Tel. +49(0) # Fax +49(0) # Katalog mit den Produkten der Firma Larodan, die wir vertreten.
|
|
|
- Matthew Shepherd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Katalog mit den Produkten der Firma Larodan, die wir vertreten. Inhalt Alphabetischer Index Seitennummer Acyl-L-Carnitines Native 50 Deuterium Labelled 52 Bile Acids & Methyl Esters 152 Cholesterol & Esters 108 Coenzyme A & Fatty Acid CoA Esters 54 Conjugated Linoleic Acids (CLA) Analytical Standards 20 FFA/ Esters/ Triglycerides in bulk 29 Dicarboxylic Acids & Dimethyl Esters 116 Dolichols & Phosphates 148 Eicosanoids 48 Fatty Acids & Methyl Esters straight chain Saturated & Unsaturated 4 EPA & DHA Esters in bulk 28 Fatty Acids - Unusual / Methyl Esters Conjugated Polyene 20 Odd-Numbered Polyunsaturated 22 Other Unusual 24 Fatty Acids & Methyl Esters methyl branched/ cyclopropyl Phytanic & Pristanic Native and Deuterium labelled 56 Iso & Anteiso methyl Branched 62 Cyclopropyl 63 Fatty Acids & Methyl Esters Oxygenated/ Oxylipin related Hydroxy 44 Dihydroxy 46 Epoxy 36 Oxo 46 Fatty Acids & Methyl Esters Hydroxy (synthetic) Hydroxy 64 3-Hydroxy 66 Omega-Hydroxy 69 Other Microbiological 70 1/202
2 Fatty Acids Deuterium labelled Perdeuterated 95 α-deuterated 97 ω-deuterated 98 Polyunsaturated 99 Miscellaneous 101 Fatty Acids 13C labelled 102 Fatty Alcohols 105 Gangliosides & Derivatives 142 Glycerides Monoglycerides - Saturated/ Unsaturated 71 Diglycerides Single/ Mixed Fatty Acids 76 Triglycerides - Single/ Mixed Fatty Acids 84 Triglycerides 13C-Labelled 103 Hydrocarbons Aliphatic 153 Isoprenoid 157 Kits Fatty Acids/ Methyl Esters 157 Glycerides 164 Aliphatic Hydrocarbons 163 Phosphoglycerides 165 Phospholipids 164 Plant Sterols 164 Larodan Reference Mixtures Glycoshingolipid Mixtures 165 FAME Mixtures 166 Oil Mixtures 181 Methyl Branched FAME Mixtures 177 Glyceride Mixtures 182 Mixed Lipid Mixtures 184 Polar Lipids Mixture 188 Polyprenol Mixtures 186 Free Fatty Acid Mixtures 179 n-paraffin Mixture 188 Fish Oil FAME Mixture 189 Metabolic Research Products Long Chain Fatty Acids Deuteriumlabelled 101 2/202
3 Acylglycines/ Miscellaneous 13C/ Deuteriumlabelled 103 Oligoprenyl Phosphates Oxylipines 31 Hydroperoxides 32 Hydroxides 33 Ketones 36 Epoxides 37 Diols 38 Allene-Oxide-Synthase- -derived 38 Divinyl-Ether-Synthase- -derived 39 Epoxy Alcohol Synthase / Peroxygenase-derived 41 Lyase-derived 44 Others 45 D-myo-Phosphatidylinositol Phosphates Phospholipids 120 Natural PC, PE, PI, PA, PG, CL, PS, LPC, LPE, LPI, LPG 120 Semisynthetic GPC, PC, PE, PA, PG, PS, LPC, LPG 125 Deuterium Labelled 100 Di-O-Alkyl 131 Plant Leaf Lipids 145 Plant Sterols & Steryl Glucosides 145 Plasmalogens 124 Polyprenols & Monophosphates 146 Sialic Acid & Derivatives 143 Sphingolipids Sphingosines 132 Ceramides 134 Cerebrosides 137 Sphingomyelins 139 Fluorescent 140 Wax Esters C12-C Nomenclature Geometrical Isomers In this catalogue we use two systems to descibe the geometry of structures having carbon-carbon double bonds (geometric isomers). Cis/ trans denomination is used to indicate C=C configuration of common unsaturated fatty acids of natural origin, i.e. from vegetable and animal fats and oils. 3/202
4 A more distinct nomenclature, the Z/E-system, was introduced in the 1950 s by Cahn, Ingold and Prelog. For fatty acids and derivatives cis is equivalent to Z and trans to E, which is not always the case for other kinds of molecules. Fatty Acids & Derivatives Saturated n-fatty Acids (n-carboxylic) Bulk discounts are available on larger quantities. Other esters, such as ethyl esters can be offered on request. Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids occur, as triglycerides, mainly in plants and animals, such as in oil bearing seeds and fruits, tallow, lard and marine oils. In natural fats and oils, even numbered fatty acids are the predominant ones - odd numbered are rare. Larodan and CPS provide a growing range of high purity fatty acids and esters for research and analytical purposes. In this catalogue you will find new lines of fatty acids and metabolites under special headings. Im Katalog werden neben den Mengen die Bestellnummern angegeben Saturated n-fatty Acids Gesättigte n-fettsäuren Propionic Acid No. of C: 3:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Butyric Acid No. of C: 4:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Pentanoic Acid No. of C: 5:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g /202
5 10 g Hexanoic Acid (Caproic Acid) No. of C: 6:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Heptanoic Acid No. of C: 7:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Octanoic Acid (Caprylic Acid) No. of C: 8:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Nonanoic Acid (Pelargonic Acid) No. of C: 9:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Decanoic Acid (Capric Acid) No. of C: 10:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Undecanoic Acid No. of C: 11:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Dodecanoic Acid (Lauric Acid) No. of C: 12:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Tridecanoic Acid No. of C: 13:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 5/202
6 100 mg g g Tetradecanoic Acid (Myristic Acid) No. of C: 14:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Pentadecanoic Acid No. of C: 15:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Hexadecanoic Acid (Palmitic Acid) No. of C: 16:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Heptadecanoic Acid (Margaric Acid) No. of C: 17:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Octadecanoic Acid (Stearic Acid) No. of C: 18:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Nonadecanoic Acid No. of C: 19:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Eicosanoic Acid(Arachidic Acid) No. of C: 20:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g /202
7 Heneicosanoic Acid No. of C: 21:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg mg g Docosanoic Acid (Behenic Acid) No. of C: 22:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Tricosanoic Acid No. of C: 23:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg mg g Tetracosanoic Acid (Lignoceric Acid) No. of C: 24:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg mg g Pentacosanoic Acid No. of C: 25:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg mg Hexacosanoic Acid (Cerotic Acid) No. of C: 26:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg mg g Heptacosanoic Acid No. of C: 27:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 97+% 25 mg mg Octacosanoic Acid (Montanic Acid) No. of C: 28:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg mg Nonacosanoic Acid 7/202
8 No. of C: 29:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg mg Triacontanoic Acid(Melissic Acid) No. of C: 30:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 98+% 25 mg mg Hentriacontanoic Acid No. of C: 31:0 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% Saturated n-fatty Acid Methyl Esters Methyl Propionate No. of C: 3:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Butyrate No. of C: 4:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Pentanoate No. of C: 5:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Hexanoate No. of C: 6:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Heptanoate No. of C: 7:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g /202
9 5 g Methyl Octanoate No. of C: 8:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Nonanoate No. of C: 9:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Decanoate No. of C: 10:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Undecanoate No. of C: 11:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Dodecanoate No. of C: 12:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Tridecanoate No. of C: 13:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Tetradecanoate No. of C: 14:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Pentadecanoate No. of C: 15:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 9/202
10 100 mg g g Methyl Hexadecanoate No. of C: 16:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Heptadecanoate No. of C: 17:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Octadecanoate No. of C: 18:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Nonadecanoate No. of C: 19:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Eicosanoate No. of C: 20:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g Methyl Heneicosanoate No. of C: 21:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg mg g Methyl Docosanoate No. of C: 22:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg g g /202
11 Methyl Tricosanoate No. of C: 23:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg mg g Methyl Tetracosanoate No. of C: 24:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg mg g Methyl Pentacosanoate No. of C: 25:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg mg Methyl Hexacosanoate No. of C: 26:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg mg g Methyl Heptacosanoate No. of C: 27:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg mg Methyl Octacosanoate No. of C: 28:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg mg Methyl Nonacosanoate No. of C: 29:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg mg Methyl Triacontanoate No. of C: 30:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 98% 25 mg mg Methyl Hentriacontanoate No. of C: 31:0 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg /202
12 100 mg Unsaturated n-fatty Acids Ungesättigte Fettsäuren 10-Hydroxy-2tr-Decenoic Acid (Royal Jelly Acid) No. of C: 10:1 Mw: Documentation: Not included Purity: 98% 50 mg c-Undecenoic Acid No. of C: 11:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg c-Dodecenoic Acid No. of C: 12:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg c-Tridecenoic Acid No. of C: 13:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Myristoleic Acid (9c) No. of C: 14:1 Mw: 226. Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Myristelaidic Acid (9tr) No. of C: 14:1 Mw: 226. Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg c-Pentadecenoic Acid No. of C: 15:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg tr-Pentadecenoic Acid No. of C: 15:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg mg Palmitoleic Acid (9c) No. of C: 16:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg /202
13 5 x 100 mg Palmitelaidic Acid (9tr) No. of C: 16:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg tr-Hexadecenoic Acid No. of C: 16:1 Mw: Documentation: Not included Purity: 98% c-Heptadecenoic Acid No. of C: 17:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg tr-Heptadecenoic Acid No. of C: 17:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg x 25 mg Oleic Acid (9c) No. of C: 18:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 1 g g Elaidic Acid (9tr) No. of C: 18:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 1 g x 1 g Petroselinic Acid (6c) No. of C: 18:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Vaccenic Acid (11c) No. of C: 18:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Transvaccenic Acid (11tr) No. of C: 18:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Ricinoleic Acid (9c, 12OH) No. of C: 18:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 13/202
14 100 mg x 100 mg Ricinelaidic Acid (9tr, 12OH) No. of C: 18:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Linoleic Acid (9c, 12c) No. of C: 18:2 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 1 g g Linoelaidic Acid (9tr, 12tr)) No. of C: 18:2 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Linolenic Acid (9c, 12c, 15c) No. of C: 18:3 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Linolenic Acid (9c, 12c, 15c) No. of C: 18:3 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: min. 80% 1 kg Gamma Linolenic Acid (6c, 9c, 12c) No. of C: 18:3 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg c,9c,12c,15c-Octadecatetraenoic Acid (Stearidonic acid) No. of C: 18:4 Mw: mg c-Eicosenoic Acid No. of C: 20:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg tr-Eicosenoic Acid No. of C: 20:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg x 25 mg c,14c-Eicosadienoic Acid No. of C: 20:2 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 14/202
15 100 mg x 100 mg c,14c,17c-Eicosatrienoic Acid No. of C: 20:3 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Homogamma Linolenic Acid (8c,11c,14c) No. of C: 20:3 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg mg Arachidonic Acid (5c,8c,11c,14c) No. of C: 20:4 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg mg Omega3-Arachidonic Acid (8c,11c,14c,17c)) No. of C: 20:4 Mw: Documentation: CoA Purity: 98% 1 mg mg c,8c,11c,14c,17c-Eicosapentaenoic Acid No. of C: 20:5 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Erucic Acid (13c-Docosenoic Acid) No. of C: 22:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Brassidic Acid (13tr-Docosenoic Acid) No. of C: 22:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg c,16c-Docosadienoic Acid No. of C: 22:2 Mw: Documentation: Not included Purity: 99+% 25 mg x 25 mg c,16c,19c-Docosatrienoic Acid No. of C: 22:3 Mw: Documentation: Not included Purity: 99+% 25 mg x 25 mg /202
16 7c,10c,13c,16c-Docosatetraenoic Acid No. of C: 22:4 Mw: Documentation: Not included Purity: 99+% 25 mg x 25 mg c,7c,10c,13c,16c-Docosapentaenoic Acid No. of C: 22:5 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg c,10,13c,16c,19c-Docosapentaenoic Acid No. of C: 22:5 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg c,7c,10c,13c,16c,19c-Docosahexaenoic Acid No. of C: 22:6 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Nervonic Acid (15c) No. of C: 24:1 Mw: Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg c, 12c, 15c, 18c, 21c-Tetracosapentaenoic Acid No. of C: 24:5 Mw: mg c, 9c, 12c, 15c, 18c, 21c-Tetracosahexaenoic Acid No. of C: 24:6 Mw: mg Unsaturated n-fatty Acid Methyl Esters Methyl 10c-Undecenoate No. of C: 11:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl 11c-Dodecenoate No. of C: 12:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl 12c-Tridecenoate No. of C: 13:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 16/202
17 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Myristoleate (9c) No. of C: 14:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Myristelaidate (9tr) No. of C: 14:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg Methyl 10c-Pentadecenoate No. of C: 15:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg Methyl -10tr-Pentadecenoate No. of C: 15:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg mg Methyl Palmitoleate (9c) No. of C: 16:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Palmitelaidate (9tr) No. of C: 16:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl 10c-Heptadecenoate No. of C: 17:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl 10tr-Heptadecenoate No. of C: 17:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg x 25 mg Methyl Oleate (9c) No. of C: 18:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 1 g g /202
18 Methyl Elaidate (9tr) No. of C: 18:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 1 g x 1 g Methyl Petroselinoate (6c) No. of C: 18:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Vaccenate (11c) No. of C: 18:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Transvaccenate (11tr) No. of C: 18:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Ricinoleate ( 9c, 12OH) No. of C: 18:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Ricinelaidate ( 9tr, 12OH) No. of C: 18:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Linoleate (9c, 12c) No. of C: 18:2 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 1 g g Methyl Linoelaidate (9tr, 12tr) No. of C: 18:2 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Linolenate (9c, 12c, 15c) No. of C: 18:3 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Gamma Linolenate (6c, 9c, 12c) No. of C: 18:3 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 18/202
19 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Octadecatetraenoate (6c, 9c, 12c, 15c) (Methyl Stearidonate) No. of C: 18:4 5 mg Methyl 11c-Eicosenoate No. of C: 20:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl 11tr-Eicosenoate No. of C: 20:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg x 25 mg Methyl 11c,14c- Eicosadienoate No. of C: 20:2 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Eicosatrienoate (11c, 14c, 17c) No. of C: 20:3 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Hommo-gammalinolenate (8c, 11c, 14c) No. of C: 20:3 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg mg Methyl Arachidonate (5c, 8c, 11c, 14c) No. of C: 20:4 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg mg Omega3-Methyl Arachidonate (8c, 11c,14c, 17c ) No. of C: 20:4 Documentation: CoA Purity: 98% 1 mg mg Methyl Eicosapentaenoate (5c, 8c, 11c, 14c, 17c) No. of C: 20:5 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Erucate (13c) 19/202
20 No. of C: 22:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Brassidate ( 13tr) No. of C: 22:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Docosadienoate (13c, 16c) No. of C: 22:2 Documentation: Not included Purity: 99+% 25 mg x 25 mg Methyl Docosatrienoate(13c, 16c, 19c) No. of C: 22:3 Documentation: Not included Purity: 99+% 25 mg x 25 mg Methyl Docosatetraenoate (7c, 10c, 13c, 16c) No. of C: 22:4 Documentation: Not included Purity: 99+% 25 mg x 25 mg Methyl Docosapentaenoate (4c,7c,10c,13c,16c) No. of C: 22:5 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 25 mg Methyl Docosapentaenoate ( 7c, 10c, 13c, 16c, 19c) No. of C: 22:5 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Docosahexaenoate ( 4c, 7c, 10c, 13c, 16c, 19c) No. of C: 22:6 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl Nervonate ( 15c) No. of C: 24:1 Documentation: GC Purity: 99+% 100 mg x 100 mg Methyl (9c, 12c, 15c, 18c, 21c)-Tetracosapentaenoate No. of C: 24:5 5 mg Methyl (6c, 9c, 12c, 15c, 18c, 21c)-Tetracosahexaenoate 20/202
21 No. of C: 24:6 5 mg CLAs Analytical Standards 9c,11tr-Octadecadienoic Acid Documentation: Not included Purity: 98+% 25 mg g g c,11c-Octadecadienoic Acid Documentation: Not included Purity: 96+% 25 mg g tr,11tr-Octadecadienoic Acid Documentation: Not included Purity: 98% 25 mg tr,12c-Octadecadienoic Acid Documentation: Not included Purity: 98+% 25 mg g Methyl 9c,11tr-Octadecadienoate Documentation: Not included Purity: 98+% 25 mg Methyl 9c,11c-Octadecadienoate Documentation: Not included Purity: 96+% 25 mg Methyl 9tr,11tr-Octadecadienoate Documentation: Not included Purity: 98% 25 mg Methyl 10tr,12c-Octadecadienoate Documentation: Not included Purity: 98+% 25 mg /202
22 Unusual Fatty Acids Fatty acid biosynthesis by de novo pathways or by pathways involving elongation of preformed molecules takes place by successive addition of two carbons from either malonyl-coa or acetyl-coa, and this is the reason why the overwhelming part of naturally occurring fatty acids have even-numbered acyl chains. Furthermore, because of the specificities of acyl desaturases, most polyunsaturated fatty acids of natural origin possess two or more copies of the Zconfigured element (-CH=CH-CH2-)n. For this reason even the simplest of the naturally occurring polyunsaturated fatty acids, i.e. linoleic acid (n = 2), will possess a bis-allylic methylene group located between double bonds: (-CH=CHCH2-CH=CH-CH2-). The lowered carbon-hydrogen bond dissociation energy of this methylene group makes it unusually reactive and explains the susceptibility of polyunsaturated fatty acids to e.g. autoxidation and base-catalyzed isomerization as well as their conversions by enzymes like lipoxygenases, cyclooxygenases and conjugases. In addition to the dioxygenase and monooxygenase classes of enzymes, which introduce molecular oxygen into fatty acids to produce the oxylipin family of compounds, acyl chains can be modified by a large number of unorthodox desaturases. Such enzymes are especially common in the plant kingdom and are frequently active during seed development. Examples are the desaturases which introduce the 5(Z) double bond in 5(Z),9(Z)- octadecadienoic acid (taxoleic acid) and 5(Z),9(Z),12(Z)-octadecatrienoic acid (pinolenic acid), the desaturase which convert linoleic acid into 9(Z)- octadecen-12-ynoic acid (crepenynic acid), and the conjugase-type of desaturases which catalyze the dehydrogenation of linoleic acid into α- leostearic, α-calendic and punicic acids. It should be noted that the fatty acids in this category are non-oxygenated, occur in esterified form in plant lipids, and are as a rule isolated together with conventional fatty acids. Larodan takes special interest in the isolation of uncommon fatty acids from natural origin and also applies synthetic methods for modification of existing fatty acids. In this way we can provide a collection of unusual fatty acids, most of which are not available from other commercial sources. Conjugated Polyene Fatty Acids / Methyl Esters 22/202
23 Recent research has revealed new biological roles of Conjugated PUFAs, e.g. Conjugated Linoleic acid and alpha-parinaric acid act as high affinity binding ligands and activators of peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR). Others (trienoic and tetraenoic acids) display potent cytotoxic activity in cell cultures. A review article on Conjugated PUFAs is available on our web site. 8(E),10(E)-Octadecadienoic Acid 2 mg (E),10(E)-Octadecadienoic Acid Methyl Ester 2 mg (E),13(E)-Octadecadienoic Acid 2 mg (E),13(E)-Octadecadienoic Acid Methyl Ester Documentation: GS-MS / HPLC Purity: 97+% 2 mg (Z),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic Acid (alpha-eleostearic) 25 mg (E),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic Acid (beta-eleostearic) 25 mg (E),10(E),12(Z)-Octadecatrienoic Acid (alpha-calendic) 25 mg (E),10(E),12(E)-Octadecatrienoic Acid (beta-calendic) 25 mg (Z),11(E),13(Z)-Octadecatrienoic Acid (Punicic) 25 mg (Z),10(E),12(Z)-Octadecatrienoic Acid (Jacaric) 25 mg (E),11(E),13(Z)-Octadecatrienoic Acid (Catalpic) 23/202
24 5 mg (Z),11(E),13(E),15(Z)-Octadecatetraenoic Acid (alpha-parinaric) 250 mg Odd-Numbered PUFAs Odd-numbered fatty acids are formed inter alia by the alpha-oxidation pathway. 8(Z),11(Z),14(Z)-Heptadecatrienoic Acid 5 mg (Z),13(Z)-Nonadecadienoic acid 5 mg (Z),10(Z),13(Z)-Nonadecatrienoic Acid 5 mg (Z),13(Z),16(Z)-Nonadecatrienoic Acid 5 mg (Z),15(Z),18(Z)-Heneicosatrienoic Acid 5 mg (Z),12(Z),15(Z)-Heneicosatrienoic Acid 5 mg (Z),9(Z),12(Z),15(Z)-Heneicosatetraenoic Acid 5 mg (Z),9(Z),12(Z),15(Z),18(Z)-Heneicosapentaenoic Acid 5 mg (Z),11(Z),14(Z),17(Z),20(Z)-Tricosapentaenoic Acid 5 mg /202
25 5(Z),8(Z),11(Z),14(Z),17(Z),20(Z)-Tricosahexaenoic Acid 5 mg Odd-Numbered PUFA Methyl Esters 8(Z),11(Z),14(Z)-Heptadecatrienoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (Z),13(Z)-Nonadecadienoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (Z),10(Z),13(Z)-Nonadecatrienoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (Z),13(Z),16(Z)-Nonadecatrienoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (Z),15(Z),18(Z)-Heneicosatrienoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (Z),12(Z),15(Z)-Heneicosatrienoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (Z),9(Z),12(Z),15(Z)-Heneicosatetraenoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (Z),9(Z),12(Z),15(Z),18(Z)-Heneicosapentaenoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (Z),11(Z),14(Z),17(Z),20(Z)-Tricosapentaenoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (Z),8(Z),11(Z),14(Z),17(Z),20(Z)-Tricosahexaenoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg /202
26 Other Unusual PUFAs 9(Z),12(Z)-Hexadecadienoic acid 5 mg (Z), 10(Z), 13(Z)-Hexadecatrienoic Acid 5 mg (Z)-Hexadecenoic acid (Sapienic acid) 5mg Octadecynoic acid (Stearolic acid) 5mg (E)-Octadecenoic Acid 5 mg (Z)-Octadecen-12-ynoic Acid (Crepenynic) 25 mg (E)-Octadecen-9-ynoic Acid (Santalbic or Ximenynic) 25 mg (Z),12(E)-Octadecadienoic Acid 5 mg b-4 9(E),12(Z)-Octadecadienoic Acid 5 mg c-4 5(Z),9(Z)-Octadecadienoic Acid (Taxoleic) 5 mg (E),9(Z),12(Z)-Octadecatrienoic Acid (Columbinic) 5 mg (Z),9(Z),12(Z)-Octadecatrienoic Acid (Pinolenic) 5 mg Oxalinolenic Acid 26/202
27 2 mg (Z),9(Z)-Octadecadienoic Acid 2 mg (Z)-Eicosenoic Acid (Gadoleic) 5 mg (E),8(Z),11(Z),14(Z)-Eicosatetraenoic Acid 5 mg (E),8(Z),11(Z),14(Z)-Eicosatetraenoic Acid (5(E)-Arachidonic) 1 mg (Z),8Z),11(Z)-Eicosatrien-1,20-dioic acid 2 mg (Z),8(Z),11(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid (Mead acid) Documentation: GC-MS / HPLC Purity: 98% 2 mg ,7-Eicosadiynoic acid 5 mg (E),10(Z),13(Z),16(Z)-Docosatetraenoic Acid 5 mg (E),7(Z),10(Z),13(Z),16(Z)-Docosapentaenoic Acid 5 mg (E),7(Z),10(Z),13(Z),16(Z),19(Z)-Docosahexaenoic Acid 5 mg (E),7(Z),10(Z),13(Z),16(Z),19(Z)-Docosahexaenoic Acid 1 mg (E)-Tetracosenoic Acid (trans-nervonic) 5 mg (E),6(Z), 9(Z), 12(Z), 15(Z), 18(Z), 21(Z)-Tetracosaheptaenoic Acid 27/202
28 5 mg Other Unusual PUFA Methyl Esters Methyl 9(Z),12(Z)-Hexadecadienoate 5 mg Methyl (7(Z), 10(Z), 13(Z))-Hexadecatrienoate 5 mg (Z)-Hexadecenoic acid Methyl Ester(Sapienic acid) 5mg Octadecynoic acid Methyl Ester(Stearolic acid) 5mg (E)-Octadecenoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (Z)-Octadecen-12-ynoic acid (Crepenynic) Methyl Ester 25 mg (E)-Octadecen-9-ynoic acid (Santalbic or Ximenynic) Methyl Ester 25 mg (Z),12(E)-Octadecadienoic acid Methyl Ester Documentation: GC-MS/HPLC Purity: 97+% 5 mg b-4 9(E),12(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg c-4 5(Z),9(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid (Taxoleic) Methyl Ester 5 mg (E),9(Z),12(Z)-Octadecatrienoic acid (Columbinic) Methyl Ester 5 mg (Z),9(Z),12(Z)-Octadecatrienoic acid (Pinolenic) Methyl Ester 28/202
29 5 mg (Z),9(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid Methyl Ester 2 mg (Z)-Eicosenoic acid (Gadoleic) Methyl Ester 5 mg (E),8(Z),11(Z),14(Z)-Eicosatetraenoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (E),8(Z),11(Z),14(Z)-Eicosatetraenoic acid (5(E)-Arachidonic) Methyl Ester 1 mg (Z),8(Z),11(Z)-Eicosatrien-1,20-dioic acid Methyl Ester Documentation: GC-MS - HPLC Purity: 97+% 2 mg (Z),8(Z),11(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid (Mead acid) Methyl Ester Documentation: GC-MS / HPLC Purity: 98% 2 mg (E),10(Z),13(Z),16(Z)-Docosatetraenoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (E),7(Z),10(Z),13(Z),16(Z)-Docosapentaenoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (E),7(Z),10(Z),13(Z),16(Z),19(Z)-Docosahexaenoic acid Methyl Ester 5 mg (E),7(Z),10(Z),13(Z),16(Z),19(Z)-Docosahexaenoic acid Methyl Ester 1 mg (E)-Tetracosenoic acid Methyl Ester (trans-nervonic) 5 mg (E),6(Z), 9(Z), 12(Z), 15(Z),18(Z),21(Z)-Tetracosaheptaenoic Acid Methyl Ester 29/202
30 5 mg Omega-3 Fish Oil Fatty Acid Products EPA (5c,8c,11c,14c,17c) Documentation: GC Purity: 90% 1 g g g EPA Methyl Ester Documentation: GC Purity: 90% 1 g g g EPA Ethyl Ester Documentation: GC Purity: 90% 1 g g g DHA (4c,7c,10c,13c,16c,19c) Documentation: GC Purity: 90% 1 g g g DHA Methyl Ester Documentation: GC Purity: 90% 1 g g g DHA Ethyl Ester Documentation: GC Purity: 90% 1 g g g /202
31 CLAs Conjugated Linoleic Acids / Bulk Linoleic acids occur naturally as natural Octadienoic acid (9c,12c) and related isomers, so called Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) having double bonds in 9,11 or 10,12 positions (cis/trans). CLA isomers have been shown to be biologically active, e.g. suppressing cancer diseases and inhibiting development of atherosclerosis. Larodan offers selected CLAs for analytical and larger scale experiments (bulk). The analytical standards are listed in the Fatty Acid section. CLAs in bulk Free Fatty Acids Methyl/ Ethyl Esters Triglycerides CLA 9c,11tr Free Fatty Acid Documentation: Data sheet Purity: 89-94% 1 g g g g g CLA 9c,11tr Methyl Ester Documentation: Data sheet Purity: 89-94% 1 g g g g g CLA 9c,11tr Ethyl Ester Documentation: Data sheet Purity: 89-94% 1 g g g g g CLA 9c,11tr Triglyceride 31/202
32 Documentation: Data sheet Purity: 89-94% 1 g g g g g CLA 10tr,12c Free Fatty Acid Documentation: Data sheet Purity: 89-94% 1 g g g g g CLA 10tr,12c Methyl Ester Documentation: Data sheet Purity: 89-94% 1 g g g g g CLA 10tr,12c Ethyl Ester Documentation: Data sheet Purity: 89-94% 1 g g g g g CLA 10tr,12c Triglyceride Documentation: Data sheet Purity: 89-94% 1 g g g g g /202
33 Oxylipins Fatty acid hydroperoxides can be enzymatically produced in plants by lipoxygenase- or α-dioxygenase-catalyzed oxygenation. Further conversion by secondary enzymes results in an array of oxygenated derivatives belonging to the oxylipin family of compounds. The name "oxylipin" was introduced in 1990 as an encompassing term for fatty acid derivatives of all chain lengths formed by mono- or dioxygenase-catalyzed oxygenations. Although it is a general term which is unspecific for lengths of acyl chains, it has so far found most use to denote linoleic and linolenic acid-derived products in the plant fatty acid field. Interest in oxylipins to a large part stems from their involvement in plant development and their role as defensive agents in plants attacked by fungi, insects and bacteria. The Larodan company has supplied oxylipins for a multitude of studies on plants oxylipins and is actively involved in research aimed at elucidating the antimicrobial effects of oxylipins as well as more specific projects dealing e.g. with the structures of complex lipids containing 12-oxophytodienoic acid and with the mechanism of the hydroperoxide lyase reaction. Many oxylipins are unstable and/or rapidly inactivated by metabolic degradation. Research at Larodan with the aim of obtaining oxylipin analogs with enhanced metabolic stability has recently resulted in a series of β- oxidation-stable 3-oxa oxylipins, and limited quantities of the precursor of such analogs, i.e. 3-oxalinolenic acid, is now available from Larodan. The almost hundred different oxylipins provided by Larodan range from fatty acid hydroperoxides produced by lipoxygenases (LOX) to a multitude of derivatives generated from hydroperoxides by chemical transformations or by secondary plant enzymes such as allene oxide synthase (AOS), divinyl ether synthase (DES), hydroperoxide lyase (HPL), epoxy alcohol synthase (EAS) and peroxygenase (POX). Hydroperoxides 13(S)-HPOD [13(S)-hydroperoxy-9(Z),11(E)-octadecadienoic acid] 1 mg a-1 5 x 1 mg a 13-LOX product of linoleic acid. Serves as the substrate for secondary enzymes like AOS, HPL, DES and POX. 33/202
34 λmax (EtOH) 234 nm, ε 27,000 13(R,S)-Hydroperoxy-9(Z),11(E)-octadecadienoic Acid 100 microgram b- Primary autoxidation product of linoleic acid. λmax (EtOH) 234 nm, ε 27,000 13(R,S)-Hydroperoxy-9(E),11(E)-octadecadienoic Acid 100 microgram c- Primary autoxidation product of linoleic acid. λmax (EtOH) 230 nm. 9(S)-HPOD [9(S)-hydroperoxy-10(E),12(Z)-octadecadienoic acid] 1 mg a-1 5 x 1 mg a- 9-LOX product of linoleic acid. Serves as the substrate for secondary enzymes like AOS, HPL, DES and POX. λmax (EtOH) 234 nm, ε = 27,000 9(R,S)-Hydroperoxy-10(E),12(Z)-octadecadienoic Acid 100 microgram c- Primary autoxidation product of linoleic acid. λmax (EtOH) 234 nm, ε 27,000 9(R,S)-Hydroperoxy-10(E),12(E)-octadecadienoic Acid 100 microgram d- Primary autoxidation product of linoleic acid. λmax (EtOH) 230 nm. 13(S)-HPOT [13(S)-hydroperoxy-9(Z),11(E),15(Z)-octadecatrienoic acid] 1 mg x 1 mg LOX product of linolenic acid. Serves as the substrate for secondary enzymes like AOS, HPL, DES and POX. λmax (EtOH) 235 nm, ε 27,000 9(S)-HPOT [9(S)-hydroperoxy-10(E),12(Z),15(Z)-octadecatrienoic acid] 1 mg a-1 5 x 1 mg a-38 9-LOX product of linolenic acid. Serves as the substrate for secondary enzymes like AOS, HPL, DES and POX. λmax (EtOH) 235 nm, ε 27,000 34/202
35 11(S)-Hydroperoxy-7(Z),9(E),13(Z)-hexadecatrienoic Acid 100 microgram x 100 microgram LOX product of 7,10,13-hexadecatrienoic acid. λmax (EtOH) 235 nm, ε 27,000 2(R,S)-Hydroperoxy-9(Z)-octadecenoic Acid 100 microgram c-39 Chemical oxygenation product of oleic acid. 2(R,S)-Hydroperoxyhexadecanoic acid 1mg Chemical oxygenation product of palmitic acid Hydroxides 13(S)-HOD [13(S)-hydroxy-9(Z),11(E)-octadecadienoic acid] 1 mg a-1 5 x 1 mg a-38 Chemical or enzymatical reduction product of the corresponding hydroperoxide. λmax (EtOH) 234 nm, ε 27,000 13(R,S)-Hydroxy-9(Z),11(E)-octadecadienoic acid 100 microgram f-39 Chemical or enzymatical reduction product of the corresponding hydroperoxide. λmax (EtOH) 234 nm, ε 27,000 13(R,S)-Hydroxy-9(E),11(E)-octadecadienoic acid 100 microgram g-39 Chemical or enzymatical reduction product of the corresponding hydroperoxide. λmax (EtOH) 230 nm 9(S)-HOD [9(S)-hydroxy-10(E),12(Z)-octadecadienoic acid] 1 mg b-1 5 x 1 mg b-38 35/202
36 Chemical or enzymatical reduction product of the corresponding hydroperoxide. λmax (EtOH) 234 nm, ε = 27,000 9(R,S)-Hydroxy-10(E),12(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 100 microgram e-39 Chemical or enzymatical reduction product of the corresponding hydroperoxide. λmax (EtOH) 234 nm, ε 27,000 9(R,S)-Hydroxy-10(E),12(E)-octadecadienoic acid 100 microgram f-39 Chemical or enzymatical reduction product of the corresponding hydroperoxide. λmax (EtOH) 230 nm 10(R,S)-Hydroxy-8(E),12(Z)-octadecadienoic Acid 100 microgram b-39 Reduction product of hydroperoxide formed on singlet oxygen oxygenation of linoleic acid. 11(R)-Hydroxy-9(Z),12(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 100 microgram b-39 Enzymatic bis-allylic oxidation product of linoleic acid. The methyl ester is supplied. 11(R,S)-Hydroxy-9(Z),12(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 100 microgram c-39 Nonenzymatic bis-allylic oxidation product of linoleic acid. The methyl ester is supplied. 12(R,S)-Hydroxy-9(Z),13(E)-octadecadienoic Acid 100 microgram c-39 Reduction product of hydroperoxide formed on singlet oxygen oxygenation of linoleic acid. 15(R)-Hydroxy-9(Z),12(Z)-octadecadienoic Acid (Avenoleic) 100 microgram d-39 5 x 100 microgram d-40 Monooxygenase product of linoleic acid 15(R,S)-Hydroxy-9(Z),12(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 36/202
37 100 microgram e-39 Reduction product of 15-oxolinoleic acid 13(S)-HOT [13(S)-hydroxy-9(Z),11(E),15(Z)-octadecatrienoic acid] 1 mg x 1 mg Chemical or enzymatical reduction product of the corresponding hydroperoxide. λmax (EtOH) 234 nm, ε 27,000 9(S)-HOT [9(S)-hydroxy-10(E),12(Z),15(Z)-octadecatrienoic acid] 1 mg b-1 5 x 1 mg b-38 Chemical or enzymatical reduction product of the corresponding hydroperoxide. λmax (EtOH) 235 nm, ε 27,000 13(S)-Hydroxy-6(Z),9(Z),11(E)-octadecatrienoic acid [13(S)-HOTω6] 1 mg Chemical or enzymatical reduction product of the 13(S)-hydroperoxide derivative of γ-linolenic acid. λmax (EtOH) 235 nm, ε 27,000 11(S)-Hydroxy-7(Z),9(E),13(Z)-hexadecatrienoic Acid 100 microgram x 100 microgram Chemical or enzymatical reduction product of the corresponding hydroperoxide. λmax (EtOH) 234 nm, ε 27,000 12(S)-Hydroxy-5(Z),8(E),10(E)-heptadecatrienoic acid [12(S)-HHT] 100 microgram x 100 microgram Degradation product of prostaglandin H2. λmax (EtOH) 231 nm 2(R,S)-Hydroxy-9(Z)-octadecenoic acid 100 microgram d-39 Chemical or enzymatical reduction product of the corresponding hydroperoxide. 2(R)-Hydroxy-9(Z),12(Z),15(Z)-octadecatrienoic acid 37/202
38 5 mg a-4 Secondary α-dioxygenase product of linolenic acid 2(R,S)-Hydroxy-9(Z),12(Z),15(Z)-octadecatrienoic acid 1 mg b-1 Reduction product of 2-oxolinolenic acid Ketones 13-Oxo-9(Z),11(E)-octadecadienoic Acid [13-KOD] 1 mg b-1 5 x 1 mg b-38 Secondary 13-LOX product of linoleic acid. λmax (EtOH) 278 nm, ε 24,000 9-Oxo-10(E),12(Z)-octadecadienoic Acid [ 9-KOD] 1 mg c-1 5 x 1 mg c-38 Secondary 9-LOX product of linoleic acid λmax (EtOH) 278 nm, ε 24, Oxo-9(Z),11(E),15(Z)-octadecatrienoic Acid [13-KOT] 1 mg b-1 Secondary 13-LOX product of linolenic acid. λmax (EtOH) 280 nm, ε 24,000 9-Oxo-10(E),12(Z),15(Z)-octadecatrienoic Acid [9-KOT] 1 mg c-1 5 x 1 mg c-38 Secondary 9-LOX product of linolenic acid. λmax (EtOH) 278 nm, ε 24,000 2-Oxo-9(Z),12(Z),15(Z)-octadecatrienoic acid 1 mg Secondary α-dioxygenase product of linolenic acid. 15-Oxo-9(Z),12(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 100 microgram Dehydrogenation product of avenoleic acid. 38/202
39 Epoxides (±)-cis-12,13--9(z)-octadecenoic Acid ((±)-Vernolic) 1 mg a-1 Epoxidation product of linoleic acid 12(S),13(R)-Epoxy-9(Z)-octadecenoic Acid ((+)-Vernolic) 25 mg b-7 Methyl ester 25 mg b-7 Epoxygenase/peroxygenase product of linoleic acid. 12(R),13(S)-Epoxy-9(Z)-octadecenoic Acid ((-)-Vernolic) 5 mg c-4 Epoxygenase/peroxygenase product of linoleic acid. (±)-cis-9,10-epoxy-12(z)-octadecenoic Acid ((±)-Coronaric) 1 mg d-1 Epoxidation product of linoleic acid. 9(R),10(S)-Epoxy-12(Z)-octadecenoic Acid ((+)-Coronaric) 5 mg e-4 Epoxygenase/peroxygenase product of linoleic acid. (±)-cis-12,13-epoxy-9(z),15(z)-octadecadienoic Acid 1 mg a-1 Epoxidation product of linolenic acid. (±)-trans-5,6-epoxy-9(z),12(z)-octadecadienoic Acid 1 mg b-1 Epoxidation product of columbinic acid. (±)-cis-5,6-epoxy-9(z),12(z)-octadecadienoic acid 1 mg c-1 Epoxidation product of pinolenic acid. (±)-cis-11,12-epoxy-14(z)-eicosenoic Acid 39/202
40 1mg Epoxidation product of 11,14-eicosadienoic acid. (±)-cis-14,15-epoxy-11(z)-eicosenoic Acid ((±)-Alchornic) 1 mg Epoxidation product of 11,14-eicosadienoic acid. (±)-cis-4,5-epoxy-7(z),10(z),13(z),16(z),19(z)-docosapentaenoic acid 1 mg Epoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid. The methyl ester is supplied. 10,13-epoxy-10,12-octadecadienoic Acid 1 mg Nonenzymatical degradation product of many oxylipins. Diols (±)-threo-9,10-dihydroxy-12(z)-octadecenoic Acid 5 mg a-4 Chemical or enzymatical hydrolysis product of coronaric acid. (±)-threo-12,13-dihydroxy-9(z)-octadecenoic Acid 5 mg b-4 Chemical or enzymatical hydrolysis product of vernolic acid. (±)-threo-12,13-dihydroxy-9(z),15(z)-octadecadienoic Acid 1 mg Chemical or enzymatical hydrolysis product of cis-12,13-epoxy-9(z),15(z)- octadecadienoic acid. (±)-erythro-5,6-dihydroxy-9(z),12(z)-octadecadienoic Acid 1mg Chemical and enzymatical hydrolysis product of trans-5,6-epoxy-9(z),12(z)- octadecadienoic acid. 40/202
41 Allene Oxide Synthase derived Oxylipins 13-Hydroxy-12-oxo-9(Z)-octadecenoic Acid 100 microgram a-39 α-ketol derived from 13(S)-HPOD. 9-Hydroxy-12-oxo-10(E)-octadecenoic Acid 50 microgram a-41 5 x 50 microgram a-42 γ-ketol derived from 13(S)-HPOD. λmax (EtOH) 224 nm 9-Hydroxy-10-oxo-12(Z)-octadecenoic acid 100 microgram b-39 α-ketol derived from 9(S)-HPOD. 10-Oxo-11-phytoenoic Acid [side chain cis isomer] 100 microgram a-39 5 x 100 microgram a-40 Cyclopentenone derived from 9(S)-HPOD. The racemic side chain cis isomer is provided. λmax (EtOH) 220 nm, ε 12, Hydroxy-12-oxo-9(Z),15(Z)-octadecadienoic Acid 100 microgram a-39 α-ketol derived from 13(S)-HPOT. 9-Hydroxy-10-oxo-12(Z),15(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 100 microgram b-39 α-ketol derived from 9(S)-HPOT. 9-Hydroxy-12-oxo-10(E),15(Z)-octadecadienoic Acid 50 microgram x 50 microgram γ-ketol derived from 13(S)-HPOT. λmax (EtOH) 224 nm 12-Oxo-10,15(Z)-phytodienoic Acid [side chain cis isomer, mainly 9(S),13(S)] 41/202
42 100 microgram a-39 5 x 100 microgram a-40 Cyclopentenone derived from 13(S)-HPOT. The material consists of >90% of the natural 9(S),13(S)-isomer. λmax (EtOH) 220 nm, ε 12,500 Divinyl Ether Synthase derived Oxylipins Colneleic Acid [9-[1 (E),3 (Z)-nonadienyloxy]-8(E)-nonenoic acid] 100 microgram x 100 microgram Divinyl ether fatty acid formed from 9(S)-HPOD (potato/tomato type DES). λmax (EtOH) 250 nm, ε 30,000 Etheroleic Acid [12-[1 (E)-hexenyloxy]-9(Z),11(E)-dodecadienoic acid] 100 microgram x 100 microgram Divinyl ether fatty acid formed from 13(S)-HPOD (garlic type DES). λmax (EtOH) 250 nm, ε 30,000 ω-5(z)-etheroleic Acid [12-[1 (Z)-hexenyloxy]-9(Z),11(E)-dodecadienoic acid] 100 microgram a-39 5 x 100 microgram a-40 Divinyl ether fatty acid formed from 13(S)-HPOD (Ranunculus acris type DES). λmax (EtOH) 250 nm, ε 30,000 11(Z)-Etheroleic acid [12-[1 (E)-hexenyloxy]-9(Z),11(Z)-dodecadienoic acid] 50 microgram b-41 Divinyl ether fatty acid from 13(S)-HPOD (Ranunculus lingua type DES). λmax (EtOH) 253 nm Colnelenic Acid [9-[1 (E),3 (Z),6 (Z)-nonatrienyloxy]-8(E)-nonenoic acid] 100 microgram x 100 microgram /202
43 Divinyl ether fatty acid formed from 9(S)-HPOT (potato/tomato type DES). λmax (EtOH) 253 nm Etherolenic Acid [12-[1 (E),3 (Z)-hexadienyloxy]-9(Z),11(E)- dodecadienoic acid] contains up to 30% of the ω-5(z) isomer. Isomeric composition indicated for each sample 100 microgram x 100 microgram Divinyl ether fatty acid from 13(S)-HPOT (garlic type DES). λmax (EtOH) 268 nm, ε 41,000 ω-5(z)-etherolenic Acid [12-[1 (Z),3 (Z)- hexadienyloxy]-9(z),11(e)- dodecadienoic acid] 100 microgram x 100 microgram Divinyl ether fatty acid from 13(S)-HPOT (Ranunculus type DES). λmax (EtOH) 267 nm, ε 41,000 Dorignic Acid (14-[1 (E)-hexenyloxyl]-8(Z),11(Z),13(E)-tetradecatrienoic acid) 100 microgram Divinyl ether fatty acid from 15(S)-HPET (garlic type DES). λmax (EtOH) 252 nm Epoxy Alcohol Synthase / Peroxygenase-derived Oxylipins 10(S),11(S)-Epoxy-9(S)-hydroxy-12(Z)-octadecenoic acid - threo isomer also available 100 microgram a-39 5 x 100 microgram a-40 Epoxy alcohol synthase product of 9(S)-HPOD. The methyl ester is supplied. 11(S),12(S)-Epoxy-13(S)-hydroxy-9(Z)-octadecenoic acid - threo isomer also available 100 microgram b-39 43/202
44 5 x 100 microgram b-40 Putative epoxy alcohol synthase product of 13(S)-HPOD. The methyl ester i supplied. 9(S),10(S)-Epoxy-11(S)-hydroxy-12(Z)-octadecenoic acid - threo isomer also available 100 microgram c-39 5 x 100 microgram c-40 Degradation product of 9(S)-HPOD. The methyl ester is supplied. 12(S),13(S)-Epoxy-11(S)-hydroxy-9(Z)-octadecenoic acid - threo isomer also available 100 microgram d-39 5 x 100 microgram d-40 Degradation product of 13(S)-HPOD. The methyl ester is supplied. 12(R),13(S)-Epoxy-9(S)-hydroxy-10(E)-octadecenoic acid 50 microgram a-41 5 x 50 microgram a-42 Epoxy alcohol synthase product of 9(S)-HPOD. The methyl ester is supplied. 9(S),10(R)-Epoxy-13(S)-hydroxy-11(E)-octadecenoic acid 50 microgram b-41 5 x 50 microgram b-42 Putative epoxy alcohol synthase product of 13(S)-HPOD. The methyl ester is supplied. 10(S),11(S)-Epoxy-9(S)-hydroxy-12(Z),15(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 100 microgram a-39 5 x 100 microgram a-40 Epoxy alcohol synthase product of 9(S)-HPOT. The methyl ester is supplied. 11(S),12(S)-Epoxy-13(S)-hydroxy-9(Z),15(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 100 microgram b-39 5 x 100 microgram b-40 Putative epoxy alcohol synthase product of 13(S)-HPOT. The methyl ester i supplied. 9(S),10(S)-Epoxy-11(S)-hydroxy-12(Z),15(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 44/202
45 100 microgram c-39 5 x 100 microgram c-40 Degradation product of 9(S)-HPOT. The methyl ester is supplied. 12(S),13(S)-Epoxy-11(S)-hydroxy-9(Z),15(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 100 microgram d-39 5 x 100 microgram d-40 Degradation product of 13(S)-HPOT. The methyl ester is supplied. 12(R),13(S)-Epoxy-9(S)-hydroxy-10(E),15(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 50 microgram a-41 5 x 50 microgram a-42 Epoxy alcohol synthase product of 9(S)-HPOT. The methyl ester is supplied. 9(S),10(R)-Epoxy-13(S)-hydroxy-11(E),15(Z)-octadecadienoic acid 50 microgram b-41 5 x 50 microgram b-42 Putative epoxy alcohol synthase product of 13(S)-HPOT. The methyl ester is supplied. 9(S),10(S),11(R)-Trihydroxy-12(Z)-octadecenoic Acid 100 microgram x 100 microgram Chemical or enzymatical hydrolysis product of 10(S),11(S)-epoxy-9(S)- hydroxy-12(z)-octadecenoic acid 9(S),12(S),13(S)-Trihydroxy-10(E)-octadecenoic Acid 100 microgram x 100 microgram Chemical or enzymatical hydrolysis product of 12(R),13(S)-epoxy-9(S)- hydroxy-10(e)-octadecenoic acid 9(S),10(S),13(S)-Trihydroxy-11(E)-octadecenoic Acid 100 microgram x 100 microgram Chemical and enzymatical hydrolysis product of 9(S),10(R)-epoxy-13(S)- hydroxy-11(e)-octadecenoic acid 45/202
46 9(S),10(S),11(R)-Trihydroxy-12(Z),15(Z)-octadecadienoic Acid 100 microgram x 100 microgram Chemical or enzymatical hydrolysis product of 10(S),11(S)-epoxy-9(S)- hydroxy-12(z),15(z)-octadecadienoic acid 9(S),12(S),13(S)-Trihydroxy-10(E),15(Z)-octadecadienoic Acid 100 microgram x 100 microgram Chemical or enzymatical hydrolysis product of 12(R),13(S)-epoxy-9(S)- hydroxy-10(e),15(z)-octadecadienoic acid 9(S),10(S),13(S)-Trihydroxy-11(E),15(Z)-octadecadienoic Acid 100 microgram x 100 microgram Chemical or enzymatical hydrolysis product of 9(S),10(R)-epoxy-13(S)- hydroxy-11(e),15(z)-octadecadienoic acid Lyase-derived Oxylipins 3(Z)-Nonenal 5 mg Short-chain aldehyde formed from linoleic acid. 9-Oxononanoic Acid 5 mg Oxo-acid formed from Linoleic and Linolenic acid. 12-Oxo-9(Z)-dodecenoic Acid 5 mg x 5 mg Oxo-acid formed from linoleic and linolenic acids. 12-Oxo-10(E)-dodecenoic Acid (Traumatin) 5 mg /202
The Conditions of Sale apply to the written text in this Catalogue superseding earlier texts related to such conditions.
 Conditions of Sale Validity Intention of Use The Conditions of Sale apply to the written text in this Catalogue superseding earlier texts related to such conditions. Our products are intended for research
Conditions of Sale Validity Intention of Use The Conditions of Sale apply to the written text in this Catalogue superseding earlier texts related to such conditions. Our products are intended for research
Fats and Lipids (Ans570)
 Fats and Lipids (Ans570) Outlines Fats and Lipids Structure, nomenclature Phospholipids, Sterols, and Lipid Derivatives Lipid Oxidation Roles of fat in food processing and dietary fat Lipid and fat analysis:
Fats and Lipids (Ans570) Outlines Fats and Lipids Structure, nomenclature Phospholipids, Sterols, and Lipid Derivatives Lipid Oxidation Roles of fat in food processing and dietary fat Lipid and fat analysis:
MPS Advanced Plant Biochemistry Course
 MPS 587 - Advanced Plant Biochemistry Course Lipids section guest lecture: Philip Bates Post-doc Browse lab Office: 453 Clark Hall Email: phil_bates@wsu.edu Lecture 9 Lipids I 1. What is a lipid? 2. Fatty
MPS 587 - Advanced Plant Biochemistry Course Lipids section guest lecture: Philip Bates Post-doc Browse lab Office: 453 Clark Hall Email: phil_bates@wsu.edu Lecture 9 Lipids I 1. What is a lipid? 2. Fatty
CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS AR-15-QD
 Eurofins Sample Code: 464-2015-09040561 Sample Description: Fermented Cod Liver Oil Client Sample Code: 29442 PO Number: Credit Card on file Client Code: QD0006557 attn: Dr. Jie Zhang Nutrition Analysis
Eurofins Sample Code: 464-2015-09040561 Sample Description: Fermented Cod Liver Oil Client Sample Code: 29442 PO Number: Credit Card on file Client Code: QD0006557 attn: Dr. Jie Zhang Nutrition Analysis
Highly Reproducible Detailed cis/trans FAMEs Analysis Ensured by New Optimized Rt-2560 Column Manufacturing and Application-Specific QC Test
 Highly Reproducible Detailed cis/trans FAMEs Analysis Ensured by New Optimized Rt-2560 Manufacturing and Application-Specific QC Test By Kristi Sellers and Rebecca Stevens Restek s Rt-2560 GC column is
Highly Reproducible Detailed cis/trans FAMEs Analysis Ensured by New Optimized Rt-2560 Manufacturing and Application-Specific QC Test By Kristi Sellers and Rebecca Stevens Restek s Rt-2560 GC column is
Trans FAT LABELING an Industry Perspective
 Trans FAT LABELING an Industry Perspective National Nutrition Database Conference 28 th Edition June 24-26, 2004 Iowa City, IA Trans FAT LABELING an Industry Perspective Christine Wold QRO Product Labeling
Trans FAT LABELING an Industry Perspective National Nutrition Database Conference 28 th Edition June 24-26, 2004 Iowa City, IA Trans FAT LABELING an Industry Perspective Christine Wold QRO Product Labeling
NEW! 200 m GC Columns for Detailed Analysis of cis/trans FAME Isomers
 Order: 00--00 (U.S.) -- (Global) NEW! 00 m GC Columns for Detailed Analysis of cis/trans FAME Isomers Leonard M. Sidisky, R&D Manager; and Michael D. Buchanan, Product Manager mike.buchanan@sial.com Over
Order: 00--00 (U.S.) -- (Global) NEW! 00 m GC Columns for Detailed Analysis of cis/trans FAME Isomers Leonard M. Sidisky, R&D Manager; and Michael D. Buchanan, Product Manager mike.buchanan@sial.com Over
Biological role of lipids
 Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Erythrocyte Essential Fatty Acids
 Biolab reference: PHWN\ABCD\A12 Referred by: Dr.. Patient: Mr Sample Patient Date of birth: 16/01/969 Your reference: Date: 04/01/2012 Sex: Male Sample date: 03/01/2012 Erythrocyte Essential Fatty Acids
Biolab reference: PHWN\ABCD\A12 Referred by: Dr.. Patient: Mr Sample Patient Date of birth: 16/01/969 Your reference: Date: 04/01/2012 Sex: Male Sample date: 03/01/2012 Erythrocyte Essential Fatty Acids
Column Selection for the Analysis of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Application
 Column Selection for the Analysis of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Application Food Analysis Authors Frank David Research Institute for Chromatography President Kennedy Park B- Kortrijk, Belgium Pat Sandra
Column Selection for the Analysis of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Application Food Analysis Authors Frank David Research Institute for Chromatography President Kennedy Park B- Kortrijk, Belgium Pat Sandra
Introduction to the Study of Lipids
 Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES. Lipid Chemistry NO. OF CARBONS COMMON NAME GENEVA NAME STRUCTURE
 ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES I. Common Saturated Fatty Acids NO. OF CARBONS COMMON NAME GENEVA NAME STRUCTURE 4 Butyric Tetranoic CH 3 (CH 2 ) 2 COOH 6 Caproic Hexanoic CH 3 (CH
ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES I. Common Saturated Fatty Acids NO. OF CARBONS COMMON NAME GENEVA NAME STRUCTURE 4 Butyric Tetranoic CH 3 (CH 2 ) 2 COOH 6 Caproic Hexanoic CH 3 (CH
Analysis of FAMEs Using Cold EI GC/MS for Enhanced Molecular Ion Selectivity
 APPLICATION NOTE Gas Chromatography/ Mass Spectrometry Author: Adam Patkin PerkinElmer, Inc. Shelton, CT Analysis of FAMEs Using GC/MS for Enhanced Molecular Ion Selectivity Introduction Characterization
APPLICATION NOTE Gas Chromatography/ Mass Spectrometry Author: Adam Patkin PerkinElmer, Inc. Shelton, CT Analysis of FAMEs Using GC/MS for Enhanced Molecular Ion Selectivity Introduction Characterization
Chapter 8. Functions of Lipids. Structural Nature of Lipids. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2.
 BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
Lipids are broadly classified in to simple, complex and derived, which are further subdivided into different groups.
 Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
Structure SMILES IUPAC name Name MW Plate description CAS Catalog number Concentration Solvent Plate part number
 H CCCCCCCCCC()= decanoic acid Decanoic acid 1723 Fatty Acid Library 334-48-5 BL-135 10mM DMS 2803 H CCCCCCCCCCC()= undecanoic acid Undecanoic acid 1863 Fatty Acid Library 112-37-8 BL-136 10mM DMS 2803
H CCCCCCCCCC()= decanoic acid Decanoic acid 1723 Fatty Acid Library 334-48-5 BL-135 10mM DMS 2803 H CCCCCCCCCCC()= undecanoic acid Undecanoic acid 1863 Fatty Acid Library 112-37-8 BL-136 10mM DMS 2803
Certificate of Analysis Standard Reference Material 3275
 National Institute of Standards & Technology Certificate of Analysis Standard Reference Material 3275 Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids in Fish Oil This Standard Reference Material (SRM) is intended primarily
National Institute of Standards & Technology Certificate of Analysis Standard Reference Material 3275 Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids in Fish Oil This Standard Reference Material (SRM) is intended primarily
Improving the Analysis of 37 Fatty Acid Methyl Esters
 Application Note Food Testing Improving the Analysis of 37 Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Using Three Types of Capillary GC columns Authors Yun Zou Agilent Technologies (Shanghai) Co.Ltd, Shanghai 200131 P.R.China
Application Note Food Testing Improving the Analysis of 37 Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Using Three Types of Capillary GC columns Authors Yun Zou Agilent Technologies (Shanghai) Co.Ltd, Shanghai 200131 P.R.China
DET REPORT NO. 69 JUNE 2015
 1.) THINKING BEYOND THE NPD BOX - INEXPENSIVE CONVERSION OF NPD EQUIPMENT TO MULTIPLE MODES OF SELECTIVE GC DETECTION. 2.) GC-CCID DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN SATURATE VS. UNSATURATE AND MONO-UNSATURATE VS.
1.) THINKING BEYOND THE NPD BOX - INEXPENSIVE CONVERSION OF NPD EQUIPMENT TO MULTIPLE MODES OF SELECTIVE GC DETECTION. 2.) GC-CCID DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN SATURATE VS. UNSATURATE AND MONO-UNSATURATE VS.
Optimising. membranes
 Optimising Neuronal membranes Lipids are classified as 1. Simple lipids oils and fats 2. Complex lipids a) Phospholipids b) Glycosphingolipids containing a fatty acid, sphingosine and a CHO c) Lipoproteins
Optimising Neuronal membranes Lipids are classified as 1. Simple lipids oils and fats 2. Complex lipids a) Phospholipids b) Glycosphingolipids containing a fatty acid, sphingosine and a CHO c) Lipoproteins
ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS General Chemistry of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerols
 ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS General Chemistry of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerols I. Common Saturated Fatty Acids NO. OF CARBONS COMMON NAME GENEVA NAME STRUCTURE 4 Butyric Tetranoic
ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS General Chemistry of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerols I. Common Saturated Fatty Acids NO. OF CARBONS COMMON NAME GENEVA NAME STRUCTURE 4 Butyric Tetranoic
OBJECTIVE. Lipids are largely hydrocarbon derivatives and thus represent
 Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
High-Resolution GC Analyses of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (FAMEs)
 High-Resolution GC Analyses of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (s) Fatty acid methyl esters (s) analysis is an important tool both for characterizing fats and oils and for determining the total fat content in
High-Resolution GC Analyses of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (s) Fatty acid methyl esters (s) analysis is an important tool both for characterizing fats and oils and for determining the total fat content in
FOOD TECHNOLOGY FACT SHEET
 FAPC-196 Robert M. Kerr Food & Agricultural Products Center Nurhan Turgut Dunford FAPC Oil/oilseed Specialist FOOD TECHNOLOGY FACT SHEET Adding Value to OKLAHOMA 405-744-6071 www.fapc.biz fapc@okstate.edu
FAPC-196 Robert M. Kerr Food & Agricultural Products Center Nurhan Turgut Dunford FAPC Oil/oilseed Specialist FOOD TECHNOLOGY FACT SHEET Adding Value to OKLAHOMA 405-744-6071 www.fapc.biz fapc@okstate.edu
Lipids and Classification:
 Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Food Analysis Standards
 Food Chemists routinely use AccuStandard's comprehensive program of Analytical Reference Materials for their Food Analysis. These include, Vitamin Standards, Preservative Standards and Antimicrobial Standards.
Food Chemists routinely use AccuStandard's comprehensive program of Analytical Reference Materials for their Food Analysis. These include, Vitamin Standards, Preservative Standards and Antimicrobial Standards.
FAMEs Analyses High-Resolution GC Analyses of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters
 APPLICATIONS NOTE FAMEs Analyses High-Resolution GC Analyses of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) analysis is an important tool both for characterizing fats and oils and for determining
APPLICATIONS NOTE FAMEs Analyses High-Resolution GC Analyses of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) analysis is an important tool both for characterizing fats and oils and for determining
Physical properties. Carboxylic acids. Boiling points of Carboxylic Acids 3/19/2012
 R H Carboxylic acid Carboxylic acids Ionization R _ Carboxylate ion + H (proton) 1 Physical properties Carboxylic acids are polar, and form hydrogen bonds with each other. At high temperatures, in vapour
R H Carboxylic acid Carboxylic acids Ionization R _ Carboxylate ion + H (proton) 1 Physical properties Carboxylic acids are polar, and form hydrogen bonds with each other. At high temperatures, in vapour
AOAC Official Method Determination of Labeled Fatty Acids Content in Milk Products and Infant Formula
 AOAC Official Method 2012.13 Determination of Labeled Fatty Acids Content in Milk Products and Infant Formula Capillary Gas Chromatography First Action 2012 A. Scope The method involves the quantification
AOAC Official Method 2012.13 Determination of Labeled Fatty Acids Content in Milk Products and Infant Formula Capillary Gas Chromatography First Action 2012 A. Scope The method involves the quantification
Separation of 37 Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Utilizing a High-Efficiency 10 m Capillary GC Column with Optimization in Three Carrier Gases
 APPLICATION NOTE Separation of 37 Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Utilizing a High-Efficiency 10 m Capillary GC Column with Optimization in Three Carrier Gases No. 21557 Aaron L. Lamb Thermo Fisher Scientific,
APPLICATION NOTE Separation of 37 Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Utilizing a High-Efficiency 10 m Capillary GC Column with Optimization in Three Carrier Gases No. 21557 Aaron L. Lamb Thermo Fisher Scientific,
3 Lipids. 3.1 Foreword
 3 Lipids 3.1 Foreword Lipids are formed from structural units with a pronounced hydrophobicity. This solubility characteristic, rather than a common structural feature, is unique for this class of compounds.
3 Lipids 3.1 Foreword Lipids are formed from structural units with a pronounced hydrophobicity. This solubility characteristic, rather than a common structural feature, is unique for this class of compounds.
Classification, functions and structure
 Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
CHEMISTRY OF OILS AND FATS. Albert J. Dijkstra
 CHEMISTRY F ILS AND FATS Albert J. Dijkstra Production vegetable oil (m tonnes) Seven oil seeds 2008/09 2009/10 2010/11 2011/12 total 396.7 444.1 455.7 441.4 Soya bean 211.6 260.2 263.6 238.7 ther 185.1
CHEMISTRY F ILS AND FATS Albert J. Dijkstra Production vegetable oil (m tonnes) Seven oil seeds 2008/09 2009/10 2010/11 2011/12 total 396.7 444.1 455.7 441.4 Soya bean 211.6 260.2 263.6 238.7 ther 185.1
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
Lipids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8
 Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
Lipids ON HPLC COLUMNS
 Lipids N HPLC CLUMNS No.TI17E cis - trans Isomers of 9-octadecenoic acid 2 1 1 2 mau 5 1 15 2 min Cadenza CD-C18, 15 x 4.6 mm ACN / water / formic acid = 9 / 1 /.5.8 ml/min, 37 C UV at 215 nm, 3.7 MPa
Lipids N HPLC CLUMNS No.TI17E cis - trans Isomers of 9-octadecenoic acid 2 1 1 2 mau 5 1 15 2 min Cadenza CD-C18, 15 x 4.6 mm ACN / water / formic acid = 9 / 1 /.5.8 ml/min, 37 C UV at 215 nm, 3.7 MPa
Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerides (TG) in liver. Mobilization of stored fat and oxidation of fatty acids
 Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerides (TG) in liver Mobilization of stored fat and oxidation of fatty acids Activation of hormone sensitive lipase This enzyme is activated when phosphorylated (3,5 cyclic AMPdependent
Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerides (TG) in liver Mobilization of stored fat and oxidation of fatty acids Activation of hormone sensitive lipase This enzyme is activated when phosphorylated (3,5 cyclic AMPdependent
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM. Fatty Acid Elongation and Desaturation
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM I. Fatty acid elongation A. General 1. At least 60% of fatty acids in triacylglycerols are C18. 2. Free palmitic acid (16:0) synthesized in cytoplasm is elongated
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM I. Fatty acid elongation A. General 1. At least 60% of fatty acids in triacylglycerols are C18. 2. Free palmitic acid (16:0) synthesized in cytoplasm is elongated
Experiment 12 Lipids. Structures of Common Fatty Acids Name Number of carbons
 Experiment 12 Lipids Lipids are a class of biological molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. There are many different categories of lipids and each category has different
Experiment 12 Lipids Lipids are a class of biological molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. There are many different categories of lipids and each category has different
Fats Can Be Good For You!
 Fats Can Be Good For You! Fat Quiz (True or False) 1. Excess fat in the diet is a major cause of heart disease. 2. Saturated fats raise cholesterol levels. 3. The saturated fats in butter and coconut oil
Fats Can Be Good For You! Fat Quiz (True or False) 1. Excess fat in the diet is a major cause of heart disease. 2. Saturated fats raise cholesterol levels. 3. The saturated fats in butter and coconut oil
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Serum and synovial fluid lipidomic profiles predict obesity-associated osteoarthritis, synovitis, and wound repair Chia-Lung Wu 1,2, Kelly A. Kimmerling 1,2, Dianne Little 3,
Supplementary Information Serum and synovial fluid lipidomic profiles predict obesity-associated osteoarthritis, synovitis, and wound repair Chia-Lung Wu 1,2, Kelly A. Kimmerling 1,2, Dianne Little 3,
Chem 5 PAL Worksheet Lipids Smith text Chapter 15
 Chem 5 PAL Worksheet Lipids Smith text Chapter 15 Principle: Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long (usually > 14) carbon chains which can be saturated (no carbon-carbon double bonds) are unsaturated
Chem 5 PAL Worksheet Lipids Smith text Chapter 15 Principle: Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long (usually > 14) carbon chains which can be saturated (no carbon-carbon double bonds) are unsaturated
FATTY ACIDS IN PLASMA BY GC/MS - Code GC75010
 FATTY ACIDS IN PLASMA BY GC/MS - Code GC75010 BIOCHEMISTRY The term fatty acids (abbreviation FA, English Fatty Acids) are indicated aliphatic monocarboxylic acids. They are, with few exceptions, long
FATTY ACIDS IN PLASMA BY GC/MS - Code GC75010 BIOCHEMISTRY The term fatty acids (abbreviation FA, English Fatty Acids) are indicated aliphatic monocarboxylic acids. They are, with few exceptions, long
FATTY ACIDS (FAs) SIMPLE AND COMPLEX LIPIDS
 FATTY ACIDS (FAs) SIMPLE AND COMPLEX LIPIDS Dicarboxylic acids, ketone bodies. Department of General Chemistry Structure and classification of lipids Lipids can be divided into five categories, on the
FATTY ACIDS (FAs) SIMPLE AND COMPLEX LIPIDS Dicarboxylic acids, ketone bodies. Department of General Chemistry Structure and classification of lipids Lipids can be divided into five categories, on the
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules
 Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Introduction to Lipid Chemistry
 Introduction to Lipid Chemistry Benjamin Schwartz Ontario SCC Education Day September 18, 2018 Lipid knowledge for the personal care industry What is a Lipid? Lipids are fatty acids and their derivatives,
Introduction to Lipid Chemistry Benjamin Schwartz Ontario SCC Education Day September 18, 2018 Lipid knowledge for the personal care industry What is a Lipid? Lipids are fatty acids and their derivatives,
Chapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids
 common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
INTEGRATIVE MEDICINE BLOOD - EDTA Result Range Units
 D Collected : 00-00-0000 INTEGRATIVE MEDICINE BLOOD - EDTA Result Range Units RED CELL FATTY ACID PROFILE Red Cell Fatty Acid Summary Saturated Fats, Total 36.99 19.30-39.40 Monounsaturated Fats, Total
D Collected : 00-00-0000 INTEGRATIVE MEDICINE BLOOD - EDTA Result Range Units RED CELL FATTY ACID PROFILE Red Cell Fatty Acid Summary Saturated Fats, Total 36.99 19.30-39.40 Monounsaturated Fats, Total
ANNEX. to the. COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No /..
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, XXX SANCO/10387/2013 Rev. 1 ANNEX (POOL/E3/2013/10387/10387R1-EN ANNEX.doc) D030733/02 [ ](2014) XXX draft ANNEX 1 ANNEX to the COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No /.. granting
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, XXX SANCO/10387/2013 Rev. 1 ANNEX (POOL/E3/2013/10387/10387R1-EN ANNEX.doc) D030733/02 [ ](2014) XXX draft ANNEX 1 ANNEX to the COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No /.. granting
N a t i o n a l M e a s u r e m e n t I n s t i t u t e
 Page: 1 of 5 Client : KIMBERLEY WILD GUBINGE Job No. : KIMB10/170116 MUNGET ABORIGINAL CORPORATION Quote No. : QT-02094 PENDER BAY Order No. : DAMPIER PENINSULA WA 6725 Date Sampled : Date Received : 16-JAN-2017
Page: 1 of 5 Client : KIMBERLEY WILD GUBINGE Job No. : KIMB10/170116 MUNGET ABORIGINAL CORPORATION Quote No. : QT-02094 PENDER BAY Order No. : DAMPIER PENINSULA WA 6725 Date Sampled : Date Received : 16-JAN-2017
MCQS ON LIPIDS. Dr. RUCHIKA YADU
 MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 5 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 25 th 2013 Mohammad Abu Dosh Sheet 5.. Lipids ( Dr. Nafith ) : Classification of fatty acids : - they are classified depending on the existence of double bonds to : 1) Saturated
5 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 25 th 2013 Mohammad Abu Dosh Sheet 5.. Lipids ( Dr. Nafith ) : Classification of fatty acids : - they are classified depending on the existence of double bonds to : 1) Saturated
ESSENTIAL FATTY ACIDS - RED CELL
 Healthscope Functional Pathology 1868 Dandenong Road, Clayton, Victoria 3168, Australia www.functionalpathology.com.au ABN 62 006 823 089 T 1300 55 44 80 F 03 8540 5555 infofp@healthscope.com.au LAB No:
Healthscope Functional Pathology 1868 Dandenong Road, Clayton, Victoria 3168, Australia www.functionalpathology.com.au ABN 62 006 823 089 T 1300 55 44 80 F 03 8540 5555 infofp@healthscope.com.au LAB No:
Saba Al Fayoumi. Nour Hamdan. Bann Khraisat. Dr. Mamoun Ahram
 9 Saba Al Fayoumi Nour Hamdan Bann Khraisat Dr. Mamoun Ahram Proteoglycans and glycoproteins have been previously discussed and the differences between them have been noted. Protein glycosylation (protein-linked
9 Saba Al Fayoumi Nour Hamdan Bann Khraisat Dr. Mamoun Ahram Proteoglycans and glycoproteins have been previously discussed and the differences between them have been noted. Protein glycosylation (protein-linked
Chapter 11: Lipids. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
Lipids. Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals. Storage Lipids: derivatives of fatty acids. 11/21/10
 1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids
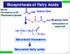 Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids CH 511 ource b-oxidation of FA Glycolysis of glucose n H CoA Acetyl CoA CoA Malonyl CoA Carboxylation of acetyl CoA H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 n-1 CoA aturated thioesters aturated fatty
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids CH 511 ource b-oxidation of FA Glycolysis of glucose n H CoA Acetyl CoA CoA Malonyl CoA Carboxylation of acetyl CoA H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 n-1 CoA aturated thioesters aturated fatty
Fatty acids and cardiovascular health: current evidence and next steps
 Fatty acids and cardiovascular health: current evidence and next steps Emanuele Di Angelantonio, MD, PhD Department of Public Health and Primary Care NICE guidelines on fatty acids Eliminate the use of
Fatty acids and cardiovascular health: current evidence and next steps Emanuele Di Angelantonio, MD, PhD Department of Public Health and Primary Care NICE guidelines on fatty acids Eliminate the use of
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1
 Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
26.1 Acetyl Coenzyme A
 Chapter 26 Lipids Lipids Lipids are naturally occurring substances grouped together on the basis of a common property they they are more soluble in nonpolar solvents than in water. Some of the most important
Chapter 26 Lipids Lipids Lipids are naturally occurring substances grouped together on the basis of a common property they they are more soluble in nonpolar solvents than in water. Some of the most important
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids
 I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
Table S1. Identified metabolites in rats plasma
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Table S1. Identified metabolites in rats plasma NO Retention time Metabolites Level
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Table S1. Identified metabolites in rats plasma NO Retention time Metabolites Level
: Overview of EFA metabolism
 Figure 1 gives an overview of the metabolic fate of the EFAs when consumed in the diet. The n-6 and n-3 PUFAs when consumed in the form of dietary triglyceride from various food sources undergoes digestion
Figure 1 gives an overview of the metabolic fate of the EFAs when consumed in the diet. The n-6 and n-3 PUFAs when consumed in the form of dietary triglyceride from various food sources undergoes digestion
CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS
 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS Schizochytrium DHA-Rich Algal Oil T=0, Lot#BY120306 Date received: 05/09/2012 NDI#: 11072012 Analysis for: Source-Omega LLC Attention: Scott Doughman 11312 US 15-501 North, Suite
CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS Schizochytrium DHA-Rich Algal Oil T=0, Lot#BY120306 Date received: 05/09/2012 NDI#: 11072012 Analysis for: Source-Omega LLC Attention: Scott Doughman 11312 US 15-501 North, Suite
Part 4. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
 MASS SPECTRA OF PYRROLIDIE DERIVATIVES Part 4. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids As was described for dienes, the interpretation of mass spectra of pyrrolidides is similar to that for monoenes in that it is
MASS SPECTRA OF PYRROLIDIE DERIVATIVES Part 4. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids As was described for dienes, the interpretation of mass spectra of pyrrolidides is similar to that for monoenes in that it is
REP15/FO Appendix III 1. PROPOSED DRAFT CODEX STANDARD FOR FISH OILS (at Step 5 of the Procedure)
 REP15/FO Appendix III 1 PROPOSED DRAFT CODEX STANDARD FOR FISH OILS (at Step 5 of the Procedure) Appendix III 1. Scope This Standard applies to the fish oils described in section 2 that are presented in
REP15/FO Appendix III 1 PROPOSED DRAFT CODEX STANDARD FOR FISH OILS (at Step 5 of the Procedure) Appendix III 1. Scope This Standard applies to the fish oils described in section 2 that are presented in
Use natural fish oil with 2g daily dose? Yes Use other omega-3? Replicate test? Date of birth
 Fatty Acid Analysis NORSAN Fatty Acid Analysis Analyse-ID RL44UA52 Date of analysis 31.03.2017 Country GB Sex Male Use natural fish oil with 2g daily dose? Yes Use other omega-3? No Replicate test? Yes
Fatty Acid Analysis NORSAN Fatty Acid Analysis Analyse-ID RL44UA52 Date of analysis 31.03.2017 Country GB Sex Male Use natural fish oil with 2g daily dose? Yes Use other omega-3? No Replicate test? Yes
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
Fatty acids, cardiovascular disease and diabetes
 Fatty acids, cardiovascular disease and diabetes Rajiv Chowdhury, Nita Forouhi 28 th October 2015 Workshop on nutritional biomarkers A joint PHRI/MRC Epidemiology Unit Initiative Population nutrient goal
Fatty acids, cardiovascular disease and diabetes Rajiv Chowdhury, Nita Forouhi 28 th October 2015 Workshop on nutritional biomarkers A joint PHRI/MRC Epidemiology Unit Initiative Population nutrient goal
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE. Fatty acids and heart disease. Kay-Tee Khaw
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE Fatty acids and heart disease Kay-Tee Khaw Bristol 3 October 2013 Yerushalmy J Hilleboe HE NY State J Med 1957 Coronary heart disease death rates in relation to blood cholesterol
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE Fatty acids and heart disease Kay-Tee Khaw Bristol 3 October 2013 Yerushalmy J Hilleboe HE NY State J Med 1957 Coronary heart disease death rates in relation to blood cholesterol
4 Types of Organic Polar Reactions
 Objective 10 Apply Reactivity Principles to Elimination Reactions: identify structural features (alpha C, H on beta C, LG) Use curved arrows to predict product. Compare E1 vs. E2 mechanisms. 4 Types of
Objective 10 Apply Reactivity Principles to Elimination Reactions: identify structural features (alpha C, H on beta C, LG) Use curved arrows to predict product. Compare E1 vs. E2 mechanisms. 4 Types of
Lipid Structure and Function
 Lipid Structure and Function ommon Physical Properties of Lipids Soluble in non-polar organic solvents ontain,, O Sometimes N & P Includes fats and oils mostly triglycerides Fat: solid at room temperature
Lipid Structure and Function ommon Physical Properties of Lipids Soluble in non-polar organic solvents ontain,, O Sometimes N & P Includes fats and oils mostly triglycerides Fat: solid at room temperature
Lecture: 26 OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS
 Lecture: 26 OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS Fatty acids obtained by hydrolysis of fats undergo different oxidative pathways designated as alpha ( ), beta ( ) and omega ( ) pathways. -oxidation -Oxidation of fatty
Lecture: 26 OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS Fatty acids obtained by hydrolysis of fats undergo different oxidative pathways designated as alpha ( ), beta ( ) and omega ( ) pathways. -oxidation -Oxidation of fatty
Lecture 25: Polymers and Biopolymers
 Lecture 25: Polymers and Biopolymers In the previous lecture we learned that by using carbon as the primary backbone, we can create a seemingly endless array of molecules built on covelent bonds to carbon.
Lecture 25: Polymers and Biopolymers In the previous lecture we learned that by using carbon as the primary backbone, we can create a seemingly endless array of molecules built on covelent bonds to carbon.
Figure 1 Separation of Ginger oil by (a) Cold Maceration (b) Hot Extraction (c) Liquid- Liquid Extraction -
 Effect of Methods of Separation on Ginger Oil Method of extractions affects how many components of a sample is successfully extracted from the sample. Figure one shows the chromatogram obtained for ginger
Effect of Methods of Separation on Ginger Oil Method of extractions affects how many components of a sample is successfully extracted from the sample. Figure one shows the chromatogram obtained for ginger
Lipids Definition. Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
BCM 221 LECTURES OJEMEKELE O.
 BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202
 General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
Comparison of Nutrients, Nutrient Ratios and Other Food Components in NDSR and the ASA24
 Comparison of Nutrients, Nutrient Ratios and Other Food Components in and the Category Primary Energy Sources Alcohol Total Fat Total Protein Energy (kilocalories) Total Carbohydrate Energy (kilojoules)
Comparison of Nutrients, Nutrient Ratios and Other Food Components in and the Category Primary Energy Sources Alcohol Total Fat Total Protein Energy (kilocalories) Total Carbohydrate Energy (kilojoules)
Recap: A little chemistry helps to understand a lot of biology
 Recap: A little chemistry helps to understand a lot of biology Covalent Bonds Polar and Non-Polar Electronegativity is key! Non-covalent bonds: Intra and inter molecular interactions Hydrogen Bonds Ionic
Recap: A little chemistry helps to understand a lot of biology Covalent Bonds Polar and Non-Polar Electronegativity is key! Non-covalent bonds: Intra and inter molecular interactions Hydrogen Bonds Ionic
COMMISSION DIRECTIVE 2004/4/EC
 22.1.2004 L 15/25 COMMISSION DIRECTIVE 2004/4/EC of 15 January 2004 amending Directive 96/3/EC granting a derogation from certain provisions of Council Directive 93/43/EEC on the hygiene of foodstuffs
22.1.2004 L 15/25 COMMISSION DIRECTIVE 2004/4/EC of 15 January 2004 amending Directive 96/3/EC granting a derogation from certain provisions of Council Directive 93/43/EEC on the hygiene of foodstuffs
LIPID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
Biochemical changes and fatty acid profiling of consecutively used fried groundnut oil
 2018; 6(2): 231-236 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2018; 6(2): 231-236 2018 IJCS Received: 01-01-2018 Accepted: 02-02-2018 NP Bodar UK Kandoliya Dr. PJ Rathod NV Bhadja VK Bajaniya Dr. BA Golakiya
2018; 6(2): 231-236 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2018; 6(2): 231-236 2018 IJCS Received: 01-01-2018 Accepted: 02-02-2018 NP Bodar UK Kandoliya Dr. PJ Rathod NV Bhadja VK Bajaniya Dr. BA Golakiya
Fatty Acid Mass Spectrometry Protocol Updated 10/11/2007 By Daren Stephens
 Fatty Acid Mass Spectrometry Protocol Updated 10/11/2007 By Daren Stephens Synopsis: This protocol describes the standard method for extracting and quantifying free fatty acids found in cells and media
Fatty Acid Mass Spectrometry Protocol Updated 10/11/2007 By Daren Stephens Synopsis: This protocol describes the standard method for extracting and quantifying free fatty acids found in cells and media
Part 1: General Structure & Function of Lipids
 CND/S 412 Biochemistry Lipids Part 1: General Structure & Function of Lipids Jess Keane BSc PG Cert mntoi jess@cnelm.co.uk Lipid Classification Fatty Acids (FAs) - monomers Triglycerides: 3 FAs esterified
CND/S 412 Biochemistry Lipids Part 1: General Structure & Function of Lipids Jess Keane BSc PG Cert mntoi jess@cnelm.co.uk Lipid Classification Fatty Acids (FAs) - monomers Triglycerides: 3 FAs esterified
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE
 BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
Non-Conjugated Double Bonds
 1 H-NMR Spectroscopy of Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives Non-Conjugated Double Bonds The introduction of one double bond gives rise to several peaks in the NMR spectrum compared to the saturated chains
1 H-NMR Spectroscopy of Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives Non-Conjugated Double Bonds The introduction of one double bond gives rise to several peaks in the NMR spectrum compared to the saturated chains
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 10 Lipids
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids Storage lipids: TG lipid 의기능 : 1 Energy source 3 Electrical insulator 2 Thermal insulator 4 Membrane 의구성성분, 방수, 부력, cofactor, signaling 등 지방대사이상 : obesity, atherosclerosis,
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids Storage lipids: TG lipid 의기능 : 1 Energy source 3 Electrical insulator 2 Thermal insulator 4 Membrane 의구성성분, 방수, 부력, cofactor, signaling 등 지방대사이상 : obesity, atherosclerosis,
Macromolecules: introduction on structural features and most important functions
 Macromolecules: introduction on structural features and most important functions 1 Outline Atomic and molecular composition of living matter Carbohydrates Nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides Aminoacids
Macromolecules: introduction on structural features and most important functions 1 Outline Atomic and molecular composition of living matter Carbohydrates Nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides Aminoacids
Lipids and Fatty Acids
 Lipids and Fatty Acids Objectives: 1. What are Lipids? properties glycerolipids vs. isoprenoids glycerolipid structure glycerolipid nomenclature 2. Fatty acid biosynthesis ellular localization Substrate
Lipids and Fatty Acids Objectives: 1. What are Lipids? properties glycerolipids vs. isoprenoids glycerolipid structure glycerolipid nomenclature 2. Fatty acid biosynthesis ellular localization Substrate
Dr. Dicken Weatherby's "Foundations of Functional Diagnosis" Training INSIDER S GUIDE. Dicken Weatherby, N.D.
 Dr. Dicken Weatherby's "Foundations of Functional Diagnosis" Training INSIDER S GUIDE Functional Diagnosis of Essential fatty acids By http://www.fmtrainingcenter.com Limits of Liability & Disclaimer of
Dr. Dicken Weatherby's "Foundations of Functional Diagnosis" Training INSIDER S GUIDE Functional Diagnosis of Essential fatty acids By http://www.fmtrainingcenter.com Limits of Liability & Disclaimer of
Fundamentals of Oils & Fats by Albert J. Dijkstra, PhD
 Fundamentals of ils & Fats by Albert J. Dijkstra, PhD Ignace Debruyne, PhD ignace.debruyne@gmail.com Fundamentals of Edible il Processing and Refining Saturday, May 3, 2014 Topics to be discussed Composition
Fundamentals of ils & Fats by Albert J. Dijkstra, PhD Ignace Debruyne, PhD ignace.debruyne@gmail.com Fundamentals of Edible il Processing and Refining Saturday, May 3, 2014 Topics to be discussed Composition
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson
 Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Interpretive Guide for Fatty Acids
 Name Potential Responses Metabolic Association Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Alpha Linolenic L Add flax and/or fish oil Essential fatty acid Eicosapentaenoic L Eicosanoid substrate Docosapentaenoic L Add fish
Name Potential Responses Metabolic Association Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Alpha Linolenic L Add flax and/or fish oil Essential fatty acid Eicosapentaenoic L Eicosanoid substrate Docosapentaenoic L Add fish
STANDARD FOR FISH OILS CODEX STAN Adopted in 2017.
 STANDARD FOR FISH OILS CODEX STAN 329-2017 Adopted in 2017. CODEX STAN 329-2017 2 1. SCOPE This Standard applies to the fish oils described in section 2 that are presented in a state for human consumption.
STANDARD FOR FISH OILS CODEX STAN 329-2017 Adopted in 2017. CODEX STAN 329-2017 2 1. SCOPE This Standard applies to the fish oils described in section 2 that are presented in a state for human consumption.
