Bo Tian, Chunfeng Song, Hui Li, Wenqian Zhang, Qirui Chen, Shuo Chen, Yili Fu, Xiaoxing Hu, Bin You, Tong Li, Bin Hu, Shengcai Hou
|
|
|
- Lesley Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article The significance of perioperative coagulation and fibrinolysis related parameters after lung surgery for predicting venous thromboembolism: a prospective, single center study Bo Tian, Chunfeng Song, Hui Li, Wenqian Zhang, Qirui Chen, Shuo Chen, Yili Fu, Xiaoxing Hu, Bin You, Tong Li, Bin Hu, Shengcai Hou Department of Thoracic Surgery, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing , China Contributions: (I) Conception and design: B Tian, C Song, H Li; (II) Administrative support: H Li, B Hu, S Hou; (III) Provision of study materials or patients: W Zhang, Q Chen, S Chen, Y Fu, X Hu, B You, T Li; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: B Tian, C Song; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: B Tian; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors. Correspondence to: Hui Li. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing , China. huilee@vip.sina.com. Background: The high incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) has been perceived in post thoracic surgery patients. However, the significance of perioperative coagulation and fibrinolysis related parameters after lung surgery for VTE predicting is not clear. To investigate that, we conducted a prospective single center study. Methods: A total of 111 patients undergoing lung surgery were enrolled in this study, included 52 primary lung cancer patients and 59 benign lung disease patients from July 2016 to March Preoperative and postoperative days 1, 3, and 5 coagulation and fibrinolysis related parameters were tested, including antithrombin (AT), fibrinogen degradation product (FDP), prothrombin time (PT), prothrombin time activity (PA), prothrombin time ratio (PR), international normalized ratio (INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), plasma fibrinogen (FBG), thrombin time (TT) and D-Dimer. The Doppler ultrasonography was performed before and after surgery for deep venous thrombosis (DVT) confirmation. Patients with new postoperative DVT, unexplained dyspnea, hemoptysis, chest pain, or high Caprini score ( 9) were received further computer tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) for pulmonary embolism (PE). We used the area under receiver-operating-characteristic (ROC) curve to discriminate patients between those who developed VTE and those who did not. Single factor analysis was utilized to define risk factors associated with VTE. Results: The overall incidence of VTE was 16.2% (18/111). The incidence of VTE in primary lung cancer patients was 23.1% (12/52), much higher than that in benign lung diseases 10.2% (6/59), but did not reach statistical significance (P=0.066). Among 18 VTE patients, 83.3% was DVT, 16.7% was DVT + PE and 72.2% was muscular veins of the calf thrombosis. D-Dimer was much higher in VTE group than that in non-vte group preoperatively and at postoperative days 1, 3 (0.64±0.24 vs. 0.33±0.06, P=0.007; 3.14±0.75 vs. 1.51±0.09, P=0.005, and 1.88±0.53 vs. 0.76±0.05, P=0.001, respectively). And the ROC curve areas of preoperative and postoperative days 1, 3 of D-Dimer were 0.70, 0.71 and 0.74, respectively. And FDP was much higher in VTE group than that in non-vte group at postoperative day 3 (6.78±1.43 vs. 3.79±0.15, P=0.004). But AT, PT, PA, PR, INR, APTT, FBG and TT there were no significantly difference. Conclusions: The overall incidence of VTE after lung surgery was 16.2%. The patients with preoperative high D-Dimer should receive VTE prophylaxis. Keywords: Lung surgery; venous thromboembolism (VTE); coagulation Submitted Nov 13, Accepted for publication Mar 16, doi: /jtd View this article at:
2 2224 Tian et al. VTE after lung surgery Introduction Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a common postoperative syndrome and a common cause of postoperative death, nevertheless it is also a preventable disease. VTE, which consisting pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep venous thrombosis (DVT), is a major cause of morbidity and mortality after the surgery. Especially the malignant tumor surgery characterizes a greater incidence of postoperative VTE. PE and DVT are same disease expressed differently by parts and stages. Virchow triad including hypercoagulability, stasis and endothelial injury that contribute to the development of venous thrombosis. The surgery and tumor are the main causation of acquired hypercoagulability (1,2). The overall incidence of VTE after operation is approximately 0.8% to 1.6% (3,4), whereas the incidence of VTE after lung cancer surgery is higher than that, from 0.2% to 19% (5). A previous study show that the mortality rate of patients with VTE increase 6-fold, and half of the postoperative deaths are caused by VTE, about 2/3 VTE events occur before discharge (6). During the process of VTE formation, the activation of coagulation and fibrinolysis system is accompanied. Four phases are included in the typical clotting process, the initiation and formation of platelet plug; clotting process propagation by coagulation cascade; the termination of clotting by antithrombotic mechanisms; clot removal by fibrinolysis (7). The operation injures tissue directly, large number of tissue factor (TF) enters the blood in a short time and activate the exogenous coagulation system. Surgery also damages endothelial cells, exposes the elements such as subcutaneous collagen and so endogenous coagulation system could be activated. Therefore, exogenous coagulation starts firstly and then exogenous coagulation system activates endogenous coagulation system in order to maintain and complete blood coagulation process. At the same time fibrinolysis system is activated. However, the significance of perioperative coagulation and fibrinolysis related parameters after lung surgery for VTE predicting is not clear. To investigate that, we conduct a prospective single center study. Methods Patients A single center, prospective study was performed with data collected from patients who had undergone lung resection at Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital from July 2016 to March The color Doppler ultrasonography was performed before and after operation for DVT confirmation. Patients with new postoperative DVT, unexplained dyspnea, hemoptysis, chest pain, or high Caprini score ( 9), highly suspected PE, further computer tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) examination was required. The VTE incidence was evaluated before discharge. Preoperative and postoperative days 1, 3, and 5 coagulation and fibrinolysis related parameters were test, including antithrombin (AT), fibrinogen degradation product (FDP), prothrombin time (PT), prothrombin time activity (PA), prothrombin time ratio (PR), international normalized ratio (INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), plasma fibrinogen (FBG), thrombin time (TT) and D-Dimer. We used the area under the receiver-operating-characteristic (ROC) curve to discriminate between patients between those who developed VTE and those who did not. Single factor analysis was constructed to define risk factors that associated with VTE. The institutional research ethics committee of the Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital approved the study, and all of the patients signed the informed consent preoperatively. Inclusion criteria The medical records of consecutive patients who underwent lung resection but without VTE prevention were reviewed. All the patients underwent open or video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) procedure. Exclusion criteria Patients received any perioperative prophylaxis or anticoagulation with heparin, warfarin, aspirin or lowmolecular-weight heparin; patients had been confirmed with DVT or PE before surgery; patients with missing information, especially those who did not undergo VTE related imaging examine, coagulation and fibrinolysis related parameters blood test before or after surgery. Statistical analysis Continuous variables were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), or medians compared by analysis of Student s t-test or Wilcoxon test. Categorical variables were compared by either the χ 2 test or Fisher s exact test. We used the area under the receiver-operating-characteristic (ROC) curve to discriminate patients between the patients who developed VTE and those who did not. In this study, the area under the ROC curve between 0.5 and 0.7, between 0.7
3 Journal of Thoracic Disease, Vol 10, No 4 April and 0.9 and >0.9 were considered low, moderate and high, respectively. Single factor analysis was constructed to define risk factors associated with VTE. All statistical analyses were carried out with SPSS 23.0 and SigmaPlot 12.0 for Windows. The null hypothesis was rejected for P<0.05. Results From department of Thoracic Surgery, Beijing Chao- Yang Hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University, 111 patients were enrolled in this study, included 52 primary lung cancer patients and 59 benign lung disease patients admitted for lung surgery from July 2016 to March Among those patients, there was no difference about sex, the mean age at the time of surgery was 62.8 years of VTE patients and 52.3 years of non-vte patients (P=0.001). Postoperative VTE incidence was correlated with increasing ASA scores. The VTE incidence in the 1 2 and 3 5 groups was 12.9% and 50.0% respectively. The high-asa patients group had significant higher incidence than the low- ASA group (P=0.010). BMI, postoperative hospital stay, operative time and intraoperative bleeding, of VTE patients were higher than those of non-vte patients (25.2±1.1 vs. 23.3±0.4, P=0.058; 8.6±1.2 vs. 7.2±0.3, P=0.589; 189.1±15.5 vs ±7.9, P=0.183, and 202.8±44.5 vs ±17.9, P=0.484, respectively), but no significant differences were got. And we did not find that postoperative VTE was correlated with operative procedures, type of resection, pathology, lung cancer postoperative stages (Table 1). The overall VTE incidence was 16.2% (18 of 111). The VTE incidence after primary lung cancer surgery was 23.1% (12 of 52), which was higher than that of benign lung diseases 10.2% (6 of 59), but did not reach statistical significance (P=0.066). And VTE incidence of open surgery was higher than that of VATS surgery 25.0% vs. 13.8% (P=0.314). When the complexity of the surgery increased from wedge/ segmentectomy to bilobectomy, the incidence increased from 14.3% to 33.3% (P=0.684). Among 18 VTE lung cancer patients, 83.3% was DVT [15] and 16.7% was DVT + PE [3]; 13 patients (72.2%) manifested muscular veins of the calf thrombosis (Table 2). Preoperative and postoperative days 1, 3 D-Dimer of VTE(+) patients was much higher than that of VTE( ) patients, which were 0.64±0.24 vs. 0.33±0.06, P=0.007; 3.14±0.75 vs. 1.51±0.09, P=0.005 and 1.88±0.53 vs. 0.76±0.05, P=0.001, respectively. But at day 5, D-Dimer has no statistical difference between VTE(+) patients and VTE( ) patients (2.53±0.38 vs. 1.88±0.12, P=0.099). And postoperative days 3 FDP of VTE(+) patients was much higher than that of VTE( ) patients, which was 6.78±1.43 vs. 3.79±0.15, P= But for other parameters, there were no significantly difference (Table 3). And the ROC curve areas of preoperative and postoperative days 1, 3, 5 of D-Dimer were 0.70, 0.71, 0.74 and 0.62, respectively (Figure 1). When we took Youden index as the cutoff point, Pre-D-Dimer Youden index >0.15, the sensitivity was 94.4%, specificity was 44.1% (P=0.007), D1-D-Dimer Youden index >1.26, the sensitivity was 83.3%, specificity was 47.3% (P=0.005), D3-D-Dimer Youden index >0.95, the sensitivity was 66.7%, specificity was 74.2% (P=0.001), D5-D-Dimer Youden index >3.44, the sensitivity was 33.3%, specificity was 92.5% (P=0.099) (Table 4). Discussion The high VTE incidence has been perceived in post-surgery patients. VTE is the most common complication and the main cause of death in the thoracic surgery after operation. This study finds out that the overall VTE incidence is 16.2%. The VTE incidence after primary lung cancer surgery is 23.1%, which is much higher than that of benign lung diseases (10.2%). This finding is consistent with recent study (5). Lung cancer may be responsible for the higher incidence of thrombotic events associated with cancer, but do not reach statistical significance. Among those 111 patients, the median age at the time of surgery was 62.8 years old for the VTE patients and 52.3 years old for the non- VTE patients. VTE is a predominant disease for older ages (8). Postoperative VTE incidence is correlated with increasing ASA scores. The VTE incidence in the 1 2 and 3 5 groups was 12.9% and 50.0% respectively. The high- ASA patients group had significant higher incidence than the low-asa group. Older and high ASA patients are seems more likely to have VTE after operation. In this study, we found that postoperative VTE incidence did not correlate with lung cancer pathology and postoperative stages, while previous literature showed that the VTE incidence of adenocarcinoma histology was 2-fold of squamous cell carcinoma (9). VTE is more common in late-stage cancer patients, and its incidence increases with the tumor progression after operation (10). The product of TF and mucin by adenocarcinomas may be related to this higher risk (11). And also we find open surgery VTE incidence is higher than VATS surgery, which are 25.0% and 13.8% respectively. In addition, the VTE incidence of wedge/ segmentectomy and bilobectomy operation are 14.3% and
4 2226 Tian et al. VTE after lung surgery Table 1 General and operation information for patients Variable VTE(+) (n=18) VTE( ) (n=93) Z value/t value/χ 2 value P value Sex Male Female 8 40 Age (years) 62.8± ± BMI (kg/m 2 ) 25.2± ± ASA Operative procedures VATS Open 6 18 Type of resection * Wedge/segmentectomy 5 30 Lobectomy Lobectomy + wedge 1 6 Bilobectomy 2 4 Postoperative hospital stay (days) 8.6± ± Operative time (min) 189.1± ± Intraoperative bleeding (ml) 202.8± ± Pathology Benign 6 53 Cancer Postoperative stages * I 4 22 II 2 6 III 4 9 IV 0 0 *, Fisher s exact test. VTE, venous thromboembolism; BMI, body mass index; VATS, video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. 33.3% respectively, which means that when the complexity of the surgery increases, the VTE incidence is elevated too. And BMI, postoperative hospital stay, operative time and intraoperative bleeding of VTE patients are higher than those of non-vte patients. A literature demonstrated that prevalence of VTE is 8.9% after total pneumonectomy (12). VTE incidence is higher than we thought previously, the different time of examination could be one reason which caused this different outcome. In some researches, patients received Ultrasound examination for lower limb venous only when they complained with lower limb swelling, pain and so on. However, in our study, Ultrasound examination was routinely performed before and after the surgery in order to get an accurate and timely diagnosis with VTE.
5 Journal of Thoracic Disease, Vol 10, No 4 April Table 2 VTE information for patients Variable Cases (n=18) Ratio DVT(+)PE( ) DVT( )PE(+) 0 0 DVT(+)PE(+) VTE, venous thromboembolism; DVT, deep venous thrombosis; PE, pulmonary embolism. Table 3 (continued) Variable INR VTE(+) (n=18) VTE( ) (n=93) Z value/t value/χ 2 value P value Pre-op 1.02± ± D1 1.09± ± D3 1.05± ± D5 1.05± ± Table 3 Perioperative coagulation and fibrinolysis related parameters results Variable AT (%) VTE(+) (n=18) VTE( ) (n=93) Z value/t value/χ 2 value P value Pre-op 89.73± ± D ± ± D ± ± D ± ± FDP (μg/ml) Pre-op 2.21± ± D ± ± D3 6.78± ± D5 7.46± ± PT (s) Pre-op 12.10± ± D ± ± D ± ± D ± ± PA (%) PR Pre-op 90.30± ± D ± ± D ± ± D ± ± Pre-op 1.04± ± D1 1.10± ± D3 1.07± ± D5 1.08± ± Table 3 (continued) APTT (s) Pre-op 28.60± ± D ± ± D ± ± D ± ± FBG (mg/dl) Pre-op ± ± D ± ± D ± ± D ± ± TT (s) Pre-op 18.00± ± D ± ± D ± ± D ± ± D-Dimer (mg/l) Pre-op 0.64± ± D1 3.14± ± D3 1.88± ± D5 2.53± ± VTE, venous thromboembolism; AT, antithrombin; FDP, fibrinogen degradation product; PT, prothrombin time; PA, prothrombin time activity; PR, prothrombin time ratio; INR, international normalized ratio; APTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; FBG, plasma fibrinogen; TT, thrombin time. Because VTE usually develops before significant clinical manifestation occurs, we showed the VTE incidence in postoperative patients is higher than that in other studies, indicating that the real incidence may be underestimated previously. Among 18 VTE patients, VTE mainly happens in deep
6 2228 Tian et al. VTE after lung surgery vein thrombosis, with an occupation of 83.3% over total population, while pure PE is less likely to happen, with an incidence rate of 0%. It is reported that PE was confirmed in 15.2% of postoperative deaths by autopsy, indicating that it is a frequently fatal postoperative complication (13). Among those 18 patients, 13 (72.2%) of which manifested distal isolated calf muscular venous thrombosis. It is generally acknowledged that the calf muscular venous thrombosis has a lower venous extend risk than axial venous thrombosis (such as fibular venous and femoral venous thrombosis) (14). Whether to apply anticoagulation therapy for calf muscular venous thrombosis is still controversial, presently in our department we have taken standardize anticoagulation therapy, and closely follow-up with post operational visit, the therapeutic effect and risks still remain to be observed. A literature demonstrated that the fatal recurrence rate of Sensitivity ROC curves Pre-D-Dimer, A=0.70 D1-D-Dimer, A=0.71 D3-D-Dimer, A=0.74 D5-D-Dimer, A= Specifity Figure 1 ROC curves of preoperative and postoperative days 1, 3 and 5 of D-Dimer. ROC, receiver-operating-characteristic. VTE is as high as 5% to 9% in patients, yet the occurrence of postoperative VTE is occult, and lack of characteristic clinical manifestations (15). It is mainly diagnosed by lower limb venous color Doppler ultrasonography and the CT imaging of pulmonary blood vessels. Once DVT patients form PE, it will cause serious damage to the patient s health, even lead to sudden death. Malignant tumor patients with VTE have a poorer prognosis, the average survival period is much shorter. Perioperative VTE is the second most common complication for inpatients and the third most common cause of mortality, leading to the delay of postoperative recovery, increase treatment costs and longer hospital stays. This will further induce a great adverse effect on the prognosis of surgical patients and become one of the most important causes of unanticipated death after surgery (16), so the prevention of VTE is very important. Although a previous meta-analysis (17) stated that the incidence of DVT patients with pharmacological thromboprophylaxis was relatively decreased compared with those without, the incidence of bleeding events also has been found out experienced a significant increase. A significant difference has been detected at the time of the first dose usage preoperatively, but no clue on postoperative patients. A literature (18) demonstrated that it is safe and feasible to take preoperative use of heparin for thromboprophylaxis in Chinese patients. However, due to the usage risks of heparin, the timing of anticoagulation is important. In our study, preoperative and postoperative days 1, 3 D-Dimer of VTE(+) patients is much higher than that of VTE( ) patients, which are 0.64±0.24 vs. 0.33±0.06, P=0.007; 3.14±0.75 vs. 1.51±0.09, P=0.005 and 1.88±0.53 vs. 0.76±0.05, P=0.001, respectively. And postoperative days 3 FDP of VTE(+) patients is much higher than that of VTE( ) patients, which is 6.78±1.43 vs. 3.79±0.15, P= Patients with VTE positive have shown a significant increase of D-Dimer before surgery, almost 2-fold higher, suggesting that such patients show a preoperative state Table 4 Perioperative ROC curve area and Youden index and corresponding sensitivity and specificity of D-Dimer Variable ROC curve area 95% confidence interval Youden index Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) P value Pre-D-Dimer > D1-D-Dimer > D3-D-Dimer > D5-D-Dimer > ROC, receiver-operating-characteristic.
7 Journal of Thoracic Disease, Vol 10, No 4 April of thrombosis. And the postoperative D-Dimer is rapidly elevated, with significant statistical differences between the first and third day after surgery. D-Dimer is cross linked fibrin fibrinolysis enzyme hydrolysis to produce a specific molecular markers, and its level reflects the extent of the secondary fibrinolysis inside body, can be used as high coagulation state in the body and an important index of hyper fibrinolysis. And the ROC curve areas of preoperative and postoperative days 1, 3, 5 of D-Dimer are 0.70, 0.71, 0.74 and 0.62, respectively. When take Youden index as the cutoff point, D3-D-Dimer Youden index >0.95, the sensitivity is 66.7%, specificity is 74.2%. From the ROC curve area preoperative and postoperative days 1, 3 D-Dimer have a moderate discrimination between patients who develop VTE and those who do not. And D3-D-Dimer has the highest ROC curve area, and corresponding sensitivity and specificity is both high. So we think the patients with preoperative high D-Dimer should receive VTE prophylaxis. But further research is still needed to confirm it. The main objective of the treatment of deep vein thrombosis is to prevent PE, especially in the early stage of the course of the disease, since the thrombus and the wall of blood vessels are not tight and easy to fall off. In order to avoid the serious threat of PE, all high-risk patients with DVT, such as the patients with femoral head fracture, larger orthopedic or pelvic surgery and the elderly with high blood viscosity should be prevented in advance. The ninth edition antithrombotic and thrombolysis therapy evidence-based guidelines were published in 2012 by American thoracic society (American College of Chest Physicians, ACCP) (19), suggesting VTE therapy and prevention for orthopedic surgery patients. But there are no specific guidelines about VTE therapy and prevention after thoracic surgery. Actually, in China, prophylaxis is not the routine management in most hospitals after thoracic surgery. The main reason is majority of thoracic surgeons in China does not realize the high incidence of postoperative VTE. Secondly, there are no relevant data from China to support prophylaxis after thoracic surgery. Through the early questionnaires survey researched on 1,150 thoracic surgery doctors found that 46.9% of thoracic surgeons did not prevent against VTE, 56.2% of them think that no thoracic surgery related guidelines is the main reason that they did not take the prevention and 99.6% of those doctors considered that VTE prevention was quite necessary. Therefore, through this research, we find out a relatively accurate data on the incidence of postoperative VTE after lung surgery, but this is just a single center study, in order to indicate the most meaningful risk factors that could explain the prevalence of postoperative VTE, set the most suitable risk score standard for Chinese patients, and eventually develop the specialists consensus and guidelines on VTE prevention for Chinese thoracic surgery, there are many works need to do. Acknowledgements Thank you for my wife Fuli Liu, for taking care of our child and family while I am studying for my doctorate. Footnote Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Ethical Statement: This study was approved by the Institutional Research Ethics Committee of Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University (ID: 2017-Ke-1). All the patients signed the informed consent preoperatively. The study outcomes will not affect the future management of the patients. References 1. Bagot CN, Arya R. Virchow and his triad: a question of attribution. Br J Haematol 2008;143: Goldhaber SZ. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;56: Nelson RE, Grosse SD, Waitzman NJ, et al. Using multiple sources of data for surveillance of postoperative venous thromboembolism among surgical patients treated in Department of Veterans Affairs hospitals, Thromb Res 2015;135: Merkow RP, Bilimoria KY, McCarter MD, et al. Postdischarge venous thromboembolism after cancer surgery: extending the case for extended prophylaxis. Ann Surg 2011;254: Christensen TD, Vad H, Pedersen S, et al. Venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing operations for lung cancer: a systematic review. Ann Thorac Surg 2014;97: Agnelli G, Bolis G, Capussotti L, et al. A clinical outcomebased prospective study on venous thromboembolism after cancer surgery: project. Ann Surg 2006;243:89-95.
8 2230 Tian et al. VTE after lung surgery 7. Muciño-Bermejo J, Carrillo-Esper R, Uribe M, et al. Coagulation abnormalities in the cirrhotic patient. Ann Hepatol 2013;12: Cushman M, Tsai AW, White RH, et al. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in two cohorts: the longitudinal investigation of thromboembolism etiology. Am J Med 2004;117: Chew HK, Davies AM, Wun T, et al. The incidence of venous thromboembolism among patients with primary lung cancer. J Thromb Haemost 2008;6: Yang Y, Zhou Z, Niu XM, et al. Clinical analysis of postoperative venous thromboembolism risk factors in lung cancer patients. J Surg Oncol 2012;106: Corrales-Rodriguez L, Blais N. Lung cancer associated venous thromboembolic disease: a comprehensive review. Lung Cancer 2012;75: Raja S, Idrees JJ, Blackstone EH, et al. Routine venous thromboembolism screening after pneumonectomy: The more you look, the more you see. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2016;152: e Daddi G, Milillo G, Lupattelli L, et al. Postoperative pulmonary embolism detected with multislice computed tomography in lung surgery for cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;132: Kearon C, Akl EA, Ornelas J, et al. Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 2016;149: Douketis JD, Gu CS, Schulman S, et al. The risk for fatal pulmonary embolism after discontinuing anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism. Ann Intern Med 2007;147: Heit JA. The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism in the community. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008;28: Guo Q, Huang B, Zhao J, et al. Perioperative Pharmacological Thromboprophylaxis in Patients With Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Surg 2017;265: Deng HY, Shi CL, Li G, et al. The safety profile of preoperative administration of heparin for thromboprophylaxis in Chinese patients intended for thoracoscopic major thoracic surgery: a pilot randomized controlled study. J Thorac Dis 2017;9: Gould MK, Garcia DA, Wren SM, et al. Prevention of VTE in nonorthopedic surgical patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012;141:e227S-e277S. Cite this article as: Tian B, Song C, Li H, Zhang W, Chen Q, Chen S, Fu Y, Hu X, You B, Li T, Hu B, Hou S. The significance of perioperative coagulation and fibrinolysis related parameters after lung surgery for predicting venous thromboembolism: a prospective, single center study. J Thorac Dis 2018;10(4): doi: /jtd
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients. David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center
 DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM. Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow
 CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK?
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Approach to Thrombosis
 Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT?
 How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies
 VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies VTE in Surgical Patients: Recognizing the Patients at Risk Pathogenesis of thrombosis: Virchow s triad and VTE Risk Hypercoagulability
VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies VTE in Surgical Patients: Recognizing the Patients at Risk Pathogenesis of thrombosis: Virchow s triad and VTE Risk Hypercoagulability
Effect of low molecular weight heparin on venous thromboembolism disease in thoracotomy patients with cancer
 Original Article Effect of low molecular weight heparin on venous thromboembolism disease in thoracotomy patients with cancer Jun Dong 1, Jia Wang 2, Yuan Feng 2, Li-Ping Qi 3, Hua Fang 1, Guo-Dong Wang
Original Article Effect of low molecular weight heparin on venous thromboembolism disease in thoracotomy patients with cancer Jun Dong 1, Jia Wang 2, Yuan Feng 2, Li-Ping Qi 3, Hua Fang 1, Guo-Dong Wang
AN AUDIT: THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PATIENTS AT NORTHWICK PARK AND CENTRAL MIDDLESEX HOSPITALS
 The West London Medical Journal 2010 Vol 2 No 4 pp 19-24 AN AUDIT: THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PATIENTS AT NORTHWICK PARK AND CENTRAL MIDDLESEX HOSPITALS Soneji ND Agni NR Acharya MN Anjari
The West London Medical Journal 2010 Vol 2 No 4 pp 19-24 AN AUDIT: THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PATIENTS AT NORTHWICK PARK AND CENTRAL MIDDLESEX HOSPITALS Soneji ND Agni NR Acharya MN Anjari
Jessica Bryan, Natalia Evans, Karlyn Henderson, & Whitney Parks
 Jessica Bryan, Natalia Evans, Karlyn Henderson, & Whitney Parks 1. What is the most common cause of death in hospitalized patients? 1. Hospital-acquired infection 2. Pulmonary embolism 3. Myocardial infarction
Jessica Bryan, Natalia Evans, Karlyn Henderson, & Whitney Parks 1. What is the most common cause of death in hospitalized patients? 1. Hospital-acquired infection 2. Pulmonary embolism 3. Myocardial infarction
Primary VTE Prophylaxis. Ponlapat Rojnuckarin, MD PhD Chulalongkorn University Bangkok, Thailand
 Primary VTE Prophylaxis Ponlapat Rojnuckarin, MD PhD Chulalongkorn University Bangkok, Thailand A 70-yr-old female before THA BMI 31 kg/m 2 with varicose vein What do you recommend for VTE prevention?
Primary VTE Prophylaxis Ponlapat Rojnuckarin, MD PhD Chulalongkorn University Bangkok, Thailand A 70-yr-old female before THA BMI 31 kg/m 2 with varicose vein What do you recommend for VTE prevention?
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
Venous Thrombo-Embolism. John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH
 Venous Thrombo-Embolism John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH overview The statistics Pathogenesis Prophylaxis Treatment Agent Duration Incidental VTE Recurrence of VTE IVC filters CVC related thrombosis
Venous Thrombo-Embolism John de Vos Consultant Haematologist RSCH overview The statistics Pathogenesis Prophylaxis Treatment Agent Duration Incidental VTE Recurrence of VTE IVC filters CVC related thrombosis
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy. Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016
 Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis
 Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis Veerendra Chadachan Senior Consultant Dept of General Medicine (Vascular Medicine and Hypertension) Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Case scenario
Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis Veerendra Chadachan Senior Consultant Dept of General Medicine (Vascular Medicine and Hypertension) Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Case scenario
What s New in DVT & PE
 What s New in DVT & PE Mark Buch MD CM CCFP(EM) Attending physician Emergency Department Jewish General Hospital Family Physician and Medical Director GMF Santé Mont-Royal Objectives: Review the diagnostic
What s New in DVT & PE Mark Buch MD CM CCFP(EM) Attending physician Emergency Department Jewish General Hospital Family Physician and Medical Director GMF Santé Mont-Royal Objectives: Review the diagnostic
Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism
 Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Benjamin Hohlfelder Samuel Z. Goldhaber Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Cardiovascular Division Harvard Medical School Brigham and
Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Benjamin Hohlfelder Samuel Z. Goldhaber Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Cardiovascular Division Harvard Medical School Brigham and
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40114 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Exter, Paul L. den Title: Diagnosis, management and prognosis of symptomatic and
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40114 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Exter, Paul L. den Title: Diagnosis, management and prognosis of symptomatic and
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Outline of This Presentation
 Slide 1 Current Approaches to Venous Thromboembolism Prevention in Orthopedic Patients Hujefa Vora, MD Maria Fox, RN June 9, 2017 Slide 2 Slide 3 Outline of This Presentation Pathophysiology of venous
Slide 1 Current Approaches to Venous Thromboembolism Prevention in Orthopedic Patients Hujefa Vora, MD Maria Fox, RN June 9, 2017 Slide 2 Slide 3 Outline of This Presentation Pathophysiology of venous
D-dimer Value more than 3.6 μg/ml is Highly Possible Existence Deep Vein Thrombosis
 Original Contribution This is Advance Publication Article Kurume Medical Journal, 60, 00-00, 2013 D-dimer Value more than 3.6 μg/ml is Highly Possible Existence Deep Vein Thrombosis SHINICHI NATA, SHINICHI
Original Contribution This is Advance Publication Article Kurume Medical Journal, 60, 00-00, 2013 D-dimer Value more than 3.6 μg/ml is Highly Possible Existence Deep Vein Thrombosis SHINICHI NATA, SHINICHI
Venous thrombosis is common and often occurs spontaneously, but it also frequently accompanies medical and surgical conditions, both in the community
 Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
RISK FACTORS. Cancer type. Cancer stage
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS RISK FACTORS The link between cancer and thrombosis is well established, with malignancy recognised as the most important individual risk factor for venous thromboembolism
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS RISK FACTORS The link between cancer and thrombosis is well established, with malignancy recognised as the most important individual risk factor for venous thromboembolism
10/24/2013. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy:
 Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy: Heparin-Induced (HIT) Michael H. Creer, MD Professor of Pathology Director, Clinical Laboratories, Medical Co- Director, Hematopathology and Chief, Division
Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy: Heparin-Induced (HIT) Michael H. Creer, MD Professor of Pathology Director, Clinical Laboratories, Medical Co- Director, Hematopathology and Chief, Division
Disclosures. DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Questions To Ask. Dr. Susanna Shin - DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) None
 Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Primary VTE Thromboprophylaxis
 Primary VTE Thromboprophylaxis Controversies in Hematology 53 rd Annual Meeting of Thai Society of Hematology Bundarika Suwanawiboon, MD Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Faculty of Medicine
Primary VTE Thromboprophylaxis Controversies in Hematology 53 rd Annual Meeting of Thai Society of Hematology Bundarika Suwanawiboon, MD Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Faculty of Medicine
Thrombophilia. Diagnosis and Management. Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI
 Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Anticoagulation for prevention of venous thromboembolism
 Anticoagulation for prevention of venous thromboembolism Original article by: Michael Tam Note: updated in June 2009 with the eighth edition (from the seventh) evidence-based clinical practice guidelines
Anticoagulation for prevention of venous thromboembolism Original article by: Michael Tam Note: updated in June 2009 with the eighth edition (from the seventh) evidence-based clinical practice guidelines
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
Venous Thrombosis in Asia
 Venous Thrombosis in Asia Pantep Angchaisuksiri, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Mahidol University, Thailand Adjunct Associate Professor, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, USA Venous Thromboembolism
Venous Thrombosis in Asia Pantep Angchaisuksiri, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Mahidol University, Thailand Adjunct Associate Professor, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, USA Venous Thromboembolism
CADTH Rapid Response Report: ASA for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Evidence for Clinical Benefit and Harm
 CADTH Rapid Response Report: ASA for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Evidence for Clinical Benefit and Harm P. Timothy Pollak, MD, PhD University of Calgary Rocky Mountain/ACP Internal Medicine Meeting,
CADTH Rapid Response Report: ASA for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Evidence for Clinical Benefit and Harm P. Timothy Pollak, MD, PhD University of Calgary Rocky Mountain/ACP Internal Medicine Meeting,
Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders
 SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
PE and DVT. Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP
 PE and DVT Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call +256777363201 Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP OBJECTIVES DEFINE DVT AND P.E PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DVT CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF DVT/PE INVESTIGATE DVT MANAGEMENT
PE and DVT Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call +256777363201 Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP OBJECTIVES DEFINE DVT AND P.E PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DVT CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF DVT/PE INVESTIGATE DVT MANAGEMENT
VTE in the Trauma Population
 VTE in the Trauma Population Erik Peltz, D.O. February 11 th, 2015 * contributions from Eduardo Gonzalez, M.D. University of Colorado T-32 Research Fellow The problem. VTE - Scope of the Problem One of
VTE in the Trauma Population Erik Peltz, D.O. February 11 th, 2015 * contributions from Eduardo Gonzalez, M.D. University of Colorado T-32 Research Fellow The problem. VTE - Scope of the Problem One of
Results from RE-COVER RE-COVER II RE-MEDY RE-SONATE EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 Assessment of the safety and efficacy of dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa ) in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) and the prevention of recurrent DVT and PE Results from
Assessment of the safety and efficacy of dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa ) in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) and the prevention of recurrent DVT and PE Results from
The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT
 The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT Mr Chung Sim Lim Consultant Vascular Surgeon and Honorary Lecturer Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust and University College London NIHR UCLH Biomedical Research
The Evidence Base for Treating Acute DVT Mr Chung Sim Lim Consultant Vascular Surgeon and Honorary Lecturer Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust and University College London NIHR UCLH Biomedical Research
Top Ten Reasons For Failure To Prevent Postoperative Thrombosis
 Top Ten Reasons For Failure To Prevent Postoperative Thrombosis Joseph A. Caprini, MD, MS, FACS, RVT, FACCWS Louis W. Biegler Chair of Surgery NorthShore University HealthSystem, Evanston, IL Clinical
Top Ten Reasons For Failure To Prevent Postoperative Thrombosis Joseph A. Caprini, MD, MS, FACS, RVT, FACCWS Louis W. Biegler Chair of Surgery NorthShore University HealthSystem, Evanston, IL Clinical
UC SF. Division of General Internal Medicine UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA SAN FRANCISCO, DIVISION OF HOSPITAL MEDICINE
 Updates in the Management of Venous Thromboembolism Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical Director, Anticoagulation Clinic Venous Thromboembolism
Updates in the Management of Venous Thromboembolism Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical Director, Anticoagulation Clinic Venous Thromboembolism
A VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM (VTE) TOWN HALL: Answering Your Top Questions on Treatment and Secondary Prevention
 A VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM (VTE) TOWN HALL: Answering Your Top Questions on Treatment and Secondary Prevention This handout is a supplemental resource to an educational video activity released on Medscape
A VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM (VTE) TOWN HALL: Answering Your Top Questions on Treatment and Secondary Prevention This handout is a supplemental resource to an educational video activity released on Medscape
Postsurgical Home Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Clinical Position Statement Postsurgical Home Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Effective: October 2017 Next Review: September 2018 CLINICAL POSITION STATEMENT Postsurgical
Clinical Position Statement Postsurgical Home Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Effective: October 2017 Next Review: September 2018 CLINICAL POSITION STATEMENT Postsurgical
Σάββας Σουρμελής Διευθυντής Β Ορθοπαιδικής Κλινικής ΔΘΚΑ «Υγεία» Αναγνώριση παραγόντων κινδύνου της φλεβικής θρόμβωσης.
 Σάββας Σουρμελής Διευθυντής Β Ορθοπαιδικής Κλινικής ΔΘΚΑ «Υγεία» Αναγνώριση παραγόντων κινδύνου της φλεβικής θρόμβωσης. VTE: deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) PE Migration Embolus
Σάββας Σουρμελής Διευθυντής Β Ορθοπαιδικής Κλινικής ΔΘΚΑ «Υγεία» Αναγνώριση παραγόντων κινδύνου της φλεβικής θρόμβωσης. VTE: deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) PE Migration Embolus
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Perioperative VTE prophylaxis (ACCP 9 th edition Guidelines) Gamal Marey SUNY Downstate Medical Center 10/16/2014
 Perioperative VTE prophylaxis (ACCP 9 th edition Guidelines) Gamal Marey SUNY Downstate Medical Center 10/16/2014 Case Presentation 75 y/o AAM Rectal bleeding & obstructive symptoms 11/12 Obstructing mass
Perioperative VTE prophylaxis (ACCP 9 th edition Guidelines) Gamal Marey SUNY Downstate Medical Center 10/16/2014 Case Presentation 75 y/o AAM Rectal bleeding & obstructive symptoms 11/12 Obstructing mass
DVT and Pulmonary Embolus. Dr Piers Blombery BSc(Biomed), MBBS (Hons), FRACP, FRCPA Consultant Haematologist Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre
 DVT and Pulmonary Embolus Dr Piers Blombery BSc(Biomed), MBBS (Hons), FRACP, FRCPA Consultant Haematologist Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Overview Structure of deep and superficial venous system of upper
DVT and Pulmonary Embolus Dr Piers Blombery BSc(Biomed), MBBS (Hons), FRACP, FRCPA Consultant Haematologist Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Overview Structure of deep and superficial venous system of upper
Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital Foundation Trust
 MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) IN THE COMMUNITY SETTING & ANTICOAGULATION CLINICS THE PAST, PRESENT AND THE FUTURE Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital
MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) IN THE COMMUNITY SETTING & ANTICOAGULATION CLINICS THE PAST, PRESENT AND THE FUTURE Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital
Inferior Venacaval Filters Valuable vs. Dangerous Valuable Annie Kulungowski. Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 24, 2008
 Inferior Venacaval Filters Valuable vs. Dangerous Valuable Annie Kulungowski Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 24, 2008 History of Vena Cava Filters Virchow-1846-Proposes PE originate from veins
Inferior Venacaval Filters Valuable vs. Dangerous Valuable Annie Kulungowski Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 24, 2008 History of Vena Cava Filters Virchow-1846-Proposes PE originate from veins
Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales
 Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales Merimbula, 6 th November 2010 University of Sydney Department of Surgery Westmead Hospital
Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales Merimbula, 6 th November 2010 University of Sydney Department of Surgery Westmead Hospital
Risk factors for DVT. Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Anticoagulation (cont d) Diagnosis 1/5/2018. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Early Ambulation Reduces the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism After Total Knee Replacement. Marilyn Szekendi, PhD, RN
 Early Ambulation Reduces the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism After Total Knee Replacement Marilyn Szekendi, PhD, RN ANA 7 th Annual Nursing Quality Conference, February 2013 Research Team Banafsheh Sadeghi,
Early Ambulation Reduces the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism After Total Knee Replacement Marilyn Szekendi, PhD, RN ANA 7 th Annual Nursing Quality Conference, February 2013 Research Team Banafsheh Sadeghi,
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule
 Original Article Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule Xuan Zhang*, Hong-Hong Yan, Jun-Tao Lin, Ze-Hua Wu, Jia Liu, Xu-Wei Cao, Xue-Ning Yang From
Original Article Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule Xuan Zhang*, Hong-Hong Yan, Jun-Tao Lin, Ze-Hua Wu, Jia Liu, Xu-Wei Cao, Xue-Ning Yang From
Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D.
 In low-risk patients with isolated calf DVT (IDDVT), what is the morbidity risk of treating with repeat ultrasound/observation versus anticoagulation? Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D. Clinical Scenario:
In low-risk patients with isolated calf DVT (IDDVT), what is the morbidity risk of treating with repeat ultrasound/observation versus anticoagulation? Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D. Clinical Scenario:
Adam Goldfarb, M.A., D.C., D.E.S.S. Introduction
 Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis following Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery: A Review of the Biomedical Research Literature and Evidence-Based Policy in the United States. Adam Goldfarb, M.A., D.C.,
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis following Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery: A Review of the Biomedical Research Literature and Evidence-Based Policy in the United States. Adam Goldfarb, M.A., D.C.,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
Protocol. Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for (10128) (Formerly Outpatient Use of Limb Pneumatic Compression Devices for ) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 03/15
Postsurgical Outpatient Use of Limb Compression Devices for (10128) (Formerly Outpatient Use of Limb Pneumatic Compression Devices for ) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 03/15
Annals of RSCB Vol. XVII, Issue 1/2012
 CORRELATIONS BETWEEN ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION AND GLYCEMIA IN VENOUS THROMBOSIS PATHOGENESIS Codruţa Bădescu 1, Oana Bădulescu 2, Manuela Ciocoiu 2, Magda Bădescu 2, M. Costuleanu 2 1 DEPARTMENT OF INTERNAL
CORRELATIONS BETWEEN ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION AND GLYCEMIA IN VENOUS THROMBOSIS PATHOGENESIS Codruţa Bădescu 1, Oana Bădulescu 2, Manuela Ciocoiu 2, Magda Bădescu 2, M. Costuleanu 2 1 DEPARTMENT OF INTERNAL
Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism After Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
 Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism After Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Masaki Nagashima 1,2 Toshiro Otani 3 Hiroyuki Seki 1,2 Kenichiro Takeshima 2 Nobuto Origuchi 4 Ken Ishii
Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism After Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Masaki Nagashima 1,2 Toshiro Otani 3 Hiroyuki Seki 1,2 Kenichiro Takeshima 2 Nobuto Origuchi 4 Ken Ishii
4/30/2018 CLOT+ In patients with an acute proximal deep vein thrombosis, pharmacomechanical catheter-directed thrombolysis does not reduce t
 In patients with an acute proximal deep vein thrombosis, pharmacomechanical catheter-directed thrombolysis does not reduce the rate of post-thrombotic syndrome Question In patients who have symptomatic
In patients with an acute proximal deep vein thrombosis, pharmacomechanical catheter-directed thrombolysis does not reduce the rate of post-thrombotic syndrome Question In patients who have symptomatic
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism
 Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease
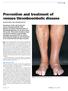 REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Checked!
 Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Checked! William Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto National Lead, VTE Prevention, Safer
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: Checked! William Geerts, MD, FRCPC Director, Thromboembolism Program, Sunnybrook HSC Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto National Lead, VTE Prevention, Safer
Society of Trauma Nurses TraumaCon 03/22/2018
 Prophylaxis Against Venous Thromboemblism (VTE) in Pediatric Trauma Society of Trauma Nurses TraumaCon 03/22/2018 Arash Mahajerin, MD, MSCr Hematology, CHOC Children s Specialists Orange, CA Disclosure
Prophylaxis Against Venous Thromboemblism (VTE) in Pediatric Trauma Society of Trauma Nurses TraumaCon 03/22/2018 Arash Mahajerin, MD, MSCr Hematology, CHOC Children s Specialists Orange, CA Disclosure
Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance Independent Medical Education
 Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance Independent Medical Education Request for Educational Support (RFE) Date August 23, 2018 RFE Requestor Information RFE Code Name: Sylvia Nashed, PharmD, RPh Title:
Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance Independent Medical Education Request for Educational Support (RFE) Date August 23, 2018 RFE Requestor Information RFE Code Name: Sylvia Nashed, PharmD, RPh Title:
VTE in Children: Practical Issues
 VTE in Children: Practical Issues Wasil Jastaniah MBBS,FAAP,FRCPC Consultant Pediatric Hem/Onc/BMT May 2012 Top 10 Reasons Why Pediatric VTE is Different 1. Social, ethical, and legal implications. 2.
VTE in Children: Practical Issues Wasil Jastaniah MBBS,FAAP,FRCPC Consultant Pediatric Hem/Onc/BMT May 2012 Top 10 Reasons Why Pediatric VTE is Different 1. Social, ethical, and legal implications. 2.
Risk assessment of lower-limb deep vein thrombosis in patients with lumbar spondylolisthesis: A retrospective study.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (13): 6043-6047 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Risk assessment of lower-limb deep vein thrombosis in patients with lumbar spondylolisthesis: A retrospective study. Sen Liu
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (13): 6043-6047 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Risk assessment of lower-limb deep vein thrombosis in patients with lumbar spondylolisthesis: A retrospective study. Sen Liu
Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism. João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal
 Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal Disclosures João Morais On the last year JM received honoraria
Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal Disclosures João Morais On the last year JM received honoraria
Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after Total Hip/Knee Replacement: A Population-based Taiwan Study
 IMPROVING PATIENT SAFETY Preventing & Managing Venous Thromboembolism Session 8 Data Driving Strategies for VTE Prevention and Management 3/30/2012; 15.35-15.55 Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after
IMPROVING PATIENT SAFETY Preventing & Managing Venous Thromboembolism Session 8 Data Driving Strategies for VTE Prevention and Management 3/30/2012; 15.35-15.55 Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after
Donald M. Arnold, MD; Susan R. Kahn, MD, MSc; and Ian Shrier, MD, PhD
 Missed Opportunities for Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism* An Evaluation of the Use of Thromboprophylaxis Guidelines Donald M. Arnold, MD; Susan R. Kahn, MD, MSc; and Ian Shrier, MD, PhD Objectives:
Missed Opportunities for Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism* An Evaluation of the Use of Thromboprophylaxis Guidelines Donald M. Arnold, MD; Susan R. Kahn, MD, MSc; and Ian Shrier, MD, PhD Objectives:
ASH 2011: Clinically Relevant Highlights Regarding Venous Thromboembolism and Anticoagulation
 ASH 2011: Clinically Relevant Highlights Regarding Venous Thromboembolism and Anticoagulation Stephan Moll Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology-Oncology, University of North Carolina School of
ASH 2011: Clinically Relevant Highlights Regarding Venous Thromboembolism and Anticoagulation Stephan Moll Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology-Oncology, University of North Carolina School of
Clinical Policy: Dalteparin (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date:
 Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 11.17 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
Clinical Policy: (Fragmin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.207 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 11.17 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
Objectives. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis. Case VTE WHY DO IT? Question: Who Is At Risk?
 Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
LIMB COMPRESSION DEVICES FOR VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS
 PROPHYLAXIS Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent
PROPHYLAXIS Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent
Predicting Venous Thromboembolic Complications following Neurosurgical Procedures
 1 Predicting Venous Thromboembolic Complications following Neurosurgical Procedures David Dornbos III, Varun Shah, Blake Priddy, Victoria Schunemann, Ciarán Powers Venous Thromboembolic (VTE) Complications
1 Predicting Venous Thromboembolic Complications following Neurosurgical Procedures David Dornbos III, Varun Shah, Blake Priddy, Victoria Schunemann, Ciarán Powers Venous Thromboembolic (VTE) Complications
Dave Duddleston, MD VP and Medical Director Southern Farm Bureau Life
 Dave Duddleston, MD VP and Medical Director Southern Farm Bureau Life Sources of Risk for Venous Diseases Pulmonary embolism (thrombus) Bleeding from anticoagulation Mortality from underlying disease Chronic
Dave Duddleston, MD VP and Medical Director Southern Farm Bureau Life Sources of Risk for Venous Diseases Pulmonary embolism (thrombus) Bleeding from anticoagulation Mortality from underlying disease Chronic
Episode 88 DOACs Part 1: Use & Misuse, DVT & Atrial Fibrillation
 Older age: In patients >80 years old with atrial fibrillation dose reductions may be required for the DOACs for stroke prevention Episode 88 DOACs Part 1: Use & Misuse, DVT & Atrial Fibrillation With Dr.
Older age: In patients >80 years old with atrial fibrillation dose reductions may be required for the DOACs for stroke prevention Episode 88 DOACs Part 1: Use & Misuse, DVT & Atrial Fibrillation With Dr.
Duration of Therapy for Venous Thromboembolism
 Duration of Therapy for Venous Thromboembolism Michael B Streiff, MD FACP Associate Professor of Medicine and Pathology Medical Director, Johns Hopkins Anticoagulation Service Chairman, VTE Guideline Committee
Duration of Therapy for Venous Thromboembolism Michael B Streiff, MD FACP Associate Professor of Medicine and Pathology Medical Director, Johns Hopkins Anticoagulation Service Chairman, VTE Guideline Committee
Venous Thromboembolism National Hospital Inpatient Quality Measures
 Venous Thromboembolism National Hospital Inpatient Quality Measures Presentation Overview Review venous thromboembolism as a new mandatory measure set Outline measures with exclusions and documentation
Venous Thromboembolism National Hospital Inpatient Quality Measures Presentation Overview Review venous thromboembolism as a new mandatory measure set Outline measures with exclusions and documentation
Disclosures. What is a Specialty Vein Clinic? Prevalence of Venous Disease. Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach.
 Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach Disclosures Ed Boyle, MD Andrew Jones, MD Dr. Ed Boyle and Dr. Andrew Jones disclose Grants/research support: Medtronic, BTG International, Clearflow,
Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach Disclosures Ed Boyle, MD Andrew Jones, MD Dr. Ed Boyle and Dr. Andrew Jones disclose Grants/research support: Medtronic, BTG International, Clearflow,
Mutidisciplinary cooperation on VTE prevention and managment
 Mutidisciplinary cooperation on VTE prevention and managment TAO YANG Dpartment of vascular surgery Shanxi DAYI Hospita Tai yuan Shanxi China Disclosure Speaker name: Tao Yang... I have the following potential
Mutidisciplinary cooperation on VTE prevention and managment TAO YANG Dpartment of vascular surgery Shanxi DAYI Hospita Tai yuan Shanxi China Disclosure Speaker name: Tao Yang... I have the following potential
What are blood clots?
 What are blood clots? Dr Matthew Fay GP Principal The Willows Medical Practice- Queensbury GPwSI and Co-Founder Westcliffe Cardiology Service GP Partner Westcliffe Medical Group Created 5/31/18 Dr. Matthew
What are blood clots? Dr Matthew Fay GP Principal The Willows Medical Practice- Queensbury GPwSI and Co-Founder Westcliffe Cardiology Service GP Partner Westcliffe Medical Group Created 5/31/18 Dr. Matthew
Perioperative Management of the Anticoagulated Patient
 Perioperative Management of the Anticoagulated Patient Citywide Resident Perioperative Medical Consultation Conference 5/5/17 Matthew Eisen, MD Director, Anticoagulation Services MetroHealth Medical Center
Perioperative Management of the Anticoagulated Patient Citywide Resident Perioperative Medical Consultation Conference 5/5/17 Matthew Eisen, MD Director, Anticoagulation Services MetroHealth Medical Center
Safety of Arthrocentesis and Joint Injection in Patients Receiving Anticoagulation at Therapeutic Levels
 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Safety of Arthrocentesis and Joint Injection in Patients Receiving Anticoagulation at Therapeutic Levels Imdad Ahmed, MBBS, a,b Elie Gertner, MD a,b a Department of Internal Medicine,
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Safety of Arthrocentesis and Joint Injection in Patients Receiving Anticoagulation at Therapeutic Levels Imdad Ahmed, MBBS, a,b Elie Gertner, MD a,b a Department of Internal Medicine,
Epidemiology of Thrombosis in Patients with Malignancy. Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism. Chew HK, Arch Int Med, Feb Blom et al, JAMA, Feb 2005
 Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism Objectives 1. Epidemiology of thrombosis in patients with malignancy 2. Anticancer agents and thrombosis 3. Current treatment protocols at UHN 4. Prevention of DVT 5.
Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism Objectives 1. Epidemiology of thrombosis in patients with malignancy 2. Anticancer agents and thrombosis 3. Current treatment protocols at UHN 4. Prevention of DVT 5.
Updates in Management of Venous Thromboembolic Disease
 Updates in Management of Venous Thromboembolic Disease November 7 th 2018 UHN Emergency Conference Susan Jenkins RN(EC) NP-Adult Thrombosis and Hemostasis Program University Health Network Disclosures
Updates in Management of Venous Thromboembolic Disease November 7 th 2018 UHN Emergency Conference Susan Jenkins RN(EC) NP-Adult Thrombosis and Hemostasis Program University Health Network Disclosures
Pulmonary Thromboembolism
 Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Frequently Asked Questions about Cancer Associated Thrombosis
 + Frequently Asked Questions about Cancer Associated Thrombosis Atlantic Canada Oncology Group Annual Meeting June 13 th, 2015 Sudeep Shivakumar, Dalhousie University + Conflict of Interest Disclosures
+ Frequently Asked Questions about Cancer Associated Thrombosis Atlantic Canada Oncology Group Annual Meeting June 13 th, 2015 Sudeep Shivakumar, Dalhousie University + Conflict of Interest Disclosures
NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE. Measure Information Form. Performance Measure Name: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Last Updated: Version 4.3 NQF-ENORSE VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANARS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form Measure Set: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Set Measure Set I #: Performance Measure Name: Venous
Last Updated: Version 4.3 NQF-ENORSE VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANARS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form Measure Set: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Set Measure Set I #: Performance Measure Name: Venous
Key words: cardiac rehabilitation; coronary bypass; deep vein thrombosis; prevention; prophylaxis
 Deep Vein Thrombosis Among Patients Entering Cardiac Rehabilitation After Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery* Marco Ambrosetti, MD; Mario Salerno, MD; Mara Zambelli, MD; Filippo Mastropasqua, MD; Roberto Tramarin,
Deep Vein Thrombosis Among Patients Entering Cardiac Rehabilitation After Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery* Marco Ambrosetti, MD; Mario Salerno, MD; Mara Zambelli, MD; Filippo Mastropasqua, MD; Roberto Tramarin,
Clinical Policy Title: Genetic testing for G1691A polymorphism factor V Leiden
 Clinical Policy Title: Genetic testing for G1691A polymorphism factor V Leiden Clinical Policy Number: 05.01.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: July 15, 2015 Most Recent Review Date:
Clinical Policy Title: Genetic testing for G1691A polymorphism factor V Leiden Clinical Policy Number: 05.01.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: July 15, 2015 Most Recent Review Date:
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction There are several disorders which carry an increased risk of thrombosis, clots that interfere with normal circulation, including: venous thromboembolism (VTE), comprising both deep
Chapter 1 Introduction There are several disorders which carry an increased risk of thrombosis, clots that interfere with normal circulation, including: venous thromboembolism (VTE), comprising both deep
New Guidance in AT10 Clive Kearon, MD, PhD,
 New Guidance in AT10 Clive Kearon, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Medicine, McMaster University; Program Director, McMaster Clinical Investigator Program, McMaster University Head, Clinical Thromboembolism
New Guidance in AT10 Clive Kearon, MD, PhD, Professor, Department of Medicine, McMaster University; Program Director, McMaster Clinical Investigator Program, McMaster University Head, Clinical Thromboembolism
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin
 Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2016 Section: Prescription Drugs
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2016 Section: Prescription Drugs
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine
 Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Slide 1: Perioperative Management of Anticoagulation
 Perioperative Management of Anticoagulation by Steven L. Cohn, MD, FACP Director, Medical Consultation Service, Kings County Hospital Center, Clinical Professor of Medicine, SUNY Downstate, Brooklyn, NY
Perioperative Management of Anticoagulation by Steven L. Cohn, MD, FACP Director, Medical Consultation Service, Kings County Hospital Center, Clinical Professor of Medicine, SUNY Downstate, Brooklyn, NY
EAST MULTICENTER STUDY DATA DICTIONARY
 EAST MULTICENTER STUDY DATA DICTIONARY Does the Addition of Daily Aspirin to Standard Deep Venous Thrombosis Prophylaxis Reduce the Rate of Venous Thromboembolic Events? Data Entry Points and appropriate
EAST MULTICENTER STUDY DATA DICTIONARY Does the Addition of Daily Aspirin to Standard Deep Venous Thrombosis Prophylaxis Reduce the Rate of Venous Thromboembolic Events? Data Entry Points and appropriate
Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism
 Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism Ethan Cumbler M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Hospitalist Medicine Section University of Colorado Denver May 2010 No Conflicts of Interest Objectives
Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism Ethan Cumbler M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Hospitalist Medicine Section University of Colorado Denver May 2010 No Conflicts of Interest Objectives
