Highly efficient gene silencing activity of sirna embedded in a nanostructured gyroid cubic lipid matrix
|
|
|
- Alannah Elliott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Highly efficient gene silencing activity of sirna embedded in a nanostructured gyroid cubic lipid matrix Cecília Leal *, Nathan F. Bouxsein, Kai K. Ewert and Cyrus R. Safinya * Physics, Materials, and Molecular, Cellular & Developmental Biology Departments, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA 93106, USA Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to C.L. (cecilal@mrl.ucsb.edu) or C.R.S. (safinya@mrl.ucsb.edu). Supplementary information S1
2 Figure S1: Chemical structure of the lipids used in this work. All lipids are commercially available. They bear similar, oleic acid tails to prevent lateral demixing of the membranes. Similar to conventional lipids, GM (also termed monoolein) has a very low solubility in water (10-6 M) but is able to swell in water giving rise to a variety of liquid crystalline mesophases 1. GM H H DTAP N + Cl - DPC P - N + Figure S2: In order to investigate the effect of the nucleic acid length on the stability of the cubic phase structure, we used the same lipid system (DTAP/GM) to prepare complexes with long DNA (highly polymerized calf thymus (HPCT) DNA, USB). For DTAP/GM HPCT DNA complexes, no cubic phase was observed at any Φ GM. (a) Synchrotron SAXS scans of DTAP/GM DNA complexes at varied Φ GM, displaying the inverted hexagonal (H C II ) and the lamellar (L C α ) phase. In the lamellar phase (L C α ), the characteristic correlation between DNA molecules gives rise to a broad peak at q DNA that shifts to lower q (larger interhelical differences) as the content of neutral lipid increases. The lamellar phase is obtained up to Φ GM =0.70. At this point, coexistence with the inverse hexagonal phase (H C II ) is observed (Φ GM = 0.70 and 0.75). At higher Φ GM, the H C II phase is found exclusively. At no Φ GM did we find evidence for a cubic phase of CL DNA complexes. Generally, gyroid cubic phases have a lattice spacing of the order of 100 Å 2. The sirna used in this study (19 bp with 2nt 3 overhangs) is a short, rod-like molecule with a length ( 52 Å) much shorter than its persistence length (between 500 Å and 1000 Å), and an S2
3 aspect ratio of about two. Thus, its inclusion in a bicontinuous lipid matrix can be performed without disruption of the cubic structure. In contrast, the average length of HPCT DNA molecules is many times their persistence length of 500 Å to 1000 Å and the energetic cost associated with bending the semi-flexible DNA to incorporate it within the curved water channels of the cubic phase appears to inhibit formation of this phase. Instead, the 2D inverse hexagonal phase, which requires minimal DNA bending, is retained even at very high Φ GM. (b) Unit cell spacing (d and a H ) obtained for the DTAP/GM DNA complexes at ρ = 1 in ptimem buffer. The lattice spacings obtained for the DTAP/GM DNA complex phases are a few Angstroms smaller than those obtained for the corresponding sirna complexes. At Φ GM = 0.50, the lamellar phase spacing d = 2π/q 001 equals Å for DNA complexes and Å for sirna complexes, with the difference closely matching the difference in diameter (sirna = 26 Å and DNA = 20 Å) of the nucleic acids. S3
4 Figure S3: Unit cell dimensions (a, a H, and d, for the cubic, inverse hexagonal, and lamellar phases, respectively) obtained for DTAP/GM-siRNA complexes at charge ratios ρ = 1 (blue triangle), ρ = 0.5 (red square), ρ = 2 (black circle) in two different aqueous environments (low conductivity water (left) and ptimem cell culture medium (right)). The amount of sirna was kept constant in all samples, while the amount of lipid was varied to achieve the desired charge ratio. There is no significant difference between the spacings obtained for the different aqueous environments. In addition, the various phases display essentially the same lattice spacings for all charge ratios. G, However, the phase transition from the cubic phase (Q sirna II ) to the inverse hexagonal phase (H sirna II ) occurs at higher molar fractions of GM for negatively charged complexes (ρ = 0.5) than for electroneutral (ρ = 1) and positively charged complexes (ρ = 2). In other words, the cubic phase is stabilized for a narrower range of Φ GM (Φ GM 0.80 at ρ = 0.5 vs. Φ GM 0.75 at ρ = 1 and ρ = 2 in ptimem). This fact is even more evident in water, where the cubic phase is only stabilized for Φ GM 0.85 at ρ = 0.5. The cell culture medium ptimem contains salts, and the resulting electrostatic screening seems to allow the cubic phase to form for a wider range of Φ GM. It appears that the cubic phase is less able than the inverted hexagonal phase to accommodate a lipid/sirna charge mismatch in the regime of excess sirna (ρ = 0.5). S4
5 Table S1 Small-angle X-ray results for experiments presented in Figure 2 q (1/Å) b a (Å) e hkl a h + k + l LIPIDS c Lipid-siRNA d LIPIDS c Lipid-siRNA d not observed not observed / Lipid-siRNA d. Dilute regime (Fig. 2e) a hkl are the lattice indices, b q is the X-ray wave vector, c LIPIDS refers to DTAP/GM (Φ GM =0.85) with 30 wt% water, d Lipid-siRNA is the DTAP/GM sirna (Φ GM =0.85) complex, and e a is the lattice spacing of the Ia3d cubic phase given by a = π h + k + l q References 1. Larsson, K. Lipids-molecular organization, physical functions and technical applications. (The oily press Ltd, Dundee; 1994). 2. Larsson, K. Two cubic phases in monoolein-water system. Nature 304, (1983). 3. Complete author list for reference 9 in the manuscript: Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; Garrigue, A.; Wang, G. P.; Soulier, J.; Lim, A.; Morillon, E.; Clappier, E.; Caccavelli, L.; Delabesse, E.; Beldjord, K.; Asnafi, V.; Macintyre, E.; Dal Cortivo, L.; Radford, I.; Brousse, N.; Sigaux, F.; Moshous, D.; Hauer, J.; Borkhardt, A.; Belohradsky, B. H.; Wintergerst, U.; Velez, M. C.; Leiva, L.; Sorensen, R.; Wulffraat, N.; Blanche, S.; Bushman, F. D.; Fischer, A.; Cavazzana-Calvo, M. S5
6 S6
Supplementary Information: Supplementary Note 1: Confirmation of Complex 3D Self-Assembly and Assignment of Lyotropic Phases
 Supplementary Information: Supplementary Note 1: Confirmation of Complex 3D Self-Assembly and Assignment of Lyotropic Phases This section shows SAXS patterns from different lyotropic phases we observed
Supplementary Information: Supplementary Note 1: Confirmation of Complex 3D Self-Assembly and Assignment of Lyotropic Phases This section shows SAXS patterns from different lyotropic phases we observed
Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Phase Behaviour in Amphiphile-Protic Ionic Liquid Systems
 Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Phase Behaviour in Amphiphile-Protic Ionic Liquid Systems Zhengfei Chen, 1,2 Tamar L. Greaves, 2 Celesta Fong, 2 Rachel A. Caruso, 1,2* Calum J. Drummond 2* 1 PFPC, School
Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Phase Behaviour in Amphiphile-Protic Ionic Liquid Systems Zhengfei Chen, 1,2 Tamar L. Greaves, 2 Celesta Fong, 2 Rachel A. Caruso, 1,2* Calum J. Drummond 2* 1 PFPC, School
SAXS on lipid structures
 Practical Course in Biophysics, Experiment R2b SAXS on lipid structures Summer term 2015 Room: Advisor: X-ray lab at LS Rädler, NU111 Stefan Fischer Tel: +49-(0)89-2180-1459 Email: stefan.f.fischer@physik.lmu.de
Practical Course in Biophysics, Experiment R2b SAXS on lipid structures Summer term 2015 Room: Advisor: X-ray lab at LS Rädler, NU111 Stefan Fischer Tel: +49-(0)89-2180-1459 Email: stefan.f.fischer@physik.lmu.de
TUTORIAL IN SMALL ANGLE X-RAY SCATTERING ANALYSIS
 TUTORIAL IN SMALL ANGLE X-RAY SCATTERING ANALYSIS at the Abdus Salam International Center of Theoretical Physics (ICTP) Heinz Amenitsch Sigrid Bernstorff Michael Rappolt Trieste, 15. May 2006 (14:30-17:15)
TUTORIAL IN SMALL ANGLE X-RAY SCATTERING ANALYSIS at the Abdus Salam International Center of Theoretical Physics (ICTP) Heinz Amenitsch Sigrid Bernstorff Michael Rappolt Trieste, 15. May 2006 (14:30-17:15)
8 Influence of permeation modulators on the behaviour of a SC lipid model mixture
 8 Influence of permeation modulators on the behaviour of a SC lipid model mixture 8.1 Introduction In the foregoing parts of this thesis, a model membrane system of SC lipids has been developed and characterized.
8 Influence of permeation modulators on the behaviour of a SC lipid model mixture 8.1 Introduction In the foregoing parts of this thesis, a model membrane system of SC lipids has been developed and characterized.
Cationic Liposome-Microtubule Complexes: Lipid-Protein Bio-Nanotubes with Open or Closed Ends
 Science Highlight October 2005 Cationic Liposome-Microtubule Complexes: Lipid-Protein Bio-Nanotubes with Open or Closed Ends Uri Raviv *,, Daniel J. Needleman *,, Youli Li *,, Herbert P. Miller, Leslie
Science Highlight October 2005 Cationic Liposome-Microtubule Complexes: Lipid-Protein Bio-Nanotubes with Open or Closed Ends Uri Raviv *,, Daniel J. Needleman *,, Youli Li *,, Herbert P. Miller, Leslie
Structure of DNA-CTAB-hexanol complexes
 Structure of DNA-CTAB-hexanol complexes Rema Krishnaswamy, 1 Georg Pabst, 2 Michael Rappolt, 2 V. A. Raghunathan, 1 and A. K. Sood 3 1 Raman Research Institute, Bangalore 560 080, India 2 Institute of
Structure of DNA-CTAB-hexanol complexes Rema Krishnaswamy, 1 Georg Pabst, 2 Michael Rappolt, 2 V. A. Raghunathan, 1 and A. K. Sood 3 1 Raman Research Institute, Bangalore 560 080, India 2 Institute of
Development and Application of HIV Vectors Pseudotyped with HIV Envelopes
 16 Development and Application of HIV Vectors Pseudotyped with HIV Envelopes Koichi Miyake and Takashi Shimada Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Division of Gene Therapy Research Center
16 Development and Application of HIV Vectors Pseudotyped with HIV Envelopes Koichi Miyake and Takashi Shimada Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Division of Gene Therapy Research Center
Membrane structure correlates to function of LLP2 on the cytoplasmic tail of HIV-1 gp41 protein
 Membrane structure correlates to function of LLP2 on the cytoplasmic tail of HIV-1 gp41 protein Alexander L. Boscia 1, Kiyotaka Akabori 1, Zachary Benamram 1, Jonathan A. Michel 1, Michael S. Jablin 1,
Membrane structure correlates to function of LLP2 on the cytoplasmic tail of HIV-1 gp41 protein Alexander L. Boscia 1, Kiyotaka Akabori 1, Zachary Benamram 1, Jonathan A. Michel 1, Michael S. Jablin 1,
Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology
 Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology Instability of Lipid Membrane Benxin Jing a, Marie Hutin c, Erin Connor a, Leroy Cronin c,* and Yingxi Zhu a,b,* a Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology Instability of Lipid Membrane Benxin Jing a, Marie Hutin c, Erin Connor a, Leroy Cronin c,* and Yingxi Zhu a,b,* a Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry)
 051117 Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry) (Figures from Heimenz Colloid Sci.) 1) Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules (molecules having one end hydrophobic and the other hydrophilic) and are
051117 Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry) (Figures from Heimenz Colloid Sci.) 1) Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules (molecules having one end hydrophobic and the other hydrophilic) and are
and controllable behavior - Supplementary Information
 Metastability in lipid based particles exhibits temporally deterministic and controllable behavior - Supplementary Information Guy Jacoby, Keren Cohen, Kobi Barkan, Yeshayahu Talmon, Dan Peer, Roy Beck
Metastability in lipid based particles exhibits temporally deterministic and controllable behavior - Supplementary Information Guy Jacoby, Keren Cohen, Kobi Barkan, Yeshayahu Talmon, Dan Peer, Roy Beck
Designing swollen lipid nanoparticles at physiologically relevant conditions
 1 Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Bachelor of Science Designing swollen lipid nanoparticles at physiologically relevant conditions Biyun Zhang 2 nd May 2017 Abstract
1 Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Bachelor of Science Designing swollen lipid nanoparticles at physiologically relevant conditions Biyun Zhang 2 nd May 2017 Abstract
Self-Assembly. Lecture 3 Lecture 3 Surfactants Self-Assembly
 Self-Assembly Lecture 3 Lecture 3 Surfactants Self-Assembly Anionic surfactants unsaturated omega-3 3 fatty acids rd carbon from the metyl end has double bond saturated Non-ionic surfactants Cationic surfactants
Self-Assembly Lecture 3 Lecture 3 Surfactants Self-Assembly Anionic surfactants unsaturated omega-3 3 fatty acids rd carbon from the metyl end has double bond saturated Non-ionic surfactants Cationic surfactants
Millicient A. Firestone, Amanda C. Wolf, and Sonke Seifert. Chris Bianchi 4/30/12
 Small-Angle X-ray Scattering of the Interaction of Poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(propylene oxide)-b- Poly(ethylene oxide)triblock Copolymers with Lipid Bilayers Millicient A. Firestone, Amanda C. Wolf, and
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering of the Interaction of Poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(propylene oxide)-b- Poly(ethylene oxide)triblock Copolymers with Lipid Bilayers Millicient A. Firestone, Amanda C. Wolf, and
Phase Diagram, Stability, and Overcharging of Lamellar Cationic Lipid DNA Self-Assembled Complexes
 Biophysical Journal Volume 77 August 1999 915 924 915 Phase Diagram, Stability, and Overcharging of Lamellar Cationic Lipid DNA Self-Assembled Complexes I. Koltover, T. Salditt, and C. R. Safinya Materials
Biophysical Journal Volume 77 August 1999 915 924 915 Phase Diagram, Stability, and Overcharging of Lamellar Cationic Lipid DNA Self-Assembled Complexes I. Koltover, T. Salditt, and C. R. Safinya Materials
Thermotropic structural changes of saturated-cationic-lipid DNA complexes
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 January 1999 Europhys. Lett., 45 (1), pp. 90-96 (1998) Thermotropic structural changes of saturated-cationic-lipid DNA complexes R. Zantl 1,F.Artzner 1,G.Rapp 2 and J. O. Rädler 1
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 January 1999 Europhys. Lett., 45 (1), pp. 90-96 (1998) Thermotropic structural changes of saturated-cationic-lipid DNA complexes R. Zantl 1,F.Artzner 1,G.Rapp 2 and J. O. Rädler 1
Self-assembled Multicompartment Liquid Crystalline Lipid Carriers for Protein, Peptide, and Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery
 Supporting Information Self-assembled Multicompartment Liquid Crystalline Lipid Carriers for Protein, Peptide, and Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery Angelina Angelova, Borislav Angelov, Rada Mutafchieva, Sylviane
Supporting Information Self-assembled Multicompartment Liquid Crystalline Lipid Carriers for Protein, Peptide, and Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery Angelina Angelova, Borislav Angelov, Rada Mutafchieva, Sylviane
Solution Behaviour of Polyethylene Oxide, Nonionic Gemini Surfactants
 Solution Behaviour of Polyethylene Oxide, Nonionic Gemini Surfactants A thesis submitted to The University of Sydney in fulfilment of the requirements for the admission to the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Solution Behaviour of Polyethylene Oxide, Nonionic Gemini Surfactants A thesis submitted to The University of Sydney in fulfilment of the requirements for the admission to the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Transitions between Distinct Compaction Regimes in Complexes of Multivalent Cationic Lipids and DNA
 836 Biophysical Journal Volume 95 July 2008 836 846 Transitions between Distinct Compaction Regimes in Complexes of Multivalent Cationic Lipids and DNA Oded Farago,* Kai Ewert, y Ayesha Ahmad, y Heather
836 Biophysical Journal Volume 95 July 2008 836 846 Transitions between Distinct Compaction Regimes in Complexes of Multivalent Cationic Lipids and DNA Oded Farago,* Kai Ewert, y Ayesha Ahmad, y Heather
PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY Physical and Mathematical Sciences 2018, 52(3), p. 217 221 P h y s i c s STUDY OF THE SWELLING OF THE PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER, DEPENDING ON THE ANGLE BETWEEN THE
PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY Physical and Mathematical Sciences 2018, 52(3), p. 217 221 P h y s i c s STUDY OF THE SWELLING OF THE PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER, DEPENDING ON THE ANGLE BETWEEN THE
Synthesis and Characterization of Degradable Multivalent Cationic Lipids with Disulfide-Bond Spacers for Gene Delivery
 Accepted Manuscript Synthesis and Characterization of Degradable Multivalent Cationic Lipids with Disulfide-Bond Spacers for Gene Delivery Rahau S. Shirazi, Kai K. Ewert, Cecilia Leal, Ramsey N. Majzoub,
Accepted Manuscript Synthesis and Characterization of Degradable Multivalent Cationic Lipids with Disulfide-Bond Spacers for Gene Delivery Rahau S. Shirazi, Kai K. Ewert, Cecilia Leal, Ramsey N. Majzoub,
ISM08. Surfactants II Chapters 3 and 4
 ISM08 Surfactants II Chapters 3 and 4 1 Topics Emulsions Foam Curvature Laplace pressure Packing factor Lyotropic phases Membranes and vesicles 2 Emulsions Emulsions are dispersions of immiscible or partially
ISM08 Surfactants II Chapters 3 and 4 1 Topics Emulsions Foam Curvature Laplace pressure Packing factor Lyotropic phases Membranes and vesicles 2 Emulsions Emulsions are dispersions of immiscible or partially
Supporting information
 S1 Supporting information Biodegradable Injectable Polymer Systems Exhibiting Temperature-Responsive Irreversible Sol-to-Gel Transition by Covalent Bond Formation Yasuyuki YOSHIDA 1,2, Keisuke KAWAHARA
S1 Supporting information Biodegradable Injectable Polymer Systems Exhibiting Temperature-Responsive Irreversible Sol-to-Gel Transition by Covalent Bond Formation Yasuyuki YOSHIDA 1,2, Keisuke KAWAHARA
H 2 O. Liquid, solid, and vapor coexist in the same environment
 Water H 2 O Liquid, solid, and vapor coexist in the same environment WATER MOLECULES FORM HYDROGEN BONDS Water is a fundamental requirement for life, so it is important to understand the structural and
Water H 2 O Liquid, solid, and vapor coexist in the same environment WATER MOLECULES FORM HYDROGEN BONDS Water is a fundamental requirement for life, so it is important to understand the structural and
Lipid Bilayer Based Binding Surfaces for Nucleic Acids
 Lipid Bilayer Based Binding Surfaces for Nucleic Acids Caitlin Kreutz Major: Biology Mentor: Emin Oroudjev Faculty Advisor: Helen Hansma Funding By: National Institutes of Health July 28 th, 2005 Main
Lipid Bilayer Based Binding Surfaces for Nucleic Acids Caitlin Kreutz Major: Biology Mentor: Emin Oroudjev Faculty Advisor: Helen Hansma Funding By: National Institutes of Health July 28 th, 2005 Main
DEVELOPMENT OF TERNARY PHASE DIAGRAM: OPTICAL AND MECHANICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF WATER/TAPIOCA STARCH/TRITON X-100 LIQUID CRYSTAL
 DEVELOPMENT OF TERNARY PHASE DIAGRAM: OPTICAL AND MECHANICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF WATER/TAPIOCA STARCH/TRITON X-100 LIQUID CRYSTAL By Muhd Fazreel B Muhammad Rosli A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment
DEVELOPMENT OF TERNARY PHASE DIAGRAM: OPTICAL AND MECHANICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF WATER/TAPIOCA STARCH/TRITON X-100 LIQUID CRYSTAL By Muhd Fazreel B Muhammad Rosli A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment
Water Interactions with Membrane Proteins & Other Biomolecules from 1. H-X Heteronuclear Correlation NMR. Mei Hong Department of Chemistry, MIT
 Water Interactions with Membrane Proteins & Other Biomolecules from 1 H-X Heteronuclear Correlation NMR Mei Hong Department of Chemistry, MIT 4 th Winter School on Biomolecular Solid-State NMR, Stowe,
Water Interactions with Membrane Proteins & Other Biomolecules from 1 H-X Heteronuclear Correlation NMR Mei Hong Department of Chemistry, MIT 4 th Winter School on Biomolecular Solid-State NMR, Stowe,
c = pc p regime III: surface tension nearly constant because chemical potential depends only weakly on surfactant concentration chemical potential:
 regime III: surface tension nearly constant because chemical otential deends only weakly on surfactant concentration chemical otential: below CMC: c c s i.e. total surfactant concentration unimer concentration
regime III: surface tension nearly constant because chemical otential deends only weakly on surfactant concentration chemical otential: below CMC: c c s i.e. total surfactant concentration unimer concentration
Supplementary Material: Orientational order of carbon nanotube guests in a nematic host suspension of colloidal viral rods.
 Supplementary Material: Orientational order of carbon nanotube guests in a nematic host suspension of colloidal viral rods Nicolas Puech, 1 Matthew Dennison, 2 Christophe Blanc, 3 Paul van der Schoot,
Supplementary Material: Orientational order of carbon nanotube guests in a nematic host suspension of colloidal viral rods Nicolas Puech, 1 Matthew Dennison, 2 Christophe Blanc, 3 Paul van der Schoot,
AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes Michael J. Higgins
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes Michael J. Higgins
Characterizing the mesophase behavior of hydrated 9.9 MAG at 20 C and at increasing concentrations of DDM by SAXS.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterizing the mesophase behavior of hydrated 9.9 MAG at 20 C and at increasing concentrations of DDM by SAXS. Individual panels show I/2 SAXS profiles at the specified concentration
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterizing the mesophase behavior of hydrated 9.9 MAG at 20 C and at increasing concentrations of DDM by SAXS. Individual panels show I/2 SAXS profiles at the specified concentration
New multivalent cationic lipids reveal bell curve for transfection efficiency versus membrane charge density: lipid DNA complexes for gene delivery
 RESEARC ARTICLE TE JURAL F GEE MEDICIE J Gene Med 2005; 7: 739 748. Published online 31 January 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DI: 10.1002/jgm.717 ew multivalent cationic lipids
RESEARC ARTICLE TE JURAL F GEE MEDICIE J Gene Med 2005; 7: 739 748. Published online 31 January 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DI: 10.1002/jgm.717 ew multivalent cationic lipids
Formation of multistranded β-lactoglobulin amyloid fibrils and their stimuli responsive magnetic behaviour in the lyotropic liquid crystals
 Formation of multistranded β-lactoglobulin amyloid fibrils and their stimuli responsive magnetic behaviour in the lyotropic liquid crystals Sreenath Bolisetty Prof. Raffaele Mezzenga Food & Soft Materials
Formation of multistranded β-lactoglobulin amyloid fibrils and their stimuli responsive magnetic behaviour in the lyotropic liquid crystals Sreenath Bolisetty Prof. Raffaele Mezzenga Food & Soft Materials
Supplementary Figure S1. Statistical measurements on particle size and aspect ratio of
 Supplementary Figure S1. Statistical measurements on particle size and aspect ratio of as-prepared Cd 0.5 Zn 0.5 S nanocrystals. a,b,c, Histograms of the particle size distribution of the three-type of
Supplementary Figure S1. Statistical measurements on particle size and aspect ratio of as-prepared Cd 0.5 Zn 0.5 S nanocrystals. a,b,c, Histograms of the particle size distribution of the three-type of
THE INS AND OUTS OF YOUR SKIN. Emma Sparr Physical Chemistry Lund University
 THE INS AND OUTS OF YOUR SKIN Emma Sparr Physical Chemistry Lund University The skin - A Responding Barrier Membrane stratum corneum (10 20 µm) Water CO 2 Temperature ph 5.5 O 2 Moisturizers, Drugs etc
THE INS AND OUTS OF YOUR SKIN Emma Sparr Physical Chemistry Lund University The skin - A Responding Barrier Membrane stratum corneum (10 20 µm) Water CO 2 Temperature ph 5.5 O 2 Moisturizers, Drugs etc
by the cosurfactant hexanol. Earlier work on lipid-dna systems [1] has shown that
![by the cosurfactant hexanol. Earlier work on lipid-dna systems [1] has shown that by the cosurfactant hexanol. Earlier work on lipid-dna systems [1] has shown that](/thumbs/80/81966900.jpg) Chapter 4 Influence of hexanol on the structure of CTAB-DNA and CTAB-SHN-DNA complexes 4.1 Introduction This chapter deals with the structural transformations of CTAB-DNA complexes induced by the cosurfactant
Chapter 4 Influence of hexanol on the structure of CTAB-DNA and CTAB-SHN-DNA complexes 4.1 Introduction This chapter deals with the structural transformations of CTAB-DNA complexes induced by the cosurfactant
Supplementary Fig. 1.
 Supplementary Fig. 1. (a,b,e,f) SEM and (c,d,g,h) TEM images of (a-d) TiO 2 mesocrystals and (e-h) NiO mesocrystals. The scale bars in the panel c, d, g, and h are 500, 2, 50, and 5 nm, respectively. SAED
Supplementary Fig. 1. (a,b,e,f) SEM and (c,d,g,h) TEM images of (a-d) TiO 2 mesocrystals and (e-h) NiO mesocrystals. The scale bars in the panel c, d, g, and h are 500, 2, 50, and 5 nm, respectively. SAED
Phase behavior of charged lipid bilayer membranes with added electrolyte
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 119, NUMBER 2 8 JULY 2003 Phase behavior of charged lipid bilayer membranes with added electrolyte Shigeyuki Komura, a) Hisashi Shirotori, and Tadashi Kato Department
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 119, NUMBER 2 8 JULY 2003 Phase behavior of charged lipid bilayer membranes with added electrolyte Shigeyuki Komura, a) Hisashi Shirotori, and Tadashi Kato Department
A SUCROSE SOLUTIONS APPLICATIION TO THE STUDY OF MODEL BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES
 Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research A 470 (2001) 409-416 A SUCROSE SOLUTIONS APPLICATIION TO THE STUDY OF MODEL BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES M.A. Kiselev *, P. Lesieur #, A.M. Kisselev *, D. Lombardo
Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research A 470 (2001) 409-416 A SUCROSE SOLUTIONS APPLICATIION TO THE STUDY OF MODEL BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES M.A. Kiselev *, P. Lesieur #, A.M. Kisselev *, D. Lombardo
Chapter 12: Membranes. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 12: Membranes Voet & Voet: Pages 390-415 Slide 1 Membranes Essential components of all living cells (define boundry of cells) exclude toxic ions and compounds; accumulation of nutrients energy
Chapter 12: Membranes Voet & Voet: Pages 390-415 Slide 1 Membranes Essential components of all living cells (define boundry of cells) exclude toxic ions and compounds; accumulation of nutrients energy
Biology 4410 First Examination Version B
 Biology 4410 Spring 2006 Name First Examination Version B This examination consists of two parts, a multiple-choice section and an essay section. Be sure to put your name on both the mark-sense sheet and
Biology 4410 Spring 2006 Name First Examination Version B This examination consists of two parts, a multiple-choice section and an essay section. Be sure to put your name on both the mark-sense sheet and
Structure and Phase Behaviour of Binary Mixtures of Cholesterol with DPPC and DMPC
 Chapter 3 Structure and Phase Behaviour of Binary Mixtures of Cholesterol with DPPC and DMPC 3.1 Introduction As discussed in chapter 1, phospholipids and cholesterol are important constituents of plasma
Chapter 3 Structure and Phase Behaviour of Binary Mixtures of Cholesterol with DPPC and DMPC 3.1 Introduction As discussed in chapter 1, phospholipids and cholesterol are important constituents of plasma
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. Characterization of Aqueous Oleic Acid/Oleate Dispersions by
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Characterization of Aqueous Oleic Acid/Oleate Dispersions by Fluorescent Probes and Raman Spectroscopy Keishi Suga, Dai Kondo, Yoko Otsuka, Yukihiro Okamoto, and Hiroshi Umakoshi*
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Characterization of Aqueous Oleic Acid/Oleate Dispersions by Fluorescent Probes and Raman Spectroscopy Keishi Suga, Dai Kondo, Yoko Otsuka, Yukihiro Okamoto, and Hiroshi Umakoshi*
The sponge phase of a mixed surfactant system
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 308 (2007) 485 490 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The sponge phase of a mixed surfactant system A. Maldonado a,,r.ober b, T. Gulik-Krzywicki c,w.urbach d, D. Langevin
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 308 (2007) 485 490 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The sponge phase of a mixed surfactant system A. Maldonado a,,r.ober b, T. Gulik-Krzywicki c,w.urbach d, D. Langevin
Modified Liposomes with Biomaterials Delivery Applications
 Modified Liposomes with Biomaterials Delivery Applications Dr. Rahau Shirazi ACS Meeting Newcastle, Australia November 8th, 2013 utline Motivation and Background Focus Future Direction Liposomes Delivery
Modified Liposomes with Biomaterials Delivery Applications Dr. Rahau Shirazi ACS Meeting Newcastle, Australia November 8th, 2013 utline Motivation and Background Focus Future Direction Liposomes Delivery
Cellular Neurophysiology I Membranes and Ion Channels
 Cellular Neurophysiology I Membranes and Ion Channels Reading: BCP Chapter 3 www.bioelectriclab All living cells maintain an electrical potential (voltage) across their membranes (V m ). Resting Potential
Cellular Neurophysiology I Membranes and Ion Channels Reading: BCP Chapter 3 www.bioelectriclab All living cells maintain an electrical potential (voltage) across their membranes (V m ). Resting Potential
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Minicircle topoisomer generation. a, Generation of supercoiled topoisomers. Minicircles were nicked with the sequence-specific nicking endonuclease, Nb.BbvCI.
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Minicircle topoisomer generation. a, Generation of supercoiled topoisomers. Minicircles were nicked with the sequence-specific nicking endonuclease, Nb.BbvCI.
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: Competing Interactions between Various Entropic Forces towards Assembly of Pt 3 Ni Octahedra into a Body-Centered- Cubic Superlattice Ruipeng Li, Jun Zhang, Rui Tan, # Frauke Gerdes,
Supporting Information: Competing Interactions between Various Entropic Forces towards Assembly of Pt 3 Ni Octahedra into a Body-Centered- Cubic Superlattice Ruipeng Li, Jun Zhang, Rui Tan, # Frauke Gerdes,
57 pp RNA RNA. SeV Hemagglutinating Virus of Japan HVJ 1 15,384. TEL FAX
 57 pp.29-362007 2. RNA RNA 305-0856 1-25-11 TEL 029-838-0540 FAX 029-839-1123 E-mail iida@dnavec-corp.com 31 17 4 2006 1. SeV Hemagglutinating Virus of JapanHVJ 1 2,15,20 150-250 nm 15,384 RNA 1950 1957
57 pp.29-362007 2. RNA RNA 305-0856 1-25-11 TEL 029-838-0540 FAX 029-839-1123 E-mail iida@dnavec-corp.com 31 17 4 2006 1. SeV Hemagglutinating Virus of JapanHVJ 1 2,15,20 150-250 nm 15,384 RNA 1950 1957
Neutron reflectivity in biology and medicine. Jayne Lawrence
 Neutron reflectivity in biology and medicine Jayne Lawrence Why neutron reflectivity studies? build up a detailed picture of the structure of a surface in the z direction n e u tro n s in n e u tro n s
Neutron reflectivity in biology and medicine Jayne Lawrence Why neutron reflectivity studies? build up a detailed picture of the structure of a surface in the z direction n e u tro n s in n e u tro n s
Chemistry and Physics of Lipids
 Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 164 (11) 177 183 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Chemistry and Physics of Lipids journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chemphyslip Review Pivotal surfaces
Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 164 (11) 177 183 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Chemistry and Physics of Lipids journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chemphyslip Review Pivotal surfaces
Vesicle Adhesion and Fusion Studied by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering
 Biophysical Journal, Volume 114 Supplemental Information Vesicle Adhesion and Fusion Studied by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering Karlo Komorowski, Annalena Salditt, Yihui Xu, Halenur Yavuz, Martha Brennich,
Biophysical Journal, Volume 114 Supplemental Information Vesicle Adhesion and Fusion Studied by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering Karlo Komorowski, Annalena Salditt, Yihui Xu, Halenur Yavuz, Martha Brennich,
In previous chapters we have shown the influence of organic salts on the phase behaviour of
 Chapter 5 Phase Behaviour of SDS-PTHC-Water System: An Unusual Phase Sequence from Hexagonal to Lamellar 5.1 Introduction In previous chapters we have shown the influence of organic salts on the phase
Chapter 5 Phase Behaviour of SDS-PTHC-Water System: An Unusual Phase Sequence from Hexagonal to Lamellar 5.1 Introduction In previous chapters we have shown the influence of organic salts on the phase
Small angle neutron scattering study of mixed micelles of oppositely charged surfactants
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 71, No. 5 journal of November 2008 physics pp. 1039 1043 Small angle neutron scattering study of mixed micelles of oppositely charged surfactants J V JOSHI 1,,
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 71, No. 5 journal of November 2008 physics pp. 1039 1043 Small angle neutron scattering study of mixed micelles of oppositely charged surfactants J V JOSHI 1,,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Abstract. Keywords: Zinc Oxide, Eu doped ZnO, Dy doped ZnO, Thin film INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFORMATION AND COMPUTING SCIENCE ISSN NO:
 Synthesis and Structural study of Rare Earth activated ZnO Thin film Pawan Kumar Department of Physics, University Institute of Sciences, Chandigarh University, Gharuan (Mohali), Punjab (India) e-mail-pawan.uis@cumail.in
Synthesis and Structural study of Rare Earth activated ZnO Thin film Pawan Kumar Department of Physics, University Institute of Sciences, Chandigarh University, Gharuan (Mohali), Punjab (India) e-mail-pawan.uis@cumail.in
Effect of Unsaturated Acyl Chains on Structural Transformations in Triacylglycerols. Oleksandr Mykhaylyk. Chris Martin
 Effect of Unsaturated Acyl hains on Structural Transformations in Triacylglycerols leksandr Mykhaylyk Department of hemistry, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, S3 7HF, UK hris Martin STF Daresbury Laboratory,
Effect of Unsaturated Acyl hains on Structural Transformations in Triacylglycerols leksandr Mykhaylyk Department of hemistry, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, S3 7HF, UK hris Martin STF Daresbury Laboratory,
Liquid crystals; biological and artificial membranes
 Liquid crystals; biological and artificial membranes Dr. István Voszka Liquid crystals: Intermediate state between liquids and crystalline solids anisotropic liquids. (anisotropy = the physical properties
Liquid crystals; biological and artificial membranes Dr. István Voszka Liquid crystals: Intermediate state between liquids and crystalline solids anisotropic liquids. (anisotropy = the physical properties
Membrane Protein Crystallization In Meso: Lipid Type-Tailoring of the Cubic Phase
 Biophysical Journal Volume 83 December 2002 3393 3407 3393 Membrane Protein Crystallization In Meso: Lipid Type-Tailoring of the Cubic Phase Vadim Cherezov,* Jeffrey Clogston, Yohann Misquitta, Wissam
Biophysical Journal Volume 83 December 2002 3393 3407 3393 Membrane Protein Crystallization In Meso: Lipid Type-Tailoring of the Cubic Phase Vadim Cherezov,* Jeffrey Clogston, Yohann Misquitta, Wissam
Insertional oncogenesis in 4 patients after retrovirus-mediated gene therapy of SCID-X1
 Research article Insertional oncogenesis in 4 patients after retrovirus-mediated gene therapy of SCID-X1 Salima Hacein-Bey-Abina, 1,2 Alexandrine Garrigue, 2 Gary P. Wang, 3 Jean Soulier, 4 Annick Lim,
Research article Insertional oncogenesis in 4 patients after retrovirus-mediated gene therapy of SCID-X1 Salima Hacein-Bey-Abina, 1,2 Alexandrine Garrigue, 2 Gary P. Wang, 3 Jean Soulier, 4 Annick Lim,
Phase behaviour of the CTAB SHN water system
 Chapter 2 Phase behaviour of the CTAB SHN water system 2.1 Introduction This chapter deals with the different liquid crystalline phases exhibited by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) sodium-3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate
Chapter 2 Phase behaviour of the CTAB SHN water system 2.1 Introduction This chapter deals with the different liquid crystalline phases exhibited by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) sodium-3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate
1.2 introduction to the cell. me239 mechanics of the cell. 1.2 introduction to the cell. 1.2 introduction to the cell.
 2. introduction to mechanics prokaryotic cells Figure 1.1 Prokaryotic cell. Cell without a nucleus. the inner life of a cell, viel & lue, harvard [2006] me239 mechanics of the cell 1 eukaryotic cells 1.2
2. introduction to mechanics prokaryotic cells Figure 1.1 Prokaryotic cell. Cell without a nucleus. the inner life of a cell, viel & lue, harvard [2006] me239 mechanics of the cell 1 eukaryotic cells 1.2
Membranes & Membrane Proteins
 School on Biomolecular Simulations Membranes & Membrane Proteins Vani Vemparala The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai November 13 2007 JNCASR, Bangalore Cellular Environment Plasma membrane extracellular
School on Biomolecular Simulations Membranes & Membrane Proteins Vani Vemparala The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai November 13 2007 JNCASR, Bangalore Cellular Environment Plasma membrane extracellular
Membranes 5357 Review Membrane Binding. Protein Binding Domains
 Review Membrane Binding Protein Binding Domains Protein Binding Domains C1, C2 and FYVE are seen in 100s of proteins and bind to polyphosporylated inositol and are used to regulate protein activity and
Review Membrane Binding Protein Binding Domains Protein Binding Domains C1, C2 and FYVE are seen in 100s of proteins and bind to polyphosporylated inositol and are used to regulate protein activity and
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Salipro lipid particles.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Salipro lipid particles. (a) Gel filtration analysis of Saposin A after incubation with the indicated detergent solubilised lipid solutions. The generation of Saposin A-lipid complexes
Supplementary Figure 1 Salipro lipid particles. (a) Gel filtration analysis of Saposin A after incubation with the indicated detergent solubilised lipid solutions. The generation of Saposin A-lipid complexes
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Biological membranes are composed of lipid bilayers
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Biological membranes are composed of lipid bilayers
MemMeso TM MD1-86. MemMeso TM A 96-condition crystallization screen specifically for use with mesophases. (LCP compatible). Features of MemMeso:
 MemMeso TM MD1-86 MemMeso TM A 96-condition crystallization screen specifically for use with mesophases. (LCP compatible). MD1-86 is a targeted sparse matrix presented as a 96 x 10 ml conditions. Features
MemMeso TM MD1-86 MemMeso TM A 96-condition crystallization screen specifically for use with mesophases. (LCP compatible). MD1-86 is a targeted sparse matrix presented as a 96 x 10 ml conditions. Features
Liquid Crystalline Phases of DNA
 Jožef Stefan Institute & Faculty of Mathemaitcs and Physics Liquid Crystalline Phases of DNA Author: Huang Peng Adviser: Prof. Dr. Rudi Podgornik Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Igor Muševič 5. June 2011 Liquid
Jožef Stefan Institute & Faculty of Mathemaitcs and Physics Liquid Crystalline Phases of DNA Author: Huang Peng Adviser: Prof. Dr. Rudi Podgornik Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Igor Muševič 5. June 2011 Liquid
Xianren Zhang ( 张现仁 )
 The interaction between nanoparticles and membranes: from cytotoxicity to drug delivery Xianren Zhang ( 张现仁 ) zhangxr@mail.buct.edu.cn State Key Laboratory of Organic-Inorganic Composites, Beijing University
The interaction between nanoparticles and membranes: from cytotoxicity to drug delivery Xianren Zhang ( 张现仁 ) zhangxr@mail.buct.edu.cn State Key Laboratory of Organic-Inorganic Composites, Beijing University
Life s molecular diversity is based on the. properties of carbon. Chain Ring Branching chain
 Carbon Compounds Life s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon Chain Ring Branching chain The Chemistry of Carbon : carbon based Carbon can make 4 covalent bonds The foundation of organic
Carbon Compounds Life s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon Chain Ring Branching chain The Chemistry of Carbon : carbon based Carbon can make 4 covalent bonds The foundation of organic
Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation
 Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation Hang Yu, 1, 2, a) Wei Han, 1, 3, b) Wen Ma, 1, 2 1, 2, 3, c) and Klaus Schulten 1) Beckman
Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation Hang Yu, 1, 2, a) Wei Han, 1, 3, b) Wen Ma, 1, 2 1, 2, 3, c) and Klaus Schulten 1) Beckman
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information for Chemical Synthesis of Blue-emitting Metallic Zinc Nano-hexagons Nguyen T. Mai, Trinh T. Thuy, Derrick M. Mott and Shinya Maenosono* School of Materials Science, Japan Advanced
Supplementary Information for Chemical Synthesis of Blue-emitting Metallic Zinc Nano-hexagons Nguyen T. Mai, Trinh T. Thuy, Derrick M. Mott and Shinya Maenosono* School of Materials Science, Japan Advanced
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Uncropped version of Fig. 2a. RM indicates that the translation was done in the absence of rough mcirosomes. (b) LepB construct containing the GGPG-L6RL6-
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Uncropped version of Fig. 2a. RM indicates that the translation was done in the absence of rough mcirosomes. (b) LepB construct containing the GGPG-L6RL6-
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/11/e1701208/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Competitive chiral induction in a 2D molecular assembly: Intrinsic chirality versus coadsorber-induced chirality This
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/11/e1701208/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Competitive chiral induction in a 2D molecular assembly: Intrinsic chirality versus coadsorber-induced chirality This
Phase Transition Behaviours of the Supported DPPC Bilayer. Investigated by Sum Frequency Generation (SFG) and Atomic Force
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2015 Supporting Information for Phase Transition Behaviours of the Supported DPPC Bilayer
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2015 Supporting Information for Phase Transition Behaviours of the Supported DPPC Bilayer
Supplementary Material
 10.1071/CH15728_AC The Authors 2016 Australian Journal of Chemistry 2016, 69(8), 846-855 Supplementary Material Structural Diversity and Properties of Six Zn II /Cd II Coordination Polymers Based on a
10.1071/CH15728_AC The Authors 2016 Australian Journal of Chemistry 2016, 69(8), 846-855 Supplementary Material Structural Diversity and Properties of Six Zn II /Cd II Coordination Polymers Based on a
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Predicted structure of the most stable {110} antiphase boundary defect in magnetite (model APB-I). a) The same structure as that shown in Fig. 1b (main text)
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Predicted structure of the most stable {110} antiphase boundary defect in magnetite (model APB-I). a) The same structure as that shown in Fig. 1b (main text)
DIFFERENT APPROACHES TO CRYSTALLIZATION OF MEMBRANE PROTEINS
 OnLine Journal of Biological Sciences, 2012, 12 (3), 118-122 ISSN: 1608-4217 2012 Doiphode and Singh, This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 3.0 license doi:10.3844/ojbssp.2012.118.122
OnLine Journal of Biological Sciences, 2012, 12 (3), 118-122 ISSN: 1608-4217 2012 Doiphode and Singh, This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 3.0 license doi:10.3844/ojbssp.2012.118.122
The Interaction between Lipid Bilayers and Biological Membranes. Chapter 18
 The Interaction between Lipid Bilayers and Biological Membranes Chapter 18 Introduction Membrane & Phospholipid Bilayer Structure Membrane Lipid bilayer 2 Introduction Forces Acting between Surfaces in
The Interaction between Lipid Bilayers and Biological Membranes Chapter 18 Introduction Membrane & Phospholipid Bilayer Structure Membrane Lipid bilayer 2 Introduction Forces Acting between Surfaces in
Protein directed assembly of lipids
 Protein directed assembly of lipids D. Nordin, O. Yarkoni, L. Donlon, N. Savinykh, and D.J. Frankel SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Supported bilayer preparation 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
Protein directed assembly of lipids D. Nordin, O. Yarkoni, L. Donlon, N. Savinykh, and D.J. Frankel SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Supported bilayer preparation 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
ULTRA THIN INDIUM TIN OXIDE FILMS ON VARIOUS SUBSTRATES BY PULSED LASER DEPOSITION
 ULTRA THIN INDIUM TIN OXIDE FILMS ON VARIOUS SUBSTRATES BY PULSED LASER DEPOSITION X. W. Sun 1, D. H. Kim 2, and H. S. Kwok 1 1 Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Hong Kong University of
ULTRA THIN INDIUM TIN OXIDE FILMS ON VARIOUS SUBSTRATES BY PULSED LASER DEPOSITION X. W. Sun 1, D. H. Kim 2, and H. S. Kwok 1 1 Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Hong Kong University of
2.2 Properties of Water
 2.2 Properties of Water I. Water s unique properties allow life to exist on Earth. A. Life depends on hydrogen bonds in water. B. Water is a polar molecule. 1. Polar molecules have slightly charged regions
2.2 Properties of Water I. Water s unique properties allow life to exist on Earth. A. Life depends on hydrogen bonds in water. B. Water is a polar molecule. 1. Polar molecules have slightly charged regions
Supplement 2 - Quantifying sample mosaicity
 Supplement 2 - Quantifying sample mosaicity Supplementary information for: Order parameters and areas in fluid-phase oriented lipid membranes using wide angle x-ray scattering Thalia T. Mills, Gilman E.
Supplement 2 - Quantifying sample mosaicity Supplementary information for: Order parameters and areas in fluid-phase oriented lipid membranes using wide angle x-ray scattering Thalia T. Mills, Gilman E.
Cell Transport. Movement of molecules
 Cell Transport Movement of molecules TEKS Students will investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis and transport of molecules Homeostasis The maintaining of a stable body system
Cell Transport Movement of molecules TEKS Students will investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis and transport of molecules Homeostasis The maintaining of a stable body system
Original Articles in Scientific international Journals
 Original Articles in Scientific international Journals 1. Gene therapy for transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 2018. Accepted for publication. 2. Gene transfer into hematopoietic stem cells
Original Articles in Scientific international Journals 1. Gene therapy for transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 2018. Accepted for publication. 2. Gene transfer into hematopoietic stem cells
Neutron and Softmatter
 Neutron and Softmatter Hideki Seto IMSS/J-PARC Center, KEK SOKENDAI So# Ma'er Polymer Liquid Crystal polymeric liquid crystal liquid crystal polymer amphiphilic polymer lyotropic liquid crystal liquid
Neutron and Softmatter Hideki Seto IMSS/J-PARC Center, KEK SOKENDAI So# Ma'er Polymer Liquid Crystal polymeric liquid crystal liquid crystal polymer amphiphilic polymer lyotropic liquid crystal liquid
CHAPTER 6. BLUE GREEN AND UV EMITTING ZnO NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED THROUGH A NON AQUEOUS ROUTE
 71 CHAPTER 6 BLUE GREEN AND UV EMITTING ZnO NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED THROUGH A NON AQUEOUS ROUTE 6.1 INTRODUCTION Several techniques such as chemical vapour deposition, electrochemical deposition, thermal
71 CHAPTER 6 BLUE GREEN AND UV EMITTING ZnO NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED THROUGH A NON AQUEOUS ROUTE 6.1 INTRODUCTION Several techniques such as chemical vapour deposition, electrochemical deposition, thermal
SeQuant ZIC -HILIC For all who expect more...
 SeQuant ZIC -ILIC For all who expect more... The better choice for PLC and LC/MS of all types of polar and hydrophilic compounds EMD Millipore Corp. is a subsidiary of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Poor
SeQuant ZIC -ILIC For all who expect more... The better choice for PLC and LC/MS of all types of polar and hydrophilic compounds EMD Millipore Corp. is a subsidiary of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Poor
176 YMC Chiral Columns
 176 YMC Chiral Columns YMC Chiral Columns 177 Chiral Columns Content YMC Chiral NEA(R)(S)... 178-181 YMC Chiral CD BR... 182-185 Ordering Information... 186 HPLC Columns for Optical Isomer Separation Introduction
176 YMC Chiral Columns YMC Chiral Columns 177 Chiral Columns Content YMC Chiral NEA(R)(S)... 178-181 YMC Chiral CD BR... 182-185 Ordering Information... 186 HPLC Columns for Optical Isomer Separation Introduction
Molecular modeling of the pathways of vesicle membrane interaction. Tongtao Yue and Xianren Zhang
 Molecular modeling of the pathways of vesicle membrane interaction Tongtao Yue and Xianren Zhang I. ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI): METHODS Dissipative particle dynamics method The dissipative
Molecular modeling of the pathways of vesicle membrane interaction Tongtao Yue and Xianren Zhang I. ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI): METHODS Dissipative particle dynamics method The dissipative
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Supporting Information Modulating Interactions between Ligand-Coated Nanoparticles and Phase-Separated
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Supporting Information Modulating Interactions between Ligand-Coated Nanoparticles and Phase-Separated
Sponge Phases and Nanoparticle Dispersions in Aqueous Mixtures of Mono- and Diglycerides
 pubs.acs.org/langmuir Sponge Phases and Nanoparticle Dispersions in Aqueous Mixtures of Mono- and Diglycerides Maria Valldeperas,*, Małgorzata Wisńiewska,, Maor Ram-On,, Ellina Kesselman,,# Dganit Danino,,#
pubs.acs.org/langmuir Sponge Phases and Nanoparticle Dispersions in Aqueous Mixtures of Mono- and Diglycerides Maria Valldeperas,*, Małgorzata Wisńiewska,, Maor Ram-On,, Ellina Kesselman,,# Dganit Danino,,#
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes. Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment.
 Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
PLEASE DO NOT REMOVE THIS PAGE
 Thank you for downloading this document from the RMIT ResearchR Repository Citation: Kent, B, Garvey, C, enne, T, Porcar,, Garamus, V and Bryant, G, 'Measurement of glucose exclusion from the fully hydrated
Thank you for downloading this document from the RMIT ResearchR Repository Citation: Kent, B, Garvey, C, enne, T, Porcar,, Garamus, V and Bryant, G, 'Measurement of glucose exclusion from the fully hydrated
Supplemental Data Figure S1 Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells.
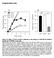 Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Microfluidic Approaches for Membrane Protein Crystallization
 Microfluidic Approaches for Membrane Protein Crystallization Sarah L. Perry, Griffin W. Roberts, Sameer Talreja, Joshua D. Tice, Robert B. Gennis, Charles F. Zukoski, and Paul J.A. Kenis Background and
Microfluidic Approaches for Membrane Protein Crystallization Sarah L. Perry, Griffin W. Roberts, Sameer Talreja, Joshua D. Tice, Robert B. Gennis, Charles F. Zukoski, and Paul J.A. Kenis Background and
