Bevacizumab plus chemotherapy in elderly patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: single center experience
|
|
|
- Brent Bennett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 226 research article Bevacizumab plus chemotherapy in elderly patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: single center experience Janja Ocvirk 1,2, Maja Ebert Moltara 1,Tanja Mesti 1, Marko Boc 1, Martina Rebersek 1, Neva Volk 1, Jernej Benedik 1, Zvezdana Hlebanja 1 1 Department of Medical Oncology, Institute of Oncology Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia 2 Faculty of Medicine, University of Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia Received 3 September 2014 Accepted 7 October 2014 Correspondence to: Assoc. Prof. Janja Ocvirk, M.D., Ph.D., Institute of Oncology Ljubljana, Zaloška 2, Ljubljana. Phone: ; Fax: ; jocvirk@onko-i.si Disclosure: No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed. Background. Metastatic colorectal cancer (mcrc) is mainly a disease of elderly, however, geriatric population is underrepresented in clinical trials. Patient registries represent a tool to assess and follow treatment outcomes in this patient population. The aim of the study was with the help of the patients register to determine the safety and efficacy of bevacizumab plus chemotherapy in elderly patients who had previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. Patients and methods. The registry of patients with mcrc was designed to prospectively evaluate the safety and efficacy of bevacizumab-containing chemotherapy as well as selection of patients in routine clinical practice. Patient baseline clinical characteristics, pre-specified bevacizumab-related adverse events, and efficacy data were collected, evaluated and compared according to the age categories. Results. Between January 2008 and December 2010, 210 patients with mcrc (median age 63, male 61.4%) started bevacizumab-containing therapy in the 1 st line setting. Majority of the 210 patients received irinotecan-based chemotherapy (68%) as 1 st line treatment and 105 patients (50%) received bevacizumab maintenance therapy. Elderly ( 70 years) patients presented 22.9% of all patients and they had worse performance status (PS 1/2, 62.4%) than patients in < 70 years group (PS 1/2, 35.8%). Difference in disease control rate was mainly due to inability to assess response in elderly group (64.6% in elderly and 77.8% in < 70 years group, p = 0.066). The median progression free survival was 10.2 (95% CI, ) and 11.3 (95% CI, ) months in elderly and < 70 years group, respectively (p = 0.58). The median overall survival was 18.5 (95% CI, ) and 27.4 (95% CI, ) months for elderly and < 70 years group, respectively (p = 0.03). Three-year survival rate was 26% and 37.6% in elderly vs. < 70 years group (p = 0.03). Overall rates of bevacizumab-related adverse events were similar in both groups: proteinuria 21/22 %, hypertension 25/19 %, haemorrhage 2/4 % and thromboembolic events 10/6 %, for elderly and < 70 years group, respectively. Conclusions. In routine clinical practice, the combination of bevacizumab and chemotherapy is effective and welltolerated regimen in elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Key words: metastatic colorectal cancer; bevacizumab; chemotherapy; elderly Introduction As with many cancers, metastatic colorectal cancer (mcrc) is mainly a disease of elderly population. However, geriatric population is underrepresented in clinical trials. The median age at diagnosis for patients with CRC is 72 years, while the median age of patients in clinical trials is 63 years. 1 In Slovenia, 44% of colorectal cancer cases were diagnosed in people aged 70 years and over. 2 Age together with performance status and comorbidities is one of the most important factors when deciding doi: /raon
2 Ocvirk J et al. / Bevacizumab plus chemotherapy in elderly patients 227 on treatment regimen. 3 Studies show that close to half of the elderly patients with stage III colon cancer do not receive chemotherapy, although most of the studies and meta-analysis have reported similar response rate (ORR), overall survival (OS), time to progression (TTP) and tolerability for elderly and younger patients in adjuvant and metastatic setting. 4-6 Addition of bevacizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor, to the chemotherapy backbone regimens improves progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival in first-line and second-line treatment and when continued beyond first progression in mcrc. 7 Data from large observational studies, subgroup analysis and pooled analysis of randomized trials have suggested that the survival benefits associated with the use of bevacizumab in the first-line treatment are similar in elderly and general population With the introduction of bevacizumab as standard of care for mcrc patients in Slovenia 14, our centre has created patient registry to prospectively assess patient selection as well as efficacy and safety of bevacizumab containing chemotherapy in routine clinical practice. This registry enabled data capturing of the mcrc management in geriatric population that is usually excluded in clinical research and comparison of clinical outcomes to their younger counterparts. The aim of the study was with the help of the patients register to determine the safety and efficacy of bevacizumab plus chemotherapy in elderly patients who had previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. Patients and methods Patient clinical baseline characteristics, pre-specified bevacizumab-related adverse events, and efficacy data were prospectively collected within local patient registry from 210 mcrc patients who started bevacizumab-containing chemotherapy in the 1 st line setting. Patient clinical characteristics (primary tumour treatments, an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group [ECOG] performance status [PS], metastatic burden), rate of bevacizumab-related toxicities, metastasectomy rate, ORR, PFS and OS were evaluated. The study was done in accordance with the principles of Good Clinical Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by national ethics committee. All patients provided written informed consent for data collection. Statistical analysis Statistical analyses were performed on the intentto-treat (ITT) population e.g. patients who received at least one dose of bevacizumab. Patient characteristics and toxicity data were summarized descriptively by the age group. Proportions of categorical variables were compared using the chi-square test. Survival analyses were performed using the Kaplan-Meier method, which provided medians and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The differences in survival were evaluated using the log rank test; the follow-up time for this comparison was limited to 3 years, which is the minimum period available for all the patients. Results Patient characteristics The data from 210 patients (median age 63, males 61.4%) treated with bevacizumab-containing chemotherapy (B-CTX) in the 1 st line setting in routine clinical practice were included in the evaluation. The patients with mcrc started B-CTX treatment between January 2008 and December 2010 and were followed for outcomes at our centre until December The ECOG PS at baseline was 0 in 58%, 1 in 38% and 2 in 4% of all patients. Subgroup Elderly patients ( 70 years, n = 48) presented 22.9% of all patients and they had worse performance status (PS1/2 62.4%) than patients in < 70 years group (PS1/2 35.8%). Patient characteristics are described in Table 1. Metastatic disease was the first diagnosis in 63% of patients < 70 years old, while in the elderly patients only 45.8% had mcrc as the first diagnosis of CRC. Treatment Bevacizumab 5 mg/kg every two weeks or 7.5 mg/ kg every three weeks was administered in combination with chemotherapy (CTX) to the patients with mcrc. Majority of 210 patients received irinotecan-based chemotherapy (68%) as 1 st line treatment and 105 patients (50%) received bevacizumab maintenance therapy. The patients in < 70 years group received mainly irinotecan-based chemotherapy (66%) - capecitabine plus irinotecan (XELIRI) 58.6%, capecitabine plus oxaliplatin (XELOX) 27.8%, leucovorin, fluorouracil plus irinotecan (FOLFIRI) 6.8%, leucovorin, fluorouracil plus oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) 4.9%, monotherapy capecitabine or irinotecan 1.8%. Median duration
3 228 Ocvirk J et al. / Bevacizumab plus chemotherapy in elderly patients TABLE 1. Patient characteristics at baseline Characteristics Gender, n (%) Age < 70 y (n = 162) Age 70 y (n = 48) Age Men 96 (60) 33 (70) Women 64 (40) 14 (30) FIGURE 1. Kaplan-Meier survival curves for Progression Free Survival and Overall Survival in patients aged < 70 years and 70 years. Median, years Range, years ECOG performance status, n (%) TABLE 2. Efficacy outcomes Outcomes Best response, n (%) Age < 70 y (n = 162) Age 70 y (n = 48) Complete 9 (6) 4 (8) Partial 60 (37) 13 (27) Stable disease 57 (35) 14 (29) Progressive disease 21 (13) 6 (13) Not evaluable 7 (4) 6 (13) Overall response rate, % (95% CI) 69 (43) 17 (35) Disease-control rate, % (95% CI) 126 (78) 31 (65) Progression free survival, months Median (95% CI) 11.3 ( ) 10.2 ( ) Overall survival, months Median (95% CI) 27.4 ( ) 18.5 ( ) Metastasectomy, n (%) 32 (21.2) 6 (15) (64) 18 (38) 1 52 (32) 27 (56) 2 6 (4) 3 (6) Site of metastatic disease, n (%) Liver 112 (69) 35 (73) Lung 39 (24) 12 (25) Lymph nodes 42 (26) 12 (25) Bones 6 (4) 3 (6) Other 64 (40) 13 (27) Primary tumour location, n (%) Colon only 106 (65) 31 (65) Rectum only 56 (35) 16 (33) Colon and rectum 0 1 (2) Adjuvant chemotherapy, n (%) 50 (31) 18 (38) Previous radiotherapy, n (%) 30 (19) 9 (19) Surgical resection, n (%) 132 (82) 42 (88) CI = confidence interval of B-CTX was 24 weeks (range 3 to 36) and the median number of treatment cycles was 8 (range 1 to 16). In this group of patients, maintenance bevacizumab was administered to 83 patients (51%), with median number of cycles 6 (range 1 to 70). The backbone chemotherapy in patients aged 70 years was also mostly irinotecan (75%) - XELIRI 60.4%, XELOX 14.6%, FOLFIRI 10.4%, FOLFOX 6.2%, monotherapy capecitabine or irinotecan 8.4%. Median duration of B-CTX in elderly was 17 weeks (range 3 to 36) and the median number of treatment cycles was 6 (range 1 to 12). Twenty one patients (44%) received maintenance bevacizumab with median number of cycles 5 (range 1 to 51). Treatment interruption was reported in 20.4% of patients in < 70 years group and 14.6% of patients 70 years group. Two main reasons for bevacizumab discontinuation in < 70 years group were disease progression (49% of all patients that discontinued) and adverse events (25%). In 70 years group bevacizumab was discontinued due to disease progression (35%) and adverse events (20%), but 15% of patients were lost to follow-up. Efficacy Efficacy data are summarized in Table 2. Difference in disease control rate (DCR) was mainly due to inability to assess response in elderly group (64.6% in elderly and 77.8% in < 70 years group). ORR and DCR did not differ significantly between the two groups (p = and p = 0.066, respectively). The median PFS was 10.2 (95% CI, ) and 11.3 (95% CI, ) months in elderly and < 70 years group, respectively (p = 0.58) (Figure 1). The median OS was 18.5 (95% CI,
4 Ocvirk J et al. / Bevacizumab plus chemotherapy in elderly patients ) and 27.4 (95% CI, ) months for elderly and < 70 years group, respectively (p = 0.03) (Figure 1). Metastasectomy was performed in 6 (15%) of elderly patients and 32 (21.2%) patients in < 70 years group. Three-year survival rate was 26% (95% CI, ) and 37.6% (95% CI, ) in elderly vs. < 70 years group (p = 0.03). In elderly patients, 15 patients received secondline therapy, all of them receiving bevacizumab in combination with subsequent chemotherapy. In patients aged < 70 years, 101 patients received second-line therapy, out of which 76% contained bevacizumab. Toxicity Adverse events related to bevacizumab were reported in 123 (75.9%) and 38 (79.2%) patients in < 70 years and 70 years group, respectively. Adverse events of special interest to bevacizumab are summarized in Table 3 (epistaxis excluded). A case of vesico-rectal fistula was reported in the patient aged < 70 years (rectal cancer with previous radiotherapy). One case of acute myocardial infarction was reported in each group. One patient on capecitabine monotherapy from elderly group presented with adverse event with an outcome death (heart failure). The incidence of adverse event that led to bevacizumab discontinuation was 19% in both age groups. The incidence of adverse event that led to bevacizumab dose interruption was 10.5% and 10% in patients aged < 70 and 70 years, respectively. Discussion Randomized studies, subgroup and pooled analysis, along with large observational studies suggest that bevacizumab containing first-line chemotherapy is efficacious and safe in elderly patients with mcrc. Randomized phase II trial of bevacizumab or placebo added to 5-FU in elderly patients not suitable for irinotecan treatment reported significantly longer PFS in patients who received bevacizumab versus placebo (9.2 months versus 5.5 months, respectively, hazard ratio, 0.5; p = ). 15 Furthermore, results from phase III trial AVEX showed that in patients over age of 70 years and non-fit for oxaliplatin or irinotecan-based chemotherapy, PFS was significantly longer in the group of patients who received bevacizumab plus capecitabine versus the capecitabine alone group TABLE 3. Targeted adverse events Adverse event < 70 years (n = 162) No. of patients (%) Grade1 Grade2 Grade3 Grade4 (9.1 versus 5.1 months, p < ). 16 The subanalysis of the BICC-C study (bevacizumab + FOLFIRI or mifl) reported no difference in efficacy and safety for mcrc patients > 70 years compared with patients 70 years (PFS 7.6 months compared to 10.7 months, p = 0.14, with FOLFIRI/Bev ORR 57% > 70 years and 58% 70 years). 11 Pooled analysis of four randomized trials (three first-line and one second-line treatment, n = 3,007)), where patients were treated with fluoropyrimidinebased chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab, showed that addition of bevacizumab to CTX significantly prolonged PFS in older and younger patients with similar magnitude of PFS benefit (hazard ratios were 0.59, 0.58 and 0.54 in patients aged < 65 years, 65 years and 70 years, respectively). In addition, OS in both older and younger patients was statistically significantly prolonged by addition of bevacizumab to CTX (median OS was 19.9 months in patients aged < 65 years, 17.9 months in patients 65 years and 17.4 months in those aged 70 years). 13 Recent results from phase II study BECOX suggest that bevacizumab plus XELOX is effective and well tolerated in elderly mcrc patients with time to progression of 11.1 months, median OS of 20.4 months and ORR of 46%. 17 Bevacizumab-containing CTX outcomes from routine clinical practice were monitored and/or reported in mcrc patients registries such as prospective US BRiTE registry (n = 1,953) 9 or retrospective Czech (n = 3,187) and French (n = 1,322) registries. 10,18 These large first-line setting registries confirmed similarity of clinical benefit between Total Hypertension 11 (6.8) 15 (9.3) 5 (3.1) 0 (0) 30 (18.5) Thromboembolism 1 (0.6) 4 (2.5) 4 (2.5) 0 (0) 9 (5.6) Proteinuria 23 (14.2) 11 (6.8) 2 (1.2) 0 (0) 36 (22.2) Hemorrhage 4 (2.5) 1 (0.6) 0 (0) 1 (0.6) 6 (3.7) Infection 4 (2.5) 1 (0.6) 4 (2.5) 0 (0) 8 (4.9) > 70 years (n = 48) Hypertension 3 (6.2) 6 (12.5) 2 (4.2) 0 (0) 12 (25) Thromboembolism 0 (0) 1 (2.1) 2 (4.2) 2 (4.2) 5 (10.4) Proteinuria 7 (14.6) 3 (6.2) 0 (0) 0 (0) 10 (20.8) Hemorrhage 0 (0) 0 (0) 1 (2.1) 0 (0) 1 (2.1) Infection 0 (0) 1 (2.1) 0 (0) 0 (0) 1 (2.1)
5 230 Ocvirk J et al. / Bevacizumab plus chemotherapy in elderly patients younger and older patients, previously reported in randomized clinical trials and pooled analysis. Safety profile for all these studies is generally similar in older and younger patients, except for thromboembolic events, which were more common in the older group. Within local registry of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, we have assessed efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in combination with various chemotherapy regimens and compared data between two age groups - patients aged below and over 70 years. While other registries as backbone chemotherapy reported use of primarily oxaliplatine-based first line chemotherapy (FOLFOX followed by XELOX or FOLFIRI) with trend of increased monotherapy use in elderly population, in our centre backbone chemotherapy was in majority of patients (68%) irinotecan-based. Specifically, bevacizumab was administered mainly with XELIRI (58.6% in < 70 years group and 60.4% in 70 years group) followed by XELOX (27.8% in < 70 years group and 14.6% in 70 years group) with low rate of monotherapy use (1.8% and 8.4% for < 70 years and 70 years, respectively). Although median duration of B-CTX in elderly was 17 weeks and in patients aged < 70 years was 24 weeks, maintenance with bevacizumab was well tolerated in both groups with median number of cycles 6 and 5 for < 70 years (51% of patients) and 70 years group (44% of patients), respectively. ORR and DCR did not differ significantly between the two groups (p = and p = 0.066, respectively) which is in concordance with other studies. The median PFS of 10.2 and 11.3 months in elderly and < 70 years group, respectively (p = 0.58) is also comparable to findings in other studies. In BRiTE registry, even after adjusting for significant baseline covariates such as ECOG PS or site and surgical resection of primary tumour, decreasing median OS in older age cohorts was observed. 9 Similarly, in our study median OS was 18.5 and 27.4 months for elderly and < 70 years group, respectively (p = 0.03). This can be partially explained by worse PS in elderly (PS1/2 62.4%) than patients in < 70 years group (PS1/2 35.8%). Selection bias and influence of comorbidities and presence of synchronous metastasis that were not captured cannot be excluded. In the registry, only bevacizumab-associated adverse event information was collected. A disadvantage of our registry was lack of data for chemotherapy induced adverse events. This was not in scope of the registry, as in an earlier retrospective study from our group, where we compared XELIRI/ bevacizumab to FOLFIRI/bevacizumab (age range years), we have reported similar efficacy and safety data between two chemotherapy regimens, but with more grade 3/4 neutropenia in FOLFIRI/ bevacizumab combination, and more grade 3/4 diarrhoea in XELIRI/bevacizumab, findings confirmed also by other studies. 19,20 The rates of most bevacizumab-targeted adverse events in the older patient group were similar to rates in the patients aged < 70 years. They were also comparable to previously reported overall rates of adverse events. 9,13,15 The most common bevacizumab-associated adverse events were hypertension and proteinuria, with hypertension being slightly more observed in elderly (25% vs. 18.5%). No grade 4 or 5 hypertensive events were recorded. Thromboembolic events were reported in 10.4% of elderly patients compared to 5.6% in patients aged < 70 years. The increase of arterial thromboembolism in elderly treated with bevacizumab, but no change in venous thromboembolic events, was previously reported in pooled analysis of four randomized trials as well as in large patient registry. 9,13 Conclusions Our single centre experience present new set of data confirming PFS and OS benefit of bevacizumab containing, predominantly irinotecan-based firstline chemotherapy in mcrc patients in routine clinical practice. This benefit was observed in both elderly and patients aged < 70 years with manageable safety profile. Proper selection of patients with mcrc can result in a safe and beneficial B-CTX treatment results in older patients with similar outcomes to their younger counterparts, therefore, chronological age does not present exclusion to treatment with bevacizumab. Acknowledgements The independent analysis of data was performed by Institute for Biostatistics and Medical Informatics at University of Ljubljana, Slovenia. This research was partially supported by Roche. References 1. Schmoll HJ, Van Cutsem E, Stein A, Valentini V, Glimelius B, Haustermans K, et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for management of patients with colon and rectal cancer. A personalized approach to clinical decision making. Ann Oncol 2012; 23:
6 Ocvirk J et al. / Bevacizumab plus chemotherapy in elderly patients Cancer in Slovenia Ljubljana: Institute of Oncology Ljubljana, Epidemiology and Cancer Registry, Cancer Registry of Republic of Slovenia; Zwitter M, Kovac V, Rajer M, Vrankar M, Smrdel U. Two schedules of chemotherapy for patients with non-small cell lung cancer in poor performance status: a phase II randomized trial. Anticancer Drugs 2010; 21: Sundararajan V, Mitra N, Jacobson JS, Grann VR, Heitjan DF, Neugut AI. Survival associated with 5-fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy among elderly patients with node positive colon cancer. Ann Intern Med 2002; 136: Folprecht G, Cunningham D, Ross P, Glimelius B, Di Costanzo F, Wils J, et al. Efficacy of 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy in elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A pooled analysis of clinical trials. Ann Oncol 2004; 15: Köhne CH, Folprecht G, Goldberg RM, Mitry E, Rougier P. Chemotherapy in elderly patients with colorectal cancer. Oncologist 2008; 13: Ocvirk J. Advances in the treatment of metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Radiol Oncol 2009; 43: Van Cutsem E, Rivera F, Berry S, Kretzschmar A, Michael M, DiBartolomeo M, et al. Safety and efficacy of first-line bevacizumab with FOLFOX, XELOX, FOLFIRI and fluoropyrimidines in metastatic colorectal cancer: the BEAT study. Ann Oncol 2009; 29: Kozloff MF, Berlin J, Flynn PJ, Kabbinavar F, Ashby M, Dong W, et al. Clinical outcomes in elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer receiving bevacizumab and chemotherapy: results from the BRiTE observational cohort study. Oncology 2010; 78: Slavicek L, Pavlik T, Tomasek J, Bortlicek Z, Buchler T, Melichar B, et al. Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results from the Czech population-based registry. BMC Gastroenterology 2014; 14: Jackson NA, Barrueco J, Soufi-Mahjoubi R, Marshall J, Mitchell E, Zhang X, et al. Comparing safety and efficacy of first-line irinotecan/fluoropirimidine combinations in elderly versus nonelderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer 2009; 115: Price TJ, Zannino D, Wilson K, Simes J, Cassidy J, Van Hazel GA, et al. Bevacizumab is equally effective and no more toxic in elderly patients with advanced colorectal cancer: a subgroup analysis from the AGITG MAX trial: an international randomised controlled trial of capecitabine, bevacizumab and mytomycin C. Ann Oncol 2012; 23: Cassidy J, Saltz LB, Giantonio BJ, Kabbinavar FF, Hurwitz HI, Rohr UP. Effect of bevacizumab in older patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: pooled analysis of four randomized studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2010; 136: Mesti T, Boshkoska BM, Kos M, Tekavčič M, Ocvirk J. The cost of systemic therapy for metastatic colorectal carcinoma in Slovenia: Discrepancy analysis between cost and reimbursement. Radiol Oncol 2015; 49: Kabbinavar FF, Schulz J, McCleod, Patel T, Hamm JT, Hecht JR, et al. Addition of bevacizumab to bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin in first-line metastatic colorectal cancer: results of randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: Cunningham D, Lang I, Marcuello E, Lorusso V, Ocvirk J, Shin DB, et al. Bevacizumab plus capecitabine versus capecitabine alone in elderly patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer (AVEX): an open label, randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2013; 14: Feliu J, Salud A, Safont MJ, Garcia-Girón C, Aparicio J, Vera R, et al. First-line bevacizumab and capecitabine-oxaliplatine in elderly patients with mcrc: GEMCAD phase II BECOX study. Br J Cancer 2014; 111: Doat S, Thiébaut A, Samson S, Ricordeau P, Guillemont D, Mitry E. Elderly patients with colorectal cancer: treatment modalities and survival in France. National data from the ThInDiT cohort study. Eur J Cancer 2014; 50: Ocvirk J, Rebersek M, Boc M. Bevacizumab in first-line therapy of metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective comparison of FOLFIRI and XELIRI. Anticancer Res 2011; 31: Ducreux M, Adenis A, Pignon J-P, François E, Chauffert B, Ichanté JL, et al. Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab-based combination regimens in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: Final results from a randomised phase ii study of bevacizumab plus5-fluorouracil, leucovorin plus irinotecan versus bevacizumab plus capecitabine plus irinotecan (FNCLCC ACCORD 13/0503 study). Eur J Cancer 2013; 49:
Targeted Therapies in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Update
 Targeted Therapies in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Update ASCO 2007: Targeted Therapies in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Update Bevacizumab is effective in combination with XELOX or FOLFOX-4 Bevacizumab
Targeted Therapies in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Update ASCO 2007: Targeted Therapies in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Update Bevacizumab is effective in combination with XELOX or FOLFOX-4 Bevacizumab
Incorporating biologics in the management of older patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
 Incorporating biologics in the management of older patients with metastatic colorectal cancer D Papamichael MB BS MD FRCP Cyprus Oncology Centre GSK Satellite Symposium SIOG APAC Singapore 12-13 July 2014
Incorporating biologics in the management of older patients with metastatic colorectal cancer D Papamichael MB BS MD FRCP Cyprus Oncology Centre GSK Satellite Symposium SIOG APAC Singapore 12-13 July 2014
Bevacizumab is currently licensed for the following indication relevant for this NICE review:
 Roche Executive Summary Context Bevacizumab (Avastin) is a humanized (93% human) murine monoclonal antibody which binds to and neutralizes VEGF, a powerful pro-angiogenic glycoprotein produced by both
Roche Executive Summary Context Bevacizumab (Avastin) is a humanized (93% human) murine monoclonal antibody which binds to and neutralizes VEGF, a powerful pro-angiogenic glycoprotein produced by both
Tobias Engel Ayer Botrel 1,2*, Luciana Gontijo de Oliveira Clark 1, Luciano Paladini 1 and Otávio Augusto C. Clark 1
 Botrel et al. BMC Cancer (2016) 16:677 DOI 10.1186/s12885-016-2734-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab plus chemotherapy compared to chemotherapy alone in previously untreated
Botrel et al. BMC Cancer (2016) 16:677 DOI 10.1186/s12885-016-2734-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab plus chemotherapy compared to chemotherapy alone in previously untreated
Management of Advanced Colorectal Cancer in Older Patients
 Review Article [1] April 15, 2005 By Stuart M. Lichtman, MD, FACP [2] Many elderly individuals have substantial life expectancy, even in the setting of significant illness. There is evidence to indicate
Review Article [1] April 15, 2005 By Stuart M. Lichtman, MD, FACP [2] Many elderly individuals have substantial life expectancy, even in the setting of significant illness. There is evidence to indicate
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. M. Bakogeorgos, G. Mountzios, G. Kotsantis, P. Economopoulou, N. Fytrakis, N. Kentepozidis. Summary.
 JBUON 2013; 18(3): 629-634 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Chemotherapy compliance, tolerance and efficacy in elderly and non-elderly
JBUON 2013; 18(3): 629-634 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Chemotherapy compliance, tolerance and efficacy in elderly and non-elderly
MEETING SUMMARY ESMO 2018, Munich, Germany. Dr. Jenny Seligmann University of Leeds, UK HIGHLIGHTS ON COLORECTAL CANCER
 MEETING SUMMARY ESMO 2018, Munich, Germany Dr. Jenny Seligmann University of Leeds, UK HIGHLIGHTS ON COLORECTAL CANCER DISCLAIMER Please note: The views expressed within this presentation are the personal
MEETING SUMMARY ESMO 2018, Munich, Germany Dr. Jenny Seligmann University of Leeds, UK HIGHLIGHTS ON COLORECTAL CANCER DISCLAIMER Please note: The views expressed within this presentation are the personal
How Old is Too Old for Chemotherapy in Early C olon Colon Cancer: Role of Geriatric Assessments Winson Y. Cheung, MD, MPH, FRCPC
 How Old is Too Old for Chemotherapy in Early Colon Cancer: Role of Geriatric Assessments Winson Y. Cheung, MD, MPH, FRCPC British Columbia Cancer Agency - Vancouver CAGPO - October 20, 2013 1 About Me
How Old is Too Old for Chemotherapy in Early Colon Cancer: Role of Geriatric Assessments Winson Y. Cheung, MD, MPH, FRCPC British Columbia Cancer Agency - Vancouver CAGPO - October 20, 2013 1 About Me
Jonathan Dickinson, LCL Xeloda
 Xeloda A blockbuster in the making Jonathan Dickinson, LCL Xeloda Xeloda unique tumor-activated mechanism Delivering more cancer-killing agent straight into cancer Highly effective comparable efficacy
Xeloda A blockbuster in the making Jonathan Dickinson, LCL Xeloda Xeloda unique tumor-activated mechanism Delivering more cancer-killing agent straight into cancer Highly effective comparable efficacy
Treatment of the elderly metastatic colorectal cancer patient: SIOG Recommendations
 Treatment of the elderly metastatic colorectal cancer patient: SIOG Recommendations D Papamichael MB BS FRCP On behalf of the SIOG CRC in the Elderly Task Force Madrid 10/11/07 8 th Meeting of the International
Treatment of the elderly metastatic colorectal cancer patient: SIOG Recommendations D Papamichael MB BS FRCP On behalf of the SIOG CRC in the Elderly Task Force Madrid 10/11/07 8 th Meeting of the International
ADVANCED COLORECTAL CANCER: UNRESECTABLE OR BORDERLINE RESECTABLE (GROUP 1) CHEMOTHERAPY +/- TARGETED AGENTS. Andrés Cervantes. Professor of Medicine
 ADVANCED COLORECTAL CANCER: UNRESECTABLE OR BORDERLINE RESECTABLE (GROUP 1) CHEMOTHERAPY +/- TARGETED AGENTS Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine 1995 One option Advances in the treatment of mcrc 2000
ADVANCED COLORECTAL CANCER: UNRESECTABLE OR BORDERLINE RESECTABLE (GROUP 1) CHEMOTHERAPY +/- TARGETED AGENTS Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine 1995 One option Advances in the treatment of mcrc 2000
OVERALL CLINICAL BENEFIT
 cetuximab plus FOLFIRI to convert unresectable liver metastatses to resectable, perc confirmed that neither the FIRE-3 study nor the CRYSTAL study were designed to assess resectability and, in the absence
cetuximab plus FOLFIRI to convert unresectable liver metastatses to resectable, perc confirmed that neither the FIRE-3 study nor the CRYSTAL study were designed to assess resectability and, in the absence
The efficacy of bevacizumab in Chinese patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and its effect in different line setting*
 Chinese-German J Clin Oncol DOI 10.1007/s10330-014-1295-2 April 2014, Vol. 13, No. 4, P169 P173 The efficacy of bevacizumab in Chinese patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and its effect in different
Chinese-German J Clin Oncol DOI 10.1007/s10330-014-1295-2 April 2014, Vol. 13, No. 4, P169 P173 The efficacy of bevacizumab in Chinese patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and its effect in different
Does it matter which chemotherapy regimen you partner with the biologic agents?
 Does it matter which chemotherapy regimen you partner with the biologic agents? Yes, it does matter! Axel Grothey Disclosures Research Funding to MAYO Clinic Genentech Bayer Eisai Pfizer Imclone Potential
Does it matter which chemotherapy regimen you partner with the biologic agents? Yes, it does matter! Axel Grothey Disclosures Research Funding to MAYO Clinic Genentech Bayer Eisai Pfizer Imclone Potential
Il paziente anziano con malattia oncologica avanzata: il tumore del colon-retto
 Milano 05.10.2018 Il paziente anziano con malattia oncologica avanzata: il tumore del colon-retto Salvatore Corallo U.O.C. Oncologia Medica IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori Milano CRC in elderly patients
Milano 05.10.2018 Il paziente anziano con malattia oncologica avanzata: il tumore del colon-retto Salvatore Corallo U.O.C. Oncologia Medica IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori Milano CRC in elderly patients
Conflicts of Interest GI Malignancies: An Update on Current Treatment Options
 Conflicts of Interest GI Malignancies: An Update on Current Treatment Options Nothing to disclose Trevor McKibbin, PharmD, MS, BCOP Clinical Specialist, Hematology/Oncology Winship Cancer Institute of
Conflicts of Interest GI Malignancies: An Update on Current Treatment Options Nothing to disclose Trevor McKibbin, PharmD, MS, BCOP Clinical Specialist, Hematology/Oncology Winship Cancer Institute of
EVIDENCE IN BRIEF OVERALL CLINICAL BENEFIT
 of the clinical trial data for this outcome. Therefore, perc considered that the cost-effectiveness of cetuximab plus FOLFIRI would be at the higher end of the EGP s range of best estimates. Therefore,
of the clinical trial data for this outcome. Therefore, perc considered that the cost-effectiveness of cetuximab plus FOLFIRI would be at the higher end of the EGP s range of best estimates. Therefore,
DALLA CAPECITABINA AL TAS 102
 DALLA CAPECITABINA AL TAS 102 Milano 29 settembre 2016 LE PROSPETTIVE NELLA RICERCA Armando Santoro Humanitas Cancer Center THE 1,2.AND 3 LINE CHEMOTHERAPY IN CRC M BEVACIZUMAB AFLIBERCET RAS wt RAS mu
DALLA CAPECITABINA AL TAS 102 Milano 29 settembre 2016 LE PROSPETTIVE NELLA RICERCA Armando Santoro Humanitas Cancer Center THE 1,2.AND 3 LINE CHEMOTHERAPY IN CRC M BEVACIZUMAB AFLIBERCET RAS wt RAS mu
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Efficacy and Safety of Bevacizumab in Chinese Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.16.6559 Efficacy and Safety of Bevacizumab in Chinese Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer RESEARCH ARTICLE Efficacy and Safety of Bevacizumab in Chinese
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.16.6559 Efficacy and Safety of Bevacizumab in Chinese Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer RESEARCH ARTICLE Efficacy and Safety of Bevacizumab in Chinese
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 25 January 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta242
 Cetuximab, bevacizumab and panitumumab for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer after first- line chemotherapy: Cetuximab (monotherapy or combination chemotherapy), bevacizumab (in combination
Cetuximab, bevacizumab and panitumumab for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer after first- line chemotherapy: Cetuximab (monotherapy or combination chemotherapy), bevacizumab (in combination
State of the Art: Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Dr. Iain Tan
 State of the Art: Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Dr. Iain Tan Consultant GI Medical Oncologist National Cancer Centre Singapore Clinician Scientist, Genome Institute of Singapore OS (%) Overall survival
State of the Art: Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Dr. Iain Tan Consultant GI Medical Oncologist National Cancer Centre Singapore Clinician Scientist, Genome Institute of Singapore OS (%) Overall survival
Development of Conventional Chemotherapy in mcrc BSC vs. Chemo, Biochemical modulation, Oral fluoropyrimidines, Developmentof combination chemotherapy
 ESMO Preceptorship Colorectal Cancer Colorectal ESMO Cancer Preceptorship Valencia May Program 20-21st 2016 Prague May 22-23rd 2014 Development of Conventional Chemotherapy in mcrc BSC vs. Chemo, Biochemical
ESMO Preceptorship Colorectal Cancer Colorectal ESMO Cancer Preceptorship Valencia May Program 20-21st 2016 Prague May 22-23rd 2014 Development of Conventional Chemotherapy in mcrc BSC vs. Chemo, Biochemical
MÁS ALLA DE LA PRIMERA LÍNEA: SECUENCIA DE TRATAMIENTO. Dra. Ruth Vera Complejo Hospitalario de Navarra
 MÁS ALLA DE LA PRIMERA LÍNEA: SECUENCIA DE TRATAMIENTO Dra. Ruth Vera Complejo Hospitalario de Navarra GOALS Prolongation of survival Cure Improving tumour-related symptoms Stopping tumour progression
MÁS ALLA DE LA PRIMERA LÍNEA: SECUENCIA DE TRATAMIENTO Dra. Ruth Vera Complejo Hospitalario de Navarra GOALS Prolongation of survival Cure Improving tumour-related symptoms Stopping tumour progression
GRACE: Geriatric patients treated with Avastin in CRC multiple lines
 GRACE: Geriatric patients treated with Avastin in CRC multiple lines Continuous treatment with bevacizumab in elderly patients with mcrc: A phase IV prospective, open-label, single-arm trial to evaluate
GRACE: Geriatric patients treated with Avastin in CRC multiple lines Continuous treatment with bevacizumab in elderly patients with mcrc: A phase IV prospective, open-label, single-arm trial to evaluate
Bevacizumab 5mg/kg Therapy 14 days
 INDICATIONS FOR USE: Bevacizumab 5mg/kg Therapy 14 days Regimen Code 00211a *Reimbursement status Hospital INDICATION ICD10 In combination with fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy C18 for treatment of
INDICATIONS FOR USE: Bevacizumab 5mg/kg Therapy 14 days Regimen Code 00211a *Reimbursement status Hospital INDICATION ICD10 In combination with fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy C18 for treatment of
Chemotherapy of colon cancers
 Chemotherapy of colon cancers Stage distribution Stage I : 15% T 1,2 NO Stage IV: 20 25% M+ Stage II : 20 30% T3,4 NO Stage III N+: 30 40% clinical stages I, II, or III colon cancer are at risk for having
Chemotherapy of colon cancers Stage distribution Stage I : 15% T 1,2 NO Stage IV: 20 25% M+ Stage II : 20 30% T3,4 NO Stage III N+: 30 40% clinical stages I, II, or III colon cancer are at risk for having
Original article. E. Mitry 1 *, J.-Y. Douillard 2, E. Van Cutsem 3, D. Cunningham 4, E. Magherini 5, D. Mery-Mignard 5, L. Awad 5 & P.
 Original article Annals of Oncology 15: 1013 1017, 2004 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh267 Predictive factors of survival in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: an individual data analysis of 602 patients
Original article Annals of Oncology 15: 1013 1017, 2004 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh267 Predictive factors of survival in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: an individual data analysis of 602 patients
Chemotherapy for resectable liver mets: Options and Issues. Herbert Hurwitz Duke University Medical Center Durham, North Carolina, USA
 Chemotherapy for resectable liver mets: Options and Issues Herbert Hurwitz Duke University Medical Center Durham, North Carolina, USA Chemotherapy regimens in 1 st line mcrc Standard FOLFOX-Bev FOLFIRI-Bev
Chemotherapy for resectable liver mets: Options and Issues Herbert Hurwitz Duke University Medical Center Durham, North Carolina, USA Chemotherapy regimens in 1 st line mcrc Standard FOLFOX-Bev FOLFIRI-Bev
Retrospective analysis of the effect of CAPOX and mfolfox6 dose intensity on survival in colorectal patients in the adjuvant setting
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CAPOX AND mfolfox6 DOSE INTENSITY AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES IN STAGE III CRC, Mamo et al. Retrospective analysis of the effect of CAPOX and mfolfox6 dose intensity on survival in colorectal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE CAPOX AND mfolfox6 DOSE INTENSITY AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES IN STAGE III CRC, Mamo et al. Retrospective analysis of the effect of CAPOX and mfolfox6 dose intensity on survival in colorectal
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
Systemic Therapy for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Patterns of Chemotherapy and Biologic Therapy Use in US Medical Oncology Practice
 Original Contribution Systemic Therapy for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Patterns of Chemotherapy and Biologic Therapy Use in US Medical Oncology Practice By Gregory P. Hess, MD, MSc, Peter Feng Wang,
Original Contribution Systemic Therapy for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Patterns of Chemotherapy and Biologic Therapy Use in US Medical Oncology Practice By Gregory P. Hess, MD, MSc, Peter Feng Wang,
Panel Two: Evidence for Use of Maintenance Therapy
 Panel Two: Evidence for Use of Maintenance Therapy Evidence for Use of Maintenance Therapy Richard L. Schilsky University of Chicago Comprehensive Cancer Center What is maintenance therapy? The continued
Panel Two: Evidence for Use of Maintenance Therapy Evidence for Use of Maintenance Therapy Richard L. Schilsky University of Chicago Comprehensive Cancer Center What is maintenance therapy? The continued
research article Introduction
 research article 285 Efficacy of first-line systemic treatment in correlation with BRAF V600E and different KRAS mutations in metastatic colorectal cancer a single institution retrospective analysis Martina
research article 285 Efficacy of first-line systemic treatment in correlation with BRAF V600E and different KRAS mutations in metastatic colorectal cancer a single institution retrospective analysis Martina
Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results from the Czech population-based registry
 Slavicek et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2014, 14:53 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results from the Czech population-based
Slavicek et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2014, 14:53 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results from the Czech population-based
Academia Pharma Intersect: Key Words. Bevacizumab FOLFOX protocol FOLFIRI protocol Safety Treatment outcome
 The Oncologist Academia Pharma Intersect: Gastrointestinal Cancer Treatment Patterns and Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Initially Treated with FOLFOX Bevacizumab or FOLFIRI
The Oncologist Academia Pharma Intersect: Gastrointestinal Cancer Treatment Patterns and Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Initially Treated with FOLFOX Bevacizumab or FOLFIRI
Bevacizumab in first-line treatment of elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: German community-based observational cohort study results
 Hofheinz et al. BMC Cancer 2014, 14:761 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bevacizumab in first-line treatment of elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: German community-based observational cohort
Hofheinz et al. BMC Cancer 2014, 14:761 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bevacizumab in first-line treatment of elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: German community-based observational cohort
Cancer Cell Research 14 (2017)
 Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer Ping Xu, Hongmei Li*, Xiaoyan Zhang Department of
Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer Ping Xu, Hongmei Li*, Xiaoyan Zhang Department of
EVIDENCE IN BRIEF OVERALL CLINICAL BENEFIT
 information aligned with the expected toxicity profile of panitumumab, which is well-known as panitumumab is already used as a third-line therapy for patients with mcrc. perc also noted QoL did not deteriorate
information aligned with the expected toxicity profile of panitumumab, which is well-known as panitumumab is already used as a third-line therapy for patients with mcrc. perc also noted QoL did not deteriorate
Tumors in the Randomized German AIO study KRK-0306
 FOLFIRI plus Cetuximab versus FOLFIRI plus Bevacizumab as First- Line Treatment for Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mcrc): Analysis of Patients with KRAS-Mutated Tumors in the Randomized German
FOLFIRI plus Cetuximab versus FOLFIRI plus Bevacizumab as First- Line Treatment for Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mcrc): Analysis of Patients with KRAS-Mutated Tumors in the Randomized German
Konzepte bei der Therapie des metastasierten kolorektalen Karzinoms
 21. Ärzte Fortbildungskurs in Klinischer Onkologie 24.-26. Februar 2011 Kantonspital St. Gallen / Schweiz Konzepte bei der Therapie des metastasierten kolorektalen Karzinoms Claus-Henning Köhne Klinik
21. Ärzte Fortbildungskurs in Klinischer Onkologie 24.-26. Februar 2011 Kantonspital St. Gallen / Schweiz Konzepte bei der Therapie des metastasierten kolorektalen Karzinoms Claus-Henning Köhne Klinik
Cetuximab with Chemotherapy as Treatment for Stage III Colon or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
 Cetuximab with Chemotherapy as Treatment for Stage III Colon or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Cetuximab with Chemotherapy (CT) as First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mcrc): Analysis of
Cetuximab with Chemotherapy as Treatment for Stage III Colon or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Cetuximab with Chemotherapy (CT) as First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mcrc): Analysis of
Adjuvant therapies for large bowel cancer Wasantha Rathnayake, MD
 LEADING ARTICLE Adjuvant therapies for large bowel cancer Wasantha Rathnayake, MD Consultant Clinical Oncologist, National Cancer Institute, Maharagama, Sri Lanka. Key words: Large bowel; Cancer; Adjuvant
LEADING ARTICLE Adjuvant therapies for large bowel cancer Wasantha Rathnayake, MD Consultant Clinical Oncologist, National Cancer Institute, Maharagama, Sri Lanka. Key words: Large bowel; Cancer; Adjuvant
Κίκα Πλοιαρχοπούλου. Παθολόγος Ογκολόγος Ευρωκλινική Αθηνών
 Κίκα Πλοιαρχοπούλου Παθολόγος Ογκολόγος Ευρωκλινική Αθηνών Time (months) Survival outcomes in mcrc have progressively improved over the past two decades Treatment options for many patients Multidisciplinary
Κίκα Πλοιαρχοπούλου Παθολόγος Ογκολόγος Ευρωκλινική Αθηνών Time (months) Survival outcomes in mcrc have progressively improved over the past two decades Treatment options for many patients Multidisciplinary
COMETS: COlorectal MEtastatic Two Sequences
 COMETS: COlorectal MEtastatic Two Sequences A Phase III Multicenter Trial Comparing Two Different Sequences of Second/Third Line Therapy (Irinotecan/Cetuximab Followed By FOLFOX-4 vs. FOLFOX-4 Followed
COMETS: COlorectal MEtastatic Two Sequences A Phase III Multicenter Trial Comparing Two Different Sequences of Second/Third Line Therapy (Irinotecan/Cetuximab Followed By FOLFOX-4 vs. FOLFOX-4 Followed
MEETING SUMMARY ASCO GI, SATURDAY JANUARY 17 TH 2015
 Supported by an Independent Educa1onal Grant from MEETING SUMMARY ASCO GI, SATURDAY JANUARY 17 TH 2015 BY DR. GUILLEM ARGILES, BARCELONA, SPAIN Cancers of the Lower GI Tract RAISE: A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND,
Supported by an Independent Educa1onal Grant from MEETING SUMMARY ASCO GI, SATURDAY JANUARY 17 TH 2015 BY DR. GUILLEM ARGILES, BARCELONA, SPAIN Cancers of the Lower GI Tract RAISE: A RANDOMIZED, DOUBLE-BLIND,
1 st LINE ANTI-VEGF TREATMENT OF METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER (CRC)
 1 st LINE ANTI-VEGF TREATMENT OF METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER (CRC) Role of the VEGF Pathway in Oncogenesis The Role of Angiogenesis in Cancer Somatic mutation Small avascular tumor Tumor secretion of
1 st LINE ANTI-VEGF TREATMENT OF METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER (CRC) Role of the VEGF Pathway in Oncogenesis The Role of Angiogenesis in Cancer Somatic mutation Small avascular tumor Tumor secretion of
SIOG CRC Guidelines D Papamichael MB BS FRCP Cyprus Oncology Centre SIOG 2014 Special SIOG Guidelines Session
 SIOG CRC Guidelines D Papamichael MB BS FRCP Cyprus Oncology Centre SIOG 2014 Special SIOG Guidelines Session Lisbon October 25 th Outline Background Surgery in older adults Adjuvant therapy - Single agent
SIOG CRC Guidelines D Papamichael MB BS FRCP Cyprus Oncology Centre SIOG 2014 Special SIOG Guidelines Session Lisbon October 25 th Outline Background Surgery in older adults Adjuvant therapy - Single agent
Opinion 17 October 2012
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 17 October 2012 VECTIBIX 20 mg/ml, concentrate for solution for infusion B/1 vial of 5 ml (CIP code: 3400957181857)
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 17 October 2012 VECTIBIX 20 mg/ml, concentrate for solution for infusion B/1 vial of 5 ml (CIP code: 3400957181857)
Management Of Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in Lebanese Hospitals and Associated Direct Cost: A Multicenter Cohort Study
 Management Of Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in Lebanese Hospitals and Associated Direct Cost: A Multicenter Cohort Study Henaine AM; Chahine G; Massoud M; Salameh P; Awada S; Lahoud N; El
Management Of Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in Lebanese Hospitals and Associated Direct Cost: A Multicenter Cohort Study Henaine AM; Chahine G; Massoud M; Salameh P; Awada S; Lahoud N; El
Q11: WHAT IS THE CURRENT STANDARD FIRST LINE TREATMENT FOR METASTATIC INOPERABLE COLORECTAL CANCER?
 Q11: WHAT IS THE CURRENT STANDARD FIRST LINE TREATMENT FOR METASTATIC INOPERABLE COLORECTAL CANCER? Version 11/24/2011 3:08 PM Q11 TABLE OF CONTENTS SCIENTIFIC REPORT... 6 1 INTRODUCTION... 6 1.1 PICO...
Q11: WHAT IS THE CURRENT STANDARD FIRST LINE TREATMENT FOR METASTATIC INOPERABLE COLORECTAL CANCER? Version 11/24/2011 3:08 PM Q11 TABLE OF CONTENTS SCIENTIFIC REPORT... 6 1 INTRODUCTION... 6 1.1 PICO...
Adjuvant/neoadjuvant systemic treatment of colorectal cancer
 5th ESO-ESMO Eastern Europe and Balkan Region Masterclass in Medical Oncology Belgrade, June 19 th 2018 Adjuvant/neoadjuvant systemic treatment of colorectal cancer Carlotta Antoniotti Polo Oncologico
5th ESO-ESMO Eastern Europe and Balkan Region Masterclass in Medical Oncology Belgrade, June 19 th 2018 Adjuvant/neoadjuvant systemic treatment of colorectal cancer Carlotta Antoniotti Polo Oncologico
A clinical study of metastasized rectal cancer treatment: assessing a multimodal approach
 Med Oncol (2014) 31:839 DOI 10.1007/s12032-014-0839-1 ORIGINAL PAPER A clinical study of metastasized rectal cancer treatment: assessing a multimodal approach Michaela Jung Annica Holmqvist Xiao-Feng Sun
Med Oncol (2014) 31:839 DOI 10.1007/s12032-014-0839-1 ORIGINAL PAPER A clinical study of metastasized rectal cancer treatment: assessing a multimodal approach Michaela Jung Annica Holmqvist Xiao-Feng Sun
FIRST LINE 5-FU-BASED CHEMOTHERAPY WITH/ WITHOUT BEVACIZUMAB FOR METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: ONE CENTER EXPERIENCE RESULTS
 PROCEEDINGS FIRST LINE 5-FU-BASED CHEMOTHERAPY WITH/ WITHOUT BEVACIZUMAB FOR METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: ONE CENTER EXPERIENCE RESULTS Assia Konsoulova, Ivan Donev, Nikolay Conev, Sonya Draganova, Trifon
PROCEEDINGS FIRST LINE 5-FU-BASED CHEMOTHERAPY WITH/ WITHOUT BEVACIZUMAB FOR METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: ONE CENTER EXPERIENCE RESULTS Assia Konsoulova, Ivan Donev, Nikolay Conev, Sonya Draganova, Trifon
A Single-Center Phase 2 Trial. Bevacizumab is a humanized immunoglobulin G1 murine antibody directed against all isoforms of
 Bevacizumab in Association With de Gramont 5-Fluorouracil/Folinic Acid in Patients With Oxaliplatin-, Irinotecan-, and Cetuximab-Refractory Colorectal Cancer A Single-Center Phase 2 Trial Bruno Vincenzi,
Bevacizumab in Association With de Gramont 5-Fluorouracil/Folinic Acid in Patients With Oxaliplatin-, Irinotecan-, and Cetuximab-Refractory Colorectal Cancer A Single-Center Phase 2 Trial Bruno Vincenzi,
Adverse Effects of Chemotherapy Regimens Used in Colorectal Cancer Patients in a Referral Cancer Center in North of Iran,
 2016 jpc.tums.ac.ir Adverse Effects of Chemotherapy Regimens Used in Colorectal Cancer Patients in a Referral Cancer Center in North of Iran, 2008-2014 Ebrahim Salehifar 1*, Shayeste Gheibi 2, Ghasem Janbabaei
2016 jpc.tums.ac.ir Adverse Effects of Chemotherapy Regimens Used in Colorectal Cancer Patients in a Referral Cancer Center in North of Iran, 2008-2014 Ebrahim Salehifar 1*, Shayeste Gheibi 2, Ghasem Janbabaei
Colon Cancer Molecular Target Agents
 Colon Cancer Molecular Target Agents Ci Caio Max SR S. Rocha Lima, M.D. MD Professor of Medicine CDi CoDiretor Cl Colorectal tlheptobiliary, Pancreatic SDG, and Phase I Unit University of Miami & Silvester
Colon Cancer Molecular Target Agents Ci Caio Max SR S. Rocha Lima, M.D. MD Professor of Medicine CDi CoDiretor Cl Colorectal tlheptobiliary, Pancreatic SDG, and Phase I Unit University of Miami & Silvester
First line treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer
 First line treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer Claus-Henning Köhne University Clinic Onkology and Haematology North West German Cancer Center (NWTZ) A non authorised version of ESMO guidelines was
First line treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer Claus-Henning Köhne University Clinic Onkology and Haematology North West German Cancer Center (NWTZ) A non authorised version of ESMO guidelines was
Cytotoxic Chemotherapy for Advanced Colorectal Cancer
 Review Article [1] November 02, 2005 By Scott Kopetz, MD [2] and Paulo M. Hoff, MD, FACP [3] Several developments in the past few years have incrementally progressed the field and provided additional insights
Review Article [1] November 02, 2005 By Scott Kopetz, MD [2] and Paulo M. Hoff, MD, FACP [3] Several developments in the past few years have incrementally progressed the field and provided additional insights
The role of Maintenance treatment Appropriate endpoints according to ESMO consensus
 ESMO Preceptorship Programme Colorectal Cancer Singapore-October 20-22 2016 JY Douillard, MD, PhD, CMO ESMO The role of Maintenance treatment Appropriate endpoints according to ESMO consensus MAINTENANCE
ESMO Preceptorship Programme Colorectal Cancer Singapore-October 20-22 2016 JY Douillard, MD, PhD, CMO ESMO The role of Maintenance treatment Appropriate endpoints according to ESMO consensus MAINTENANCE
New Options in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Jeffrey A. Bubis, DO, FACOI, FACP Fleming Island Baptist South Palatka
 New Options in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Jeffrey A. Bubis, DO, FACOI, FACP Fleming Island Baptist South Palatka 4 th most frequently diagnosed CA in the US 2 nd leading cause of CA death in the US Incidence
New Options in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Jeffrey A. Bubis, DO, FACOI, FACP Fleming Island Baptist South Palatka 4 th most frequently diagnosed CA in the US 2 nd leading cause of CA death in the US Incidence
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Technology Appraisals. Patient Access Scheme Submission Template
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals Patient Access Scheme Submission Template Bevacizumab in combination with fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy for the first-line
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals Patient Access Scheme Submission Template Bevacizumab in combination with fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy for the first-line
Bevacizumab 7.5mg/kg Therapy 21 days
 INDICATIONS FOR USE: Bevacizumab 7.5mg/kg Therapy 21 days INDICATION ICD10 Regimen Code *Reimbursement status In combination with fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy for C18 00214a Hospital treatment of
INDICATIONS FOR USE: Bevacizumab 7.5mg/kg Therapy 21 days INDICATION ICD10 Regimen Code *Reimbursement status In combination with fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy for C18 00214a Hospital treatment of
Targeted therapies in colorectal cancer: the dos, don ts, and future directions
 Editorial Targeted therapies in colorectal cancer: the dos, don ts, and future directions Marwan Fakih City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center, 1500 E Duarte St, Duarte, CA 91010, USA Corresponding to:
Editorial Targeted therapies in colorectal cancer: the dos, don ts, and future directions Marwan Fakih City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center, 1500 E Duarte St, Duarte, CA 91010, USA Corresponding to:
JY Douillard MD, PhD Professor of Medical Oncology
 ESMO Preceptorship Colorectal Cancer Colorectal ESMO Cancer Preceptorship Vienna 26-27 Program October 2015 Prague May 22-23rd 2014 Review of the ESMO Consensus Conference on metastatic colo-rectal cancer
ESMO Preceptorship Colorectal Cancer Colorectal ESMO Cancer Preceptorship Vienna 26-27 Program October 2015 Prague May 22-23rd 2014 Review of the ESMO Consensus Conference on metastatic colo-rectal cancer
Current Status of Adjuvant Therapy for Colorectal Cancer
 Review Article [1] May 01, 2004 By Michael J. O connell, MD [2] Adjuvant therapy with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy in addition to surgery improves outcome for patients with high-risk carcinomas
Review Article [1] May 01, 2004 By Michael J. O connell, MD [2] Adjuvant therapy with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy in addition to surgery improves outcome for patients with high-risk carcinomas
Cost-effectiveness of Cetuximab and Panitumumab in First-line Treatment for Patients with KRAS Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in Ontario
 Cost-effectiveness of Cetuximab and Panitumumab in First-line Treatment for Patients with KRAS Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in Ontario Emmanuel Ewara, Dr. Greg Zaric, Dr. Stephen Welch, Dr. Sisira
Cost-effectiveness of Cetuximab and Panitumumab in First-line Treatment for Patients with KRAS Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in Ontario Emmanuel Ewara, Dr. Greg Zaric, Dr. Stephen Welch, Dr. Sisira
Clinical CRC registries of the Czech Society for Oncology
 Clinical CRC registries of the Czech Society for Oncology Why do we have problems with equity and early access to the innovative CRC therapy? Prof. MUDr. Rostislav Vyzula, CSc., MUDr. Jiří Tomášek, doc.
Clinical CRC registries of the Czech Society for Oncology Why do we have problems with equity and early access to the innovative CRC therapy? Prof. MUDr. Rostislav Vyzula, CSc., MUDr. Jiří Tomášek, doc.
Review of the ESMO consensus conference on metastatic CRC Basis strategies ad groups (RAS, BRAF, etc) Michel Ducreux
 Review of the ESMO consensus conference on metastatic CRC Basis strategies ad groups (RAS, BRAF, etc) Michel Ducreux 2 ESMO consensus on mcrc 2016 Chairs: Co-Chairs of working groups E Van Cutsem A Sobrero
Review of the ESMO consensus conference on metastatic CRC Basis strategies ad groups (RAS, BRAF, etc) Michel Ducreux 2 ESMO consensus on mcrc 2016 Chairs: Co-Chairs of working groups E Van Cutsem A Sobrero
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Aflibercept (Zaltrap) for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer September 5, 2014
 pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Aflibercept (Zaltrap) for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer September 5, 2014 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This report
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Aflibercept (Zaltrap) for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer September 5, 2014 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This report
4.3 Input parameters Patient
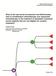 Table of Content 1 Introduction -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 7 Summary -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Table of Content 1 Introduction -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 7 Summary -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Irinotecan (CPT-11) in Patients with Advanced Colon Carcinoma Relapsing after 5-Fluorouracil-Leucovorin Combination
 Clinical Report Chemotherapy 2002;48:94 99 Irinotecan (CPT-11) in Patients with Advanced Colon Carcinoma Relapsing after 5-Fluorouracil-Leucovorin Combination N.B. Tsavaris a A. Polyzos b K. Gennatas c
Clinical Report Chemotherapy 2002;48:94 99 Irinotecan (CPT-11) in Patients with Advanced Colon Carcinoma Relapsing after 5-Fluorouracil-Leucovorin Combination N.B. Tsavaris a A. Polyzos b K. Gennatas c
S u p p o r t e d b y a n i n d e p e n d e n t E d u c a t i o n a l G r a n t f r o m B a y e r
 EXPERTS KNOWLEDGE SHARE with Prof. Köhne, Dr. Modest and Dr. Vecchione Madrid (Spain) Sunday September 10 th 2017 S u p p o r t e d b y a n i n d e p e n d e n t E d u c a t i o n a l G r a n t f r o m
EXPERTS KNOWLEDGE SHARE with Prof. Köhne, Dr. Modest and Dr. Vecchione Madrid (Spain) Sunday September 10 th 2017 S u p p o r t e d b y a n i n d e p e n d e n t E d u c a t i o n a l G r a n t f r o m
RECONSIDERING THE BENEFIT OF INTERMITTENT VERSUS CONTINUOUS TREATMENT IN THE MAINTENANCE TREATMENT SETTING OF METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER
 RECONSIDERING THE BENEFIT OF INTERMITTENT VERSUS CONTINUOUS TREATMENT IN THE MAINTENANCE TREATMENT SETTING OF METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER SUNAKAWA, Y, 1 BEKAIISAAB, T, 2 AND STINTZING, S. 3 SELECTED HIGHLIGHTS
RECONSIDERING THE BENEFIT OF INTERMITTENT VERSUS CONTINUOUS TREATMENT IN THE MAINTENANCE TREATMENT SETTING OF METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER SUNAKAWA, Y, 1 BEKAIISAAB, T, 2 AND STINTZING, S. 3 SELECTED HIGHLIGHTS
Chemotherapy re-challenge response rate in metastatic colorectal cancer
 Original Article Chemotherapy re-challenge response rate in metastatic colorectal cancer Alexandra E. Chambers 1, Jacob Frick 1, Natalee Tanner 1, Richard Gerkin 2, Madappa Kundranda 3, Tomislav Dragovich
Original Article Chemotherapy re-challenge response rate in metastatic colorectal cancer Alexandra E. Chambers 1, Jacob Frick 1, Natalee Tanner 1, Richard Gerkin 2, Madappa Kundranda 3, Tomislav Dragovich
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Venook AP, Niedzwiecki D, Lenz H-J, et al. Effect of first-line chemotherapy combined with cetuximab or bevacizumab on overall survival in patients with KRAS wild-type advanced
Supplementary Online Content Venook AP, Niedzwiecki D, Lenz H-J, et al. Effect of first-line chemotherapy combined with cetuximab or bevacizumab on overall survival in patients with KRAS wild-type advanced
Case Report Management of a Patient with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Liver Metastases
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine, Article ID 790192, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/790192 Case Report Management of a Patient with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Liver Metastases Muhammad
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine, Article ID 790192, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/790192 Case Report Management of a Patient with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Liver Metastases Muhammad
Effective Panitumumab Treatment in Patients with Heavily Pre-treated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Case Series
 Effective Panitumumab Treatment in Patients with Heavily Pre-treated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Case Series ALEXANDROS A. TZOVARAS, ATHANASSIOS KARAGIANNIS, CHARALAMBIA MARGARI, GEORGIA BARLA and
Effective Panitumumab Treatment in Patients with Heavily Pre-treated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Case Series ALEXANDROS A. TZOVARAS, ATHANASSIOS KARAGIANNIS, CHARALAMBIA MARGARI, GEORGIA BARLA and
Understanding predictive and prognostic markers
 Understanding predictive and prognostic markers Professor Aimery de Gramont Chairman of ARCAD Foundation and GERCOR, Paris FRANCE Understanding predictive and prognostic markers Aimery de Gramont Prognostic
Understanding predictive and prognostic markers Professor Aimery de Gramont Chairman of ARCAD Foundation and GERCOR, Paris FRANCE Understanding predictive and prognostic markers Aimery de Gramont Prognostic
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(1): /ISSN: /IJCEM Guoliang Zhang, Xile Zhou, Caizhao Lin
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(1):1434-1445 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003370 Original Article Efficacy of chemotherapy plus bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(1):1434-1445 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003370 Original Article Efficacy of chemotherapy plus bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal
Bevacizumab 10mg/kg 14 days
 INDICATIONS FOR USE: Bevacizumab 10mg/kg 14 days Regimen Code 00212a *Reimbursement status Hospital INDICATION ICD10 In combination with fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy C18 for treatment of adult patients
INDICATIONS FOR USE: Bevacizumab 10mg/kg 14 days Regimen Code 00212a *Reimbursement status Hospital INDICATION ICD10 In combination with fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy C18 for treatment of adult patients
Adjuvant therapy in older adults: controversies and challenges - Colorectal cancer -
 International Society of Geriatric Oncology Lisbon October 23 rd 25t h 2014 Adjuvant therapy in older adults: controversies and challenges - Colorectal cancer - Claus-Henning Köhne Klinik für Onkologie
International Society of Geriatric Oncology Lisbon October 23 rd 25t h 2014 Adjuvant therapy in older adults: controversies and challenges - Colorectal cancer - Claus-Henning Köhne Klinik für Onkologie
A retrospective analysis of the safety and efficacy of apatinib in treating advanced metastatic colorectal cancer
 Oncology and Translational Medicine DOI 10.1007/s10330-017-0235-5 October 2017, Vol. 3, No. 5, P210 P216 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A retrospective analysis of the safety and efficacy of apatinib in treating advanced
Oncology and Translational Medicine DOI 10.1007/s10330-017-0235-5 October 2017, Vol. 3, No. 5, P210 P216 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A retrospective analysis of the safety and efficacy of apatinib in treating advanced
General Information, efficacy and safety data
 Horizon Scanning in Oncology Horizon Scanning in Oncology 23 rd Prioritization 2 nd quarter 2015 General Information, efficacy and safety data Eleen Rothschedl Anna Nachtnebel Priorisierung XXIII HSS Onkologie
Horizon Scanning in Oncology Horizon Scanning in Oncology 23 rd Prioritization 2 nd quarter 2015 General Information, efficacy and safety data Eleen Rothschedl Anna Nachtnebel Priorisierung XXIII HSS Onkologie
METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: TUMOR MUTATIONAL ANALYSIS AND ITS IMPACT ON CHEMOTHERAPY SUMA SATTI, MD
 METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: TUMOR MUTATIONAL ANALYSIS AND ITS IMPACT ON CHEMOTHERAPY SUMA SATTI, MD INTRODUCTION Second leading cause of cancer related death in the United States. 136,830 cases in 2014
METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: TUMOR MUTATIONAL ANALYSIS AND ITS IMPACT ON CHEMOTHERAPY SUMA SATTI, MD INTRODUCTION Second leading cause of cancer related death in the United States. 136,830 cases in 2014
Unresectable or boarderline resectable disease
 ESMO Preceptorship Colorectal Cancer Nov 2016 Barcelona Unresectable or boarderline resectable disease Claus-Henning Köhne Klinik für Onkologie und Hämatologie North West German Cancer Center (NWTZ) Learning
ESMO Preceptorship Colorectal Cancer Nov 2016 Barcelona Unresectable or boarderline resectable disease Claus-Henning Köhne Klinik für Onkologie und Hämatologie North West German Cancer Center (NWTZ) Learning
Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer
 Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine DISCLOSURE OF INTEREST Employment: None Consultant or Advisory Role: Merck Serono, Roche, Beigene, Bayer, Servier, Lilly,
Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine DISCLOSURE OF INTEREST Employment: None Consultant or Advisory Role: Merck Serono, Roche, Beigene, Bayer, Servier, Lilly,
Targeted Agents as Maintenance Therapy. Karen Kelly, MD Professor of Medicine UC Davis Cancer Center
 Targeted Agents as Maintenance Therapy Karen Kelly, MD Professor of Medicine UC Davis Cancer Center Disclosures Genentech Advisory Board Maintenance Therapy Defined Treatment Non-Progressing Patients Drug
Targeted Agents as Maintenance Therapy Karen Kelly, MD Professor of Medicine UC Davis Cancer Center Disclosures Genentech Advisory Board Maintenance Therapy Defined Treatment Non-Progressing Patients Drug
Cetuximab plus 5-FU/FA/oxaliplatin (FOLFOX-4) in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a large-scale Phase II study (OPUS)
 Cetuximab plus 5-FU/FA/oxaliplatin (FOLFOX-4) in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a large-scale Phase II study (OPUS) C Bokemeyer, E Staroslawska, A Makhson, I Bondarenko, JT Hartmann,
Cetuximab plus 5-FU/FA/oxaliplatin (FOLFOX-4) in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a large-scale Phase II study (OPUS) C Bokemeyer, E Staroslawska, A Makhson, I Bondarenko, JT Hartmann,
Comparison of first-line bevacizumab in combination with mfolfox6 or XELOX in metastatic colorectal cancer
 JBUON 2015; 20(2): 460-467 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of first-line bevacizumab in combination with mfolfox6 or
JBUON 2015; 20(2): 460-467 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of first-line bevacizumab in combination with mfolfox6 or
Clinical Studies. Keywords: metastatic; colorectal cancer; bevacizumab; curative-intent; R0 metastasectomy
 British Journal of Cancer (2009) 101, 1033 1038 All rights reserved 0007 0920/09 $32.00 www.bjcancer.com Surgery with curative-intent in patients treated with first-line chemotherapy plus bevacizumab for
British Journal of Cancer (2009) 101, 1033 1038 All rights reserved 0007 0920/09 $32.00 www.bjcancer.com Surgery with curative-intent in patients treated with first-line chemotherapy plus bevacizumab for
Low-dose capecitabine (Xeloda) for treatment for gastrointestinal cancer
 Med Oncol (2014) 31:870 DOI 10.1007/s12032-014-0870-2 ORIGINAL PAPER Low-dose capecitabine (Xeloda) for treatment for gastrointestinal cancer Jasmine Miger Annika Holmqvist Xiao-Feng Sun Maria Albertsson
Med Oncol (2014) 31:870 DOI 10.1007/s12032-014-0870-2 ORIGINAL PAPER Low-dose capecitabine (Xeloda) for treatment for gastrointestinal cancer Jasmine Miger Annika Holmqvist Xiao-Feng Sun Maria Albertsson
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
/m 2 Oxaliplatin 85 1 Q2W 1-3 Leucovorin Q2W 5-FU Q2W 5-FU Q2W
 癌症診療指引33 Adjuvant therapy of colon cancer mfolfox6 Oxaliplatin 85 1 Q2W 1-3 FOLFOX4 Oxaliplatin 85 1 Q2W 9 Leucovorin 200 1-2 Q2W 5-FU 400 1-2 Q2W 5-FU 600 1-2 Q2W FLOX Oxaliplatin 85 1,15,29 Q8W 4 Leucovorin
癌症診療指引33 Adjuvant therapy of colon cancer mfolfox6 Oxaliplatin 85 1 Q2W 1-3 FOLFOX4 Oxaliplatin 85 1 Q2W 9 Leucovorin 200 1-2 Q2W 5-FU 400 1-2 Q2W 5-FU 600 1-2 Q2W FLOX Oxaliplatin 85 1,15,29 Q8W 4 Leucovorin
What to do after 1 st line failure?
 ESMO Preceptorship Programme Colorectal Cancer Singapore 20-22 nd 2016 JY Douillard MD PhD ESMO CMO What to do after 1 st line failure? mcrc: How to maximize survival? Improving 1st line therapy efficacy
ESMO Preceptorship Programme Colorectal Cancer Singapore 20-22 nd 2016 JY Douillard MD PhD ESMO CMO What to do after 1 st line failure? mcrc: How to maximize survival? Improving 1st line therapy efficacy
2015 EUROPEAN CANCER CONGRESS
 2015 EUROPEAN CANCER CONGRESS 25-29 September 2015 Vienna, Austria SUMMARY The European Cancer Congress (ECC 2015) combined the 40th European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) congress with the 18th
2015 EUROPEAN CANCER CONGRESS 25-29 September 2015 Vienna, Austria SUMMARY The European Cancer Congress (ECC 2015) combined the 40th European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) congress with the 18th
JY Douillard MD, PhD Professor of Medical Oncology
 Colorectal Cancer ESMO Preceptorship Program Prague May 22-23rd 2014 Review of the ESMO Consensus Conference on metastatic colo-rectal cancer Basic strategy and groups (RASwt/mut, BRAF mut) JY Douillard
Colorectal Cancer ESMO Preceptorship Program Prague May 22-23rd 2014 Review of the ESMO Consensus Conference on metastatic colo-rectal cancer Basic strategy and groups (RASwt/mut, BRAF mut) JY Douillard
Is There a New Standard of Care for Adjuvant Therapy in Colon Cancer? When is 3 Months Enough?
 Is There a New Standard of Care for Adjuvant Therapy in Colon Cancer? When is 3 Months Enough? Jeffrey Meyerhardt, MD, MPH Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Boston, MA 1 Disclosure Ad Board: Genentech Honorarium:
Is There a New Standard of Care for Adjuvant Therapy in Colon Cancer? When is 3 Months Enough? Jeffrey Meyerhardt, MD, MPH Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Boston, MA 1 Disclosure Ad Board: Genentech Honorarium:
Factors associated with delayed time to adjuvant chemotherapy in stage iii colon cancer
 Curr Oncol, Vol. 21, pp. 181-186 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.3747/co.21.1963 DELAYED TIME TO ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors associated with delayed time to adjuvant chemotherapy in stage
Curr Oncol, Vol. 21, pp. 181-186 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.3747/co.21.1963 DELAYED TIME TO ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors associated with delayed time to adjuvant chemotherapy in stage
Rationale for VEGFR-targeted Therapy in RCC
 Rationale for VEGFR-targeted Therapy in RCC EIKCS, Budapest, May 2013 Tim Eisen Tim Eisen - Disclosures Company Research Support Advisory Board Trial Management Group Honoraria Astra Zeneca + + + Astellas
Rationale for VEGFR-targeted Therapy in RCC EIKCS, Budapest, May 2013 Tim Eisen Tim Eisen - Disclosures Company Research Support Advisory Board Trial Management Group Honoraria Astra Zeneca + + + Astellas
Case 1 Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: What Therapy Should I Select First?
 Case 1 Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: What Therapy Should I Select First? Marc Peeters, MD, PhD Head of the Oncology Department Antwerp University Hospital Antwerp, Belgium marc.peeters@uza.be 71-year-old
Case 1 Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: What Therapy Should I Select First? Marc Peeters, MD, PhD Head of the Oncology Department Antwerp University Hospital Antwerp, Belgium marc.peeters@uza.be 71-year-old
