Constipation is a common and distressing pediatric problem, with a prevalence ranging from 7% to 30% in both western
|
|
|
- Melanie Walsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) in Infants with Functional Chronic Constipation: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study Paola Coccorullo, MD, Caterina Strisciuglio, MD, Massimo Martinelli, MD, Erasmo Miele, MD, Luigi Greco, MD, and Annamaria Staiano, MD Objectives To evaluate the beneficial effects of Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) in infants with functional chronic constipation. Study design A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study was conducted from January 2008 to December 2008 in 44 consecutive infants at least 6 months old (mean age SD, SD; male/female, 24/ 20) admitted to the Gastrointestinal Endoscopy and Motility Unit of the Department of Pediatrics, University Federico II of Naples, with a diagnosis of functional chronic constipation. The 44 infants with chronic constipation were randomly assigned to 2 groups: group A (n = 22) received supplementation with the probiotic L reuteri (DSM 17938) and group B (n = 22) received an identical placebo. Primary outcome measures were frequency of bowel movements per week, stool consistency, and presence of inconsolable crying episodes, recorded in a daily diary by parents. Results Infants receiving L reuteri (DSM 17938) had a significantly higher frequency of bowel movements than infants receiving a placebo at week 2 (P =.042), week 4 (P =.008), and week 8 (P =.027) of supplementation. In the L reuteri group, the stool consistency was reported as hard in 19 infants (86.4%) at baseline, in 11 infants (50%) at week 2, and in 4 infants (18.2%) at weeks 4 and 8. However, there was no significant difference between L reuteri and placebo groups in the stool consistency at all weeks (P =.63, week 2; P =.38, week 4; P =.48, week 8). Similarly, there was no statistically difference in the 2 groups in the presence of inconsolable crying episodes. No adverse effects were reported. Conclusions The administration of L reuteri (DSM 17938) in infants with chronic constipation had a positive effect on bowel frequency, even when there was no improvement in stool consistency and episodes of inconsolable crying episodes. Because of their safety profile, probiotics may be an attractive option in the treatment of functional constipation. (J Pediatr 2010;-:---). Constipation is a common and distressing pediatric problem, with a prevalence ranging from 7% to 30% in both western and non-western countries. 1 No organic cause is found in 90% to 95% of children with constipation. 2 Only 60% of children with constipation have successful treatment with laxatives, 3 and a sizable proportion of children needs long-term therapy. After 1 year of treatment, constipation persisted in 53% of children, and 52% of them were still constipated 5 years later. 4 Moreover, approximately 30% of children beyond puberty continue to struggle with constipation symptoms, such as infrequent, painful evacuation of stools and fecal incontinence. 3 Development of new therapeutic strategies is necessary to treat these challenging patients more effectively. There is growing interest in the use of probiotics in organic and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Probiotics are reported to be effective in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease, traveller diarrhea, and constipation. 5,6 One rationale for using probiotics to treat constipation is a report of dysbiosis in the intestinal flora of patients with chronic constipation. 7 Functional constipation in children therefore would seem, on the whole, to induce no bacterial overgrowth, but only changes in selected bacterial species. The stools of the children with constipation showed a disturbed microbiota characterized by a high clostridia count in comparison with other genera (bacteroides and Escherichia coli) and a substantial frequency of clostridia and enterobacteriaceae species, which are rarely isolated in healthy children. In addition, probiotics might improve intestinal motility; bifidobacteria and lactobacilli produce lactic acid, acetic acid, and other acids, resulting in a lowering of ph in the colon. A lower ph enhances peristalsis of the colon and subsequently decreases colonic transit time, which is beneficial in the treatment of constipation. 8 A limited number of studies have been published about the effects of probiotics on constipation in children, but so far there is no hard evidence to recommend the use of probiotics in children affected by chronic constipation. The aim of our study was to evaluate the beneficial effects of Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938), one of the few endogenous Lactobacillus species in the human gastrointestinal tract, in infants with functional chronic constipation. From the Department of Pediatrics, University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy Noos (Italy) provided probiotic and placebo for the study and it payed for color reproduction charges. The authors declare no conflicts of interest. BM Bowel movement /$ - see front matter. Copyright Ó 2010 Mosby Inc. All rights reserved /j.jpeds
2 THE JOURNAL OF PEDIATRICS Vol. -, No. - Methods A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study was conducted from January 2008 to December 2008 in 44 consecutive formula-fed infants >6 months of age (mean age SD, SD; male/female: 24/20) referred for functional chronic constipation to the Gastrointestinal Endoscopy and Motility Unit of the Department of Pediatrics, University Federico II of Naples, Italy. Functional constipation is defined by the Rome III Criteria as having at least two of these symptoms: #2 defecations per week; history of excessive stool retention and painful or hard bowel movements; presence of a large fecal mass in the rectum; history of large-diameter stools. 9 Infants with organic causes of constipation such as Hirschsprung s disease, spinal bifida (occulta), hypothyroidism or other metabolic or renal abnormalities, and mental retardation, infants taking oral laxatives or antibiotics, and infants who were fed breast milk and formula with the addition of probiotics, prebiotics, or both were excluded. Probiotic or prebiotic food supplements were not allowed through the study period. Weaning started in a standard fashion at 5 months of age with fruit followed by weaning purees with a dose of 0.5 g/kg/ day of fiber, according to guideline proposed by the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. 10 At enrollment, a medical history was collected and all patients underwent clinical examination, including rectal digital examination. The 44 infants were randomly assigned to 2 groups according to an automatically generated randomization list: group A (n = 22) received supplementation with the probiotic L reuteri (DSM 17938), and group B (n = 22) was given an identical placebo. L reuteri (DSM 17938) was administered at a dose of 10 8 colony-forming units in 5 drops of a commercially available oil suspension (Reuterin, Noos S.r.l.; BioGaia AB, Stockholm, Sweden), 30 minutes after feeding, once per day for 8 weeks. This oil suspension is stable for 24 months at 2 C to 8 C (as documented by the manufacturer). During the study period, parents were instructed to keep the product refrigerated. Excellent compliance has been defined as no violation of the protocol for the study product intake. The use of laxatives was not allowed during the treatment period, whereas glycerin suppository was used only when there was no defecation for >5 days. Parents received a stool diary to record the frequency of daily bowel movements, stool consistency, inconsolable crying episodes, and the use of enema of their children. Evaluation was conducted during the visits at the outpatient clinic 2, 4, and 8 weeks after the study start. During each visit, the physician assessed the patient s diary and examined the child. Treatment success was defined as $3 defecation per week, and stool consistency was defined as hard, normal, and watery. The interpretation of inconsolable infant crying was left to the mothers. Mothers were asked to report the number of crying episodes that were difficult to soothe in their babies. Primary outcome measures were frequency of bowel movements per week, stool consistency, and presence of inconsolable crying episodes. Secondary outcome was comparison of the frequency of defecation, stool consistency, and presence of inconsolable crying episodes in the two groups. Informed consent was obtained from parents of all the enrolled patients, and the study was approved by the independent ethics committee of the University of Naples, Federico II. Statistical Analysis All data were stored in a common database and statistically analyzed with SPSS software version 8.0 (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois). Comparisons in proportions were made with the c 2 test. The Fischer exact test was dependent on the number of observations. A P value <.05 was considered to be statistically significant. The power evaluation for both univariate and multivariate tests has been computed with the SPSS Multivariate Anova: population rate, 2.9%; smallest difference, 25%; first type error, 0.05; second type error, 0.05; P <.05; power, 95%; case/control, 1/1. Results Forty-four infants >6 months old with chronic constipation were enrolled, and all patients completed the study. Of the 44 infants with constipation, 22 were assigned randomly to treatment with L reuteri (DSM 17938), and 22 were assigned to receive a placebo. The study groups were well matched in age, sex, and constipation characteristics. Age, sex, and baseline characteristics are shown in the Table. No differences have been identified in the diet of infants treated with L reuteri and that of the placebo group. The frequency of bowel movements (BMs) per week increased in infants who received L reuteri (DSM 17938) (Figure 1). The frequency of BMs was 2.82 per week at week 0, compared with 4.77 at week 8 (P =.0001; 95% CI, 2.75 to 1.16). In addition, infants treated with L reuteri had a significantly higher defecation frequency than placebo at week 2 of treatment (P =.042), at week 4 of treatment (P =.008), and at week 8 of treatment (P =.027). In the L reuteri group, the stool consistency was reported to be hard in 19 infants (86.4%) at baseline, in 11 infants (50%) Table. Age, sex, and baseline characteristics L reuteri group (n = 22) Placebo group (n = 22) Age, months (mean SD) Sex (female/male) 14/8 6/16 BMs/week 1-2/week 31.8% 50% 3-4/week 50% 27.3% 5-7/week 18.2% 22.7% Hard BMs 66.4% 59.1% Rectal impaction 72.7% 52.4% 2 Coccorullo et al
3 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Figure 1. Frequency of BMs in the L reuteri and placebo groups. Infants treated with L reuteri had a significantly higher defecation frequency than infants in the placebo group at week 2 of treatment (P =.042), at week 4 (P =.008), and at week 8 (P =.027). Figure 3. Inconsolable crying episodes in the L reuteri and placebo groups. There was no statistically significant difference in the 2 groups in the presence of inconsolable crying episodes at week 0, 2, 4, 8. at week 2, and in 4 infants (18.2%) at weeks 4 and 8 (P =.34, week 2; P =.01, week 4; P =.01, week 8). However, there was no statistically significant difference between the L reuteri and placebo groups in the stool consistency at all weeks (P =.63, week 2; P =.38, week 4; P = 0.48, week 8; Figure 2). During the study period, we observed a significant increase of inconsolable crying episodes in the L reuteri group (P =.02), whereas a trend toward significance was found in the placebo group (P =.08). In addition, there was no statistically significant difference in the 2 groups in the presence of inconsolable crying episodes at all weeks (P =.64, week 2; P =.50, week 4; P =.66, week 8; Figure 3). Compliance with the study preparation was excellent in 94.6% of the infants in the L reuteri group and in 86.9% of the infants in the placebo group. No adverse effects such as vomiting, bloating, and increased flatulence were reported. Figure 2. Stool consistency in the L reuteri and placebo groups. There was no statistically significant difference in the 2 groups in the stool consistency at all weeks (P =.63, week 2; P =.38, week 4; P =.48, week 8). Discussion This study demonstrates a significant efficacy of L reuteri (DSM 17938) on functional chronic constipation of infants. The frequency of BMs significantly increased from 2.82 per week at week 0 to 4.77 at week 8 (P =.0001). Subjects treated with L reuteri (DSM 17938) had a significantly higher defecation frequency than subjects receiving a placebo at week 2 of treatment (P =.042), at week 4 (P =.008), and at week 8 (P =.027). We found a significant improvement of stool consistency in the L reuteri group during treatment, but no significant difference was shown when comparing the 2 groups. Similarly, there was no statistically significant difference in the 2 groups in the presence of inconsolable crying episodes. There were no clinical adverse events related to L reuteri (DSM 17938). However, we observed a significant increase of inconsolable crying episodes in the L reuteri group and a trend toward significance was shown in the placebo group. This seems to be in contrast to earlier studies, but we could hypothesize that the pathogenesis of the inconsolable crying episodes in this cohort is different from that of the infantile colics, which affect infants aged <6 months. 9,11 Because of the considerable variation in infant cry characteristics, it is impossible to define what is normal crying behavior and what is abnormal crying behavior. Bias cannot explain our findings. Because this study was based on parental reports, social, cultural, and environmental differences in maternal perceptions of crying might be an explanation. We do not believe that the increase of inconsolable crying episodes was related to the use of L reuteri, because we observed a higher rate of inconsolable crying episodes in both groups during the treatment. In addition, L reuteri was well tolerated, and no adverse events associated with this supplementation were reported in any of the existing trials in children Loening-Baucke showed that the prevalence rate for constipation, defined by the NASPGHAN and the Rome II criteria, in the first year of life was 2.9% Symptoms develops Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) in Infants with Functional Chronic Constipation: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo- Controlled Study 3
4 THE JOURNAL OF PEDIATRICS Vol. -, No. - during the first year of life in approximately 40% of children with functional constipation; peak incidence occurs at the time of toilet training, between 2 and 4 years of age. 18,19 Constipation in infants often corresponds with the change from breast milk to commercial formula or with the introduction of solids in their diet. In some babies, an acute episode of constipation may occur in association with a change in the diet. Passage of dry and hard stools may cause anal fissures and pain. Genetic predisposition may play a role because constipation often dates back to the first months of life, and many patients have a positive family history of constipation. 20 A study by van den Berg et al evaluating the clinical course of severe functional constipation in early childhood demonstrated that, 6 months after initial evaluation, only 69% of the children had recovered, and a relapse in 15% of them was observed within 3 years. 21 In addition, it has been demonstrated that early age of onset and family history of constipation are predictive of persistence. 22 Despite therapy, constipation is still present in 30% of children after puberty. 3 It is clear that an early therapeutic intervention could beneficially contribute to the outcome of constipation in infant. Although there is evidence that gut flora is important in gut motility, there is little evidence that gut flora is abnormal in constipation. 23,24 Hyams et al had evaluated the stool characteristics of young infants and found that breastfed infants as group passed twice as many BMs than infants receiving cow s milk formulas and that infants receiving soy formula had hard/firm stools significantly more often than breastfed and other formula-fed infants. 25 This data may be related to differences in microflora. The number of bifidobacteria is higher in breastfed babies. Breast milk has an optimal whey protein composition, rich in a-lactalbumin, lactose, and with low phosphorus content. Part of the lactose escapes digestion and is fermented, releasing water (that moves into lumen to soften stools) and short-chain fatty acids (that lower the ph and provide fuel for bifidobacteria). Lactose passes through normal digestion, resulting in the production of lactic acid, which has a low buffering capacity. Because of this, intestinal ph decreases and bifidobacteria proliferate. 26 In adults, one double-blind, randomized trial showed that L casei Shirota improved gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with chronic constipation. 27 A small non-randomized open clinical trial in elderly subjects showed that supplementation with a combination of L rhamnosus and Propionibacterium freudenreichii increased defecation frequency compared with a group receiving L reuteri and an unsupplemented group. No reduction in laxatives use was observed. 28 A randomized controlled trial addressed the use of probiotics in the treatment of children with constipation and concluded that Lactobacillus GG was not an effective adjunct to lactulose. 29 In addition, a recent double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study in children with chronic constipation showed an increase in defecation frequency, but there was no statistically significant difference in efficacy between magnesium oxide and Lactobacillus casei rhamnosus (Lcr35). 30 A pilot non-randomized, non-placebo controlled study showed that a mixture of probiotics, containing Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, has positive effects on frequency of bowel movements, stool frequency, number of fecal incontinence episodes, and presence of abdominal pain. 31 In our study, we recruited infants >6 months old to avoid subjects with dyschezia. Dyschezia is seen in the first few months of life and can occur several times a day. The symptoms improve without intervention, and parents should abstain from rectal stimulation. 15 In conclusion, this prospective, placebo-controlled, double-blind study demonstrates the efficiency and safety of L reuteri DMS in infants with functional constipation to increase stool frequency. On the basis of our results, probiotics as a natural, safe, and well-tolerated treatment may provide a simple and attractive way to treat infantile functional chronic constipation. A possible link between constipation and changes in intestinal flora needs to be evaluated in the future. n The authors would like to thank these pediatricians who made this study possible: Teresa Cazzato, Luigi Morcaldi, Ettore Napoleone, and Domenico Simeone. Submitted for publication Nov 24, 2009; last revision received Mar 26, 2010; accepted Apr 27, Reprint requests: Annamaria Staiano, MD, Department of Pediatrics, University Federico II, Via S Pansini, 5, Naples, Italy. staiano@ unina.it. References 1. van den Berg MM, Benninga MA, Di Lorenzo C. Epidemiology of childhood constipation: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101: Loening-Baucke V. Chronic constipation in children. Gastroenterology 1993;105: van Ginkel R, Reitsma JB, Büller HA, van Wijk MP, Taminiau JA, Benninga MA. Childhood constipation: longitudinal follow-up beyond puberty. Gastroenterology 2003;125: Staiano A, Andreotti MR, Greco L, Basile P, Auricchio S. Long-term follow-up of children with chronic idiopathic constipation. Dig Dis Sci 1994;39: Doron S, Gorbach SL. Probiotics: their role in the treatment and prevention of disease. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2006;4: Kruis W. Review article: antibiotics and probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004;20(Suppl. 4): Zoppi G, Cinquetti M, Luciano A, Benini A, Muner A, Bertazzoni Minelli E. The intestinal ecosystem in chronic functional constipation. Acta Paediatr 1998;87: Picard C, Fioramonti J, Francois A, Robinson T, Neant F, Matuchansky C. Review article: bifidobacteria as probiotic agents physiological effects and clinical benefits. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005;22: Hyman PE, Milla PJ, Benninga MA, Davidson GP, Fleisher DF, Taminiau J. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: neonate/ toddler. Gastroenterology 2006;130: Williams CL, Bollella M, Wynder EL. A new recommendation for dietary fiber in childhood. Pediatrics 1995;96(5 Pt 2): Savino F, Pelle E, Palumeri E, Oggero R, Miniero R. Lactobacillus reuteri (American type culture collection strain 55730) versus simethicone in the treatment of infantile colic: a prospective randomized study. Pediatrics 2007;119:e Connolly E, Abrahamsson T, Bjorksten B. Safety of D(-)-lactic acid producing bacteria in the human infant. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2005; 41: Coccorullo et al
5 ORIGINAL ARTICLES 13. Ogden NS, Bielory L. Probiotics: a complementary approach in the treatment and prevention of pediatric atopic disease. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2005;5: Rosenfeldt V, Benfeldt E, Valerius NH, Paerregaard A, Michaelsen KF. Effect of probiotics on gastrointestinal symptoms and small intestinal permeability in children with atopic dermatitis. J Pediatr 2004;145: Loening-Baucke V. Prevalence, symptoms and outcome of constipation in infants and toddlers. J Pediatr 2005;146: Baker SS, Liptak GS, Colletti RB, Croffie JM, Lorenzo Di, Ector W, et al. Constipation in infants and children: evaluation and treatment. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1999;29: Rasquin-Weber A, Hyman PE, Cucchiara S, Fleisher DR, Hyams JS, Milla PJ, et al. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gut 1999;45:SII Caplan A, Walker L, Rasquin A. Validation of the Pediatric Rome II criteria for functional gastrointestinal disorders using the questionnaire on pediatric gastrointestinal symptoms. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2005; 41: Voskuijl WP, Heijmans J, Heijmans HS, Taminiau JA, Benninga MA. Use of Rome II criteria in childhood defecation disorders: applicability in clinical and research practice. J Pediatr 2004;145: Masi P, Miele E, Staiano A. Pediatric anorectal disorders. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2008;37: van den Berg MM, van Rossum CH, de Lorin F, Reitsma JB, Di Lorenzo C, Benninga MA. Functional constipation in infants: a follow up study. J Pediatr 2005;147: Staiano A, Andreotti MR, Greco L, Basile P, Auricchio S. Long-term follow-up of children with chronic idiopathic constipation. Dig Dis Sci 1994;39: Szajewska H, Setty M, Mrukowicz J, Guandalini S. Probiotics in gastrointestinal diseases in children: hard and not-so-hard evidence of efficacy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2006;42: Husebye E, Hellstrom PM, Sundler F, Chen J, Midtvedt T. Influence of microbial species on small intestinal myoelectirc activity and transit in germ free rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2001;280:G Hyams JS, Treem WR, Etienne NL, Weinerman H, MacGilpin D, Hine P, et al. Effect of infant formula on stool charcteristics of young infants. Pediatrics 1995;95: Vandenplas Y, Benninga M. Probiotics and functional gastrointestinal disorders in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2009;48:S Koebnick C, Wagner I, Leitzmann P, Stern U, Zunft HJ. Probiotic beverage containing Lactobacillus casei Shirota improves gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with chronic constipation. Can J Gastroenterol 2003;17: Möllenbrink M, Bruckschen E. Treatment of chronic constipation with physiologic Escherichia coli bacteria. Results of a clinical study of the effectiveness and tolerance of microbiological therapy with the E coli Nissle 1917 strain (Mutaflor) Med Klin (Munich) 1994;89: Banaszkiewicz A, Szajewska H. Ineffectiveness of Lactobacillus GG as an adjunct to lactulose for the treatment of constipation in children: a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial. J Pediatr 2005; 146: Bu LN, Chang MH, Ni YH, Chen HL, Cheng CC. Lactobacillus casei rhamnosus Lcr35 in children with chronic constipation. Pediatr Int 2007;49: Bekkali NL, Bongers ME, Van den Berg MM, Liem O, Benninga MA. The role of a probiotics mixture in the treatment of childhood constipation: a pilot study. Nutr J 2007;6:17. Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) in Infants with Functional Chronic Constipation: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo- Controlled Study 5
ORIGINAL PAPER ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL PAPER Available from: URL: http://www.jgld.ro/2014/4/9 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15403/jgld.2014.1121.234.elr The Effect of Lactobacillus reuteri Supplementation in Adults with Chronic Functional
ORIGINAL PAPER Available from: URL: http://www.jgld.ro/2014/4/9 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15403/jgld.2014.1121.234.elr The Effect of Lactobacillus reuteri Supplementation in Adults with Chronic Functional
Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation in childhood
 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
Constipation in childhood is characterized by a low defecation frequency in combination with either involuntary loss of
 USE OF ROME II CRITERIA IN CHILDHOOD DEFECATION DISORDERS: APPLICABILITY IN CLINICAL AND RESEARCH PRACTICE WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL, MD, JAROM HEIJMANS, HUGO S. A. HEIJMANS, MD, PHD, JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,MD,PHD,
USE OF ROME II CRITERIA IN CHILDHOOD DEFECATION DISORDERS: APPLICABILITY IN CLINICAL AND RESEARCH PRACTICE WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL, MD, JAROM HEIJMANS, HUGO S. A. HEIJMANS, MD, PHD, JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,MD,PHD,
The involuntary loss of feces in the underwear after. Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence.
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol. glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide, lactulose. treatment of functional constipation in children
 Original article Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulosein treatment of functional constipation in children Hossein Saneian 1, Neda Mostofizadeh 2 1 Assistant
Original article Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulosein treatment of functional constipation in children Hossein Saneian 1, Neda Mostofizadeh 2 1 Assistant
The Effect of Adding Synbiotics to Polyethylene Glycol in Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 5357-5367) The Effect of Adding Synbiotics to Polyethylene Glycol in Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study M Mahdavi 1, *MR
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 5357-5367) The Effect of Adding Synbiotics to Polyethylene Glycol in Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study M Mahdavi 1, *MR
Systematic review of randomised controlled trials: Probiotics for functional constipation
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v16.i1.69 World J Gastroenterol 2010 January 7; 16(1): 69-75 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) 2010 Baishideng. All rights
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v16.i1.69 World J Gastroenterol 2010 January 7; 16(1): 69-75 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) 2010 Baishideng. All rights
Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children VIKRANT KHANNA*, UJJAL PODDAR AND SURENDER KUMAR YACHHA From the Departments of Pediatric Gastroenterology and
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children VIKRANT KHANNA*, UJJAL PODDAR AND SURENDER KUMAR YACHHA From the Departments of Pediatric Gastroenterology and
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014
 Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
Constipation in children
 Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
TREATMENT SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION
 SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION One of the most common functional GI disorders
SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION One of the most common functional GI disorders
Functional Gut Disorders in Infants
 Disclosures Functional Gut Disorders in Infants Speaker fees - Nutricia Neocate, Merck Serono, AstraZeneca, Aspen Nutritionals Consultancy fees - Nutricia Neocate, Danone Early Life Nutrition, Nestle Health
Disclosures Functional Gut Disorders in Infants Speaker fees - Nutricia Neocate, Merck Serono, AstraZeneca, Aspen Nutritionals Consultancy fees - Nutricia Neocate, Danone Early Life Nutrition, Nestle Health
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Specific nutritional care in children The role of food in children with functional gastrointestinal disorders M. Benninga (NL) The role of food in children with functional
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Specific nutritional care in children The role of food in children with functional gastrointestinal disorders M. Benninga (NL) The role of food in children with functional
השפעת חיידקים פרוביוטיים
 השפעת חיידקים פרוביוטיים החיים בחלל )המעי(... על רון שאול יחידת גסטרו ילדים מרכז רפואי רמב"ם Introduction The intestinal microflora primarily in the large bowel consists mostly on benign bacterial species
השפעת חיידקים פרוביוטיים החיים בחלל )המעי(... על רון שאול יחידת גסטרו ילדים מרכז רפואי רמב"ם Introduction The intestinal microflora primarily in the large bowel consists mostly on benign bacterial species
Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone. Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club
 Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club Objectives Brief overview of constipation Review of article Discussion Constipation in Children 3-5% of all
Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club Objectives Brief overview of constipation Review of article Discussion Constipation in Children 3-5% of all
A Synbiotic Infant Formula with High Magnesium Content Improves Constipation and Quality of Life
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 https://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2018.21.1.28 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2018 January 21(1):28-33 Original Article PGHN A Synbiotic Infant Formula with High Magnesium
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 https://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2018.21.1.28 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2018 January 21(1):28-33 Original Article PGHN A Synbiotic Infant Formula with High Magnesium
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
Chronic constipation, often accompanied by encopresis. Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty. Patients and Methods
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2003;125:357 363 Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty RIJK VAN GINKEL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, HANS A. BÜLLER, MICHIEL P. VAN WIJK,* JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,* and
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2003;125:357 363 Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty RIJK VAN GINKEL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, HANS A. BÜLLER, MICHIEL P. VAN WIJK,* JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,* and
Study summaries L. casei 431
 This binder provides you with summaries of selected publications on Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei L. casei 431. The publications are clinical studies performed in humans documenting the effects
This binder provides you with summaries of selected publications on Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei L. casei 431. The publications are clinical studies performed in humans documenting the effects
Probiotics in Pediatric Health. AANP Annual Convention
 Probiotics in Pediatric Health AANP Annual Convention Don Brown, ND July 12, 2017 Human Microbiome Richness and Metabolic Markers Human gut microbial composition was studied in 292 Danish adults Individuals
Probiotics in Pediatric Health AANP Annual Convention Don Brown, ND July 12, 2017 Human Microbiome Richness and Metabolic Markers Human gut microbial composition was studied in 292 Danish adults Individuals
Probiotics for management of infantile colic: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials
 Systematic review/meta-analysis Probiotics for management of infantile colic: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials Department of Paediatrics, Medical University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland
Systematic review/meta-analysis Probiotics for management of infantile colic: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials Department of Paediatrics, Medical University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland
Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate.
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
Synbiotic preparation in men suffering from functional constipation: a randomised controlled trial
 Published 30 July 2011, doi:10.4414/smw.2011.13239 Cite this as: Synbiotic preparation in men suffering from functional constipation: a randomised controlled trial Rouzbeh Fateh a, Shahrokh Iravani b,
Published 30 July 2011, doi:10.4414/smw.2011.13239 Cite this as: Synbiotic preparation in men suffering from functional constipation: a randomised controlled trial Rouzbeh Fateh a, Shahrokh Iravani b,
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands
 Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka
 Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2, Sachith Mettananda 3, Priyantha Perera 1, Sanofer
Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2, Sachith Mettananda 3, Priyantha Perera 1, Sanofer
Clinical Report: Probiotics and Prebiotics in Pediatrics
 www.medscape.com Authors and Disclosures Author(s) Dan W. Thomas, MD Professor of Pediatrics, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California; Head, Division of Gastroenterology
www.medscape.com Authors and Disclosures Author(s) Dan W. Thomas, MD Professor of Pediatrics, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California; Head, Division of Gastroenterology
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children
 Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Formulations and Availability 900 BILLION 5,319 HIGH POTENCY PROBIOTIC PEDIATRIC ADULT GERIATRIC PROVEN BY RESEARCH. HIGH-POTENCY. NO SHORTCUTS.
 Formulations and Availability S TU D I E S PE R D I S E A S E 39 LIVER Liver Disease, Cirrhosis, Liver Failure, Hepatic Encephalopathy S TU D I E S PE R AG E G RO U P Visbiome Regular Product Code: 693-0412-01
Formulations and Availability S TU D I E S PE R D I S E A S E 39 LIVER Liver Disease, Cirrhosis, Liver Failure, Hepatic Encephalopathy S TU D I E S PE R AG E G RO U P Visbiome Regular Product Code: 693-0412-01
Authors and Disclosures
 Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
The role of nutrition in optimum gastrointestinal health
 The role of nutrition in optimum gastrointestinal health Kelly A. Tappenden, Ph.D., R.D., FASPEN Kraft Foods Human Nutrition Endowed Professor University Distinguished Teacher-Scholar University of Illinois
The role of nutrition in optimum gastrointestinal health Kelly A. Tappenden, Ph.D., R.D., FASPEN Kraft Foods Human Nutrition Endowed Professor University Distinguished Teacher-Scholar University of Illinois
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 11 Page November 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i11.139 The Effect of Synbiotics on the Duration
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i11.139 The Effect of Synbiotics on the Duration
Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation
 Pediatr Radiol (2010) 40:1789 1793 DOI 10.1007/s00247-010-1725-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation Fredericus T. Kokke & Judith S. Sittig & Annemiek de Bruijn
Pediatr Radiol (2010) 40:1789 1793 DOI 10.1007/s00247-010-1725-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation Fredericus T. Kokke & Judith S. Sittig & Annemiek de Bruijn
Chronic constipation in the elderly
 Chronic constipation in the elderly 1 Dec,2011 R 2 Natta Asanaleykha Epidemiology Definition Scope The impact of chronic constipation in the elderly Pathophysiology Evaluation the elderly patient with
Chronic constipation in the elderly 1 Dec,2011 R 2 Natta Asanaleykha Epidemiology Definition Scope The impact of chronic constipation in the elderly Pathophysiology Evaluation the elderly patient with
Is a multispecies probiotic mixture effective in constipation during pregnancy? 'A pilot study'
 de Milliano et al. Nutrition Journal 2012, 11:80 RESEARCH Open Access Is a multispecies probiotic mixture effective in constipation during pregnancy? 'A pilot study' Inge de Milliano 1, Merit M Tabbers
de Milliano et al. Nutrition Journal 2012, 11:80 RESEARCH Open Access Is a multispecies probiotic mixture effective in constipation during pregnancy? 'A pilot study' Inge de Milliano 1, Merit M Tabbers
The Gut Microbiome: 101 Justin Carlson University of Minnesota
 The Gut Microbiome: 101 Justin Carlson University of Minnesota Where are we now? 360 B.C. 2003 Human Gut Microbes Associated With Obesity Ley et al., Nature. 2006. Consumer Driven Science For Better of
The Gut Microbiome: 101 Justin Carlson University of Minnesota Where are we now? 360 B.C. 2003 Human Gut Microbes Associated With Obesity Ley et al., Nature. 2006. Consumer Driven Science For Better of
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
Homeopathic Products. Evidence??
 Homeopathic Products Principle of analogy or Law of Similars Small or infinitesimal doses (3X-30C) Avogadro s number=6x10 23 = ~23X Succussion and potentization (see http://www.boiron.com/en/htm/02_medi_hom
Homeopathic Products Principle of analogy or Law of Similars Small or infinitesimal doses (3X-30C) Avogadro s number=6x10 23 = ~23X Succussion and potentization (see http://www.boiron.com/en/htm/02_medi_hom
The impact of the microbiome on brain and cognitive development
 The Gut-Brain Axis The impact of the microbiome on brain and cognitive development Diane Stadler, PhD, RD Oregon Health & Sciences University, Portland, Oregon Lao-American Nutrition Institute With acknowledgements
The Gut-Brain Axis The impact of the microbiome on brain and cognitive development Diane Stadler, PhD, RD Oregon Health & Sciences University, Portland, Oregon Lao-American Nutrition Institute With acknowledgements
Constipation is a common disorder in children,
 The Effect of Anorectal Manometry on the Outcome of Treatment in Severe Childhood Constipation: A Randomized, Controlled Trial Rijk van Ginkel, MD*; Hans A. Büller, PhD ; Guy E. Boeckxstaens, PhD ; Roos
The Effect of Anorectal Manometry on the Outcome of Treatment in Severe Childhood Constipation: A Randomized, Controlled Trial Rijk van Ginkel, MD*; Hans A. Büller, PhD ; Guy E. Boeckxstaens, PhD ; Roos
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews
 PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews The effect of probiotics on functional constipation: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials EIRINI DIMIDI, STEPHANOS CHRISTODOULIDES,
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews The effect of probiotics on functional constipation: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials EIRINI DIMIDI, STEPHANOS CHRISTODOULIDES,
Seppo Salminen Mimi Tang
 Koletzko B. (ed): Pediatric Nutrition in Practice. Basel, Karger, 2008, pp 80 84 1 General Aspects of Childhood Nutrition 1.8 Gut Microbiota in Infants Seppo Salminen Mimi Tang Key Words M i c r o b i
Koletzko B. (ed): Pediatric Nutrition in Practice. Basel, Karger, 2008, pp 80 84 1 General Aspects of Childhood Nutrition 1.8 Gut Microbiota in Infants Seppo Salminen Mimi Tang Key Words M i c r o b i
Issue 3, September usio
 Issue 3, September 2014 usio 1 Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota Research Update IMPROVEMENT IN INTESTINAL HEALTH 1. A probiotic fermented milk drink containing Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota improves
Issue 3, September 2014 usio 1 Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota Research Update IMPROVEMENT IN INTESTINAL HEALTH 1. A probiotic fermented milk drink containing Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota improves
Carbohydrates effects on the production of reuterin by Lactobacillus reuteri
 Carbohydrates effects on the production of reuterin by Lactobacillus reuteri An experiment in biology by Micah Forshee Mentored by Dr. Daniel Sharda Preview Introduction to microbiome and project at hand
Carbohydrates effects on the production of reuterin by Lactobacillus reuteri An experiment in biology by Micah Forshee Mentored by Dr. Daniel Sharda Preview Introduction to microbiome and project at hand
9/18/2018. The Physiological Roles of the Intestinal Microbiota. Learning Objectives
 The Physiological Roles of the Intestinal Microbiota Kelly A. Tappenden, Ph.D., R.D., FASPEN Professor and Head, Kinesiology and Nutrition University Distinguished Teacher-Scholar University of Illinois
The Physiological Roles of the Intestinal Microbiota Kelly A. Tappenden, Ph.D., R.D., FASPEN Professor and Head, Kinesiology and Nutrition University Distinguished Teacher-Scholar University of Illinois
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin
 Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report
 Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report 1. Private practice, Quebec, Canada. Email: nathaelle@chirostmartin.com By Nathaëlle Martin-Marcotte,
Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report 1. Private practice, Quebec, Canada. Email: nathaelle@chirostmartin.com By Nathaëlle Martin-Marcotte,
Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 4 August 2010; 595-601 Original article Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol a, Lakkana Rerksuppaphol b
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 4 August 2010; 595-601 Original article Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol a, Lakkana Rerksuppaphol b
The role of gut microbiome in IBS
 The role of gut microbiome in IBS Chung Owyang, MD H. Marvin Pollard Professor of Internal Medicine Professor of Molecular and Integrative Physiology Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Director, Pollard
The role of gut microbiome in IBS Chung Owyang, MD H. Marvin Pollard Professor of Internal Medicine Professor of Molecular and Integrative Physiology Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Director, Pollard
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
Probiotics for Primary Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infection
 Probiotics for Primary Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infection Objectives Review risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Describe guideline recommendations for CDI prevention Discuss
Probiotics for Primary Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infection Objectives Review risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Describe guideline recommendations for CDI prevention Discuss
The Effect of Probiotic Lactobacillus Reuteri on Reducing the Period of Restlessness in Infants with Colic
 Original Article J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 17, Issu 5; May 2015. P:7-11 The Effect of Probiotic Lactobacillus Reuteri on Reducing the Period of Restlessness in Infants with Colic Z. Akbarian Rad (MD) 1,
Original Article J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 17, Issu 5; May 2015. P:7-11 The Effect of Probiotic Lactobacillus Reuteri on Reducing the Period of Restlessness in Infants with Colic Z. Akbarian Rad (MD) 1,
Microbiome GI Disorders
 Microbiome GI Disorders Prof. Ram Dickman Neurogastroenterology Unit Rabin Medical Center Israel 1 Key Points Our gut microbiota Were to find them? Symbiosis or Why do we need them? Dysbiosis or when things
Microbiome GI Disorders Prof. Ram Dickman Neurogastroenterology Unit Rabin Medical Center Israel 1 Key Points Our gut microbiota Were to find them? Symbiosis or Why do we need them? Dysbiosis or when things
Human Anatomy rectum
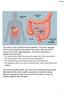 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
ESPEN Congress Vienna Networking with your microbiota Specific evidence-based indications. H. Lochs (Germany)
 ESPEN Congress Vienna 2009 Networking with your microbiota Specific evidence-based indications H. Lochs (Germany) Probiotics Evidence based indications H. Lochs Medizinische Klinik mit Schwerpunkt Gastroenterologie,
ESPEN Congress Vienna 2009 Networking with your microbiota Specific evidence-based indications H. Lochs (Germany) Probiotics Evidence based indications H. Lochs Medizinische Klinik mit Schwerpunkt Gastroenterologie,
Constipation an Old Friend. Presented by Dr. Keith Harris
 Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Does The Use Of Probiotics Treat Abdominal Pain In Children Between The Ages Of 4 And 18 With Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Does The Use Of Probiotics Treat Abdominal
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Does The Use Of Probiotics Treat Abdominal
Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders. TERRAGASTRO - Good health starts in the gut
 Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE Referred to as gastrointestinal diseases, they are common disorders which affect the esophagus,
Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE Referred to as gastrointestinal diseases, they are common disorders which affect the esophagus,
Presented by Megan R. Sanctuary, MS University of California at Davis
 Effects of supplementation with Bifidobacterium infantis in combination with bioactive milk components on gastrointestinal symptoms in children with autism Presented by Megan R. Sanctuary, MS University
Effects of supplementation with Bifidobacterium infantis in combination with bioactive milk components on gastrointestinal symptoms in children with autism Presented by Megan R. Sanctuary, MS University
Identify electrolytes that should be monitored whenever prolonged or severe diarrhea is present
 Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
The Intestinal Microbiota and the Developing Immune System
 The Intestinal Microbiota and the Developing Immune System 4 Feb 2016 The Intestinal Microbiota 10 fold more bacterial cells than human cells 100-1000 fold more bacterial genes than human genes Why does
The Intestinal Microbiota and the Developing Immune System 4 Feb 2016 The Intestinal Microbiota 10 fold more bacterial cells than human cells 100-1000 fold more bacterial genes than human genes Why does
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
Bacteriology. Mycology. Patient: SAMPLE PATIENT DOB: Sex: MRN: Rare. Rare. Positive. Brown. Negative *NG. Negative
 Patient: SAMPLE PATIENT DOB: Sex: MRN: 3.2 0.9-26.8 U/g 1.2 0.2-3.3 mg/g 2.2 1.3-8.6 micromol/g 1.1 1.3-23.7 mg/g 1.1 0.2-3.5 mg/g Rare 1.0 0.2-8.8 mg/g Rare 4.4 2.6-32.4 mg/g 64.6 >= 13.6 micromol/g Bacteriology
Patient: SAMPLE PATIENT DOB: Sex: MRN: 3.2 0.9-26.8 U/g 1.2 0.2-3.3 mg/g 2.2 1.3-8.6 micromol/g 1.1 1.3-23.7 mg/g 1.1 0.2-3.5 mg/g Rare 1.0 0.2-8.8 mg/g Rare 4.4 2.6-32.4 mg/g 64.6 >= 13.6 micromol/g Bacteriology
The Global Trends in Evaluation and Regulations of Intestine related Functional Foods
 The Global Trends in Evaluation and Regulations of Intestine related Functional Foods Keun Uk Ji, M.D. Department of Human and Food Seoul National University, College of Ecology E mail : geji@bifido.com
The Global Trends in Evaluation and Regulations of Intestine related Functional Foods Keun Uk Ji, M.D. Department of Human and Food Seoul National University, College of Ecology E mail : geji@bifido.com
!Microbiology Profile, stool
 LAB #: F000000-0000-0 PATIENT: Sample Patient ID: P12345 SEX: Female AGE: 37 CLIENT #: 12345 DOCTOR: Doctor's Data, Inc. 3755 Illinois Ave. St. Charles, IL 60174!Microbiology Profile, stool BACTERIOLOGY
LAB #: F000000-0000-0 PATIENT: Sample Patient ID: P12345 SEX: Female AGE: 37 CLIENT #: 12345 DOCTOR: Doctor's Data, Inc. 3755 Illinois Ave. St. Charles, IL 60174!Microbiology Profile, stool BACTERIOLOGY
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST
 COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
Emerging Probiotic Research: A Guide to the Use of Probiotics in Clinical Practice
 Emerging Probiotic Research: A Guide to the Use of Probiotics in Clinical Practice Donald Brown, ND April 13, 2010 Probiotics WHO Definition: Live microorganisms, which when administered in adequate amounts,
Emerging Probiotic Research: A Guide to the Use of Probiotics in Clinical Practice Donald Brown, ND April 13, 2010 Probiotics WHO Definition: Live microorganisms, which when administered in adequate amounts,
Immunity & Metabolism Human Microbiome Systems Nutrition. Food Bioactives Asian Consumers
 INFANT HEALTH Clare Wall, PhD, Assoc. Professor, The University of Auckland, and Martin Kussmann, PhD, Professor, The Liggins Institute, The University of Auckland. Chief Scientist HVN On behalf of the
INFANT HEALTH Clare Wall, PhD, Assoc. Professor, The University of Auckland, and Martin Kussmann, PhD, Professor, The Liggins Institute, The University of Auckland. Chief Scientist HVN On behalf of the
Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up
 1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
THE EFFECT OF PROBIOTIC, OHHIRA OMX CAPSULES, IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE NON-BLOODY DIARRHEA IN INFANTS 3-24 MONTHS OF AGE
 THE EFFECT OF PROBIOTIC, OHHIRA OMX CAPSULES, IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE NON-BLOODY DIARRHEA IN INFANTS - MONTHS OF AGE Hazel T. Valdoria, MD., Felizardo N. Gatcheco, MD. INTRODUCTION Diarrheal diseases
THE EFFECT OF PROBIOTIC, OHHIRA OMX CAPSULES, IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE NON-BLOODY DIARRHEA IN INFANTS - MONTHS OF AGE Hazel T. Valdoria, MD., Felizardo N. Gatcheco, MD. INTRODUCTION Diarrheal diseases
7/30/2018. Nutricia North America 1. Learning Objectives
 Probiotics, Prebiotics and the Role of the Infant Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Allergic Disease Kelly Tappenden, Ph.D, R.D. Kelly Tappenden, Ph.D, R.D. Professor and Department Head Department of
Probiotics, Prebiotics and the Role of the Infant Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Allergic Disease Kelly Tappenden, Ph.D, R.D. Kelly Tappenden, Ph.D, R.D. Professor and Department Head Department of
PROBIOTIC RESEARCH REVIEW
 Probiotics in the Prevention of Eczema: A Randomised Controlled Trial (Allen at al. 2014) The probiotic formula that is used in GENESTRA BRANDS HMF Baby B and HMF Baby F was found to safely and effectively
Probiotics in the Prevention of Eczema: A Randomised Controlled Trial (Allen at al. 2014) The probiotic formula that is used in GENESTRA BRANDS HMF Baby B and HMF Baby F was found to safely and effectively
Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:255-261 Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation Hasan Karami* 1, MD; Mohammad Khademloo 2,
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:255-261 Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation Hasan Karami* 1, MD; Mohammad Khademloo 2,
EED INTERVENTIONS: PRE- AND PRO-BIOTIC SAFETY
 EED INTERVENTIONS: PRE- AND PRO-BIOTIC SAFETY Produced by: Dietrich, C.; Kidane, L.; Babigumira, J. Agenda Agenda Timeline Project Background and Objectives Key Takeaways Approach & Rationale Methods Results
EED INTERVENTIONS: PRE- AND PRO-BIOTIC SAFETY Produced by: Dietrich, C.; Kidane, L.; Babigumira, J. Agenda Agenda Timeline Project Background and Objectives Key Takeaways Approach & Rationale Methods Results
What can we learn from the clinical studies in infants (on thickeners)?
 What can we learn from the clinical studies in infants (on thickeners)? Dominique Turck Member of the FAF WG Re-evaluation of FA in foods for infants below 16 weeks of age FA Stakeholders Workshop 30 November
What can we learn from the clinical studies in infants (on thickeners)? Dominique Turck Member of the FAF WG Re-evaluation of FA in foods for infants below 16 weeks of age FA Stakeholders Workshop 30 November
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation. Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class
 Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider
 Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider Elizabeth Coss, MD General Gastroenterologist Audie Murphy Veterans Hospital UT Health This presentation does not
Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider Elizabeth Coss, MD General Gastroenterologist Audie Murphy Veterans Hospital UT Health This presentation does not
PROBIOTICS. The Ultimate Flora Difference
 In the Refrigerator Section! PROBIOTICS High-Potency Daily, Critical Care and Targeted Probiotic Formulas to Improve Regularity, Strengthen Natural Defenses and Promote Overall Digestion * The ReNew Life
In the Refrigerator Section! PROBIOTICS High-Potency Daily, Critical Care and Targeted Probiotic Formulas to Improve Regularity, Strengthen Natural Defenses and Promote Overall Digestion * The ReNew Life
Fonterra Probiotics: From guts to glory
 Fonterra Probiotics: From guts to glory James Dekker April 16, 2015 Host Institution Probiotic bacteria Live micro-organisms which, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the
Fonterra Probiotics: From guts to glory James Dekker April 16, 2015 Host Institution Probiotic bacteria Live micro-organisms which, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination
 Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT
 Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study is to find out if there is any relationship between
Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study is to find out if there is any relationship between
The Cow s Milk-related Symptom Score. CoMiSS TM. An awareness tool. to recognize cow s milk-related symptoms in infants and young children
 The Cow s Milk-related Symptom Score CoMiSS TM An awareness tool to recognize cow s milk-related symptoms in infants and young children Background SYMPTOMS RELATED TO INTAKE OF COW S MILK Many infants
The Cow s Milk-related Symptom Score CoMiSS TM An awareness tool to recognize cow s milk-related symptoms in infants and young children Background SYMPTOMS RELATED TO INTAKE OF COW S MILK Many infants
Health Benefits of Prebiotic Dietary Fiber
 Health Benefits of Prebiotic Dietary Fiber JENNIFER ERICKSON, PhD, RD Objectives Provide some background on dietary fiber To define the term "prebiotic dietary fiber" To discuss potential health effects
Health Benefits of Prebiotic Dietary Fiber JENNIFER ERICKSON, PhD, RD Objectives Provide some background on dietary fiber To define the term "prebiotic dietary fiber" To discuss potential health effects
A Randomized Open Label Comparative Clinical Study of a Probiotic against a Symbiotic in the Treatment of Acute Diarrhoea in Children
 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(9): 96-100 I J M R
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(9): 96-100 I J M R
Hygiene Hypothesis: 10 years later. Christina Ciaccio MD, MSc Assistant Professor The University of Chicago
 Hygiene Hypothesis: 10 years later Christina Ciaccio MD, MSc Assistant Professor The University of Chicago none Disclosures Definitions Microbe: Microscopic organism Microbiota: Microbial community Definition
Hygiene Hypothesis: 10 years later Christina Ciaccio MD, MSc Assistant Professor The University of Chicago none Disclosures Definitions Microbe: Microscopic organism Microbiota: Microbial community Definition
Probiotics and Health
 Probiotics and Health March 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 2 BACKGROUND AND DEFINITIONS... 4 FUNCTIONAL GASTROINTESTIINAL DISORDERS... 5 Irritable bowel syndrome... 5 Constipation... 6 INFLAMMATORY
Probiotics and Health March 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 2 BACKGROUND AND DEFINITIONS... 4 FUNCTIONAL GASTROINTESTIINAL DISORDERS... 5 Irritable bowel syndrome... 5 Constipation... 6 INFLAMMATORY
Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in childhood constipation: a study using a Delphi technique
 BMJ Paediatrics Open To cite: Kuizenga-Wessel S, Steutel NF, Benninga MA, et al. Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in childhood constipation: a study using a Delphi technique. BMJ Paediatrics
BMJ Paediatrics Open To cite: Kuizenga-Wessel S, Steutel NF, Benninga MA, et al. Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in childhood constipation: a study using a Delphi technique. BMJ Paediatrics
Gut Lung Axis Implication of the Gut Microbiota beyond its niche
 Gut Lung Axis Implication of the Gut Microbiota beyond its niche Reema Subramanian PhD Candidate (4 th year) Supervisor: Prof. Margaret Ip Department of Microbiology, CUHK Joint Graduate Student Seminar
Gut Lung Axis Implication of the Gut Microbiota beyond its niche Reema Subramanian PhD Candidate (4 th year) Supervisor: Prof. Margaret Ip Department of Microbiology, CUHK Joint Graduate Student Seminar
Symposium 9. Evidence based or gut reaction
 Symposium 9 Ch i E t l F d Choosing Enteral Feeds Evidence based or gut reaction All enteral feeds should contain fibre Ceri Green Global Medical Department Numico Clinical Nutrition Division Schiphol,
Symposium 9 Ch i E t l F d Choosing Enteral Feeds Evidence based or gut reaction All enteral feeds should contain fibre Ceri Green Global Medical Department Numico Clinical Nutrition Division Schiphol,
The importance of early complementary feeding in the development of oral tolerance: Concerns and controversies
 The importance of early complementary feeding in the development of oral tolerance: Concerns and controversies Prescott SL, Smith P, Tang M, Palmer DJ, Sinn J, Huntley SJ, Cormack B. Heine RG. Gibson RA,
The importance of early complementary feeding in the development of oral tolerance: Concerns and controversies Prescott SL, Smith P, Tang M, Palmer DJ, Sinn J, Huntley SJ, Cormack B. Heine RG. Gibson RA,
How to to approach a child with recurrent abdominal pain?
 How to to approach a child with recurrent abdominal pain? Alexandra Papadopoulou Athens Interconnected Alexandra Papadopoulou Children s Hospitals Athens Interconnected Children s Hospitals «Ag Sofia»
How to to approach a child with recurrent abdominal pain? Alexandra Papadopoulou Athens Interconnected Alexandra Papadopoulou Children s Hospitals Athens Interconnected Children s Hospitals «Ag Sofia»
Murdoch Childrens Research Institute and The Royal Children s Hospital Centre for Community Child Health
 Is Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 effective for the treatment of infant colic? Results from an international individual participant data meta-analysis (IPDMA) Murdoch Childrens Research Institute and
Is Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 effective for the treatment of infant colic? Results from an international individual participant data meta-analysis (IPDMA) Murdoch Childrens Research Institute and
Diet during pregnancy. and atopic disease
 Diet during pregnancy and atopic disease 1. Elimination diet 2. Probiotics 3. LCPUFA 4. Conclusions Maternal elimination diet during pregnancy? NO! Prescription of of an an antigen avoidance diet to to
Diet during pregnancy and atopic disease 1. Elimination diet 2. Probiotics 3. LCPUFA 4. Conclusions Maternal elimination diet during pregnancy? NO! Prescription of of an an antigen avoidance diet to to
Dr Warren Hyer Consultant Paediatric Gastroenterologist
 Dr Warren Hyer Consultant Paediatric Gastroenterologist Probiotics a cure for all? No conflict of interest to declare Aims To change your opinion of probiotic use in children To base your decision on high
Dr Warren Hyer Consultant Paediatric Gastroenterologist Probiotics a cure for all? No conflict of interest to declare Aims To change your opinion of probiotic use in children To base your decision on high
OPO fats By Dr. Annie Salsberg, N.D.
 1 of 5 An inside look at and how y increase absorption of calcium and essential fatty acids while improving digestive health. Close up portrait of eight mounth old baby What are? According to FDA regulations,
1 of 5 An inside look at and how y increase absorption of calcium and essential fatty acids while improving digestive health. Close up portrait of eight mounth old baby What are? According to FDA regulations,
Constipation An Overview. Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment
 CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
Laboratory report. Test: Leaky gut test. Sample material: stool. John Doe Main St 1 Anytown
 1 / 5 Verisana LAB John Doe Main St 1 Anytown Surname, First name Doe, John DOB 02/13/1980 Sex male Laboratory # 20020181 Date collected 01/25/2018 Date received 02/01/2018 Report date 02/13/2018 Laboratory
1 / 5 Verisana LAB John Doe Main St 1 Anytown Surname, First name Doe, John DOB 02/13/1980 Sex male Laboratory # 20020181 Date collected 01/25/2018 Date received 02/01/2018 Report date 02/13/2018 Laboratory
William Chey, MD University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI
 Lin Chang, MD David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, CA William Chey, MD University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI Mark Pimentel, MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Accredited by Jointly
Lin Chang, MD David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, CA William Chey, MD University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI Mark Pimentel, MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Accredited by Jointly
Module Four: The GI System Module Five: The Gut Microbiome. The GI System. LLiana Shanti, CN
 Module Four: The GI System Module Five: The Gut Microbiome The GI System LLiana Shanti, CN www.healthmasteryinstitute.com Review Review Review The Gut Hippocrates has been quoted as saying death sits in
Module Four: The GI System Module Five: The Gut Microbiome The GI System LLiana Shanti, CN www.healthmasteryinstitute.com Review Review Review The Gut Hippocrates has been quoted as saying death sits in
