Epidemiology: Closing the Gap
|
|
|
- Candice James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Integrating Basic Biology and Epidemiology: Closing the Gap for Risk Assessment R. Julian Preston National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Research Triangle Park, NC NAS/NRC 2014
2 The Issue Current attempts to estimate cancer and noncancer risks from radiation exposures at low doses (<100mGy) and low dose rates (<5mGy per hour) have resulted in significant uncertainties. A major component of these uncertainties is a consequence of an almost complete reliance on human epidemiology data obtained at relatively high doses for estimating effects at low doses and dose rates. The human data are clearly very important in risk assessment but their limitations have to be overcome. Enhancement in risk estimates cannot be achieved solely by designing and conducting larger and more directed epidemiology studies.
3 A Possible Solution A greater use has to be made of basic biology data from animal models and in vitro systems together with enhanced computational approaches to improve the quantitation of adverse health effects at low doses and dose rates. Some data of the types needed are already available from some 60 years of extensive research. Others will be available from studies that are underway and from future studies that are already feasible. A valuable review in this regard is that of Boss et al., Radiat Res 181, , 2014 (Linking the history of radiation biology to the hallmarks of cancer). An approach of this general type has been used in risk assessment for environmental chemicals for which epidemiology data are nearly always absent.
4 Definitions (I) An adverse outcome pathway is an analytical construct that describes a sequential chain of causally linked key events at different levels of biological organization that lead to an adverse health effect. A key event is an empirically observable precursor step that is itself a necessary element of an adverse outcome pathway or is a biologically based marker for such an element.
5 Definitions (II) When evaluating biological endpoints for use in risk assessment it is useful to differentiate between biomarkers of exposure, biomarkers of effect and bioindicators of cancer or noncancer effects. Biomarkers of exposure and early effect include : DNA adducts mutations in reporter genes, mutations in genes not known to be related to cancer, chromosome alterations in non-target genes. These can be used to inform the shape of the dose response for an adverse health outcome. Bioindicators are alterations that are specifically related to the development of an apical endpoint and include: mutations in cancerrelated genes or chromosome translocations associated with specific cancers when identified in the target tissue. These bioindicators can be used to inform the dose response for an apical endpoint in a qualitative and quantitative manner. Bioindicators are thus the key events along an adverse outcome pathway and are considered the most informative biological outcome in a risk assessment framework.
6 Biologically-Based Dose-Response (BBDR) Models BBDR models combine the use of epidemiology, laboratory animal studies and cellular and molecular data in order to parameterize the model. The selection of parameters can be guided by a knowledge of the key events that lead to cancer development (adverse outcome pathway) in response to radiation. The challenge in simple terms is to: 1. Understand a sufficient amount of the relevant biology 2. Acquire enough knowledge to parameterize the model 3. Develop the computational model
7 Schematic representation of an adverse outcome pathway (AOP) for ionizing radiation-induced cancer and non-cancer diseases showing each step along the proposed pathway and the linked key events. AOP Steps Interaction with Radiation Energy Deposition Macro-Molecular Alterations Cellular Responses Organ Responses Adverse Outcome Key Events Exposure of target tissue Single, double and multiple DNA breaks Protein oxidation Free Radical formation Chromosome alterations Gene activation Protein production Altered signaling Cell killing and tissue disruption Altered physiology Disrupted homeostasis Altered tissue development/function Impaired development Impaired reproduction Cancer and noncancer effects
8 Key questions for testing AOP confidence 1. How well characterized is the AOP? 2. How well are the initiating and other key events causally linked to the outcome? 3. What are the limitations in the evidence in support of the AOP? 4. Is the AOP specific to certain tissues, life stages or age classes? 5. Are the initiating and key events expected to be conserved across taxa? OECD, 2012
9 Research Program The need is for the conduct of targeted research aimed at enhancing the risk assessment process at low doses and low dose rates. To do this the approach will be to identify and evaluate informative bioindicators of an apical response (cancer or noncancer) and use these to set parameters for a BBDR model. Based on our current knowledge, this is a viable approach although not a short term venture. These research activities have to be viewed in the context of ongoing and proposed epidemiology studies. Any viable approach has to be an integration of the biology and the epidemiology.
10 A parallelogram approach for utilizing laboratory animal and in vitro cell data to estimate human cancer and non-cancer risks for ionizing radiation Bioindicators for laboratory animal cells in vitro Experimental Bioindicators for human cells in vitro Experimental Bioindicators/adverse outcomes for laboratory animals in vivo Calculated/ Measured Calculated/ Measured Bioindicators/adverse health outcomes for humans in vivo
11 What Is Available? It is important to note that this is not pie in the sky ; significant advances using this general approach have been made in the arena of environmental chemicals. For example, Adverse Outcome Pathways: From Research to Regulation ( For key events, the knowledge of the molecular basis for cancer and, to a lesser extent, for noncancer diseases is increasing very rapidly. New techniques such as ultra high speed sequencing are fueling this. (Note Hanahan and Weinberg s Hallmarks of Cancer ) Predictive biologically-based models have been developed (e.g., Moolgavkar et al., 1979,1981; Little, 2010; Shuryak et al., 2010; Luebeck et al., 2013) and are becoming more relevant to the state of knowledge. Recent computational advances make linking molecular/cellular events to adverse outcomes much for readily feasible.
12 What is Needed? Increased knowledge of key events for radiation-induced adverse health outcomes. Are there radiation signatures of response? Development or enhancement of adverse outcome pathways. Identification and evaluation of key events/bioindicators. Development of new and improved BBDR models. Epidemiology studies directed to low dose and low doserate exposures.
BRIDGE THE GAP A Human Pathways Approach to Disease Research
 BRIDGE THE GAP A Human Pathways Approach to Disease Research BIOMED 21 Brussels December 8 th, 2015 Brigitte Landesmann Systems Toxicology Unit and EURL ECVAM Institute for Health and Consumer Protection
BRIDGE THE GAP A Human Pathways Approach to Disease Research BIOMED 21 Brussels December 8 th, 2015 Brigitte Landesmann Systems Toxicology Unit and EURL ECVAM Institute for Health and Consumer Protection
Application of human epidemiological studies to pesticide risk assessment
 Workshop What does the future hold for harmonised human health risk assessment of plant protection products? Application of human epidemiological studies to pesticide risk assessment Antonio F. Hernández,
Workshop What does the future hold for harmonised human health risk assessment of plant protection products? Application of human epidemiological studies to pesticide risk assessment Antonio F. Hernández,
María José Mesa López
 María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3
 Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Genome Editing Research for Translational Toxicology Solutions
 Genome Editing Research for Translational Toxicology Solutions REBECCA FRY, PH.D. Carol Remmer Angle Distinguished Professor and Associate Chair Director, UNC Superfund Research Program Director, Graduate
Genome Editing Research for Translational Toxicology Solutions REBECCA FRY, PH.D. Carol Remmer Angle Distinguished Professor and Associate Chair Director, UNC Superfund Research Program Director, Graduate
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)
 TECHNICAL REPORT APPROVED: 06 April 2017 doi:10.2903/sp.efsa.2017.en-1210 Outcome of the preliminary pesticides peer review meeting on the assessment of endocrine disrupting properties in mammalian toxicology
TECHNICAL REPORT APPROVED: 06 April 2017 doi:10.2903/sp.efsa.2017.en-1210 Outcome of the preliminary pesticides peer review meeting on the assessment of endocrine disrupting properties in mammalian toxicology
MIE KE2 AO Mutations per LacZ mutant. [van Delft and Baan 1995] [O'Brien et al. 2014]
![MIE KE2 AO Mutations per LacZ mutant. [van Delft and Baan 1995] [O'Brien et al. 2014] MIE KE2 AO Mutations per LacZ mutant. [van Delft and Baan 1995] [O'Brien et al. 2014]](/thumbs/88/115815301.jpg) Table I. Empirical data for male rodents exposed to germ cells for ENU. Dose (mg/kg) a Alkyl Adducts per nucleotide in male germ cells b MIE KE2 AO Mutations per LacZ mutant nucleotide in Time of frequency
Table I. Empirical data for male rodents exposed to germ cells for ENU. Dose (mg/kg) a Alkyl Adducts per nucleotide in male germ cells b MIE KE2 AO Mutations per LacZ mutant nucleotide in Time of frequency
Individual Sensitivity
 Individual Sensitivity Why do we care about Individual Sensitivity? This IS an issue at high doses (for deterministic effects in radiation therapy) It is not known whether Individual Sensitivity is an
Individual Sensitivity Why do we care about Individual Sensitivity? This IS an issue at high doses (for deterministic effects in radiation therapy) It is not known whether Individual Sensitivity is an
Best practices to develop artificial intelligence models for predicting multilevel effects in Adverse Outcome Pathways (AOP)
 Best practices to develop artificial intelligence models for predicting multilevel effects in Adverse Outcome Pathways (AOP) Altox Ltda Senior Data Scientist, Toxicology and Drug Discovery Specialist 2
Best practices to develop artificial intelligence models for predicting multilevel effects in Adverse Outcome Pathways (AOP) Altox Ltda Senior Data Scientist, Toxicology and Drug Discovery Specialist 2
William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc.
 Biological Responses at Low Radiation Doses: Advances in Radiation Biology and Potential ti Implications for Radiation Exposure Regulations. William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Biological Responses at Low Radiation Doses: Advances in Radiation Biology and Potential ti Implications for Radiation Exposure Regulations. William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Long-term Epidemiological Studies on Radiation Effects in A-bomb Survivors
 Consultancy Meeting on Science, Technology and Society Perspectives on Nuclear Science, Radiation and Human Health: The International Perspective 23 May 2017 Hiroshima, Japan Long-term Epidemiological
Consultancy Meeting on Science, Technology and Society Perspectives on Nuclear Science, Radiation and Human Health: The International Perspective 23 May 2017 Hiroshima, Japan Long-term Epidemiological
DISCUSSION GROUP 3. Mechanism of carcinogenicity. EFSA Scientific Colloquium on Acrylamide carcinogenicity, 22/23 May
 DISCUSSION GROUP 3 Mechanism of carcinogenicity EFSA Scientific Colloquium on Acrylamide carcinogenicity, 22/23 May 2008 1 1. Review the recent evidence for the mutagenicity and genotoxicity of acrylamide
DISCUSSION GROUP 3 Mechanism of carcinogenicity EFSA Scientific Colloquium on Acrylamide carcinogenicity, 22/23 May 2008 1 1. Review the recent evidence for the mutagenicity and genotoxicity of acrylamide
Rare Disease Workshop 5: Post Marketing Confirmatory Studies in Rare Diseases
 Rare Disease Workshop 5: Post Marketing Confirmatory Studies in Rare Diseases Susan Boynton, VP, Global Regulatory Affairs, Shire Mary O'Donovan, Senior Director, Regulatory Affairs & Policy, Biomarin
Rare Disease Workshop 5: Post Marketing Confirmatory Studies in Rare Diseases Susan Boynton, VP, Global Regulatory Affairs, Shire Mary O'Donovan, Senior Director, Regulatory Affairs & Policy, Biomarin
Distinguishing between Mode and Mechanism of Action
 Distinguishing between Mode and Mechanism of Action Michael Dourson Toxicology Excellence for Risk Assessment Center University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Conflict of Interest Statement The research
Distinguishing between Mode and Mechanism of Action Michael Dourson Toxicology Excellence for Risk Assessment Center University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Conflict of Interest Statement The research
Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure
 Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure Balázs G. Madas, Imre Balásházy MTA Centre for Energy Research,, Hungary balazs.madas@energia.mta.hu Low
Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure Balázs G. Madas, Imre Balásházy MTA Centre for Energy Research,, Hungary balazs.madas@energia.mta.hu Low
A Novel Bottom Up Approach to Bounding Potential Human Cancer Risks from Endogenous Chemicals
 A Novel Bottom Up Approach to Bounding Potential Human Cancer Risks from Endogenous Chemicals Thomas B. Starr, PhD TBS Associates, Raleigh NC Alliance for Risk Assessment Workshop Crystal City VA 28 May
A Novel Bottom Up Approach to Bounding Potential Human Cancer Risks from Endogenous Chemicals Thomas B. Starr, PhD TBS Associates, Raleigh NC Alliance for Risk Assessment Workshop Crystal City VA 28 May
Is a Linear Extrapolation of Cancer Risks to Very Low Doses Justified?
 Is a Linear Extrapolation of Cancer Risks to Very Low Doses Justified? May 3, 2000 Radiation Research Society Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA Daniel J. Strom Risk Analysis & Health Protection Richland, Washington
Is a Linear Extrapolation of Cancer Risks to Very Low Doses Justified? May 3, 2000 Radiation Research Society Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA Daniel J. Strom Risk Analysis & Health Protection Richland, Washington
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program
 U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program Update November 2010 ISCORS NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research The Department of Energy Office of
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program Update November 2010 ISCORS NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research The Department of Energy Office of
Mechanism underlying individual radiosensitivity of breast and head and neck cancer patients
 Mechanism underlying individual radiosensitivity of breast and head and neck cancer patients Siamak Haghdoost Centre for Radiation Protection Research Stockholm University WP6 DoReMi Individual variability
Mechanism underlying individual radiosensitivity of breast and head and neck cancer patients Siamak Haghdoost Centre for Radiation Protection Research Stockholm University WP6 DoReMi Individual variability
Question #1 Controls on cell growth and division turned on and off
 Lesson Overview 10.3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Question #1 Controls on cell growth and division turned on and off When cells are grown in the laboratory, most cells will divide until they come into contact
Lesson Overview 10.3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Question #1 Controls on cell growth and division turned on and off When cells are grown in the laboratory, most cells will divide until they come into contact
Deciphering multiple stressor effects of gamma radiation and uranium on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): Transcriptomics-based mixture modeling
 Deciphering multiple stressor effects of gamma radiation and uranium on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): Transcriptomics-based mixture modeling Y. Song, J. Asselman, K.A.C. De Schamphelaere, B. Salbu, and
Deciphering multiple stressor effects of gamma radiation and uranium on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): Transcriptomics-based mixture modeling Y. Song, J. Asselman, K.A.C. De Schamphelaere, B. Salbu, and
Concepts and Case Study Template for Surrogate Endpoints Workshop. Lisa M. McShane, Ph.D. Biometric Research Program National Cancer Institute
 Concepts and Case Study Template for Surrogate Endpoints Workshop Lisa M. McShane, Ph.D. Biometric Research Program National Cancer Institute Medical Product Development GOAL is to improve how an individual
Concepts and Case Study Template for Surrogate Endpoints Workshop Lisa M. McShane, Ph.D. Biometric Research Program National Cancer Institute Medical Product Development GOAL is to improve how an individual
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA
 LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
Chapter 7. What is Radiation Biology? Ionizing Radiation. Energy Transfer Determinants 09/21/2014
 Chapter 7 Molecular & Cellular Radiation Biology What is Radiation Biology? A branch of biology concerned with how ionizing radiation effects living systems. Biological damage that occurs from different
Chapter 7 Molecular & Cellular Radiation Biology What is Radiation Biology? A branch of biology concerned with how ionizing radiation effects living systems. Biological damage that occurs from different
MELODI statement 2018 Gap analysis
 MELODI statement 2018 Gap analysis MELODI (Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative) is a European Platform dedicated to low dose ionizing radiation risk research. The purpose of the MELODI Association
MELODI statement 2018 Gap analysis MELODI (Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative) is a European Platform dedicated to low dose ionizing radiation risk research. The purpose of the MELODI Association
Chromosomal Mutations
 Notes 2/17 Chromosomal Mutations A chromosome mutation is an unpredictable change that occurs in a chromosome. These changes are most often brought on by problems that occur during meiosis or by mutagens
Notes 2/17 Chromosomal Mutations A chromosome mutation is an unpredictable change that occurs in a chromosome. These changes are most often brought on by problems that occur during meiosis or by mutagens
TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK
 Norges teknisk-naturvitenskaplige universitet Institutt for fysikk EKSAMENSOPPGÅVER med løysingsforslag Examination papers with solution proposals TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK Biophysics of Ionizing Radiation
Norges teknisk-naturvitenskaplige universitet Institutt for fysikk EKSAMENSOPPGÅVER med løysingsforslag Examination papers with solution proposals TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK Biophysics of Ionizing Radiation
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis
 Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis University of Dundee Medical School Eric G Wright Professor of Experimental Haematology The
Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis University of Dundee Medical School Eric G Wright Professor of Experimental Haematology The
SOFIT: Sociotechnical and Organizational Factors for Insider Threat
 SOFIT: Sociotechnical and Organizational Factors for Insider Threat Frank L. Greitzer, Justin Purl, Yung Mei Leong, D.E. (Sunny) Becker, PsyberAnalytix Human Resources Research Organization Independent
SOFIT: Sociotechnical and Organizational Factors for Insider Threat Frank L. Greitzer, Justin Purl, Yung Mei Leong, D.E. (Sunny) Becker, PsyberAnalytix Human Resources Research Organization Independent
Breast Cancer and Biotechnology Jacquie Bay, Jo Perry, Michal Denny and Peter Lobie
 LENScience Senior Biology Seminar Series Breast Cancer and Biotechnology Jacquie Bay, Jo Perry, Michal Denny and Peter Lobie Breast Cancer Each year in New Zealand, approximately 2,400 women and 20 men
LENScience Senior Biology Seminar Series Breast Cancer and Biotechnology Jacquie Bay, Jo Perry, Michal Denny and Peter Lobie Breast Cancer Each year in New Zealand, approximately 2,400 women and 20 men
Radiation Carcinogenesis
 Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Mutations. Any change in DNA sequence is called a mutation.
 Mutations Mutations Any change in DNA sequence is called a mutation. Mutations can be caused by errors in replication, transcription, cell division, or by external agents. Mutations Mutations can be harmful.
Mutations Mutations Any change in DNA sequence is called a mutation. Mutations can be caused by errors in replication, transcription, cell division, or by external agents. Mutations Mutations can be harmful.
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
How to overcome limitations of new approach methodologies in the context of regulatory science
 How to overcome limitations of new approach methodologies in the context of regulatory science Romualdo Benigni Istituto Superiore di Sanita romualdo.benigni@gmail.com Chemical Risk Assessment into this
How to overcome limitations of new approach methodologies in the context of regulatory science Romualdo Benigni Istituto Superiore di Sanita romualdo.benigni@gmail.com Chemical Risk Assessment into this
Lecture -2- Environmental Biotechnology
 Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
Recommendations from Programmatic Review on Disease Pathway Management. Date: June 12, 2010
 Recommendations from Programmatic Review on Disease Pathway Management Date: June 12, 2010 Cancer Quality Council of Ontario: Context CQCO founded in 2002 on the recommendations of Ministry review of cancer
Recommendations from Programmatic Review on Disease Pathway Management Date: June 12, 2010 Cancer Quality Council of Ontario: Context CQCO founded in 2002 on the recommendations of Ministry review of cancer
5 3 Mutations.notebook April 10, 2017
 Mutations Lesson 3 Mar 14 4:21 PM How can mutations affect an organism? How is cancer related to mutations and the cell cycle? Mar 14 4:22 PM 1 I. How can mutations affect an organism? A. Some traits are
Mutations Lesson 3 Mar 14 4:21 PM How can mutations affect an organism? How is cancer related to mutations and the cell cycle? Mar 14 4:22 PM 1 I. How can mutations affect an organism? A. Some traits are
Computer modeling of radiation effects
 Computer modeling of radiation effects 20th International CODATA Conference 25 October 2006, Beijing Noriyuki B. Ouchi and Kimiaki Saito Radiation Effects Analysis Research Group, Nuclear Science and Engineering
Computer modeling of radiation effects 20th International CODATA Conference 25 October 2006, Beijing Noriyuki B. Ouchi and Kimiaki Saito Radiation Effects Analysis Research Group, Nuclear Science and Engineering
OA Biomarkers: What is required for validation and qualification? Part I. Evaluation Frameworks
 OA Biomarkers: What is required for validation and qualification? Part I. Evaluation Frameworks Michael C. Nevitt, PhD Dept of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of California, San Francisco OAI
OA Biomarkers: What is required for validation and qualification? Part I. Evaluation Frameworks Michael C. Nevitt, PhD Dept of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of California, San Francisco OAI
Challenges in environmental risk assessment (ERA) for birds and mammals and link to endocrine disruption (ED) Katharina Ott, BASF SE, Crop Protection
 Challenges in environmental risk assessment (ERA) for birds and mammals and link to endocrine disruption (ED) Katharina Ott, BASF SE, Crop Protection Charles River Symposium, Den Bosch, 3rd October 2017
Challenges in environmental risk assessment (ERA) for birds and mammals and link to endocrine disruption (ED) Katharina Ott, BASF SE, Crop Protection Charles River Symposium, Den Bosch, 3rd October 2017
Lecture 13 Radiation Onclolgy
 Lecture 13 Radiation Onclolgy Radiation Oncology: Tumors attacked with ionizing radiation Photons (gamma rays) High Energy Electrons Protons Other particles Brachytherapy: implants of beta emitters Ionizing
Lecture 13 Radiation Onclolgy Radiation Oncology: Tumors attacked with ionizing radiation Photons (gamma rays) High Energy Electrons Protons Other particles Brachytherapy: implants of beta emitters Ionizing
Pathology of Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC) A rare tumor
 Pathology of Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC) A rare tumor Jelle Wesseling 1, John Martens 2, Gabe Sonke 1, Carolien Schröder 3 1: Netherlands Cancer Institute Antoni van Leeuwenhoek Hospital, Amsterdam
Pathology of Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC) A rare tumor Jelle Wesseling 1, John Martens 2, Gabe Sonke 1, Carolien Schröder 3 1: Netherlands Cancer Institute Antoni van Leeuwenhoek Hospital, Amsterdam
Approaches to Integrating Evidence From Animal and Human Studies in Chemical Assessments
 Approaches to Integrating Evidence From Animal and Human Studies in Chemical Assessments Kris Thayer, National Center for Environmental Assessment (NCEA) Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) Division
Approaches to Integrating Evidence From Animal and Human Studies in Chemical Assessments Kris Thayer, National Center for Environmental Assessment (NCEA) Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) Division
1/31/2014. Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public
 Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS
 MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS How do different alleles arise? ( allele : form of a gene; specific base sequence at a site on DNA) Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS How do different alleles arise? ( allele : form of a gene; specific base sequence at a site on DNA) Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350.
 Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned. Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago
 The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago Regulatory Organizations NCRP (Nat l Council on Radiation
The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago Regulatory Organizations NCRP (Nat l Council on Radiation
pharmaceuticals volume 100 A A review of human carcinogens iarc monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans
 pharmaceuticals volume 100 A A review of human carcinogens This publication represents the views and expert opinions of an IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, which met
pharmaceuticals volume 100 A A review of human carcinogens This publication represents the views and expert opinions of an IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, which met
Objectives. Morphology and IHC. Flow and Cyto FISH. Testing for Heme Malignancies 3/20/2013
 Molecular Markers in Hematologic Malignancy: Ways to locate the needle in the haystack. Objectives Review the types of testing for hematologic malignancies Understand rationale for molecular testing Marcie
Molecular Markers in Hematologic Malignancy: Ways to locate the needle in the haystack. Objectives Review the types of testing for hematologic malignancies Understand rationale for molecular testing Marcie
METHODOLOGIES FOR INTERMITTENT AND SHORT-TERM EXPOSURE TO CARCINOGENS SUBCOMMITTEE
 METHODOLOGIES FOR INTERMITTENT AND SHORT-TERM EXPOSURE TO CARCINOGENS SUBCOMMITTEE Mission The mission of the MISTEC Subcommittee is to develop methodologies for establishing appropriate dose-metrics to
METHODOLOGIES FOR INTERMITTENT AND SHORT-TERM EXPOSURE TO CARCINOGENS SUBCOMMITTEE Mission The mission of the MISTEC Subcommittee is to develop methodologies for establishing appropriate dose-metrics to
Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment with Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
 Q: How is the strength of recommendation determined in the new molecular testing guideline? A: The strength of recommendation is determined by the strength of the available data (evidence). Strong Recommendation:
Q: How is the strength of recommendation determined in the new molecular testing guideline? A: The strength of recommendation is determined by the strength of the available data (evidence). Strong Recommendation:
EFSA Scientific Colloquium No. 17, June 2012, Parma, Italy. Dieter Schrenk Food Chemistry and Toxicology University of Kaiserslautern 2012
 EFSA Scientific Colloquium No. 17, 14-15 June 2012, Parma, Italy Dieter Schrenk Food Chemistry and Toxicology University of Kaiserslautern 2012 Thesis: The ideal risk assessment (in search of the relevant
EFSA Scientific Colloquium No. 17, 14-15 June 2012, Parma, Italy Dieter Schrenk Food Chemistry and Toxicology University of Kaiserslautern 2012 Thesis: The ideal risk assessment (in search of the relevant
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF
 BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
The European Commission s science and knowledge service
 The European Commission s science and knowledge service Joint Research Centre Creating and Using an AOP 13 th March 2018 Brigitte Landesmann DISCLAIMER: This presentation and its contents do not constitute
The European Commission s science and knowledge service Joint Research Centre Creating and Using an AOP 13 th March 2018 Brigitte Landesmann DISCLAIMER: This presentation and its contents do not constitute
IGEM team SIAT-SCIE Modelling part - an intuitive summary
 IGEM team SIAT-SCIE Modelling part - an intuitive summary Dsup - the key protein that protects tardigrades from lethal dosage of radiation Part 0 - Kinetic based model st edition backup The primary focus
IGEM team SIAT-SCIE Modelling part - an intuitive summary Dsup - the key protein that protects tardigrades from lethal dosage of radiation Part 0 - Kinetic based model st edition backup The primary focus
Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection
 1 Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection Cari Borrás, D.Sc., FACR, FAAPM Radiological Physics and Health Services Consultant Adjunct Assistant Professor (Radiology) GWU School
1 Review of the Radiobiological Principles of Radiation Protection Cari Borrás, D.Sc., FACR, FAAPM Radiological Physics and Health Services Consultant Adjunct Assistant Professor (Radiology) GWU School
What is the effect of radiation on astronauts? What damage can it do?
 Radiation in depth What is the effect of radiation on astronauts? What damage can it do? One of the biggest challenges in sending astronauts to destinations beyond the International Space Station, which
Radiation in depth What is the effect of radiation on astronauts? What damage can it do? One of the biggest challenges in sending astronauts to destinations beyond the International Space Station, which
Data and Knowledge Fusion: Supporting Toxicology, Health Effects Endpoints Analysis & Human Health Risk Assessment
 Data and Knowledge Fusion: Supporting Toxicology, Health Effects Endpoints Analysis & Human Health Risk Assessment OpenTox Asia May 17-18, 2017 Asish Mohapatra Health Canada Disclaimer This presentation
Data and Knowledge Fusion: Supporting Toxicology, Health Effects Endpoints Analysis & Human Health Risk Assessment OpenTox Asia May 17-18, 2017 Asish Mohapatra Health Canada Disclaimer This presentation
5.1. KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 68 Reinforcement Unit 2 Resource Book
 5.1 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Cells have a regular pattern of growth, DNA duplication, and division that is called the cell cycle.
5.1 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Cells have a regular pattern of growth, DNA duplication, and division that is called the cell cycle.
MELODI Multidisciplinary European Low dose Initiative. First Draft of Strategic Research Agenda (SRA) Date: 11 October 2010
 MELODI Multidisciplinary European Low dose Initiative First Draft of Strategic Research Agenda (SRA) Date: 11 October 2010 Authors: Dietrich AVERBECK, IRSN/CEA Consultant, Leader of WP2 of DoReMi, Emeritus
MELODI Multidisciplinary European Low dose Initiative First Draft of Strategic Research Agenda (SRA) Date: 11 October 2010 Authors: Dietrich AVERBECK, IRSN/CEA Consultant, Leader of WP2 of DoReMi, Emeritus
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
> Low-frequency magnetic fields and cancer
 > Environmental studies > Non-ionizing radiation > Low-frequency magnetic fields and cancer Assessment of scientific studies in the low dose range. Status as of August 2008 Summary of the publication «Niederfrequente
> Environmental studies > Non-ionizing radiation > Low-frequency magnetic fields and cancer Assessment of scientific studies in the low dose range. Status as of August 2008 Summary of the publication «Niederfrequente
ARCHITECTURAL RESEARCH METHODS
 ARCHITECTURAL RESEARCH METHODS ARCHITECTURAL RESEARCH METHODS 1) Interpretive - Historical Research 2) Qualitative Research 3) Correlational Research 4) Experimental / Quasi-Experimental Research 5) Simulation
ARCHITECTURAL RESEARCH METHODS ARCHITECTURAL RESEARCH METHODS 1) Interpretive - Historical Research 2) Qualitative Research 3) Correlational Research 4) Experimental / Quasi-Experimental Research 5) Simulation
Signaling Hypergraphs
 Signaling Hypergraphs Anna Ritz Department of Computer Science, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA SIAM Talk March 19, 2015 Cells in the Human Body www.thetahealth.com Cellular Communication: Wound Healing
Signaling Hypergraphs Anna Ritz Department of Computer Science, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA SIAM Talk March 19, 2015 Cells in the Human Body www.thetahealth.com Cellular Communication: Wound Healing
Non-Targeted Effects. Break out Session 1 H.Métivier Rapporteur
 Non-Targeted Effects Break out Session 1 H.Métivier Rapporteur Non-Targeted Effects The group discussed the non-targeted effects and their potential impacts on RP system. However, after a fruitful and
Non-Targeted Effects Break out Session 1 H.Métivier Rapporteur Non-Targeted Effects The group discussed the non-targeted effects and their potential impacts on RP system. However, after a fruitful and
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
NexGen Risk Assessment
 NexGen Risk Assessment Daniel Krewski, PhD, MHA Professor and Director McLaughlin Centre for Population Heath Risk Assessment & Risk Sciences International January 12, 2011 McLaughlin Centre for Population
NexGen Risk Assessment Daniel Krewski, PhD, MHA Professor and Director McLaughlin Centre for Population Heath Risk Assessment & Risk Sciences International January 12, 2011 McLaughlin Centre for Population
Simple Cancer Screening Based on Urinary Metabolite Analysis
 FEATURED ARTICLES Taking on Future Social Issues through Open Innovation Life Science for a Healthy Society with High Quality of Life Simple Cancer Screening Based on Urinary Metabolite Analysis Hitachi
FEATURED ARTICLES Taking on Future Social Issues through Open Innovation Life Science for a Healthy Society with High Quality of Life Simple Cancer Screening Based on Urinary Metabolite Analysis Hitachi
Name: BIOS 703 MIDTERM EXAMINATIONS (5 marks per question, total = 100 marks)
 Name: BIOS 703 MIDTERM EXAMINATIONS (5 marks per question, total = 100 marks) You will have 75 minutest to complete this examination. Some of the questions refer to Crizotinib in ROS1- Rearranged Non Small-
Name: BIOS 703 MIDTERM EXAMINATIONS (5 marks per question, total = 100 marks) You will have 75 minutest to complete this examination. Some of the questions refer to Crizotinib in ROS1- Rearranged Non Small-
Radiation Health Effects
 Radiation Health Effects Elena Buglova Incident and Emergency Centre Department of Nuclear Safety and Security Content Historical background Primary target for cell damage Deterministic effects Stochastic
Radiation Health Effects Elena Buglova Incident and Emergency Centre Department of Nuclear Safety and Security Content Historical background Primary target for cell damage Deterministic effects Stochastic
Paolo Vineis Imperial College London. The New World of Omics in Environmental Epidemiology. Zurich, June 21, 2018
 Paolo Vineis Imperial College London The New World of Omics in Environmental Epidemiology Zurich, June 21, 2018 An evolutionary perspective Cancer is the product of mutations, selection (evolutionary branching),
Paolo Vineis Imperial College London The New World of Omics in Environmental Epidemiology Zurich, June 21, 2018 An evolutionary perspective Cancer is the product of mutations, selection (evolutionary branching),
The Research Roadmap Checklist
 1/5 The Research Roadmap Checklist Version: December 1, 2007 All enquires to bwhitworth@acm.org This checklist is at http://brianwhitworth.com/researchchecklist.pdf The element details are explained at
1/5 The Research Roadmap Checklist Version: December 1, 2007 All enquires to bwhitworth@acm.org This checklist is at http://brianwhitworth.com/researchchecklist.pdf The element details are explained at
WHO Research Agenda for RF fields
 WHO Research Agenda for RF fields Dr E. van Deventer 1 Outline Introduction The WHO RF Research Agenda Motivation Background Content Discussion 2 3 Established in 1996 Coordinated by WHO HQ (SDE/PHE/RAD)
WHO Research Agenda for RF fields Dr E. van Deventer 1 Outline Introduction The WHO RF Research Agenda Motivation Background Content Discussion 2 3 Established in 1996 Coordinated by WHO HQ (SDE/PHE/RAD)
1, 2, 3-Trichloropropane (TCP): Assessment of Risks from Drinking Water
 1, 2, 3-Trichloropropane (TCP): Assessment of Risks from Drinking Water 1, 2, 3-Trichloropropane (TCP): Assessment of Risks from Drinking Water Prepared for Alaimo Group (Engineers and Architects) 200
1, 2, 3-Trichloropropane (TCP): Assessment of Risks from Drinking Water 1, 2, 3-Trichloropropane (TCP): Assessment of Risks from Drinking Water Prepared for Alaimo Group (Engineers and Architects) 200
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Competitive Edge Performance
 Competitive Edge Performance Competitive Edge Performance is a high quality nutritional supplement company that addresses the demanding needs of today s athletes, regardless of their fitness level, with
Competitive Edge Performance Competitive Edge Performance is a high quality nutritional supplement company that addresses the demanding needs of today s athletes, regardless of their fitness level, with
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions Linkage Analysis Question Question 8.1 Affected members of the pedigree above have an autosomal dominant disorder, and cytogenetic analyses using conventional
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions Linkage Analysis Question Question 8.1 Affected members of the pedigree above have an autosomal dominant disorder, and cytogenetic analyses using conventional
The breast advice for managing radiotherapy induced skin reactions
 15/05/2016 The breast advice for managing radiotherapy induced skin reactions Margaret Hjorth Nurse Unit Manager Epworth Radiation Oncology 1 15/05/2016 What is Radiotherapy? Use of high energy radiation
15/05/2016 The breast advice for managing radiotherapy induced skin reactions Margaret Hjorth Nurse Unit Manager Epworth Radiation Oncology 1 15/05/2016 What is Radiotherapy? Use of high energy radiation
Risk Assessment Report on styrene. Human Health Part
 Scientific Committee on Health and Environmental Risks SCHER Risk Assessment Report on styrene Human Health Part CAS No.: 100-42-6 EINECS no.: 202-851-5 SCHER adopted this opinion at its 23 rd plenary
Scientific Committee on Health and Environmental Risks SCHER Risk Assessment Report on styrene Human Health Part CAS No.: 100-42-6 EINECS no.: 202-851-5 SCHER adopted this opinion at its 23 rd plenary
Toxicology. Toxicity. Human Health Concerns. Health Effects of Hazardous Materials
 Human Health Concerns Health Effects of Hazardous Materials Toxicology Study of the nature, effects, and detection of poisons in organisms Humans are obvious focal point Other species and ecosystem function
Human Health Concerns Health Effects of Hazardous Materials Toxicology Study of the nature, effects, and detection of poisons in organisms Humans are obvious focal point Other species and ecosystem function
IPCS WORKSHOP ON ISSUES IN CANCER RISK ASSESSMENT. Meeting Report
 IPCS WORKSHOP ON ISSUES IN CANCER RISK ASSESSMENT Fraunhofer Institute of Toxicology and Aerosol Research, Hannover, Germany, 27-30 January 1998 Meeting Report 1. The Workshop was opened by Ms Sonich-Mullin
IPCS WORKSHOP ON ISSUES IN CANCER RISK ASSESSMENT Fraunhofer Institute of Toxicology and Aerosol Research, Hannover, Germany, 27-30 January 1998 Meeting Report 1. The Workshop was opened by Ms Sonich-Mullin
Multistep Carcinogenesis
 Multistep Carcinogenesis M.Rosemann, Institute for Radiation Biology Helmholtz Center Munich, Research Centre for Health and Environment The Hallmarks of Cancer D.Hanahan, Cell 2011 The Hallmarks of Cancer
Multistep Carcinogenesis M.Rosemann, Institute for Radiation Biology Helmholtz Center Munich, Research Centre for Health and Environment The Hallmarks of Cancer D.Hanahan, Cell 2011 The Hallmarks of Cancer
Glioblastoma pathophysiology: or a
 Glioblastoma pathophysiology: A or a? M.J. van den Bent The Brain Tumor Center at Erasmus MC Cancer Center Rotterdam, the Netherlands Pathophysiology: pathophysiology seeks to explain the physiological
Glioblastoma pathophysiology: A or a? M.J. van den Bent The Brain Tumor Center at Erasmus MC Cancer Center Rotterdam, the Netherlands Pathophysiology: pathophysiology seeks to explain the physiological
Regulation of Cell Division
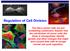 Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Garbay Catherine CNRS, LIG, Grenoble
 Garbay Catherine CNRS, LIG, Grenoble Sensors capturing world-wide information in the physical, cyber or social realms Open data initiatives, Web 4.0, crowdsourcing Multi-sensory immersion: skinput, novel
Garbay Catherine CNRS, LIG, Grenoble Sensors capturing world-wide information in the physical, cyber or social realms Open data initiatives, Web 4.0, crowdsourcing Multi-sensory immersion: skinput, novel
Inherited Cancer Syndromes and the DNA Damage Response
 Inherited Cancer Syndromes and the DNA Damage Response Inherited Breast Cancer and DNA Double- Strand Break Repair Michal Goldberg Department of GeneGcs The Hebrew University Cancer Hub, March 2014 Hallmarks
Inherited Cancer Syndromes and the DNA Damage Response Inherited Breast Cancer and DNA Double- Strand Break Repair Michal Goldberg Department of GeneGcs The Hebrew University Cancer Hub, March 2014 Hallmarks
AZA Research Priorities
 AZA Research Priorities Association of Zoos & Aquariums Research & Technology Committee Position Summary: The application of research findings to meet critical needs is a key to the successful accomplishment
AZA Research Priorities Association of Zoos & Aquariums Research & Technology Committee Position Summary: The application of research findings to meet critical needs is a key to the successful accomplishment
Regulating the Cell Cycle. Lesson Overview THINK ABOUT IT. How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide?
 THINK ABOUT IT How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide? Controls on Cell Division How is the cell cycle regulated? The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins both inside
THINK ABOUT IT How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide? Controls on Cell Division How is the cell cycle regulated? The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins both inside
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Core Concepts in Radiation Exposure 4/10/2015. Ionizing Radiation, Cancer, and. James Seward, MD MPP
 Ionizing Radiation, Cancer, and Causation James P. Seward, MD MPP FACOEM Clinical Professor of Medicine, UCSF American Occupational Health Conf May 4, 2015 Ionizing Radiation, Cancer, and Causation James
Ionizing Radiation, Cancer, and Causation James P. Seward, MD MPP FACOEM Clinical Professor of Medicine, UCSF American Occupational Health Conf May 4, 2015 Ionizing Radiation, Cancer, and Causation James
Estimating Risk of Low Radiation Doses (from AAPM 2013) María Marteinsdóttir Nordic Trauma,
 Estimating Risk of Low Radiation Doses (from AAPM 2013) María Marteinsdóttir Nordic Trauma, 20140521 Stochastic effects Linear No Threshold - LNT-model Uncertain Material produced by William R. Hendee
Estimating Risk of Low Radiation Doses (from AAPM 2013) María Marteinsdóttir Nordic Trauma, 20140521 Stochastic effects Linear No Threshold - LNT-model Uncertain Material produced by William R. Hendee
cells divide? Growth Development Repair Asexual reproduction Formation of gametes
 mitosis and meiosis cells divide? Growth Development Repair Asexual reproduction Formation of gametes How does a cell know when to divide? the cell cycle A repeating process of cell growth and division
mitosis and meiosis cells divide? Growth Development Repair Asexual reproduction Formation of gametes How does a cell know when to divide? the cell cycle A repeating process of cell growth and division
Implementing scientific evidence into clinical practice guidelines
 Evidence Based Dentistry Implementing scientific evidence into clinical practice guidelines Asbjørn Jokstad University of Oslo, Norway 15/07/2004 1 PRACTICE GUIDELINES IN DENTISTRY (Medline) 2100 1945
Evidence Based Dentistry Implementing scientific evidence into clinical practice guidelines Asbjørn Jokstad University of Oslo, Norway 15/07/2004 1 PRACTICE GUIDELINES IN DENTISTRY (Medline) 2100 1945
Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle
 Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Vocabulary: Cyclin Cancer Key Concepts: How is the cell cycle regulated? How are cancer cells different from other cells? I. Introduction A. An Interesting Fact About
Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Vocabulary: Cyclin Cancer Key Concepts: How is the cell cycle regulated? How are cancer cells different from other cells? I. Introduction A. An Interesting Fact About
HESI Biological Significance of DNA Adducts Project Committee
 HESI Biological Significance of DNA Adducts Project Committee Presenter: Gary Williams, M.D. (New York Medical College) Chair: Lynn H. Pottenger, Ph.D., DABT (The Dow Chemical Company) Vice-Chair: Robert
HESI Biological Significance of DNA Adducts Project Committee Presenter: Gary Williams, M.D. (New York Medical College) Chair: Lynn H. Pottenger, Ph.D., DABT (The Dow Chemical Company) Vice-Chair: Robert
Cancer Treatment by Alternating Electric Fields (TTFields); Physical Basis & Clinical Trial Results. Madrid, March 2015
 1 Cancer Treatment by Alternating Electric Fields (TTFields); Physical Basis & Clinical Trial Results Madrid, March 2015 2 Cancer Treatments Surgical - whenever possible, Effective mostly in Early stages,
1 Cancer Treatment by Alternating Electric Fields (TTFields); Physical Basis & Clinical Trial Results Madrid, March 2015 2 Cancer Treatments Surgical - whenever possible, Effective mostly in Early stages,
CONTROL OF CELL DIVISION
 CONTROL OF CELL DIVISION Regulation of cell division is necessary to determine when and how cells should divide. Types of Regulators: Internal regulators: Cyclins proteins that regulate the timing of the
CONTROL OF CELL DIVISION Regulation of cell division is necessary to determine when and how cells should divide. Types of Regulators: Internal regulators: Cyclins proteins that regulate the timing of the
Radiation Effects. Radiobiology Steve Curtis Desert Research Institute
 Radiation Effects Radiobiology Steve Curtis Desert Research Institute Background Radiation Cosmic Terrestrial In our Bodies Total Radiation About 300 mr per year Equals about 15 X-Rays Over half is from
Radiation Effects Radiobiology Steve Curtis Desert Research Institute Background Radiation Cosmic Terrestrial In our Bodies Total Radiation About 300 mr per year Equals about 15 X-Rays Over half is from
