Serum CYFRA 21-1 (cytokeratin-19 fragments) is a useful tumour marker for detecting disease relapse and assessing treatment efficacy in breast cancer
|
|
|
- Georgia Clark
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 British Journal of Cancer (00) 9, 7 7 All rights reserved /0 $ Serum CYFRA - (cytokeratin-9 fragments) is a useful tumour marker for detecting disease relapse and assessing treatment efficacy in breast cancer B Nakata*,, T Takashima, Y Ogawa, T Ishikawa and K Hirakawa Department of Surgical Oncology, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, -- Asahimachi, Abeno-ku, Osaka -, Japan The usefulness of serum CYFRA - (cytokeratin-9 fragments) in monitoring the recurrence of breast cancer and in evaluating therapeutic effects was studied retrospectively. The sera from 7 patients with primary breast cancer or recurrent disease were measured for CYFRA -, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), and carbohydrate antigen - (CA -) levels. The positive rates of serum CYFRA - for stage IV (n ¼ ) or recurrent disease (n ¼ ) were. and.%, respectively, while those of serum CEA were.7 and.9%, and those of serum CA - were. and.%. The elevated preoperative levels of serum CYFRA - decreased to normal levels after curative operation, whereas the levels remained abnormally high after noncurative operation. There was a significantly high frequency of recurrence in patients with elevated levels of serum CYFRA - preoperatively compared to those with normal levels of the marker preoperatively. The serum CYFRA - levels were well correlated with response to chemotherapy. The positive rate of serum CYFRA - alone was higher than that of an assay combining CEA with CA -, in both primary and recurrent cases (. vs. and. vs.%, respectively). These observations suggest that serum CYFRA - may be a reliable marker of recurrence or therapeutic efficacy. British Journal of Cancer (00) 9, 7 7. doi:./sj.bjc Published online 7 July 00 Keywords: CYFRA -; cytokeratin-9 fragments; breast cancer; monitoring; carcinoembryonic antigen; carbohydrate antigen - The clinical usefulness of serum tumour markers for breast cancer surveillance has not yet been established. Indeed, until sufficient data on this subject are obtained, the American Society of Oncology (ASCO) recommends against the routine use of even well-known antigens such as carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and carbohydrate antigen - (CA -) after primary treatment or in monitoring responses to treatment (American Society of Oncology, 00). For economic reasons, and to minimise radiation exposure, it is not possible to carry out the imaging studies, such as chest and abdominal computed tomography (CT) and bone scintigraphy, for follow-up and evaluation of therapeutic effect every months. Therefore, it is clearly a worthwhile goal to find a reliable serum tumour marker with high sensitivity and high specificity for breast cancer. We previously reported that the positive rates of serum CYFRA -, which reacts specifically with cytokeratin-9 fragments, in patients with stage IV or recurrent breast cancer were as high as those for CA - and superior to those for CEA. We also previously demonstrated that serum CYFRA - titre had prognostic predictive value in patients with breast cancer (Nakata et al, 000). In this study, we measured serum CYFRA - titres prior to and after treatment in patients with breast cancer to observe the potential impact of the use of serum CYFRA - in monitoring for recurrence and in evaluating therapeutic efficacy. *Correspondence: B Nakata; bunzo@med.osaka-cu.ac.jp Received February 00; revised June 00; accepted June 00; published online 7 July 00 PATIENTS AND METHODS Patients The Department of Surgical Oncology of Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine first began to use a combination assay of serum CYFRA -, CEA, and CA - for diagnosis and follow-up of patients with breast cancer in January 999. Between January 999 and May 00, a total of 0 patients were treated for breast cancer at Osaka City University Hospital, but in 7 (.%) of these cases serum CYFRA - titres were not measured because the patients doctors were not yet familiar with the combination assay system. These 7 cases were excluded from this analysis, leaving 7 patients in whom breast cancer was retrospectively investigated in the present study. Among these 7 patients, 9 were patients with primary tumours (untreated tumours) in whom sera were obtained from within weeks prior to resection and at every months after resection according to our follow-up system using the serum tumour markers CYFRA -, CEA, and CA -. These 9 patients also underwent routine imaging studies, including chest X-ray, abdominal ultrasonography/ct, and bone scintigraphy, every months as part of our follow-up system. Among these 9 patients (median follow-up time after operation:. months; range: months), (.9%) developed recurrent disease, and seven patients with high preoperative levels of serum CYFRA - happened to be measured in the early period of 7 days postoperation. In the remaining patients ( with primary breast cancer and, as in the fully assayed patients, with recurrent cancer), sera were
2 7 obtained only once due to the doctors unfamiliarity with the combination assay system. The Union Internationale Contre le Cancer (UICC) stages of the 0 patients with primary breast cancer were as follows: stage 0 (n ¼ ), stage I (n ¼ ), stage II (n ¼ ), stage III (n ¼ 7), and stage IV (n ¼ ) (Table ). The staging was based on the complete pathological findings and imaging studies for each patient. As described above, the total number of recurrent cases was, among which patients were measured for serum CYFRA - serially and patients were assessed only once. In patients, a change in serum CYFRA - levels was observed during chemotherapy. Among them, four patients were treated neoadjuvantly for primary tumours and distant metastases (lung (n ¼ ), liver (n ¼ ), and bone (n ¼ )). The other patients were treated for recurrent metastases (bone (n ¼ ), bone þ liver (n ¼ ), lung (n ¼ ), lung þ bone (n ¼ ), and lymph node (n ¼ )). All lesions except bone metastases were measurable by CT or ultrasonography, and bony lesions were evaluable by bone scintigraphy. Objective responses were classified according to World Health Organisation criteria (World Health Organization, 979). Measurement of tumour markers Serum CYFRA - was measured by a solid-phase immunoradiometric assay based on the two-site sandwich method using a CYFRA - kit (CIS Biointernational, Gif Yvette, France) (Sarwar et al, 99). The measurement of serum CEA was completed in a counting immunoassay. Serum CA - was measured by a twostep sandwich immunoradiometric assay. The cutoff values of CYFRA -, CEA, and CA - recommended by the manufacturers were.0 ng ml,. ng ml, and 0 U ml, respectively. Measurement of estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PgR) ER status and PgR status were determined by an enzyme-linked immunoassay, and tumours with more than fmol mg protein were considered to be positive. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed using nonparametric methods. The Kruskal Wallis one-way analysis was used for multiple comparison of the UICC staging groups 0 IV. The Mann Table Serum CYFRA -, CEA, and CA - titres of 0 patients with primary breast cancer according to stage Variables CYFRA - (ng ml ) Serum CYFRA - in breast cancer CEA (ng ml ) CA - (U ml ) Cutoff value.0. 0 UICC staging Median (range) Median (range) Median (range) 0(n¼) 0. (0..). (.0.). (..) I(n¼). (0..0). (0. 9.). (. 0.) II (n ¼ ). (0..).0 (0.9 9.). (.7 ) III (n ¼ 7). (0. ). (0..).9 (. ) IV (n ¼ ). (. ).7 (..7) 7. (. 70) Kruskal Wallis test Po0.000 P ¼ 0. Po0.000 Mann Whitney U-test P-value P-value P-value Stage 0 vs I IV Stage 0 I vs II IV Stage 0 II vs III IV Stage 0 III vs IV o o0.000 CEA¼ carcinoembryonic antigen; CA ¼ carbohydrate antigen. UICC ¼ Union Internationale Contre le Cancer. Whitney U-test was used for comparisons between pairs of independent groups divided according to UICC staging, ER status, and PgR status. The w test (Fisher s exact method) was used to compare between variables. P-values o0.0 were considered to be statistically significant. RESULTS Serum CYFRA - titre according to ER and PgR status The serum CYFRA - levels of the 7 ER-positive tumours were not different from those of the ER-negative tumours (median values:. vs. ng ml, respectively; P ¼ 0.079). The serum CYFRA - levels of the 77 PgR-positive tumours were not different from those of the 7 PgR-negative tumours (median values:. vs. ng ml, respectively; P ¼ 0.7). Serum tumour marker level in each stage for primary breast cancer The serum CYFRA -, CEA, and CA - titres of all 0 primary cases are shown in Table. The serum CYFRA - and CA - levels were significantly different among stages 0 IV (the Kruskal Wallis one-way analysis; both, Po0.000), although the serum CEA levels were not. Table demonstrates the difference between the serum levels of the two groups according to UICC staging in each tumour marker examined based on the results of the Mann Whitney U-test. The serum CEA levels were not significantly different between any two groups. The serum CYFRA - and CA - levels were significantly different between all pairs of groups except 0 vs I IV, although the P-values for CA - were a little smaller than those for CYFRA -. Figure compares the positive rates of serum CYFRA -, CEA, and CA - for each stage grouping. No tumour marker was elevated for stage 0. Among these three markers, CYFRA - had the highest rate of positivity in stages I IV. At stage IV, of patients (.%) showed elevated levels of both serum CYFRA - and CA -. Serum tumour marker level for recurrent breast cancer Among the recurrent cases,.% ( of ) were positive for serum CYFRA -, whereas.9% (six of ) and.% (nine of ) were positive for serum CEA and CA -, respectively (Figure ). When the w test was used to examine the rate of positivity for each of the three tumour markers in the sera of patients with recurrence, significant differences between CYFRA - and CEA (Po0.000) and between CYFRA - and CA - Positive rate (%) Stage 0 Stage I Stage II Stage III Stage IV Figure Comparison of the positive rates of serum CYFRA - (solid bar), CEA (open bar), and CA - (striped bar) at each stage. British Journal of Cancer (00) 9(), 7 7
3 CYFRA - CEA Primary case CA - CYFRA - CEA (Po0.000) were observed. However, there was no difference between CEA and CA - (P ¼ 0.0). Changes in serum CYFRA - levels by resection The sera from 9 patients with primary tumours were measured pre- and postoperatively. All patients with negative preoperative serum CYFRA - titres had normal levels postoperatively. However, among the five such patients who developed a later recurrence, four showed elevated levels of serum CYFRA -. One of these patients, who had an ipsilateral recurrence after breast conservation therapy, had a normal serum CYFRA - titre (Figure ). Among the patients with elevated levels of serum CYFRA - preoperatively, 9 (.9%) showed a decrement to within the normal range postoperatively. Among these 9 patients, six (0.7%) developed recurrent tumours by months postoperatively and all showed elevated levels of serum CYFRA -. Of the six patients in whom the serum CYFRA - levels continued to be elevated postoperatively, three underwent noncurative operation for lung, liver, or bone metastases; two developed bony recurrences at and 0 months after operation; and the sixth patient has so far shown no evidence of recurrence after curative operation (Figure ). Among the recurrent patients whose serum CYFRA - was monitored serially, two patients showed elevated serum CYFRA - titres before the detection of metastatic lesions by imaging studies. Both of these patients developed liver metastases and showed elevated levels of CYFRA - at or months, respectively, before the detection of tumours by CT scan. In the CA - Recurrent case Figure Distribution of patients with elevated levels of serum CYFRA -, CEA, and CA - in primary and recurrent breast cancer. The number in each area is the number of patients with elevated levels of tumour markers. CYFRA - (ng ml ) 9 7. Multiple (M) Multiple (M) Ipsilateral breast (M) Preoperation Postoperation At recurrence Lung (M) Chest wall (9M) Figure Change of serum CYFRA - titres of patients within normal levels at preoperation. The recurrent site is demonstrated for each case, and the recurrent time after operation is shown within parentheses. Serum CYFRA - in breast cancer CYFRA - (ng ml ) 9 7. (Lung, liver) (Bone) (Bone) Multiple (M). Bone (M) Multiple (M) Bone (M) Chest wall (M) Bone (0M) Lung (M) Chest wall (0M) Preoperation Postoperation At recurrence Figure Changes in serum CYFRA - titres of patients with elevated levels at preoperation. Residual sites are within parentheses. A recurrent site is demonstrated for each case, and the postoperation time until recurrence is shown within parentheses. The open circle indicates a patient with an elevated level of serum CYFRA - at postoperation, who nevertheless has shown no evidence of relapse. CYFRA - (ng ml ) 9 7 Figure operation. Pre 7 9 Days after curative operation The decrement of serum CYFRA - titre after curative other patients, the dates of tumour detection by imaging studies were almost identical to the dates of detection by elevation of serum CYFRA -. The reason for this may have been related to our follow-up system, in which the measurement of tumour markers and imaging studies were simultaneously ordered. Another possible reason may have been that, in all patients, imaging studies were immediately performed whenever the serum CYFRA - was found to be elevated. The sera from seven patients with elevated serum CYFRA - levels (median:. ng ml ; range:. ng ml ) preoperatively were measured within weeks after operation. All the serum CYFRA - titres decreased to within the normal range during this period (Figure ). These data demonstrate how quickly the marker decreased in the sera of these patients. Relation between serum CYFRA - levels and recurrence Among the 9 primary breast cancer patients with pre- and postoperative serum CYFRA - data, patients underwent potentially curative operation. These data were analysed to examine the association between serum CYFRA - level and disease recurrence. As shown in Table, the patients in whom serum CYFRA - levels were elevated both pre- and postoperatively had the greatest frequency of recurrence. In patients in whom the serum CYFRA - levels were elevated preoperatively and normal postoperatively, the frequency of recurrence was 7 British Journal of Cancer (00) 9(), 7 7
4 7 Table - Serum CYFRA - in breast cancer Comparison of frequency of disease recurrence after potentially curative operation according to pre- and postoperative levels of serum CYFRA Serum CYFRA - (ng ml ) Number of patients Group Preoperation Postoperation Recurrence No recurrence Total A o o (.0%) 79 B. o (0.7%) 9 C.. (.%) According to serum CYFRA - levels at pre- and postoperation, the patients were divided into groups A, B, and C. Frequencies of recurrences were different between A and B (P ¼ 0.0), A and C (P ¼ 0.0), and A and B+C (P ¼ 0.007), but not B and C (P ¼ 0.), examined by w test (Fisher s exact method). CYFRA - (ng ml ) Figure 0 7 Prechemotherapy 97 7 Postchemotherapy : Progressive disease : Stable disease : Partial response Change in serum CYFRA - titres after chemotherapy. Combination assay of tumour markers for breast cancer Figure demonstrates the positive case number for each tumour marker. Among the 0 patients with primary tumours, (%) showed normal serum levels of all tumour markers and (.%) had elevated CYFRA - levels. Also among the primary cases,, six, and two patients showed elevated levels of serum CYFRA alone, CEA alone, and CA - alone, respectively. The rates of positivity for CYFRA -, CEA, and CA - among the 0 primary tumour cases were.,., and.%, respectively. The rate of positivity for all three markers in the combined assay was %; CYFRA - combined with CEA was.%; CYFRA - with CA - was.%; and CEA with CA - was.% among these 0 patients. Among the patients with recurrent tumours, (.%) had elevated CYFRA - levels. Three of the recurrent patients (.%) showed normal serum levels of all tumour markers. These marker-negative tumours occurred in the lung, the axillary lymph node, or the ipsilateral breast, respectively. Among recurrent cases,, 0, and one patients showed elevated levels of serum CYFRA alone, CEA alone, and CA - alone, respectively. The positive rates of CYFRA -, CEA, and CA - for recurrent tumours were.,., and.%, respectively. In recurrent cases, the positive rate of the combined assay using all three markers was.%; CYFRA - combined with CEA was.%; CYFRA - with CA - was.%; and CEA with CA - was %. 0.7%. Only % of the patients with normal levels of serum CYFRA - preoperatively developed recurrences. The frequency of recurrence in patients with elevated levels of serum CYFRA - preoperatively was significantly higher than that in patients with preoperatively normal levels of the marker (P ¼ 0.007). Changes in serum CYFRA - levels after chemotherapy Figure demonstrates the changes in serum CYFRA - levels before and after chemotherapy. These patients were administered intensive chemotherapeutic regimens, such as CAF (cyclophosphamide þ adriamycin þ -fluorouracil), FEC (-fluorouracil þ epirubicin þ cyclophosphamide), or taxane with or without herceptin. The serum CYFRA - levels in five of seven patients with postoperative recurrence decreased to within the normal range after chemotherapy, and those of the other two patients with extremely high levels (7 and ng ml ) prior to chemotherapy decreased to approximately and % of the prechemotherapy levels after chemotherapy, respectively. In the four patients with stable disease, chemotherapy reduced the serum CYFRA - levels to approximately 0 90% of the prechemotherapy levels. In the three patients with progressive disease, the serum CYFRA - levels were increased by 0 00% following chemotherapy. DISCUSSION It has been well demonstrated that breast cancer cells express fragments of cytokeratin-9 (Moll et al, 9; Brotheric et al, 99; Sheard et al, 00), which is one of the various kinds of cytokeratins comprising the intermediate filaments of the cytoskeleton (Moll et al, 9). Serum fragments of cytokeratin-9 can be detected using anti-cyfra - antibody (Pujol et al, 99). Most of the epitopes that are detectable by clinically useful tumour markers such as CEA, CA -, CA 9-9, and alpha-fetoprotein are glycoproteins shed from the cell surface. CYFRA - is unique in that its epitope is a polypeptide, which is most likely released following cell death (Stieber et al, 99; Sheard et al, 00). Elevated levels of serum CYRFA - titres have been observed in various malignancies, especially in lung cancer (Molina et al, 99). Healthy individuals with an abnormal level of serum CYFRA - are quite rare (Molina et al, 99; Nakata et al, 99; Giovanella et al, 00). Patients with nonmalignant disease also showed almost no elevation of serum CYFRA -, except in cases of cirrhosis, renal failure, or infectious lung disease. In previous studies, 0 0% of patients with one of these three benign diseases showed elevated levels of serum CYRFA - (Molina et al, 99; Nakata et al, 99). However, little is known about this tumour marker for breast cancer (Molina et al, 99; Nakata et al, 000; Giovanella et al, 00; Rodriguez et al, 00). British Journal of Cancer (00) 9(), 7 7
5 Our previous report demonstrated that, in patients with stage IV or recurrent disease, the positive rate of serum CYFRA - was as high as that of CA - and superior to that of CEA (Nakata et al, 000). In this study, we measured serum CYFRA - in a new series of patients, and the results for primary breast cancer were the same, except that the positive rate of serum CYFRA - for recurrent disease was higher than that of serum CA - (Figures and ). Rodriguez et al (00) examined the serum CYFRA -, CEA, and CA - titres in their 0 patients with metastatic breast cancers and found that CYFRA - was a sensitive tumour marker for breast cancer when compared with CEA or CA -, supporting our results. However, contrary to our results, Giovanella et al (00) reported that serum CYFRA - was less accurate for the evaluation of primary and recurrent breast cancer than serum CA -. The low diagnostic value of CYFRA - in breast cancer reported by Giovanella et al should be due to their higher serum CYFRA - cutoff value (. ng ml ) compared to our cutoff value (.0 ng ml ), although both studies used the same CYFRA - kit (CIS Biointernational). Our cutoff value was decided by the manufacturer s recommendation, while Giovanella et al used the cutoff value originally selected for lung cancer and benign lung diseases. Giovanella et al described that they could not employ a lower cutoff in a breast disease setting, because % of the healthy individuals in their series showed a high level above. ng ml. In our study, the serum marker levels among each stage were examined by nonparametric analyses, and CYFRA - and CA - were correlated significantly with stage, although CEA was not (Table ). However, as described in our previous report (Nakata et al, 000) and as shown in this report, the measurement of serum CYFRA - cannot be a potential screening test due to the low positive rate for early breast cancer. We also demonstrated in a previous report (Nakata et al, 000) that serum CYFRA - has not only a high positive rate for breast cancer but also high specificity for breast cancer, that is, patients with benign mammary disease did not show elevated levels of serum CYFRA -. Molina et al (99) also reported that only % (one of ) of patients with benign mammary disease had elevated levels of serum CYFRA -. The time course of serum CYFRA - titre during treatment has not been investigated previously. We observed 9 patients with primary tumour at pre- and postoperation. We surveyed these patients and found that of them had had a recurrent tumour. Among the patients with elevated levels of serum CYFRA - at preoperation, only six patients had abnormal levels of this tumour marker at postoperation. Among the six cases, the high levels in three cases were attributable to residual tumours, while the high Serum CYFRA - in breast cancer levels in two cases were probably due to micrometastasis (Figure ). These results suggest that serum CYFRA - may be a good marker for surgical curability. Moreover, we found that the high serum titre of CYFRA - at preoperation decreased to a normal level within weeks after curative operation (Figure ). All but one of the patients who developed recurrent disease showed elevated levels of CYFRA -, and the one exception had an ipsilateral recurrence after breast conservation therapy (Figures and ). These results suggest that serum CYFRA - might be a reliable marker of recurrent disease. Among the patients with normal levels of serum CYFRA - preoperatively, five developed recurrences and four of these demonstrated elevated levels of this tumour marker. This indicates the potential usefulness of the marker for monitoring disease relapse, even in cases with normal levels of serum CYFRA - at preoperation. Moreover, the preoperative abnormal levels of CYFRA - were significantly related to higher incidence of the disease relapse (Table ). The leading time of a tumour marker elevation before manifestation of relapse by imaging studies is an important subject. However, our retrospective study demonstrated only two anecdotal cases in which the leading times of serum CYFRA - were months. To investigate the leading time, a prospective study may be required, in that serum CYFRA - should be measured monthly. The chemotherapeutic effects of CYFRA - correlated well with the changes in serum levels of CYFRA - between pre- and postchemotherapy (Figure ). Partial response efficacy may be assessed by changes in serum CYFRA - when the elevated titre decreases to % or less of the preoperative value, or when the normal range is reached at postchemotherapy. We observed that the positive rates of serum CYFRA - alone in primary and recurrent cases were superior to those of the assay combining CEA with CA -. The assays combining CYFRA - with CEA or CA - increased the positive rate modestly, increased the positive rate by or.% in primary cases, and 0 or.9% in recurrent cases, respectively (Figure ). These findings indicated that serum CYFRA - may be useful even in a single assay, when a combination assay using two or more tumour markers is not feasible economically. In conclusion, the measurement of serum CYFRA - may be useful for detecting disease relapse and for assessing surgical and chemotherapeutic efficacy. However, the patient number in this study was too small to draw any definitive conclusions. Further prospective studies using greater numbers of patients are required before serum CYFRA - can be recommended for routine clinical use. 77 REFERENCES American Society of Oncology (00) 000 Update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in breast and colorectal cancer: clinical practice guideline of the American Society of Oncology. J Clin Oncol 9: 7 Brotheric I, Robson CN, Browell DA, Shenfine J, White MD, Cunliffe WJ, Shenton BK, Egan M, Webb LA, Lunt LG, Young JR, Higgs MJ (99) Cytokeratin expression in breast cancer: phenotypic changes associated with disease progression. Cytometry : 0 0 Giovanella L, Ceriani L, Giardina G, Bardelli D, Tanzi F, Garancini S (00) Serum cytokeratin fragment. (CYFRA.) as tumour marker for breast cancer: comparison with carbohydrate antigen. (CA.) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). Clin Chem Lab Med 0: 9 0 Molina R, Agusti C, Filella X, Jo J, Joseph J, Gimenez N, Ballesta AM (99) Study of a new tumor marker, CYFRA -, in malignant and nonmalignant diseases. Tumour Biol : Moll R, Franke WW, Schiller DL (9) The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell : Nakata B, Chung YS, Kato Y, Ogawa M, Ogawa Y, Inui A, Maeda K, Sawada T, Sowa M (99) significance of serum CYFRA - in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 7: 9 Nakata B, Ogawa Y, Ishikawa T, Ikeda K, Kato Y, Nishino H, Hirakawa K (000) Serum CYFRA - is one of the most reliable tumor markers for breast carcinoma. Cancer 9: 90 Pujol JL, Grenier J, Daures JP, Daver A, Pujol H, Michel FB (99) Serum fragment of cytokeratin subunit 9 measured by CYFRA - immunoradiometric assay as a marker of lung cancer. Cancer Res : Rodriguez CA, Cruz JJ, Martin T, Gomez A, Olaverri A, Hernandez M (00) Letter and author reply: serum CYFRA - is one of the most reliable tumor marker for breast carcinoma. Cancer 9: 70 7 Sarwar M, Tomiyoshi K, Inoue T, Fukazawa K, Endo K (99) CYFRA - as a tumor marker used in measuring the serum fragment of cytokeratin subunit 9 by immunoradiometric assay. Ann Nucl Med : 0 0 British Journal of Cancer (00) 9(), 7 7
6 7 Serum CYFRA - in breast cancer Sheard MA, Vojtesek B, Simickova M, Valik D (00) Release of cytokeratin- and -9 fragments (TPS and CYFRA -) into the extracellular space during apoptosis. J Cell Biochem : Stieber P, Bodenmuller H, Banauch D, Hasholzner U, Dessauer A, Ofenloch-Hahnle B, Jaworek D, Fateh-Moghadam A (99) Cytokeratin 9 fragments: a new marker for non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Biochem : 0 0 World Health Organization (979) WHO Handbook for Reporting Results of Cancer Treatment, Offset Publication No. Geneva: World Health Organization British Journal of Cancer (00) 9(), 7 7
Recently, serum tumor marker CYFRA 21-1 has shown a high
 670 CORRESPONDENCE Serum CYFRA 21-1 Is One of the Most Reliable Tumor Markers for Breast Carcinoma Recently, serum tumor marker CYFRA 21-1 has shown a high sensitivity and specificity in patients with
670 CORRESPONDENCE Serum CYFRA 21-1 Is One of the Most Reliable Tumor Markers for Breast Carcinoma Recently, serum tumor marker CYFRA 21-1 has shown a high sensitivity and specificity in patients with
Index. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) 465 469 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adjuvant therapy, preoperative for gastric cancer, staging and, 339 B Breast cancer, metabolic
Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) 465 469 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adjuvant therapy, preoperative for gastric cancer, staging and, 339 B Breast cancer, metabolic
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 15: 927-931, 2005 927 Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy YOSUKE TANAKA 1, HIRONORI MAEDA 2, YASUHIRO OGAWA 3, AKIHITO NISHIOKA 3, SATOSHI
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 15: 927-931, 2005 927 Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy YOSUKE TANAKA 1, HIRONORI MAEDA 2, YASUHIRO OGAWA 3, AKIHITO NISHIOKA 3, SATOSHI
The right middle lobe is the smallest lobe in the lung, and
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Impact of Superior Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastases on Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Located in the Right Middle Lobe Yukinori Sakao, MD, PhD,* Sakae Okumura, MD,* Mun Mingyon,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Impact of Superior Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastases on Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Located in the Right Middle Lobe Yukinori Sakao, MD, PhD,* Sakae Okumura, MD,* Mun Mingyon,
Preoperative CA 15-3 and CEA serum levels as predictor for breast cancer outcomes
 Annals of Oncology 19: 675 681, 2008 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdm538 Published online 23 November 2007 Preoperative CA 15-3 and CEA serum levels as predictor for breast cancer outcomes B.-W. Park 1,4 *, J.-W.
Annals of Oncology 19: 675 681, 2008 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdm538 Published online 23 November 2007 Preoperative CA 15-3 and CEA serum levels as predictor for breast cancer outcomes B.-W. Park 1,4 *, J.-W.
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Serum Tumor Markers for Breast Malignancies Page 1 of 9 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Serum Tumor Markers for Breast Malignancies Professional
Serum Tumor Markers for Breast Malignancies Page 1 of 9 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Serum Tumor Markers for Breast Malignancies Professional
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Intensive post-operative follow-up of breast cancer patients with tumour markers: CEA, TPA or CA15.3 vs MCA and MCA-CA15.3 vs CEA-TPA-CA15.3 panel in the early detection
Author's response to reviews Title: Intensive post-operative follow-up of breast cancer patients with tumour markers: CEA, TPA or CA15.3 vs MCA and MCA-CA15.3 vs CEA-TPA-CA15.3 panel in the early detection
The prognostic value of the tumour marker Cyfra 21-1 in carcinoma of head and neck and its role in early detection of recurrent disease
 doi: 10.1054/ bjoc.2000.1502, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on http://www.bjcancer.com The prognostic value of the tumour marker Cyfra 21-1 in carcinoma of head and neck and its role in
doi: 10.1054/ bjoc.2000.1502, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on http://www.bjcancer.com The prognostic value of the tumour marker Cyfra 21-1 in carcinoma of head and neck and its role in
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Doppler ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis, and color Doppler
 - - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
- - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
Carcinoembryonic Antigen
 Other Names/Abbreviations CEA 190.26 - Carcinoembryonic Antigen Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is a protein polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring
Other Names/Abbreviations CEA 190.26 - Carcinoembryonic Antigen Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is a protein polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring
It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue
 59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
PET/CT in breast cancer staging
 PET/CT in breast cancer staging Anni Morsing Consultant, PhD, DMSc Rigshospitalet 1 18F- FDG PET/CT for breastcancer staging Where is the clinical impact? To which women should 18F- FDG PET/CT be offered?
PET/CT in breast cancer staging Anni Morsing Consultant, PhD, DMSc Rigshospitalet 1 18F- FDG PET/CT for breastcancer staging Where is the clinical impact? To which women should 18F- FDG PET/CT be offered?
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, INDIA. Department of Pediatric Surgery, Medical Oncology, and Radiology
 All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, INDIA Department of Pediatric Surgery, Medical Oncology, and Radiology Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney- rare renal neoplasm second most common renal
All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, INDIA Department of Pediatric Surgery, Medical Oncology, and Radiology Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney- rare renal neoplasm second most common renal
Breast Cancer. Most common cancer among women in the US. 2nd leading cause of death in women. Mortality rates though have declined
 Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Cytokeratin19-2g2, a Novel Fragment of Cytokeratin19 in Serum, Indicating a More Invasive Behavior and Worse Prognosis in Breast Cancer Patients
 Cytokeratin19-2g2, a Novel Fragment of Cytokeratin19 in Serum, Indicating a More Invasive Behavior and Worse Prognosis in Breast Cancer Patients Yanan Kong 1,2., Junye Wang 2,4., Wanli Liu 2,3, Qiaolun
Cytokeratin19-2g2, a Novel Fragment of Cytokeratin19 in Serum, Indicating a More Invasive Behavior and Worse Prognosis in Breast Cancer Patients Yanan Kong 1,2., Junye Wang 2,4., Wanli Liu 2,3, Qiaolun
Xiang Hu*, Liang Cao*, Yi Yu. Introduction
 Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
Breast Cancer. Saima Saeed MD
 Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Breast Cancer Breast Managed Clinical Network
 Initial Evaluation Clinical Stage Pre-Treatment Evaluation Treatment and pathological stage Less than 4 positive lymph nodes Adjuvant Treatment ER Positive HER2 Negative (see page 2 & 3 ) HER2 Positive
Initial Evaluation Clinical Stage Pre-Treatment Evaluation Treatment and pathological stage Less than 4 positive lymph nodes Adjuvant Treatment ER Positive HER2 Negative (see page 2 & 3 ) HER2 Positive
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
ANZUP SURVEILLANCE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR METASTATIC TESTICULAR CANCER POST-CHEMOTHERAPY
 ANZUP SURVEILLANCE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR METASTATIC TESTICULAR CANCER POST-CHEMOTHERAPY Note: These surveillance recommendations are provided as recommendations only. Clinicians should take into account
ANZUP SURVEILLANCE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR METASTATIC TESTICULAR CANCER POST-CHEMOTHERAPY Note: These surveillance recommendations are provided as recommendations only. Clinicians should take into account
4/13/2010. Silverman, Buchanan Breast, 2003
 Tailoring Breast Cancer Treatment: Has Personalized Medicine Arrived? Judith Luce, M.D. San Francisco General Hospital Avon Comprehensive Breast Care Center Outline First, treatment of DCIS Sorting risk
Tailoring Breast Cancer Treatment: Has Personalized Medicine Arrived? Judith Luce, M.D. San Francisco General Hospital Avon Comprehensive Breast Care Center Outline First, treatment of DCIS Sorting risk
Although the international TNM classification system
 Prognostic Significance of Perioperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis of 1,000 Consecutive Resections for Clinical Stage I Disease Morihito Okada, MD, PhD, Wataru
Prognostic Significance of Perioperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis of 1,000 Consecutive Resections for Clinical Stage I Disease Morihito Okada, MD, PhD, Wataru
Clinical Management Guideline for Breast Cancer
 Initial Evaluation Clinical Stage Pre-Treatment Evaluation Treatment and pathological stage Adjuvant Treatment Less than 4 positive lymph nodes ER Positive HER2 Negative (see page 2 & 3 ) Primary Diagnosis:
Initial Evaluation Clinical Stage Pre-Treatment Evaluation Treatment and pathological stage Adjuvant Treatment Less than 4 positive lymph nodes ER Positive HER2 Negative (see page 2 & 3 ) Primary Diagnosis:
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 15 February 2006
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 15 February 2006 Taxotere 20 mg, concentrate and solvent for solution for infusion B/1 vial of Taxotere and 1 vial
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 15 February 2006 Taxotere 20 mg, concentrate and solvent for solution for infusion B/1 vial of Taxotere and 1 vial
Liver Cancer And Tumours
 Liver Cancer And Tumours What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood from all parts of the body, cancer cells from elsewhere can
Liver Cancer And Tumours What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood from all parts of the body, cancer cells from elsewhere can
Lung cancer is a major cause of cancer deaths worldwide.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Factors in 3315 Completely Resected Cases of Clinical Stage I Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in Japan Teruaki Koike, MD,* Ryosuke Tsuchiya, MD, Tomoyuki Goya, MD, Yasunori Sohara,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Factors in 3315 Completely Resected Cases of Clinical Stage I Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in Japan Teruaki Koike, MD,* Ryosuke Tsuchiya, MD, Tomoyuki Goya, MD, Yasunori Sohara,
Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1
 Page 1 Sponsor Novartis UK Limited Generic Drug Name Letrozole/FEM345 Therapeutic Area of Trial Localized ER and/or PgR receptor positive breast cancer Study Number CFEM345EGB07 Protocol Title This study
Page 1 Sponsor Novartis UK Limited Generic Drug Name Letrozole/FEM345 Therapeutic Area of Trial Localized ER and/or PgR receptor positive breast cancer Study Number CFEM345EGB07 Protocol Title This study
Lung Cancer in Women: A Different Disease? James J. Stark, MD, FACP
 Lung Cancer in Women: A Different Disease? James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Director of Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical
Lung Cancer in Women: A Different Disease? James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Director of Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical
Case Scenario 1. 2/15/2011 The patient received IMRT 45 Gy at 1.8 Gy per fraction for 25 fractions.
 Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
TUMOR M ARKERS MARKERS
 TUMOR MARKERS M.Shekarabi IUMS Definition Many cancers are associated with the abnormal production of some molecules l which h can be measured in plasma. These molecules are known as tumor markers. A good
TUMOR MARKERS M.Shekarabi IUMS Definition Many cancers are associated with the abnormal production of some molecules l which h can be measured in plasma. These molecules are known as tumor markers. A good
Keywords Breast cancer Brain metastasis Lapatinib Capecitabine. Introduction
 Int Canc Conf J (2013) 2:9 13 DOI 10.1007/s13691-012-0054-x CASE REPORT HER2-positive recurrent breast cancer and metastases of breast cancer, including life-threatening metastases to the brain and dura
Int Canc Conf J (2013) 2:9 13 DOI 10.1007/s13691-012-0054-x CASE REPORT HER2-positive recurrent breast cancer and metastases of breast cancer, including life-threatening metastases to the brain and dura
Cancer Prevention & Control in Adolescent & Young Adult Survivors
 + Cancer Prevention & Control in Adolescent & Young Adult Survivors NCPF Workshop July 15-16, 2013 Patricia A. Ganz, MD UCLA Schools of Medicine & Public Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center + Overview
+ Cancer Prevention & Control in Adolescent & Young Adult Survivors NCPF Workshop July 15-16, 2013 Patricia A. Ganz, MD UCLA Schools of Medicine & Public Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center + Overview
Physician Follow-Up and Guideline Adherence in Post- Treatment Surveillance of Colorectal Cancer
 Physician Follow-Up and Guideline Adherence in Post- Treatment Surveillance of Colorectal Cancer Gabriela M. Vargas, MD Kristin M. Sheffield, PhD, Abhishek Parmar, MD, Yimei Han, MS, Kimberly M. Brown,
Physician Follow-Up and Guideline Adherence in Post- Treatment Surveillance of Colorectal Cancer Gabriela M. Vargas, MD Kristin M. Sheffield, PhD, Abhishek Parmar, MD, Yimei Han, MS, Kimberly M. Brown,
Molecular Imaging and Cancer
 Molecular Imaging and Cancer Cancer causes one in every four deaths in the United States, second only to heart disease. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, more than 512,000
Molecular Imaging and Cancer Cancer causes one in every four deaths in the United States, second only to heart disease. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, more than 512,000
BR-MA, GI-MA and OM-MA: Immunoassays for the Tumor Markers CA15-3, CA19-9 and CA125
 BR-MA, GI-MA and OM-MA: Immunoassays for the Tumor Markers CA15-3, CA19-9 and CA125 Paul E. C. Sibley, Ph.D. EURO/DPC Limited BR-MA, GI-MA and OM-MA: Immunoassays for the Tumor Markers CA15-3, CA19-9 and
BR-MA, GI-MA and OM-MA: Immunoassays for the Tumor Markers CA15-3, CA19-9 and CA125 Paul E. C. Sibley, Ph.D. EURO/DPC Limited BR-MA, GI-MA and OM-MA: Immunoassays for the Tumor Markers CA15-3, CA19-9 and
Monitoring Metastatic Breast Cancer with Serum HER-2/neu: Individual Patient Profiles
 Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, a global leader in clinical diagnostics, provides healthcare professionals in hospital, reference, and physician office laboratories and point-of-care settings with the
Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, a global leader in clinical diagnostics, provides healthcare professionals in hospital, reference, and physician office laboratories and point-of-care settings with the
PET IMAGING (POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPY) FACT SHEET
 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Dr Sneha Shah Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai.
 Dr Sneha Shah Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai. Topics covered Lymphomas including Burkitts Pediatric solid tumors (non CNS) Musculoskeletal Ewings & osteosarcoma. Neuroblastomas Nasopharyngeal carcinomas
Dr Sneha Shah Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai. Topics covered Lymphomas including Burkitts Pediatric solid tumors (non CNS) Musculoskeletal Ewings & osteosarcoma. Neuroblastomas Nasopharyngeal carcinomas
Indeterminate Pulmonary Nodules in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
 Indeterminate Pulmonary Nodules in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Jai Sule 1, Kah Wai Cheong 2, Stella Bee 2, Bettina Lieske 2,3 1 Dept of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, University Surgical Cluster,
Indeterminate Pulmonary Nodules in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Jai Sule 1, Kah Wai Cheong 2, Stella Bee 2, Bettina Lieske 2,3 1 Dept of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, University Surgical Cluster,
Understanding Tumor Markers for Breast and Colorectal Cancers. A Patient s Guide. Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology
 Cover Layout 1 A Patient s Guide Understanding Tumor Markers for Breast and Colorectal Cancers Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology ... Cover Layout 2 A Patient s Guide Understanding
Cover Layout 1 A Patient s Guide Understanding Tumor Markers for Breast and Colorectal Cancers Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology ... Cover Layout 2 A Patient s Guide Understanding
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown. Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC
 Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Surgical Management of Pulmonary Metastases. Dr AG Jacobs Principal Specialist Dept Cardiothoracic Surgery Steve Biko Academic Hospital
 Surgical Management of Pulmonary Metastases Dr AG Jacobs Principal Specialist Dept Cardiothoracic Surgery Steve Biko Academic Hospital Introduction Lungs 2 nd most common site of metastatic deposition
Surgical Management of Pulmonary Metastases Dr AG Jacobs Principal Specialist Dept Cardiothoracic Surgery Steve Biko Academic Hospital Introduction Lungs 2 nd most common site of metastatic deposition
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125. Learning Outcomes
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125 Learning Outcomes Upon completion of this exercise, participants will be able to: discuss the use of CA 125 levels in monitoring patients undergoing treatment for ovarian
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125 Learning Outcomes Upon completion of this exercise, participants will be able to: discuss the use of CA 125 levels in monitoring patients undergoing treatment for ovarian
Causation Issues. Delay in Diagnosis of Cancer Cases. Prof Pat Price Imperial College London
 Causation Issues Delay in Diagnosis of Cancer Cases Prof Pat Price Imperial College London office@patprice.co.uk www.patprice.co.uk Faculty of Advocates Annual conference 18 th June 2018 EVIDENCE BASED
Causation Issues Delay in Diagnosis of Cancer Cases Prof Pat Price Imperial College London office@patprice.co.uk www.patprice.co.uk Faculty of Advocates Annual conference 18 th June 2018 EVIDENCE BASED
Imaging Surveillance in Women with a History of Treated Breast Cancer. Wei Tse Yang, M.D.
 Imaging Surveillance in Women with a History of Treated Breast Cancer Wei Tse Yang, M.D. Breast Cancer 1. Extent 2. Response 3. Recurrence Surveillance Breast Cancer 1. Extent 2. Response Surveillance
Imaging Surveillance in Women with a History of Treated Breast Cancer Wei Tse Yang, M.D. Breast Cancer 1. Extent 2. Response 3. Recurrence Surveillance Breast Cancer 1. Extent 2. Response Surveillance
Best Papers. F. Fusco
 Best Papers UROLOGY F. Fusco Best papers - 2015 RP/RT Oncological outcomes RP/RT IN ct3 Utilization trends RP/RT Complications Evolving role of elnd /Salvage LND This cohort reflects the current clinical
Best Papers UROLOGY F. Fusco Best papers - 2015 RP/RT Oncological outcomes RP/RT IN ct3 Utilization trends RP/RT Complications Evolving role of elnd /Salvage LND This cohort reflects the current clinical
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER
 MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
PET/CT Frequently Asked Questions
 PET/CT Frequently Asked Questions General Q: Is FDG PET specific for cancer? A: No, it is a marker of metabolism. In general, any disease that causes increased metabolism can result in increased FDG uptake
PET/CT Frequently Asked Questions General Q: Is FDG PET specific for cancer? A: No, it is a marker of metabolism. In general, any disease that causes increased metabolism can result in increased FDG uptake
In 1989, Deslauriers et al. 1 described intrapulmonary metastasis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Intrapulmonary Metastases Kanji Nagai, MD,* Yasunori Sohara, MD, Ryosuke Tsuchiya, MD, Tomoyuki Goya, MD, and Etsuo Miyaoka,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Intrapulmonary Metastases Kanji Nagai, MD,* Yasunori Sohara, MD, Ryosuke Tsuchiya, MD, Tomoyuki Goya, MD, and Etsuo Miyaoka,
Background: Case Report: Conclusions: Neoplasm Metastasis Breast Neoplasms therapy Aromatase Inhibitors. MeSH Keywords:
 ISSN 1941-5923 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.890023 Received: 2013.11.11 Accepted: 2013.12.08 Published: 2014.02.24 Long-term complete remission of metastatic breast cancer, induced by a steroidal aromatase inhibitor
ISSN 1941-5923 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.890023 Received: 2013.11.11 Accepted: 2013.12.08 Published: 2014.02.24 Long-term complete remission of metastatic breast cancer, induced by a steroidal aromatase inhibitor
Name of Policy: Serum Tumor Markers for Breast and Gastrointestinal Malignancies
 Name of Policy: Serum Tumor Markers for Breast and Gastrointestinal Malignancies Policy #: 195 Latest Review Date: October 2013 Category: Medical Policy Grade: A Background/Definitions: As a general rule,
Name of Policy: Serum Tumor Markers for Breast and Gastrointestinal Malignancies Policy #: 195 Latest Review Date: October 2013 Category: Medical Policy Grade: A Background/Definitions: As a general rule,
ARTICLE IN PRESS. doi: /j.ijrobp METAPLASTIC CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST: A RETROSPECTIVE REVIEW
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.024 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. xx, No. x, pp. xxx, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/05/$ see front matter
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.024 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. xx, No. x, pp. xxx, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/05/$ see front matter
UK CAA Oncology Certification Charts
 UK CAA Oncology Certification Charts 1. Colorectal 2. Malignant Melanoma 3. Germ Cell Tumour of Testis 4. Renal Cell Carcinoma 5. Breast Carcinoma 6. Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Note: All Class 1 cases
UK CAA Oncology Certification Charts 1. Colorectal 2. Malignant Melanoma 3. Germ Cell Tumour of Testis 4. Renal Cell Carcinoma 5. Breast Carcinoma 6. Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Note: All Class 1 cases
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of WSAVA http://www.ivis.org 14(Fri)
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of WSAVA http://www.ivis.org 14(Fri)
Breast Cancer Basics. Clinical Oncology for Public Health Professionals. Ben Ho Park, MD, PhD
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Vinorelbine, methotrexate and fluorouracil (VMF) as first-line therapy in metastatic breast cancer: a randomized phase II trial
 Original article Annals of Oncology 14: 699 703, 2003 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdg199 Vinorelbine, methotrexate and fluorouracil (VMF) as first-line therapy in metastatic breast cancer: a randomized phase II
Original article Annals of Oncology 14: 699 703, 2003 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdg199 Vinorelbine, methotrexate and fluorouracil (VMF) as first-line therapy in metastatic breast cancer: a randomized phase II
Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer
 Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer Chiun Sheng Huang, MD, PhD, MPH Professor and Chairman Department of Surgery Director of Breast Care Center National Taiwan University Hospital
Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer Chiun Sheng Huang, MD, PhD, MPH Professor and Chairman Department of Surgery Director of Breast Care Center National Taiwan University Hospital
Citation for published version (APA): Francken, A. B. (2007). Primary and metastatic melanoma: aspects of follow-up and staging s.n.
 University of Groningen Primary and metastatic melanoma Francken, Anne Brecht IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Primary and metastatic melanoma Francken, Anne Brecht IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Dr. Shari Srinivasan, Consultant Chemical Pathologist, Tallaght Hospital, Dublin 24, Ireland
 Draft Laboratory Testing for Tumour Markers V1.0 Authors Dr. Shari Srinivasan, Consultant Chemical Pathologist, Tallaght Hospital, Dublin 24, Ireland Dr. Gerard Boran, Consultant Chemical Pathologist,
Draft Laboratory Testing for Tumour Markers V1.0 Authors Dr. Shari Srinivasan, Consultant Chemical Pathologist, Tallaght Hospital, Dublin 24, Ireland Dr. Gerard Boran, Consultant Chemical Pathologist,
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL RECTAL CANCER GI Site Group Rectal Cancer Authors: Dr. Jennifer Knox, Dr. Mairead McNamara 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. SCREENING AND
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL RECTAL CANCER GI Site Group Rectal Cancer Authors: Dr. Jennifer Knox, Dr. Mairead McNamara 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. SCREENING AND
Gastrinoma: Medical Management. Haley Gallup
 Gastrinoma: Medical Management Haley Gallup Also known as When to put your knife down Gastrinoma Definition and History Diagnosis Historic Management Sporadic vs MEN-1 Defining surgical candidates Nonsurgical
Gastrinoma: Medical Management Haley Gallup Also known as When to put your knife down Gastrinoma Definition and History Diagnosis Historic Management Sporadic vs MEN-1 Defining surgical candidates Nonsurgical
COLORECTAL CANCER 44
 COLORECTAL CANCER 44 Colorectal Cancer Highlights from the 2009 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Edited by Stuart M. Lichtman, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Commack,
COLORECTAL CANCER 44 Colorectal Cancer Highlights from the 2009 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Edited by Stuart M. Lichtman, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Commack,
Prognostic value of serum CYFRA in patients with anal canal squamous cell carcinoma treated with radio(chemo)therapy
 Gauthé et al. BMC Cancer (2018) 18:417 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4335-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Prognostic value of serum CYFRA 21-1 1 in patients with anal canal squamous cell carcinoma treated with
Gauthé et al. BMC Cancer (2018) 18:417 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4335-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Prognostic value of serum CYFRA 21-1 1 in patients with anal canal squamous cell carcinoma treated with
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine. Dara Colasurdo Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine,
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2012 Does The Use Of Intravenous Zoledronic
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2012 Does The Use Of Intravenous Zoledronic
4/22/2010. Hakan Korkmaz, MD Assoc. Prof. of Otolaryngology Ankara Dıșkapı Training Hospital-Turkey.
 Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Head Neck Surgeon Perspective Hakan Korkmaz, MD Assoc. Prof. of Otolaryngology Ankara Dıșkapı Training Hospital-Turkey Thyroid gland Small endocrine gland:
Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Head Neck Surgeon Perspective Hakan Korkmaz, MD Assoc. Prof. of Otolaryngology Ankara Dıșkapı Training Hospital-Turkey Thyroid gland Small endocrine gland:
Quiz. b. 4 High grade c. 9 Unknown
 Quiz 1. 10/11/12 CT scan abdomen/pelvis: Metastatic liver disease with probable primary colon malignancy. 10/17/12 Colonoscopy with polypectomy: Adenocarcinoma of sigmoid colon measuring at least 6 mm
Quiz 1. 10/11/12 CT scan abdomen/pelvis: Metastatic liver disease with probable primary colon malignancy. 10/17/12 Colonoscopy with polypectomy: Adenocarcinoma of sigmoid colon measuring at least 6 mm
* * * * Supplementary Figure 1. DS Lv CK HSA CK HSA. CK Col-3. CK Col-3. See overleaf for figure legend. Cancer cells
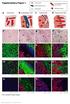 Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Intro to Cancer Therapeutics
 An Intro to Cancer Therapeutics Christopher R. Chitambar, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Froedtert and Medical College of Wisconsin Clinical Cancer Center cchitamb@mcw.edu Intro
An Intro to Cancer Therapeutics Christopher R. Chitambar, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Froedtert and Medical College of Wisconsin Clinical Cancer Center cchitamb@mcw.edu Intro
Resection of retroperitoneal residual mass after chemotherapy in patients with nonseminomatous testicular cancer
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.31/ No. 2/2001 Resection of retroperitoneal residual mass after chemotherapy in patients with nonseminomatous testicular cancer AHMET ÖZET 1, ALİ AYDIN YAVUZ 1, MURAT BEYZADEOĞLU
Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.31/ No. 2/2001 Resection of retroperitoneal residual mass after chemotherapy in patients with nonseminomatous testicular cancer AHMET ÖZET 1, ALİ AYDIN YAVUZ 1, MURAT BEYZADEOĞLU
A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma. in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis. of Lymph Node Metastasis
 Kitakanto Med J 2002 ; 52 : 189-193 189 A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis of Lymph Node Metastasis Susumu Kawate,' Susumu Ohwada,'
Kitakanto Med J 2002 ; 52 : 189-193 189 A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis of Lymph Node Metastasis Susumu Kawate,' Susumu Ohwada,'
THE RELEVANCE OF SOME TUMORAL MARKERS IN PATIENTS WITH PANCREATIC CANCER
 THE RELEVANCE OF SOME TUMORAL MARKERS IN PATIENTS WITH PANCREATIC CANCER DANIEL TIMOFTE 1, RADU DANILA 1*, ALIN CIOBICA 2, CORNELIU DIACONU 1, ROXANA LIVADARIU 3, LIDIA IONESCU 1 Keywords: pancreatic cancer,
THE RELEVANCE OF SOME TUMORAL MARKERS IN PATIENTS WITH PANCREATIC CANCER DANIEL TIMOFTE 1, RADU DANILA 1*, ALIN CIOBICA 2, CORNELIU DIACONU 1, ROXANA LIVADARIU 3, LIDIA IONESCU 1 Keywords: pancreatic cancer,
Real-world outcomes of postmastectomy radiotherapy in breast cancer patients with 1 3 positive lymph nodes: a retrospective study
 Journal of Radiation Research, 2014, 55, 121 128 doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrt084 Advance Access Publication 20 June 2013 Real-world outcomes of postmastectomy radiotherapy in breast cancer patients with 1 3 positive
Journal of Radiation Research, 2014, 55, 121 128 doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrt084 Advance Access Publication 20 June 2013 Real-world outcomes of postmastectomy radiotherapy in breast cancer patients with 1 3 positive
Solitary Contralateral Adrenal Metastases after Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma
 Original Report ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2004.39 Solitary Contralateral Adrenal after Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma Nikolaos Antoniou, M.D. and Demetrios Karanastasis, M.D. General Hospital
Original Report ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2004.39 Solitary Contralateral Adrenal after Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma Nikolaos Antoniou, M.D. and Demetrios Karanastasis, M.D. General Hospital
Serum Ca 15-3: A Useful Tumor Marker in the Prognostication of Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/awch.1782 Serum Ca 15-3: A Useful Tumor Marker in the Prognostication of Locally Advanced Breast Cancer Mohd Rafey 1, Kafil Akhtar 1 *, Atia Z Rab 2 and Shahid A Siddiqui
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/awch.1782 Serum Ca 15-3: A Useful Tumor Marker in the Prognostication of Locally Advanced Breast Cancer Mohd Rafey 1, Kafil Akhtar 1 *, Atia Z Rab 2 and Shahid A Siddiqui
The Itracacies of Staging Patients with Suspected Lung Cancer
 The Itracacies of Staging Patients with Suspected Lung Cancer Gerard A. Silvestri, MD,MS, FCCP Professor of Medicine Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC silvestri@musc.edu Staging Lung
The Itracacies of Staging Patients with Suspected Lung Cancer Gerard A. Silvestri, MD,MS, FCCP Professor of Medicine Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC silvestri@musc.edu Staging Lung
PMRT for N1 breast cancer :CONS. Won Park, M.D., Ph.D Department of Radiation Oncology Samsung Medical Center
 PMRT for N1 breast cancer :CONS Won Park, M.D., Ph.D Department of Radiation Oncology Samsung Medical Center DBCG 82 b & c Overgaard et al Radiot Oncol 2007 1152 pln(+), 8 or more nodes removed Systemic
PMRT for N1 breast cancer :CONS Won Park, M.D., Ph.D Department of Radiation Oncology Samsung Medical Center DBCG 82 b & c Overgaard et al Radiot Oncol 2007 1152 pln(+), 8 or more nodes removed Systemic
Tumor Markers Yesterday, Today & Tomorrow. Steven E. Zimmerman M.D. Vice President & Chief Medical Director
 Tumor Markers Yesterday, Today & Tomorrow Steven E. Zimmerman M.D. Vice President & Chief Medical Director Tumor Marker - Definition Substances produced by cancer cells or other cells in response to cancer
Tumor Markers Yesterday, Today & Tomorrow Steven E. Zimmerman M.D. Vice President & Chief Medical Director Tumor Marker - Definition Substances produced by cancer cells or other cells in response to cancer
Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors for gastric cancer patients with bone metastasis
 Mikami et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2017) 15:8 DOI 10.1186/s12957-016-1091-2 RESEARCH Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors for gastric cancer patients with bone metastasis Open Access
Mikami et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2017) 15:8 DOI 10.1186/s12957-016-1091-2 RESEARCH Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors for gastric cancer patients with bone metastasis Open Access
BOWEL CANCER. Causes of bowel cancer
 A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
FDG-PET/CT in Gynaecologic Cancers
 Friday, August 31, 2012 Session 6, 9:00-9:30 FDG-PET/CT in Gynaecologic Cancers (Uterine) cervical cancer Endometrial cancer & Uterine sarcomas Ovarian cancer Little mermaid (Edvard Eriksen 1913) honoring
Friday, August 31, 2012 Session 6, 9:00-9:30 FDG-PET/CT in Gynaecologic Cancers (Uterine) cervical cancer Endometrial cancer & Uterine sarcomas Ovarian cancer Little mermaid (Edvard Eriksen 1913) honoring
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Qian Liu, Jian-Jun Bi, Yan-Tao Tian, Qiang Feng, Zhao-Xu Zheng, Zheng Wang* Abstract. Introduction. Materials and Methods
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Outcome after Simultaneous Resection of Gastric Primary Tumour and Synchronous Liver Metastases: Survival Analysis of a Single-center Experience in China Qian Liu, Jian-Jun Bi, Yan-Tao
RESEARCH ARTICLE Outcome after Simultaneous Resection of Gastric Primary Tumour and Synchronous Liver Metastases: Survival Analysis of a Single-center Experience in China Qian Liu, Jian-Jun Bi, Yan-Tao
Clinical indications for positron emission tomography
 Clinical indications for positron emission tomography Oncology applications Brain and spinal cord Parotid Suspected tumour recurrence when anatomical imaging is difficult or equivocal and management will
Clinical indications for positron emission tomography Oncology applications Brain and spinal cord Parotid Suspected tumour recurrence when anatomical imaging is difficult or equivocal and management will
Clinical Study Colorectal Carcinoma with Extremely Low CA19-9
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2009, Article ID 780263, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/780263 Clinical Study Colorectal Carcinoma with Extremely Low CA19-9 Yutaka J. Kawamura, Aika Tokumitsu,
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2009, Article ID 780263, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/780263 Clinical Study Colorectal Carcinoma with Extremely Low CA19-9 Yutaka J. Kawamura, Aika Tokumitsu,
Radiotherapy Physics and Equipment
 Radiological Sciences Department Radiotherapy Physics and Equipment RAD 481 Lecture s Title: Introduction Dr. Mohammed EMAM Ph.D., Paris-Sud 11 University Vision :IMC aspires to be a leader in applied
Radiological Sciences Department Radiotherapy Physics and Equipment RAD 481 Lecture s Title: Introduction Dr. Mohammed EMAM Ph.D., Paris-Sud 11 University Vision :IMC aspires to be a leader in applied
Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary
 Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary.. Definition Histologic evidence of malignancy in the cervical lymph node (s) with no apparent primary site of original tumour Diagnosis after a thorough
Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary.. Definition Histologic evidence of malignancy in the cervical lymph node (s) with no apparent primary site of original tumour Diagnosis after a thorough
Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
Effective local and systemic therapy is necessary for the cure of Ewing tumor Most chemotherapy regimens are a combination of cyclophosphamide,
 Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules
 Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules YASUHIRO ITO, TAKUYA HIGASHIYAMA, YUUKI TAKAMURA, AKIHIRO MIYA, KAORU KOBAYASHI, FUMIO MATSUZUKA, KANJI KUMA
Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules YASUHIRO ITO, TAKUYA HIGASHIYAMA, YUUKI TAKAMURA, AKIHIRO MIYA, KAORU KOBAYASHI, FUMIO MATSUZUKA, KANJI KUMA
Mauricio Camus Appuhn Associate Professor Chief, Department of Surgical Oncology, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile
 May 18-20, 2017 18 a 20 de Maio / 2017 Castro's Park Hotel Surgery for metastatic breast cancer: the controversy of local surgery for metastatic breast cancer Cirurgia em câncer de mama metastático: a
May 18-20, 2017 18 a 20 de Maio / 2017 Castro's Park Hotel Surgery for metastatic breast cancer: the controversy of local surgery for metastatic breast cancer Cirurgia em câncer de mama metastático: a
DRAFT GUIDANCE. This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only.
 Guidance for Industry Pathologic Complete Response in Neoadjuvant Treatment of High-Risk Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Use as an Endpoint to Support Accelerated Approval DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document
Guidance for Industry Pathologic Complete Response in Neoadjuvant Treatment of High-Risk Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Use as an Endpoint to Support Accelerated Approval DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document
CEA, CA 15-3 and CYFRA 21-1 in serum and pleural fluid of patients with pleural effusion.
 Eur Respir J, 1996, 9, 17 23 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.96.09017 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1996 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 CEA, CA 15-3 and CYFRA 21-1 in
Eur Respir J, 1996, 9, 17 23 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.96.09017 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1996 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 CEA, CA 15-3 and CYFRA 21-1 in
TUMOUR MARKERS: RATIONALE USE. Mathias M. Müller, Marietta Vogl. Page 37. Table 1. History of tumour markers
 TUMOUR MARKERS: RATIONALE USE Mathias M. Müller, Marietta Vogl similar in women and men. Just the incidence for the cancer of the lung differs: 6.7 % in women and 15.4 % in men. Table 1. History of tumour
TUMOUR MARKERS: RATIONALE USE Mathias M. Müller, Marietta Vogl similar in women and men. Just the incidence for the cancer of the lung differs: 6.7 % in women and 15.4 % in men. Table 1. History of tumour
After primary tumor treatment, 30% of patients with malignant
 ESTS METASTASECTOMY SUPPLEMENT Alberto Oliaro, MD, Pier L. Filosso, MD, Maria C. Bruna, MD, Claudio Mossetti, MD, and Enrico Ruffini, MD Abstract: After primary tumor treatment, 30% of patients with malignant
ESTS METASTASECTOMY SUPPLEMENT Alberto Oliaro, MD, Pier L. Filosso, MD, Maria C. Bruna, MD, Claudio Mossetti, MD, and Enrico Ruffini, MD Abstract: After primary tumor treatment, 30% of patients with malignant
Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011
 Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011 Robert W. Carlson, M.D. Professor of Medicine Stanford University Chair, NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines Panel Selection of
Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011 Robert W. Carlson, M.D. Professor of Medicine Stanford University Chair, NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines Panel Selection of
Comparison of the serum fibrin fibrinogen degradation products with cytokeratin 19 fragment as biomarkers in patients with lung cancer
 BIOMEDICAL REPORTS 2: 737-742 Comparison of the serum fibrin fibrinogen degradation products with cytokeratin 19 fragment as biomarkers in patients with lung cancer HEE JIN SO 1, SEOK IL HONG 1,2, JIN
BIOMEDICAL REPORTS 2: 737-742 Comparison of the serum fibrin fibrinogen degradation products with cytokeratin 19 fragment as biomarkers in patients with lung cancer HEE JIN SO 1, SEOK IL HONG 1,2, JIN
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CANCER
 20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
