Copyright 2009 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 7260, Medical Imaging 2009:
|
|
|
- Alban Hunt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Copyright 2009 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 7260, Medical Imaging 2009: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of SPIE. One print or electronic copy may be made for personal use only. Systematic or multiple reproduction, distribution to multiple locations via electronic or other means, duplication of any material in this paper for a fee or for commercial purposes, or modification of the content of the paper are prohibited.
2 Quantitative Assessment of Emphysema from Whole Lung CT Scans: Comparison with Visual Grading Brad M. Keller *a, Anthony P. Reeves b, Tatiyana V. Apanasovich c, Jianwei Wang d, David F. Yankelevitz d, Claudia I. Henschke d a Department of Biomedical Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA; b School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA; c Department of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, Jefferson Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA, USA; d Department of Radiology, Weill Medical College of Cornell University, New York, NY, USA; ABSTRACT Emphysema is a disease of the lungs that destroys the alveolar air sacs and induces long-term respiratory dysfunction. CT scans allow for imaging of the anatomical basis of emphysema and for visual assessment by radiologists of the extent present in the lungs. Several measures have been introduced for the quantification of the extent of disease directly from CT data in order to add to the qualitative assessments made by radiologists. In this paper we compare emphysema index, mean lung density, histogram percentiles, and the fractal dimension to visual grade in order to evaluate the predictability of radiologist visual scoring of emphysema from low-dose CT scans through quantitative scores, in order to determine which measures can be useful as surrogates for visual assessment. All measures were computed over nine divisions of the lung field (whole lung, individual lungs, and upper/middle/lower thirds of each lung) for each of 148 low-dose, whole lung scans. In addition, a visual grade of each section was also given by an expert radiologist. One-way ANOVA and multinomial logistic regression were used to determine the ability of the measures to predict visual grade from quantitative score. We found that all measures were able to distinguish between normal and severe grades (p<0.01), and between mild/moderate and all other grades (p<0.05). However, no measure was able to distinguish between mild and moderate cases. Approximately 65% prediction accuracy was achieved from using quantitative score to predict visual grade, with 73% if mild and moderate cases are considered as a single class. Keywords: CT, computer aided diagnosis, COPD, emphysema, lung disease, visual score 1. INTRODUCTION High-resolution, multi-row detector computed tomography has allowed radiologists to view the underlying anatomical basis of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD), particularly emphysema, from CT scans. Emphysema is clinically defined as the destruction and breakdown of the alveolar air sacs in the lung into large, coalescing pockets of anatomically dead-air space, emphysematous regions are visually described in CT images as being regions of lung parenchyma that are of a significantly low density. This has allowed for qualitative scoring of the disease state of an individual by radiologists. Computer-based scoring systems have been developed that extend this concept to allow for quantitative evaluation of emphysema from CT scans, with the majority of methods focusing on the use of density information as the primary index, either through relative area, such as the emphysema index, or distribution of regions, such as the fractal dimension. The emphysema index, also referred to as low attenuation area percentage (LAA%), developed by Müller [1], is the most well known of all these measures. Both visual and quantitative scoring have been showing to be relatively accurate in quantifying emphysema. [2] Little work has gone into the evaluation of using quantitative measurements as a surrogate scoring system for visual scoring. The purpose of this work is to evaluate the predictability of radiologist visual scoring of emphysema, both globally and of sub-regions of the lung parenchyma, from low-dose CT scans through the analysis of four commonly used quantitative measurements. This work focuses on the four most commonly used scores reported in the literature: the emphysema index [3][4], the n-th percentile of the histogram [5][3], the mean lung density [6][7] and the fractal dimension [8][9]. Medical Imaging 2009: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, edited by Nico Karssemeijer, Maryellen L. Giger Proc. of SPIE Vol. 7260, SPIE CCC code: /09/$18 doi: / Proc. of SPIE Vol
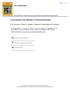
3 a) b) c) d) Fig. 1. Visual representation of Emphysema Distribution in Whole Lung a) Mild Emphysema 3D visualization b) Severe Emphysema 3D visualization c) Mild Emphysema CT slice d) Severe Emphysema CT slice Proc. of SPIE Vol
4 2. METHOD The introduction of high-resolution, multi-row detector CT has allowed radiologists to view the underlying anatomical basis of emphysema from CT scans. Given that emphysema is defined as the destruction and breakdown of the alveolar air sacs in the lung, emphysematous regions are visually described as being regions of lung parenchyma that are of a significantly low density. This allows for a qualitative scoring of the extent to which an individual has emphysema present in the lungs by radiologists investigating COPD and its effects. Computer-based scoring methods and systems have been developed that extend this concept to allow for quantitative evaluation of emphysema from CT scans. Emphysema index (EI) is the standard quantification measure of emphysema from lung CT-scans. Other commonly used and evaluated measures include mean lung density(mld), histogram percentiles(hist), and the fractal dimension(fd). All of these measures have been promoted as measures for quantification of the underlying anatomical basis for emphysema. However, little work to date has compared these four common measures to radiological visual scoring simultaneously. Therefore, this work focuses on the predictability of visual scores from quantitative measures. Figure 1 gives visual distributions of mild and severe emphysema in a whole lung scan. Four primary measures were investigated in this work. The emphysema index is the classic measure of pulmonary emphysema and is the relative volume of the lung parenchyma that falls below a given density threshold. In this study, that threshold is set to -910 H.U. as that threshold is believed to cover. The emphysema index is also commonly called the percent low attenuation area (%LAA). The second measure of interest is the N th percentile of the histogram. The histogram percentile is an empirical percentile, with the observation used in this case as the voxel densities of the lung, giving the density level at which N% of the lung pixel densities will fall below. Effectively the HIST measure returns the threshold needed to get an EI of N. In this work, N is set to be the 15 th percentile. The third measure is the fractal dimension. This returns a value that is indicative of the distribution of emphysema region sizes within the lung. The final measure is the mean lung density. In order to determine the predictability of the visual grade from these measures, and thus which measures correlate most closely with radiologist observations, 148 low-dose, whole lung scans were randomly selected from a database of patients with known smoking history. Each scan was graded on the extent of emphysema present based on expert radiologist visual interpretation and was classified normal, mild, moderate, or severe. Nine classifications of the level of presence of emphysema in the lung was given by the radiologist for each of the 148 whole-lung scans. A single classification was given for the whole scan overall, for each of the two lungs independently, and for each of the three divisions of each lung independently (upper, middle, and lower third). The three classification schema can be considered as a global, lung, and six-partition schema. For each of the nine established divisions, the emphysema index and fractal dimension were computed at a -910 HU threshold using in-house software developed for use by radiologists in the Weill Medical College of Cornell University. The algorithms used were similar to the ones described by Müller et al. [1] and Mishima et al. [10] respectively. Mean lung density and the 15th percentile of the histogram were also computed using the same software. One-way ANOVA using F-test and all pairwise comparisons among means are tested using Tukey-Kramer s HSD test were performed to show that means of objective scores associated with each visual score are significantly different from another. The equation for Tukey-Kramer s HSD is given below, t S = M i M MSE n h j where i and j represent the pair of means to be tested, M i - M j is the difference between the i-th and j-th means, MSE is the Mean Square Error, and n h is the harmonic mean of the sample sizes of groups i and j. The critical value of ts is determined from the distribution of the studentized range. The number of means in the experiment is used in the determination of the critical value, and this critical value is used for all comparisons among means. If t s surpasses this critical value, the two means are considered significantly different. All statistical computations and tests in this work were performed with the use of the R statistical software package [11]. Proc. of SPIE Vol
5 Table 1: Confusion Matrices of Classification of Emphysema Index to True Visual Grade in the six-partitioned lung segments Above) Mild and Moderate as separate classes Below) Mild and Moderate as a single class EI Visual Normal Mild Moderate Severe Normal Mild Moderate Severe EI Visual Normal Mildmoderate Severe Normal Mild-moderate Severe Table. 2. Classification Accuracies for Measures and Lung Division Schema Left) Mild and Moderate as separate classes Right) Mild and Moderate as a single class Global Lung Regional EI 64.2% 67.2% 62.3% HIST 65.5% 67.2% 61.9% MLD 59.5% 62.1% 58.4% FD 66.2% 67.9% 59.5% Global Lung Regional EI 73.0% 73.6% 68.5% HIST 77.0% 75.7% 70.5% MLD 67.6% 67.6% 64.4% FD 75.0% 74.6% 64.2% In order to determine the overall usefulness in using quantitative score to predict the subjective visual score for a given lung region, multinomial logistic regression was used to compute the probability that a objective score would predict a visual grade and classification accuracy was computed using each measure. Finally, a pair-wise implementation of the McNemar s test was used to determine if the four objective scores are significantly different in predicting visual score. 3. DATA All scans used in this study were acquired at the Weill Medical College of Cornell University using a whole lung, low dose protocol. 148 total scans were acquired in this manner. 135 scans were at 1.25mm slice thickness acquired at 120 kvp; 13 scans were at 5mm slice thickness acquired at 140 kvp. All scans underwent the same visual grading procedure and quantitative scoring methods. Proc. of SPIE Vol
6 Emphysema Index Score vs. Visual Grade Emphysema Index Score normal mild moderate severe Visual Grade Fig. 2. Box plot of distributions of Emphysema Index vs. Visual Grade. Both normal and severe grades were shown to be statistically different from all groups (p<0.05) for all three lung partition schema. Of particular interest is the large overlap between mild and moderate emphysema scores. Proc. of SPIE Vol
7 4. RESULTS We found that for all measures, both normal and severe grades were shown to be statistically different from all groups (p<0.05) for all three lung partition schema. However mild and moderate did not show statistical significance, and a large overlap in the ranges of scores for mild and moderate was found, with moderate cases tending to have quantitative scores in the upper range of mild cases. Figure 2 provides a box-plot that shows this effect for emphysema index in the six-partition schema. The average correct classification rate of visual score from quantitative measurements was approximately 65%, with greatest confusion occurring between mild and moderate grades due to the classification schema failing to separate mild and moderate cases, classifying all moderate cases as mild or severe. Accuracies of over 75% could be achieved when mild and moderate were combined into single class to minimize this confusion. Table 1 illustrates this effect for emphysema index on the regional level of the lungs. Overall, FD, EI, and HIST were found to be superior to MLD at the global and lung levels (p<0.1) and EI and HIST being superior to FD and MLD at the regional level (p<0.1) for predicting visual grade from quantitative score. Table 2 gives the overall classification accuracies for the four measures across the three lung division analysis for both the four visual grade scoring method and three visual grade scoring method. 5. DISCUSSION Little work has been done comparing multiple measures simultaneously to visual grading. Simultaneous comparison is important to show true advantages between various methods. This work shows that automated measures show good agreement with visual grade, particularly emphysema index, and these scores could be used as surrogate scores for the interpretation and assessment of emphysema severity in lung CT scans. The findings in this work show that the quantitative scores can most easily distinguish between normal and severe cases of emphysema, regardless of the lung partition schema used. All four quantitative measures could also distinguish between normal and mild cases as well as between moderate and severe, although the distinction between these groups is not as clear as between normal and severe cases. However, no measure at any level was able to distinguish between mild and severe cases. The primary reason for this outcome is that in general, an average increase in emphysema score can be seen for the various measures when advancing visual grade from mild to moderate, the variation of scores falling within the mild case is enough to provide large overlap between scores of the mild and moderate cases. This is most clearly seen in figure 2, where approximately 50% of the moderate scores for emphysema index are shown to fall within a single quartile of the mild case. When the two categories are combined, we find that overall accuracies of classification increase for the measures by 10-15%, indicating that misclassification of moderate cases is the largest single source of error. Another possible reason is that there were fewer moderate observations as opposed to mild or severe, which, when combined with the reason above, could have ultimately biased the multinomial logistic regression to not classify observations as moderate. When we compare the accuracy rates of three lung-division schema, a trend towards increased prediction accuracy of visual scores increases as we analyze larger sub-regions of the lung parenchyma at once, for example each whole lung individually versus analyzing the 3 divisions of a single lung, as is shown in Table 2. There are two possible explanations for this occurrence. The first is that the by analyzing divisions of a lung, the sample-size of the measurements taken increases substantially, which could account for increased accuracy in the larger. The second possible explanation is that the measures were originally designed to be used on whole lung scans, so that smaller variations within a sub-region could cause increased error rates, such as increased noise in the apices of the lungs. Normally, local variations would have a larger lung volume to be averaged against, thus mitigating their effects on the measures accuracy, but the limited regional volume could allow for the variations to have a larger effect. This could be considered a limitation of the measures for local analysis. Proc. of SPIE Vol
8 6. CONCLUSION This work shows that there is a strong relationship between visual grade and quantitative measures when distinguishing between normal, mild/moderate, and severe cases. We also find that 65% predictability is possible for all divisions of the lung, with EI and HIST being the most indicative of visual grade. The prediction accuracy can be further increased to 75% if mild and moderate cases can be grouped as a single class. Given that automated measures show good agreement with visual grade, quantitative measures could be used as surrogate scores for the interpretation and assessment of emphysema severity in lung CT scans. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This research was supported in part by NIH grant R33CA and the Flight Attendants' Medical Research Institute. Drs. Henschke, Yankelevitz and Reeves are co-inventors on a patent and other pending patents which are owned by Cornell Research Foundation (CRF) who non-exclusively licenses them to General Electric for technology involving detection and characterization of nodules in many medical situations, including measurement of nodules. They receive royalties from CRF pursuant to Cornell policy, which in turn is consistent with the Bayh-Dole Act. They are also inventors on a pending patent application for lesion measurement. Dr. Yankelevitz is an inventor on a pending patent owned by PneumRx related to biopsy needles, serves as a medical advisor to them, and holds an equity interest in PneumRx. REFERENCES [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] Muller, N.L., Staples, C.A., Miller, R.R. and R.T. Abboud, Density Mask. An Objective Method to Quantitate Emphysema Using Computed Tomography, Chest 94(4), (1988). Park KJ, Bergin CJ, and Clausen JL, Quantitation of Emphysema with Three-dimensional CT Densitometry: Comparison with Two-dimensional Analysis, Visual Emphysema Scores, and Pulmonary Function Test Results, Radiology 211, (1999). Uppaluri, R., Mitsa, T., Sonka, M., Hoffman, E.A. and McLennan, G. Quantification of Pulmonary Emphysema from Lung Computed Tomography Images, Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156(1), (1997). Madani, A., de Maertelaer, V., Zanen, J. and P.A. Gevenois., Pulmonary Emphysema: Radiation Dose and Section Thickness at Multidetector CT Quantification Comparison with Macroscopic and Microscopic Morphometry, Radiology 243, (2007). Gould, G.A., MacNee, W., McLean, A., Warren, P. M., Redpath, A., Best, J. J., Lamb, D. and Flenley, D. C., CT Measurements of Lung Density in Life can Quantitate Distal Airspace Enlargement an Essential Defining Feature of Human Emphysema, Am Rev Respir Dis 137, (1988). Best AC, Lynch AM, Bozic CM, Miller D, Grunwald GK, Lynch DA, Quantitative CT Indexes in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Relationship with Physiologic Impairment, Radiology 228, (2003). Ley S, Zaporozhan J, Morbach A, Eberle B, Gast KK, Heussel CP, Biedermann A, Mayer E, Schmiedeskamp J, Stepniak A, Schreiber WG, Kauczor HU, Functional Evaluation of Emphysema Using Diffusion-Weighted 3Helium-Magnetic Resonance Imaging, High-Resolution Computed Tomography, and Lung Function Tests, Investigative Radiology.39(7), (2004). Hoffman EA, Reinhardt JM, Sonka M, Simon BA, Guo J, Saba O, Chon Deokiee, Samrah S, Shikata H, Tschirren J, Palagyi K, Beck KC, McLennan G, Characterization of the interstitial lung diseases via density-based and texturebased analysis of computed tomography images of lung structure and function, Academic Radiology 10(10), (2003) Coxson HO, Whittall KP, Nakano Y, Rogers RM, Sciurba FC, Keenan RJ, Hogg JC, Selection of patients for lung volume reduction surgery using a power law analysis of the computed tomographic scan, Thorax. 58(6), (2003). Mishima, M., Hirai, T., Itoh, H., Nakano, Y., Sakai, H., Nishimura, K., Muro, S., Oku, Y., Chin, K., Ohi, M., Nakamura, T., Bates, J.H. T., Alencar, A. M. and Suki, B., Complexity of Terminal Airspace Geometry Assessed Proc. of SPIE Vol
9 [11] by Lung Computed Tomography in Normal Subjects and Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Proc Natl Acad Sci 96(16), (1999). R Development Core Team (2007). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN , url: Proc. of SPIE Vol
Copyright 2008 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6915, Medical Imaging 2008:
 Copyright 2008 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6915, Medical Imaging 2008: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as an
Copyright 2008 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6915, Medical Imaging 2008: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as an
doi: /
 Yiting Xie ; Yu Maw Htwe ; Jennifer Padgett ; Claudia Henschke ; David Yankelevitz ; Anthony P. Reeves; Automated aortic calcification detection in low-dose chest CT images. Proc. SPIE 9035, Medical Imaging
Yiting Xie ; Yu Maw Htwe ; Jennifer Padgett ; Claudia Henschke ; David Yankelevitz ; Anthony P. Reeves; Automated aortic calcification detection in low-dose chest CT images. Proc. SPIE 9035, Medical Imaging
doi: /
 Yiting Xie ; Matthew D. Cham ; Claudia Henschke ; David Yankelevitz ; Anthony P. Reeves; Automated coronary artery calcification detection on low-dose chest CT images. Proc. SPIE 9035, Medical Imaging
Yiting Xie ; Matthew D. Cham ; Claudia Henschke ; David Yankelevitz ; Anthony P. Reeves; Automated coronary artery calcification detection on low-dose chest CT images. Proc. SPIE 9035, Medical Imaging
Quantitative CT in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Inspiratory and Expiratory Assessment
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research kira et al. CT of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Masanori kira 1 Kazushige Toyokawa 1 Yoshikazu Inoue 2 Toru rai
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research kira et al. CT of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Masanori kira 1 Kazushige Toyokawa 1 Yoshikazu Inoue 2 Toru rai
Copyright 2009 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 7260, Medical Imaging 2009:
 Copyright 2009 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 7260, Medical Imaging 2009: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as an
Copyright 2009 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 7260, Medical Imaging 2009: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as an
Copyright 2008 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6915, Medical Imaging 2008:
 Copyright 2008 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6915, Medical Imaging 2008: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as an
Copyright 2008 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6915, Medical Imaging 2008: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as an
Chapter 11. Summary and general discussion
 Chapter 11 Summary and general discussion Low Dose Computed Tomography of the Chest: Applications and Limitations INTRODUCTION The introduction of spiral, multidetector-row computed tomography (CT) has
Chapter 11 Summary and general discussion Low Dose Computed Tomography of the Chest: Applications and Limitations INTRODUCTION The introduction of spiral, multidetector-row computed tomography (CT) has
Copyright 2007 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, volume 6514, Medical Imaging
 Copyright 2007 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, volume 6514, Medical Imaging 2007: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as
Copyright 2007 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, volume 6514, Medical Imaging 2007: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as
Copyright 2007 IEEE. Reprinted from 4th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, April 2007.
 Copyright 27 IEEE. Reprinted from 4th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, April 27. This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the
Copyright 27 IEEE. Reprinted from 4th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, April 27. This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the
Radiologic characterization of emphysema's pattern of distribution - a subjective approach
 Radiologic characterization of emphysema's pattern of distribution - a subjective approach Poster No.: C-0866 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Praia, C. Maciel, J. Pereira, J. Albuquerque,
Radiologic characterization of emphysema's pattern of distribution - a subjective approach Poster No.: C-0866 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Praia, C. Maciel, J. Pereira, J. Albuquerque,
Copyright 2008 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6915, Medical Imaging 2008:
 Copyright 28 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 695, Medical Imaging 28: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as an electronic
Copyright 28 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 695, Medical Imaging 28: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as an electronic
Fractal analysis of low attenuation clusters on computed tomography in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Tanabe et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018) 18:144 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0714-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Fractal analysis of low attenuation clusters on computed tomography in chronic
Tanabe et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018) 18:144 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0714-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Fractal analysis of low attenuation clusters on computed tomography in chronic
A comparative study of machine learning methods for lung diseases diagnosis by computerized digital imaging'"
 A comparative study of machine learning methods for lung diseases diagnosis by computerized digital imaging'" Suk Ho Kang**. Youngjoo Lee*** Aostract I\.' New Work to be 1 Introduction Presented U Mater~al
A comparative study of machine learning methods for lung diseases diagnosis by computerized digital imaging'" Suk Ho Kang**. Youngjoo Lee*** Aostract I\.' New Work to be 1 Introduction Presented U Mater~al
Quantitative Assessment of Air Trapping in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Using Inspiratory and Expiratory Volumetric MDCT
 Chest Imaging Original Research Matsuoka et al. MDCT of Air Trapping in COPD Chest Imaging Original Research Shin Matsuoka 12 Yasuyuki Kurihara 1 Kunihiro Yagihashi 1 Makoto Hoshino 3 Naoto Watanabe 3
Chest Imaging Original Research Matsuoka et al. MDCT of Air Trapping in COPD Chest Imaging Original Research Shin Matsuoka 12 Yasuyuki Kurihara 1 Kunihiro Yagihashi 1 Makoto Hoshino 3 Naoto Watanabe 3
Patient selection for lung volume reduction surgery. Patient Selection for Lung Volume Reduction Surgery*
 Patient Selection for Lung Volume Reduction Surgery* An Objective Model Based on Prior Clinical Decisions and Quantitative CT Analysis David S. Gierada, MD; Roger D. Yusen, MD; Ian A. Villanueva, BS; Thomas
Patient Selection for Lung Volume Reduction Surgery* An Objective Model Based on Prior Clinical Decisions and Quantitative CT Analysis David S. Gierada, MD; Roger D. Yusen, MD; Ian A. Villanueva, BS; Thomas
Automated CT Image Evaluation of the Lung: A Morphology-Based Concept
 434 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 20, NO. 5, MAY 2001 Automated CT Image Evaluation of the Lung A Morphology-Based Concept R. A. Blechschmidt*, Member, IEEE, R. Werthschützky, and U. Lörcher
434 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 20, NO. 5, MAY 2001 Automated CT Image Evaluation of the Lung A Morphology-Based Concept R. A. Blechschmidt*, Member, IEEE, R. Werthschützky, and U. Lörcher
APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES
 APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES Volume 4, Issue 7 Newsletter Date: July 2012 APSR EDUCATION PUBLICATION Inside this issue: Quantitative imaging of airways Small-Airway Obstruction and Emphysema in Chronic Obstructive
APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES Volume 4, Issue 7 Newsletter Date: July 2012 APSR EDUCATION PUBLICATION Inside this issue: Quantitative imaging of airways Small-Airway Obstruction and Emphysema in Chronic Obstructive
Kerstin Cederlund, MD, PhD; Ulf Tylén, MD, PhD; Lennart Jorfeldt, MD, PhD; and Peter Aspelin, MD, PhD
 Classification of Emphysema in Candidates for Lung Volume Reduction Surgery* A New Objective and Surgically Oriented Model for Describing CT Severity and Heterogeneity Kerstin Cederlund, MD, PhD; Ulf Tylén,
Classification of Emphysema in Candidates for Lung Volume Reduction Surgery* A New Objective and Surgically Oriented Model for Describing CT Severity and Heterogeneity Kerstin Cederlund, MD, PhD; Ulf Tylén,
Normal variance in emphysema index measurements in 64 multidetector-row computed tomography
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 14, NUMBER 4, 2013 Normal variance in emphysema index measurements in 64 multidetector-row computed tomography Bruno Hochhegger, 1 Klaus L. Irion, 2
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 14, NUMBER 4, 2013 Normal variance in emphysema index measurements in 64 multidetector-row computed tomography Bruno Hochhegger, 1 Klaus L. Irion, 2
Advances in imaging. N.L. Müller
 Eur Respir J 2001; 18: 867 871 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 SERIES 0THORACIC IMAGING 0 Edited by P.A. Gevenois, A. Bankier
Eur Respir J 2001; 18: 867 871 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 SERIES 0THORACIC IMAGING 0 Edited by P.A. Gevenois, A. Bankier
Pulmonary emphysema is a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and worldwide the sixth and 12th most common cause of mortality and morbidity, respecti
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH THORACIC IMAGING Afarine Madani, MD Viviane De Maertelaer, PhD Jacqueline Zanen, PhD Pierre Alain Gevenois, MD, PhD Pulmonary Emphysema: Radiation Dose and Section Thickness at Multidetector
ORIGINAL RESEARCH THORACIC IMAGING Afarine Madani, MD Viviane De Maertelaer, PhD Jacqueline Zanen, PhD Pierre Alain Gevenois, MD, PhD Pulmonary Emphysema: Radiation Dose and Section Thickness at Multidetector
Core to Rind Distribution of Severe Emphysema Predicts Outcome of Lung Volume Reduction Surgery
 Core to Rind Distribution of Severe Emphysema Predicts Outcome of Lung Volume Reduction Surgery YASUTAKA NAKANO, HARVEY O. COXSON, SOREL BOSAN, ROBERT M. ROGERS, FRANK C. SCIURBA, ROBERT J. KEENAN, KEITH
Core to Rind Distribution of Severe Emphysema Predicts Outcome of Lung Volume Reduction Surgery YASUTAKA NAKANO, HARVEY O. COXSON, SOREL BOSAN, ROBERT M. ROGERS, FRANK C. SCIURBA, ROBERT J. KEENAN, KEITH
SPIRATION VALVE SYSTEM Patient Selection for the Treatment of Emphysema Based on Clinical Literature.
 SPIRATION VALVE SYSTEM Patient Selection for the Treatment of Emphysema Based on Clinical Literature. SPIRATION VALVE SYSTEM The Spiration Valve System is a device placed in the lung airway to treat severely
SPIRATION VALVE SYSTEM Patient Selection for the Treatment of Emphysema Based on Clinical Literature. SPIRATION VALVE SYSTEM The Spiration Valve System is a device placed in the lung airway to treat severely
THE BENEFITS OF BIG DATA
 THE BENEFITS OF BIG DATA Disclosures I am a named inventor on a number of patents and patent applications relating to the evaluation of pulmonary nodules on CT scans of the chest which are owned by Cornell
THE BENEFITS OF BIG DATA Disclosures I am a named inventor on a number of patents and patent applications relating to the evaluation of pulmonary nodules on CT scans of the chest which are owned by Cornell
Automated quantification of radiological patterns predicts survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES Automated quantification of radiological patterns predicts survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Fabien Maldonado 1,5, Teng Moua 1,5, Srinivasan Rajagopalan
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES Automated quantification of radiological patterns predicts survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Fabien Maldonado 1,5, Teng Moua 1,5, Srinivasan Rajagopalan
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF EMPHYSEMA FROM WHOLE-LUNG, LOW-DOSE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IMAGES
 QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF EMPHYSEMA FROM WHOLE-LUNG, LOW-DOSE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IMAGES A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Cornell University in Partial Fulllment of the
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF EMPHYSEMA FROM WHOLE-LUNG, LOW-DOSE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IMAGES A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Cornell University in Partial Fulllment of the
By choosing to view this document, you agree to all provisions of the copyright laws protecting it.
 Copyright 2009 IEEE. Reprinted from 31 st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2009. EMBC 2009. Sept. 2009. This material is posted here with permission
Copyright 2009 IEEE. Reprinted from 31 st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2009. EMBC 2009. Sept. 2009. This material is posted here with permission
Sang Min Lee, M.D., Jin Hur, M.D., Tae Hoon Kim, M.D., Sang Jin Kim, M.D., Hyung Jung Kim, M.D. 2
 Quantitative Assessment of Lung Volumes using Multidetector Row Computed Tomography (MDCT) in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 1 Sang Min Lee, M.D., Jin Hur, M.D., Tae Hoon Kim,
Quantitative Assessment of Lung Volumes using Multidetector Row Computed Tomography (MDCT) in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 1 Sang Min Lee, M.D., Jin Hur, M.D., Tae Hoon Kim,
Quantification of Pulmonary Emphysema from Lung Computed Tomography Images
 Quantification of Pulmonary Emphysema from Lung Computed Tomography Images RENUKA UPPALURI, THEOPHANO MITSA, MILAN SONKA, ERIC A. HOFFMAN, and GEOFFREY MCLENNAN Departments of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Quantification of Pulmonary Emphysema from Lung Computed Tomography Images RENUKA UPPALURI, THEOPHANO MITSA, MILAN SONKA, ERIC A. HOFFMAN, and GEOFFREY MCLENNAN Departments of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
VA PARTNERSHIP Increase ACCESS to LUNG SCREENING
 VA PARTNERSHIP Increase ACCESS to LUNG SCREENING Project PI: Drew Moghanaki, MD, MPH Clinical Co-PI: Claudia Henschke, PhD, MD Technical Co-PI: Rick Avila, MS Sponsored by the Bristol-Myers Squibb Foundation
VA PARTNERSHIP Increase ACCESS to LUNG SCREENING Project PI: Drew Moghanaki, MD, MPH Clinical Co-PI: Claudia Henschke, PhD, MD Technical Co-PI: Rick Avila, MS Sponsored by the Bristol-Myers Squibb Foundation
Computed Tomography-Based Centrilobular Emphysema Subtypes Relate with Pulmonary Function
 Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.net 54 The Open Respiratory Medicine Journal, 213, 7, 54-59 Computed Tomography-Based Centrilobular Emphysema s Relate with Pulmonary Function Mamoru
Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.net 54 The Open Respiratory Medicine Journal, 213, 7, 54-59 Computed Tomography-Based Centrilobular Emphysema s Relate with Pulmonary Function Mamoru
Parametric response mapping
 Parametric response mapping Utility of a novel imaging biomarker in pulmonary disease Dharshan Vummidi MD, Lama VN MD, Yanik G MD, Kazerooni EA MD, Meilan Han MD, Galban C PhD Radiology, Pulmonary & Critical
Parametric response mapping Utility of a novel imaging biomarker in pulmonary disease Dharshan Vummidi MD, Lama VN MD, Yanik G MD, Kazerooni EA MD, Meilan Han MD, Galban C PhD Radiology, Pulmonary & Critical
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 25, NO. 4, APRIL
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 25, NO. 4, APRIL 2006 435 On Measuring the Change in Size of Pulmonary Nodules Anthony P. Reeves*, Senior Member, IEEE, Antoni B. Chan, David F. Yankelevitz,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 25, NO. 4, APRIL 2006 435 On Measuring the Change in Size of Pulmonary Nodules Anthony P. Reeves*, Senior Member, IEEE, Antoni B. Chan, David F. Yankelevitz,
clinical investigations Preoperative Severity of Emphysema Predictive of Improvement After Lung Volume Reduction Surgery* Use of CT Morphometry
 clinical investigations Preoperative Severity of Emphysema Predictive of Improvement After Lung Volume Reduction Surgery* Use of CT Morphometry Robert M. Rogers, MD, FCCP; Harvey O. Coxson, PhD; Frank
clinical investigations Preoperative Severity of Emphysema Predictive of Improvement After Lung Volume Reduction Surgery* Use of CT Morphometry Robert M. Rogers, MD, FCCP; Harvey O. Coxson, PhD; Frank
Three Cuts Method for Identification of COPD
 ORIGINAL REPORT Three Cuts Method for Identification of COPD Mohammad-Parsa Hosseini 1,2, Hamid Soltanian-Zadeh 2,3, and Shahram Akhlaghpoor 4 1 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, Wayne State
ORIGINAL REPORT Three Cuts Method for Identification of COPD Mohammad-Parsa Hosseini 1,2, Hamid Soltanian-Zadeh 2,3, and Shahram Akhlaghpoor 4 1 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, Wayne State
Detection and Severity Scoring of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Using Volumetric Analysis of Lung CT Images ABSTRACT
 chest imaging Iran J Radiol. 2012;9(1):22-27. DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.6759 Iranian Journal of RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGYwww.iranjradiol.com Detection and Severity Scoring of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
chest imaging Iran J Radiol. 2012;9(1):22-27. DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.6759 Iranian Journal of RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGYwww.iranjradiol.com Detection and Severity Scoring of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Impact of Exacerbations on Emphysema Progression in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Impact of Exacerbations on Emphysema Progression in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Naoya Tanabe 1, Shigeo Muro 1, Toyohiro Hirai 1, Tsuyoshi Oguma 1, Kunihiko Terada 1, Satoshi Marumo 1, Daisuke
Impact of Exacerbations on Emphysema Progression in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Naoya Tanabe 1, Shigeo Muro 1, Toyohiro Hirai 1, Tsuyoshi Oguma 1, Kunihiko Terada 1, Satoshi Marumo 1, Daisuke
Regional Comparisons of CT Air Trapping and MRI Ventilation Defect Percent in Asthma
 Regional Comparisons of CT Air Trapping and MRI Ventilation Defect Percent in Asthma V. A. Zavaletta 1, D.G. Mummy 4, T. Lampkins 4, W. Zha 4, M. L. Schiebler 1, N. Jarjour 3, L. Denlinger 3, and S.B.
Regional Comparisons of CT Air Trapping and MRI Ventilation Defect Percent in Asthma V. A. Zavaletta 1, D.G. Mummy 4, T. Lampkins 4, W. Zha 4, M. L. Schiebler 1, N. Jarjour 3, L. Denlinger 3, and S.B.
Quantitative evaluation by high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of patients with asthma and emphysema
 19 Evaluation by HRCT in asthma and emphysema Quantitative evaluation by high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of patients with asthma and emphysema Fumihiro Mitsunobu, Takashi Mifune, Kozo Ashida,
19 Evaluation by HRCT in asthma and emphysema Quantitative evaluation by high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of patients with asthma and emphysema Fumihiro Mitsunobu, Takashi Mifune, Kozo Ashida,
Densitometry for assessment of effect of Lung Volume Reduction. Surgery for emphysema
 ERJ Express. Published on March 1, 2007 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00056206 Densitometry for assessment of effect of Lung Volume Reduction Surgery for emphysema 1 Jan Stolk, 2 Michel I.M. Versteegh, 1 Leon
ERJ Express. Published on March 1, 2007 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00056206 Densitometry for assessment of effect of Lung Volume Reduction Surgery for emphysema 1 Jan Stolk, 2 Michel I.M. Versteegh, 1 Leon
AUR, Acad Radiol 2003; 10:
 Characterization of the Interstitial Lung Diseases via Density-Based and Texture-Based Analysis of Computed Tomography Images of Lung Structure and Function 1 Eric A. Hoffman, PhD, Joseph M. Reinhardt,
Characterization of the Interstitial Lung Diseases via Density-Based and Texture-Based Analysis of Computed Tomography Images of Lung Structure and Function 1 Eric A. Hoffman, PhD, Joseph M. Reinhardt,
Automated Detection System for Pulmonary Emphysema on 3D Chest Images
 Automated Detection System for Pulmonary Emphysema on 3D Chest Images Takeshi Hara, Akira Yamamoto, Xiangrong Zhou, Shingo Iwano*, Shigeki Itoh*, Hiroshi Fujita, and Takeo Ishigaki* Department of Intelligent
Automated Detection System for Pulmonary Emphysema on 3D Chest Images Takeshi Hara, Akira Yamamoto, Xiangrong Zhou, Shingo Iwano*, Shigeki Itoh*, Hiroshi Fujita, and Takeo Ishigaki* Department of Intelligent
Functional Impairment in Emphysema: Contribution of Airway Abnormalities and Distribution of Parenchymal Disease
 Functional Impairment in Emphysema Chest Imaging Original Research Zelena A. Aziz 1 Athol U. Wells 2 Sujal R. Desai 3 Stephen M. Ellis 4 Amanda E. Walker 5 Sharyn MacDonald 6 David M. Hansell 1 Aziz ZA,
Functional Impairment in Emphysema Chest Imaging Original Research Zelena A. Aziz 1 Athol U. Wells 2 Sujal R. Desai 3 Stephen M. Ellis 4 Amanda E. Walker 5 Sharyn MacDonald 6 David M. Hansell 1 Aziz ZA,
Normal Range of Emphysema and Air Trapping on CT in Young Men
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Mets et al. CT of Emphysema and Air Trapping Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Onno M. Mets 1 Robert A. van Hulst 2,3 Colin Jacobs 4,5 Bram van Ginneken
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Mets et al. CT of Emphysema and Air Trapping Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Onno M. Mets 1 Robert A. van Hulst 2,3 Colin Jacobs 4,5 Bram van Ginneken
MSc. eng. Artur Wujcicki. Ventilation-perfusion lung imaging by filtering MR image sequence
 TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF LODZ FACULTY OF ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONIC, COMPUTER AND CONTROL ENGINEERING INSTITUTE OF ELECTRONICS MSc. eng. Artur Wujcicki Abstract of Ph.D. Thesis Ventilation-perfusion lung imaging
TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF LODZ FACULTY OF ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONIC, COMPUTER AND CONTROL ENGINEERING INSTITUTE OF ELECTRONICS MSc. eng. Artur Wujcicki Abstract of Ph.D. Thesis Ventilation-perfusion lung imaging
Emphysema Scores Predict Death From COPD and Lung Cancer
 CHEST Original Research Emphysema Scores Predict Death From COPD and Lung Cancer Javier J. Zulueta, MD, FCCP ; Juan P. Wisnivesky, MD, DrPH ; Claudia I. Henschke, PhD, MD ; Rowena Yip, MPH ; Ali O. Farooqi,
CHEST Original Research Emphysema Scores Predict Death From COPD and Lung Cancer Javier J. Zulueta, MD, FCCP ; Juan P. Wisnivesky, MD, DrPH ; Claudia I. Henschke, PhD, MD ; Rowena Yip, MPH ; Ali O. Farooqi,
Research Protocol: Project summary
 Research Protocol: First clinical study with AiDA on patients as presented in the manuscript Can a single-breath nanoaerosol inhalation detect emphysema? A case-control study Project summary Nanoparticles
Research Protocol: First clinical study with AiDA on patients as presented in the manuscript Can a single-breath nanoaerosol inhalation detect emphysema? A case-control study Project summary Nanoparticles
Airway wall thickness associated with forced expiratory volume in 1 second decline and development of airflow limitation
 ERJ Express. Published on January 22, 2015 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00020714 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IN PRESS CORRECTED PROOF Airway wall thickness associated with forced expiratory volume in 1 second decline
ERJ Express. Published on January 22, 2015 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00020714 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IN PRESS CORRECTED PROOF Airway wall thickness associated with forced expiratory volume in 1 second decline
CREATIS UMR CNRS 5520 INSERM U
 Helium-3 MRI: Clinical applications of quantitative measurements of regional lung ventilation Y Berthezène Hôpital de la Croix Rousse- CREATIS UMR CNRS 5520 INSERM U 630 Lyon-France For a variety of lung
Helium-3 MRI: Clinical applications of quantitative measurements of regional lung ventilation Y Berthezène Hôpital de la Croix Rousse- CREATIS UMR CNRS 5520 INSERM U 630 Lyon-France For a variety of lung
Copyright 2003 IEEE. Reprinted from IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 22, no. 10, pp , Oct
 Copyright 2003 IEEE. Reprinted from IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 22, no. 10, pp. 1259-1274, Oct. 2003. This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE
Copyright 2003 IEEE. Reprinted from IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 22, no. 10, pp. 1259-1274, Oct. 2003. This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE
May-Lin Wilgus. A. Study Purpose and Rationale
 Utility of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis Program in the Evaluation of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules Detected on Computed Tomography Scans: A Prospective Observational Study May-Lin Wilgus A. Study Purpose and
Utility of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis Program in the Evaluation of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules Detected on Computed Tomography Scans: A Prospective Observational Study May-Lin Wilgus A. Study Purpose and
An application to pulmonary emphysema classification based on model of texton learning by sparse representation
 An application to pulmonary emphysema classification based on model of texton learning by sparse representation Min Zhang* a, Xiangrong Zhou a, Satoshi Goshima b, Huayue Chen c, Chisako Muramatsu a, Takeshi
An application to pulmonary emphysema classification based on model of texton learning by sparse representation Min Zhang* a, Xiangrong Zhou a, Satoshi Goshima b, Huayue Chen c, Chisako Muramatsu a, Takeshi
Quantitative Computed Tomography in COPD: Possibilities and Limitations
 Lung (2012) 190:133 145 DOI 10.1007/s00408-011-9353-9 Quantitative Computed Tomography in COPD: Possibilities and Limitations O. M. Mets P. A. de Jong B. van Ginneken H. A. Gietema J. W. J. Lammers Received:
Lung (2012) 190:133 145 DOI 10.1007/s00408-011-9353-9 Quantitative Computed Tomography in COPD: Possibilities and Limitations O. M. Mets P. A. de Jong B. van Ginneken H. A. Gietema J. W. J. Lammers Received:
Lung Region Segmentation using Artificial Neural Network Hopfield Model for Cancer Diagnosis in Thorax CT Images
 Automation, Control and Intelligent Systems 2015; 3(2): 19-25 Published online March 20, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/acis) doi: 10.11648/j.acis.20150302.12 ISSN: 2328-5583 (Print); ISSN:
Automation, Control and Intelligent Systems 2015; 3(2): 19-25 Published online March 20, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/acis) doi: 10.11648/j.acis.20150302.12 ISSN: 2328-5583 (Print); ISSN:
Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema; prevalence and follow up among health-care personnel
 Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema; prevalence and follow up among health-care personnel Poster No.: C-0698 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Chae, G. Jin, S. Chon, Y. Lee;
Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema; prevalence and follow up among health-care personnel Poster No.: C-0698 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Chae, G. Jin, S. Chon, Y. Lee;
Automatic recognition of lung lobes and fissures from multi-slice CT images
 Automatic recognition of lung lobes and fissures from multi-slice CT images Xiangrong Zhou* a, Tatsuro Hayashi a, Takeshi Hara a, Hiroshi Fujita a, Ryujiro Yokoyama b, Takuji Kiryu b, Hiroaki Hoshi b a
Automatic recognition of lung lobes and fissures from multi-slice CT images Xiangrong Zhou* a, Tatsuro Hayashi a, Takeshi Hara a, Hiroshi Fujita a, Ryujiro Yokoyama b, Takuji Kiryu b, Hiroaki Hoshi b a
( ) (COPD) , Vol.J91-D No.7 pp MR PET/CT (COPD) 91.2%, 89.7% PET/CT. 99.3% 5mm 5.61
 ( ) (COPD) CT, Vol.J91-D No.7 pp.1715-17292008 CTMRI PET/CT ( )(COPD) CT MR PET/CT 8 CT CT 40 40 91.2%, 89.7% CT CT 80 99.3%5mm 5.61 CT CT CT CT CT 3 CT BMD 526 99.24% 98.39% CT GUI CADe CT 99.3% 5mm 5.61
( ) (COPD) CT, Vol.J91-D No.7 pp.1715-17292008 CTMRI PET/CT ( )(COPD) CT MR PET/CT 8 CT CT 40 40 91.2%, 89.7% CT CT 80 99.3%5mm 5.61 CT CT CT CT CT 3 CT BMD 526 99.24% 98.39% CT GUI CADe CT 99.3% 5mm 5.61
HRCT Versus Volume Rendering (Three Colors, Three Densities Lung Images) in Diagnosis of Small Airway Disease: A Comparative Study
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 1, March: 359-364, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net HRCT Versus Volume Rendering (Three Colors, Three Densities Lung Images) in Diagnosis of Small Airway Disease:
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 1, March: 359-364, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net HRCT Versus Volume Rendering (Three Colors, Three Densities Lung Images) in Diagnosis of Small Airway Disease:
Copyright 2007 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, volume 6514, Medical Imaging
 Copyright 2007 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, volume 6514, Medical Imaging 2007: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as
Copyright 2007 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, volume 6514, Medical Imaging 2007: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as
Quantitative assessment of emphysema distribution in smokers and patients with a 1 -antitrypsin deficiency
 Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 94 100 Quantitative assessment of emphysema distribution in smokers and patients with a 1 -antitrypsin deficiency Trine Stavngaard, Saher B. Shaker, Asger Dirksen Department
Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 94 100 Quantitative assessment of emphysema distribution in smokers and patients with a 1 -antitrypsin deficiency Trine Stavngaard, Saher B. Shaker, Asger Dirksen Department
Understanding the contribution of native tracheobronchial structure to lung function: CT assessment of airway morphology in never smokers
 Diaz et al. Respiratory Research (2015) 16:23 DOI 10.1186/s12931-015-0181-y RESEARCH Open Access Understanding the contribution of native tracheobronchial structure to lung function: CT assessment of airway
Diaz et al. Respiratory Research (2015) 16:23 DOI 10.1186/s12931-015-0181-y RESEARCH Open Access Understanding the contribution of native tracheobronchial structure to lung function: CT assessment of airway
Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A. Lynch, MB Disclosures Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A Lynch, MB Consultant: t Research support: Perceptive Imaging Boehringer Ingelheim
Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A. Lynch, MB Disclosures Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A Lynch, MB Consultant: t Research support: Perceptive Imaging Boehringer Ingelheim
Imaging biomarkers for patient selection and treatment planning in emphysema
 Review Imaging biomarkers for patient selection and treatment planning in emphysema Emphysema is a disease that causes destruction of lung tissue and an overall reduction in lung compliance as air becomes
Review Imaging biomarkers for patient selection and treatment planning in emphysema Emphysema is a disease that causes destruction of lung tissue and an overall reduction in lung compliance as air becomes
CT Screening for Lung Cancer: Frequency and Significance of Part-Solid and Nonsolid Nodules
 Claudia I. Henschke 1 David F. Yankelevitz 1 Rosna Mirtcheva 1 Georgeann McGuinness 2 Dorothy McCauley 1 0lli S. Miettinen 3 for the ELCAP Group Received June 19, 2001; accepted after revision November
Claudia I. Henschke 1 David F. Yankelevitz 1 Rosna Mirtcheva 1 Georgeann McGuinness 2 Dorothy McCauley 1 0lli S. Miettinen 3 for the ELCAP Group Received June 19, 2001; accepted after revision November
Identification of Missed Pulmonary Nodules on Low Dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Studies Using an Automatic Detection System
 Identification of Missed Pulmonary Nodules on Low Dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Studies Using an Automatic Detection System Carol L. Novak *a, Li Fan a, Jianzhong Qian a, Guo-Qing Wei a, David P. Naidich
Identification of Missed Pulmonary Nodules on Low Dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Studies Using an Automatic Detection System Carol L. Novak *a, Li Fan a, Jianzhong Qian a, Guo-Qing Wei a, David P. Naidich
Lung transplantation is the ultimate treatment for. Functional Analysis in Single-Lung Transplant Recipients*
 Functional Analysis in Single-Lung Transplant Recipients* A Comparative Study of High-Resolution CT, 3 He- MRI, and Pulmonary Function Tests Julia Zaporozhan, MS; Sebastian Ley, MD; Klaus Kurt Gast, MD;
Functional Analysis in Single-Lung Transplant Recipients* A Comparative Study of High-Resolution CT, 3 He- MRI, and Pulmonary Function Tests Julia Zaporozhan, MS; Sebastian Ley, MD; Klaus Kurt Gast, MD;
LUNG NODULE SEGMENTATION FOR COMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSIS
 LUNG NODULE SEGMENTATION FOR COMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSIS Manjula.T 1 Sheela.S 2 Shanthala.C.P 3 1 Fourth Sem M.Tech (CSE), CIT Gubbi, Tumkur. Email: manjula.t44@gmail.com 2 Asst. Professor, Dept of CSE, CIT
LUNG NODULE SEGMENTATION FOR COMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSIS Manjula.T 1 Sheela.S 2 Shanthala.C.P 3 1 Fourth Sem M.Tech (CSE), CIT Gubbi, Tumkur. Email: manjula.t44@gmail.com 2 Asst. Professor, Dept of CSE, CIT
Respiratory Research. Open Access. Abstract. BioMed Central
 Respiratory Research BioMed Central Research Exploring the optimum approach to the use of CT densitometry in a randomised placebo-controlled study of augmentation therapy in alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency
Respiratory Research BioMed Central Research Exploring the optimum approach to the use of CT densitometry in a randomised placebo-controlled study of augmentation therapy in alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency
Small Pulmonary Nodules: Our Preliminary Experience in Volumetric Analysis of Doubling Times
 Small Pulmonary Nodules: Our Preliminary Experience in Volumetric Analysis of Doubling Times Andrea Borghesi, MD Davide Farina, MD Roberto Maroldi, MD Department of Radiology University of Brescia Brescia,
Small Pulmonary Nodules: Our Preliminary Experience in Volumetric Analysis of Doubling Times Andrea Borghesi, MD Davide Farina, MD Roberto Maroldi, MD Department of Radiology University of Brescia Brescia,
C hronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) develops
 837 CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE Relationship between peripheral airway dysfunction, airway obstruction, and neutrophilic inflammation in COPD R A O Donnell, C Peebles, J A Ward, A Daraker, G
837 CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE Relationship between peripheral airway dysfunction, airway obstruction, and neutrophilic inflammation in COPD R A O Donnell, C Peebles, J A Ward, A Daraker, G
Visual Assessment of CT Findings in Smokers With Nonobstructed Spirometric Abnormalities in The COPDGene Study
 88 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Original Research. Visual Assessment of CT Findings in Smokers With Nonobstructed Spirometric Abnormalities in The COPDGene Study
88 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Original Research. Visual Assessment of CT Findings in Smokers With Nonobstructed Spirometric Abnormalities in The COPDGene Study
CT-Densitometry A structure-based quantitative analysis of lung-ct in emphysema
 CT-Densitometry A structure-based quantitative analysis of lung-ct in emphysema R.A. Blechschmidt and U. Lörcher Department of Radiology, Deutsche Klinik für Diagnostik Aukammallee 33, 65191 Wiesbaden,
CT-Densitometry A structure-based quantitative analysis of lung-ct in emphysema R.A. Blechschmidt and U. Lörcher Department of Radiology, Deutsche Klinik für Diagnostik Aukammallee 33, 65191 Wiesbaden,
Computed tomography-quantified emphysema distribution is associated with lung function decline
 Eur Respir J 2012; 40: 844 850 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00186311 CopyrightßERS 2012 Computed tomography-quantified emphysema distribution is associated with lung function decline Firdaus A.A. Mohamed Hoesein*,
Eur Respir J 2012; 40: 844 850 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00186311 CopyrightßERS 2012 Computed tomography-quantified emphysema distribution is associated with lung function decline Firdaus A.A. Mohamed Hoesein*,
USEFULNESS OF HRCT IN DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY INVOLVEMENT IN SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS
 USEFULNESS OF HRCT IN DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY INVOLVEMENT IN SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS Brestas P., Vergadis V., Emmanouil E., Malagari K. 2 nd Dept of Radiology, University of Athens, Greece ABSTRACT
USEFULNESS OF HRCT IN DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY INVOLVEMENT IN SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS Brestas P., Vergadis V., Emmanouil E., Malagari K. 2 nd Dept of Radiology, University of Athens, Greece ABSTRACT
Low Grade Coal Worker's Pneumoconiosis
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-181 (Print) 1600-04 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Low Grade Coal Worker's Pneumoconiosis P. A. Gevenois, E. Pichot, F. Dargent, S. Dedeire,
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-181 (Print) 1600-04 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Low Grade Coal Worker's Pneumoconiosis P. A. Gevenois, E. Pichot, F. Dargent, S. Dedeire,
Detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment using Image Differences and Clinical Features
 Detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment using Image Differences and Clinical Features L I N L I S C H O O L O F C O M P U T I N G C L E M S O N U N I V E R S I T Y Copyright notice Many of the images in
Detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment using Image Differences and Clinical Features L I N L I S C H O O L O F C O M P U T I N G C L E M S O N U N I V E R S I T Y Copyright notice Many of the images in
Chapter 6. Hester Gietema Cornelia Schaefer-Prokop Willem Mali Gerard Groenewegen Mathias Prokop. Accepted for publication in Radiology
 Chapter 6 Interscan variability of semiautomated volume measurements in intraparenchymal pulmonary nodules using multidetector-row computed tomography: Influence of inspirational level, nodule size and
Chapter 6 Interscan variability of semiautomated volume measurements in intraparenchymal pulmonary nodules using multidetector-row computed tomography: Influence of inspirational level, nodule size and
A VIRTUAL TRAINING SYSTEM FOR CHEST RADIOGRAM INTERPRETATIONS USING ANATOMICAL HUMAN STRUCTURES IN HIGH-RESOLUTION CT IMAGES
 A VIRTUAL TRAINING SYSTEM FOR CHEST RADIOGRAM INTERPRETATIONS USING ANATOMICAL HUMAN STRUCTURES IN HIGH-RESOLUTION CT IMAGES T. Hara*, X. Zhou*, H. Fujita*, I. Kurimoto*, T. Kiryu**, R. Yokoyama**, H.
A VIRTUAL TRAINING SYSTEM FOR CHEST RADIOGRAM INTERPRETATIONS USING ANATOMICAL HUMAN STRUCTURES IN HIGH-RESOLUTION CT IMAGES T. Hara*, X. Zhou*, H. Fujita*, I. Kurimoto*, T. Kiryu**, R. Yokoyama**, H.
Original Article. Sang Ok Park, MD 1, Joon Beom Seo, MD 1, Namkug Kim, PhD 1, Young Kyung Lee, MD 2, Jeongjin Lee, PhD 3, Dong Soon Kim, MD 4
 Original Article DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.297 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):297-307 Comparison of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia: Quantification
Original Article DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.297 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):297-307 Comparison of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia: Quantification
Factors influencing the decline in lung density in a Danish lung cancer screening cohort
 Eur Respir J 2012; 40: 1142 1148 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00207911 CopyrightßERS 2012 Factors influencing the decline in lung density in a Danish lung cancer screening cohort Saher B. Shaker*, Asger Dirksen*,
Eur Respir J 2012; 40: 1142 1148 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00207911 CopyrightßERS 2012 Factors influencing the decline in lung density in a Danish lung cancer screening cohort Saher B. Shaker*, Asger Dirksen*,
Learning Objectives. 1. Identify which patients meet criteria for annual lung cancer screening
 Disclosure I, Taylor Rowlett, DO NOT have a financial interest /arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict of interest in the context
Disclosure I, Taylor Rowlett, DO NOT have a financial interest /arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict of interest in the context
Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose?
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
SIMONETTA BALDI, MASSIMO MINIATI, CALOGERO RICCARDO BELLINA, LUIGI BATTOLLA, GIOSUÉ CATAPANO, ENRICO BEGLIOMINI, DAVIDE GIUSTINI, and CARLO GIUNTINI
 Relationship between Extent of Pulmonary Emphysema by High-resolution Computed Tomography and Lung Elastic Recoil in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease SIMONETTA BALDI, MASSIMO MINIATI,
Relationship between Extent of Pulmonary Emphysema by High-resolution Computed Tomography and Lung Elastic Recoil in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease SIMONETTA BALDI, MASSIMO MINIATI,
Interobserver Variability in the Determination of Upper Lobe- Predominant Emphysema*
 CHEST Interobserver Variability in the Determination of Upper Lobe- Predominant Emphysema* Original Research Craig P. Hersh, MD, MPH; George R. Washko, MD; Francine L. Jacobson, MD, MPH; Ritu Gill, MBBS;
CHEST Interobserver Variability in the Determination of Upper Lobe- Predominant Emphysema* Original Research Craig P. Hersh, MD, MPH; George R. Washko, MD; Francine L. Jacobson, MD, MPH; Ritu Gill, MBBS;
Segmentation-Based Quantitation of Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis, Pre- and Post-Lavage, Using High-Resolution Computed Tomography
 -61- Segmentation-Based Quantitation of Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis, Pre- and Post-Lavage, Using High-Resolution Computed Tomography Tessa Sundaram Cook 1, Nicholas Tustison 1, Gang Song 2, Suyash Awate
-61- Segmentation-Based Quantitation of Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis, Pre- and Post-Lavage, Using High-Resolution Computed Tomography Tessa Sundaram Cook 1, Nicholas Tustison 1, Gang Song 2, Suyash Awate
BronCare: clinical multimedia system for new therapies assessment in asthma
 BronCare: clinical multimedia system for new therapies assessment in asthma A. SARAGAGLIA, C. FETITA, and F. PRETEUX ARTEMIS Project Unit, GET/INT, Evry, FRANCE 9, Rue Charles Fourier, 91011, Evry-France
BronCare: clinical multimedia system for new therapies assessment in asthma A. SARAGAGLIA, C. FETITA, and F. PRETEUX ARTEMIS Project Unit, GET/INT, Evry, FRANCE 9, Rue Charles Fourier, 91011, Evry-France
Growth Pattern Analysis of Murine Lung Neoplasms by Advanced Semi-Automated Quantification of Micro-CT Images
 Growth Pattern Analysis of Murine Lung Neoplasms by Advanced Semi-Automated Quantification of Micro-CT Images Minxing Li 1., Artit Jirapatnakul 2., Alberto Biancardi 2, Mark L. Riccio 3, Robert S. Weiss
Growth Pattern Analysis of Murine Lung Neoplasms by Advanced Semi-Automated Quantification of Micro-CT Images Minxing Li 1., Artit Jirapatnakul 2., Alberto Biancardi 2, Mark L. Riccio 3, Robert S. Weiss
Validation of lung densitometry threshold at CT for the distinction between senile lung and emphysema in elderly subjects
 Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 2011; 75: 3, 162-166 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validation of lung densitometry threshold at CT for the distinction between senile lung and emphysema in elderly subjects M. Bellia 1, A. Benfante
Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 2011; 75: 3, 162-166 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validation of lung densitometry threshold at CT for the distinction between senile lung and emphysema in elderly subjects M. Bellia 1, A. Benfante
Imaging Emphysema 3-Helium MR Imaging
 Imaging Emphysema 3-Helium MR Imaging Edwin J.R. van Beek MD PhD MEd FRCR Professor of Radiology and Medicine Carver College of Medicine, University of Iowa, USA. Permanent Visiting Professor of Radiology,
Imaging Emphysema 3-Helium MR Imaging Edwin J.R. van Beek MD PhD MEd FRCR Professor of Radiology and Medicine Carver College of Medicine, University of Iowa, USA. Permanent Visiting Professor of Radiology,
Compute-aided Differentiation of Focal Liver Disease in MR Imaging
 1063 Compute-aided Differentiation of Focal Liver Disease in MR Imaging Xuejun Zhang a, Masayuki Kanematsu b, Hiroshi Fujita c, Takeshi Hara c, Hiroshi Kondo b, Xiangrong Zhou c, Wenguang Li a and Hiroaki
1063 Compute-aided Differentiation of Focal Liver Disease in MR Imaging Xuejun Zhang a, Masayuki Kanematsu b, Hiroshi Fujita c, Takeshi Hara c, Hiroshi Kondo b, Xiangrong Zhou c, Wenguang Li a and Hiroaki
Nestor L. Müller, MD, PhD Professor Emeritus of Radiology University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC, Canada
 Atlas of Interstitial Lung Disease Pathology Pathology with High Resolution CT Correlations First Edition Andrew Churg, MD Professor of Pathology University of British Columbia Pathologist, Vancouver General
Atlas of Interstitial Lung Disease Pathology Pathology with High Resolution CT Correlations First Edition Andrew Churg, MD Professor of Pathology University of British Columbia Pathologist, Vancouver General
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
of the right B 10 fourth, r = 0.476, p < ; B 10
 Yamashiro et al. CT of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Tsuneo Yamashiro 1,2 Shin Matsuoka 3 Raúl San José Estépar 4 Mark T. Dransfield 5 Alejandro Diaz 6,7
Yamashiro et al. CT of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Tsuneo Yamashiro 1,2 Shin Matsuoka 3 Raúl San José Estépar 4 Mark T. Dransfield 5 Alejandro Diaz 6,7
Division of Medicine, "Division of Rehabilitation, Misasa Medical Center, Okayama University Medical and Dental School
 35 Low attenation area in asthma and Difference in low attenuation area (LAA) of the lungs on high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) between asthma and in relation to cigarette smoking Fumihiro Mitsunobu,
35 Low attenation area in asthma and Difference in low attenuation area (LAA) of the lungs on high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) between asthma and in relation to cigarette smoking Fumihiro Mitsunobu,
Automated Detection of Polyps from Multi-slice CT Images using 3D Morphologic Matching Algorithm: Phantom Study
 Automated Detection of Polyps from Multi-slice CT Images using 3D Morphologic Matching Algorithm: Phantom Study Yonghum Na, Jin Sung Kim, Bruce R Whiting, K. Ty Bae Electronic Radiology Laboratory, Mallinckrodt
Automated Detection of Polyps from Multi-slice CT Images using 3D Morphologic Matching Algorithm: Phantom Study Yonghum Na, Jin Sung Kim, Bruce R Whiting, K. Ty Bae Electronic Radiology Laboratory, Mallinckrodt
Malignant solitary pulmonary nodules: assessment of mass growth rate and doubling time at follow-up CT
 Original Article Malignant solitary pulmonary nodules: assessment of mass growth rate and doubling time at follow-up CT Jingxu Li*, Tingting Xia*, Xinguan Yang, Xiao Dong, Jiamin Liang, Nanshan Zhong,
Original Article Malignant solitary pulmonary nodules: assessment of mass growth rate and doubling time at follow-up CT Jingxu Li*, Tingting Xia*, Xinguan Yang, Xiao Dong, Jiamin Liang, Nanshan Zhong,
Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using Linear Discriminative Analysis and Quadratic Discriminative Analysis
 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
Pulmonary Nodule Volumetric Measurement Variability as a Function of CT Slice Thickness and Nodule Morphology
 CT of Pulmonary Nodules Chest Imaging Original Research Myria Petrou 1 Leslie E. Quint 1 in Nan 2 Laurence H. aker 3 Petrou M, Quint LE, Nan, aker LH Keywords: chest, lung disease, MDCT, oncologic imaging,
CT of Pulmonary Nodules Chest Imaging Original Research Myria Petrou 1 Leslie E. Quint 1 in Nan 2 Laurence H. aker 3 Petrou M, Quint LE, Nan, aker LH Keywords: chest, lung disease, MDCT, oncologic imaging,
Effect of Emphysema on CT Scan Measures of Airway Dimensions in Smokers
 CHEST Original Research Effect of Emphysema on CT Scan Measures of Airway Dimensions in Smokers Alejandro A. Diaz, MD ; MeiLan K. Han, MD ; Carolyn E. Come, MD, MPH ; Raúl San José Estépar, PhD ; James
CHEST Original Research Effect of Emphysema on CT Scan Measures of Airway Dimensions in Smokers Alejandro A. Diaz, MD ; MeiLan K. Han, MD ; Carolyn E. Come, MD, MPH ; Raúl San José Estépar, PhD ; James
