I-Cell Disease: Biochemical Studies
|
|
|
- Barrie Holt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JULES G. LEROY, MAE WAN HO, MONICA C. MACBRINN, KLAUS ZIELKE, JACK JACOB, AND JOHN S. O'BRIEN 132 ] Pediat. Res. 6: 52-5 (12) Acid hydrolases lipids I-cell disease lysosome I-Cell Disease: Biochemical Studies Department of Genetics, Antwerp State University, Antwerp, Belgium, and Department of Neurosciences, University of California, San Diego, School of Medicine, La Jolla, California, USA Extract Six patients with I-cell disease (ICD) are studied. Multiple acid hydrolase deficiencies are demonstrated in cultured skin fibroblasts. These include /3-galactosidase (2% of normal), /3-glucosaminidase (8% of normal), /3-glucuronidase (% of normal), a-galactosidase (% of normal), and arylsulfatase A (5% of normal). Acid hydrolases found not to be deficient include /3-glucosidase and acid phosphatase. In brain and visceral organs, only /3-galactosidase is deficient (2% of normal in brain; % of normal in liver). A nonspecific accumulation of lipids of all classes occurs in skin fibroblasts (2-3 times normal), but not in brain or visceral organs. No accumulation of acid mucopolysaccharides is demonstrated in skin fibroblasts or liver. Speculation I-cell disease may represent a unique opportunity for the study of control of intracellular levels of lysosomal enzymes. Introduction "I-cell" or "inclusion cell" disease (ICD) is a hereditary disorder of childhood, named from the phase contrast appearance o cultured skin fibroblasts from affected patients. The cytoplasm of cultured fibroblasts is filled with granular inclusions [6]. Recently I-cell disease has also been called mucolipidosis II [16]. The disease presents clinically [] as a slowly progressive disorder with severe growth retardation, skeletal dysplasia, psychomotor retardation, gingival hyperplasia, coarsening of facial features similar to those seen in the Hurler syndrome (MPS type I), and fatal outcome within the 1st decade. The corneas of ICD patients are only occasionally cloudy, hepatosplenomegaly is minimal or absent, and urinary excretion of acid mucopolysaccharides (AMPS) is normal. Pedigree analyses indicate that ICD is transmitted as an autosomal recessive trait []. The nature of the cytoplasmic inclusions in cultured skin fibroblasts is unknown. Ultrastructural studies [5, 20] suggest they are storage cytosomes, possibly derived from lysosomes. In this report we present the results of chemical analyses of the storage material in I-cells as well as the activity of lysosomal hydrolases in these cells. Postmortem analyses of frozen tissues from two patients with I-cell disease are also presented. Subjects Materials and Methods LG,, OW, SS, US, and have been described clinically by Leroy et al. []. BE and JB have been studied by Tondeur et al. [20] and by Eggermont et al. [8], respectively. Patient CM is currently being followed at the Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland. 52
2 I-cell disease 53 Cultures of Skin Fibroblasts Fibroblast cultures were obtained from skin biopsies and propagated in media F- containing 15% fetal calf serum according to methods published previously [6]. For chemical analyses as well as for enzyme studies, cultures of control and patient cell strains were started simultaneously, using in each instance a similar number of cells. All cultures were harvested between 5 and days after they had reached confluency, at which time the cell number had become five times that of the inoculum. Organs Specimens of liver, brain, kidney, and spleen, obtained at autopsy, were frozen and kept at 20 until analysis. Enzyme Assays Af-Acetyl-jS-D-glucosaminidase, /3-D-galactosidase, /3-Dglucosidase, /3-D-glucuronidase, /3-D-xylosidase, «-D-galactosidase, and «-D-mannosidase were assayed fluorometrically by measuring 4-methylumbelliferone released from the appropriate glycosidic derivatives [24] (Table I). The concentrations of homogenates used were 1: (w/v) for liver, skin biopsies, spleen, and kidney; 1:20 (w/v) for brain; and 1: (v/v) for cultured skin fibroblasts. The reaction was stopped with 1 ml M glycine carbonate buffer, ph, and fluorescence was measured with a Turner fluorometer at an excitation wavelength of 365 xufj, and an emission wavelength of 4 mfn. 4-Methylumbelliferone dissolved in the same glycine-carbonate buffer was used as the standard. Arylsulfatase A activity was assayed according to the method of Percy and Brady [14], using p-nitrocatecholsulfate as substrate. Acid phosphatase was assayed spectrophotometrically [] with p-nitrophenylphosphate [25] as substrate. Lipid Analyses Frozen brain and liver obtained at autopsy were available from patients and. Control tissues were obtained from patients ranging in age from 13 days to 55 years who expired from noncerebral causes. Lipid analysis was carried out on cultured fibroblasts from patients LG and, both their parents, and five control subjects. Lipids were extracted by treating the samples with chloroform-methanol, 2:1, in a nitrogen atmosphere as previously described [12]. After evaporation of the solvent, the amount of lipid present was determined by weighing the lipid extract and the nonlipid residue. Two-dimensional thin layer chromatography [13] was carried out using plates coated with Silica Gel G to compare visually the total lipid composition of the patients' tissues or fibroblasts with that of control subjects. Thin layer plates were stained with iodine vapor or charred with potassium dichromatesulfuric acid to visualize lipids. Galactolipids were also stained with orcinol-sulfuric acid, and gangliosides were stained with resorcinol. Lipids in the patients' tissues were quantified by the method of Suzuki [1] using silica gel-coated plates; phosphorus, hexose, and cholesterol contents were determined after each lipid was scraped from the chromatoplates. Total ganglioside-sialic acid in the patients' tissues was determined by the resorcinol method [1]. Analyses of Acid Mucopolysaccharides Isolation of acid mucopolysaccharides [18] was carried out by extracting specimens (2 mg wet wt) with 20 volumes chloroform-methanol, 2:1. After the solvent-extracted residue was dried overnight in a desiccator, it was homogenized in 2 ml 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (ph.5) and digested with Pronase [26] at a final concentration of 0.25 mg/ml for 24 hr at. The undigested residue was removed by centrifugation. Three volumes of ethanol saturated with NaCl were added to the supernate, and crude mucopolysac- Table I. Conditions of enzyme assays Enzyme Composition Buffer-substrate M ph Substrate cone, nim Additions llomogenate, ^liters Buffersubstrate, ^liters Incubation, 0-Galactosidase -Glucosaminidase /3-Glucuronidase ^-Glucosidase a-galactosidase a-mannosidase M NaCl 0.1% human albumin , 20 30, 60
3 54 LEROY ET AL. charides were precipitated at 4 for 12 hr. The precipitate was dissolved in 2 ml 0.5 M acetic acid in 5% sodium acetate and reprecipitated with 4 volumes ethanol. The precipitate was dissolved in 2 ml 0.01 M sodium phosphate buffer (ph.0) with 0.01 M NaCl and incubated with 5 /J a-amylase [2] for 2 hr at 3. Crude mucopolysaccharides were then precipitated with 4 volumes ethanol and washed with 80% ethanol. Table. Acid hydrolase activities 1 (3-Glucuronidase /S-Xylosidase /3-GIucosidase /3-Galactosidase /3-GIucosarainidase a-galactosidase «-Mannosidase Arylsulfatase A Acid phosphatase Skin fibroblasts LG BE CM JB Parents Mother of LG Father of LG Mother of Father of N Skin biopsies CM LH OW SS US N Liver CM TV Gray matter N ,-A Enzyme activity is expressed as m^tmoles substrate cleaved per mg protein per hr at 3
4 I-cell disease 55 The dried powder was redissolved in distilled water for determination of uronic acid and hexosamine. Uronic acid was determined according to the method of Bitter and Muir [1]. Hexosamine was determined according to the method of Boas [2]. Enzyme Assays Results Skin fibroblasts from patients with ICD were markedly deficient in /J-galactosidase, /3-glucosaminidase, /3-glucuronidase, a-galactosidase, and arylsulfatase A activities (Table II). Normal activities were found for /3-glucosidase and acid phosphatase. Skin biopsies from ICD patients were also deficient in /?-galactosidase and /?-glucosaminidase activities as compared with samples from control subjects (Table II). In the liver and cerebral grey matter from patients with ICD, the activities of all enzymes tested fell within the normal range with the exception of /3-galactosidase, which was reduced to about % of the control value in the liver and to 25% of the control value in gray matter. Reduced levels of /3-galactosidase were also found in spleen and kidney. The reduction of /3-galactosidase activity was demonstrated using both jfc>-nitrophenyland 4-methylumbelliferyl-galactosides as substrates. The enzyme deficiencies in skin fibroblasts and the ys-galactosidase deficiency in other tissues were not due to the presence of soluble endogenous inhibitors. This was demonstrated by mixing homogenates of fibroblasts or frozen tissues from control subjects with those from each patient. The mixtures were assayed for enzyme specific activity; assays of all enzymes which were reduced in activity gave the expected intermediate reduction of specific activity in the mixed homogenates. Lipid Analysis The lipid contents of brain, liver, and spleen from patients and were within normal limits. Twodimensional thin layer chromatography of lipid extracts from each organ demonstrated no apparent alteration in the proportions of triglycerides, cholesterol, cholesterol esters, free fatty acids, phosphatidyl ethanolamine, phosphatidyl serine, lecithin, sphingomyelin, phosphatidyl inositol, cardiolipin, gangliosides, or other glycolipids. Cerebral ganglioside patterns in both patients appeared within normal limits. The lipid content of I-cell fibroblasts was increased approximately three times those of controls (Table III). Nonetheless, thin layer chromatography of fibroblast lipid extracts and fractionation of lipids by diethylaminoethyl cellulose chromatography [12] revealed no change in relative percentage of any single lipid. Uniform increases of all fibroblast lipids was apparent, including cholesterol, glycerophosphatides, and glycosphingolipids. Lipid analyses of fibroblasts from parents of two patients gave lipid contents which were higher than the mean of control values; the values fell in the high normal range (Table III). Mucopolysaccharide Analyses No difference was found between the contents of mucopolysaccharides in liver of two ICD patients and in that of control subjects when mucopolysaccharides were quantified on the basis of their uronic acid and hexosamine contents. The content of total mucopolysaccharides in I-cell fibroblasts was also not significantly different from that of normal fibroblasts (Table IV). Discussion We know of no disorder, other than I-cell disease, which involves deficiencies of multiple lysosomal hydrolases in cultured skin fibroblasts. This is useful in the differential diagnosis of ICD from clinically similar disorders such as Hurler's syndrome (MPS I), fucosidosis, and generalized gangliosidosis (GM^-gangliosidosis type I) []. In cultured skin fibroblasts, no deficiency of any of the lysosomal hydrolases assayed occurs in Hurler's syndrome [4], only crfucosidase is deficient in fucosidosis [21, 23], and only /}-galactosidase is deficient in generalized gangliosidosis [15]. Deficiencies of multiple lysosomal hydrolases were also demonstrated in the fibroblasts of the patient studied by Lightbody et al. [], who have confirmed our preliminary results [8]. It is of interest to note that in four parental strains of fibroblasts, the activity of all hydrolases is not inter- Table III. Lipid content of I-cell fibroblasts Subject Patient LG LG's mother LG's father Patient 's mother 's father (5) Lipid content, % dry \vt (-1)
5 56 LEROY ET AL. Table IV. Acid mucopolysaccharide content Skin fibroblasts Parents Mother of Father of Mother o( Control subjects no. 45 no. 51 Liver Control subjects A68-2 A68-3 A68-4 A68-5 A68-6 A68-8 AMPS, ixg/mg protein Chondroitin sulfate was used as standard in an assay for uronic acid. AMPS: acid mucopolysaccharides. mediate between mutant and control strains, but normal (Table II). In our patients with ICD the only lysosomal hydrolase found to be deficient in postmortem tissues is p- galactosidase. Lucksinger et al. [] also reported this to be the only lysosomal hydrolase enzyme deficient in repeated liver biopsies o their patient with I-cell disease. However, in five patients studied by Van Hoof and Hers [21], two had a deficiency of /J-galactosidase in liver and three did not. This inconsistency could be due to heterogeneity among patients with I-cell disease or variability of the /3-gaIactosidase deficiency. A nonspecific accumulation of lipids occurs in cultured skin fibroblasts from patients with ICD. The relationship of the lipid accumulation to the fundamental defect is not clear. Examination of postmortem tissues from patients with I-cell disease demonstrated no significant accumulation of total lipids or of any specific lipid. Moreover, no single lipid was found to accumulate within I-cell fibroblasts, indicating that I- cell disease is not a lipidosis in the classical sense. The acid mucopolysaccharide content of cultured fibroblasts and of liver from patients with I-cell disease is also not elevated, demonstrating that I-cell disease does not involve hepatic mucopolysaccharide storage. For these reasons it appears to be inappropriate to designate I-cell disease as a "mucolipidosis" [16], since neither mucopolysaccharides nor lipids were found to accumulate in the tissues we had available for study. The cause of multiple enzyme deficiencies in cultured skin fibroblasts in I-cell disease is unknown. This multiple enzyme deficiency appears to be present in vivo, at least in fresh skin (although not in other organs). Wiesmann et al. [22] have reported excessive leakage of some acid hydrolases into the culture media in skin fibroblasts from an I-cell patient. Preliminary studies in our laboratory are in accordance with this finding. Further exploration of the cellular and molecular biology of I-cell disease is indicated in order to achieve understanding of the fundamental defect in this remarkable disease. Summary Multiple acid hydrolase deficiencies were demonstrated in cultured skin fibroblasts from patients with I-cell disease. These deficiencies may be due to excessive leakage of enzymes from the cells. In brain and visceral organs, only /3-galactosidase was deficient. A nonspecific accumulation of all classes of lipids occurred in skin fibroblasts, but not in brain or visceral organs. No accumulation of acid mucopolysaccharides was found in skin fibroblasts or in liver. I-cell disease does not present as a classical lipid or mucopolysaccharide storage disorder. The characteristic multiple enzyme deficiencies in skin fibroblasts serve to distinguish it from clinically similar disorders. References and Notes 1. BITTER, T., AND MUIR, H. M.: A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal. Biochem., 4: 330 (162). 2. BOAS, N. F.: Method for the determination of hexosamines in tissues. J. Biol. Chem., 204: 553 (153). 3. EGGERMONT, E.: Connatale vorm van gargoylisme. In: Abstracts of Annual Meeting of Belgian Society of Pediatrics, Louvain, Belgium, p. (10). 4. FLUHARTY, A. L., et al.: Acid glycosidases in mucopolysaccharidoses fibroblasts. Biochem. Med., 4: 1 (10). 5. HANAI, J., LEROY, J. G., AND O'BRIEN, J. S.: Ultrastructure of cultured fibroblasts in I-cell disease. Amer. J. Dis. Child., 122: 34 (11). 6. LEROY, J. G., AND DEMARS, R. I.: Mutant enzymatic and cytological phenotypes in cultured human fibroblasts. Science, 15: 804 (16).. LEROY, J. G., et al.: I-cell disease, a clinical picture. J. Pediat., : 360 (11).
6 I-cell disease 5 8. LEROY, J. G., et al.: I-cell disease, entity detected in cell culture. Bull. Eur. Soc. Hum. Genet., 3: 40 (16).. LIGHTBODY, J., et al.: I-cell disease: multiple lysosomal enzyme defect. Lancet, i: 451 (11).. LUCKSINGER, V., et al.: I-cell disease. New Engl. J. Med., 282: 134 (10).. MACBRINN, M. C, et al.: (3-Galactosidase deficiency in the Hurler syndrome. New Engl. J. Med., 281: 338 (16). 12. O'BRIEN, J. S., AND SAMPSON, E. L.: Lipid composition of the normal human brain: gray matter, white matter and myelin. J. Lipid Res., 6: 53 (165). 13. PARSONS, J. G., AND PATTON, S.: TWO dimensional thin-layer chromatogiaphy of polar lipids from milk and mammary tissue. J. Lipid Res., 8: 66 (16). 14. PERCY, A. K., AND BRADY, R. O.: Metachromatic leukodystrophy: diagnosis with samples of venous blood. Science, 161: 54 (168). 15. SLOAN, H. R., et al.: 3-Galactosidase in tissue culture derived from human skin and bone marrow: enzyme defect in CM,- gangliosidosis. Pediat. Res., 3: 532 (16). 16. SPRANGER, J. W., AND WIEDEMANN, H. R.: The genetic mucolipidoses. Humangenetik, : 3 (10). 1. SUZUKI, K.: A simple and accurate micromethod for quantitative determination of ganglioside patterns. Life Sci., 3: 122 (164). 18. SUZUKI, K., SUZUKI, K., AND KAMOSHITA, S.: Chemical pathology of GMj-gangliosidosis (generalized gangliosidosis). J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 28: 25 (16). 1. ENNERHOLM, L.: Quantitative estimation of sialic acids; II. A colorimetric resorcinol-hydrochloric acid method. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 24: 604 (15). 20. TONDEUR, M., et al.: Clinical, biochemical and ultrastructural studies in a case of chondrodystrophy presenting the I-cell phenotype in tissue culture. J. Pediat. : 366 (11). 21. VAN HOOF, F., AND HERS, H. G.: The abnormalities of lysosomal enzymes in mucopolysaccharidoses. Eur. J. Biochem., : 34 (168). 22. WIESMANN, U. N., et al.: Multiple lysosomal enzyme deficiency due to enzyme leakage. New Engl. J. Med., 284: (11). 23. ZIELKE, K., OKADA, S., AND O'BRIEN, J. S.: Fucosidosis: diagnosis by serum assay of a-l-fucosidase. J. Lab. Clin. Med., : 164 (12). 24. Koch Light, England. 25. Sigma Chemical Company, St. Louis, Mo. 26. B grade, Calbiochem, Los Angeles, Calif. 2. Dog pancreas, Sigma Chemical Company, St. Louis, Mo. 28. Informed consent for publication of clinical data on the subjects reported herein has been granted by parties involved. 2. We thank Drs. A. C. Crocker, J. M. Opitz, J. Spranger, M. Feingold, H. Loeb, E. Eggermont, and V. McKusick for referring patients to us. Dr. R. I. DeMars has kindly supplied us with some of the skin fibrobiast strains used in these studies. 30. Excellent technical assistance was given by Mrs. A. De Becker, L. Tennant, L. Veath, and Miss M. Roemans. 31. This work was supported by the Fonds voor Geneeskundig wetenschappelijk onderzoek, Brussels, Belgium and by grants from the National Foundation, the National Genetics Foundation, the National Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, the National Institutes of Health Grant no. NB08682, and the National Institutes of Health Program Grant no. GM Requests for reprints should be addressed to: JOHN S. O'BRIEN, M.D., Department of Neurosciences, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, Calif. 203 (USA). 33. Accepted for publication May 23, 12. Copyright 12 International Pcdiatric Research Foundation, Inc. Printed in U.S.A.
The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders
 The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders Dr Guy Besley, formerly Willink Biochemical Genetics Unit, Manchester Children s Hospital, Manchester M27 4HA, UK. Lysosomal disorders What
The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders Dr Guy Besley, formerly Willink Biochemical Genetics Unit, Manchester Children s Hospital, Manchester M27 4HA, UK. Lysosomal disorders What
METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS. Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry
 METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry STORAGE AND MEMBRANE LIPIDS STORAGE LIPIDS Mainly as triacylglycerols (triglycerides) in adipose cells Constitute
METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry STORAGE AND MEMBRANE LIPIDS STORAGE LIPIDS Mainly as triacylglycerols (triglycerides) in adipose cells Constitute
Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases
 Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases M. Rohrbach, MD, PhD FMH Pädiatrie und FMH Medizinische Genetik Abteilung Stoffwechsel Universitätskinderklinik Zürich Lysosomal storage disorders
Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases M. Rohrbach, MD, PhD FMH Pädiatrie und FMH Medizinische Genetik Abteilung Stoffwechsel Universitätskinderklinik Zürich Lysosomal storage disorders
 Title Spot Test Method Convenient in Column Chromatography for Det Author(s) Morita, Shigeru; Hanai, Tetsuya Citation Bulletin of the Institute for Chemi University (1975), 53(3): 279-283 Issue Date 1975-09-16
Title Spot Test Method Convenient in Column Chromatography for Det Author(s) Morita, Shigeru; Hanai, Tetsuya Citation Bulletin of the Institute for Chemi University (1975), 53(3): 279-283 Issue Date 1975-09-16
Glycoproteins and Mucins. B.Sopko
 Glycoproteins and Mucins B.Sopko Content Glycoproteins: Structures and Linkages Interconversions and activation of dietary sugars Other pathways of sugar nucleotide metabolism Biosynthesis of oligosaccharides
Glycoproteins and Mucins B.Sopko Content Glycoproteins: Structures and Linkages Interconversions and activation of dietary sugars Other pathways of sugar nucleotide metabolism Biosynthesis of oligosaccharides
Quantitation and Identification of Urine Mucopolysaccharides. George Gray MetBioNet Workshop 2008
 Quantitation and Identification of Urine Mucopolysaccharides George Gray MetBioNet Workshop 2008 The Big Questions What are we measuring? Where does it come from? How do we measure it? What are we measuring?
Quantitation and Identification of Urine Mucopolysaccharides George Gray MetBioNet Workshop 2008 The Big Questions What are we measuring? Where does it come from? How do we measure it? What are we measuring?
(From the Division q[ Human Genetics, Department of Medicine, CorneU University Medical College, New York 10021) Materials and Methods
 OYSTER CILIARY INHIBITION BY CYSTIC FIBROSIS CULTURE MEDIUM* BY B. SHANNON DANES ANn ALEXANDER G. BEARN (From the Division q[ Human Genetics, Department of Medicine, CorneU University Medical College,
OYSTER CILIARY INHIBITION BY CYSTIC FIBROSIS CULTURE MEDIUM* BY B. SHANNON DANES ANn ALEXANDER G. BEARN (From the Division q[ Human Genetics, Department of Medicine, CorneU University Medical College,
Consequently, lipoprotein fractions have been analyzed
 THE PHOSPHOLIPID COMPOSITION OF HUMAN SERUM LIPOPROTEIN FRACTIONS SEPARATED BY ULTRACENTRIFUGATION * BY GERALD B. PHILLIPS (From the Departments of Biochemistry and Medicine, College of Physicians and
THE PHOSPHOLIPID COMPOSITION OF HUMAN SERUM LIPOPROTEIN FRACTIONS SEPARATED BY ULTRACENTRIFUGATION * BY GERALD B. PHILLIPS (From the Departments of Biochemistry and Medicine, College of Physicians and
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson
 Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Colorimetric determination of free
 Colorimetric determination of free fatty acids in biological fluids KOICHI ITAYA and MICHIO UI Department of Biological Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hokkaido University School of Medicine,
Colorimetric determination of free fatty acids in biological fluids KOICHI ITAYA and MICHIO UI Department of Biological Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hokkaido University School of Medicine,
SEASONAL CHANGES OF AVOCADO LIPIDS DURING FRUIT DEVELOPMENT AND STORAGE
 California Avocado Society 1968 Yearbook 52: 102-108 SEASONAL CHANGES OF AVOCADO LIPIDS DURING FRUIT DEVELOPMENT AND STORAGE Yoshio Kikuta Present address: Department of Botany, Faculty of Agriculture,
California Avocado Society 1968 Yearbook 52: 102-108 SEASONAL CHANGES OF AVOCADO LIPIDS DURING FRUIT DEVELOPMENT AND STORAGE Yoshio Kikuta Present address: Department of Botany, Faculty of Agriculture,
4. Determination of fat content (AOAC, 2000) Reagents
 94 ANALYTICAL METHODS 1. Determination of moisture content (AOAC, 2000) 1. Dry the empty dish and lid in the oven at 105 C for 3 h and transfer to desiccator to cool. Weigh the empty dish and lid. 2. Weigh
94 ANALYTICAL METHODS 1. Determination of moisture content (AOAC, 2000) 1. Dry the empty dish and lid in the oven at 105 C for 3 h and transfer to desiccator to cool. Weigh the empty dish and lid. 2. Weigh
Beta Hexosaminidase Activity Assay Kit
 Product Manual Beta Hexosaminidase Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number MET-5095 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Hexosaminidase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes
Product Manual Beta Hexosaminidase Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number MET-5095 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Hexosaminidase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes
the shoreline and the surrounding water was exposed to menhaden chum. Every 15mins,
 Supplemental Methods: Shark Capture A gill net (450 x 10 with 4 5/8 stretched mesh) was positioned perpendicular to the shoreline and the surrounding water was exposed to menhaden chum. Every 15mins, the
Supplemental Methods: Shark Capture A gill net (450 x 10 with 4 5/8 stretched mesh) was positioned perpendicular to the shoreline and the surrounding water was exposed to menhaden chum. Every 15mins, the
Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit
 Product Manual Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit Catalog Number MET- 5019 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Phosphatidic Acid (PA) is a critical precursor
Product Manual Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit Catalog Number MET- 5019 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Phosphatidic Acid (PA) is a critical precursor
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP
 CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J.) (Accepted
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J.) (Accepted
Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム
 Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム Add the following next to Description: Identification Dissolve 1 mg each of Heparin Sodium and Heparin Sodium Reference Standard for physicochemical test in 1 ml of water, and
Heparin Sodium ヘパリンナトリウム Add the following next to Description: Identification Dissolve 1 mg each of Heparin Sodium and Heparin Sodium Reference Standard for physicochemical test in 1 ml of water, and
TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010)
 June 2010 TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
June 2010 TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Tenofoviri disoproxili fumaras)
 C 19 H 30 N 5 O 10 P. C 4 H 4 O 4 Relative molecular mass. 635.5. Chemical names. bis(1-methylethyl) 5-{[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl}-5-oxo-2,4,6,8-tetraoxa-5-λ 5 - phosphanonanedioate
C 19 H 30 N 5 O 10 P. C 4 H 4 O 4 Relative molecular mass. 635.5. Chemical names. bis(1-methylethyl) 5-{[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl}-5-oxo-2,4,6,8-tetraoxa-5-λ 5 - phosphanonanedioate
Date of commencement: February Principal Investigator Dr. Jayesh J. Sheth CASE RECORD FORM
 ICMR-FRIGE-MULTICENTRIC LSDs Project Foundation for Research in Genetics & Endocrinology [FRIGE], FRIGE House, Jodhpur Gam road, Satellite, Ahmedabad-380015 Tel no: 079-26921414, Fax no: 079-26921415 E-mail:
ICMR-FRIGE-MULTICENTRIC LSDs Project Foundation for Research in Genetics & Endocrinology [FRIGE], FRIGE House, Jodhpur Gam road, Satellite, Ahmedabad-380015 Tel no: 079-26921414, Fax no: 079-26921415 E-mail:
Total lipid and membrane lipid analysis of normal animal and human lenses
 Total lipid and membrane lipid analysis of normal animal and human lenses J. Stevens Andrews and Thomas Leonard-Martin Comparisons of lens fiber cell membrane isolation methods were made. Although membrane
Total lipid and membrane lipid analysis of normal animal and human lenses J. Stevens Andrews and Thomas Leonard-Martin Comparisons of lens fiber cell membrane isolation methods were made. Although membrane
Manual (Second edition)
 Reagent for RNA Extraction ISOGENⅡ Manual (Second edition) Code No. 311-07361 Code No. 317-07363 NIPPON GENE CO., LTD. Table of contents I Product description 1 II Product content 1 III Storage 1 IV Precautions
Reagent for RNA Extraction ISOGENⅡ Manual (Second edition) Code No. 311-07361 Code No. 317-07363 NIPPON GENE CO., LTD. Table of contents I Product description 1 II Product content 1 III Storage 1 IV Precautions
FIXATION OF TISSUES MODULE 5.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 5.2 AIMS OF FIXATION 5.3 PRINCIPLE OF FIXATION. Notes
 MODULE Fixation of Tissues 5 FIXATION OF TISSUES 5.1 INTRODUCTION It is a process by which the cells or tissues are fixed in chemical and partly physical state so that they can withstand subsequent treatment
MODULE Fixation of Tissues 5 FIXATION OF TISSUES 5.1 INTRODUCTION It is a process by which the cells or tissues are fixed in chemical and partly physical state so that they can withstand subsequent treatment
MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS
 December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
Best Practice Guidelines for the Biochemical Investigation of Patients with Foetal and Neonatal Hydrops
 National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Best Practice Guidelines for the Biochemical Investigation of Patients with Foetal and Neonatal Hydrops INTRODUCTION Hydrops is defined as the presence of skin oedema
National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Best Practice Guidelines for the Biochemical Investigation of Patients with Foetal and Neonatal Hydrops INTRODUCTION Hydrops is defined as the presence of skin oedema
Opinion on the safety assessment of phospholipds obtained from egg yolk as food produced using a new process
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL XXIV CONSUMER POLICY AND CONSUMER HEALTH PROTECTION Directorate B - Scientific opinions on health matters Unit B3 - Management of scientific committees II SCIENTIFIC
EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL XXIV CONSUMER POLICY AND CONSUMER HEALTH PROTECTION Directorate B - Scientific opinions on health matters Unit B3 - Management of scientific committees II SCIENTIFIC
II- Compound Lipids. 1- Phospholipids
 II- ompound Lipids ompound (conjugated) lipids are lipids conjugated with other substances. They include: 1- Phospholipids formed of lipid, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base. 2- Glycolipids, formed
II- ompound Lipids ompound (conjugated) lipids are lipids conjugated with other substances. They include: 1- Phospholipids formed of lipid, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base. 2- Glycolipids, formed
DAG (Diacylglycerol) Assay Kit
 Product Manual DAG (Diacylglycerol) Assay Kit Catalog Number MET-5028 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Diacylglycerols (DAG) are key intermediates in the
Product Manual DAG (Diacylglycerol) Assay Kit Catalog Number MET-5028 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Diacylglycerols (DAG) are key intermediates in the
The effect of phosphatidyl choline on the degradation of phosphatidyl ethanolamine by the phospholipase of post-heparin plasma or snake venom
 The effect of phosphatidyl choline on the degradation of phosphatidyl ethanolamine by the phospholipase of post-heparin plasma or snake venom WILLIAM C. VOGEL, J. L. KOPPEL, and J. H. OLWIN Coagulation
The effect of phosphatidyl choline on the degradation of phosphatidyl ethanolamine by the phospholipase of post-heparin plasma or snake venom WILLIAM C. VOGEL, J. L. KOPPEL, and J. H. OLWIN Coagulation
Lipid Chemistry. Presented By. Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair
 Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids
 I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO
 COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO Induction by Dibutyryl Cyclic-AMP I. PASTAN and S. HI. WOLLMAN. Froml the National Institute of Arthritis and Metabolic Diseases and the National Cancer
COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO Induction by Dibutyryl Cyclic-AMP I. PASTAN and S. HI. WOLLMAN. Froml the National Institute of Arthritis and Metabolic Diseases and the National Cancer
9( )- Hydroxyoctadecadienoic Acid ELISA
 Package Insert 9( )- Hydroxyoctadecadienoic Acid ELISA 96 Wells For Research Use Only v. 1.0 Eagle Biosciences, Inc. 82 Broad Street, Suite 383, Boston, MA 02110 Phone: 866-419-2019 Fax: 617-419-1110 INTRODUCTION
Package Insert 9( )- Hydroxyoctadecadienoic Acid ELISA 96 Wells For Research Use Only v. 1.0 Eagle Biosciences, Inc. 82 Broad Street, Suite 383, Boston, MA 02110 Phone: 866-419-2019 Fax: 617-419-1110 INTRODUCTION
Lipids. Lipids. Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague
 Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) ARTESUNATI COMPRESSI ARTESUNATE TABLETS
 December 2009 ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
December 2009 ARTESUNATE TABLETS: Final text for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (December 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
Supporting Information
 Notes Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, Vol. 34, No. 1 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.1.xxx Supporting Information Chemical Constituents of Ficus drupacea Leaves and their α-glucosidase Inhibitory
Notes Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, Vol. 34, No. 1 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.1.xxx Supporting Information Chemical Constituents of Ficus drupacea Leaves and their α-glucosidase Inhibitory
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical properties of SDS-stable low molecular weight alkaline serine protease from Citrullus Colocynthis Muhammad Bashir Khan, 1,3 Hidayatullah khan, 2 Muhammad
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical properties of SDS-stable low molecular weight alkaline serine protease from Citrullus Colocynthis Muhammad Bashir Khan, 1,3 Hidayatullah khan, 2 Muhammad
Akiyoshi HOSONO and Fumisaburo. (Faculty of Agriculture, Shinshu University, Ina, Nagano-Ken, Japan) (Received for Publication on May, 7, 1970)
 The lipolytic properties of Candida mycoderma and Debaryomyces kloeckeri isolated from limburger cheese and some properties of the lipases produced by these yeasts Akiyoshi HOSONO and Fumisaburo TOKITA
The lipolytic properties of Candida mycoderma and Debaryomyces kloeckeri isolated from limburger cheese and some properties of the lipases produced by these yeasts Akiyoshi HOSONO and Fumisaburo TOKITA
ISOLATION AND PURIFICATION OF A SEROLOGICALLY ACTIVE PHOSPHOLIPID FROM BEEF HEART
 SOLATON AND PURFCATON OF A SEROLOGCALLY ACTVE PHOSPHOLPD FROM BEEF HEART BY MARY C. PANGBORN (From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Albany) (Received for
SOLATON AND PURFCATON OF A SEROLOGCALLY ACTVE PHOSPHOLPD FROM BEEF HEART BY MARY C. PANGBORN (From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Albany) (Received for
Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples:
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples: Sample preparation for serum proteome analysis Sample
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples: Sample preparation for serum proteome analysis Sample
Fatty Acid Methylation Kits
 Methyl esterification kit for fatty acids analysis Fatty Acid Methylation Kits Below are two methods for efficiently preparing fatty acid samples for GC analysis. Neither method requires high temperatures,
Methyl esterification kit for fatty acids analysis Fatty Acid Methylation Kits Below are two methods for efficiently preparing fatty acid samples for GC analysis. Neither method requires high temperatures,
CYTIDINE. Enzymatic synthesis of cytidine diphosphate diglyceride
 Enzymatic synthesis of cytidine diphosphate diglyceride JAMES R. CARTER* and EUGENE P. KENNEDY Department of Biological Chemistry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts ABSTRACT Evidence is presented
Enzymatic synthesis of cytidine diphosphate diglyceride JAMES R. CARTER* and EUGENE P. KENNEDY Department of Biological Chemistry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts ABSTRACT Evidence is presented
IN RECENT YEARS several systems of TLC for the separation. Separation of neutral glycosphingolipids and sulfatides by thin-layer chromatography
 Separation of neutral glycosphingolipids and sulfatides by thin-layer chromatography VLADIMIR P. SKIPSKI, ANSON F. SMOLOWE,* and MARION BARCLAY Division of Experimental Chemotherapy, Sloan-Kettering Institute
Separation of neutral glycosphingolipids and sulfatides by thin-layer chromatography VLADIMIR P. SKIPSKI, ANSON F. SMOLOWE,* and MARION BARCLAY Division of Experimental Chemotherapy, Sloan-Kettering Institute
RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS. Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012)
 July 2012 RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-sixth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
July 2012 RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-sixth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
[GANN, 59, ; October, 1968] CHANGES IN ALDOLASE ISOZYME PATTERNS OF HUMAN CANCEROUS TISSUES
![[GANN, 59, ; October, 1968] CHANGES IN ALDOLASE ISOZYME PATTERNS OF HUMAN CANCEROUS TISSUES [GANN, 59, ; October, 1968] CHANGES IN ALDOLASE ISOZYME PATTERNS OF HUMAN CANCEROUS TISSUES](/thumbs/87/96205960.jpg) [GANN, 59, 415-419; October, 1968] UDC 616-006-092.18 CHANGES IN ALDOLASE ISOZYME PATTERNS OF HUMAN CANCEROUS TISSUES Kiyoshi TSUNEMATSU, Shin-ichi YOKOTA, and Tadao SHIRAISHI (Third Department of Internal
[GANN, 59, 415-419; October, 1968] UDC 616-006-092.18 CHANGES IN ALDOLASE ISOZYME PATTERNS OF HUMAN CANCEROUS TISSUES Kiyoshi TSUNEMATSU, Shin-ichi YOKOTA, and Tadao SHIRAISHI (Third Department of Internal
Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit
 Product Manual Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit Catalog Number STA-616 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cholesterol is a lipid sterol
Product Manual Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit Catalog Number STA-616 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cholesterol is a lipid sterol
ARTENIMOLUM ARTENIMOL. Adopted revised text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia
 February 2012 ARTENIMOLUM ARTENIMOL Adopted revised text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted at the Forty-sixth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
February 2012 ARTENIMOLUM ARTENIMOL Adopted revised text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted at the Forty-sixth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
Mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses
 J. clin. Path., 27, Suppl. (Roy. Coll. Path.), 8, 64-93 Mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses F. VAN HOOF From the Laboratoire de Chimie Physiologique, Universite Catholique de Louvain, and International
J. clin. Path., 27, Suppl. (Roy. Coll. Path.), 8, 64-93 Mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses F. VAN HOOF From the Laboratoire de Chimie Physiologique, Universite Catholique de Louvain, and International
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Antiradical and antioxidant activity of flavones from Scutellariae baicalensis radix
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Antiradical and antioxidant activity of flavones from Scutellariae baicalensis radix Dorota Woźniak A, Andrzej Dryś B, and Adam Matkowski* A A Department of Pharmaceutical Biology
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Antiradical and antioxidant activity of flavones from Scutellariae baicalensis radix Dorota Woźniak A, Andrzej Dryś B, and Adam Matkowski* A A Department of Pharmaceutical Biology
Phospholipase D Activity of Gram-Negative Bacteria
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Dec. 1975, p. 1148-1152 Copyright 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 124, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Phospholipase D Activity of Gram-Negative Bacteria R. COLE AND P. PROULX*
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Dec. 1975, p. 1148-1152 Copyright 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 124, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Phospholipase D Activity of Gram-Negative Bacteria R. COLE AND P. PROULX*
B. 1% (w/v) Salicin Substrate Solution (Salicin) (Prepare 50 ml in Reagent A using Salicin, Sigma Prod. No. S-0625.)
 SIGMA QUALITY CONTROL TEST PROCEDURE (Q]\PDWLFÃ$VVD\ÃRIÃ */8&26,'$6( PRINCIPLE: 'Glucoside + H 2 O Glucosidase > D-Glucose + an Alcohol CONDITIONS: T = 37 C, ph = 5.0, A 540nm, Light path = 1 cm METHOD:
SIGMA QUALITY CONTROL TEST PROCEDURE (Q]\PDWLFÃ$VVD\ÃRIÃ */8&26,'$6( PRINCIPLE: 'Glucoside + H 2 O Glucosidase > D-Glucose + an Alcohol CONDITIONS: T = 37 C, ph = 5.0, A 540nm, Light path = 1 cm METHOD:
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Dauvillée et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907424106 Fig. S1. Iodine screening of the C. cohnii mutant bank. Each single colony was grown on rich-medium agar plates then vaporized with iodine.
Supporting Information Dauvillée et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907424106 Fig. S1. Iodine screening of the C. cohnii mutant bank. Each single colony was grown on rich-medium agar plates then vaporized with iodine.
Substrate Specificity and Salt Inhibition of Five Proteinases Isolated from the Pyloric Caeca and Stomach of Sardine
 Agric. Biol. Chem., 46 (6), 1565~1569, 1982 1565 Substrate Specificity and Salt Inhibition of Five Proteinases Isolated from the Pyloric Caeca and Stomach of Sardine Minoru Noda, Thanh Vo Van, Isao Kusakabe
Agric. Biol. Chem., 46 (6), 1565~1569, 1982 1565 Substrate Specificity and Salt Inhibition of Five Proteinases Isolated from the Pyloric Caeca and Stomach of Sardine Minoru Noda, Thanh Vo Van, Isao Kusakabe
Monitoring intracellular activity of Arylsulfatase B on its natural substrates in a functional bioassay using LIF-CZE
 Monitoring intracellular activity of Arylsulfatase B on its natural substrates in a functional bioassay using LIF-CZE Erno Pungor Jr; Charles M. Hague; Ginger Chen; Jeffrey F. Lemontt; William S. Prince
Monitoring intracellular activity of Arylsulfatase B on its natural substrates in a functional bioassay using LIF-CZE Erno Pungor Jr; Charles M. Hague; Ginger Chen; Jeffrey F. Lemontt; William S. Prince
Enzyme Derived Pig Livers. By Shoei ISEKI and Haruko YAMAMOTO Department of Legal Medicine, School of Medicine, Gunma University, Maebashi
 No. 4] Proc. Japan Acad., 44 (1968) 269 62. A-Decomposing Human and Enzyme Derived Pig Livers from By Shoei ISEKI and Haruko YAMAMOTO Department of Legal Medicine, School of Medicine, Gunma University,
No. 4] Proc. Japan Acad., 44 (1968) 269 62. A-Decomposing Human and Enzyme Derived Pig Livers from By Shoei ISEKI and Haruko YAMAMOTO Department of Legal Medicine, School of Medicine, Gunma University,
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 26 Done by حسام أبو عوض Corrected by Zaid Emad Doctor فيصل الخطيب 1 P a g e A small note about phosphatidyl inositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) before moving on: This molecule is found in the membrane
number 26 Done by حسام أبو عوض Corrected by Zaid Emad Doctor فيصل الخطيب 1 P a g e A small note about phosphatidyl inositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) before moving on: This molecule is found in the membrane
Overview on the identification of different classes of. lipids by HPTLC (High Performance Thin Layer. Chromatography) and ITLC (Immuno Thin Layer
 Overview on the identification of different classes of lipids by HPTLC (High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography) and ITLC (Immuno Thin Layer Chromatography) Iuliana Popa 1, Marie-Jeanne David 2, Daniel
Overview on the identification of different classes of lipids by HPTLC (High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography) and ITLC (Immuno Thin Layer Chromatography) Iuliana Popa 1, Marie-Jeanne David 2, Daniel
Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010)
 June 2010 KANAMYCIN ACID SULFATE: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WH Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
June 2010 KANAMYCIN ACID SULFATE: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WH Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
CYCLOSERINI CAPSULAE - CYCLOSERINE CAPSULES (AUGUST 2015)
 August 2015 Document for comment 1 2 3 4 5 CYCLOSERINI CAPSULAE - CYCLOSERINE CAPSULES DRAFT PROPOSAL FOR THE INTERNATIONAL PHARMACOPOEIA (AUGUST 2015) DRAFT FOR COMMENT 6 Should you have any comments
August 2015 Document for comment 1 2 3 4 5 CYCLOSERINI CAPSULAE - CYCLOSERINE CAPSULES DRAFT PROPOSAL FOR THE INTERNATIONAL PHARMACOPOEIA (AUGUST 2015) DRAFT FOR COMMENT 6 Should you have any comments
Enzymatic Assay of ß-GLUCOSIDASE (EC )
 PRINCIPLE: ß-D-Glucoside + H 2 O ß-Glucosidase > D-Glucose + an Alcohol CONDITIONS: T = 37 C, ph = 5.0, A 540nm, Light path = 1 cm METHOD: Colorimetric 1 REAGENTS: A. 100 mm Sodium Acetate Buffer, ph 5.0
PRINCIPLE: ß-D-Glucoside + H 2 O ß-Glucosidase > D-Glucose + an Alcohol CONDITIONS: T = 37 C, ph = 5.0, A 540nm, Light path = 1 cm METHOD: Colorimetric 1 REAGENTS: A. 100 mm Sodium Acetate Buffer, ph 5.0
OCR (A) Biology A-level
 OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 2.2: Biological molecules Notes Water Water is a very important molecule which is a major component of cells, for instance: Water is a polar molecule due to uneven distribution
OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 2.2: Biological molecules Notes Water Water is a very important molecule which is a major component of cells, for instance: Water is a polar molecule due to uneven distribution
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 4 Membrane Organization and Transport Across Membranes Lecture 1 Cell Membrane and Transport
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 4 Membrane Organization and Transport Across Membranes Lecture 1 Cell Membrane and Transport
The development of a detection method discriminating for
 1 2 3 The development of a detection method discriminating for mannosylerythritol lipids and acylglycerols Simon Van Kerrebroeck 1, *, Hannes Petit, Joeri Beauprez 1, Inge N.A. Van Bogaert 1, Wim Soetaert
1 2 3 The development of a detection method discriminating for mannosylerythritol lipids and acylglycerols Simon Van Kerrebroeck 1, *, Hannes Petit, Joeri Beauprez 1, Inge N.A. Van Bogaert 1, Wim Soetaert
Supporting Information File S2
 Pulli et al. Measuring Myeloperoxidase Activity in Biological Samples Page 1 of 6 Supporting Information File S2 Step-by-Step Protocol Reagents: Sucrose (Sigma, S3089) CaCl 2 (Sigma, C5770) Heparin Sodium
Pulli et al. Measuring Myeloperoxidase Activity in Biological Samples Page 1 of 6 Supporting Information File S2 Step-by-Step Protocol Reagents: Sucrose (Sigma, S3089) CaCl 2 (Sigma, C5770) Heparin Sodium
Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA0820 500 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA0820 500 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
M1.(a) 1. Fewer children / less likely that children with asthma eat fish; Accept converse.
 M.(a). Fewer children / less likely that children with asthma eat fish; Accept converse.. Fewer children / less likely that children with asthma eat oily fish; MP and Allow use of numbers.. Little / only
M.(a). Fewer children / less likely that children with asthma eat fish; Accept converse.. Fewer children / less likely that children with asthma eat oily fish; MP and Allow use of numbers.. Little / only
THE SITE OF STEROL AND SQUALENE SYNTHESIS IN THE HUMAN SKIN123
 THE SITE OF STEROL AND SQUALENE SYNTHESIS IN THE HUMAN SKIN123 N. NICOLAIDES, PH.D. AND STEPHEN ROTHMAN, M.D. In earlier work (1) it was demonstrated that human scalp skin is an efficient organ for synthesizing
THE SITE OF STEROL AND SQUALENE SYNTHESIS IN THE HUMAN SKIN123 N. NICOLAIDES, PH.D. AND STEPHEN ROTHMAN, M.D. In earlier work (1) it was demonstrated that human scalp skin is an efficient organ for synthesizing
TechNotes. Gangliosides. 1. Applications
 TechNotes Gangliosides Gangliosides are a large group of sialylated glycosphingolipids that are widely expressed in mammalian tissues. Gangliosides are found in most tissues of the body, but they are particularly
TechNotes Gangliosides Gangliosides are a large group of sialylated glycosphingolipids that are widely expressed in mammalian tissues. Gangliosides are found in most tissues of the body, but they are particularly
Organic and biochemical synthesis of monolignol biosynthetic pathway intermediates
 Jie Liu 2012-2-8 Organic and biochemical synthesis of monolignol biosynthetic pathway intermediates 1. Organic synthesis of 5-hydroxyferulic acid Malonic acid 3, 4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 0.1
Jie Liu 2012-2-8 Organic and biochemical synthesis of monolignol biosynthetic pathway intermediates 1. Organic synthesis of 5-hydroxyferulic acid Malonic acid 3, 4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxy-benzaldehyde 0.1
CYCLOSERINE Proposal for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (August 2012)
 August 2012 RESTRICTED CYCLOSERINE Proposal for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (August 2012) Draft for comment This document was provided by a quality control expert. Should you have any comments
August 2012 RESTRICTED CYCLOSERINE Proposal for revision of The International Pharmacopoeia (August 2012) Draft for comment This document was provided by a quality control expert. Should you have any comments
Chairman: DR B. D. CORNER
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (August 1977) 53, 441-448. SESSION II Chairman: DR B. D. CORNER Catabolic disorders of complex carbohydrates J. W. SPRANGER M.D. Children's Hospital, Johannes Gutenberg University,
Postgraduate Medical Journal (August 1977) 53, 441-448. SESSION II Chairman: DR B. D. CORNER Catabolic disorders of complex carbohydrates J. W. SPRANGER M.D. Children's Hospital, Johannes Gutenberg University,
LEVONORGESTREL AND ETHINYLESTRADIOL TABLETS. (January 2012) DRAFT FOR COMMENT
 January 2012 RESTRICTED DRAFT PROPOSAL FOR The International Pharmacopoeia LEVONORGESTREL AND ETHINYLESTRADIOL TABLETS (January 2012) DRAFT FOR COMMENT This document was provided by a quality control expert.
January 2012 RESTRICTED DRAFT PROPOSAL FOR The International Pharmacopoeia LEVONORGESTREL AND ETHINYLESTRADIOL TABLETS (January 2012) DRAFT FOR COMMENT This document was provided by a quality control expert.
Lipid changes in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1972, 35, 658-663 B. P. HUGHES From the Muscular Dystrophy Research Laboratory, Institute of Neurology, The National Hospital, London SUMMARY Thin layer
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1972, 35, 658-663 B. P. HUGHES From the Muscular Dystrophy Research Laboratory, Institute of Neurology, The National Hospital, London SUMMARY Thin layer
HYDROXYPROPYLCELLULOSE, LOW SUBSTITUTED Stage 4, Revision 1 CP: USP BRIEFING NOTE
 002-0901PDG.pdf HYDROXYPROPYLCELLULOSE, LOW SUBSTITUTED Stage 4, Revision 1 CP: USP BRIEFING NOTE Compared to the Stage 4, document the following changes are proposed: 1. Assay: a determination of the
002-0901PDG.pdf HYDROXYPROPYLCELLULOSE, LOW SUBSTITUTED Stage 4, Revision 1 CP: USP BRIEFING NOTE Compared to the Stage 4, document the following changes are proposed: 1. Assay: a determination of the
Biochemical Techniques 06 Salt Fractionation of Proteins. Biochemistry
 . 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 2 1. Objectives Understanding the concept of protein fractionation Understanding protein fractionation with salt 2. Concept Map 3.
. 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 2 1. Objectives Understanding the concept of protein fractionation Understanding protein fractionation with salt 2. Concept Map 3.
THE CHEMISTRY OF THE LIPIDS OF TUBERCLE BACILLI
 THE CHEMISTRY OF THE LIPIDS OF TUBERCLE BACILLI LXXII. FATTY ACIDS OCCURRING IN THE WAX PREPARED FROM TUBERCULIN RESIDUES. CONCERNING MYCOCEROSIC ACID* BY LEONARD G. GINGER? AND R. J. ANDERSON (From the
THE CHEMISTRY OF THE LIPIDS OF TUBERCLE BACILLI LXXII. FATTY ACIDS OCCURRING IN THE WAX PREPARED FROM TUBERCULIN RESIDUES. CONCERNING MYCOCEROSIC ACID* BY LEONARD G. GINGER? AND R. J. ANDERSON (From the
Cholesterol determination using protein-templated fluorescent gold nanocluster probes
 Electronic Supplementary Information for Cholesterol determination using protein-templated fluorescent gold nanocluster probes Xi Chen and Gary A. Baker* Department of Chemistry, University of Missouri-Columbia,
Electronic Supplementary Information for Cholesterol determination using protein-templated fluorescent gold nanocluster probes Xi Chen and Gary A. Baker* Department of Chemistry, University of Missouri-Columbia,
Abdallah Q& Razi. Faisal
 27 & Ahmad Attari م ح م د ي وس ف Abdallah Q& Razi Faisal Sphingophospolipids - The backbone of sphingophospholipids is sphingosine, unlike glycerophospholipids with a glycerol as the backbone. Which contains
27 & Ahmad Attari م ح م د ي وس ف Abdallah Q& Razi Faisal Sphingophospolipids - The backbone of sphingophospholipids is sphingosine, unlike glycerophospholipids with a glycerol as the backbone. Which contains
Title Revision n date
 A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
Semimicro Determination of Cellulose in Biological Materials
 A*N-ALYTICAL BIOCtIEIVIISTRY 3:2, 420--424 (1969) Semimicro Determination of Cellulose in Biological Materials DAVID M. UPDEGRAFF Chemical Division, Denver Research Institute, University of Denver, Denver,
A*N-ALYTICAL BIOCtIEIVIISTRY 3:2, 420--424 (1969) Semimicro Determination of Cellulose in Biological Materials DAVID M. UPDEGRAFF Chemical Division, Denver Research Institute, University of Denver, Denver,
Gargoylism: Hydrolysis of 0 - Galactosides
 Gargoylism: Hydrolysis of 0 - Galactosides and Tissue Accumulation of Galactose- and Mannose-Containing Compounds Bj6RN HULTBERG, PER-ARNE OCKERMAN, and Apm DAHLQVIST From the Laboratory of Clinical Chemistry
Gargoylism: Hydrolysis of 0 - Galactosides and Tissue Accumulation of Galactose- and Mannose-Containing Compounds Bj6RN HULTBERG, PER-ARNE OCKERMAN, and Apm DAHLQVIST From the Laboratory of Clinical Chemistry
Blueberry scorch virus Reagent Set DAS ELISA, Alkaline phosphatase label for BlScV Catalog number: SRA 19100
 List of contents Lot number Blueberry scorch virus Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150
List of contents Lot number Blueberry scorch virus Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150
21 Virginiamycin OH O. For chickens (except for broilers) broilers. Added amount 5~15 5~15 10~20 10~20
 21 Virginiamycin H H H H H H Virginiamycin M 1 C 28 H 35 3 7 MW: 525.6 CAS o.: 21411-53-0 Virginiamycin S 1 C 43 H 49 7 10 MW: 823.9 CAS o.: 23152-29-6 [Summary of virginiamycin] Virginiamycin (VM) is
21 Virginiamycin H H H H H H Virginiamycin M 1 C 28 H 35 3 7 MW: 525.6 CAS o.: 21411-53-0 Virginiamycin S 1 C 43 H 49 7 10 MW: 823.9 CAS o.: 23152-29-6 [Summary of virginiamycin] Virginiamycin (VM) is
Metabolism of acylglycerols and sphingolipids. Martina Srbová
 Metabolism of acylglycerols and sphingolipids Martina Srbová Types of glycerolipids and sphingolipids 1. Triacylglycerols function as energy reserves adipose tissue (storage of triacylglycerol), lipoproteins
Metabolism of acylglycerols and sphingolipids Martina Srbová Types of glycerolipids and sphingolipids 1. Triacylglycerols function as energy reserves adipose tissue (storage of triacylglycerol), lipoproteins
BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON CARBOHYDRATES. XL. Preparation of Mucoitin* from Umbilical Cords.
 The Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 28, No. 3. BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON CARBOHYDRATES. XL. Preparation of Mucoitin* from Umbilical Cords. MASAMI BY SUZUKI. (From the Medico-Chemical Institute, Hokkaido Imperial
The Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 28, No. 3. BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON CARBOHYDRATES. XL. Preparation of Mucoitin* from Umbilical Cords. MASAMI BY SUZUKI. (From the Medico-Chemical Institute, Hokkaido Imperial
Supporting Information. First synthetic entry to the trimer stage of 5,6-dihydroxyindole polymerization: orthoalkynylaniline-based
 Supporting Information First synthetic entry to the trimer stage of 5,6-dihydroxyindole polymerization: orthoalkynylaniline-based access to the missing 2,7 :2,7 -triindole Luigia Capelli, Paola Manini,*
Supporting Information First synthetic entry to the trimer stage of 5,6-dihydroxyindole polymerization: orthoalkynylaniline-based access to the missing 2,7 :2,7 -triindole Luigia Capelli, Paola Manini,*
(From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, New Jersey)
 CRYSTALLIZATION OF SALT-FREE CHYMOTRYPSINOGEN AND CHYMOTRYPSIN FROM SOLUTION IN DILUTE ETHYL ALCOHOL BY M. KUNITZ (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, New
CRYSTALLIZATION OF SALT-FREE CHYMOTRYPSINOGEN AND CHYMOTRYPSIN FROM SOLUTION IN DILUTE ETHYL ALCOHOL BY M. KUNITZ (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, New
Newborn Screening for Lysosomal Storage Diseases in Missouri. Outline
 Newborn Screening for Lysosomal Storage Diseases in Missouri Dr. Kathy Grange Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University Outline Brief overview of clinical
Newborn Screening for Lysosomal Storage Diseases in Missouri Dr. Kathy Grange Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University Outline Brief overview of clinical
THE EFFECT OF FLUORINE UPON THE PHOSPHATASE CONTENT OF PLASMA, BONES, AND TEETH OF ALBINO RATS
 THE EFFECT OF FLUORINE UPON THE PHOSPHATASE CONTENT OF PLASMA, BONES, AND TEETH OF ALBINO RATS BY MARGARET CAMMACK SMITH AND EDITH M. LANTZ (From the Department oj Nutrition, Agricultural Experiment Station,
THE EFFECT OF FLUORINE UPON THE PHOSPHATASE CONTENT OF PLASMA, BONES, AND TEETH OF ALBINO RATS BY MARGARET CAMMACK SMITH AND EDITH M. LANTZ (From the Department oj Nutrition, Agricultural Experiment Station,
Membrane biochemistry. Red blood cell ghost Only plasmalemma Size known (7 µm) Gorter & Grendel 1925 Tension on surface Enough lipid for 2 layers
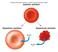 Membrane biochemistry Red blood cell ghost Only plasmalemma Size known (7 µm) Gorter & Grendel 1925 Tension on surface Enough lipid for 2 layers Fig. 6.5 Osmosis water moves passively from high WATER
Membrane biochemistry Red blood cell ghost Only plasmalemma Size known (7 µm) Gorter & Grendel 1925 Tension on surface Enough lipid for 2 layers Fig. 6.5 Osmosis water moves passively from high WATER
Examination of Chemicals in Trap Cases. (Phenolphthalein)
 Introduction Examination of Chemicals in Trap Cases (Phenolphthalein) Although a number of different techniques using different chemicals such as fluorescent dyes, starch powder, phenolphthalein powders
Introduction Examination of Chemicals in Trap Cases (Phenolphthalein) Although a number of different techniques using different chemicals such as fluorescent dyes, starch powder, phenolphthalein powders
SKIN LIPIDS OF A NORMAL AND A MUTANT (ASEBIC) MOUSE STRAIN*
 TRE JOURNAL OF IN'VESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1986 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 47, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. SKIN LIPIDS OF A NORMAL AND A MUTANT (ASEBIC) MOUSE STRAIN* DAVID I. WILKINSON, PHD.
TRE JOURNAL OF IN'VESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1986 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 47, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. SKIN LIPIDS OF A NORMAL AND A MUTANT (ASEBIC) MOUSE STRAIN* DAVID I. WILKINSON, PHD.
Phosphatase Activity of Drosophila Salivary Glands
 Phosphatase Activity of Drosophila Salivary Glands BY W. L. DOYLE (From the Department of Anatomy, University of Chicago) THE presence of alkaline phosphatase in chromosomes has been demonstrated by means
Phosphatase Activity of Drosophila Salivary Glands BY W. L. DOYLE (From the Department of Anatomy, University of Chicago) THE presence of alkaline phosphatase in chromosomes has been demonstrated by means
(LM pages 91 98) Time Estimate for Entire Lab: 2.5 to 3.0 hours. Special Requirements
 Laboratory 7 Chemical Aspects of Digestion (LM pages 91 98) Time Estimate for Entire Lab: 2.5 to 3.0 hours Special Requirements Incubation. Students should start these sections at the beginning of the
Laboratory 7 Chemical Aspects of Digestion (LM pages 91 98) Time Estimate for Entire Lab: 2.5 to 3.0 hours Special Requirements Incubation. Students should start these sections at the beginning of the
Data sheet. TBARS Assay kit. (Colorimetric/Fluorometric) Kit Contents. MDA-TBA Adduct. 2-Thiobarbituric Acid. Cat. No: CA995.
 Data sheet Cat. No: CA995 TBARS Assay kit (Colorimetric/Fluorometric) Introduction Oxidative stress in the cellular environment results in the formation of highly reactive and unstable lipid hydroperoxides.
Data sheet Cat. No: CA995 TBARS Assay kit (Colorimetric/Fluorometric) Introduction Oxidative stress in the cellular environment results in the formation of highly reactive and unstable lipid hydroperoxides.
ASSAY OF SPHINGOMYELINASE ACTIVITY
 ASSAY OF SPHINGOMYELINASE ACTIVITY Protocol for Protein Extraction Stock Solution 1. Leupeptin/hydrochloride (FW 463.0,
ASSAY OF SPHINGOMYELINASE ACTIVITY Protocol for Protein Extraction Stock Solution 1. Leupeptin/hydrochloride (FW 463.0,
Separation of Plasma and Serum and Their Proteins from Whole Blood
 Separation of Plasma and Serum and Their Proteins from Whole Blood BCH 471 [Practical] BLOOD COMPOSITION Other names to blood cells Red blood cells (erythrocytes) White blood cells (leukocytes) Platelets
Separation of Plasma and Serum and Their Proteins from Whole Blood BCH 471 [Practical] BLOOD COMPOSITION Other names to blood cells Red blood cells (erythrocytes) White blood cells (leukocytes) Platelets
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd
 ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enzyme-activatable Probe with a Self-immolative Linker for Rapid and Sensitive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enzyme-activatable Probe with a Self-immolative Linker for Rapid and Sensitive
Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable. Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors
 Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors Yu Zhao, Jianming Kang, Chung-Min Park, Powell E. Bagdon, Bo Peng, and Ming Xian * Department of Chemistry, Washington
Thiol-Activated gem-dithiols: A New Class of Controllable Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Donors Yu Zhao, Jianming Kang, Chung-Min Park, Powell E. Bagdon, Bo Peng, and Ming Xian * Department of Chemistry, Washington
