International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (2): 165-171, March - April, 2006 Are Prostate Carcinoma Clinical Stages T1c and T2 Similar? Athanase Billis,
Clinical Urology Are Clinical Stages T1c and T2 Similar? International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (2): 165-171, March - April, 2006 Are Prostate Carcinoma Clinical Stages T1c and T2 Similar? Athanase Billis,
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Original Article Clinicopathologic Features of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Young Adults: A Comparison Study with Renal Cell Carcinoma in Older Patients
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol (29) 2, 489-493 www.ijcep.com/ijcep8122 Original Article Clinicopathologic Features of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Young Adults: A Comparison Study with Renal Cell Carcinoma in Older
Int J Clin Exp Pathol (29) 2, 489-493 www.ijcep.com/ijcep8122 Original Article Clinicopathologic Features of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Young Adults: A Comparison Study with Renal Cell Carcinoma in Older
Ben Xu 1, Yue Mi 1, Li-qun Zhou 1, Jie Jin 1, Qian Zhang 1* and Guang-fu Chen 2* WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY
 Xu et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2014, 12:111 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma: a potential
Xu et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2014, 12:111 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma: a potential
American Journals of Cancer Case Reports. A Rare Case of Rectal Metastasis from Sarcomatoid Variant of Urothelial Carcinoma: A Case Report
 American Journals of Cancer Case Reports Lin JYJ et al. American Journals of Cancer Case Reports 2014, 3:1-5 http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajccr Page 1 of 5 Vol 3 Article ID 20140539, 5 pages Case Report
American Journals of Cancer Case Reports Lin JYJ et al. American Journals of Cancer Case Reports 2014, 3:1-5 http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajccr Page 1 of 5 Vol 3 Article ID 20140539, 5 pages Case Report
NAACCR Webinar Series 1
 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data: Kidney 1 Questions Please use the Q&A panel to submit your questions Send questions to All Panelist 2 Fabulous Prizes 3 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar
NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data: Kidney 1 Questions Please use the Q&A panel to submit your questions Send questions to All Panelist 2 Fabulous Prizes 3 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar
Comparison of prognosis between patients with renal cell carcinoma on hemodialysis and those with renal cell carcinoma in the general population
 DOI 10.1007/s10147-015-0812-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of prognosis between patients with renal cell carcinoma on hemodialysis and those with renal cell carcinoma in the general population Yasunobu
DOI 10.1007/s10147-015-0812-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of prognosis between patients with renal cell carcinoma on hemodialysis and those with renal cell carcinoma in the general population Yasunobu
Case 4: 7- year- old boy. [Chief complaint] Gross Hematuria
![Case 4: 7- year- old boy. [Chief complaint] Gross Hematuria Case 4: 7- year- old boy. [Chief complaint] Gross Hematuria](/thumbs/89/98875170.jpg) Case 4: 7- year- old boy [Chief complaint] Gross Hematuria [History of present illness] He visited an urological clinic because of gross hematuria from one day before the consulta?on. A renal tumor with
Case 4: 7- year- old boy [Chief complaint] Gross Hematuria [History of present illness] He visited an urological clinic because of gross hematuria from one day before the consulta?on. A renal tumor with
Tumor necrosis is a strong predictor for recurrence in patients with pathological T1a renal cell carcinoma
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 125-130, 2015 Tumor necrosis is a strong predictor for recurrence in patients with pathological T1a renal cell carcinoma KEIICHI ITO 1, KENJI SEGUCHI 1, HIDEYUKI SHIMAZAKI 2, EIJI TAKAHASHI
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 125-130, 2015 Tumor necrosis is a strong predictor for recurrence in patients with pathological T1a renal cell carcinoma KEIICHI ITO 1, KENJI SEGUCHI 1, HIDEYUKI SHIMAZAKI 2, EIJI TAKAHASHI
Various kinds of cystic tumor or tumor-like lesions in the kidney :radiologic-pathologic correlation.
 Various kinds of cystic tumor or tumor-like lesions in the kidney :radiologic-pathologic correlation. Poster No.: C-0299 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S.-J. Lee, J.-H. Yoon, Y.
Various kinds of cystic tumor or tumor-like lesions in the kidney :radiologic-pathologic correlation. Poster No.: C-0299 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S.-J. Lee, J.-H. Yoon, Y.
Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult. by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department
 Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department Various hereditary, acquired, and neoplastic conditions can
Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department Various hereditary, acquired, and neoplastic conditions can
Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma of Different Histological Subtypes in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 382-386 CASE REPORT Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma of Different Histological Subtypes in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Ki Yong Na Hyun-Soo Kim
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 382-386 CASE REPORT Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma of Different Histological Subtypes in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Ki Yong Na Hyun-Soo Kim
Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT
 Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT during follow- up. ALT, AST, Alk Phos and bilirubin were
Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT during follow- up. ALT, AST, Alk Phos and bilirubin were
Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions
 Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE. Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT
 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE AUTHORS : PROSTATE CHAPTER
2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE AUTHORS : PROSTATE CHAPTER
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 02 Page February 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i2.08 Pattern of Renal Tumors: A Tertiary
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i2.08 Pattern of Renal Tumors: A Tertiary
Disclosure. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None. Off Label Usage None MFMER slide-1
 Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency
 Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency World Health Organization Available in Feb 2016 Frame work for reporting Major contributing
Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency World Health Organization Available in Feb 2016 Frame work for reporting Major contributing
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Comparison of Imaging and Pathologic Findings
 Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Hindman et al. Multilocular ystic Renal ell arcinoma Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Nicole M. Hindman 1 Morton. osniak 1 ndrew. Rosenkrantz 1 Stephanie
Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Hindman et al. Multilocular ystic Renal ell arcinoma Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Nicole M. Hindman 1 Morton. osniak 1 ndrew. Rosenkrantz 1 Stephanie
Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1991, 36
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Large Periureteral Lipoma Associa Hydronephrosis. Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Imamura, Atushi Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Large Periureteral Lipoma Associa Hydronephrosis. Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Imamura, Atushi Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
Microcystic transitional cell carcinoma: a rare tumor of the urinary bladder
 PATHOLOGICA 2017;109:151-155 Case report Microcystic transitional cell carcinoma: a rare tumor of the urinary bladder M. TRIKI 1, L. AYADI 1, R. KALLEL 1, S. CHARFI 1, I. SAGUEM 1, N. MHIRI 2, T.S. BOUDAWARA
PATHOLOGICA 2017;109:151-155 Case report Microcystic transitional cell carcinoma: a rare tumor of the urinary bladder M. TRIKI 1, L. AYADI 1, R. KALLEL 1, S. CHARFI 1, I. SAGUEM 1, N. MHIRI 2, T.S. BOUDAWARA
Case 1. Clinical history
 Case 1 Case 1 Clinical history 17-month-old boy with a kidney tumor found during routine childhood care program. CT scan showed a solid mass. Chemotherapy was given for 4 weeks using actinomycin D and
Case 1 Case 1 Clinical history 17-month-old boy with a kidney tumor found during routine childhood care program. CT scan showed a solid mass. Chemotherapy was given for 4 weeks using actinomycin D and
6/5/2010. Renal vein invasion & Capsule Penetration (T3a) Adrenal Gland involvement (T4 vs. M1) Beyond Gerota s Fascia? (?T4).
 GU Cancer Staging: Updates and Challenging Areas 13 th Current Issues in Surgical Pathology San Francisco, CA June 5, 2010 Jeffry P. Simko, PhD, MD Associate Professor Departments of Urology and Anatomic
GU Cancer Staging: Updates and Challenging Areas 13 th Current Issues in Surgical Pathology San Francisco, CA June 5, 2010 Jeffry P. Simko, PhD, MD Associate Professor Departments of Urology and Anatomic
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017
 Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
Renal Mass Biopsy: Needed Now More than Ever
 Renal Mass Biopsy: Needed Now More than Ever Stuart G. Silverman, MD, FACR Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director, Abdominal Imaging and Intervention Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston,
Renal Mass Biopsy: Needed Now More than Ever Stuart G. Silverman, MD, FACR Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director, Abdominal Imaging and Intervention Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston,
Renal masses - the role of diagnostic imaging
 Renal masses - the role of diagnostic imaging Poster No.: C-2471 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Rai#; Bjelovar/HR Keywords: Cysts, Cancer, Structured reporting, Ultrasound, MR,
Renal masses - the role of diagnostic imaging Poster No.: C-2471 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Rai#; Bjelovar/HR Keywords: Cysts, Cancer, Structured reporting, Ultrasound, MR,
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer
 Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Characteristic Enhancement Patterns of Renal Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma: a case report and literature review
 J Radiol Sci 2015; 40: 51-56 Characteristic Enhancement Patterns of Renal Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma: a case report and literature review I-Chang LIn 1 nan-han Lu 1 KaI-Jen LIn 2 VICtor C. LIn 3 Department
J Radiol Sci 2015; 40: 51-56 Characteristic Enhancement Patterns of Renal Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma: a case report and literature review I-Chang LIn 1 nan-han Lu 1 KaI-Jen LIn 2 VICtor C. LIn 3 Department
Guidelines on Renal Cell
 Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma (Text update March 2009) B. Ljungberg (Chairman), D.C. Hanbury, M.A. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, P.F.A. Mulders, J-J. Patard, I.C. Sinescu Introduction Renal cell carcinoma
Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma (Text update March 2009) B. Ljungberg (Chairman), D.C. Hanbury, M.A. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, P.F.A. Mulders, J-J. Patard, I.C. Sinescu Introduction Renal cell carcinoma
Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL
 Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL Overview Principles Individual organs Small pieces Partial resections Whole organs Data recording and data sets Principles You are working for the patient
Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL Overview Principles Individual organs Small pieces Partial resections Whole organs Data recording and data sets Principles You are working for the patient
Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Prognostic Relevance of the Histological Subtype of Renal Cell Carcinoma
 Clinical Urology Prognostic Relevance of the Histological Subtype of RCC International Braz J Urol Vol. 34(1): 3-8, January - February, 2008 Prognostic Relevance of the Histological Subtype of Renal Cell
Clinical Urology Prognostic Relevance of the Histological Subtype of RCC International Braz J Urol Vol. 34(1): 3-8, January - February, 2008 Prognostic Relevance of the Histological Subtype of Renal Cell
Update on 2015 WHO Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma 1/3/ Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. All rights reserved.
 1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
Division of Oncology, S Orsola-Malpighi Hospital, Bologna, Italy. Department of Surgery, Cordoba University Medical School, Cordoba, Spain
 Prostate cancer glands with cribriform architecture and with glomeruloid features should be considered as Gleason pattern 4 and not pattern 3 Daniele Minardi,1, Roberta Mazzucchelli,, Marina Scarpelli,
Prostate cancer glands with cribriform architecture and with glomeruloid features should be considered as Gleason pattern 4 and not pattern 3 Daniele Minardi,1, Roberta Mazzucchelli,, Marina Scarpelli,
RCC in ADPKD / CKD / ESRD
 RCC in ADPKD / CKD / ESRD FOIU 2018 David A. Goldfarb, MD,FACS Professor of Surgery, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio
RCC in ADPKD / CKD / ESRD FOIU 2018 David A. Goldfarb, MD,FACS Professor of Surgery, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio
2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
PITFALLS AND TRAPS IN THE DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING OF RENAL TUMOURS OF CHILDHOOD. Gordan M. Vujanić Cardiff, U.K.
 PITFALLS AND TRAPS IN THE DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING OF RENAL TUMOURS OF CHILDHOOD Gordan M. Vujanić Cardiff, U.K. RENAL TUMOURS OF CHILDHOOD - CLASSIFICATION (2016) Nephroblastic tumours Mesenchymal tumours
PITFALLS AND TRAPS IN THE DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING OF RENAL TUMOURS OF CHILDHOOD Gordan M. Vujanić Cardiff, U.K. RENAL TUMOURS OF CHILDHOOD - CLASSIFICATION (2016) Nephroblastic tumours Mesenchymal tumours
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman
 the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
Citation American Journal of Surgery, 196(5)
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Multifocal branch-duct pancreatic i neoplasms Tajima, Yoshitsugu; Kuroki, Tamotsu Amane; Adachi, Tomohiko; Mishima, T Kanematsu, Takashi Citation American
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Multifocal branch-duct pancreatic i neoplasms Tajima, Yoshitsugu; Kuroki, Tamotsu Amane; Adachi, Tomohiko; Mishima, T Kanematsu, Takashi Citation American
DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES
 DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON Case 1 43 year-old female,
DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON Case 1 43 year-old female,
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sun, 25 Nov 2018 12:22:24 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 06/07/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sun, 25 Nov 2018 12:22:24 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 06/07/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 18 CBULP 2011 041 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 18 CBULP 2011 041 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma: A case report and literature review
 Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma: A case report and literature review Michael Reiter 1*, Ryan Schwope 1, Arthur Clarkson 2 1. Department of Radiology, Brooke Army Medical Center, San Antonio USA 2. Department
Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma: A case report and literature review Michael Reiter 1*, Ryan Schwope 1, Arthur Clarkson 2 1. Department of Radiology, Brooke Army Medical Center, San Antonio USA 2. Department
Clinical analysis of 29 cases of nasal mucosal malignant melanoma
 1166 Clinical analysis of 29 cases of nasal mucosal malignant melanoma HUANXIN YU and GANG LIU Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Tianjin Huanhu Hospital, Tianjin 300060, P.R. China
1166 Clinical analysis of 29 cases of nasal mucosal malignant melanoma HUANXIN YU and GANG LIU Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Tianjin Huanhu Hospital, Tianjin 300060, P.R. China
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CARCINOMA
 GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CARCINOMA B. Ljungberg (chairman), D.C. Hanbury, M.A. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, P.F.A. Mulders, J-J. Patard, I.C. Sinescu Introduction This EAU guideline was prepared to help urologists
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CARCINOMA B. Ljungberg (chairman), D.C. Hanbury, M.A. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, P.F.A. Mulders, J-J. Patard, I.C. Sinescu Introduction This EAU guideline was prepared to help urologists
Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology
 PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology No Conflict of Interest Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona F.Algaba Section of Pathology PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology
PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology No Conflict of Interest Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona F.Algaba Section of Pathology PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology
Prognostic factors in localized renal cell cancer
 Original Article PROGNOSTIC FACTORS IN LOCALIZED RENAL CELL CANCER KNIGHT and STADLER Prognostic factors in localized renal cell cancer David A. Knight and Walter M. Stadler Section of Hematology/Oncology,
Original Article PROGNOSTIC FACTORS IN LOCALIZED RENAL CELL CANCER KNIGHT and STADLER Prognostic factors in localized renal cell cancer David A. Knight and Walter M. Stadler Section of Hematology/Oncology,
3/23/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Pathologic Staging Updates in Lung Cancer T STAGE OUTLINE SURVIVAL ACCORDING TO SIZE ONLY
 Pathologic Staging Updates in Lung Cancer Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content of CME
Pathologic Staging Updates in Lung Cancer Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content of CME
Renal tumours: use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology. Dr Lisa Browning John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford
 Renal tumours: use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Dr Lisa Browning John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford Renal tumours: the use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Classification of RCC
Renal tumours: use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Dr Lisa Browning John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford Renal tumours: the use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Classification of RCC
Renal Parenchymal Neoplasms
 Renal Parenchymal Neoplasms د. BENIGN TUMORS : Benign renal tumors include adenoma, oncocytoma, angiomyolipoma, leiomyoma, lipoma, hemangioma, and juxtaglomerular tumors. Renal Adenomas : The adenoma is
Renal Parenchymal Neoplasms د. BENIGN TUMORS : Benign renal tumors include adenoma, oncocytoma, angiomyolipoma, leiomyoma, lipoma, hemangioma, and juxtaglomerular tumors. Renal Adenomas : The adenoma is
Malignant transformation in benign cystic teratomas, dermoids of the ovary
 European JournalofObstetrics& Gynecology andreproductivebiology, 29 (1988) 197-206 197 Elsevier EJO 00716 Malignant transformation in benign cystic teratomas, dermoids of the ovary S. Chadha 1 and A. Schaberg
European JournalofObstetrics& Gynecology andreproductivebiology, 29 (1988) 197-206 197 Elsevier EJO 00716 Malignant transformation in benign cystic teratomas, dermoids of the ovary S. Chadha 1 and A. Schaberg
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer
 Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Is renal cryoablation becoming an effective alternative to partial nephrectomy?
 Is renal cryoablation becoming an effective alternative to partial nephrectomy? J GARNON 1, G TSOUMAKIDOU 1, H LANG 2, A GANGI 1 1 department of interventional radiology 2 department of urology University
Is renal cryoablation becoming an effective alternative to partial nephrectomy? J GARNON 1, G TSOUMAKIDOU 1, H LANG 2, A GANGI 1 1 department of interventional radiology 2 department of urology University
Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder
 Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder Overview of kidney tumors Benign and malignant Of the benign: papillary adenoma -cortical -small (0.5cm) -in 40% of population -clinically insignificant The most common
Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder Overview of kidney tumors Benign and malignant Of the benign: papillary adenoma -cortical -small (0.5cm) -in 40% of population -clinically insignificant The most common
GUIDELINES ON PROSTATE CANCER
 10 G. Aus (chairman), C. Abbou, M. Bolla, A. Heidenreich, H-P. Schmid, H. van Poppel, J. Wolff, F. Zattoni Eur Urol 2001;40:97-101 Introduction Cancer of the prostate is now recognized as one of the principal
10 G. Aus (chairman), C. Abbou, M. Bolla, A. Heidenreich, H-P. Schmid, H. van Poppel, J. Wolff, F. Zattoni Eur Urol 2001;40:97-101 Introduction Cancer of the prostate is now recognized as one of the principal
Renal tumors of adults
 Renal tumors of adults Urinary Tract Tumors 2%-3% of all cancers in adults. The most common malignant tumor of the kidney is renal cell carcinoma. Tumors of the lower urinary tract are twice as common
Renal tumors of adults Urinary Tract Tumors 2%-3% of all cancers in adults. The most common malignant tumor of the kidney is renal cell carcinoma. Tumors of the lower urinary tract are twice as common
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
Cystoscopy in children presenting with hematuria should not be overlooked
 Ped Urol Case Rep 2015; 2(3):7-11 DOI: 10.14534/PUCR.2015310303 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Cystoscopy
Ped Urol Case Rep 2015; 2(3):7-11 DOI: 10.14534/PUCR.2015310303 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Cystoscopy
Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma
 49 Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma Loredana Miglietta a Maria Angela Parodi b Luciano Canobbio b Luca Anselmi c a Medical
49 Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma Loredana Miglietta a Maria Angela Parodi b Luciano Canobbio b Luca Anselmi c a Medical
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CANCER
 20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS
 Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS SUBATHRA K* Department of pathology,
Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS SUBATHRA K* Department of pathology,
Surgically Discovered Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Invading Inferior Vena Cava with Coexisting Renal Cell Carcinoma
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 5 9 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.6 Surgically Discovered Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Invading Inferior Vena Cava with Coexisting
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 5 9 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.6 Surgically Discovered Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Invading Inferior Vena Cava with Coexisting
Carcinoma of the Renal Pelvis and Ureter Histopathology
 Carcinoma of the Renal Pelvis and Ureter Histopathology Reporting Proforma (NEPHROURETERECTOMY AND URETERECTOMY) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family
Carcinoma of the Renal Pelvis and Ureter Histopathology Reporting Proforma (NEPHROURETERECTOMY AND URETERECTOMY) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family
Original Article APMC-276
 Original Article APMC-276 The Clinical Value of Immediate Second Transurethral Resection in Patients with High Grade Non-Muscle Inasive Bladder Cancer (HG-NMIBC) Syed Saleem Abbas Jafri, Zafar Iqbal Khan
Original Article APMC-276 The Clinical Value of Immediate Second Transurethral Resection in Patients with High Grade Non-Muscle Inasive Bladder Cancer (HG-NMIBC) Syed Saleem Abbas Jafri, Zafar Iqbal Khan
Multifocal Lung Cancer
 Multifocal Lung Cancer P. De Leyn, MD, PhD Department of Thoracic Surgery University Hospitals Leuven Belgium LEUVEN LUNG CANCER GROUP Department of Thoracic Surgery Department of Pneumology Department
Multifocal Lung Cancer P. De Leyn, MD, PhD Department of Thoracic Surgery University Hospitals Leuven Belgium LEUVEN LUNG CANCER GROUP Department of Thoracic Surgery Department of Pneumology Department
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007
 International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
RENAL EPITHELIAL TUMORS 2009: THE ROLE OF ELECTRON MICROSCOPY IN UNDERSTANDING PATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS, AND CLASSIFICATION.
 RENAL EPITHELIAL TUMORS 2009: THE ROLE OF ELECTRON MICROSCOPY IN UNDERSTANDING PATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS, AND CLASSIFICATION. Guillermo A. Herrera MD Nephrocor, Tempe, Arizona Epithelial renal cell tumors
RENAL EPITHELIAL TUMORS 2009: THE ROLE OF ELECTRON MICROSCOPY IN UNDERSTANDING PATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS, AND CLASSIFICATION. Guillermo A. Herrera MD Nephrocor, Tempe, Arizona Epithelial renal cell tumors
1/25/13 Right partial nephrectomy followed by completion right radical nephrectomy.
 History and Physical Case Scenario 1 45 year old white male presents with complaints of nausea, weight loss, and back pain. A CT of the chest, abdomen and pelvis was done on 12/8/12 that revealed a 12
History and Physical Case Scenario 1 45 year old white male presents with complaints of nausea, weight loss, and back pain. A CT of the chest, abdomen and pelvis was done on 12/8/12 that revealed a 12
S1.04 PRINCIPAL CLINICIAN G1.01 COMMENTS S2.01 SPECIMEN LABELLED AS G2.01 *SPECIMEN DIMENSIONS (PROSTATE) S2.03 *SEMINAL VESICLES
 Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Although current American Cancer Society guidelines
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffuse Adenosis of the Peripheral Zone in Prostate Needle Biopsy and Prostatectomy Specimens Tamara L. Lotan, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract: We have observed a group of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffuse Adenosis of the Peripheral Zone in Prostate Needle Biopsy and Prostatectomy Specimens Tamara L. Lotan, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract: We have observed a group of
Baker Alabbadi MD*, Ali Alasmar MD*, Ayman Alqarallah MD*, Nizar Saaydah MD* ABSTRACT
 Renal Cell Carcinoma Clinical Presentation and Histopathological Findings: A Retrospective Analysis of a Jordanian Population at King Hussein Medical Center Baker Alabbadi MD*, Ali Alasmar MD*, Ayman Alqarallah
Renal Cell Carcinoma Clinical Presentation and Histopathological Findings: A Retrospective Analysis of a Jordanian Population at King Hussein Medical Center Baker Alabbadi MD*, Ali Alasmar MD*, Ayman Alqarallah
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 46/Sep 22, 2014 Page 11296
 CT SPECTRUM OF GIANT RETROPERITONEAL LIPOSARCOMAS WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION Shashikumar M. R 1, Rajendra Kumar N. L 2, C. P. Nanjaraj 3, Nishanth R. K 4, Vishwanath Joshi 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
CT SPECTRUM OF GIANT RETROPERITONEAL LIPOSARCOMAS WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION Shashikumar M. R 1, Rajendra Kumar N. L 2, C. P. Nanjaraj 3, Nishanth R. K 4, Vishwanath Joshi 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Comparison of Radiological Criteria (RECIST - MASS - SACT -Choi) in Antiangiogenic Therapy of Renal Cell Carcinoma
 Universal Journal of Public Health 4(5): 239-243, 2016 DOI: 10.13189/ujph.2016.040503 http://www.hrpub.org Comparison of Radiological Criteria (RECIST - MASS - SACT -Choi) in Antiangiogenic Therapy of
Universal Journal of Public Health 4(5): 239-243, 2016 DOI: 10.13189/ujph.2016.040503 http://www.hrpub.org Comparison of Radiological Criteria (RECIST - MASS - SACT -Choi) in Antiangiogenic Therapy of
Diagnosis and treatment of cystic renal cell carcinoma
 Zhang et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2013, 11:158 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of cystic renal cell carcinoma Jiexiu Zhang, Bianjiang Liu,
Zhang et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2013, 11:158 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of cystic renal cell carcinoma Jiexiu Zhang, Bianjiang Liu,
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a
 G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a Conventional adrenocortical neoplasm. Each of the below parameters is scored 0 when absent and 1 when present. 3 or more of these
G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a Conventional adrenocortical neoplasm. Each of the below parameters is scored 0 when absent and 1 when present. 3 or more of these
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Patient Selection for Ablative Therapies. Adrian D Joyce Leeds UK
 Patient Selection for Ablative Adrian D Joyce Leeds UK Therapy Renal Cell Ca USA: 30,000 new cases annually >12,000 deaths RCC accounts for 3% of all adult malignancy 40% of patients will die from their
Patient Selection for Ablative Adrian D Joyce Leeds UK Therapy Renal Cell Ca USA: 30,000 new cases annually >12,000 deaths RCC accounts for 3% of all adult malignancy 40% of patients will die from their
Chronic inflammation of long-standing duration has
 Inflammatory Atrophy of the Prostate Prevalence and Significance Athanase Billis, MD; Luis A. Magna, MD Context. Recently, prostatic atrophy associated with chronic inflammation has been linked to carcinoma
Inflammatory Atrophy of the Prostate Prevalence and Significance Athanase Billis, MD; Luis A. Magna, MD Context. Recently, prostatic atrophy associated with chronic inflammation has been linked to carcinoma
