Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio
|
|
|
- Andrew Hill
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio
2 Risk and Odds Risk is a probability as calculated from one outcome probability = ALL possible outcomes Odds is opposed to probability, and is calculated from one outcome Odds = all OTHER outcomes Both are measures of likelihood but differ in Denominator 0 Risk (or probability) 1 whereas 0 Odds
3 Calculation Examples The probability and the odds of flipping a coin and getting a head Outcome: H Other outcome: T All possible outcome: H, T probability = Odds = one outcome ALL possible outcomes = 1 2 = 0.5 one outcome all OTHER outcomes = 1 1 = 1: 1 The probability and the odds of flipping a coin twice and getting two heads Outcome: HH Other outcome: HT, TH, TT All possible outcome: HH, HT, TH, TT one outcome probability = = 1 = 0.25 ALL possible outcomes 4 one outcome Odds = = 1 = 1: 3 all OTHER outcomes 3
4 Another Example The probability and the odds of having 2 short-hair kittens in a litter with 5 kittens Outcome: 2 short-hair kittens (S S) Other outcome: 3 long-hair kittens (L L L) All possible outcome: S S L L L probability = Odds = one outcome ALL possible outcomes = 2 5 = 0.4 one outcome all OTHER outcomes = 2 3 = 2: The probability and the odds of having 4 short-hair kittens in a litter with 5 kittens Outcome: 4 short-hair kittens (S S S S) Other outcome: 1 long-hair kittens (L) All possible outcome: S S S S L one outcome probability = = 4 = 0.8 ALL possible outcomes 5 one outcome Odds = = 4 = 4: 1 = 4 all OTHER outcomes 1
5 Graphical Representations of Risk and Odds Risk = Odds =
6 Epidemiology Wiki definition: Epidemiology is the study and analysis about the distribution and determinants of health and diseases in defined population Many types of epidemiological studies Randomized control study Cohort study Case-control study
7 Epidemiological studies: Some assessments Experimental study or Observational study If a researcher assigns mixture of participants to groups (i.e. randomization), it s the experimental study If the researcher does not assign participants to any groups, but let participants characteristics determined which group they should fall in, it s an observational study Directionality Forward study the exposure is known, then follow up to see what outcomes occurred Backward study the outcomes are occurred, then exposure is determined Timing Prospective the study starts before the outcome occurred Retrospective the study starts after the outcomes occurred
8 Epidemiology Study Types: Cohort study An observational study; forward directionality; prospective timing, or can be a retrospective timing Conceptually, Start with a population of disease-free individuals Identify individuals that are exposed to a risk factor(s) and those that are NOT exposed to the same risk factor(s) then follow up both groups over time to find out the risk of specific outcomes (e.g. diseases) occurring in each individual Relative Risk is used to determined association between the exposure and the outcomes Hypotheses (tentative!!!) Ho: Proportions of the outcome in exposed and unexposed groups are equal H1: Proportions of the outcome in exposed and unexposed groups are not equal
9 Cohort study time Exposure e.g. smoking outcome e.g. lung cancer smoke not smoke Lung cancer No Lung cancer versus
10 Breast cancer and Hormone replacement therapy in the million-women study Outcome Exposure Breast cancer No breast cancer Used HRT ,936 Never used HRT ,863 Question: what is the risk of using HRT on breast cancer occurrence in women? Outcome Exposure Breast cancer No breast cancer Used HRT a b Never used HRT c d The Lancet 362:
11 Relative Risk (RR) and confident intervals Outcome Exposure Breast cancer No breast cancer Used HRT a b Relative Risk = Never used HRT c d a a + b c c + d limits = ln(rr) ±z b a a + b + d c c + d CI = e lower limit upper limit, e
12 Interpretation of RR If RR = 1 or CI includes 1, there is no risk for the outcome to the exposed group nor the unexposed group If RR is more than 1 and CI does not includes 1, the relative risk of the outcome in the exposed group was increased by 1 RR 100% relative to the unexposed group Or the risk of the outcome has RR times more likely to occur in the exposed group than in the unexposed group If RR is less than 1 and CI does not includes 1 in its range, the relation risk of the outcome in the exposed group was reduced by 1 RR 100% relative to the unexposed group
13 Breast cancer and Hormone replacement therapy in the million-women study Risk HRT = Risk No HRT = = = Outcome Exposure Breast cancer No breast cancer Used HRT ,936 Never used HRT ,863 Reletive Risk = Risk HRT = Risk No HRT = limit a = limit a = ln limit b = ln limit b = CI = e.5573, e.6120 CI = 1.746,1.958
14 Relative Risk (RR) and confident intervals Exposure Outcome Breast cancer No breast cancer Used HRT ,936 Never used HRT ,863 RR=1.824 with CI=(1.746,1.958) RR is significantly different from 1, reject Ho then accept H1 stating that proportions of breast cancer in both groups are not equal Interpretation: Relative risk of breast cancer in women who used HRT is increased by %=82.4% relative to women who did not use HRT. Or the risk of breast cancer is 1.8 times more likely to occur in women who used HRT than in the women who did not use HRT.
15 Exposure Cardiovascular diseases among users of estrogen with progestin as compared to nonusers Outcome Major coronary disease No disease Estrogen with progestin 8 27, Not Used , RR = Τ = with CI=(0.103,0.419) RR is significantly different from 1, reject Ho ten accept H1 stating that proportions of breast cancer in both groups are not equal Interpretation: Relative risk of major coronary disease is reduced by % = 79.2% in users of estrogen with progestin relative to users who has not used any hormone Or the risk of major coronary disease is 0.2 times less likely to occur in user who of estrogen with progestin than in users who do not use any hormone. Risk = = Adapted from NEJM 1996:
16 Epidemiology Study Types: Case-Control study An observational study; backward directionality; retrospective timing Conceptually, Start with the case, i.e. a group of individuals having the outcomes (e.g. disease), and the control, i.e. a group of individuals not having the outcomes, then look back in time in both groups to find out what exposure(s) in both case and control that lead to specific outcomes or diseases Odds ratio is used to determined association Hypotheses (tentative!!!) Ho: Proportions of the exposure in case and control are equal H1: Proportions of the exposure in case and control are not equal
17 Case-Control study time Exposure e.g. smoking outcome e.g. lung cancer Smoking Not smoking Lung cancer No Lung cancer versus
18 Hay fever and eczema in 11 years old children Eczema Hay fever Yes (case) No (control) Yes No Case is children with hay fever and control is children without hay fever. Exposure is the children has experienced eczema or not. What is the odds of children having hay fever will develop eczema compared to children without hay fever? Eczema Hay fever Yes (case) No (control) Yes a b BMJ May 27; 320(7247): No c d
19 Odds ratio (OR) and confident intervals Eczema Hey fever Yes (case) No (control) Yes a b No c d Odds Ratio = aτ c b d limits = ln(or) ±z 1 a + 1 b + 1 c + 1 d CI = e lower limit upper limit, e
20 Interpretation of OR If OR = 1 or CI includes 1, the odds are equal for the case group and the control group to experience the exposures If OR is more than 1 and CI does not includes 1, the odds of the exposure in the case group was higher relative to the control group If OR is less than 1 and CI does not includes 1, the odd of the exposure in the case group was lower relative to the control group Normally, there should be switched the case and the control (NOT shuffling data!) so that OR is greater than 1
21 Odds ratio (OR) and confident intervals Odds Ratio = = Hey fever Eczema Yes (case) No (control) Yes No limit a = ln(4.893) 1.96 limit b = ln(4.893) limit a = limit b = CI = e 1.386, e CI = 3.998,5.998
22 Hay fever and eczema in 11 years old children Eczema Hay fever Yes (case) No (control) Yes No OR = with CI=(3.998,5.998) OR is significantly different from 1, reject Ho then accept H1 stating that proportions of eczema developed in the case and the control are not equal Interpretation: children having hay fever has the odds of times to develop eczema compared to children without hay fever BMJ May 27; 320(7247): 1468.
23 Leukemia and parental smoking in pregnancy Leukemia Yes (case) No (control) Smoking Yes No Case is patients with leukemia and control is patients without leukemia. Exposure is whether or not there is parental smoking during pregnancy. What is the odd of patients with leukemia (the case) to have been exposed to parental smoking in pregnancy?
24 Leukemia and parental smoking in pregnancy Smoking Leukemia Yes (case) No (control) Yes No Odds = = OR = 0.433Τ = with CI=(1.096,2.042) OR is significantly different from 1, reject Ho then accept H1 stating that proportions of exposing to parental smoking in pregnancy in case and control are not equal Interpretation: In patients with leukemia (case group), the odds is times to have been exposed to parental smoking in pregnancy
25 Choosing a test [after a thought!] If you want to know whether or not the observation deviates from the theory choose the test for goodness of fit If you have only 2 outcomes, use binomial test; else, use 2 test If observations is less than 1000, you may find exact probability [you are using a computer, aren t you?]; else, asymptotic probability will suffice it However, you want to find association between 2 nominal variables, a) You may choose 2 test or Fisher s exact test for a test of independence if what you really want to know is whether one or more categories in variable A affect one or more categories in variable B; or b) You may choose 2 test for a test of homogeneity if you just want to know whether proportions of one category in variable A are equal in 2 or more groups (=variable B); or c) You may choose to find relative risk if you want to know causality of the outcome (=one of two categories in variable A) in 2 different exposed groups from the cohort study; or d) You may choose to find odds ratio if you want to know odds of the exposure (=one of two categories in variable A) in the case and control groups from the case-control study
26 Strength of association by crosstab 2 test For 2x2 tables, i.e. 2 binary nominal variables Phi that is defined as φ = χ2 Example: if 2 = and n=150, then φ = = 0.25 For table larger than 2x2 tables n Cramer s V that is defined as V = n min(r 1,c 1) Example: if 2 = , n=566, r=4 rows and c=3 columns, so r-1=4-1=3 and c-1=3-1=2, then V = = = χ 2
27 Interpretation of Phi and Cramer s V Reminder: Phi and Cramer s V are the measures of association between two nominal variables, i.e. how strong the association is Both Phi and Cramer s V do not identify the pattern nor direction To assess the pattern of association, interpret the column percentages in the bivariate table Here the guideline Measure of association Between 0.00 and 0.10 Between 0.11 and 0.30 Greater than 0.30 Strength of association Weak Moderate Strong
Reflection Questions for Math 58B
 Reflection Questions for Math 58B Johanna Hardin Spring 2017 Chapter 1, Section 1 binomial probabilities 1. What is a p-value? 2. What is the difference between a one- and two-sided hypothesis? 3. What
Reflection Questions for Math 58B Johanna Hardin Spring 2017 Chapter 1, Section 1 binomial probabilities 1. What is a p-value? 2. What is the difference between a one- and two-sided hypothesis? 3. What
observational studies Descriptive studies
 form one stage within this broader sequence, which begins with laboratory studies using animal models, thence to human testing: Phase I: The new drug or treatment is tested in a small group of people for
form one stage within this broader sequence, which begins with laboratory studies using animal models, thence to human testing: Phase I: The new drug or treatment is tested in a small group of people for
Contingency Tables Summer 2017 Summer Institutes 187
 Contingency Tables 87 Overview ) Types of Variables ) Comparing () Categorical Variables Contingency (two-way) tables Tests 3) x Tables Sampling designs Testing for association Estimation of effects Paired
Contingency Tables 87 Overview ) Types of Variables ) Comparing () Categorical Variables Contingency (two-way) tables Tests 3) x Tables Sampling designs Testing for association Estimation of effects Paired
Analyzing Discrete Data
 Analyzing Discrete Data Kwang Woo Ahn, PhD Sponsored by the Clinical and Translational Science Institute (CTSI) and the Department of Population Health / Division of Biostatistics Speaker disclosure In
Analyzing Discrete Data Kwang Woo Ahn, PhD Sponsored by the Clinical and Translational Science Institute (CTSI) and the Department of Population Health / Division of Biostatistics Speaker disclosure In
Welcome to this third module in a three-part series focused on epidemiologic measures of association and impact.
 Welcome to this third module in a three-part series focused on epidemiologic measures of association and impact. 1 This three-part series focuses on the estimation of the association between exposures
Welcome to this third module in a three-part series focused on epidemiologic measures of association and impact. 1 This three-part series focuses on the estimation of the association between exposures
Comparing Proportions between Two Independent Populations. John McGready Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Strategies for Data Analysis: Cohort and Case-control Studies
 Strategies for Data Analysis: Cohort and Case-control Studies Post-Graduate Course, Training in Research in Sexual Health, 24 Feb 05 Isaac M. Malonza, MD, MPH Department of Reproductive Health and Research
Strategies for Data Analysis: Cohort and Case-control Studies Post-Graduate Course, Training in Research in Sexual Health, 24 Feb 05 Isaac M. Malonza, MD, MPH Department of Reproductive Health and Research
Strategies for data analysis: case-control studies
 Strategies for data analysis: case-control studies Gilda Piaggio UNDP/UNFPA/WHO/World Bank Special Programme of Research, Development and Research Training in Human Reproduction World Health Organization
Strategies for data analysis: case-control studies Gilda Piaggio UNDP/UNFPA/WHO/World Bank Special Programme of Research, Development and Research Training in Human Reproduction World Health Organization
Biostatistics 513 Spring Homework 1 Key solution. See the Appendix below for Stata code and output related to this assignment.
 Biostatistics 513 Spring 2010 Homework 1 Key solution * Question will be graded for points, the remaining question is credit/no credit. See the Appendix below for Stata code and output related to this
Biostatistics 513 Spring 2010 Homework 1 Key solution * Question will be graded for points, the remaining question is credit/no credit. See the Appendix below for Stata code and output related to this
Binary Diagnostic Tests Paired Samples
 Chapter 536 Binary Diagnostic Tests Paired Samples Introduction An important task in diagnostic medicine is to measure the accuracy of two diagnostic tests. This can be done by comparing summary measures
Chapter 536 Binary Diagnostic Tests Paired Samples Introduction An important task in diagnostic medicine is to measure the accuracy of two diagnostic tests. This can be done by comparing summary measures
Is There An Association?
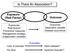 Is There An Association? Exposure (Risk Factor) Outcome Exposures Risk factors Preventive measures Management strategy Independent variables Outcomes Dependent variable Disease occurrence Lack of exercise
Is There An Association? Exposure (Risk Factor) Outcome Exposures Risk factors Preventive measures Management strategy Independent variables Outcomes Dependent variable Disease occurrence Lack of exercise
Epidemiologic study designs
 Epidemiologic study designs and critical appraisal of scientific papers Rolf H.H. Groenwold, MD, PhD Bio sketch MD, PhD in epidemiology Associate professor of Epidemiology at UMC Utrecht Research focus
Epidemiologic study designs and critical appraisal of scientific papers Rolf H.H. Groenwold, MD, PhD Bio sketch MD, PhD in epidemiology Associate professor of Epidemiology at UMC Utrecht Research focus
Epidemiology: Overview of Key Concepts and Study Design. Polly Marchbanks
 Epidemiology: Overview of Key Concepts and Study Design Polly Marchbanks Lecture Outline (1) Key epidemiologic concepts - Definition - What epi is not - What epi is - Process of epi research Lecture Outline
Epidemiology: Overview of Key Concepts and Study Design Polly Marchbanks Lecture Outline (1) Key epidemiologic concepts - Definition - What epi is not - What epi is - Process of epi research Lecture Outline
PFIZER INC. What is the difference in incidence of fracture in women who ever or never used DMPA for contraception?
 PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
Gender Analysis. Week 3
 Gender Analysis Week 3 1 Objectives 1. Understand how to practically conduct gender analysis 2. Learn and apply measures of frequency and association 2 100 75 50 25 0 Measures of Disease Frequency and
Gender Analysis Week 3 1 Objectives 1. Understand how to practically conduct gender analysis 2. Learn and apply measures of frequency and association 2 100 75 50 25 0 Measures of Disease Frequency and
Data that can be classified as belonging to a distinct number of categories >>result in categorical responses. And this includes:
 This sheets starts from slide #83 to the end ofslide #4. If u read this sheet you don`t have to return back to the slides at all, they are included here. Categorical Data (Qualitative data): Data that
This sheets starts from slide #83 to the end ofslide #4. If u read this sheet you don`t have to return back to the slides at all, they are included here. Categorical Data (Qualitative data): Data that
How to describe bivariate data
 Statistics Corner How to describe bivariate data Alessandro Bertani 1, Gioacchino Di Paola 2, Emanuele Russo 1, Fabio Tuzzolino 2 1 Department for the Treatment and Study of Cardiothoracic Diseases and
Statistics Corner How to describe bivariate data Alessandro Bertani 1, Gioacchino Di Paola 2, Emanuele Russo 1, Fabio Tuzzolino 2 1 Department for the Treatment and Study of Cardiothoracic Diseases and
Stratified Tables. Example: Effect of seat belt use on accident fatality
 Stratified Tables Often, a third measure influences the relationship between the two primary measures (i.e. disease and exposure). How do we remove or control for the effect of the third measure? Issues
Stratified Tables Often, a third measure influences the relationship between the two primary measures (i.e. disease and exposure). How do we remove or control for the effect of the third measure? Issues
Section D. Another Non-Randomized Study Design: The Case-Control Design
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
GATE: Graphic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology picture, 2 formulas & 3 acronyms
 GATE: Graphic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology 1991-2015 1 picture, 2 formulas & 3 acronyms 1 GATE: Graphic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology Graphic Architectural Tool for Epidemiology Graphic Approach To
GATE: Graphic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology 1991-2015 1 picture, 2 formulas & 3 acronyms 1 GATE: Graphic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology Graphic Architectural Tool for Epidemiology Graphic Approach To
POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN BIOETHICS (PGDBE) Term-End Examination June, 2016 MHS-014 : RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
 No. of Printed Pages : 12 MHS-014 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN BIOETHICS (PGDBE) Term-End Examination June, 2016 MHS-014 : RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 70 PART A Attempt all questions.
No. of Printed Pages : 12 MHS-014 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN BIOETHICS (PGDBE) Term-End Examination June, 2016 MHS-014 : RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 70 PART A Attempt all questions.
Risk Study. Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics. Definition
 Risk Study Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics What is Risk? Definition The probability of some untoward event The likelihood that people who are exposed to certain factors (risk factors)
Risk Study Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics What is Risk? Definition The probability of some untoward event The likelihood that people who are exposed to certain factors (risk factors)
Measuring association in contingency tables
 Measuring association in contingency tables Patrick Breheny April 3 Patrick Breheny University of Iowa Introduction to Biostatistics (BIOS 4120) 1 / 28 Hypothesis tests and confidence intervals Fisher
Measuring association in contingency tables Patrick Breheny April 3 Patrick Breheny University of Iowa Introduction to Biostatistics (BIOS 4120) 1 / 28 Hypothesis tests and confidence intervals Fisher
General Biostatistics Concepts
 General Biostatistics Concepts Dongmei Li Department of Public Health Sciences Office of Public Health Studies University of Hawai i at Mānoa Outline 1. What is Biostatistics? 2. Types of Measurements
General Biostatistics Concepts Dongmei Li Department of Public Health Sciences Office of Public Health Studies University of Hawai i at Mānoa Outline 1. What is Biostatistics? 2. Types of Measurements
Case-control studies. Hans Wolff. Service d épidémiologie clinique Département de médecine communautaire. WHO- Postgraduate course 2007 CC studies
 Case-control studies Hans Wolff Service d épidémiologie clinique Département de médecine communautaire Hans.Wolff@hcuge.ch Outline Case-control study Relation to cohort study Selection of controls Sampling
Case-control studies Hans Wolff Service d épidémiologie clinique Département de médecine communautaire Hans.Wolff@hcuge.ch Outline Case-control study Relation to cohort study Selection of controls Sampling
Survey research (Lecture 1) Summary & Conclusion. Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2015 Creative Commons Attribution 4.
 Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2015 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 3. Descriptives & graphing 4. Correlation
Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2015 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 3. Descriptives & graphing 4. Correlation
Survey research (Lecture 1)
 Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2015 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 3. Descriptives & graphing 4. Correlation
Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2015 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 3. Descriptives & graphing 4. Correlation
Constructing a Bivariate Table:
 Introduction Bivariate Analysis: A statistical method designed to detect and describe the relationship between two nominal or ordinal variables (typically independent and dependent variables). Cross-Tabulation:
Introduction Bivariate Analysis: A statistical method designed to detect and describe the relationship between two nominal or ordinal variables (typically independent and dependent variables). Cross-Tabulation:
Summary & Conclusion. Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2016 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
 Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2016 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research and design 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 2. Univariate
Summary & Conclusion Lecture 10 Survey Research & Design in Psychology James Neill, 2016 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Overview 1. Survey research and design 1. Survey research 2. Survey design 2. Univariate
In the 1700s patients in charity hospitals sometimes slept two or more to a bed, regardless of diagnosis.
 Control Case In the 1700s patients in charity hospitals sometimes slept two or more to a bed, regardless of diagnosis. This depicts a patient who finds himself lying with a corpse (definitely a case ).
Control Case In the 1700s patients in charity hospitals sometimes slept two or more to a bed, regardless of diagnosis. This depicts a patient who finds himself lying with a corpse (definitely a case ).
Confounding and Interaction
 Confounding and Interaction Why did you do clinical research? To find a better diagnosis tool To determine risk factor of disease To identify prognosis factor To evaluate effectiveness of therapy To decide
Confounding and Interaction Why did you do clinical research? To find a better diagnosis tool To determine risk factor of disease To identify prognosis factor To evaluate effectiveness of therapy To decide
ONLINE MATERIAL THAT ACCOMPANIES CHAPTER 11. Box 1. Assessing additive interaction using ratio measures
 ONLINE MATERIAL THAT ACCOMPANIES CHAPTER 11 Box 1. Assessing additive interaction using ratio measures Often times we may not be able to estimate risk or rate differences when assessing interaction. For
ONLINE MATERIAL THAT ACCOMPANIES CHAPTER 11 Box 1. Assessing additive interaction using ratio measures Often times we may not be able to estimate risk or rate differences when assessing interaction. For
Binary Diagnostic Tests Two Independent Samples
 Chapter 537 Binary Diagnostic Tests Two Independent Samples Introduction An important task in diagnostic medicine is to measure the accuracy of two diagnostic tests. This can be done by comparing summary
Chapter 537 Binary Diagnostic Tests Two Independent Samples Introduction An important task in diagnostic medicine is to measure the accuracy of two diagnostic tests. This can be done by comparing summary
Section F. Measures of Association: Risk Difference, Relative Risk, and the Odds Ratio
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
S160 #15. Comparing Two Proportions, Part 3 Odds Ratio. JC Wang. March 15, 2016
 S60 #5 Comparing Two Proportions, Part 3 JC Wang March 5, 206 Outline Odds Odds 2 JC Wang WMU) S60 #5 S60, Lecture 5 2 / The odds that an event occurs is Odds = Odds Probability that event occurs Probability
S60 #5 Comparing Two Proportions, Part 3 JC Wang March 5, 206 Outline Odds Odds 2 JC Wang WMU) S60 #5 S60, Lecture 5 2 / The odds that an event occurs is Odds = Odds Probability that event occurs Probability
Kathryn M. Rexrode, MD, MPH. Assistant Professor. Division of Preventive Medicine Brigham and Women s s Hospital Harvard Medical School
 Update: Hormones and Cardiovascular Disease in Women Kathryn M. Rexrode, MD, MPH Assistant Professor Division of Preventive Medicine Brigham and Women s s Hospital Harvard Medical School Overview Review
Update: Hormones and Cardiovascular Disease in Women Kathryn M. Rexrode, MD, MPH Assistant Professor Division of Preventive Medicine Brigham and Women s s Hospital Harvard Medical School Overview Review
Complex Traits Activity INSTRUCTION MANUAL. ANT 2110 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Professor Julie J. Lesnik
 Complex Traits Activity INSTRUCTION MANUAL ANT 2110 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Professor Julie J. Lesnik Introduction Human variation is complex. The simplest form of variation in a population
Complex Traits Activity INSTRUCTION MANUAL ANT 2110 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Professor Julie J. Lesnik Introduction Human variation is complex. The simplest form of variation in a population
INTRODUCTION TO EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY DESIGNS PHUNLERD PIYARAJ, MD., MHS., PHD.
 INTRODUCTION TO EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY DESIGNS PHUNLERD PIYARAJ, MD., MHS., PHD. 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of this section, you will be able to: Provide a definition of epidemiology Describe the major types
INTRODUCTION TO EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY DESIGNS PHUNLERD PIYARAJ, MD., MHS., PHD. 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of this section, you will be able to: Provide a definition of epidemiology Describe the major types
Announcement. Homework #2 due next Friday at 5pm. Midterm is in 2 weeks. It will cover everything through the end of next week (week 5).
 Announcement Homework #2 due next Friday at 5pm. Midterm is in 2 weeks. It will cover everything through the end of next week (week 5). Political Science 15 Lecture 8: Descriptive Statistics (Part 1) Data
Announcement Homework #2 due next Friday at 5pm. Midterm is in 2 weeks. It will cover everything through the end of next week (week 5). Political Science 15 Lecture 8: Descriptive Statistics (Part 1) Data
An Introduction to Epidemiology
 An Introduction to Epidemiology Wei Liu, MPH Biostatistics Core Pennington Biomedical Research Center Baton Rouge, LA Last edited: January, 14 th, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction.................................................................
An Introduction to Epidemiology Wei Liu, MPH Biostatistics Core Pennington Biomedical Research Center Baton Rouge, LA Last edited: January, 14 th, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction.................................................................
Does Mirena use Increase Peri-menopausal Breast Cancer Development? Maccabi Health Services (MHS) Perspective and Recent Danish Study
 Does Mirena use Increase Peri-menopausal Breast Cancer Development? Maccabi Health Services (MHS) Perspective and Recent Danish Study Nava Siegelmann Danieli, Itzhak Katzir, Janet Vesterman Landes, Yaakov
Does Mirena use Increase Peri-menopausal Breast Cancer Development? Maccabi Health Services (MHS) Perspective and Recent Danish Study Nava Siegelmann Danieli, Itzhak Katzir, Janet Vesterman Landes, Yaakov
Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club. A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology. August, 2013
 Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology August, 2013 Rationale for EBM Conscientious, explicit, and judicious use Beyond clinical experience and physiologic
Evidence-Based Medicine Journal Club A Primer in Statistics, Study Design, and Epidemiology August, 2013 Rationale for EBM Conscientious, explicit, and judicious use Beyond clinical experience and physiologic
Measuring association in contingency tables
 Measuring association in contingency tables Patrick Breheny April 8 Patrick Breheny Introduction to Biostatistics (171:161) 1/25 Hypothesis tests and confidence intervals Fisher s exact test and the χ
Measuring association in contingency tables Patrick Breheny April 8 Patrick Breheny Introduction to Biostatistics (171:161) 1/25 Hypothesis tests and confidence intervals Fisher s exact test and the χ
Conditional probability
 Conditional probability February 12, 2012 Once you eliminate the impossible, whatever remains, however improbable, must be the truth. Flip a fair coin twice. If you get TT, re-roll. Flip a fair coin twice.
Conditional probability February 12, 2012 Once you eliminate the impossible, whatever remains, however improbable, must be the truth. Flip a fair coin twice. If you get TT, re-roll. Flip a fair coin twice.
BMI 541/699 Lecture 16
 BMI 541/699 Lecture 16 Where we are: 1. Introduction and Experimental Design 2. Exploratory Data Analysis 3. Probability 4. T-based methods for continous variables 5. Proportions & contingency tables -
BMI 541/699 Lecture 16 Where we are: 1. Introduction and Experimental Design 2. Exploratory Data Analysis 3. Probability 4. T-based methods for continous variables 5. Proportions & contingency tables -
Observational Study Designs. Review. Today. Measures of disease occurrence. Cohort Studies
 Observational Study Designs Denise Boudreau, PhD Center for Health Studies Group Health Cooperative Today Review cohort studies Case-control studies Design Identifying cases and controls Measuring exposure
Observational Study Designs Denise Boudreau, PhD Center for Health Studies Group Health Cooperative Today Review cohort studies Case-control studies Design Identifying cases and controls Measuring exposure
Proportions, risk ratios and odds ratios
 Applied Biostatistics Proportions, risk ratios and odds ratios Martin Bland Professor of Health Statistics University of York http://www-users.york.ac.uk/~mb55/ Risk difference Difference between proportions:
Applied Biostatistics Proportions, risk ratios and odds ratios Martin Bland Professor of Health Statistics University of York http://www-users.york.ac.uk/~mb55/ Risk difference Difference between proportions:
Basic Biostatistics. Chapter 1. Content
 Chapter 1 Basic Biostatistics Jamalludin Ab Rahman MD MPH Department of Community Medicine Kulliyyah of Medicine Content 2 Basic premises variables, level of measurements, probability distribution Descriptive
Chapter 1 Basic Biostatistics Jamalludin Ab Rahman MD MPH Department of Community Medicine Kulliyyah of Medicine Content 2 Basic premises variables, level of measurements, probability distribution Descriptive
Two-sample Categorical data: Measuring association
 Two-sample Categorical data: Measuring association Patrick Breheny October 27 Patrick Breheny University of Iowa Biostatistical Methods I (BIOS 5710) 1 / 40 Introduction Study designs leading to contingency
Two-sample Categorical data: Measuring association Patrick Breheny October 27 Patrick Breheny University of Iowa Biostatistical Methods I (BIOS 5710) 1 / 40 Introduction Study designs leading to contingency
115 remained abstinent. 140 remained abstinent. Relapsed Remained abstinent Total
 Chapter 10 Exercises 1. Intent-to-treat analysis: Example 1 In a randomized controlled trial to determine whether the nicotine patch reduces the risk of relapse among smokers who have committed to quit,
Chapter 10 Exercises 1. Intent-to-treat analysis: Example 1 In a randomized controlled trial to determine whether the nicotine patch reduces the risk of relapse among smokers who have committed to quit,
Day 11: Measures of Association and ANOVA
 Day 11: Measures of Association and ANOVA Daniel J. Mallinson School of Public Affairs Penn State Harrisburg mallinson@psu.edu PADM-HADM 503 Mallinson Day 11 November 2, 2017 1 / 45 Road map Measures of
Day 11: Measures of Association and ANOVA Daniel J. Mallinson School of Public Affairs Penn State Harrisburg mallinson@psu.edu PADM-HADM 503 Mallinson Day 11 November 2, 2017 1 / 45 Road map Measures of
CONCEPTUALIZING A RESEARCH DESIGN
 CONCEPTUALIZING A RESEARCH DESIGN Detty Nurdiati Dept of Obstetrics & Gynecology Fac of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta, Indonesia Conceptualizing a Research Design The Research Design The
CONCEPTUALIZING A RESEARCH DESIGN Detty Nurdiati Dept of Obstetrics & Gynecology Fac of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta, Indonesia Conceptualizing a Research Design The Research Design The
Fixed Effect Combining
 Meta-Analysis Workshop (part 2) Michael LaValley December 12 th 2014 Villanova University Fixed Effect Combining Each study i provides an effect size estimate d i of the population value For the inverse
Meta-Analysis Workshop (part 2) Michael LaValley December 12 th 2014 Villanova University Fixed Effect Combining Each study i provides an effect size estimate d i of the population value For the inverse
Lecture Outline. Biost 517 Applied Biostatistics I. Purpose of Descriptive Statistics. Purpose of Descriptive Statistics
 Biost 517 Applied Biostatistics I Scott S. Emerson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Biostatistics University of Washington Lecture 3: Overview of Descriptive Statistics October 3, 2005 Lecture Outline Purpose
Biost 517 Applied Biostatistics I Scott S. Emerson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Biostatistics University of Washington Lecture 3: Overview of Descriptive Statistics October 3, 2005 Lecture Outline Purpose
W e have previously described the disease impact
 606 THEORY AND METHODS Impact numbers: measures of risk factor impact on the whole population from case-control and cohort studies R F Heller, A J Dobson, J Attia, J Page... See end of article for authors
606 THEORY AND METHODS Impact numbers: measures of risk factor impact on the whole population from case-control and cohort studies R F Heller, A J Dobson, J Attia, J Page... See end of article for authors
Learning Objectives 9/9/2013. Hypothesis Testing. Conflicts of Interest. Descriptive statistics: Numerical methods Measures of Central Tendency
 Conflicts of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose Biostatistics Kevin M. Sowinski, Pharm.D., FCCP Last-Chance Ambulatory Care Webinar Thursday, September 5, 2013 Learning Objectives For
Conflicts of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose Biostatistics Kevin M. Sowinski, Pharm.D., FCCP Last-Chance Ambulatory Care Webinar Thursday, September 5, 2013 Learning Objectives For
9/4/2013. Decision Errors. Hypothesis Testing. Conflicts of Interest. Descriptive statistics: Numerical methods Measures of Central Tendency
 Conflicts of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose Biostatistics Kevin M. Sowinski, Pharm.D., FCCP Pharmacotherapy Webinar Review Course Tuesday, September 3, 2013 Descriptive statistics:
Conflicts of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose Biostatistics Kevin M. Sowinski, Pharm.D., FCCP Pharmacotherapy Webinar Review Course Tuesday, September 3, 2013 Descriptive statistics:
Beyond Controlling for Confounding: Design Strategies to Avoid Selection Bias and Improve Efficiency in Observational Studies
 September 27, 2018 Beyond Controlling for Confounding: Design Strategies to Avoid Selection Bias and Improve Efficiency in Observational Studies A Case Study of Screening Colonoscopy Our Team Xabier Garcia
September 27, 2018 Beyond Controlling for Confounding: Design Strategies to Avoid Selection Bias and Improve Efficiency in Observational Studies A Case Study of Screening Colonoscopy Our Team Xabier Garcia
Do the sample size assumptions for a trial. addressing the following question: Among couples with unexplained infertility does
 Exercise 4 Do the sample size assumptions for a trial addressing the following question: Among couples with unexplained infertility does a program of up to three IVF cycles compared with up to three FSH
Exercise 4 Do the sample size assumptions for a trial addressing the following question: Among couples with unexplained infertility does a program of up to three IVF cycles compared with up to three FSH
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables.
 bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
GATE: Graphic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology picture, 2 formulas & 3 acronyms
 1 GATE: Graphic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology 1991-2016 1 picture, 2 formulas & 3 acronyms 2 GATE: Graphic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology Graphic Architectural Tool for Epidemiology Graphic Approach
1 GATE: Graphic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology 1991-2016 1 picture, 2 formulas & 3 acronyms 2 GATE: Graphic Appraisal Tool for Epidemiology Graphic Architectural Tool for Epidemiology Graphic Approach
Embedding pragmatic trials within databases of electronic health records / disease registries Tjeerd van Staa
 Embedding pragmatic trials within databases of electronic health records / disease registries Tjeerd van Staa London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine Utrecht University The big-data revolution in
Embedding pragmatic trials within databases of electronic health records / disease registries Tjeerd van Staa London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine Utrecht University The big-data revolution in
1. Below is the output of a 2 (gender) x 3(music type) completely between subjects factorial ANOVA on stress ratings
 SPSS 3 Practice Interpretation questions A researcher is interested in the effects of music on stress levels, and how stress levels might be related to anxiety and life satisfaction. 1. Below is the output
SPSS 3 Practice Interpretation questions A researcher is interested in the effects of music on stress levels, and how stress levels might be related to anxiety and life satisfaction. 1. Below is the output
Common Statistical Issues in Biomedical Research
 Common Statistical Issues in Biomedical Research Howard Cabral, Ph.D., M.P.H. Boston University CTSI Boston University School of Public Health Department of Biostatistics May 15, 2013 1 Overview of Basic
Common Statistical Issues in Biomedical Research Howard Cabral, Ph.D., M.P.H. Boston University CTSI Boston University School of Public Health Department of Biostatistics May 15, 2013 1 Overview of Basic
Supplementary Table 4. Study characteristics and association between OC use and endometrial cancer incidence
 Supplementary Table 4. characteristics and association between OC use and endometrial cancer incidence a Details OR b 95% CI Covariates Region Case-control Parslov, 2000 (1) Danish women aged 25 49 yr
Supplementary Table 4. characteristics and association between OC use and endometrial cancer incidence a Details OR b 95% CI Covariates Region Case-control Parslov, 2000 (1) Danish women aged 25 49 yr
WEIGHING UP THE RISKS OF HRT. Department of Endocrinology Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital
 WEIGHING UP THE RISKS OF HRT V. Nicolaou Department of Endocrinology Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Background Issues surrounding post menopausal hormonal therapy (PMHT) are complex given: Increased
WEIGHING UP THE RISKS OF HRT V. Nicolaou Department of Endocrinology Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Background Issues surrounding post menopausal hormonal therapy (PMHT) are complex given: Increased
Haemostasis, thrombosis risk and hormone replacement therapy
 Haemostasis, thrombosis risk and hormone replacement therapy Serge Motte Brussels 13.05.17 - MY TALK TODAY The coagulation cascade and its regulation Effects of hormone replacement therapy on haemostasis
Haemostasis, thrombosis risk and hormone replacement therapy Serge Motte Brussels 13.05.17 - MY TALK TODAY The coagulation cascade and its regulation Effects of hormone replacement therapy on haemostasis
Uterine Fibroid on Women's Fertility and Pregnancy Outcome in Delta State, Nigeria
 Uterine Fibroid on Women's Fertility and Pregnancy Outcome in Delta State, Nigeria Osuji, G.A Obubu, M.* Obiora-Ilouno H.O Department of Statistics, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Nigeria Abstract The
Uterine Fibroid on Women's Fertility and Pregnancy Outcome in Delta State, Nigeria Osuji, G.A Obubu, M.* Obiora-Ilouno H.O Department of Statistics, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Nigeria Abstract The
Overview of Study Designs
 Overview of Study Designs Kyoungmi Kim, Ph.D. July 13 & 20, 2016 This seminar is jointly supported by the following NIH-funded centers: We are video recording this seminar so please hold questions until
Overview of Study Designs Kyoungmi Kim, Ph.D. July 13 & 20, 2016 This seminar is jointly supported by the following NIH-funded centers: We are video recording this seminar so please hold questions until
Sections 10.7 and 10.9
 Sections 10.7 and 10.9 Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 205: Elementary Statistics for the Biological and Life Sciences 1 / 24 10.7 confidence interval for p 1
Sections 10.7 and 10.9 Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 205: Elementary Statistics for the Biological and Life Sciences 1 / 24 10.7 confidence interval for p 1
Sensitivity Analysis in Observational Research: Introducing the E-value
 Sensitivity Analysis in Observational Research: Introducing the E-value Tyler J. VanderWeele Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health Departments of Epidemiology and Biostatistics 1 Plan of Presentation
Sensitivity Analysis in Observational Research: Introducing the E-value Tyler J. VanderWeele Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health Departments of Epidemiology and Biostatistics 1 Plan of Presentation
Results. NeuRA Treatments for internalised stigma December 2017
 Introduction Internalised stigma occurs within an individual, such that a person s attitude may reinforce a negative self-perception of mental disorders, resulting in reduced sense of selfworth, anticipation
Introduction Internalised stigma occurs within an individual, such that a person s attitude may reinforce a negative self-perception of mental disorders, resulting in reduced sense of selfworth, anticipation
Biostatistics and Epidemiology Step 1 Sample Questions Set 2. Diagnostic and Screening Tests
 Biostatistics and Epidemiology Step 1 Sample Questions Set 2 Diagnostic and Screening Tests 1. A rare disorder of amino acid metabolism causes severe mental retardation if left untreated. If the disease
Biostatistics and Epidemiology Step 1 Sample Questions Set 2 Diagnostic and Screening Tests 1. A rare disorder of amino acid metabolism causes severe mental retardation if left untreated. If the disease
Confounding in influenza VE studies in seniors, and possible solutions
 Confounding in influenza VE studies in seniors, and possible solutions Michael L. Jackson Group Health Research Institute 4 th December, 2012 1 Outline Focus is on non-specific outcomes (e.g. community-acquired
Confounding in influenza VE studies in seniors, and possible solutions Michael L. Jackson Group Health Research Institute 4 th December, 2012 1 Outline Focus is on non-specific outcomes (e.g. community-acquired
Controlling Bias & Confounding
 Controlling Bias & Confounding Chihaya Koriyama August 5 th, 2015 QUESTIONS FOR BIAS Key concepts Bias Should be minimized at the designing stage. Random errors We can do nothing at Is the nature the of
Controlling Bias & Confounding Chihaya Koriyama August 5 th, 2015 QUESTIONS FOR BIAS Key concepts Bias Should be minimized at the designing stage. Random errors We can do nothing at Is the nature the of
INVESTIGATION SLEEPLESS DRIVERS
 50644_05_ch5_p407-482.qxd 5/10/05 12:08 PM Page 420 420 5.1 COMPARING TWO SAMPLES ON A CATEGORICAL RESPONSE retain the penny and the proportion of female students at this university who would vote to retain
50644_05_ch5_p407-482.qxd 5/10/05 12:08 PM Page 420 420 5.1 COMPARING TWO SAMPLES ON A CATEGORICAL RESPONSE retain the penny and the proportion of female students at this university who would vote to retain
Epidemiologic Study Designs. (RCTs)
 Epidemiologic Study Designs Epidemiologic Study Designs Experimental (RCTs) Observational Analytical Descriptive Case-Control Cohort + cross-sectional & ecologic Epidemiologic Study Designs Descriptive
Epidemiologic Study Designs Epidemiologic Study Designs Experimental (RCTs) Observational Analytical Descriptive Case-Control Cohort + cross-sectional & ecologic Epidemiologic Study Designs Descriptive
Epidemiologic Methods and Counting Infections: The Basics of Surveillance
 Epidemiologic Methods and Counting Infections: The Basics of Surveillance Ebbing Lautenbach, MD, MPH, MSCE University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine Nothing to disclose PENN Outline Definitions / Historical
Epidemiologic Methods and Counting Infections: The Basics of Surveillance Ebbing Lautenbach, MD, MPH, MSCE University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine Nothing to disclose PENN Outline Definitions / Historical
Bias. A systematic error (caused by the investigator or the subjects) that causes an incorrect (overor under-) estimate of an association.
 Bias A systematic error (caused by the investigator or the subjects) that causes an incorrect (overor under-) estimate of an association. Here, random error is small, but systematic errors have led to
Bias A systematic error (caused by the investigator or the subjects) that causes an incorrect (overor under-) estimate of an association. Here, random error is small, but systematic errors have led to
Research Methodology Workshop. Study Type
 Research Methodology Workshop Study Type What type of question? Frequency: how common is it? Aetiology: What caused this? Intervention: Does this intervention work? Diagnosis or test evaluation: How accurate
Research Methodology Workshop Study Type What type of question? Frequency: how common is it? Aetiology: What caused this? Intervention: Does this intervention work? Diagnosis or test evaluation: How accurate
EPIDEMIOLOGY. Training module
 1. Scope of Epidemiology Definitions Clinical epidemiology Epidemiology research methods Difficulties in studying epidemiology of Pain 2. Measures used in Epidemiology Disease frequency Disease risk Disease
1. Scope of Epidemiology Definitions Clinical epidemiology Epidemiology research methods Difficulties in studying epidemiology of Pain 2. Measures used in Epidemiology Disease frequency Disease risk Disease
WHI, HERS y otros estudios: Su significado en la clinica diária. Manuel Neves-e-Castro
 WHI, HERS y otros estudios: Su significado en la clinica diária III Congreso Ecuatoriano de Climaterio Menopausia y Osteoporosis por Manuel Neves-e-Castro (Lisboa-Portugal) Julho, 2003 Machala The published
WHI, HERS y otros estudios: Su significado en la clinica diária III Congreso Ecuatoriano de Climaterio Menopausia y Osteoporosis por Manuel Neves-e-Castro (Lisboa-Portugal) Julho, 2003 Machala The published
The Multiethnic Cohort Study
 VOL. 13 ISSUE 1 FALL 2013 Multiethnic Cohort Update The Multiethnic Cohort Study (MEC) celebrates 20 years of ground-breaking research thanks to all of you who completed our surveys. It s hard to believe
VOL. 13 ISSUE 1 FALL 2013 Multiethnic Cohort Update The Multiethnic Cohort Study (MEC) celebrates 20 years of ground-breaking research thanks to all of you who completed our surveys. It s hard to believe
Research Article An Estrogen Model: The Relationship between Body Mass Index, Menopausal Status, Estrogen Replacement Therapy, and Breast Cancer Risk
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume 202, Article ID 792375, 8 pages doi:0.55/202/792375 Research Article An Estrogen Model: The Relationship between
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume 202, Article ID 792375, 8 pages doi:0.55/202/792375 Research Article An Estrogen Model: The Relationship between
THERAPY WORKSHEET: page 1 of 2 adapted from Sackett 1996
 THERAPY WORKSHEET: page 1 of 2 adapted from Sackett 1996 Citation: Are the results of this single preventive or therapeutic trial valid? Was the assignment of patients to treatments randomised? -and was
THERAPY WORKSHEET: page 1 of 2 adapted from Sackett 1996 Citation: Are the results of this single preventive or therapeutic trial valid? Was the assignment of patients to treatments randomised? -and was
Bias and confounding. Mads Kamper-Jørgensen, associate professor, Section of Social Medicine
 Bias and confounding Mads Kamper-Jørgensen, associate professor, maka@sund.ku.dk PhD-course in Epidemiology l 7 February 2017 l Slide number 1 The world according to an epidemiologist Exposure Outcome
Bias and confounding Mads Kamper-Jørgensen, associate professor, maka@sund.ku.dk PhD-course in Epidemiology l 7 February 2017 l Slide number 1 The world according to an epidemiologist Exposure Outcome
Contraception and gynecological pathologies
 1 Contraception and gynecological pathologies 18 years old, 2 CMI normal First menstruation at 14 years old Irregular (every 2/3 months), painful + She does not need contraception She is worried about
1 Contraception and gynecological pathologies 18 years old, 2 CMI normal First menstruation at 14 years old Irregular (every 2/3 months), painful + She does not need contraception She is worried about
Today: Binomial response variable with an explanatory variable on an ordinal (rank) scale.
 Model Based Statistics in Biology. Part V. The Generalized Linear Model. Single Explanatory Variable on an Ordinal Scale ReCap. Part I (Chapters 1,2,3,4), Part II (Ch 5, 6, 7) ReCap Part III (Ch 9, 10,
Model Based Statistics in Biology. Part V. The Generalized Linear Model. Single Explanatory Variable on an Ordinal Scale ReCap. Part I (Chapters 1,2,3,4), Part II (Ch 5, 6, 7) ReCap Part III (Ch 9, 10,
Menopausal hormone therapy currently has no evidence-based role for
 IN PERSPECTIVE HT and CVD Prevention: From Myth to Reality Nanette K. Wenger, M.D. What the studies show, in a nutshell The impact on coronary prevention Alternative solutions Professor of Medicine (Cardiology),
IN PERSPECTIVE HT and CVD Prevention: From Myth to Reality Nanette K. Wenger, M.D. What the studies show, in a nutshell The impact on coronary prevention Alternative solutions Professor of Medicine (Cardiology),
Lessons in biostatistics
 Lessons in biostatistics The test of independence Mary L. McHugh Department of Nursing, School of Health and Human Services, National University, Aero Court, San Diego, California, USA Corresponding author:
Lessons in biostatistics The test of independence Mary L. McHugh Department of Nursing, School of Health and Human Services, National University, Aero Court, San Diego, California, USA Corresponding author:
Epidemiologic Measure of Association
 Measures of Disease Occurrence: Epidemiologic Measure of Association Basic Concepts Confidence Interval for population characteristic: Disease Exposure Present Absent Total Yes A B N 1 = A+B No C D N 2
Measures of Disease Occurrence: Epidemiologic Measure of Association Basic Concepts Confidence Interval for population characteristic: Disease Exposure Present Absent Total Yes A B N 1 = A+B No C D N 2
Biostatistics 3. Developed by Pfizer. March 2018
 BROUGHT TO YOU BY Biostatistics 3 Developed by Pfizer March 2018 This learning module is intended for UK healthcare professionals only. Job bag: PP-GEP-GBR-0986 Date of preparation March 2018. Agenda I.
BROUGHT TO YOU BY Biostatistics 3 Developed by Pfizer March 2018 This learning module is intended for UK healthcare professionals only. Job bag: PP-GEP-GBR-0986 Date of preparation March 2018. Agenda I.
MS&E 226: Small Data
 MS&E 226: Small Data Lecture 10: Introduction to inference (v2) Ramesh Johari ramesh.johari@stanford.edu 1 / 17 What is inference? 2 / 17 Where did our data come from? Recall our sample is: Y, the vector
MS&E 226: Small Data Lecture 10: Introduction to inference (v2) Ramesh Johari ramesh.johari@stanford.edu 1 / 17 What is inference? 2 / 17 Where did our data come from? Recall our sample is: Y, the vector
Health Studies 315. Clinical Epidemiology: Evidence of Risk and Harm
 Health Studies 315 Clinical Epidemiology: Evidence of Risk and Harm 1 Patients encounter (possibly) risky exposures Alcohol during pregnancy (fetal risk) Electromagnetic fields (cancer risk) Vasectomy
Health Studies 315 Clinical Epidemiology: Evidence of Risk and Harm 1 Patients encounter (possibly) risky exposures Alcohol during pregnancy (fetal risk) Electromagnetic fields (cancer risk) Vasectomy
CHAPTER 3 DATA ANALYSIS: DESCRIBING DATA
 Data Analysis: Describing Data CHAPTER 3 DATA ANALYSIS: DESCRIBING DATA In the analysis process, the researcher tries to evaluate the data collected both from written documents and from other sources such
Data Analysis: Describing Data CHAPTER 3 DATA ANALYSIS: DESCRIBING DATA In the analysis process, the researcher tries to evaluate the data collected both from written documents and from other sources such
Comparison And Application Of Methods To Address Confounding By Indication In Non- Randomized Clinical Studies
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Masters Theses 1911 - February 2014 Dissertations and Theses 2013 Comparison And Application Of Methods To Address Confounding By Indication
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Masters Theses 1911 - February 2014 Dissertations and Theses 2013 Comparison And Application Of Methods To Address Confounding By Indication
PSY 216: Elementary Statistics Exam 4
 Name: PSY 16: Elementary Statistics Exam 4 This exam consists of multiple-choice questions and essay / problem questions. For each multiple-choice question, circle the one letter that corresponds to the
Name: PSY 16: Elementary Statistics Exam 4 This exam consists of multiple-choice questions and essay / problem questions. For each multiple-choice question, circle the one letter that corresponds to the
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Table 1. Distribution of Participants Characteristics by Treatment Group at Baseline - The Vitamin D and calcium (CaD) Trial of the Women s Health Initiative (WHI) Study,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Table 1. Distribution of Participants Characteristics by Treatment Group at Baseline - The Vitamin D and calcium (CaD) Trial of the Women s Health Initiative (WHI) Study,
5.3: Associations in Categorical Variables
 5.3: Associations in Categorical Variables Now we will consider how to use probability to determine if two categorical variables are associated. Conditional Probabilities Consider the next example, where
5.3: Associations in Categorical Variables Now we will consider how to use probability to determine if two categorical variables are associated. Conditional Probabilities Consider the next example, where
NORTH SOUTH UNIVERSITY TUTORIAL 1
 NORTH SOUTH UNIVERSITY TUTORIAL 1 REVIEW FROM BIOSTATISTICS I AHMED HOSSAIN,PhD Data Management and Analysis AHMED HOSSAIN,PhD - Data Management and Analysis 1 DATA TYPES/ MEASUREMENT SCALES Categorical:
NORTH SOUTH UNIVERSITY TUTORIAL 1 REVIEW FROM BIOSTATISTICS I AHMED HOSSAIN,PhD Data Management and Analysis AHMED HOSSAIN,PhD - Data Management and Analysis 1 DATA TYPES/ MEASUREMENT SCALES Categorical:
