Review Article Technical Advances in Skin Sparing Mastectomy
|
|
|
- August Pitts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Surgical Oncology Volume 2011, Article ID , 7 pages doi: /2011/ Review Article Technical Advances in Skin Sparing Mastectomy Grant W. Carlson 1, 2 1 Division of Plastic Surgery, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA 30322, USA 2 Winship Cancer Institute, Emory University, 1365C Clifton Road, Atlanta, GA 30327, USA Correspondence should be addressed to Grant W. Carlson, grant carlson@emory.org Received 12 November 2010; Accepted 3 March 2011 Academic Editor: C. H. Yip Copyright 2011 Grant W. Carlson. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Skin sparing mastectomy has resulted in marked improvement in the aesthetic results of immediate breast reconstruction. Mature data has confirmed its oncological safety in the treatment of breast cancer. The procedure has gained wide acceptance and has undergone numerous technical advances since its introduction over twenty years ago. Careful patient selection and choice of skin incisions are necessary to avoid complications. 1. Introduction The term skin sparing mastectomy (SSM) was first used by Toth and Lappert in 1991 [2]. They described preoperative planning of mastectomy incisions in an attempt to maximize skin preservation and facilitate immediate breast reconstruction (IBR). The procedure removes the breast, nippleareola complex, previous biopsy incisions, and skin overlying superficial tumors [3]. Preservation of the inframammary fold (IMF) and native skin greatly enhances the aesthetic result of breast reconstruction. The operation has been adopted for patients with early breast cancer treated by total mastectomy and immediate reconstruction but has not gained universal acceptance. Most surgeons surveyed agree that the procedure improves the cosmetic results of immediate breast reconstruction [4]. Despite numerous studies that have demonstrated the oncological safety of the procedure compared to traditional total mastectomy, there are still concerns about the oncological safety [1, 5 9]. One international survey of over 1,000 surgeons found that 78% of respondents believed that the current published literature demonstrated that SSM does notresultinhigherlocalrecurrenceratesofbreastcancer, 25% did not believe the data [9]. Despite these concerns, the utilization of skin sparing mastectomy continues to increase [10]. 2. Completeness of Mastectomy The breast is a modified cutaneous gland or skin appendage. It is enclosed between the superficial and deep layers of the superficial fascia of the anterior abdominal wall. The superficial layer is a very delicate but definite structure. Large axial vessels lie deep to this plane and send vertical branches to the subdermal plexus. This layer allows the surgeon to dissect the skin flaps in a relatively avascular plane and include minimal mammary tissue. Cooper s ligaments are peripheral projections of breast tissue in fibrous processes, which fuse with the superficial layer of the superficial fascia [11]. Skiles demonstrated that these projections were intimately associated with the skin and concluded in order to excise the whole breast that a large amount of skin need be sacrificed or the dissection kept as close to it as run a risk of skin slough [12]. Beer et al. examined breast tissue from 62 reduction specimens for the presence of the superficial fascia [13]. They found the superficial fascia was absent in 44% of the inferior breast quadrants examined. When it was present, no breast tissue was found beyond it. Torresan et al. studied the skin that would have been preserved in SSM in 42 mastectomy specimens [14]. They found that the presence of breast tissue was significantly associated with skin flaps thicker than 5 mm. They found no correlation between the presence of
2 2 International Surgical Oncology Type I Type II (a) (b) Type III Type IV (c) (d) Figure 1: Types of skin sparing mastectomy [1]. breast tissue in the skin flaps and age, body mass index, or menopausal status. Hicken outlined the extent of mammary tissue in 1940 by injecting X-ray contrast material into the lactiferous ducts of 385 mastectomy specimens [15]. He found that in 95% of cases the ducts ascended into the axilla, 15% passed into the epigastric space, and 2% followed the lateral chest wall beyond the anterior border of the latissimus dorsi muscle. This study defined the classic boundaries of a mastectomy: the clavicle, rectus sheath, midline of the sternum, and the anterior border of the latissimus dorsi muscle. The fascial relationships of the breast facilitate its removal along defined tissue planes. The inferior extent to breast tissue, except in rare cases, stops at the separation of the superficial and deep layers of the superficial fascia of the abdominal wall. Cooper stated that at the... abdominal margin, the gland is turned upon itself at its edge, and forms a kind of hem [11]. The zone of adherence of the superficial fascial to the underlying chest wall in this region is the inframammary fold [16]. It occurs at the inferior margin of the pectoralis major muscle at the 6th and occasionally the 7th rib. Its presence has been demonstrated
3 International Surgical Oncology 3 Figure 2: Type I SSM Tennis Racquet Incision. (a) in the 8th month fetus, and its location is fixed throughout life [17]. It generally contains fat, which may become firm and indurated in patients with large, ptotic breasts. Breast cancer is extremely rare in this location. Haagenson, in his large experience, cited only 26 cases of breast cancer occurring in the region of the IMF [18]. Preservation of the inframammary fold leaves minimal amount of breast tissue and does not appreciably effect the completeness of a mastectomy [19]. All forms of mastectomy leave residual breast tissue. The differences between the various mastectomy techniques are in terms of the amount of microscopic breast tissue left behind in the skin. These small differences have not been shown to impact the local recurrence of breast cancer [1, 5 8]. 3. Types of Skin Sparing Mastectomy The type of skin sparing mastectomy has been classified by the type of incision used and the amount of skin removed (Figure 1) [1]. Factors influencing incision choice include previous biopsies, tumor location and depth, and the type of reconstruction planned. A periareolar incision or Type I SSM is commonly used in prophylactic cases and for nonpalpable cancers diagnosed by needle biopsy. In patients with small diameter areola, a lateral extension or tennis racquet incision is sometimes necessary to improve exposure to the axillary tail, or to provide access for breast reconstruction (Figure 2). If implant/expander reconstruction is planned, the circular incision can be converted to an elliptical incision. The incision should be obliquely oriented toward the axilla to reduce flattening of the central breast mound. A purse string closure of the circumareolar incision has been described in patients with small to medium sized breasts undergoing immediate implant reconstruction [20]. In the author s opinion, the closure is slow to heal and the resultant scar can make nipple reconstruction difficult. Previous incisions impact the amount of skin preservation in SSM. The wide adoption of imaging directed stereotaxic core biopsy has reduced the number of excisional (b) Figure 3: Type II SSM and TRAM Flap Reconstruction. breast biopsies. Today, excisional biopsy incisions usually result from failed attempts at breast conservation. The ablative surgeon must be aware of the depth and extent of tumor involvement prior to final decision planning. A Type II SSM is used when a superficial tumor or previous biopsy is in proximity to the areola. In autologous reconstruction, the flap skin can be used to fill the defect (Figure 3). In implantbased reconstruction, the skin is closed to facilitate breast shape. Type III SSM is used when the superficial tumor or previous incision was remote from the areola, usually in the upper quadrants of the breast. Care must be taken to ensure the viability of the intervening skin. A Type IV SSM is used in large, ptotic breasts when a reduction is planned on the opposite breast. A common problem with this technique is the occurrence of native skin flap necrosis of the most distal portions of the flap, particularly at the T junction. Skoll has described a modification of the Wise pattern to avoid this complication [21]. The area between the vertical limbs of the T and an additional 2cm outside the horizontal limbs are deepithelialized but not resected. Bostwick first described using Wise pattern mastectomy incisions for prophylactic mastectomies and immediate implant reconstruction [22]. He released
4 4 International Surgical Oncology (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Figure 4: (a) Intraoperative photograph showing Wise pattern incisions with de-epithelialization of the skin. The area in yellow will be resected as part of the Type IV SSM. This excision leaves a rim of dermis along the vertical limbs of the skin excision. (b) The inferior skin flap is elevated down to the inframammary fold. (c) The de-epithelialized inferior skin flap is draped over the tissue expander and sutured to the released inferior border of the pectoralis major muscle. Back cuts are made to allow inset of the dermal flap. (d) The skin flaps just prior to closure. The de-epithelialized vertical limbs serve as a buttress. (e) Preoperative appearance. (f) Postoperative appearance after type IV SSM and implant reconstruction using an inferior dermal flap. the pectoralis major muscle and used a deepithelialized inferior skin flap to allow placement of definitive silicone prosthesis. Other authors have built on Bostwick s work, using an inferior dermal pedicle to cover the prosthesis with acceptable complication rates (Table 1). The technique can obviate the need for an acellular dermal matrix and provide adermalbuttresstoreducewoundhealingcomplications (Figure 4).
5 International Surgical Oncology 5 Figure 5: Scissoring of the fingers can assist in deep dissection obviating the need for deep retractors. (a) Table 1: Series of Type IV skin sparing mastectomy using an inferior dermal flap. Author N Type of reconstruction Native skin necrosis (%) Implant removal (%) Hammond et al. [33] 12 Expander 8 8 Nava et al. [34] 30 Implant Derderian et al. [35] 20 Expander/ADM 25 0 Losken et al. [36] 34 Expander ADM acellular dermal matrix. (b) 4. Skin Flap Elevation The skin flaps are elevated superficial to the enveloping fascia of the breast. The skin flap thickness depends on the location on the breast and body habitus of the patient. Breast tissue extends closer to the skin in the lower quadrants and the subcutaneous tissue is thicker in the upper, outer quadrant of the breast. The skin flaps generally are two to five mm. in thickness. Exposure of the white dermis indicates the plane is too superficial to assure skin viability. Electrical cautery on low blended coagulation current is preferred by many surgeons for flap elevation because it is quicker with less blood loss. Care must be taken to avoid thermal injury to the skin. The majority of the blood vessels lie deep to the fascia, but perforating vessels to the skin are encountered and controlled with coagulation current. The infiltration of the breast with dilute epinephrine solution has been described to facilitate sharp dissection of the skin flaps and reduce blood loss [23]. Skin retraction is performed with double pronged skin hooks. The flaps must be handled carefully, and the use of deep abdominal retractors is avoided. Scissoring of the fingers of the nondominant hand can assist in the deep dissection (Figure 5). Because the skin opening is small, the flaps are elevated in a centripetal fashion to assist in exposure. Skin flap viability is usually assessed on clinical grounds but the use of epinephrine solution and blue dye that is used in sentinel lymph node mapping may make this difficult. Fluoroscein dye may be helpful in select cases, especially (c) Figure 6: ((a), (b)) After excision of the necrotic tissue, the pectoralis major interface with acellular dermal matrix is exposed. (c) Appearance after expansion and placement of permanent implants. those where implant reconstruction is used, but it tends to underestimate skin viability [24]. Intraoperative indocyanine green angiography has been shown to have a high sensitivity and specificity in predicting native skin flap necrosis after SSM [25]. Superiorly, the breast falls away from the skin as the clavicle is approached. The fascia is followed down to the
6 6 International Surgical Oncology Table 2: Risk factors for native skin flap necrosis after SSM [1]. Factor Total N (%) Native skin flap necrosis N (%) SSM Type Type I 232 (36.7) 22 (9.5) Type II 293 (46.2) 28 (13) Type III 40 (6.3) 10 (25) Type IV 68 (10.8) 18 (26.5) Tobacco 79 (12.5) 16 (20.3) Radiation 21 (3.3) 5 (23.8) Overall 633 (100) 88 (13.9) pectoralis major muscle. Medially, the fascia is not as defined and the dissection ends at the border of the sternum. Perforating vessels of the internal mammary artery are frequently encountered along the sternal border and can be controlled with the cautery. Attempts should be made to preserve these vessels in cases using type IV SSM to improve skin flap blood supply. These perforators can be used as donor vessels in free flap breast reconstruction. Inferiorly, the dissection follows the superficial layer of the fascia to its junction with the deep layer (Figure 4). The skin is adherent to the anterior abdominal wall at this juncture. This fascial junction occurs at the inferior edge of the pectoralis major muscle. Laterally, the dissection continues over the pectoralis muscle toward the humerus enabling removal of the axillary tail. If an axillary incision is required, a tunnel is developed between it and the chest incision. The breast is mobilized laterally over the serratus anterior muscle. The axillary dissection is performed in continuity with the breast tail and the specimen is removed en bloc through the central incision. 5. Native Skin Flap Necrosis The reported incidence of native skin flap necrosis after SSM has been reported to be 10% to 22% when followed by IBR [1, 26, 27]. It can vary in severity from superficial epidermolysis to full thickness skin loss. Predisposing factors include: preoperative radiation, tobacco smoking, incision type, obesity, breastsize, and age [28 31]. Skin flap elevation with the scalpel or cautery appears to have similar skin necrosis rates [30]. There are conflicting reports as to its impact of epinephrine infiltration on mastectomy flap viability [29, 30]. A review of the Emory University experience found that Type III and IV incisions, tobacco smoking, and preoperative radiation predisposed to native skin flap necrosis (Table 2) [28]. Davies et al. found that periareolar incisions had a significantly lower rates of complications compared to Wise pattern or tennis racquet incisions [30]. The management of native skin flap necrosis depends on its depth and extent and the type of reconstruction performed. Skin necrosis after expander reconstruction should be managed aggressively to prevent exposure and the development of infection necessitating implant removal (Figure 6). Antony et al. reported their experience with 58 cases of mastectomy skin flap necrosis following tissue expander reconstruction [32]. Nine patients required removal of the expander because of the large area of skin loss. The remaining patients underwent skin excision and primary closure. Three of these patients (6%) subsequently developed infection necessitating expander removal. 6. Summary The use of skin sparing mastectomy has been one of the greatest advancements in immediate breast reconstruction in the last two decades. It is technically more challenging than traditional mastectomy and requires close coordination between the oncologic and reconstructive surgeons. Proper patient selection and meticulous technique are necessary to avoid wound complications. References [1] G. W. Carlson, J. Bostwick, T. M. Styblo et al., Skin-sparing mastectomy: oncologic and reconstructive considerations, Annals of Surgery, vol. 225, no. 5, pp , [2] B. A. Toth and P. Lappert, Modified skin incisions for mastectomy: the need for plastic surgical input in preoperative planning, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,vol.87,no.6,pp , [3] G. W. Carlson, Skin sparing mastectomy: anatomic and technical considerations, American Surgeon,vol.62,no.2,pp , [4] J. Shen, J. Ellenhorn, D. Qian, D. Kulber, and J. Aronowitz, Skin-sparing mastectomy: a survey based approach to defining standard of care, American Surgeon, vol. 74, no. 10, pp , [5] S. S. Kroll, A. Khoo, S. Eva et al., Local recurrence risk after skin-sparing and conventional mastectomy: a 6-year followup, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 104, no. 2, pp , [6]S.Lanitis,P.P.Tekkis,G.Sgourakis,N.Dimopoulos,R.Al Mufti, and D. J. Hadjiminas, Comparison of skin-sparing mastectomy versus non-skin-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies, Annals of Surgery, vol. 251, no. 4, pp , [7] L. A. Newman, H. M. Kuerer, K. K. Hunt et al., Presentation, treatment, and outcome of local recurrence after skin- sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction, Annals of Surgical Oncology, vol. 5, no. 7, pp , [8] R. M. Simmons, S. K. Fish, L. Gayle et al., Local and distant recurrence rates in skin-sparing mastectomies compared with non-skin-sparing mastectomies, Annals of Surgical Oncology, vol. 6, no. 7, pp , [9] R. J. Bleicher, N. M. Hansen, and A. E. Giuliano, Skin-sparing mastectomy. specialty bias and worldwide lack of consensus, Cancer, vol. 98, no. 11, pp , [10] W. J. Sotheran and R. M. Rainsbury, Skin-sparing mastectomy in the UK a review of current practice, Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England, vol. 86, no. 2, pp , [11] A. Cooper, On the Anatomy of the Breast, Longmans, London, UK, [12] H. Skiles, Contributions to the surgical anatomy of the breast, Edinburgh Medical Journal, vol. 37, p. 1099, [13] G. M. Beer, Z. Varga, S. Budi, B. Seifert, and V. E. Meyer, Incidence of the superficial fascia and its relevance in skinsparing mastectomy, Cancer, vol. 94, no. 6, pp , 2002.
7 International Surgical Oncology 7 [14] R. Z. Torresan, C. C. D. Santos, H. Okamura, and M. Alvarenga, Evaluation of residual glandular tissue after skinsparing mastectomies, Annals of Surgical Oncology, vol. 12, no. 12, pp , [15] N. F. Hicken, Mastectomy: a clinical pathologic study demonstrating why most mastectomies result in incomplete removal of the mammary gland, Archives of Surgery, vol. 40, pp. 6 14, [16] T. E. Lockwood, Superficial fascial system (SFS) of the trunk and extremities: a new concept, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 87, no. 6, pp , [17] D. Garnier, R. Angonin, P. Foulon, J. P. Chavoin, B. Ricbourg, and M. Costagliola, Le sillon sous-mammaire: mythe ou re alite? Annales de Chirurgie Plastique et Esthetique, vol. 36, no. 4, pp , [18] C. D. Haagenson, Disease of the Breast, W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, Pa, USA, 2nd edition, [19]G.W.Carlson,N.Grossl,M.M.Lewis,J.R.Temple,andT. M. Styblo, Preservation of the inframammary fold: what are we leaving behind? Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 98, no. 3, pp , [20] B. A. Toth and S. P. Daane, Purse-string mastectomy with immediate prosthetic reconstruction: an improved skinsparing technique for small breasts, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 111, no. 7, pp , [21] P. J. Skoll and D. A. Hudson, Skin-sparing mastectomy using a modified wise pattern, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 110, no. 1, pp , [22] J. Bostwick, Total mastectomy with breast skin and volume reduction using an inverted T incision, in Plastic and Reconstructive Breast Surgery, pp , Quality Medical Publishing, St. Louis, Mo, USA, [23] A. Shoher, R. Hekier, and A. Lucci Jr., Mastectomy performed with scissors following tumescent solution injection, Journal of Surgical Oncology, vol. 83, no. 3, pp , [24] J. B. McCraw, B. Myers, and K. D. Shanklin, The value of fluorescein in predicting the viability of arterialized flaps, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 60, no. 5, pp , [25] M. I. Newman, M. C. Samson, J. F. Tamburrino, and K. A. Swartz, Intraoperative laser-assisted indocyanine green angiography for the evaluation of mastectomy flaps in immediate breast reconstruction, JournalofReconstructive Microsurgery, vol. 26, no. 7, pp , [26] T. J. Meretoja, S. Rasia, K. A. J. Von Smitten, S. L. Asko- Seljavaara, H. O. M. Kuokkanen, and T. A. Jahkola, Late results of skin-sparing mastectomy followed by immediate breast reconstruction, British Surgery, vol. 94, no. 10, pp , [27] S. A. Slavin, S. J. Schnitt, R. B. Duda et al., Skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction: oncologic risks and aesthetic results in patients with early-stage breast cancer, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 102, no. 1, pp , [28] G. W. Carlson, T. M. Styblo, R. H. Lyles et al., The use of skin sparing mastectomy in the treatment of breast cancer: the Emory experience, Surgical Oncology, vol. 12, no. 4, pp , [29] Y. S. Chun, K. Verma, H. Rosen et al., Use of tumescent mastectomy technique as a risk factor for native breast skin flap necrosis following immediate breast reconstruction, American Surgery, vol. 201, no. 2, pp , [30] K. Davies, L. Allan, P. Roblin, D. Ross, and J. Farhadi, Factors affecting post-operative complications following skin sparing mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction, Breast, vol. 20, no. 1, pp , [31] C. S. Hultman, S. Daiza, and L. T. Furlow, Skin-sparing mastectomy flap complications after breast reconstruction: review of incidence, management, and outcome, Annals of Plastic Surgery, vol. 50, no. 3, pp , [32] A.K.Antony,B.M.Mehrara,C.M.McCarthyetal., Salvage of tissue expander in the setting of mastectomy flap necrosis: a 13-year experience using timed excision with continued expansion, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 124, no. 2, pp , [33] D. C. Hammond, P. A. Capraro, E. B. Ozolins, and J. F. Arnold, Use of a skin-sparing reduction pattern to create a combination skin-muscle flap pocket in immediate breast reconstruction, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 110, no. 1, pp , [34] M. B. Nava, U. Cortinovis, J. Ottolenghi et al., Skin-reducing mastectomy, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 118, no. 3, pp , [35] C. A. Derderian, N. S. Karp, and M. Choi, Wise-pattern breast reconstruction: modification using alloderm and a vascularized dermal-subcutaneous pedicle, Annals of Plastic Surgery, vol. 62, no. 5, pp , [36] A. Losken, B. Collins, and G. W. Carlson, Dual plane prosthetic reconstruction using the modified wise pattern mastectomy and fasciocutaneous flap in women with macromastia, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, vol. 126, no. 3, pp , 2010.
8 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery. Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University
 Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Breast Reconstruction Options
 Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Skin Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 14, No. 4, December: 259-266, 2002 Skin Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction OMAYA NASSAR, M.D. The Department of Surgical Oncology, National
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 14, No. 4, December: 259-266, 2002 Skin Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction OMAYA NASSAR, M.D. The Department of Surgical Oncology, National
Skin sparing mastectomy: Technique and suggested methods of reconstruction
 Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2014) 26, 153 159 Cairo University Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute www.nci.cu.adu.eg www.sciencedirect.com Full Length Article Skin
Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2014) 26, 153 159 Cairo University Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute www.nci.cu.adu.eg www.sciencedirect.com Full Length Article Skin
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy. Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD
 How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
Modified Radical Mastectomy
 Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Circumareolar Mastopexy
 Circumareolar Mastopexy and Moderate Reduction drien iache n mastopexy the problems created by the doughnut-type excision and scarring are relatively minimal, because the breast tissue is not excised and
Circumareolar Mastopexy and Moderate Reduction drien iache n mastopexy the problems created by the doughnut-type excision and scarring are relatively minimal, because the breast tissue is not excised and
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction
 Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative
 Il trattamento delle complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative Dr. Christian Rizzetto UOC Chirurgia Senologica - Breast
Il trattamento delle complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative Dr. Christian Rizzetto UOC Chirurgia Senologica - Breast
Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities
 Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander.
 Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts. Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA
 The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
Superior Pedicle Vertical Scar Mammaplasty: Surgical Technique
 Superior Pedicle Vertical Scar Mammaplasty: Surgical Technique 4 Foad Nahai A man honours himself by not displaying all the knowledge he has acquired. Folk Tradition Introduction I first tried the vertical
Superior Pedicle Vertical Scar Mammaplasty: Surgical Technique 4 Foad Nahai A man honours himself by not displaying all the knowledge he has acquired. Folk Tradition Introduction I first tried the vertical
AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
Clinical Study Breast-Volume Displacement Using an Extended Glandular Flap for Small Dense Breasts
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 359842, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2011/359842 Clinical Study Breast-Volume Displacement Using an Extended Glandular Flap for Small Dense Breasts Tomoko Ogawa,
Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 359842, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2011/359842 Clinical Study Breast-Volume Displacement Using an Extended Glandular Flap for Small Dense Breasts Tomoko Ogawa,
Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate surgical options
 A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
Mitchell Buller, MEng, a Adee Heiman, BA, a Jared Davis, MD, b ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Nicolás Ajkay, MD, FACS, c and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD, FACS b
 Immediate Breast Reconstruction of a Nipple Areolar Lumpectomy Defect With the L-Flap Skin Paddle Breast Reduction Design and Contralateral Reduction Mammoplasty Symmetry Procedure: Optimizing the Oncoplastic
Immediate Breast Reconstruction of a Nipple Areolar Lumpectomy Defect With the L-Flap Skin Paddle Breast Reduction Design and Contralateral Reduction Mammoplasty Symmetry Procedure: Optimizing the Oncoplastic
PRINCIPLES OF BREAST SURGERY & COMPLICATIONS
 PRINCIPLES OF BREAST SURGERY & COMPLICATIONS Adam Cichowitz The Royal Melbourne Hospital ANATOMY Lies in subcutaneous tissue Base: midline to midaxillary line, 2nd to 6th rib Overlies pec major, serratus
PRINCIPLES OF BREAST SURGERY & COMPLICATIONS Adam Cichowitz The Royal Melbourne Hospital ANATOMY Lies in subcutaneous tissue Base: midline to midaxillary line, 2nd to 6th rib Overlies pec major, serratus
Kentaro Tanaka, 1 Hiroki Mori, 1 Mutsumi Okazaki, 1 Aya Nishizawa, 2 and Hiroo Yokozeki Introduction. 2. Case Presentation
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 259326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/259326 Case Report Long-Term Treatment Outcome after Only Popliteal Lymph Node Dissection for
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 259326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/259326 Case Report Long-Term Treatment Outcome after Only Popliteal Lymph Node Dissection for
ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY. Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services. Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow
 Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
Tor Chiu. Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161
 18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
Case Study. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis.
 Case Study TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication Challenge Insulin-dependent diabetes
Case Study TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication Challenge Insulin-dependent diabetes
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer
 Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
A Combined Practice. Why Its Worked. Barriers to Breast Reconstruction. As a breast oncologist the patient gets seemless care
 A Combined Practice A Combined Breast Oncology and Plastic Surgery Practice Why It Works Anne M. Wallace, MD, FACS Director, Comprehensive Breast Health Center Professor of Clinical Surgery, Surgical Oncology
A Combined Practice A Combined Breast Oncology and Plastic Surgery Practice Why It Works Anne M. Wallace, MD, FACS Director, Comprehensive Breast Health Center Professor of Clinical Surgery, Surgical Oncology
Clinical Study Retrospective Comparison of Non-Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Skin-Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate Breast Reconstruction
 International Surgical Oncology Volume 2011, Article ID 876520, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2011/876520 Clinical Study Retrospective Comparison of Non-Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Skin-Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate
International Surgical Oncology Volume 2011, Article ID 876520, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2011/876520 Clinical Study Retrospective Comparison of Non-Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Skin-Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate
BREAST CANCER SURGERY. Dr. John H. Donohue
 Dr. John H. Donohue HISTORY References to breast surgery in ancient Egypt (ca 3000 BCE) Mastectomy described in numerous medieval texts Petit formulated organized approach in 18 th Century Improvements
Dr. John H. Donohue HISTORY References to breast surgery in ancient Egypt (ca 3000 BCE) Mastectomy described in numerous medieval texts Petit formulated organized approach in 18 th Century Improvements
Breast Reconstruction Surgery
 Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap
 Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
The decision to repair a partial mastectomy CME. State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction.
 CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction
 Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix used in the repair of rippling
 Clinical case study Strattice Tissue Matrix Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix used in the repair of rippling Steven Teitelbaum, MD* Santa Monica, CA Case summary A 48-year-old woman with a history
Clinical case study Strattice Tissue Matrix Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix used in the repair of rippling Steven Teitelbaum, MD* Santa Monica, CA Case summary A 48-year-old woman with a history
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
The Use of Vertical Scar Techniques in Reconstructive Surgery
 The Use of Vertical Scar Techniques in Reconstructive Surgery 12 Moustapha Hamdi, Phillip Blondeel, Koenraad Van Landuyt, Stan Monstrey H e who does not possess a thing cannot give it. Folk tradition Introduction
The Use of Vertical Scar Techniques in Reconstructive Surgery 12 Moustapha Hamdi, Phillip Blondeel, Koenraad Van Landuyt, Stan Monstrey H e who does not possess a thing cannot give it. Folk tradition Introduction
ONCOLOGIC AND COSMETIC CHALLENGES DO NOT ROUTINELY OPPOSE BREAST CONSERVING SURGERY IN RETRO-AREOLA PRIMARY LESIONS
 ONCOLOGIC AND COSMETIC CHALLENGES DO NOT ROUTINELY OPPOSE BREAST CONSERVING SURGERY IN RETRO-AREOLA PRIMARY LESIONS SURGERY SYMPOSIUM Ines Buccimazza Breast Unit Department of Surgery Nelson R. Mandela
ONCOLOGIC AND COSMETIC CHALLENGES DO NOT ROUTINELY OPPOSE BREAST CONSERVING SURGERY IN RETRO-AREOLA PRIMARY LESIONS SURGERY SYMPOSIUM Ines Buccimazza Breast Unit Department of Surgery Nelson R. Mandela
International Journal of Surgery
 International Journal of Surgery xxx (2010) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Experience with the Wise mammaplasty skin resection
International Journal of Surgery xxx (2010) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Experience with the Wise mammaplasty skin resection
Pocket Conversion Made Easy: A Simple Technique Using Alloderm to Convert Subglandular Breast Implants to the Dual-Plane Position
 Breast Surgery Pocket Conversion Made Easy: A Simple Technique Using Alloderm to Convert Subglandular Breast Implants to the Dual-Plane Position M. Mark Mofid, MD; and Navin K. Singh, MD Background: The
Breast Surgery Pocket Conversion Made Easy: A Simple Technique Using Alloderm to Convert Subglandular Breast Implants to the Dual-Plane Position M. Mark Mofid, MD; and Navin K. Singh, MD Background: The
The evolution of mastectomies in the oncoplastic breast surgery era
 Perspective The evolution of mastectomies in the oncoplastic breast surgery era Gustavo Zucca-Matthes 1,2, Andrea Manconi 3, Rene Aloísio da Costa Viera 1,2, Rodrigo Augusto Depieri Michelli 2, Angelo
Perspective The evolution of mastectomies in the oncoplastic breast surgery era Gustavo Zucca-Matthes 1,2, Andrea Manconi 3, Rene Aloísio da Costa Viera 1,2, Rodrigo Augusto Depieri Michelli 2, Angelo
Augmentation of the Ptotic Breast: Simultaneous Periareolar Mastopexy/Breast Augmentation By: Laurence Kirwan, M.D., F.R.C.S
 Augmentation of the Ptotic Breast: Simultaneous Periareolar Mastopexy/Breast Augmentation By: Laurence Kirwan, M.D., F.R.C.S Background: Submusculofascial augmentation of the ptotic breast can result in
Augmentation of the Ptotic Breast: Simultaneous Periareolar Mastopexy/Breast Augmentation By: Laurence Kirwan, M.D., F.R.C.S Background: Submusculofascial augmentation of the ptotic breast can result in
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications
 Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
NIPPLE SPARING MASTECTOMY
 NIPPLE SPARING MASTECTOMY 29th Annual Montefiore-Einstein Controversies in Surgery Symposium Virgilio Sacchini, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Professor of Clinical Surgery Weill Cornell Medical
NIPPLE SPARING MASTECTOMY 29th Annual Montefiore-Einstein Controversies in Surgery Symposium Virgilio Sacchini, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Professor of Clinical Surgery Weill Cornell Medical
NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 42 yo female healthy athlete Right breast mass. Past medical history: none Family history: aunt with Breast cancer Candidates for nipple-sparing mastectomy
NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 42 yo female healthy athlete Right breast mass. Past medical history: none Family history: aunt with Breast cancer Candidates for nipple-sparing mastectomy
Aesthetic Subunits of the Breast
 Aesthetic Subunits of the Breast Scott L. Spear, M.D., and Steven P. Davison, D.D.S., M.D. Washington, D.C. Surgery for breast cancer has traditionally addressed the breast as if it were a geometric circle
Aesthetic Subunits of the Breast Scott L. Spear, M.D., and Steven P. Davison, D.D.S., M.D. Washington, D.C. Surgery for breast cancer has traditionally addressed the breast as if it were a geometric circle
Vertical mammaplasty has been developed
 BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
Extending breast conservation and other new oncoplastic techniques
 Extending breast conservation and other new oncoplastic techniques Dick Rainsbury BSBR 11-12 November 2013 Liverpool What s the maximum volume of the breast which can be resected during lumpectomy without
Extending breast conservation and other new oncoplastic techniques Dick Rainsbury BSBR 11-12 November 2013 Liverpool What s the maximum volume of the breast which can be resected during lumpectomy without
Alireza Bakhshaeekia and Sina Ghiasi-hafezi. 1. Introduction. 2. Patients and Methods
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 0, Article ID 4578, 4 pages doi:0.55/0/4578 Clinical Study Comparing the Alteration of Nasal Tip Sensibility and Sensory Recovery Time following Open Rhinoplasty with
Plastic Surgery International Volume 0, Article ID 4578, 4 pages doi:0.55/0/4578 Clinical Study Comparing the Alteration of Nasal Tip Sensibility and Sensory Recovery Time following Open Rhinoplasty with
Breast Reduction By Dr. Tarek Ahmed Said Professor of Plastic Surgery Cairo University 2017
 Breast Reduction By Dr. Tarek Ahmed Said Professor of Plastic Surgery Cairo University 2017 Reduction Mammaplasty SAFE Good Size Reduction Minimal Scar Aesthetic & Long Lasting Breast Shape Reduction Mammaplasty
Breast Reduction By Dr. Tarek Ahmed Said Professor of Plastic Surgery Cairo University 2017 Reduction Mammaplasty SAFE Good Size Reduction Minimal Scar Aesthetic & Long Lasting Breast Shape Reduction Mammaplasty
Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 421245, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/421245 Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor Akira Sugamata, 1 Naoki Yoshizawa,
Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 421245, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/421245 Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor Akira Sugamata, 1 Naoki Yoshizawa,
Incorporating Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy Into Your Practice. Michael Howard, MD, FACS Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS
 Incorporating Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy Into Your Practice Michael Howard, MD, FACS Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS 1 Disclosures Michael Howard, MD Scientific Advisor, EO2 Concepts Karol Gutowski, MD Speaker's
Incorporating Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy Into Your Practice Michael Howard, MD, FACS Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS 1 Disclosures Michael Howard, MD Scientific Advisor, EO2 Concepts Karol Gutowski, MD Speaker's
Breast Surgery: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
 Breast Surgery: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow Baptist Hospital Gladys L. Giron, MD, FACS October 11,2014 Homestead Hospital Baptist Children s Hospital Doctors Hospital Baptist Cardiac & Vascular Institute
Breast Surgery: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow Baptist Hospital Gladys L. Giron, MD, FACS October 11,2014 Homestead Hospital Baptist Children s Hospital Doctors Hospital Baptist Cardiac & Vascular Institute
Breast Reconstruction. Westmead Breast Cancer Institute
 Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: Page 1 of 8
 Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Chest Wall Tumors and Reconstruction: Lateral Chest Wall. Dr. Robert Kelly
 Chest Wall Tumors and Reconstruction: Lateral Chest Wall Dr. Robert Kelly THORACIC PROGRAMME: ADVANCES IN CHEST WALL SURGERY AND OSTEOSYNTHESIS Dr. José Ribas Milanez de Campos Assistant, Professor, Department
Chest Wall Tumors and Reconstruction: Lateral Chest Wall Dr. Robert Kelly THORACIC PROGRAMME: ADVANCES IN CHEST WALL SURGERY AND OSTEOSYNTHESIS Dr. José Ribas Milanez de Campos Assistant, Professor, Department
In a second stage or a second operation that tissue expander is removed through the same incision and the implant is placed within the chest pocket.
 Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Review Article Oncoplastic Approaches to Breast Conservation
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Journal of Breast Cancer Volume 2011, Article ID 303879, 16 pages doi:10.4061/2011/303879 Review Article Oncoplastic Approaches to Breast Conservation Dennis
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Journal of Breast Cancer Volume 2011, Article ID 303879, 16 pages doi:10.4061/2011/303879 Review Article Oncoplastic Approaches to Breast Conservation Dennis
Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
Figure 1. Anatomy of the breast
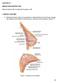 CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop
 Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:333 340 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9612-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop André Auersvald Luiz Augusto Auersvald Received: 28 April
Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:333 340 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9612-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop André Auersvald Luiz Augusto Auersvald Received: 28 April
Despite breast reduction being one of the BREAST. Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction?
 BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
-primarily by apposition of the anterior rectus
 2 Component separation Cop HARVEY CHIM, KAREN KIM EVANS, AND SAMIR MARDINI Mater al Introduction 7 Preoperative markings 7 Intraoperative details 9 Technique modification: Component separation with preservation
2 Component separation Cop HARVEY CHIM, KAREN KIM EVANS, AND SAMIR MARDINI Mater al Introduction 7 Preoperative markings 7 Intraoperative details 9 Technique modification: Component separation with preservation
Chapter 1 SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE BREAST
 Chapter 1 SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE BREAST Mahmoud El-Tamer and Sunny Mitchell Breast Service, Department of Surgery, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065, USA Women s Breast Center,
Chapter 1 SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE BREAST Mahmoud El-Tamer and Sunny Mitchell Breast Service, Department of Surgery, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065, USA Women s Breast Center,
Exercise & Breast Cancer Recovery
 Exercise & Breast Cancer Recovery LEARNING OBJECTIVES Demonstrate an understanding of the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer Demonstrate an understanding of how breast cancer surgery and treatment
Exercise & Breast Cancer Recovery LEARNING OBJECTIVES Demonstrate an understanding of the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer Demonstrate an understanding of how breast cancer surgery and treatment
SINGLE-STAGE BREAST RECONSTRUCTION WITH WISE PATTERN AND INFERIOR AUTODERM FLAP FOR MAMMARY HYPERTROPHY
 Volume 4 Number 1 PLSTI SURGRY Pulse News 35 SINGL-STG RST RONSTRUTION WITH WIS PTTRN N INRIOR UTORM LP OR MMMRY HYPRTROPHY Jaime S. Schwartz, M reast reconstruction with prosthetic devices has become
Volume 4 Number 1 PLSTI SURGRY Pulse News 35 SINGL-STG RST RONSTRUTION WITH WIS PTTRN N INRIOR UTORM LP OR MMMRY HYPRTROPHY Jaime S. Schwartz, M reast reconstruction with prosthetic devices has become
Updates in Breast Care. Truth or Hype. History of Breast Cancer Surgery. Dr Karen Barbosa 5/3/2017 4/20/2017
 Updates in Breast Care Dr Karen Barbosa 4/20/2017 Truth or Hype Princess Bust Developer Sears, Roebuck and Co. 1897 Promised to make the breast round, firm and beautiful History of Breast Cancer Surgery
Updates in Breast Care Dr Karen Barbosa 4/20/2017 Truth or Hype Princess Bust Developer Sears, Roebuck and Co. 1897 Promised to make the breast round, firm and beautiful History of Breast Cancer Surgery
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine. Breast. Dr. Ahmed Salman. Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology
 Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Breast Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The breasts are specialized accessory glands of the skin that secretes milk. They are situated
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Breast Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The breasts are specialized accessory glands of the skin that secretes milk. They are situated
Techniques for Reduction of Larger Breasts
 Techniques for Reduction of Larger Breasts Tolbert S. Wilkinson s discussed earlier, circumareolar surgery was initially performed only for smaller mastopexies; in time its use gradually expanded to include
Techniques for Reduction of Larger Breasts Tolbert S. Wilkinson s discussed earlier, circumareolar surgery was initially performed only for smaller mastopexies; in time its use gradually expanded to include
The progress in microsurgical procedures has led
 Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Breast Reconstruction
 Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Alexander C Vlantis. Total Laryngectomy 57
 07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
INNOVATIVE RECONSTRUCTIVE STRATEGIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY
 INNOVATIVE RECONSTRUCTIVE STRATEGIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY Jane L. Kakkis, MD, MPH Breast Surgeon, Director Orange Coast Memorial Medical Center, Fountain Valley, CA USA WHEN RADIATION IS NECESSARY
INNOVATIVE RECONSTRUCTIVE STRATEGIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY Jane L. Kakkis, MD, MPH Breast Surgeon, Director Orange Coast Memorial Medical Center, Fountain Valley, CA USA WHEN RADIATION IS NECESSARY
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps
 Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
The vertical reduction mammaplasty was first
 Special Topic Technical Refinements of the Vertical Mammaplasty: A Modified Lejour Approach Steven G. Wallach, MD Dr. Wallach is Assistant Clinical Professor of Plastic Surgery, Albert Einstein College
Special Topic Technical Refinements of the Vertical Mammaplasty: A Modified Lejour Approach Steven G. Wallach, MD Dr. Wallach is Assistant Clinical Professor of Plastic Surgery, Albert Einstein College
Breast Cancer Reconstruction
 Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Aesthetic surgery techniques after excision of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a case report
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 556 560 CASE REPORT Aesthetic surgery techniques after excision of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a case report G. Dagregorio a, *, V. Darsonval b a Department
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 556 560 CASE REPORT Aesthetic surgery techniques after excision of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a case report G. Dagregorio a, *, V. Darsonval b a Department
Journal of Breast Cancer
 CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2013 June; 16(2): 236-243 bdominal dvancement Flap as Oncoplastic reast Conservation: Report of Seven Cases and Their Cosmetic Results Tomoko Ogawa, Noriko
CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2013 June; 16(2): 236-243 bdominal dvancement Flap as Oncoplastic reast Conservation: Report of Seven Cases and Their Cosmetic Results Tomoko Ogawa, Noriko
The Effect of Acellular Dermal Matrix in Implant-Based Immediate Breast Reconstruction with Latissimus Dorsi Flap
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.14730/.2017.23.1.17 Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg 2017;23(1):17-23 pissn: 2234-0831 eissn: 2288-9337 The Effect Acellular Dermal Matrix in Implant-Based Immediate Breast
ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.14730/.2017.23.1.17 Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg 2017;23(1):17-23 pissn: 2234-0831 eissn: 2288-9337 The Effect Acellular Dermal Matrix in Implant-Based Immediate Breast
Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps
 BREAST SURGERY Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps Albert Losken, MD, FACS, Claire S. Nicholas, MD, Ximena A. inell, MD, and Grant W.
BREAST SURGERY Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps Albert Losken, MD, FACS, Claire S. Nicholas, MD, Ximena A. inell, MD, and Grant W.
Treatment of Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Implant-Based Reconstruction with a Vascularized Dermal Sling
 Treatment of Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Implant-Based Reconstruction with a Vascularized Dermal Sling Idea and Innovation Bok Ki Jung 1, Ji Hae Nahm 2, Dae Hyun Lew 1, Dong Won
Treatment of Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Implant-Based Reconstruction with a Vascularized Dermal Sling Idea and Innovation Bok Ki Jung 1, Ji Hae Nahm 2, Dae Hyun Lew 1, Dong Won
Allograft Based Breast Reconstruction: Opportunity for a Second Look
 Allograft Based Breast Reconstruction: Opportunity for a Second Look Martin I. Newman, MD, FACS Director of Resident Education and Associate Program Director Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Allograft Based Breast Reconstruction: Opportunity for a Second Look Martin I. Newman, MD, FACS Director of Resident Education and Associate Program Director Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
PUBLISHED VERSION.
 PUBLISHED VERSION Shay Keren, Gad Dotan, Leah Leibovitch, Dinesh Selva, and Igal Leibovitch Indocyanine green assisted removal of orbital lacrimal duct cysts in children Ophthalmology, 2015; 2015:130215-1-130215-5
PUBLISHED VERSION Shay Keren, Gad Dotan, Leah Leibovitch, Dinesh Selva, and Igal Leibovitch Indocyanine green assisted removal of orbital lacrimal duct cysts in children Ophthalmology, 2015; 2015:130215-1-130215-5
Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 129632, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/129632 Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 129632, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/129632 Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
National Mastectomy & Breast Reconstruction Audit Datasheet - Mastectomy +/- Immediate Reconstruction
 Patient Registration data Surname Forename NHS/Private Hospital Number Date of birth Postcode Ethnicity Patient-reported outcomes consent Has this patient consented to being sent outcome questionnaires?
Patient Registration data Surname Forename NHS/Private Hospital Number Date of birth Postcode Ethnicity Patient-reported outcomes consent Has this patient consented to being sent outcome questionnaires?
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy PRE-DETERMINATION
Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy PRE-DETERMINATION
Oncoplastic Breast Surgery
 Disclosures Oncoplastic Breast Surgery Newfoundlander OAGS 2016 Dr Renee Hanrahan General Surgeon Oncologic and Reconstructive Breast Surgeon Objectives What is Oncoplastic Surgery Define Oncoplastic Surgery
Disclosures Oncoplastic Breast Surgery Newfoundlander OAGS 2016 Dr Renee Hanrahan General Surgeon Oncologic and Reconstructive Breast Surgeon Objectives What is Oncoplastic Surgery Define Oncoplastic Surgery
MICHAEL R. ZENN, M.D. INFORMATION ABOUT BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 MICHAEL R. ZENN, M.D. INFORMATION ABOUT BREAST RECONSTRUCTION The purpose of breast reconstruction is to restore body image and to enable you to wear all types of clothes without restriction. Most women
MICHAEL R. ZENN, M.D. INFORMATION ABOUT BREAST RECONSTRUCTION The purpose of breast reconstruction is to restore body image and to enable you to wear all types of clothes without restriction. Most women
Nipple Sparing Mastectomy: Tips & Tricks. Rebecca Nelson, MD MSc FRCSC Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon, Burnaby Hospital
 Nipple Sparing Mastectomy: Tips & Tricks Rebecca Nelson, MD MSc FRCSC Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon, Burnaby Hospital Nipple Sparing Mastectomy (NSM) Introduction & Technique Safety Evidence Indications/Contraindications
Nipple Sparing Mastectomy: Tips & Tricks Rebecca Nelson, MD MSc FRCSC Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon, Burnaby Hospital Nipple Sparing Mastectomy (NSM) Introduction & Technique Safety Evidence Indications/Contraindications
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER
 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER Effective Date: September 2013 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the Alberta Provincial
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER Effective Date: September 2013 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the Alberta Provincial
Technique Guide. A natural product for a natural repair. Post-Mastectomy Breast Reconstruction
 A natural product for a natural repair. Acellular Dermal Matrix Tissue In Conjunction With Soft Tissue Repair Technique Guide Post-Mastectomy Breast Reconstruction This Technique Guide contains the opinions
A natural product for a natural repair. Acellular Dermal Matrix Tissue In Conjunction With Soft Tissue Repair Technique Guide Post-Mastectomy Breast Reconstruction This Technique Guide contains the opinions
