International Journal of Laboratory Hematology AUTOMATIC CLASSIFICATION OF ATYPICAL LYMPHOID B CELLS USING DIGITAL BLOOD IMAGE PROCESSING
|
|
|
- Junior Eaton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AUTOMATIC CLASSIFICATION OF ATYPICAL LYMPHOID B CELLS USING DIGITAL BLOOD IMAGE PROCESSING Journal: Manuscript ID: IJLH R Manuscript Type: Original Article Date Submitted by the Author: n/a Complete List of Authors: Alférez, Santiago; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Matemàtica Aplicada III Merino, Anna; Hospital Clinic, Core Lab. Cytology Unit.; Hospital Clinic, Hemotherapy-Hemostasis Mujica, Luis; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Matemàtica Aplicada III Ruiz, Magda; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Matemàtica Aplicada III Bigorra, Laura; Hospital Clinic, Hemotherapy-Hemostasis Rodellar, Jose; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Matemàtica Aplicada III Keywords: Morphology, Laboratory Automation, Leukocytes, Lymphoma
2 Page of TITLE PAGE AUTOMATIC CLASSIFICATION OF ATYPICAL LYMPHOID B CELLS USING DIGITAL BLOOD IMAGE PROCESSING Running Head: Digital image classification of atypical lymphoid cells Authors: Santiago Alférez (), Anna Merino (), Luis E Mujica (), Magda Ruiz (), Laura Bigorra (), José Rodellar () Institutions of the authors: () Servei d Hemoterapia-Hemostasia. Centre de Diagnóstic Biomédic. Hospital Clínic de Barcelona. Spain. () Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya. Spain Anna Merino: Dept. Hemotherapy-Hemostasis. Hospital Clinic. Villarroel 0, 00 Barcelona, Spain; Telephone ; Fax +-; amerino@clinic.ub.es Keywords: atypical lymphoid cells, hematological cytology, digital image processing, automatic cell classification, peripheral blood, morphological analysis. List of abbreviations: PB, CLL, HCL, N, FCM, WHO, AC, WT, WBC. "The authors have nothing to disclose."
3 Page of ABSTRACT: Introduction: There are automated systems for digital peripheral blood (PB) cell analysis, but they operate most effectively in non-pathological blood samples. The objective of this work was to design a methodology to improve the automatic classification of abnormal lymphoid cells. Methods: We analyzed 0 digital images of individual lymphoid cells from PB films obtained in the CellaVision DM: 0 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) cells, 00 Hairy Cell Leukemia (HCL) cells and 0 normal lymphocytes (N). We implemented the Watershed Transformation to segment the nucleus, the cytoplasm and the peripheral cell region. We extracted features and then the clustering Fuzzy C-Means (FCM) was applied in two steps for the lymphocyte classification. Results: The images were automatically clustered in three groups, one of them with % of the HCL cells. The set of the remaining cells was clustered again using FCM and texture features. The two new groups contained. % of the N cells and. % of the CLL cells, respectively. Conclusion: The approach has been able to automatically classify with high precision types of lymphoid cells. The addition of more descriptors and other classification techniques will allow extending the classification to other classes of atypical lymphoid cells.
4 Page of MAIN BODY OF TEXT INTRODUCTION Peripheral blood (PB) is an organic fluid easily accessible and its study is the initial analytical step in the diagnosis of most of the hematological and non hematological diseases (). Frequently, the blood smear provides the primary or the only evidence of a specific diagnosis, remaining an important diagnostic tool even in the age of molecular analysis (). Morphological evaluation of leukemia and lymphoma cells is essential for their diagnosis and classification. In the World Health Organization (WHO) classification, atypical cell morphology, along with immunophenotype and genetic changes, remains essential in defining lymphoid neoplasms (). Despite the significant improvements during the last years in hematology analyzers, no significant progress has been made in terms of automatic classification of atypical PB cells. These devices are limited to identifying normally circulating leukocytes and flagging abnormal cells, without being able to classify the abnormal leukocytes. The close collaboration between cytologists, mathematicians and engineers over the last few years has made possible the development of automatic methodologies for digital image processing of normal blood cells. Some equipments are able to pre-classify cells in different categories by applying neural networks, extracting a large number of measurements and parameters that describe the most significant cell morphological characteristics (). These systems, when integrated in the daily routine, represent an interesting technological advance since they are able to pre-classify most of the normal blood cells in PB ().
5 Page of Atypical lymphoid cells are the most difficult pathological cells to classify using morphology features only (), so that few studies of automatic classification of these cells with satisfactory results have been published. In most of the previous studies, the lymphoid cell classification has been addressed with pattern recognition systems in order to separate the cells into categories (-0). Nevertheless, the image processing techniques used in some of the papers are not useful for the current digital images, since the present acquisition technology is based on charge-coupled device sensors (). Morphological distinction between various types of lymphoid cells requires experience and skill and, moreover, objective values do not exist to define cytological variables. CLL cells are typically small lymphocytes with clumped chromatin and scant cytoplasm. HCL cells are larger than normal lymphocytes (N) and they have abundant weakly basophilic cytoplasm with irregular hairy margins. This paper presents a new methodology for lymphocyte recognition to allow the automatic classification of abnormal lymphoid cells circulating in PB in some B lymphoid neoplasms, such us Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) and Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) cells. MATERIAL AND METHODS Blood sample preparation and digital image acquisition Samples from patients with CLL and HCL were included in the study. The diagnoses were established by clinical and morphological findings as well as characteristic immunophenotype of the lymphoid cells. Specifically, CLL cells had the phenotype CD+,
6 Page of CD+, CD+, CD+, weak CD0+, CD0-, FMC- and dim surface immunoglobulin (sig) expression. All the patients with HCL had lymphoid cells with the phenotype CDc+, CD+, FMC+, CD0+ and CD+. Blood samples were obtained from the routine workload of the Core Laboratory of the Hospital Clínic of Barcelona. Venous blood was collected into tubes containing K EDTA as anticoagulant. The samples were analyzed by a cell counter Advia 0 (Siemens Healthcare Diagnosis, Deerfield, USA) and PB films were automatically stained with May-Grünwald- Giemsa in the SP000i (Sysmex, Japan, Kobe) within hours of blood collection. The quality of the smears and cell morphology was assessed by hematologists prior to the image study. We selected 0 lymphoid cell images from PB films, where 0 images were lymphocytes from healthy patients, 00 were lymphoid cells from patients with HCL and 0 were lymphoid cells from patients with CLL. Each individual cell image had a resolution of x 0 pixels and they were obtained by the CellaVision DM system (Lund, Sweden). Novel method for lymphocyte classification In this study we developed a novel method for lymphocyte recognition based on steps: ) color segmentation; ) feature extraction; and ) classification. They are shortly described in the remaining of this section..-color segmentation A digital blood image is composed of a finite number of pixels. Each one has a particular location and color value, which can be represented in several spectral components or color spaces: RGB, HSV, Lab, among others (). The goal of the segmentation procedure is to
7 Page of separate lymphoid cells captured by microscope from other objects in the image (,, ). In this work, lymphoid cell segmentation was obtained using the Watershed transformation (WT), which was applied only on the gradient of the green component from RGB color space (). As a final result, different regions of the cell were identified (segmented): the cytoplasm, the nucleus and the peripheral zone around the cell..-feature extraction The objective of this stage is to obtain information about the objects in the image under analysis. A number of features were used in this work, which are related respectively to: geometry (0), texture (0), basophilia intensity (), and cytoplasm external profile (). They are summarized as follows: Geometric features These features are quantitative geometric interpretations of the cell and nucleus shapes. For each cell and nucleus we calculated: areas, diameters, perimeters and conic eccentricities. Then, nucleus/cytoplasm ratio was calculated by dividing the respective areas. The nucleus eccentricity relative to the cell center was calculated as the distance between the center of the cell and the nucleus (). Texture features Several statistical measures were used to describe the texture of the cytoplasm and nucleus regions (). The skewness measures the asymmetry of the shape; the kurtosis, the relative flatness; the energy, the uniformity; and the entropy, the variability. In addition, the mean and the standard deviation were calculated. Other second-order statistical features were considered: contrast, homogeneity, correlation, energy, entropy and difference variance (). Granulometrical features of the nucleus The granulometry estimates the size distribution of the bright and dark spots on the image. The granulometrical curve places the information from the dark spots on the left (negative
8 Page of coordinates) and the information from the bright spots on the right (positive coordinates) (). From the granulometrical curve of the lymphoid cell, we calculated four features: mean, standard deviation, skewness and kurtosis, in order to discriminate the different types of nuclear texture and improve chromatin description. Basophilia features of the cytoplasm Cytoplasmic basophilia can be estimated by color analysis. The Lab color space is characterized by its approximation to human perception. Therefore, the means of the intensities for each color component are appropriate to represent the basophilia degree of the cytoplasm (). Cytoplasmic profile feature In this paper we propose a novel method to characterize the cytoplasmic profile. It estimates the projections of the cytoplasm using the peripheral region around the cell segmented by WT. This feature is obtained by using thresholding segmentation to the green component and counting the pixels of this region.. Classification In this work, the main objective of the classification step was to obtain an automatic clustering using the features extracted from each image in order to analyze how they can provide relevant information for the detection of normal, HCL or CLL lymphoid cells. All features were stored in a data matrix, which was used as the input data for the classification. The unsupervised classification methodology Fuzzy c-mean (FCM) was applied. Similar input data were grouped in each cluster with certain membership degree (). Finally, the maximum membership value was considered to select the cluster for each lymphoid cell.
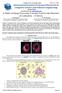
9 Page of RESULTS In the first step, WT was effective in separating the nucleus of the cell. Besides, it allowed segmenting more regions, specifically the outer profile of the cytoplasm, which is crucial to extract the useful information to discriminate different types of lymphocytes. Moreover, its computational cost was low. Figure shows the images corresponding to the different stages that we obtained applying the WT segmentation to the lymphoid cells. The lymphoid original cell stained with MGG is shown in Figure A. The WT was applied only on the gradient of the green component from RGB color space (Figure B). Since the gradient highlights the edges (high intensity changes) of the objects, some external and internal markers were included as minimum values over the gradient image to improve the delimitation of the different regions as shown in Figure C. Thereby, the over-segmentation was avoided and only the entire lymphoid cell was separated (the darkest region on Figure D). Once the entire lymphoid cell was separated, new markers were imposed (Figure E) and the WT was applied again to segment the nucleus (Figure F). Afterwards, mathematical morphology operations were performed in order to improve the quality of the regions from the nucleus and cytoplasm. Finally, different regions of the cell were identified: the cytoplasm, the nucleus and the peripheral zone around the cell (Figures G and H). Corresponding to the second step (feature extraction), Figure shows an example of N, HCL and CLL lymphoid cell images (Figure A) and their granulometrical curves. Figure B shows how these curves discriminate the types of nuclear texture in the different lymphoid cells, improving chromatin description. In order to obtain information from each curve, four features were calculated: mean, standard deviation, skewness and kurtosis.
10 Page of Figure displays an example of cytoplasmic profile feature extraction obtained in one of the hairy cell images. After the segmentation of the cell (Figure A), the peripheral zone around the cell was selected (Figure B). The histogram representation of this region showed an intermediate lobe that contained most of these hairy projections (Figure C). Then, the presence or absence of these projections was determined (Figure D). Finally, this area was quantified. The novel cytoplasmic profile feature proposed in this work was decisive for the detection of the hairy cells. Figure shows the characteristic cytoplasmic profile feature for all the cells. HCL cells showed very high values of this feature compared with CLL and N lymphoid cells. Afterwards, for the classification step, the features of the 0 available cells were used to create the data matrix. It was automatically clustered into groups using FCM producing membership functions. Since every cell pertains to one of the groups with different degrees of membership, we used the criterion that each lymphoid cell belongs to the group with the highest membership value. The left part of Table gives a summary of the whole data obtained in the first FCM classification step. This shows an excellent classification on the group because it included % of the HCL cells. However, the groups and contained.% of normal lymphoid cells and.% of CLL cells, respectively. Figure contains plots corresponding to each group. The horizontal axis represents each individual cell, while the vertical axis gives its membership value. These values represent the probability of belonging to each group, their sum being equal to. In every plot, the data set was sorted in this way: the first 0 images belong to N lymphocytes, the following 00 to HCL cells and the last 0 to CLL cells. From Figure, it was clear to assure that both the normal cells and the CLL cells do not belong to group due to their low membership values. It was also clear that HCL cells had high probability of belonging to group. On the contrary, from Figure it
11 Page 0 of was difficult to infer to which group ( or ) belong the normal and the CLL cells due to the high variance of their membership values in groups and. In order to improve the classification, once the HCL group was identified, the set of the remaining cells was clustered again using FCM. In this new clustering process, only two types were considered (N and CLL cells) and only the texture features were used. The right part of Table gives a report of the results in this step: the percentage of normal lymphoid cells increased to. % in the new group and the percentage of CLL cells increased to. % in the new group. In this case, this was clear enough to distinguish these two types of cells, because their membership values were quite different for a significant percentage of cells as observed in the right part of Table. DISCUSSION In this study, a group composed by normal and two types of atypical lymphoid cells (HCL and CLL) has been analyzed. HCL and CLL cells were selected in our work for their representative morphology and the large number of these cells that we found in the routine workload in our laboratory. Cell morphology is subject to variability in slide making and staining procedures. In order to minimize this variability, the images used in this work were obtained in a standard and reproducible way using automatic staining and the Cellavision DM analyzer. The system scanned the slides identifying different types of white blood cells (WBC). It takes digital cell images and uses artificial neural networks to analyze them (, ). The analyzer pre-classifies WBC but is not able to separate the different abnormal lymphoid cells circulating in PB in some B cell lymphoid neoplasms (0). 0
12 Page of Since atypical lymphoid cells are the most difficult ones to be classified using only morphology features (), in this work a new methodology is proposed combining segmentation, feature extraction and classification algorithms. We showed that this automated image-based methodology extracted granulometrical, basophilia and cytoplasmic profile features in an objective and reproducible way. Then, this methodology could help to provide a new generation of automated systems to assist in the diagnosis through hematological cytology. Our results showed that texture descriptors were the most relevant in CLL lymphoid cell discrimination. Moreover, nuclear characteristics are important features in morphological diagnosis. The nuclear staining pattern reflects chromatin organizations and, in addition, the CLL cells typically contain clumped chromatin (). Therefore it supplies a good descriptor. In a previous work (), granulometry was used to describe cytoplasmic profile feature. Although that work showed good segmentation and description results, it was not completed with further studies towards the discrimination among different groups of similar diagnosis. In our work, a novel cytoplasmic profile feature is proposed based on a simple thresholding of the peripheral zone around the cell. As we expected, this feature was crucial for the HCL cells detection, since in PB stained with MGG they show a soft, blue-gray cytoplasm with hair-like cytoplasmic projection (). On the other hand, this feature could be used for the detection of another atypical lymphoid cells with cytoplasmic villous, such us the splenic marginal zone lymphoma.
13 Page of Concerning to the classification process, features (geometrical and second-order statistical features) were used in () to automate the classical microscopic diagnosis, obtaining good results in the classification of CLL cells but only with respect to the different normal types of leucocytes from PB. In our work, features are used adding other geometrical and second-order statistical features as well as basophilia, granulometrical, first-order statistical and cytoplasmic profile features. In addition, we distinguish types of lymphoid cells: normal, CLL and HCL cells. It is relevant to remark that, up to our knowledge, hairy cells have never been automatically classified before. One of the main contributions of this work is the segmentation methodology of the peripheral region of the cell, in addition to the nucleus and cytoplasm, which allows proposing a new cytoplasmic profile feature describing information about the villous. This enables to achieve an accurate classification of HCL cells. In summary, the methodology presented in this paper has been able to discriminate between groups of lymphoid cells with encouraging results. The overall goal is to combine medical, engineering and mathematical backgrounds to provide more objective and reproducible estimation of the lymphoid cell morphology than the standard microscopy analysis. The addition of more descriptors and other classification techniques to the developed methodology will allow extending to other classes of atypical lymphoid cells. We are progressing with further work in this direction, in order that this methodology could be useful in clinical practice.
14 Page of ACKNOWLEDGMENTS S. Alférez acknowledges to the Technical University of Catalonia for the PhD grant within the Biomedical Engineering program. L. Bigorra acknowledges the support of Fundación J.L. Castaño for a research grant.
15 Page of REFERENCE LIST. Houwen B. The differential cell count. Lab Hematol 00;:-00.. Bain BJ. Diagnosis from the blood smear. N Engl J Med 00;:-0.. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. France: IARC Press; 00.. Ceelie H, Dinkelaar RB, van Gelder W, Examination of peripheral blood films using automated microscopy; evaluation of Diffmaster Octavia and Cellavision DM. J Clin Pathol 00;0:-.. Briggs C, Longair I, Slavik M, Thwaite K, Mills R, Thavaraja V, et al. Can automated blood film analysis replace the manual differential? An evaluation of the CellaVision DM automated image analysis system. Int J Lab Hematol 00;:-0.. Gutiérrez G, Merino A, Domingo A, Jou JM, Reverter JC. EQAS for peripheral blood morphology in Spain: a -year experience. Int J Lab Hematol 00;0:0-.. Bergmann M, Heyn H, Müller-Hermelink HK, Harms H, Aus HM. Automated recognition of cell images in high grade malignant lymphoma and reactive follicular hyperplasia. Anal Cell Pathol 0; :-.. Sabino DMU, Da Fontoura Costa L, Rizzatti EG, Zago MA, A texture approach to leukocyte recognition, Real-Time Imaging 00; 0:0-.. Angulo J, Klossa J, Flandrin G. Ontology-based lymphocyte population description using mathematical morphology on color blood images. Cell Mol Biol 00; :-. 0. Tuzel O, Yang L, Meer P, Foran DJ. Classification of hematologic malignancies using texton signatures. Pattern Anal Applic 00;0(): 0.. González RC, Woods RE. Digital Image Processing. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice
16 Page of Hall; 00.. Xu C, Prince JL. Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans Image Process ;:-.. Sadeghian F, Seman Z, Ramli AR, Abdul Kahar BH, Saripan M-I. A framework for white blood cell segmentation in microscopic blood images using digital image processing. Biol Proced Online 00; :-0.. Alférez E, Merino A, Mujica L, Rodellar J, Morphological features using digital image processing in lymphoid neoplasias [Abstract]. Int J Lab Hematol 0; (Suppl.):.. Beucher S, Meyer F. The morphological approach to segmentation: the watershed transformation. In Dougherty E, ed. Mathematical Morphology in Image Processing. New York: Marcel Dekker : -.. Materka A, Strzeleck M, Texture analysis methods - a review. Technical University of Lodz, Institute of Electronics, COST B report, Brussels,. Available from: Haralick RM, Shanmugan K, Dinstein I, Textural features for image classification, IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern ; :0-.. Angulo J. A mathematical morphology approach to the analysis of the shape of cells. In Bonilla LL, Moscoso M, Platero G, Vega JM, eds. Progress in Industrial Mathematics at ECMI 00. Leganes, Spain: Springer 00: -.. Pal NR, Bezdek JC. On cluster validity for the fuzzy c-means model. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst ; : Merino A, Brugués R, Garcia R, Kinder M, Bedini JL, Escolar G. Comparative study
17 Page of of peripheral blood morphology by conventional microscopy and Cellavision DM in hematological and non hematological diseases [Abstract]. Int J Lab Hematol 0; (Suppl.):.. Jahanmehr SH, Rogers M, Zheng J, Lai R, Wang C. Quantitation of cytological parameters of malignant lymphocytes using computerized image analysis. Int J Lab Hematol 00; 0:-.. Summers TA, Jaffe ES. Hairy cell leukemia diagnostic criteria and differential diagnosis. Leuk Lymphoma 0; :-0.
18 Page of TABLES AND FIGURE CAPTION LIST Table. Two steps classification process. First, different classes of data were obtained. Each group has cells of the types, i.e. the group has % of the HCL cells. A second Fuzzy C-means (FCM) was applied using the texture features only. It resulted in two new groups with.% of N lymphoid cells and.% of CLL cells, respectively. Type FCM step FCM step Group Group Group New group New group N. % 0 %. %. %. % HCL % % % % 0 % CLL 0 %. %. %. %. % N: normal lymphoid cells HCL: Hairy Cell Leukemia cells CLL: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia cells
19 Page of Figure Captions Figure. Different stages of the Watershed segmentation (WT): The original cell (A) was processed to obtain the external and internal markers (C). The WT was calculated on the gradient of green component (B). The markers limit the WT to segment the cell (D). Once the lymphoid cell was separated its edges are used as the new external marker and the thinned mask of the nucleus as the new internal marker (E) in the WT to segment the nucleus (F). Finally the watershed lines (G) showed the regions of interest: the nucleus, the cytoplasm (H) and the peripheral zone around the cell. Figure. Normal (N), HCL and CLL lymphocytes (A) and their corresponding granulometric curves (B), which places the information from the dark spots on the left (negative coordinates) and the information from the bright spots on the right (positive coordinates). Figure. Stages to calculate the HCL cell cytoplasmic feature. After the cell segmentation (A), the peripheral zone around the cell was selected (B). The histogram representation of this region showed an intermediate lobe that contained most of the hairy projections (C). Then, the presence of these projections was determined (D). Finally, this area was quantified. Figure. Cytoplasmic profile feature in N, HCL and CLL lymphoid cells. HCL cells showed very high values of this feature compared with CLL and N lymphoid cells. Figure. Membership function of each type of cell: normal lymphocytes (Normal), hairy cells (HCL) and lymphoid cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The horizontal axis represents the cells, while the vertical axis represents the probability of belonging to each group. The horizontal line for each type of cell represents the mean of their membership values in each group.
20 Page of Different stages of the Watershed segmentation (WT): The original cell (A) was processed to obtain the external and internal markers (C). The WT was calculated on the gradient of green component (B). The markers limit the WT to segment the cell (D). Once the lymphoid cell was separated its edges are used as the new external marker and the thinned mask of the nucleus as the new internal marker (E) in the WT to segment the nucleus (F). Finally the watershed lines (G) showed the regions of interest: the nucleus, the cytoplasm (H) and the peripheral zone around the cell. xmm ( x DPI)
21 Page 0 of Normal (N), HCL and CLL lymphocytes (A) and their corresponding granulometric curves (B), which places the information from the dark spots on the left (negative coordinates) and the information from the bright spots on the right (positive coordinates). x0mm ( x DPI)
22 Page of Stages to calculate the HCL cell cytoplasmic feature. After the cell segmentation (A), the peripheral zone around the cell was selected (B). The histogram representation of this region showed an intermediate lobe that contained most of the hairy projections (C). Then, the presence of these projections was determined (D). Finally, this area was quantified. 0xmm (00 x 00 DPI)
23 Page of Cytoplasmic profile feature in N, HCL and CLL lymphoid cells. HCL cells showed very high values of this feature compared with CLL and N lymphoid cells. 0xmm (00 x 00 DPI)
24 Page of Membership function of each type of cell: normal lymphocytes (Normal), hairy cells (HCL) and lymphoid cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The horizontal axis represents the cells, while the vertical axis represents the probability of belonging to each group. The horizontal line for each type of cell represents the mean of their membership values in each group. xmm (00 x 00 DPI)
Optimizing morphology through blood cell image analysis
 Received: 05 January 2018 Accepted: 22 March 2018 DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.12832 REVIEW ARTICLE Optimizing morphology through blood cell image analysis A. Merino 1 L. Puigví 2 L. Boldú 1 S. Alférez 2 J. Rodellar
Received: 05 January 2018 Accepted: 22 March 2018 DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.12832 REVIEW ARTICLE Optimizing morphology through blood cell image analysis A. Merino 1 L. Puigví 2 L. Boldú 1 S. Alférez 2 J. Rodellar
Cancer Cells Detection using OTSU Threshold Algorithm
 Cancer Cells Detection using OTSU Threshold Algorithm Nalluri Sunny 1 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Mithinti Srikanth 2 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Kodali
Cancer Cells Detection using OTSU Threshold Algorithm Nalluri Sunny 1 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Mithinti Srikanth 2 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Kodali
Computerized Detection System for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia in Blood Microscopic Images
 Computerized Detection System for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia in Blood Microscopic Images Yogesh Ambadas Gajul 1, Rupali Shelke 2 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics Engineering, Walchand Institute
Computerized Detection System for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia in Blood Microscopic Images Yogesh Ambadas Gajul 1, Rupali Shelke 2 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics Engineering, Walchand Institute
Early Detection of Lung Cancer
 Early Detection of Lung Cancer Aswathy N Iyer Dept Of Electronics And Communication Engineering Lymie Jose Dept Of Electronics And Communication Engineering Anumol Thomas Dept Of Electronics And Communication
Early Detection of Lung Cancer Aswathy N Iyer Dept Of Electronics And Communication Engineering Lymie Jose Dept Of Electronics And Communication Engineering Anumol Thomas Dept Of Electronics And Communication
A Robust Feature Extraction and Selection Method for the Recognition of Lymphocytes versus Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
 2012 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science Applications and Technologies A Robust Feature Extraction and Selection Method for the Recognition of Lymphocytes versus Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
2012 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science Applications and Technologies A Robust Feature Extraction and Selection Method for the Recognition of Lymphocytes versus Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Case 3. Ann T. Moriarty,MD
 Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Morphometric Characterization of Small Cell Lymphocytic Lymphoma
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2014; 4(79): 179-183 10.1515/arsm-2015-0002 Chisoi Anca 1, Aşchie Mariana 2, Poinăreanu I. 2 Morphometric Characterization of Small Cell Lymphocytic Lymphoma 1 Spitalul Clinic Judetean
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2014; 4(79): 179-183 10.1515/arsm-2015-0002 Chisoi Anca 1, Aşchie Mariana 2, Poinăreanu I. 2 Morphometric Characterization of Small Cell Lymphocytic Lymphoma 1 Spitalul Clinic Judetean
Keywords: Leukaemia, Image Segmentation, Clustering algorithms, White Blood Cells (WBC), Microscopic images.
 Volume 6, Issue 10, October 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Study on
Volume 6, Issue 10, October 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Study on
COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) DETECTION OF ACUTE LEUKEMIA USING WHITE BLOOD CELLS SEGMENTATION BASED ON BLOOD SAMPLES
 International INTERNATIONAL Journal of Electronics JOURNAL and Communication OF ELECTRONICS Engineering & Technology AND (IJECET), COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) ISSN 0976 6464(Print)
International INTERNATIONAL Journal of Electronics JOURNAL and Communication OF ELECTRONICS Engineering & Technology AND (IJECET), COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) ISSN 0976 6464(Print)
Unsupervised MRI Brain Tumor Detection Techniques with Morphological Operations
 Unsupervised MRI Brain Tumor Detection Techniques with Morphological Operations Ritu Verma, Sujeet Tiwari, Naazish Rahim Abstract Tumor is a deformity in human body cells which, if not detected and treated,
Unsupervised MRI Brain Tumor Detection Techniques with Morphological Operations Ritu Verma, Sujeet Tiwari, Naazish Rahim Abstract Tumor is a deformity in human body cells which, if not detected and treated,
A ROBUST MORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL LEUKEMIC CELLS POPULATIONS IN ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA
 A ROBUST MORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL LEUKEMIC CELLS POPULATIONS IN ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA 1 TRUPTI A. KULKARNI, 2 DILIP S. BHOSALE 1 E & TC Department JSPM s, Bhivarabai Sawant
A ROBUST MORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL LEUKEMIC CELLS POPULATIONS IN ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA 1 TRUPTI A. KULKARNI, 2 DILIP S. BHOSALE 1 E & TC Department JSPM s, Bhivarabai Sawant
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology
 Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
ANALYSIS AND DETECTION OF BRAIN TUMOUR USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES
 ANALYSIS AND DETECTION OF BRAIN TUMOUR USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES P.V.Rohini 1, Dr.M.Pushparani 2 1 M.Phil Scholar, Department of Computer Science, Mother Teresa women s university, (India) 2 Professor
ANALYSIS AND DETECTION OF BRAIN TUMOUR USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES P.V.Rohini 1, Dr.M.Pushparani 2 1 M.Phil Scholar, Department of Computer Science, Mother Teresa women s university, (India) 2 Professor
Dharmesh A Sarvaiya 1, Prof. Mehul Barot 2
 Detection of Lung Cancer using Sputum Image Segmentation. Dharmesh A Sarvaiya 1, Prof. Mehul Barot 2 1,2 Department of Computer Engineering, L.D.R.P Institute of Technology & Research, KSV University,
Detection of Lung Cancer using Sputum Image Segmentation. Dharmesh A Sarvaiya 1, Prof. Mehul Barot 2 1,2 Department of Computer Engineering, L.D.R.P Institute of Technology & Research, KSV University,
Automated Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Region Growing Algorithm by Extracting Feature
 Automated Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Region Growing Algorithm by Extracting Feature Shraddha P. Dhumal 1, Ashwini S Gaikwad 2 1 Shraddha P. Dhumal 2 Ashwini S. Gaikwad ABSTRACT In this paper, we propose
Automated Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Region Growing Algorithm by Extracting Feature Shraddha P. Dhumal 1, Ashwini S Gaikwad 2 1 Shraddha P. Dhumal 2 Ashwini S. Gaikwad ABSTRACT In this paper, we propose
Segmentation of Tumor Region from Brain Mri Images Using Fuzzy C-Means Clustering And Seeded Region Growing
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 18, Issue 5, Ver. I (Sept - Oct. 2016), PP 20-24 www.iosrjournals.org Segmentation of Tumor Region from Brain
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 18, Issue 5, Ver. I (Sept - Oct. 2016), PP 20-24 www.iosrjournals.org Segmentation of Tumor Region from Brain
Identification of Sickle Cells using Digital Image Processing. Academic Year Annexure I
 Academic Year 2014-15 Annexure I 1. Project Title: Identification of Sickle Cells using Digital Image Processing TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.1 Abstract 1-1 1.2 Motivation 1-1 1.3 Objective 2-2 2.1 Block Diagram
Academic Year 2014-15 Annexure I 1. Project Title: Identification of Sickle Cells using Digital Image Processing TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.1 Abstract 1-1 1.2 Motivation 1-1 1.3 Objective 2-2 2.1 Block Diagram
Research Article. Automated grading of diabetic retinopathy stages in fundus images using SVM classifer
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(1):537-541 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Automated grading of diabetic retinopathy stages
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(1):537-541 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Automated grading of diabetic retinopathy stages
Performance evaluation and relevance of the CellaVision TM DM96 system in routine analysis and in patients with malignant hematological diseases
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF LABORATORY HEMATOLOGY Performance evaluation and relevance of the CellaVision TM DM96 system in routine analysis and in patients with malignant hematological diseases
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF LABORATORY HEMATOLOGY Performance evaluation and relevance of the CellaVision TM DM96 system in routine analysis and in patients with malignant hematological diseases
Patterns of Lymphoid Neoplasia in Peripheral Blood. Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Disclosure
 Patterns of Lymphoid Neoplasia in Peripheral Blood Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Disclosure Dr Baltrucki has received an honorarium for his participation as a faculty presenter in this
Patterns of Lymphoid Neoplasia in Peripheral Blood Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Leon F. Baltrucki, M.D. Disclosure Dr Baltrucki has received an honorarium for his participation as a faculty presenter in this
EARLY STAGE DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER USING CT-SCAN IMAGES BASED ON CELLULAR LEARNING AUTOMATE
 EARLY STAGE DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER USING CT-SCAN IMAGES BASED ON CELLULAR LEARNING AUTOMATE SAKTHI NEELA.P.K Department of M.E (Medical electronics) Sengunthar College of engineering Namakkal, Tamilnadu,
EARLY STAGE DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER USING CT-SCAN IMAGES BASED ON CELLULAR LEARNING AUTOMATE SAKTHI NEELA.P.K Department of M.E (Medical electronics) Sengunthar College of engineering Namakkal, Tamilnadu,
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering. Review Paper Volume-5, Issue-12 E-ISSN:
 International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access Review Paper Volume-5, Issue-12 E-ISSN: 2347-2693 Different Techniques for Skin Cancer Detection Using Dermoscopy Images S.S. Mane
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access Review Paper Volume-5, Issue-12 E-ISSN: 2347-2693 Different Techniques for Skin Cancer Detection Using Dermoscopy Images S.S. Mane
ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANT NEOPLASTIC USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES
 ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANT NEOPLASTIC USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES N.R.Raajan, R.Vijayalakshmi, S.Sangeetha School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, SASTRA University Thanjavur, India nrraajan@ece.sastra.edu,
ANALYSIS OF MALIGNANT NEOPLASTIC USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES N.R.Raajan, R.Vijayalakshmi, S.Sangeetha School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, SASTRA University Thanjavur, India nrraajan@ece.sastra.edu,
Letter to the Editor. Effect of edta-anticoagulated whole blood storage on cell morphology examination. A need for standardization
 International Journal of Laboratory Hematology LETTER TO THE EDITOR The Official journal of the International Society for Laboratory Hematology INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF LABORATORY HEMATOLOGY Letter to
International Journal of Laboratory Hematology LETTER TO THE EDITOR The Official journal of the International Society for Laboratory Hematology INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF LABORATORY HEMATOLOGY Letter to
Lung Tumour Detection by Applying Watershed Method
 International Journal of Computational Intelligence Research ISSN 0973-1873 Volume 13, Number 5 (2017), pp. 955-964 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Lung Tumour Detection by Applying
International Journal of Computational Intelligence Research ISSN 0973-1873 Volume 13, Number 5 (2017), pp. 955-964 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Lung Tumour Detection by Applying
Blood Microscopic Image Segmentation & Acute Leukemia Detection Tejashri G. Patil *, V. B. Raskar E & TC Department & S.P. Pune, Maharashtra, India
 International Journal of Emerging Research in Management &Technology Research Article September 215 Blood Microscopic Image Segmentation & Acute Leukemia Detection Tejashri G. Patil *, V. B. Raskar E &
International Journal of Emerging Research in Management &Technology Research Article September 215 Blood Microscopic Image Segmentation & Acute Leukemia Detection Tejashri G. Patil *, V. B. Raskar E &
Classification of mammogram masses using selected texture, shape and margin features with multilayer perceptron classifier.
 Biomedical Research 2016; Special Issue: S310-S313 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Classification of mammogram masses using selected texture, shape and margin features with multilayer perceptron classifier.
Biomedical Research 2016; Special Issue: S310-S313 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Classification of mammogram masses using selected texture, shape and margin features with multilayer perceptron classifier.
AUTOMATIC BRAIN TUMOR DETECTION AND CLASSIFICATION USING SVM CLASSIFIER
 AUTOMATIC BRAIN TUMOR DETECTION AND CLASSIFICATION USING SVM CLASSIFIER 1 SONU SUHAG, 2 LALIT MOHAN SAINI 1,2 School of Biomedical Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Kurukshetra, Haryana -
AUTOMATIC BRAIN TUMOR DETECTION AND CLASSIFICATION USING SVM CLASSIFIER 1 SONU SUHAG, 2 LALIT MOHAN SAINI 1,2 School of Biomedical Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Kurukshetra, Haryana -
COMPARATIVE STUDY ON FEATURE EXTRACTION METHOD FOR BREAST CANCER CLASSIFICATION
 COMPARATIVE STUDY ON FEATURE EXTRACTION METHOD FOR BREAST CANCER CLASSIFICATION 1 R.NITHYA, 2 B.SANTHI 1 Asstt Prof., School of Computing, SASTRA University, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu, India-613402 2 Prof.,
COMPARATIVE STUDY ON FEATURE EXTRACTION METHOD FOR BREAST CANCER CLASSIFICATION 1 R.NITHYA, 2 B.SANTHI 1 Asstt Prof., School of Computing, SASTRA University, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu, India-613402 2 Prof.,
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Final Project Report. Detection of Cervical Cancer in Pap Smear Images
 Final Project Report Detection of Cervical Cancer in Pap Smear Images Hana Sarbortova COMPSCI/ECE/ME 539 Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems University of Wisconsin - Madison December
Final Project Report Detection of Cervical Cancer in Pap Smear Images Hana Sarbortova COMPSCI/ECE/ME 539 Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems University of Wisconsin - Madison December
Detection and Classification of Lung Cancer Using Artificial Neural Network
 Detection and Classification of Lung Cancer Using Artificial Neural Network Almas Pathan 1, Bairu.K.saptalkar 2 1,2 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, SDMCET, Dharwad, India 1 almaseng@yahoo.co.in,
Detection and Classification of Lung Cancer Using Artificial Neural Network Almas Pathan 1, Bairu.K.saptalkar 2 1,2 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, SDMCET, Dharwad, India 1 almaseng@yahoo.co.in,
NAÏVE BAYESIAN CLASSIFIER FOR ACUTE LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA DETECTION
 NAÏVE BAYESIAN CLASSIFIER FOR ACUTE LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA DETECTION Sriram Selvaraj 1 and Bommannaraja Kanakaraj 2 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, P.S.N.A College of Engineering and Technology,
NAÏVE BAYESIAN CLASSIFIER FOR ACUTE LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA DETECTION Sriram Selvaraj 1 and Bommannaraja Kanakaraj 2 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, P.S.N.A College of Engineering and Technology,
Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood
 Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood JONATHAN DEGEL, MASIH SHOKRANI OBJECTIVE: The objectives of this study were to validate the Polymorphprep
Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood JONATHAN DEGEL, MASIH SHOKRANI OBJECTIVE: The objectives of this study were to validate the Polymorphprep
Kathleen Finnegan MS MT(ASCP)SHCM
 Kathleen Finnegan MS MT(ASCP)SHCM Discuss the history of hematology automation and digital differentials. Discuss the HemoFAXS Hematology Analysis System by Tissue Gnostics. Review automated microscopy
Kathleen Finnegan MS MT(ASCP)SHCM Discuss the history of hematology automation and digital differentials. Discuss the HemoFAXS Hematology Analysis System by Tissue Gnostics. Review automated microscopy
Analysis of Microscopic Images of Blood Cells for Detection of Leukemia
 Analysis of Microscopic Images of Blood Cells for Detection of Leukemia Purnima.S 1, Manikandan.S 2, Mohan Raj. S 3, Nishanth. A 4, Selvakumar. A 5 1 Asst.Professor, 2,3,4,5 UG Scholar, Department of Biomedical
Analysis of Microscopic Images of Blood Cells for Detection of Leukemia Purnima.S 1, Manikandan.S 2, Mohan Raj. S 3, Nishanth. A 4, Selvakumar. A 5 1 Asst.Professor, 2,3,4,5 UG Scholar, Department of Biomedical
COMPUTERIZED SYSTEM DESIGN FOR THE DETECTION AND DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG NODULES IN CT IMAGES 1
 ISSN 258-8739 3 st August 28, Volume 3, Issue 2, JSEIS, CAOMEI Copyright 26-28 COMPUTERIZED SYSTEM DESIGN FOR THE DETECTION AND DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG NODULES IN CT IMAGES ALI ABDRHMAN UKASHA, 2 EMHMED SAAID
ISSN 258-8739 3 st August 28, Volume 3, Issue 2, JSEIS, CAOMEI Copyright 26-28 COMPUTERIZED SYSTEM DESIGN FOR THE DETECTION AND DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG NODULES IN CT IMAGES ALI ABDRHMAN UKASHA, 2 EMHMED SAAID
The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow
 The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow Anna Porwit Lund University Faculty of Medicine Dept. of Clinical Sciences Div. Oncology and Pathology anna.porwit@med.lu.se Disclosure of speaker s interests
The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow Anna Porwit Lund University Faculty of Medicine Dept. of Clinical Sciences Div. Oncology and Pathology anna.porwit@med.lu.se Disclosure of speaker s interests
Almost any suspected tumor can be aspirated easily and safely. Some masses are more risky to aspirate including:
 DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
Earlier Detection of Cervical Cancer from PAP Smear Images
 , pp.181-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2017.147.26 Earlier Detection of Cervical Cancer from PAP Smear Images Asmita Ray 1, Indra Kanta Maitra 2 and Debnath Bhattacharyya 1 1 Assistant Professor
, pp.181-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2017.147.26 Earlier Detection of Cervical Cancer from PAP Smear Images Asmita Ray 1, Indra Kanta Maitra 2 and Debnath Bhattacharyya 1 1 Assistant Professor
A Hierarchical Artificial Neural Network Model for Giemsa-Stained Human Chromosome Classification
 A Hierarchical Artificial Neural Network Model for Giemsa-Stained Human Chromosome Classification JONGMAN CHO 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Inje University, Gimhae, 621-749, KOREA minerva@ieeeorg
A Hierarchical Artificial Neural Network Model for Giemsa-Stained Human Chromosome Classification JONGMAN CHO 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Inje University, Gimhae, 621-749, KOREA minerva@ieeeorg
LOCATING BRAIN TUMOUR AND EXTRACTING THE FEATURES FROM MRI IMAGES
 Research Article OPEN ACCESS at journalijcir.com LOCATING BRAIN TUMOUR AND EXTRACTING THE FEATURES FROM MRI IMAGES Abhishek Saxena and Suchetha.M Abstract The seriousness of brain tumour is very high among
Research Article OPEN ACCESS at journalijcir.com LOCATING BRAIN TUMOUR AND EXTRACTING THE FEATURES FROM MRI IMAGES Abhishek Saxena and Suchetha.M Abstract The seriousness of brain tumour is very high among
1 Introduction. Abstract: Accurate optic disc (OD) segmentation and fovea. Keywords: optic disc segmentation, fovea detection.
 Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering 2017; 3(2): 533 537 Caterina Rust*, Stephanie Häger, Nadine Traulsen and Jan Modersitzki A robust algorithm for optic disc segmentation and fovea detection
Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering 2017; 3(2): 533 537 Caterina Rust*, Stephanie Häger, Nadine Traulsen and Jan Modersitzki A robust algorithm for optic disc segmentation and fovea detection
A comparative study of machine learning methods for lung diseases diagnosis by computerized digital imaging'"
 A comparative study of machine learning methods for lung diseases diagnosis by computerized digital imaging'" Suk Ho Kang**. Youngjoo Lee*** Aostract I\.' New Work to be 1 Introduction Presented U Mater~al
A comparative study of machine learning methods for lung diseases diagnosis by computerized digital imaging'" Suk Ho Kang**. Youngjoo Lee*** Aostract I\.' New Work to be 1 Introduction Presented U Mater~al
Brain Tumor Detection using Watershed Algorithm
 Brain Tumor Detection using Watershed Algorithm Dawood Dilber 1, Jasleen 2 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Amity University, Noida, U.P, India 1 P.G. Student, Department
Brain Tumor Detection using Watershed Algorithm Dawood Dilber 1, Jasleen 2 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Amity University, Noida, U.P, India 1 P.G. Student, Department
Blood Cell Morphology. Pr François MULLIER, Pr Bernard CHATELAIN BHS course, October 12th, 2013
 Blood Cell Morphology Pr François MULLIER, Pr Bernard CHATELAIN BHS course, October 12th, 2013 Blood cell morphology Validation of the hematology counter parameters (PLT count, MCV ) Lack of sensitivity
Blood Cell Morphology Pr François MULLIER, Pr Bernard CHATELAIN BHS course, October 12th, 2013 Blood cell morphology Validation of the hematology counter parameters (PLT count, MCV ) Lack of sensitivity
Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (2016)
 Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (216) Performance Evaluation of the XN-55 Automated Hematology Analyzer Body Fluid Mode Considerations for Operational Conditions for Cell Counting with Cerebrospinal
Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (216) Performance Evaluation of the XN-55 Automated Hematology Analyzer Body Fluid Mode Considerations for Operational Conditions for Cell Counting with Cerebrospinal
AUTOMATIC DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DETECTION USING GABOR FILTER WITH LOCAL ENTROPY THRESHOLDING
 AUTOMATIC DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DETECTION USING GABOR FILTER WITH LOCAL ENTROPY THRESHOLDING MAHABOOB.SHAIK, Research scholar, Dept of ECE, JJT University, Jhunjhunu, Rajasthan, India Abstract: The major
AUTOMATIC DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DETECTION USING GABOR FILTER WITH LOCAL ENTROPY THRESHOLDING MAHABOOB.SHAIK, Research scholar, Dept of ECE, JJT University, Jhunjhunu, Rajasthan, India Abstract: The major
Natural Scene Statistics and Perception. W.S. Geisler
 Natural Scene Statistics and Perception W.S. Geisler Some Important Visual Tasks Identification of objects and materials Navigation through the environment Estimation of motion trajectories and speeds
Natural Scene Statistics and Perception W.S. Geisler Some Important Visual Tasks Identification of objects and materials Navigation through the environment Estimation of motion trajectories and speeds
BraTS : Brain Tumor Segmentation Some Contemporary Approaches
 BraTS : Brain Tumor Segmentation Some Contemporary Approaches Mahantesh K 1, Kanyakumari 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, S. J. B Institute of Technology, BGS,
BraTS : Brain Tumor Segmentation Some Contemporary Approaches Mahantesh K 1, Kanyakumari 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, S. J. B Institute of Technology, BGS,
Image analysis in IHC overview, considerations and applications
 Image analysis in IHC overview, considerations and applications Rasmus Røge, MD, Institute of Pathology, Aalborg University Hospital NordiQC workshop September 2016 Aalborg, Denmark Outline Theory Image
Image analysis in IHC overview, considerations and applications Rasmus Røge, MD, Institute of Pathology, Aalborg University Hospital NordiQC workshop September 2016 Aalborg, Denmark Outline Theory Image
Next-Gen Analytics in Digital Pathology
 Next-Gen Analytics in Digital Pathology Cliff Hoyt, CTO Cambridge Research & Instrumentation April 29, 2010 Seeing life in a new light 1 Digital Pathology Today Acquisition, storage, dissemination, remote
Next-Gen Analytics in Digital Pathology Cliff Hoyt, CTO Cambridge Research & Instrumentation April 29, 2010 Seeing life in a new light 1 Digital Pathology Today Acquisition, storage, dissemination, remote
NAILFOLD CAPILLAROSCOPY USING USB DIGITAL MICROSCOPE IN THE ASSESSMENT OF MICROCIRCULATION IN DIABETES MELLITUS
 NAILFOLD CAPILLAROSCOPY USING USB DIGITAL MICROSCOPE IN THE ASSESSMENT OF MICROCIRCULATION IN DIABETES MELLITUS PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0841 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDE : DR.AMBEDKAR INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
NAILFOLD CAPILLAROSCOPY USING USB DIGITAL MICROSCOPE IN THE ASSESSMENT OF MICROCIRCULATION IN DIABETES MELLITUS PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0841 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDE : DR.AMBEDKAR INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
Estimation of Breast Density and Feature Extraction of Mammographic Images
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 2 Issue 11 April 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Estimation of Breast Density and Feature Extraction of Mammographic Images
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 2 Issue 11 April 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Estimation of Breast Density and Feature Extraction of Mammographic Images
Local Fuzzy c-means Clustering for Medical Spectroscopy Images
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 5, 211, no. 3, 1449-1458 Local Fuzzy c-means Clustering for Medical Spectroscopy Images Andrés Barrea CIEM - Universidad Nacional de Córdoba abarrea@mate.uncor.edu Abstract
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 5, 211, no. 3, 1449-1458 Local Fuzzy c-means Clustering for Medical Spectroscopy Images Andrés Barrea CIEM - Universidad Nacional de Córdoba abarrea@mate.uncor.edu Abstract
Texture analysis in Medical Imaging: Applications in Cancer
 Texture analysis in Medical Imaging: in Cancer Angel Alberich-Bayarri, PhD alberich_ang@gva.es angel@quibim.com 1 Biomedical Imaging Research Group (GIBI230) La Fe Polytechnics and University Hospital
Texture analysis in Medical Imaging: in Cancer Angel Alberich-Bayarri, PhD alberich_ang@gva.es angel@quibim.com 1 Biomedical Imaging Research Group (GIBI230) La Fe Polytechnics and University Hospital
A Survey on Localizing Optic Disk
 International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 14 (2014), pp. 1355-1359 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com A Survey on Localizing
International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 14 (2014), pp. 1355-1359 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com A Survey on Localizing
NUCLEI SEGMENTATION OF MICROSCOPY IMAGES OF THYROID NODULES VIA ACTIVE CONTOURS AND K-MEANS CLUSTERING
 1 st International Conference on Experiments/Process/System Modelling/Simulation/Optimization 1 st IC-EpsMsO Athens, 6-9 July, 2005 IC-EpsMsO NUCLEI SEGMENTATION OF MICROSCOPY IMAGES OF THYROID NODULES
1 st International Conference on Experiments/Process/System Modelling/Simulation/Optimization 1 st IC-EpsMsO Athens, 6-9 July, 2005 IC-EpsMsO NUCLEI SEGMENTATION OF MICROSCOPY IMAGES OF THYROID NODULES
Final Project Report Sean Fischer CS229 Introduction
 Introduction The field of pathology is concerned with identifying and understanding the biological causes and effects of disease through the study of morphological, cellular, and molecular features in
Introduction The field of pathology is concerned with identifying and understanding the biological causes and effects of disease through the study of morphological, cellular, and molecular features in
Enhanced Detection of Lung Cancer using Hybrid Method of Image Segmentation
 Enhanced Detection of Lung Cancer using Hybrid Method of Image Segmentation L Uma Maheshwari Department of ECE, Stanley College of Engineering and Technology for Women, Hyderabad - 500001, India. Udayini
Enhanced Detection of Lung Cancer using Hybrid Method of Image Segmentation L Uma Maheshwari Department of ECE, Stanley College of Engineering and Technology for Women, Hyderabad - 500001, India. Udayini
Segmentation and Analysis of Cancer Cells in Blood Samples
 Segmentation and Analysis of Cancer Cells in Blood Samples Arjun Nelikanti Assistant Professor, NMREC, Department of CSE Hyderabad, India anelikanti@gmail.com Abstract Blood cancer is an umbrella term
Segmentation and Analysis of Cancer Cells in Blood Samples Arjun Nelikanti Assistant Professor, NMREC, Department of CSE Hyderabad, India anelikanti@gmail.com Abstract Blood cancer is an umbrella term
Segmentation of vertebrae in lateral lumbar spinal X-ray images
 Segmentation of vertebrae in lateral lumbar spinal X-ray images Eduardo A. Ribeiro, Marcello H. Nogueira-Barbosa, Rangaraj M. Rangayyan, Paulo M. Azevedo-Marques School of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, University
Segmentation of vertebrae in lateral lumbar spinal X-ray images Eduardo A. Ribeiro, Marcello H. Nogueira-Barbosa, Rangaraj M. Rangayyan, Paulo M. Azevedo-Marques School of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, University
Abstract. Background. Objective
 Molecular epidemiology of clinical tissues with multi-parameter IHC Poster 237 J Ruan 1, T Hope 1, J Rheinhardt 2, D Wang 2, R Levenson 1, T Nielsen 3, H Gardner 2, C Hoyt 1 1 CRi, Woburn, Massachusetts,
Molecular epidemiology of clinical tissues with multi-parameter IHC Poster 237 J Ruan 1, T Hope 1, J Rheinhardt 2, D Wang 2, R Levenson 1, T Nielsen 3, H Gardner 2, C Hoyt 1 1 CRi, Woburn, Massachusetts,
MRI Image Processing Operations for Brain Tumor Detection
 MRI Image Processing Operations for Brain Tumor Detection Prof. M.M. Bulhe 1, Shubhashini Pathak 2, Karan Parekh 3, Abhishek Jha 4 1Assistant Professor, Dept. of Electronics and Telecommunications Engineering,
MRI Image Processing Operations for Brain Tumor Detection Prof. M.M. Bulhe 1, Shubhashini Pathak 2, Karan Parekh 3, Abhishek Jha 4 1Assistant Professor, Dept. of Electronics and Telecommunications Engineering,
EXTRACT THE BREAST CANCER IN MAMMOGRAM IMAGES
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 96-105, Article ID: IJCIET_10_02_012 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=10&itype=02
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 96-105, Article ID: IJCIET_10_02_012 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=10&itype=02
Computer Assisted System for Features Determination of Lung Nodule from Chest X-ray Image
 Computer Assisted System for Features Determination of Lung Nodule from Chest X-ray Image Manoj R. Tarambale Marathwada Mitra Mandal s College of Engineering, Pune Dr. Nitin S. Lingayat BATU s Institute
Computer Assisted System for Features Determination of Lung Nodule from Chest X-ray Image Manoj R. Tarambale Marathwada Mitra Mandal s College of Engineering, Pune Dr. Nitin S. Lingayat BATU s Institute
Automatic Detection of Malaria Parasite from Blood Images
 Volume 1, No. 3, May 2012 ISSN 2278-1080 The International Journal of Computer Science & Applications (TIJCSA) RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at http://www.journalofcomputerscience.com/ Automatic Detection
Volume 1, No. 3, May 2012 ISSN 2278-1080 The International Journal of Computer Science & Applications (TIJCSA) RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at http://www.journalofcomputerscience.com/ Automatic Detection
BONE CANCER DETECTION USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK
 ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138(Online) BONE CANCER DETECTION USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK 1 Asuntha A, 2 Andy Srinivasan 1 Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engg., SRM Institute
ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138(Online) BONE CANCER DETECTION USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK 1 Asuntha A, 2 Andy Srinivasan 1 Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engg., SRM Institute
Edge Detection Techniques Based On Soft Computing
 International Journal for Science and Emerging ISSN No. (Online):2250-3641 Technologies with Latest Trends 7(1): 21-25 (2013) ISSN No. (Print): 2277-8136 Edge Detection Techniques Based On Soft Computing
International Journal for Science and Emerging ISSN No. (Online):2250-3641 Technologies with Latest Trends 7(1): 21-25 (2013) ISSN No. (Print): 2277-8136 Edge Detection Techniques Based On Soft Computing
Brain Tumor segmentation and classification using Fcm and support vector machine
 Brain Tumor segmentation and classification using Fcm and support vector machine Gaurav Gupta 1, Vinay singh 2 1 PG student,m.tech Electronics and Communication,Department of Electronics, Galgotia College
Brain Tumor segmentation and classification using Fcm and support vector machine Gaurav Gupta 1, Vinay singh 2 1 PG student,m.tech Electronics and Communication,Department of Electronics, Galgotia College
An efficient method for Segmentation and Detection of Brain Tumor in MRI images
 An efficient method for Segmentation and Detection of Brain Tumor in MRI images Shubhangi S. Veer (Handore) 1, Dr. P.M. Patil 2 1 Research Scholar, Ph.D student, JJTU, Rajasthan,India 2 Jt. Director, Trinity
An efficient method for Segmentation and Detection of Brain Tumor in MRI images Shubhangi S. Veer (Handore) 1, Dr. P.M. Patil 2 1 Research Scholar, Ph.D student, JJTU, Rajasthan,India 2 Jt. Director, Trinity
A Bag of Words Approach for Discriminating between Retinal Images Containing Exudates or Drusen
 A Bag of Words Approach for Discriminating between Retinal Images Containing Exudates or Drusen by M J J P Van Grinsven, Arunava Chakravarty, Jayanthi Sivaswamy, T Theelen, B Van Ginneken, C I Sanchez
A Bag of Words Approach for Discriminating between Retinal Images Containing Exudates or Drusen by M J J P Van Grinsven, Arunava Chakravarty, Jayanthi Sivaswamy, T Theelen, B Van Ginneken, C I Sanchez
Lung Cancer Detection by Using Artificial Neural Network and Fuzzy Clustering Methods
 American Journal of Biomedical Engineering 2012, 2(3): 136-142 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajbe.20120203.08 Lung Cancer Detection by Using Artificial Neural Network and Fuzzy Clustering Methods Fatma Taher 1,*, Naoufel
American Journal of Biomedical Engineering 2012, 2(3): 136-142 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajbe.20120203.08 Lung Cancer Detection by Using Artificial Neural Network and Fuzzy Clustering Methods Fatma Taher 1,*, Naoufel
Characterization of Human Sperm Components for an Accu. an Accurate Morphological Analysis. Violeta Chang. June, 2014
 Characterization of Human Sperm Components for an Accurate Morphological Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Chile June, 2014 Outline 1 Introduction The Basic Problem That We Studied
Characterization of Human Sperm Components for an Accurate Morphological Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Chile June, 2014 Outline 1 Introduction The Basic Problem That We Studied
Type II Fuzzy Possibilistic C-Mean Clustering
 IFSA-EUSFLAT Type II Fuzzy Possibilistic C-Mean Clustering M.H. Fazel Zarandi, M. Zarinbal, I.B. Turksen, Department of Industrial Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology, P.O. Box -, Tehran, Iran
IFSA-EUSFLAT Type II Fuzzy Possibilistic C-Mean Clustering M.H. Fazel Zarandi, M. Zarinbal, I.B. Turksen, Department of Industrial Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology, P.O. Box -, Tehran, Iran
A New Approach For an Improved Multiple Brain Lesion Segmentation
 A New Approach For an Improved Multiple Brain Lesion Segmentation Prof. Shanthi Mahesh 1, Karthik Bharadwaj N 2, Suhas A Bhyratae 3, Karthik Raju V 4, Karthik M N 5 Department of ISE, Atria Institute of
A New Approach For an Improved Multiple Brain Lesion Segmentation Prof. Shanthi Mahesh 1, Karthik Bharadwaj N 2, Suhas A Bhyratae 3, Karthik Raju V 4, Karthik M N 5 Department of ISE, Atria Institute of
Gray Zones and Double Hits Distinguishing True Burkitt Lymphoma from Other High-Grade B-NHLs Burkitt Lymphoma Burkitt-Like Lymphoma DLBCL Patrick Tres
 Gray Zones and Double Hits Distinguishing True Burkitt Lymphoma from Other High-Grade B-NHLs Burkitt Lymphoma Burkitt-Like Lymphoma DLBCL Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco
Gray Zones and Double Hits Distinguishing True Burkitt Lymphoma from Other High-Grade B-NHLs Burkitt Lymphoma Burkitt-Like Lymphoma DLBCL Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DIFFERENTIATING IMMATURE PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Detection Of Red Lesion In Diabetic Retinopathy Using Adaptive Thresholding Method
 Detection Of Red Lesion In Diabetic Retinopathy Using Adaptive Thresholding Method Deepashree Devaraj, Assistant Professor, Instrumentation Department RVCE Bangalore. Nagaveena M.Tech Student, BMSP&I,
Detection Of Red Lesion In Diabetic Retinopathy Using Adaptive Thresholding Method Deepashree Devaraj, Assistant Professor, Instrumentation Department RVCE Bangalore. Nagaveena M.Tech Student, BMSP&I,
arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 8 Mar 2018
![arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 8 Mar 2018 arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 8 Mar 2018](/thumbs/87/97094636.jpg) Automated soft tissue lesion detection and segmentation in digital mammography using a u-net deep learning network Timothy de Moor a, Alejandro Rodriguez-Ruiz a, Albert Gubern Mérida a, Ritse Mann a, and
Automated soft tissue lesion detection and segmentation in digital mammography using a u-net deep learning network Timothy de Moor a, Alejandro Rodriguez-Ruiz a, Albert Gubern Mérida a, Ritse Mann a, and
Brain Tumour Detection of MR Image Using Naïve Beyer classifier and Support Vector Machine
 International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology 2018 IJSRCSEIT Volume 3 Issue 3 ISSN : 2456-3307 Brain Tumour Detection of MR Image Using Naïve
International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology 2018 IJSRCSEIT Volume 3 Issue 3 ISSN : 2456-3307 Brain Tumour Detection of MR Image Using Naïve
Detection of Abnormalities of Retina Due to Diabetic Retinopathy and Age Related Macular Degeneration Using SVM
 Science Journal of Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing 2016; 5(1): 1-7 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/cssp doi: 10.11648/j.cssp.20160501.11 ISSN: 2326-9065 (Print); ISSN: 2326-9073 (Online)
Science Journal of Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing 2016; 5(1): 1-7 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/cssp doi: 10.11648/j.cssp.20160501.11 ISSN: 2326-9065 (Print); ISSN: 2326-9073 (Online)
Keywords Fuzzy Logic, Fuzzy Rule, Fuzzy Membership Function, Fuzzy Inference System, Edge Detection, Regression Analysis.
 Volume 6, Issue 3, March 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Modified Fuzzy
Volume 6, Issue 3, March 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Modified Fuzzy
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa
 Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
A Review on Brain Tumor Detection in Computer Visions
 International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 14 (2014), pp. 1459-1466 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com A Review on Brain
International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 14 (2014), pp. 1459-1466 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com A Review on Brain
Implementation of Brain Tumor Detection using Segmentation Algorithm & SVM
 Implementation of Brain Tumor Detection using Segmentation Algorithm & SVM Swapnil R. Telrandhe 1 Amit Pimpalkar 2 Ankita Kendhe 3 telrandheswapnil@yahoo.com amit.pimpalkar@raisoni.net ankita.kendhe@raisoni.net
Implementation of Brain Tumor Detection using Segmentation Algorithm & SVM Swapnil R. Telrandhe 1 Amit Pimpalkar 2 Ankita Kendhe 3 telrandheswapnil@yahoo.com amit.pimpalkar@raisoni.net ankita.kendhe@raisoni.net
A REVIEW ON CLASSIFICATION OF BREAST CANCER DETECTION USING COMBINATION OF THE FEATURE EXTRACTION MODELS. Aeronautical Engineering. Hyderabad. India.
 Volume 116 No. 21 2017, 203-208 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu A REVIEW ON CLASSIFICATION OF BREAST CANCER DETECTION USING COMBINATION OF
Volume 116 No. 21 2017, 203-208 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu A REVIEW ON CLASSIFICATION OF BREAST CANCER DETECTION USING COMBINATION OF
Statistics-Based Initial Contour Detection of Optic Disc on a Retinal Fundus Image Using Active Contour Model
 Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 33(4): 388-393 388 Statistics-Based Initial Contour Detection of Optic Disc on a Retinal Fundus Image Using Active Contour Model Huang-Tsun Chen 1 Chuin-Mu
Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 33(4): 388-393 388 Statistics-Based Initial Contour Detection of Optic Disc on a Retinal Fundus Image Using Active Contour Model Huang-Tsun Chen 1 Chuin-Mu
Automated Detection of Vascular Abnormalities in Diabetic Retinopathy using Morphological Entropic Thresholding with Preprocessing Median Fitter
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 3 September 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-784X Automated Detection of Vascular Abnormalities in Diabetic Retinopathy using Morphological
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 3 September 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-784X Automated Detection of Vascular Abnormalities in Diabetic Retinopathy using Morphological
Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology, India
 Volume 4, Issue 1, January 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Segmented
Volume 4, Issue 1, January 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Segmented
CME/SAM. Abstract. Hematopathology / CD103 and CD123 in B-Cell Neoplasia
 Hematopathology / CD103 and CD123 in B-Cell Neoplasia Characteristic CD103 and CD123 Expression Pattern Defines Hairy Cell Leukemia Usefulness of CD123 and CD103 in the Diagnosis of Mature B-Cell Lymphoproliferative
Hematopathology / CD103 and CD123 in B-Cell Neoplasia Characteristic CD103 and CD123 Expression Pattern Defines Hairy Cell Leukemia Usefulness of CD123 and CD103 in the Diagnosis of Mature B-Cell Lymphoproliferative
Brain Tumor Segmentation: A Review Dharna*, Priyanshu Tripathi** *M.tech Scholar, HCE, Sonipat ** Assistant Professor, HCE, Sonipat
 International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 4 Issue 09 Pages 4467-4471 2016 Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Brain Tumor Segmentation: A Review Dharna*, Priyanshu
International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 4 Issue 09 Pages 4467-4471 2016 Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Brain Tumor Segmentation: A Review Dharna*, Priyanshu
Evaluation of the Diagnostic Performance of the Sysmex XT-2000i Automated Hematology Analyzer in the Detection of Immature Granulocytes
 Evaluation of the Diagnostic Performance of the Sysmex XT-2000i Automated Hematology Analyzer in the Detection of Immature Granulocytes A. M. CENCI *1, M. MACONI *2, and B. CASOLARI *1 *1 Laboratory of
Evaluation of the Diagnostic Performance of the Sysmex XT-2000i Automated Hematology Analyzer in the Detection of Immature Granulocytes A. M. CENCI *1, M. MACONI *2, and B. CASOLARI *1 *1 Laboratory of
COMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM FOR BRAIN TUMOR DETECTION USING K-MEANS CLUSTERING
 COMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM FOR BRAIN TUMOR DETECTION USING K-MEANS CLUSTERING Urmila Ravindra Patil Tatyasaheb Kore Institute of Engineering and Technology, Warananagar Prof. R. T. Patil Tatyasaheb
COMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM FOR BRAIN TUMOR DETECTION USING K-MEANS CLUSTERING Urmila Ravindra Patil Tatyasaheb Kore Institute of Engineering and Technology, Warananagar Prof. R. T. Patil Tatyasaheb
Analysis & Classification of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia using KNN Algorithm
 Analysis & Classification of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia using KNN Algorithm Pratik M. Gumble Dept of Electronics & Telecommunication C.O.E.T.Sipna Amravati, India pratikmgumble@gmail.com Dr.S.V.Rode
Analysis & Classification of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia using KNN Algorithm Pratik M. Gumble Dept of Electronics & Telecommunication C.O.E.T.Sipna Amravati, India pratikmgumble@gmail.com Dr.S.V.Rode
Incorporating Differentials Into Every Complete Blood Count. Paige Flowers, LVT Dogwood Veterinary Internal Medicine
 Incorporating Differentials Into Every Complete Blood Count Paige Flowers, LVT Dogwood Veterinary Internal Medicine Complete Blood Count Diagnostic performed to evaluate the quantity and morphology of
Incorporating Differentials Into Every Complete Blood Count Paige Flowers, LVT Dogwood Veterinary Internal Medicine Complete Blood Count Diagnostic performed to evaluate the quantity and morphology of
ADVANCED HAEMATOLOGY BATTLE OF THE BANDS. Dennis B. DeNicola, DVM, PhD, DACVP IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. Westbrook, Maine, USA BACKGROUND
 ADVANCED HAEMATOLOGY BATTLE OF THE BANDS Dennis B. DeNicola, DVM, PhD, DACVP IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. Westbrook, Maine, USA BACKGROUND The identification of immature neutrophils (bands, metamyelocytes,
ADVANCED HAEMATOLOGY BATTLE OF THE BANDS Dennis B. DeNicola, DVM, PhD, DACVP IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. Westbrook, Maine, USA BACKGROUND The identification of immature neutrophils (bands, metamyelocytes,
A dynamic approach for optic disc localization in retinal images
 ISSN 2395-1621 A dynamic approach for optic disc localization in retinal images #1 Rutuja Deshmukh, #2 Karuna Jadhav, #3 Nikita Patwa 1 deshmukhrs777@gmail.com #123 UG Student, Electronics and Telecommunication
ISSN 2395-1621 A dynamic approach for optic disc localization in retinal images #1 Rutuja Deshmukh, #2 Karuna Jadhav, #3 Nikita Patwa 1 deshmukhrs777@gmail.com #123 UG Student, Electronics and Telecommunication
Performance Evaluation of the CellaVision DM96 System WBC Differentials by Automated Digital Image Analysis Supported by an Artificial Neural Network
 Hematopathology / DIGITAL IMAGE ANALYSIS IN HEMATOLOGY Performance Evaluation of the CellaVision DM96 System WBC Differentials by Automated Digital Image Analysis Supported by an Artificial Neural Network
Hematopathology / DIGITAL IMAGE ANALYSIS IN HEMATOLOGY Performance Evaluation of the CellaVision DM96 System WBC Differentials by Automated Digital Image Analysis Supported by an Artificial Neural Network
Automated Approach for Qualitative Assessment of Breast Density and Lesion Feature Extraction for Early Detection of Breast Cancer
 Automated Approach for Qualitative Assessment of Breast Density and Lesion Feature Extraction for Early Detection of Breast Cancer 1 Spandana Paramkusham, 2 K. M. M. Rao, 3 B. V. V. S. N. Prabhakar Rao
Automated Approach for Qualitative Assessment of Breast Density and Lesion Feature Extraction for Early Detection of Breast Cancer 1 Spandana Paramkusham, 2 K. M. M. Rao, 3 B. V. V. S. N. Prabhakar Rao
