Yorkshire & Humber Neonatal ODN (South) Clinical Guideline
|
|
|
- Emory Phelps
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Yorkshire & Humber Neonatal ODN (South) Clinical Guideline Title: Extravasation Injuries in Neonates Author: Dr Pauline Adiotomre, Lynn Elliot Date Written: March 2005, Reviewed July 2018 by Dr Pauline Adiotomre & Dr Cath Smith Next Review Date: July 2021 Date Ratified: 6 September 2018 This clinical guideline has been developed to ensure appropriate evidence based standards of care throughout the Yorkshire & Humber Neonatal ODN (South). The appropriate use and interpretation of this guideline in providing clinical care remains the responsibility of the individual clinician. If there is any doubt discuss with a senior colleague. Best practice recommendations represent widely used evidence-based practice and high quality standards that all Neonatal Units across the Network should implement. Subsequent suggested recommendations may be put into practice in local units. However, alternative appropriate local guidelines may also exist. A. Summary Aim of guideline Prevention and management of extravasation injuries. Extravasation injuries require review regarding the need for treatment. Treatments include Dressingshydrocolloids hydrogels Topical therapies- 2% Glyceryltrinitrate ointment (GTN). Glyceryltrinitrate patch Hyaluronidase irrigation The treatment required will depend on the drug extravasated, the site and extent of the injury and the gestation of the infant. Note hyaluronidase is no longer recommended for use in extremely preterm infants.
2 B. Full guideline 1. Background EPIDEMIOLOGY OF EXTRAVASATION INJURIES Extravasation is the non-intentional leakage of infused fluid into surrounding tissue which may cause tissue damage¹. The prevalence of extravasation injuries causing skin necrosis in 31 regional neonatal units in the United Kingdom was 38 per 1000 babies². Infants of 26 weeks gestation or less were more likely to have injuries, which was likely to occur when parenteral nutrition was given via intravenous cannulae. Other fluids implicated in extravasation injuries were 10% dextrose with calcium and blood. Dopamine and other vasoactive fluids can also cause this injury with tissue ischaemia³. Preterm babies are at high risk as they have most immature skin which is easily damaged, require longer duration of intravenous therapy and have difficult venous access. 2. Aim Prevention and management of extravasation injuries. 3. Areas outside remit if applicable None applicable 4. Core guideline: 4.1 PREVENTION Use percutaneous long lines for the administration of total parenteral nutrition and glucose concentrations greater than 12.5%. When running dextrose 12.5% peripherally the site should be very closely observed and observations documented. Consideration should be given to placing central access to avoid extravasation. Avoid scalp vein cannula where possible Secure cannulae with transparent dressing to ensure visibility at insertion site. Hourly recording of observation of cannula site for oedema, firmness or discolouration. Percutaneous long line for long term calcium supplementation. However, if calcium supplementation is only short term, this can be given via a peripheral cannula, the site of which must be monitored closely There is currently no evidence that monitoring infusion pump pressures reduces the incidence of extravasation injuries 4.
3 4.2 STAGING OF EXTRAVASATION 5 Stage Characteristics Absence of redness and swelling. Flushes with difficulty. Take IV device out. Slight swelling at site. Presence of redness. Good pulse below site. 1-2 seconds capillary refill below site. Take IV device out. Elevate extremity. Moderate swelling above or below site. Blanching. Good pulse below extravasation site. 1-2 seconds capillary refill below extravasation site. Skin cool to touch. Follow management below. Severe swelling above or below site. Blanching. Pain at site. Decreased or absent pulse. Capillary refill greater than 4 seconds. Skin cool to touch. Skin breakdown or necrosis. Follow management below. 4.3 WOUND ASSESSMENT 1 This should include the site, size of injury, level of exudate, state of healing and possibility of infection. Exudate is more pronounced during the inflammatory phase of wound healing and should be graded as low, medium or large. This is however subjective. There are 4 stages of wound healing (wound status)-: a) Necrotic stage - the surface of wound may initially be covered with devitalised tissue which is unbroken if area of damage is away from the cannulation site. b) Slough stage - slough is composed of dead white cells and can be mistaken for pus often with lack of signs of infection such as redness, swelling, heat and loss of movement. c) Granulating stage - granulation tissue develops quickly when wound bed is clean and gives a red appearance. This is highly vascular and bleeds easily if damaged. Care should be taken during dressing change or handling to prevent damage and bleeding. d) Epithelisation stage - this is the last stage of healing when the epithelial cells move from the wound edges towards the centre. Wound bed has a pink appearance at this stage.
4 4.4 MANAGEMENT Stop the intravenous infusion. Take the IV device out after an attempt has been made to aspirate the area through the device. There is no consensus on the management of extravasation injuries in babies. From the survey in 31 regional neonatal units common treatments were- Exposing wounds to the air Infiltration with hyaluronidase and saline Occlusive dressing ². Leaving the wound exposed to the air is not considered an optimal treatment as dry scab is thought to delay epithelisation. Infiltration with hyaluronidase and saline 6 is an invasive procedure and British National Formulary has advised caution in the use of hyaluronidase in infants 7 and to control speed and total volume and therefore avoid overhydration especially in renal impairment. Although occlusive dressings keep the wound moist which aids healing, no clinical trials have compared the out come of treatment with occlusive dressings to that of infiltration with hyaluronidase and saline. Features of optimum dressing¹ Small dressing size or dressing that can be cut to size. Can be used in a humidified environment. Allows full range of movement at joint sites. Minimum risk of further tissue damage on removal. Reduces epithermal water loss through wound bed 4.5 WOUND DRESSING Those currently used are: Hydrocolloids These have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of extravasation injuries in the preterm population 8. They have many of the features of an optimum dressing with an extended wear time of 7 days which is achievable during the granulation and epithelisation stages for wound healing. Because the absorption properties are limited dressing will need to be changed daily when level of exudate is high to prevent strike through. Hydrocolloid dressings are suitable for softening eschars or promoting granulation. Examples of hydrocolloids are:- Duoderm and Granuflex dressings with or without Granuflex paste. Hydrogels These create a moist environment and lead to reduced scarring when used in preterm infants 9. Hydrogels prevent the growth of bacteria and have a mild
5 bactericidal property. The gel is applied directly to the extravasation injury and either covered with a film dressing (like tegaderm or opsite) or the affected limb is placed inside a sterile transparent plastic bag. Additional gel may be delivered into the bag with a syringe and a quill to ensure the wound is covered at all times 10. Neck of bag should be closed using surgical tape but ensure the tape doesn t come in contact with the baby s skin. Dressing should be changed every 2 to 3 days but daily if any clinical evidence of wound infection. In this case appropriate antibiotics should be initiated. To change the dressing slide the bag off the limb and irrigate wound with sterile isotonic saline. It is not necessary to dry the wound. One of the hydrogels is intrasite gel. Film dressings Film dressings like tegaderm and opsite should be used as secondary dressings over hydrogels. Dry dressing is considered not to be effective. 4.6 OTHER STRATEGIES THAT CAN BE CONSIDERED OR USED 2% Glyceryl trinitrate ointment. This is used for severe peripheral tissue ischaemia caused by vasospasm from indwelling arterial catheterisation or dopamine (or other vasoactive drugs) extravasation. Glyceryl trinitrate is well absorbed topically through intact skin. It causes relaxation of the vascular smooth muscle and increases collateral circulation to localized areas of peripheral ischaemia 3. Local vasodilating effects are often noted 15 to 30 minutes after topical application. Dose : 4mm Glyceryl trinitrate ointment/ kg ( or 2mg as 0.1 ml in a syringe ) applied as a thin film to the affected area 3,11,12. Glyceryl trinitrate can be reapplied 8 hourly if the desired local effect is not attained and no adverse or systemic effects occur. It has the potential to cause hypotension therefore monitor vital signs. Glyceryl Trinitrate patch 13,14 GTN patch can be used to manage extravasation injury associated with intense local vasoconstriction. Glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) is a powerful local vasodilator and the patch containing 25 mg (releasing 5 mg per 24 hours) can be applied to the ischaemic area for one hour. As it is a patch, it may not cover edges of the affected area. Infiltration with hyaluronidase and saline flushout 6,15,16 It is not advisable to use hyaluronidase in extreme preterm babies as it is felt not to provide any extra benefit 1 but can cause further tissue
6 damage 2. Outcome is better where irrigation with saline is done within 1 to 6 hours of the injury 17,18 Equipment: - 1% Lignocaine (up to 0.3 ml/kg maximum) units/ml vial of hyaluronidase - Normal saline for injection - 1 ml syringes - Sterile scalpel blade - Size 19G cannula - 3 way tap - 20 ml syringe - 25G needles - Sterile towel - Dressing pack - Sterile gloves - Chlorhexidine solution - Water proof sheet Clean the discoloured area and surrounding skin with Chlorhexidine solution and place on sterile towel. Place a sterile bowl underneath towel. Infiltrate area with 1% Lignocaine. Inject units hyaluronidase into the subcutaneous tissue beneath the damaged skin. Do not use for extravasation injuries due to vaso-constrictive agents or in extreme preterm babies Make four small punctures in the tissue plane with a scalpel blade around the affected area approximately 5mm long. Insert the 19G cannula subcutaneously through one of the puncture sites and remove the needle Using a 20 ml syringe attached to a three-way tap, inject normal saline into the area. This should flow out freely from the other three incisions. Repeat the process injecting normal saline through each incision and using up to 500 ml of normal saline depending on size of wound and of baby. The following has been suggested for different weights of babies 17 : <1000g 200ml g 300ml > 2000g 500ml If the limb gets oedematous, excess fluid can be removed by massaging towards the incisions. Dress area with sterile non-stick dressing such as Mepitel or Intrasite conformable gel dressing. The stab wounds should not be closed as they may drain for a while. Check wound 6 hourly for the next 1 day 19 If baby not already on antibiotics give 1 dose of IV flucloxacillin Elevate limb for 24 hours
7 saline flush out technique A combination of strategies may be required in managing extravasation injuries. The wound dressing used will depend on the wound status. If there is clinical suggestion of infection baby should be screened for infection and started on appropriate antibiotics. Where intra-arterial line vasospasm is responsible for the peripheral ischaemia, take the line out. 4.7 DOCUMENTATION Detailed account of action taken when there was concern about patency of cannula or any swelling around the cannula site before the extravasation. Clear documentation of the causative agent, the site and size of the injury, an assessment of the wound and rationale for choice of dressing product used. Care plan for the treatment. Photograph of wound with scale included. Parents informed and documented. Complete an incident form. Observe and document a change in colour and decrease in swelling hourly for six hours then every six hours then at start of each shift as appropriate With each dressing change document state of the wound bed, change in size of wound, details of replacement dressing and planned date of review.
8 4.8 FURTHER ACTIONS Parents to be involved with wound care which should form part of the discharge planning if wound not completely healed by the time infant is ready for discharge. Plastic surgeons to be involved especially in extravasation injuries in term babies. Liaise with Tissue Viability nurse where possible. 5. Audit criteria Adherence to guideline in managing extravasation injuries 6. References 1. Irving V. Managing extravasation injuries in preterm neonates. Nurs Times.2001;97(35): Wilkins CE, Emmerson AJ. Extravasation injuries on regional neonatal units. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed.2004;89(3):F Wong AF, McCulloch LM et al.treatment of peripheral tissue ischaemia with topical nitroglycerin ointment in neonates. J Pediatr. 1992;121(6): Gnanalingham MG, Irving V, Shaw NJ.Consensus on neonatal infusion pumps and pressure monitoring. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005;90(1):F Montgomery LA, Haurahan K, Kottam K et al. Guideline for IV infiltrations in pediatric patients. Pediatr Nurs 1999 ; 25(2) : 167-9, Davies J, Gault D, Buchdahl R. Preventing the scars of neonatal intensive care. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1994;70:F British National Formulary.London: BMJ Books, 2002; Young T, et al. The use of a hydrocolloid dressing in the treatment of iatrogenic neonatal skin trauma. In: Proceedings of the 6 th European Conference on Advances in Wound Management London: Macmillan. 9. Thomas,S et al. A new approach to the management of extravasation injury in neonates. Pharmaceutical Journal. 1987;239: Thomas S, Rowe HN, et al. The management of extravasation injury in neonates. ml. 11. Mosalli, R et al. Topical nitroglycerine for neonatal arterial associated peripheral ischaemia following cannulation: A case report and comprehensive literature review. Case Reports in Pediatrics Plum M et al.alternative pharmacological management of vasopressor extravasation in the absence of phentolamine. Pharmacy and Therapeutics. 2017;42(9) O Reilly C, McKay FMA, Duffty P, Lloyd D. Glyceryl trinitrate in skin necrosis caused by extravasation of parenteral nutrition. Lancet ; 2 (8610) : Reynolds B.C. Neonatal extravasation injury: Case report. Infant. 2007; 3(6):
9 15. Gault D.T. Extravasation injuries. Br J Plast Surg. 1993; 46(2): Casanova D, Bardot J, Magalon G. Emergency treatment of accidental infusion leakage in the newborn: report of 14 cases. Br J Plastic Surgeon. 2001; 54 : Harris P.A, Bradley S, Moss A.L. Limiting the damage of iatrogenic extravasation injury in neonates. Plastic Reconstructive Surgery 2001; 107(3): Rose V, Turner M, Harris P.A, Moss A.L.H. Emergency treatment of accidental infusion leakage in the newborn. Br J Plast Surg 2002; 55(1): NW Newborn Clinical Guideline. Recognition and management of infiltration injuries (including clysis). May 2010
Risk factors and drugs/infusion commonly associated with tissue damage include: Extreme Prematurity Dextrose greater than 12.
 Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Clinical Guideline Extravasation injuries Extravasation is defined as the inadvertent leakage of infused fluid into the surrounding tissue. The resultant damage to tissue can
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Clinical Guideline Extravasation injuries Extravasation is defined as the inadvertent leakage of infused fluid into the surrounding tissue. The resultant damage to tissue can
Extravasation injuries. Amendments Date Page(s) Comments Approved by 03/16 ALL Completely updated guideline
 Note: Guidance comments are written in italics Extravasation injuries Amendments Date Page(s) Comments Approved by 03/16 ALL Completely updated guideline Compiled by: In Consultation with: Ratified by:
Note: Guidance comments are written in italics Extravasation injuries Amendments Date Page(s) Comments Approved by 03/16 ALL Completely updated guideline Compiled by: In Consultation with: Ratified by:
ASHFORD & ST PETER S HOSPITALS NHS TRUST Neonatal Unit. Neonatal Skin and Wound Care Guideline
 ASHFORD & ST PETER S HOSPITALS NHS TRUST Neonatal Unit Neonatal Skin and Wound Care Guideline Contents Preventative measures 2 Initiating wound care 3 Wound classification and management 4 Recommended
ASHFORD & ST PETER S HOSPITALS NHS TRUST Neonatal Unit Neonatal Skin and Wound Care Guideline Contents Preventative measures 2 Initiating wound care 3 Wound classification and management 4 Recommended
SOUTHERN HEALTH & SOCIAL CARE TRUST. Children & Young People s Directorate Procedure/Guidelines/Protocol Checklist & Version Control Sheet
 Children & Young People s Directorate Procedure/Guidelines/Protocol Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1 Name of Procedure/Guidelines/ Protocol: PROCEDURE FOR PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL CANNULATION 2 Purpose of
Children & Young People s Directorate Procedure/Guidelines/Protocol Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1 Name of Procedure/Guidelines/ Protocol: PROCEDURE FOR PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL CANNULATION 2 Purpose of
CHEST DRAIN PROTOCOL
 CHEST DRAIN PROTOCOL Rationale The pleural membranes have an important role in effective lung expansion. The visceral pleura is a thin, smooth, serous membrane covering the surface of the lungs and is
CHEST DRAIN PROTOCOL Rationale The pleural membranes have an important role in effective lung expansion. The visceral pleura is a thin, smooth, serous membrane covering the surface of the lungs and is
IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Serum Osmolality 275 to 295 Isotonic
 1 IV Fluids Nursing B23 2 Objectives 3 Serum Osmolality Serum osmolality solute concentration of a solution Higher osmolality means greater pulling power for water Normal serum osmolality is 275 to 295
1 IV Fluids Nursing B23 2 Objectives 3 Serum Osmolality Serum osmolality solute concentration of a solution Higher osmolality means greater pulling power for water Normal serum osmolality is 275 to 295
IV Fluids. Nursing B23. Objectives. Serum Osmolality
 IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Discuss the purpose of IV Discuss nursing interventions in IV therapy Identify complications of IV therapy Differentiate between peripheral line, central line, and PICC
IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Discuss the purpose of IV Discuss nursing interventions in IV therapy Identify complications of IV therapy Differentiate between peripheral line, central line, and PICC
NOTTINGHAM CHILDREN S HOSPITAL Nursing Guideline. P07 Care and Management of Children with a Totally Implantable Venous Access Device (Portacath).
 NOTTINGHAM CHILDREN S HOSPITAL Nursing Guideline P07 Care and Management of Children with a Totally Implantable Venous Access Device (Portacath). Introduction A Portacath is a central venous access device
NOTTINGHAM CHILDREN S HOSPITAL Nursing Guideline P07 Care and Management of Children with a Totally Implantable Venous Access Device (Portacath). Introduction A Portacath is a central venous access device
Successful IV Starts Revised February 2014
 Successful IV Starts Revised February 2014 Why Intravenous Therapy? Used for access to the body s circulation Indications: Administer fluids, blood, medications, and nutrition Obtain laboratory specimens
Successful IV Starts Revised February 2014 Why Intravenous Therapy? Used for access to the body s circulation Indications: Administer fluids, blood, medications, and nutrition Obtain laboratory specimens
St George Hospital Renal Department Internal Only
 RENAL VASCULAR ACCESS CANNULATION POLICY AND PROCEDURE SUMMARY: A functioning arteriovenous fistula (AVF) or arteriovenous graft (AVG) is paramount in the maintenance of regular and optimal haemodialysis
RENAL VASCULAR ACCESS CANNULATION POLICY AND PROCEDURE SUMMARY: A functioning arteriovenous fistula (AVF) or arteriovenous graft (AVG) is paramount in the maintenance of regular and optimal haemodialysis
NEONATAL SKIN AND WOUND CARE
 NEONATAL SKIN AND WOUND CARE Objectives Review the different categories of wounds seen in neonates and children. Understand the physiologic and structural differences between neonatal skin and adult skin.
NEONATAL SKIN AND WOUND CARE Objectives Review the different categories of wounds seen in neonates and children. Understand the physiologic and structural differences between neonatal skin and adult skin.
DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED
 10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
IV Link Staff. Infection Prevention & Control A Learning Package for IV Link Staff
 IV Link Staff Infection Prevention & Control A Learning Package for IV Link Staff Purpose This learning package provides key infection prevention messages and direction for knowledge that you require as
IV Link Staff Infection Prevention & Control A Learning Package for IV Link Staff Purpose This learning package provides key infection prevention messages and direction for knowledge that you require as
2. Indications Infusion of hyperosmolar medication, e.g. TPN. Administration of vasoactive/irritant drugs.
 Policy and Procedure for Insertion and care of Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters by Neonatal Staff (see Ch 8 TPN) 1. Introduction The peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) is an intravenous
Policy and Procedure for Insertion and care of Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters by Neonatal Staff (see Ch 8 TPN) 1. Introduction The peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) is an intravenous
ASSESSMENT AND CARE Monitor for the following and remove catheter if there is: redness, pain, swelling, firm tissue, exudates, bleeding or leakage.
 POLICY An Indwelling subcutaneous catheter may be inserted when an infant requires regular subcutaneous injections (At least one subcutaneous injection per day). SUPPORTIVE DATA In the NICU medications
POLICY An Indwelling subcutaneous catheter may be inserted when an infant requires regular subcutaneous injections (At least one subcutaneous injection per day). SUPPORTIVE DATA In the NICU medications
Managing Wounds. Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse
 Managing Wounds Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse First things first.. Assess, measure and photograph Know what you re dealing with, look at anatomical position and the bigger picture to look for extra
Managing Wounds Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse First things first.. Assess, measure and photograph Know what you re dealing with, look at anatomical position and the bigger picture to look for extra
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds
 Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
Advazorb. Hydrophilic foam dressing range
 Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
Children s Acute Transport Service
 Children s Acute Transport Service Vascular Access Document Control Information Author Ramnarayan Author Position Consultant, CATS Document Owner Polke Document Owner Position CATS Co-ordinator Document
Children s Acute Transport Service Vascular Access Document Control Information Author Ramnarayan Author Position Consultant, CATS Document Owner Polke Document Owner Position CATS Co-ordinator Document
Table of Contents. Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings
 Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Skin Integrity and Wound Care
 Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
Insertion of a totally implantable vascular access device (TIVAD)
 Insertion of a totally implantable vascular access device (TIVAD) What is a TIVAD? A TIVAD is a long hollow tube that is inserted into one of the large veins in your body. One end of the tube sits in a
Insertion of a totally implantable vascular access device (TIVAD) What is a TIVAD? A TIVAD is a long hollow tube that is inserted into one of the large veins in your body. One end of the tube sits in a
2. Advanced wound therapies... 4 (i) Maggots... 4 (ii) Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT)... 4
 Contents: Wound management Medicines Formulary 1. Interactive dressings... 2 (i) Hydrocolloid dressings... 2 (ii) Hydrogel dressings... 2 (iii) Alginate dressings... 2 (iv) Fibrous absorbent dressings...
Contents: Wound management Medicines Formulary 1. Interactive dressings... 2 (i) Hydrocolloid dressings... 2 (ii) Hydrogel dressings... 2 (iii) Alginate dressings... 2 (iv) Fibrous absorbent dressings...
3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing Description 3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing is used
 3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing Description 3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing is used to cover and protect catheter sites and to secure devices
3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing Description 3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing is used to cover and protect catheter sites and to secure devices
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment. Michelle Greenwood. Lorraine Grothier. Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust
 Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Central venous access devices for children with lysosomal storage disorders
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Central venous access devices for children with lysosomal storage disorders This information explains about central
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Central venous access devices for children with lysosomal storage disorders This information explains about central
Drawtex: a unique dressing that can be tailor-made to fit wounds
 BRITISH JOURNAL OF Drawtex: a unique dressing that can be tailor-made to fit wounds Linda Russell, Amanda Evans This article is reprinted from the British Journal of Nursing, 1999, Vol 8, No 15, pp 1022-1026
BRITISH JOURNAL OF Drawtex: a unique dressing that can be tailor-made to fit wounds Linda Russell, Amanda Evans This article is reprinted from the British Journal of Nursing, 1999, Vol 8, No 15, pp 1022-1026
Guidelines for the Care and Maintenance of Intravenous Access Devices in Paediatric Patients
 Guidelines for the Care and Maintenance of Intravenous Access Devices in Paediatric Patients These guidelines have been adapted for local use from the Collaborative Intravenous Nursing Services regional
Guidelines for the Care and Maintenance of Intravenous Access Devices in Paediatric Patients These guidelines have been adapted for local use from the Collaborative Intravenous Nursing Services regional
PATIENT CARE PLAN FOR CARE OF PERIPHERAL MIDLINE. Manufacturers specific recommendations should be noted and adhered to by individual practitioners.
 PATIENT CARE PLAN FOR CARE OF PERIPHERAL MIDLINE The care plan is designed to be used in conjunction with CINS Guidelines for vascular devices. Manufacturers specific recommendations should be noted and
PATIENT CARE PLAN FOR CARE OF PERIPHERAL MIDLINE The care plan is designed to be used in conjunction with CINS Guidelines for vascular devices. Manufacturers specific recommendations should be noted and
Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide)
 Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide) A Guide for Patients in the Home Phone Number: Nurse/Contact: Central Venous Catheters This manual is a guide for
Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide) A Guide for Patients in the Home Phone Number: Nurse/Contact: Central Venous Catheters This manual is a guide for
PRODIGY Quick Reference Guide
 PRODIGY Quick Venous leg ulcer infected How do I assess a venous leg ulcer? Chronic venous insufficiency and venous hypertension result from damage to the valves in the veins of the leg and inadequate
PRODIGY Quick Venous leg ulcer infected How do I assess a venous leg ulcer? Chronic venous insufficiency and venous hypertension result from damage to the valves in the veins of the leg and inadequate
Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice.
 Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice. Nutrition Successful wound management depends on appropriate nutritional support. Poor nutrition is recognised as one of the major causes of poor
Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice. Nutrition Successful wound management depends on appropriate nutritional support. Poor nutrition is recognised as one of the major causes of poor
Emergency clamp should always be readily available in case of accidental catheter fracture
 Note: Please see individual policies for further information. Flushing best practice: Always use a 10 diameter syringe or larger when first accessing and when flushing vascular access device (VAD) Use
Note: Please see individual policies for further information. Flushing best practice: Always use a 10 diameter syringe or larger when first accessing and when flushing vascular access device (VAD) Use
Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome
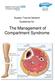 Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome Management of Compartment Syndrome Control Page Version: 1 Category number: Approved by: Date approved: Name of author: and
Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome Management of Compartment Syndrome Control Page Version: 1 Category number: Approved by: Date approved: Name of author: and
GP Practice Woundcare Formulary
 Agreed jointly by Ipswich and East Suffolk and West Suffolk Clinical Commissioning Groups GP Practice Woundcare Formulary Version 28 October 2017 Formulary items should be prescribed wherever possible.
Agreed jointly by Ipswich and East Suffolk and West Suffolk Clinical Commissioning Groups GP Practice Woundcare Formulary Version 28 October 2017 Formulary items should be prescribed wherever possible.
WOUNDS. Emergency Procedures in PT
 WOUNDS Emergency Procedures in PT Types of Wounds Abrasions uppermost layer scraped away, minor capillary bleeding occurs, nerve endings exposed Lacerations skin tear with edges jagged and uneven Incisions
WOUNDS Emergency Procedures in PT Types of Wounds Abrasions uppermost layer scraped away, minor capillary bleeding occurs, nerve endings exposed Lacerations skin tear with edges jagged and uneven Incisions
Venepuncture and Cannulation. Louise Smith Clinical Nurse Specialist
 Venepuncture and Cannulation Louise Smith Clinical Nurse Specialist Outcomes By the end of this session you will be aware of: Basic anatomy Preparation procedures including patient identification Equipment
Venepuncture and Cannulation Louise Smith Clinical Nurse Specialist Outcomes By the end of this session you will be aware of: Basic anatomy Preparation procedures including patient identification Equipment
ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Central Venous Access Devices
 For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Central Venous Access Devices Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Central Venous Access Devices Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
Central Venous Catheter Insertion: Assisting
 Approved by: Central Venous Catheter Insertion: Assisting Gail Cameron Senior Director, Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Santiago Ensenat Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal
Approved by: Central Venous Catheter Insertion: Assisting Gail Cameron Senior Director, Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Santiago Ensenat Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal
Standard Operational Procedure. Drainage of Malignant Ascites (Abdominal Paracentesis)
 Standard Operational Procedure Drainage of Malignant Ascites (Abdominal Paracentesis) Background Cancers that involve the peritoneum can cause fluid to build up within the abdominal cavity. This is most
Standard Operational Procedure Drainage of Malignant Ascites (Abdominal Paracentesis) Background Cancers that involve the peritoneum can cause fluid to build up within the abdominal cavity. This is most
2. Need for serial arterial blood gas determinations. 2. Anticipation of the initiation of thrombolytic therapy
 I. Subject: Arterial Cannulation II. Policy: Arterial cannulation will be performed upon a physician's order by Cardiopulmonary and Respiratory Therapy personnel certified in the arterial catheterization
I. Subject: Arterial Cannulation II. Policy: Arterial cannulation will be performed upon a physician's order by Cardiopulmonary and Respiratory Therapy personnel certified in the arterial catheterization
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to to view current policies.
 If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5575 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5575 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
Peripheral Arterial Lines: Insertion and Care
 1 MCN for Neonatology West of Scotland Neonatal Guideline Peripheral Arterial Lines: Insertion and Care This Guideline is applicable to all Medical and nursing staff working in neonatal units in the West
1 MCN for Neonatology West of Scotland Neonatal Guideline Peripheral Arterial Lines: Insertion and Care This Guideline is applicable to all Medical and nursing staff working in neonatal units in the West
Anseong Factory : 70-17, Wonam-ro, Wongok-myeon, Anseong-si, Gyeonggi-do , REPUBLIC OF KOREA
 Care for tomorrow The Solution for Management HQ & Factory : 7, Hyeongjero4Beon-gil, Namsa-myeon, Cheoin-gu, Yong-in-si, Gyeonggi-do 449-884, REPUBLIC OF KOREA TEL: +8-3-33-33 / FAX: +8-3-33-34 Anseong
Care for tomorrow The Solution for Management HQ & Factory : 7, Hyeongjero4Beon-gil, Namsa-myeon, Cheoin-gu, Yong-in-si, Gyeonggi-do 449-884, REPUBLIC OF KOREA TEL: +8-3-33-33 / FAX: +8-3-33-34 Anseong
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy)
 Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
4.0 Definitions. Subcutaneous: is defined as the loose connective tissue between the epidermis and the muscle.
 Status: Protocol: Specifies the procedures to be followed, only in exceptional circumstances should these not be followed. Title: Protocol on subcutaneous (SC) fluids (hypodermoclysis) administration Written
Status: Protocol: Specifies the procedures to be followed, only in exceptional circumstances should these not be followed. Title: Protocol on subcutaneous (SC) fluids (hypodermoclysis) administration Written
Advanced Wound Care. Cut Shape Innovate
 Advanced Wound Care Cut Shape Innovate Vacutex incorporates a patented three layer construction of poly-cotton elements that promotes an accelerated capillary action on wound interfaces. Effectively lifting,
Advanced Wound Care Cut Shape Innovate Vacutex incorporates a patented three layer construction of poly-cotton elements that promotes an accelerated capillary action on wound interfaces. Effectively lifting,
Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home
 Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home The purpose
Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home The purpose
SAMPLE. HLTEN406A Undertake basic wound care. Learner resource. HLT07 Health Training Package. Version 2
 HLT07 Health Training Package HLTEN406A Undertake basic wound care Learner resource Version 2 Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit Meadowbank Acknowledgments The TAFE NSW Training and Education
HLT07 Health Training Package HLTEN406A Undertake basic wound care Learner resource Version 2 Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit Meadowbank Acknowledgments The TAFE NSW Training and Education
MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM
 SUBJECT Venipuncture of Arteriovenous Fistula/Graft MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM SECTION CODE 30.30.01 30.30 Vascular Access AUTHORIZATION Professional Advisory Committee, Manitoba Renal Program Nursing Practice
SUBJECT Venipuncture of Arteriovenous Fistula/Graft MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM SECTION CODE 30.30.01 30.30 Vascular Access AUTHORIZATION Professional Advisory Committee, Manitoba Renal Program Nursing Practice
MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM
 SUBJECT Venipuncture of Arteriovenous Fistula/Graft MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM SECTION CODE 30.20.01 30.20 Vascular Access AUTHORIZATION Professional Advisory Committee, Manitoba Renal Program Nursing Practice
SUBJECT Venipuncture of Arteriovenous Fistula/Graft MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM SECTION CODE 30.20.01 30.20 Vascular Access AUTHORIZATION Professional Advisory Committee, Manitoba Renal Program Nursing Practice
Burn Wound Assessment and Infections
 Burn Wound Assessment and Infections Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Family Health:
Burn Wound Assessment and Infections Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Family Health:
Extravasation Management of Non- Chemotherapeutic Agents
 Extravasation Management of Non- Chemotherapeutic Agents Sarah M. Martin, PharmD, MBA St John Medical Center Tulsa, OK Objectives Review non-chemotherapeutic agents that can cause extravasation Explain
Extravasation Management of Non- Chemotherapeutic Agents Sarah M. Martin, PharmD, MBA St John Medical Center Tulsa, OK Objectives Review non-chemotherapeutic agents that can cause extravasation Explain
Education for Self Administration of Intravenous Therapy HOME IV THERAPY PICC. Portacath
 HOME IV THERAPY PICC Portacath Who To contact Cardio-Respiratory Integrated Specialist Services (CRISS) Office hours 0800 1630 hours Ph: 364 0167 Weekends and after hours, phone Christchurch Hospital operator
HOME IV THERAPY PICC Portacath Who To contact Cardio-Respiratory Integrated Specialist Services (CRISS) Office hours 0800 1630 hours Ph: 364 0167 Weekends and after hours, phone Christchurch Hospital operator
IV therapy. By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN. Copyright 2016, 2013, 2010, 2006, 2002 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
 IV therapy By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN 1 IV Therapy Types of solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Caution: Too rapid or excessive infusion of any IV fluid has the potential to cause serious problems
IV therapy By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN 1 IV Therapy Types of solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Caution: Too rapid or excessive infusion of any IV fluid has the potential to cause serious problems
STOMA CARE. Amendments Date Page(s) Comments Approved by 03/16 ALL Updated Guideline
 Note: Guidance comments are written in italics STOMA CARE Amendments Date Page(s) Comments Approved by 03/16 ALL Updated Guideline Compiled by: In Consultation with: Ratified by: Alice D Souza Neonatal
Note: Guidance comments are written in italics STOMA CARE Amendments Date Page(s) Comments Approved by 03/16 ALL Updated Guideline Compiled by: In Consultation with: Ratified by: Alice D Souza Neonatal
Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types. Summary
 Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care
 Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter
 Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to to view current policies.
 If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5555 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5555 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
Chapter 14 8/23/2016. Surgical Wound Care. Wound Classifications. Wound Healing. Classified According to. Phases
 Chapter 14 Surgical Wound Care All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Wound Classifications Classified According to Cause Incision
Chapter 14 Surgical Wound Care All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Wound Classifications Classified According to Cause Incision
Wound Management for Nurses/Technicians What do we need to know?
 Wound Management for Nurses/Technicians What do we need to know? Laura Owen European Specialist in Small Animal Surgery Lecturer in Small Animal Surgery, University of Cambridge The Acute Open Wound PPE
Wound Management for Nurses/Technicians What do we need to know? Laura Owen European Specialist in Small Animal Surgery Lecturer in Small Animal Surgery, University of Cambridge The Acute Open Wound PPE
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment
 Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE
 SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE Chapter 34 1 skin integrity: intact skin refers to the presence of normal skin layer uninterrupted by wound 2 WOUNDS DISRUPTION IN THE INTEGRITY OF BODY TISSUE CLASSIFIED AS:
SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE Chapter 34 1 skin integrity: intact skin refers to the presence of normal skin layer uninterrupted by wound 2 WOUNDS DISRUPTION IN THE INTEGRITY OF BODY TISSUE CLASSIFIED AS:
IV Catheter Placement
 Year Group: BVSc3 + Document number: CSL_A06 Equipment for this station: Equipment list: IV catheter model, with giving set and red fluid bag IV catheter Bung or T-port Tape two strips cut to size before
Year Group: BVSc3 + Document number: CSL_A06 Equipment for this station: Equipment list: IV catheter model, with giving set and red fluid bag IV catheter Bung or T-port Tape two strips cut to size before
Cannulating AV Fistula using Buttonhole Technique
 Nephrology Directorate Subject: Objective: Prepared by: Cannulating AV Fistula using Buttonhole Technique To enable the safe insertion and removal of needles into arteriovenous fistulae using the buttonhole
Nephrology Directorate Subject: Objective: Prepared by: Cannulating AV Fistula using Buttonhole Technique To enable the safe insertion and removal of needles into arteriovenous fistulae using the buttonhole
Wound Care per HHVNA Wound Product Formulary
 Venous Ulcers ABI of 0.9-1.2 = normal blood flow An ABI MUST be obtained prior to inititiation of compression therapy. Compression is the Gold Standard of care to promote wound of venous ulcers. Elevation
Venous Ulcers ABI of 0.9-1.2 = normal blood flow An ABI MUST be obtained prior to inititiation of compression therapy. Compression is the Gold Standard of care to promote wound of venous ulcers. Elevation
CLINICAL GUIDELINES FOR LARVAL THERAPY (MAGGOTS)
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES FOR LARVAL THERAPY (MAGGOTS) Introduction The use of maggots for wound debridement has a long history and the introduction of sterile maggots specifically bred for wound management
CLINICAL GUIDELINES FOR LARVAL THERAPY (MAGGOTS) Introduction The use of maggots for wound debridement has a long history and the introduction of sterile maggots specifically bred for wound management
SDMA Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products
 Version 7 - February 2015 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Traditional Wound Dressings Wound Dressings Packs Swabs Swabs Swab Products Adhesive Tapes Taping Sheets Absorbent Wadding Absorbent Dressings
Version 7 - February 2015 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Traditional Wound Dressings Wound Dressings Packs Swabs Swabs Swab Products Adhesive Tapes Taping Sheets Absorbent Wadding Absorbent Dressings
Central Venous Access Devices. Stephanie Cunningham Amy Waters
 Central Venous Access Devices Stephanie Cunningham Amy Waters 5 Must Know Facts About CVAD s 1) What are CVAD s? 2) What are CVAD s used for? 3) How are these devices put in? 4) What are the complications
Central Venous Access Devices Stephanie Cunningham Amy Waters 5 Must Know Facts About CVAD s 1) What are CVAD s? 2) What are CVAD s used for? 3) How are these devices put in? 4) What are the complications
TOTALLY IMPLANTED VENOUS ACCESS DEVICES
 Information for Parents/Carers TOTALLY IMPLANTED VENOUS ACCESS DEVICES This leaflet tells you about having a totally implanted venous access device (Port). It explains what is involved and what the benefits
Information for Parents/Carers TOTALLY IMPLANTED VENOUS ACCESS DEVICES This leaflet tells you about having a totally implanted venous access device (Port). It explains what is involved and what the benefits
Intravenous therapy and medication. ELCT Health Department Quality Assurance 2007
 Intravenous therapy and medication ELCT Health Department Quality Assurance 2007 Intravenous therapy and medication the procedure is absolutely sterile, everything should be handled remaining sterility
Intravenous therapy and medication ELCT Health Department Quality Assurance 2007 Intravenous therapy and medication the procedure is absolutely sterile, everything should be handled remaining sterility
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: INTERMITTENT FLUID AND MEDICATION THERAPY Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN I, LPN II Per Job Description 03/81 8/09
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: INTERMITTENT FLUID AND MEDICATION THERAPY Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN I, LPN II Per Job Description 03/81 8/09
BLOOD COLLECTION GUIDELINES
 I. Patient Identification Lee Memorial Health System Lee County, FL CLINICAL LABORATORY BLOOD COLLECTION GUIDELINES A. Inpatient / Outpatient with armband 1. When possible, ask patient to state their name
I. Patient Identification Lee Memorial Health System Lee County, FL CLINICAL LABORATORY BLOOD COLLECTION GUIDELINES A. Inpatient / Outpatient with armband 1. When possible, ask patient to state their name
Burns Management in the Emergency Department
 Management in the Emergency Department (Referral Proforma) Time/Date of injury (24hr) Patient demographic data sticker Airway Please remember to protect C-spine until clinically cleared as stable Administer
Management in the Emergency Department (Referral Proforma) Time/Date of injury (24hr) Patient demographic data sticker Airway Please remember to protect C-spine until clinically cleared as stable Administer
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017
 Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
Education for self administration of intravenous therapy HOME IV THERAPY. 30 minute - Baxter Pump Tobramycin
 HOME IV THERAPY Tobramycin Tobramycin Check the order on the drug chart This can change when the results from your blood test come through. Your doctor will change the order, if required. A copy of the
HOME IV THERAPY Tobramycin Tobramycin Check the order on the drug chart This can change when the results from your blood test come through. Your doctor will change the order, if required. A copy of the
Caring for a Nephrostomy and what is Ureteric Stenting
 Useful contacts: Macmillan Cancer Support Tel: 0808 808 00 00 www.macmillan.org.uk Buckinghamshire Healthcare NHS Trust Cancer Education, Information & Support Service Tel: 01296 316954 How can I help
Useful contacts: Macmillan Cancer Support Tel: 0808 808 00 00 www.macmillan.org.uk Buckinghamshire Healthcare NHS Trust Cancer Education, Information & Support Service Tel: 01296 316954 How can I help
To standardize wound care and prevent infection in compromised patients who have a Berlin Heart Ventricular Assist Device (VAD).
 PURPOSE To standardize wound care and prevent infection in compromised patients who have a Berlin Heart Ventricular Assist Device (VAD). POLICY STATEMENTS Dressing change should be done no sooner than
PURPOSE To standardize wound care and prevent infection in compromised patients who have a Berlin Heart Ventricular Assist Device (VAD). POLICY STATEMENTS Dressing change should be done no sooner than
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017
 Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
Tissue Viability Service Wound Management Primary Care Formulary 2017 WMPF/TVS: March 2017 Review date: March 2019 Product Group Current Product Sizes Price per Item Hydrogel 1st Activheal Hydrogel 2nd
Vascular access device selection & placement. Alisa Seangleulur, MD Anesthesiology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University
 Vascular access device selection & placement Alisa Seangleulur, MD Anesthesiology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University How to make the right choice of vascular access device.. Peripheral
Vascular access device selection & placement Alisa Seangleulur, MD Anesthesiology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University How to make the right choice of vascular access device.. Peripheral
BASINGSTOKE AND NORTH HAMPSHIRE NHS FOUNDATION TRUST. Clinical Policy for Peripheral Venous Cannula Insertion and Management (Adults)
 BASINGSTOKE AND NORTH HAMPSHIRE NHS FOUNDATION TRUST Clinical Policy for Peripheral Venous Cannula Insertion and Management (Adults) Reviewed in accordance with The Health and Social Care Act 2008: Code
BASINGSTOKE AND NORTH HAMPSHIRE NHS FOUNDATION TRUST Clinical Policy for Peripheral Venous Cannula Insertion and Management (Adults) Reviewed in accordance with The Health and Social Care Act 2008: Code
Acute and Chronic WOUND ASSESSMENT. Wound Assessment OBJECTIVES ITEMS TO CONSIDER
 WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
Basic Dressing Categories
 Category of Dressing Examples Advantages/Indications Disadvantages/Contraindications Hydrofiber Aquacel AG - ConvaTec Aquacel - Convatec Excellent for absorbing excess exudate These dressings form a gel
Category of Dressing Examples Advantages/Indications Disadvantages/Contraindications Hydrofiber Aquacel AG - ConvaTec Aquacel - Convatec Excellent for absorbing excess exudate These dressings form a gel
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT
 TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Booklet
 Aintree University Hospital FT PICC Booklet: a real world example This local booklet is an example used in the NICE medical technology guidance adoption support resource for SecurAcath for securing percutaneous
Aintree University Hospital FT PICC Booklet: a real world example This local booklet is an example used in the NICE medical technology guidance adoption support resource for SecurAcath for securing percutaneous
Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products
 Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products Version 9 March 2018 Surgical Dressing Manufacturers Association 2018 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Wound Dressings Swabs Taping Traditional Wound
Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products Version 9 March 2018 Surgical Dressing Manufacturers Association 2018 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Wound Dressings Swabs Taping Traditional Wound
Nephrostomy Tube Care
 Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers
 A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers Background: The concept of increasing the oxygen concentration in healing wounds developed originally with hyperbaric oxygen therapy and from the fact
A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers Background: The concept of increasing the oxygen concentration in healing wounds developed originally with hyperbaric oxygen therapy and from the fact
1. Purpose Documentation Description.1 4. References 8 5. Cross-References.8 6. Development of the guideline.8
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE For use in (clinical areas): For use by (staff groups): For use for (patients): Document owner: Status: Oncology/Haematology Unit (excluding Paediatrics) Oncologists, Haematologists,
CLINICAL GUIDELINE For use in (clinical areas): For use by (staff groups): For use for (patients): Document owner: Status: Oncology/Haematology Unit (excluding Paediatrics) Oncologists, Haematologists,
BLOOD CULTURE POLICY FOR PAEDIATRICS
 BLOOD CULTURE POLICY FOR PAEDIATRICS 1. INTRODUCTION Blood culture to detect bacteraemia is an important investigation with major implications for the diagnosis of patients with infection and the selection
BLOOD CULTURE POLICY FOR PAEDIATRICS 1. INTRODUCTION Blood culture to detect bacteraemia is an important investigation with major implications for the diagnosis of patients with infection and the selection
To you who will receive a T-Port PATIENT INFORMATION
 To you who will receive a T-Port PATIENT INFORMATION T-Port Patient information What is a T-Port? Why this booklet The purpose of this handout is to help you understand how it is to receive and live with
To you who will receive a T-Port PATIENT INFORMATION T-Port Patient information What is a T-Port? Why this booklet The purpose of this handout is to help you understand how it is to receive and live with
Curraheen, Co. Cork. Guidelines on the Management and Care of Central Venous Access Devices
 Curraheen, Co. Cork. Guidelines on the Management and Care of Central Venous Access Devices Date re-approved: 27 th Jan 2015. Version No: 2 Revision Due: 2018 Index code: CLIN028 Disclaimer: The information
Curraheen, Co. Cork. Guidelines on the Management and Care of Central Venous Access Devices Date re-approved: 27 th Jan 2015. Version No: 2 Revision Due: 2018 Index code: CLIN028 Disclaimer: The information
Galen ( A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing
 Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
CARE OF A TUNNELED CATHETER (HICKMAN & BROVIAC ) with a Needleless Connector (MicroClave Clear)
 CARE OF A TUNNELED CATHETER (HICKMAN & BROVIAC ) with a Needleless Connector (MicroClave Clear) Table of Contents Part 1 Learning about the Catheter...2 Part 2 Caring for Your Child s Catheter...3 A. Preventing
CARE OF A TUNNELED CATHETER (HICKMAN & BROVIAC ) with a Needleless Connector (MicroClave Clear) Table of Contents Part 1 Learning about the Catheter...2 Part 2 Caring for Your Child s Catheter...3 A. Preventing
Resources to Guide the Management of Suspected Infection in Chronic Wounds
 Resources to Guide the Management of Suspected Infection in Chronic Wounds Health Improvement Scotland published their 13th Health Technology Assessment (HTA 13) in December 2015 entitled, Antimicrobial
Resources to Guide the Management of Suspected Infection in Chronic Wounds Health Improvement Scotland published their 13th Health Technology Assessment (HTA 13) in December 2015 entitled, Antimicrobial
PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Question What is Vacutex? How does Vacutex work? Does Vacutex prevent maceration to the surrounding skin? Does Vacutex adhere to the wound face?
PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Question What is Vacutex? How does Vacutex work? Does Vacutex prevent maceration to the surrounding skin? Does Vacutex adhere to the wound face?
Standard Operating Procedure for cannulation
 Standard Operating Procedure for cannulation Effective date: 26.07.2017 Review due date: 31.03.2019 Original Author Name: Richard Metcalfe Position: PhD Student Date: 05.12.2012 Reviewer Name: Pippa Heath
Standard Operating Procedure for cannulation Effective date: 26.07.2017 Review due date: 31.03.2019 Original Author Name: Richard Metcalfe Position: PhD Student Date: 05.12.2012 Reviewer Name: Pippa Heath
NovoSorb BTM. A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold. Regenerating tissue. Changing lives.
 NovoSorb BTM A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold Regenerating tissue. Changing lives. Overview NovoSorb BTM is a unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold that delivers good cosmetic and
NovoSorb BTM A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold Regenerating tissue. Changing lives. Overview NovoSorb BTM is a unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold that delivers good cosmetic and
