Indium 11 1 autologous leucocyte scanning in lobar
|
|
|
- Aubrey Farmer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thorax 1985;4: Indium 11 1 autologous leucocyte scanning in lobar pneumonia and lung abscesses SETHNA H SAVERYMUTTU, GARETH PHILLIPS, J PETER LAVENDER A MICHAEL PETERS, From the Departments of Medicine and Diagnostic Radiology, Royal Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital, London ABSTRACT Indium 111 leucocyte scanning was used to examine the kinetics of granulocyte localisation in five patients with lobar pneumonia and four patients with lung abscess. Lung abscesses showed dense accumulation of labelled granulocytes within four hours of injection. In contrast, in all cases of lobar pneumonia granulocytes failed to accumulate over a period of up to 24 hours despite evidence of adequate perfusion and of uptake in inflammation elsewhere. These results suggest that the recruitment of granulocytes to lobar pneumonia may be terminated early in its clinical course. Indium I 1 (11 ( In) autologous leucocyte scanning has been extensively used for localisation of intraabdominal abscesses.12 More recently the potential for studying other conditions with an inflammatory component has been developed. For instance, the technique has been used to demonstrate the kinetics of labelled leucocytes in inflamed bowel. After injection ' ' 'In labelled leucocytes migrate to and accumulate in diseased bowel within a matter of minutes, pass into the bowel lumen over the following few hours, and are subsequently excreted over the next four days.36 Address for reprint requests: Dr SHS Saverymuttu, Medicine II, St George's Hospital Medical School, London SW17B. Accepted 24 June 1985 Table 1 Details of the patients Unlike an intra-abdominal abscess, but like bowel, the parenchyma of the lung provides a portal of exit for granulocytes when it is inflamed. This is reflected by the presence of granulocytes in sputum, analogous to faecal granulocytes in inflammatory bowel disease. The aim of this study therefore was to examine the kinetics of granulocyte localisation in lobar pneumonia and in lung abscess to see how far they resembled or differed from the kinetics in inflammatory bowel disease. Method Nine patients were studied, five with lobar pneumonia and four with lung abscess. The clinical details are Patient Age Diagnosis Associated Sputum Sputum White cell Duration (days) before scan (y) condition culture leucocytes count (x 15/l) Treatment Symptoms 1 68 Lung abscess Diabetes Proteus II Lung abscess Renal failure Klebsiella Lung abscess Bronchogenic E coli carcinoma 4 78 Lung abscess - E coli Lobar - Strep Indefinite: vague pneumonia pneumoniae symptoms of malaise 2 weeks 6 6 Lobar - Strep pneumonia pneumoniae 7 8 Lobar - Strep pneumonia pneumoniae 8 71 Lobar Chronic Normal flora Indefinite: vague pneumonia Bronchitis symptoms of malaise 4 weeks 9 16 Lobar Post-operative pneumonia 925 Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 December Downloaded from on 27 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
2 926 Saverymuttu, Phillips, Peters, Lavender Table 2 Radiological features and detection of indium 111 in patients with lung abscess and patients with pneumonia Patient No Radiological site of abscess or pneumonia Time after injection of.. lin granulocytes 4 min 3 h h Abscess I R middle lobe R middle lobe ND R lower and middle lobes L lower lobe ND + + Pneumonia 5 R upper lobe ND R middle lobe 7 R middle lobe 8 R middle lobe L lower lobe R-right; L-left; ND-not done; + indicates radioactivity present and - radioactivity absent. summarised in table 1. Autologous granulocytes were separated and labelled, without removal from plasma, as previously described.7 This method ensures that granulocyte indium Ill activity does not vary with peripheral count and that the artefactual pulmonary leucocyte sequestration seen after labelling in saline is avoided. The administered activity was about 2 pci. Abdominal and chest scans were performed 4 minutes, 3-4 hours, and 24 hours after return of the labelled granulocytes and compared with radiological findings. In some patients dynamic gamma camera imaging was performed over the lung fields immediately after injection. Time-activity curves based on symmetrical and similar sized regions of interest over normal and affected lung were constructed with a computer (MDS A2) on line to the gamma camera. Results The scanning and radiological findings are summarised in table 2. In the four patients with lung abscesses, who were studied one to 12 days after continuous treatment with antibiotics, the chest radiograph showed evidence of cavitation (fig 1). Early scans were performed 4 minutes after return of the labelled granulocytes in two of the four patients. In one a focal area of increased activity corresponding to the site of the abscess was seen, while in the other the scan was normal. In all four patients later scans three to four hours and 24 hours after the return of the cells, were clearly positive over the abscess site (fig 2). Abdominal scans at 24 hours showed activity in the large bowel in three of the four, representing swallowed labelled granulocytes. Three of the four Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 December Downloaded from Fig 1 (a) Patient 2: Anteroposterior and (b) lateral chest radiographs showed a multiloculated abscess in the right lower lobe. on 27 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
3 Indiuhn 111 autologous leucocyte scanning in lobar pneumonia and lung abscesses (I)..X t t, t 4.Q abscesses resolved with antibiotic treatment; the remaining patient died but necropsy was not performed. No repeat studies were performed. All five cases of lobar pneumonia showed characteristic radiological changes (fig 3). Streptococcus pneumoniae was the cause in three patients. No Abscess2 (I) Fig 2 (a) White cell scan of the chest and upper abdomen ofpatient 2 showing focal uptake corresponding to the right lower lobe abscess. Other areas offocal uptake correspond to the spleen and subclavian lines respectively. Only faint activity is seen in the liver. (b) Diagram of white cell scan. organism was isolated in the other two. The patients were studied one to 13 days after the start of antibiotic treatment, when all except one had leucocytes in the sputum. Scans were negative at the site of the pneumonia in all five cases at all times (fig 4). Furthermore, apart from splenic uptake and uptake in an infected (ael (b) Fig 3 (a) Posteroanterior and (b) lateral chest radio-graphs ofpatient 5 showing consolidation in the right upper lobe. r 927 Subclavialn Line Spleeni Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 December Downloaded from on 27 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
4 928 Fig 4 (a) White cell scan of the thorax ofpatient 5 showing uptake of indium 111 in spleen, liver, and bone marrow but no focal pulmonary uptake. (b) Diagram of white cell scan. surgical wound in case 9, no abdominal activity was seen. All five patients showed progressive radiological clearance from the time of scanning. In patient 9 the pneumonia developed six days post operatively. This patient had been on routine perioperative antibiotics during that period and this might explain the failure to detect an organism. There was no evidence to suggest an alternative explanation for the consolidation and the patient's condition improved with antibiotics and physiotherapy alone. On dynamic imaging in the two patients with abscess, the time-activity curves recorded over the x L. = 45 (6-) C: m 3 15 Saverymuttu, Phillips, Peters, Lavender * Normal lung o ~~~~~~ ~~~~~ - I I I time from injection (min) Fig 5 Time-activity curves recorded by dynamic gamma camera imaging anteriorly over the chest after injection of granulocytes labelled with indium 111 in a patient with a lung abscess. Open circles-region over affected lung; closed circles-similar sized symmetrical region over unaffected opposite lung. The ordinate indicates the count rate per computer matrix point normalised to the maximum count rate recorded over unaffected lung. abscess regions were similar in shape to those recorded over unaffected lung up to about 2 minutes after injection of granulocytes labelled with indium 1 11, although the count rate per pixel was less over the abscess (with abnormal:normal ratios one minute after injection of.59 and.32). From 2 minutes, however, the count rate over the abscess increased (fig 5). In the three patients with pneumonia who underwent dynamic imaging the initial count rate per pixel was again less over the affected region (with abnormal:normal ratios at one minute of.71,.7 and.66) (fig 6). In contrast to the findings in lung abscess, however, the count rate over consolidated lung showed no subsequent tendency to increase in relation to the normal region. Discussion The finding that "'1In labelled granulocytes fail to Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 December Downloaded from on 27 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
5 Indium III autologous leucocyte scanning in lobar pneumonia and lung abscesses Secondly, there may be appreciable impairment of perfusion, thereby limiting vascular access. Results of. ventilation-perfusion scanning suggest, however, 6 - that there is adequate, though reduced, perfusion of * Normal lung. o Pneumonia 1) x L- a) CL co O o *. I time from injection (min) Fig 6 Time-activity curves recorded by dynamic gamma camera imaging anteriorly over the chest after injection of granulocytes labelled with indium 111 in a patient with lobar pneumonia. Open circles-region over affected lung; closed circles-similar sized symmetric region over unaffected opposite lung. The ordinate indicates the count rate per computer matrix point normalised to the maximum count rate recorded over unaffected lung. Discussion The finding that "'In labelled granulocytes fail to localise in lobar pneumonia is surprising particularly in view of the accumulating reports of the effectiveness of this technique in widely varying conditions. In addition to the well known uptake in abscess, recent studies have demonstrated visualisation by "'In leucocyte scanning of ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease,34 ischaemic bowel,8 osteomyelitis,9 pancreatitis, 1 prosthetic vascular graft infection,"1 and a renal transplant undergoing rejection.'2 The number of false negative scans is very low in all such inflammatory lesions, suggesting that there is almost always migration of cells from the circulating pool. Several explanations of our negative scans in lobar pneumonia are possible. Firstly, the cells may be damaged during the separation and labelling procedure. The technique used here, however, been shown to result consistently in normal granulocyte biodistribution and rapid accumulation in septic foci.513 Furthermore, in postoperative lobar pneumonia (case 9), the infected abdominal wound site was visualised, indicating normal migration to that focus. I consolidated lobes.14 Furthermore, the immediate signals from "'In labelled granulocyte achieved with dynamic imaging indicated that, although inflow was reduced in the affected regions, it was clearly not decreased sufficiently to produce any appreciable reduction in vascular access, and indeed not reduced to any greater extent than inflow into the abscess. Thirdly, although all patients with lobar pneumonia were receiving antibiotic treatment, previous studies have shown that this does not prevent localisation of "'In labelled granulocytes in inflammatory sites.12 Indeed, all of the patients with lung abscess were scanned while receiving antibiotic treatment. A further possible explanation for these negative scans in lobar pneumonia is that recruitment of fresh leucocytes might have ceased before the injection of labelled granulocytes and that, whatever the intravescular kinetics of granulocytes, there was no extravascular granulocyte migration after this time. The presence of sputum leucocytes at the time of scanning is difficult to reconcile with this, in view of the short intravascular half life of granulocytes approximately about seven hours, and suggests that granulocytes have a considerable postmigration life span and that they are capable of remaining viable in lung parenchyma for some time. Evidence to support this implication has been lacking until recently, when Bueshcer et al'5 were able to study granulocyte life span in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease receiving leucocyte transfusions for a chest infection. They showed that granulocytes were present in sputum for at least 42 hours after their disappearance from the blood. This suggests that granulocytes can be present in sputum for an appreciable time after the termination of granulocyte recruitment into an infective chest lesion. We suggest that this last explanation is the most likely. Unlike other inflammatory conditions studied with "'In granulocytes, in lobar pneumonia there is no breakdown of tissue architecture and it is possible that the alveolar air spaces become filled with exudate soon after the onset of infection, so that further granulocytes are unable to gain access and recruitment ceases. The mechanism of cessation of recruitment could be mechanical but seems more likely to be due to biological factors. Uptake of "'In granulocytes into lobar pneumonia has been recorded in the dog within 24 hours of its induction. '6 This stage of active granulocyte recruitment was probably completed in our cases before imaging. Indeed, in at least two patients with white cells were injected within 48 hours of-- t-he onset of pneumonia, suggesting that Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 December Downloaded from on 27 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
6 93 recruitment is terminated before this. Such a limited period of recruitment in lobar pneumonia may be contrasted with lung abscess, in which granulocyte migration into the septic focus continues pari passu with tissue destruction. We are grateful to Miss Sally Barnes for typing this manuscript and to Miss Belinda Henderson and Miss Penny George for technical assistance. References 1 McDougall I, Baumert J, Lantieri R. Evaluation of 111-indium leucocyte whole body scanning. AJR 1979;133: Coleman R, Black R, Welch D, Maxwell G. Indium labelled leucocytes in the evaluation of suspected abdominal abscesses Am J Surg 198;139: Segal A, Munro J, Ensell J, Sarner M. Indium-111- tagged leucocytes in the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet 1981;i: Saverymuttu SH, Peters AM, Lavender JP, Hodgson HJF, Chadwick VS. 111-Indium autologous leucocytes in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 1983;24: Saverymuttu SH, Peters AM, Reavy HJ, Lavender JP. Measurement of granulocyte migration and accumulation in inflammation in man. Clin Exp Immunol 1983;52: Saverymuttu SH, Peters AM, Lavender JP, Pepys MB, Hodgson HJF, Chadwick VS. Quantitative faecal 111-indium labelled leukocyte excretion in the assess- Saverymuttu, Phillips, Peters, Lavender ment of disease activity in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 1983;85: Saverymuttu SH, Peters AM, Reavy HJ, Danpure HJ, Osman S, Lavender JP. Lung transit of 111-indium labelled granulocytes-relationship to labelling techniques. Scand J Haemtol 1983;3: Gray HW, Cuthbert I, Richards JR. Clinical imaging with I I I-indium-leucocytes. Uptake in bowel infarction. J Nuci Med 1981;22: Raptopolous V, Doherty PW, Goss TP, et al. Acute osteomyelitis. Advantages of white cell scans in early detection. AJR 1982;139: Anderson JR, Spence RAJ, Laird JD, Ferguson WR, Kennedy TL. Initial experience with indium-l1lautologous leucocyte imaging in patients with acute pancreatitis. Br Med J 1983;287: Wilson DG, Seabold JE, Lieberman LM. Detection of aorto arterial graft infections by leukocyte scintigraphy. Clin Nucl Med 1983;8: Forstrom LA, Loken MK, Cook A, et al. Indiumlabelled leukocytes in the diagnosis of rejection and cystomeyelovirus infection in renal transplant patients. Clin Nucl Med 1981;6: Peters AM, Saverymuttu SH, Reavy HJ, Danpure HJ, Osman S, Lavender JP. Imaging inflammation with 111-In troplonate labelled leucocytes. J Nucl Med 1983;24: Lavender JP, Irvine H, Armstrong JD. Krypton-81m ventilation scanning: acute respiratory disease. AJR 1981;136: Buescher S, Gallin J. Leukocyte transfusions in chronic granulomatous disease. New EnglJ Med 1982;37: Lichter JP, Konopkar G, Hartman MT, Moser KM, Sprag RG. The in-vivo behaviour of granulocytes labelled with indium-ill in a canine model of pneumoccal pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis 1984;129:62-6. Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 December Downloaded from on 27 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
inflammatory bowel disease
 Gut, 1985, 26, 955-96 '1lndium autologous granulocytes in the detection of inflammatory bowel S H SAVERYMUTTU, A M PETERS, M E CROFTON, H REES, J P LAVENDER, H J F HODGSON, AND V S CHADWICK From the Departments
Gut, 1985, 26, 955-96 '1lndium autologous granulocytes in the detection of inflammatory bowel S H SAVERYMUTTU, A M PETERS, M E CROFTON, H REES, J P LAVENDER, H J F HODGSON, AND V S CHADWICK From the Departments
No Difference in Sensitivity for Occult Infection Between Tropolone- and Oxine-Labeled Indium-Ill Leukocytes
 No Difference in Sensitivity for Occult Infection Between Tropolone- and Oxine-Labeled Indium-Ill Leukocytes Frederick L. Datz, Richard A. Bedont, William J. Baker, Naomi P. Alazraki, and Andrew Taylor,
No Difference in Sensitivity for Occult Infection Between Tropolone- and Oxine-Labeled Indium-Ill Leukocytes Frederick L. Datz, Richard A. Bedont, William J. Baker, Naomi P. Alazraki, and Andrew Taylor,
Radiolabelled leucocytes: a new diagnostic tool in
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1984, 59, 62-66 Radiolabelled leucocytes: a new diagnostic tool in occult infection/inflammation I GORDON AND G VIVIAN Department of Paediatric Radiology, Hospital for
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1984, 59, 62-66 Radiolabelled leucocytes: a new diagnostic tool in occult infection/inflammation I GORDON AND G VIVIAN Department of Paediatric Radiology, Hospital for
INFECTION & INFLAMMATION IMAGING
 INFECTION & INFLAMMATION IMAGING Radiopharmaceutical Drug Interactions & Other Interesting Case Studies MICHELLE RUNDIO, CNMT NCT MBA PCI NUCLEAR IN-111 WHITE BLOOD CELL IMAGING Interactions, Imaging Parameters
INFECTION & INFLAMMATION IMAGING Radiopharmaceutical Drug Interactions & Other Interesting Case Studies MICHELLE RUNDIO, CNMT NCT MBA PCI NUCLEAR IN-111 WHITE BLOOD CELL IMAGING Interactions, Imaging Parameters
Location and Activity of Ulcerative and Crohn's Colitis by Indium 111 Leukocyte Scan
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1983;84:388-93 Location and Activity of Ulcerative and Crohn's Colitis by Indium 111 Leukocyte Scan A Prospective Comparison Study DAVID T. STEIN, GARY M. GRAY, PETER B. GREGORY, MALCOLM
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1983;84:388-93 Location and Activity of Ulcerative and Crohn's Colitis by Indium 111 Leukocyte Scan A Prospective Comparison Study DAVID T. STEIN, GARY M. GRAY, PETER B. GREGORY, MALCOLM
Splenic atrophy in adult coeliac disease:
 Gut, 1981, 22, 628-632 Splenic atrophy in adult coeliac disease: is it reversible? P N TREWBY, P M CHIPPING, S J PALMER, P D ROBERTS, S M LEWIS, AND J S STEWART From the Departments of Gastroenterology
Gut, 1981, 22, 628-632 Splenic atrophy in adult coeliac disease: is it reversible? P N TREWBY, P M CHIPPING, S J PALMER, P D ROBERTS, S M LEWIS, AND J S STEWART From the Departments of Gastroenterology
Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline fo r. exametazime (HMPAO) labeled leukocyte
 Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline fo r Tc-99m Exametazime (HMPAO) Labeled Leuko cy t e S c i n t i g r a p hy for Suspected Infe c t i o n / I n f l a m m a t i o n version 2.0, approved
Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline fo r Tc-99m Exametazime (HMPAO) Labeled Leuko cy t e S c i n t i g r a p hy for Suspected Infe c t i o n / I n f l a m m a t i o n version 2.0, approved
squamous-cell carcinoma1
 Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
tomography Assessment of bronchiectasis by computed Reid' into three types-cystic, varicose, andcylindrical.
 Thorax 1985;40:920-924 Assessment of bronchiectasis by computed tomography IM MOOTOOSAMY, RH REZNEK, J OSMAN, RSO REES, MALCOLM GREEN From the Departments of Diagnostic Radiology and Chest Medicine, St
Thorax 1985;40:920-924 Assessment of bronchiectasis by computed tomography IM MOOTOOSAMY, RH REZNEK, J OSMAN, RSO REES, MALCOLM GREEN From the Departments of Diagnostic Radiology and Chest Medicine, St
Joseph Garland, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman, MD. Round Pneumonia. Joseph Garland, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman, MD
 Round Pneumonia Joseph Garland, HMS IV Case 1: Mr. H Mr. H is a 45-year-old man who presents with a 4 day history of full-body myalgias, headaches and fever to 103 F. He also complains of sharp leftsided
Round Pneumonia Joseph Garland, HMS IV Case 1: Mr. H Mr. H is a 45-year-old man who presents with a 4 day history of full-body myalgias, headaches and fever to 103 F. He also complains of sharp leftsided
Early Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscesses associated with Pylephlebitis Mimic
 Early Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscesses associated with Pylephlebitis Mimic Hepatocellular Carcinoma Chih-Hao Shen, MD 3, Jung-Chung Lin, MD, PhD 2, Hsuan-Hwai Lin, MD 1, You-Chen Chao, MD 1, and Tsai-Yuan
Early Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscesses associated with Pylephlebitis Mimic Hepatocellular Carcinoma Chih-Hao Shen, MD 3, Jung-Chung Lin, MD, PhD 2, Hsuan-Hwai Lin, MD 1, You-Chen Chao, MD 1, and Tsai-Yuan
Indium ill-labeled white blood cell scans after vascular prosthetic reconstruction
 Indium ill-labeled white blood cell scans after vascular prosthetic reconstruction Marc M. Sedwitz, M.D., Richard J. Davies, M.D., Harold T. Pretorius, M.D., Ph.D., and Tony E. Vasquez, M.D., San Diego,
Indium ill-labeled white blood cell scans after vascular prosthetic reconstruction Marc M. Sedwitz, M.D., Richard J. Davies, M.D., Harold T. Pretorius, M.D., Ph.D., and Tony E. Vasquez, M.D., San Diego,
ENTEROCOLITIDES CAN YOU TELL THEM APART ON MDCT? Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Medical Center University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois
 ENTEROCOLITIDES CAN YOU TELL THEM APART ON MDCT? Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Medical Center University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois SCBT/MR 2010 San Diego, California March 8, 2010 13:40-14:00
ENTEROCOLITIDES CAN YOU TELL THEM APART ON MDCT? Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Medical Center University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois SCBT/MR 2010 San Diego, California March 8, 2010 13:40-14:00
Comparative radiographic features of community
 Thorax 1984;39:28-33 Comparative radiographic features of community acquired legionnaires' disease, pneumococcal pneumonia, mycoplasma pneumonia, and psittacosis JT MACFARLANE, AC MILLER, WH RODERICK SMITH,
Thorax 1984;39:28-33 Comparative radiographic features of community acquired legionnaires' disease, pneumococcal pneumonia, mycoplasma pneumonia, and psittacosis JT MACFARLANE, AC MILLER, WH RODERICK SMITH,
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia
 Difference Between Pleural Effusion and Pneumonia www.differencebetween.com Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia Pleural effusion and pneumonia are two conditions that affect our respiratory
Difference Between Pleural Effusion and Pneumonia www.differencebetween.com Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia Pleural effusion and pneumonia are two conditions that affect our respiratory
Circulating human leucocyte elastase in patients with
 Gut, 1985, 26, 136-1311 Circulating human leucocyte elastase in patients with inflammatory bowel disease E ADEYEMI, S NEUMANN, V S CHADWICK, H J F HODGSON, AND M B PEPYS From the Gastroenterology Unit,
Gut, 1985, 26, 136-1311 Circulating human leucocyte elastase in patients with inflammatory bowel disease E ADEYEMI, S NEUMANN, V S CHADWICK, H J F HODGSON, AND M B PEPYS From the Gastroenterology Unit,
Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection
 Thorax (1970), 25, 41. Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection 0. SERIKI, A. ADEYOKUNNU, T. 0. DE LA CRUZ Departments of Paediatrics and Surgery, University College Hospital, Ibadan,
Thorax (1970), 25, 41. Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection 0. SERIKI, A. ADEYOKUNNU, T. 0. DE LA CRUZ Departments of Paediatrics and Surgery, University College Hospital, Ibadan,
Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction
 Thlorax (1973), 28, 198. Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction S. TALBOT, B. S. WORTHINGTON, and E. J. ROEBUCK General Hospital, Nottingham A comparative analysis of the radiographic
Thlorax (1973), 28, 198. Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction S. TALBOT, B. S. WORTHINGTON, and E. J. ROEBUCK General Hospital, Nottingham A comparative analysis of the radiographic
04/03/2013. Second Annual BIR SPECT/CT Symposium London, UK 25/02/2013. NMD: Al-Jahra Hospital. NMD: Al-Jahra Hospital
 Second Annual BIR SPECT/CT Symposium London, UK 25/02/2013 1 Muhammad Umar Khan, FCPS Al-Jahra Hospital; PET/CT Suite: Kuwait Cancer Control Center 25/02/2012 SPECT/CT in Imaging Infection Kuwait 25/02/2013
Second Annual BIR SPECT/CT Symposium London, UK 25/02/2013 1 Muhammad Umar Khan, FCPS Al-Jahra Hospital; PET/CT Suite: Kuwait Cancer Control Center 25/02/2012 SPECT/CT in Imaging Infection Kuwait 25/02/2013
Primary hyperparathyroidism (HPT) has an incidence of
 Dual-Phase Tc-Sestamibi Imaging: Its Utility in Parathyroid Hyperplasia and Use of Immediate/ Delayed Image Ratios to Improve Diagnosis of Hyperparathyroidism Leonie Gordon, MD; William Burkhalter, MD;
Dual-Phase Tc-Sestamibi Imaging: Its Utility in Parathyroid Hyperplasia and Use of Immediate/ Delayed Image Ratios to Improve Diagnosis of Hyperparathyroidism Leonie Gordon, MD; William Burkhalter, MD;
Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology
 Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Russell Tucker, DVM, DACVR Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual
Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Russell Tucker, DVM, DACVR Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual
Serum amyloid A protein and C-reactive protein levels in pulmonary tuberculosis: relationship to amyloidosis
 Thorax 1984;39:196-2 Serum amyloid A protein and C-reactive protein levels in pulmonary tuberculosis: relationship to amyloidosis FC DE BEER, AE NEL, RP GIE, PR DONALD, AF STRACHAN From the Departments
Thorax 1984;39:196-2 Serum amyloid A protein and C-reactive protein levels in pulmonary tuberculosis: relationship to amyloidosis FC DE BEER, AE NEL, RP GIE, PR DONALD, AF STRACHAN From the Departments
PULMONARY EMERGENCIES
 EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
Medical and Surgical Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia
 Medical and Surgical Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia Ahmed Al-Salem Medical and Surgical Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia Ahmed Al-Salem Department of Surgery Dar A lalafia Medical Company Qatif
Medical and Surgical Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia Ahmed Al-Salem Medical and Surgical Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia Ahmed Al-Salem Department of Surgery Dar A lalafia Medical Company Qatif
Role of imaging (images) in my practice. Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases
 Role of imaging (images) in my practice Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases Medical images: My thoughts Images are just images Subject to the intellect of the interpreter View it in conjuction
Role of imaging (images) in my practice Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases Medical images: My thoughts Images are just images Subject to the intellect of the interpreter View it in conjuction
Chronic immune colitis in rabbits
 Chronic immune colitis in rabbits A. S. MEE, J. E. McLAUGHLIN, H. J. F. HODGSON, AND D. P. JEWELL Gut, 1979, 20, 1-5 From the Academic Department of Medicine and Department of Histopathology, Royal Free
Chronic immune colitis in rabbits A. S. MEE, J. E. McLAUGHLIN, H. J. F. HODGSON, AND D. P. JEWELL Gut, 1979, 20, 1-5 From the Academic Department of Medicine and Department of Histopathology, Royal Free
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Leucocytscintigraphy. Lene Rørdam Senior Consultant DMSci Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine Bispebjerg University Hospital
 Leucocytscintigraphy Lene Rørdam Senior Consultant DMSci Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine Bispebjerg University Hospital Indications for leucocytscintigraphy in the past Inflammatory
Leucocytscintigraphy Lene Rørdam Senior Consultant DMSci Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine Bispebjerg University Hospital Indications for leucocytscintigraphy in the past Inflammatory
Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients
 Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children. Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital
 FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
Detection of abscesses and infection in soft tissues, particularly in patients without localizing findings.
 NUCLEAR MEDICINE SERVICES SUBJECT: WHITE BLOOD CELL STUDY Overview Indications The White Blood Cell Study demonstrates the distribution of labeled autologous white blood cells within the body at various
NUCLEAR MEDICINE SERVICES SUBJECT: WHITE BLOOD CELL STUDY Overview Indications The White Blood Cell Study demonstrates the distribution of labeled autologous white blood cells within the body at various
Imaging of white blood cells with Scintimun
 Imaging of white blood cells with Scintimun APRAMEN Réunion, Mardi 8 février 2011, Paris Wolf S. Richter SCINTIMUN : IgG1 antibody targeting white blood cells Tc-99m kit; murine IgG1 antibody target: NCA-95
Imaging of white blood cells with Scintimun APRAMEN Réunion, Mardi 8 février 2011, Paris Wolf S. Richter SCINTIMUN : IgG1 antibody targeting white blood cells Tc-99m kit; murine IgG1 antibody target: NCA-95
and localized ground glass opacities, or bronchiolar focal or multifocal micronodules;
 E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
Radiology. Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions
 Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Lecture Notes. Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia
 Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lung scanning in carcinoma of the bronchus
 Thorax (1971), 26, 23. Lung scanning in carcinoma of the bronchus R. H. SECKER WALKER, J. L. PROVAN1, J. A. JACKSON, and J. GOODWIN The Medical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School, University
Thorax (1971), 26, 23. Lung scanning in carcinoma of the bronchus R. H. SECKER WALKER, J. L. PROVAN1, J. A. JACKSON, and J. GOODWIN The Medical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School, University
Fibrin thrombi, a cause of clindamycin-associated
 Gut, 1976, 17, 483487 Fibrin thrombi, a cause of clindamycin-associated colitis? W. V. BOGOMOLETZ From the Department of Pathology, Queen Mary's Hospital, London summary Rectal biopsies from five patients
Gut, 1976, 17, 483487 Fibrin thrombi, a cause of clindamycin-associated colitis? W. V. BOGOMOLETZ From the Department of Pathology, Queen Mary's Hospital, London summary Rectal biopsies from five patients
IN THE SPREAD OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 Thorax (1951), 6, 417. THE IMPORTANCE OF SLEEPING POSTURE IN THE SPREAD OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY W. H. HELM From the London Chest Hospital (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION AUGUST 22, 195 1) When an infective
Thorax (1951), 6, 417. THE IMPORTANCE OF SLEEPING POSTURE IN THE SPREAD OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY W. H. HELM From the London Chest Hospital (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION AUGUST 22, 195 1) When an infective
Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
 Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Dr Neetu Talwar Senior Consultant, Pediatric Pulmonology Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram Study To compare
Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Dr Neetu Talwar Senior Consultant, Pediatric Pulmonology Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram Study To compare
Effects of posture on the distribution of pulmonary
 Thorax 1989;44:48-484 Effects of posture on the distribution of pulmonary ventilation and perfusion in children and adults U BHUYAN, A M PETERS, I GORDON, H DAVIES, P HELMS From the Departments of Paediatric
Thorax 1989;44:48-484 Effects of posture on the distribution of pulmonary ventilation and perfusion in children and adults U BHUYAN, A M PETERS, I GORDON, H DAVIES, P HELMS From the Departments of Paediatric
8/14/2017. Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features
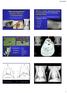 What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
Lung Allograft Dysfunction
 Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
UC Irvine Western Journal of Emergency Medicine: Integrating Emergency Care with Population Health
 UC Irvine Western Journal of Emergency Medicine: Integrating Emergency Care with Population Health Title Analysis of Urobilinogen and Urine Bilirubin for Intra-Abdominal Injury in Blunt Trauma Patients
UC Irvine Western Journal of Emergency Medicine: Integrating Emergency Care with Population Health Title Analysis of Urobilinogen and Urine Bilirubin for Intra-Abdominal Injury in Blunt Trauma Patients
Radiology Pathology Conference
 Radiology Pathology Conference Nadia F. Yusaf, M.D. PGY-3 1/29/2010 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2010 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 90 Case 1 60 year- old man presents
Radiology Pathology Conference Nadia F. Yusaf, M.D. PGY-3 1/29/2010 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2010 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 90 Case 1 60 year- old man presents
Bronchography in chronic bronchitis
 Bronchography in chronic bronchitis A. G. OGILVIE Wood Cottage, Thropton, Morpeth, Northumnberland Thorax (1975), 30, 631. Ogilvie, A. G. (1975). Thorax, 30, 631-635. Bronchography in chronic bronchitis.
Bronchography in chronic bronchitis A. G. OGILVIE Wood Cottage, Thropton, Morpeth, Northumnberland Thorax (1975), 30, 631. Ogilvie, A. G. (1975). Thorax, 30, 631-635. Bronchography in chronic bronchitis.
ARDS during Neutropenia. D Mokart DAR IPC GRRRRROH 2010
 ARDS during Neutropenia D Mokart DAR IPC GRRRRROH 2010 Definitions Neutropenia is a decrease in circulating neutrophil white cells in the peripheral blood. neutrophil count of 1,000 1,500 cells/ml = mild
ARDS during Neutropenia D Mokart DAR IPC GRRRRROH 2010 Definitions Neutropenia is a decrease in circulating neutrophil white cells in the peripheral blood. neutrophil count of 1,000 1,500 cells/ml = mild
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that
PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA
 Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency
 Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency Poster No.: C-2233 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Vanhoutte, M. Lefere, R. Vanslembrouck, D. Bielen, G. De 1 1 2 1 1
Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency Poster No.: C-2233 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Vanhoutte, M. Lefere, R. Vanslembrouck, D. Bielen, G. De 1 1 2 1 1
production Comparison of thin section computed tomography with bronchography for identifying bronchiectatic segments in patients with chronic sputum
 Thorax 1990;45:135-139 Host Defence Unit, Department of Thoracic Medicine, National Heart and Lung Institute, London N C Munro D C Currie P J Cole Department of Radiology, Brompton Hospital, London J C
Thorax 1990;45:135-139 Host Defence Unit, Department of Thoracic Medicine, National Heart and Lung Institute, London N C Munro D C Currie P J Cole Department of Radiology, Brompton Hospital, London J C
Pathology of Pneumonia
 Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure SPHINCTER OF ODDI STUDY (Tc-99m-Mebrofenin)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure SPHINCTER OF ODDI STUDY (Tc-99m-Mebrofenin) Overview Indications The successively demonstrates hepatic perfusion, hepatocyte clearance, hepatic
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure SPHINCTER OF ODDI STUDY (Tc-99m-Mebrofenin) Overview Indications The successively demonstrates hepatic perfusion, hepatocyte clearance, hepatic
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs) Overview Indications The White Blood Cell Migration Study demonstrates the distribution
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs) Overview Indications The White Blood Cell Migration Study demonstrates the distribution
Protecting the Lungs
 Protecting the Lungs PGA New York 12/07 Disclosures: Peter Slinger MD, FRCPC University of Toronto 58 y.o. Male, Chronic Gallstone Pancreatitis, Open Cholecystectomy 100 pack/year smoker Dyspnea > 1 block
Protecting the Lungs PGA New York 12/07 Disclosures: Peter Slinger MD, FRCPC University of Toronto 58 y.o. Male, Chronic Gallstone Pancreatitis, Open Cholecystectomy 100 pack/year smoker Dyspnea > 1 block
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism
 Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Proctocolitis and Crohn's disease of the colon:
 and of the colon: a comparison of the clinical course J. E. LENNARD-JONES, JEAN K. RITCHIE, AND W. J. ZOHRAB From St Mark's Hospital, London Gut, 1976, 17, 477-482 SUMMARY This study suggests that proctocolitis
and of the colon: a comparison of the clinical course J. E. LENNARD-JONES, JEAN K. RITCHIE, AND W. J. ZOHRAB From St Mark's Hospital, London Gut, 1976, 17, 477-482 SUMMARY This study suggests that proctocolitis
InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index
 InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index Long-Term Acute Care (LTAC) Criteria The Index is an alphabetical listing of conditions and/or diagnoses designed to guide the user to the criteria subset where a specific
InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index Long-Term Acute Care (LTAC) Criteria The Index is an alphabetical listing of conditions and/or diagnoses designed to guide the user to the criteria subset where a specific
ISF criteria (International sepsis forum consensus conference of infection in the ICU) Secondary peritonitis
 Appendix with supplementary material. This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Supplementary Tables Table S1. Definitions
Appendix with supplementary material. This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Supplementary Tables Table S1. Definitions
Comparison of Different Scoring System in Predicting the Severity and Prognosis of Acute Pancreatitis
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 5 Ver. 3 (May. 2018), PP 56-60 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of Different Scoring System
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 5 Ver. 3 (May. 2018), PP 56-60 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of Different Scoring System
Case Discussion. Nutrition in IBD. Rémy Meier MD. Ulcerative colitis. Crohn s disease
 26.08.2017 Case Discussion Nutrition in IBD Crohn s disease Ulcerative colitis Rémy Meier MD Case Presentation 30 years old female, with diarrhea for 3 months Shool frequency 3-4 loose stools/day with
26.08.2017 Case Discussion Nutrition in IBD Crohn s disease Ulcerative colitis Rémy Meier MD Case Presentation 30 years old female, with diarrhea for 3 months Shool frequency 3-4 loose stools/day with
Case 1. What does the CXR show? How would you manage this patient? Discussion overleaf.
 Tutorial of the week cerebral challenge. This has previously been published in Update in anaesthesia. Examples of investigations demonstrating typical appearances of commonly encountered conditions are
Tutorial of the week cerebral challenge. This has previously been published in Update in anaesthesia. Examples of investigations demonstrating typical appearances of commonly encountered conditions are
Paediatrics. John Buscombe
 Paediatrics John Buscombe Renal disease n Use of most radiopharmaceuticals limited as excreted via kidneys n However some role for infection specific studies in no-working kidneys Eg Infected polycystic
Paediatrics John Buscombe Renal disease n Use of most radiopharmaceuticals limited as excreted via kidneys n However some role for infection specific studies in no-working kidneys Eg Infected polycystic
Value of serum magnesium estimation in diagnosing myocardial infarction and predicting dysrhythmias after coronary artery bypass grafting
 Thorax 1983;38:946-95 Value of serum magnesium estimation in diagnosing myocardial infarction and predicting dysrhythmias after coronary artery bypass grafting RICHARD W BUNTON From the Department of Cardiothoracic
Thorax 1983;38:946-95 Value of serum magnesium estimation in diagnosing myocardial infarction and predicting dysrhythmias after coronary artery bypass grafting RICHARD W BUNTON From the Department of Cardiothoracic
Hyperandrogenism and polycystic ovary syndrome are clear casual factors (trends) which result in hirsuitism and acne.
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Indication: Treatment of moderate to severe acne related to androgen-sensitivity (with or without seborrhoea) and/or hirsutism,
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Indication: Treatment of moderate to severe acne related to androgen-sensitivity (with or without seborrhoea) and/or hirsutism,
Pathogenic organisms in the sputum of patients
 Thorax (1967), 22, 265. Pathogenic organisms in the sputum of patients with chronic bronchitis 0. L. WADE, P. C. ELMES, AND EILEEN BARTLEY From the Department of Therapeutics and Pharmacology and the Department
Thorax (1967), 22, 265. Pathogenic organisms in the sputum of patients with chronic bronchitis 0. L. WADE, P. C. ELMES, AND EILEEN BARTLEY From the Department of Therapeutics and Pharmacology and the Department
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!!
 The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
Gastrointestinal tract
 Gastrointestinal tract Colloidal liver-spleen imaging Presented by: Jehad Felemban Introduction: To obtain better anatomic display of liver and spleen architecture, we use (CT Ultrasound). (Radionuclide
Gastrointestinal tract Colloidal liver-spleen imaging Presented by: Jehad Felemban Introduction: To obtain better anatomic display of liver and spleen architecture, we use (CT Ultrasound). (Radionuclide
Contrast-enhanced small bowel ultrasound in the assessment of the small bowel in patients with Crohn s Disease
 Contrast-enhanced small bowel ultrasound in the assessment of the small bowel in patients with Crohn s Disease C.F. Healy 1, D. Ferguson 1, S. Jepson 1, B. Salh 2, F. Donnellan 2, N. Chatur 2, A. C. Harris
Contrast-enhanced small bowel ultrasound in the assessment of the small bowel in patients with Crohn s Disease C.F. Healy 1, D. Ferguson 1, S. Jepson 1, B. Salh 2, F. Donnellan 2, N. Chatur 2, A. C. Harris
Empyema due to Klebsiella pneumoniae
 Thorax (1967), 22, 170. Empyema due to Klebsiella pneumoniae J. M. REID, R. S. BARCLAY, J. G. STEVENSON, T. M. WELSH, AND N. McSWAN From thle Cardio-thoracic Unit, Mearnskirk Hospital, Renifrewshire Three
Thorax (1967), 22, 170. Empyema due to Klebsiella pneumoniae J. M. REID, R. S. BARCLAY, J. G. STEVENSON, T. M. WELSH, AND N. McSWAN From thle Cardio-thoracic Unit, Mearnskirk Hospital, Renifrewshire Three
Information for patients (and their families) waiting for liver transplantation
 Information for patients (and their families) waiting for liver transplantation Waiting list? What is liver transplant? Postoperative conditions? Ver.: 5/2017 1 What is a liver transplant? Liver transplantation
Information for patients (and their families) waiting for liver transplantation Waiting list? What is liver transplant? Postoperative conditions? Ver.: 5/2017 1 What is a liver transplant? Liver transplantation
Positioning Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis
 Positioning Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS Acting Chief, Gastrointestinal Unit Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Sequential Therapies
Positioning Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS Acting Chief, Gastrointestinal Unit Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Sequential Therapies
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum. Elective Student S. C.
 Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi
 Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
Radiochromated Erythrocytes in Gastrointestinal Tract
 Radiochromated Erythrocytes in Gastrointestinal Tract 16 th ISORBE meeting Pretoria, March 2013 Annare Ellmann Stellenbosch University and Tygerberg Hospital History Successful labelling of red blood cells
Radiochromated Erythrocytes in Gastrointestinal Tract 16 th ISORBE meeting Pretoria, March 2013 Annare Ellmann Stellenbosch University and Tygerberg Hospital History Successful labelling of red blood cells
Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University.
 Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University. Chronic transmural inflammatory process of the bowel & affects any part of the gastro -intestinal tract from the mouth to the
Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University. Chronic transmural inflammatory process of the bowel & affects any part of the gastro -intestinal tract from the mouth to the
Diagnosis of old anterior myocardial infarction in
 Br Heart J 1981; 45: 522-26 Diagnosis of old anterior myocardial infarction in emphysema with poor R wave progression in anterior chest leads GRAHAM J HART, PETER A BARRETT, PETER F BARNABY, ELIZABETH
Br Heart J 1981; 45: 522-26 Diagnosis of old anterior myocardial infarction in emphysema with poor R wave progression in anterior chest leads GRAHAM J HART, PETER A BARRETT, PETER F BARNABY, ELIZABETH
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
Frequency of Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer with Double Contrast Barium Enema
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.3, September 2002 Frequency of Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer with Double Contrast Barium Enema Najeeb S Jamsheer, MD, FRCR* Neelam. Malik, MD, MNAMS** Objective: To
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.3, September 2002 Frequency of Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer with Double Contrast Barium Enema Najeeb S Jamsheer, MD, FRCR* Neelam. Malik, MD, MNAMS** Objective: To
Fariba Rezaeetalab Associate Professor,Pulmonologist
 Fariba Rezaeetalab Associate Professor,Pulmonologist rezaitalabf@mums.ac.ir Patient related risk factors Procedure related risk factors Preoperative risk assessment Risk reduction strategies Age Obesity
Fariba Rezaeetalab Associate Professor,Pulmonologist rezaitalabf@mums.ac.ir Patient related risk factors Procedure related risk factors Preoperative risk assessment Risk reduction strategies Age Obesity
Is follow up chest X-ray required in children with round pneumonia?
 Is follow up chest X-ray required in children with round pneumonia? McCrossan, P., McNaughten, B., Shields, M., & Thompson, A. (2017). Is follow up chest X-ray required in children with round pneumonia?
Is follow up chest X-ray required in children with round pneumonia? McCrossan, P., McNaughten, B., Shields, M., & Thompson, A. (2017). Is follow up chest X-ray required in children with round pneumonia?
Body MRI from the Liver to the Bladder
 Body MRI from the Liver to the Bladder I Want You! Audience Participation Methodist Hospital Continuing Education Seminar Jordan Swensson, MD November 7, 2015 Objectives Observe the uses of MRI for organs
Body MRI from the Liver to the Bladder I Want You! Audience Participation Methodist Hospital Continuing Education Seminar Jordan Swensson, MD November 7, 2015 Objectives Observe the uses of MRI for organs
Chapter 16. Lung Abscess. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lung Abscess 1 EDA PM C AFC RB A B Figure 16-1. Lung abscess. A, Cross-sectional view of lung abscess. B, Consolidation and (C) excessive bronchial secretions are common secondary anatomic alterations
Chapter 16 Lung Abscess 1 EDA PM C AFC RB A B Figure 16-1. Lung abscess. A, Cross-sectional view of lung abscess. B, Consolidation and (C) excessive bronchial secretions are common secondary anatomic alterations
Lugano classification: Role of PET-CT in lymphoma follow-up
 CAR Educational Exhibit: ID 084 Lugano classification: Role of PET-CT in lymphoma follow-up Charles Nhan 4 Kevin Lian MD Charlotte J. Yong-Hing MD FRCPC Pete Tonseth 3 MD FRCPC Department of Diagnostic
CAR Educational Exhibit: ID 084 Lugano classification: Role of PET-CT in lymphoma follow-up Charles Nhan 4 Kevin Lian MD Charlotte J. Yong-Hing MD FRCPC Pete Tonseth 3 MD FRCPC Department of Diagnostic
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
Informed Consent Gastrectomy
 Informed Consent Gastrectomy Department of Surgery, Nagasaki University Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences Important things you need to know Patient choice is an important part of your care. You have
Informed Consent Gastrectomy Department of Surgery, Nagasaki University Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences Important things you need to know Patient choice is an important part of your care. You have
A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia
 7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 258. A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia P. H. FITZGERALD From the Cytogenetics Unit*, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 258. A Complex Pattern of Chromosome Abnormalities in the Acute Phase of Chronic Granulocytic Leukaemia P. H. FITZGERALD From the Cytogenetics Unit*, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch,
To Study The Cinico-Radiological Features And Associated Co-Morbid Conditions
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 16 (July. 2018), PP 58-62 www.iosrjournals.org To study the clinico-radiological features
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 16 (July. 2018), PP 58-62 www.iosrjournals.org To study the clinico-radiological features
Biodistribution on Tc-99m labeled somatostatin receptor-binding peptide (Depreotide, NeoTec) planar and SPECT studies
 ORIGINL RTICLE nnals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 3, 213 219, 2002 iodistribution on Tc-99m labeled somatostatin receptor-binding peptide (Depreotide, NeoTec) planar and SPECT studies Wei-Jen SHIH,
ORIGINL RTICLE nnals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 3, 213 219, 2002 iodistribution on Tc-99m labeled somatostatin receptor-binding peptide (Depreotide, NeoTec) planar and SPECT studies Wei-Jen SHIH,
Outcomes of Patients with Preoperative Weight Loss following Colorectal Surgery
 Outcomes of Patients with Preoperative Weight Loss following Colorectal Surgery Zhobin Moghadamyeghaneh MD 1, Michael J. Stamos MD 1 1 Department of Surgery, University of California, Irvine Nothing to
Outcomes of Patients with Preoperative Weight Loss following Colorectal Surgery Zhobin Moghadamyeghaneh MD 1, Michael J. Stamos MD 1 1 Department of Surgery, University of California, Irvine Nothing to
Abbreviated Prescribing Information
 Abbreviated Prescribing Information balance 1.5% glucose, 1.75 mmol/l calcium, solution for peritoneal dialysis balance 2.3% glucose, 1.75 mmol/l calcium, solution for peritoneal dialysis balance 4.25%
Abbreviated Prescribing Information balance 1.5% glucose, 1.75 mmol/l calcium, solution for peritoneal dialysis balance 2.3% glucose, 1.75 mmol/l calcium, solution for peritoneal dialysis balance 4.25%
5/9/2015. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Common things are common, but not always the answer
 Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Lung abscess in childhood
 Thorax (1968), 23, 216. PATRICIA H. MARK AND J. A. PETER TURNER' Froml the Depattmenit of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, and the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada Lung
Thorax (1968), 23, 216. PATRICIA H. MARK AND J. A. PETER TURNER' Froml the Depattmenit of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, and the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada Lung
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections
 Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
