Resident Short Review. Fabry Nephropathy. Prudence Colpart, MD; Sophie Félix, MD
|
|
|
- Annabel Melton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Resident Short Review Fabry disease is a rare X-linked recessive lysosomal storage disease. Multiple mutations of the GLA gene lead to a deficient or absent activity of the lysosomal enzyme a- galactosidase A, resulting in progressive glycotriaosylceramide accumulation in many organs. Low a-galactosidase A activity and mutations in the GLA gene confirm the diagnosis. Clinical signs are multisystemic, heterogeneous, and progressive. Renal, cardiac, and neurovascular involvements are the main life-threatening complications, highlighting the importance of an early initiation of enzyme replacement therapy improving long-term outcome. Fabry nephropathy lesions are characterized by a cell vacuolization of glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and arteries and by ultrastructural myelin bodies. The main histologic differential diagnoses are toxicity of lysosomal inhibitors and other renal lipidoses. Renal biopsies are not necessary for diagnosis but have an important role in the evaluation of disease evolution and treatment efficiency, which is a major challenge for improving outcome and quality of life. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2017;141: ; doi: /arpa RS) Fabry Nephropathy Prudence Colpart, MD; Sophie Félix, MD no residual a-galactosidase A activity, displaying all the characteristic signs of the disease. Clinical signs and symptoms vary widely in heterozygous females. This phenotypic heterogeneity is due to lyonization, a process whereby one copy of the X-chromosome is randomly inactivated in all the cells of the female embryo, so that heterozygous females are essentially a mosaic of normal and mutant cells in varying proportions. 2 Accumulation of Gb3 occurs within lysosomes throughout the body, leading to progressive organ damage resulting in a heterogeneous and multisystemic disease. The delay in diagnosis is estimated at 12 to 15 years. CLINICAL FEATURES Disease manifestations appear in childhood, later for girls than for boys. 3 Pain is a frequent sign characterized by intense episodic burning of the soles and hands. Neurologic symptoms also include acroparaesthesia, hypohidrosis, hearing loss, tinnitus, and vertigo. Angiokeratoma, purple papules on upper thighs and mucosal areas, is a typical but not specific symptom. Classical ophthalmologic signs are cornea verticillata and Fabry cataract. Gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain and diarrhea might be Fabry disease is a panethnic lipidosis first described in found. Osteopenia and osteoporosis are more frequent as 1898 by Johannes Fabry and William Anderson. It is the compared to the general population. A quiescent stage of second most frequent lysosomal storage disease after the disease is described in the second to third decade of life. Gaucher disease. Its incidence rate is estimated at between As the disease progresses, renal, cardiovascular, and 1 in and 1 in births worldwide by the Fabry cerebrovascular complications appear around the age of 30 Outcome Survey, the biggest European Fabry disease years. Renal involvement often begins with proteinuria. It database. 1 seems to be the most important predictor for renal progression. 4 Glycotriaosylceramide deposits, in all renal PATHOGENESIS cell types, lead to gradual deterioration of renal function progressing to end-stage renal disease, requiring hemodialysis or renal transplant in the fourth or fifth decade of life. The GLA gene consists of 7 exons situated in position q22.1 on chromosome X, which code a-galactosidase A. Cardiac symptoms include dyspnea, angina, arrhythmia, This lysosomal enzyme hydrolyzes the glycotriaosylceramides (Gb3) into galactoses and lactosylceramides. More and conduction disorders responsible for syncope and sudden death. It results from myocardial infarction, terminal than 475 mutations of GLA gene have been reported, cardiac failure, and malignant arrhythmias. Transient resulting in a deficiency or a lack in a-galactosidase A, ischemic attacks and ischemic strokes are the main which leads to Gb3 lysosomal accumulation in many tissues. cerebrovascular complications. Fabry disease follows a recessive X-linked pattern of inheritance. Classically, it affects hemizygous males with Atypical male variants have a milder phenotype than the classical Fabry disease, which is caused by a residual a- galactosidase A activity that varies between 2% and 20% of Accepted for publication October 13, normal activity, associated with certain types of GLA From the Department of Pathology, University Hospital of mutations. Renal or cardiac variants have disease manifestations confined to the kidneys and the heart, respectively, Besançon, CHRU, Besançon, France. The authors have no relevant financial interest in the products or without other systemic involvement. Heterozygous females companies described in this article. Reprints: Prudence Colpart, MD, Department of Pathology, generally present an asymptomatic clinical form. However, University Hospital of Besançon, CHRU, 3, bd Alexandre Fleming, an equally severe form of the disease can occur in females as Besançon Cedex, France ( prue7@hotmail.fr). in males. Random inactivation of 1 chromosome X in the Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, August 2017 Fabry Nephropathy Colpart & Félix 1127
2 cells of various tissues and organs (lyonization) explains the phenotypic heterogeneity in females. 6 The European consensus on laboratory diagnostics of Fabry disease recommends the assessment of a-galactosidase A activity in plasma and leukocytes in males. However, GLA gene molecular analysis is necessary to confirm the diagnosis in heterozygous females because they express highly variable levels of the enzyme owing to lyonization. 7 HISTOPATHOLOGY FINDINGS On light microscopy, glomeruli show a vacuolization of podocytes, mesangial or endothelial cells, and sometimes, glomerular parietal epithelial cells, due to Gb3 inclusions. 8,9 Vacuolization is also present in epithelial cells of distal tubules, Henle loops, and collecting ducts. The involvement of proximal tubular epithelial cells is uncommon. Vascular lesions include depositions in myocytes and endothelial cells, sometimes associated with hyaline deposits in the media of arteries and arterioles (Figure 1, A through C). Glycotriaosylceramide accumulation leads to procoagulant and proinflammatory effects, resulting in focal, segmental, and global glomerulosclerosis, interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, and thickening of vascular walls. 10 With progression of the disease, there is fusion of podocyte foot processes in association with increasing proteinuria. A decrease in endothelial fenestration and a duplication of the glomerular basement membrane have been reported. 11,12 Characteristic cytoplasmic deposits of Gb3 are removed during routine paraffin processing. On frozen sections, Gb3 can be demonstrated with several approaches, including staining with periodic acid Schiff, Hale, Luxol fast blue, Oil red O, and Sudan black. On light microscopy, a good morphologic method to demonstrate Fabry deposits is to use tissues fixed in glutaraldehyde, embedded in Epon, and stained with toluidine blue dye, which yields dark blue cytoplasmic inclusions in glomeruli, tubules, and arteries (Figure 2, A through D). ANCILLARY STUDIES Immunofluorescence is not contributory, showing no specific deposits. However, this technique is useful to eliminate more common renal diseases causing proteinuria (such as immunoglobulin A nephropathy and type I membranous glomerulonephritis), especially in cases of Fabry disease at early stages presenting an isolated proteinuria. Under polarized light, inclusions exhibit birefringence and orange autofluorescence on tissues stained with hematoxylin-eosin-saffron. Ultrastructural analysis shows intracellular osmiophilic, lamellated membrane structures with a concentric pattern called myelin bodies or with elongated stripes called zebra bodies. The periodicity of the lamellated membrane structures is estimated to be 4 to 5 nm on routine thin sections and 14 to 15 nm on frozen sections, owing to better tissue preservation. They have the same topography as on light microscopy (Figure 2, A through D). DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES The main histologic differential diagnoses are other nephropathies with foamy podocytes, such as lysosomal inhibitor toxicity and other renal lipidoses (GM1 gangliosidosis, I-cell disease, Hurler syndrome, Niemann-Pick disease, Farber disease, and infantile nephrosialidosis). 13,14 Ultrastructural morphology and cellular distribution of Figure 1. Fabry nephropathy on light microscopy. A, Cytoplasm of podocytes appears expanded, foamy, pale, and lacy owing to lipid deposits. B, Vacuolization of distal tubular epithelial cells. C, Hyaline deposits (arrow) in the media of an artery (hematoxylin-eosin-saffron, original magnification 3200 [A]; Masson trichrome, original magnification 3400 [B]; periodic acid Schiff, original magnification 3200 [C]) Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, August 2017 Fabry Nephropathy Colpart & Félix
3 Figure 2. Fabry nephropathy on toluidine blue stained semithin sections and by electron microscopy (frozen tissues). A, Dense, dark blue granules in the cytoplasm of distal tubular epithelial cells. B, Myelin bodies in a distal tubule. C, Glycotriaosylceramides in the cytoplasm of endothelial cells (red arrow) and myocytes (blue arrow). D, Zebra bodies in an arteriole (toluidine blue, original magnifications 3400 [A] and [C]; electron micrograph, original magnifications [B] and [D]). Courtesy of Viviane Gnemmi, MD (CHRU de Lille, France). lysosomal storage material are the most useful criteria to differentiate Fabry disease from its mimics (Table). Indeed, no other renal lipidosis shows prominent and widespread myelin bodies in podocytes, mesangial cells, endothelial cells, proximal tubules, interstitial cells, and arterial endothelial cells. For example, curvilinear and granular osmiophilic deposits found in Batten disease and the membrane-bound vacuoles containing fibrillogranular material in Hurler syndrome have a completely different aspect from Fabry myelin bodies. Moreover, Niemann-Pick disease can show myelin-like figures, but they are absent from mesangial cells and arterial cells contrary to Fabry disease. The main alternative diagnostic consideration is iatrogenic renal lipidosis, which has ultrastructural morphologic features not distinguishable from Fabry myelin bodies. 15 Iatrogenic renal lipidoses have been reported in association with different lysosomal inhibitors (chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, amiodarone), which inhibit lysosomal enzyme a-galactosidase A. Because of the inability to distinguish genetic and iatrogenic conditions based on morphologic grounds alone, a diagnosis of Fabry disease must be confirmed by the demonstration of decreased a-galactosidase A activity and/or a mutation in the GLA gene. Therefore, myelin-like inclusions are not entirely specific for Fabry disease, although they are highly characteristic. Certain drugs can cause cellular injury indistinguishable from classic Fabry disease. This needs to be kept in mind in the evaluation of typical pathologic lesions in case of history of exposure to lysosomal inhibitors. CURRENT TREATMENT Since 2001, Fabry disease treatment has been revolutionized by the introduction of an intravenous enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) using recombinant human a- galactosidase A. In Europe, there are currently 2 commercially available enzyme preparations. Agalsidase alpha (Replagal, Shire, Cambridge, Massachusetts) is infused at a dose of 0.2 mg/kg every 2 weeks. Agalsidase beta (Fabrazyme, Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, Massachusetts) is used at a dose of 1 mg/kg every 2 weeks. The safety and efficiency of both enzymes have been assessed in Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, August 2017 Fabry Nephropathy Colpart & Félix 1129
4 Pathologic Entity Histologic Differential Diagnoses of Fabry Nephropathy on Electron Microscopy a Podocyte Mesangial Cell Endothelial Cell Cellular Distribution Proximal Tubule Distal Henle Tubule Loop Interstitium Artery Electron Microscopy Fabry disease þ þ þ þ þ þ Osmiophilic, lamellated membrane structures with a concentric pattern (myelin bodies) or with elongated stripes (zebra bodies); diameter: lm; lamellar periodicity: 4 15 nm Chloroquine þ þ þ þ þ þ Myelin-like lamellated bodies, toxicity GM1 gangliosidosis curvilinear bodies þ þ þ Membrane-bound empty vacuoles occasionally containing stacks or concentric lamellar material (periodicity: nm) I-cell disease þ /þ /þ Membrane-bound empty vacuoles occasionally containing fibrillogranular or lamellar material (residual membranous structures) Hurler syndrome þ /þ Membrane-bound, empty vacuoles or containing fibrillogranular material Niemann-Pick disease þ þ þ þ þ Concentrically laminated, tightly packed myelin-like figures Farber disease þ þ Osmiophilic granules and bundles of curvilinear structures (periodicity: nm) Infantile nephrosialidosis þ þ þ þ Membrane-bound, almost empty vacuoles containing occasional granular and electron-dense material Gaucher disease þ Membrane-bound packets of lipid material arranged in microtubules (diameter: nm) LCAT deficiency þ þ /þ Heterogeneous lipid deposits (partly electron lucent, partly osmiophilic), curvilinear and granular debris in epimembranous, intramembranous, subendothelial, and mesangial locations Metachromatic leukodystrophy /þ þ þ Stacked lamellar disks (6 8 nm) in honeycomb or parallel array Batten disease /þ þ þ þ Membrane-bound, rectilinear, curvilinear, or granular cytoplasmic inclusions, granular osmiophilic deposits Sandhoff disease þ Electron-dense, finely granular or lamellated bodies arranged in concentric or parallel stacks Refsum disease /þ þ þ þ Perinuclear cytoplasmic vacuoles and membranebound vesicles (glomerular, tubular epithelial cells), crystalloid, quadrangular, microtubular inclusions (400 Å) (distal tubules, loop of Henle) Wolman disease þ þ Cholesterol clefts and neutral lipids (dropletlike structures) Abbreviations: LCAT, lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase; þ, presence of stored material; /þ, stored material rarely present. a Empty entries denote absence of stored material Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, August 2017 Fabry Nephropathy Colpart & Félix
5 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Therapeutic management of Fabry disease is multidisciplinary, including specific treatment with ERT, symptomatic and prophylactic therapy. Histologically, there is a total clearance of Gb3 lysosomal accumulation in endothelial and mesangial cells after 11 months of ERT by agalsidase alpha or beta. Posttherapeutic effects on myocyte inclusions are more moderate. The reduction of Gb3 in podocytes and tubular epithelial cells is milder than in other cells. The podocyte clearance is correlated with the cumulative dose of agalsidase. 16 This observation is another argument for early ERT introduction to improve symptomatology, quality of life, and prognosis. The International Study Group of Fabry Nephropathy scored histologic changes on light microscopy and toluidine blue stained semithin sections. 17 The score quantifies Gb3 density deposition (mild, moderate, and severe) in glomeruli, interstitium, and vessels and progressive lesions (glomerulosclerosis, ischemic glomeruli, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis). Some studies have underlined the role of kidney biopsies for the follow-up of the disease evolution to identify the presence of significant histologic changes before the decrease of renal function. 17,18 PROGNOSIS Cardiac morbimortality is the primary cause of death in Fabry disease. Average life expectancy is approximately 50 years in males and 70 years in females. CONCLUSIONS Fabry disease is a lysosomal storage disease involving many organs. Clinical symptoms are heterogeneous and aspecific. The diagnosis is established by a low a-galactosidase A activity and the identification of a mutation in the GLA gene. Histologically, renal involvement is characterized by vacuolization in glomerular cells, tubular epithelial cells, and vascular cells. Toluidine blue is particularly useful to reveal Gb3 deposits and electron microscopy examination shows myelin or zebra bodies. The progression of kidney disease is characterized by segmental and global glomerulosclerosis, tubular atrophy, and interstitial fibrosis. Histologic evidence is not needed for the diagnosis of Fabry disease. However, renal biopsy is an important tool to evaluate the renal progression of the disease and the efficiency of ERT. References 1. Mehta A, Clarke JT, Giugliani R, et al. Natural course of Fabry disease: changing pattern of causes of death in FOS Fabry Outcome Survey. J Med Genet. 2009;46(8): Garman SC, Garboczi DN. The molecular defect leading to Fabry Disease: structure of human a-galactosidase. J Mol Biol. 2004;337(2): Germain DP. Fabry disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010;5: Wanner C, Oliveira JP, Ortiz A, et al. prognostic indicators of renal disease progression in adults with Fabry disease: natural history data from the Fabry Registry. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5(12): Sessa A, Meroni M, Battini G, et al. Renal involvement in Anderson-Fabry disease. J Nephrol. 2003;16(2): Nakao S, Kodama C, Takenaka T, et al. Fabry disease: detection of undiagnosed hemodialysis patients and identification of a renal variant phenotype. Kidney Int. 2003;64(3): Gal A, Hughes DA, Winchester B. Toward a consensus in the laboratory diagnostics of Fabry disease: recommendations of a European expert group. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2011;34(2): D Agati VD, Jennette JC, Silva FG. Hereditary nephropathies. In: D Agati VD, Jennette JC, Silva FG, eds. AFIP Atlas of Nontumor Pathology Non-Neoplastic Kidney Diseases. 1st ed. Silver Spring, MD: ARP Press; 2005: Colvin RB. Fabry disease. In: Colvin RB, Chang A, eds. Diagnostic Pathology: Kidney Diseases. 2nd ed. Salt Lake City, UT: Amirsys; 2011: Fischer EG, Moore MJ, Lager DJ. Fabry disease: a morphologic study of 11 cases. Mod Pathol. 2006;19(10): Kanai T, Yamagata T, Ito T, et al. Foot process effacement with normal urinalysis in classic Fabry Disease. JIMD Rep. 2011;1: Najafian B, Svarstad E, Bostad L, et al. Podocyte injury and GL-3 accumulation are progressive in young patients with Fabry disease. Kidney Int. 2011;79(6): Faraggiana T, Churg J. Renal lipidoses: a review. Hum Pathol. 1987;18(7): Merscher S, Fornoni A. Podocyte pathology and nephropathy sphingolipids in glomerular diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014;5: Albay D, Adler SG, Philipose J, Calescibetta CC, Romansky SG, Cohen AH. Chloroquine induced lipidosis mimicking Fabry disease. Mod Pathol. 2005;18(5): Thurberg BL, Rennke H, Colvin RB, et al. Globotriaosylceramide accumulation in the Fabry kidney is cleared from multiple cell types after enzyme replacement therapy. Kidney Int. 2002;62(6): Fogo AB, Bostad L, Svarstad E, et al. Scoring system for renal pathology in Fabry disease: report of the International Study Group of Fabry Nephropathy (ISGFN). Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25(7): Noël LH, Laurent B, Grünfeld JP. La biopsie rénale dans la maladie de Fabry: étude multicentrique française. Nephrol Ther. 2012;8(6): Arch Pathol Lab Med Vol 141, August 2017 Fabry Nephropathy Colpart & Félix 1131
NEPHROPATHOLOGY- ELECTRON MICROSCOPY SEMINAR: CASE 2
 NEPHROPATHOLOGY- ELECTRON MICROSCOPY SEMINAR: CASE 2 ABSTRACT We present the case of a 32 years old woman with nephrotic range proteinuria. The proteinuria was first detected on a routine medical checkup,
NEPHROPATHOLOGY- ELECTRON MICROSCOPY SEMINAR: CASE 2 ABSTRACT We present the case of a 32 years old woman with nephrotic range proteinuria. The proteinuria was first detected on a routine medical checkup,
What s hiding behind IgA nephropathy?
 What s hiding behind IgA nephropathy? Bauerova L. Department of Pathology, the First Faculty of Medicine and General Hospital, Charles University Prague (nephropathology training: Department of Clinical
What s hiding behind IgA nephropathy? Bauerova L. Department of Pathology, the First Faculty of Medicine and General Hospital, Charles University Prague (nephropathology training: Department of Clinical
The use of pathology surrogate markers in Fabry Disease. Beth L. Thurberg MD PhD Vice President of Pathology Genzyme
 Disclaimer: Presentation slides from the Rare Disease Workshop Series are posted by the EveryLife Foundation for Rare Diseases for educational purposes only. They are for use by drug development professionals
Disclaimer: Presentation slides from the Rare Disease Workshop Series are posted by the EveryLife Foundation for Rare Diseases for educational purposes only. They are for use by drug development professionals
Hemizygous Fabry disease associated with IgA nephropathy: A case report
 1 Hemizygous Fabry disease associated with IgA nephropathy: A case report Fabry disease and IgA nephropathy Homare Shimohata 1, 3, Keigyou Yoh 1, Kenji Takada 2, Hiroaki Tanaka 2, Joichi Usui 1, Kouichi
1 Hemizygous Fabry disease associated with IgA nephropathy: A case report Fabry disease and IgA nephropathy Homare Shimohata 1, 3, Keigyou Yoh 1, Kenji Takada 2, Hiroaki Tanaka 2, Joichi Usui 1, Kouichi
FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D.
 FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D. Director, International Center for Fabry Disease Dean for Genetic & Genomic
FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D. Director, International Center for Fabry Disease Dean for Genetic & Genomic
Ordering Physician. Collected REVISED REPORT. Performed. IgG IF, Renal MCR. Lambda IF, Renal MCR. C1q IF, Renal. MCR Albumin IF, Renal MCR
 RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Medication Policy Manual. Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru391 Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015 Committee Approval Date: March 13, 2015 Next Review Date: March 2016 Effective Date: July
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru391 Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015 Committee Approval Date: March 13, 2015 Next Review Date: March 2016 Effective Date: July
Fabry disease: when to suspect it and how to treat it
 Fabry disease: when to suspect it and how to treat it Catalina Martín Cleary Alberto Ortiz Arduán, MD, PhD IIS-Fundacion Jimenez Diaz, UAM IRSIN, REDINREN Madrid, Spain Conflict of interest Consultant:
Fabry disease: when to suspect it and how to treat it Catalina Martín Cleary Alberto Ortiz Arduán, MD, PhD IIS-Fundacion Jimenez Diaz, UAM IRSIN, REDINREN Madrid, Spain Conflict of interest Consultant:
Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report:
 Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report: Proximal tubulopathy and light chain deposition disease presented as severe pulmonary hypertension with right-sided cardiac dysfunction and nephrotic
Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report: Proximal tubulopathy and light chain deposition disease presented as severe pulmonary hypertension with right-sided cardiac dysfunction and nephrotic
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Fabry Disease and the Kidneys
 Department of Human Genetics Division of Medical Genetics Lysosomal Storage Disease Center www.genetics.emory.edu Fabry Disease and the Kidneys What is Fabry Disease? Fabry disease (FD) is an X-linked
Department of Human Genetics Division of Medical Genetics Lysosomal Storage Disease Center www.genetics.emory.edu Fabry Disease and the Kidneys What is Fabry Disease? Fabry disease (FD) is an X-linked
Heart disease. Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS
 Heart disease Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS You have been given this brochure because your heart condition may be linked to Fabry disease, which is a rare,
Heart disease Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS You have been given this brochure because your heart condition may be linked to Fabry disease, which is a rare,
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease
 Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing proteinuria & haematuria Highlight diagnostic pitfalls Nephrotic
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing proteinuria & haematuria Highlight diagnostic pitfalls Nephrotic
Assessment report. for
 Assessment report for FABRAZYME agalsidase beta Assessment report on the shortage of Fabrazyme Overview of Shortage Period: Spontaneous Reports from June 2009 through 15 September and Registry Data from
Assessment report for FABRAZYME agalsidase beta Assessment report on the shortage of Fabrazyme Overview of Shortage Period: Spontaneous Reports from June 2009 through 15 September and Registry Data from
The principal characteristics of some of the more common heredofamilial
 Heredofamilial and Congenital Glomerular Disorders rthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The principal characteristics of some of the more common heredofamilial and congenital glomerular disorders are described
Heredofamilial and Congenital Glomerular Disorders rthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The principal characteristics of some of the more common heredofamilial and congenital glomerular disorders are described
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard
 Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: GLA DISORDER: Fabry disease HGNC ID: 4296 OMIM ID: 301500 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: GLA DISORDER: Fabry disease HGNC ID: 4296 OMIM ID: 301500 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic
Fabry disease: An underrecognized cause of proteinuria
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2008 International Society of Nephrology the renal consult Fabry disease: An underrecognized cause of proteinuria FC Fervenza 1, R Torra 2 and DJ Lager 3 1 Department
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2008 International Society of Nephrology the renal consult Fabry disease: An underrecognized cause of proteinuria FC Fervenza 1, R Torra 2 and DJ Lager 3 1 Department
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease
 Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease Herzinsuffizienzlunch Basel, 11.09.2018 Christiane Gruner Kardiologie, UniversitätsSpital Zürich Content Background / epidemiology Differential diagnosis Clinical presentations
Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease Herzinsuffizienzlunch Basel, 11.09.2018 Christiane Gruner Kardiologie, UniversitätsSpital Zürich Content Background / epidemiology Differential diagnosis Clinical presentations
Familial DDD associated with a gain-of-function mutation in complement C3.
 Familial DDD associated with a gain-of-function mutation in complement C3. Santiago Rodríguez de Córdoba, Centro de investigaciones Biológicas, Madrid Valdés Cañedo F. and Vázquez- Martul E., Complejo
Familial DDD associated with a gain-of-function mutation in complement C3. Santiago Rodríguez de Córdoba, Centro de investigaciones Biológicas, Madrid Valdés Cañedo F. and Vázquez- Martul E., Complejo
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome
 Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
CHAPTER 2. Primary Glomerulonephritis
 2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
Fabry Disease Glossary
 Fabry Disease Glossary A Acroparesthesia: A tingling sensation in the hands and feet. Angiokeratoma: Localized collection of thin-walled blood vessels covered by a cap of warty material. Also described
Fabry Disease Glossary A Acroparesthesia: A tingling sensation in the hands and feet. Angiokeratoma: Localized collection of thin-walled blood vessels covered by a cap of warty material. Also described
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus. With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs
 Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
NEPHROTIC SYNDROME OF ACQUIRED SYPHILIS-A MORPHOLOGICAL AND ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY
 NEPHROTIC SYNDROME OF ACQUIRED SYPHILIS-A MORPHOLOGICAL AND ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 3 To 7 A.H. Nagi, I.A. Naveed, A. Rashid ( Department of Pathology, Allama
NEPHROTIC SYNDROME OF ACQUIRED SYPHILIS-A MORPHOLOGICAL AND ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 3 To 7 A.H. Nagi, I.A. Naveed, A. Rashid ( Department of Pathology, Allama
Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis
 J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
C1q nephropathy the Diverse Disease
 C1q nephropathy the Diverse Disease Danica Galešić Ljubanović School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Dubrava University Hospital Zagreb, Croatia Definition Dominant or codominant ( 2+), mesangial staining
C1q nephropathy the Diverse Disease Danica Galešić Ljubanović School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Dubrava University Hospital Zagreb, Croatia Definition Dominant or codominant ( 2+), mesangial staining
The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced
 Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
FIBRILLARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, PITFALLS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
 FIBRILLARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, PITFALLS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Guillermo A. Herrera MD Louisiana State University, Shreveport Fibrils in bundles 10-20 nm d Diabetic fibrillosis
FIBRILLARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, PITFALLS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Guillermo A. Herrera MD Louisiana State University, Shreveport Fibrils in bundles 10-20 nm d Diabetic fibrillosis
Monoclonal Gammopathies and the Kidney. Tibor Nádasdy, MD The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
 Monoclonal Gammopathies and the Kidney Tibor Nádasdy, MD The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH Monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance (MGRS) Biopsies at OSU (n=475) between 2007 and 2016 AL or AH
Monoclonal Gammopathies and the Kidney Tibor Nádasdy, MD The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH Monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance (MGRS) Biopsies at OSU (n=475) between 2007 and 2016 AL or AH
THE URINARY SYSTEM. The cases we will cover are:
 THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness
 Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Running Title: Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Professor Perry Elliott MBBS; MD; FRCP; FESC; FACC Chair of Cardiovascular
Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Running Title: Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Professor Perry Elliott MBBS; MD; FRCP; FESC; FACC Chair of Cardiovascular
THE URINARY SYSTEM. The cases we will cover are:
 THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders
 The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders Dr Guy Besley, formerly Willink Biochemical Genetics Unit, Manchester Children s Hospital, Manchester M27 4HA, UK. Lysosomal disorders What
The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders Dr Guy Besley, formerly Willink Biochemical Genetics Unit, Manchester Children s Hospital, Manchester M27 4HA, UK. Lysosomal disorders What
Light-Chain Mediated Acute Tubular Interstitial Nephritis. A Poorly Recognized Pattern of Renal Disease in Patients With Plasma Cell Dyscrasia
 Light-Chain Mediated Acute Tubular Interstitial Nephritis A Poorly Recognized Pattern of Renal Disease in Patients With Plasma Cell Dyscrasia Xin Gu, MD; Guillermo A. Herrera, MD Context. Acute renal failure
Light-Chain Mediated Acute Tubular Interstitial Nephritis A Poorly Recognized Pattern of Renal Disease in Patients With Plasma Cell Dyscrasia Xin Gu, MD; Guillermo A. Herrera, MD Context. Acute renal failure
A Unique Disease Uniquely Experienced
 A Unique Disease Uniquely Experienced Understanding Fabry disease a serious, progressive disorder with complex pathology 1 Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder. 1 Caused by a deficiency
A Unique Disease Uniquely Experienced Understanding Fabry disease a serious, progressive disorder with complex pathology 1 Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder. 1 Caused by a deficiency
Fabry nephropathy: a review how can we optimize the management of Fabry nephropathy?
 Waldek and Feriozzi BMC Nephrology 2014, 15:72 REVIEW Open Access Fabry nephropathy: a review how can we optimize the management of Fabry nephropathy? Stephen Waldek 1* and Sandro Feriozzi 2 Abstract Fabry
Waldek and Feriozzi BMC Nephrology 2014, 15:72 REVIEW Open Access Fabry nephropathy: a review how can we optimize the management of Fabry nephropathy? Stephen Waldek 1* and Sandro Feriozzi 2 Abstract Fabry
HRZZ project: Genotype-Phenotype correlation in Alport's syndrome and Thin Glomerular Basement Membrane Nephropathy. Patohistological Aspects
 HRZZ project: Genotype-Phenotype correlation in Alport's syndrome and Thin Glomerular Basement Membrane Nephropathy Patohistological Aspects Petar Šenjug, MD 1 Professor Danica Galešić Ljubanović, MD,
HRZZ project: Genotype-Phenotype correlation in Alport's syndrome and Thin Glomerular Basement Membrane Nephropathy Patohistological Aspects Petar Šenjug, MD 1 Professor Danica Galešić Ljubanović, MD,
PAEDIATRIC MANAGEMENT KDIGO. Uma Ramaswami FRCPCH, MD Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust
 PAEDIATRIC MANAGEMENT Uma Ramaswami FRCPCH, MD Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust Disclosure of Interests UR has received travel grants and lecture fees from Shire HGT, Amicus and Genzyme; and advisory
PAEDIATRIC MANAGEMENT Uma Ramaswami FRCPCH, MD Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust Disclosure of Interests UR has received travel grants and lecture fees from Shire HGT, Amicus and Genzyme; and advisory
GALAFOLD (migalastat) oral capsule
 GALAFOLD (migalastat) oral capsule Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage
GALAFOLD (migalastat) oral capsule Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage
ataxia, head tremors and mild inappentence, was given palliative care
 2013-5-2 Cerebellum, Spleen-Raccoon Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION :College of Veterinary Medicine UC Davies Signalment: Wild-caught juvenile male raccoon, ( Procyon lotor)
2013-5-2 Cerebellum, Spleen-Raccoon Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION :College of Veterinary Medicine UC Davies Signalment: Wild-caught juvenile male raccoon, ( Procyon lotor)
Diabetic Nephropathy. Introduction/Clinical Setting. Pathologic Findings Light Microscopy. J. Charles Jennette
 12 Diabetic Nephropathy J. Charles Jennette Introduction/Clinical Setting Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome in a patient with diabetes mellitus that is characterized by persistent albuminuria,
12 Diabetic Nephropathy J. Charles Jennette Introduction/Clinical Setting Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome in a patient with diabetes mellitus that is characterized by persistent albuminuria,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
Dense deposit disease with steroid pulse therapy
 Case Report Dense deposit disease with steroid pulse therapy Jun Odaka, Takahiro Kanai, Takane Ito, Takashi Saito, Jun Aoyagi, and Mariko Y Momoi Abstract Treatment of dense deposit disease DDD has not
Case Report Dense deposit disease with steroid pulse therapy Jun Odaka, Takahiro Kanai, Takane Ito, Takashi Saito, Jun Aoyagi, and Mariko Y Momoi Abstract Treatment of dense deposit disease DDD has not
Case # 2 3/27/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Clinical history. Clinical history. Laboratory findings
 Case # 2 Christopher Larsen, MD Arkana Laboratories Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content
Case # 2 Christopher Larsen, MD Arkana Laboratories Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content
Examination of the light microscopic slide of renal biopsy specimens by utilizing Low-vacuum scanning electron microscope
 SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2017 Vol. 9 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Examination of the light microscopic slide of renal biopsy specimens by utilizing
SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2017 Vol. 9 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Examination of the light microscopic slide of renal biopsy specimens by utilizing
C3 Glomerulonephritis versus C3 Glomerulopathies?
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Kidneycentric Kidneycentric 2016 C3 Glomerulonephritis versus C3 Glomerulopathies? T. Keefe Davis Washington University School of Medicine
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Kidneycentric Kidneycentric 2016 C3 Glomerulonephritis versus C3 Glomerulopathies? T. Keefe Davis Washington University School of Medicine
CHAPTER 2 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
 CHAPTER 2 Sunita Bavanandan Lim Soo Kun 19 5th Report of the 2.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main primary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the years 2005-2012. Minimal change
CHAPTER 2 Sunita Bavanandan Lim Soo Kun 19 5th Report of the 2.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main primary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the years 2005-2012. Minimal change
Index. electron microscopy, 81 immunofluorescence microscopy, 80 light microscopy, 80 Amyloidosis clinical setting, 185 etiology/pathogenesis,
 A Acute antibody-mediated rejection (Acute AMR) clinical features, 203 clinicopathologic correlations, 206 pathogenesis, 205 206 204 205 light microscopy, 203 204 Acute cellular rejection (ACR) clinical
A Acute antibody-mediated rejection (Acute AMR) clinical features, 203 clinicopathologic correlations, 206 pathogenesis, 205 206 204 205 light microscopy, 203 204 Acute cellular rejection (ACR) clinical
RENAL EVENING SPECIALTY CONFERENCE
 RENAL EVENING SPECIALTY CONFERENCE Harsharan K. Singh, MD The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships No conflicts of interest to disclose. CLINICAL HISTORY
RENAL EVENING SPECIALTY CONFERENCE Harsharan K. Singh, MD The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships No conflicts of interest to disclose. CLINICAL HISTORY
Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis
 Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis MPGN is characterizedby alterations in the GBM and mesangium and by proliferation of glomerular cells. 5% to 10% of cases of 1ry nephrotic syndrome in children
Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis MPGN is characterizedby alterations in the GBM and mesangium and by proliferation of glomerular cells. 5% to 10% of cases of 1ry nephrotic syndrome in children
Globotriaosylceramide accumulation in the Fabry kidney is cleared from multiple cell types after enzyme replacement therapy
 Kidney International, Vol. 62 (2002), pp. 1933 1946 GENETIC DISORDERS DEVELOPMENT Globotriaosylceramide accumulation in the Fabry kidney is cleared from multiple cell types after enzyme replacement therapy
Kidney International, Vol. 62 (2002), pp. 1933 1946 GENETIC DISORDERS DEVELOPMENT Globotriaosylceramide accumulation in the Fabry kidney is cleared from multiple cell types after enzyme replacement therapy
Glomerular pathology-2 Nephritic syndrome. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 Glomerular pathology-2 Nephritic syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: inflammation proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls
Glomerular pathology-2 Nephritic syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: inflammation proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls
Fabry Outcome Survey
 Fabry Outcome Survey Annual Report 2016 Reporting Period: 17-04-2001 to 05-01-2017 This report has been prepared by Shire Outcome Surveys, on behalf of the FOS Steering Committee Date of preparation: August
Fabry Outcome Survey Annual Report 2016 Reporting Period: 17-04-2001 to 05-01-2017 This report has been prepared by Shire Outcome Surveys, on behalf of the FOS Steering Committee Date of preparation: August
Fabry disease: a review of current management strategies
 Fabry disease: a review of current management strategies A. MEHTA 1, M. BECK 2, F. EYSKENS 3, C. FELICIANI 4, I. KANTOLA 5, U. RAMASWAMI 6, A. ROLFS 7, A. RIVERA 8, S. WALDEK 9, D.P. GERMAIN 10 1 Lysosomal
Fabry disease: a review of current management strategies A. MEHTA 1, M. BECK 2, F. EYSKENS 3, C. FELICIANI 4, I. KANTOLA 5, U. RAMASWAMI 6, A. ROLFS 7, A. RIVERA 8, S. WALDEK 9, D.P. GERMAIN 10 1 Lysosomal
Case Report Copious Podocyturia without Proteinuria and with Normal Renal Function in a Young Adult with Fabry Disease
 Case Reports in Nephrology Volume 2015, Article ID 257628, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/257628 Case Report Copious Podocyturia without Proteinuria and with Normal Renal Function in a Young Adult
Case Reports in Nephrology Volume 2015, Article ID 257628, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/257628 Case Report Copious Podocyturia without Proteinuria and with Normal Renal Function in a Young Adult
Crescentic Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)
 Crescentic Glomerulonephritis (RPGN) Background Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) is defined as any glomerular disease characterized by extensive crescents (usually >50%) as the principal histologic
Crescentic Glomerulonephritis (RPGN) Background Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) is defined as any glomerular disease characterized by extensive crescents (usually >50%) as the principal histologic
Glomerular diseases with organized deposits
 Glomerular diseases with organized deposits Banu Sis, MD, FRCPC University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada Ulusal Patoloji Kongresi, Manavgat, Antalya 8/11/2012 What is an organized deposit? A number
Glomerular diseases with organized deposits Banu Sis, MD, FRCPC University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada Ulusal Patoloji Kongresi, Manavgat, Antalya 8/11/2012 What is an organized deposit? A number
Chronic Active Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Native and Transplanted Kidneys
 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 36, no.3, 2006 319 Case Reports: Chronic Active Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Native and Transplanted Kidneys Ping
Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 36, no.3, 2006 319 Case Reports: Chronic Active Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Native and Transplanted Kidneys Ping
Pedigree analysis of Mexican families with Fabry disease as a powerful tool for identification of heterozygous females
 Pedigree analysis of Mexican families with Fabry disease as a powerful tool for identification of heterozygous females B.E. Gutiérrez-Amavizca 1,2, R. Orozco-Castellanos 3,4, J. R. Padilla-Gutiérrez 5,
Pedigree analysis of Mexican families with Fabry disease as a powerful tool for identification of heterozygous females B.E. Gutiérrez-Amavizca 1,2, R. Orozco-Castellanos 3,4, J. R. Padilla-Gutiérrez 5,
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
Pathology of Complement Mediated Renal Disease
 Pathology of Complement Mediated Renal Disease Mariam Priya Alexander, MD Associate Professor of Pathology GN Symposium Hong Kong Society of Nephrology July 8 th, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 The complement
Pathology of Complement Mediated Renal Disease Mariam Priya Alexander, MD Associate Professor of Pathology GN Symposium Hong Kong Society of Nephrology July 8 th, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 The complement
Long-term follow-up of juvenile acute nonproliferative glomerulitis (JANG)
 Pediatr Nephrol (2007) 22:1957 1961 DOI 10.1007/s00467-007-0555-6 BRIEF REPORT Long-term follow-up of juvenile acute nonproliferative glomerulitis (JANG) Teruo Fujita & Kandai Nozu & Kazumoto Iijima &
Pediatr Nephrol (2007) 22:1957 1961 DOI 10.1007/s00467-007-0555-6 BRIEF REPORT Long-term follow-up of juvenile acute nonproliferative glomerulitis (JANG) Teruo Fujita & Kandai Nozu & Kazumoto Iijima &
Case Report Early Renal Involvement in a Girl with Classic Fabry Disease
 Hindawi Case Reports in Nephrology Volume 2017, Article ID 9543079, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9543079 Case Report Early Renal Involvement in a Girl with Classic Fabry Disease Fernando Perretta,
Hindawi Case Reports in Nephrology Volume 2017, Article ID 9543079, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9543079 Case Report Early Renal Involvement in a Girl with Classic Fabry Disease Fernando Perretta,
Thin basement membrane syndrome in adults
 J Clin Pathol 1987;40:318-322 Thin basement membrane syndrome in adults S ABE, Y AMAGASAKI,* S IYORI,t K KONISHI, E KATO, H SAKAGUCHI,: K SHIMOYAMA** From the Department of Internal Medicine and tpathology,
J Clin Pathol 1987;40:318-322 Thin basement membrane syndrome in adults S ABE, Y AMAGASAKI,* S IYORI,t K KONISHI, E KATO, H SAKAGUCHI,: K SHIMOYAMA** From the Department of Internal Medicine and tpathology,
Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases
 Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases M. Rohrbach, MD, PhD FMH Pädiatrie und FMH Medizinische Genetik Abteilung Stoffwechsel Universitätskinderklinik Zürich Lysosomal storage disorders
Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases M. Rohrbach, MD, PhD FMH Pädiatrie und FMH Medizinische Genetik Abteilung Stoffwechsel Universitätskinderklinik Zürich Lysosomal storage disorders
Fabry Disease: A complex multisystem disorder
 Fabry Disease: A complex multisystem disorder Dr. Bertram Henderson Division of Clinical Genetics, UFS/FPA 1 2 Speaker Disclosure The speaker has received sponsorship from Sanofi Genzyme to attend workshops,
Fabry Disease: A complex multisystem disorder Dr. Bertram Henderson Division of Clinical Genetics, UFS/FPA 1 2 Speaker Disclosure The speaker has received sponsorship from Sanofi Genzyme to attend workshops,
Galafold (migalastat) or Fabrazyme (agalsidase beta) Prior Authorization Criteria:
 Request for Prior Authorization for Fabry Disease Medications Website Form www.highmarkhealthoptions.com Submit request via: Fax - 1-855-476-4158 All requests for Galafold (migalastat) or Fabrazyme (agalsidase
Request for Prior Authorization for Fabry Disease Medications Website Form www.highmarkhealthoptions.com Submit request via: Fax - 1-855-476-4158 All requests for Galafold (migalastat) or Fabrazyme (agalsidase
Clinical history. 73 yo man with chest pain Systemic hypertension and WG Stress EKG N Stress echocardiogram: Cardiac catheterization: no CAD
 CASE 8 Clinical history 73 yo man with chest pain Systemic hypertension and WG Stress EKG N Stress echocardiogram: Concentric hypertrophy Hypokinesis of LV-Inf Cardiac catheterization: no CAD Technique
CASE 8 Clinical history 73 yo man with chest pain Systemic hypertension and WG Stress EKG N Stress echocardiogram: Concentric hypertrophy Hypokinesis of LV-Inf Cardiac catheterization: no CAD Technique
Clinical features and diagnosis of Fabry disease
 Clinical features and diagnosis of Fabry disease Monique E Cho, MD Jeffrey B Kopp, MD UpToDate performs a continuous review of over 375 journals and other resources. Updates are added as important new
Clinical features and diagnosis of Fabry disease Monique E Cho, MD Jeffrey B Kopp, MD UpToDate performs a continuous review of over 375 journals and other resources. Updates are added as important new
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features.
 Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Natural History and Treatment of Renal Involvement in Fabry Disease
 J Am Soc Nephrol 13: S139 S143, 2002 Natural History and Treatment of Renal Involvement in Fabry Disease MARY BRANTON,* RAPHAEL SCHIFFMANN, and JEFFREY B. KOPP* *Kidney Disease Section, National Institute
J Am Soc Nephrol 13: S139 S143, 2002 Natural History and Treatment of Renal Involvement in Fabry Disease MARY BRANTON,* RAPHAEL SCHIFFMANN, and JEFFREY B. KOPP* *Kidney Disease Section, National Institute
Nephritic vs. Nephrotic Syndrome
 Page 1 of 18 Nephritic vs. Nephrotic Syndrome Terminology: Glomerulus: A network of blood capillaries contained within the cuplike end (Bowman s capsule) of a nephron. Glomerular filtration rate: The rate
Page 1 of 18 Nephritic vs. Nephrotic Syndrome Terminology: Glomerulus: A network of blood capillaries contained within the cuplike end (Bowman s capsule) of a nephron. Glomerular filtration rate: The rate
FABRY DISEASE 12/30/2012. Ataxia-Telangiectasia. Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease
 Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease ES ROACH,MD. Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease Conjunctival lesions Corneal lesions Lesions of iris & lens Retinal vascular lesions
Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease ES ROACH,MD. Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease Conjunctival lesions Corneal lesions Lesions of iris & lens Retinal vascular lesions
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Overview of glomerular diseases
 Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane
Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology
 Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
Fundamentals of Renal Pathology
 Fundamentals of Renal Pathology Fundamentals of Renal Pathology Agnes B. Fogo, Arthur H. Cohen, J. Charles Jennette, Jan A. Bruijn, Robert B. Colvin Agnes B. Fogo, M.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Fundamentals of Renal Pathology Fundamentals of Renal Pathology Agnes B. Fogo, Arthur H. Cohen, J. Charles Jennette, Jan A. Bruijn, Robert B. Colvin Agnes B. Fogo, M.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Journal of Nephropathology
 www.nephropathol.com DOI: 10.15171/jnp.2018.24 J Nephropathol. 2018;7(3):101-105 Journal of Nephropathology Relationship of CD147 kidney expression with various pathologic lesions, biochemical and demographic
www.nephropathol.com DOI: 10.15171/jnp.2018.24 J Nephropathol. 2018;7(3):101-105 Journal of Nephropathology Relationship of CD147 kidney expression with various pathologic lesions, biochemical and demographic
Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Landi Lombard Endocrinologist Kuilsrivier
 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Landi Lombard Endocrinologist Kuilsrivier Classification of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Amino acid disorders eg Phenylketonuria Organic acidemias eg Maple syrup urine disease
Inborn Errors of Metabolism Landi Lombard Endocrinologist Kuilsrivier Classification of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Amino acid disorders eg Phenylketonuria Organic acidemias eg Maple syrup urine disease
Primer: histopathology of calcineurin-inhibitor toxicity in renal allografts
 Primer: histopathology of calcineurin-inhibitor toxicity in renal allografts Peter Liptak and Bela Ivanyi* SUMMARY Calcineurin inhibitors (ciclosporin and tacrolimus) can cause acute and chronic nephrotoxicity.
Primer: histopathology of calcineurin-inhibitor toxicity in renal allografts Peter Liptak and Bela Ivanyi* SUMMARY Calcineurin inhibitors (ciclosporin and tacrolimus) can cause acute and chronic nephrotoxicity.
Lab 3, case 1. Is this an example of nephrotic or nephritic syndrome? Why? Which portion of the nephron would you expect to be abnormal?
 Lab 3, case 1 12-year-old Costa Rican boy is brought into clinic by his parents because of dark brownish-red urine over the last 24 hours. The family has been visiting friends in Indianapolis for two weeks.
Lab 3, case 1 12-year-old Costa Rican boy is brought into clinic by his parents because of dark brownish-red urine over the last 24 hours. The family has been visiting friends in Indianapolis for two weeks.
Clinical Appearance and Management of Fabry Nephropathy in Greece
 BANTAO Journal 2010; 8 (2): 75-80 BJ BANTAO Journal Original article Clinical Appearance and Management of Fabry Nephropathy in Greece Andrikos K. Emilios 1, Iatrou E. Christos 2, Boletis N. John 3, Diamandopoulos
BANTAO Journal 2010; 8 (2): 75-80 BJ BANTAO Journal Original article Clinical Appearance and Management of Fabry Nephropathy in Greece Andrikos K. Emilios 1, Iatrou E. Christos 2, Boletis N. John 3, Diamandopoulos
Genetics of Steroid Resistant Nephrotic syndrome. Velibor Tasic University Children s Hospital Skopje, Macedonia
 Genetics of Steroid Resistant Nephrotic syndrome Velibor Tasic University Children s Hospital Skopje, Macedonia Nephrotic syndrome - definition Oedema Massive proteinuria (> 50mg/kg/d or> 40mg/m2/h Hypoalbuminemia
Genetics of Steroid Resistant Nephrotic syndrome Velibor Tasic University Children s Hospital Skopje, Macedonia Nephrotic syndrome - definition Oedema Massive proteinuria (> 50mg/kg/d or> 40mg/m2/h Hypoalbuminemia
Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary
 Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff 2017 B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary Treatment of allograft dysfunction should rely on the biopsy findings
Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff 2017 B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary Treatment of allograft dysfunction should rely on the biopsy findings
Fine structural appearances of glomerular capillaries in a case of malignant hypertension
 J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 579-583 Fine structural appearances of glomerular capillaries in a case of malignant hypertension R. F. MACADAM From the University Department of Pathology, Western Infirmary,
J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 579-583 Fine structural appearances of glomerular capillaries in a case of malignant hypertension R. F. MACADAM From the University Department of Pathology, Western Infirmary,
A Case of Podocytic Infolding Glomerulopathy with Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
 Published online: August 8, 2013 1664 5510/13/0032 0110$38.00/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Published online: August 8, 2013 1664 5510/13/0032 0110$38.00/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Morbus Fabry. Bruno Conti Rossini. Sostituto primario Ospedale Regionale di Locarno
 Morbus Fabry Bruno Conti Rossini Sostituto primario Ospedale Regionale di Locarno Problem: Anesthesiologic ambulatory preanesthetic consultation for peripartal epidural anesthesia the call: we have a pregnant
Morbus Fabry Bruno Conti Rossini Sostituto primario Ospedale Regionale di Locarno Problem: Anesthesiologic ambulatory preanesthetic consultation for peripartal epidural anesthesia the call: we have a pregnant
Lysosomes. Gr: lysis solution, soma body. Membrane bounded vesicles. Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies m.
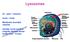 Lysosomes Gr: lysis solution, soma body Membrane bounded vesicles Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies 0.05 0.5 m. Lysosomes No. varies from a few to several hundred per cell, in different
Lysosomes Gr: lysis solution, soma body Membrane bounded vesicles Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies 0.05 0.5 m. Lysosomes No. varies from a few to several hundred per cell, in different
RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT. J. H. Helderman,MD,FACP,FAST
 RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT J. H. Helderman,MD,FACP,FAST Vanderbilt University Medical Center Professor of Medicine, Pathology and Immunology Medical Director, Vanderbilt Transplant
RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT J. H. Helderman,MD,FACP,FAST Vanderbilt University Medical Center Professor of Medicine, Pathology and Immunology Medical Director, Vanderbilt Transplant
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE
 HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
2 nd Latin American Fabry Round Table
 2 nd Latin American Fabry Round Table FABRY DISEASE AND THE KIDNEY KIDNEY PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC PATHWAYS OF DISEASE REVISITED FOCUS ON THE PODOCYTE AND OTHER ISSUES HERNÁN TRIMARCHI CHIEF NEPHROLOGY AND RENAL
2 nd Latin American Fabry Round Table FABRY DISEASE AND THE KIDNEY KIDNEY PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC PATHWAYS OF DISEASE REVISITED FOCUS ON THE PODOCYTE AND OTHER ISSUES HERNÁN TRIMARCHI CHIEF NEPHROLOGY AND RENAL
Thin basement membrane nephropathy cannot be diagnosed reliably in deparaffinized, formalin-fixed tissue
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2007) 22: 1228 1232 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl838 Advance Access publication 3 February 2007 Technical Note Thin basement membrane nephropathy cannot be diagnosed reliably in deparaffinized,
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2007) 22: 1228 1232 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl838 Advance Access publication 3 February 2007 Technical Note Thin basement membrane nephropathy cannot be diagnosed reliably in deparaffinized,
