Development of Biomimetic Surfaces by Vesicle Fusion
|
|
|
- Reynold Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Development of Biomimetic Surfaces by Vesicle Fusion Dimitris Stroumpoulis Department of hemical Engineering - University of alifornia, Santa Barbara
2 Introduction
3 Fibronectin Integrin System ell Surface Receptor Integrin family: Adhesive Ligand: GRGDSP 10Å 30-40Å PSR Integrins Binding RGD α 5 β 1 α 8 β 1 α v β 1 α v β 3 α v β 5 α v β 6 α 2 β 1 α 3 β 1 α 4 β 1 α 7 β 1 (weak) α v β 8 α IIb β 3 Image adapted from Leahy, D.L. et al., 1996, ell 84:155
4 Intelligent Biomaterials: Minimize non-specific interactions with EM Allow selective interaction with cells Mimic EM (Biomimetics) Motivation Design Goals: ontrol Microenvironment of ells Direct ell Behavior
5 Surface Biofunctionalization Arrange Ligands on Surface: Accessibility onformation oncentration Lateral Motion Peptide Ligand Polar eadgroup (small) / Tails (bulky) Planar Bilayer Properties of Lipid Bilayers: Bending easier than stretching Flip flop times are high ( s) Residence time (10 4 s)
6 Langmuir Blodgett-Deposition ompress amphiphiles on the air-water interface Transfer solid monolayer onto substrate 'ollapse 2 Deposition Surface pressure 'Solid' 'Liquid' 'Gas Phosphatidylethanolamine GRGDSP PEG120 1 Area per molecule ompression Isotherm
7 DS1 Vesicle Fusion Vesicle Solution on Surface Planar Bilayer Vesicle Fusion ydrophilic Substrate Diffusion Adsorption and deformation Rupture Spreading Rupture propagation Lateral diffusion
8 Ellipsometry Angle of Incidence Reflected Beam Incident Beam Detector Laser Source r E p i E p Polarizer Analyzer r E s δ r δ i i E s Birefringence Modulator Substrate Plane of Incidence y = 2 Im() r 2 Im( r) Re ( 2 2 n n ) () r + Im() r 2 2 2π n1 + n2 Δy = 2 λ n 1 2 ( 2 2 )( 2 2 n n n n ) 1 2 Δz r = r r p s = E E E E r p i p r s i s e i δ δ ) ( r i
9 Refractive Index of a Single Bilayer R (bulk) R (Monolayer) Alkanes (bulk) (From Petrov et al, J. Phys. hem. 103 (1999) ) Assuming n of one DMP Bilayer n of one Monolayer (=28) z = 40Å (for y max = 0.035) Good overage eadgroup Area of DMP 59Å 2 Γ M = 3.8 mg/m 2
10 The Model (From Self Assembly Driven by ydrophobic Interactions at Alkanethiol Monolayers: Mechanism of Formation of ybrid Bilayer Membranes, J. B. ubbard, V. Silin, A. L. Plant, Biophysical hemistry 75 (1998) ) x 1-D Mass Equation: t = D 2 2 x Initial ondition: (x, t = 0) = o Mixed Boundary ondition: D x Surface = K Surface Where K: adsorption rate constant of mass (cm/s) o : bulk concentration of lipids (mg/ml) D: diffusion coefficient of mass close to surface (cm 2 /s) J Surface = K o e 2 K t D K erfc( D 1/2 t 1/2 )
11 General and Limiting ases dγ dt Γ(t) = β J = [1- ] J surface I: Γ(t=0) = 0 Γ M surface General Solution: Γ(t) = Γ M {1 e K Γ M o D [ (e 2 K K 2 t D erfc 2 K t 2 1) + D K Dt π ] } haracteristic Time of Adsorption: τ = D/K 2 For t/τ >> 1 (Diffusion Limited ase): Γ(t) = Γ M (1 e Γ o M (2 D t D ) π K ) For t/τ << 1 (Adsorption Limited ase): Γ(t) = Γ M (1 e K Γ o M t )
12 Results (Limiting ases Fittings) Diffusion Limited ase Adsorption Limited ase Lipid concentration 0, mg ml -1 Maximum Surface coverage Γ m, mg cm -2 Diffusion coefficient D, cm 2 s -1 Lipid concentration 0, mg ml -1 Maximum Surface coverage Γ m, mg cm -2 Adsorption rate constant K, cm s
13 Effect of Peptide Amphiphile Presence on the Kinetics 2 ( 14 ) 2 linker 2 G R G D S P 0.09 mg/ml 10% mole PA DMP ase Diffusion Limited Adsorption Limited Adsorption rate constant K, cm s Diffusion coefficient D, cm 2 s Kinetics not Interrupted by PA presence
14 Fluorescence Visualization DP - PA 1,2-dihexadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphoethanolamine, triethylammonium salt (Texas Red DPE - Molecular Probes) 2 mm DP PA 0hrs DP PA 2hrs
15 PA for ell Adhesion ontrols the presentation of RGD, a peptide sequence important for cell adhesion, i.e vesicles, bilayers, etc. Focused on two peptide amphiphiles with different spacer groups, 2 and polyethylene oxide (PE). Tails Spacer ead 2 2
16 Experimental Procedure Vesicle formation 100 nm ydration - Extrusion Bilayer formation Fusion ~ 5 nm Glass Substrate Addition of cells Incubation
17 Adhesion & Spreading Evaluation Inertia motion caused by mild microscope stage shaking determines adhesion. Scion Imaging software is used to determine the shape factor.
18 Results EggP Bilayer 200 μm 200 μm Average Shape Factor (4 hours) o Adhesion
19 Results 10% 2 -RGD Bilayer 200 μm 200 μm Average Shape Factor (3 hours) o Adhesion
20 Results 10 % PE-RGD Bilayer 200 μm 200 μm Average Shape Factor (4 hours) Adhesion
21 oncentration Effect 100 μm 100 μm 5% PE-RGD 10% PE-RGD (2 hours) Adhesion
22 Surface oncentration Gradients Supported bilayers present a physically relevant substrate to study cell-em protein interactions Active protein sequences can be presented in a control manner using peptide amphiphiles There is a drive for the development of multifunctionalmulticomponent surfaces Further understanding of how specific ligand-integrin interactions modulate cell function is required Gradients of membrane bounded ligands can provide a useful tool to study this problem Vesicle fusion is the most efficient method to make surface gradients in a membrane environment
23 Ligand oncentration ell Spreading A 200 μm 200 μm B D 200 μm 200 μm Figure: I3T3 cells cultured on supported membranes after 4 hours. Membranes in (A) & (B) are 99% EggP and 1% Texas Red DPE while in () & (D) 94% EggP, 5% (16)2-Glu-PE-GRGDSP and 1% Texas Red DPE. Pictures (A) and () are in optical mode, while (B) and (D) in fluorescent mode on the same surface spot respectively.
24 Ligand oncentration ell Migration MIRSPY RESEAR AD TEIQUE 43: (1998)
25 Steps to a oncentration Gradient Barriers ydrophilic Substrate Patterning ydrophilic Substrate
26 Different ways to make barriers Materials: Au, Al, r, Ti Al 2 3, Ti 2 Fibronectin, BSA Polymerized Bilayers hemical ature of Barrier not topography Blocks Diffusion Techniques: Standard Photolithography (metals) Polymerization Microcontact Printing Spread - eutral and Low P Deep Abrasion (R<<10 nm) Stable - igh P "Micropattern Formation in Supported Lipid Membranes", Jay T. Groves and Steven G. Boxer, Acc. of hem. Res., 35, (2002).
27 hrome Grid 1 mm 5 μm EggP Bilayer 200 μm
28 Different ways to pattern Photolithographic Patterning (Photoactivatable peptides) Microprinting Direct Pipetting Microfluidic Flow "Micropattern Formation in Supported Lipid Membranes", Jay T. Groves and Steven G. Boxer, Acc. of hem. Res., 35, (2002).
29 Microfluidic etworks
30 onstruction Si 2 Si μm SU-8 Mask Mask Si 2 3mm Si 2
31 Evaluation
32 SEM
33 Testing 1 mm Intensity vs Position Intensity Position (mm)
34 onclusions Ellipsometry was used to study the kinetics of VF on Si 2 Bilayer formation from vesicles is adsorption limited Fluorescence microscopy was used to visualize the membranes Peptide accessibility and density are important for cell binding Surface composition gradients are useful in studying cellular function modulation induced by ligand-integrin interactions on a biomimetic membrane A novel technique was developed to control the microenvironment of cells in 2-D
35 Acknowledgments Dr. Alejandro Parra Ellipsometry Dr. aining Zhang PE chemistry ing ao lean-room Processing This work was partially supported by the MRSE Program of the ational Science Foundation under Award o. DMR , the ational Science Foundation IRT Award o. TS , and the Army Research ffice through the Institute for ollaborative Biotechnologies.
Electronic Supporting Information
 Modulation of raft domains in a lipid bilayer by boundary-active curcumin Manami Tsukamoto a, Kenichi Kuroda* b, Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy* c, Kazuma Yasuhara* a Electronic Supporting Information Contents
Modulation of raft domains in a lipid bilayer by boundary-active curcumin Manami Tsukamoto a, Kenichi Kuroda* b, Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy* c, Kazuma Yasuhara* a Electronic Supporting Information Contents
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Rupture of Lipid Membranes Induced by Amphiphilic Janus Nanoparticles Kwahun Lee, Liuyang Zhang, Yi Yi, Xianqiao Wang, Yan Yu* Department of Chemistry, Indiana University, Bloomington,
Supporting Information for Rupture of Lipid Membranes Induced by Amphiphilic Janus Nanoparticles Kwahun Lee, Liuyang Zhang, Yi Yi, Xianqiao Wang, Yan Yu* Department of Chemistry, Indiana University, Bloomington,
NANO 243/CENG 207 Course Use Only
 L9. Drug Permeation Through Biological Barriers May 3, 2018 Lipids Lipid Self-Assemblies 1. Lipid and Lipid Membrane Phospholipid: an amphiphilic molecule with a hydrophilic head and 1~2 hydrophobic tails.
L9. Drug Permeation Through Biological Barriers May 3, 2018 Lipids Lipid Self-Assemblies 1. Lipid and Lipid Membrane Phospholipid: an amphiphilic molecule with a hydrophilic head and 1~2 hydrophobic tails.
Chemical Surface Transformation 1
 Chemical Surface Transformation 1 Chemical reactions at Si H surfaces (inorganic and organic) can generate very thin films (sub nm thickness up to µm): inorganic layer formation by: thermal conversion:
Chemical Surface Transformation 1 Chemical reactions at Si H surfaces (inorganic and organic) can generate very thin films (sub nm thickness up to µm): inorganic layer formation by: thermal conversion:
The Transport and Organization of Cholesterol in Planar Solid-Supported Lipid Bilayer Depend on the Phospholipid Flip-Flop Rate
 Supporting Information The Transport and Organization of Cholesterol in Planar Solid-Supported Lipid Bilayer Depend on the Phospholipid Flip-Flop Rate Ting Yu, 1,2 Guangnan Zhou, 1 Xia Hu, 1,2 Shuji Ye
Supporting Information The Transport and Organization of Cholesterol in Planar Solid-Supported Lipid Bilayer Depend on the Phospholipid Flip-Flop Rate Ting Yu, 1,2 Guangnan Zhou, 1 Xia Hu, 1,2 Shuji Ye
Flip-Flop Induced Relaxation Of Bending Energy: Implications For Membrane Remodeling
 Biophysical Journal, Volume 97 Supporting Material Flip-Flop Induced Relaxation Of Bending Energy: Implications For Membrane Remodeling Raphael Jeremy Bruckner, Sheref S. Mansy, Alonso Ricardo, L. Mahadevan,
Biophysical Journal, Volume 97 Supporting Material Flip-Flop Induced Relaxation Of Bending Energy: Implications For Membrane Remodeling Raphael Jeremy Bruckner, Sheref S. Mansy, Alonso Ricardo, L. Mahadevan,
Transport and Concentration of Charged Molecules in a Lipid Membrane
 Transport and Concentration of Charged Molecules in a Lipid Membrane Johannes S. Roth 1, Matthew R. Cheetham 1,2, and Stephen D. Evans* 1 1 University of Leeds, 2 Current Address: University of Oxford
Transport and Concentration of Charged Molecules in a Lipid Membrane Johannes S. Roth 1, Matthew R. Cheetham 1,2, and Stephen D. Evans* 1 1 University of Leeds, 2 Current Address: University of Oxford
Physical Cell Biology Lecture 10: membranes elasticity and geometry. Hydrophobicity as an entropic effect
 Physical Cell Biology Lecture 10: membranes elasticity and geometry Phillips: Chapter 5, Chapter 11 and Pollard Chapter 13 Hydrophobicity as an entropic effect 1 Self-Assembly of Lipid Structures Lipid
Physical Cell Biology Lecture 10: membranes elasticity and geometry Phillips: Chapter 5, Chapter 11 and Pollard Chapter 13 Hydrophobicity as an entropic effect 1 Self-Assembly of Lipid Structures Lipid
Patterning and Composition Arrays of Supported Lipid Bilayers by Microcontact Printing
 3400 Langmuir 2001, 17, 3400-3405 Patterning and Composition Arrays of Supported Lipid Bilayers by Microcontact Printing Jennifer S. Hovis and Steven G. Boxer* Department of Chemistry, Stanford University,
3400 Langmuir 2001, 17, 3400-3405 Patterning and Composition Arrays of Supported Lipid Bilayers by Microcontact Printing Jennifer S. Hovis and Steven G. Boxer* Department of Chemistry, Stanford University,
Biological Membranes. Lipid Membranes. Bilayer Permeability. Common Features of Biological Membranes. A highly selective permeability barrier
 Biological Membranes Structure Function Composition Physicochemical properties Self-assembly Molecular models Lipid Membranes Receptors, detecting the signals from outside: Light Odorant Taste Chemicals
Biological Membranes Structure Function Composition Physicochemical properties Self-assembly Molecular models Lipid Membranes Receptors, detecting the signals from outside: Light Odorant Taste Chemicals
Neutron reflectivity in biology and medicine. Jayne Lawrence
 Neutron reflectivity in biology and medicine Jayne Lawrence Why neutron reflectivity studies? build up a detailed picture of the structure of a surface in the z direction n e u tro n s in n e u tro n s
Neutron reflectivity in biology and medicine Jayne Lawrence Why neutron reflectivity studies? build up a detailed picture of the structure of a surface in the z direction n e u tro n s in n e u tro n s
Protein directed assembly of lipids
 Protein directed assembly of lipids D. Nordin, O. Yarkoni, L. Donlon, N. Savinykh, and D.J. Frankel SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Supported bilayer preparation 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
Protein directed assembly of lipids D. Nordin, O. Yarkoni, L. Donlon, N. Savinykh, and D.J. Frankel SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Supported bilayer preparation 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
Colloid chemistry. Lecture 10: Surfactants
 Colloid chemistry Lecture 10: Surfactants Applications of surfactants: cleaning/detergents (40%); textiles; cosmetics; pharmacy; paint; food; etc. Etymology Surfactant micelles surfactant molecule spherical
Colloid chemistry Lecture 10: Surfactants Applications of surfactants: cleaning/detergents (40%); textiles; cosmetics; pharmacy; paint; food; etc. Etymology Surfactant micelles surfactant molecule spherical
Phosphatidylcholines are a class of glycerophospholipids which along with other phospholipids
 Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of glycerophospholipids which along with other phospholipids account for more than half of the lipids in most membranes. Phosphatidylcholines can further
Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of glycerophospholipids which along with other phospholipids account for more than half of the lipids in most membranes. Phosphatidylcholines can further
Self-assembly and phase behavior
 Self-assembly and phase behavior Amphiphiles and surface tension Lyotropic phases Micelles Key parameters for micellisation Critical packing parameter Other lyotropic phases Special lyotropic phases: vesicles
Self-assembly and phase behavior Amphiphiles and surface tension Lyotropic phases Micelles Key parameters for micellisation Critical packing parameter Other lyotropic phases Special lyotropic phases: vesicles
Methods and Materials
 a division of Halcyonics GmbH Anna-Vandenhoeck-Ring 5 37081 Göttingen, Germany Application Note Micostructured lipid bilayers ANDREAS JANSHOFF 1), MAJA GEDIG, AND SIMON FAISS Fig.1: Thickness map of microstructured
a division of Halcyonics GmbH Anna-Vandenhoeck-Ring 5 37081 Göttingen, Germany Application Note Micostructured lipid bilayers ANDREAS JANSHOFF 1), MAJA GEDIG, AND SIMON FAISS Fig.1: Thickness map of microstructured
Model for measurement of water layer thickness under lipid bilayers by surface plasmon resonance
 Model for measurement of water layer thickness under lipid bilayers by surface plasmon resonance Koyo Watanabe Unit of Measurement Technology, CEMIS-OULU, University of Oulu, PO Box 51, 87101 Kajaani,
Model for measurement of water layer thickness under lipid bilayers by surface plasmon resonance Koyo Watanabe Unit of Measurement Technology, CEMIS-OULU, University of Oulu, PO Box 51, 87101 Kajaani,
Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography.
 Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography. Representative low-magnification scanning electron micrographs of a) Black silicon (bsi) and b) Diplacodes bipunctata dragonfly
Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography. Representative low-magnification scanning electron micrographs of a) Black silicon (bsi) and b) Diplacodes bipunctata dragonfly
Solid supported lipid bilayers: From biophysical studies to sensor design
 Surface Science Reports 61 (2006) 429 444 www.elsevier.com/locate/surfrep Solid supported lipid bilayers: From biophysical studies to sensor design Edward T. Castellana, Paul S. Cremer Department of Chemistry,
Surface Science Reports 61 (2006) 429 444 www.elsevier.com/locate/surfrep Solid supported lipid bilayers: From biophysical studies to sensor design Edward T. Castellana, Paul S. Cremer Department of Chemistry,
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Biomimetic membrane systems on graphene based sensordevices for biomedical diagnoses application
 Biomimetic membrane systems on graphene based sensordevices for biomedical diagnoses application Supervisors: Christoph Nowak (NTU/AIT), Erik Reimhult (BOKU), Bo Liedberg (NTU) and Wolfgang Knoll (AIT)
Biomimetic membrane systems on graphene based sensordevices for biomedical diagnoses application Supervisors: Christoph Nowak (NTU/AIT), Erik Reimhult (BOKU), Bo Liedberg (NTU) and Wolfgang Knoll (AIT)
CHARACTERIZATION OF THE ADHESION OF CALCIUM OXALATE MONOHYDRATE CRYSTALS ON PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANES BY ELLIPSOMETRY
 CHARACTERIZATION OF THE ADHESION OF CALCIUM OXALATE MONOHYDRATE CRYSTALS ON PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANES BY ELLIPSOMETRY By ANNE-SOPHIE WIDEDE BOURIDAH A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY
CHARACTERIZATION OF THE ADHESION OF CALCIUM OXALATE MONOHYDRATE CRYSTALS ON PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANES BY ELLIPSOMETRY By ANNE-SOPHIE WIDEDE BOURIDAH A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY
Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology
 Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology Instability of Lipid Membrane Benxin Jing a, Marie Hutin c, Erin Connor a, Leroy Cronin c,* and Yingxi Zhu a,b,* a Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology Instability of Lipid Membrane Benxin Jing a, Marie Hutin c, Erin Connor a, Leroy Cronin c,* and Yingxi Zhu a,b,* a Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
Xianren Zhang ( 张现仁 )
 The interaction between nanoparticles and membranes: from cytotoxicity to drug delivery Xianren Zhang ( 张现仁 ) zhangxr@mail.buct.edu.cn State Key Laboratory of Organic-Inorganic Composites, Beijing University
The interaction between nanoparticles and membranes: from cytotoxicity to drug delivery Xianren Zhang ( 张现仁 ) zhangxr@mail.buct.edu.cn State Key Laboratory of Organic-Inorganic Composites, Beijing University
Supported Lipid Bilayers with Phosphatidylethanolamine as the Major Component
 Supporting Information for: Supported Lipid Bilayers with Phosphatidylethanolamine as the Major Component Anne M. Sendecki 1, Matthew F. Poyton 1, Alexis J. Baxter 1, Tinglu Yang, 1 Paul S. Cremer 1,2
Supporting Information for: Supported Lipid Bilayers with Phosphatidylethanolamine as the Major Component Anne M. Sendecki 1, Matthew F. Poyton 1, Alexis J. Baxter 1, Tinglu Yang, 1 Paul S. Cremer 1,2
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes. Reading Assignments. Selective and Semi-permeable Barriers
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lipid surface concentration estimation, conversion of fluorescence
 Lipid surface concentration estimation, conversion of fluorescence intensity, and data analysis In order to be able to fit the catalysis data with the kinetic model we proposed, the fluorescence intensity
Lipid surface concentration estimation, conversion of fluorescence intensity, and data analysis In order to be able to fit the catalysis data with the kinetic model we proposed, the fluorescence intensity
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/6/e1700338/dc1 Supplementary Materials for HIV virions sense plasma membrane heterogeneity for cell entry Sung-Tae Yang, Alex J. B. Kreutzberger, Volker Kiessling,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/6/e1700338/dc1 Supplementary Materials for HIV virions sense plasma membrane heterogeneity for cell entry Sung-Tae Yang, Alex J. B. Kreutzberger, Volker Kiessling,
AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes Michael J. Higgins
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes Michael J. Higgins
Carbohydrates. And Lipids. - Polymers. -Carbohydrates monomers and polymers. - Lipids. Principles of Building Polymers: MODULAR DESIGN
 Lecture 5 Sept 9, 2005 MARMLEULES #1 arbohydrates Lecture outline: - Polymers -arbohydrates monomers and polymers And Lipids - Lipids Principles of Building Polymers: - biological polymers are built from
Lecture 5 Sept 9, 2005 MARMLEULES #1 arbohydrates Lecture outline: - Polymers -arbohydrates monomers and polymers And Lipids - Lipids Principles of Building Polymers: - biological polymers are built from
LOCALISATION, IDENTIFICATION AND SEPARATION OF MOLECULES. Gilles Frache Materials Characterization Day October 14 th 2016
 LOCALISATION, IDENTIFICATION AND SEPARATION OF MOLECULES Gilles Frache Materials Characterization Day October 14 th 2016 1 MOLECULAR ANALYSES Which focus? LOCALIZATION of molecules by Mass Spectrometry
LOCALISATION, IDENTIFICATION AND SEPARATION OF MOLECULES Gilles Frache Materials Characterization Day October 14 th 2016 1 MOLECULAR ANALYSES Which focus? LOCALIZATION of molecules by Mass Spectrometry
THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHREYER HONORS COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
 THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHREYER HONORS COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING CHOLERA TOXIN BINDING STUDIES ON ALUMINUM OXIDE COATED SUBSTRATES FOR BIO-SENSING APPLICATIONS MARIA POLUCH
THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHREYER HONORS COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING CHOLERA TOXIN BINDING STUDIES ON ALUMINUM OXIDE COATED SUBSTRATES FOR BIO-SENSING APPLICATIONS MARIA POLUCH
Supporting Information. Magnetic Field and Chirality Effects on Electrochemical Charge Transfer Rates: Spin. Dependent Electrochemistry
 Supporting Information Magnetic Field and Chirality Effects on Electrochemical Charge Transfer Rates: Spin Dependent Electrochemistry Prakash Chandra Mondal, 1 Claudio Fontanesi, 1,2 David H. Waldeck,
Supporting Information Magnetic Field and Chirality Effects on Electrochemical Charge Transfer Rates: Spin Dependent Electrochemistry Prakash Chandra Mondal, 1 Claudio Fontanesi, 1,2 David H. Waldeck,
Calcium-dependent Hydrolysis of Supported Planar Lipids Were Triggered by honey bee venom Phospholipase A 2 with Right Orientation at Interface
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Calcium-dependent Hydrolysis of Supported Planar Lipids Were Triggered by honey
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Calcium-dependent Hydrolysis of Supported Planar Lipids Were Triggered by honey
Chemistry 1506: Allied Health Chemistry 2. Section 8: Lipids. Biochemical Esters and Hydrocarbons. Outline
 hemistry 1506 Dr. unter s lass Section 8 Notes - Page 1/21 hemistry 1506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 Section 8: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons utline SETIN 8.1 INTRDUTIN...2 SETIN SETIN SETIN 8.2
hemistry 1506 Dr. unter s lass Section 8 Notes - Page 1/21 hemistry 1506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 Section 8: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons utline SETIN 8.1 INTRDUTIN...2 SETIN SETIN SETIN 8.2
Single Giant Vesicle Rupture Events Reveal Multiple Mechanisms of Glass-Supported Bilayer Formation
 1988 Biophysical Journal Volume 92 March 2007 1988 1999 Single Giant Vesicle Rupture Events Reveal Multiple Mechanisms of Glass-Supported Bilayer Formation Chiho Hamai,* Paul S. Cremer, y and Siegfried
1988 Biophysical Journal Volume 92 March 2007 1988 1999 Single Giant Vesicle Rupture Events Reveal Multiple Mechanisms of Glass-Supported Bilayer Formation Chiho Hamai,* Paul S. Cremer, y and Siegfried
MARTINI Coarse-Grained Model of Triton TX-100 in Pure DPPC. Monolayer and Bilayer Interfaces. Supporting Information
 MARTINI Coarse-Grained Model of Triton TX-100 in Pure DPPC Monolayer and Bilayer Interfaces. Antonio Pizzirusso a, Antonio De Nicola* a, Giuseppe Milano a a Dipartimento di Chimica e Biologia, Università
MARTINI Coarse-Grained Model of Triton TX-100 in Pure DPPC Monolayer and Bilayer Interfaces. Antonio Pizzirusso a, Antonio De Nicola* a, Giuseppe Milano a a Dipartimento di Chimica e Biologia, Università
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Biological membranes are composed of lipid bilayers
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Biological membranes are composed of lipid bilayers
2R v. R v. R l c. Reminder: self assembly. Packing parameter (shape factor): v/a 0. spherical micelles : v/a 0 <1/3 <1/2
 Reminder: self assembly a 0 Packing parameter (shape factor): v/a 0 l c spherical micelles : v/a 0 l c
Reminder: self assembly a 0 Packing parameter (shape factor): v/a 0 l c spherical micelles : v/a 0 l c
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
A. Membrane Composition and Structure. B. Animal Cell Adhesion. C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport. D. Active Transport
 Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Chemistry 506: Allied Health Chemistry 2. Chapter 17: Lipids. Biochemical Esters and Hydrocarbons
 hemistry 506 Dr. unter s lass hapter 17. hemistry 506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 1 hapter 17: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons Introduction to General, rganic & Biochemistry, 5 th Edition by Bettelheim
hemistry 506 Dr. unter s lass hapter 17. hemistry 506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 1 hapter 17: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons Introduction to General, rganic & Biochemistry, 5 th Edition by Bettelheim
Surfactants. The Basic Theory. Surfactants (or surface active agents ): are organic compounds with at least one lyophilic. Paints and Adhesives
 Surfactants Surfactants (or surface active agents ): are organic compounds with at least one lyophilic ( solvent-loving ) group and one lyophobic ( solvent-fearing ) group in the molecule. In the simplest
Surfactants Surfactants (or surface active agents ): are organic compounds with at least one lyophilic ( solvent-loving ) group and one lyophobic ( solvent-fearing ) group in the molecule. In the simplest
SAXS on lipid structures
 Practical Course in Biophysics, Experiment R2b SAXS on lipid structures Summer term 2015 Room: Advisor: X-ray lab at LS Rädler, NU111 Stefan Fischer Tel: +49-(0)89-2180-1459 Email: stefan.f.fischer@physik.lmu.de
Practical Course in Biophysics, Experiment R2b SAXS on lipid structures Summer term 2015 Room: Advisor: X-ray lab at LS Rädler, NU111 Stefan Fischer Tel: +49-(0)89-2180-1459 Email: stefan.f.fischer@physik.lmu.de
The electrical properties of ZnO MSM Photodetector with Pt Contact Electrodes on PPC Plastic
 Journal of Electron Devices, Vol. 7, 21, pp. 225-229 JED [ISSN: 1682-3427 ] Journal of Electron Devices www.jeldev.org The electrical properties of ZnO MSM Photodetector with Pt Contact Electrodes on PPC
Journal of Electron Devices, Vol. 7, 21, pp. 225-229 JED [ISSN: 1682-3427 ] Journal of Electron Devices www.jeldev.org The electrical properties of ZnO MSM Photodetector with Pt Contact Electrodes on PPC
Pressure Modulation of the Enzymatic Activity of. Phospholipase A2, a Putative Membraneassociated
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Pressure Modulation of the Enzymatic Activity of Phospholipase A2, a Putative Membraneassociated Pressure Sensor Saba Suladze, Suleyman Cinar, Benjamin Sperlich, and Roland Winter*
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Pressure Modulation of the Enzymatic Activity of Phospholipase A2, a Putative Membraneassociated Pressure Sensor Saba Suladze, Suleyman Cinar, Benjamin Sperlich, and Roland Winter*
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes. Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment.
 Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
Supplementary Information Membrane tension increases fusion efficiency of model membranes in the presence of SNAREs
 Supplementary Information Membrane tension increases fusion efficiency of model membranes in the presence of SNAREs Torben-Tobias Kliesch, Jörn Dietz, Laura Turco, Partho Halder, Elena Alexandra Polo,
Supplementary Information Membrane tension increases fusion efficiency of model membranes in the presence of SNAREs Torben-Tobias Kliesch, Jörn Dietz, Laura Turco, Partho Halder, Elena Alexandra Polo,
Microtubule Teardrop Patterns
 Supporting Information Microtubule Teardrop Patterns Kosuke Okeyoshi 1, Ryuzo Kawamura 1, Ryo Yoshida 2, and Yoshihito Osada 1 * 1 RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198,
Supporting Information Microtubule Teardrop Patterns Kosuke Okeyoshi 1, Ryuzo Kawamura 1, Ryo Yoshida 2, and Yoshihito Osada 1 * 1 RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198,
Fluid Mozaic Model of Membranes
 Replacement for the 1935 Davson Danielli model Provided explanation for Gortner-Grendel lack of lipid and permitted the unit membrane model. Trans membrane protein by labelling Fry & Edidin showed that
Replacement for the 1935 Davson Danielli model Provided explanation for Gortner-Grendel lack of lipid and permitted the unit membrane model. Trans membrane protein by labelling Fry & Edidin showed that
Second harmonic spectroscopy: detection and orientation of molecules at a biomembrane interface
 24 March 2000 Chemical Physics Letters 319 2000 435 439 www.elsevier.nlrlocatercplett Second harmonic spectroscopy: detection and orientation of molecules at a biomembrane interface J.S. Salafsky, K.B.
24 March 2000 Chemical Physics Letters 319 2000 435 439 www.elsevier.nlrlocatercplett Second harmonic spectroscopy: detection and orientation of molecules at a biomembrane interface J.S. Salafsky, K.B.
Endocytosis of Nanoparticles
 Endocytosis of Nanoparticles Reinhard Lipowsky Theory & Bio-Systems, MPI-CI, Potsdam Motivation: Cellular Uptake of NPs Dissecting Endocytosis into Adhesion + Engulfment + Fission Quantitative Relationships
Endocytosis of Nanoparticles Reinhard Lipowsky Theory & Bio-Systems, MPI-CI, Potsdam Motivation: Cellular Uptake of NPs Dissecting Endocytosis into Adhesion + Engulfment + Fission Quantitative Relationships
Molecular modeling of the pathways of vesicle membrane interaction. Tongtao Yue and Xianren Zhang
 Molecular modeling of the pathways of vesicle membrane interaction Tongtao Yue and Xianren Zhang I. ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI): METHODS Dissipative particle dynamics method The dissipative
Molecular modeling of the pathways of vesicle membrane interaction Tongtao Yue and Xianren Zhang I. ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI): METHODS Dissipative particle dynamics method The dissipative
Chapter 12: Membranes. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 12: Membranes Voet & Voet: Pages 390-415 Slide 1 Membranes Essential components of all living cells (define boundry of cells) exclude toxic ions and compounds; accumulation of nutrients energy
Chapter 12: Membranes Voet & Voet: Pages 390-415 Slide 1 Membranes Essential components of all living cells (define boundry of cells) exclude toxic ions and compounds; accumulation of nutrients energy
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Fabrication processes of bud-mimicking PDMS patterns based on a combination of colloidal, soft, and photo-lithography a-d, The polystyrene (PS) particles
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Fabrication processes of bud-mimicking PDMS patterns based on a combination of colloidal, soft, and photo-lithography a-d, The polystyrene (PS) particles
Membrane structure correlates to function of LLP2 on the cytoplasmic tail of HIV-1 gp41 protein
 Membrane structure correlates to function of LLP2 on the cytoplasmic tail of HIV-1 gp41 protein Alexander L. Boscia 1, Kiyotaka Akabori 1, Zachary Benamram 1, Jonathan A. Michel 1, Michael S. Jablin 1,
Membrane structure correlates to function of LLP2 on the cytoplasmic tail of HIV-1 gp41 protein Alexander L. Boscia 1, Kiyotaka Akabori 1, Zachary Benamram 1, Jonathan A. Michel 1, Michael S. Jablin 1,
Supporting Information. Photopolymerization of dienoyl lipids creates planar supported poly(lipid) membranes with retained fluidity
 Supporting Information Photopolymerization of dienoyl lipids creates planar supported poly(lipid) membranes with retained fluidity Kristina S. Orosz, 1 Ian W. Jones, 1 John P. Keogh, 1 Christopher M. Smith,
Supporting Information Photopolymerization of dienoyl lipids creates planar supported poly(lipid) membranes with retained fluidity Kristina S. Orosz, 1 Ian W. Jones, 1 John P. Keogh, 1 Christopher M. Smith,
List of Figure. Figure 1.1. Selective pathways for the metabolism of arachidonic acid
 List of Figure Figure 1.1. Selective pathways for the metabolism of arachidonic acid Figure 1.2. Arachidonic acid transformation to ω and ω-1 hydroxylase 14 19 reaction mediated by cytochrome P450 enzyme
List of Figure Figure 1.1. Selective pathways for the metabolism of arachidonic acid Figure 1.2. Arachidonic acid transformation to ω and ω-1 hydroxylase 14 19 reaction mediated by cytochrome P450 enzyme
Light and X-ray triggered liposomal gene/drug delivery system for cancer therapy
 Light and X-ray triggered liposomal gene/drug delivery system for cancer therapy Wei Deng, 1 Wenjie Chen, 2 Sandhya Clement, 1 Anna Guller, 1 Alexander Engel, 3 Ewa Goldys 1 1 The Graduate School of Biomedical
Light and X-ray triggered liposomal gene/drug delivery system for cancer therapy Wei Deng, 1 Wenjie Chen, 2 Sandhya Clement, 1 Anna Guller, 1 Alexander Engel, 3 Ewa Goldys 1 1 The Graduate School of Biomedical
Constructing supported lipid bilayers from native cell membranes
 Tommy Dam LTH Master of Science in Engineering, Engineering Nanoscience Constructing supported lipid bilayers from native cell membranes Supervisor Peter Jönsson Division of Physical Chemistry, Lund University
Tommy Dam LTH Master of Science in Engineering, Engineering Nanoscience Constructing supported lipid bilayers from native cell membranes Supervisor Peter Jönsson Division of Physical Chemistry, Lund University
Coarse grained simulations of Lipid Bilayer Membranes
 Coarse grained simulations of Lipid Bilayer Membranes P. B. Sunil Kumar Department of Physics IIT Madras, Chennai 600036 sunil@iitm.ac.in Atomistic MD: time scales ~ 10 ns length scales ~100 nm 2 To study
Coarse grained simulations of Lipid Bilayer Membranes P. B. Sunil Kumar Department of Physics IIT Madras, Chennai 600036 sunil@iitm.ac.in Atomistic MD: time scales ~ 10 ns length scales ~100 nm 2 To study
Patterning Adjacent Supported Lipid Bilayers of Desired Composition To Investigate Receptor-Ligand Binding under Shear Flow
 10252 Langmuir 2004, 20, 10252-10259 Patterning Adjacent Supported Lipid Bilayers of Desired Composition To Investigate Receptor-Ligand Binding under Shear Flow Kelley A. Burridge,, Michael A. Figa, and
10252 Langmuir 2004, 20, 10252-10259 Patterning Adjacent Supported Lipid Bilayers of Desired Composition To Investigate Receptor-Ligand Binding under Shear Flow Kelley A. Burridge,, Michael A. Figa, and
This week s topic will be: Evidence for the Fluid Mosaic Model. Developing theories, testing hypotheses and techniques for visualizing cells
 Tutorials, while not mandatory, will allow you to improve your final grade in this course. Thank you for your attendance to date. These notes are not a substitute for the discussions that we will have
Tutorials, while not mandatory, will allow you to improve your final grade in this course. Thank you for your attendance to date. These notes are not a substitute for the discussions that we will have
Supplemental Data Figure S1 Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells.
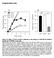 Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane is selectively permeable, (allowing some substances to cross more easily than others) PM is flexible bends and changes shape
CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane is selectively permeable, (allowing some substances to cross more easily than others) PM is flexible bends and changes shape
Shape Transformations of Lipid Bilayers Following Rapid Cholesterol
 Biophysical Journal, Volume 111 Supplemental Information Shape Transformations of Lipid Bilayers Following Rapid Cholesterol Uptake Mohammad Rahimi, David Regan, Marino Arroyo, Anand Bala Subramaniam,
Biophysical Journal, Volume 111 Supplemental Information Shape Transformations of Lipid Bilayers Following Rapid Cholesterol Uptake Mohammad Rahimi, David Regan, Marino Arroyo, Anand Bala Subramaniam,
Emulsification. An Introduction to the Emulsification of Lipids within a Watery Environment. By Noel Ways
 Emulsification An Introduction to the Emulsification of Lipids within a Watery Environment By Noel Ways To begin the process of understanding emulsification, let's start with water. First, we note that
Emulsification An Introduction to the Emulsification of Lipids within a Watery Environment By Noel Ways To begin the process of understanding emulsification, let's start with water. First, we note that
Supplementary Figure 1. Overview of steps in the construction of photosynthetic protocellular systems
 Supplementary Figure 1 Overview of steps in the construction of photosynthetic protocellular systems (a) The small unilamellar vesicles were made with phospholipids. (b) Three types of small proteoliposomes
Supplementary Figure 1 Overview of steps in the construction of photosynthetic protocellular systems (a) The small unilamellar vesicles were made with phospholipids. (b) Three types of small proteoliposomes
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION selective permeability permits some substances to cross it more easily than others Figure 7.1 Scientists studying the plasma Reasoned that it must be a phospholipid bilayer
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION selective permeability permits some substances to cross it more easily than others Figure 7.1 Scientists studying the plasma Reasoned that it must be a phospholipid bilayer
Cellular Transport Notes
 Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information An efficient broadband and omnidirectional light-harvesting scheme employing the hierarchical structure based on ZnO nanorod/si 3 N 4 -coated Si microgroove on 5-inch single crystalline
Supporting Information An efficient broadband and omnidirectional light-harvesting scheme employing the hierarchical structure based on ZnO nanorod/si 3 N 4 -coated Si microgroove on 5-inch single crystalline
Name Class Date. cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell. MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory.
 Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
Chapter 7: Membranes
 Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Kinetic Pathway of Antimicrobial Peptide Magainin 2-Induced Pore Formation in Lipid Membranes
 ISSP International Workshop on Soft Matter Physics: Biomembranes and Vesicles on 24 Aug. 2010, at IPMU Lecture Hall Kinetic Pathway of Antimicrobial Peptide Magainin 2-Induced Pore Formation in Lipid Membranes
ISSP International Workshop on Soft Matter Physics: Biomembranes and Vesicles on 24 Aug. 2010, at IPMU Lecture Hall Kinetic Pathway of Antimicrobial Peptide Magainin 2-Induced Pore Formation in Lipid Membranes
COR 011 Lecture 9: ell membrane structure ept 19, 2005
 COR 011 Lecture 9: ell membrane structure ept 19, 2005 Cell membranes 1. What are the functions of cell membranes? 2. What is the current model of membrane structure? 3. Evidence supporting the fluid mosaic
COR 011 Lecture 9: ell membrane structure ept 19, 2005 Cell membranes 1. What are the functions of cell membranes? 2. What is the current model of membrane structure? 3. Evidence supporting the fluid mosaic
Femtosecond Laser Applications in NiTi
 Femtosecond Laser Applications in NiTi Professor Luísa Coutinho IST-UTL Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade Técnica de Lisboa, Portugal Objectives Analyze beam/material interaction of femtosecond
Femtosecond Laser Applications in NiTi Professor Luísa Coutinho IST-UTL Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade Técnica de Lisboa, Portugal Objectives Analyze beam/material interaction of femtosecond
Effect of Unsaturated Acyl Chains on Structural Transformations in Triacylglycerols. Oleksandr Mykhaylyk. Chris Martin
 Effect of Unsaturated Acyl hains on Structural Transformations in Triacylglycerols leksandr Mykhaylyk Department of hemistry, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, S3 7HF, UK hris Martin STF Daresbury Laboratory,
Effect of Unsaturated Acyl hains on Structural Transformations in Triacylglycerols leksandr Mykhaylyk Department of hemistry, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, S3 7HF, UK hris Martin STF Daresbury Laboratory,
Spectrum on skin Jonathan Hadgraft & Majella Lane
 Spectrum on skin Jonathan Hadgraft & Majella Lane The School of Pharmacy, University of London radiofrequency microwave far infra red uv x rays γ rays log ν / Hz 5 6 7 8 9 10 111213141516171819 20 λ 3km
Spectrum on skin Jonathan Hadgraft & Majella Lane The School of Pharmacy, University of London radiofrequency microwave far infra red uv x rays γ rays log ν / Hz 5 6 7 8 9 10 111213141516171819 20 λ 3km
Physical effects underlying the transition from primitive to modern cell membranes
 Physical effects underlying the transition from primitive to modern cell membranes Itay Budin and Jack W. Szostak* *To whom correspondence should be addressed. Email: szostak@molbio.mgh.harvard.edu This
Physical effects underlying the transition from primitive to modern cell membranes Itay Budin and Jack W. Szostak* *To whom correspondence should be addressed. Email: szostak@molbio.mgh.harvard.edu This
Raman spectroscopy methods for detecting and imaging supported lipid bilayers
 Spectroscopy 24 (2010) 113 117 113 DOI 10.3233/SPE-2010-0426 IOS Press Raman spectroscopy methods for detecting and imaging supported lipid bilayers Claire S. Sweetenham and Ioan Notingher Nanoscience
Spectroscopy 24 (2010) 113 117 113 DOI 10.3233/SPE-2010-0426 IOS Press Raman spectroscopy methods for detecting and imaging supported lipid bilayers Claire S. Sweetenham and Ioan Notingher Nanoscience
CWDHS Mr. Winch Grade 12 Biology
 The Cell Membrane Overview Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
The Cell Membrane Overview Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
MIMICKING ANHYDROBIOSIS ON SOLID SUPPORTED LIPID BILAYERS. A Thesis VANESSA ALYSS CHAPA
 MIMICKING ANYDRBISIS N SLID SUPPRTED LIPID BILAYERS A Thesis by VANESSA ALYSS CAPA Submitted to the ffice of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
MIMICKING ANYDRBISIS N SLID SUPPRTED LIPID BILAYERS A Thesis by VANESSA ALYSS CAPA Submitted to the ffice of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY Physical and Mathematical Sciences 2018, 52(3), p. 217 221 P h y s i c s STUDY OF THE SWELLING OF THE PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER, DEPENDING ON THE ANGLE BETWEEN THE
PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY Physical and Mathematical Sciences 2018, 52(3), p. 217 221 P h y s i c s STUDY OF THE SWELLING OF THE PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER, DEPENDING ON THE ANGLE BETWEEN THE
Microfluidic Approaches for Membrane Protein Crystallization
 Microfluidic Approaches for Membrane Protein Crystallization Sarah L. Perry, Griffin W. Roberts, Sameer Talreja, Joshua D. Tice, Robert B. Gennis, Charles F. Zukoski, and Paul J.A. Kenis Background and
Microfluidic Approaches for Membrane Protein Crystallization Sarah L. Perry, Griffin W. Roberts, Sameer Talreja, Joshua D. Tice, Robert B. Gennis, Charles F. Zukoski, and Paul J.A. Kenis Background and
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Lectures 16-17: Biological Membranes: Life in Two Dimensions
 Lectures 16-17: Biological Membranes: Life in Two Dimensions Lecturer: Brigita Urbanc Office: 1-909 (E-mail: brigita@drexel.edu) Course website: www.physics.drexel.edu/~brigita/courses/biophys_011-01/
Lectures 16-17: Biological Membranes: Life in Two Dimensions Lecturer: Brigita Urbanc Office: 1-909 (E-mail: brigita@drexel.edu) Course website: www.physics.drexel.edu/~brigita/courses/biophys_011-01/
Fusion (%) = 100 (B-A)/(C-A)
 6 Fusion (%) = 1 (B-A)/(C-A) fluorescence, a.u. x 1 C 1 B A 6 1 A Supplementary Figure 1. Fusion of lipid vesicles studied with cobalt-calcein liquid content transfer assay. An example of fusion % calibration
6 Fusion (%) = 1 (B-A)/(C-A) fluorescence, a.u. x 1 C 1 B A 6 1 A Supplementary Figure 1. Fusion of lipid vesicles studied with cobalt-calcein liquid content transfer assay. An example of fusion % calibration
Spatially Selective Manipulation of Supported Lipid Bilayers by Laminar Flow: Steps Toward Biomembrane Microfluidics
 1624 Langmuir 2003, 19, 1624-1631 Spatially Selective Manipulation of Supported Lipid Bilayers by Laminar Flow: Steps Toward Biomembrane Microfluidics Lance Kam and Steven G. Boxer* Department of Chemistry,
1624 Langmuir 2003, 19, 1624-1631 Spatially Selective Manipulation of Supported Lipid Bilayers by Laminar Flow: Steps Toward Biomembrane Microfluidics Lance Kam and Steven G. Boxer* Department of Chemistry,
Rate Dependent Rupture of Solid-Supported Phospholipid Bilayers. Sarah S Ng
 Rate Dependent Rupture of Solid-Supported Phospholipid Bilayers by Sarah S Ng Submitted to the Department of Materials Science and Engineering in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
Rate Dependent Rupture of Solid-Supported Phospholipid Bilayers by Sarah S Ng Submitted to the Department of Materials Science and Engineering in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
Phospholipids. Extracellular fluid. Polar hydrophilic heads. Nonpolar hydrophobic tails. Polar hydrophilic heads. Intracellular fluid (cytosol)
 Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
ก Chirality Control on Lipid Nanotubule Morphology Investigated by Circular Dichroism 1, 1, 2, 2,,
 ก Chirality Control on Lipid Nanotubule Morphology Investigated by Circular Dichroism 1, 1, 2, 2,, ก 3, 1 Yuwathida Jantippana 1, Weerawat Intaratat 1, Wisit Singhsomroje 2, Sujint Wangsuya 2, Piboon Pantu
ก Chirality Control on Lipid Nanotubule Morphology Investigated by Circular Dichroism 1, 1, 2, 2,, ก 3, 1 Yuwathida Jantippana 1, Weerawat Intaratat 1, Wisit Singhsomroje 2, Sujint Wangsuya 2, Piboon Pantu
Supplementary information for Effects of Stretching Speed on. Mechanical Rupture of Phospholipid/Cholesterol Bilayers: Molecular
 Supplementary information for Effects of Stretching Speed on Mechanical Rupture of Phospholipid/Cholesterol Bilayers: Molecular Dynamics Simulation Taiki Shigematsu, Kenichiro Koshiyama*, and Shigeo Wada
Supplementary information for Effects of Stretching Speed on Mechanical Rupture of Phospholipid/Cholesterol Bilayers: Molecular Dynamics Simulation Taiki Shigematsu, Kenichiro Koshiyama*, and Shigeo Wada
Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry)
 051117 Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry) (Figures from Heimenz Colloid Sci.) 1) Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules (molecules having one end hydrophobic and the other hydrophilic) and are
051117 Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry) (Figures from Heimenz Colloid Sci.) 1) Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules (molecules having one end hydrophobic and the other hydrophilic) and are
Supporting Information. Maximizing the Supported Bilayer Phenomenon: LCP Liposomes Comprised Exclusively
 S-1 Supporting Information Maximizing the Supported Bilayer Phenomenon: LCP Liposomes Comprised Exclusively of PEGylated Phospholipids for Enhanced Systemic and Lymphatic Delivery Matthew T. Haynes and
S-1 Supporting Information Maximizing the Supported Bilayer Phenomenon: LCP Liposomes Comprised Exclusively of PEGylated Phospholipids for Enhanced Systemic and Lymphatic Delivery Matthew T. Haynes and
Structural, Optical & Surface Morphology of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanorods in Molten Solution
 Journal of Materials Science and Engineering B 6 (3-4) (2016) 68-73 doi: 10.17265/2161-6221/2016.3-4.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Structural, Optical & Surface Morphology of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanorods in Molten
Journal of Materials Science and Engineering B 6 (3-4) (2016) 68-73 doi: 10.17265/2161-6221/2016.3-4.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Structural, Optical & Surface Morphology of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanorods in Molten
1.4 Page 1 Cell Membranes S. Preston 1
 AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport Page 1 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport from your syllabus l. Cell Membrane Structure 1. Read and
AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport Page 1 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport from your syllabus l. Cell Membrane Structure 1. Read and
Topic 7b: Biological Membranes
 Topic 7b: Biological Membranes Overview: Why does life need a compartment? Nature of the packaging what is it made of? properties? New types of deformations in 2D Applications: Stretching membranes, forming
Topic 7b: Biological Membranes Overview: Why does life need a compartment? Nature of the packaging what is it made of? properties? New types of deformations in 2D Applications: Stretching membranes, forming
Polarization and Circular Dichroism (Notes 17)
 Polarization and Circular Dichroism - 2014 (Notes 17) Since is vector, if fix molec. orient., E-field interact (absorb) with molecule differently when change E-orientation (polarization) Transitions can
Polarization and Circular Dichroism - 2014 (Notes 17) Since is vector, if fix molec. orient., E-field interact (absorb) with molecule differently when change E-orientation (polarization) Transitions can
Simulation of Membrane and Cell Culture Permeability and Transport. Michael B. Bolger and Viera Lukacova Simulations Plus, Inc.
 Simulation of Membrane and Cell Culture Permeability and Transport Michael B. Bolger and Viera Lukacova Simulations Plus, Inc. utline Models of microscopic membrane kinetics Calculation of membrane entry
Simulation of Membrane and Cell Culture Permeability and Transport Michael B. Bolger and Viera Lukacova Simulations Plus, Inc. utline Models of microscopic membrane kinetics Calculation of membrane entry
