Small bowel polyps and tumours: endoscopic detection and treatment by double-balloon enteroscopy
|
|
|
- Iris McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Small bowel polyps and s: endoscopic detection and treatment by double-balloon enteroscopy L. C. FRY*,1,H.NEUMANN*,1,D.KUESTER, R.KUHNà, M.BELLUTTI*,P.MALFERTHEINER*& K. MONKEMULLER* *Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Infectious Diseases; Department of Pathology and àdepartment of Surgery, Otto-von- Guericke University, Magdeburg, Germany Correspondence to: Dr K. Mönkemüller, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Infectious Diseases, Otto-von-Guericke University, Leipziger Str. 44, Magdeburg, Germany. 1 LCF and HN contributed equally to this study. Publication data Submitted 21 August 2008 First decision 4 September 2008 Resubmission 18 September 2008 Resubmission 29 September 2008 Accepted 29 September 2008 Epub Accepted Article 3 October 2008 SUMMARY Background Double-balloon enteroscopy has allowed us not only to inspect deeply the small bowel but also to carry out interventions for diseases of the small bowel. Aim To evaluate the utility of double-balloon enteroscopy for the diagnosis and therapy of these lesions. Methods All patients undergoing double-balloon enteroscopy for evaluation of small bowel polyps and s during a 3.75-year period at a university referral hospital were studied. The types of polyps and s as well as endoscopic technique of removal, surgery and complications were documented. Results The incidence of small bowel polyps and s in-patients undergoing DBE was 9.6%. A total of 40 double-balloon enteroscopy procedures were performed in 29 patients [13 female (44.8%), mean age 51 years, range 22 74]. The following lesions were found most frequently: adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome, n = 8; hamartomas, n = 4 (Peutz-Jeghers and Cronkhite Canada syndromes), jejunal adenocarcinoma n = 5, neuroendocrine n = 4 and others n =6. Conclusions The incidence of small bowel s in those in-patients who were undergoing double-balloon enteroscopy was 10%. Double-balloon enteroscopy is useful for the diagnosis and treatment of small bowel polyps and s. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 29, ª 2008 The Authors 135 doi: /j x
2 136 L. C. FRY et al. INTRODUCTION The major indications for double-balloon enteroscopy are evaluation of patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding and suspected Crohn s disease. 1 5 Small bowel polyps and s are an important cause of small bowel pathology occurring most frequently in familial and nonfamilial polyposis syndromes. 6 8 However, other important small bowel s include adenocarcinoma, neuroendocrine s and others. 8, 9 Until recently, radiological methods and capsule endoscopy were the major methods to investigate small bowel disorders. 10, 11 However, neither radiological methods nor capsule endoscopy permits biopsy, resection or mucosal marking of polyps and s. Until only a few years ago, primary surgical resection with or without intraoperative endoscopy and polypectomy were the only available means of treating polyps in the mid-small bowel in these patients. 12 The advent of double-balloon enteroscopy has increased our diagnostic and therapeutic armamentarium for various small bowel disorders. 1 5 The aims of this study were to evaluate the feasibility and utility of double-balloon enteroscopy for the diagnosis of and therapy of these lesions. METHODS Consecutive patients who underwent double-balloon enteroscopy at the University of Magdeburg Medical Centre (Universitätsklinikum Magdeburg, Otto von Guericke University, Magdeburg, Germany) were included and their data recorded in a prospectively collected database. This study evaluated a period of 3.75 years and comprises all patients who were found to have polyps or masses of the small bowel. The study was approved by the ethics committee of the University of Magdeburg and conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration. The patients provided written informed consent to undergo endoscopy with doubleballoon enteroscopy. Double-balloon enteroscopy (DBE) was performed using Fujinon enteroscopes (Fujinon FN 450P 5 20, EN-450T5, Fuji, Fujinon Corp., Japan). The characteristic technical details of double-balloon enteroscopy have been presented in detail elsewhere. 1, 5 Briefly, the depth of insertion of the endoscope into the small bowel is estimated by recording the net advancement of the endoscope for each push-and-pull manoeuvre on a standardized documentation sheet. 13 At any point during the procedure and at the end, all of the figures recorded are added and the length of small bowel that has been visualized can be estimated. During doubleballoon enteroscopy, careful attention must be given not to insufflate too much air, because this induces intestinal loop formation and impedes deep advancement. In addition, water combined with Simethicone to reduce bubble formation is used routinely. During intubation, it is important to straighten the enteroscope and resolve any loops formed during insertion. 13 Patients underwent small bowel cleansing on the day before the procedure using 2 L of a standard colon lavage solution (Kleanprep, Marburg, Germany) and then underwent the procedure after an overnight fast. A small bowel relaxant [Buscopan (butyl scopolamine), Boehringer Ingelheim, Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany] was administered if the bowel motility was increased or if a therapeutic intervention was performed. Fluoroscopy to determine the position of the enteroscope was performed using a Philips C-arm (Philips, Best, Holland). All procedures were performed using conscious sedation with propofol (Disoprivan, Propofol, Braun, Melsungen, Germany). Conscious sedation was administered by one physician. Polyps were defined as any mucosal protuberance, either sessile or pedunculated. Sessile lesions larger than 3 cm were considered masses. The polyp or mass was considered submucosal if the overlying mucosa was intact. The size of polyps and masses was estimated with the use of an open biopsy forceps. All patients with familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome underwent an additional endoscopy with the side viewing duodenoscope (Olympus, Hamburg, Germany) to evaluate the ampulla of Vater. Small bowel polyposis was defined according to the Spigelman score modified by Saurin. 14 This modified Spigelman Saurin classification takes into account the updated Vienna classification for gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasias (i.e. low or high grade dysplasia), whereas traditional Spigelman classification classifies adenomas into mild, moderate and severe dysplasia. 15 In the modified Spigelman Saurin classification, points are given for the number of polyps (1 point for one to four polyps, 2 points for five to 20 polyps and 3 points for >20 polyps), polyp size (1 point for 1 4 mm, 2 points for 5 10 mm, 3 points for >10 mm), histology (1 point for tubular adenoma, 2 points for tubolovillous and 3 points for villous adenoma) and dysplasia (1 point for low grade dysplasia, 3 points for high grade dysplasia). Stage 0: no polyp; stage I: 1 to 4 points; stage II: 5 to 6 points; stage III; 7 to 8 points;
3 DOUBLE-BALLOON ENTEROSCOPY SMALL BOWEL POLYPS AND TUMOURS 137 and stage IV: 9 t 12 points. 14, 15 Advanced adenoma (neoplasia) was defined as an adenomatous polyp >10 mm or with severe dysplasia. 14 All patients with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome received genetic counselling and genetic testing. Familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome patients underwent testing for the adenomatous polyposis coli mutation and patients with Peutz- Jeghers syndrome were tested for the STK11 germline mutation. The diagnosis of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome or familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome was based on standard criteria. 16 Determination of the primary route of insertion (oral or antegrade vs. anal or retrograde) The choice of either the oral or the anal route depended on the suspected location of the lesions within the small bowel based on the clinical manifestations, results of laboratory, radiological and previous radiological and endoscopic examinations. If a patient had undergone capsule endoscopy, we used the results of this test to guide the insertion route. Capsule endoscopy was not available at our institution until the latter part of In cases of obscure overt gastrointestinal bleeding, the route of insertion was dictated by the colour of the stool; in cases of maelena, the oral approach was preferred, whereas in the presence of haematochaezia, the anal approach was used first. If one double-balloon enteroscopy route did not yield any diagnosis, the opposite route was used for the second investigation. To confirm total enteroscopy, we performed India ink marking of the small bowel. Total enteroscopy was also confirmed if the coecum or colon could be visualized when using the oral approach. In case total enteroscopy was not possible in high risk patients with familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome, they also underwent capsule endoscopy. Complications of DBE were defined according to standard criteria. 17 Removal of polyps was performed using either mucosectomy or polypectomy techniques, but always preceded by submucosal injection of epinephrine-saline solution (1:10 000). All s were biopsied. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize baseline demographics and clinical characteristics. RESULTS During the study period, we performed a total of 402 double-balloon enteroscopies in 301 patients. Small bowel s and or polyps were detected in 29 patients (9.6%) in whom a total of 40 double-balloon enteroscopies were performed. The demographic, clinical, endoscopic and surgical findings of the study cohort are presented in Tables 1 and 2. The most common indications for double-balloon enteroscopy were obscure gastrointestinal bleeding and evaluation of small bowel polyps in-patients with familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome (Table 2). In seven patients, the double-balloon enteroscopy was performed because of suspicious finding on capsule endoscopy (Figure 1). The following polyps and s were found most frequently: adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome, n = 8 (Figure 1); hamartomas, n = 4 (Peutz-Jeghers and Cronkhite Canada syndromes) (Figure 2) and jejunal adenocarcinoma n =5 (Figure 3), neuroendocrine n =4 (Figure 4) (Tables 1 and 2). Technical results The route for double-balloon enteroscopy in patients with positive findings was oral in 34 and anal in 6. The mean duration of the procedure was 75 min, range 25 min to 115 min. The mean radiation exposure was 185 dgy cm 2 (range 0 556). The mean small bowel insertion was 300 cm, range cm (excluding failed cases). There were two failed doubleballoon enteroscopies: in a patient with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, jejunal intubation via the oral route was only successful to 40 cm because of multiple adhesions. In one anal double-balloon enteroscopy in a patient with neuroendocrine, it was only possible to visualize 20 cm of terminal ileum, but a submucosal lesion was detected and confirmed as a neuroendocrine during laparotomy. Endoscopic and histological results The most commonly diagnosed mass lesions were adenocarcinomas (n = 5) and neuroendocrine s (n = 4). Adenocarcinomas appeared either as a stenosing or hemicircumferential mass (Table 1) (Figure 4). In one patient with adenocarcinoma, double-balloon enteroscopy was useful to remove a lodged capsule. Neuroendocrine appeared as yellow submucosal masses, thickened folds or ulcerated actively bleeding lesions (Table 1). In two patients with neuroendocrine, endoscopic haemostatic therapy using argon plasma coagulation was employed to
4 138 L. C. FRY et al. Table 1. Clinical, demographic and endoscopic characteristics of patients diagnosed with small bowel s N Age Gender Route Indication Finding Histology Technical aspects Evolution 1 75 F Oral Anaemia, Stenosing Adenocarcinoma Extraction of CE Surgery CE: jejunal 2 72 M Oral Anaemia Hemicircumferential Adenocarcinoma Biopsies Surgery 3 56 F Oral Anaemia, CE: Tumour and capsule retention Stenosing Adenocarcinoma Biopsies but they were negative Surgery 4 72 F Oral Anaemia, CE: suspected Large mass Adenocarcinoma Biopsies + India ink marking Surgery 5 38 M Oral Maelena, Large mass Adenocarcinoma Biopsies Chemotherapy liver metastasis 6 48 M Oral Anaemia Submucosal GIST Biopsies Surgery 7 61 F Oral Maelena Submucosal GIST Biopsies Surgery 8 48 F Oral Haematochaezia Bleeding ulcerated NET Biopsies, APC, Surgery India ink marking 9 68 M Oral Haematochaezia Bleeding ulcerated NET Biopsies, India Surgery ink marking F Anal Liver Submucosal NET Biopsies negative Surgery metastasis of a NET In terminal ileum F Anal Metastatic NET Tumour with NET No biopsies could Surgery central erosion be obtained M Oral Haematochaezia, CE: small bowel with invagination Jejunal Histology negative Biopsies, India ink marking Surgery: Leiomyoma M Oral CE: suspected small bowel infiltration of lymphoma M Anal Bleeding, CE: several s Irregular mucosa suspicious of lymphoma infiltration Large mucosal s B-cell lymphoma B-celllymphoma Biopsies Biopsies Chemotherapy Chemotherapy DBE, double-balloon enteroscopy; SB, small bowel; FAP, familial adenomatous polyposis; PJS, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome; CE, capsule endoscopy, GI, gastrointestinal, GIST, gastrointestinal stromal ; NET, neuroendocrine. stop the active bleeding. Gastrointestinal stromal s appeared as large, submucosal lesions with grey rubbery surface. Both lymphomas appeared as submucosal lesions with intact overlying mucosa. Except for the patient with testicular metastasis, who expired as a result of his underlying illness, all other patients with s underwent exploratory laparotomy. The surgeon was able to locate the lesions in all patients. The polyps found in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome were adenomas of various sizes and histological grades (Table 1). The mean Spigelman Saurin score was 4.1, range 2 8. The polyps were flat with a whitish surface (Figure 1). Two patients were found to have advanced jejunal adenomas (Figure 1). Six patients were found to have mutations involving exon 15 of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene. The advanced lesions were removed with mucosectomy technique. All patients with Peutz- Jeghers syndrome and the patient with Cronkhite Canada syndrome were found to have hamartomas. All polyps larger than 15 mm were removed using snare electrocautery. Nine double-balloon enteroscopies were performed in three patients with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. The average number of polyps removed during one session was 10 (range 3 32). The patients with diffuse small bowel polyposis and nodular lymphoid
5 DOUBLE-BALLOON ENTEROSCOPY SMALL BOWEL POLYPS AND TUMOURS 139 Table 2. Clinical, demographic and endoscopic characteristics of patients diagnosed with small bowel polyps N DBE Age Gender Route Indication* Finding Type of polyp(s) Endoscopic technical aspects 1 42 F Oral FAP Polyps in duodenum, jejunum and ileum M Oral FAP Papillary adenoma no small bowel polyps Tubulovillous adenomas with LGIN Adenomas, LGIN Polypectomy >5 polyps with snare and APC surveillance 2 Oral FAP Jejunal polyps Adenomas, LGIN APC 3 31 F Oral FAP Small bowel polyps Adenomas, LGIN APC M Oral FAP Jejunal polyps Adenomas with LGIN Mucosectomy, polypectomy + APC 2 Oral FAP Jejunal polyps APC M Oral FAP Jejunal polyps No histology APC 2 Oral FAP Jejunal polyps Advanced adenomas with LGIN Mucosectomy, polypectomy + APC M Oral FAP 1 jejunal polyp adenoma surveillance 2 Anal FAP No polyps n a surveillance 7 22 M Oral FAP Duodenal polyps adenomas surveillance 8 46 F Oral FAP Jejunal polyps adenomas with LGIN APC F Oral PJS small Hamartomas Polypectomy bowel polyps*** 2 Oral PJS 20 small bowel polyps Hamartomas Polypectomy 3 Oral PJS Small bowel polyps Hamartomas Polypectomy M Oral PJS 18 jejunal polyps*** Hamartomas Polypectomy, bleeding: epinephrine injection 2 Anal PJS Colonic polyps Hamartomas, Polypectomy adenomas M Oral PJS 12 small bowel polyps*** Hamartomas Polypectomy 2 Oral PJS 8 small bowel polyps Hamartomas Polypectomy 12 polyps 3 Oral PJS 3 small bowel polyps Hamartomas Polypectomy 4 Oral PJS 5 small bowel polyps Hamartomas polypectomy M Oral Diarrhoea Small bowel polyps NLH Medical treatment F Oral Diarrhoea Pseudopolyps Atrophy, NLH Medical treatment F Oral CCS, diarrhoea Sessile polyps, elongated villi Hamartomas, mucosal atrophy** Steroids m Oral Haematochaezia Normal 2 Anal Ileal mass*** Lipoma Surgery * Indication: FAP, surveillance; PJS, recurrent abdominal pain (intussusception) and prophylactic removal or polyps. ** The patient with CCS also had colonic polyps: serrated adenomas, juvenile polyps, pseudopolyps and hamartomas. DBE, double-balloon enteroscopy: this column indicates the number of DBEs per patient. LGIN, low grade intraepithelial neoplasia; APC, argon plasma coagulation; CCS, Cronkhite-Canada syndrome; NLH, nodular lymphoid hyperplasia. *** These patients had 1-5 polyps or lesions larger than 3 cm (per definition these were masses, see text). hyperplasia did not require any endoscopic therapeutic intervention. The only major complication was bleeding after polypectomy in a patient with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. One patient suffered from temporary oxygen desaturation (<92%) during the procedure, which responded to increased oxygen administration.
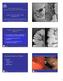
6 140 L. C. FRY et al. Figure 1. Advanced adenoma in a patient with familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome (FAP). Note the sessile polyp with whitish mucosal discoloration. Advanced adenomas are polyps >10 mm in FAP. Figure 3. Surgical specimen demonstrating a stenosing adenocarcinoma of the small bowel. Figure 2. Large pedunculated polyp in a patient with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. These polyps have a tendency to grow larger over time and result in bleeding or intussusception. Although we did not observe any case of pancreatitis, one patient had significant abdominal pain and bloating after the procedure, which subsided after the passage of large amounts of flatus. DISCUSSION Figure 4. Large submucosal mass diagnosed as a neuroendocrine. In this study, we found that the relative incidence of small bowel s in-patients undergoing doubleballoon enteroscopy was 9.6%. Whereas doubleballoon enteroscopy was useful for the diagnosis of various types of polyps and s its major endoscopic therapeutic impact was evident in-patients with familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome, Peutz- Jeghers syndrome and single polyps. However, even in-patients with endoscopically unresectable lesions, double-balloon enteroscopy was useful for the diagnosis and or localization of the lesion. Until only recently, primary surgical resection and intraoperative endoscopy and polypectomy were the only available possibilities to treat polyps in the midsmall bowel in-patients with polyps. 12, 15 Doubleballoon enteroscopy has changed this approach and now it is possible to not only perform endoscopic
7 DOUBLE-BALLOON ENTEROSCOPY SMALL BOWEL POLYPS AND TUMOURS 141 surveillance and diagnoses these lesions but also to resect them. 18, 19 Although there are few case reports and series documenting the feasibility of double-balloon enteroscopy in-patients with polyposis syndromes, our study has the advantage of having focused on all patients with small bowel polyps and s undergoing double-balloon enteroscopy. Knowledge of the data on the incidence and management of these lesions inpatients undergoing double-balloon enteroscopy is useful for several reasons. First, the endoscopist performing double-balloon enteroscopy should be trained and prepared to resect these polyps. Repeating double-balloon enteroscopy carries the risk of complications; albeit low, it is associated with significant morbidity and even mortality. 17, 20 Thus, in cases where a polypectomy is anticipated, double-balloon enteroscopy should be performed in a specialized centre. Second, knowledge of the incidence and management of small bowel polyps and s is important for planning the endoscopic infrastructure required for the performance of doubleballoon enteroscopy. Currently, double-balloon enteroscopy is mainly performed for obscure gastrointestinal bleeding and suspected Crohn s disease. 1 5 However, our data and those from other studies suggest that polyps and s are a major reason for performing doubleballoon enteroscopy. 21 Third, knowledge of the complications associated with small polypectomy is important. Therapeutic double-balloon enteroscopy is associated with approximately 1 5% incidence of complications, the most frequent ones being pancreatitis, bleeding and perforation. 17, 18, 20, 22 In our series, the incidence of major complications was 3%, consisting of one episode of bleeding. However, minor complications such as oxygen desaturation and abdominal discomfort can also occur as a consequence of double-balloon enteroscopy. We did not aim to investigate the utility of doubleballoon enteroscopy for the surveillance of polyposis syndromes. This topic has been addressed in recent publications. 14 Nevertheless, it is important to emphasize that patients with familial and nonfamilial polyposis syndromes are at increased risk of small bowel polyps and adenocarcinoma. In patients with familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome, the risk increases in parallel to the Spigelman Saurin score or if there are mutations in exon 15. 5, 7, 23, 24 Thus, genetic testing, as it was performed in our study, might be of help to select patients for small bowel investigation. Doubleballoon enteroscopy will allow the elimination of small bowel adenomas using either polypectomy or argon plasma coagulation. 25 In-patients with adenocarcinoma and submucosal masses such as neuroendocrine and gastrointestinal stromal s, we found that double-balloon enteroscopy was most useful for establishing a diagnosis. We want to emphasize that an important aspect about submucosal s is that endoscopic resection should not be attempted. Double-balloon enteroscopy serves the main purpose of localizing these lesions. A recent study reported on the feasibility of combined double-balloon enteroscopy and laparoscopy for the management of various small bowel disease including angiodysplasias, Meckel s diverticula, gastrointestinal stromal and adenocarcinoma. 26 It is important to stress that double-balloon enteroscopy can be a time-consuming procedure and it is not always possible to visualize the entire small bowel. Thus, capsule endoscopy may play an important role in the evaluation of patients with small bowel polyps and s. If no lesions are found, capsule endoscopy may obviate the need for an invasive double-balloon enteroscopy and if a lesion is detected, it would point to the diseased segment to be investigated with the double balloon enteroscope. Therefore, capsule endoscopy and double-balloon enteroscopy should be viewed as tests complementing each other. Our study has the potential limitations of being a single-centre study in a university setting with its associated bias and that it was not a prospective study. Because the study was not population-based, but rather reflects a consecutive series of local and referred patients, the term incidence may be a relative term. However, to our knowledge, this is the largest endoscopic experience focusing on the diagnosis and management of both small bowel polyps and s using balloon enteroscopy. In addition, the data collection was performed prospectively and thoroughly, including definition of polyps and s and usage of standard endoscopic, histological and international criteria for polyposis syndromes, including genetic testing. In summary, we have shown that the relative incidence of small bowel polyps and s in-patients undergoing double-balloon enteroscopy is 9.6%. We also demonstrated that double-balloon enteroscopy is a useful method for the diagnosis and endoscopic therapy of polyps and localization of s. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Declaration of personal and funding interests: None.
8 142 L. C. FRY et al. REFERENCES 1 Yamamoto H, Kita H, Sunada K, et al. Clinical outcomes of double-balloon endoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of small-intestinal diseases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 2: Schäfer C, Rothfuss K, Kreichgauer HP, Stange EF. Efficacy of double-balloon enteroscopy in the evaluation and treatment of bleeding and non-bleeding small bowel disease. Z Gastroenterol 2007; 45: Heine GD, Hadithi M, Groenen MJ, et al. Double-balloon enteroscopy: indications, diagnostic yield, and complications in a series of 275 patients with suspected small-bowel disease. Endoscopy 2006; 38: Zhong J, Ma T, Zhang C, et al. A retrospective study of the application on double-balloon enteroscopy in 378 patients with suspected small-bowel diseases. Endoscopy 2007; 39: Mönkemüller K, Weigt J, Treiber G, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic impact of double-balloon enteroscopy. Endoscopy 2006; 38: Galiatsatos P, Foulkes WD. Familial adenomatous polyposis. Am J Gastroenterol 2006; 101: Brosens LA, van Hattem WA, Jansen M, et al. Gastrointestinal polyposis syndromes. Curr Mol Med 2007; 7: Ward EM, Wolfsen HC. Review article: the non-inherited gastrointestinal polyposis syndromes. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002; 16: Minardi AJ Jr, Zibari GB, Aultman DF, McMillan RW, McDonald JC. Small-bowel tumors. J Am Coll Surg 1998; 186: Marmo R, Rotondano G, Piscopo R, Bianco MA, Cipolletta L. Meta-analysis: capsule enteroscopy vs. conventional modalities in diagnosis of small bowel diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: Goldstein JL, Eisen GM, Lewis B, et al. Small bowel mucosal injury is reduced in healthy subjects treated with celecoxib compared with ibuprofen plus omeprazole, as assessed by video capsule endoscopy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007; 25: Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Penetrante RB, Herrera L, et al. Intraoperative small bowel enteroscopy in familial adenomatous and familial juvenile polyposis. Gastrointest Endosc 1995; 42: May A, Nachbar L, Schneider M, et al. Push-and-pull enteroscopy using the double-balloon technique: method of assessing depth of insertion and training of the enteroscopy technique using the Erlangen Endo-Trainer. Endoscopy 2005; 37: Saurin JC, Gutknecht C, Napoleon B, et al. Surveillance of duodenal adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis reveals high cumulative risk of advanced disease. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: Spigelman AD, Williams CB, Talbot IC, et al. Upper gastrointestinal cancer in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet 1989; 2: Giardiello FM, Brensinger JD, Petersen GM. AGA technical review on hereditary colorectal cancer and genetic testing. Gastroenterology 2001; 121: Mensink PB, Haringsma J, Kucharzik T, et al. Complications of double-balloon enteroscopy: a multicenter survey. Endoscopy 2007; 39: Plum N, May AD, Manner H, Ell C. Peutz- Jeghers syndrome: endoscopic detection and treatment of small bowel polyps by double-balloon enteroscopy. Z Gastroenterol 2007; 45: Ross AS, Dye C, Prachand VN. Laparoscopic-assisted double-balloon enteroscopy for small-bowel polyp surveillance and treatment in patients with Peutz- Jeghers syndrome. Gastrointest Endosc 2006; 64: Möschler O, May AD, Müller MK, Ell C. DBE-Studiengruppe Deutschland. Complications in double-balloon-enteroscopy: results of the German DBE register. Z Gastroenterol 2008; 46: Pasha SF, Leighton JA, Das A, et al. Double-balloon enteroscopy and capsule endoscopy have comparable diagnostic yield in small-bowel disease: a metaanalysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008; 6: Spahn TW, Kampmann W, Eilers M, et al. Small-bowel perforation after endoscopic resection of a Peutz-Jeghers polyp in an infant using double-balloon enteroscopy. Endoscopy 2007; 39: E Mönkemüller K, Fry LC, Ebert M, et al. Feasibility of double-balloon enteroscopy-assisted chromoendoscopy of the small bowel in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Endoscopy 2007; 39: Saurin JC, Ligneau B, Ponchon T, et al. The influence of mutation site and age on the severity of duodenal polyposis in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Gastrointest Endosc 2002; 55: Giardiello FM, Brensinger JD, Tersmette AC, et al. Very high risk of cancer in familial Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Gastroenterology 2000; 119: Yeh TS, Liu KH, Su MY, Lin CH, Chiu CT, Tseng JH. Laparoscopically assisted bowel surgery in an era of double-balloon enteroscopy: from inside to outside. Surg Endosc Epub ahead of print: DOI /s
Deep Enteroscopy Methods to Diagnose Small Bowel IBD
 Deep Enteroscopy Methods to Diagnose Small Bowel IBD Name: Institution: Peter Draganov University of Florida, Gainesville, FL Overview Types of enteroscopy Enteroscopy equipment Enetoscopy do and don'ts
Deep Enteroscopy Methods to Diagnose Small Bowel IBD Name: Institution: Peter Draganov University of Florida, Gainesville, FL Overview Types of enteroscopy Enteroscopy equipment Enetoscopy do and don'ts
Colonic Polyp. Najmeh Aletaha. MD
 Colonic Polyp Najmeh Aletaha. MD 1 Polyps & classification 2 Colorectal cancer risk factors 3 Pathogenesis 4 Surveillance polyp of the colon refers to a protuberance into the lumen above the surrounding
Colonic Polyp Najmeh Aletaha. MD 1 Polyps & classification 2 Colorectal cancer risk factors 3 Pathogenesis 4 Surveillance polyp of the colon refers to a protuberance into the lumen above the surrounding
Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Presented by Dr. 張瀚文
 Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding Presented by Dr. 張瀚文 Definition Obscure: : hard to understand; not clear. Overt: : public; not secret. Occult: : hidden from the knowledge
Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding Presented by Dr. 張瀚文 Definition Obscure: : hard to understand; not clear. Overt: : public; not secret. Occult: : hidden from the knowledge
Long-term Outcome of Patients With Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding Investigated by Double-Balloon Endoscopy
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:151 158 Long-term Outcome of Patients With Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding Investigated by Double-Balloon Endoscopy SATOSHI SHINOZAKI, HIRONORI YAMAMOTO,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:151 158 Long-term Outcome of Patients With Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding Investigated by Double-Balloon Endoscopy SATOSHI SHINOZAKI, HIRONORI YAMAMOTO,
Double-Balloon Enteroscopy and Capsule Endoscopy Have Comparable Diagnostic Yield in Small-Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:671 676 Double-Balloon Enteroscopy and Capsule Endoscopy Have Comparable Diagnostic Yield in Small-Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis SHABANA F. PASHA, JONATHAN
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:671 676 Double-Balloon Enteroscopy and Capsule Endoscopy Have Comparable Diagnostic Yield in Small-Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis SHABANA F. PASHA, JONATHAN
Investigating obscure gastrointestinal bleeding: capsule endoscopy or double balloon enteroscopy?
 REVIEW Investigating obscure gastrointestinal bleeding: capsule endoscopy or double balloon enteroscopy? J. Westerhof, R.K. Weersma, J.J. Koornstra * Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University
REVIEW Investigating obscure gastrointestinal bleeding: capsule endoscopy or double balloon enteroscopy? J. Westerhof, R.K. Weersma, J.J. Koornstra * Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University
Approximately 5% of patients presenting with gastrointestinal
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:664 669 Long-Term Outcomes After Double-Balloon Enteroscopy for Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding LAUREN B. GERSON,* MELISSA A. BATENIC, SHARESE L. NEWSOM,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:664 669 Long-Term Outcomes After Double-Balloon Enteroscopy for Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding LAUREN B. GERSON,* MELISSA A. BATENIC, SHARESE L. NEWSOM,
Imaging Evaluation of Polyps. CT Colonography: Sessile Adenoma. Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon Objectives
 Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon: Pathology and Imaging of the Colon and Rectum Angela D. Levy and Leslie H. Sobin Washington, DC Drs. Levy and Sobin have indicated that they have no relationships which, in the
Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon: Pathology and Imaging of the Colon and Rectum Angela D. Levy and Leslie H. Sobin Washington, DC Drs. Levy and Sobin have indicated that they have no relationships which, in the
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy
 Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY COLORECTAL POLYPS P Goldberg POLYP A polyp is a localised elevated lesion arising from a epithelial surface. If it has a stalk it is called a pedunculated polyp
OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY COLORECTAL POLYPS P Goldberg POLYP A polyp is a localised elevated lesion arising from a epithelial surface. If it has a stalk it is called a pedunculated polyp
Gastric Polyps. Bible class
 Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
GI Polyp syndromes in children. Screening and surveillance, surgery.
 Dr Warren Hyer Consultant Paediatric Gastroenterologist St Mark s Hospital, UK GI Polyp syndromes in children Screening and surveillance, surgery. No conflict of interests to declare Objectives Understand
Dr Warren Hyer Consultant Paediatric Gastroenterologist St Mark s Hospital, UK GI Polyp syndromes in children Screening and surveillance, surgery. No conflict of interests to declare Objectives Understand
Proposed Scoring System to Determine Small Bowel Mass Lesions Using Capsule Endoscopy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proposed Scoring System to Determine Small Bowel Mass Lesions Using Capsule Endoscopy Li-Rung Shyung, Shee-Chan Lin, Shou-Chuan Shih, Wen-Hsiung Chang,* Cheng-Hsin Chu, Tsang-En Wang Background/Purpose:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proposed Scoring System to Determine Small Bowel Mass Lesions Using Capsule Endoscopy Li-Rung Shyung, Shee-Chan Lin, Shou-Chuan Shih, Wen-Hsiung Chang,* Cheng-Hsin Chu, Tsang-En Wang Background/Purpose:
Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role
 Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role Dr. Christos G. Toumpanakis MD PhD FRCP Consultant in Gastroenterology/Neuroendocrine Tumours Hon. Senior Lecturer University
Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role Dr. Christos G. Toumpanakis MD PhD FRCP Consultant in Gastroenterology/Neuroendocrine Tumours Hon. Senior Lecturer University
3/31/12 DOUBLE BALLOON ENTEROSCOPY DOUBLE BALLOON ENTEROSCOPE DOUBLE BALLOON ENTEROSCOPY ASAD ULLAH ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
 ASAD ULLAH ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER DOUBLE BALLOON ENTEROSCOPE v Double balloon enteroscope was developed by Dr. Hironori Yamamoto in Japan. In 2001, he first reported the use of this
ASAD ULLAH ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER DOUBLE BALLOON ENTEROSCOPE v Double balloon enteroscope was developed by Dr. Hironori Yamamoto in Japan. In 2001, he first reported the use of this
Research Article Small Bowel Endoscopy Diagnostic Yield and Reasons of Obscure GI Bleeding in Chinese Patients
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice, Article ID 437693, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/437693 Research Article Small Bowel Endoscopy Diagnostic Yield and Reasons of Obscure GI Bleeding in Chinese
Gastroenterology Research and Practice, Article ID 437693, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/437693 Research Article Small Bowel Endoscopy Diagnostic Yield and Reasons of Obscure GI Bleeding in Chinese
Advanced techniques for resection of large polyps. John G. Lee, MD February 2, 2018
 Advanced techniques for resection of large polyps John G. Lee, MD February 2, 2018 Background 1cm - large polyp on screening 2cm - large for polypectomy 3cm giant polyp 10-15% of polyps can t be removed
Advanced techniques for resection of large polyps John G. Lee, MD February 2, 2018 Background 1cm - large polyp on screening 2cm - large for polypectomy 3cm giant polyp 10-15% of polyps can t be removed
Classification of polyposis syndromes two major groups. Adenomatous polyposis syndromes. Hamartomatous polyposis syndromes
 Hereditary polyposis syndromes Classification of polyposis syndromes two major groups adenomatous and non-adenomatous polyposis syndromes Adenomatous polyposis syndromes Familial adenomatous polyposis(fap)
Hereditary polyposis syndromes Classification of polyposis syndromes two major groups adenomatous and non-adenomatous polyposis syndromes Adenomatous polyposis syndromes Familial adenomatous polyposis(fap)
Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah
 Original Article Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the diagnostic
Original Article Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the diagnostic
Endoscopic techniques for surveillance and treatment of FAP
 Endoscopic techniques for surveillance and treatment of FAP Evelien Dekker MD PhD Department of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Academic Medical Center Amsterdam The Netherlands FAP: endoscopic surveillance
Endoscopic techniques for surveillance and treatment of FAP Evelien Dekker MD PhD Department of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Academic Medical Center Amsterdam The Netherlands FAP: endoscopic surveillance
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
 Familial Adenomatous Polyposis 1 in 10,000 incidence 100 s to 1000 s of colonic adenomas by teens Cancer risk: colon, gastric, duodenum (periampulla), small bowel, pancreas, papillary thyroid, childhood
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis 1 in 10,000 incidence 100 s to 1000 s of colonic adenomas by teens Cancer risk: colon, gastric, duodenum (periampulla), small bowel, pancreas, papillary thyroid, childhood
Capsule Endoscopy Professor Anthony Morris
 Capsule Endoscopy Professor Anthony Morris Consultant Gastroenterologist Director, National Endoscopy Training Centre, Royal Liverpool University Hospitals President, British Society of Gastroenterology
Capsule Endoscopy Professor Anthony Morris Consultant Gastroenterologist Director, National Endoscopy Training Centre, Royal Liverpool University Hospitals President, British Society of Gastroenterology
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal surgery prior as factor in laparoscopic colorectal surgery, 554 555 Abscess(es) CRC presenting as, 539 540 Adenocarcinoma of
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal surgery prior as factor in laparoscopic colorectal surgery, 554 555 Abscess(es) CRC presenting as, 539 540 Adenocarcinoma of
True obscure causes hemobilia, hemosuccus pancreaticus, vasculitis
 Endoscopic Techniques for Small Bowel Imaging Going Where No Man Has Gone Before! Jonathan A. Leighton, MD, FACG, FASGE Mayo Clinic in Arizona 2014 ACG Governors/ASGE Best Practices Course January 2014
Endoscopic Techniques for Small Bowel Imaging Going Where No Man Has Gone Before! Jonathan A. Leighton, MD, FACG, FASGE Mayo Clinic in Arizona 2014 ACG Governors/ASGE Best Practices Course January 2014
Occult and Overt GI Bleeding: Small Bowel Imaging. Outline of Talk
 Occult and Overt GI Bleeding: Small Bowel Imaging Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc Director of Clinical Research, GI Fellowship Program California Pacific Medical Center San Francisco, CA Outline of Talk Definition
Occult and Overt GI Bleeding: Small Bowel Imaging Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc Director of Clinical Research, GI Fellowship Program California Pacific Medical Center San Francisco, CA Outline of Talk Definition
The Spiral Enteroscopy Experience in 101 Consecutive Patients: Safety and Efficacy Using the Discovery SB
 The Spiral Enteroscopy Experience in 101 Consecutive Patients: Safety and Efficacy Using the Discovery SB Akerman, Paul A. 1 ; Cantero, Daniel 2 ; Avila, Jose 2 ; Pangtay, Jesus 3 ; Agrawal, Deepak 1 Introduction:
The Spiral Enteroscopy Experience in 101 Consecutive Patients: Safety and Efficacy Using the Discovery SB Akerman, Paul A. 1 ; Cantero, Daniel 2 ; Avila, Jose 2 ; Pangtay, Jesus 3 ; Agrawal, Deepak 1 Introduction:
Kentaro Tominaga, Kenya Kamimura, Junji Yokoyama and Shuji Terai
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1700-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Usefulness of Capsule Endoscopy and Double-balloon Enteroscopy for the Diagnosis of Multiple Carcinoid Tumors in the Small Intestine:
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1700-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Usefulness of Capsule Endoscopy and Double-balloon Enteroscopy for the Diagnosis of Multiple Carcinoid Tumors in the Small Intestine:
Roles of Capsule Endoscopy and Single-Balloon Enteroscopy in Diagnosing Unexplained Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2016;49:56-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.49.1.56 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Roles of Capsule Endoscopy and Single-Balloon Enteroscopy in
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2016;49:56-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.49.1.56 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Roles of Capsule Endoscopy and Single-Balloon Enteroscopy in
YES NO UNKNOWN. Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE SIGNIFICANCE/BURDEN OF DISEASE NEXT STEPS. YES ( 1 of above)
 Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: SMAD4, BMPR1A DISORDER: Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome HGNC ID: 6670, 1076 OMIM ID: 174900, 175050 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource,
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: SMAD4, BMPR1A DISORDER: Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome HGNC ID: 6670, 1076 OMIM ID: 174900, 175050 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource,
Pathology reports, related operative reports and consult letters must be provided with a request for assessment.
 Page 1 of 6 Polyposis Syndromes Inherited risk for colorectal cancer is associated with a number of polyposis syndromes (genes), some of which are well-defined and others are less common. Identification
Page 1 of 6 Polyposis Syndromes Inherited risk for colorectal cancer is associated with a number of polyposis syndromes (genes), some of which are well-defined and others are less common. Identification
Occult small bowel bleeding - Video capsule first
 Occult small bowel bleeding - Video capsule first Prof. Joseph Sung The Chinese University of Hong Kong Disclosure of Potential Conflict of Interest: Nothing to Disclose Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Occult small bowel bleeding - Video capsule first Prof. Joseph Sung The Chinese University of Hong Kong Disclosure of Potential Conflict of Interest: Nothing to Disclose Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Prospective Comparison of Push Enteroscopy and Push-and-Pull Enteroscopy in Patients with Suspected Small-Bowel Bleeding
 American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2006 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00745.x Published by Blackwell Publishing Prospective Comparison of Push Enteroscopy
American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2006 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00745.x Published by Blackwell Publishing Prospective Comparison of Push Enteroscopy
Laboratory Technique ROLE OF CAPSULE ENDOSCOPY IN OBSCURE GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDING
 Laboratory Technique ROLE OF CAPSULE ENDOSCOPY IN OBSCURE GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDING J. JAIN* ABSTRACT Capsule endoscopy (CE) is a safe, non invasive technique for evaluation of small bowel (SB) lesions.
Laboratory Technique ROLE OF CAPSULE ENDOSCOPY IN OBSCURE GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDING J. JAIN* ABSTRACT Capsule endoscopy (CE) is a safe, non invasive technique for evaluation of small bowel (SB) lesions.
But.. Capsule Endoscopy. Guidelines (OMED ECCO) Why is Enteroscopy so Important? 4/19/2017
 Dr. Elizabeth Odstrcil Digestive Health Associates of Texas April 22, 2017 But.. Capsules fail to reach the cecum in as many as 25% of patients Patients with known CD have a risk of capsule retention of
Dr. Elizabeth Odstrcil Digestive Health Associates of Texas April 22, 2017 But.. Capsules fail to reach the cecum in as many as 25% of patients Patients with known CD have a risk of capsule retention of
Alberta Colorectal Cancer Screening Program (ACRCSP) Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines
 Alberta Colorectal Cancer Screening Program (ACRCSP) Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines June 2013 ACRCSP Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines - 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Background... 3 Terms, Definitions
Alberta Colorectal Cancer Screening Program (ACRCSP) Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines June 2013 ACRCSP Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines - 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Background... 3 Terms, Definitions
Yoshimasa Maeda, Kosaku Moribata, Hisanobu Deguchi, Izumi Inoue, Takao Maekita, Mikitaka Iguchi, Hideyuki Tamai, Jun Kato * and Masao Ichinose
 Maeda et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2015) 15:132 DOI 10.1186/s12876-015-0362-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Video capsule endoscopy as the initial examination for overt obscure gastrointestinal bleeding
Maeda et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2015) 15:132 DOI 10.1186/s12876-015-0362-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Video capsule endoscopy as the initial examination for overt obscure gastrointestinal bleeding
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Small Bowel Bleeding
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Small Bowel Bleeding Lauren B. Gerson, MD, MSc, FACG 1, Jeff L. Fidler 2, MD, David R. Cave, MD, PhD, FACG 3, Jonathan A. Leighton, MD, FACG 4 1 Division
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Small Bowel Bleeding Lauren B. Gerson, MD, MSc, FACG 1, Jeff L. Fidler 2, MD, David R. Cave, MD, PhD, FACG 3, Jonathan A. Leighton, MD, FACG 4 1 Division
Risk factors for advanced duodenal and ampullary adenomatosis in familial adenomatous polyposis: a prospective, single-center study
 Risk factors for advanced duodenal and ampullary adenomatosis in familial adenomatous polyposis: a prospective, single-center study Authors M. Sulbaran 1,F.G.Campos 2, U. Ribeiro Jr. 2,H.S.Kishi 3,P.Sakai
Risk factors for advanced duodenal and ampullary adenomatosis in familial adenomatous polyposis: a prospective, single-center study Authors M. Sulbaran 1,F.G.Campos 2, U. Ribeiro Jr. 2,H.S.Kishi 3,P.Sakai
Summary. Cezary ŁozińskiABDF, Witold KyclerABCDEF. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 2007; 12(4):
 Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 2007; 12(4): 201-206 Original Paper Received: 2006.12.19 Accepted: 2007.04.02 Published: 2007.08.31 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical Analysis
Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 2007; 12(4): 201-206 Original Paper Received: 2006.12.19 Accepted: 2007.04.02 Published: 2007.08.31 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical Analysis
25/11/ / upper G.I. bleeding sources 20/ lower G.I. bleeding sources. scaricato da 1
 U.S.L. AVEZZANO - SULMONA Ospedale SS Filippo e Nicola U.O. ENDOSCOPIA DIGESTIVA (Direttore Dott. Antonio Sedici) double-balloon balloon enteroscopy new gold standard for small-bowel imaging? A. Sedici
U.S.L. AVEZZANO - SULMONA Ospedale SS Filippo e Nicola U.O. ENDOSCOPIA DIGESTIVA (Direttore Dott. Antonio Sedici) double-balloon balloon enteroscopy new gold standard for small-bowel imaging? A. Sedici
SMALL BOWEL ADENOCARCINOMA. Dr. C. Jeske
 SMALL BOWEL ADENOCARCINOMA Dr. C. Jeske Case presentation 54 year old female. Presents with OJ and weight loss. Abdominal examination only reveals a palpable gallbladder. ERCP reveals a circumferential
SMALL BOWEL ADENOCARCINOMA Dr. C. Jeske Case presentation 54 year old female. Presents with OJ and weight loss. Abdominal examination only reveals a palpable gallbladder. ERCP reveals a circumferential
Clinical Outcome of Endoscopic Resection for Nonampullary Duodenal Tumors
 2016.10.20 The 9 th Nottingham Endoscopy Masterclass 9:50-10:10 Clinical Outcome of Endoscopic Resection for Nonampullary Duodenal Tumors Satoru Nonaka, MD, PhD Endoscopy Division National Cancer Center
2016.10.20 The 9 th Nottingham Endoscopy Masterclass 9:50-10:10 Clinical Outcome of Endoscopic Resection for Nonampullary Duodenal Tumors Satoru Nonaka, MD, PhD Endoscopy Division National Cancer Center
Polypectomy and Local Resections of the Colorectum Structured Pathology Reporting Proforma
 Polypectomy and Local Resections of the Colorectum Structured Pathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.03). Family name Given name(s) Date of birth
Polypectomy and Local Resections of the Colorectum Structured Pathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.03). Family name Given name(s) Date of birth
Page 1. Is the Risk This High? Dysplasia in the IBD Patient. Dysplasia in the Non IBD Patient. Increased Risk of CRC in Ulcerative Colitis
 Screening for Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Francis A. Farraye MD, MSc Clinical Director, Section of Gastroenterology Co-Director, Center for Digestive Disorders Boston Medical Center
Screening for Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Francis A. Farraye MD, MSc Clinical Director, Section of Gastroenterology Co-Director, Center for Digestive Disorders Boston Medical Center
colorectal cancer Colorectal cancer hereditary sporadic Familial 1/12/2018
 colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
Adenoma to Carcinoma Pathway
 It is widely accepted that more than 95% of colorectal cancers arise from adenomatous polyps, which are generally defined as benign lesions with dysplastic epithelium that have variable potential for malignancy.
It is widely accepted that more than 95% of colorectal cancers arise from adenomatous polyps, which are generally defined as benign lesions with dysplastic epithelium that have variable potential for malignancy.
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation. See specific types, e.g., Thermal ablation Achalasia, 53 75 described, 53 features of, 53 management of past options, 54 POEM
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation. See specific types, e.g., Thermal ablation Achalasia, 53 75 described, 53 features of, 53 management of past options, 54 POEM
Dysplasia 4/19/2017. How do I practice Chromoendoscopy for Surveillance of Colitis? SCENIC: Polypoid Dysplasia in UC. Background
 SCENIC: Polypoid in UC Definition How do I practice for Surveillance of Colitis? Themos Dassopoulos, M.D. Director, BSW Center for IBD Themistocles.Dassopoulos@BSWHealth.org Tel: 469-800-7189 Cell: 314-686-2623
SCENIC: Polypoid in UC Definition How do I practice for Surveillance of Colitis? Themos Dassopoulos, M.D. Director, BSW Center for IBD Themistocles.Dassopoulos@BSWHealth.org Tel: 469-800-7189 Cell: 314-686-2623
The Usefulness of Capsule Endoscopy for Small Bowel Tumors
 FOCUSED REVIEW SERIES: Current Issues and Future Directions of Small Bowel Endoscopic Evaluation Clin Endosc 2016;49:21-25 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.49.1.21 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443
FOCUSED REVIEW SERIES: Current Issues and Future Directions of Small Bowel Endoscopic Evaluation Clin Endosc 2016;49:21-25 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.49.1.21 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443
GI EMERGENCIES Acute Abdominal Pain
 GI EMERGENCIES Acute Abdominal Pain Marcia Cruz-Correa, MD, PhD, AGAF. FASGE Associate Professor of Medicine, Biochemistry, Surgery Director Translational Research University of Puerto Rico Comprehensive
GI EMERGENCIES Acute Abdominal Pain Marcia Cruz-Correa, MD, PhD, AGAF. FASGE Associate Professor of Medicine, Biochemistry, Surgery Director Translational Research University of Puerto Rico Comprehensive
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus).
 THE COLON This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus). 3 4 5 This part is responsible for formation of stool. The large intestine (colon- coloured
THE COLON This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus). 3 4 5 This part is responsible for formation of stool. The large intestine (colon- coloured
For identification, support and follow up related to Familial Gastrointestinal Cancer conditions. South Island Cancer Nurses Network September 2013
 For identification, support and follow up related to Familial Gastrointestinal Cancer conditions South Island Cancer Nurses Network September 2013 Who are we? Specialist multidisciplinary team: Nurse coordinators,
For identification, support and follow up related to Familial Gastrointestinal Cancer conditions South Island Cancer Nurses Network September 2013 Who are we? Specialist multidisciplinary team: Nurse coordinators,
Hyperplastische Polyps Innocent bystanders?
 Hyperplastische Polyps Innocent bystanders?? K. Geboes P th l i h O tl dk d Pathologische Ontleedkunde, KULeuven Content Historical Classification Relation Hyperplastic polyps carcinoma The concept cept
Hyperplastische Polyps Innocent bystanders?? K. Geboes P th l i h O tl dk d Pathologische Ontleedkunde, KULeuven Content Historical Classification Relation Hyperplastic polyps carcinoma The concept cept
Wireless Capsule Endoscopy as a Diagnostic Technique in Disorders of the Small Bowel, Esophagus and Colon. Original Policy Date
 MP 6.01.23 Wireless Capsule Endoscopy as a Diagnostic Technique in Disorders of the Small Bowel, Esophagus and Colon Medical Policy Section Radiology Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review
MP 6.01.23 Wireless Capsule Endoscopy as a Diagnostic Technique in Disorders of the Small Bowel, Esophagus and Colon Medical Policy Section Radiology Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review
Session I. Clinical Application of Capsule Endoscopy and Enteroscopy: Based on Updated Clinical Guidelines and Evidences
 Symposium: Gut Image Study Group Session I. Clinical Application of Capsule Endoscopy and Enteroscopy: Based on Updated Clinical Guidelines and Evidences Small Bowel Tumors Jin Su Kim Department of Internal
Symposium: Gut Image Study Group Session I. Clinical Application of Capsule Endoscopy and Enteroscopy: Based on Updated Clinical Guidelines and Evidences Small Bowel Tumors Jin Su Kim Department of Internal
Colorectal Cancer Screening
 Recommendations from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer Colorectal Cancer Screening Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Kaltenbach T, Levin TR, Lieberman D, Robertson
Recommendations from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer Colorectal Cancer Screening Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Kaltenbach T, Levin TR, Lieberman D, Robertson
How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD?
 How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD? Name: Institution: Helmut Neumann, MD, PhD, FASGE University Medical Center Mainz What do we know? Patients with IBD carry an increased risk of developing
How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD? Name: Institution: Helmut Neumann, MD, PhD, FASGE University Medical Center Mainz What do we know? Patients with IBD carry an increased risk of developing
Large polyps: EMR, ESD, TEM and segmental resection. Terry Phang 2017 SON fall update
 Large polyps: EMR, ESD, TEM and segmental resection Terry Phang 2017 SON fall update Key Points: Large polyps No RCT re: Recurrence, complications Piecemeal vs en bloc: EMR vs ESD Partial vs full-thickness:
Large polyps: EMR, ESD, TEM and segmental resection Terry Phang 2017 SON fall update Key Points: Large polyps No RCT re: Recurrence, complications Piecemeal vs en bloc: EMR vs ESD Partial vs full-thickness:
SMALL BOWEL GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDING
 SMALL BOWEL GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDING Giovanni DI NARDO giovanni.dinardo@uniroma1.it UOC Gastroenterologia ed Epatologia Pediatrica Dipartimento di Pediatria, Sapienza - Università di Roma (Direttore:
SMALL BOWEL GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDING Giovanni DI NARDO giovanni.dinardo@uniroma1.it UOC Gastroenterologia ed Epatologia Pediatrica Dipartimento di Pediatria, Sapienza - Università di Roma (Direttore:
Occult GI Bleed. July 2015
 Occult GI Bleed July 2015 Occult GI Bleed Occult vs Obscure Occult positive FOB and/or IDA, but no evidence of visible blood loss to pt or physician Obscure GI bleed that persist/ recurs without obvious
Occult GI Bleed July 2015 Occult GI Bleed Occult vs Obscure Occult positive FOB and/or IDA, but no evidence of visible blood loss to pt or physician Obscure GI bleed that persist/ recurs without obvious
27
 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 Diagnosis:? Diagnosis: Juvenile Polyposis with BMPR1A Mutation 36 Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome Rare Autosomal Dominant Disorder with Multiple Juvenile Polyps in GI Tract Juvenile
26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 Diagnosis:? Diagnosis: Juvenile Polyposis with BMPR1A Mutation 36 Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome Rare Autosomal Dominant Disorder with Multiple Juvenile Polyps in GI Tract Juvenile
Benchmarking For Colonoscopy. Technology and Technique to Improve Adenoma Detection
 Benchmarking For Colonoscopy Technology and Technique to Improve Adenoma Detection Objectives 1. Review the latest data on performance characteristics and efficacy for colon cancer prevention 2. Highlight
Benchmarking For Colonoscopy Technology and Technique to Improve Adenoma Detection Objectives 1. Review the latest data on performance characteristics and efficacy for colon cancer prevention 2. Highlight
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. 1 Approach to the patient with gross gastrointestinal bleeding. Grace H. Elta, Mimi Takami
 1 Approach to the patient with gross gastrointestinal bleeding Grace H. Elta, Mimi Takami Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a common clinical problem that requires more than 300 000 hospitalizations annually
1 Approach to the patient with gross gastrointestinal bleeding Grace H. Elta, Mimi Takami Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a common clinical problem that requires more than 300 000 hospitalizations annually
Objectives. Definitions. Colorectal Cancer Screening 5/8/2018. Payam Afshar, MS, MD Kaiser Permanente, San Diego. Colorectal cancer background
 Colorectal Cancer Screening Payam Afshar, MS, MD Kaiser Permanente, San Diego Objectives Colorectal cancer background Colorectal cancer screening populations Colorectal cancer screening modalities Colonoscopy
Colorectal Cancer Screening Payam Afshar, MS, MD Kaiser Permanente, San Diego Objectives Colorectal cancer background Colorectal cancer screening populations Colorectal cancer screening modalities Colonoscopy
Historical. Note: The parenthetical numbers in the Clinical Indications section refer to the source documents cited in the References Section below.
 Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Colonoscopy Guideline #: CG-SURG-01 Current Effective Date: 01/21/2015 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 05/15/2014 Description Colonoscopy describes the direct visual inspection
Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Colonoscopy Guideline #: CG-SURG-01 Current Effective Date: 01/21/2015 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 05/15/2014 Description Colonoscopy describes the direct visual inspection
Wireless Capsule Endoscopy to Diagnose Disorders of the Small Bowel, Esophagus, and Colon
 Wireless Capsule Endoscopy to Diagnose Disorders of the Small Bowel, Esophagus, and Colon Policy Number: 6.01.33 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2003 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield
Wireless Capsule Endoscopy to Diagnose Disorders of the Small Bowel, Esophagus, and Colon Policy Number: 6.01.33 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2003 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield
References. GI Biopsies. What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD
 What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
Capsule Endoscopy and Deep Enteroscopy
 Capsule Endoscopy and Deep Enteroscopy Are they complementary? ACG Governors / ASGE 2012 Best Practices Course January 29, 2012 The Hyatt Regency Huntington Beach, California John A. Martin, MD Disclosure
Capsule Endoscopy and Deep Enteroscopy Are they complementary? ACG Governors / ASGE 2012 Best Practices Course January 29, 2012 The Hyatt Regency Huntington Beach, California John A. Martin, MD Disclosure
Bowel obstruction and tumors
 Bowel obstruction and tumors Intestinal Obstruction Obstruction of the GI tract may occur at any level, but the small intestine is most often involved because of its relatively narrow lumen. Causes: Hernias
Bowel obstruction and tumors Intestinal Obstruction Obstruction of the GI tract may occur at any level, but the small intestine is most often involved because of its relatively narrow lumen. Causes: Hernias
Impact of balloon-assisted enteroscopy on the diagnosis and management of suspected and established small-bowel Crohn s disease
 THIEME E201 Impact of balloon-assisted enteroscopy on the diagnosis and management of suspected and established small-bowel Crohn s disease Authors Institution Udayakumar Navaneethan, John J. Vargo, K.
THIEME E201 Impact of balloon-assisted enteroscopy on the diagnosis and management of suspected and established small-bowel Crohn s disease Authors Institution Udayakumar Navaneethan, John J. Vargo, K.
Small Bowel Metastatic Cancer Observed With Double Balloon Enteroscopy in a Patient With a Past History of Multiple Cancers
 CASE REPORT ISSN 1598-9100(Print) ISSN 2288-1956(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5217/ir.2015.13.4.350 Intest Res 2015;13(4):350-354 Small Bowel Metastatic Cancer Observed With Double Balloon Enteroscopy
CASE REPORT ISSN 1598-9100(Print) ISSN 2288-1956(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5217/ir.2015.13.4.350 Intest Res 2015;13(4):350-354 Small Bowel Metastatic Cancer Observed With Double Balloon Enteroscopy
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia
 Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
EMR, ESD and Beyond. Peter Draganov MD. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida
 EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy. Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital
 Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital Colon Cancer Colon cancer is common. 1 in 20 people in the UK will develop the disease 19 000
Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital Colon Cancer Colon cancer is common. 1 in 20 people in the UK will develop the disease 19 000
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Aberrant crypt foci, chromocolonoscopy for, 539 540 Absorptive stains, for chromocolonoscopy, 522 524 Accessories, for colonoscopy, 680 684
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Aberrant crypt foci, chromocolonoscopy for, 539 540 Absorptive stains, for chromocolonoscopy, 522 524 Accessories, for colonoscopy, 680 684
HHS Public Access Author manuscript Gastrointest Endosc. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 April 29.
 Endoscopic papillectomy: risk factors for incomplete resection and recurrence during long-term follow-up Wiriyaporn Ridtitid, MD 1,2, Damien Tan, MD 1, Suzette E. Schmidt, BSN 1, Evan L. Fogel, MD 1, Lee
Endoscopic papillectomy: risk factors for incomplete resection and recurrence during long-term follow-up Wiriyaporn Ridtitid, MD 1,2, Damien Tan, MD 1, Suzette E. Schmidt, BSN 1, Evan L. Fogel, MD 1, Lee
malignant polyp Daily Challenges in Digestive Endoscopy for Endoscopists and Endoscopy Nurses BSGIE Annual Meeting 18/09/2014 Mechelen
 Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Colorectal Neoplasia. Dr. Smita Devani MBChB, MRCP. Consultant Physician and Gastroenterologist Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi
 Colorectal Neoplasia Dr. Smita Devani MBChB, MRCP Consultant Physician and Gastroenterologist Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Case History BT, 69yr male Caucasian History of rectal bleeding No change
Colorectal Neoplasia Dr. Smita Devani MBChB, MRCP Consultant Physician and Gastroenterologist Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Case History BT, 69yr male Caucasian History of rectal bleeding No change
Hereditary Gastric Cancer
 Hereditary Gastric Cancer Dr Bastiaan de Boer Consultant Pathologist Department of Anatomical Pathology PathWest Laboratory Medicine, QE II Medical Centre Clinical Associate Professor School of Pathology
Hereditary Gastric Cancer Dr Bastiaan de Boer Consultant Pathologist Department of Anatomical Pathology PathWest Laboratory Medicine, QE II Medical Centre Clinical Associate Professor School of Pathology
Digestive Health Southwest Endoscopy 2016 Quality Report
 Digestive Health 2016 Quality Report Our 2016 our quality and value management program focused on one primary area of interest: Performing high quality colonoscopy High quality Colonoscopy We selected
Digestive Health 2016 Quality Report Our 2016 our quality and value management program focused on one primary area of interest: Performing high quality colonoscopy High quality Colonoscopy We selected
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R
 170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
COLORECTAL CARCINOMA
 QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS MANAGEMENT OF COLORECTAL CARCINOMA Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Colorectal Surgeons Malaysian Society of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Malaysian
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS MANAGEMENT OF COLORECTAL CARCINOMA Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Colorectal Surgeons Malaysian Society of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Malaysian
for the gastroenterologist
 Original Article Singapore Med.1 2007, 48 (1) : 50 Early experience with double balloon enteroscopy: a leap forward for the gastroenterologist Ang D, Luman W, Ooi CJ Department of Gastroenterology and
Original Article Singapore Med.1 2007, 48 (1) : 50 Early experience with double balloon enteroscopy: a leap forward for the gastroenterologist Ang D, Luman W, Ooi CJ Department of Gastroenterology and
Enteroscopy in children
 Review Article Enteroscopy in children Giovanni Di Nardo 1,2, Carlo Calabrese 3, Roberto Conti Nibali 4, Arianna De Matteis 5, Emanuele Casciani 2,6, Luigi Martemucci 1, Giuseppe Pagliaro 7 and Nico Pagano
Review Article Enteroscopy in children Giovanni Di Nardo 1,2, Carlo Calabrese 3, Roberto Conti Nibali 4, Arianna De Matteis 5, Emanuele Casciani 2,6, Luigi Martemucci 1, Giuseppe Pagliaro 7 and Nico Pagano
FINAL HISTOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS: Villo-adenomatous polyp with in-situ-carcinomatous foci (involving both adenomatous and villous component).
 SOLITARY VILLO ADENOMATOUS POLYP WITH CARCINOMATOUS CHANGES RECTUM: A Divvya B 1, M. Valluvan 2, Rehana Tippoo 3, P. Viswanathan 4, R. Baskaran 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, M. Valluvan, Rehana
SOLITARY VILLO ADENOMATOUS POLYP WITH CARCINOMATOUS CHANGES RECTUM: A Divvya B 1, M. Valluvan 2, Rehana Tippoo 3, P. Viswanathan 4, R. Baskaran 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, M. Valluvan, Rehana
Razvan I. Arsenescu, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Digestive Diseases EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER
 Razvan I. Arsenescu, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Digestive Diseases EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER Epidemiology of CRC Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common and lethal disease Environmental
Razvan I. Arsenescu, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Digestive Diseases EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER Epidemiology of CRC Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common and lethal disease Environmental
EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER. Epidemiology of CRC
 Razvan I. Arsenescu, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Digestive Diseases EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER Epidemiology of CRC Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common and lethal disease Environmental
Razvan I. Arsenescu, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Digestive Diseases EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER Epidemiology of CRC Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common and lethal disease Environmental
URGENT CAPSULE ENDOSCOPY IS USEFUL IN SEVERE OBSCURE-OVERT GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDING
 Digestive Endoscopy (2009) 21, 87 92 doi:10.1111/j.1443-1661.2009.00838.x ORIGINAL ARTICLE URGENT CAPSULE ENDOSCOPY IS USEFUL IN SEVERE OBSCURE-OVERT GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDING Nuno Almeida,Pedro Figueiredo,Sandra
Digestive Endoscopy (2009) 21, 87 92 doi:10.1111/j.1443-1661.2009.00838.x ORIGINAL ARTICLE URGENT CAPSULE ENDOSCOPY IS USEFUL IN SEVERE OBSCURE-OVERT GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDING Nuno Almeida,Pedro Figueiredo,Sandra
The Usefulness of Capsule Endoscopy
 The Usefulness of Capsule Endoscopy David J. Hass, MD, FACG Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Gastroenterology Center of Connecticut Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding
The Usefulness of Capsule Endoscopy David J. Hass, MD, FACG Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Gastroenterology Center of Connecticut Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행
 Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Familial and Hereditary Colon Cancer
 Familial and Hereditary Colon Cancer Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, FACG, FASGE, FACP GI Section Chief, Minneapolis VAMC Associate Professor, Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, University of
Familial and Hereditary Colon Cancer Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, FACG, FASGE, FACP GI Section Chief, Minneapolis VAMC Associate Professor, Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, University of
Double-balloon endoscopy as the primary method for small-bowel video capsule endoscope retrieval
 Double-balloon endoscopy as the primary method for small-bowel video capsule endoscope retrieval Stijn J. B. Van Weyenberg 1, Sietze T. Van Turenhout 1, Gerd Bouma 1, Jan Hein T. M. Van Waesberghe 2, Donald
Double-balloon endoscopy as the primary method for small-bowel video capsule endoscope retrieval Stijn J. B. Van Weyenberg 1, Sietze T. Van Turenhout 1, Gerd Bouma 1, Jan Hein T. M. Van Waesberghe 2, Donald
Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation
 Anatomic Pathology / LARGE COLORECTAL ADENOMAS AND PATHOLOGIC EVALUATION Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation Elizabeth D. Euscher, MD, 1 Theodore H. Niemann, MD, 1 Joel G. Lucas,
Anatomic Pathology / LARGE COLORECTAL ADENOMAS AND PATHOLOGIC EVALUATION Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation Elizabeth D. Euscher, MD, 1 Theodore H. Niemann, MD, 1 Joel G. Lucas,
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD
 Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Screening & Surveillance Guidelines
 Chapter 2 Screening & Surveillance Guidelines I. Eligibility Coloradans ages 50 and older (average risk) or under 50 at elevated risk for colon cancer (personal or family history) that meet the following
Chapter 2 Screening & Surveillance Guidelines I. Eligibility Coloradans ages 50 and older (average risk) or under 50 at elevated risk for colon cancer (personal or family history) that meet the following
GIQIC18 Appropriate follow-up interval of not less than 5 years for colonoscopies with findings of 1-2 tubular adenomas < 10 mm
 GI Quality Improvement Consortium, Ltd. (GIQuIC) 1 Following is an overview of the clinical quality measures in GIQuIC that can be reported to CMS for the Quality performance category of the Merit-Based
GI Quality Improvement Consortium, Ltd. (GIQuIC) 1 Following is an overview of the clinical quality measures in GIQuIC that can be reported to CMS for the Quality performance category of the Merit-Based
Barrett s esophagus. Barrett s neoplasia treatment trends
 Options for endoscopic treatment of Barrett s esophagus Patrick S. Yachimski, MD MPH Director of Pancreatobiliary Endoscopy Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition
Options for endoscopic treatment of Barrett s esophagus Patrick S. Yachimski, MD MPH Director of Pancreatobiliary Endoscopy Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition
Colon and Rectum: 2018 Solid Tumor Rules
 2018 SEER Solid Tumor Manual 2018 KCR SPRING TRAINING Colon and Rectum: 2018 Solid Tumor Rules 1 Colon and Rectum Solid Tumor Rules Separate sections for: Introduction Changes from 2007 MP/H rules Equivalent
2018 SEER Solid Tumor Manual 2018 KCR SPRING TRAINING Colon and Rectum: 2018 Solid Tumor Rules 1 Colon and Rectum Solid Tumor Rules Separate sections for: Introduction Changes from 2007 MP/H rules Equivalent
