The relationship between hip internal rotation. and groin pain in elite Australian Rules Football. players. Ngaire McKay. Jenny Hynes.
|
|
|
- Scott Bryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The relationship between hip internal rotation and groin pain in elite Australian Rules Football players. Ngaire McKay Jenny Hynes Patrick McLaughlin 1
2 Abstract A prospective study was performed in order to examine the relationship of internal hip rotation to groin pain in Australian Rules Football Players. 101 subjects were tested using a plurimeter placed on the lateral aspect of the tibia whilst lying prone on a plinth. Subjects were tested twice at an interval of six weeks and episodes of groin pain that occurred between the first and second testing dates were recorded. In players who experienced bilateral groin pain in the six week period between testing a loss of internal rotation was found. In contrast an increase in rotation was found in players suffering from unilateral groin pain. Though the degree of change in rotation was not found to be statistically significant, a definite trend was identifiable. A high rate of recurrence of groin injuries was also found. This study may have implications for the treatment and prevention of groin injuries in the athletic population and in particular Australian Rules football players. 2
3 Introduction Diagnosis of groin pain especially osteitis pubis (OP) is an area of ongoing concern and frustration to medical practitioners in the sporting field (Andrews and Carek 1998). The incidence of groin strains and osteitis pubis consistently rose in the AFL between seasons Each AFL club averaged an incidence of 3.9 new groin strains or osteitis pubis cases per season in 2002, compared to 3.5 new cases in 2001 and 3 new cases per club per year in In the season 2002, groin strains and osteitis pubis were second only to anterior cruciate ligament injuries in terms of number of matches missed (Orchard and Seward 2002). First described by Beer in 1924, OP is not a new condition (Rodriguez et al 2001). In the athletic population OP was first documented by Spinelli in 1932 who noted the condition in fencers (Vitanzo et al 2001). Fricker et al (1991) described OP as groin pain that emanates from the area of the pubic symphysis including the lower rectus abdominis and upper adductors. Pain is reported during and or after exercise (particularly running and or kicking) and the most common clinical sign is tenderness on palpation of the pubic bones and or pubic symphysis. Clinical diagnosis may be supported by radiological findings on MRI such as increased signal intensity within the pubic bone marrow and irregularity of the pubic symphysis (Verrall et al, 2001). In some cases, standard AP radiographs of the pelvis will display erosion, resorption, and sclerosis of the pubic bones (Holt et al, 1995). However, in early or mild disease radiographic findings may be normal (Morelli and Smith 2001). Early diagnosis is vital and according to Vitanzo et al (2001), diagnosis of OP should be considered immediately in any active patient presenting with persistent abdominal, pelvic or groin pain. Other groin injuries include adductor strains, adductor tendonitis, 3
4 osteomyelitis and fracture of the pubic symphysis. Though considered to be of unknown etiology (Batt et al 1995), there are a number of suggested contributing factors for both groin pain and OP. One such factor is periosteal trauma which may result from a variety of causes which include direct force or microtrauma related to athletic activity (Williams et al 2000). OP may also occur as a result of infection, inflammation or injury (Fricker et al 1991) and has been associated with parturition, trauma, non-urologic surgery, urinary tract infections and arthritic disorders (Vitanzo et al 2001). For the purposes of this study we are only concerned with groin pain in the athletic population. In a study of 59 patients, including 50 male patients presenting to sports medicine clinics having been diagnosed as having OP, Fricker et al (1991) noted that on examination men experienced tenderness over one or both of the superior pubic ramii, and had decreased hip rotation which was either unilateral or bilateral. Although the loss of internal rotation was noted the authors were not able to conclude if the loss had predisposed subjects to the condition or was a result of it. Thus the need for a prospective study as opposed to a retrospective study was presented. The authors also suggest that pelvic malalignment and sacroiliac dysfunction may play a role, but this was not investigated within this study. Highlighting the chronic nature of the condition, Fricker et al reported an average recovery time of 15 months. Morelli and Smith (2001) noted the possible implication of decreased internal hip range of motion and fixation of the sacroiliac joint as causing excessive stress on the pubic symphysis and OP as a possible sequale. Rodriguez et al. (2001) proposed shear stress at the symphysis as being capable of causing sacroiliac dysfunction in osteitis pubis sufferers if hip internal rotation is limited in either flexion or extension. As this study 4
5 was based on a single case study, however, it has poor external validity when applied to a larger population. Gilbert et al (2001) investigated passive hip rotation in elite Australian Rules footballers. Seventy nine (79) players aged years were tested in the study. The authors undertook a number of testing procedures in order to determine a reliable clinical test that, allowed for reproducibility in the clinical setting, whilst establishing normative data for the sample population. The authors found measurement of hip internal rotation to be reliable when using a method they developed based on past clinical tests. This method involved the subject lying prone in 0 of hip flexion, and measuring hip internal rotation using a plurimeter. The research concluded that the clinical test could be the basis for ongoing research into the effect of hip rotation in Australian Rules Footballers with respect to hip/groin/pelvic injury (Gilbert et al 2001). In the aforementioned study Gilbert et al (2001) noted a significant difference in the mean values for the players who had a history of groin injury compared to those with no history of groin pain, for passive internal rotation of the hip when measured at 90 0 of hip flexion. Players with a past history of groin pain were found to have decreased ROM bilaterally, compared to those without a history of groin pain. These findings warrant further investigation. No significant difference was found when considering leg dominance of the sample population. Though some authors refer to the influence of limited hip range of motion, the evidence appears to be anecdotal, observed during research into other possible 5
6 mechanisms rather than as primary research focused on hip internal rotation and its influence on groin pain (Fricker et al1991, Morelli and Smith 2001, Rodriguez et al 2001). They report a loss of internal rotation in one or both hips to be found in those with OP. Whether or not loss of rotation is the cause or result of groin pain is as yet unclear. This study aimed to establish whether a relationship between groin pain and hip internal rotation may exist. Limitations were also present in that none of the research into groin pain appears to describe how the limitation of hip rotation was measured. Ongoing research is required to further investigate these factors, and possibly make an impact on the prevention and management of the condition. 6
7 Methods Participants were Australian Rules players from three Melbourne based Australian Football League clubs. Any player on the club s list who was physically capable of performing the testing procedure was included in the study, regardless of concurrent injuries. To be included in the study, players were required to be available for both testing dates six weeks apart. A total of 101 players were tested. Of those players involved in the study, the youngest was 18 years of age, and the oldest player 31 years of age. The mean age was 22.7 ± 3.52 years. Players weight varied from 74.5kg to 120kg with a mean of ± 9.07kg. Players filled out a questionnaire prior to first round testing. The questionnaire included a general player profile, lower limb and groin injury history, as well as current injury status. All players signed an informed consent form and the study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee. Testing was performed on two separate occasions during the AFL season. The first testing date was just after the midseason break, with the subsequent testing date being in the second last round of the season, six weeks following 1 st round testing. The AFL has a home and away season of 22 rounds. Measurements were taken using a procedure adapted from Gilbert et al (2001), which were as follows: Participants were asked to stand comfortably with their feet hip width apart. The distance between the mid-points of each popliteal fossa was measured and recorded. A plurimeter was placed on the lateral part of each tibia, just superior to the lateral malleolus and an angle was recorded. 7
8 Participants were then instructed to lie prone on a treatment table with their feet hanging slightly off the edge of the table. For the purposes of consistency, the distance between the two popliteal fossas was required to be the same when prone as it had been with the participant standing. To ensure the pelvis remained level during hip rotation a spirit level was placed on the participant s sacrum at approximately the level of the posterior superior iliac spines. Participants were then instructed to completely relax in order for the tester to passively flex the knees. The plurimeter was placed on the lateral aspect of the tibia before internally rotating the hips and an angle recorded at the end of passive hip rotation as palpated by the tester. In order to calculate total hip internal rotation, the standing angle of the tibia is added to the prone angle. Insert Figure 1 here Six weeks following initial testing, the tester returned to each club and performed subsequent measurements, following the same procedure. Participants were also asked at this time to verbally report any episodes of groin pain, which they had experienced since the previous testing date to the tester, who in turn recorded the information on to the survey. 8
9 Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version Inter and intra-rater reliabilities of the testing procedure were calculated using a Pearson Correlation. A one way between groups ANOVA with post hoc comparisons was performed in order to establish significance of the data including change in rotation on the right and left legs and changes in asymmetry between the right and left legs from the first to the second testing dates. SPSS was used to draw mean plots for easier visual analysis of the data. 9
10 Results To enhance reliability of the results, intra and inter-rater reliability was assessed prior to testing. For the intra-rater reliabilities the sample population was taken at random from a local football team. A Pearson correlation co-efficient of r = 0.85 was reported when the above method was repeated twice on 10 players, 10 minutes apart. Interrater reliability was performed with another tester proficient in the testing procedure. Pearson s r was calculated at an overall value of For this part of the study, 10 students were assessed by each tester, two minutes apart. On the right leg, the maximum internal rotation recorded was 50, whilst the lowest rotation was 8. On the left leg the maximum internal rotation was recorded at 50, and the minimum was 6. Insert Table 1 here There was minimal variation in hip rotation from the general population of subjects when compared with those with a history of groin pain, or groin pain experienced between testing dates (Table 1). This represents a non significant difference. Of the 101 subjects tested, 48 (47.5%) had previously reported a history of groin injury lasting for 3 or more weeks. During this study eighteen (18) players reported experiencing groin pain in the 6week period between the first and second measurements. In those who developed groin pain, 3 reported groin pain on the left side, 6 on the right side and 9 players experienced bilateral groin pain. 10
11 Figure 2.1 shows the change in right hip rotation from the first to the second testing date in those who had experienced groin pain. Internal rotation of the right hip decreased for those players who experienced bilateral groin pain, varied very little in those players that experienced right sided groin pain and increased by a mean of 2.33 in those with left sided groin pain. Insert Figure 2.1 here Insert Figure 2.2 here Figure 2.2 shows the difference in left hip rotation from the first to the second measurements in those players who had reported experiencing groin pain between testing dates. Those who experienced bilateral groin pain had a decrease in their left hip rotation, whilst those with unilateral right or left sided groin pain were shown to have some increase in their hip rotation. All changes were non-significant. Insert Figure 2.3 here Insert Figure 2.4 here Figure 2.4 shows the average difference between right and left hip internal rotation in those players who experienced groin pain in the six weeks between measurements, as measured in the second round of testing. Those who reported experiencing pain in their left groin, show a 5.3 variation in rotation from their left to right legs. Subjects reporting right sided groin pain had an asymmetry of 2.5 and those with bilateral pain were asymmetrical by 1.3, this appears as a negative on the graph as the first number was smaller than the second. Subjects with groin pain in the second round of testing had a mean increase in asymmetry by almost 2 when compared to first round testing. First round measurements of asymmetry between the right and left legs are shown in Figure 2.3. The trends are very similar from the first to the second testing 11
12 date. Those with bilateral groin pain did however have a greater asymmetry on the first testing date, compared with the second. This may be indicative of asymmetry between the right and left hips having an influence on the development of groin pain. 12
13 Discussion One hundred and one (101) participants took part in this study. Of these, 47.5% reported a previous episode of groin pain lasting for three or more weeks. This finding is consistent with other studies of groin pain in Australian Rules Footballers. One such study reported groin pain as being experienced in 45% of tested AFL subjects (Verrall et al 2001). In this study, 18 players (17.8%) experienced groin pain in the 6 week period between testing dates, 13 of the 18 had a past history of groin pain lasting 3 or more weeks. Of the 13, nine players had experienced no groin pain for more than a year prior to their current injury. This supports the high rate of recurrence reported by many including the AFL s own Injury Report. The present study suggests a recurrence rate of 72%. When taking into account players who had experienced groin pain earlier in the current season, a recurrence rate of 50% is seen. This figure is higher than what has been previously reported in other studies. There were five cases of groin pain which had developed with no prior history. Changes in internal hip rotation over the six week period were not found to be statistically significant, though some trends can be seen. Players who experience bilateral groin pain were shown to have a loss of internal rotation in both the left and right hips. Those with unilateral groin pain had an increase in rotation in both legs regardless of which side the pain was reported on. It does however appear that the increase in rotation will be greatest on the side of the reported pain. The incidence of groin pain in the sporting population is thought to comprise between 2 and 5 percent of all sporting injuries and is more prevalent in athletes participating in sports such as ice hockey, long distance running, skiing and high jumping (Morelli and Smith 2001). It may comprise as many as 5-7% of all injuries in soccer players (Morelli and Smith 13
14 2001). Rodriguez et al (2001) also report that osteitis pubis represented 3-5% of all injuries sustained in a professional soccer team over an eight year period. These figures are similar to those reported to have occurred in the AFL injury report between 1997 and 2002 with groin strains and osteitis pubis representing between 3-4 percent of injuries (Orchard and Seward 2002). Although hip rotation has been proposed in various studies as a predisposing factor to developing groin pain across a number of sporting activities (soccer, Australian rules football, long distance running and ice hockey), it has never been formally investigated (Fricker et al 1991, Gilbert et al 2001, Morelli and Smith 2001 and Rodriguez et al 2001). There remains a paucity in the literature with respect to mechanisms of injury in the development of groin pain, especially osteitis pubis. Some limitations exist in this study. Firstly the six week time frame between initial and follow up testing may not have been sufficient to gauge the degree of change in internal hip rotation. Given that the majority of cases of osteitis pubis were reported to occur during pre season, in future studies it would be advisable to have base line measurements performed prior to the pre season, then again before the beginning of the season proper and finally at the end of the home and away season. This would allow for a much better representation of any changes in rotation. This study focused only on hip internal rotation and its implications for groin pain. Although it is likely that hip internal rotation does play a role in groin pain and osteitis pubis, it remains a multifactorial problem and a multitude of other factors need to be clinically considered for these patients. 14
15 Conclusion The link between groin pain and hip internal rotation remains unclear. Trends identified in this study suggest that groin pain and osteitis pubis may be influenced by hip internal rotation, however further investigation is required in order to understand the clinical significance and the reasons for bilateral groin pain being responsible for a decrease in hip internal rotation whilst unilateral pain appears to increase hip internal rotation. Ongoing research is crucial in order to broaden the current understanding of mechanisms of injury contributing to groin pain. 15
16 References Batt ME et al (1995): Osteitis pubis in collegiate football players. Medical Journal of sports exercise 27(5): Fricker PA et al (1991): Osteitis pubis in athletes. Infection, inflammatory or injury? Sports medicine 12(4): Gilbert et al (2001): Passive Hip Rotation Range of Motion in Elite Australian Rules Footballers. Masters in Manipulative Physiotherapy, University of South Australia. Morelli and Smith (2001): Groin injuries in athletes. American Family Physician 64(8): O Kane (1999): Anterior hip pain. American Family Physician 60(6): Orchard and Seward (2002): AFL Injury Report. Rodriguez, Christina et a.l (2001): Osteitis pubis syndrome in the professional soccer athlete: A case report. Journal of Athletic Training 36(4): Verrall, GM et al. (2001): Incidence of pubic marrow oedema in Australian rules football players: relation to groin pain. British Journal of Sport Medicine 35(1): Vitanzo et al (2001): Solving a perplexing problem. The Physician and Sportsmedicine 29(7): Williams et al (2000): Osteitis pubis and instability of the pubic symphysis: when nonoperative measures fail. The American Journal of Sports Medicine 28(3):
17 Figure 1 Plurimeter placed on lateral shin 17
18 Table 1: Mean Internal Hip Rotation of Sample Population compared with those with a History of Groin Pain of Greater than 3 or more Weeks. Mean internal hip rotation 1 st Testing Date 2 nd Testing Date Right hip (all players, n = 101) Left Hip (all players n = 101) Right hip (subjects with >3 week history of groin pain, n = 48) Left hip (subjects with >3 week history of groin pain, n = 48) Right hip (players without groin pain in the 6 weeks between testing, n = 83) Left hip (players without groin pain in the 6 weeks between testing, n = 83) Right Hip (players who experienced groin pain in the six weeks between testing, n = 18) Left Hip (players who experienced groin pain in the six weeks between testing, n = 18)
19 2Mean of DiffR Figure 2.1 Difference of Right Hip Internal Rotation between Measurements in Players Experiencing Groin Pain yes, left Yes, right Yes, Bilateral injury between 1st and 2nd 19
20 Figure 2.2 Difference of Left Hip Internal Rotation between Measurements in Players Experiencing groin pain Mean of DiffL yes, left Yes, right Yes, Bilateral injury between 1st and 2nd 20
21 8Mean of RvLdiff Figure Asymmetry between Right and Left Hip Internal Rotation Found in First Round Testing in players with groin pain yes, left Yes, right Yes, Bilateral injury between 1st and 2nd 21
22 6Mean of RvLdiff2 Figure 2.4 Asymmetry between Right and Left Hip Internal Rotation Found in Second Round Testing in players with groin pain yes, left Yes, right Yes, Bilateral injury between 1st and 2nd 22
Doc, I've done my groin. Groin Pain. Peter Brukner. Doc, I've done my groin 1. acute chronic
 Doc, I've done my groin Peter Brukner Associate Professor in Sports Medicine Centre for Sports Medicine Research and Education School of Physiotherapy 9/22/2006 The University of Melbourne Groin Pain acute
Doc, I've done my groin Peter Brukner Associate Professor in Sports Medicine Centre for Sports Medicine Research and Education School of Physiotherapy 9/22/2006 The University of Melbourne Groin Pain acute
PREVIEW ONLY 3/04/2013. Andrew Ellis. Dr John Read IMAGING OF GROIN PAIN. Click to minimize panel and see whole screen
 Be sure to convert to your own time zone at Andrew Ellis BSc (Ex. Sci), M. Phty IMAGING OF GROIN PAIN World Health Webinars CEO World Health Webinars (Australia/NZ) Host Presented by: Dr John Read Will
Be sure to convert to your own time zone at Andrew Ellis BSc (Ex. Sci), M. Phty IMAGING OF GROIN PAIN World Health Webinars CEO World Health Webinars (Australia/NZ) Host Presented by: Dr John Read Will
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS
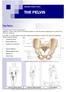 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS The Pelvis The pelvis has 3 joints connecting it together 2 sacro-iliac joints at the back (posterior) and the pubic symphysis joint which is at the front (anterior). A
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS The Pelvis The pelvis has 3 joints connecting it together 2 sacro-iliac joints at the back (posterior) and the pubic symphysis joint which is at the front (anterior). A
11/11/2016. Hip FAI & Core Muscle Deficiency: Diagnosis and Treatment. Disclosures. Differential Diagnosis. Consultant, Smith and Nephew
 Hip FAI & Core Muscle Deficiency: Diagnosis and Treatment FORE Baseball Sports Medicine Game-Changing Concepts November 4, 2016 T. Sean Lynch, MD Assistant Professor New York-Presbyterian/ Columbia University
Hip FAI & Core Muscle Deficiency: Diagnosis and Treatment FORE Baseball Sports Medicine Game-Changing Concepts November 4, 2016 T. Sean Lynch, MD Assistant Professor New York-Presbyterian/ Columbia University
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
G roin pain is associated with many sports and
 446 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical examination of athletes with groin pain: an intraobserver and interobserver reliability study PHölmich, L R Hölmich, A M Bjerg... Br J Sports Med 2004;38:446 451. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2003.004754
446 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical examination of athletes with groin pain: an intraobserver and interobserver reliability study PHölmich, L R Hölmich, A M Bjerg... Br J Sports Med 2004;38:446 451. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2003.004754
G roin pain is associated with many sports and
 446 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical examination of athletes with groin pain: an intraobserver and interobserver reliability study PHölmich, L R Hölmich, A M Bjerg... See end of article for authors affiliations...
446 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical examination of athletes with groin pain: an intraobserver and interobserver reliability study PHölmich, L R Hölmich, A M Bjerg... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Tier 2 MSK Clinic GP Message of the Month June Sportsman s groin (inguinal disruption).
 Tier 2 MSK Clinic GP Message of the Month June 2014 Sportsman s groin (inguinal disruption). This month s MoM presents a case of bilateral inguinal disruption (ID) presenting as chronic (right) groin pain.
Tier 2 MSK Clinic GP Message of the Month June 2014 Sportsman s groin (inguinal disruption). This month s MoM presents a case of bilateral inguinal disruption (ID) presenting as chronic (right) groin pain.
Connecting the Core. Rationale. Physiology. Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS. Athletes have been inundated with terminology
 Connecting the Core Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS Athletes have been inundated with terminology and references to core development in recent years. However, little has been conveyed to these athletes on what
Connecting the Core Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS Athletes have been inundated with terminology and references to core development in recent years. However, little has been conveyed to these athletes on what
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know
 Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know Üstün Aydıngöz, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara, Turkey ustunaydingoz@yahoo.com No conflicts of interest
Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know Üstün Aydıngöz, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara, Turkey ustunaydingoz@yahoo.com No conflicts of interest
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001)
 Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
A Prediction model for the prevention of soccer injuries amongst
 A Prediction model for the prevention of soccer injuries amongst youth players SUMMARY Background: Football (Soccer) is arguably the most popular sport in the international sporting arena. A survey conducted
A Prediction model for the prevention of soccer injuries amongst youth players SUMMARY Background: Football (Soccer) is arguably the most popular sport in the international sporting arena. A survey conducted
Lower Limb. Hamstring Strains. Risk Factors. Dr. Peter Friis 27/04/15. 16% missed games AFL 6-15% injury in rugby 30% recurrent
 Lower Limb Dr. Peter Friis MB BS FACSP Sports Physician Hamstring Strains 16% missed games AFL 6-15% injury in rugby 30% recurrent Risk Factors Modifiable Warm up Fatigue Strength Flexibility L/Spine Pelvic
Lower Limb Dr. Peter Friis MB BS FACSP Sports Physician Hamstring Strains 16% missed games AFL 6-15% injury in rugby 30% recurrent Risk Factors Modifiable Warm up Fatigue Strength Flexibility L/Spine Pelvic
emoryhealthcare.org/ortho
 COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER. Planes of Lumbar Pelvic Femoral (Back, Pelvic, Hip) Muscle Function
 BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
Sports Medicine and Radiology
 Sports Medicine and Radiology The judicious utilization of a thorough history and physical examination and appropriately applied imaging studies will allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of athletic
Sports Medicine and Radiology The judicious utilization of a thorough history and physical examination and appropriately applied imaging studies will allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of athletic
Dr Sanjay Pandanaboyana
 Dr Sanjay Pandanaboyana General and Laparoscopic Surgeon Specialist General Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgeon Auckland 16:30-16:50 It's Just a Hernia! Its just a hernia! Mr. Sanjay Pandanaboyana MS,
Dr Sanjay Pandanaboyana General and Laparoscopic Surgeon Specialist General Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgeon Auckland 16:30-16:50 It's Just a Hernia! Its just a hernia! Mr. Sanjay Pandanaboyana MS,
6/05/2018. Aspetar, Qatar. Why the Bermuda triangle of Sports Medicine?
 Why the Bermuda triangle of Sports Medicine? Complex anatomy Mul factorial ae ology diagnos c difficulty Variability in terminology/classification systems Clinical reasoning for hip and groin pain navigating
Why the Bermuda triangle of Sports Medicine? Complex anatomy Mul factorial ae ology diagnos c difficulty Variability in terminology/classification systems Clinical reasoning for hip and groin pain navigating
Hip Pain in the Athlete: A Diagnostic Challenge
 : A Diagnostic Challenge Matthew Gimre MD Sports Medicine 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Conference Presented June 17, 2017 on: Month day, Year Presented to: Insert relevant presenter information Calibri
: A Diagnostic Challenge Matthew Gimre MD Sports Medicine 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Conference Presented June 17, 2017 on: Month day, Year Presented to: Insert relevant presenter information Calibri
CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT
 SPORTS REHABILITATION CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT A case study and rationale for treatment Written by Joanne Kemp and Kay Crossley, Australia BACKGROUND The hip joint and FAI
SPORTS REHABILITATION CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT A case study and rationale for treatment Written by Joanne Kemp and Kay Crossley, Australia BACKGROUND The hip joint and FAI
Differential diagnosis of hip and groin pain in athletes. Kristian Thorborg, Specialist in Sportsphysiotherapy, Ph.D., Post-doctoral fellow
 Differential diagnosis of hip and groin pain in athletes Kristian Thorborg, Specialist in Sportsphysiotherapy, Ph.D., Post-doctoral fellow , Denmark City Arthroscopic Centre Amager, University Amager Airport
Differential diagnosis of hip and groin pain in athletes Kristian Thorborg, Specialist in Sportsphysiotherapy, Ph.D., Post-doctoral fellow , Denmark City Arthroscopic Centre Amager, University Amager Airport
Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes
 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes John P Salvo, MD Sports Medicine Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA EATA Annual Meeting January, 2011 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Anatomy History Physical Exam
Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes John P Salvo, MD Sports Medicine Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA EATA Annual Meeting January, 2011 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Anatomy History Physical Exam
5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival. 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: Back
 Low Back Pain 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: Back Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn by the start of class, we'll have you out of
Low Back Pain 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: Back Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn by the start of class, we'll have you out of
Incidence of pubic bone marrow oedema in Australian rules football players: relation to groin pain
 28 SPORTSMEDvSA Sports Medicine Clinic, Adelaide, Australia G M Verrall Department of Radiology, Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide J P Slavotinek Perrett Medical Imaging, Adelaide GTFon Correspondence
28 SPORTSMEDvSA Sports Medicine Clinic, Adelaide, Australia G M Verrall Department of Radiology, Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide J P Slavotinek Perrett Medical Imaging, Adelaide GTFon Correspondence
 GROIN DISRUPTION MR O J A GILMORE MS FRCS FRCS (ED) F. INST. SPORTS MED. 5% ALL SPORTS INJURIES AFFECT GROIN PATIENT S REFERRED with GROIN PAIN 1980-2008 TOTAL 7273 MALE 7030 (97%) FEMALE 273 (3%) PATIENT
GROIN DISRUPTION MR O J A GILMORE MS FRCS FRCS (ED) F. INST. SPORTS MED. 5% ALL SPORTS INJURIES AFFECT GROIN PATIENT S REFERRED with GROIN PAIN 1980-2008 TOTAL 7273 MALE 7030 (97%) FEMALE 273 (3%) PATIENT
STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN
 STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN Written by Kristian Thorborg, Denmark INTRODUCTION Hip and groin pain is a common problem often related to physical functioning and sports activities.
STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN Written by Kristian Thorborg, Denmark INTRODUCTION Hip and groin pain is a common problem often related to physical functioning and sports activities.
3 Movements of the Trunk. Flexion Rotation Extension
 3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Hip and groin pain in athletes Tak, I.J.R. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Hip and groin pain in athletes Tak, I.J.R. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Tak, I. J. R. (2017). Hip and groin pain in athletes: Morphology,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Hip and groin pain in athletes Tak, I.J.R. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Tak, I. J. R. (2017). Hip and groin pain in athletes: Morphology,
Information within the handout. Brief Introduction Anatomy & Biomechanics Assessment & Diagnosis Treatment through Muscle Energy
 Manual Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment for Somatic Dysfunction of the Pelvis Through Muscle Energy Greenman s Priciples of Manual Medicine (5 th Ed.)- Lisa DeStefano,DO Speaker disclosure I declare I
Manual Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment for Somatic Dysfunction of the Pelvis Through Muscle Energy Greenman s Priciples of Manual Medicine (5 th Ed.)- Lisa DeStefano,DO Speaker disclosure I declare I
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These
7) True/False: Rigid motor strategies are the most effective way to handle high forces
 The Sacro-Iliac Joint 1) Which of the following make up part of the SIJ provocative physical examination? A. Gaenslen s, FABERS, stork, joint distraction B. Fortin finger test, joint compression, thigh
The Sacro-Iliac Joint 1) Which of the following make up part of the SIJ provocative physical examination? A. Gaenslen s, FABERS, stork, joint distraction B. Fortin finger test, joint compression, thigh
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics)
 Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
REPETITIVE STRESS SYNDROME AND ITS EFFECTS ON THE LOWER PELVIS
 REPETITIVE STRESS SYNDROME AND ITS EFFECTS ON THE LOWER PELVIS Kim Turney Body Arts and Science International Comprehensive Global Feb 2018 London, UK ABSTRACT In many lines of work people are subjected
REPETITIVE STRESS SYNDROME AND ITS EFFECTS ON THE LOWER PELVIS Kim Turney Body Arts and Science International Comprehensive Global Feb 2018 London, UK ABSTRACT In many lines of work people are subjected
POSTURE ANALYSIS. What is good posture?
 POSTURE ANALYSIS What is good posture? Posture is the position in which you hold your body upright against gravity while standing or sitting. Good posture involves training your body to stand, walk, sit
POSTURE ANALYSIS What is good posture? Posture is the position in which you hold your body upright against gravity while standing or sitting. Good posture involves training your body to stand, walk, sit
THE ROLE OF THE MID-TORSO IN SPEED DEVELOPMENT
 THE ROLE OF THE MID-TORSO IN SPEED DEVELOPMENT The mid-torso is made up of 4 major muscle groups: 1. Rectus Abdominus Origin Base of sternum and bottom ribs Insertion Pubis bone (as part of the pelvis)
THE ROLE OF THE MID-TORSO IN SPEED DEVELOPMENT The mid-torso is made up of 4 major muscle groups: 1. Rectus Abdominus Origin Base of sternum and bottom ribs Insertion Pubis bone (as part of the pelvis)
AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM
 AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or providers of commercial services discussed in this CME
AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or providers of commercial services discussed in this CME
Football and netball season A review of the apophysis and the acute shoulder: assessment. Simon Locke Sport and Exercise Physician
 Football and netball season A review of the apophysis and the acute shoulder: assessment Simon Locke Sport and Exercise Physician Apophyseal injuries; How to diagnose and manage? Goals for tonight Recognise
Football and netball season A review of the apophysis and the acute shoulder: assessment Simon Locke Sport and Exercise Physician Apophyseal injuries; How to diagnose and manage? Goals for tonight Recognise
Apophysiolysis of the pelvic area in adolescents.
 Apophysiolysis of the pelvic area in adolescents. Poster No.: C-0077 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Derks, R. E. Westerbeek, R. Van Dijk; Deventer/NL Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Apophysiolysis of the pelvic area in adolescents. Poster No.: C-0077 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Derks, R. E. Westerbeek, R. Van Dijk; Deventer/NL Keywords: Musculoskeletal
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention. Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS
 ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
Lateral knee injuries
 Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast episode 051 with Matt Konopinski Get your free trial of online Physio education at Orthopaedic timeframes Traditionally Orthopaedic
Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast episode 051 with Matt Konopinski Get your free trial of online Physio education at Orthopaedic timeframes Traditionally Orthopaedic
The Footballers 7 Deadly Sins
 The Footballers 7 Deadly Sins CONTENTS 1. Not enough core strength 2. Not enough balance retraining 3. Not enough hamstring strength 4. Too many ACL Injuries 5. Not enough flexibility/warming up 6. Not
The Footballers 7 Deadly Sins CONTENTS 1. Not enough core strength 2. Not enough balance retraining 3. Not enough hamstring strength 4. Too many ACL Injuries 5. Not enough flexibility/warming up 6. Not
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
BACK SPASM. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
Static Back. Instructions: Purpose: Hold this ecise for 05 min. prepared for Pain Free Posture MN
 1 Static Back Hold this ecise for 05 min. 1. Lie on your back with your legs up over a block or chair 2. Place your arms out to the sides at 45 degrees from your body with palms up 3. Relax your upper
1 Static Back Hold this ecise for 05 min. 1. Lie on your back with your legs up over a block or chair 2. Place your arms out to the sides at 45 degrees from your body with palms up 3. Relax your upper
Pilates for Brachialis Tendonitis (Tennis Elbow)
 Pilates for Brachialis Tendonitis (Tennis Elbow) Sally Dunford September 2017 Wimbledon, UK Abstract Tennis Elbow is a term used to describe a painful condition in which the tendons of the elbow are overloaded
Pilates for Brachialis Tendonitis (Tennis Elbow) Sally Dunford September 2017 Wimbledon, UK Abstract Tennis Elbow is a term used to describe a painful condition in which the tendons of the elbow are overloaded
Ricki Shah, M.D., Nirav Shelat, D.O., Georges Y. El-Khoury, M.D., D. Lee Bennett, M.A., M.B.A., M.D.
 vulsion Injuries of the Pelvis Ricki Shah, M.D., Nirav Shelat, D.O., Georges Y. El-Khoury, M.D., D. Lee ennett, M.., M..., M.D. Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology, University of Iowa Hospitals & linics,
vulsion Injuries of the Pelvis Ricki Shah, M.D., Nirav Shelat, D.O., Georges Y. El-Khoury, M.D., D. Lee ennett, M.., M..., M.D. Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology, University of Iowa Hospitals & linics,
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT ***
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
Approaching the Irritable Hip antero-medial hip and groin pain
 Approaching the Irritable Hip antero-medial hip and groin pain Dr John P Best, FACSP, FFSEM Sports and Exercise Medicine Conjoint Lecturer UNSW Antero-medial Hip and Groin Pain Incidence and Causes 5-10%
Approaching the Irritable Hip antero-medial hip and groin pain Dr John P Best, FACSP, FFSEM Sports and Exercise Medicine Conjoint Lecturer UNSW Antero-medial Hip and Groin Pain Incidence and Causes 5-10%
Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic. Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack
 Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack Developed by: Mark Jansz (Health & Fitness Advisor) AV Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Version
Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack Developed by: Mark Jansz (Health & Fitness Advisor) AV Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Version
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
Apophysis. Apophyseal Avulsion. Apophyseal avulsion injuries 3/2/2017
 Apophysis 0 Differentiate from Epiphysis: The end of long bones which undergo endochondral ossification to produce longitudinal growth of the bones. i.e. growth plates 0 Apophysis refers to any eminence,
Apophysis 0 Differentiate from Epiphysis: The end of long bones which undergo endochondral ossification to produce longitudinal growth of the bones. i.e. growth plates 0 Apophysis refers to any eminence,
Movement Patterns and Muscular Function Before and After Onset of Sports-Related Groin Pain: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis.
 Movement Patterns and Muscular Function Before and After Onset of Sports-Related Groin Pain: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Kloskowska, P; Morrissey, D; Small, C; Malliaras, P; Barton, C The Author(s)
Movement Patterns and Muscular Function Before and After Onset of Sports-Related Groin Pain: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Kloskowska, P; Morrissey, D; Small, C; Malliaras, P; Barton, C The Author(s)
A rotator cuff injury is a strain or tear in the group of tendons and muscles that hold your shoulder joint together and help move your shoulder.
 Rotator Cuff Injury What is a rotator cuff injury? A rotator cuff injury is a strain or tear in the group of tendons and muscles that hold your shoulder joint together and help move your shoulder. How
Rotator Cuff Injury What is a rotator cuff injury? A rotator cuff injury is a strain or tear in the group of tendons and muscles that hold your shoulder joint together and help move your shoulder. How
Sports Hernias. Matthew Gimre, MD ATC Conference, June 20, 2015
 Sports Hernias Matthew Gimre, MD ATC Conference, June 20, 2015 Sports hernia: So what is it? An injury to the rectus abdominis-common adductor aponeurosis, at the anterior/inferior aspect of the pubic
Sports Hernias Matthew Gimre, MD ATC Conference, June 20, 2015 Sports hernia: So what is it? An injury to the rectus abdominis-common adductor aponeurosis, at the anterior/inferior aspect of the pubic
Hip & Groin pain. M Hassabi (MD) Assistant professor Department of Sports & Exercise Medicine Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences
 Hip & Groin pain M Hassabi (MD) Assistant professor Department of Sports & Exercise Medicine Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences EPIDEMIOLOGY Groin pain and injury is common with sports that
Hip & Groin pain M Hassabi (MD) Assistant professor Department of Sports & Exercise Medicine Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences EPIDEMIOLOGY Groin pain and injury is common with sports that
APPROACH TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF GROIN PAIN. Alexandra Myers, D.O., M.S.H.S. February 22, 2018 OPSC Annual Convention
 APPROACH TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF GROIN PAIN Alexandra Myers, D.O., M.S.H.S. February 22, 2018 OPSC Annual Convention OVERVIEW Review the entities that may contribute to groin pain Discuss the approach to making
APPROACH TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF GROIN PAIN Alexandra Myers, D.O., M.S.H.S. February 22, 2018 OPSC Annual Convention OVERVIEW Review the entities that may contribute to groin pain Discuss the approach to making
DEEP SQUAT. Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet
 APPENDIX 9 SCORING CRITERIA DEEP SQUAT Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet Upper torso is parallel with tibia
APPENDIX 9 SCORING CRITERIA DEEP SQUAT Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet Upper torso is parallel with tibia
Knee-Joint Position Sense: The Relationship Between Open and Closed Kinetic Chain Tests
 J Sport Rehabil. 2005;14:356-362 2005 Human Kinetics, Inc. Knee-Joint Position Sense: The Relationship Between Open and Closed Kinetic Chain Tests Lee Herrington Context: Authors have investigated knee
J Sport Rehabil. 2005;14:356-362 2005 Human Kinetics, Inc. Knee-Joint Position Sense: The Relationship Between Open and Closed Kinetic Chain Tests Lee Herrington Context: Authors have investigated knee
9/26/2012. Basic Terminology. Basic Terminology continued. Kinesiology Terminology. Kinesiology = The study of movement
 Kinesiology Terminology Basic Terminology Kinesiology = The study of movement This definition is so broad. What other fields of study come together to create kinesiology? Yes!! And it relates them all
Kinesiology Terminology Basic Terminology Kinesiology = The study of movement This definition is so broad. What other fields of study come together to create kinesiology? Yes!! And it relates them all
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
FUNCTIONAL TESTING GUIDELINES FOR ACL RECONSTRUCTION TESTING INSTRUCTIONS FOR CLINICIANS
 FUNCTIONAL TESTING GUIDELINES FOR ACL RECONSTRUCTION TESTING INSTRUCTIONS FOR CLINICIANS A number of criteria should be met before advanced functional testing of ACL reconstruction or ACL deficient knees
FUNCTIONAL TESTING GUIDELINES FOR ACL RECONSTRUCTION TESTING INSTRUCTIONS FOR CLINICIANS A number of criteria should be met before advanced functional testing of ACL reconstruction or ACL deficient knees
Rehabilitation of an ACL injury in a 29 year old male with closed kinetic chain exercises: A case study
 Abstract Objective: This paper will examine a rehabilitation program for a healthy 29 year old male who sustained an incomplete tear of the left ACL. Results: Following a 9 week treatment plan focusing
Abstract Objective: This paper will examine a rehabilitation program for a healthy 29 year old male who sustained an incomplete tear of the left ACL. Results: Following a 9 week treatment plan focusing
Conservative Correction of Leg-Length Discrepancies of 10 mm or Less for the Relief of Chronic Low Back Pain
 Conservative Correction of Leg-Length Discrepancies of 10 mm or Less for the Relief of Chronic Low Back Pain Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation November 2005, Volume 86, Issue 11, pp 2075-2080
Conservative Correction of Leg-Length Discrepancies of 10 mm or Less for the Relief of Chronic Low Back Pain Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation November 2005, Volume 86, Issue 11, pp 2075-2080
Knee Injuries. PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS. Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain
 Knee Injuries PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain Result from either a direct blow from the lateral side in a medial direction or a severe outward twist Greater injury
Knee Injuries PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain Result from either a direct blow from the lateral side in a medial direction or a severe outward twist Greater injury
 Today we will cover: Exercise for the back L-S spine S-I joint Pelvis www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Toward Developing Scientifically Justified Low Back Rehabilitation Exercises Use evidence to support clinical
Today we will cover: Exercise for the back L-S spine S-I joint Pelvis www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Toward Developing Scientifically Justified Low Back Rehabilitation Exercises Use evidence to support clinical
Chapter 20: The Spine The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 20: The Spine Anatomy of the Spine Prevention of Injuries to the Spine Cervical Spine Muscle Strengthening Muscles of the neck resist hyperflexion, hyperextension and rotational forces Prior
Chapter 20: The Spine Anatomy of the Spine Prevention of Injuries to the Spine Cervical Spine Muscle Strengthening Muscles of the neck resist hyperflexion, hyperextension and rotational forces Prior
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries
 A Patient s Guide to Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries Introduction An ankle injury common to athletes is the ankle syndesmosis injury. This type of injury is sometimes called a high ankle sprain because it involves
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries Introduction An ankle injury common to athletes is the ankle syndesmosis injury. This type of injury is sometimes called a high ankle sprain because it involves
2015 AFL Injury Survey
 2015 AFL Injury Survey Collaborators: AFL Doctors Association AFL Physiotherapists Association AFL Football Operations Department 1 Key Indicators Table 1 Key indicators for all injuries over the 24 seasons
2015 AFL Injury Survey Collaborators: AFL Doctors Association AFL Physiotherapists Association AFL Football Operations Department 1 Key Indicators Table 1 Key indicators for all injuries over the 24 seasons
Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete. Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute
 Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute Disclosures None Baseball Hip Injuries - Background Abdominal/groin injuries
Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute Disclosures None Baseball Hip Injuries - Background Abdominal/groin injuries
ASSESSMENT OF FLEXIBILITY
 Name: Date ASSESSMENT OF FLEXIBILITY Objective The purpose of this lab is to gain an assessment of the participant s flexibility. A number of key joints and movement patterns will be assessed to gain an
Name: Date ASSESSMENT OF FLEXIBILITY Objective The purpose of this lab is to gain an assessment of the participant s flexibility. A number of key joints and movement patterns will be assessed to gain an
LEG LENGTH INEQUALITY: Sports Medicine Perspective
 LEG LENGTH INEQUALITY: Sports Medicine Perspective Debra A. Zillmer, M.D. M&M Orthopaedics, Ltd 18 Year Old Experienced Cross Country Runner: Sept Sr Year Pain in left lower leg with running Pain now prevents
LEG LENGTH INEQUALITY: Sports Medicine Perspective Debra A. Zillmer, M.D. M&M Orthopaedics, Ltd 18 Year Old Experienced Cross Country Runner: Sept Sr Year Pain in left lower leg with running Pain now prevents
Lesson 24. A & P Hip
 Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Relationship between Body Core Stabilization and Athletic Function in. Football, Basketball and Swimming Athletes
 Relationship between Body Core Stabilization and Athletic Function in Football, Basketball and Swimming Athletes Fatemeh Pouya (Msc) 1, Farahnaz Ghaffarinejad (Msc) 2 1. Department of Anatomy, Kerman University
Relationship between Body Core Stabilization and Athletic Function in Football, Basketball and Swimming Athletes Fatemeh Pouya (Msc) 1, Farahnaz Ghaffarinejad (Msc) 2 1. Department of Anatomy, Kerman University
C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle
 C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle 1. 2 coxal bones (a.k.a hip bones): -bony pelvis is made up of hip bones, sacrum, & coccyx -pelvic bones are large & heavy & attach to the axial skeleton via sacrum/coccyx
C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle 1. 2 coxal bones (a.k.a hip bones): -bony pelvis is made up of hip bones, sacrum, & coccyx -pelvic bones are large & heavy & attach to the axial skeleton via sacrum/coccyx
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Spine. After completing this lesson, you should be able to identify:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Positioning for Exams of the Spine. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-15. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to identify: 4-1. Identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Positioning for Exams of the Spine. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-15. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to identify: 4-1. Identify
Inguinal-related groin pain
 Inguinal-related groin pain Adam Weir @adamweirsports Aspetar Sports Groin Pain Centre @Aspetar Talk structure Case Terminology Definition Pathology? Imaging Treatment Rehab protocol History 31 yr male
Inguinal-related groin pain Adam Weir @adamweirsports Aspetar Sports Groin Pain Centre @Aspetar Talk structure Case Terminology Definition Pathology? Imaging Treatment Rehab protocol History 31 yr male
Exam of the Knee and Ankle I HAVE NO FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES RELEVANT TO THIS PRESENTATION
 Exam of the Knee and Ankle I HAVE NO FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES RELEVANT TO THIS PRESENTATION Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or
Exam of the Knee and Ankle I HAVE NO FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES RELEVANT TO THIS PRESENTATION Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or
Case report. Your Diagnosis?
 Case report 18 year Male Panel beater referred with a tibial shin syndrome with pain of 6 months. Pain over the anterolateral aspect of leg, bilateral and is precipitated walking 10 minutes. Your Diagnosis?
Case report 18 year Male Panel beater referred with a tibial shin syndrome with pain of 6 months. Pain over the anterolateral aspect of leg, bilateral and is precipitated walking 10 minutes. Your Diagnosis?
Beginner and advanced exercises for the abdominal and lower back muscles
 Beginner and advanced exercises for the abdominal and lower back muscles Professionally managed by: Mission: The National Institute for Fitness and Sport is committed to enhancing human health, physical
Beginner and advanced exercises for the abdominal and lower back muscles Professionally managed by: Mission: The National Institute for Fitness and Sport is committed to enhancing human health, physical
Hamstring Strain. 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) Website: philip-bayliss.com.
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Hamstring Strain The hamstring muscles are very susceptible to tears, strains and other common sporting
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Hamstring Strain The hamstring muscles are very susceptible to tears, strains and other common sporting
AACPDM IC#21 DFEO+PTA 1
 Roles of Distal Femoral Extension Osteotomy and Patellar Tendon Advancement in the Treatment of Severe Persistent Crouch Gait in Adolescents and Young Adults with Cerebral Palsy Instructional Course #21
Roles of Distal Femoral Extension Osteotomy and Patellar Tendon Advancement in the Treatment of Severe Persistent Crouch Gait in Adolescents and Young Adults with Cerebral Palsy Instructional Course #21
Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dora Street, Hurstville
 www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville WHEN SCIATICA IS NOT SCIATICA, WHAT DO YOU LOOK FOR? What do you look for, where? Low Back pain
www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville WHEN SCIATICA IS NOT SCIATICA, WHAT DO YOU LOOK FOR? What do you look for, where? Low Back pain
The Role of the Rectus Abdominis in Predicting and Preventing Low Back Pain
 The Role of the Rectus Abdominis in Predicting and Preventing Low Back Pain What causes low back pain? The causes of low back pain and complicated and varied, but the pain we feel is in most cases the
The Role of the Rectus Abdominis in Predicting and Preventing Low Back Pain What causes low back pain? The causes of low back pain and complicated and varied, but the pain we feel is in most cases the
AFL Injury Report: Season 2007
 AFL Injury Report: Season 2007 Dr John Orchard, Dr Hugh Seward (AFLMOA) Released May 28th 2008 Highlights: Presents findings from the 16th consecutive year of injury surveillance for the AFL, the last
AFL Injury Report: Season 2007 Dr John Orchard, Dr Hugh Seward (AFLMOA) Released May 28th 2008 Highlights: Presents findings from the 16th consecutive year of injury surveillance for the AFL, the last
Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis
 Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
PHYSICAL TRAINING INSTRUCTORS MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5. Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1. Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3
 TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5 Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1 Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3 Exercise No 33: Bicycle Crunch 4 Exercise No 34: Straight Leg U Crunches 5 Exercise No 35: Bent Knee U Crunch
TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5 Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1 Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3 Exercise No 33: Bicycle Crunch 4 Exercise No 34: Straight Leg U Crunches 5 Exercise No 35: Bent Knee U Crunch
KNEE EXAMINATION. Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective. EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine
 KNEE EXAMINATION Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective Dr P O CONNOR Emergency Medicine Physician EUSEM 10/09/2018 EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine Musculoskeletal Medicine becoming
KNEE EXAMINATION Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective Dr P O CONNOR Emergency Medicine Physician EUSEM 10/09/2018 EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine Musculoskeletal Medicine becoming
Professional Baseball Chiropractic Society Workshop. January 18-20, 2018
 Professional Baseball Chiropractic Society Workshop January 18-20, 2018 Dr. Craig Couillard Team Chiropractor and Soft Tissue Specialist for the St. Paul Saints What is a Sport s Hernia? What is the current
Professional Baseball Chiropractic Society Workshop January 18-20, 2018 Dr. Craig Couillard Team Chiropractor and Soft Tissue Specialist for the St. Paul Saints What is a Sport s Hernia? What is the current
H amstring injuries are common in sprinting, dancing,
 106 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk factors for hamstring injuries in community level Australian football B J Gabbe, C F Finch, K L Bennell, H Wajswelner... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
106 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk factors for hamstring injuries in community level Australian football B J Gabbe, C F Finch, K L Bennell, H Wajswelner... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Soccer syndrome - Common presentations and manual diagnostic techniques for pelvic malalignment syndrome
 American Journal of Sports Science 2014; 2(6): 141-154 Published online November 10, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajss) doi: 10.11648/j.ajss.20140206.11 ISSN: 2330-8559 (Print); ISSN:
American Journal of Sports Science 2014; 2(6): 141-154 Published online November 10, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajss) doi: 10.11648/j.ajss.20140206.11 ISSN: 2330-8559 (Print); ISSN:
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
The Spine.
 The Spine www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Characteristics of Vertebrae Cervical Spine 1 and 2 Sacrum and Coccyx Curves Lordotic in the Spine Kyphotic Lordotic Ligamentous Support Muscles of the Spine Spinal
The Spine www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Characteristics of Vertebrae Cervical Spine 1 and 2 Sacrum and Coccyx Curves Lordotic in the Spine Kyphotic Lordotic Ligamentous Support Muscles of the Spine Spinal
FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT
 THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
MR findings in patients with athletic pubalgia: our experience
 MR findings in patients with athletic pubalgia: our experience Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: P. Schvartzman, A. Fernandez Viña, F. Olmos Cantarero, J. 1 2 1 1
MR findings in patients with athletic pubalgia: our experience Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: P. Schvartzman, A. Fernandez Viña, F. Olmos Cantarero, J. 1 2 1 1
405 Firemans Ave LaVale, Maryland 21502
 Dec 19, 2016 CHIEF COMPLAINT: Iris presents with a chief complaint involving her lower lumbar and sacral region, left sacroiliac region and left anterior hip and groin. ONSET OF SYMPTOMS Iris states this
Dec 19, 2016 CHIEF COMPLAINT: Iris presents with a chief complaint involving her lower lumbar and sacral region, left sacroiliac region and left anterior hip and groin. ONSET OF SYMPTOMS Iris states this
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation
 Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
By Dr. Ellyn Robinson
 Issue: 15.03 April 2005 Stretching The Field At Boston College, coaches are making flexibility a focal point of their strength and conditioning program with great results. By Dr. Ellyn Robinson Ellyn Robinson,
Issue: 15.03 April 2005 Stretching The Field At Boston College, coaches are making flexibility a focal point of their strength and conditioning program with great results. By Dr. Ellyn Robinson Ellyn Robinson,
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults
 What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
