BRONCHOPULMONARY CARCINOMA
|
|
|
- Phyllis Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 425. THE DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF PLEURAL BIOPSY IN BRONCHOPULMONARY CARCINOMA BY WALTER PAGEL AND SUSAN GOLDFARB From the Department of Pathology, Clare Hall Hospital, Herts (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION DECEMBER 21, 1959) The diagnosis of bronchopulmonary carcinoma was either corroborated or arrived at in 13 out of a total of 26 cases by pleural biopsy. Taken as a whole, pleural biopsy is inferior to repeated examination of the pleural exudate for neoplastic cells. In individual observations, however, the former can be found positive at a time when neither the pleural fluid nor any other material provide a diagnostic clue. In an instance of primary pleural growth (mesothelioma) its nature was recognizable in the pleural biopsy material. Pleural biopsy can correctly lead to the diagnostic exclusion of growth in favour of tuberculosis. Pleural biopsy can be suggestive of the rheumatic aetiology of changes. A pleural biopsy positive for carcinoma can be obtained on both sides. All stages, from early submesothelial deposition of individual neoplastic cells to the dense infiltration of the subserous connective and fat tissue, were observed. The diagnostic usefulness of pleural needle biopsies has been pointed out on several occasions (Hill, Hensler, and Breckler, 1958; Mestitz, Purves, and Pollard, 1958; Leggat, 1959; Karlish, 1959a, b). The results were particularly impressive in the large series (228 biopsies) presented by Mestitz et al. (1958). However, no unanimity has been reached as to the real usefulness of the method and this seems to be the reason why it has not yet been adopted generally and routinely. Informative individual case reports are therefore still called for, and those given in the present paper from a comparatively small series largely confirm the favourable view arrived at before. However, while helpful in certain instances, the method does not appear to be indispensable and not infrequently fails at a time when other diagnostic methods, such as the examination of pleural fluid and bronchial biopsy, have led to the desired result. The Present Series The series comprises a total of 26 cases in which pleural biopsy was performed uniformly with the Adams (or Harefield) needle on one or several occasions for the diagnosis of bronchopulmonary carcinoma. It was positive in 13 cases and negative in 13. 2M1 In all 13 positive cases the diagnosis was confirmed: in six by bronchial biopsy, in four by suggestive bronchoscopic findings, and in six by examination of the pleural fluid and/or sputum for neoplastic cells. Of the 13 negative pleural biopsies, seven were in cases of carcinoma. It should be expected that a positive pleural biopsy implies the presence of neoplastic cells in the pleural fluid, and indeed the longer and more often this is searched the higher will be the yield of neoplastic cells. However, the pleural fluid can be found devoid of neoplastic cells at a time when the pleural biopsy does reveal carcinoma. This was found in two cases of the present series. Against this there were three cases in which the reverse was seen, namely, neoplastic cells in the pleural fluid with a negative pleural biopsy. The latter event should be more common in view of the proximity of many lung tumours to the visceral pleural lymphatics. In our small series pleural biopsy was thus indicative of bronchopulmonary carcinoma in about half the cases and failed to do so in roughly one-fourth. It therefore compares unfavourably with examination of the pleural exudate which failed only in one-fifth of the cases (in 12 out of 67 cases) examined at Clare Hall Hospital in
2 426 WALTER PA GEL and Case Reports Of the individual cases the following are noteworthy: (1) A man, aged 56 years, with one month's history of pain in the chest, cough, and dyspnoea, presented with a right pleural effusion that was aspirated several times. Bronchoscopy showed stenosis of the right upper lobe bronchus, but the bronchial biopsy was negative. A subsequent pleural biopsy was positive. In this instance the positive pleural biopsy formed the only pathological evidence of carcinoma. On its strength no further investigations were made, as the radiological extent of the growth and the general condition of the patient rendered it inoperable. (2) In a man, aged 62 years, with four months' history of cough, sputum, and dyspnoea, a left pleural effusion was found on x-ray examination. This was aspirated several times. On bronchoscopy narrowing of the left stem bronchus was found. Both the bronchial biopsy and pleural fluid were negative. Pleural biopsy was, however, positive. Squamous-celled carcinoma was diagnosed from the pleural biopsy on two occasions at a time when no evidence was forthcoming from the bronchial biopsy and the pleural fluid. Bronchoscopically, however, a suggestive stenosis was seen. (3) This patient, a man aged 67, had a two years' history of hoarseness of the voice. He then developed gastric symptoms for which he was investigated. Radiographs showed a large mass in the right upper zone. Bronchoscopy showed a narrowing of the lower trachea and stenosis of the right main bronchus. Bronchial biopsy did not reveal any neoplastic changes. The pleural biopsy, however, contained units of squamous-celled carcinoma. This case was almost a replica of the previous one. Carcinoma was found in the pleural biopsy, with a negative bronchial biopsy in spite of bronchoscopic findings suggestive of bronchial stenosis. (4) In a man, aged 57 years, with six months' history of cough, dyspnoea, and haemoptysis, the chest radiograph showed multiple bilateral opacities. There was a small right pleural effusion. Oat-celled carcinoma was found in several pleural biopsies and in an enlarged right supraclavicular lymph node, but no neoplastic cells were seen in the sputum. In this instance a positive pleural biopsy antedated any other positive findings by about one month. (5) In a man, aged 59 years, with progressive dyspnoea for two years a left pleural effusion was diagnosed. Though numerous aspirations were performed, only later were neoplastic cells found in the SUSAN GOLDFARB fluid. No changes could be seen on bronchoscopy. The needle biopsy was, however, positive (Fig. 1). Later, following an aspiration, he developed a pneumothorax. Radiographs taken at that time showed deposits on the thoracic wall. In this case a growth that was most probably pleural in origin was discovered by pleural biopsy. The naked-eye appearance was of multiple, patchy, intrapleural deposits of a white growth (Fig. 2). Involvement of lung tissue was not demonstrable, either by naked eye or by histological examination, nor could any intrabronchial deposit be detected in a narrow series of sections through the specimen. Histologically the growth consisted of tubular pseudo-adenomatous units showing central clefts lined by low cuboidal cells with scanty mitoses (Fig. 3). The growth conformed in type with what has been described as pleural mesothelioma or primary pleural tumour (Eisenstadt, 1956; Smart and Hinson, 1957; Forse and Haug, 1958). Particular reference should be made to the cases collected by McCaughey (1958) and his Figs. 10 and 11. In the present instance neither papillary structures nor neoplastic pleomorphic spindlecelled stroma, as often seen in these tumours, could be found. Bronchoscopy and bronchial biopsy had been negative, but neoplastic cells were observed in the pleural fluid, though only after the diagnosis had been made from the pleural biopsy. (6) In a man, aged 67 years, a pleural effusion containing neoplastic cells (Fig. 4) developed six months after a negative chest radiograph. Bronchoscopy showed narrowing of the left stem bronchus. A bronchial biopsy, however, was negative, whereas a pleural biopsy showed carcinoma (Fig. 5). A case of oat-celled carcinoma of the bronchus proved by pleural biopsy on two occasions, on which neither the bronchial biopsy nor the sputum provided any evidence. On the other hand, such evidence was forthcoming from the pleural fluid. (7) In a man, aged 68 years, with a history of chronic bronchitis and recent haemoptysis, the sputum was found to contain neoplastic cells (Fig. 6). After pleural effusion had developed, squamous-celled carcinoma was proved by pleural biopsy (Fig. 7), and a neoplastic mass blocking the left stem bronchus was seen bronchoscopically. Bronchial biopsy confirmed the pleural biopsy findings (Fig. 8). This observation is reported in detail because of the scantiness of carcinomatous units in the pleural biopsy, calling for a careful and prolonged search, including cytological examination under oil immersion. In the present instance only one
3 4 1 '4 f..1. n i PLEURAL BIOPSY IN BRONCHOPULMONARY CARCINOMA 427 Z~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 44 liv.~ 47%~ 45. ~ I ~~~~~~R PII FIG. I.-Case 5: Primary pleural growth (mesothelioma) in a man aged 59. Pleural biopsy x 100 showed multiple clefts lined by uniformly low cuboidal "epithelia." FiG. 2. -Case 5:.OAq-~~I.5 1IIG. 3.--Case 5: Histological aspects of growth x 100. The same pattern of clefts lined by " epithelium " as seen in Fig. 1, limited to visceral pleura, encroaching on but not infiltrating lung. Specimen showing multiple patchy deposits in tlhe visceral pleura. Fro. 4.-Case 6: Positive pleural. negative bronchial biopsy in a man aged 67. Neoplastic unit from pleural exudate x 400.
4 FIG. 5.-Case 6: Pleural biopsy x 100. Dense infiltration of subserous fat tissue with oat-celled carcinoma. FIG. 6.-Case 7 illustrating scantiness of carcinoma cell units in pleural biopsy in a man aged 68 years. Neoplastic cells in sputum x 400. s~~ ~.. ~ ~~~~~~~4ef FIG. 7.-Case 7: Pleural biopsy x 400 showing scanty units of carcinoma (arrows). Bronchial biopsy x 40 showing squamous-celled carcinoma. FIG. 9.-Case 8: Pleural biopsy with tuberculous changes in a woman aged 35. Pleural biopsy x 100, "clearance" area. Peripherally a giant cell (arrowed) of the Langhans type. W 9 FIG. 10.-Case 8 The same as Fig. 9. Close-up of giant cell (x 400).
5 S * t sx.fr,eo~uj - ns,o...fig. PLEURAL BIOPSY IN BRONCHOPULMONARY CARCINOMA 429 JIMIL~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ S 'M.~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~. _ 13.-ase 9: Second pleural biopsy taken eight days 1 palisading" of cells with tendency to conflue r s F ~, 1 FIG. 11.-Case 8: Specimen of tuberculoma in the right lower lobe with >,_ marginal epituberculosis. S, f i 0X#{ 4 (~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~showing; 4... _~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ FIG. 12.-Case 9: Pleural biopsy suggesting rheumatic aetiology in a man aged 53 years. Macrophages and a giant cell of the Langhans type x 400. ii,4 later ene FIG. 14.-Case 4: Pleural biopsy x 100 in a man aged 57 years. Endolymphatic unit (U) and scattered neoplastic cells (S), M muscle, F fibrin clot.
6 am lmbk-:-. NM&:,>- J! in, a w: 0 FIG. 15.* WALTER PA GEL and "wv Pkb SUSAN GOLDFARB FIG. 15.-Case 11: Pleural biopsy showing the earliest stage of micro-deposit in the parietal pleura, one individual and a small cluster of neoplastic cells in a submesothelial lymph space (arrows) x 100. The mesothelial strip forms the extreme outer margin of the picture. FIG. 16.-Case 11, the same as in Fig. 15 x 400. FIG. 17.-Case 11: Stage subsequent to that shown in Figs. 15 and 16. Two solid units of carcinoma are shown in a deep lymph space (arrow) x 100. FIG Case 11: The same as Fig. 17 x 400. :^4 r..* :: a s * ; i.c:-.~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~..fs > *74A_ aw. 4b4 ''o. ^ _..~~~f FIG. 16 FIG. 18 FIG. 17 qbmml". %;. Qx-,%*:...:.. I , 4. C:Ṣ. _.t# such unit was found in many sections examined. It was situated in a lymph space. Before the positive pleural biopsy, neoplastic cells had been seen in the sputum, but only later was a positive bronchial biopsy obtained. Discussion From the present series, however small, it is evident that pleural biopsy can be useful in (a) corroborating the diagnosis of bronchopulmonary carcinoma suggested or arrived at by other means; (b) rendering bronchial biopsy unnecessary ; (c) furnishing a positive result in a case with a negative bronchial biopsy. As a rule persistent search for neoplastic cells in the pleural fluid will eventually lead to a positive result without pleural biopsy. The latter may be attempted, however, in the absence of exudate and lead to a positive result. This was seen in the only case of the present series in which the tuberculous nature
7 PLEURAL BIOPSY IN of a mass in the lung was correctly suggested by pleural biopsy. The patient was a woman, aged 35 (Case 8), with a shadow suspicious of carcinoma in the right lower lobe, in spite of some history of tuberculosis treated with drugs. A pleural biopsy showed chronic inflammatory changes around an area of "clearance" and fibrosis with a solitary large giant cell of the Langhans type at the periphery (Figs. 9 and 10). The segment of the right lower lobe containing the suspicious change was then removed. It contained a tuberculoma (Fig. 11) with a broad peripheral zone of chronic collapse containing many non-caseating tuberculoid nodules that were rich in giant cells of the Langhans as well as the foreign body type. Both the naked-eye and histological changes closely resemble those observed in epituberculosis (Pagel, Simmonds, and Macdonald, 1953) and in this instance-are due to chemotherapy. The presence in a pleural biopsy of giant cells of the Langhans type in itself is no proof of tuberculosis. This is illustrated by a case in which pleural biopsy suggested a rheumatic aetiology. A man aged 53 years (Case 9), with recurrent multiple rheumatoid arthritis of 16 years' standing, developed, during a period of exacerbation, a unilateral pleural effusion. A pleural biopsy showed large mononuclear cells with a tendency to form giant cells of the Langhans type (Fig. 12). In a second pleural biopsy taken eight days later no giant cells of the Langhans type were seen, but there was distinct palisading of mononuclear cells with a tendency to form syncytia (Fig. 13). The changes were reminiscent of those seen in the cellular parts of rheumatic infiltrates. A suspicion of tuberculous aetiology (as suggested by the first pleural biopsy) could not be confirmed by clinical, radiological, or bacteriological evidence. A pleural biopsy positive for carcinoma can be obtained on both sides. This was seen in a man aged 52 years (Case 10) with a shadow suspicious of growth in the right lower zone of the chest. The pleural exudate from both sides contained many neoplastic-looking cells. Pleural biopsies taken from both sides likewise showed units of carcinoma. In the present series, in all positive cases a real infiltration of the pleural membrane by neoplastic cells or units was demonstrated compared with a merely superficial adhesion of neoplastic units BRONCHOPULMONARY CARCINOMA deposited from the pleural fluid. The pictures observed fall into three categories: (a) Deepseated and extensive infiltration of the subserous fat tissue (Fig. 5); (b) patchy units lying in isolated lymph spaces, sometimes scanty and difficult to trace (Fig. 7); (c) superficial, but submesothelial infiltration, of isolated neoplastic cells or small groups mixed with blood or fibrin (Figs. 14, 15, and 16). The latter pictures illustrate the very early stages in the involvement of the pleural membrane in a marginal submesothelial lymph space. This is followed by larger units collecting in lymph spaces (Figs. 17 and 18). Both these stages were seen in two pleural biopsies taken simultaneously in a man aged 46 with squamouscelled carcinoma of the right main bronchus with pleural effusion (Case 11): the second stage was close to the growth itself where it was adherent to the parietal pleura, whereas the earlier changes of superficial submesothelial infiltration were found in a pleural strip remote from the former site Ȧ point of more general interest that emerges from the examination of pleural biopsies in bronchopulmonary carcinoma is the comparatively frequent presence of deposits in the parietal pleura. Perhaps this is less surprising in view of the pleural effusion that is present in most cases in which pleural biopsy is attempted, indicating an early involvement of the visceral pleura. Nevertheless the common occurrence of micro-deposits in the parietal membrane appears to be a subject worthy of systematic clinicopathological studies, with particular reference to the prognostic significance of such deposits. The authors are indebted to Mr. R. Laird, Mr. T. W. Stephens, and Mr. G. C. W. James, senior surgeons, and to Dr. F. A. H. Simmonds, Dr. T. A. W. Edwards, and Dr. N. Macdonald, senior physicians, at Clare Hall Hospital, for case reports, encouragement, and help, and to Mrs. M. K. Barry for the photographic work. REFERENCES 431 Eisenstadt, H. B. (1956). Dis. Chest, 30, 549. Forse, M. A., and Haug, W. A. (1958). Amer. Rev. Tubere., 78, 268. Hill. H. E., Hensler, N. M., and Breckler, I. A. (1958). Ibid., 78, 8. Karlish, A. J. (1959a). Brit. med. J., 2, (1959b). Tubercle (Lond.), 40, 230, 396. Leggat, P. 0. (1959). Brit. med. J., 2, 478. McCaughey, W. T. E. (1958). J. Path. Bact., 76, 517. Mestitz. P., Purves, M. J., and Pollard, A. C. (1958). Lancet, 2, Pagel, W., Simmonds, F. A. H., and Macdonald, N. (1953). Pulmonary Tuberculosis, 3rd ed. Oxford University Press, London. Smart, J., and Hinson, K. F. W. (1957). Brit. J. Tuberc. Dis. Chest, 51, 319.
PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA
 Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
CASE REPORTS. Inflammatory Polyp of the Bronchus. V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS
 Thorax (1951), 6, 375. PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN BY COLIN A. ROSS From Shotley Bridge Hospital and Poole Sanatorium (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JULY 9, 1951) The literature concerning
Thorax (1951), 6, 375. PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN BY COLIN A. ROSS From Shotley Bridge Hospital and Poole Sanatorium (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JULY 9, 1951) The literature concerning
An Update: Lung Cancer
 An Update: Lung Cancer Andy Barlow Consultant in Respiratory Medicine Lead Clinician for Lung Cancer (West Herts Hospitals NHS Trust) Lead for EBUS-Harefield Hospital (RB&HFT) Summary Lung cancer epidemiology
An Update: Lung Cancer Andy Barlow Consultant in Respiratory Medicine Lead Clinician for Lung Cancer (West Herts Hospitals NHS Trust) Lead for EBUS-Harefield Hospital (RB&HFT) Summary Lung cancer epidemiology
TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE
 Thorax (1954), 9, 2 1. TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE BY PETER BEACONSFIELD, H. S. COULTHARD, AND F. G. KERGIN From the Toronto Hospital for the
Thorax (1954), 9, 2 1. TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE BY PETER BEACONSFIELD, H. S. COULTHARD, AND F. G. KERGIN From the Toronto Hospital for the
Metastatic carcinoma of the pleura
 Metastatic carcinoma of the pleura P C. MEYER From the Central Histological Laboratory, Whittington Hospital, London, N.19 Pleural secondaries are a frequent finding at necropsy in cases of carcinomatosis,
Metastatic carcinoma of the pleura P C. MEYER From the Central Histological Laboratory, Whittington Hospital, London, N.19 Pleural secondaries are a frequent finding at necropsy in cases of carcinomatosis,
Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!!
 The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
Primary chondrosarcoma of lung
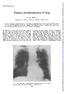 Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Basaloid carcinoma of the anal canal
 J. clin. Path. (1967), 0, 18 Basaloid carcinoma of the anal canal LILLIAN S. C. PANG AND B. C. MORSON From the Research Department, St. Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The pathology and results of treatment
J. clin. Path. (1967), 0, 18 Basaloid carcinoma of the anal canal LILLIAN S. C. PANG AND B. C. MORSON From the Research Department, St. Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The pathology and results of treatment
New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma
 July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
IN THE SPREAD OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 Thorax (1951), 6, 417. THE IMPORTANCE OF SLEEPING POSTURE IN THE SPREAD OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY W. H. HELM From the London Chest Hospital (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION AUGUST 22, 195 1) When an infective
Thorax (1951), 6, 417. THE IMPORTANCE OF SLEEPING POSTURE IN THE SPREAD OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY W. H. HELM From the London Chest Hospital (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION AUGUST 22, 195 1) When an infective
Chapter 8. Other Important Tests and Procedures. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
Collaborative Stage. Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG
 Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Case Scenario 1. The patient agreed to a CT guided biopsy of the left upper lobe mass. This was performed and confirmed non-small cell carcinoma.
 Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
Empyema in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 181 Empyema in rheumatoid arthritis P. A. DIEPPE From the Brompton Hospital, Fulham Road, London Dieppe, P. A. (1975). Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases, 34, 181. Empyema in
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 181 Empyema in rheumatoid arthritis P. A. DIEPPE From the Brompton Hospital, Fulham Road, London Dieppe, P. A. (1975). Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases, 34, 181. Empyema in
Bronchial carcinosarcoma
 Bronchial carcinosarcoma Carolina Carcano 1*, Edward Savage 2, Maria Julia Diacovo 3, Jacobo Kirsch 1 1. Division of Radiology, Cleveland Clinic Florida, Weston, Fl, USA 2. Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular
Bronchial carcinosarcoma Carolina Carcano 1*, Edward Savage 2, Maria Julia Diacovo 3, Jacobo Kirsch 1 1. Division of Radiology, Cleveland Clinic Florida, Weston, Fl, USA 2. Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular
Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Carcinoma of the lung and diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
 J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 486-491 Carcinoma of the lung and diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis B. FOX AND R. A. RISDON From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, Charing Cross Hospital Medical School,
J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 486-491 Carcinoma of the lung and diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis B. FOX AND R. A. RISDON From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, Charing Cross Hospital Medical School,
Report of two cases. and disorders of fat metabolism. as nose drops, sprays, or laxatives, these lesions
 Thorax (1973), 28, 214. Paraffinoma of lung: Report of two cases JOHN BORRIE and JAMES F. lipoid pneumonia GWYNNE Departments of Thoracic Surgery and Pathology, University of Otago Medical School and Southern
Thorax (1973), 28, 214. Paraffinoma of lung: Report of two cases JOHN BORRIE and JAMES F. lipoid pneumonia GWYNNE Departments of Thoracic Surgery and Pathology, University of Otago Medical School and Southern
Lung Cytology: Lessons Learned from Errors in Practice
 Lung Cytology: Lessons Learned from Errors in Practice Stephen S. Raab, M.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine Eastern Health and Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John s, NL and University of Washington,
Lung Cytology: Lessons Learned from Errors in Practice Stephen S. Raab, M.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine Eastern Health and Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John s, NL and University of Washington,
[1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the
![[1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the [1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the](/thumbs/84/89127006.jpg) 'ca -.101 6II.25:6II.OI8.86 NERVES AND NERVE ENDINGS IN THE VISCERAL PLEURA OF THE CAT. BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN. (From the Unit Laboratories, University College Hospital Medical School.) (Received September
'ca -.101 6II.25:6II.OI8.86 NERVES AND NERVE ENDINGS IN THE VISCERAL PLEURA OF THE CAT. BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN. (From the Unit Laboratories, University College Hospital Medical School.) (Received September
Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis?
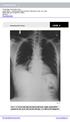 1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1959, 16, 318. LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS BY R. ABBEY SMITH Fronm the Thoracic Surgical Unit, King Edward VII Memorial Chest Hospital, Warwick (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1959, 16, 318. LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS BY R. ABBEY SMITH Fronm the Thoracic Surgical Unit, King Edward VII Memorial Chest Hospital, Warwick (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER
Mixed glandular and squamous-cell carcinoma
 Thorax (1967), 22, 431. Mixed glandular and squamous-cell carcinoma of the bronchus DAVID J. B. ASHLEY AND H. DUNCAN DAVIES From the Pathology Department, Morriston Hospital, Swansea A group of 26 examples
Thorax (1967), 22, 431. Mixed glandular and squamous-cell carcinoma of the bronchus DAVID J. B. ASHLEY AND H. DUNCAN DAVIES From the Pathology Department, Morriston Hospital, Swansea A group of 26 examples
Diagnosis of Cancer of the Lung by the Cytologic Method*
 Diagnosis of Cancer of the Lung by the Cytologic Method* GEORGE N. PAPANICOLAOU, M.D., Ph.D. and HENRY A. CROMWELL, M.D.-- New York, New York The application of the fixation and staining technique developed
Diagnosis of Cancer of the Lung by the Cytologic Method* GEORGE N. PAPANICOLAOU, M.D., Ph.D. and HENRY A. CROMWELL, M.D.-- New York, New York The application of the fixation and staining technique developed
Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
Lung Cancer: A review of 589 Malaysian patients
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 43 No. 4 December 1988 Lung Cancer: A review of 589 Malaysian patients Prathap Gopal, MBBS(Mal), FRCP(Lond), AM(Mal), FCCP(USA) Kuppusamy Iyawoo, MBBS(Mal), MRCP(I) Hooi Lai Ngoh,
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 43 No. 4 December 1988 Lung Cancer: A review of 589 Malaysian patients Prathap Gopal, MBBS(Mal), FRCP(Lond), AM(Mal), FCCP(USA) Kuppusamy Iyawoo, MBBS(Mal), MRCP(I) Hooi Lai Ngoh,
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul. Epidemiology. Risk factors/aetiology
 Slide 1 Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul Department of Thoracic Oncology Papworth Hospital Slide 2 Epidemiology Second most common cancer in the UK (after breast). 38 000 new
Slide 1 Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul Department of Thoracic Oncology Papworth Hospital Slide 2 Epidemiology Second most common cancer in the UK (after breast). 38 000 new
Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis)
 Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis) Sevda Sener Cömert, MD, FCCP. SBU, Kartal Dr.Lütfi Kırdar Training and Research Hospital Department of Pulmonary
Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis) Sevda Sener Cömert, MD, FCCP. SBU, Kartal Dr.Lütfi Kırdar Training and Research Hospital Department of Pulmonary
Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease
 Thorax (1966), 21, 230. Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease DEWI DAVIES From Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Notts Rheumatoid nodules in the lung, in the absence of exposure to mineral dust, are uncommon.
Thorax (1966), 21, 230. Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease DEWI DAVIES From Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Notts Rheumatoid nodules in the lung, in the absence of exposure to mineral dust, are uncommon.
Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis: A Case Detected by Breast Cancer Screening Examination
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 9016517, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9016517 Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 9016517, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9016517 Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis:
squamous-cell carcinoma1
 Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
THE CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF THE TENSION LESIONS OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA IN INFANCY
 Thorax (1960), 15, 233. THE CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF THE TENSION LESIONS OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA IN INFANCY BY JAMES S. DAVIDSON From the Royal Infirmary, Bradford (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION APRIL
Thorax (1960), 15, 233. THE CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF THE TENSION LESIONS OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA IN INFANCY BY JAMES S. DAVIDSON From the Royal Infirmary, Bradford (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION APRIL
B REAST STAGING FORM. PATHOLOGIC Extent of disease through completion of definitive surgery. CLINICAL Extent of disease before any treatment
 B REAST STAGING FORM Extent of disease before any treatment y clinical staging completed after neoadjuvant therapy but before subsequent surgery (DCIS) (LCIS) (Paget s) mi a b c a b c d TUMOR SIZE: S TAGE
B REAST STAGING FORM Extent of disease before any treatment y clinical staging completed after neoadjuvant therapy but before subsequent surgery (DCIS) (LCIS) (Paget s) mi a b c a b c d TUMOR SIZE: S TAGE
Isolated anthracosis: benign but neglected cause of bronchial stenosis and obstruction
 Isolated anthracosis: benign but neglected cause of bronchial stenosis and obstruction Poster No.: C-0143 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Kahkouee, R. Pourghorban, M. Bitarafan,
Isolated anthracosis: benign but neglected cause of bronchial stenosis and obstruction Poster No.: C-0143 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Kahkouee, R. Pourghorban, M. Bitarafan,
Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary
 Thorax, 1980, 35, 936-940 Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary neoplasm (Blesovsky's syndrome) C R PAYNE, P JAQUES, AND I From the Brompton Hospital, London H KERR ABSTRACT Six cases are reported
Thorax, 1980, 35, 936-940 Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary neoplasm (Blesovsky's syndrome) C R PAYNE, P JAQUES, AND I From the Brompton Hospital, London H KERR ABSTRACT Six cases are reported
THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS
 Thorax (1956), 11, 241. THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF RADIATION FIBROSIS OF THE LUNGS* BY WILLIAM M. ROSS From Newcastle Regional Hospital Board (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY 23,
Thorax (1956), 11, 241. THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF RADIATION FIBROSIS OF THE LUNGS* BY WILLIAM M. ROSS From Newcastle Regional Hospital Board (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY 23,
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
CARCINOMA OF THE BRONCHUS
 Thorax (1951), 6, 1. CARCINOMA OF THE BRONCHUS A REPORT ON THE FIRST FIVE YEARS' WORK OF THE JOINT CONSULTATION CLINIC FOR NEOPLASTIC DISEASES OF THE BROMPTON HOSPITAL AND THE ROYAL CANCER HOSPITAL BY
Thorax (1951), 6, 1. CARCINOMA OF THE BRONCHUS A REPORT ON THE FIRST FIVE YEARS' WORK OF THE JOINT CONSULTATION CLINIC FOR NEOPLASTIC DISEASES OF THE BROMPTON HOSPITAL AND THE ROYAL CANCER HOSPITAL BY
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results
 AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Survey Tool 1 Survey Development, Delivery, Analysis THANKS to NCRA for the following work Developed survey with input from partners
AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Survey Tool 1 Survey Development, Delivery, Analysis THANKS to NCRA for the following work Developed survey with input from partners
Lung cancer in women
 Thorax (1969), 24, 446. Lung cancer in women DAVID J. B. ASHLEY AND H. DUNCAN DAVIES From Morristoll Hospital, Swantsea Eighty-three instances of lung cancer in women are presented. The frequency of the
Thorax (1969), 24, 446. Lung cancer in women DAVID J. B. ASHLEY AND H. DUNCAN DAVIES From Morristoll Hospital, Swantsea Eighty-three instances of lung cancer in women are presented. The frequency of the
North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
 THIS DOCUMENT IS North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Non Small Cell Lung Cancer [Based on WOSCAN NSCLC CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN] UNCONTROLLED
THIS DOCUMENT IS North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Non Small Cell Lung Cancer [Based on WOSCAN NSCLC CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN] UNCONTROLLED
Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema
 Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema Poster No.: P-0025 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Lee, C.-K. Park; Guri/KR Keywords: Neoplasia, Biopsy, PET-CT, CT, Thorax, Lung DOI:
Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema Poster No.: P-0025 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Lee, C.-K. Park; Guri/KR Keywords: Neoplasia, Biopsy, PET-CT, CT, Thorax, Lung DOI:
Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection
 Thorax (1970), 25, 41. Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection 0. SERIKI, A. ADEYOKUNNU, T. 0. DE LA CRUZ Departments of Paediatrics and Surgery, University College Hospital, Ibadan,
Thorax (1970), 25, 41. Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection 0. SERIKI, A. ADEYOKUNNU, T. 0. DE LA CRUZ Departments of Paediatrics and Surgery, University College Hospital, Ibadan,
TUBERCULOUS PERICARDIAL EFFUSION
 BY S. SUZMAN From the Cardiographic Department, Guy's Hospital Received June 22, 1942 Tuberculous pericardial effusion is not common; and so the case described is of interest on account of the patient's
BY S. SUZMAN From the Cardiographic Department, Guy's Hospital Received June 22, 1942 Tuberculous pericardial effusion is not common; and so the case described is of interest on account of the patient's
Reactive mesothelial proliferation: a necropsy study
 Thorax 1981 ;36:901-905 Reactive mesothelial proliferation: a necropsy study CD SHELDON, AMANDA HERBERT, PJ GALLAGHER From the Department ofpathology, Southampton University General Hospital, Southampton
Thorax 1981 ;36:901-905 Reactive mesothelial proliferation: a necropsy study CD SHELDON, AMANDA HERBERT, PJ GALLAGHER From the Department ofpathology, Southampton University General Hospital, Southampton
B REAST STAGING FORM. PATHOLOGIC Extent of disease through completion of definitive surgery. CLINICAL Extent of disease before any treatment
 B REAST STAGING FORM CLINICAL Extent of disease before any treatment y clinical staging completed after neoadjuvant therapy but before subsequent surgery (DCIS) (LCIS) (Paget s) mi c a b c d TUMOR SIZE:
B REAST STAGING FORM CLINICAL Extent of disease before any treatment y clinical staging completed after neoadjuvant therapy but before subsequent surgery (DCIS) (LCIS) (Paget s) mi c a b c d TUMOR SIZE:
What is lung cancer? Contents
 13 11 20 Information and support What is lung cancer? Contents About the lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Different types of lung cancer Causes Symptoms Information reviewed by About the lungs
13 11 20 Information and support What is lung cancer? Contents About the lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Different types of lung cancer Causes Symptoms Information reviewed by About the lungs
Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma
 Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma A. S. SOORAE AND R. ABBEY SMITH Thorax, 1977, 32, 19-25 From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Walsgrave Hospital, Clifford Bridge Road, Coventry
Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma A. S. SOORAE AND R. ABBEY SMITH Thorax, 1977, 32, 19-25 From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Walsgrave Hospital, Clifford Bridge Road, Coventry
Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse. Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p
 Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
Collecting Cancer Data: Lung
 Collecting Cancer Data: Lung NAACCR 2011 2012 Webinar Series 2/2/2012 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this
Collecting Cancer Data: Lung NAACCR 2011 2012 Webinar Series 2/2/2012 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Thoracic Surgery; An Overview
 Thoracic Surgery What we see Thoracic Surgery; An Overview James P. Locher, Jr, MD Methodist Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery Lung cancer Mets Fungus and TB Lung abcess and empyema Pleural based disease
Thoracic Surgery What we see Thoracic Surgery; An Overview James P. Locher, Jr, MD Methodist Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery Lung cancer Mets Fungus and TB Lung abcess and empyema Pleural based disease
Α 78-year-old female who presents with a non-resolving pneumonia: what is your diagnosis?
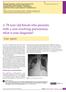 Evangelia Panagiotidou 1, Serafeim-Chrysovalantis Kotoulas 1, Maria Kilmpasani 2, Nikoleta Pastelli 2, Sofia Akritidou 1, Evangelos Chatzopoulos 1, Vasilis Bikos 1, Vasilios Bagalas 1, Katalin Fekete-Passa
Evangelia Panagiotidou 1, Serafeim-Chrysovalantis Kotoulas 1, Maria Kilmpasani 2, Nikoleta Pastelli 2, Sofia Akritidou 1, Evangelos Chatzopoulos 1, Vasilis Bikos 1, Vasilios Bagalas 1, Katalin Fekete-Passa
Radiology Pathology Conference
 Radiology Pathology Conference Sharlin Johnykutty,, MD, Cytopathology Fellow Sara Majewski, MD, Radiology Resident Friday, August 28, 2009 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights
Radiology Pathology Conference Sharlin Johnykutty,, MD, Cytopathology Fellow Sara Majewski, MD, Radiology Resident Friday, August 28, 2009 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights
A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka
 A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka Author s Details: (1) Dushantha Madegedara (2) Asela Rasika Bandara (3) Sachini Seneviratne (4) Samadara Nakandala (5) Rathnayake R.M.D.H.M - (1) (2)
A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka Author s Details: (1) Dushantha Madegedara (2) Asela Rasika Bandara (3) Sachini Seneviratne (4) Samadara Nakandala (5) Rathnayake R.M.D.H.M - (1) (2)
Diagnostic accuracy of cytology and biopsy in
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 294-299 Diagnostic accuracy of cytology and biopsy in primary bronchial carcinoma C R PAYNE, P G I STOVIN, V BARKER, S McVITTIE, AND J E STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard,
Thorax, 1979, 34, 294-299 Diagnostic accuracy of cytology and biopsy in primary bronchial carcinoma C R PAYNE, P G I STOVIN, V BARKER, S McVITTIE, AND J E STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard,
Well-differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Pleura Diagnosed by Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgical Pleural Biopsy : A Case Report
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 25 1, 67 72, March 2013 Case Report Well-differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Pleura Diagnosed by Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgical Pleural Biopsy : A Case Report Yuri TOMITA
Showa Univ J Med Sci 25 1, 67 72, March 2013 Case Report Well-differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Pleura Diagnosed by Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgical Pleural Biopsy : A Case Report Yuri TOMITA
Undergraduate Teaching
 Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma
 Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma G. HEFIN ROBERTS AND G. M. CAMPBELL From the Pathology Department, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 577-582 SYNOPSIS The exfoliative
Exfoliative cytology of diffuse mesothelioma G. HEFIN ROBERTS AND G. M. CAMPBELL From the Pathology Department, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow J. clin. Path., 1972, 25, 577-582 SYNOPSIS The exfoliative
FIBROMA OF THE VISCERAL PLEURA*
 Thorax (1953), 8, 180. FIBROMA OF THE VISCERAL PLEURA* BY SIR CLEMENT PRICE THOMAS AND C. E. DREW From the Brompton and Westminster Hospitals, London Intrathoracic fibromas are rare tumours, but as might
Thorax (1953), 8, 180. FIBROMA OF THE VISCERAL PLEURA* BY SIR CLEMENT PRICE THOMAS AND C. E. DREW From the Brompton and Westminster Hospitals, London Intrathoracic fibromas are rare tumours, but as might
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax. Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem
 Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Respiratory Medicine
 Respiratory Medicine This document is based on the handout from the Medicine for Finals course. The notes provided here summarise key aspects, focusing on areas that are popular in clinical examinations.
Respiratory Medicine This document is based on the handout from the Medicine for Finals course. The notes provided here summarise key aspects, focusing on areas that are popular in clinical examinations.
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Award Top Quizzes For Residents
 Award Top Quizzes For Residents Giovanni Negri, MD, Bolzano (Italy) Eva M. Wojcik MD, Department of Pathology, Loyola University, Chicago (USA) Esther D. Rossi MD, PhD, MIAC, Division of Anatomic Pathology
Award Top Quizzes For Residents Giovanni Negri, MD, Bolzano (Italy) Eva M. Wojcik MD, Department of Pathology, Loyola University, Chicago (USA) Esther D. Rossi MD, PhD, MIAC, Division of Anatomic Pathology
CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY
 Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit
 Page1 Original Article NJR 2011;1(1):1 7;Available online at www.nranepal.org Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit S
Page1 Original Article NJR 2011;1(1):1 7;Available online at www.nranepal.org Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit S
PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1
 5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
Atypical radiologic appearances of pulmonary tuberculosis in non-hiv adult patients
 Atypical radiologic appearances of pulmonary tuberculosis in non-hiv adult patients Poster No.: R-0200 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. N. Jeon, K. Bae, M. J. Park Keywords:
Atypical radiologic appearances of pulmonary tuberculosis in non-hiv adult patients Poster No.: R-0200 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. N. Jeon, K. Bae, M. J. Park Keywords:
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
PLEURAL TUM:OURS. required thoracoscopy, were referred to this unit. During the period when 3,000 patients with
 Thorax (1962), 17, 111. PLEURAL TUM:OURS BY B. T. LE ROUX From the Department of Clinical Surgery, University of Edinburgh The commonest pleural tumour is a metastasis, and the commonest source of such
Thorax (1962), 17, 111. PLEURAL TUM:OURS BY B. T. LE ROUX From the Department of Clinical Surgery, University of Edinburgh The commonest pleural tumour is a metastasis, and the commonest source of such
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
Carcinoma of the Lung
 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 1 I - NUMBER 3 0 MARCH 1971 Carcinoma of the Lung M. L. Dillon, M.D., and
THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 1 I - NUMBER 3 0 MARCH 1971 Carcinoma of the Lung M. L. Dillon, M.D., and
Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell lymphocyte proliferative disease
 Du et al. Respiratory Research (2018) 19:247 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0941-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell
Du et al. Respiratory Research (2018) 19:247 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0941-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell
Two malignant pleural mesotheliomas with unusual histological features
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 375-379 Two malignant pleural mesotheliomas with unusual histological features B GOLDSTEIN From the National Research Institute for Occupational Diseases of the South African Medical
Thorax, 1979, 34, 375-379 Two malignant pleural mesotheliomas with unusual histological features B GOLDSTEIN From the National Research Institute for Occupational Diseases of the South African Medical
Concordance of cytology and histopathology of intra-thoracic lesions
 Original article: Concordance of cytology and histopathology of intra-thoracic lesions *Dr.Prasanthi cherukuri 1, Dr.B.V.Madhavi 2 1Assitant Proferssor, Gitam institute of Medical sciences and research,visakhapatnam,
Original article: Concordance of cytology and histopathology of intra-thoracic lesions *Dr.Prasanthi cherukuri 1, Dr.B.V.Madhavi 2 1Assitant Proferssor, Gitam institute of Medical sciences and research,visakhapatnam,
RESECTION OF TUBERCULOUS STRICTURES OF THE MAIN BRONCHI IN THREE CASES
 Thorax (1955), 10, 229. RESECTION OF TUBERCULOUS STRICTURES OF THE MAIN BRONCHI IN THREE CASES BY J. W. JACKSON, P. H. JONES, AND T. HOLMES SELLORS From the London Chest and Harefield Hospitals (RECEIVED
Thorax (1955), 10, 229. RESECTION OF TUBERCULOUS STRICTURES OF THE MAIN BRONCHI IN THREE CASES BY J. W. JACKSON, P. H. JONES, AND T. HOLMES SELLORS From the London Chest and Harefield Hospitals (RECEIVED
Chief Complain. For chemotherapy
 Chief Complain For chemotherapy Present Illness 93.12 Progressive weakness of R t arm for 1 year X-ray: peneative lesion over right proximal humorous Bone scan: multiple increased intake Biopsy of distal
Chief Complain For chemotherapy Present Illness 93.12 Progressive weakness of R t arm for 1 year X-ray: peneative lesion over right proximal humorous Bone scan: multiple increased intake Biopsy of distal
OBJECTIVES. Solitary Solid Spiculated Nodule. What would you do next? Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules.
 Organ Imaging : September 25 2015 OBJECTIVES Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules Dr. Elsie T. Nguyen Dr. Kazuhiro Yasufuku 1. To review guidelines for follow up and management
Organ Imaging : September 25 2015 OBJECTIVES Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules Dr. Elsie T. Nguyen Dr. Kazuhiro Yasufuku 1. To review guidelines for follow up and management
WELLNESS INITIATIVE NOW
 WELLNESS INITIATIVE NOW To promote personal well-being, fitness and nutrition for all TDCJ employees. November 2008 Lung cancer is cancer that forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining
WELLNESS INITIATIVE NOW To promote personal well-being, fitness and nutrition for all TDCJ employees. November 2008 Lung cancer is cancer that forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
THE DIAGNOSIS AND SURGICAL ASSESSMENT OF CARCINOMA OF THE BRONCHUS
 POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1966), 42, 207 Current Surveys THE DIAGNOSIS AND SURGICAL ASSESSMENT OF CARCINOMA OF THE BRONCHUS H. C. NOHL-OSER, M.A., D.M., F.R.C.S. Consuiltant Thoracic Surgeon to Harefield, Hillingdont
POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1966), 42, 207 Current Surveys THE DIAGNOSIS AND SURGICAL ASSESSMENT OF CARCINOMA OF THE BRONCHUS H. C. NOHL-OSER, M.A., D.M., F.R.C.S. Consuiltant Thoracic Surgeon to Harefield, Hillingdont
Let s Talk TB A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year
 A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Barry Rabinovitch, MD, FRCP(C) Author Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD co-author and Series Editor Barry Rabinovitch is an assistant
A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Barry Rabinovitch, MD, FRCP(C) Author Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD co-author and Series Editor Barry Rabinovitch is an assistant
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
OSAMA A. ABDULMAJID, ABDELMOMEN M. EBEID, MOHAMED M. MOTAWEH, and IBRAHIM S. KLEIBO
 Aspirated foreign bodies in the tracheobronchial tree: report of 250 cases Thorax (1976), 31, 635. OSAMA A. ABDULMAJID, ABDELMOMEN M. EBEID, MOHAMED M. MOTAWEH, and IBRAHIM S. KLEIBO Thoracic Surgical
Aspirated foreign bodies in the tracheobronchial tree: report of 250 cases Thorax (1976), 31, 635. OSAMA A. ABDULMAJID, ABDELMOMEN M. EBEID, MOHAMED M. MOTAWEH, and IBRAHIM S. KLEIBO Thoracic Surgical
Lung Cancer in a Sample of Iraqi Patients Yousif A. Al-Rahim M.B.Ch.,B F.I.C.M.S/CM
 Lung Cancer in a Sample of Iraqi Patients Yousif A. Al-Rahim M.B.Ch.,B F.I.C.M.S/CM Background: Lung cancer is responsible for the most cancer deaths in both men and women throughout the world. Deaths
Lung Cancer in a Sample of Iraqi Patients Yousif A. Al-Rahim M.B.Ch.,B F.I.C.M.S/CM Background: Lung cancer is responsible for the most cancer deaths in both men and women throughout the world. Deaths
Educational Objectives. Managing Lung Cancer From the Solitary Pulmonary Nodule to Complex Cases: A Multidisciplinary Approach.
 Managing Lung Cancer From the Solitary Pulmonary Nodule to Complex Cases: A Multidisciplinary Approach Robert A. Meguid, MD, MPH, FACS Assistant Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Surgical Director, Surgical
Managing Lung Cancer From the Solitary Pulmonary Nodule to Complex Cases: A Multidisciplinary Approach Robert A. Meguid, MD, MPH, FACS Assistant Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Surgical Director, Surgical
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules
 Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi
 Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery
 Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery Sometimes seen on Chest X-ray (CXR) Common incidental findings on computed tomography (CT) chest and abdomen done for other reasons Most lung cancers discovered
Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery Sometimes seen on Chest X-ray (CXR) Common incidental findings on computed tomography (CT) chest and abdomen done for other reasons Most lung cancers discovered
