Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Perspective
|
|
|
- Myron O’Brien’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective McMonagle et al. MRI of the PL Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective J. Scott McMonagle 1 lyde. Helms 1 William E. Garrett, Jr. 2 Emily N. Vinson 1 McMonagle JS, Helms, Garrett WE Jr, Vinson EN Keywords: MRI, mucoid degeneration, posterior cruciate ligament DOI: /JR Received June 21, 2011; accepted after revision October 23, Presented at the 2011 annual meeting of the merican Roentgen Ray Society, hicago, IL. 1 Department of Radiology, Duke University Health System, ox 3808, Durham, N ddress correspondence to J. S. McMonagle (jscottmcm@gmail.com). 2 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Duke University Health System, Durham, N. JR 2013; 201: X/13/ merican Roentgen Ray Society Tram-Track ppearance of the Posterior ruciate Ligament (PL): orrelations With Mucoid Degeneration, Ligamentous Stability, and Differentiation From PL Tears OJETIVE. The purpose of our study was to describe the MRI findings in the posterior cruciate ligament (PL) analogous to mucoid degeneration in the anterior cruciate ligament (L); to correlate MRI findings in the PL with ligamentous stability; to differentiate the PL tram-track appearance from the appearance of PL tears; and to emphasize the coexistence of PL and L mucoid degeneration, cruciate ganglia, and meniscal cysts. ONLUSION. The tram-track PL appearance commonly coexists with L mucoid degeneration; ganglia; and, less frequently, meniscal cysts. oth PL tears and MRI findings suggestive of PL mucoid degeneration show ligament thickening and increased PL signal intensity. Tram-track PLs are usually asymptomatic and typically have no ligamentous instability. lthough the MRI appearances of complete tears, partial tears, and chronic degeneration of the anterior cruciate ligament (L) have been thoroughly described, comparable studies in the literature about the posterior cruciate ligament (PL) are lacking. In particular, the MRI appearance of L mucoid degeneration was first described in 1999 [1]. Since then, our understanding of L mucoid degeneration has evolved and is now well established [2 5]. Histologic evaluations of cruciate ligaments harvested from cadavers and from patients undergoing knee replacement surgery have long described a link between degenerative changes in the L and those in the PL, particularly mucoid degeneration [6 8]. Despite the association of mucoid degeneration of the cruciate ligaments and the long-standing reports about the MRI appearance of L mucoid degeneration, only a few studies in the radiology literature describe the MRI appearance of mucoid degeneration of the PL [9, 10]. This discrepancy was highlighted at our institution s weekly sports medicine conference when an orthopedic surgeon showed a knee MRI examination that revealed diffuse PL thickening and increased signal intensity both of which are MRI findings associated with a PL tear [11]. However, this index patient had normal results on a posterior drawer examination. Homogeneous increased signal intensity that extends longitudinally throughout a thickened PL with an intact rim of peripher- al fibers (Fig. 1) is an appearance analogous to the classic celery stalk morphology of L mucoid degeneration [4]. Given the stability of the PL on physical examination and the MRI appearance of the PL being similar to mucoid degeneration in the L, we postulated that these MRI findings represent mucoid degeneration of the PL. Ultimately, findings from a physical examination performed of the index patient under anesthesia were normal and knee arthroscopy revealed an intact PL with a bulbous morphology and a diffuse yellowish hue, which was called PL mucoid degeneration by the orthopedic surgeon. The purpose of this study was to evaluate tram-track longitudinal intraligamentous PL signal-intensity abnormalities, which is similar to the MRI appearance of mucoid degeneration of the L. We also sought to differentiate this longitudinal intraligamentous PL signalintensity abnormality from PL tears and to determine the incidence of coexistent L mucoid degeneration, cruciate ganglia, and parameniscal and intrameniscal cysts. Materials and Methods Institutional review board approval and a waiver of informed consent were obtained for this retrospective study. fter our index case, we encountered five additional knee MRI examinations that had findings similar to the index case. We then conducted a retrospective review of our institution s knee MRI database of records over an 8-year period (12,972 cases). We searched for the key- 394 JR:201, ugust 2013
2 MRI of the PL Fig year-old man with posterior knee pain. Sagittal fat-suppressed T2- weighted MR image (TR/TE, 4000/70) of posterior cruciate ligament (PL) shows diffuse thickening and longitudinally increased signal intensity with peripheral rim of hypointense PL fibers (arrows). t arthroscopy, PL was intact, was bulbous in morphology, and had yellowish hue. words PL cyst, PL signal, and abnormal PL, which yielded 61 MRI studies. ll imaging studies were performed on a 1.5-T unit (Signa, GE Healthcare) according to our standard knee MRI protocol: sagittal fat-suppressed spin-echo proton density images (TR range/te, /20) and sagittal, axial, and coronal fat-suppressed fast spin-echo (FSE) T2-weighted images (TR range/te range, /57 80). The number of signals acquired was 2 for the FSE sequences and 1 for the proton density sequences. The echo-train length was 8 10 for the FSE sequences. slice thickness of 4 mm with a 0.4-mm interslice gap was used. The FOV was 16 cm, and the matrix size was These MRI examinations were retrospectively reviewed in consensus by two musculoskeletal radiologists with 5 and 33 years experience and one musculoskeletal radiology fellow. ased on our index case, the imaging criteria of PL mucoid degeneration included homogeneous longitudinal increased signal intensity in the PL in all planes on proton density and T2 images with an adjacent welldefined intact rim of hypointense PL fibers that give the PL a tram-track appearance. In an attempt to prevent potential inclusion of injured PLs, patients were excluded if they had a clinical history of knee trauma or MRI findings indicative of prior knee injury. Of the 61 patients from our database search, 47 were excluded: 23 patients had a clinical history of acute trauma, 11 had MRI findings of an acute L tear, four had an L-deficient knee, and nine had bone contusions with an intact L. Thus, there were 20 patients in the PL mucoid degeneration group: our index case, the five cases subsequently encountered in the reading room, and 14 examinations from the retrospective search. Each case fulfilled the defined imaging criteria of PL mucoid degeneration. There were eight women (40%) and 12 men (60%) with a mean age of 51.7 years (age range, years). In an effort to differentiate MRI findings of PL mucoid degeneration from those of PL tears, we included for review an equal number of patients with surgically proven PL tears. This group included seven women (35%) and 13 men (65%) with a mean age of 35.2 years (age range, years). Several different parameters for these 40 studies 20 examinations that met the imaging criteria for PL mucoid degeneration and 20 examinations of surgically proven PL tears were then retrospectively evaluated, again in consensus. Reviewers were blinded to the preliminary consensus interpretations and therefore did not know if the study had been included as PL mucoid degeneration or as a surgically proven PL tear. Using the imaging criteria of PL mucoid degeneration, the reviewers first decided whether the study represented PL mucoid degeneration or a PL tear. The transverse anteroposterior diameter of the vertical portion of each PL was measured on sagittal T2-weighted images. The PL was evaluated for the presence or absence of complete fiber disruption. The intrasubstance signal intensity of each PL on proton density weighted and T2-weighted sequences was graded as hyperintense (isointense to fluid), intermediate (increased signal intensity but less than signal intensity of joint fluid), or hypointense (normal PL signal intensity). The relative signal intensities on proton density and T2 images were then compared with each other. oexistent MRI findings of L mucoid degeneration, ganglia involving or adjacent to the PL, intrameniscal cysts, parameniscal cysts, and intraosseous cysts at either the femoral or tibial PL attachments were noted. The electronic medical records of all patients were reviewed: Each patient s presenting symptoms, the clinical assessment of the PL by an orthopedic specialist, and arthroscopic results, if available, were recorded. Results The tram-track appearance, our inclusion criterion, reliably differentiated all 20 of the PLs included as the mucoid degeneration group from the 20 PLs with surgically proven tears. Of the 20 PL tears, 19 (95%) showed amorphous or heterogeneously striated increased signal intensity without adjacent welldefined or intact peripheral fibers on both proton density weighted and T2-weighted images; these findings were easily differentiated from the tram-track appearance. Only on sagittal images, one of the PL tears (5%) showed linear, longitudinally oriented increased intraligamentous signal intensity that was somewhat similar to the tram-track appearance (Fig. 2). However, although the peripheral rim of fibers appeared intact on sagittal images, the peripheral fibers were clearly discontinuous on both the coronal and axial images. Further, the longitudinally oriented increased signal intensity throughout this PL tear was heterogeneous and had a striated look, with multiple separate lines of increased signal intensity as is often seen in PL tears; it was not a single solid and homogeneous streak of increased signal intensity, further differentiating it from the tram-track appearance [11]. y contrast, all 20 PLs in the mucoid degeneration group had a tram-track appearance created by homogeneous, longitudinal increased signal intensity with discrete borders surrounded by intact hypointense PL fibers validated on all three imaging planes (Fig. 3). Further, evaluation in all three planes distinguished adjacent structures, such as the meniscofemoral ligaments, oriented perpendicular to the PL that could erroneously appear as part of an intact peripheral rim if the PL had been evaluated in only a single plane. The tram-track appearance was seen throughout the entire length of 18 PLs (90%). One of the tram-track PLs (5%) had intraligamentous signal intensity that involved only the proximal half of the PL, whereas another (5%) had intraligamentous increased signal intensity with an intact peripheral rim of fibers that extended through the proximal and middle thirds of the PL but that spared the distal third of the PL. In the 20 patients with MRI findings that met the imaging criteria for PL mucoid degeneration, 19 PLs (95%) measured 7 mm or more in anteroposterior diameter on sagittal T2-weighted images. The average PL JR:201, ugust
3 McMonagle et al. Fig year-old man with severe knee pain after motor vehicle crash., Sagittal fat-suppressed proton density weighted MR image (TR/TE, 2000/20) shows thickening and multiple linear, longitudinally oriented intrasubstance striations of posterior cruciate ligament (PL) and few peripheral hypointense PL fibers (arrows). and, xial (4000/65) () and coronal (4000/60) () fat-suppressed T2-weighted images show abnormal thickening and multiple heterogeneous linear striations of intermediate signal intensity throughout PL, in contrast to homogeneous and solid intrasubstance signal intensity of mucoid degeneration. dditionally, peripheral rim of hypointense fibers (arrows) is not intact on axial or coronal images. t surgery, this PL was described as torn. thickness for PL mucoid degeneration was 8.5 mm, with a range of 6 12 mm. mong the surgically proven PL tears, 17 PLs (85%) had a transverse anteroposterior diameter that measured 7 mm or more. PL tears had an average PL thickness of 8.8 mm and a range of 4 13 mm. Ten of the 20 PLs (50%) from the surgically proven PL tear group appeared completely disrupted or avulsed. Partial fiber discontinuity was seen in none of the PL tear group. Four (40% of the total) of the ligaments were proximal tears with complete fiber disruption from the femoral attachment, three (30%) tears were midsubstance, and three (30%) PLs were completely disrupted from the tibial attachment; two of these three distal tears also involved small avulsed and retracted tibial cortical bone fragments. y contrast, conforming to the criteria of the tram-track appearance, PLs in the mucoid degeneration group had no disruption of the PL fibers. Hyperintense signal intensity was seen more often in the PL mucoid degeneration group than in PL tears (Table 1). Seven PLs in the mucoid degeneration group (35%) had hyperintense intrasubstance signal on proton density images, whereas only one PL tear (5%) had hyperintense signal intensity on proton density images. None of the PLs in the mucoid degeneration group had hypointense signal intensity on proton density weighted or T2-weighted images. y comparison, the PL tear group had hypointense signal intensity on T2-weighted images in six of 20 PLs (30%), and the majority of PL tears, 14 of 20 (70%), showed intermediate signal intensity. In all 20 of the PL tears (100%), the signal intensity on proton density images was relatively higher than on T2-weighted images. The majority of PLs in the mucoid degeneration group, 14 of 20 (70%), also had relatively increased signal intensity on proton density images when compared with the signal intensity on T2-weighted images. In nine of the 20 patients with PLs with a tram-track appearance (45%), coexistent MRI findings of L mucoid degeneration were also present (Fig. 4). coincident ganglion exerted mass effect on, emanated from, or was immediately adjacent to the PL in 16 (80%) of the PLs in the mucoid degeneration group (Fig. 5). Intrameniscal cysts were present in five knees in the PL mucoid degeneration group (25%), three in the lateral meniscus and two in the medial meniscus, and parameniscal cysts were noted in two patients (10%), one adjacent to the lateral meniscus posterior horn and one adjacent to the medial meniscus posterior body. Intraosseous cysts were noted in four of the 20 patients (20%) in the PL mucoid degeneration group: Two were adjacent to the tibial attachment of the PL and two were adjacent to the femoral attachment. oexistent L mucoid degeneration was not seen in any of the patients with surgically proven PL tears (0%). ganglion was adjacent to the PL in four of the 20 (20%) PL tears. Two intrameniscal cysts (10%) and one parameniscal cyst (5%) were present in the PL tear group. Review of each patient s electronic medical record showed that knee pain was the most common presenting symptom, seen in all 20 patients with tram-track PLs. However, 18 of these 20 patients (90%) had additional MRI findings that were likely the primary cause of knee pain. ll 20 patients with a tram-track PL appearance (100%) had a Table 1: Posterior ruciate Ligament (PL) Intrasubstance Signal Intensity MRI Sequence PL Intrasubstance Signal Intensity Hyperintense a Intermediate b Hypointense c PL mucoid degeneration Proton density 7 (35) 13 (65) 0 (0) FSE T2 4 (20) 16 (80) 0 (0) PL tears Proton density 1 (5) 18 (90) 1 (5) FSE T2 0 (0) 14 (70) 6 (30) Note Data presented are no. (%) of patients. FSE T2 = fast spin-echo T2-weighted. a Isointense to fluid. b Increased signal intensity but less than signal intensity of joint fluid. c Normal PL signal intensity. 396 JR:201, ugust 2013
4 MRI of the PL negative posterior drawer test on physical examination by an orthopedic specialist. Two patients (10%) in this group also had posterior knee pain with knee flexion beyond 90 and one patient (5%) had posterior midline knee tenderness to palpation. Of the 20 patients with a tram-track PL appearance, six (30%) had subsequent arthroscopy; all six patients had no ligamentous instability during their examination under anesthesia. Five of the PLs were described as normal and intact, whereas the sixth PL, our index case, was intact but also was bulbous with a diffuse yellowish hue. Discussion The true incidence of PL mucoid degeneration is difficult to assess because it is, as in our patient population, typically asymptomatic and incidentally noted. s a point of reference, ergin et al. [2] reported that the incidence of mucoid degeneration in the L is 1.0% (44/4221). The incidence of Fig year-old woman with chronic left knee pain with stable posterior cruciate ligament (PL) on clinical examination. and, xial (TR/TE, 4000/65) (), coronal (4000/68) (), and sagittal (4000/68) () fat-suppressed T2-weighted MR images show typical appearance of PL mucoid degeneration (arrows) with increased intraligamentous signal intensity and peripheral rim of intact hypointense PL fibers., Sagittal image shows anterior meniscofemoral ligament (arrowhead) that is adjacent to but separate from intact peripheral PL rim (arrows). PL mucoid degeneration in our retrospective study population was 0.1% (14/12,972). The normal appearance of the PL on MRI is that of a broad curvilinear band of low signal intensity on proton density weighted and T2-weighted images that is usually 6 mm or less in anteroposterior diameter. In 2008, Rodriguez et al. [11] reported two MRI findings that are highly suggestive of a torn PL: an anteroposterior diameter of 7 mm or more and increased intrasubstance signal intensity in the PL, particularly with PLs showing relatively higher signal intensity on proton density images than T2-weighted images. However, PL thickening and increased signal intensity do not always equate to a functionally torn PL: 19 of the 20 PLs that met the imaging criteria for mucoid degeneration (95%) were greater than 7 mm in anteroposterior diameter and 14 (70%) PLs in the mucoid degeneration group had signal intensity that was relatively higher on proton density weighted images than on T2-weighted images. s a result, neither PL thickness nor relatively higher signal intensity is a reliable discriminator and additional imaging criteria that differentiate PL degenerative changes from PL tears are requisite. The tram-track appearance was the best MRI finding for distinguishing between PL mucoid degeneration and PL tears in this small series. nalogous to intrameniscal cysts, which are isointense to fluid in only 8.4% of the cases [12], the majority of PL intrasubstance signal intensity, particularly in our tram-track PL group, was not fluid signal intensity. Instead, PLs in both study groups were usually intermediate on proton density and T2-weighted imaging, 65% and 80% for PL mucoid degeneration versus 90% and 70% for PL tears, respectively. PLs in the mucoid degeneration group were more likely to have intrasubstance signal intensity isointense to fluid on proton density images, 35%, as compared with only 5% of PL tears. Relative signal intensities, Fig year-old man with anterior knee pain and normal findings on anterior and posterior drawer clinical examinations., onsecutive coronal fat-suppressed T2-weighted MR images (TR/TE, 3700/50) show increased signal intensity and thickening of both anterior cruciate ligament (L) and posterior cruciate ligament (PL); these findings are consistent with L (black arrows) and PL (white arrows) mucoid degeneration. JR:201, ugust
5 McMonagle et al. however, cannot reliably distinguish between PL mucoid degeneration and PL tears, increasing the importance of additional MRI criteria such as the tram-track appearance. ergin et al. [2] reported that L mucoid degeneration involved the entire L in 93% of cases; similarly, the majority of our PLs with a tram-track appearance, 18 of 20 (90%), involved the entire length of the PL. One of the patients in our series had undergone subsequent knee MRI 2 and 6 years after the initial MRI examination. The transverse and longitudinal dimensions of the hyperintense intraligamentous signal intensity enlarged with each subsequent examination (Fig. 6), suggesting that just as degenerative changes of osteoarthritis progress over time, so too does the extent of PL mucoid degeneration proceed. Fig year-old man who presented with 6-week history of posterior knee pain and fullness and no history of trauma. Sagittal fat-suppressed T2-weighted MR image (TR/TE, 3700/50) shows complex ganglion (arrow) that exerts mass effect on adjacent proximal posterior cruciate ligament (PL). Longitudinal tram-track appearance of PL mucoid degeneration is also seen. PL ganglion was aspirated at surgery and PL was described as normal and intact. The posterior drawer examination is the most accurate clinical test, with a reported sensitivity of 90% and specificity of 99% for orthopedic surgeons with fellowship training in sports medicine [13]. However, the accuracy of the posterior drawer test significantly decreases with distracting injuries, when even subtle internal or external rotation of the tibia is present, or even when the knee is not precisely at 90 of flexion. The positive likelihood ratio of the posterior drawer test also significantly decreases for less experienced providers and those without dedicated training [13]. Thus, physical examination of the PL is highly valuable for assessing the functional competency of the ligament, but it is not without limitations. ll of the patients in our PL mucoid degeneration group had physical examinations that included a posterior drawer test. Further, the results were reported as either normal or no laxity for all 20 PLs that had a tram-track appearance. ll of the PLs in the surgically proven PL tear group, by contrast, had been preoperatively noted to have grade II or grade III PL laxity. Investigators have reported that the majority of PL tears (62%) involve stretching deformation and, as a result, do not have complete fiber avulsion or disruption [11]. In the group with a surgically proven PL tear, 10 of the 20 PLs (50%) showed fiber disruption. onsequently, although fiber disruption indicates a torn PL, visualization of intact PL fibers poorly correlates with functional competence of the PL. y comparison, all 20 PLs (100%) that had a tram-track appearance with an intact peripheral rim of PL fibers on all imaging planes (i.e., the inclusion criteria for this study) had a mechanically intact PL. Similar to patients with L mucoid degeneration who rarely complain of knee instability and typically have a negative Lachman sign [2], patients with PL mucoid degeneration typically do not have ligamentous instability. ll six tram-track PL patients who subsequently underwent surgery also had a normal posterior drawer examination under anesthesia. dditionally, all six patients had an intact ligament at arthroscopy; in one patient, the PL also had a bulbous appearance and yellowish hue. The arthroscopic appearance of these tram-track PLs resembles the two possible arthroscopic appearances of L mucoid degeneration: normal or bulbous with a yellowish hue [14]. lthough no specimens were obtained in our PL mucoid degeneration Fig year-old female triathlete with patellofemoral pain., Sagittal T2-weighted MR image (TR/TE, 3300/70) at initial presentation shows tram-track appearance (arrow) involving only proximal half of posterior cruciate ligament (PL) (transverse dimension, 4.3 mm; longitudinal dimension, 12.0 mm). Patient did not have meniscofemoral ligament., Sagittal T2-weighted MR image (4000/60) obtained 2 years after shows intraligamentous tram-track appearance (arrow). PL has increased in transverse dimension (5.5 mm) and longitudinal dimension (13.6 mm) since initial examination., Most recent sagittal T2-weighted MR image (3400/63) obtained 6 years after shows continued increase in transverse (7.5 mm) and longitudinal (18.2 mm) size of tram-track appearance (arrow) relative to both earlier studies. t arthroscopy, PL was reported as normal. 398 JR:201, ugust 2013
6 MRI of the PL group, Shoji et al. [10] described a PL with MRI findings identical to our group that was arthroscopically excised and revealed mucoid degeneration at histologic examination. The cause of cruciate ligament mucoid degeneration remains controversial. ergin et al. [2] described the coexistence of L mucoid degeneration with L ganglia and intraosseous cysts. The coincident association between ganglia and PL mucoid degeneration, seen in 16 of our patients (80%), suggests that these two entities may also share a common pathogenesis in the PL. Some investigators have suggested that ganglia are a product of connective tissue mucoid degeneration [15, 16], whereas others theorize that a congenital abnormality or previous injury facilitates and possibly predisposes cruciate ligaments to degenerative ganglion formation [17]. Nine of our patients (45%) had MRI findings of both L and PL mucoid degeneration, further supporting a common pathogenesis among degeneration of the L and PL, similar to what has previously been reported in cadavers and in patients undergoing knee replacement surgery [6 8]. Seven meniscal cysts (35%) five intrameniscal cysts and two parameniscal cysts were seen in our tram-track PL group. ecause meniscal cysts are reportedly found in 8% of knee MRI studies [12], the increased prevalence of meniscal cysts in our tramtrack PL patients suggests a common degenerative pathway or at least that some patients, for anatomic or biomechanical reasons, are more predisposed to soft-tissue degenerative changes throughout the knee. This study was limited by its retrospective and observational design. In an attempt to exclude injured PLs, we chose to exclude patients with a preceding episode of trauma or with MRI findings indicative of a prior knee injury. Our assumption of no prior knee injury relies heavily on each patient s reported clinical history; obviously we cannot guarantee that each patient with tram-track PL findings had absolutely no prior or remote history of knee trauma. Potential selection bias was unavoidable given the inclusion criteria for the PL tram-track group. Partial PL tears, which might have imaging features similar to or overlapping with those described with mucoid degeneration, were also potentially excluded from the study. Mild or nonspecific repetitive trauma and even healed partial tears have been espoused as potential causes of mucoid degeneration in the L [15]; similar causality for PL mucoid degeneration can be suggested and, to date, have not been definitively refuted. McIntyre et al. [3] described L mucoid degeneration that progressed to an atraumatic complete L tear. Significant selection bias was also present in our surgically proven PL tear group because progression to surgery implied clinical instability of the PL. ecause most PL tears are not treated surgically, there is uncertain clinical significance of distinguishing between PL tears and PL mucoid degeneration. This study is further limited by lack of direct histologic correlation; five of the six tram-track PLs that proceeded to arthroscopy had a normal appearance, similar to arthroscopic findings in cases of L mucoid degeneration. In summary, although the pathogenesis of cruciate ligament mucoid degeneration remains unknown, it is important that MRI findings suggestive of PL mucoid degeneration be differentiated from chronic or acute interstitial, partial, and complete PL tears given their respective and important differences in ligamentous stability and the practical implications for clinical management. linical correlation in our study population indicates that the tram-track PL appearance is usually asymptomatic and typically has no ligamentous laxity. The tramtrack PL appearance further informs clinical decision-making by allowing the radiologist to discriminate between mechanically unstable torn PLs and mechanically intact PLs. oexistent MRI findings suggest associations between PL and L mucoid degeneration, ganglia, and potentially even meniscal cysts. References 1. Kumar, ickerstaff DR, Grimwood JS, Suvarna SK. Mucoid cystic degeneration of the cruciate ligament. J one Joint Surg r 1999; 81: ergin D, Morrison W, arrino J, Nallamshetty SN, artolozzi R. nterior cruciate ligament ganglia and mucoid degeneration: coexistence and clinical correlation. JR 2004; 182: McIntyre J, Moelleken S, Tirman P. Mucoid degeneration of the anterior cruciate ligament mistaken for ligamentous tears. Skeletal Radiol 2001; 30: Papadopoulou P. The celery stalk sign. Radiology 2007; 245: Roberts, Towers JD, Spangehl MJ, arrino J, Morrison W. dvanced MR imaging of the cruciate ligaments. Magn Reson Imaging lin N m 2007; 15: Stubbs G, Dahlstrom J, Papantoniou P, herian M. orrelation between macroscopic changes of arthrosis and the posterior cruciate ligament histology in the osteoarthritic knee. NZ J Surg 2005; 75: llain J, Goutallier D, Voisin M. Macroscopic and histological assessments of the cruciate ligaments in arthrosis of the knee. cta Orthop Scand 2001; 72: Hodler J, Haghighi P, Trudell D, Resnick D. The cruciate ligaments of the knee: correlation between MR appearance and gross and histologic findings in cadaveric specimens. JR 1992; 159: Viana SL, Fernandes JL, Mendonca JL, Freitas FM. Diffuse intrasubstance signal abnormalities of the posterior cruciate ligament: the counterpart of the mucoid degeneration of the anterior cruciate ligament? case series. JR-TR 2008; 91: Shoji T, Fujimoto E, Sasashige Y. Mucoid degeneration of the posterior cruciate ligament: a case report. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol rthrosc 2010; 18: Rodriguez W Jr, Vinson EN, Helms, Toth P. MRI appearance of posterior cruciate ligament tears. JR 2008; 191: nderson JJ, onnor GF, Helms. New observations on meniscal cysts. Skeletal Radiol 2010; 39: Rubinstein R Jr, Shelbourne KD, Mcarroll JR, VanMeter D, Rettig. The accuracy of the clinical examination in the setting of posterior cruciate ligament injuries. m J Sports Med 1994; 22: Makino, Pascual-Garrido, Rolon, Isola M, Muscolo DL. Mucoid degeneration of the anterior cruciate ligament: MRI, clinical, intraoperative, and histological findings. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol rthrosc 2011; 19: Fealy S, Kenter K, Dines JS, Warren RF. Mucoid degeneration of the anterior cruciate ligament. rthroscopy 2001; 17:E Liu SH, Osti L, Mirzayan R. Ganglion cysts of the anterior cruciate ligament: a case report and review of the literature. rthroscopy 1994; 10: Levine J. ganglion of the anterior cruciate ligament. Surgery 1948; 24: JR:201, ugust
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Mucoid degeneration of the posterior cruciate ligament
 Mucoid degeneration of the posterior cruciate ligament Poster No.: C-2278 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: P. Papadopoulou, I. Kalaitzoglou, I. Tsifoundoudis,
Mucoid degeneration of the posterior cruciate ligament Poster No.: C-2278 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: P. Papadopoulou, I. Kalaitzoglou, I. Tsifoundoudis,
MRI Appearance of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations William Rodriguez, Jr. 1 Emily N. Vinson 1 Clyde. Helms 1 lison P. Toth 2 Rodriguez W Jr, Vinson EN, Helms C,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations William Rodriguez, Jr. 1 Emily N. Vinson 1 Clyde. Helms 1 lison P. Toth 2 Rodriguez W Jr, Vinson EN, Helms C,
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
The Meniscal Roots: Gross Anatomic Correlation with 3-T MRI Findings
 rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
Knee: Cruciate Ligaments
 72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
What s your diagnosis?
 Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
Downloaded from by on 12/22/17 from IP address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.205.8 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.205.8. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay MR Imaging of the natomy of and Injuries
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.205.8 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.205.8. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay MR Imaging of the natomy of and Injuries
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
Rotator Cable: MRI Study of Its Appearance in the Intact Rotator Cuff With Anatomic and Histologic Correlation
 Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel
 ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
MENISCAL INJURY. Meniscus. Anterior Roots. Medial Meniscus. Lateral Meniscus. Posterior Roots. MRI and Arthroscopic Findings
 Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries
 MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears
 Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast Necessary?
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
MRI of Acute Meniscal Injury Associated with Tibial Plateau Fractures: Prevalence, Type, and Location
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Mustonen et al. MRI of Meniscal Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research ntti O. T. Mustonen 1 Mika P. Koivikko 1 Jan Lindahl 2 Seppo K. Koskinen 1 Mustonen
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Mustonen et al. MRI of Meniscal Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research ntti O. T. Mustonen 1 Mika P. Koivikko 1 Jan Lindahl 2 Seppo K. Koskinen 1 Mustonen
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works
 UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
Validation of MRI Classification System for Tibial Stress Injuries
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kijowski et al. MRI lassification for Tibial Stress Injuries Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Richard Kijowski 1 James hoi 2 Kazuhiko Shinki 3 lejandro
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kijowski et al. MRI lassification for Tibial Stress Injuries Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Richard Kijowski 1 James hoi 2 Kazuhiko Shinki 3 lejandro
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
Original Report MR Imaging of Infrapatellar Plica Injury OBJECTIVE. CONCLUSION. Materials and Methods
 R. Lee Cothran 1 Philip M. McGuire 1,2 Clyde A. Helms 1 Nancy M. Major 1 David E. Attarian 3 Received October 25, 2001; accepted after revision October 11, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Box 3808, Duke
R. Lee Cothran 1 Philip M. McGuire 1,2 Clyde A. Helms 1 Nancy M. Major 1 David E. Attarian 3 Received October 25, 2001; accepted after revision October 11, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Box 3808, Duke
n avulsion fracture of the head of the fibula has been described as an important
 Guo-Shu Huang 1 Joseph S. Yu 2 Muhammad Munshi 3 Wing P. Chan 4 Chian-Her Lee 5 Cheng-Yu Chen 1 Donald Resnick 3 Received December 6, 2001; accepted after revision July 30, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology,
Guo-Shu Huang 1 Joseph S. Yu 2 Muhammad Munshi 3 Wing P. Chan 4 Chian-Her Lee 5 Cheng-Yu Chen 1 Donald Resnick 3 Received December 6, 2001; accepted after revision July 30, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology,
LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION
 LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION R. ŚMIGIELSKI, B. DOMINIK, U, ZDANOWICZ, Z. GAJEWSKI, K. SKIERBISZEWSKA, K. SIEWRUK,
LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION R. ŚMIGIELSKI, B. DOMINIK, U, ZDANOWICZ, Z. GAJEWSKI, K. SKIERBISZEWSKA, K. SIEWRUK,
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics
 Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE
 MENISCAL ANATOMY ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE MENISCAL ABNORMALITIES MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL FUNCTION load transmission shock absorption stability The menisci DO NOT function as primary stabilizers
MENISCAL ANATOMY ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE MENISCAL ABNORMALITIES MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL FUNCTION load transmission shock absorption stability The menisci DO NOT function as primary stabilizers
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations
 MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 706241, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/706241 Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst Shoji Fukuta,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 706241, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/706241 Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst Shoji Fukuta,
MRI of ligaments. Ligament biomechanics Spine Shoulder Elbow Hand/wrist Pelvis/hip Knee Foot/ankle
 MRI of ligaments Chang Ho Kang M.D. Korea University Anam Hospital Spine Shoulder Elbow Hand/wrist Pelvis/hip Knee Foot/ankle Introduction Ligament Fibrous connective tissue Attaches bone to bone Holds
MRI of ligaments Chang Ho Kang M.D. Korea University Anam Hospital Spine Shoulder Elbow Hand/wrist Pelvis/hip Knee Foot/ankle Introduction Ligament Fibrous connective tissue Attaches bone to bone Holds
Relationship between Mucoid Degeneration of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament and Posterior Tibial Slope in Patients with Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2016;28(1):34-38 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2016.28.1.34 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Mucoid Degeneration
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2016;28(1):34-38 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2016.28.1.34 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Mucoid Degeneration
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life
 Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life Poster No.: P-0089 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Hirtler, S. Röhrich, F. Kainberger; Vienna/AT Keywords:
Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life Poster No.: P-0089 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Hirtler, S. Röhrich, F. Kainberger; Vienna/AT Keywords:
Original Report. Sonography of Tears of the Distal Biceps Tendon. Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. Adler 3
 Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. dler 3 Received October 15, 1999; accepted after revision March 21, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican Roentgen Ray Society, Washington, DC, May 2000.
Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. dler 3 Received October 15, 1999; accepted after revision March 21, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican Roentgen Ray Society, Washington, DC, May 2000.
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Outcome of Arthroscopic Treatment of Mucoid Degeneration of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:307-314 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.3.307 Outcome of Arthroscopic Treatment of Mucoid Degeneration of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament Diego
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:307-314 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.3.307 Outcome of Arthroscopic Treatment of Mucoid Degeneration of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament Diego
Normal Anatomy and Strains of the Deep Musculotendinous Junction of the Proximal Rectus Femoris: MRI Features
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of the Proximal Rectus Femoris Musculotendinous Junction Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Soterios Gyftopoulos 1 Zehava
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of the Proximal Rectus Femoris Musculotendinous Junction Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Soterios Gyftopoulos 1 Zehava
Anterolateral Ligament. Bradd G. Burkhart, MD Orlando Orthopaedic Center Sports Medicine
 Anterolateral Ligament Bradd G. Burkhart, MD Orlando Orthopaedic Center Sports Medicine What in the world? TIME magazine in November 2013 stated: In an age filled with advanced medical techniques like
Anterolateral Ligament Bradd G. Burkhart, MD Orlando Orthopaedic Center Sports Medicine What in the world? TIME magazine in November 2013 stated: In an age filled with advanced medical techniques like
MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
MRI Characteristics of Healed and Unhealed Peripheral Vertical Meniscal Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kijowski et al. MRI of Peripheral Meniscal Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Richard Kijowski 1 Humberto G. Rosas 1 Kenneth S. Lee 1 rnold Cheung
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kijowski et al. MRI of Peripheral Meniscal Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Richard Kijowski 1 Humberto G. Rosas 1 Kenneth S. Lee 1 rnold Cheung
Intramuscular Rotator Cuff Cysts: Association with Tendon Tears on MRI and Arthroscopy
 Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Palle Lalitha, 1 M. Ch. Balaji Reddy, 1 K. Jagannath Reddy, 1 Vijaya Kumari 2 1 Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Palle Lalitha, 1 M. Ch. Balaji Reddy, 1 K. Jagannath Reddy, 1 Vijaya Kumari 2 1 Department
Differential Diagnosis
 Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review of Treatments
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional
 MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional Isotropic SPACE. Poster No.: C-1792 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.-W. Lee, Y. M. Jeong, J. A. Sim, S. Ahn; Incheon/KR
MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional Isotropic SPACE. Poster No.: C-1792 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.-W. Lee, Y. M. Jeong, J. A. Sim, S. Ahn; Incheon/KR
Elbow Effusions in Trauma in Adults and Children: Is There an Occult Fracture?
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
Imaging the Knee 17/10/2017. Friction syndrome Common in runners or cyclists Fluid between ITB and Lateral femoral condyle
 17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
Diagnostic Utility of MRI and MR Arthrography for Detection of Ligamentum Teres Tears: A Retrospective Analysis of 187 Patients With Hip Pain
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Datir et al. MRI and MR for Ligamentum Teres Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research bhijit Datir 1 Minzhi Xing 1 Jian Kang 2 Paul Harkey 1 parna Kakarala
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Datir et al. MRI and MR for Ligamentum Teres Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research bhijit Datir 1 Minzhi Xing 1 Jian Kang 2 Paul Harkey 1 parna Kakarala
Simon M. Thompson, Tom M. Cross, Meryvn J. Cross & David G. Wood
 Medial meniscal cyst as a cause of painful erosion of the tibial plateau Simon M. Thompson, Tom M. Cross, Meryvn J. Cross & David G. Wood Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy ISSN 0942-2056 Volume
Medial meniscal cyst as a cause of painful erosion of the tibial plateau Simon M. Thompson, Tom M. Cross, Meryvn J. Cross & David G. Wood Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy ISSN 0942-2056 Volume
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177)
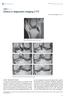 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
High Prevalence of Abnormal MR Findings of the Distal Semimembranosus Tendon: Contributing Factors Based on Demographic, Radiographic, and MR Features
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Yoon et al. MRI of the Distal Semimembranosus Tendon Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Min A Yoon 1 Ja-Young Choi Hyun Kyong Lim Hye Jin Yoo Sung Hwan
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Yoon et al. MRI of the Distal Semimembranosus Tendon Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Min A Yoon 1 Ja-Young Choi Hyun Kyong Lim Hye Jin Yoo Sung Hwan
Sensitivity of MR Arthrography in the Evaluation of Acetabular Labral Tears
 MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
MR Imaging of the Medial Collateral Ligament Bursa: Findings in Patients and Anatomic Data Derived from Cadavers
 Michel De Maeseneer 1 Maryam Shahabpour 1 Frans Van Roy 2 Anita Goossens 3 Filip De Ridder 1 Jan Clarijs 2 Michel Osteaux 1 Received October 9, 2000; accepted after revision April 17, 2001. 1 Department
Michel De Maeseneer 1 Maryam Shahabpour 1 Frans Van Roy 2 Anita Goossens 3 Filip De Ridder 1 Jan Clarijs 2 Michel Osteaux 1 Received October 9, 2000; accepted after revision April 17, 2001. 1 Department
Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions
 KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Periosteal stripping of the MCL
 Periosteal stripping of the MCL Poster o.: P-0014 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. Pedersen; Toensberg/O Keywords: Musculoskeletal soft tissue, Musculoskeletal joint, Anatomy, MR,
Periosteal stripping of the MCL Poster o.: P-0014 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. Pedersen; Toensberg/O Keywords: Musculoskeletal soft tissue, Musculoskeletal joint, Anatomy, MR,
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological
 The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury, is one
 )3( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY EDITORIAL Medial Collateral Ligament Injury; A New Classification Based on MRI and Clinical Findings. A Guide for Patient Selection and Early
)3( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY EDITORIAL Medial Collateral Ligament Injury; A New Classification Based on MRI and Clinical Findings. A Guide for Patient Selection and Early
doi: /j.knee
 doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2013.04.016 Title page (a) title: Oblique coronal and oblique sagittal MRI for diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament tears and evaluation of anterior cruciate ligament remnant tissue
doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2013.04.016 Title page (a) title: Oblique coronal and oblique sagittal MRI for diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament tears and evaluation of anterior cruciate ligament remnant tissue
Subchondroplasty: What the Radiologist Needs to Know
 Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective gten et al. Subchondroplasty Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective hristoph. gten 1,2,3 Daniel J. Kaplan 3,4 Laith M. Jazrawi 3,4 hristopher J. urke 2,3
Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective gten et al. Subchondroplasty Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective hristoph. gten 1,2,3 Daniel J. Kaplan 3,4 Laith M. Jazrawi 3,4 hristopher J. urke 2,3
Key words: arthroscopy, orthopaedic examination, magnetic resonance imaging, knee injury.
 Original paper Videosurgery Arthroscopic verification of objectivity of the orthopaedic examination and magnetic resonance imaging in intra-articular knee injury. Retrospective study Julian Dutka, Michał
Original paper Videosurgery Arthroscopic verification of objectivity of the orthopaedic examination and magnetic resonance imaging in intra-articular knee injury. Retrospective study Julian Dutka, Michał
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2023/14
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2023/14 BEFORE: A. T. Patterson: Vice-Chair HEARING: November 3, 2014 at Toronto Oral DATE OF DECISION: April 17, 2015 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2015
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2023/14 BEFORE: A. T. Patterson: Vice-Chair HEARING: November 3, 2014 at Toronto Oral DATE OF DECISION: April 17, 2015 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2015
Imaging the Athlete s Knee. Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado
 Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
MRI of Osteochondral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle: Incidence and Pattern of Injury After Transient Lateral Dislocation of the Patella
 Sanders et al. MRI of Osteochond ral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:1332 1337 0361 803X/06/1875
Sanders et al. MRI of Osteochond ral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:1332 1337 0361 803X/06/1875
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study
 Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Traumatic and non-traumatic isolated horizontal meniscal tears of the knee in patients less than 40 years of age
 DOI 10.1007/s00590-012-1028-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Traumatic and non-traumatic isolated horizontal meniscal tears of the knee in patients less than 40 years of age Jung-Ryul Kim Byung-Guk Kim Jin-Woo Kim Jin-Hyun
DOI 10.1007/s00590-012-1028-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Traumatic and non-traumatic isolated horizontal meniscal tears of the knee in patients less than 40 years of age Jung-Ryul Kim Byung-Guk Kim Jin-Woo Kim Jin-Hyun
Sport Specific MRI. The symptoms of the majority, if not all sports injuries are experienced when upright, and weight-bearing
 Sport Specific MRI The symptoms of the majority, if not all sports injuries are experienced when upright, and weight-bearing A complete, accurate MRI assessment can only be made when in the position of
Sport Specific MRI The symptoms of the majority, if not all sports injuries are experienced when upright, and weight-bearing A complete, accurate MRI assessment can only be made when in the position of
Sonographic Detection of Baker s Cysts: Comparison with MR Imaging
 Eric E. Ward 1 Jon. Jacobson 2 David P. Fessell 2 Curtis W. Hayes 2 Marnix van Holsbeeck 1 Received June 20, 2000; accepted after revision ugust 14, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican
Eric E. Ward 1 Jon. Jacobson 2 David P. Fessell 2 Curtis W. Hayes 2 Marnix van Holsbeeck 1 Received June 20, 2000; accepted after revision ugust 14, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican
Depiction of Lateral Ligament Complex of the Ankle using 3D MRI in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Chronic Ankle Instability.
 Depiction of Lateral Ligament Complex of the Ankle using 3D MRI in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Chronic Ankle Instability. Satoshi Yamaguchi, M.D. 1, Hiroshi Matsumoto, R.T. 2, Atsuya Watanabe, M.D.
Depiction of Lateral Ligament Complex of the Ankle using 3D MRI in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Chronic Ankle Instability. Satoshi Yamaguchi, M.D. 1, Hiroshi Matsumoto, R.T. 2, Atsuya Watanabe, M.D.
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation
 A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
Ultrasound of the Knee
 Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder
 Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Jin Wan Kim, Youn Soo Hwang, Kyu Pill Moon, Kyung Taek Kim, Joon Yeon Song
 Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.14517/aosm15022 pissn 2289-005X eissn 2289-0068 rthroscopic fixation with a cannulated screw for avulsion fractures of the tibial spine in children: a report of two cases
Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.14517/aosm15022 pissn 2289-005X eissn 2289-0068 rthroscopic fixation with a cannulated screw for avulsion fractures of the tibial spine in children: a report of two cases
MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee
 Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Acute Injury of the Articular Cartilage and Subchondral Bone: A Common but Unrecognized Lesion in the Immature Knee
 Rachel S. Oeppen 1,2 Susan. Connolly 3 Jenny T. encardino 4 Diego Jaramillo 1 Received May 19, 2003; accepted after revision July 28, 2003. 1 Department of Pediatric Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital,
Rachel S. Oeppen 1,2 Susan. Connolly 3 Jenny T. encardino 4 Diego Jaramillo 1 Received May 19, 2003; accepted after revision July 28, 2003. 1 Department of Pediatric Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital,
Posterior Medial Meniscus Root Ligament Lesions: MRI Classification and Associated Findings
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choi et al. MRI of Posterior Medial Meniscus Root Ligament Lesions Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Ja-Young Choi 1 Eric Y. Chang 2,3 Guilherme M. Cunha
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choi et al. MRI of Posterior Medial Meniscus Root Ligament Lesions Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Ja-Young Choi 1 Eric Y. Chang 2,3 Guilherme M. Cunha
Pellegrini-Stieda Syndrome: Report Of Two Cases. M Akinkunmi, S Vijayvargiya, C Prakash, M Kayode, G Awosanya
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 M Akinkunmi, S Vijayvargiya, C Prakash, M Kayode, G Awosanya Citation M Akinkunmi, S Vijayvargiya, C Prakash, M Kayode, G Awosanya.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 M Akinkunmi, S Vijayvargiya, C Prakash, M Kayode, G Awosanya Citation M Akinkunmi, S Vijayvargiya, C Prakash, M Kayode, G Awosanya.. The Internet
Posterior Cruciate Ligament Resection for Ganglion Cyst and Associated Ligament Degeneration
 Case Report & Literature Review Posterior Cruciate Ligament Resection for Ganglion Cyst and ssociated Ligament Degeneration Denis Nam, MD, lec Macaulay, S, Michael Cross, MD, Michael K. Shindle, MD, and
Case Report & Literature Review Posterior Cruciate Ligament Resection for Ganglion Cyst and ssociated Ligament Degeneration Denis Nam, MD, lec Macaulay, S, Michael Cross, MD, Michael K. Shindle, MD, and
BAD RESULTS OF CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF ACL TEARS IN CHILDREN. Guy BELLIER PARIS France
 BAD RESULTS OF CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF ACL TEARS IN CHILDREN Guy BELLIER PARIS France TREATMENT OF ACL TEARS IN CHILDREN CONTROVERSIAL DIAGNOSIS clinical exam X-rays (stress) M.R.I. arthroscopy ACL TEARS
BAD RESULTS OF CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF ACL TEARS IN CHILDREN Guy BELLIER PARIS France TREATMENT OF ACL TEARS IN CHILDREN CONTROVERSIAL DIAGNOSIS clinical exam X-rays (stress) M.R.I. arthroscopy ACL TEARS
Case Report Reverse Segond Fracture Associated with Anteromedial Tibial Rim and Tibial Attachment of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Avulsion Fractures
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9637153, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9637153 Case Report Reverse Segond Fracture Associated with Anteromedial Tibial Rim and Tibial
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9637153, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9637153 Case Report Reverse Segond Fracture Associated with Anteromedial Tibial Rim and Tibial
A comparative study of MRI versus arthroscopic findings in ACL and meniscal injuries of the knee
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
MRI Features of Cortical Desmoid in Acute Knee Trauma
 Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective La Rocca Vieira et al. MRI of ortical Desmoid Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.206.187 on 12/15/17 from
Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective La Rocca Vieira et al. MRI of ortical Desmoid Musculoskeletal Imaging linical Perspective Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.206.187 on 12/15/17 from
