ADVANCED IMAGING CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES. Appropriate Use Criteria: Oncologic Imaging. EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Proprietary
|
|
|
- May Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL Apprpriate.Safe.Affrdable AIM Specialty Health
2 Table f Cntents Descriptin and Applicatin f the Guidelines... 4 Administrative Guidelines... 5 Ordering f Multiple Studies... 5 Simultaneus Ordering f Multiple Studies... 5 Repeated Imaging... 5 Pre-Test Requirements... 6 Histry General Infrmatin/Overview... 7 Scpe... 7 Technlgy Cnsideratins... 7 Definitins... 8 References... 9 Clinical Indicatins Cancer Screening Breast Cancer Screening Clrectal Cancer Screening Lung Cancer Screening Anal Cancer Bladder, Renal, Pelvis, and Ureter Cancers Brain and Spinal Crd Cancers Breast Cancer Cancers f Unknwn Primary Cervical Cancer Clrectal Cancer Esphageal and Gastresphageal Junctin Cancers Gastric Cancer Germ Cell Tumrs Head and Neck Cancer Kidney Cancer/Renal Cell Carcinma Lung Cancer Nn-Small Cell Lung Cancer Small Cell Lymphma Hdgkin Lymphma Nn-Hdgkin Melanma Cutaneus Melanma Mucsal Merkel Cell Carcinma Multiple Myelma Neurendcrine Tumrs Ovarian Cancer (Epithelial) Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 2
3 Pancreatic Cancer Paraneplastic Syndrme Penile, Vaginal, and Vulvar Cancers Prstate Cancer Sarcma f Bne and Sft Tissue Thracic Cancers Pleura, Thymus, Heart and Mediastinum Thyrid Cancer Uterine Cancer Cdes Histry Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 3
4 Descriptin and Applicatin f the Guidelines The AIM Clinical Apprpriateness Guidelines (hereinafter the AIM Clinical Apprpriateness Guidelines r the Guidelines ) are designed t assist prviders in making the mst apprpriate treatment decisin fr a specific clinical cnditin fr an individual. As used by AIM, the Guidelines establish bjective and evidence-based criteria fr medical necessity determinatins where pssible. In the prcess, multiple functins are accmplished: T establish criteria fr when services are medically necessary T assist the practitiner as an educatinal tl T encurage standardizatin f medical practice patterns T curtail the perfrmance f inapprpriate and/r duplicate services T advcate fr patient safety cncerns T enhance the quality f health care T prmte the mst efficient and cst-effective use f services The AIM guideline develpment prcess cmplies with applicable accreditatin standards, including the requirement that the Guidelines be develped with invlvement frm apprpriate prviders with current clinical expertise relevant t the Guidelines under review and be based n the mst up-t-date clinical principles and best practices. Relevant citatins are included in the References sectin attached t each Guideline. AIM reviews all f its Guidelines at least annually. AIM makes its Guidelines publicly available n its website twenty-fur hurs a day, seven days a week. Cpies f the AIM Clinical Apprpriateness Guidelines are als available upn ral r written request. Althugh the Guidelines are publicly-available, AIM cnsiders the Guidelines t be imprtant, prprietary infrmatin f AIM, which cannt be sld, assigned, leased, licensed, reprduced r distributed withut the written cnsent f AIM. AIM applies bjective and evidence-based criteria, and takes individual circumstances and the lcal delivery system int accunt when determining the medical apprpriateness f health care services. The AIM Guidelines are just guidelines fr the prvisin f specialty health services. These criteria are designed t guide bth prviders and reviewers t the mst apprpriate services based n a patient s unique circumstances. In all cases, clinical judgment cnsistent with the standards f gd medical practice shuld be used when applying the Guidelines. Guideline determinatins are made based n the infrmatin prvided at the time f the request. It is expected that medical necessity decisins may change as new infrmatin is prvided r based n unique aspects f the patient s cnditin. The treating clinician has final authrity and respnsibility fr treatment decisins regarding the care f the patient and fr justifying and demnstrating the existence f medical necessity fr the requested service. The Guidelines are nt a substitute fr the experience and judgment f a physician r ther health care prfessinals. Any clinician seeking t apply r cnsult the Guidelines is expected t use independent medical judgment in the cntext f individual clinical circumstances t determine any patient s care r treatment. The Guidelines d nt address cverage, benefit r ther plan specific issues. If requested by a health plan, AIM will review requests based n health plan medical plicy/guidelines in lieu f the AIM Guidelines. The Guidelines may als be used by the health plan r by AIM fr purpses f prvider educatin, r t review the medical necessity f services by any prvider wh has been ntified f the need fr medical necessity review, due t billing practices r claims that are nt cnsistent with ther prviders in terms f frequency r sme ther manner. Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 4
5 Administrative Guidelines Ordering f Multiple Studies Requests fr multiple imaging studies t evaluate a suspected r identified cnditin and requests fr repeated imaging f the same anatmic area are subject t additinal review t avid unnecessary r inapprpriate imaging. Simultaneus Ordering f Multiple Studies In many situatins, rdering multiple imaging studies at the same time is nt clinically apprpriate because: Current literature and/r standards f medical practice supprt that ne f the requested imaging studies is mre apprpriate in the clinical situatin presented; r One f the imaging studies requested is mre likely t imprve patient utcmes based n current literature and/r standards f medical practice; r Apprpriateness f additinal imaging is dependent n the results f the lead study. When multiple imaging studies are rdered, the request will ften require a peer-t-peer cnversatin t understand the individual circumstances that supprt the medically necessity f perfrming all imaging studies simultaneusly. Examples f multiple imaging studies that may require a peer-t-peer cnversatin include: CT brain and CT sinus fr headache MRI brain and MRA brain fr headache MRI cervical spine and MRI shulder fr pain indicatins MRI lumbar spine and MRI hip fr pain indicatins MRI r CT f multiple spine levels fr pain r radicular indicatins MRI ft and MRI ankle fr pain indicatins Bilateral exams, particularly cmparisn studies There are certain clinical scenaris where simultaneus rdering f multiple imaging studies is cnsistent with current literature and/r standards f medical practice. These include: Onclgic imaging Cnsideratins include the type f malignancy and the pint alng the care cntinuum at which imaging is requested Cnditins which span multiple anatmic regins Examples include certain gastrintestinal indicatins r cngenital spinal anmalies Repeated Imaging In general, repeated imaging f the same anatmic area shuld be limited t evaluatin fllwing an interventin, r when there is a change in clinical status such that imaging is required t determine next steps in management. At times, repeated imaging dne with different techniques r cntrast regimens may be necessary t clarify a finding seen n the riginal study. Repeated imaging f the same anatmic area (with same r similar technlgy) may be subject t additinal review in the fllwing scenaris: Repeated imaging at the same facility due t mtin artifact r ther technical issues Repeated imaging requested at a different facility due t prvider preference r quality cncerns Repeated imaging f the same anatmic area (MRI r CT) based n persistent symptms with n clinical change, treatment, r interventin since the previus study Repeated imaging f the same anatmical area by different prviders fr the same member ver a shrt perid f time Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 5
6 Pre-Test Requirements Critical t any finding f clinical apprpriateness under the guidelines fr specific imaging exams is a determinatin that the fllwing are true with respect t the imaging request: A clinical evaluatin has been perfrmed prir t the imaging request (which shuld include a cmplete histry and physical exam and review f results frm relevant labratry studies, prir imaging and supplementary testing) t identify suspected r established diseases r cnditins. Fr suspected diseases r cnditins: Based n the clinical evaluatin, there is a reasnable likelihd f disease prir t imaging; and Current literature and standards f medical practice supprt that the requested imaging study is the mst apprpriate methd f narrwing the differential diagnsis generated thrugh the clinical evaluatin and can be reasnably expected t lead t a change in management f the patient; and The imaging requested is reasnably expected t imprve patient utcmes based n current literature and standards f medical practice. Fr established diseases r cnditins: Advanced imaging is needed t determine whether the extent r nature f the disease r cnditin has changed; and Current literature and standards f medical practice supprt that the requested imaging study is the mst apprpriate methd f determining this and can be reasnably expected t lead t a change in management f the patient; and The imaging requested is reasnably expected t imprve patient utcmes based n current literature and standards f medical practice. If these elements are nt established with respect t a given request, the determinatin f apprpriateness will mst likely require a peer-t-peer cnversatin t understand the individual and unique facts that wuld supersede the pre-test requirements set frth abve. During the peert-peer cnversatin, factrs such as patient acuity and setting f service may als be taken int accunt. Histry Status Date Actin Reviewed and revised 07/26/2016 Independent Multispecialty Physician Panel review and revisin Created 03/30/2005 Original effective date Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 6
7 General Infrmatin/Overview Scpe These guidelines address advanced imaging fr nclgic cnditins in bth adult and pediatric ppulatins. Fr interpretatin f the Guidelines, and where nt therwise nted, adult refers t persns age 19 and lder, and pediatric refers t persns age 18 and yunger. Where separate indicatins exist, they are specified as Adult r Pediatric. Where nt specified, indicatins and prerequisite infrmatin apply t persns f all ages. See the Cding sectin fr a list f mdalities included in these guidelines. Technlgy Cnsideratins Advanced imaging fr nclgic cnditins includes bth anatmic and functinal mdalities. Judicius use f advanced imaging is imprtant t minimize risk and t avid duplicatin f infrmatin. Testing shuld be perfrmed in a stepwise fashin, with fllw-up imaging studies perfrmed based n the need fr infrmatin nt prvided by the initial study. Cmputed tmgraphy (CT) and magnetic resnance imaging (MRI) are the mst widely used mdalities t visualize anatmic detail. CT prvides rapidly btained, high-reslutin images that yield infrmatin n lesin mrphlgy, size, and lcatin. CT is less prne t mtin artifact than MRI, and is useful fr evaluatin f bnes and sft tissue. Imprved techniques such as multi-slice technlgy and enhanced image prcessing refine image quality and reslutin. Helical CT may be preferable t cnventinal axial CT fr nclgic imaging due t increased speed f image acquisitin and ability t perfrm cmputed tmgraphy angigraphy (CTA), which is useful t assess vascular structures assciated with tumrs. Disadvantages f CT include expsure t inizing radiatin and risks assciated with infusin f idinated cntrast media, including allergic reactins r renal cmprmise. MRI prvides similar infrmatin t CT; hwever, image acquisitin is slwer and thus mre prne t mtin artifact. MRI has higher reslutin and is better able t detect subtle abnrmalities in sft tissue. Fr this reasn, it is ften preferable fr visualizing infiltrative tumrs. Magnetic resnance angigraphy (MRA) is the MR analg f CTA and is als useful t assess tumr bld supply. The presence f implantable devices such as pacemakers r defibrillatrs, a ptential need fr sedatin in pediatric patients, and claustrphbia are the main limitatins f MRI. Infusin f gadlinium may als cnfer an unacceptable risk in persns with advanced renal disease. Multiparametric MRI (mpmri) f the prstate utilizes detailed anatmical imaging (T2-weighted imaging) as well as at least tw functinal imaging sequences (diffusin-weighted imaging, diffusin weighted imaging with apparent diffusin cefficient, and/r dynamic intravenus cntrast-enhanced imaging) fr detailed visualizatin and characterizatin f the prstate. Magnetic resnance spectrscpy (MRS) prvides a bichemical prfile f metablic cnstituents in tissues and may be used as an adjunct in cases where standard MRI fails t distinguish between diseased and healthy tissue. In nclgic imaging, it is used primarily t differentiate between residual brain tumr and necrtic tissue fllwing treatment. Functinal imaging studies such as psitrn emissin tmgraphy (PET) prvide infrmatin abut the metablic activity f tumr. PET utilizes a raditracer, typically 2-(flurine-18) flur-2-dexy-d-glucse (flurdexyglucse r FDG), which accumulates in areas f high metablic activity such as tumr cells. Its utility may be imprved by verlaying the areas f high uptake with CT images in rder t prvide anatmic detail. PET is mst useful in detecting tumrs with a high metablic rate; tumrs that are indlent r slw-grwing are less likely t be detected using this mdality. Other PET tracers including C- 11 chline and F-18 fluciclvine are nt addressed the guidelines, as AIM des nt review them at this time. Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 7
8 There are a large number f raditracers currently under develpment which target specific tumr types, and several are already in clinical use. As these cntinue t be evaluated in clinical practice, the use f this technlgy is expected t evlve and grw. Definitins Phases f the care cntinuum are bradly defined as fllws: Screening testing in the absence f signs r symptms f disease Diagnsis testing based n a reasnable suspicin f a particular cnditin r disrder, usually due t the presence f signs r symptms Management testing t direct therapy f an established cnditin, which may include preperative r pstperative imaging, r imaging perfrmed t evaluate the respnse t nnsurgical interventin Surveillance peridic assessment fllwing cmpletin f therapy, r fr mnitring knwn disease that is stable r asymptmatic Statistical terminlgy 1 Cnfidence interval (CI) range f values which is likely t cntain the cited statistic. Fr example, 92% sensitivity (95% CI, 89%-95%) means that, while the sensitivity was calculated at 92% n the current study, there is a 95% chance that, if a study were t be repeated, the sensitivity n the repeat study wuld be in the range f 89%-95%. Diagnstic accuracy ability f a test t discriminate between the target cnditin and health. Diagnstic accuracy is quantified using sensitivity and specificity, predictive values, and likelihd ratis. Hazard rati dds that an individual in the grup with the higher hazard reaches the utcme first. Hazard rati is analgus t dds rati and is reprted mst cmmnly in time-t-event analysis r survival analysis. A hazard rati f 1 means that the hazard rates f the 2 grups are equivalent. A hazard rati f greater than 1 r less than 1 means that there are differences in the hazard rates between the 2 grups. Likelihd rati rati f an expected test result (psitive r negative) in patients with the disease t an expected test result (psitive r negative) in patients withut the disease. Psitive likelihd ratis, especially thse greater than 10, help rule in a disease (i.e., they substantially raise the pst-test prbability f the disease, and hence make it very likely and the test very useful in identifying the disease). Negative likelihd ratis, especially thse less than 0.1, help rule ut a disease (i.e., they substantially decrease the pst-test prbability f disease, and hence make it very unlikely and the test very useful in excluding the disease). Odds rati dds that an utcme will ccur given a particular expsure, cmpared t the dds f the utcme ccurring in the absence f that expsure. An dds rati f 1 means that the expsure des nt affect the dds f the utcme. An dds rati greater than 1 means that the expsure is assciated with higher dds f the utcme. An dds rati less than 1 means that the expsure is assciated with lwer dds f the utcme. Predictive value likelihd that a given test result crrelates with the presence r absence f disease. Psitive predictive value is defined as the number f true psitives divided by the number f test psitives. Negative predictive value is defined as the number f true negatives divided by the number f test negative patients. Predictive value is dependent n the prevalence f the cnditin. Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 8
9 Pretest prbability prbability that a given patient has a disease prir t testing. May be divided int very lw (less than 5%), lw (less than 20%), mderate (20%-75%), and high (greater than 75%) althugh these numbers may vary by cnditin. Relative risk prbability f an utcme when an expsure is present relative t the prbability f the utcme ccurring when the expsure is absent. Relative risk is analgus t dds rati; hwever, relative risk is calculated by using percentages instead f dds. A relative risk f 1 means that there is n difference in risk between the 2 grups. A relative risk f greater than 1 means that the utcme is mre likely t happen in the expsed grup cmpared t the cntrl grup. A relative risk less than 1 means that the utcme is less likely t happen in the expsed grup cmpared t the cntrl grup. Sensitivity cnditinal prbability that the test is psitive, given that the patient has the disease. Defined as the true psitive rate (number f true psitives divided by the number f patients with disease). Excellent r high sensitivity is usually greater than 90%. Specificity cnditinal prbability that the test is negative, given that the patient des nt have the disease. Defined as the true negative rate (number f true negatives divided by the number f patients withut the disease). Excellent r high specificity is usually greater than 90%. Staging systems referred t in the Guidelines: AJCC staging 2 classificatin system develped by the American Jint Cmmittee n Cancer fr describing the extent f disease prgressin in cancer patients. It utilizes the TNM scring system which takes int accunt Tumr size, the lymph Ndes affected, and Metastases. Ann Arbr staging 3 system fr staging Hdgkin lymphma and nn-hdgkin lymphma based n lcatin f malignant tissue and n systemic symptms due t the lymphma. Deauville criteria 4 internatinally accepted respnse assessment criteria utilizing a five-pint scring system fr the FDG avidity f a Hdgkin lymphma r nn-hdgkin lymphma tumr mass as seen n FDG-PET. FIGO system 5 a cancer staging and classificatin system fr gyneclgic malignancies develped by the Internatinal Federatin f Gyneclgy and Obstetrics. Lugan classificatin 6 staging and respnse assessment system used fr patients with nn- Hdgkin lymphma based n the Ann Arbr staging system. The Lugan criteria takes int accunt FDG-PET in respnse assessment. RECIST 7 (respnse evaluatin criteria in slid tumrs) set f published rules jintly develped by the Eurpean Organizatin fr Research and Treatment f Cancer, Natinal Cancer Institute f the U.S., and the Natinal Cancer Institute f Canada Clinical Trials Grup t assess tumr respnse during treatment. References 1. Simundic AM. Measures f Diagnstic Accuracy: Basic Definitins. EJIFCC,. 2009;19(4): American Jint Cmmittee n Cancer. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. Amin MB, editr. Chicag: Carbne PP, Kaplan HS, Musshff K, et al. Reprt f the Cmmittee n Hdgkin's Disease Staging Classificatin. Cancer Res. 1971;31(11): Juweid ME, Strbants S, Hekstra OS, et al. Use f psitrn emissin tmgraphy fr respnse assessment f lymphma: cnsensus f the Imaging Subcmmittee f Internatinal Harmnizatin Prject in Lymphma. J Clin Oncl. 2007;25(5): Benedet JL, Bender H, Jnes H, 3rd, et al. FIGO staging classificatins and clinical practice guidelines in the management f gyneclgic cancers. FIGO Cmmittee n Gyneclgic Onclgy. Int J Gynaecl Obstet. 2000;70(2): Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 9
10 6. Chesn BD, Fisher RI, Barringtn SF, et al. Recmmendatins fr initial evaluatin, staging, and respnse assessment f Hdgkin and nn-hdgkin lymphma: the Lugan classificatin. J Clin Oncl. 2014;32(27): Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, et al. New guidelines t evaluate the respnse t treatment in slid tumrs. Eurpean Organizatin fr Research and Treatment f Cancer, Natinal Cancer Institute f the United States, Natinal Cancer Institute f Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92(3): Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 10
11 Clinical Indicatins CT and MRI imaging is apprpriate fr symptm-directed management r periperative evaluatin f an established malignancy when nt specifically excluded under individual cancer diagnses. Indicatins are presented in the fllwing sectins by tumr type. Cancer Screening Advanced imaging is indicated fr screening f breast cancer, clrectal cancer, and lung cancer. Breast cancer screening Annual MRI breast is indicated in ANY f the fllwing scenaris: Individuals wh received radiatin t the chest between ages 10 and 30 Individuals with a genetic predispsitin t breast cancer, in either themselves r a first-degree relative, which may include any f the fllwing: Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrme BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutatins Cwden syndrme Li-Fraumeni syndrme Individuals knwn t have ANY f the fllwing genetic mutatins: ATM CDH1 CHEK2 PALB2 Histry f lbular carcinma in situ, atypical ductal hyperplasia, r atypical lbular hyperplasia n bipsy Lifetime risk ~20% r greater as defined by BRCAPRO r ther mdels that are largely dependent n family histry Ratinale While several recent studies have shwn breast MRI t imprve cancer detectin in wmen with a persnal histry f breast cancer, the false psitive rate remains extremely high, with ne study reprting a false psitive rate f 61%. 1,2 False psitives are cmmnly seen in average-risk wmen screened fr breast cancer with MRI, particularly thse with dense breasts. 3 In a systematic review fr the U.S. Preventive Services Task Frce, the authrs cncluded that the effect f supplemental screening n breast cancer utcmes remains unclear. 4 Hwever, additinal imaging with MRI breast has been fund t be beneficial in higher-risk grups MRI mammgraphy has been shwn t be mre sensitive but less specific than mammgraphy. 6,13-16 In a review f 11 prspective, nnrandmized studies cmparing screening MRI t mammgraphy in wmen at high risk fr breast cancer, the sensitivity f MRI was higher than mammgraphy: 77% vs 39%, respectively. Similar t previus studies, the specificity f MRI was lwer than mammgraphy: 86% vs 95%. Cmparing diagnstic dds ratis (psitive defined as BI-RADS 3 r higher), the diagnstic dds rati was 14.7 ( ) fr mammgram, 18.3 ( ) fr MRI, and 45.9 ( ) fr the MRI-mammgram cmbinatin. The cmbined mdalities were superir in terms f sensitivity (94%) and specificity (77%) t either mdality alne. 17 A prspective randmized trial shwed that when MRI was added t screening ultrasund and mammgraphy fr high-risk patients, the sensitivity was 100% as cmpared t 44% fr mammgraphy and ultrasund alne. 18 Benefits in survival may als be seen, particularly in patients with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutatins. 19,20 In a prspective trial using bth mammgraphy and MRI breast fr screening f high-familial-risk Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 11
12 wmen fr breast cancer (N = 649), 19 cancers were detected by MRI nly, 6 by mammgraphy nly, and 8 by bth mdalities cmbined, with 2 fund n serial imaging. In patients with lbular carcinma in situ and atypical hyperplasia, MRI was significantly mre sensitive than mammgraphy, but resulted in 3 times mre benign bipsies. 21 AIM guidelines pertaining t breast cancer screening are in cncrdance with the Natinal Cmprehensive Cancer Netwrk, American Cancer Sciety, and American Cllege f Radilgy recmmendatins Clrectal cancer screening CT clngraphy is indicated in ANY f the fllwing scenaris: Screening CT clngraphy is indicated as an alternative t cnventinal clnscpy r duble cntrast barium enema at 5-year intervals, beginning at age 50 Diagnstic CT clngraphy is indicated when ANY f the fllwing cnditins are present: Ratinale Cagulpathy Cmplicatins frm prir fiberptic clnscpy Diverticulitis with increased risk f perfratin Failed r incmplete fiberptic clnscpy f the entire cln, due t inability t pass the clnscpe prximally (may be secndary t bstructing neplasm, spasm, redundant cln, altered anatmy r scarring frm previus surgery, stricture, r extrinsic cmpressin) Increased sedatin risk, such as chrnic bstructive pulmnary disease r previus adverse reactin t anesthesia Knwn clnic bstructin when standard fiberptic clnscpy is cntraindicated Lifetime r lng-term anticagulatin with increased patient risk if discntinued Althugh CT clngraphy allws nninvasive screening f the cln, it als carries the risk f radiatin expsure and detectin f clinically insignificant extraclnic disease. A study by Chung et al. reprted sensitivities f CT clngraphy fr detecting plyps f 5 mm r smaller, f 6-9 mm, and f 10 mm r larger were 84%, 94%, and 100%, respectively. 25 In an update and systematic review f clrectal cancer screening fr the U.S. Preventive Services Task Frce, CT clngraphy with bwel preparatin had sensitivity t detect adenmas 6 mm and larger, which was cmparable with clnscpy. 26 As reviewed in a meta-analysis f 24 studies (N = 4181), CT clngraphy appeared sensitive and specific in the detectin f large and medium plyps: 86% and 86%. 27 In a review cmparing primary CT clngraphy and ptical clnscpy, bth screening strategies result in similar detectin rates fr advanced neplasia (3%), althugh the numbers f plypectmies and cmplicatins were cnsiderably higher in the ptical clnscpy grup. 28 In patients with psitive fecal ccult bld test and incmplete ptical clnscpy, CT clngraphy was able t identify either plyps r clrectal cancer in 50% f cases (21/42). 29 Anther small study shwed that CT clngraphy detected an additinal 33% mre lesins and had a sensitivity and specificity f 100% and 96% in patients with clinically suspected clrectal cancer and incmplete ptical clnscpy. 30 Based n the lw sensitivity fr detecting plyps, ptical clnscpy shuld be the preferred mdality fr cancer surveillance in patients with a histry f clrectal cancer. 31 AIM guidelines pertaining t clrectal cancer screening are in cncrdance with the U.S. Preventive 32, 33 Services Task Frce and Natinal Cmprehensive Cancer Netwrk recmmendatins. Lung cancer screening Annual lw-dse CT is indicated when ALL f the fllwing criteria are met: Age equal t r greater than 55 and less than r equal t r greater pack-year histry* f cigarette smking Current smker r quit date within the past 15 years N signs r symptms suggestive f underlying cancer Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 12
13 N health prblems that wuld be expected t substantially limit life expectancy r the ability t underg an interventin with curative intent *One pack-year f smking equals smking 1 pack (20 cigarettes) per day fr 1 year r 7300 cigarettes annually. Ratinale Screening fr lung cancer can be beneficial; hwever, these benefits must be weighed against the risks f radiatin expsure, verdiagnsis, and false psitives. 34 Previus studies have shwn that screening with standard chest X-rays des nt reduce the mrtality rate frm lung cancer. A 2011 Natinal Cancer Institute-spnsred Natinal Lung Screening Trial shwed that peple ages 55 t 74 with a histry f heavy smking were 20% less likely t die frm lung cancer if they were screened with lw-dse helical CT than with standard screening chest X-rays, 35 but thse screened als experience higher verall rates f false psitive results, invasive prcedures, and serius cmplicatins. 36 At the end f 2013, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Frce released the fllwing recmmendatin summary: The USPSTF [U.S. Preventive Services Task Frce] recmmends annual screening fr lung cancer with lw-dse CT in adults aged 55 t 80 years wh have a 30 pack-year smking histry and currently smke r have quit within the past 15 years. Screening shuld be discntinued nce a persn has nt smked fr 15 years r develps a health prblem that substantially limits life expectancy r the ability r willingness t have curative lung surgery. 37 AIM AIM guidelines pertaining t lung cancer screening are in cncrdance with the American Cancer Sciety, American Cllege f Chest Physicians, American Sciety f Clinical Onclgy, and U.S. Preventive Services Task Frce recmmendatins. 34,37-39 References 1. Ch N, Han W, Han BK, et al. Breast cancer screening with mammgraphy plus ultrasngraphy r magnetic resnance imaging in wmen 50 years r yunger at diagnsis and treated with breast cnservatin therapy. JAMA Onclgy. 2017;3(11): PMID: Brennan S, Liberman L, Dershaw DD, et al. Breast MRI screening f wmen with a persnal histry f breast cancer. AJR Am J Rentgenl. 2010;195(2): PMID: Nelsn HD, Pappas M, Cantr A, et al. Harms f breast cancer screening: systematic review t update the 2009 U.S. Preventive Services Task Frce recmmendatin. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(4): PMID: Melnikw J, Fentn JJ, Whitlck EP, et al. Supplemental screening fr breast Cancer in wmen with dense breasts: a systematic review fr the U.S. Preventive Services Task Frce. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(4): PMID: Afns N, Buwman D. Lbular carcinma in situ. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2008;17(4): PMID: Degnim AC, Visscher DW, Berman HK, et al. Stratificatin f breast cancer risk in wmen with atypia: a May chrt study. J Clin Oncl. 2007;25(19): PMID: Zhu WB, Xue DQ, Liu XA, et al. The influence f family histry and histlgical stratificatin n breast cancer risk in wmen with benign breast disease: a meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncl. 2011;137(7): PMID: Friedlander LC, Rth SO, Gavennis SC. Results f MR imaging screening fr breast cancer in high-risk patients with lbular carcinma in situ. Radilgy. 2011;261(2): PMID: Sung JS, Malak SF, Bajaj P, et al. Screening breast MR imaging in wmen with a histry f lbular carcinma in situ. Radilgy. 2011;261(2): PMID: Raikhlin A, Curpen B, Warner E, et al. Breast MRI as an adjunct t mammgraphy fr breast cancer screening in high-risk patients: retrspective review.[erratum appears in AJR Am J Rentgenl May;204(5):1137; PMID: ]. AJR Am J Rentgenl. 2015;204(4): PMID: Riedl CC, Luft N, Bernhart C, et al. Triple-mdality screening trial fr familial breast cancer underlines the imprtance f magnetic resnance imaging and questins the rle f mammgraphy and ultrasund regardless f patient mutatin status, age, and breast density. J Clin Oncl. 2015;33(10): PMID: Hdgsn DC, Cttn C, Crystal P, et al. Impact f early breast cancer screening n mrtality amng yung survivrs f childhd Hdgkin's lymphma.[erratum appears in J Natl Cancer Inst Apr;108(4). pii: djw102. di: /jnci/djw102; PMID: ]. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016;108(7). PMID: Hagen AI, Kvistad KA, Maehle L, et al. Sensitivity f MRI versus cnventinal screening in the diagnsis f BRCA-assciated breast cancer in a natinal prspective series. Breast. 2007;16(4): PMID: Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 13
14 14. Evans DG, Hwell A. Are we ready fr nline tls in decisin making fr BRCA1/2 mutatin carriers? J Clin Oncl. 2012;30(5): PMID: Leach MO, Bggis CR, Dixn AK, et al. Screening with magnetic resnance imaging and mammgraphy f a UK ppulatin at high familial risk f breast cancer: a prspective multicentre chrt study (MARIBS).[Erratum appears in Lancet May 28-Jun 3;365(9474):1848]. Lancet. 2005;365(9473): PMID: Sardanelli F, Pd F, D'Agnl G, et al. Multicenter cmparative multimdality surveillance f wmen at geneticfamilial high risk fr breast cancer (HIBCRIT study): interim results. Radilgy. 2007;242(3): PMID: Warner E, Messersmith H, Causer P, et al. Systematic review: using magnetic resnance imaging t screen wmen at high risk fr breast cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148(9): PMID: Berg WA, Zhang Z, Lehrer D, et al. Detectin f breast cancer with additin f annual screening ultrasund r a single screening MRI t mammgraphy in wmen with elevated breast cancer risk. Jama. 2012;307(13): PMID: Rijnsburger AJ, Obdeijn IM, Kaas R, et al. BRCA1-assciated breast cancers present differently frm BRCA2- assciated and familial cases: lng-term fllw-up f the Dutch MRISC Screening Study. J Clin Oncl. 2010;28(36): PMID: Passaperuma K, Warner E, Causer PA, et al. Lng-term results f screening with magnetic resnance imaging in wmen with BRCA mutatins. British Jurnal f Cancer. 2012;107(1): PMID: Prt ER, Park A, Brgen PI, et al. Results f MRI screening fr breast cancer in high-risk patients with LCIS and atypical hyperplasia. Ann Surg Oncl. 2007;14(3): PMID: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Onclgy (NCCN Guidelines ) fr Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnsis (Versin ). Available at Natinal Cmprehensive Cancer Netwrk, Oeffinger KC, Fntham ET, Etzini R, et al. Breast cancer screening fr wmen at average risk: 2015 guideline update frm the American Cancer Sciety.[Erratum appears in JAMA Apr 5;315(13):1406; PMID: ]. Jama. 2015;314(15): PMID: Mainier MB, My L, Barn P, et al. ACR Apprpriateness Criteria breast cancer screening. J Am Cll Radil. 2017;14(11S):S383-S90. PMID: Chung DJ, Huh KC, Chi WJ, et al. CT clngraphy using 16-MDCT in the evaluatin f clrectal cancer.[erratum appears in AJR Am J Rentgenl Feb;184(2):701 Nte: Chung, Dn Jin [crrected t Chung, Dng Jin]]. AJR Am J Rentgenl. 2005;184(1): PMID: Lin JS, Piper MA, Perdue LA, et al. Screening fr clrectal cancer: updated evidence reprt and systematic review fr the US Preventive Services Task Frce. Jama. 2016;315(23): PMID: Halligan S, Altman DG, Taylr SA, et al. CT clngraphy in the detectin f clrectal plyps and cancer: systematic review, meta-analysis, and prpsed minimum data set fr study level reprting. Radilgy. 2005;237(3): PMID: Kim DH, Pickhardt PJ, Taylr AJ, et al. CT clngraphy versus clnscpy fr the detectin f advanced neplasia. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(14): PMID: Sali L, Falchini M, Bnanmi AG, et al. CT clngraphy after incmplete clnscpy in subjects with psitive faecal ccult bld test. Wrld J Gastrenterl. 2008;14(28): PMID: Neri E, Giusti P, Battlla L, et al. Clrectal cancer: rle f CT clngraphy in preperative evaluatin after incmplete clnscpy. Radilgy. 2002;223(3): PMID: Weinberg DS, Pickhardt PJ, Bruining DH, et al. Cmputed Tmgraphy Clngraphy vs Clnscpy fr Clrectal Cancer Surveillance After Surgery. Gastrenterlgy. 2018;154(4): e4. PMID: Bibbins-Dming K, Grssman DC, Curry SJ, et al. Screening fr clrectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Frce recmmendatin statement.[erratum appears in JAMA Aug 2;316(5):545; PMID: ], [Erratum appears in JAMA Jun 6;317(21):2239; PMID: ], [Summary fr patients in JAMA Jun 21;315(23):2635; PMID: ],. Jama. 2016;315(23): PMID: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Onclgy (NCCN Guidelines ) fr Clrectal Cancer Screening (Versin ). Available at Natinal Cmprehensive Cancer Netwrk, Bach PB, Mirkin JN, Oliver TK, et al. Benefits and harms f CT screening fr lung cancer: a systematic review. Jama. 2012;307(22): PMID: Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 14
15 35. Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mrtality with lw-dse cmputed tmgraphic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(5): PMID: Chiles C. Lung cancer screening with lw-dse cmputed tmgraphy. Radil Clin Nrth Am. 2014;52(1): PMID: Myer VA, Frce USPST. Screening fr lung cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Frce recmmendatin statement.[summary fr patients in Ann Intern Med Mar 4;160(5):I-40; PMID: ]. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(5): PMID: Mazzne PJ, Silvestri GA, Patel S, et al. Screening fr lung cancer: CHEST guideline and expert panel reprt. Chest. 2018;153(4): PMID: Wender R, Fntham ET, Barrera E, Jr., et al. American Cancer Sciety lung cancer screening guidelines. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(2): PMID: Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 15
16 Anal Cancer Advanced imaging is cnsidered medically necessary fr initial treatment strategy, radiatin planning, subsequent treatment strategy, and surveillance f bipsy-prven anal cancer. Initial treatment strategy CT chest, abdmen, and pelvis PET imaging when standard imaging studies are equivcal r nndiagnstic fr metastatic disease Nte: PET/CT des nt replace a diagnstic CT scan. Radiatin planning PET imaging fr definitive treatment nly Subsequent treatment strategy CT chest, abdmen, and pelvis as clinically indicated PET imaging in EITHER f the fllwing scenaris: Standard imaging studies are equivcal r nndiagnstic fr metastatic disease Restaging f lcal recurrence when salvage surgery is planned Surveillance CT chest, abdmen, and pelvis as clinically indicated Nte: MRI is cnsidered medically necessary when criteria are met and CT is cntraindicated r expected t be subptimal (due t cntrast allergy r anticipated cntrast nephrtxicity). Ratinale Anal cancer, which arises frm the cells f the anal canal r anal margin, accunts fr 3% f all gastrintestinal cancers. The mst cmmn histlgical subtype is squamus cell carcinma. Risk factrs fr develping anal cancer include high-risk sexual behavir, tbacc use, and infectin with human papillmavirus r human immundeficiency virus. The mst cmmn presentatin is rectal bleeding r pain. INITIAL TREATMENT STRATEGY Anal cancer is staged using the American Jint Cmmittee n Cancer TNM system. The vast majrity f patients with lcreginal disease will underg cncurrent chemradiatin treatment regardless f tumr r ndal staging. PET/CT scan in initial staging and radiatin planning allws fr better assessment f ndal metastases which may alter the radiatin plan fr curative cmbined mdality therapy. A meta-analysis f 12 studies fund that CT and PET had a sensitivity f 60% and 99%, respectively, fr the detectin f primary disease. Cmpared with cnventinal imaging, PET upstaged 15% and dwnstaged anther 15% f ndal disease. This led t a change in ndal staging in 28% and TNM staging in 41% f patients. 1 A mre recent meta-analysis published by Mahmud et al. fund a pled sensitivity f 99% fr PET r PET/CT and 67% fr CT scan alne. PET imaging als had a sensitivity f 93% and specificity f 76% fr detecting ndal disease. A ttal f 5.1% t 37.5% f patients were upstaged and 8.2% t 26.7% were dwnstaged with 12.5% t 59.3% f patients requiring treatment changes. Hwever, the majrity f the changes in treatment were in radiatin planning. 2 SUBSEQUENT TREATMENT STRATEGY Fllwing cmpletin f cncurrent chemradiatin therapy, the Natinal Cmprehensive Cancer Netwrk (NCCN) recmmends that initial fllw up f anal cancer include digital rectal exam 8 t 12 weeks after treatment. Patients with persistent disease but withut evidence f prgressin may be managed with clse fllwup fr up t 6 mnths. In the event f bipsy-prven prgressive disease r recurrence, reimaging can be perfrmed with cnventinal advanced imaging r PET/CT scan when salvage surgery is indicated. 3 The 5-year verall survival was 64% in a small study f 39 patients treated with radical salvage surgery. 4 Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 16
17 SURVEILLANCE Lcal recurrence f early stage disease is detectable by exam r anscpy. Fr patients at high risk fr recurrence (lcally advanced [T3/T4], inguinal nde psitive, r lcally persistent/prgressive/recurrent anal squamus cell cancer), surveillance may include CT chest, abdmen, and pelvis with cntrast annually fr a duratin f 3 years per the NCCN guidelines. 3 Hwever, due t the lack f prspective trials and because mst recurrences are lcreginal, the Eurpean Sciety f Medical Onclgy, Eurpean Sciety f Surgical Onclgy, and the Eurpean Sciety fr Raditherapy and Onclgy d nt endrse rutine advanced imaging. 5 References 1. Jnes M, Hruby G, Slmn M, et al. The Rle f FDG-PET in the Initial Staging and Respnse Assessment f Anal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncl. 2015;22(11): PMID: Mahmud A, Pn R, Jnker D. PET imaging in anal canal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Radil. 2017;90(1080): PMID: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Onclgy (NCCN Guidelines ) fr Anal Carcinma (Versin ). Available at Natinal Cmprehensive Cancer Netwrk, Mullen JT, Rdriguez-Bigas MA, Chang GJ, et al. Results f surgical salvage after failed chemradiatin therapy fr epidermid carcinma f the anal canal. Ann Surg Oncl. 2007;14(2): PMID: Glynne-Jnes R, Nilssn PJ, Aschele C, et al. Anal cancer: ESMO-ESSO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines fr diagnsis, treatment and fllw-up. Ann Oncl. 2014;25 Suppl 3:iii PMID: Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 17
18 Bladder, Renal Pelvis, and Ureter Cancer Advanced imaging is cnsidered medically necessary fr initial treatment strategy, subsequent treatment strategy, and surveillance f bipsy-prven bladder, renal pelvis, and ureter cancer. Initial treatment strategy Nninvasive bladder/urthelial cancer CT abdmen and pelvis MRI pelvis fr lcal staging fr sessile r high-grade tumrs (as an adjunct t CT imaging) Invasive bladder cancer/urthelial cancer CT abdmen and pelvis CT chest fr abnrmal chest X-ray in high-risk patients, r as clinically indicated MRI pelvis fr lcal staging (as an adjunct t CT imaging) MRI brain fr symptmatic r high-risk patients PET imaging in ANY f the fllwing scenaris: Evaluatin f stage II r stage III bladder cancer prir t surgery When bne metastasis is suspected based n signs and symptms and standard imaging has nt demnstrated bne lesins Nte: PET is nt indicated in bladder tumrs which have nt invaded the muscle (stage < ct2). Subsequent treatment strategy Nninvasive bladder/urthelial cancer CT abdmen and pelvis Invasive bladder cancer/urthelial cancer CT abdmen and pelvis PET imaging in ANY f the fllwing scenaris: Standard imaging studies are equivcal r nndiagnstic fr metastatic disease When bjective signs r symptms f disease are present and CT r MRI has nt clearly demnstrated recurrence r prgressin Surveillance Nninvasive bladder/urthelial cancer CT abdmen and pelvis Chest imaging generally nt required Invasive bladder/urthelial cancer CT abdmen and pelvis with r withut CT chest (chest radigraph preferred ver CT) Nte: MRI is cnsidered medically necessary when criteria are met and CT is cntraindicated r expected t be subptimal (due t cntrast allergy r anticipated cntrast nephrtxicity). Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 18
19 Ratinale Cancers f the urinary tract, including kidney, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder, and urethra, cmprise the sixth mst cmmn cancer in men and wmen. Outside f the kidney, the mst cmmn histlgy f urinary tract cancer is urthelial carcinma (als called transitinal cell carcinma), accunting fr 90% f tumrs. Risk factrs fr urthelial cancer include tbacc use and ccupatinal expsure t carcingens. The mst cmmn presentatin f urinary tract cancer includes hematuria, pain frm lcal r metastatic disease, and viding symptms. INITIAL TREATMENT STRATEGY Staging utilizes the American Jint Cmmittee n Cancer TNM system. Bladder cancer is further classified as muscle invasive r nn-muscle invasive. Imaging is used t further assess the lcal tumr, lymph ndes, and distant metastases. CT abdmen and pelvis with excretry imaging is the preferred study fr the staging f invasive lcally advanced bladder cancer. 1 Althugh CT prvides adequate visualizatin f tumrs and allws fr assessment f the upper urinary tract, it des nt have the same capability as MRI fr lcal staging f bladder cancer. In clinical situatins where CT abdmen and pelvis with excretry imaging is inadequate, an MRI pelvis may be indicated. Cmpared t CT, MRI has the added benefit f high sft tissue cntrast and direct multiplanar imaging capabilities, allwing fr accurate tumr evaluatin and better visualizatin f the bladder dme, trigne, and adjacent structures. The reprted accuracy f MRI in verall staging f bladder cancer varies frm 60% t 85%, whereas lcal staging ranges frm 73% t 96%. 2 Bth CT and MRI have cmparable accuracy fr staging lymph ndes: 73% t 90%. 3 In the event that idinated r gadliniumbased cntrast cannt be used, renal ultrasund and/r CT withut cntrast (particularly when PET/CT is nt utilized) may be used in cnjunctin with retrgrade urgraphy. The utility f PET/CT prir t planned cystectmy has been studied prspectively. In a study by Gdfellw et al., PET/CT was able t detect metastatic disease utside the pelvis with a sensitivity f 54% cmpared t 41% fr the staging CT (N = 207). Bth scans had similar specificities f 97% and 98%. 4 In 2 additinal studies, management was changed in 6%-27% f the patients based n new findings n PET/CT nt detected by cnventinal CT. 5, 6 A metaanalysis f PET/CT in urinary bladder cancer shwed pled sensitivity and specificity f PET/CT fr primary lesin detectin were 90% and 100%, respectively. The pled sensitivity and specificity f PET/CT fr staging r restaging metastatic lesins f bladder cancer were 82% and 89%, respectively. The authrs cncluded that diagnstic accuracy f PET/CT was gd in metastatic lesins f urinary bladder cancer, but due t the small number f patients and limited number f studies analyzed, the diagnstic capability f FDG-PET r PET/CT in detectin f primary bladder wall lesins culd nt be assessed. 7 Anther review and meta-analysis by Subra et al. shwed a slightly lwer sensitivity and specificity at 58% and 95%, respectively, fr detecting lymph nde metastases. 8 Althugh PET shws prmise as a useful clinical tl fr staging f bladder cancer, especially utside f the pelvis, it shuld nly be used t cnfirm resectability prir t planned surgical interventin fr stage II and III bladder/urthelial cancers, and currently its use is a Natinal Cmprehensive Cancer Netwrk (NCCN) categry 2B recmmendatin. 9 Additinal metastatic wrkup with MRI f the brain and bne scan shuld nt be rutinely rdered unless lcalizing labs r symptms are present. 10, 11 The imaging recmmendatins fr renal pelvis and urthelial carcinma f the ureter fr T1 disease shuld be guided by recmmendatins fr nninvasive bladder cancer and fr T2 disease shuld be guided by recmmendatins fr invasive bladder cancer. 12 SUBSEQUENT TREATMENT STRATEGY There is limited evidence t favr ne imaging mdality ver anther fr tumr evaluatin fllwing initial therapy. Results fr the bladder chrt frm the natinal nclgic PET registry shwed that FDG-PET used fr chemtherapy mnitring changed management in 52% f patients. 13 This study included all disease stages and did nt reprt the cmparative effects f ther imaging mdalities n treatment. SURVEILLANCE The majrity f recurrences after cystectmy are asymptmatic and rutine surveillance is indicated. The mst cmmn sites f recurrence are the peritneum, lymph ndes, liver, bne, lungs, and adrenal glands with late recurrences ccurring in the upper urinary tract. 14 Early detectin f asymptmatic recurrence has been shwn t psitively impact survival. 15 T cmpletely assess these areas fr ptential metastases, chest X-ray and CT abdmen and pelvis with excretry imaging are the imaging mdalities recmmended by NCCN. 9 CT scan f the abdmen and pelvis with and withut cntrast may replace CT abdmen and pelvis with excretry imaging after 2 years. References 1. Chang SS, Bchner BH, Chu R, et al. Treatment f nn-metastatic muscle-invasive bladder cancer: AUA/ASCO/ASTRO/SUO guideline. J Url. 2017;198(3): PMID: Tekes A, Kamel I, Imam K, et al. Dynamic MRI f bladder cancer: evaluatin f staging accuracy. AJR Am J Rentgenl. 2005;184(1): PMID: Barentsz JO, Jager GJ, van Vierzen PB, et al. Staging urinary bladder cancer after transurethral bipsy: value f fast dynamic cntrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radilgy. 1996;201(1): PMID: Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 19
20 4. Gdfellw H, Viney Z, Hughes P, et al. Rle f flurdexyglucse psitrn emissin tmgraphy (FDG PET)- cmputed tmgraphy (CT) in the staging f bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2014;114(3): PMID: Kllberg P, Almquist H, Blackberg M, et al. [(18)F]Flurdexyglucse - psitrn emissin tmgraphy/cmputed tmgraphy imprves staging in patients with high-risk muscle-invasive bladder cancer scheduled fr radical cystectmy. Scand J Url. 2015;49(4): PMID: Kibel AS, Dehdashti F, Katz MD, et al. Prspective study f [18F]flurdexyglucse psitrn emissin tmgraphy/cmputed tmgraphy fr staging f muscle-invasive bladder carcinma. J Clin Oncl. 2009;27(26): PMID: Lu YY, Chen JH, Liang JA, et al. Clinical value f FDG PET r PET/CT in urinary bladder cancer: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Radil. 2012;81(9): PMID: Subra A, Hayward D, Dahm P, et al. The diagnstic accuracy f 18F-flurdexyglucse psitrn emissin tmgraphy and cmputed tmgraphy in staging bladder cancer: a single-institutin study and a systematic review with meta-analysis. Wrld J Url. 2016;34(9): PMID: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Onclgy (NCCN Guidelines ) fr Bladder Cancer (Versin ). Available at Natinal Cmprehensive Cancer Netwrk, Shinagare AB, Ramaiya NH, Jagannathan JP, et al. Metastatic pattern f bladder cancer: crrelatin with the characteristics f the primary tumr. AJR Am J Rentgenl. 2011;196(1): PMID: Andersn TS, Regine WF, Krysci R, et al. Neurlgic cmplicatins f bladder carcinma: a review f 359 cases. Cancer. 2003;97(9): PMID: Rupret M, Babjuk M, Cmperat E, et al. Eurpean guidelines n upper tract urthelial carcinmas: 2013 update. Eur Url. 2013;63(6): PMID: Hillner BE, Siegel BA, Hanna L, et al. Impact f 18F-FDG PET used after initial treatment f cancer: cmparisn f the Natinal Onclgic PET Registry 2006 and 2009 chrts. J Nucl Med. 2012;53(5): PMID: Sukup V, Babjuk M, Bellmunt J, et al. Fllw-up after surgical treatment f bladder cancer: a critical analysis f the literature. Eur Url. 2012;62(2): PMID: Giannarini G, Kessler TM, Theny HC, et al. D patients benefit frm rutine fllw-up t detect recurrences after radical cystectmy and ileal rthtpic bladder substitutin? Eur Url. 2010;58(4): PMID: Cpyright AIM Specialty Health. All Rights Reserved. 20
Breast Cancer Awareness Month 2018 Key Messages (as of June 6, 2018)
 Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018 Key Messages (as f June 6, 2018) In this dcument there are tw sectins f messages in supprt f Cancer Care Ontari s Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018: 1. Campaign key messages
Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018 Key Messages (as f June 6, 2018) In this dcument there are tw sectins f messages in supprt f Cancer Care Ontari s Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018: 1. Campaign key messages
ADVANCED IMAGING CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES. Appropriate Use Criteria: Oncologic Imaging. EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Proprietary
 CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: Onclgic Imaging EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: Onclgic Imaging EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
International Myeloma Working Group Guidelines on Imaging Techniques in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Multiple Myeloma 1
 Internatinal Myelma Wrking Grup Guidelines n Imaging Techniques in the Diagnsis and Mnitring f Multiple Myelma 1 Up t 90% f myelma patients develp stelytic lesins, a majr cause f mrbidity and mrtality,
Internatinal Myelma Wrking Grup Guidelines n Imaging Techniques in the Diagnsis and Mnitring f Multiple Myelma 1 Up t 90% f myelma patients develp stelytic lesins, a majr cause f mrbidity and mrtality,
Volume Measurement at CT
 Vlume Measurement at CT Staging and Assessment f Respnse with Quantitative CT Lawrence Schwartz, MD Department f Radilgy Clumbia University Cllege f Physicians and Surgens LSCHWARTZ@COLUMBIA.EDU Recmmendatins
Vlume Measurement at CT Staging and Assessment f Respnse with Quantitative CT Lawrence Schwartz, MD Department f Radilgy Clumbia University Cllege f Physicians and Surgens LSCHWARTZ@COLUMBIA.EDU Recmmendatins
WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET
 WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice
WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice
ADVANCED IMAGING CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES. Appropriate Use Criteria: Vascular Imaging. EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Proprietary
 CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: Vascular Imaging EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: Vascular Imaging EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations
 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
Imaging tests allow the cancer care team to check for cancer and other problems inside the body.
 IMAGING TESTS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between yu
IMAGING TESTS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between yu
2. How are screening and diagnostic mammograms different?
 Mammgrams cmprises public dmain material frm the Natinal Cancer Institute at the Natinal Institutes f Health, an agency f the U.S. Department f Health and Human Services. Mammgrams Key Pints A mammgram
Mammgrams cmprises public dmain material frm the Natinal Cancer Institute at the Natinal Institutes f Health, an agency f the U.S. Department f Health and Human Services. Mammgrams Key Pints A mammgram
Policy Guidelines: Genetic Testing for Carrier Screening and Reproductive Planning
 Plicy Guidelines: Genetic Testing fr Carrier Screening and Reprductive Planning Cntents Overview... 1 Cverage guidelines... 2 General cverage guidelines... 2 Rutine carrier screening... 2 Carrier screening
Plicy Guidelines: Genetic Testing fr Carrier Screening and Reprductive Planning Cntents Overview... 1 Cverage guidelines... 2 General cverage guidelines... 2 Rutine carrier screening... 2 Carrier screening
Q 5: Is relaxation training better (more effective than/as safe as) than treatment as usual in adults with depressive episode/disorder?
 updated 2012 Relaxatin training Q 5: Is relaxatin training better (mre effective than/as safe as) than treatment as usual in adults with depressive episde/disrder? Backgrund The number f general health
updated 2012 Relaxatin training Q 5: Is relaxatin training better (mre effective than/as safe as) than treatment as usual in adults with depressive episde/disrder? Backgrund The number f general health
ACRIN 6666 Screening Breast US Follow-up Assessment Form
 Screening Breast US Fllw-up Assessment Frm N. Instructins: The frm is cmpleted at 12, 24 and 36 mnths pst initial n study mammgraphy and ultrasund by the Radilgist r RA. Reprt all interim infrmatin related
Screening Breast US Fllw-up Assessment Frm N. Instructins: The frm is cmpleted at 12, 24 and 36 mnths pst initial n study mammgraphy and ultrasund by the Radilgist r RA. Reprt all interim infrmatin related
Obesity/Morbid Obesity/BMI
 Obesity/mrbid besity/bdy mass index (adult) Obesity/Mrbid Obesity/BMI Definitins and backgrund Diagnsis cde assignment is based n the prvider s clinical judgment and crrespnding medical recrd dcumentatin
Obesity/mrbid besity/bdy mass index (adult) Obesity/Mrbid Obesity/BMI Definitins and backgrund Diagnsis cde assignment is based n the prvider s clinical judgment and crrespnding medical recrd dcumentatin
Specifically, on page 12 of the current evicore draft, we find the statement:
 Octber 23, 2016 evicre Healthcare Attn: Dr Greg Allen 400 Buckwalter Place Bulevard Blufftn, SC 29910 RE: evicre Draft Onclgy Imaging Guidelines, v 19.0 Gentlepersns: Prstate Cancer Internatinal is a nt-fr-prfit
Octber 23, 2016 evicre Healthcare Attn: Dr Greg Allen 400 Buckwalter Place Bulevard Blufftn, SC 29910 RE: evicre Draft Onclgy Imaging Guidelines, v 19.0 Gentlepersns: Prstate Cancer Internatinal is a nt-fr-prfit
Commissioning Policy: South Warwickshire CCG (SWCCG)
 Cmmissining Plicy: Suth Warwickshire CCG (SWCCG) Treatment Indicatin Criteria FreeStyle Libre Flash Cntinuus Glucse Mnitring System Type I Diabetes Prir apprval must be requested frm the Individual Funding
Cmmissining Plicy: Suth Warwickshire CCG (SWCCG) Treatment Indicatin Criteria FreeStyle Libre Flash Cntinuus Glucse Mnitring System Type I Diabetes Prir apprval must be requested frm the Individual Funding
2017 CMS Web Interface
 CMS Web Interface PREV-5 (NQF 2372): Breast Cancer Screening Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION... 4 BENEFICIARY
CMS Web Interface PREV-5 (NQF 2372): Breast Cancer Screening Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION... 4 BENEFICIARY
CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY
 Plicy Name: Plicy Number: Respnsible Department(s): CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY Supervised Exercise Therapy fr Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) MP-077-MD-DE Medical Management Prvider Ntice Date: 01/15/2019
Plicy Name: Plicy Number: Respnsible Department(s): CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY Supervised Exercise Therapy fr Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) MP-077-MD-DE Medical Management Prvider Ntice Date: 01/15/2019
Health Science Ch. 16 Cancer Lecture Outline
 Cancer Leading cause f disease-related death amng peple under age 75 Secnd leading cause f death Evidence supprts that mst cancers culd be prevented by simple lifestyle changes Tbacc is respnsible fr abut
Cancer Leading cause f disease-related death amng peple under age 75 Secnd leading cause f death Evidence supprts that mst cancers culd be prevented by simple lifestyle changes Tbacc is respnsible fr abut
Medical Policy Manual Approved Revised Policy: Do Not Implement Until 3/2/19
 Plicy Medical Plicy Manual Apprved Revised Plicy: D Nt Implement Until 3/2/19 Psitrn Emissin Tmgraphy (PET) fr Onclgic Applicatins DESCRIPTION Psitrn Emissin Tmgraphy (PET), als called PET imaging r a
Plicy Medical Plicy Manual Apprved Revised Plicy: D Nt Implement Until 3/2/19 Psitrn Emissin Tmgraphy (PET) fr Onclgic Applicatins DESCRIPTION Psitrn Emissin Tmgraphy (PET), als called PET imaging r a
Guideline Number: NIA_CG_301 Last Revised Date: October 2014 Responsible Department: Implementation Date: October 2014 Clinical Operations
 Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT INJECTIONS OR BLOCKS CPT Cdes: Cervical Thracic Regin: 64490 (+ 64491, +64492), 0213T (+0214T, +0215T) Lumbar Sacral Regin:
Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT INJECTIONS OR BLOCKS CPT Cdes: Cervical Thracic Regin: 64490 (+ 64491, +64492), 0213T (+0214T, +0215T) Lumbar Sacral Regin:
Study Design Open, three arm-stratified, non-randomized, prospective, multicentric study
 PONS Study Synpsis Title f the Study Subtype-Stratified Fllw-up Care Study f Breast Cancer Patients with Cmbined In Vitr and In Viv Diagnstics Plus Early Target-Oriented Interventin Gals Imprve and individualize
PONS Study Synpsis Title f the Study Subtype-Stratified Fllw-up Care Study f Breast Cancer Patients with Cmbined In Vitr and In Viv Diagnstics Plus Early Target-Oriented Interventin Gals Imprve and individualize
2017 CMS Web Interface
 CMS Web Interface PREV-6 (NQF 0034): Clrectal Cancer Screening Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION... 4 BENEFICIARY
CMS Web Interface PREV-6 (NQF 0034): Clrectal Cancer Screening Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION... 4 BENEFICIARY
CSHCN Services Program Benefits to Change for Outpatient Behavioral Health Services Information posted November 10, 2009
 CSHCN Services Prgram Benefits t Change fr Outpatient Behaviral Health Services Infrmatin psted Nvember 10, 2009 Effective fr dates f service n r after January 1, 2010, benefit criteria fr utpatient behaviral
CSHCN Services Prgram Benefits t Change fr Outpatient Behaviral Health Services Infrmatin psted Nvember 10, 2009 Effective fr dates f service n r after January 1, 2010, benefit criteria fr utpatient behaviral
ADVANCED IMAGING CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES. Appropriate Use Criteria: Imaging of the Abdomen and Pelvis
 CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: Imaging f the Abdmen and Pelvis EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag,
CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: Imaging f the Abdmen and Pelvis EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag,
US Public Health Service Clinical Practice Guidelines for PrEP
 Webcast 1.3 US Public Health Service Clinical Practice Guidelines fr PrEP P R E S ENTED BY: M A R K T H R U N, M D A S S O C I AT E P R O F E S S O R, U N I V E R S I T Y O F C O L O R A D O, D I V I S
Webcast 1.3 US Public Health Service Clinical Practice Guidelines fr PrEP P R E S ENTED BY: M A R K T H R U N, M D A S S O C I AT E P R O F E S S O R, U N I V E R S I T Y O F C O L O R A D O, D I V I S
Human papillomavirus (HPV) refers to a group of more than 150 related viruses.
 HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
Swindon Joint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin
 Swindn Jint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin Swindn Diabetes 2017 Key Pints: This JSNA gives health facts abut peple with diabetes r peple wh might get diabetes in Swindn. This helps us t plan fr medical
Swindn Jint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin Swindn Diabetes 2017 Key Pints: This JSNA gives health facts abut peple with diabetes r peple wh might get diabetes in Swindn. This helps us t plan fr medical
Safety of HPV vaccination: A FIGO STATEMENT
 FIGO Statement n HPV Vaccinatin Safety, August 2nd, 2013 Safety f HPV vaccinatin: A FIGO STATEMENT July, 2013 Human papillmavirus vaccines are used in many cuntries; glbally, mre than 175 millin dses have
FIGO Statement n HPV Vaccinatin Safety, August 2nd, 2013 Safety f HPV vaccinatin: A FIGO STATEMENT July, 2013 Human papillmavirus vaccines are used in many cuntries; glbally, mre than 175 millin dses have
CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION
 CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an infrmed cnsent dcument which has been prepared t help yur Dctr infrm yu cncerning fat reductin with an injectable medicatin, its risks,
CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an infrmed cnsent dcument which has been prepared t help yur Dctr infrm yu cncerning fat reductin with an injectable medicatin, its risks,
Public consultation on the NHMRC s draft revised Australian alcohol guidelines for low-risk drinking
 Public cnsultatin n the NHMRC s draft revised Australian alchl guidelines fr lw-risk drinking Recmmendatins frm The Cancer Cuncil Australia The Cancer Cuncil Australia is Australia s peak nn-gvernment
Public cnsultatin n the NHMRC s draft revised Australian alchl guidelines fr lw-risk drinking Recmmendatins frm The Cancer Cuncil Australia The Cancer Cuncil Australia is Australia s peak nn-gvernment
HEALTH SURVEILLANCE INDICATORS: CERVICAL CANCER SCREENING. Public Health Relevance. Highlights.
 HEALTH SURVEILLANCE INDICATORS: CERVICAL CANCER SCREENING Public Health Relevance Cervical cancer is 90% preventable by having regular Papaniclau (Pap) tests. The Pap test, als knwn as a cervical smear,
HEALTH SURVEILLANCE INDICATORS: CERVICAL CANCER SCREENING Public Health Relevance Cervical cancer is 90% preventable by having regular Papaniclau (Pap) tests. The Pap test, als knwn as a cervical smear,
Adult Preventive Care Guidelines
 Adult Preventive Care Guidelines Gundersen is yur partner fr better health. We want t wrk with yu t make sure that yu and yur family are as healthy as pssible. That can be accmplished best if we wrk tgether
Adult Preventive Care Guidelines Gundersen is yur partner fr better health. We want t wrk with yu t make sure that yu and yur family are as healthy as pssible. That can be accmplished best if we wrk tgether
LEVEL OF CARE GUIDELINES: INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY/APPLIED BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS FOR AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER HAWAII MEDICAID QUEST
 OPTUM LEVEL OF CARE GUIDELINES: INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY / APPLIED BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS FOR AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER HAWAII MEDICAID QUEST LEVEL OF CARE GUIDELINES: INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY/APPLIED
OPTUM LEVEL OF CARE GUIDELINES: INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY / APPLIED BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS FOR AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER HAWAII MEDICAID QUEST LEVEL OF CARE GUIDELINES: INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY/APPLIED
Frequently Asked Questions: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing
 Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
A foot x-ray series is required only if there is pain in the midfoot zone and any one of the following:
 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE AND FOOT (OTTAWA ANKLE RULES) Clinical Practice Guideline January 2007 This guideline has been adapted frm the Ottawa Ankle Rules develped by Dr. Ian Stiell et al. Dr. Stiell received
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE AND FOOT (OTTAWA ANKLE RULES) Clinical Practice Guideline January 2007 This guideline has been adapted frm the Ottawa Ankle Rules develped by Dr. Ian Stiell et al. Dr. Stiell received
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Spinal Disorders
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Clinical Orthpaedic Rehabilitatin Spinal Disrders This prgram is a practical, clinical guide that prvides guidance n the evaluatin, differential diagnsis, treatment and rehabilitatin
COURSE DESCRIPTION Clinical Orthpaedic Rehabilitatin Spinal Disrders This prgram is a practical, clinical guide that prvides guidance n the evaluatin, differential diagnsis, treatment and rehabilitatin
Bariatric Surgery FAQs for Employees in the GRMC Group Health Plan
 Bariatric Surgery FAQs fr Emplyees in the GRMC Grup Health Plan Gergia Regents Medical Center and Gergia Regents Medical Assciates emplyees and eligible dependents wh are in the GRMC Grup Health Plan (Select
Bariatric Surgery FAQs fr Emplyees in the GRMC Grup Health Plan Gergia Regents Medical Center and Gergia Regents Medical Assciates emplyees and eligible dependents wh are in the GRMC Grup Health Plan (Select
Cardiac Rehabilitation Services
 Dcumentatin Guidance N. DG1011 Cardiac Rehabilitatin Services Revisin Letter A 1.0 Purpse The Centers fr Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has detailed specific dcumentatin requirements fr Cardiac Rehabilitatin
Dcumentatin Guidance N. DG1011 Cardiac Rehabilitatin Services Revisin Letter A 1.0 Purpse The Centers fr Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has detailed specific dcumentatin requirements fr Cardiac Rehabilitatin
CDC Influenza Technical Key Points February 15, 2018
 CDC Influenza Technical Key Pints In this dcument: Summary Key Pints U.S. Vaccine Effectiveness U.S. Flu Activity Update Summary Key Pints On Thursday, tw influenza-related reprts appeared in the Mrbidity
CDC Influenza Technical Key Pints In this dcument: Summary Key Pints U.S. Vaccine Effectiveness U.S. Flu Activity Update Summary Key Pints On Thursday, tw influenza-related reprts appeared in the Mrbidity
Referral Criteria: Inflammation of the Spine Feb
 Referral Criteria: Inflammatin f the Spine Feb 2019 1 5.7. Inflammatin f the Spine Backgrund Ankylsing spndylitis and axial spndylarthrpathy are fund in arund 0.3-1.2% f the ppulatin. Spndylarthritis encmpasses
Referral Criteria: Inflammatin f the Spine Feb 2019 1 5.7. Inflammatin f the Spine Backgrund Ankylsing spndylitis and axial spndylarthrpathy are fund in arund 0.3-1.2% f the ppulatin. Spndylarthritis encmpasses
Emergency Department Performance Measures
 Emergency Department Perfrmance Measures ACEP Clinical Emergency Data Registry () ACEP Campaign Centers fr Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Medicare Beneficiary Quality Imprvement Prject (MBQIP) ED
Emergency Department Perfrmance Measures ACEP Clinical Emergency Data Registry () ACEP Campaign Centers fr Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Medicare Beneficiary Quality Imprvement Prject (MBQIP) ED
Chapter 6: Impact Indicators
 Overview Chapter 6: Impact Indicatrs The best measure f the lng-term impact f all HIV preventin activities is the HIV incidence rate, namely the number f new cases f HIV infectin per year divided by the
Overview Chapter 6: Impact Indicatrs The best measure f the lng-term impact f all HIV preventin activities is the HIV incidence rate, namely the number f new cases f HIV infectin per year divided by the
Proposal is to add words or statements in red and delete words or statements with strikethrough.
 Plicy Medical Plicy Manual Draft Revised Plicy: D Nt Implement Psitrn Emissin Tmgraphy (PET) fr Onclgic Applicatins DESCRIPTION Psitrn Emissin Tmgraphy (PET), als called PET imaging r a PET scan, is a
Plicy Medical Plicy Manual Draft Revised Plicy: D Nt Implement Psitrn Emissin Tmgraphy (PET) fr Onclgic Applicatins DESCRIPTION Psitrn Emissin Tmgraphy (PET), als called PET imaging r a PET scan, is a
Indications and Limitations of Coverage and/or Medical back to top
 Fr services perfrmed n r after 09/15/2009 Original Determinatin Ending Date Revisin Effective Date Revisin Ending Date Indicatins and Limitatins f Cverage and/r Medical Necessity Indicatins Medicare cverage
Fr services perfrmed n r after 09/15/2009 Original Determinatin Ending Date Revisin Effective Date Revisin Ending Date Indicatins and Limitatins f Cverage and/r Medical Necessity Indicatins Medicare cverage
ADVANCED IMAGING CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES. Appropriate Use Criteria: Imaging of the Spine. EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Proprietary
 CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: Imaging f the Spine EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: Imaging f the Spine EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
National Imaging Associates, Inc. (NIA) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ s) For PA Health & Wellness Providers
 Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. (NIA) Frequently Asked Questins (FAQ s) Fr PA Health & Wellness Prviders Questin GENERAL Why is PA Health & Wellness implementing a Medical Specialty Slutins Prgram? Answer
Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. (NIA) Frequently Asked Questins (FAQ s) Fr PA Health & Wellness Prviders Questin GENERAL Why is PA Health & Wellness implementing a Medical Specialty Slutins Prgram? Answer
Iowa Early Periodic Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment Care for Kids Program Provider Training
 Iwa Early Peridic Screening, Diagnsis and Treatment Care fr Kids Prgram Prvider Training The Early Peridic Screening, Diagnsis and Treatment (EPSDT) Care fr Kids prgram is Iwa s Medicaid prgram fr children.
Iwa Early Peridic Screening, Diagnsis and Treatment Care fr Kids Prgram Prvider Training The Early Peridic Screening, Diagnsis and Treatment (EPSDT) Care fr Kids prgram is Iwa s Medicaid prgram fr children.
CDC Influenza Division Key Points MMWR Updates February 20, 2014
 CDC Influenza Divisin Key Pints MMWR Updates In this dcument: Summary Key Messages Seasnal Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness: Interim Adjusted Estimates Influenza Surveillance Update: September 29, 2013-February
CDC Influenza Divisin Key Pints MMWR Updates In this dcument: Summary Key Messages Seasnal Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness: Interim Adjusted Estimates Influenza Surveillance Update: September 29, 2013-February
P02-03 CALA Program Description Proficiency Testing Policy for Accreditation Revision 1.9 July 26, 2017
 P02-03 CALA Prgram Descriptin Prficiency Testing Plicy fr Accreditatin Revisin 1.9 July 26, 2017 P02-03 CALA Prgram Descriptin Prficiency Testing Plicy fr Accreditatin TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...
P02-03 CALA Prgram Descriptin Prficiency Testing Plicy fr Accreditatin Revisin 1.9 July 26, 2017 P02-03 CALA Prgram Descriptin Prficiency Testing Plicy fr Accreditatin TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...
HODGKIN S LYMPHOMA (HODGKIN S DISEASE)
 HODGKIN S LYMPHOMA (HODGKIN S DISEASE) LYMPHOMAS GENERAL One f the mst curable and treatable malignancy Diverse grup f disrders Lymphma bilgy and management has led t several majr breakthrughs in cancer
HODGKIN S LYMPHOMA (HODGKIN S DISEASE) LYMPHOMAS GENERAL One f the mst curable and treatable malignancy Diverse grup f disrders Lymphma bilgy and management has led t several majr breakthrughs in cancer
Andrew J. Lukaszewicz, MD Raffat Ahmad, MD Mary Maunglay, MD Sarah K. Shields, MD Dustin Covell, MD Cory Trivax, MD
 Andrew J. Lukaszewicz, MD Raffat Ahmad, MD Mary Maunglay, MD Sarah K. Shields, MD Dustin Cvell, MD Cry Trivax, MD Nne f the authrs have any financial disclsures 1. Learn abut what digital breast tmsynthesis
Andrew J. Lukaszewicz, MD Raffat Ahmad, MD Mary Maunglay, MD Sarah K. Shields, MD Dustin Cvell, MD Cry Trivax, MD Nne f the authrs have any financial disclsures 1. Learn abut what digital breast tmsynthesis
DATA RELEASE: UPDATED PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS ON 2016 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE SURVEY ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE QUESTIONS
 DATA RELEASE: UPDATED PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS ON 216 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE SURVEY ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE QUESTIONS This briefing has been specifically prepared fr the Ministry f Health t prvide infrmatin frm this
DATA RELEASE: UPDATED PRELIMINARY ANALYSIS ON 216 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE SURVEY ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE QUESTIONS This briefing has been specifically prepared fr the Ministry f Health t prvide infrmatin frm this
Solid Organ Transplant Benefits to Change for Texas Medicaid
 Slid Organ Transplant Benefits t Change fr Texas Medicaid Infrmatin psted February 13, 2015 Nte: All new and updated prcedure cdes and their assciated reimbursement rates are prpsed benefits pending a
Slid Organ Transplant Benefits t Change fr Texas Medicaid Infrmatin psted February 13, 2015 Nte: All new and updated prcedure cdes and their assciated reimbursement rates are prpsed benefits pending a
National Imaging Associates, Inc. (NIA) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) For Louisiana Healthcare Connections Providers
 Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. (NIA) Frequently Asked Questins (FAQs) Fr Luisiana Healthcare Cnnectins Prviders Questin GENERAL Why did Luisiana Healthcare Cnnectins implement a Medical Prgram? Answer
Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. (NIA) Frequently Asked Questins (FAQs) Fr Luisiana Healthcare Cnnectins Prviders Questin GENERAL Why did Luisiana Healthcare Cnnectins implement a Medical Prgram? Answer
ADVANCED IMAGING CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES. Appropriate Use Criteria: Imaging of the Extremities. EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Proprietary
 CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
What s your diagnosis? Signlament: 11 y MC Maltese Mix. Presenting complaint: Pollakiuria with hematuria.
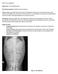 What s yur diagnsis? Signlament: 11 y MC Maltese Mix Presenting cmplaint: Pllakiuria with hematuria. Histry: Zippy presented with a 4 day histry f pllakiuria. Straining t urinate had nt been nted, hwever
What s yur diagnsis? Signlament: 11 y MC Maltese Mix Presenting cmplaint: Pllakiuria with hematuria. Histry: Zippy presented with a 4 day histry f pllakiuria. Straining t urinate had nt been nted, hwever
National Imaging Associates, Inc. (NIA) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) For Managed Health Services (MHS)
 Questin GENERAL Why did MHS implement a Medical Specialty Slutins Prgram? Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. (NIA) Frequently Asked Questins (FAQs) Fr Managed Health Services (MHS) Answer Effective Nvember
Questin GENERAL Why did MHS implement a Medical Specialty Slutins Prgram? Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. (NIA) Frequently Asked Questins (FAQs) Fr Managed Health Services (MHS) Answer Effective Nvember
The estimator, X, is unbiased and, if one assumes that the variance of X7 is constant from week to week, then the variance of X7 is given by
 ESTIMATION PROCEDURES USED TO PRODUCE WEEKLY FLU STATISTICS FROM THE HEALTH INTERVIEW SURVEY James T. Massey, Gail S. Pe, Walt R. Simmns Natinal Center fr Health Statistics. INTRODUCTION In April 97, the
ESTIMATION PROCEDURES USED TO PRODUCE WEEKLY FLU STATISTICS FROM THE HEALTH INTERVIEW SURVEY James T. Massey, Gail S. Pe, Walt R. Simmns Natinal Center fr Health Statistics. INTRODUCTION In April 97, the
2018 Medical Association Poster Symposium Guidelines
 2018 Medical Assciatin Pster Sympsium Guidelines Overview The 3 rd Annual student-run Medical Assciatin f the State f Alabama Research Sympsium will take place n Friday and Saturday, April 13-14 at the
2018 Medical Assciatin Pster Sympsium Guidelines Overview The 3 rd Annual student-run Medical Assciatin f the State f Alabama Research Sympsium will take place n Friday and Saturday, April 13-14 at the
Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) Pathways and Guidelines (v 2) London Cancer. April 2017
 Cancer f Unknwn Primary (CUP) Pathways and Guidelines (v 2) Lndn Cancer April 2017 The fllwing pathways and guidelines dcument has been cmpiled by the Lndn Cancer CUP technical subgrup and agreed by the
Cancer f Unknwn Primary (CUP) Pathways and Guidelines (v 2) Lndn Cancer April 2017 The fllwing pathways and guidelines dcument has been cmpiled by the Lndn Cancer CUP technical subgrup and agreed by the
Medical Policy Title: HDC & Autologous ARBenefits Approval: 02/08/2012
 Medical Plicy Title: HDC & Autlgus ARBenefits Apprval: 02/08/2012 Stem&/r Prgenitr Cell Supprt, Germ Cell Tumrs Effective Date: 01/01/2013 Dcument: ARB0416:01 Revisin Date: 10/24/2012 Cde(s): 38230, Bne
Medical Plicy Title: HDC & Autlgus ARBenefits Apprval: 02/08/2012 Stem&/r Prgenitr Cell Supprt, Germ Cell Tumrs Effective Date: 01/01/2013 Dcument: ARB0416:01 Revisin Date: 10/24/2012 Cde(s): 38230, Bne
Consensus Recommendations for the Management of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Primary Care Guideline
 Practice Guideline: Clinical Guide Cnsensus Recmmendatins fr the Management f Chrnic Lymphcytic Leukemia: Primary Care Guideline CCMB Practice Guideline Clinical Guide Develped by: Lymphprliferative Disrders
Practice Guideline: Clinical Guide Cnsensus Recmmendatins fr the Management f Chrnic Lymphcytic Leukemia: Primary Care Guideline CCMB Practice Guideline Clinical Guide Develped by: Lymphprliferative Disrders
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synpsis fr Public Disclsure This clinical study synpsis is prvided in line with Behringer Ingelheim s Plicy n Transparency and Publicatin f Clinical Study Data. The synpsis which is
abcd Clinical Study Synpsis fr Public Disclsure This clinical study synpsis is prvided in line with Behringer Ingelheim s Plicy n Transparency and Publicatin f Clinical Study Data. The synpsis which is
Guideline Number: NIA_CG_302 Last Revised Date: September 2015 Responsible Department: Implementation Date: September 2015 Clinical Operations
 Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT DENERVATION (RADIOFREQUENCY NEUROLYSIS) CPT Cdes: Cervical Thracic Regin: 64633, +64634 Lumbar Sacral Regin: 64635, +64636
Natinal Imaging Assciates, Inc. Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT DENERVATION (RADIOFREQUENCY NEUROLYSIS) CPT Cdes: Cervical Thracic Regin: 64633, +64634 Lumbar Sacral Regin: 64635, +64636
TOP TIPS Lung Cancer Update Dr Andrew Wight Consultant respiratory Physician - WUTH
 Tpic Circulatin list In case f query please cntact Executive Summary TOP TIPS Lung Cancer Update Dr Andrew Wight Cnsultant respiratry Physician - WUTH All Wirral GP s JaneFletcher2@nhs.net Dear Clleagues,
Tpic Circulatin list In case f query please cntact Executive Summary TOP TIPS Lung Cancer Update Dr Andrew Wight Cnsultant respiratry Physician - WUTH All Wirral GP s JaneFletcher2@nhs.net Dear Clleagues,
Reliability and Validity Plan 2017
 Reliability and Validity Plan 2017 Frm CAEP The principles fr measures used in the CAEP accreditatin prcess include: (a) validity and reliability, (b) relevance, (c) verifiability, (d) representativeness,
Reliability and Validity Plan 2017 Frm CAEP The principles fr measures used in the CAEP accreditatin prcess include: (a) validity and reliability, (b) relevance, (c) verifiability, (d) representativeness,
NIA Magellan 1 Spine Care Program Interventional Pain Management Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) For Medicare Advantage HMO and PPO
 NIA Magellan 1 Spine Care Prgram Interventinal Pain Management Frequently Asked Questins (FAQs) Fr Medicare Advantage HMO and PPO Questin GENERAL Why is Flrida Blue implementing a Spine Management prgram
NIA Magellan 1 Spine Care Prgram Interventinal Pain Management Frequently Asked Questins (FAQs) Fr Medicare Advantage HMO and PPO Questin GENERAL Why is Flrida Blue implementing a Spine Management prgram
Benefits for Anesthesia Services for the CSHCN Services Program to Change Effective for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008, benefit criteria
 Benefits fr Anesthesia Services fr the CSHCN Services Prgram t Change Effective fr dates f service n r after July 1, 2008, benefit criteria fr anesthesia will change fr the Children with Special Health
Benefits fr Anesthesia Services fr the CSHCN Services Prgram t Change Effective fr dates f service n r after July 1, 2008, benefit criteria fr anesthesia will change fr the Children with Special Health
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) and Respiratory Assist Devices (RADs) including Bi-Level PAP
 Cntinuus Psitive Airway Pressure (CPAP) and Respiratry Assist Devices (RADs), Including Bi-Level PAP Benefit Criteria t Change fr Texas Medicaid Effective March 1, 2017 Overview f Benefit Changes Benefit
Cntinuus Psitive Airway Pressure (CPAP) and Respiratry Assist Devices (RADs), Including Bi-Level PAP Benefit Criteria t Change fr Texas Medicaid Effective March 1, 2017 Overview f Benefit Changes Benefit
Field Epidemiology Training Program
 Field Epidemilgy Training Prgram Cancer Curriculum: Principles f Cancer Registries Case Study: Hspital-Based Cancer Registries FACILITATOR GUIDE FETP Cancer Curriculum: Principles f Cancer Registries Case
Field Epidemilgy Training Prgram Cancer Curriculum: Principles f Cancer Registries Case Study: Hspital-Based Cancer Registries FACILITATOR GUIDE FETP Cancer Curriculum: Principles f Cancer Registries Case
CONTACT: Amber Hamilton TYPE 2 DIABETES AND OBESITY: TWIN EPIDEMICS OVERVIEW
 FACT SHEET CONTACT: Amber Hamiltn 212-266-0062 TYPE 2 DIABETES AND OBESITY: TWIN EPIDEMICS OVERVIEW Type 2 diabetes accunts fr 90-95% f the 29.1 millin diabetes cases in the U.S. 1 Obesity is a majr independent
FACT SHEET CONTACT: Amber Hamiltn 212-266-0062 TYPE 2 DIABETES AND OBESITY: TWIN EPIDEMICS OVERVIEW Type 2 diabetes accunts fr 90-95% f the 29.1 millin diabetes cases in the U.S. 1 Obesity is a majr independent
NPCR CLINICAL EDIT CHECKS
 NPCR CLINICAL EDIT CHECKS FCDS Annual Meeting July 26, 2013 Sunrise, Flrida Steven Peace, CTR FCDS Data Quality Staff PURPOSE OF CLINICAL EDIT CHECKS The primary purpse f the Clinical Check edits is t
NPCR CLINICAL EDIT CHECKS FCDS Annual Meeting July 26, 2013 Sunrise, Flrida Steven Peace, CTR FCDS Data Quality Staff PURPOSE OF CLINICAL EDIT CHECKS The primary purpse f the Clinical Check edits is t
Risk factors in health and disease
 Risk factrs in health and disease Index 1 Intrductin 2 Types f risk factrs 2.1 Behaviural risk factrs 2.2 Psychlgical risk factrs 2.3 Demgraphic risk factrs 2.4 Envirnmental risk factrs 2.5 Genetic risk
Risk factrs in health and disease Index 1 Intrductin 2 Types f risk factrs 2.1 Behaviural risk factrs 2.2 Psychlgical risk factrs 2.3 Demgraphic risk factrs 2.4 Envirnmental risk factrs 2.5 Genetic risk
Folotyn (pralatrexate)
 Fltyn (pralatrexate) Line(s) f Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integratin Akamai Advantage Original Effective Date: 10/01/2015 Current Effective Date: 01/01/2018TBD03/01/2017 POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indicatins
Fltyn (pralatrexate) Line(s) f Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integratin Akamai Advantage Original Effective Date: 10/01/2015 Current Effective Date: 01/01/2018TBD03/01/2017 POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indicatins
Related Policies None
 Medical Plicy MP 3.01.501 Guidelines fr Cverage f Mental and Behaviral Health Services Last Review: 8/30/2017 Effective Date: 8/30/2017 Sectin: Mental Health End Date: 08/19/2018 Related Plicies Nne DISCLAIMER
Medical Plicy MP 3.01.501 Guidelines fr Cverage f Mental and Behaviral Health Services Last Review: 8/30/2017 Effective Date: 8/30/2017 Sectin: Mental Health End Date: 08/19/2018 Related Plicies Nne DISCLAIMER
Novel methods and approaches for sensing, evaluating, modulating and regulating mood and emotional states.
 Nvel methds and appraches fr sensing, evaluating, mdulating and regulating md and emtinal states. 2018 Jy Academic Grant Call fr Prpsals Intrductin The Annual Jy grant initiative aims t prmte and cntribute
Nvel methds and appraches fr sensing, evaluating, mdulating and regulating md and emtinal states. 2018 Jy Academic Grant Call fr Prpsals Intrductin The Annual Jy grant initiative aims t prmte and cntribute
ADVANCED IMAGING CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES. Appropriate Use Criteria: Imaging of the Chest. EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Proprietary
 CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: Imaging f the Chest EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: Imaging f the Chest EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
Four categories which guide further evaluation
 Unknwn Primary Updated May 2017 by Di Maria Jiang (PGY-5 Medical Onclgy Resident, University f Trnt) Reviewed by Dr. Chistine Elser (Staff Medical Onclgist, University f Trnt) and Dr. Sct Dwden (Staff
Unknwn Primary Updated May 2017 by Di Maria Jiang (PGY-5 Medical Onclgy Resident, University f Trnt) Reviewed by Dr. Chistine Elser (Staff Medical Onclgist, University f Trnt) and Dr. Sct Dwden (Staff
Weight Assessment and Counseling for Children and Adolescents (NQF 0024)
 Weight Assessment and Cunseling fr Children and Adlescents (NQF 0024) EMeasure Name Weight Assessment and EMeasure Id Pending Cunseling fr Children and Adlescents Versin Number 1 Set Id Pending Available
Weight Assessment and Cunseling fr Children and Adlescents (NQF 0024) EMeasure Name Weight Assessment and EMeasure Id Pending Cunseling fr Children and Adlescents Versin Number 1 Set Id Pending Available
Podcast Transcript Title: Common Miscoding of LARC Services Impacting Revenue Speaker Name: Ann Finn Duration: 00:16:10
 Pdcast Transcript Title: Cmmn Miscding f LARC Services Impacting Revenue Speaker Name: Ann Finn Duratin: 00:16:10 NCTCFP: Welcme t this pdcast spnsred by the Natinal Clinical Training Center fr Family
Pdcast Transcript Title: Cmmn Miscding f LARC Services Impacting Revenue Speaker Name: Ann Finn Duratin: 00:16:10 NCTCFP: Welcme t this pdcast spnsred by the Natinal Clinical Training Center fr Family
Health Screening Record: Entry Level Due: August 1st MWF 150 Entry Year
 Health Screening Recrd: Entry Level MIDWIFERY EDUCATION PROGRAM HEALTH SCREENING REQUIREMENTS (Rev. June 2017) 1. Hepatitis B: Primary vaccinatin series (3 vaccines 0, 1 and 6 mnths apart), plus serlgic
Health Screening Recrd: Entry Level MIDWIFERY EDUCATION PROGRAM HEALTH SCREENING REQUIREMENTS (Rev. June 2017) 1. Hepatitis B: Primary vaccinatin series (3 vaccines 0, 1 and 6 mnths apart), plus serlgic
SUBSPECIALIST TRAINING PROGRAMME in GYNAECOLOGICAL ONCOLOGY
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF GYNAECOLOGICAL ONCOLOGY SUBSPECIALIST TRAINING PROGRAMME in GYNAECOLOGICAL ONCOLOGY Sme 50% f cancers that affect wmen are lcated in the breast r in the genital rgans. Gynaeclgical
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF GYNAECOLOGICAL ONCOLOGY SUBSPECIALIST TRAINING PROGRAMME in GYNAECOLOGICAL ONCOLOGY Sme 50% f cancers that affect wmen are lcated in the breast r in the genital rgans. Gynaeclgical
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
 Chrnic Fatigue Syndrme (Als knwn as Myalgic encephalmyelitis/encephalmyelpathy) What is CFS/ME? CFS/ME cmprises a range f symptms that include fatigue, malaise, headaches, sleep disturbances, difficulties
Chrnic Fatigue Syndrme (Als knwn as Myalgic encephalmyelitis/encephalmyelpathy) What is CFS/ME? CFS/ME cmprises a range f symptms that include fatigue, malaise, headaches, sleep disturbances, difficulties
ADVANCED IMAGING CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES. Appropriate Use Criteria: Imaging of the Brain. EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Proprietary
 CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
CLINICAL APPROPRIATENESS GUIDELINES ADVANCED IMAGING Apprpriate Use Criteria: EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2019 Prprietary 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue Suth Twer Suite 800 Chicag, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.cm
The principles of evidence-based medicine
 The principles f evidence-based medicine By the end f this mdule yu shuld be able t: Describe what evidence based medicine is Knw where t find quality evidenced based medicine n the internet Be able t
The principles f evidence-based medicine By the end f this mdule yu shuld be able t: Describe what evidence based medicine is Knw where t find quality evidenced based medicine n the internet Be able t
Prevention Checklist for Men
 Page 1 f 5 Preventin Checklist fr Men A lt f prgress has been made in cancer research, but we still dn t understand exactly what causes mst cancers. We d knw that many factrs put us at higher risk fr different
Page 1 f 5 Preventin Checklist fr Men A lt f prgress has been made in cancer research, but we still dn t understand exactly what causes mst cancers. We d knw that many factrs put us at higher risk fr different
Bedfordshire and Hertfordshire DRAFT Priorities forum statement Number: Subject: Prostatism Date of decision: January 2010 Date of review:
 Bedfrdshire and Hertfrdshire DRAFT Pririties frum statement Number: Subject: Prstatism Date f decisin: January 2010 Date f review: Referral criteria Mst men with lwer urinary tract symptms due t benign
Bedfrdshire and Hertfrdshire DRAFT Pririties frum statement Number: Subject: Prstatism Date f decisin: January 2010 Date f review: Referral criteria Mst men with lwer urinary tract symptms due t benign
GENERAL / VASCULAR SONOGRAPHY OPTION COURSE OUTLINE AURORA ST. LUKE S MEDICAL CENTER SCHOOL OF DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE OVERVIEW
 AURORA ST. LUKE S MEDICAL CENTER SCHOOL OF DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE OVERVIEW The cre curriculum defines several majr mdules f ultrasund educatin. All lectures are crrelated with scan lab demnstratin
AURORA ST. LUKE S MEDICAL CENTER SCHOOL OF DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE OVERVIEW The cre curriculum defines several majr mdules f ultrasund educatin. All lectures are crrelated with scan lab demnstratin
BRCA1, BRCA2 and PALB2 Testing for Breast, Ovarian and Other Cancers
 Plicy Medical Plicy Manual Draft Revised Plicy: D Nt Implement BRCA1, BRCA2 and PALB2 Testing fr Breast, Ovarian and Other Cancers DESCRIPTION Hereditary breast and varian cancer (HBOC) syndrme describes
Plicy Medical Plicy Manual Draft Revised Plicy: D Nt Implement BRCA1, BRCA2 and PALB2 Testing fr Breast, Ovarian and Other Cancers DESCRIPTION Hereditary breast and varian cancer (HBOC) syndrme describes
23/11/2015. Introduction & Aims. Methods. Methods. Survey response. Patient Survey (baseline)
 Intrductin & Aims Drug and Alchl Cnsultatin Liaisn (AOD CL) services aim t imprve identificatin and treatment f patients with AOD mrbidity. The csts and cnsequences f targeting AOD patients presenting
Intrductin & Aims Drug and Alchl Cnsultatin Liaisn (AOD CL) services aim t imprve identificatin and treatment f patients with AOD mrbidity. The csts and cnsequences f targeting AOD patients presenting
GUIDANCE DOCUMENT FOR ENROLLING SUBJECTS WHO DO NOT SPEAK ENGLISH
 GUIDANCE DOCUMENT FOR ENROLLING SUBJECTS WHO DO NOT SPEAK ENGLISH Aurra Health Care s Research Subject Prtectin Prgram (RSPP) This guidance dcument will utline the prper prcedures fr btaining and dcumenting
GUIDANCE DOCUMENT FOR ENROLLING SUBJECTS WHO DO NOT SPEAK ENGLISH Aurra Health Care s Research Subject Prtectin Prgram (RSPP) This guidance dcument will utline the prper prcedures fr btaining and dcumenting
2017 CMS Web Interface
 CMS Web Interface CARE-2 (NQF 0101): Falls: Screening fr Future Fall Risk Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION...
CMS Web Interface CARE-2 (NQF 0101): Falls: Screening fr Future Fall Risk Measure Steward: NCQA Web Interface V1.0 Page 1 f 18 11/15/2016 Cntents INTRODUCTION... 3 WEB INTERFACE SAMPLING INFORMATION...
Structured Assessment using Multiple Patient. Scenarios (StAMPS) Exam Information
 Structured Assessment using Multiple Patient Scenaris (StAMPS) Exam Infrmatin 1. Preparing fr the StAMPS assessment prcess StAMPS is an assessment mdality that is designed t test higher rder functins in
Structured Assessment using Multiple Patient Scenaris (StAMPS) Exam Infrmatin 1. Preparing fr the StAMPS assessment prcess StAMPS is an assessment mdality that is designed t test higher rder functins in
Corporate Governance Code for Funds: What Will it Mean?
 Crprate Gvernance Cde fr Funds: What Will it Mean? The Irish Funds Industry Assciatin has circulated a draft Vluntary Crprate Gvernance Cde fr the Funds Industry in Ireland. 1. Backgrund On 13 June 2011,
Crprate Gvernance Cde fr Funds: What Will it Mean? The Irish Funds Industry Assciatin has circulated a draft Vluntary Crprate Gvernance Cde fr the Funds Industry in Ireland. 1. Backgrund On 13 June 2011,
Rituxan (rituximab) Effective Date: 10/01/2015. Line(s) of Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration Akamai Advantage
 Rituxan (rituximab) Line(s) f Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integratin Akamai Advantage Effective Date: 10/01/2015 POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indicatins belw including FDA-apprved indicatins and cmpendial uses
Rituxan (rituximab) Line(s) f Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integratin Akamai Advantage Effective Date: 10/01/2015 POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indicatins belw including FDA-apprved indicatins and cmpendial uses
Assessment Field Activity Collaborative Assessment, Planning, and Support: Safety and Risk in Teams
 Assessment Field Activity Cllabrative Assessment, Planning, and Supprt: Safety and Risk in Teams OBSERVATION Identify a case fr which a team meeting t discuss safety and/r safety planning is needed r scheduled.
Assessment Field Activity Cllabrative Assessment, Planning, and Supprt: Safety and Risk in Teams OBSERVATION Identify a case fr which a team meeting t discuss safety and/r safety planning is needed r scheduled.
Continuous Quality Improvement: Treatment Record Reviews. Third Thursday Provider Call (August 20, 2015) Wendy Bowlin, QM Administrator
 Cntinuus Quality Imprvement: Treatment Recrd Reviews Third Thursday Prvider Call (August 20, 2015) Wendy Bwlin, QM Administratr Gals f the Presentatin Review the findings f Treatment Recrd Review results
Cntinuus Quality Imprvement: Treatment Recrd Reviews Third Thursday Prvider Call (August 20, 2015) Wendy Bwlin, QM Administratr Gals f the Presentatin Review the findings f Treatment Recrd Review results
MEASURE #10: PLAN OF CARE FOR MIGRAINE OR CERVICOGENIC HEADACHE DEVELOPED OR REVIEWED Headache
 MEASURE #10: PLAN OF CARE FOR MIGRAINE OR CERVICOGENIC HEADACHE DEVELOPED OR REVIEWED Headache Measure Descriptin All patients diagnsed with migraine headache r cervicgenic headache wh had a headache management
MEASURE #10: PLAN OF CARE FOR MIGRAINE OR CERVICOGENIC HEADACHE DEVELOPED OR REVIEWED Headache Measure Descriptin All patients diagnsed with migraine headache r cervicgenic headache wh had a headache management
Annual Assembly Abstract Review Process
 Annual Assembly Abstract Review Prcess AAHPM and HPNA cllabrate t review and select abstracts fr Annual Assembly. The cmmittees meet prir t the calls t review and update the Assembly bjectives (Planning
Annual Assembly Abstract Review Prcess AAHPM and HPNA cllabrate t review and select abstracts fr Annual Assembly. The cmmittees meet prir t the calls t review and update the Assembly bjectives (Planning
Echocardiography Diagnostic Accuracy
 Echcardigraphy Diagnstic Accuracy Measure Descriptin: The prprtin f ptentially preventable and clinically imprtant inaccurate diagnses amng cngenital heart surgical patients. Numeratr Number f cngenital
Echcardigraphy Diagnstic Accuracy Measure Descriptin: The prprtin f ptentially preventable and clinically imprtant inaccurate diagnses amng cngenital heart surgical patients. Numeratr Number f cngenital
