Original Research Article
|
|
|
- Felicity Matthews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 E-ISSN: X Recent Advances in Biology and Medicine Original Research Article Intake of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract Decreases IL-1 and TNF-α Levels in Dyslipidemic Wistar Rat Model HATASO, USA
2 24 Original Research Article Intake of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract Decreases IL-1 and TNF-α Levels in Dyslipidemic Wistar Rat Model Sri Wahyuni 1 *, I Wayan Putu Sutirta Yasa 2 1 Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Udayana University, Denpasar, Bali, Indonesia. 2 Clinical Pathology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Udayana University, Denpasar, Bali, Indonesia. *Correspondence: sriwahjunimanuaba@gmail.com Received: Apr 8, 2017; Accepted: Apr 29, 2017; Published: May 18, 2017 Abstract Changes in consumption behavior to instant food cause various health problems, such as obesity, dislipidemia, and atherosclerosis. A study was conducted to investigate Moringa oleifera extract as an anti-inflammation product that decreases the levels of biochemical markers IL-1 and TNF-a. This experiment was done with randomized pre- and posttest control-group design, employing 40 Wistar rats separated into five groups: control group 0% M. oleifera leaf extract (P 0 ), treatment group 1 with 10% M. oleifera leaf extract (P 1 ), treatment group 2 with 15% M. oleifera leaf extract (P 2 ), treatment group 3 with 20% M. oleifera leaf extract (P 3 ), and treatment group 4 with 25% M. oleifera leaf extract (P 4 ). This research observed that intake of 20% M. oleifera leaf extract results in the highest significant decrease of 15.42% of IL-1 level ( to pg/ml) and decrease of 45.63% of TNF-α level ( to pg/ml). Therefore, it can be concluded that intake of M. oleifera leaf extract by Wistar rat has anti-inflammatory effects on chronic dyslipidemia through decrease of IL-1 and TNF-α levels and histopathology profile. Further research is required to determine whether the application of M. oleifera leaf extract (daun kelor) in humans will have similar anti-inflammation effects. Keywords: Consumption habit of fast food; Moringa oleifera leaf extract (daun kelor); Dislipidemia; Atherosclerosis. 1. INTRODUCTION It has been understood that there is a significant correlation between inflammation levels and incidents of atheroschlerosis, a trigger of coronary heart disease. Coronary heart disease presents as a result of blood circulation disturbance and abnormality of cardiac electricity or other forms of arrhythmia. This leads to disorganized myocardial contraction, blood flow obstruction, and blood flow regurgitation. All these conditions result in the return of blood flow to the heart (shunts) in each contraction, blood flow abnormality, and heart failure [1]. Atherosclerosis is a slow, progressive disease, present in large to medium arterial muscle and elastic artery. The main sites of atherosclerosis are abdominal aorta, coronary artery, popliteal artery, thorax descending aorta, carotid internal artery, and willisi circulation. Risk factors such as hypertension, chronic hypercholesterolemia, immune system disturbance, toxin, and virus are also involved in arterial endothelial wall destruction. This damage induces permeability changes of endothelial cells and leads to increase of plasma constituents, such as lipoprotein that can easily enter the artery wall. A damage to these endothelial cells could also change the properties of thrombosistein lumen artery, which can lead to adhesion of thrombosite to the blood and induce inflammation. If this damaging process continues for a long time, it will be followed by continuous atherosclerosis and will lead to thickness of tunica intima and result in disturbance of blood flow in that site [2]. Managing consumption type is one way to overcome this condition. Plasma cholesterol can be increased by rising cholesterol turnover rate. Faster cholesterol replacement can be achieved through intake of M. oleifera extract acids. These acids in metabolism act as an antioxidant that could break down saturated fatty acid chains in hyphercholesterolemia patients [3]. Hypercholesterolemia, atheroschlerotic inducer, is a multifactorial diasase that also correlates to proinflammation cytokines, such as IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-1, IL-,1 and TNF-α. Some researchers reported that atherogenic consumption could increase the formation of IL-1 and TNF-α; however, it did not significantly increase IL-1β [4-6]. Based on the background discussed above, this research was conducted to investigate M. oleifera leaf (daun kelor) extract (MOE) rich in octadecatrienoic acid is important as an anti-inflammatory agent, decreasing IL-1 and TNF-α levels in chronic dyslipidemia Wistar rats. 2. MATERIALS AND METHODS This research applied a true experimental randomized pre- and posttest control-group design to determine the role of MOE as an anti-inflammatory agent. Research was conducted using 40 Wistar rats divided into five groups: P 0 for control with 0% MOE, P 1 for treatment with 10% MOE, P 2 for treatment with 15% MOE, P 3 for treatment with 20% MOE, and P 4 for treatment with 25% MOE. The rats were fed with a high-cholesterol diet for 18 weeks to achieve chronic dyslipidemia and atheroschlerosis and then were treated with various concentration of MOE for 6 weeks. IL-1 and TNF-α levels rats serum for chronic dyslipidemia HATASO rabm.scholasticahq.com
3 Recent Advances in Biology and Medicine, Vol. 3, Pages 24-28, (pretest) and after treated (posttest) were then detected. All data obtained were analyzed statistically to determine the mean difference of treatment using one-way ANOVA at a 5% significant level. 3. RESULTS 3.1. Decrease of IL-1 Levels Mean of pre- and posttest data of IL-1 serum levels are presented in Table 1. Data in Table 1 were normally distributed with p 0.05, and their variance was also homogeneous with p The mean difference of various MOE treatments can be performed on the basis of posttest data, if, however, all pretest data are comparable. It was obtained that all the pretest data were comparable with p 0.05; therefore, mean difference of the treatment was obtained based on the posttest data and was analyzed using one-way ANOVA. There were significant differences in the treatment obtained with p 0.0; then the data were analyzed using post hoc test to measure the difference. Post hoc test results are summarized in Table Decrease of TNF-α Levels Pre- and Posttest data of the mean of TNF-α serum levels are presented in Table 3. Data in Table 3 were normally distributed with p 0.05, and their variance was also homogeneous with p All the pretest data were comparable (p 0.05); therefore, the mean difference of various treatments of MOE can only be Table 1: Serum level data for pre- and posttest mean of IL-1. IL-1 (pg/ml) Pretest Posttest MOE 0% (control) MOE 10% MOE 15% MOE 20% MOE 25% MOE 5 M. oleifera leaf extract. Table 2: Resume of post hoc test of IL-1 levels. Mean difference of IL-1 (rg/ml) p* MOE 0% (control) - MOE 10% MOE 15% MOE 20% MOE 25% MOE 10% - MOE 15% MOE 20% MOE 25% MOE 15% - MOE 20% MOE 25% MOE 20% - MOE 25% MOE 5 M. oleifera leaf extract. *Significant p Table 3: Date of the mean of TNF-α serum levels. TNF-α (pg/ml) Pretest Posttest MOE 0% (control) MOE 10% MOE 15% MOE 20% MOE 25% MOE 5 M. oleifera leaf extract. ID:
4 26 Original Research Article performed based on the posttest data analyzed using one-way ANOVA. It was obtained that there were differences between all the treatments. Then, the data were analyzed using post hoc test (LSD) to determine the difference. The post hoc test results are presented in Table Histopathology Profile Histopathology structure changes in the aortic tissue of Wistar rats with 1003 zoom and HE (hematoxylin eosin) from normal artery ( ) (Figure 1a) without the presence of leucocyte cell infiltration and dyslipidemia (pretest consumtion of fat for 8 weeks) (Figure 1b). The figure reveals the change of artery structure due to protrusion to tunica intima, an indication of mechanical endotel injury. Figure 1c represents chronic dyslipidemia due to intake of fat for 18 weeks in Wistar rats initiated with chronic dyslipidemia, leading to a narrow hole in the aortic artery ( ); there are many artery protrudes to tunica intima, and thickening of tunica media and tunica adventitia occurred. Figure 1c indicates that there is thrombocyte aggregation in the artery ( ) due to intake of fat for 18 weeks. Initiated with chronic dyslipidemia and leading to a narrow hole in the aortic artery ( ), there are many artery protrudes to tunica intima, and thickening of tunica media and tunica adventitia occurred. Figure 2 indicates that there is thrombolytic to aggregation in the artery ( ) due to intake of fat for 18 weeks. The aggregation was initially an acute change to chronic indicated by red color. Then intake of 0% MOE did not change structure. The presence of leukocyte cells, mainly monocyte cells infiltrated to the lower subendothelail tissue leads to endothelial cell destruction, that is, lumen artery experiencing inflammation compared to Figure 1a (pretest) and Figures 3-6 (picture of posttest artery histopathology structure of chronic dyslipidemia after intake of various concentration of MOE for 6 weeks (10, 15, 20, and 25%), Figure 3 indicates that the presence of thrombocyte aggregation in the artery ( ) thickens tunica media and wider tunica adventitia are indicated by red color. Intake of 15% MOE could not reduce thrombocyte aggregation. Figure 4 reveals the presence of a small thrombocyte aggregation in the artery ( ). Also, there is an aggregation in their tunica media indicated by red color. intake of 20% MOE. Figure 5 indicates no thrombocyte aggregation in the artery ( ); therefore, intake of 20% MOE results in the reduction of thrombocyte aggregation. Figure 6 indicates the appearance of thrombocyte aggregation ( ) anymore after intake of 25% SLO red color thicken of tunica media. Table 4: Resume of post hoc test of TNF-α levels. Mean difference of TNF-α (pg/ml) p* MOE 0% (control) - MOE 10% MOE 15% MOE 20% MOE25% MOE 10% - MOE 15% MOE 20% MOE 25% MOE 15% - MOE 20% MOE 25% MOE 20% - MOE 25% MOE 5 M. Oleifera leaf extract. *significant p Figure 1: (a) Histopathology profile pretest in normally Wistar rat (b) Histopathology profile pretest of consumption fat at 8 weeks in Wistar rat; (c) Histopathology profile pretest of consumption fat at 18 weeks in Wistar rat. HATASO rabm.scholasticahq.com
5 Recent Advances in Biology and Medicine, Vol. 3, Pages 24-28, Figure 2: Histopathology profile posstest P 0. Figure 3: Histopathology profile posttest P 1. Figure 4: Histopathology profile posttest P 2. Figure 5: Histopathology profile posttest P 3. Figure 6: Histopathology profile posttest P DISCUSSION The research results indicate that the highest decrease of pg/ml of TNF-α was obtained for the intake of 20% MOE. The increase of MOE to 25% could not increase TNF-α levels. This condition indicates that concentration of 25% MOE has already saturated; therefore, it could not decrease TNF-α levels any further. This was supported by the findings of Chen and Goeddel [7]; they found that there was no transcription of NF-κβ, so there was no further production of TNF-α due to saturation. Inflammation is a response of tissue damage during vascularization. This response is followed by an important process, such as endothelial process. Endothelium is an important part of blood vein that plays an important role in atheroschlerosis. Endothelium is the main target of mechanical and chemical damage due to dislipidemia risk factor. Chronic, continues, and prolong dislipidemia resulted in proinflammation response and prothrombic, which were initially acute but became chronic. This is followed by infiltration of leucocyte cells, mainly monocyte cells to lower subendothelial tissue to form macrophage cells. These cells destroy the rest of LDL-C and oxidized to form foam cells and change to ateroma [8]. The last two decades research claims that M. oleifera is effective as an anti inflammatory agent. This is because M. oleifera leaf is rich in octadecatrienoic acid. The fatty acids are a group of polyunsaturated fatty acids with double bond at the third carbon atom (from methyl group), which are known as omega-3 [4-6]. In this study, MOE which is rich in omega-3 was applied and proved to exceed an anti-inflammation effect. This anti-inflammation effect is due to activation of endothelium nuclear factor-kapa beta (ENF-κβ) on peripheral vein. ENF-κβ is a transcription factor distributed in all endothelial cells that have a role in controlling vascularization. Simopulus [9] presented that the role of omega-3 as an anti-inflammation is due to their action as an immunomodulator. In addition, their role as an anti-inflammation agent is a result of the effect of octadecatrienoic acids. These acids are a substrate for triggering the formation of cyclooxygenase and 5-lipooxyginase. These two oxygenases have vasodilator endothelium-dependent behavior to cause relaxation of ordinary coronary artery and paradoxal vasoconstruction in the atherosclerotic artery. ID:
6 28 Original Research Article Data in Table 1 indicate that there is a decrease of IL-1 levels since the intake of 10% of MOE. Even though there is a decrease of IL-1 levels caused by the treatment of 10% MOE, which is about 2.87 pg/ml, the decrease is not statistically significant, with p Then, intake of 15% MOE resulted in a significant decrease of 5.95 pg/ml of IL-1 levels, with p In addition, intake of 20% MOE has also a similar significant decrease of pg/ml of IL-1 levels, with p However, the increase of concentration to 25% MOE intake did not significantly decrease IL-1 levels, indicated by p MOE is rich in octadecatrienoic acid. These acids are grouped to alfa linolenate that has an ability as an anti-inflammation. During endothelial cells experiencing activated inflammation, it will be followed by increase of selectin and VCAM-1 expression. VICAM-1 induces monocyte adhesion. This adhesion was also induced by proinflammation cytokines, such as 1L-1β and TNF-α. These cytokines were induced by CRP protein produced as a result of IL-1 response by protease-activated receptor signaling, uptake of oxldl, through oxldl receptor-1 (LOX-1), and by interaction of CD40/CD40 ligand in artery intima [10]. IL-1 has an important role in inflammation response, and this cytokine is secreted by activated macrophage, leading to phebric and known as pyrogen endogen. IL-1 was also initiated by phase acute response and marked by protein phase acute produced by hepatocyte [11,12]. 5. CONCLUSIONS 1. Intake of 20% MOE decreases IL-1 serum levels in dyslipidemia Wistar rats around 15.42%, that is, from to pg/ml. 2. Intake of 20% MOE decreases TNF-α serum levels in dyslipidemia Wistar rats around 45.63%, that is, from to pg/ml. Acknowledgment The authors would like to thank Prof. Dr. I. Wayan Wita, SpJP; and Prof. Dr. N. Mantik Astawa, PhD; for their invaluable supervision during the doctoral study. We would also like to show our gratitude to Prof. Dr. Ir. Ida Bagus Putra Manuaba, MPhil from Udayana University, Bali, Indonesia, for sharing his pearls of wisdom with us during the course of this research. Author Contributions Both authors contributed equally. Source of Funding None Conflict of Interest None References 1. Vinay K, Abbas AK, Nelson F. Pathologic Basic of Disease. 7th ed. Elsevier Saunders, New York (2004). 2. Szmitko PE, Wang CH, Weisel RD, De-Almmeida JR, Anderson TJ, et al. New markers of inflammation and endothelial cell activation. Circulation. 2003; 108: Kanjwal M. Peripheral aterial disease the silent killer. JK-Practitioner October-December; 1(4): Stefan J, Mikko PSA, Bengt K, Nilsson J. Human monocytes/macrophages release TNF-α in response to Ox-LDL. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 16: Ahmed E. Immune mechanism in atherosclerosis. Dissertation (2001), Centrum för Molekulär Medicin, Karolinska Sjukhuset, Konferensrummet. ISSBN: Han SN, Leka LS, Lichtenstein AH, Ausman LM, Schaefer EJ, et al. Effect of hydrogenated and saturated, relative to polyunsaturated, fat on immune and inflammatory responses of adults with moderate hypercholesterolemia. J Lipid Res. 2002; 43(3): Chen G, Goeddel DV. TNFR-1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science. 2002; 296: Baraas F. Kardiologi Molekuler Radikal Bebas, Disfungsi Endotel, Aterosklerosis. Antioksidan Latihan Fisik dan Rehabilitasi Jantung. Bagian Kardiologi FKUI/RS Jantung Harapan Kita, Jakarta (2006). 9. Simopulus AP. Omega-3 fatty acids in inflammation and autoimmune diseases. J Am Coll Nutr. 2002; 21(6): Bonetti PO, Lerman LO, Lerman A. Endothelial dysfunction: a marker of atherosclerosis risk. Aterisoscler Thromb Vase Biol. 2003; 23: Coico R, Li SJ, Benyamin E. Element of innate and acquired immunity immunology. In Immunology. A Short Course. 5th ed. Editors - Coico R, Benjamini E, Sunshine G; Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons (2003), pp: Sindhughosa D, Pranamartha A. The involvement of proinflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy: Focus on interleukin 1 (IL-1), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) signaling mechanism. Bali Medical Journal. 2017; 6(1): DOI: /bmj.v6i1.299 Citation: Wahyuni S, Yasa IWPS. Intake of Moringa oleifera leaf extract decreases IL-1 and TNF-α levels in dyslipidemic Wistar rat model. Recent Adv Biol Med. 2017; 3: HATASO rabm.scholasticahq.com
INTAKE OF SARDINELLA LONGICEPS OIL AS ANTI DISLIPIDEMIA THROUGH DECREASE OF MDA ON RAT WISTAR Sri Wahjuni Biochemistry Laboratory Chemistry Departemen
 INTAKE OF SARDINELLA LONGICEPS OIL AS ANTI DISLIPIDEMIA THROUGH DECREASE OF MDA ON RAT WISTAR Sri Wahjuni Biochemistry Laboratory Chemistry Departement Faculty of Math and Science University INTRODUCTION
INTAKE OF SARDINELLA LONGICEPS OIL AS ANTI DISLIPIDEMIA THROUGH DECREASE OF MDA ON RAT WISTAR Sri Wahjuni Biochemistry Laboratory Chemistry Departement Faculty of Math and Science University INTRODUCTION
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases
 Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
Dyslipidemia Endothelial dysfunction Free radicals Immunologic
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
Catechins Green Tea Clones GMB4 Inhibit Inflammation Process of Atherosclerosis Through Decreasing TNF-Α Levels. *
 J. Islamic Pharm. Vol. 01 (01) 2016 28 Catechins Green Tea Clones GMB4 Inhibit Inflammation Process of Atherosclerosis Through Decreasing TNF-Α Levels Erna Susanti *1, Febiyanti Suratno 2 1 Pharmacy and
J. Islamic Pharm. Vol. 01 (01) 2016 28 Catechins Green Tea Clones GMB4 Inhibit Inflammation Process of Atherosclerosis Through Decreasing TNF-Α Levels Erna Susanti *1, Febiyanti Suratno 2 1 Pharmacy and
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
Cardiovascular Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School
 Low Endothelial Shear Stress Upregulates Atherogenic and Inflammatory Genes Extremely Early in the Natural History of Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Juvenile Swine Michail I. Papafaklis,
Low Endothelial Shear Stress Upregulates Atherogenic and Inflammatory Genes Extremely Early in the Natural History of Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Juvenile Swine Michail I. Papafaklis,
Depression, omega 3 fatty acid therapy 13
 Subject Index Adhesion molecules fish oil effects 12, 13 omega 3 fatty acid desaturase transfection effects on expression in endothelial cells 31 Alzheimer s disease (AD), omega 6 fatty acid/omega 3 fatty
Subject Index Adhesion molecules fish oil effects 12, 13 omega 3 fatty acid desaturase transfection effects on expression in endothelial cells 31 Alzheimer s disease (AD), omega 6 fatty acid/omega 3 fatty
The Role of Fats. Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because
 The Role of Fats Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because Fats are more energy dense than carbohydrates or protein Fats take longer to digest Emulsion
The Role of Fats Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because Fats are more energy dense than carbohydrates or protein Fats take longer to digest Emulsion
C-reactive protein: a marker or a player?
 C-reactive protein: a marker or a player? Thomas Nyström, Thomas Nyström To cite this version: Thomas Nyström, Thomas Nyström. C-reactive protein: a marker or a player?. Clinical Science, Portland Press,
C-reactive protein: a marker or a player? Thomas Nyström, Thomas Nyström To cite this version: Thomas Nyström, Thomas Nyström. C-reactive protein: a marker or a player?. Clinical Science, Portland Press,
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
THE BLOOD VESSELS. Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department.
 THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
Cho et al., 2009 Journal of Cardiology (2009), 54:
 Endothelial Dysfunction, Increased Carotid Artery Intima-media Thickness and Pulse Wave Velocity, and Increased Level of Inflammatory Markers are Associated with Variant Angina Cho et al., 2009 Journal
Endothelial Dysfunction, Increased Carotid Artery Intima-media Thickness and Pulse Wave Velocity, and Increased Level of Inflammatory Markers are Associated with Variant Angina Cho et al., 2009 Journal
Indexed, Abstracted and Cited in Various National and International Scientific Databases of the World
 Antioxidant Compounds of Gayam Seed (Inocarpus fagiferus Fosb) to Prevent Atherosclerosis through Increases of SD Activity and Improvement of Lipid Profile on Wistar Rat By I. Made Sukadana, Ida Bagus
Antioxidant Compounds of Gayam Seed (Inocarpus fagiferus Fosb) to Prevent Atherosclerosis through Increases of SD Activity and Improvement of Lipid Profile on Wistar Rat By I. Made Sukadana, Ida Bagus
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences
 ISSN: 09758585 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Isolation and Protection Effects of Methyl Gallate from Surian Leaves (Toona sureni BL Merr) Against Atherosclerosis
ISSN: 09758585 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Isolation and Protection Effects of Methyl Gallate from Surian Leaves (Toona sureni BL Merr) Against Atherosclerosis
Effects of High-carbohydrate and High Fat Diet on Formation of Foam Cells and Expression of TNF-α in Rattus Novergicus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of High-carbohydrate and High Fat Diet on Formation of Foam Cells and Expression of TNF-α in Rattus Novergicus Haidar*, Djoko W. Soeatmadji** ABSTRACT Aim: to examine the role
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of High-carbohydrate and High Fat Diet on Formation of Foam Cells and Expression of TNF-α in Rattus Novergicus Haidar*, Djoko W. Soeatmadji** ABSTRACT Aim: to examine the role
THE SAME EFFECT WAS NOT FOUND WITH SPIRITS 3-5 DRINKS OF SPIRITS PER DAY WAS ASSOCIATED WITH INCREASED MORTALITY
 ALCOHOL NEGATIVE CORRELATION BETWEEN 1-2 DRINKS PER DAY AND THE INCIDENCE OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE SOME HAVE SHOWN THAT EVEN 3-4 DRINKS PER DAY CAN BE BENEFICIAL - WHILE OTHERS HAVE FOUND IT TO BE HARMFUL
ALCOHOL NEGATIVE CORRELATION BETWEEN 1-2 DRINKS PER DAY AND THE INCIDENCE OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE SOME HAVE SHOWN THAT EVEN 3-4 DRINKS PER DAY CAN BE BENEFICIAL - WHILE OTHERS HAVE FOUND IT TO BE HARMFUL
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different?
 Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different? Trevor A Mori, Ph.D., Professor, School of Medicine and Pharmacology, Royal Perth Hospital Unit, University of Western Australia, Perth,
Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different? Trevor A Mori, Ph.D., Professor, School of Medicine and Pharmacology, Royal Perth Hospital Unit, University of Western Australia, Perth,
LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS
 LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS Patrick M. Moriarty, M.D., FACP, Director, Atherosclerosis and LDL-Apheresis Center, University of Kansas Medical
LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS Patrick M. Moriarty, M.D., FACP, Director, Atherosclerosis and LDL-Apheresis Center, University of Kansas Medical
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness. Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Hans Strijdom SA Heart Meeting November 2017
 Hans Strijdom SA Heart Meeting November 2017 HIV-infection and ART, but not high sensitivity CRP, are associated with markers of vascular function: Results from the Western Cape cohort of the EndoAfrica
Hans Strijdom SA Heart Meeting November 2017 HIV-infection and ART, but not high sensitivity CRP, are associated with markers of vascular function: Results from the Western Cape cohort of the EndoAfrica
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system
 1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
Cardiovascular System and Health. Chapter 15
 Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
NAM JUNE PAIK: Rhapsody in Video
 NAM JUNE PAIK: Rhapsody in Video 혈관연구회추계학회 2007.10.13 Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone System Kwang Kon Koh, MD, FACC, FAHA Cardiology Gachon University Gil Medical Center Incheon, Korea Cytokines oxldl Ang
NAM JUNE PAIK: Rhapsody in Video 혈관연구회추계학회 2007.10.13 Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone System Kwang Kon Koh, MD, FACC, FAHA Cardiology Gachon University Gil Medical Center Incheon, Korea Cytokines oxldl Ang
EARLY INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES TO VASCULAR DEVICES
 EARLY INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES TO VASCULAR DEVICES JAMES M. ANDERSON, MD, PhD DISTINGUISHED UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR DEPARTMENTS OF PATHOLOGY, MACROMOLECULAR SCIENCE, AND BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING CASE WESTERN
EARLY INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES TO VASCULAR DEVICES JAMES M. ANDERSON, MD, PhD DISTINGUISHED UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR DEPARTMENTS OF PATHOLOGY, MACROMOLECULAR SCIENCE, AND BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING CASE WESTERN
Invited Review. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
PPAR history of research
 PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
Nutrition & Wellness for Life 2012 Chapter 6: Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Part 1 Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis. LO1. Define the Different Forms of CVD
 Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk
 alevelbiology.co.uk Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk SPECIFICATION Many animals have a heart and circulation (mass transport to overcome limitations of diffusion in meeting the requirements of organisms).
alevelbiology.co.uk Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk SPECIFICATION Many animals have a heart and circulation (mass transport to overcome limitations of diffusion in meeting the requirements of organisms).
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012
 LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
I Made Sukadana et al /J. Pharm. Sci. & Res. Vol. 9(5), 2017,
 The Effect of Antioxidant Compounds in Ethanol Extract Inocarpus Fagiferus Fosb Seed to Expression TNF- And IL-6 Liver Cells In Hypercholesterolemia Wistar Rat I Made Sukadana* and Sri Rahayu Santi Departement
The Effect of Antioxidant Compounds in Ethanol Extract Inocarpus Fagiferus Fosb Seed to Expression TNF- And IL-6 Liver Cells In Hypercholesterolemia Wistar Rat I Made Sukadana* and Sri Rahayu Santi Departement
D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity.
 D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity. 1. Structures VITAMIN K1; Phytonadione; 2-Methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone VITAMIN K2; Menaquinone-6 and 7; N=6,7 n 2. Function
D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity. 1. Structures VITAMIN K1; Phytonadione; 2-Methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone VITAMIN K2; Menaquinone-6 and 7; N=6,7 n 2. Function
Not Hard Choices. By Dato Dr. Rajen M. 27 October 2018
 Make Choices Not Hard Choices By Dato Dr. Rajen M. 27 October 2018 Key Facts of Cardiovascular Disease 1. What is the burden of cardiovascular disease in Malaysia? 2. What causes cardiovascular disease?
Make Choices Not Hard Choices By Dato Dr. Rajen M. 27 October 2018 Key Facts of Cardiovascular Disease 1. What is the burden of cardiovascular disease in Malaysia? 2. What causes cardiovascular disease?
Lipoprotein Particle Profile
 Lipoprotein Particle Profile 50% of people at risk for HEART DISEASE are not identified by routine testing. Why is LPP Testing The Most Comprehensive Risk Assessment? u Provides much more accurate cardiovascular
Lipoprotein Particle Profile 50% of people at risk for HEART DISEASE are not identified by routine testing. Why is LPP Testing The Most Comprehensive Risk Assessment? u Provides much more accurate cardiovascular
Berries and Cardiovascular Health
 Berries and Cardiovascular Health Britt Burton-Freeman, PhD Institute for Food Safety and Health Illinois Institute of Technology bburton@iit.edu Berry Health Benefits Symposium Westlake Village CA, 2011
Berries and Cardiovascular Health Britt Burton-Freeman, PhD Institute for Food Safety and Health Illinois Institute of Technology bburton@iit.edu Berry Health Benefits Symposium Westlake Village CA, 2011
Acute coronary syndrome. Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA
 Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Can seal oil contribute to better human health?
 Can seal oil contribute to better human health? Bjarne Østerud and Edel O. Elvevoll, Faculty of Medicine and NFH, University of Tromsø E-mail: bjarne@fagmed. Historical background Old food lore of seafood
Can seal oil contribute to better human health? Bjarne Østerud and Edel O. Elvevoll, Faculty of Medicine and NFH, University of Tromsø E-mail: bjarne@fagmed. Historical background Old food lore of seafood
Relationship between serum glutathione peroxidase-1activity with endothelial dysfunction level in patients with coronary artery diseases
 Relationship between serum glutathione peroxidase-1activity with endothelial dysfunction level in patients with coronary artery diseases Introduction Reactive oxygen species (ROS),such as superoxide and
Relationship between serum glutathione peroxidase-1activity with endothelial dysfunction level in patients with coronary artery diseases Introduction Reactive oxygen species (ROS),such as superoxide and
For unclear reasons, only about 40% of patients with calcific aortic stenosis also have coronary
 Αθηροσκλήρωση και ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας. Οµοιότητες και διαφορές Ν. Μεζίλης Κλινική «Άγιος Λουκάς» Ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας: Μία ακόµα µορφή αθηρωµάτωσης; Some observations
Αθηροσκλήρωση και ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας. Οµοιότητες και διαφορές Ν. Μεζίλης Κλινική «Άγιος Λουκάς» Ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας: Μία ακόµα µορφή αθηρωµάτωσης; Some observations
 http://noodlemaz.wordpress.com/category/science/cancer/ Outline Introduction Serious nature of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) How to prevent CVD? The disease process Damage and plaque development Current
http://noodlemaz.wordpress.com/category/science/cancer/ Outline Introduction Serious nature of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) How to prevent CVD? The disease process Damage and plaque development Current
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
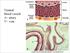 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by. Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam
 Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
 A real life example In human studies, we quantify ~120 plasma related proteins Monocytes MMP9 Macrophages TNFα IL1ß platelet derived growth factor IFNγ MMP1 MMP8 MMP13 Myeloid Related Protein14 CD40
A real life example In human studies, we quantify ~120 plasma related proteins Monocytes MMP9 Macrophages TNFα IL1ß platelet derived growth factor IFNγ MMP1 MMP8 MMP13 Myeloid Related Protein14 CD40
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com. Question Number 1(a) Answer Additional Guidance Mark NB any sign of an arrow then item to go to review. 1.
 1(a) NB any sign of an arrow then item to go to review. 1. platelets 2. prothrombin 1. ACCEPT plattelets, platellets 2. ACCEPT prothrombrin 3. fibrin 1(b) 1. prevents oxygen reaching the heart {muscle
1(a) NB any sign of an arrow then item to go to review. 1. platelets 2. prothrombin 1. ACCEPT plattelets, platellets 2. ACCEPT prothrombrin 3. fibrin 1(b) 1. prevents oxygen reaching the heart {muscle
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
The Study of Endothelial Function in CKD and ESRD
 The Study of Endothelial Function in CKD and ESRD Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body Aird WC. Circ Res 2007 Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body The endothelium should be viewed for what it is:
The Study of Endothelial Function in CKD and ESRD Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body Aird WC. Circ Res 2007 Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body The endothelium should be viewed for what it is:
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the
 The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION. Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret
 ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret Outline Inflammation in CVDs the evidence Basic Science in Cardiovascular inflammation: The Main players Inflammation as
ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret Outline Inflammation in CVDs the evidence Basic Science in Cardiovascular inflammation: The Main players Inflammation as
Facts on Fats. Ronald P. Mensink
 Facts on Fats Ronald P. Mensink Department of Human Biology NUTRIM, School for Nutrition, Toxicology and Metabolism Maastricht University Maastricht The Netherlands Outline of the Presentation Saturated
Facts on Fats Ronald P. Mensink Department of Human Biology NUTRIM, School for Nutrition, Toxicology and Metabolism Maastricht University Maastricht The Netherlands Outline of the Presentation Saturated
Endothelial dysfunction and subclinical atherosclerosis in HIV/HCV- coinfected patients in the Lower Silesia Region, Poland
 Endothelial dysfunction and subclinical atherosclerosis in HIV/HCV- coinfected patients in the Lower Silesia Region, Poland Katarzyna Barska 1,2, Wiesława Kwiatkowska 1,2, Brygida Knysz 1,3, Justyna Drelichowska
Endothelial dysfunction and subclinical atherosclerosis in HIV/HCV- coinfected patients in the Lower Silesia Region, Poland Katarzyna Barska 1,2, Wiesława Kwiatkowska 1,2, Brygida Knysz 1,3, Justyna Drelichowska
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis. Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk
 The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
KEY COMPONENTS. Metabolic Risk Cardiovascular Risk Vascular Inflammation Markers
 CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
Objectives By the end of lecture the student should:
 Objectives By the end of lecture the student should: Illustrate α oxidation of fatty acids. Understand ω oxidation of fatty acids. List sources and fates of active acetate. Discuss eicosanoids. 2- α Oxidation
Objectives By the end of lecture the student should: Illustrate α oxidation of fatty acids. Understand ω oxidation of fatty acids. List sources and fates of active acetate. Discuss eicosanoids. 2- α Oxidation
PROGRESS TOWARDS POLYUNSATURATED FATTY ACID BASED THERAPEUTICS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES: TURNING A MILLSTONE INTO A MILESTONE?
 PROGRESS TOWARDS POLYUNSATURATED FATTY ACID BASED THERAPEUTICS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES: TURNING A MILLSTONE INTO A MILESTONE? Antonio Ferrante*,, and Charles S. Hii*, *Department of Immunopathology,
PROGRESS TOWARDS POLYUNSATURATED FATTY ACID BASED THERAPEUTICS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES: TURNING A MILLSTONE INTO A MILESTONE? Antonio Ferrante*,, and Charles S. Hii*, *Department of Immunopathology,
VALVULO-METABOLIC RISK IN AORTIC STENOSIS
 January 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 1, pages 21-25) VALVULO-METABOLIC RISK IN AORTIC STENOSIS By Philippe Pibarot, DVM, PhD, FACC, FAHA Groupe de Recherche en Valvulopathies (GRV), Hôpital Laval Research Centre
January 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 1, pages 21-25) VALVULO-METABOLIC RISK IN AORTIC STENOSIS By Philippe Pibarot, DVM, PhD, FACC, FAHA Groupe de Recherche en Valvulopathies (GRV), Hôpital Laval Research Centre
Effects of the angiotensin II type-1 receptor antagonist telmisartan on endothelial activation induced by advanced glycation endproducts
 Effects of the angiotensin II type-1 receptor antagonist telmisartan on endothelial activation induced by advanced glycation endproducts Serena Del Turco, Teresa Navarra, Giuseppina Basta, Raffaele De
Effects of the angiotensin II type-1 receptor antagonist telmisartan on endothelial activation induced by advanced glycation endproducts Serena Del Turco, Teresa Navarra, Giuseppina Basta, Raffaele De
13/09/2012. Dietary fatty acids. Triglyceride. Phospholipids:
 CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES (CVD) and NUTRITION Major cause of morbidity & mortality in Canada & other developed countries e.g., majority of approved health claims on food labels relate to lowering CVD Relation
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES (CVD) and NUTRITION Major cause of morbidity & mortality in Canada & other developed countries e.g., majority of approved health claims on food labels relate to lowering CVD Relation
EXAMINATION OF OxLDL SERUM LEVEL AS THE PROGNOSIS OF ACUTE THROMBOTIC ISCHEMIC STROKE
 EXAMINATION OF OxLDL SERUM LEVEL AS THE PROGNOSIS OF ACUTE THROMBOTIC ISCHEMIC STROKE Bertha J Amaheka 1, Moh. Hasan Machfoed 1, Suhartono Taat Putra 2 1 Department of Neurology Dr M Haulussy Hospital,
EXAMINATION OF OxLDL SERUM LEVEL AS THE PROGNOSIS OF ACUTE THROMBOTIC ISCHEMIC STROKE Bertha J Amaheka 1, Moh. Hasan Machfoed 1, Suhartono Taat Putra 2 1 Department of Neurology Dr M Haulussy Hospital,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University
 Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Cardiovascular disease physiology. Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 2, 2016
 Cardiovascular disease physiology Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 2, 2016 Content Introduction The number 1 killer in America Some statistics Recommendations The disease process
Cardiovascular disease physiology Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 2, 2016 Content Introduction The number 1 killer in America Some statistics Recommendations The disease process
Prof. Isabelle Six INSERM Unit 1088 Jules Verne University of Picardie Amiens, France. Slide 1. Slide 2
 Effects of phosphate on vascular function New insights Isabelle Six, Amiens, France Chairs: Griet Glorieux, Ghent, Belgium Alberto Ortiz, Madrid, Spain Prof. Isabelle Six INSERM Unit 1088 Jules Verne University
Effects of phosphate on vascular function New insights Isabelle Six, Amiens, France Chairs: Griet Glorieux, Ghent, Belgium Alberto Ortiz, Madrid, Spain Prof. Isabelle Six INSERM Unit 1088 Jules Verne University
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry
 Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Observe the effects of atherosclerosis on the coronary artery lumen
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Palm Oil: A Preferred Healthy Dietary Choice
 Palm Oil: A Preferred Healthy Dietary Choice Kalyana Sundram, PhD Deputy Chief Executive Officer & Director, Science & Environment Malaysian Palm Oil Council (MPOC) Palm Kernel Oil (Oleochemical Applications
Palm Oil: A Preferred Healthy Dietary Choice Kalyana Sundram, PhD Deputy Chief Executive Officer & Director, Science & Environment Malaysian Palm Oil Council (MPOC) Palm Kernel Oil (Oleochemical Applications
Obesity is related to a higher inflammatory responsive state of circulating cells after stimulation of toll like receptor 2 and 4.
 Toll Like Receptor Response and traditional risk factors for atherosclerosis: Obesity is related to a higher inflammatory responsive state of circulating cells after stimulation of toll like receptor 2
Toll Like Receptor Response and traditional risk factors for atherosclerosis: Obesity is related to a higher inflammatory responsive state of circulating cells after stimulation of toll like receptor 2
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
NEUTROPHIL-PLATELET INTERACTION
 NEUTROPHIL-PLATELET INTERACTION Johnny Nijm, MD; PhD Specialist in Internal medicine, Cardiology & Clinical Physiology Department of Medicine Diagnostic, Division of Clinical Physiology, County Hospital
NEUTROPHIL-PLATELET INTERACTION Johnny Nijm, MD; PhD Specialist in Internal medicine, Cardiology & Clinical Physiology Department of Medicine Diagnostic, Division of Clinical Physiology, County Hospital
Complications of Diabetes mellitus. Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015
 Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
GLOSSARY Saturated Fatty Acids (SFA) Unsaturated Fatty Acids (UFA) Monounsaturated Fatty Acids (MUFA) Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFA) Cis
 GLOSSARY Saturated Fatty Acids (SFA) contain only single carbon-to-carbon bond. Most of the SFA occurring in nature have unbranched structures and an even number of carbon atoms. The melting point of SFA
GLOSSARY Saturated Fatty Acids (SFA) contain only single carbon-to-carbon bond. Most of the SFA occurring in nature have unbranched structures and an even number of carbon atoms. The melting point of SFA
The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories
 The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories Cardiac biomarkers in atherosclerosis Najma Asadi MD-APCP Ross and Colleagues in 1973: Response to Injury
The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories Cardiac biomarkers in atherosclerosis Najma Asadi MD-APCP Ross and Colleagues in 1973: Response to Injury
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors:
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: Risk factors are traits or habits that increase a person's chances of having cardiovascular disease. Some risk factors can be changed. These risk factors are high blood
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: Risk factors are traits or habits that increase a person's chances of having cardiovascular disease. Some risk factors can be changed. These risk factors are high blood
ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ
 ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ ΘΩΜΑΣ ΠΑΠΑΔΟΠΟΥΛΟΣ, MD, PHD ΕΠΕΜΒΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΟ ΔΙΑΒΑΛΚΑΝΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Inflammation as a cause of disease has entered the popular imagination. Diet ( macronutrients )
ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ ΘΩΜΑΣ ΠΑΠΑΔΟΠΟΥΛΟΣ, MD, PHD ΕΠΕΜΒΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΟ ΔΙΑΒΑΛΚΑΝΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Inflammation as a cause of disease has entered the popular imagination. Diet ( macronutrients )
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease. Why Animal Models of Disease? Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison
 In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Hypertension and Heart Disease. Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union
 Hypertension and Heart Disease Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union The Silent Killer High blood pressure, also known as HBP or hypertension, is a widely misunderstood medical condition
Hypertension and Heart Disease Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union The Silent Killer High blood pressure, also known as HBP or hypertension, is a widely misunderstood medical condition
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
1* (a) QWC (QWC Spelling of technical terms (shown in italics) must be correct and the answer must be organised in a logical sequence)
 1* (a) QWC (QWC Spelling of technical terms (shown in italics) must be correct and the answer must be organised in a logical sequence) 1. idea that there is a cascade of events (leading to blood clotting)
1* (a) QWC (QWC Spelling of technical terms (shown in italics) must be correct and the answer must be organised in a logical sequence) 1. idea that there is a cascade of events (leading to blood clotting)
Biomarkers of immunity and inflammation for use in nutrition interventions: ILSI Europe work on selection criteria and interpretation
 NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre in nutrition Biomarkers of immunity and inflammation for use in nutrition interventions: ILSI Europe work on selection criteria and interpretation Philip C.
NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre in nutrition Biomarkers of immunity and inflammation for use in nutrition interventions: ILSI Europe work on selection criteria and interpretation Philip C.
Weight Loss NOTES. [Diploma in Weight Loss]
![Weight Loss NOTES. [Diploma in Weight Loss] Weight Loss NOTES. [Diploma in Weight Loss]](/thumbs/82/86567947.jpg) Weight Loss NOTES [Diploma in Weight Loss] Fat s: The good, the bad and the ugly Fat s function in your body 1. Energy stores 2. Muscle fuel 3. Transportation 4. Cell membrane 5. Padding 6. Muscle fuel
Weight Loss NOTES [Diploma in Weight Loss] Fat s: The good, the bad and the ugly Fat s function in your body 1. Energy stores 2. Muscle fuel 3. Transportation 4. Cell membrane 5. Padding 6. Muscle fuel
INFLAMM-O-WARS ACTIVITY 4B. Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis. Student Activity Page 4B. Introduction. Background A LOOK AT ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Student Activity Page 4B Introduction Chances are that every one in your class knows somebody who has had a heart attack, but how many really understand what
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Student Activity Page 4B Introduction Chances are that every one in your class knows somebody who has had a heart attack, but how many really understand what
CLINICAL OUTCOME Vs SURROGATE MARKER
 CLINICAL OUTCOME Vs SURROGATE MARKER Statin Real Experience Dr. Mostafa Sherif Senior Medical Manager Pfizer Egypt & Sudan Objective Difference between Clinical outcome and surrogate marker Proper Clinical
CLINICAL OUTCOME Vs SURROGATE MARKER Statin Real Experience Dr. Mostafa Sherif Senior Medical Manager Pfizer Egypt & Sudan Objective Difference between Clinical outcome and surrogate marker Proper Clinical
PALM OLEIN BLENDING FOR TEMPERATE MARKET L/O/G/O
 PALM OLEIN BLENDING FOR TEMPERATE MARKET L/O/G/O Basic Facts on Oil Palm Originated from West Africa, palm oil is the rich source of edible oil and has become important resource of vegetable oil in the
PALM OLEIN BLENDING FOR TEMPERATE MARKET L/O/G/O Basic Facts on Oil Palm Originated from West Africa, palm oil is the rich source of edible oil and has become important resource of vegetable oil in the
Cardiovascular disease, studies at the cellular and molecular level. Linda Lowe Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century September 23, 2009
 Cardiovascular disease, studies at the cellular and molecular level Linda Lowe Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century September 23, 2009 Content Introduction The number 1 killer in America Some statistics
Cardiovascular disease, studies at the cellular and molecular level Linda Lowe Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century September 23, 2009 Content Introduction The number 1 killer in America Some statistics
Objectives. Objectives (continued) Upon completion of the learning activity the participant will be able to:
 Inflammation: Assessing, Preventing and Treating this Common Denominator in a Variety of Diseases Margaret A. Fitzgerald, DNP, FNP-BC, NP-C, FAANP, CSP, FAAN, DCC President Fitzgerald Health Education
Inflammation: Assessing, Preventing and Treating this Common Denominator in a Variety of Diseases Margaret A. Fitzgerald, DNP, FNP-BC, NP-C, FAANP, CSP, FAAN, DCC President Fitzgerald Health Education
Understanding Cholesterol Holistically
 Understanding Cholesterol Holistically Dr. Molly Force & Dr. Alicia McCubbins 213 Decatur Street, Port Townsend www.prospernaturalhealth.com (360)385-5375 This presentation is meant for educational use
Understanding Cholesterol Holistically Dr. Molly Force & Dr. Alicia McCubbins 213 Decatur Street, Port Townsend www.prospernaturalhealth.com (360)385-5375 This presentation is meant for educational use
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
