|
|
|
- Morgan Dickerson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Human Journals Research Article February 2018 Vol.:11, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Israa Mustafa Salih AL-Musawi et al. Frequency of Cholelithiasis in Sickle Cell Disease and Thalassemic Patients at Hereditary Blood Diseases Center in Karbala Teaching Hospital for Children Keywords: Cholelithiasis, Sickle cell disease, Thalassemia. ABSTRACT Abdulkareem A. Jasim 1, Israa Mustafa Salih AL- Musawi 2,*, Zahraa Alaa Abdul Zhara 3 1.C.A.B.A.P. Asst.Prof.College of Medicine,University of Karbala. 2.C.A.B.A.P. Pediatrecian Karbala Teaching Hospital for children. 3.M.B.Ch.B. Senior registrar Karbala Teaching Hospital for children. Submission: 24 January 2018 Accepted: 29 January 2018 Published: 28 February Background: Cholelithiasis is defined as formation of stones in gallbladder, it is unusual in infants, and in children but it is not rare. Hemolytic anemia (sickle cell disease and thalassemia) cause chronic hemolysis which is a risk factor for gallstones formation. Objective: To determine the frequency of cholelithiasis in patients with sickle cell disease and thalassemia treated at hereditary blood diseases center in Karbala Teaching Hospital for children in Karbala city. Methods: A retrospective study is performed by reviewing medical records of a Four hundred thirty-three patients with sickle cell disease and thalassemia, patients aged six months to 18 years, between December, the 1 st, 2015 to December the 30 th, Data collected include type of hemolytic anemia, frequency of blood transfusion, and the mode of diagnosis of cholelithiasis whether symptomatic or asymptomatic (diagnosed by doing abdominal ultrasound for each patient).results: Cholelithiasis occurred in 50 patients 32(7.39%) patients with sickle cell disease and 18 (4.15%) patients with thalassemia, with no significant difference between genders. The overall percentage of cholelithiasis was 11.54% and it increased with age. A thirtyfour (7.8%) patients with gallstones were asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis discovered by routine abdominal ultrasound and 16 (3.7%) patients were symptomatic by history of abdominal pain, jaundice, fever, nausea and vomiting. Conclusion: The frequency of cholelithiasis in patients with sickle cell disease and thalassemia in this study was significant. The frequency of gallstones in patients with sickle cell disease more than in the patients with thalassemia. The majority of patients remained asymptomatic. Patients with sickle cell disease who had infrequent blood transfusion had more chance to develop gallstones than others. In patients with beta thalassemia the frequency of gallstones where more in patients who transfused blood transfusion every 3 weeks than others.
2 INTRODUCTION When compared with adults, cholelithiasis (gallstones) is unusual in infants, and in children but it is not rare. Increased frequency of gallstones may be due to an increase in recognition of disease due to widespread use of ultrasonography (U/S) for abdominal complaints in recent years [1]. Cholelithiasis classified into three groups; hemolytic, non-hemolytic, and idiopathic [2,3,4] table (1). Table (1) ETIOLOGY OF GALLSTONES IN CHILDREN (5,6). Type Proportion Etiology of gallstone Sickle-cell disease, Hereditary spherocytosis, Thalassemia Hemolytic 20%-30% syndrome TPN, prolonged fasting ileal disease (like Crohn s disease) or Nonhemolytic bypass, congenital biliary malformations, PFIC, chronic liver resection, prematurity, furosemide therapy, cardiopulmonary 30% disease, cystic fibrosis, teenage pregnancy Idiopathic 30%-40% No predisposing factor About (20-30%) of all gallstones in children are due to Hemolytic diseases and mainly occurs after the age of 5years and is directly related to the severity and to the intensity of hemolysis. The cholelithiasis is one of the important manifestations of sickle cell disease in the digestive tract [5]. The incidence of cholelithiasis in thalassemia in children is (10-15%) [6] and increasing progressively with the age to reach (50%) in adult [7]. The highest frequency of gallstones has been reported in beta thalassemia associated with Gilbert s syndrome genotype because of the combined effect of increased bilirubin production and reduced bilirubindiphosphate-glucuronyl transferase enzyme activity [7,8]. The frequency of gallstones in patients with hereditary spherocytosis is 10-20% in children and in adult, it is 40% [9]. Gallstones are (30-40%) idiopathic mainly among adults and adolescent girls [3,4,10]. In about 30% of cases, gallstones are due to non-hemolytic causes such as use of total parenteral nutrition [which cause cholecystokinin and enterohepatic circulation impairment lead to gallbladder contraction resulting in biliary stasis, and stones], phototherapy and furosemide in the infants, congenital biliary diseases such choledochal cyst, chronic liver disease, progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis, prolonged fasting, and ileal disease or resection [2,3]. Biliary sludge or biliary pseudolithiasis has been reported complication of ceftriaxone which is reversible and disappears on discontinuation, (60% excreted unchanged into the urine and 40% in the bile, concentrate in bile 20 times more than in serum and forms an insoluble salt with calcium that deposit in gallbladder). Citation: Israa Mustafa Salih AL-Musawi et al. Ijppr.Human, 2018; Vol. 11 (3):
3 In hemolytic anemias, the liberated hemoglobin (from chronic hemolysis and also multiple blood transfusions) is broken down, and its heme component is eventually, degraded into bilirubin by the liver. Increased bilirubin production leads to formation of pigment gallstones. Even in cholesterol stones, a bilirubin nidus has been documented [11]. Patients who are homozygous have the higher incidence of gallstones development than those who are heterozygous for that particular gene defect and disease [12]. Gallstones have different types; Pigment gallstones (black or brown) which are the common type of gallstones associated with chronic haemoglobinopathies composed mainly of bilirubin and calcium salts with 20% cholesterol; Pure cholesterol gallstones; and Mixed gallstones which are more common in adults composed mostly of cholesterol (70-80%), calcium salts and bilirubin compounds (20-30%). There is variation of the frequency of cholelithiasis in the haemoglobinopathic patient with the age. As patients grow older, gallstones are more likely to develop. In Sickle Cell Disease, which is the commonest hemolytic anemia, the frequency of pigmented gallstones in SCD is directly related to the rate of hemolysis [5,13]. Stones occur in children as young as three to four years of age. The frequency of gallstones is more in patients with Hb-SS disease. The risk of gallstone in patient with Hb-SB thalassemia syndrome is moderately high. Thalassemia intermedia patients may develop gallstones, which occur more commonly than in thalassemia major [8,14]. Gallstones either asymptomatic discovered by routinely abdominal ultrasound or symptomatic inflammation of gallbladder (cholecystitis). Cholecystitis should be suspected in a patient present with right upper quadrant or epigastric pain, jaundice, vomiting, fever, and a leukocytosis. A positive Murphy's sign supports the diagnosis [15]. History, physical examination, and laboratory test findings are not enough to establish the diagnosis. In most cases, the diagnosis can be confirmed with an abdominal ultrasound with sensitivity and specificity exceeding 95%. [16]. Gallstones are usually mobile, single or multiple and characteristically cast an acoustic shadow. Biliary sludge appearing echogenic on ultrasound does not cast an acoustic shadow. A stone, as small as 1.5 mm, can be detected by ultrasonography [17]. In children 20% to 50% gallstones are radiopaque (18). If the diagnosis remains unclear, cholescintigraphy or magnetic resonance cholangiography can be obtained. Treatment of gallstones depends on the age and the symptoms of the patient. Symptomatic gallstones and complicated gallstones need cholecystectomy, but there is controversy about Citation: Israa Mustafa Salih AL-Musawi et al. Ijppr.Human, 2018; Vol. 11 (3):
4 the treatment of asymptomatic gallstones in children [19]. Asymptomatic children or children with nonspecific symptoms need monitoring and followed up till adulthood to determine their life risks for developing symptoms of gallstones. Before surgery, blood transfusion therapy is required and aimed to get the hemoglobin up to 10m g/dl to prevent potentially life-threatening Intra-and postoperative complications [20]. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is associated with lower rates of postoperative complications and a shorter hospital stay [ 21,22,23]. Aim of the study: We aim to increase the awareness about the frequency of gallstone disease with particular emphasis on its pathogenesis, genetics, risk factors and management in child patients with sickle cell disease and thalassemia treated at hereditary blood diseases center in Karbala teaching hospital for children. METHOD A retrospective study was performed by reviewing medical records of 433 patients (6 months to 18 years old) followed up till December the 30 th 2016 in hereditary blood diseases center at Karbala teaching hospital for children in Karbala city. Iraq. Data collected for this study include type of hemolytic anemia sickle cell disease or thalassemia (we exclude patients with hereditary spherocytosis), frequency of blood transfusion, treatments of hemolytic anemia, compliance with treatment, regularity of visits to the center for follow up, and complications of hemolytic anemia (namely the gallstones). the diagnosis of cholelithiasis had been done either by routine abdominal ultrasound for each patient or by history of cholecystitis. The SPSS for Windows software, version 20 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for analysis of the data. Descriptive analysis consisted of allocating continuous variables for position and dispersion and arranging categorical variables in frequency tables. The chisquare was used to determine associations or to compare proportions. A level of significance of 0.05 was adopted. The study protocol was approved by the hereditary blood diseases center, with no need for informed consent of the patients or their parents since the study was retrospective and based on records review. RESULTS A total of 433 patient records were studied. Totally the sample included 229 (52.88 %) males and 204 (47.12 %) females. The mean patients age of the patient s sample was 9.80 ± 4.70 Citation: Israa Mustafa Salih AL-Musawi et al. Ijppr.Human, 2018; Vol. 11 (3):
5 years and the age range was between 6 months and 18 years. There was no gender difference in the mean age (9.45 ± years for males and ±4.632 years for females). No significant difference in frequency of cholelithiasis between genders (P = 0.747). From 433 patients, fifty patients had gallstones, males 22 (44%) and females 28 (56%). According to the age groups studied, most of the cases are at the age group of 5-10 years 191 (44.1%) with 12 (24%) patients had gallstones while the age group years108(25%) with 12(24%) gallstones and age group of years 71(16.4 %) with 25(50 %) with gall stone these groups represented the highest numbers of patients with gallstones in the studied groups, which means the frequency of gallstones increased with age as shown in table (2). Table (2): Frequency of gallstones among Thalassemic patients and sickle cell disease patients according to age and gender. Age Boys Girls Total group (years) NO gallstones Have gallstone NO gallstones Have gallstone NO gallstones Have gallstone No % No % No % No % No % No % 6m-4 y y y y Total The sample included 249 (57.5%) patients with thalassemia and 184 (42.5%) patients were with sickle cell disease. The frequency of gallstones in thalassemia group 18(4.15%), and in sickle cell group 32(7.39%) so increase frequency of gallstones in patients with sickle cell disease than in patients with thalassemia table, (3). Table (3): Frequency according to the type of hemoglobinopathy Gall Stone Disease Have Total No Stone % % gallstone Thalassemia (57.5%) SCD (42.5%) Total (100%) Citation: Israa Mustafa Salih AL-Musawi et al. Ijppr.Human, 2018; Vol. 11 (3):
6 Table (4) show that the total number of patients of sickle cell anemia (HbSS) was 118 (27.3%) from them 16 (3.7%) (HbSS) patients had gallstones, the number of Sβ disease patients were 66 (15.2%) cases, only16 (3.7%) patients had gallstones. Beta thalassemia major was included 203(46.9%) patients from them 13(3%) have gallstones while beta thalassemia intermedia were included 33(7.6%) patients, only 5(1.1%) patients had gallstones. The overall frequency of cholelithiasis was (11.5%), was higher in patients with SS and Sβ disease and with highly significant difference (p-value 0.001). Table (4): The distribution of the subtype of disease by history of gallstone. Disease type GallStone Total No Stone Have gallstone HbSS 102(23.6%) 16(3.7%) 118(27.3%) HbS-B 50(11.5%) 16(3.7%) 66(15.2%) TM 190(43.9%) 13(3.0%) 203(46.9%) TI 28(6.5%) 5(1.1%) 33(7.6%) Alpha T 12(2.8%) 0(0%) 12(2.8%) HbE 1(0.2%) 0(0%) 1(0.2%) Total 383(88.5%) 50(11.5%) 433(100%) Chi-square p value Table (5) shows that 16 (3.7%) patients were symptomatic at the time of diagnosis of cholelithiasis and 34 (7.8%) patients asymptomatic discovered by routinely done abdominal ultrasound, for a total 50 patients with gallstones. Symptoms included nonspecific abdominal pain, abdominal pain located in the right hypochondrium radiated to back, fatty food intolerance, nausea and emesis after meals, jaundice, and fever. Patients with sickle cell anemia (Hb SS) who had gallstones, only 6(1.4%) were symptomatic. While patients with Hb S-B disease who had gallstones from them only 3(0.7%) patients were symptomatic. Five patients (1.1%) with thalassemia major who had stones were symptomatic and 2(0.5%) patients with thalassemia intermedia who had gallstones were symptomatic. This is highly significant with (p-value =0.004). Citation: Israa Mustafa Salih AL-Musawi et al. Ijppr.Human, 2018; Vol. 11 (3):
7 Thalassemia Sickle cell anemia Table (5): Symptomatic gallstone according to subtype of hemolytic disease. Have gallstone Total Disease type No stones Asymptomatic by Symptomatic Ultrasound HbSS 102 (23.6%) 10 (2.3%) 6 (1.4%) 118 (27.3%) HbS-B 50 (11.5%) 13 (3%) 3 (0.7%) 66 (15.2%) TM 190 (43.9%) 8 (1.8%) 5 (1.1%) 203 (46.9%) TI 28 (6.5%) 3 (0.7%) 2 (0.5%) 33 (7.6%) Others 13 (3%) (3%) Total 383 (88.5%) 34(7.8%) 16(3.7%) 433 (100%) Chi-square P value Regarding the 236 patients who had beta thalassemia, 12 patients had no blood transfusion, and all of them didn t have stone while only 6 patients infrequently transfused blood and had no stone, 21 patients who had 2 weekly transfused blood from them only 7 patients had stones and others had no stones. The number of patients who had three weekly transfused blood were 111 patients, from them 9 patients had stones and 102 had no gallstones, patients with 4 weekly blood transfusion were 78, from them just one patient had stone, while patients with 5 weekly transfused were 4 patients and all of them had no stone, one patient was 6 weekly transfused and had no stone, 8 weekly transfused were 3 patients from them only 1 patient had gallstone. The occurrence of gallstone in patients with thalassemia was increased with increased frequency of blood transfusion with (p-value 0.004) as shown in table (6). Table (6) Association between blood transfusion and gallstone. Gallstone Frequency of Blood Transfusions in weeks Total No BT Inf BT 2w 3w 4w 5w 6w 8w No Stone Have gall stone Total Chi square P value Gall Stone Frequency of Blood Transfusions in weeks Total No BT Inf BT 2w 3w 4w 5w 12w No Stone Have gall stone Total Chi-square P value Citation: Israa Mustafa Salih AL-Musawi et al. Ijppr.Human, 2018; Vol. 11 (3):
8 In our study we have 184 patients had sickle cell disease, 124 had no blood transfusion from them 12 had stones,46 patients had infrequently blood transfusions from them only 14 had gallstones, one patient had every two weeks transfused blood who had stone, one patient had 3 weekly transfused blood but did not have stone, while 8 patients had 4 weekly transfused blood, from them 4 patients only had stones.there were three patients had 5 weekly transfused blood only one patient and had stone, while one patient who had yearly transfused blood had no stone. The occurrence of gallstone in sickle cell patients was significantly positively associated with infrequent blood transfusion and 4 weekly transfusions with p- value DISCUSSION: In current study, we tested 433 patients (sickle cell disease and thalassemia). Totally the sample included 229 (52.88 %) males and 204 (47.12 %) females. From them, 50 (11.54%) patients had cholelithiasis, males 22 (44%) and females 28 (56%). The sex ratio of cholelithiasis was equal in childhood groups, while adolescent age group (16 18 years) was a female predilection for gallstones since males who had gallstone in this age group were 9 (18%) while females were 16 (32%). Our study is consistent with the results what was reported in Saudi Arabia, in which there is a female predilection in adolescent age group [24] (see table 2). Most of the cases who had hemolytic anemia were at the age group of 5-10 years 191(44.1%) patient from them 12(24%) patients had gallstones while the highest number of patients with gallstones in the age group from 16 to18 years 71(16.4 %) patients from them 25(50 %) patients had gallstones. This may be due to increased incidence of gallstones in patients with chronic hemolytic disease with increasing age and by the time at which bile pigment saturation in the bile increases [9]. Our study was different from Noor AL Huda's study (2015) in Basra [25] most of cases with gallstones were at age group year (66.1%). In the current study, the frequency of gallstone in patients with sickle cell disease was 7.39% while the frequency of gallstone in thalassemia syndrome was 4.15%. This percentage of gallstones in Sickle cell disease is different to what was reported by Wesdorp and Schweizer studies, which was 20% of patients [2,3] and the percentage of gallstones in thalassemia major is less than reported with Gallanello et.al [8]. The frequency of cholelithiasis in patients with sickle cell disease varies according to different studies [5]. The selection of distinct populations and different age ranges may explain some differences, but other authors have reported high rates, usually 50% [5]. The frequency of cholelithiasis in Citation: Israa Mustafa Salih AL-Musawi et al. Ijppr.Human, 2018; Vol. 11 (3):
9 sickle cell disease in our study was different to that reported by WALKER et al [5], who found frequency of cholelithiasis of 52.7% in SS disease; however, that study did not include patients with Hb S -B thalassemia, (table 3). In current study, the percentage of gallstones in HbSS and HbS B thalassemia were similar (3.7%) although the total number of patients in both diseases were different this may relate to rate of hemolysis was more in patients HbS-B thalassemia. The frequency of gallstones in patients with beta thalassemia major was 3% while in patients with thalassemia intermedia was 1.1%, this percentage were different what was reported in Italian study, which is a large study performed in 2001, gallstones were more observed in thalassemia intermedia than in Thalassemia major [9]. There are several possible explanations for this observation, including the older age of intermedia patients, the high degree of ineffective erythropoiesis, and peripheral hemolysis not suppressed by regular transfusions, (table 4). In present study, the majority of children were asymptomatic 34 (%) at the time of diagnosis of cholelithiasis and 16 (%) patients were symptomatic. This result was less than that reported by other studies in Canada (49.5%) and Italy (64.7%) [7,9]. This may be explained partly by the present of routine screening abdominal ultrasound for patients with haemoglobinopathies. The results of this study regarding ultrasound were consistent with results of other studies. [2]. This may be explained by that most of cholelithiasis remain asymptomatic until complications develop (table 5). In our study the number of patients with beta thalassemia and had gallstone who transfused blood every 3 weeks were 9 patients which represented the highest one among others, due to gallstone formation related to severity of hemolytic disease and intensity of the episodes of hemolysis [5], as multiple transfusions are a recognized risk factors for gallstone formation in thalassemia due to those patients exposed to recurrent attacks of hemolysis from more frequent blood transfusions [7] (table 6). We found that the number of patients with SCD who had gallstone and infrequent transfused blood were 14 patients which represented the high number among others because those patients complaint from hemolytic crisis as part of their disease and they suffering from occlusive crisis so lead to decrease blood supply and stasis of gallbladder contents which lead to stone formation, and patients who transfused blood every 4 week were 8 from them 4 patients had gallstone also represent high number due to recurrent attacks of hemolysis from more frequent blood transfusions(table 6) Citation: Israa Mustafa Salih AL-Musawi et al. Ijppr.Human, 2018; Vol. 11 (3):
10 CONCLUSION 1) The frequency of cholelithiasis in study population with SCD and thalassemia at hereditary blood diseases center at Karbala teaching hospital of children was 11.54%. 2) The majority of patients remained asymptomatic 34 (7.8%). 3) Patients with HbSS or Hb S-B disease were at a higher risk for the development of gallstones both of them same results (3.7%) compared to patients with beta thalassemia major and thalassemia intermedia (3%, 1.1%) respectively. 4) Most of patients were diagnosed between the ages 16 years to 18 years and were 25(50%) patients 5) Patients with SCD who had infrequent blood transfusion and who transfused blood 4 weekly had more chance to develop gallstones than other. In patients with thalassemia the frequency of gallstones more in patients who transfused blood transfusion every 3 weeks than other. RECOMMENDATIONS 1) Usefulness of abdominal ultrasound screening program in pediatric patients with hemolytic disease especially when they presented with suggestive symptoms, with special attention to age group between 16 years to 18 years. 2) Further studies should be done to identify other risk factors for the formation of gallstones in hemolytic diseases [like multiple transfusions in beta thalassemia patients and genetic factors (like UGTIA)]. 3) Cholecystectomy must be done to symptomatic patients and follow up of symptomatic patients to prevent complications like obstructive jaundice and cholangitis. REFERENCES 1. Klar A, Branski D, Akerman Y. Sludge ball, pseudolithiasis, cholelithiasis and choledocholithiasis from intrauterine life to 2 years: 13 years follow up. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2005; 40: Wesdorp I, Bosman D, de Graaff A, Aronson D, vander Blij F, Taminiau J. Clinical presentations and predisposing factors of cholelithiasis and sludge in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2000; 31: Schweizer P, Lenz MP, Kirschner HJ. Pathogenesis and symptomatology of cholelithiasis in childhood. Dig Surg 2000; 17: Citation: Israa Mustafa Salih AL-Musawi et al. Ijppr.Human, 2018; Vol. 11 (3):
11 4. Deepak J, Agarwal P, Bagdi RK, Balagopal S. Pediatric cholelithiasis and laparoscopic management: A review of twenty-two cases. J Mini Assess Surg. 2009;5(4): Walker TM, Hambleton IR, Serjeant GR. Gallstones in sickle cell disease: observations from the Jamaican cohort study. J Pediatr 2000; 136: Lotfi M, Keramati P, Assadsangabi R, Nabavizadeh SA, Karimi M. Ultrasonographic assessment of the prevalence of cholelithiasis and biliary sludge in beta-thalassemia patients in Iran. Med SciMonit 2009; 15; CR Origa R, Galanello R, Perseu L, TavazziD,Cappellini MD, Terenzani L, et al. Cholelithiasis in thalassemia major. Eur J Hematol 2008; 82: Galanello R, Piras S, Barella S, Leoni GB, Cipollina MD, Perseu L, et al. Cholelithiasis and Gilbert s syndrome in homozygour beta-thalassemia. Br J Haematol 2001; 115: Kar R, Rao S, Srinivas UM, Mishra P, Pati HP. Clinico-hematological profile of hereditary spherocytosis: experience from a tertiary care center in North India. Hematology 2009; 14: Herzog D, Bouchard G. High rate of complicated idiopathic gallstone disease in pediatric patients of a North American tertiary care center. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(10): Grünhage F, Lammert F. Gallstone disease. Pathogenesis of gallstones: A genetic perspective. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2006; 20: Tüzmen S, Tadmouri GO, Ozer A, Baig SM, Ozçelik H, Başaran S, Başak AN. Prenatal diagnosis of betathalassaemia and sickle cell anaemia in Turkey. Prenat Diagn 2000; 16: Adam S, Jonassaint J, Kruger H, et al. Surgical and obstetric outcomes in adults with sickle cell disease. Am J Med 2008; 121: Taher AT, Musallam KM, Karimi M, et al. Overview on practices in thalassemia intermedia management aiming for lowering complication rates across a region of endemicity: the optimal care study. Blood 2010; 115: Trowbridge RL, Rutkowski NK, Shojania KG. Does this patient have acute cholecystitis? JAMA 2003; 289: Millar AJW, Prasad H. Gallstone disease in children. Indian Pediatric. 2010;47(11): Poddar U, Thapa BR, Bhasin DK, Prasad A, Nagi B, Singh K. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in the management of pancreatobiliary disorders in children. J GastroenterolHepatol 2001; 16: Millar AJW. Surgical disorders of the l.kiewiet JJ, Leeuwenburgh MM, Bipat S, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic performance of imaging in acute cholecystitis. Radiology 2012; 264: National Institutes of Health. The management of sickle cell disease 2002, Accessed March 15, Available at Vichinsky EP, Haberkern CM, Neumayr L, Earles AN, Black D, Koshy MM, et al. A comparison of conservative and aggressive transfusion regimens in the perioperative management of sickle cell disease. Preoperative transfusion in sickle cell disease study group. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: Chan S, Currie J, Malik AI, Mahomed AA. Pediatric cholecystectomy: shifting goalposts in the laparoscopic era. SurgEndosc 2008; 22: Tannuri CA, Gonçalves AJ, Velhote M, Gonlçalves ME, Tannuri U. Management of gallstone disease in children: a new protocol based on the experience of a single center. J Pedia Surg. 2012; 47: Vichinsky EP, Haberkern CM, Neumayr L, Earles AN, Black D, Koshy MM, et al. A comparison of conservative and aggressive transfusion regimens in the perioperative management of sickle cell disease. Preoperative transfusion in sickle cell disease study group. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: Al-Mulhim AS, Abdulatif MM, Ali AM. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy in children with sickle cell disease. Saudi J Gastroenterol 2006; 12: Al-Huda, Noor & Al-Asadi, Jasim & Alhasani, Abbas. THE MEDICAL JOURNAL OF BASRAH UNIVERSITY. Cholelithiasis in children 16 years and below in Basrah: Epidemiological and Clinical study. The Medical Journal of Basrah University. 2015; A. Citation: Israa Mustafa Salih AL-Musawi et al. Ijppr.Human, 2018; Vol. 11 (3):
RESEARCH BRIEF. Etiology and Outcome of Cholelithiasis in Turkish Children
 RESEARCH BRIEF Etiology and Outcome of Cholelithiasis in Turkish Children * MAŞALLAH BARAN, ** YELIZ ÇAĞAN APPAK, # GÖKHAN TÜMGÖR, ** MIRAY KARAKOYUN, ** TUNÇ ÖZDEMIR AND * GÖKHAN KÖYLÜOĞLU From * Department
RESEARCH BRIEF Etiology and Outcome of Cholelithiasis in Turkish Children * MAŞALLAH BARAN, ** YELIZ ÇAĞAN APPAK, # GÖKHAN TÜMGÖR, ** MIRAY KARAKOYUN, ** TUNÇ ÖZDEMIR AND * GÖKHAN KÖYLÜOĞLU From * Department
Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis
 1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
Original Article. Study of Gall Bladder Disease in Sickle Cell Patients at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Vidarbha
 Original Article Vidarbha Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 5 July 018 Study of Gall Bladder Disease in Sickle Cell Patients at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Vidarbha 1 3 4 A H Dube, C Atkar, R Chalwade,
Original Article Vidarbha Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 5 July 018 Study of Gall Bladder Disease in Sickle Cell Patients at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Vidarbha 1 3 4 A H Dube, C Atkar, R Chalwade,
The diagnosis of gallstones in children is being made with
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: HEPATOLOGY AND NUTRITION Risk Factors, Complications, and Outcomes of Gallstones in Children: A Single-center Review Conor O. Bogue, y Amanda J. Murphy, z J. Ted Gerstle, Rahim Moineddin,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: HEPATOLOGY AND NUTRITION Risk Factors, Complications, and Outcomes of Gallstones in Children: A Single-center Review Conor O. Bogue, y Amanda J. Murphy, z J. Ted Gerstle, Rahim Moineddin,
Perioperative transfusion of patients with sickle cell disease undergoing surgery at the University Hospital of the West Indies (UHWI).
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 21 Number 2 Perioperative transfusion of patients with sickle cell disease undergoing surgery at the University Hospital of the West Indies (UHWI).
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 21 Number 2 Perioperative transfusion of patients with sickle cell disease undergoing surgery at the University Hospital of the West Indies (UHWI).
Management of gallstone disease in children: a new protocol based on the experience of a single center
 Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Sem comunidade WoS 2012 Management of gallstone disease in children: a new protocol based on the experience of a single center
Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Sem comunidade WoS 2012 Management of gallstone disease in children: a new protocol based on the experience of a single center
Cholelithiasis in Childhood: A Cohort Study in North of Iran
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Oct 2013; Vol 23 (No 5), Pp: 588-592 Cholelithiasis in Childhood: A Cohort Study in North of Iran Mohammad-Reza Esmaeili Dooki 1*, MD; Alireza Norouzi 2, MD 1. Pediatric
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Oct 2013; Vol 23 (No 5), Pp: 588-592 Cholelithiasis in Childhood: A Cohort Study in North of Iran Mohammad-Reza Esmaeili Dooki 1*, MD; Alireza Norouzi 2, MD 1. Pediatric
What Are Gallstones? GALLSTONES. Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in. the gallbladder of some people.
 What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
 GALL BLADDER Cholelithiasis (Gallstones) Gallstones afflict 10-20% of adult populations in northern hemisphere Western countries. Adult prevalence rates are higher in Latin American countries (20-40%)
GALL BLADDER Cholelithiasis (Gallstones) Gallstones afflict 10-20% of adult populations in northern hemisphere Western countries. Adult prevalence rates are higher in Latin American countries (20-40%)
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 Appendix B: Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE Post publication note: The title of this guideline changed during development. This scope was published before the guideline
Appendix B: Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE Post publication note: The title of this guideline changed during development. This scope was published before the guideline
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Comparative Study between Laparoscopic and Open Cholecystectomy for Dr. B. Hemasankararao 1,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Comparative Study between Laparoscopic and Open Cholecystectomy for Dr. B. Hemasankararao 1,
Gallstones. Farhad Zamani Prof. of Gastroenterology and Hepatology IUMS,GILDR Firoozgar Hospital December 2017
 Gallstones Farhad Zamani Prof. of Gastroenterology and Hepatology IUMS,GILDR Firoozgar Hospital December 2017 1 Gallstones Gallstones are composed of a mixture of cholesterol, calcium billirubinate,
Gallstones Farhad Zamani Prof. of Gastroenterology and Hepatology IUMS,GILDR Firoozgar Hospital December 2017 1 Gallstones Gallstones are composed of a mixture of cholesterol, calcium billirubinate,
Acute chest syndrome in children with sickle cell disease in Basra, Southern Iraq
 Original Article INTRODUCTION Sickle cell disease (SCD) represents a major public health burden because of its significant morbidity and mortality. 1 SCD is common hematologic problem in Basra, around
Original Article INTRODUCTION Sickle cell disease (SCD) represents a major public health burden because of its significant morbidity and mortality. 1 SCD is common hematologic problem in Basra, around
Background. RUQ Ultrasound Normal, Recommend Clinical Correlation. Sohail R. Shah, MD, MSHA, FACS, FAAP Texas Children s Hosptial
 RUQ Ultrasound Normal, Recommend Clinical Correlation Sohail R. Shah, MD, MSHA, FACS, FAAP Texas Children s Hosptial Background Incidence of pediatric gallbladder disease continues to rise U.S. Pediatric
RUQ Ultrasound Normal, Recommend Clinical Correlation Sohail R. Shah, MD, MSHA, FACS, FAAP Texas Children s Hosptial Background Incidence of pediatric gallbladder disease continues to rise U.S. Pediatric
ENDOSCOPIC TREATMENT OF A BILE DUCT
 HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 3, pp. 67-71 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORT
HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 3, pp. 67-71 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORT
How to Write a Life Care Plan for a Child with Hemoglobinopathy
 How to Write a Life Care Plan for a Child with Hemoglobinopathy Tamar Fleischer, BSN, MSN, CNLCP & Mona Yudkoff, RN, MPH, CRRN, CNLCP BalaCare Solutions March 2018 St. Peterburg, Florida What is Hemoglobinopathy?
How to Write a Life Care Plan for a Child with Hemoglobinopathy Tamar Fleischer, BSN, MSN, CNLCP & Mona Yudkoff, RN, MPH, CRRN, CNLCP BalaCare Solutions March 2018 St. Peterburg, Florida What is Hemoglobinopathy?
Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (3) Vol., No. 3, Issue 7, 3-7 Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis Singh DR 1, Mehta A, Dangol UMS 3 1 Lecturer, Medical Officer, 3 Lecturer, Dept.
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (3) Vol., No. 3, Issue 7, 3-7 Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis Singh DR 1, Mehta A, Dangol UMS 3 1 Lecturer, Medical Officer, 3 Lecturer, Dept.
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Retrospective Study
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 37, No. 3, September 2015 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Retrospective Study Abdullah Al-Mitwalli, LRCPI, LRCSI* Martin Corbally, MBBCh, BAO, MCh, FRCSI, FRCSEd, FRCS**
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 37, No. 3, September 2015 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Retrospective Study Abdullah Al-Mitwalli, LRCPI, LRCSI* Martin Corbally, MBBCh, BAO, MCh, FRCSI, FRCSEd, FRCS**
Sex-related differences in predicting choledocholithiasis using current American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy risk criteria
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2018) 31, 1-6 Sex-related differences in predicting choledocholithiasis using current American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy risk criteria Ankit Chhoda
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2018) 31, 1-6 Sex-related differences in predicting choledocholithiasis using current American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy risk criteria Ankit Chhoda
Gallstone Disease. PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017
 PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Gallstone Disease Dr. Muhammad Fayyaz Consultant Gastroenterologist Saidu Group of Teaching Hospitals, Saidu sharif Swat, Pakistan Abstract Gallstone disease is one
PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Gallstone Disease Dr. Muhammad Fayyaz Consultant Gastroenterologist Saidu Group of Teaching Hospitals, Saidu sharif Swat, Pakistan Abstract Gallstone disease is one
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Pre-operative prediction of difficult laparoscopic cholecystectomy
 International Surgery Journal http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20151083 Pre-operative prediction of difficult laparoscopic
International Surgery Journal http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20151083 Pre-operative prediction of difficult laparoscopic
Disclosures. Overview. Case 1. Common Bile Duct Sizes 10/14/2016. General GI + Advanced Endoscopy: NAFLD/Stones/Pancreatitis
 Disclosures General GI + Advanced Endoscopy: NAFLD/Stones/Pancreatitis 123 Blank Blank, LLC Aldo Maspons, MD Assistant Professor Director of Endoscopy Department of Pediatrics Texas Tech University Health
Disclosures General GI + Advanced Endoscopy: NAFLD/Stones/Pancreatitis 123 Blank Blank, LLC Aldo Maspons, MD Assistant Professor Director of Endoscopy Department of Pediatrics Texas Tech University Health
High Hemoglobin F in a Saudi Child Presenting with Pancytopenia
 Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Pediatric Care ISSN 2471-805X DOI: 10.21767/2471-805X.100002 High Hemoglobin F in a Saudi Child Presenting with Pancytopenia Abstract Saudi
Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Pediatric Care ISSN 2471-805X DOI: 10.21767/2471-805X.100002 High Hemoglobin F in a Saudi Child Presenting with Pancytopenia Abstract Saudi
Overview of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Procedure in the Pediatric
 Overview of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Procedure in the Pediatric 1 Malek Hassan Ibrahim Alaaullah, 2 Abadi Abdullah Hakami, 3 Qasem Ali Arishi, 4 Musleh Hussain Musleh Mubarki, 5 Mohammed Ali Zalah,
Overview of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Procedure in the Pediatric 1 Malek Hassan Ibrahim Alaaullah, 2 Abadi Abdullah Hakami, 3 Qasem Ali Arishi, 4 Musleh Hussain Musleh Mubarki, 5 Mohammed Ali Zalah,
Management of Gallbladder Disease
 Management of Gallbladder Disease Steven B. Johnson, MD, FACS, FCCM Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery Program Director, Phoenix Integrated Surgical Residency University of Arizona College of
Management of Gallbladder Disease Steven B. Johnson, MD, FACS, FCCM Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery Program Director, Phoenix Integrated Surgical Residency University of Arizona College of
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital
 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital Poster No.: C-1790 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit J. A. Maguire 1, H. Kasem 2, M. Akhtar 2, M. Strauss
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital Poster No.: C-1790 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit J. A. Maguire 1, H. Kasem 2, M. Akhtar 2, M. Strauss
Ceftriaxone Associated Nephrolithiasis in Children
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Dec 2013; Vol 23 (No 6), Pp: 643-647 Ceftriaxone Associated Nephrolithiasis in Children Azita Fesharakinia* 1, MD; Ali-Reza Ehsanbakhsh 2, MD; Nasrin Ghorashadizadeh 2,
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Dec 2013; Vol 23 (No 6), Pp: 643-647 Ceftriaxone Associated Nephrolithiasis in Children Azita Fesharakinia* 1, MD; Ali-Reza Ehsanbakhsh 2, MD; Nasrin Ghorashadizadeh 2,
Hydroxyurea and Transfusion Therapy for the Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease
 Hydroxyurea and Transfusion Therapy for the Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease A Pocket Guide for the Clinician Susan E. Creary, MD, MSc 1 John J. Strouse, MD, PhD 2 1 The Ohio State University School of
Hydroxyurea and Transfusion Therapy for the Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease A Pocket Guide for the Clinician Susan E. Creary, MD, MSc 1 John J. Strouse, MD, PhD 2 1 The Ohio State University School of
The Present Scenario of Cholecystectomy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. III (May. 2016), PP 71-75 www.iosrjournals.org The Present Scenario of Cholecystectomy
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. III (May. 2016), PP 71-75 www.iosrjournals.org The Present Scenario of Cholecystectomy
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 04 Page April 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i4.215 Isolated Gall Bladder Agenesis A Rare
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i4.215 Isolated Gall Bladder Agenesis A Rare
In The Name of God. Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst?
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 Cystic Biliary Atresia: Why Is It Important to Distinguish this from Congenital Choledochal Cyst? Hussein Ahmed Mohammed Hamdy, MRCSEd, FEBPS* Hind Mustafa
Factors influencing the conversion of Laparoscopic to Open Cholecystectomy
 Original article Factors influencing the conversion of Laparoscopic to Open Cholecystectomy Satish Kumar Bansal 1, Umesh Kumar Chhabra 1, Sandeep Kumar Goyal 1, Gopal Singal 2, Pawan Kumar Goyal 2 1 Assistant
Original article Factors influencing the conversion of Laparoscopic to Open Cholecystectomy Satish Kumar Bansal 1, Umesh Kumar Chhabra 1, Sandeep Kumar Goyal 1, Gopal Singal 2, Pawan Kumar Goyal 2 1 Assistant
Management of Gallbladder Disease. Cory Buschmann, MD PGY-5 11/28/2017
 Management of Gallbladder Disease Cory Buschmann, MD PGY-5 11/28/2017 Financial disclosures None Content Scope of gallbladder diseases Evaluation H&P Labs Imaging Cholecystectomy vs cholecystostomy Ancillary
Management of Gallbladder Disease Cory Buschmann, MD PGY-5 11/28/2017 Financial disclosures None Content Scope of gallbladder diseases Evaluation H&P Labs Imaging Cholecystectomy vs cholecystostomy Ancillary
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management
 Original Research Article Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management P. Krishna Kishore 1*, B. Manju Sruthi 2, G. Obulesu 3 1 Assistant Professor, Departmentment of General Surgery,
Original Research Article Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management P. Krishna Kishore 1*, B. Manju Sruthi 2, G. Obulesu 3 1 Assistant Professor, Departmentment of General Surgery,
Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
Medical and Surgical Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia
 Medical and Surgical Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia Ahmed Al-Salem Medical and Surgical Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia Ahmed Al-Salem Department of Surgery Dar A lalafia Medical Company Qatif
Medical and Surgical Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia Ahmed Al-Salem Medical and Surgical Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia Ahmed Al-Salem Department of Surgery Dar A lalafia Medical Company Qatif
Vesalius SCALpel : Biliary (see also: biliary/pancreatic folios) Physiology
 Vesalius SCALpel : Biliary (see also: biliary/pancreatic folios) Physiology 95% of bile acids reabsorbed; colic and chenodeoxycolic primary bile acids cholecystokinin (CCK) major stimulus of gallbladder
Vesalius SCALpel : Biliary (see also: biliary/pancreatic folios) Physiology 95% of bile acids reabsorbed; colic and chenodeoxycolic primary bile acids cholecystokinin (CCK) major stimulus of gallbladder
PROGRESSIVE FAMILIAL INTRAHEPATIC CHOLESTASIS (PFIC)
 The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. PROGRESSIVE FAMILIAL INTRAHEPATIC
The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. PROGRESSIVE FAMILIAL INTRAHEPATIC
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES
 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Jitendra Singh Yadav
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(3B):966-970 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(3B):966-970 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Downloaded from jssu.ssu.ac.ir at 13:10 IRST on Saturday October 28th 2017
 Journal of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences Vol. 21, No. 5, Nov-Dec 2013 Pages: 675-681 1392 5 21 675-681 : 3 2* 1 1392/8/ : -1-2 -3 1391/8/24 : (). :. 1390 200 :.. SPSS (%0/5) 200 (8%) (%9/5)19
Journal of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences Vol. 21, No. 5, Nov-Dec 2013 Pages: 675-681 1392 5 21 675-681 : 3 2* 1 1392/8/ : -1-2 -3 1391/8/24 : (). :. 1390 200 :.. SPSS (%0/5) 200 (8%) (%9/5)19
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha Thalassemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_thalassemia 9/2013 7/2017 7/2018 7/2017 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha Thalassemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_thalassemia 9/2013 7/2017 7/2018 7/2017 Description
Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Comparison Between Primary Closure of Common Bile Duct and T- Tube Drainage After Open Choledocholithiasis: A Hospital Based Study
 Original article: Comparison Between Primary Closure of Common Bile Duct and T- Tube Drainage After Open Choledocholithiasis: A Hospital Based Study Kali CharanBansal Principal Specialist (General surgery)
Original article: Comparison Between Primary Closure of Common Bile Duct and T- Tube Drainage After Open Choledocholithiasis: A Hospital Based Study Kali CharanBansal Principal Specialist (General surgery)
Mirizzi syndrome with an unusual type of biliobiliary fistula a case report
 Kawaguchi et al. Surgical Case Reports (2015) 1:51 DOI 10.1186/s40792-015-0052-2 CASE REPORT Mirizzi syndrome with an unusual type of biliobiliary fistula a case report Tsutomu Kawaguchi 1,2*, Tadao Itoh
Kawaguchi et al. Surgical Case Reports (2015) 1:51 DOI 10.1186/s40792-015-0052-2 CASE REPORT Mirizzi syndrome with an unusual type of biliobiliary fistula a case report Tsutomu Kawaguchi 1,2*, Tadao Itoh
Hormone related problems (Endocrinopathies and osteoporosis) Vincenzo de Sanctis Ferrara.
 Hormone related problems (Endocrinopathies and osteoporosis) Vincenzo de Sanctis Ferrara vdesanctis@libero.it 6 th EUROPEAN SYMPOSIUM ON RARE ANAEMIAS 1 st Dutch-Belgian meeting for patients and health
Hormone related problems (Endocrinopathies and osteoporosis) Vincenzo de Sanctis Ferrara vdesanctis@libero.it 6 th EUROPEAN SYMPOSIUM ON RARE ANAEMIAS 1 st Dutch-Belgian meeting for patients and health
Original Contributions
 PII S0736-4679(01)00329-8 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 21, No. 1, pp. 7 13, 2001 Copyright 2001 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/01 $ see front matter
PII S0736-4679(01)00329-8 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 21, No. 1, pp. 7 13, 2001 Copyright 2001 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/01 $ see front matter
Gall bladder cancer. Information for patients Hepatobiliary
 Gall bladder cancer Information for patients Hepatobiliary page 2 of 12 Who will provide my care? You will be cared for by a number of professionals who work together. These professionals will be specialist
Gall bladder cancer Information for patients Hepatobiliary page 2 of 12 Who will provide my care? You will be cared for by a number of professionals who work together. These professionals will be specialist
Expected and unexpected gallstones in primary care
 Expected and unexpected gallstones in primary care 7 Speets AM, Van der Graaf Y, Hoes AW, Kalmijn S, De Wit NJ, Mali WPThM. Expected and unexpected gallstones in primary care. Submitted. CHAPTER 7 Abstract
Expected and unexpected gallstones in primary care 7 Speets AM, Van der Graaf Y, Hoes AW, Kalmijn S, De Wit NJ, Mali WPThM. Expected and unexpected gallstones in primary care. Submitted. CHAPTER 7 Abstract
Subtotal cholecystectomy for complicated acute cholecystitis: a multicenter prospective observational study
 Study title Subtotal cholecystectomy for complicated acute cholecystitis: a multicenter prospective observational study Primary Investigator: Kazuhide Matsushima, MD Co-Primary investigator: Zachary Warriner,
Study title Subtotal cholecystectomy for complicated acute cholecystitis: a multicenter prospective observational study Primary Investigator: Kazuhide Matsushima, MD Co-Primary investigator: Zachary Warriner,
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Asymptomatic Gallstones GM Ref: GM061 Version: 0.2 (21 November 2018)
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Asymptomatic Gallstones GM Ref: GM061 Version: 0.2 (21 November 2018) Commissioning Statement Asymptomatic Gallstones Policy Exclusions (Alternative commissioning
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Asymptomatic Gallstones GM Ref: GM061 Version: 0.2 (21 November 2018) Commissioning Statement Asymptomatic Gallstones Policy Exclusions (Alternative commissioning
Full Case: Questions: What is sickle cell crisis?
 Full Case: 30 y/o with avascular necrosis of her right hip was admitted for a total hip arthroplasty. Her hematocrit was 22%, blood pressure was 130/90 mm Hg, and pulse was 107 beats per minute. She had
Full Case: 30 y/o with avascular necrosis of her right hip was admitted for a total hip arthroplasty. Her hematocrit was 22%, blood pressure was 130/90 mm Hg, and pulse was 107 beats per minute. She had
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/27/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 35 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/27/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 35 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Ultrasonographic Triangular Cord Sign and Gallbladder Abnormality in Diagnosis of Biliary Atresia
 Iranian Journal of Neonatology 14 Ultrasonographic Triangular Cord Sign and Gallbladder Abnormality in Diagnosis of Biliary Atresia Seyed Ali Jafari*, MD,1 Mehrzad Mehdizadeh, MD,2 Fatemeh Farahmand, MD,
Iranian Journal of Neonatology 14 Ultrasonographic Triangular Cord Sign and Gallbladder Abnormality in Diagnosis of Biliary Atresia Seyed Ali Jafari*, MD,1 Mehrzad Mehdizadeh, MD,2 Fatemeh Farahmand, MD,
A scoring system for the prediction of choledocholithiasis: a prospective cohort study
 A scoring system for the prediction of choledocholithiasis: a prospective cohort study Bilal O. Al-Jiffry, a Samah Khayat, b Elfatih Abdeen, b Tasadooq Hussain, c Mohammed Yassin d From the a Department
A scoring system for the prediction of choledocholithiasis: a prospective cohort study Bilal O. Al-Jiffry, a Samah Khayat, b Elfatih Abdeen, b Tasadooq Hussain, c Mohammed Yassin d From the a Department
A one-year study of cholelithiasis at a tertiary care hospital of South India
 International Surgery Journal Rachamalla RR et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Jul;5(7):2444-2448 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20182502
International Surgery Journal Rachamalla RR et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Jul;5(7):2444-2448 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20182502
Heme Questions and Derivatives for the USMLE Step One Exam. Winter Storm Skylar Edition
 Heme Questions and Derivatives for the USMLE Step One Exam Winter Storm Skylar Edition Howard J. Sachs, MD Howard@12DaysinMarch.com www.12daysinmarch.com Patient presents with RUQ pain. HIDA scan fails
Heme Questions and Derivatives for the USMLE Step One Exam Winter Storm Skylar Edition Howard J. Sachs, MD Howard@12DaysinMarch.com www.12daysinmarch.com Patient presents with RUQ pain. HIDA scan fails
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request
 Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy for Gallstones in Adults Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 22 December 2017 Version: 1718.3.01 Individual Funding Request
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy for Gallstones in Adults Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 22 December 2017 Version: 1718.3.01 Individual Funding Request
Acute Complications of Sickle Cell Disease
 Management of Acute Complications of Sickle Cell Disease A Pocket Guide for the Clinician Timothy McCavit, MD, MSCS 1 Payal Desai, MD 1 University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center The Ohio State University,
Management of Acute Complications of Sickle Cell Disease A Pocket Guide for the Clinician Timothy McCavit, MD, MSCS 1 Payal Desai, MD 1 University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center The Ohio State University,
Peri-Operative Management: Guidelines for Inpatient Management of Children with Sickle Cell Disease
 Version 02 Approved by Interprofessional Patient Care Committee: September 16, 2016 1.0 Background Children with Sickle Cell are at risk of developing post-operative Acute Chest Syndrome. With improvements
Version 02 Approved by Interprofessional Patient Care Committee: September 16, 2016 1.0 Background Children with Sickle Cell are at risk of developing post-operative Acute Chest Syndrome. With improvements
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst
 Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Lutheran Medical Center. Daniel H. Hunt, M.D. June 10 th, 2005
 Lutheran Medical Center Daniel H. Hunt, M.D. June 10 th, 2005 History xx y.o. pt with primary CBD stones s/p ERCP xx months earlier for attempted stone extraction resulting in post ERCP pancreatitis. Patient
Lutheran Medical Center Daniel H. Hunt, M.D. June 10 th, 2005 History xx y.o. pt with primary CBD stones s/p ERCP xx months earlier for attempted stone extraction resulting in post ERCP pancreatitis. Patient
Pediatrics. Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment. Definition. Epidemiology of Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency.
 Pediatrics Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment See online here Pyruvate kinase deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder characterized by a deficiency in the enzyme "pyruvate kinase"
Pediatrics Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment See online here Pyruvate kinase deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder characterized by a deficiency in the enzyme "pyruvate kinase"
Case 1. Intro to Gallbladder & Pancreas Pathology. Case 1 DIAGNOSIS??? Acute Cholecystitis. Acute Cholecystitis. Helen Remotti M.D.
 Cholecystitis acute chronic Gallbladder tumors Adenomyoma (benign) Adenocarcinoma Pancreatitis acute chronic Pancreatic tumors Intro to Gallbladder & Pancreas Pathology Helen Remotti M.D. Case 1 70 year
Cholecystitis acute chronic Gallbladder tumors Adenomyoma (benign) Adenocarcinoma Pancreatitis acute chronic Pancreatic tumors Intro to Gallbladder & Pancreas Pathology Helen Remotti M.D. Case 1 70 year
Prevalence, Morphology and Chemical Composition of Gallstones in 150 Cholecystectomised Patients
 MORPHOLOGY THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE AND CHEMICAL MEDICAL JOURNAL COMPOSITION GALLSTONES VOL.10, NO.1, 2011 Prevalence, Morphology and Chemical Composition of Gallstones in 150 Cholecystectomised Patients
MORPHOLOGY THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE AND CHEMICAL MEDICAL JOURNAL COMPOSITION GALLSTONES VOL.10, NO.1, 2011 Prevalence, Morphology and Chemical Composition of Gallstones in 150 Cholecystectomised Patients
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form.
 : Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Surgery Type of Article: Case Report Title: Acute cholecystitis
: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Surgery Type of Article: Case Report Title: Acute cholecystitis
Presence of choledocholithiasis in patients undergoing cholecystectomy for mild biliary pancreatitis
 Original Article Presence of choledocholithiasis in patients undergoing cholecystectomy for mild biliary pancreatitis Pradhan S 1, Shah S 2, Maharjan S 2, Shah JN 3 1 2 2 3 Professor, Patan hospital Correspondence:
Original Article Presence of choledocholithiasis in patients undergoing cholecystectomy for mild biliary pancreatitis Pradhan S 1, Shah S 2, Maharjan S 2, Shah JN 3 1 2 2 3 Professor, Patan hospital Correspondence:
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice
 Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
Management of GALLSTONE Disease and GALLBLADDER Pathology December 2017
 Commissioning Policy Management of GALLSTONE Disease and GALLBLADDER Pathology December 2017 This policy applies to patients for whom the following Clinical Commissioning Groups are responsible: NHS South
Commissioning Policy Management of GALLSTONE Disease and GALLBLADDER Pathology December 2017 This policy applies to patients for whom the following Clinical Commissioning Groups are responsible: NHS South
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain
 Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Anaemia in Pregnancy
 Anaemia in Pregnancy Definition :anaemia is a pathological condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of red blood cells is insufficient to meet the body needs. The WHO : haemoglobin concentration
Anaemia in Pregnancy Definition :anaemia is a pathological condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of red blood cells is insufficient to meet the body needs. The WHO : haemoglobin concentration
Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice
 Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice Ahmed Laving KPA Annual Scientific Conference 2018 Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Case Presentation
Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice Ahmed Laving KPA Annual Scientific Conference 2018 Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Prolonged Jaundice? >6 months >3 months >2 weeks >4 weeks Case Presentation
Gallstones. Classification
 Gallstones Nariman Karanjia Tahir Ali Abstract Gallstones are extremely common in the UK and have a major effect on healthcare resources. Presentation depends on whether the stones occlude the cystic duct
Gallstones Nariman Karanjia Tahir Ali Abstract Gallstones are extremely common in the UK and have a major effect on healthcare resources. Presentation depends on whether the stones occlude the cystic duct
Study of the degree of gall bladder wall thickness and its impact on outcomes following laparoscopic cholecystectomy in JSS Hospital
 International Surgery Journal Chandra SBJ et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Apr;5(4):1417-1421 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20181122
International Surgery Journal Chandra SBJ et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Apr;5(4):1417-1421 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20181122
Indian Journal of Medical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences July 2017;4(7) ISSN: ISSN: DOI: /zenodo Impact Factor: 3.
 GALLBLADDER DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH LAPAROSCOPIC SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY IN JORDAN, PILOT STUDY Dr. Osama T. Abu Salem*, Dr. Ibrahim Al Gwairy, Dr. Ramadan Al Hasanat & Dr. Talal Jalabneh** *Consultant Gneral
GALLBLADDER DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH LAPAROSCOPIC SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY IN JORDAN, PILOT STUDY Dr. Osama T. Abu Salem*, Dr. Ibrahim Al Gwairy, Dr. Ramadan Al Hasanat & Dr. Talal Jalabneh** *Consultant Gneral
SASKATCHEWAN REGISTERED NURSES ASSOCIATION. RNs WITH ADDITIONAL AUTHORIZED PRACTICE CLINICAL DECISION TOOL AUGUST 2017
 DEFINITION Cholelithiasis Presence of gall stones in the biliary tract. Biliary Colic Right upper quadrant pain due to obstruction of a bile duct by a gallstone. Cholecystitis Inflammation of the gallbladder
DEFINITION Cholelithiasis Presence of gall stones in the biliary tract. Biliary Colic Right upper quadrant pain due to obstruction of a bile duct by a gallstone. Cholecystitis Inflammation of the gallbladder
Abdominal Sonographic Findings in Children With Sickle Cell Anemia
 Abdominal Sonographic Findings in Children With Sickle Cell Anemia Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 26(6) 281 285 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: http://www. sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Abdominal Sonographic Findings in Children With Sickle Cell Anemia Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 26(6) 281 285 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: http://www. sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male
 Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
Pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis
 Pancreatitis Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the duodenum. The duodenum is the upper part of the small intestine. The pancreas
Pancreatitis Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the duodenum. The duodenum is the upper part of the small intestine. The pancreas
Per-operative conversion of laparoscopic cholecystectomy to open surgery: prospective study at JSS teaching hospital, Karnataka, India
 International Surgery Journal Raza M et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jan;4(1):81-85 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20163977
International Surgery Journal Raza M et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jan;4(1):81-85 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20163977
Gallstones Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Gutscharity.org.uk
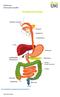 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento
 Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento https://www.google.com/search?sa=g&hl=en&q=public+disclosure&tbm=isch&tbs=simg:caqsigeahwelekju2aqaaawlelcmpwgaygpgcamskpib_1qnza7ai
Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento https://www.google.com/search?sa=g&hl=en&q=public+disclosure&tbm=isch&tbs=simg:caqsigeahwelekju2aqaaawlelcmpwgaygpgcamskpib_1qnza7ai
Objectives. Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology. RUQ: Normal Anatomy. Emergency Ultrasound: Gallbladder Location
 Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
Hemoglobinopathies Diagnosis and management
 Hemoglobinopathies Diagnosis and management Morgan L. McLemore, M.D. Hematology/Leukemia Department of Hematology and Oncology Winship Cancer Institute at Emory University mlmclem@emory.edu Disclosures
Hemoglobinopathies Diagnosis and management Morgan L. McLemore, M.D. Hematology/Leukemia Department of Hematology and Oncology Winship Cancer Institute at Emory University mlmclem@emory.edu Disclosures
Evaluation of complications and conversion rate of laparoscopic cholecystectomy in Rural Medical College
 Original article Evaluation of complications and conversion rate of laparoscopic cholecystectomy in Rural Medical College Satish Kumar Bansal 1, Sandeep Kumar Goyal 1, Umesh Kumar Chhabra 1, Pawan Kumar
Original article Evaluation of complications and conversion rate of laparoscopic cholecystectomy in Rural Medical College Satish Kumar Bansal 1, Sandeep Kumar Goyal 1, Umesh Kumar Chhabra 1, Pawan Kumar
ERCP / PTC Surgical Laparoscopic vs open Timing and order of approach
 Choledocholithiasis Which Approach and When? Lygia Stewart, MD University of California, San Francisco 2010 Naffziger Post-Graduate Course Clinical Manifestations of Choledocholithiasis Asymptomatic (no
Choledocholithiasis Which Approach and When? Lygia Stewart, MD University of California, San Francisco 2010 Naffziger Post-Graduate Course Clinical Manifestations of Choledocholithiasis Asymptomatic (no
Determination of effect of low dose vs moderate dose clofibrate on decreasing serum bilirubin in healthy term neonates
 Original Article Iran J Ped June 2007, Vol 17 (No 2), Pp:108-112 Determination of effect of low dose vs moderate dose clofibrate on decreasing serum bilirubin in healthy term neonates Mohammad Ashkan Moslehi
Original Article Iran J Ped June 2007, Vol 17 (No 2), Pp:108-112 Determination of effect of low dose vs moderate dose clofibrate on decreasing serum bilirubin in healthy term neonates Mohammad Ashkan Moslehi
CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice
 CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice Episode overview: 1) Describe heme metabolism 2) List common pre-hepatic/hepatic/post-hepatic causes of jaundice Wisecracks: 1) What are clinical signs of liver disease? 2)
CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice Episode overview: 1) Describe heme metabolism 2) List common pre-hepatic/hepatic/post-hepatic causes of jaundice Wisecracks: 1) What are clinical signs of liver disease? 2)
Comparative Study of Outcomes of Early Versus Interval Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy in Acute Calculus Cholecystitis.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. IX (April. 2017), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Study of Outcomes of Early
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. IX (April. 2017), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Study of Outcomes of Early
Epidemiology, Care and Prevention of Hemoglobinopathies
 Epidemiology, Care and Prevention of Hemoglobinopathies Nasir Al-Allawi MBChB, PhD. Professor of Hematology College of Medicine University of Dohuk, IRAQ From Research to Practice Training Course in Sexual
Epidemiology, Care and Prevention of Hemoglobinopathies Nasir Al-Allawi MBChB, PhD. Professor of Hematology College of Medicine University of Dohuk, IRAQ From Research to Practice Training Course in Sexual
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell. Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer
 Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
CLINICAL AND LABORATORY PATTERNS OF HEREDITARY HAEMOLYTIC ANEMIAS IN CHILDREN FROM CENTRAL REGION OF ROMANIA
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 6 (55) No. 2-2013 CLINICAL AND LABORATORY PATTERNS OF HEREDITARY HAEMOLYTIC ANEMIAS IN CHILDREN FROM CENTRAL REGION OF
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 6 (55) No. 2-2013 CLINICAL AND LABORATORY PATTERNS OF HEREDITARY HAEMOLYTIC ANEMIAS IN CHILDREN FROM CENTRAL REGION OF
Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases
 GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
