approach for the preparation of homogeneous plasmenylethanolamine
|
|
|
- Violet Young
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Semi-synthetic approach for the preparation of homogeneous plasmenylethanolamine utilizing phospholipase D from Streptomyces chromofuscus Robert A. Wolf* and Richard W. Gross*.t Departments of Internal Medicine* and Chemistry,t Washington University, St. Louis, MO Abstract A simple method for the preparation of homogeneous molecularspeciesofplasmenylcholine and plasmenylethanolamine was developed. The method utilized reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography to isolate homogeneous molecular species of plasmenylcholine prepared by acylation of lysoplasmenylcholine. Plasmenylcholine was directly converted toplasmenylethanolamine bytransphosphatidylation utilizing phospholipase D from Stnptomyccs chmmofuscclcs. This method permits the facile labeling of homogeneous molecular species of plasmalogens in the polar head group, the sn-2 acyl chain, or both, for the first time. - Wolf, R. A., and R. W. Gross. Semisynthetic approach for the preparation of homogeneous plasmenylethanolamine utilizing phospholipase D from Stnpfomyces chmmofusccur. J. Lipid Rw : Supplementary key words plasmalogens - phospholipase D transphosphatidylation Plasmalogens have recently been recognized as major phospholipid constituents of plasma membranes in several mammalian tissues. The striking predominance of plasmalogens in myocardial sarcolemma (l), brain (2), and peripheral nerve (3) suggests an important function of plasmalogens in electricallyactivetissues. Although plasmalogens are present in specific tissues and subcellular compartments, delineation of their biologic function remains elusive (see 4, 5 for reviews). Direct investigation of the metabolism and physicalchemical properties of plasmalogens has been impeded by the difficulty in obtaining homogeneous chemical probes. Plasmenylethanolamine is particularly difficult to prepare due to the presence of a reactive nucleophilic group (primary amine) which precludes direct acylation of lysoplasmenylethanolamine. A previous schemefor the preparation of plasmenylethanolamine utilized protection and deprotection of the amine group but the product from this previous method contained a mixture of molecular species (6). This study reports a new scheme (Fig. 1) for the rapid preparation and isolation of homogeneous molecular species of plasmenylcholine and plasmenyl- ethanolamine. This method permits, for the first time, the facile incorporation of radiolabels or physical probes into the polar head group and/or the sn-2 fatty acyl group of homogeneous molecular species of plasmenylcholine or plasmenylethanolamine. MATERIALS Oleic acid, arachidonic acid, ethanolamine, Triton X-100, bovine serum albumin, and N,N'-dicylohexylcarbodiimide were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO). N,N'-dimethyl-4-aminopyridine was purchased from Aldrich Chemical Co. (Milwaukee, WI). Derivatized rape seed oil (methyl ester) was obtained from Supelco, Inc. (Bellefonte, PA). Bovine heart lecithin was obtained from AvantiPolar Lipids, Inc. (Birmingham, AL). Anasil-OF thin-layer chromatography plateswere purchased from Analabs (North Haven, CT). Silicic acid (400 mesh) was obtained from Bio-Rad (Richmond, CA). Radiolabeled [5, 6,8, 9, 11, 12, 14, 15-3H]arachidonic acid (87.4 Ci/mmol), [1,2-'*C]ethanolamine hydrochloride (4.0 mci/mmol), and [9,10-3H]oleic acid (13.3 Ci/mmol) were obtained from New England Nuclear (Boston, MA). Phospholipase D from Streptomyces chromojiscus was purchased from Calbiochem-Behring (San Diego, CA). Aquasol-2 was obtained from New England Nuclear (Boston, MA). METHODS Phospholipid separation and analysis All synthetic products were stored under nitrogen and protected from light throughout the synthesis. Thin-layer Abbreviations: TLC, thin-layer chromatography; HPLC, high performance liquid chromatography; GLC, gas-liquid chromatography. Journal of Lipid Research Volume 26,
2 Bovine Heart Lecithin I + NaOH/MeOH Choline Lysoplasmalogen Choline Plasmalogen Ethanolamine Plasmalogen Fig. 1 The syntheticscheme for plasmenylcholineandplasmenylethanolamine synthesis. PLD, phospholipase D; DCC, N,N dicyclohexylcarbodiimide; DMAP, N,N dimethyl-4-aminopyridine. chromatography (TLC) plates were developed with chloroform-methanol-ammonium hydroxide 65:35:5. Plasmenylcholine and plasmenylethanolamine had Rf values of 0.31 and 0.48, respectively, which were similar to their diacyl analogues. Lysoplasmenylcholine had an Rf value of Silicic acid column chromatography was performed on a 2.5 x 30 cm column initially equilibrated with chloroform, and stepwise gradients of CHC13-MeOH were used to elute reaction products as described previously (7). Phospholipids purified by silicic acid chromatography appeared as a single intense spot on TLC after staining with iodine overnight. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was performed as previously described (8). Homogeneous molecular species of plasmenylcholine or plasmenylethanolamine were isolated by reverse phase HPLC. Phospholipid was applied to a Beckman Ultrasphere ODS C-18 column (4.6 mm x 25 cm, pmol of phospholipid) or for larger scale syntheses to an Altech C-18 column (16 mm x 25 cm, pmol of phospholipid) and eluted isocratically at 2 or 10 ml/min, respectively. Phospholipids were derivatized by acid methanolysis (1) and analyzed by capillary gas-liquid chromatography (GLC) as previously described (9). Peak assignments were determined by comparison with derivatized standards and GLC-mass spectrometry (1). Fast-atom bombardment mass spectrometry was performed as previously described (1). 1-0-(Z)-1 -allrenyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (lysoplasmenylcholine) Lysoplasmenylcholine was prepared by the method of Wheeldon, Schumert, and Turner (10) and purified by silicic acid column chromatography. Thin-layer chromatography of this material demonstrated a single spot (Rf = 0.10) after intense iodine staining. 1-0-(Z)-l allrenyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (plasmenylcholine) Lysoplasmenylcholine was acylated by a method adapted from Gupta, Radhakrishnan, and Khorana (11). Oleic anhydride or arachidonoyl anhydride were synthesized (Fig. 1) as described by Selinger and Lapidot (12).For preparation of radiolabeled plasmenylcholine, [5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, 15-3H]arachidonic acid (sp act 0.3 pcilpmol) or [9, 10-3H]oleic acid (sp act 280 pci/pmol) were used in the anhydride synthesis. Prior to the acylation reaction, lysoplasmenylcholine was repeatedly azeotroped with benzene. The fatty acid anhydride and lysoplasmenylcholine were dried over phosphorus pentoxide in vacuo overnight, and chloroform was freshly distilled from phosphorus pentoxide. All reagents were transferred in a dry nitrogen atmosphere into a reaction vessel containing (final concentration) lysoplasmenylcholine (50 pmol/ml of chloroform); anhydride (75 pmol/ml); and N-N -dimethyl-4-aminopyridine (50 pmol/ml) and stirred at room temperature for hr. Reaction products were identified by TLC and synthetic plasmenylcholine (Rf = 0.31) was purified by preparative TLC or silicic acid chromatography. The phospholipid class purity was established by TLC and HPLC. l-o-(z)-l -alkenyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (plasmenylethanolamine) Plasmenylethanolamine was prepared directly from the choline analogue by transphosphatidylation catalyzed by phospholipase D from Streptomyces chmmohcus. Plasmenylcholine (5 pmollml of distilled water) was sonicated at 4OC with three bursts of 2 min duration using a Branson ultrasonicator (Branson Corporation, Danbury, CT) at 30 watts output. Plasmenylcholine vesicles were transferred to a reaction vessel containing (final concentration) 40 mm Tris; 4 mm calcium chloride; 0.25% Triton X-100 (dv); 0.05% bovine serum albumin (w/v); 15% ethanolamine (v/v), and 25 unitdm1 phospholipase D at ph 8.5. This reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 20 min, and the reaction was stopped by the addition of 0.5 ml of 200 mm EDTA. The reaction products were then extracted (13) and the organic phase was filtered (1 p filter) prior to evaporation under nitrogen. Reaction products were analyzed by TLC, HPLC, and GLC. Synthetic plasmenylethanolamine was purified by preparative TLC and subsequent reverse phase HPLC. 630 Journal of Lipid Research Volume 26, 1985
3 RESULTS Characterization of 1-0-(Z)-F-alkenyl-sn-glycero- (lysoplasmenylcholine) 3-phosphocholine 0.8 Approximately 2.0 g (4.2 mmol) of lysoplasmenylcholine was routinely isolated by silicicacidcolumn chro- f 0.6 matography following alkaline methanolysis of10.0 g a (13.4 mmol) of bovine heart lecithin. Fast-atom bombardment mass spectrometry of purified lysoplasmenyl- Oo4 choline demonstrated a mixture of molecular species, with the major component at dz 480. These molecular 0.2 species were quantified by GLC (Table 1) and were corroborated by fast-atom bombardment mass spectrometry. Thus the major component of lysoplasmenylcholine utilized in the acylation reaction was 1-0-(Z)-(1'-hexa- " decenyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. TIME (Min) Fig. 2 Reverse phase HPLC of semi-synthetic plaamenylcholine. Preparation and characterization of 1-0-(Z)-l"alkeny1- Lysoplasmenylcholine was acylated with arachidonic acid, purified by 2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (plasmenylcholine) TLC, and injected onto a C-18 column withmethanol-acetonitrilewater as the mobile phaae as described in Methods. 1-0-(Z)-(1'- Approximately 75 mg (156 pmol) of lysoplasmenyl- huradecenyl)-2-arachidonoyl-m-glycero-3-ph~phocholine was eluted at choline was acylated with 100 mg (170 pmol) of arachi- 65 min. The other major reaction product, l-o-(z)-(l'-oaadecenyl)-2- arachidonoyl-m-glycero-3-pholphocholine eluted at 116 min. donoyl anhydride as described in Methods. Following silicic acid column chromatography, 61 mg (79 pmol) of plasmenylcholine was isolated (yield = 49%). As expected, mass spectrometry and GLC of plasmenylcholinerevealed a mixture of products resulting from the acylation of heterogeneous lysoplasmenylcholine. Homogeneous l-o-(z)-(l'-hexadecenyl)-2-arachidonoyl- sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine was isolated by reverse phase HPLC (Fig. 2). Of note, several of the minor peaks eluted by reverse phase HPLC contained a large molar excess of fatty acid methyl ester to dimethyl acetal after derivatization by acid methanolysis and analysis by GLC. In contrast, l-o-(z)-(l'-hexadecenyl)-2-arachidonoyl-sn- glycero-3-phosphocholine isolated by reverse phase HPLC contained stoichiometric amounts (f 2%) of the dimethyl acetal of palmitate and the fatty acidmethyl ester of arachidonic acid. Acid methanolysis and capillary GLC revealed that this purified product was essentially free of contamination by other molecular species. Fastatom bombardment mass spectrometry revealed a single TABLE 1. Characterization of 1-0-(Z)-1'-alkenylsn-glycero-3-phosphocholine m-1 5% of Total 14:O 15:O 16:O 17:O 18:O 18: 1 6*2 7 * 2 68 * 3 4*1 10 * 1 4 * 1 Lysoplasmenylcholine prepared from bovine heart lecithin was isolated by silicic acid column chromatography and aldehydes were quantified by capillary GLC after acid methanolysis. Lo 1 parent ion at d z 766 (Fig. 3), with the major fragmentation peak at dz 480 due to the loss of the sn-2 acyl group. The [5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12,14, 15-3H]arachidonoyl plasmenylcholine (sp act 0.3 pcilpol) was prepared by an identical scheme. In additional experiments, 100 mg (208 pmol) of lysoplasmenylcholine was acylated with 176 mg (322 pmol) of oleic anhydride, yielding 92 mg (124 pmol) of plasmenylcholine (yield = 60%). 1-0-(Z)-(1'-hexadecenyl)-2-oleoyl- sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine was isolated by reverse phase HPLC and was a single molecular species as ascertained by fast-atom bombardment mass spectrometry (Fig. 3) and GLC. Preparation and characterization of 1-0-(Z)-F-alkenyl- 2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (plasmenylethanolamine) 1-0-(Z)-(1'-hexadecenyl)-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine was directly converted to the ethanolamine derivative by transphosphatidylation catalyzed by phospholipase D from Streptomyces chromoficcw. Initial experiments demonstrated that this enzyme could hydrolyze the phosphoester linkage in plasmenylcholine to yield the corresponding phosphatidic acid. Inclusion of a primary alcohol such as ethanolamine in the reaction mixture resulted in the transphosphatidylation of plasmenylcholine to plasmenylethanolamine. Synthesis of plasmenylethanolamine was confirmed by incorporation of '*C-labeled ethanolamine (0.12 pci/pmol) into the reaction product. The purified plasmenylethanolamine was a single peak that comigrated with authentic phosphatidylethanolamine on straight phase HPLC (8). The Wolf and Gms Plasmalogen tranrphorphotidylation 631
4 40 z 20 r/) LU t o Lu 75 0 m /I I Fig. 3 Fast-atombombardmentmasspectrometryofplasmenylcholine. Reverse phase HPLC purified plasmenylcholine was analyzed by fast-atom bombardment mass spectrometry. The protonated parent ion peaks occurred at dz 766 for 1-O-(Z)-(l'-hexadecenyl)-2-arachidonoylsn-glyero-3-phwphocholine (panel A) and at dz 744 for 1-0-(Z)-(1'- hexadecenyl)-2-oleoyl-~n-glycero-3-phosphocholine (panel B). under identical conditions (16, 17). The identification of rapid transphosphatidylation of plasmenylcholine catalyzed by phospholipase D from Streptomyces chromopurified reaction product was a single spot on TLC fucu allows access to many different plasmalogen molecuthat comigrated with phosphatidylethanolamine. Acid lar classes and facilitates the placement of specific probes methanolysis and subsequent analysis by GLC revealed in the polar head group. that the sn-1 vinyl ether group and the sn-2 acyl group Lysoplasmenylcholine prepared by alkaline methawere present in stoichiometric amounts (f 2%) and were not altered during the transphosphatidylation reaction. In nolysis of bovine heart lecithin is contaminated by small amounts (5-796) of alkyl ether lipid. Alkyl ether contamia typical small scale reaction, 2.7 mg (3.5 pmol) of nation of purified plasmenylcholine after reverse phase 1-0-(Z)-(1'-hexadecenyl)-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phos- HPLC wasless than 2% as evidenced by the stoichiophocholine was converted to 1.3 mg (1.8 pmol) of metric ratio of dimethyl acetal to fatty acid methyl ester l-o-(z)-(l'-hexadecenyl)-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phos- in derivatized plasmenylcholine. The high ratio of fatty phoethanolamine (50% yield). In a larger scale reaction, acid methyl ester to dimethyl acetal present in minor 10 mg (13.4 pmol) of l-o-(z)-l'-alkenyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero- peaks after reverse phase HPLC suggests that alkyl ether 3-phosphocholine was converted to 4.9 mg (6.8 pmol) lipids were resolved by this technique. Resolution of other of 1-0-(Z)-1'-alkenyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanol- molecular species of plasmalogens from alkyl ether lipids amine (51% yield) with generation of 0.7 mg (1.1 pol) of by reverse phase HPLC awaits further studies. l-o-(z)-l'-alkenyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate The synthetic and chromatographic methods described (Z)-(1'-hexadecenyl)-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanol- in this study allow the rapid preparation of specifically amine was subsequently purified by reverse phase HPLC. DISCUSSION Investigation of the structure and function of plasmalogens in biologic membranes has been hampered by difficulty in preparing this class of phospholipids. This report described a new semi-synthetic route to homogeneous molecular species of plasmenylcholine and plasmenylethanolamine. This scheme obviates the need for protection and deprotection of the primary amine group in plasmenylethanolamine and facilitates the synthesis of homogeneous plasmenylcholine and plasmenylethanolamine from a common intermediate. Furthermore, it permits the introduction of specific probes into both the fatty acyl group as well as the polar head group, thus facilitating the study of both the hydrophobic and hydrophilic domains of plasmalogens. The critical steps in the semi-synthetic scheme were the separation of multiple plasmenylcholine molecular species and the enzymatic conversion of plasmenylcholine to plasmenylethanolamine. A reverse phase HPLC separation of diacyl phospholipid species has been described by Patton, Fasulo, and Robins (14) and, as this study demonstrates, identical chromatographi conditions are also useful for the separation of plasmalogen molecular species. Plasmalogens were retained longer by the reverse phase column than their diacyl counterparts, presumably reflecting their decreased polarity due to the absence of a carbonyl at the sn-1 acyl chain. Although base exchange reactions have been extensively utilized in the synthesis of diacyl glycerophospholipids employing phospholipase D from Savoy cabbage (15), plasmalogen substrates are almost completely resistant to hydrolysis or base exchange labeled homogeneous molecular species of plasmenylcholine or plasmenylethanolamine from a common intermediate (lysoplasmenylcholine). The application of these methods to the preparation of specific metabolic and physical probes should facilitate the identification of the role of plasmalogens in biologic membranes. I The authors with to thank Ms. Karen Brennan for expert technical assistance and Ms. Helen Nikolaisen for her help in preparation of this manuscript. Supported in part by NIH Grant HL in Ischemic Heart Disease, an American Heart Association Grant-in-Aid, and a Searle Scholar Award. Manuscript rcceiued 27 Noutmbn Journal of Lipid Research Volume 26, 1985
5 REFERENCES 1. Gross, R. W High plasmalogen and arachidonic acid content of canine myocardial sarcolemma: a fast atom bombardment massspectroscopic and gas chromatography-massspectroscopic characterization. Bwchistg. 23: Owens, K A two-dimensional thin-layer chromatographic procedure for estimation of plasmalogens. Bioch. J. 100: Sheltawy, C., and R. M. C. Dawson The polyphosphoinositides and other lipids of peripheral nerves. Biochon. J. 100: Snyder, F., editor Ether Lipids: Chemistry and Biology. Academic Press, NewYork,NY. 5. Mangold, H. K., and E Paltauf, editors Ether Lipids: Biochemical and Biomedical Aspects. Academic Press, New York, NY. 6. Hermetter, A., and F. Paltauf Semisynthetic preparation of choline and ethanolamine plasmalogens. Chon. P~s. Lip&. 30: Bergelson, L. D Lipid Biochemical Preparations. Elsevier-North Holland Biomedical Press, New York, NY Gross, R. W., and B. E. Sobel Isocratic high performance liquid chromatography separation of phosphoglycerides and lysophosphoglycerides. J. Chmmatogr 197: Fink, K. L., and R. W. Gross Modulation of canine myocardial sarcolemmal membrane fluidity by amphiphilic compounds. Circ. Res. 55: Wheeldon, L. W., Z. Schumert, and D.A.Turner Lipid composition of heart muscle homogenate. J. Lipid h. 6: Gupta, C. M., R. Radhakrishnan, and H. G. Khorana Glycerophospholipid synthesis: improved general method and new analogs containing photoactivatable groups, Rvc. Natl. had. Sci. USA. 7: Selinger, Z., and Y. Lapidot Synthesis of fatty acid anhydrides by reaction with dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. J. Lipid Res. 7: Bligh, E. G., and W. J. Dyer A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Pbsiol. 37: Patton, G. M., J. M. Fasulo, and S. J. Robins Separation of phospholipids and individual molecular species of phospholipids by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Lipid Res. 23: Yang, S. E, S. Freer, and A.A. Benson Transphosphatidylation by phospholipase D. J. Bwl. C h. 242: Lands, W. E. M., and P. Hart Metabolism of plasmalogen Relative reactivities ofacyl and alkenyl derivatives of glycerol-3-phosphocholine. Biochim. Biopbs. ~cta. 98: Reukonen, Mono- and dimethyl phosphatides from different subtypes of choline and ethanolamine glycerophosphatides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 152: Journal of Lipid Research Volume 26, 1985 Notes on MethoakrogY 633
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Materials and Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Materials and Methods HPLC-UV of phospholipid classes and HETE isomer determination. Fractionation of platelet lipid classes was undertaken on a Spherisorb S5W 150 x 4.6 mm column (Waters
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Materials and Methods HPLC-UV of phospholipid classes and HETE isomer determination. Fractionation of platelet lipid classes was undertaken on a Spherisorb S5W 150 x 4.6 mm column (Waters
papers on methodology
 papers on methodology Dephosphorylation and benzoylation reactions occurring in the benzoolysis of diacyl-, alkylacyl-, alk-1-enylacyl-, and acyl-lyso-glycerophosphocholines W. J. Gelsema* and H. van den
papers on methodology Dephosphorylation and benzoylation reactions occurring in the benzoolysis of diacyl-, alkylacyl-, alk-1-enylacyl-, and acyl-lyso-glycerophosphocholines W. J. Gelsema* and H. van den
Relative Quantitation of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Cell Membrane GPEtn Lipids
 Relative Quantitation of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Cell Membrane GPEtn Lipids Using the QTRAP System with mtraq Reagents Karin A. Zemski-Berry 1, John M. Hevko 2, and Robert C. Murphy 1 1 Department
Relative Quantitation of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Cell Membrane GPEtn Lipids Using the QTRAP System with mtraq Reagents Karin A. Zemski-Berry 1, John M. Hevko 2, and Robert C. Murphy 1 1 Department
Enrichment of Phospholipids from Biological Matrices with Zirconium Oxide-Modified Silica Sorbents
 Enrichment of Phospholipids from Biological Matrices with Zirconium Oxide-Modified Silica Sorbents Xiaoning Lu, Jennifer E. Claus, and David S. Bell Supelco, Div. of Sigma-Aldrich Bellefonte, PA 16823
Enrichment of Phospholipids from Biological Matrices with Zirconium Oxide-Modified Silica Sorbents Xiaoning Lu, Jennifer E. Claus, and David S. Bell Supelco, Div. of Sigma-Aldrich Bellefonte, PA 16823
Lipid Analysis ISOLATION, SEPARATION, IDENTIFICATION AND. Bridgwater, England LIPIDOMIC ANALYSIS. Fourth Edition. Invergowrie, Dundee, Scotland
 Lipid Analysis ISOLATION, SEPARATION, IDENTIFICATION AND LIPIDOMIC ANALYSIS Fourth Edition WILLIAM W.CHRISTIE MRS Lipid Analysis Unit, Scottish Crop Research Institute, Dundee, Scotland Invergowrie, and
Lipid Analysis ISOLATION, SEPARATION, IDENTIFICATION AND LIPIDOMIC ANALYSIS Fourth Edition WILLIAM W.CHRISTIE MRS Lipid Analysis Unit, Scottish Crop Research Institute, Dundee, Scotland Invergowrie, and
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION-ELIMINATION AT THE ACYL CARBON
 CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION-ELIMINATION AT THE ACYL CARBON RED ANT WAS SOURCE OF FORMIC ACID (RCOOH) Lecture 8 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2 Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION-ELIMINATION AT THE ACYL CARBON RED ANT WAS SOURCE OF FORMIC ACID (RCOOH) Lecture 8 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2 Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO
Chapter 18. Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Carboxylic Acids Organic compounds characterized by their acidity Contains COOH group (must be at
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Carboxylic Acids Organic compounds characterized by their acidity Contains COOH group (must be at
Differential susceptibility of mono- and ether phosphoglycerides to acetolysis
 Differential susceptibility of mono- and ether phosphoglycerides to acetolysis di-0-al kyl Raj Kumar, Susan T. Weintraub, and Donald J. Hanahan Departments of Biochemistry' and Pharmacology,* The University
Differential susceptibility of mono- and ether phosphoglycerides to acetolysis di-0-al kyl Raj Kumar, Susan T. Weintraub, and Donald J. Hanahan Departments of Biochemistry' and Pharmacology,* The University
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl
' Present address: lnstituto de Investigaciones Bioquimicas, Universidad
 Quantitative release of fatty acids from lipids by a simple hydrolysis procedure Marta I. Aveldafio' and Lloyd A. Horrocks Department of Physiologzcal Chemistry, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
Quantitative release of fatty acids from lipids by a simple hydrolysis procedure Marta I. Aveldafio' and Lloyd A. Horrocks Department of Physiologzcal Chemistry, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
Novel route to preparation of high purity I yso p I asm eny I et h ano I am i ne
 ~ Novel route to preparation of high purity I yso p I asm eny I et h ano I am i ne Donald J. Hanahan,"* Teri Nouchi,* Susan T. Weintraub,t and Merle S. Olson' Departments of Biochemistry* and Patho1ogy;f
~ Novel route to preparation of high purity I yso p I asm eny I et h ano I am i ne Donald J. Hanahan,"* Teri Nouchi,* Susan T. Weintraub,t and Merle S. Olson' Departments of Biochemistry* and Patho1ogy;f
Student Handout. This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have
 Student Handout This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have learned that some compounds exist as enantiomers non-identical mirror images, such as your left and right
Student Handout This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have learned that some compounds exist as enantiomers non-identical mirror images, such as your left and right
Suk Hoo Yoon Korea Food Research Institute 1/42
 Development of Phospholipases to Produce Structured Phospholipids Suk Hoo Yoon Korea Food Research Institute 1/42 Phospholipase D H H C O R R Z Fatty acyl chain -H Phosphatidic acid (PA) R O C H O - -CH
Development of Phospholipases to Produce Structured Phospholipids Suk Hoo Yoon Korea Food Research Institute 1/42 Phospholipase D H H C O R R Z Fatty acyl chain -H Phosphatidic acid (PA) R O C H O - -CH
Phospholipids Metabolism
 Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
P hospholipids : hydrolysis
 Volume 1 Number 5 The analysis of tissue J procedure and results P hospholipids : hydrolysis with pig liver G. HUBSCHER, J. N. HAWTHORNE, and P. KEMP Department of Medical Biochemistry and Pharmacology
Volume 1 Number 5 The analysis of tissue J procedure and results P hospholipids : hydrolysis with pig liver G. HUBSCHER, J. N. HAWTHORNE, and P. KEMP Department of Medical Biochemistry and Pharmacology
Differential turnover of polyunsaturated fatty acids in plasmalogen and diacyl glycerophospholipids of isolated cardiac myocytes
 Differential turnover of polyunsaturated fatty acids in plasmalogen and diacyl glycerophospholipids of isolated cardiac myocytes Steven D. DaTorre* and Michael H. Creer*-t Cardiovascular Division, Department
Differential turnover of polyunsaturated fatty acids in plasmalogen and diacyl glycerophospholipids of isolated cardiac myocytes Steven D. DaTorre* and Michael H. Creer*-t Cardiovascular Division, Department
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson
 Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Biological role of lipids
 Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
BIOCATALYTIC CONVERSION OF OTHER LIPIDS
 Chapter 6 BIOCATALYTIC CONVERSION OF OTHER LIPIDS In Chapters 4 and 5, lipase-mediated conversion of acylglycerols were presented. The Chapter 6 deals with biocatalytic modification of phospholipids, sphingolipids,
Chapter 6 BIOCATALYTIC CONVERSION OF OTHER LIPIDS In Chapters 4 and 5, lipase-mediated conversion of acylglycerols were presented. The Chapter 6 deals with biocatalytic modification of phospholipids, sphingolipids,
MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS
 December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
Phospholipase D Activity of Gram-Negative Bacteria
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Dec. 1975, p. 1148-1152 Copyright 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 124, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Phospholipase D Activity of Gram-Negative Bacteria R. COLE AND P. PROULX*
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Dec. 1975, p. 1148-1152 Copyright 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 124, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Phospholipase D Activity of Gram-Negative Bacteria R. COLE AND P. PROULX*
Supporting information
 Supporting information Figure legends Supplementary Table 1. Specific product ions obtained from fragmentation of lithium adducts in the positive ion mode comparing the different positional isomers of
Supporting information Figure legends Supplementary Table 1. Specific product ions obtained from fragmentation of lithium adducts in the positive ion mode comparing the different positional isomers of
The effect of phosphatidyl choline on the degradation of phosphatidyl ethanolamine by the phospholipase of post-heparin plasma or snake venom
 The effect of phosphatidyl choline on the degradation of phosphatidyl ethanolamine by the phospholipase of post-heparin plasma or snake venom WILLIAM C. VOGEL, J. L. KOPPEL, and J. H. OLWIN Coagulation
The effect of phosphatidyl choline on the degradation of phosphatidyl ethanolamine by the phospholipase of post-heparin plasma or snake venom WILLIAM C. VOGEL, J. L. KOPPEL, and J. H. OLWIN Coagulation
Fatty acid composition of diacyl, alkylacyl, and alkenylacyl phospholipids of control and arac h idonate-depleted rat polymorphonuclear leukocytes
 Fatty acid composition of diacyl, alkylacyl, and alkenylacyl phospholipids of control and arac h idonate-depleted rat polymorphonuclear leukocytes C. S. Ramesha and W. C. Pickett' Lipid Mediator Laboratory,
Fatty acid composition of diacyl, alkylacyl, and alkenylacyl phospholipids of control and arac h idonate-depleted rat polymorphonuclear leukocytes C. S. Ramesha and W. C. Pickett' Lipid Mediator Laboratory,
Ammonia chemical ionization mass spectrometry of intact diacyl phosphatidylcholine
 Ammonia chemical ionization mass spectrometry of intact diacyl phosphatidylcholine C. G. Crawford and R. D. Plattner Northern Regional Research Center, Agricultural Research Service, United States Department
Ammonia chemical ionization mass spectrometry of intact diacyl phosphatidylcholine C. G. Crawford and R. D. Plattner Northern Regional Research Center, Agricultural Research Service, United States Department
Lipid Analysis. Andréina Laffargue, IRD CRYMCEPT Montpellier workshop, October 17th Introduction to lipid structures
 Lipid Analysis Andréina Laffargue, IRD CRYMCEPT Montpellier workshop, October 17th 2005 Introduction to lipid structures Fatty acids Acylglycerols Glycerophospholipids Sterols Strategies involved in lipid
Lipid Analysis Andréina Laffargue, IRD CRYMCEPT Montpellier workshop, October 17th 2005 Introduction to lipid structures Fatty acids Acylglycerols Glycerophospholipids Sterols Strategies involved in lipid
Hydrolysis of Acylglycerols and Phospholipids of Milled Rice Surface Lipids During Storage 1
 RICE QUALITY AND PROCESSING Hydrolysis of Acylglycerols and Phospholipids of Milled Rice Surface Lipids During Storage 1 H.S. Lam and A. Proctor ABSTRACT The relative contribution of acylglycerols and
RICE QUALITY AND PROCESSING Hydrolysis of Acylglycerols and Phospholipids of Milled Rice Surface Lipids During Storage 1 H.S. Lam and A. Proctor ABSTRACT The relative contribution of acylglycerols and
1/3/2011. Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic
Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic
SYNTHESIS OF QUATERNARY AMMONIUM COMPOUNDS FROM NATURAL MATERIALS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 12(3), 2014, 880-884 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com SYNTHESIS OF QUATERNARY AMMONIUM COMPOUNDS FROM NATURAL MATERIALS MUHAMMAD ABDUL QADIR, MAHMOOD AHMED *, SHOUKAT HAYAT,
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 12(3), 2014, 880-884 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com SYNTHESIS OF QUATERNARY AMMONIUM COMPOUNDS FROM NATURAL MATERIALS MUHAMMAD ABDUL QADIR, MAHMOOD AHMED *, SHOUKAT HAYAT,
Chapter 8. Functions of Lipids. Structural Nature of Lipids. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2.
 BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
Title Revision n date
 A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
Chemistry 212 Fall Semester 1996 Examination #2
 Chemistry 212 Fall Semester 1996 Examination #2 University of Missouri Columbia Prof. Rainer Glaser Wednesday, October 16, 1996 103 Schlundt Hall, 8:40-9:30 featuring Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid
Chemistry 212 Fall Semester 1996 Examination #2 University of Missouri Columbia Prof. Rainer Glaser Wednesday, October 16, 1996 103 Schlundt Hall, 8:40-9:30 featuring Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid
Lipids Analysis. Lipids
 Lipids Analysis Stephen Barnes 3 5 15 Lipids Lipids are mostly very hydrophobic Most are conjugates of fatty acids of a variety of chain lengths, which have different degrees of unsaturation, cis trans
Lipids Analysis Stephen Barnes 3 5 15 Lipids Lipids are mostly very hydrophobic Most are conjugates of fatty acids of a variety of chain lengths, which have different degrees of unsaturation, cis trans
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enzyme-activatable Probe with a Self-immolative Linker for Rapid and Sensitive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enzyme-activatable Probe with a Self-immolative Linker for Rapid and Sensitive
xxi CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO PHOSPHOLIPIDS 1.1 DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS Simple lipids
 xxi CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO PHOSPHOLIPIDS 1.1 DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS 1 1.1.1 Simple lipids 2 1.1.2 Complex lipids 3 1.2 NOMENCLATURE OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS 6 1.3 SOURCES OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS
xxi CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO PHOSPHOLIPIDS 1.1 DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS 1 1.1.1 Simple lipids 2 1.1.2 Complex lipids 3 1.2 NOMENCLATURE OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS 6 1.3 SOURCES OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Rapid separation and identification of phosphatidylethanolamine molecular species
 Rapid separation and identification of phosphatidylethanolamine molecular species Jos F. H. M. Brouwers,* Elisabeth A. A. M. Vernooij, Aloysius G. M. Tielens,* and Lambert M. G. van Golde 1, * Laboratory
Rapid separation and identification of phosphatidylethanolamine molecular species Jos F. H. M. Brouwers,* Elisabeth A. A. M. Vernooij, Aloysius G. M. Tielens,* and Lambert M. G. van Golde 1, * Laboratory
Separation of Macrocyclic Lactones (Avermectins) on FLARE C18 MM & FLARE C18+ Columns
 Separation of Macrocyclic Lactones (Avermectins) on FLARE C8 MM & FLARE C8+ Columns Introduction Diamond Analytics Technical Note: T05- Avermectins are a series of 6-membered macrocyclic lactone derivatives
Separation of Macrocyclic Lactones (Avermectins) on FLARE C8 MM & FLARE C8+ Columns Introduction Diamond Analytics Technical Note: T05- Avermectins are a series of 6-membered macrocyclic lactone derivatives
Supporting Information for:
 Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
Core E Analysis of Neutral Lipids from Human Plasma June 4, 2010 Thomas J. Leiker and Robert M. Barkley
 Core E Analysis of Neutral Lipids from Human Plasma June 4, 2010 Thomas J. Leiker and Robert M. Barkley This protocol describes the extraction and direct measurement of cholesterol esters (CEs) and triacylglycerols
Core E Analysis of Neutral Lipids from Human Plasma June 4, 2010 Thomas J. Leiker and Robert M. Barkley This protocol describes the extraction and direct measurement of cholesterol esters (CEs) and triacylglycerols
Consequently, lipoprotein fractions have been analyzed
 THE PHOSPHOLIPID COMPOSITION OF HUMAN SERUM LIPOPROTEIN FRACTIONS SEPARATED BY ULTRACENTRIFUGATION * BY GERALD B. PHILLIPS (From the Departments of Biochemistry and Medicine, College of Physicians and
THE PHOSPHOLIPID COMPOSITION OF HUMAN SERUM LIPOPROTEIN FRACTIONS SEPARATED BY ULTRACENTRIFUGATION * BY GERALD B. PHILLIPS (From the Departments of Biochemistry and Medicine, College of Physicians and
Novel D-erythro N-Octanoyl Sphingosine Analogs As Chemo- and Endocrine. Resistant Breast Cancer Therapeutics
 Page 11 of 32 Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology Novel D-erythro N-Octanoyl Sphingosine Analogs As Chemo- and Endocrine Resistant Breast Cancer Therapeutics James W. Antoon, Jiawang Liu, Adharsh P. Ponnapakkam,
Page 11 of 32 Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology Novel D-erythro N-Octanoyl Sphingosine Analogs As Chemo- and Endocrine Resistant Breast Cancer Therapeutics James W. Antoon, Jiawang Liu, Adharsh P. Ponnapakkam,
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2008
 Experimental Details Unless otherwise noted, all chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company and were used as received. 2-DOS and neamine were kindly provided by Dr. F. Huang. Paromamine
Experimental Details Unless otherwise noted, all chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company and were used as received. 2-DOS and neamine were kindly provided by Dr. F. Huang. Paromamine
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1)
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 7. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 7. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR
A LDEHYDOGENIC LIPIDS were first observed in mammalian
 Evidence for the existence of cholesteryl alk-1-enyl ethers in bovine and porcine cardiac muscle JOHN R. GILBERTSON, HELGA H. GARLICH, and ROSE A. GELMAN Department of Biochemistry and Nutrition, Graduate
Evidence for the existence of cholesteryl alk-1-enyl ethers in bovine and porcine cardiac muscle JOHN R. GILBERTSON, HELGA H. GARLICH, and ROSE A. GELMAN Department of Biochemistry and Nutrition, Graduate
Facile Isolation of Carotenoid Antioxidants from Solanum lycopersicum using Flash Chromatography
 Facile Isolation of Carotenoid Antioxidants from Solanum lycopersicum using Flash Chromatography Jack E. Silver, jsilver@teledyne.com, Paul Bellinghausen, Nancy Fowler, and Ruth Pipes, Teledyne Isco, Inc.,
Facile Isolation of Carotenoid Antioxidants from Solanum lycopersicum using Flash Chromatography Jack E. Silver, jsilver@teledyne.com, Paul Bellinghausen, Nancy Fowler, and Ruth Pipes, Teledyne Isco, Inc.,
Activation of myocardial camp-dependent protein kinase by lysoplasmenylcholine
 FEBS 19630 FEBS Letters 420 (1997) 33^38 Activation of myocardial camp-dependent protein kinase by lysoplasmenylcholine Scott D. Williams, David A. Ford* Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,
FEBS 19630 FEBS Letters 420 (1997) 33^38 Activation of myocardial camp-dependent protein kinase by lysoplasmenylcholine Scott D. Williams, David A. Ford* Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Reading Study Problems Key Concepts and Skills Lecture Topics: Structures and reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives
 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Reading: Wade chapter 21, sections 21-1- 21-16 Study Problems: 21-45, 21-46, 21-48, 21-49, 21-50, 21-53, 21-56, 21-58, 21-63 Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the spectra of
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Reading: Wade chapter 21, sections 21-1- 21-16 Study Problems: 21-45, 21-46, 21-48, 21-49, 21-50, 21-53, 21-56, 21-58, 21-63 Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the spectra of
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE 1 Structures and IC50 values of compounds 13 32
 SUPPLEMETAL FIGURE 1 Structures and IC50 values of compounds 13 32 THE JURAL F UCLEAR MEDICIE Vol. 53 o. 11 ovember 2012 Synthesis of [ 19 F]1 ([ 19 F]--(2-{4-[5-(benzyloxy)pyridin-2-yl]piperazin-1-yl}-2-oxoethyl)-
SUPPLEMETAL FIGURE 1 Structures and IC50 values of compounds 13 32 THE JURAL F UCLEAR MEDICIE Vol. 53 o. 11 ovember 2012 Synthesis of [ 19 F]1 ([ 19 F]--(2-{4-[5-(benzyloxy)pyridin-2-yl]piperazin-1-yl}-2-oxoethyl)-
VaTx1 VaTx2 VaTx3. VaTx min Retention Time (min) Retention Time (min)
 a Absorbance (mau) 5 2 5 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6 2 3 4 5 6 VaTx2 High Ca 2+ Low Ca 2+ b 38.2 min Absorbance (mau) 3 2 3 4 5 3 2 VaTx2 39.3 min 3 4 5 3 2 4. min 3 4 5 Supplementary Figure. Toxin Purification For
a Absorbance (mau) 5 2 5 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6 2 3 4 5 6 VaTx2 High Ca 2+ Low Ca 2+ b 38.2 min Absorbance (mau) 3 2 3 4 5 3 2 VaTx2 39.3 min 3 4 5 3 2 4. min 3 4 5 Supplementary Figure. Toxin Purification For
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
 THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Thin layer chromatography is the best known technique of plant biochemistry. TLC is used for preliminary separation and determination of plant constituents. It is helpful for
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Thin layer chromatography is the best known technique of plant biochemistry. TLC is used for preliminary separation and determination of plant constituents. It is helpful for
LC-Based Lipidomics Analysis on QTRAP Instruments
 LC-Based Lipidomics Analysis on QTRAP Instruments Junhua Wang and Paul RS Baker SCIEX LC-Based Lipidomics Analysis Topics Covered Lipid extraction techniques Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC)
LC-Based Lipidomics Analysis on QTRAP Instruments Junhua Wang and Paul RS Baker SCIEX LC-Based Lipidomics Analysis Topics Covered Lipid extraction techniques Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC)
The First Au-Nanoparticles Catalyzed Green Synthesis of Propargylamines Via Three-Component Coupling Reaction of Aldehyde, Alkyne And Amine
 Supporting information of The First Au-anoparticles Catalyzed Green Synthesis of Propargylamines Via Three-Component Coupling Reaction of Aldehyde, Alkyne And Amine Mazaahir Kidwai a *, Vikas Bansal a,
Supporting information of The First Au-anoparticles Catalyzed Green Synthesis of Propargylamines Via Three-Component Coupling Reaction of Aldehyde, Alkyne And Amine Mazaahir Kidwai a *, Vikas Bansal a,
EXPERIMENT 8 (Organic Chemistry II) Carboxylic Acids Reactions and Derivatives
 EXPERIMENT 8 (rganic Chemistry II) Carboxylic Acids Reactions and Derivatives Pahlavan/Cherif Materials Medium test tubes (6) Test tube rack Beakers (50, 150, 400 ml) Ice Hot plate Graduated cylinders
EXPERIMENT 8 (rganic Chemistry II) Carboxylic Acids Reactions and Derivatives Pahlavan/Cherif Materials Medium test tubes (6) Test tube rack Beakers (50, 150, 400 ml) Ice Hot plate Graduated cylinders
THE DISTRIBUTION of fatty acids between the a- and. A stereospecific analysis of triglycerides
 A stereospecific analysis of triglycerides H. BROCKERHOFF Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Technological Research Laboratory, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada SUMMARY A method is presented for the analysis
A stereospecific analysis of triglycerides H. BROCKERHOFF Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Technological Research Laboratory, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada SUMMARY A method is presented for the analysis
SEASONAL CHANGES OF AVOCADO LIPIDS DURING FRUIT DEVELOPMENT AND STORAGE
 California Avocado Society 1968 Yearbook 52: 102-108 SEASONAL CHANGES OF AVOCADO LIPIDS DURING FRUIT DEVELOPMENT AND STORAGE Yoshio Kikuta Present address: Department of Botany, Faculty of Agriculture,
California Avocado Society 1968 Yearbook 52: 102-108 SEASONAL CHANGES OF AVOCADO LIPIDS DURING FRUIT DEVELOPMENT AND STORAGE Yoshio Kikuta Present address: Department of Botany, Faculty of Agriculture,
26.1 Acetyl Coenzyme A
 Chapter 26 Lipids Lipids Lipids are naturally occurring substances grouped together on the basis of a common property they they are more soluble in nonpolar solvents than in water. Some of the most important
Chapter 26 Lipids Lipids Lipids are naturally occurring substances grouped together on the basis of a common property they they are more soluble in nonpolar solvents than in water. Some of the most important
Preparation, isolation and characterization of N α -Fmoc-peptide isocyanates: Solution synthesis of oligo-α-peptidyl ureas
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Preparation, isolation and characterization of N α -Fmoc-peptide isocyanates: Solution synthesis of oligo-α-peptidyl ureas Vommina V. Suresh Babu*, Basanagoud S. Patil, and Rao Venkataramanarao
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Preparation, isolation and characterization of N α -Fmoc-peptide isocyanates: Solution synthesis of oligo-α-peptidyl ureas Vommina V. Suresh Babu*, Basanagoud S. Patil, and Rao Venkataramanarao
The four levels of protein structure are: primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure.
 Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids
 I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
 Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Classification of Lipids
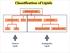 Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function Architecture of Membranes Subcellular fractionation techniques can partially separate and purify several important biological membranes, including the plasma and
Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function Architecture of Membranes Subcellular fractionation techniques can partially separate and purify several important biological membranes, including the plasma and
ciz CH2-O-P-Choline 1 NaOH GPC CH2-O-P-Choline IV V VI CH20H ?-o-co-r CH2-O-P-Choline I NaOH GPC
 Characterization of the alkyl ether species of phosphatidylcholine in bovine heart E. L. Pugh, M. Kates, and D. J. Hanahan Department of Biochemistry, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, K1N
Characterization of the alkyl ether species of phosphatidylcholine in bovine heart E. L. Pugh, M. Kates, and D. J. Hanahan Department of Biochemistry, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, K1N
Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics
 Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics Metabolomics- A realm of small molecules (
Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics Metabolomics- A realm of small molecules (
HPLC SEPARATION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS
 HPLC SEPARATION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS Abstract: The principles involved in the selection of solvents and the use of counter ions, together with the choice of column, for the separation of phospholipids by highperformance
HPLC SEPARATION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS Abstract: The principles involved in the selection of solvents and the use of counter ions, together with the choice of column, for the separation of phospholipids by highperformance
Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable. Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors
 Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors Yu Zhao, Jianming Kang, Chung-Min Park, Powell E. Bagdon, Bo Peng, and Ming Xian * Department of Chemistry, Washington
Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors Yu Zhao, Jianming Kang, Chung-Min Park, Powell E. Bagdon, Bo Peng, and Ming Xian * Department of Chemistry, Washington
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles. Chapters 20, 21 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry
 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Chapters 20, 21 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 2 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives nitrile R = CH 3 acetonitrile 3 Structure and Bonding
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Chapters 20, 21 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 2 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives nitrile R = CH 3 acetonitrile 3 Structure and Bonding
Automated Sample Preparation for Profiling Fatty Acids in Blood and Plasma using the Agilent 7693 ALS
 Automated Sample Preparation for Profiling Fatty Acids in Blood and Plasma using the Agilent 7693 ALS Application Note Clinical Research Authors Frank David and Bart Tienpont, Research Institute for Chromatography,
Automated Sample Preparation for Profiling Fatty Acids in Blood and Plasma using the Agilent 7693 ALS Application Note Clinical Research Authors Frank David and Bart Tienpont, Research Institute for Chromatography,
IAM Chromatography. Introduction
 IAM Chromatography IAM Drug Discovery Columns Introduction References: 1. Regis 1998-99 Chromatography Catalog A simple, rapid method to predict drug transport across biological barriers has been a long
IAM Chromatography IAM Drug Discovery Columns Introduction References: 1. Regis 1998-99 Chromatography Catalog A simple, rapid method to predict drug transport across biological barriers has been a long
Enantioselective synthesis of anti- and syn-β-hydroxy-α-phenyl carboxylates via boron-mediated asymmetric aldol reaction
 Enantioselective synthesis of anti- and syn-β-hydroxy-α-phenyl carboxylates via boron-mediated asymmetric aldol reaction P. Veeraraghavan Ramachandran* and Prem B. Chanda Department of Chemistry, Purdue
Enantioselective synthesis of anti- and syn-β-hydroxy-α-phenyl carboxylates via boron-mediated asymmetric aldol reaction P. Veeraraghavan Ramachandran* and Prem B. Chanda Department of Chemistry, Purdue
The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics. Outlines
 The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics Jeevan Prasain jprasain@uab.edu 6-2612 utlines Brief introduction to lipidomics Analytical methodology: MS/MS structure elucidation of phospholipids Phospholipid
The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics Jeevan Prasain jprasain@uab.edu 6-2612 utlines Brief introduction to lipidomics Analytical methodology: MS/MS structure elucidation of phospholipids Phospholipid
Changes in Composition and Structure of Triacylglycerol of Adipose Tissue and Skin from Laying Hens as Influenced by Dietary Fats
 Changes in Composition and Structure of Triacylglycerol of Adipose Tissue and Skin from Laying Hens as Influenced by Dietary Fats Akihiro HIRATA*, Tetsuya MASUDA*, Teiji KIMURA* and Yoshiyuki OHTAKE* *
Changes in Composition and Structure of Triacylglycerol of Adipose Tissue and Skin from Laying Hens as Influenced by Dietary Fats Akihiro HIRATA*, Tetsuya MASUDA*, Teiji KIMURA* and Yoshiyuki OHTAKE* *
B. 50 mm Calcium Chloride Solution (CaCl 2 ) (Prepare 25 ml in Reagent A using Calcium Chloride, Dihydrate, Sigma Prod. No. C-3881.
 SIGMA QUALITY CONTROL TEST PROCEDURE ProductInformation Enzymatic Assay of PHOSPHOLIPASE C PRINCIPLE: L-α-Lecithin + H 2 O Phospholipase C > 1,2-Diglyceride + Choline Phosphate Choline phosphate + H 2
SIGMA QUALITY CONTROL TEST PROCEDURE ProductInformation Enzymatic Assay of PHOSPHOLIPASE C PRINCIPLE: L-α-Lecithin + H 2 O Phospholipase C > 1,2-Diglyceride + Choline Phosphate Choline phosphate + H 2
Sphingomyelin with Detection in the Region of 200nm
 Biochem. J. (1976) 155, 55-6 Printed in Great Britain 55 High-Performance Liquid Chromatography of Phosphatidylcholine and Sphingomyelin with Detection in the Region of 2nm By FIROZE B. JUNGALWALA, JAMES
Biochem. J. (1976) 155, 55-6 Printed in Great Britain 55 High-Performance Liquid Chromatography of Phosphatidylcholine and Sphingomyelin with Detection in the Region of 2nm By FIROZE B. JUNGALWALA, JAMES
The development of a detection method discriminating for
 1 2 3 The development of a detection method discriminating for mannosylerythritol lipids and acylglycerols Simon Van Kerrebroeck 1, *, Hannes Petit, Joeri Beauprez 1, Inge N.A. Van Bogaert 1, Wim Soetaert
1 2 3 The development of a detection method discriminating for mannosylerythritol lipids and acylglycerols Simon Van Kerrebroeck 1, *, Hannes Petit, Joeri Beauprez 1, Inge N.A. Van Bogaert 1, Wim Soetaert
Biomolecules. Unit 3
 Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Classification, functions and structure
 Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Metabolism of plasmalogen: 11. The determination of alkenyl ethers in the
 J. Lipid Research. April 196 Volume 4, Number Metabolism of plasmalogen: 11. The determination of alkenyl ethers in the presence of free aldehydes* H. R. ARNER? and. E. M. LANDS Department of Biological
J. Lipid Research. April 196 Volume 4, Number Metabolism of plasmalogen: 11. The determination of alkenyl ethers in the presence of free aldehydes* H. R. ARNER? and. E. M. LANDS Department of Biological
Mild alkali-stable phospholipids in chicken egg yolks: characterization of 1 -alkenyl and l-alkyl-snglycero-3-phosphoethanolamine, sphingomyelin,
 Mild alkali-stable phospholipids in chicken egg yolks: characterization of 1 -alkenyl and l-alkyl-snglycero-3-phosphoethanolamine, sphingomyelin, and 1 -al kyl-sn-glycero-3-p hosphoc hol i ne Un Hoi Do
Mild alkali-stable phospholipids in chicken egg yolks: characterization of 1 -alkenyl and l-alkyl-snglycero-3-phosphoethanolamine, sphingomyelin, and 1 -al kyl-sn-glycero-3-p hosphoc hol i ne Un Hoi Do
The HPLC Preparative Scale-Up of Soybean Phospholipids Application
 The HPLC Preparative Scale-Up of Soybean Phospholipids Application Food and Flavors Authors Cliff Woodward and Ron Majors Agilent Technologies, Inc. 285 Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 1988-161 USA Abstract
The HPLC Preparative Scale-Up of Soybean Phospholipids Application Food and Flavors Authors Cliff Woodward and Ron Majors Agilent Technologies, Inc. 285 Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 1988-161 USA Abstract
Sanjog Ramdharane 1, Dr. Vinay Gaitonde 2
 JPSBR: Volume 5, Issue 2: 2015 (151-155) ISS. 2271-3681 A ew Gradient RP- HPLC Method for Quantitative Analysis of : (3-luoro-4- Morpholin-4-yl-Phenyl)-Carbamic Acid Methyl Ester and its Related Substances
JPSBR: Volume 5, Issue 2: 2015 (151-155) ISS. 2271-3681 A ew Gradient RP- HPLC Method for Quantitative Analysis of : (3-luoro-4- Morpholin-4-yl-Phenyl)-Carbamic Acid Methyl Ester and its Related Substances
Isolation, Separation, and Characterization of Organic Acids*
 In Dashek, William V., ed. Methods in plant biochemistry and molecular biology. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press: pp. 107-113. Chapter 9.1997. Isolation, Separation, and Characterization of Organic Acids* William
In Dashek, William V., ed. Methods in plant biochemistry and molecular biology. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press: pp. 107-113. Chapter 9.1997. Isolation, Separation, and Characterization of Organic Acids* William
Lecture 3 6/28/10. Membrane Lipids. Importance of Membranes. Categories of Lipids. Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7. ! Membranes are important in
 Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Diacylglycerol Metabolism and Arachidonic Acid Release in Human Fetal Membranes and Decidua Vera*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 256, No. 14, Issue of July 25, pp. 7316-7321, 1981 Printed in U.S.A. Diacylglycerol Metabolism and Arachidonic Acid Release in Human Fetal Membranes and Decidua
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 256, No. 14, Issue of July 25, pp. 7316-7321, 1981 Printed in U.S.A. Diacylglycerol Metabolism and Arachidonic Acid Release in Human Fetal Membranes and Decidua
Lecture 20. Herman Emil Fischer Nobel Prize 1902 Sugars, Esters and Purines. April 4, Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 20 April 4, 2019 Herman Emil Fischer 1852-1919 Nobel Prize 1902 Sugars, Esters and Purines Acid-catalyzed Esterification (also called Fischer esterification) CH CH 3 H H H 2 CCH 3 Please study
Lecture 20 April 4, 2019 Herman Emil Fischer 1852-1919 Nobel Prize 1902 Sugars, Esters and Purines Acid-catalyzed Esterification (also called Fischer esterification) CH CH 3 H H H 2 CCH 3 Please study
DETERMINATION OF FATTY ACIDS IN EDIBLE OILS BY CAPILARY GC
 DETERMINATION OF FATTY ACIDS IN EDIBLE OILS BY CAPILARY GC Vesna Kostik 1 University Goce Delcev Stip Faculty of Medicine Department of Pharmacy 1 WHY FATTY ACID (FA) ANALYSIS IN EDIBLE OILS The content
DETERMINATION OF FATTY ACIDS IN EDIBLE OILS BY CAPILARY GC Vesna Kostik 1 University Goce Delcev Stip Faculty of Medicine Department of Pharmacy 1 WHY FATTY ACID (FA) ANALYSIS IN EDIBLE OILS The content
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information ovel pseudo[2]rotaxanes constructed by selfassembly of dibenzyl
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information ovel pseudo[2]rotaxanes constructed by selfassembly of dibenzyl
PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM. BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. State the definition and classification of Phospholipids. 2. Describe the general structure
PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. State the definition and classification of Phospholipids. 2. Describe the general structure
Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols
 Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
notes on methodology Rapid separation of lipid classes in high yield and purity using bonded phase columns
 notes on methodology Rapid separation of lipid classes in high yield and purity using bonded phase columns M. A. Kaluzny, * L. A. Duncan,* * M. V. Merritt,' and D. E. Eppse.* Physical and Analytical Chemisty
notes on methodology Rapid separation of lipid classes in high yield and purity using bonded phase columns M. A. Kaluzny, * L. A. Duncan,* * M. V. Merritt,' and D. E. Eppse.* Physical and Analytical Chemisty
Phospholipids and acyl groups in subcellular fractions from human cerebral cortex
 Phospholipids and acyl groups in subcellular fractions from human cerebral cortex Grace Y. Sun Laboratory of Neurochemistry, Cleveland Psychiatric Institute, Cleveland, Ohio 44109 Abstract Subcellular
Phospholipids and acyl groups in subcellular fractions from human cerebral cortex Grace Y. Sun Laboratory of Neurochemistry, Cleveland Psychiatric Institute, Cleveland, Ohio 44109 Abstract Subcellular
Chem 263 Dec 1, 2016
 Chem 263 Dec 1, 2016 eactivity of Carboxylic acid Derivatives More eactive S 2 ' ' + a ' 2 - M + Less eactive Example: Acid chloride to anhydride Since an acid chloride is more reactive than an anhydride,
Chem 263 Dec 1, 2016 eactivity of Carboxylic acid Derivatives More eactive S 2 ' ' + a ' 2 - M + Less eactive Example: Acid chloride to anhydride Since an acid chloride is more reactive than an anhydride,
Esters of Carboxylic Acids These are derivatives of carboxylic acids where the hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkoxy group.
 Carboxylic acid Derivatives Carboxylic acid derivatives are described as compounds that can be converted to carboxylic acids via simple acidic or basic hydrolysis. The most important acid derivatives are
Carboxylic acid Derivatives Carboxylic acid derivatives are described as compounds that can be converted to carboxylic acids via simple acidic or basic hydrolysis. The most important acid derivatives are
A Definitive Lipidomics Workflow for Human Plasma Utilizing Off-line Enrichment and Class Specific Separation of Phospholipids
 A Definitive Lipidomics Workflow for Human Plasma Utilizing Off-line Enrichment and Class Specific Separation of Phospholipids Jeremy Netto, 1 Stephen Wong, 1 Federico Torta, 2 Pradeep Narayanaswamy, 2
A Definitive Lipidomics Workflow for Human Plasma Utilizing Off-line Enrichment and Class Specific Separation of Phospholipids Jeremy Netto, 1 Stephen Wong, 1 Federico Torta, 2 Pradeep Narayanaswamy, 2
UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry. Natura-Brasil. EA Laboratory of Dermatological Research,
 Iuliana Popa 1, Noëlle Remoué 2 and Jacques Portoukalian 3 1 UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry 2 Natura-Brasil 3 EA 41 69 Laboratory of Dermatological Research, University of Lyon I, Faculty
Iuliana Popa 1, Noëlle Remoué 2 and Jacques Portoukalian 3 1 UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry 2 Natura-Brasil 3 EA 41 69 Laboratory of Dermatological Research, University of Lyon I, Faculty
Seminar 6 Theoretical part
 Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
Supporting Information. First synthetic entry to the trimer stage of 5,6-dihydroxyindole polymerization: orthoalkynylaniline-based
 Supporting Information First synthetic entry to the trimer stage of 5,6-dihydroxyindole polymerization: orthoalkynylaniline-based access to the missing 2,7 :2,7 -triindole Luigia Capelli, Paola Manini,*
Supporting Information First synthetic entry to the trimer stage of 5,6-dihydroxyindole polymerization: orthoalkynylaniline-based access to the missing 2,7 :2,7 -triindole Luigia Capelli, Paola Manini,*
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd
 ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
Gas Chromatography/ Mass Spectrometry
 Gas Chromatography/ Mass Spectrometry Edited by H.F. Linskens and J.F. Jackson Contributors R.S. Bandurski G. Combaut A.Ehmann P.Hedden B.Janistyn H.Kameoka H.Kodama D.V.Lynch J.K.MacLeod H.Nyberg L.M.S.Palni
Gas Chromatography/ Mass Spectrometry Edited by H.F. Linskens and J.F. Jackson Contributors R.S. Bandurski G. Combaut A.Ehmann P.Hedden B.Janistyn H.Kameoka H.Kodama D.V.Lynch J.K.MacLeod H.Nyberg L.M.S.Palni
Supplemental Figure S1
 Supplemental Figure S1 GC-MS profile of total FA of BY-2 purified PM IS: h14 IS: 17: Glycerolipids 16: GIPCs 18:1,2,3 18: h22 h24 Sterols GluCER h16: 2: h2 22: h21 c23 24: h23 h25 h26 Supplemental Figure
Supplemental Figure S1 GC-MS profile of total FA of BY-2 purified PM IS: h14 IS: 17: Glycerolipids 16: GIPCs 18:1,2,3 18: h22 h24 Sterols GluCER h16: 2: h2 22: h21 c23 24: h23 h25 h26 Supplemental Figure
