Omental Transplantation for Peripheral Vascular Disease - Our Experience
|
|
|
- Alison Cummings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Omental Transplantation for Peripheral Vascular Disease - Our Experience Ashwin Pai, Sriram Bhat, HS Shankar Ram, Sheila R Pai, Shobha G Pai Vol. 3 No. 10 (October 2011) International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine & Public Health (IJCRIMPH) ISSN Journal Type: Open Access Volume 3 Number 10 Journal details including published articles and guidelines for authors can be found at: To cite this Article: Pai A, Bhat S, Shankar Ram HS, Pai SR, Pai SG. Omental Transplantation for Peripheral Vascular Disease - Our Experience. International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine & Public Health. 2011; 3(10): Article URL: Correspondence concerning this article should be addressed to Ashwin Pai (MS (Sur) MRCS (Edin) FAGE); Mangalore , Karnataka, India / Phone: / drashwinpai@gmail.com Paper publication: 28 October 2011
2 797 Omental Transplantation for Peripheral Vascular Disease - Our Experience Ashwin Pai (1) *, Sriram Bhat (2), HS Shankar Ram (3), Sheila R Pai (4),Shobha G Pai(5) 1) Assistant Prof. of Surgery, KMC Mangalore, Manipal University, India 2) Professor of Surgery, KMC Mangalore, Manipal University, India 3) Post graduate Student in Surgery, KMC Mangalore, and Manipal University, India 4) Professor of Physiology, KMC Mangalore, Manipal University, India 5) Assoc Prof of Ophthalmology, KMC Mangalore, Manipal University, India * Corresponding Author ABSTRACT Introduction /Aim: The objective of this paper is to study the efficacy of omental transplantation in peripheral vascular disease. Results: This study is a prospective study done on a group of 30 patients. This study constituted patients of the age group between years. The patients were all male. The patients were Beedi smokers (A beedi is a rolled up tobacco without filter) and on an average the patients smoked between beedis per day. The chosen cases did not have posterior tibial, anterior tibial and dorsalis pedis artery pulsations. In 20 of our cases, popliteal artery pulsation was absent. 11 cases had non-healing ulcers and 20 had dry gangrene of toe/toes or forefoot, with rest pain. The patients were assessed at post operative day 7, at 1 month and 3 months after the procedure. Intermittent claudication was relieved in 25 patients (83%). Rest pain which was present in 15 patients (50%) before the procedure was relieved in all the patients at the end of 3 months (100%). Healing of ulcer occurred in 10 out of 11 patients (91%). The healing of amputated toe site occurred in 15 out of 20 patients during 3 months follow-up (75%). The O2 saturation measured by pulseoximetry measured in all patients increased from 72% on an average to 94% after 3 months of follow-up. Conclusion: Patients presenting with terminal limb ischemia due to Thromboangitis Obliterans often have no hope for limb salvage, for such cases, omental transplantation offers a procedure which can result in improved limb circulation and limb salvage. The level of omental transplantation had no bearing on the improvement in symptoms thereby supporting the potency of omental pedicle graft to induce neoangiogenesis and thereby improving circulation of surrounding tissues. Keywords: Omentum, Omentoplasty, Omental transplant, Omental transposition, Peripheral Vascular disease, Burgers disease, Thromoboangitis Obliterans Introduction Daniel (1971) hoped omental transfer for revascularization of extremities will postpone amputation. Casten and Alday first studied omental transplantation 19. Alday and Goldsmith gave an excellent description of technique of omental lengthening. Morrison described omentum as Policeman of the abdomen. As it wraps around the structures like gall bladder, appendix and revascularises these structures when deprived of their blood supply. Hoshino 18 classified the omentum as Type I Single layered omentum
3 798 Type II Double layered omentum Goldsmith discovered lipid fraction from the omentum which exerts angiogenic properties. Omentoplasty acts by increasing the collateral circulation as it contains Angiogenic factor. 20, 21 Mechanism of Action When the procedure was introduced for patients with atherosclerosis by Casten and Aldy 19, it was thought that omental transposition works by supplying extra blood to the ischemic limb. However, this is difficult to believe, as the diameter of omental vessels is roughly one-tenth of the popliteal artery. Later studies 6, 7, 8,9,10 have demonstrated that the possible mechanism of action of omental transfer is an increase in local collateral circulation rather than any significant increase in blood flow. Goldsmith et al. have demonstrated that the omentum contains a lipid fraction which promotes neovascularisation. Thus a local action on limb musculature with increased local collateral circulation may be a possible mode 20, 21 of action. Omentum has been known to adhere to surrounding structures and develop connections with them, Hoshino et al. have seen in limbs amputated after omental transplantation that there were vascular connections of omentum with limb vasculature 18. Babu et al have seen, in the limbs amputated after omental transplantation, revascularization of muscle from omental vessels growing into it. 15 Aggarwal et al. performed postoperative angiography in 50 patients who underwent omental grafting and observed increase number of collaterals at graft site with filling of vessels distal to the block in the limbs. In an extension of the same study, 20 dogs underwent allograft omental transfer in limbs after ligation of the femoral artery in 10 of these, at the end of three weeks exploration of the graft site revealed increased number of collaterals at the graft site with filling of vessels distal to the site of the block. The authors concluded that even a blood group and human leukocyte antigen mismatched omental graft is taken up and revascularises the ischemic limb. 14 Subodh et al. performed post-operative Doppler studies and selective celiac axis angiography to study the circulation in the omental graft. In 18 of their 20 cases, the arterial pulsations were heard till the knee on Doppler study. In 2 cases in which they were not heard, there was no improvement in symptoms. However on celiac-axis angiography, the omental vessels were visualized till the thigh in only six and upto the knee in only four patients. The authors concluded that omental transposition probably works by promoting local collateralization. Similar conclusions were drawn in another study comparing free versus pedicled omental graft. 16 Materials and Methods A total of 30 patients were part of this study. The age group of the cases was between years. All the cases studied were male. The patients were Beedi smokers (A beedi is a rolled up tobacco without filter) and on an average the patients smoked between beedis per day. The chosen cases did not have posterior tibial, anterior tibial and dorsalispedis artery pulsations. In 20 of our cases, popliteal artery pulsation was absent. 11 cases had non-healing ulcers and 20 had
4 799 dry gangrene of toe/toes or forefoot, with rest pain. (Table 2) Obese and diabetic patients have not been selected since, the delineation of omental vascular pattern is difficult in obese patients and diabetic would usually have associated coronary disease and are more prone for infection. (Figures 1, 2, 3) In the post operative period, patient were given parenteral nutrition for 48 hours and switched on to oral feeds once the peristalsis returns. Routine antibiotics and analgesics were given. Patient was advised to keep the limb in extension for 2-3 days and allowed to bear weight on 4 th or 5 th day onwards. On 10 th day, sutures were removed and patient is made to walk. All patients underwent a Doppler scan of the lower limb prior to Surgery. The Doppler study was done to mainly demonstrate the block and the flow in the distal vessels Assessment of the Effect of Omentoplasty The criteria used to assess Subjective: Symptomatic improvement. Objective: 1) Improvement in the local skin temperature 2) Healing of ulcers and amputation site. 3) Measurement of oxygen saturation by pulseoximetry The patients were assessed after 7 days, 1 month and 3 months after undergoing the procedure. In all patients pulseoximetry was used to measure pre and post-operative O 2 saturation. Results Observations The youngest patient in the study was 23yrs old and the oldest 50yrs old. All of the studied patients were male. All of the patients were from low socio-economic status. Most of them were manual labourers. Clinical Presentation None of the patients were on any medications except oral analgesics before admission. All the patients in the study were non-diabetic and normotensive at the time of admission. Habituations All the patients in our study were beedi smokers (100%) (Beedis are rolled up tobacco without a filter).15 (50%) of them were also occasional alcoholics. 5 (17%) of them also used smokeless tobacco in pan chewing. Duration of smoking Around 54% of patients smoked beedis for years Amount of smoking 77% of patients smoked beedis/day Peripheral arterial pulsations The pulses were assessed both by clinical examination and a hand held Doppler probe. Correlation of symptoms with signs All the patients in the study presented with symptoms involving only one lower limb. But during clinical examination, 50% of patients, also had involvement of opposite lower limb also 3% of them had clinical involvement of upper limb also. Level of omental transplantation See Table 8.
5 800 Complications In post operative period, 10 patients had post operative infection of wounds. All of these patients were treated with regular dressing and antibiotic according to culture and sensitivity reports. 70% of these patients responded with this treatment. In 30% of these patients infection was associated with necrosis of omentum. Duration of Hospital Stay Duration of hospital stay varied from days. Most of the patients stayed for days. The length of post operative stay was increased in the patients due to wound infections and due to no improvement following the procedure in 3 patients. During follow-up the patients were assessed at 7 th day, 1 month and 3 months following intervention. O 2 Saturation by pulseoximetry was also measured in toes during follow-up examination in 10 patients. Analysis All the 30 patients in this study were males in the age group of yrs. Mean age of the patient being 36.5 yrs (Table 1). History of smoking was present in all the cases. Around 70% of patients smoked for more than 10 yrs (Table 4). About 77% of patients smoked beedis/day (Table 5). Chief symptoms were intermittent claudication, rest pain, gangrene of toes and ulceration at tip of toes or foot (Table 2). No patient underwent lumbar sympathectomy prior to omental transplantation. Clinical manifestations of the affected limb revealed absence of dorsalis pedis and anterior tibial in all the 30 patients, absence of posterior tibial in 28 patients and popliteal in 20 patients. Femoral pulsations were present in all patients. The disease was restricted to one lower limb only in 50%. In 47% it involved bilateral lower limbs and only in 3% bilateral lower limbs with upper limb (Table 6). Omental transplantation along with lumbar sympathectomy was done as a single stage procedure in 66% of patients. In 33% of patients only omental transplantation was done. The procedure was well tolerated by all the patients and there was no intra and post operative mortality. Omental transfer was possible up to below the knee in 71% of patients. However, in 23% of patients, omentum could be lengthened only up to above knee level. The time taken for surgery ranges between 2-3hrs (Tables 7-8). Amputation of toes was done simultaneously in all the 20 patients who presented with gangrene of toes. The patients were assessed post operatively in form of; Subjective Improvement in intermittent claudication and rest pain. Improvement i. Objective - Increase in skin temperature Increase oxygen saturation as measured by pulseoximetry During follow up, the patients were assessed at post operative day 7, at 1 month and 3 months after the procedure. Intermittent claudication was relieved in 25 patients (83%). Rest pain which was present in 15 patients (50%) before the procedure was relieved in all the patients at the end of 3 months (100%). Healing of ulcer occurred in
6 out of 11 patients (91%). The healing of amputated toe site occurred in 15 out of 20 patients during 3 months follow-up (75%). The O 2 saturation measured by pulseoximetry measured in all patients increased from 72% on an average to 94% after 3 months of follow-up (Tables 10 11). In 10 patients in our study, a postoperative complication in form of wound infection was noticed. In 7 of these patients (70%) the wound infection was minor and responded to the treatment given. In rest 3 of these patient (30%), necrosis of the omentum occurred which was associated with wound infection. In these patients the symptoms did not subside. All of 3 patients eventually required major amputations. No other complication was encountered in this study (Table 9). Discussion Burger s disease (Thromboangitis Obliterans) continues to be a major surgical problem. Its treatment has remained an enigma and multiple strategies have been employed. Drug therapy is of benefit only in early stages. Surgical treatment options have consisted of sympathectomy, direct arterial surgery, adrenalectomy and amputation as a last resort. With the exception of smoking, none of these measures is curative and conflicting results have been obtained. However, in patients with critical limb ischemia, surgery is required to salvage the limb. Traditionally, patients who have ischemic signs and symptoms have been offered sympathectomy despite the fact that relapses are frequent due to normalization of vasomotor tone within 2 weeks to 6 months after operation. Arterial reconstruction is usually impossible due to distal nature of the disease and carries a high failure rate. In patients who are in imminent danger of requiring major amputation, omental pedicled transplantation is a viable alternative for limb salvage and also significantly improves signs and symptoms. Greater omentum is a primitive part of gastrointestinal system containing a vast network of blood supply and lymphatics, even if deprived of its own blood supply it might survive by attacking arteries in the vicinity. Goldsmith et al. 20,21 discovered a lipid fraction from the omentum with angiogenic influences. This property of omental pedicle graft to induce neo angiogenesis and thereby improving circulation of surrounding tissues has been well established. Hence omentum has been used to revascularise the ischemic limb 7, 8, 9, 10, 11. Nishimura et al. showed an increase in muscle blood flow during exercise and reactive hyperemia by using xenon (Xe 133) clearance study 2. Babu, Menon, Vaidyanathan (in 1990) obtained relief in intermittent claudication in 92% patients with TAO, relief in intermittent claudication in 92% patients with TAO, relief from rest pain in 86%, healing of ulcers in 100% of their patients. 14% of their patients required major amputation 15 Ranwaka, Sharma (in 1999) obtained relief in intermittent claudication in 86.6%, relief from rest pain in 66.6% and healing of ulcers in 80% in their patients. 17 The results in our study are consistent with these results of some previous studies as shown in Table 12. The mechanism by which omentopexy increases vascularity of the ischemic limb is not exactly known. Probably omental transposition works by promoting local collateralization, since omentum is known to possess angiogenic factor, which stimulates the formation of capillary channels making
7 802 available collateral channels in the existing circulation. Subodh et al. (1994) 13 tried to find out the mechanism by which the omental graft increases the blood supply to the limbs. They performed Doppler ultrasound studies and celiac digital subtraction angiography to study the circulation though the omental graft. Only in 6 out of 12 patients could they visualize omental vessels till mid-thigh and only in four up to the knee joint. They concluded that omental transposition acts not by significantly supplying extra blood to the limbs but by acting locally on the limb musculature and probably causing increased collateral circulation. Although in the absence of such investigating facilities and financial constraints, we were not able to visualize omental vessels but we could certainly appreciate an excellent symptomatic relief obtained in these patients. There was immediate relief of pain; the progression of gangrene stopped, and ulcers healed, a major amputation was avoided in 90% of patients. Another interesting finding in the present series was that most of the patients experienced pain relief, immediately following surgery. Possible causes may be (i) Psychological relief that operation has been performed (ii) Bed rest (hospital admission) (iii) Supervision and almost complete stoppage of smoking leading to remission of the disease (iv) lumbar sympathectomy performed simultaneously in 2/3 rd of the patients. In the present study, objective tests were carried out to see improvement in circulation. Skin temperature increased in 90% of patients. Pulseoximetry, an excellent method of assessing limb perfusion revealed a clear benefit in tissue oxygenation after pedicled omental transplantation. Conclusion Patients presenting with critical limb ischemia due to thromboangitis obliterans often have no hope for limb salvage, for such cases, omental transplantation offers a procedure which can result in improved limb circulation and limb salvage. The level of omental transplantation had no bearing on the improvement in symptoms thereby supporting the potency of omental pedicle graft to induce neoangiogenesis and thereby improving circulation of surrounding tissues. This is a fairly simple operation, which can be performed by general surgeons. This operation does not need special instruments and can be done in all general hospitals. The postoperative care is also simple; post operatively Ryle s tube aspirations are done periodically due to presence of Gastric ileus. Secondly, wound inspection should be done to look for any infection/ discharge from the wounds. Single stage lumbar sympathectomy and omental transplantation is a better procedure in end state Thromboangitis obliterans with the advantages of a single stage operation and low cost. Immediate improvement in symptoms cannot just be explained in psychological basis as was demonstrated by increase in skin temperature and improved tissue oxygenation by pulseoximetry. The present study has short comings in form of (i) short duration of follow up (ii) no Doppler or angiographic evidence during follow up (iii). No histological
8 803 proof of neovascularization of muscles. The present study, however, proved beyond doubt, the role of omental transplantation in clinical improvement and as a limb salvage procedure in Burger s disease. By this surgery the pathological progress of the disease cannot be stopped but it can be delayed significantly. However much work needs to be done in this field. The question regarding the mechanism of action of omentum needs to be answered. Long term prospective randomized and controlled trials with longer follow up are required to establish this procedure as the first line of management in patients with Burger s disease. Conflict of Interest: None References 1. Buerger L. Thromboangitis Obliterans; a study of the vascular lesions leading to spontaneous gangrene. Am J Med Sci 1908; 136; Olin JW. Thromboangitis Obliterans (Burger s disease). New Eng J Med 2000;343; Fiessinger JN, Schafer M. Trial of iloprost versus aspirin treatment for critical limb ischemia of thromboangitis obliterans. The TAO study, Lancet 1990;335; Talwar S. Choudhary SK. Bhan A.Buerger s disease. Indian Journal of Cardiology 1998;1; Lau H, Cheng SK, Burger s disease in Hong Kong; a review of 89 cases. Aust NZ J Surg 1997; 67; Sasajima T. Kubo Y., Inaba M, Goh K. Plantar or dorsalis pedis artery bypass in Burger s disease. Ann Vasc Surg 1994;8; Stricht VJ, Goldstein M, Flamand JP, Belenger J. Evolution and prognosis of thromboangitis obliterans. J Cardiovasc surg (Torino) 1973;14; Kulin J, Lengua F, Testart J, Pajot A.F. Thromboangiosis or thromboangitis treated by adrenalectomy and sympathectomy from 1942 to 1962 J. Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1973;14; Komori K. Kawasaki K. Okazaki J., Eguchi D. Mawatari K., Okadome K., et al. Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for Burger s disease of the upper extremities. J Vasc Surg 1995; 22; Nakajima N. The change in concept and surgical treatment on Burger s disease-personal experience and review. Int J Cardiol 1998;66(Suppl.1);S273-S Nishikimi N. Fate of Limbs with failed vascular reconstruction in Burger s disease. Int J Cardiol 200;75(Suppl I); S Drummond D, Morison R. A case of ascitis due to cirrhosis of liver cured by operation. Br. Med J 1896;2;728.
9 Vineberg A, Lwin MM. Fostering a natural artery bypass for disseminated coronary artery disease by pericoronary omental strips. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1973;137; Aggarwal VK, Bajaj S. Salvage of end stage extremity by omentopexy in Buerger s disease. Indian Journal of Thoracic and cardiovascular surgery 1987; 5; Babu RD, Menon NG, Vaidyanathan S. Pedicled omental transplantation for end stage Buerger s disease as a limb salvage procedure. Indian Journal of Surgery 1990; 52; Subodh S., Mohan JC, Malik VK, Omentopexy in limbs revascularization in Buerger s disease. Indian Heart J 1994; 46; Ranwaka R, Sharma R, Mathur SN, Sachdeva G. Revascularisation of limbs by omental transfer. Ind J Surg. 1999; 61: Hoshino S, Nakayama K, Igari T, Honda K. Long term results of omental transplantation for chronic occlusive arterial diseases. Int Surg 1983; 68: Casten DF, Alday ES. Omental transfer for revascularization of the extremities. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1971; 123: Goldsmith HS, Griffith AL, Catsimpoolas N. Increased vascular perfusion after administration of an omental lipid fraction. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1986; 162: Goldsmith HS, Griffith AL, Kupferman A, Catsimpoolas N. Lipid Angiogenic factor from Omentum. JAMA 1984; 252:
10 805 Table 1: Age groups of patients studied Age group(in years) No. of patients Percentage (%) yrs 6 20% yrs % yrs % Table 2: Clinical Presentations of various cases Symptoms No. of patients Percentage (%) Intermittent claudication % Rest pain 15 50% Ulceration 11 37% Gangrene 20 66% Sensory symptoms (e.g.: paraesthesias) 7 23% Table 3: Habituations of the patients Addiction No. of patients Percentage (%) Smoking % Alcohol 15 50% Smokeless tobacco 5 17% Table 4: Duration of Smoking Duration of smoking (in yrs) No. of patients Percentage (%) 10 yrs 9 30% yrs % yrs % Table 5: Duration and amount of smoking Duration of beedis smoked No. of patients Percentage (%) <10 yrs 6 20% yrs 12 40% yrs 11 37% >30 yrs 1 3%
11 806 Table 6: Peripheral arterial Pulses Arterial Pulsation Absent Weak Normal Dorsalis Pedis Artery 30 Anterior Tibial Artery 30 Posterior Tibial Artery 28 2 Popliteal Artery Femoral Artery _ 3 27 Table 7: Extent of the disease No. of Percentage (%) patients Disease restricted to one limb 15 50% Disease involving B/L lower limbs % Disease involving B/L lower limbs and upper limbs 1 3.3% Table 8: Level of omental transplantation Level of transplantation No. of patients Percentage (%) Above knee 7 23% Below knee 21 71% Above ankle 2 6.0% Table 9: Duration of Hospital stay Duration of hospital stay No. of patients Percentage (%) <2 days 1 3% days 20 67% days % >40 days %
12 807 Table 10: Follow up Results Symptom At time diagnosis 7 th day 1 st Month 3 rd Month No. % No. % No. % Intermittent claudication % 20 66% 8 27% 5 17% Rest pain 15 50% 8 27% 5 17% - - Healing of ulcer 11 37% 11 37% 8 27% 1 3% Healing of amputated site 20 66% 20 66% 13 43% 5 17% Table 11: Oxygen Saturation of the limb during follow up O 2 Saturation of limb At the time of 7 th day 1 st month 3 rd month diagnosis 72% 80% 90% 94% Table 12: Comparison of Our Study with previous results Symtpoms % improvement In present study Baby(1990) Ranwaka (1999) Intermittent 83% 92% 86.6% claudication Rest pain 100% 86% 66.6% Ulcer healing 91% 100% 80%
13 808 Figure 1: Omentum being mobilized Figure 2: Omentum mobilized to reach till below knee
14 809 Figure 3: Skin incisions made on the limb for subcutaneous tunneling of the Omentum
Peripheral Arterial Disease Extremity
 Peripheral Arterial Disease Lower Extremity 05 Contributor Dr Steven Chong Advisors Dr Ashish Anil Dr Tay Jam Chin Introduction Risk Factors Clinical Presentation Classification History PHYSICAL examination
Peripheral Arterial Disease Lower Extremity 05 Contributor Dr Steven Chong Advisors Dr Ashish Anil Dr Tay Jam Chin Introduction Risk Factors Clinical Presentation Classification History PHYSICAL examination
Clinical and social consequences of Buerger disease
 Clinical and social consequences of Buerger disease Takashi Ohta, MD, Hiroyuki Ishioashi, MD, Minoru Hosaka, MD, and Ikuo Sugimoto, MD, Aichi, Japan Purpose: This study was undertaken to assess the clinical
Clinical and social consequences of Buerger disease Takashi Ohta, MD, Hiroyuki Ishioashi, MD, Minoru Hosaka, MD, and Ikuo Sugimoto, MD, Aichi, Japan Purpose: This study was undertaken to assess the clinical
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD
 PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
Due to Perimed s commitment to continuous improvement of our products, all specifications are subject to change without notice.
 A summary Disclaimer The information contained in this document is intended to provide general information only. It is not intended to be, nor does it constitute, medical advice. Under no circumstances
A summary Disclaimer The information contained in this document is intended to provide general information only. It is not intended to be, nor does it constitute, medical advice. Under no circumstances
Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Role of Vascular Surgeon Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai University
Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Role of Vascular Surgeon Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai University
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS
 VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer
 Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Diagnosis and management of pheripheral arterial occlusive disease
 Original article : Diagnosis and management of pheripheral arterial occlusive disease 1 Dr Shrikant kurhade, 2 Dr Pravin Namdeo shingade 1,2 Assistant Professor, Grant Govt Medical College & Sir J J Group
Original article : Diagnosis and management of pheripheral arterial occlusive disease 1 Dr Shrikant kurhade, 2 Dr Pravin Namdeo shingade 1,2 Assistant Professor, Grant Govt Medical College & Sir J J Group
Arterial Studies And The Diabetic Foot Patient
 Arterial Studies And The Patient George L. Berdejo, BA, RVT, FSVU gberdejo@wphospital.org Disclosures I have nothing to disclose! Diabetes mellitus continues to grow in global prevalence and to consume
Arterial Studies And The Patient George L. Berdejo, BA, RVT, FSVU gberdejo@wphospital.org Disclosures I have nothing to disclose! Diabetes mellitus continues to grow in global prevalence and to consume
Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Vascular Management Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai
Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Vascular Management Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists
 EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
THE popliteal artery is the second most common site of aneurysm. The
 POPLITEAL ANEURYSM Treatment by Vein Graft: Case Report A. W. HUMPHRIES, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery F. A. LeFEVRE, M.D. and V. G. dewolfe, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease THE popliteal
POPLITEAL ANEURYSM Treatment by Vein Graft: Case Report A. W. HUMPHRIES, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery F. A. LeFEVRE, M.D. and V. G. dewolfe, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease THE popliteal
What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease
 What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Sibu P. Saha, MD, MBA Professor of Surgery Chairman, Directors Council Gill Heart Institute University of Kentucky Lexington, KY Disclosure My
What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Sibu P. Saha, MD, MBA Professor of Surgery Chairman, Directors Council Gill Heart Institute University of Kentucky Lexington, KY Disclosure My
Disclosures. Tips and Tricks for Tibial Intervention. Tibial intervention overview
 Tips and Tricks for Tibial Intervention Donald L. Jacobs, MD C Rollins Hanlon Endowed Professor and Chair Chair of Surgery Saint Louis University SSM-STL Saint Louis University Hospital Disclosures Abbott
Tips and Tricks for Tibial Intervention Donald L. Jacobs, MD C Rollins Hanlon Endowed Professor and Chair Chair of Surgery Saint Louis University SSM-STL Saint Louis University Hospital Disclosures Abbott
Piazza G, Creager M. Thromboangiitis Obliterans. Circulation Apr 27; 121(16):
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Thromboangiitis Obliterans (TAO) 12 TAO, also called Buerger disease, is an inflammatory disease that most commonly affects the
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Thromboangiitis Obliterans (TAO) 12 TAO, also called Buerger disease, is an inflammatory disease that most commonly affects the
Introduction. Risk factors of PVD 5/8/2017
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
ARTERIAL BYPASS GRAFTS IN THE LEG
 The Christchurch Department of Vascular Surgery is actively involved in research projects aimed at improving treatment for patients with arterial disease. Marilyn Ollett Department of Surgery Christchurch
The Christchurch Department of Vascular Surgery is actively involved in research projects aimed at improving treatment for patients with arterial disease. Marilyn Ollett Department of Surgery Christchurch
Now That You Have the Tools
 blockosu@gmail.com Now That You Have the Tools Alan Jay Block, DPM, MS, FASPS, FACFAS Assistant Professor Dept Of Orthopeadics The Ohio State University Medical Board Kent State University Editor-in -Chief
blockosu@gmail.com Now That You Have the Tools Alan Jay Block, DPM, MS, FASPS, FACFAS Assistant Professor Dept Of Orthopeadics The Ohio State University Medical Board Kent State University Editor-in -Chief
Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot. Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017
 Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017 Case Male 67 years old Underlying DM, HTN, TVD Present with gangrene
Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017 Case Male 67 years old Underlying DM, HTN, TVD Present with gangrene
Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease. Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August
 Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August 20 2014 Outline (and for the ABIM board exam * ** ***) Prevalence* Definitions Lower Extremity: Aorta*** Claudication***
Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August 20 2014 Outline (and for the ABIM board exam * ** ***) Prevalence* Definitions Lower Extremity: Aorta*** Claudication***
EFFECT OF LUMBAR SYMPATHECTOMY ON MUSCLE CIRCULATION IN DOGS AND PATIENTS
 Nagoya J. med. Sci. 37: 71-77, 1975 EFFECT OF LUMBAR SYMPATHECTOMY ON MUSCLE CIRCULATION IN DOGS AND PATIENTS MASAFUMI HIRAI, SEIICHI KAWAI and SHIGEHIKO SHIONOY A Department of Surgery, Nagoya University
Nagoya J. med. Sci. 37: 71-77, 1975 EFFECT OF LUMBAR SYMPATHECTOMY ON MUSCLE CIRCULATION IN DOGS AND PATIENTS MASAFUMI HIRAI, SEIICHI KAWAI and SHIGEHIKO SHIONOY A Department of Surgery, Nagoya University
Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral-Popliteal and Femoral-Distal Bypass Grafts
 Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral-Popliteal and Femoral-Distal Bypass Grafts Why do you need the operation? You need this operation because you have either pain in your legs or a leg ulcer or gangrene
Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral-Popliteal and Femoral-Distal Bypass Grafts Why do you need the operation? You need this operation because you have either pain in your legs or a leg ulcer or gangrene
Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2)
 Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2) Definition Vascular surgery is the specialty concerned with the diagnosis and management of congenital and acquired diseases of the
Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2) Definition Vascular surgery is the specialty concerned with the diagnosis and management of congenital and acquired diseases of the
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing
 Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)
 Original article: Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) 1DR Anu N Gaikwad, 2 Dr Vikrant V Rasal, 3 Dr S A Kanitkar, 4 Dr Meenakshi Kalyan
Original article: Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) 1DR Anu N Gaikwad, 2 Dr Vikrant V Rasal, 3 Dr S A Kanitkar, 4 Dr Meenakshi Kalyan
Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care. Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017
 Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017 Surgeons idea Surgeons idea represents the final stage of peripheral
Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017 Surgeons idea Surgeons idea represents the final stage of peripheral
Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI
 PAD Diagnosis Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Metro Health / University of Michigan Health, Wyoming, MI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI University Hospitals Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, Cleveland, OH PAD:
PAD Diagnosis Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Metro Health / University of Michigan Health, Wyoming, MI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI University Hospitals Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, Cleveland, OH PAD:
PAD and CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA: EVALUATION AND TREATMENT 2014
 PAD and CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA: EVALUATION AND TREATMENT 2014 Van Crisco, MD, FACC, FSCAI First Coast Heart and Vascular Center, PLLC Jacksonville, FL 678-313-6695 Conflict of Interest Bayer Healthcare
PAD and CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA: EVALUATION AND TREATMENT 2014 Van Crisco, MD, FACC, FSCAI First Coast Heart and Vascular Center, PLLC Jacksonville, FL 678-313-6695 Conflict of Interest Bayer Healthcare
Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds
 Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds American Society of Podiatric Surgeons Surgical Conference September 22, 2018 Michael Maier, DPM, FACCWS Cardiovascular Medicine Cleveland Clinic Disclosures Speaker,
Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds American Society of Podiatric Surgeons Surgical Conference September 22, 2018 Michael Maier, DPM, FACCWS Cardiovascular Medicine Cleveland Clinic Disclosures Speaker,
Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease
 January 2003 Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease Grace Tye, Harvard Medical School Year III Patient D.M. CC: 44 y/o male with pain in his buttocks Occurs after walking 2 blocks. Pain is
January 2003 Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease Grace Tye, Harvard Medical School Year III Patient D.M. CC: 44 y/o male with pain in his buttocks Occurs after walking 2 blocks. Pain is
Disclosures. Critical Limb Ischemia. Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient. Vascular Testing in Critical Limb Ischemia UCSF Vascular Symposium
 Disclosures Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient None 2015 UCSF Vascular Symposium Warren Gasper, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Division of Vascular Surgery Critical Limb Ischemia Chronic Limb
Disclosures Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient None 2015 UCSF Vascular Symposium Warren Gasper, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Division of Vascular Surgery Critical Limb Ischemia Chronic Limb
Arthroplasty after previous surgery: previous vascular problems
 Arthroplasty after previous surgery: previous vascular problems Jacques Menetrey & Victoria B. Duthon Centre de médecine de l appareil locomoteur et du sport Swiss Olympic medical Center Unité d Orthopédie
Arthroplasty after previous surgery: previous vascular problems Jacques Menetrey & Victoria B. Duthon Centre de médecine de l appareil locomoteur et du sport Swiss Olympic medical Center Unité d Orthopédie
Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization:
 Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization: Long Term Result For Critical Limb Ischemia With Unreconstructable Distal Arteries Pramook Mutirangura Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj
Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization: Long Term Result For Critical Limb Ischemia With Unreconstructable Distal Arteries Pramook Mutirangura Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj
The Struggle to Manage Stroke, Aneurysm and PAD
 The Struggle to Manage Stroke, Aneurysm and PAD In this article, Dr. Salvian examines the management of peripheral arterial disease, aortic aneurysmal disease and cerebrovascular disease from symptomatology
The Struggle to Manage Stroke, Aneurysm and PAD In this article, Dr. Salvian examines the management of peripheral arterial disease, aortic aneurysmal disease and cerebrovascular disease from symptomatology
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division
 John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy
 Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy Yang-Jin Park Associate professor Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Peripheral artery
Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy Yang-Jin Park Associate professor Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Peripheral artery
Case Report Persistent Sciatic Artery Aneurysm with Lower Limb Ischemia
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine, Article ID 183969, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/183969 Case Report Persistent Sciatic Artery Aneurysm with Lower Limb Ischemia Gaurav Kesri, 1,2 Jitendra Mangtani,
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine, Article ID 183969, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/183969 Case Report Persistent Sciatic Artery Aneurysm with Lower Limb Ischemia Gaurav Kesri, 1,2 Jitendra Mangtani,
Research Article. Sanjeev Agarwal 1 *, Ritu Mehta 2, C. P. Joshi 1. DOI:
 International Surgery Journal Agarwal S et al. Int Surg J. 2016 May;3(2):537-542 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20160953
International Surgery Journal Agarwal S et al. Int Surg J. 2016 May;3(2):537-542 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20160953
FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL MEDICAL REVIEW POLICY
 FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL MEDICAL REVIEW POLICY CPT/HCPCS Codes 93925 Duplex scan of lower extremity arteries or arterial bypass grafts; complete bilateral study 93926 unilateral or limited study Policy
FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL MEDICAL REVIEW POLICY CPT/HCPCS Codes 93925 Duplex scan of lower extremity arteries or arterial bypass grafts; complete bilateral study 93926 unilateral or limited study Policy
Fluorescent Angiography: Practical uses in the Clinical Setting
 Fluorescent Angiography: Practical uses in the Clinical Setting Charles Andersen MD, FACS, MAPWCA Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation Surgery Service (Emeritus) Chief of Wound Care Service Madigan
Fluorescent Angiography: Practical uses in the Clinical Setting Charles Andersen MD, FACS, MAPWCA Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation Surgery Service (Emeritus) Chief of Wound Care Service Madigan
How to manage leg ulcers in the elderly
 How to manage leg ulcers in the elderly David Riding Clinical Research Fellow / Specialty Registrar in Vascular Surgery University of Manchester / MFT British Geriatric Society Trainees Meeting 2018 Objectives
How to manage leg ulcers in the elderly David Riding Clinical Research Fellow / Specialty Registrar in Vascular Surgery University of Manchester / MFT British Geriatric Society Trainees Meeting 2018 Objectives
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/30/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 79 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/30/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 79 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Pentoxifylline Treatment of Moderate to Severe Chronic Occlusive Arterial Disease
 Clin. Cardiol. 8, 161-165 (1985) 0 Clinical Cardiology Publishing Co., Inc. Pentoxifylline Treatment of Moderate to Severe Chronic Occlusive Arterial Disease B. Y. LEE, M.D., F.A.C.S., P. BERKOWITZ, B.S.,
Clin. Cardiol. 8, 161-165 (1985) 0 Clinical Cardiology Publishing Co., Inc. Pentoxifylline Treatment of Moderate to Severe Chronic Occlusive Arterial Disease B. Y. LEE, M.D., F.A.C.S., P. BERKOWITZ, B.S.,
Disclosures. Talking Points. An initial strategy of open bypass is better for some CLI patients, and we can define who they are
 An initial strategy of open bypass is better for some CLI patients, and we can define who they are Fadi Saab, MD, FASE, FACC, FSCAI Metro Heart & Vascular Metro Health Hospital, Wyoming, MI Assistant Clinical
An initial strategy of open bypass is better for some CLI patients, and we can define who they are Fadi Saab, MD, FASE, FACC, FSCAI Metro Heart & Vascular Metro Health Hospital, Wyoming, MI Assistant Clinical
AUTONOMIC FUNCTIONS IN BUERGER'S DISEASE
 : 470-474 AUTONOMIC FUNCTIONS IN BUERGER'S DISEASE K. SINGH* AND S. SOOD Department of Physiology, Pt. B. D. Sharma, Postgraduate, Institute of Medical Sciences (PGIMS), Rohtak - 124 001 ( Received on
: 470-474 AUTONOMIC FUNCTIONS IN BUERGER'S DISEASE K. SINGH* AND S. SOOD Department of Physiology, Pt. B. D. Sharma, Postgraduate, Institute of Medical Sciences (PGIMS), Rohtak - 124 001 ( Received on
FOR THE 18 MILLION INDIVIDUALS with diabetes mellitus in
 11 Evaluation and Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Joseph L. Mills, Sr., MD FOR THE 18 MILLION INDIVIDUALS with diabetes mellitus in the United States, foot problems ulceration, infection, and
11 Evaluation and Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Joseph L. Mills, Sr., MD FOR THE 18 MILLION INDIVIDUALS with diabetes mellitus in the United States, foot problems ulceration, infection, and
Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease
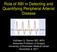 Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease Difference in AAA size between US and Surgeon 2 1 0-1 -2-3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean AAA size between US and Surgeon Kathleen G. Raman MD,
Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease Difference in AAA size between US and Surgeon 2 1 0-1 -2-3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean AAA size between US and Surgeon Kathleen G. Raman MD,
National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD
 National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD No relevant financial relationships to disclose Wound Care Referral The patient has been maximized from a vascular standpoint. She has no other options.
National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD No relevant financial relationships to disclose Wound Care Referral The patient has been maximized from a vascular standpoint. She has no other options.
Non-invasive examination
 Non-invasive examination Segmental pressure and Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) The segmental blood pressure (SBP) examination is a simple, noninvasive method for diagnosing and localizing arterial disease.
Non-invasive examination Segmental pressure and Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) The segmental blood pressure (SBP) examination is a simple, noninvasive method for diagnosing and localizing arterial disease.
Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M
 Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M The goal Treat pain Heal ulcer Preserve limb Preserve life The options Conservative Endovascular Surgical bypass Primary amputation
Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M The goal Treat pain Heal ulcer Preserve limb Preserve life The options Conservative Endovascular Surgical bypass Primary amputation
Current Status of Endovascular Therapies for Critical Limb Ischemia
 Current Status of Endovascular Therapies for Critical Limb Ischemia Bulent Arslan, MD Associate Professor of Radiology Director, Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rush University Medical Center bulent_arslan@rush.edu
Current Status of Endovascular Therapies for Critical Limb Ischemia Bulent Arslan, MD Associate Professor of Radiology Director, Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rush University Medical Center bulent_arslan@rush.edu
Access strategy for chronic total occlusions (CTOs) is crucial
 Learn How Access Strategy Impacts Complex CTO Crossing Arthur C. Lee, MD The Cardiac & Vascular Institute, Gainesville, Florida VASCULAR DISEASE MANAGEMENT 2018;15(3):E19-E23. Key words: chronic total
Learn How Access Strategy Impacts Complex CTO Crossing Arthur C. Lee, MD The Cardiac & Vascular Institute, Gainesville, Florida VASCULAR DISEASE MANAGEMENT 2018;15(3):E19-E23. Key words: chronic total
Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study
 The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
Root Cause Analysis for nontraumatic
 Root Cause Analysis for nontraumatic amputations 2016 (Full Data) Date Richard Leigh and Stella Vig, Co-Chairs London SCN Footcare Network October 2015 Outline of London RCA 2016 London Hospitals invited
Root Cause Analysis for nontraumatic amputations 2016 (Full Data) Date Richard Leigh and Stella Vig, Co-Chairs London SCN Footcare Network October 2015 Outline of London RCA 2016 London Hospitals invited
An Iranian Scoring System for Diagnosing Buerger's Disease
 ORIGINAL REPORT An Iranian Scoring System for Diagnosing Buerger's Disease Mohammad Ramin 1, Javad Salimi 2, and Alipasha Meysamie 3 1 Department of Surgery, Sina Hospital, Tehran University of Medical
ORIGINAL REPORT An Iranian Scoring System for Diagnosing Buerger's Disease Mohammad Ramin 1, Javad Salimi 2, and Alipasha Meysamie 3 1 Department of Surgery, Sina Hospital, Tehran University of Medical
UC SF. Disclosures. Vascular Assessment of the Diabetic Foot. What are the best predictors of wound healing? None. Non-Invasive Vascular Studies
 Disclosures Vascular Assessment of the Diabetic Foot What are the best predictors of wound healing? None Shant Vartanian MD Assistant Professor of Vascular Surgery UCSF Vascular Symposium April 20, 2013
Disclosures Vascular Assessment of the Diabetic Foot What are the best predictors of wound healing? None Shant Vartanian MD Assistant Professor of Vascular Surgery UCSF Vascular Symposium April 20, 2013
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY. Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS
 CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
Buerger s Disease in Tehran University of Medical Sciences Hospitals: A Fifteen Years Study
 ORIGINAL REPORT Buerger s Disease in Tehran University of Medical Sciences Hospitals: A Fifteen Years Study Javad Salimi *, Mohammad Reza Zafarghandi, Patricia Khashayar, and Mehran Ebrahimi Department
ORIGINAL REPORT Buerger s Disease in Tehran University of Medical Sciences Hospitals: A Fifteen Years Study Javad Salimi *, Mohammad Reza Zafarghandi, Patricia Khashayar, and Mehran Ebrahimi Department
AN ABNORMAL UNILATERAL ORIGIN OF DORSALIS PEDIS ARTERY- A CASE REPORT
 AN ABNORMAL UNILATERAL ORIGIN OF DORSALIS PEDIS ARTERY- A CASE REPORT Authors:- Dr. Hetal Vaishnani, Dr.Subhsh Gujar, Dr.Savita Gadekar, Dr.K.V.Bondre, Dr.G.V.Shah Department of Anatomy S.B.K.S.Medical
AN ABNORMAL UNILATERAL ORIGIN OF DORSALIS PEDIS ARTERY- A CASE REPORT Authors:- Dr. Hetal Vaishnani, Dr.Subhsh Gujar, Dr.Savita Gadekar, Dr.K.V.Bondre, Dr.G.V.Shah Department of Anatomy S.B.K.S.Medical
National Vascular Registry
 National Vascular Registry Bypass Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or postcode.
National Vascular Registry Bypass Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or postcode.
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease
 Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
Hypothesis: When compared to conventional balloon angioplasty, cryoplasty post-dilation decreases the risk of SFA nses in-stent restenosis
 Cryoplasty or Conventional Balloon Post-dilation of Nitinol Stents For Revascularization of Peripheral Arterial Segments Background: Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased risk of in-stent restenosis
Cryoplasty or Conventional Balloon Post-dilation of Nitinol Stents For Revascularization of Peripheral Arterial Segments Background: Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased risk of in-stent restenosis
Learning About. Peripheral Artery Disease
 SM A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Learning About Peripheral Artery Disease What Is Peripheral Artery Disease? Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a form of atherosclerosis the hardening and narrowing of
SM A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Learning About Peripheral Artery Disease What Is Peripheral Artery Disease? Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a form of atherosclerosis the hardening and narrowing of
Imaging Strategy For Claudication
 Who are the Debators? Imaging Strategy For Claudication Duplex Ultrasound Alone is Adequate to Select Patients for Endovascular Intervention - Pro: Dennis Bandyk MD No Disclosures PRO - Vascular Surgeon
Who are the Debators? Imaging Strategy For Claudication Duplex Ultrasound Alone is Adequate to Select Patients for Endovascular Intervention - Pro: Dennis Bandyk MD No Disclosures PRO - Vascular Surgeon
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Leg ulcer assessment and management
 Leg ulceration The views expressed in this presentation are solely those of the presenter and do not necessarily represent the views of Smith & Nephew. Smith & Nephew does not guarantee the accuracy or
Leg ulceration The views expressed in this presentation are solely those of the presenter and do not necessarily represent the views of Smith & Nephew. Smith & Nephew does not guarantee the accuracy or
Morbidity Audit and Logbook Tool SNOMED Board Reporting Terms for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION AORTA
 SNOMED s for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION Amputation above-knee Amputation of leg through tibia and fibula Amputation of the foot Amputation of toe Through knee amputation Ray amputation of
SNOMED s for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION Amputation above-knee Amputation of leg through tibia and fibula Amputation of the foot Amputation of toe Through knee amputation Ray amputation of
Treatment Strategies For Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease
 Treatment Strategies For Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Presented by Schuyler Jones, MD Duke University Medical Center & Duke Clinical Research Institute AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Review
Treatment Strategies For Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Presented by Schuyler Jones, MD Duke University Medical Center & Duke Clinical Research Institute AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Review
CHAPTER.7 CARING THE DIABETIC FOOT
 CHAPTER.7 CARING THE DIABETIC FOOT Introduction Diabetes has become a global epidemic(144). The long term complications due to diabetes impose huge social and economic burden, mental and physical misery
CHAPTER.7 CARING THE DIABETIC FOOT Introduction Diabetes has become a global epidemic(144). The long term complications due to diabetes impose huge social and economic burden, mental and physical misery
The Peripheral Vascular System
 The Peripheral Vascular System Anatomy and Physiology Arteries Arteries contain 3 concentric layers of tissue: - the intima - the media - the adventitia The intima The endothelium of the intima has metabolic
The Peripheral Vascular System Anatomy and Physiology Arteries Arteries contain 3 concentric layers of tissue: - the intima - the media - the adventitia The intima The endothelium of the intima has metabolic
Buerger s disease manifesting nodular erythema with livedo reticularis
 .Case Report Buerger s disease manifesting nodular erythema with livedo reticularis Tetsuo Takanashi*, **, Reiko Horigome***, Yasuaki Okuda*, Masato Nose**** Masayuki Matsuda**, Shu-ichi Ikeda** *Department
.Case Report Buerger s disease manifesting nodular erythema with livedo reticularis Tetsuo Takanashi*, **, Reiko Horigome***, Yasuaki Okuda*, Masato Nose**** Masayuki Matsuda**, Shu-ichi Ikeda** *Department
The present status of selfexpanding. for CLI: Why and when to use. Sean P Lyden MD Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, Ohio
 The present status of selfexpanding and balloonexpandable tibial BMS and DES for CLI: Why and when to use Sean P Lyden MD Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure Speaker name: Sean Lyden, MD I have
The present status of selfexpanding and balloonexpandable tibial BMS and DES for CLI: Why and when to use Sean P Lyden MD Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure Speaker name: Sean Lyden, MD I have
Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral to Femoral or Iliac to Femoral Crossover Bypass Graft
 Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral to Femoral or Iliac to Femoral Crossover Bypass Graft Why do you need this operation? You need this operation because you have either pain in your legs or a leg ulcer
Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral to Femoral or Iliac to Femoral Crossover Bypass Graft Why do you need this operation? You need this operation because you have either pain in your legs or a leg ulcer
Fluorescence Angiography in Limb Salvage
 Fluorescence Angiography in Limb Salvage Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor of Surgery-University Of South Carolina School of Medicine, Greenville Etiology of Lower extremity wounds Neuropathy
Fluorescence Angiography in Limb Salvage Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor of Surgery-University Of South Carolina School of Medicine, Greenville Etiology of Lower extremity wounds Neuropathy
Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010
 Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010 Goals Definition and Classification of Acute Limb Ischemia Clinical Assessment of the Vascular Patient History and Physical Diagnostic Modalities Management of Acute
Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010 Goals Definition and Classification of Acute Limb Ischemia Clinical Assessment of the Vascular Patient History and Physical Diagnostic Modalities Management of Acute
Clinical Approach to CLI and Related Diagnostics: What You Need to Know
 Clinical Approach to CLI and Related Diagnostics: What You Need to Know Ido Weinberg, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Massachusetts General Hospital None Disclosures Critical
Clinical Approach to CLI and Related Diagnostics: What You Need to Know Ido Weinberg, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Massachusetts General Hospital None Disclosures Critical
Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments. Medical Provider:
 Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments Medical Provider: Printed Name Signature Patient Name: Patient DOB: Patient SS#: Date: Dear Provider: Please indicate whether your patient s condition
Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments Medical Provider: Printed Name Signature Patient Name: Patient DOB: Patient SS#: Date: Dear Provider: Please indicate whether your patient s condition
VASCULAR WOUNDS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
 VASCULAR WOUNDS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT Lucy Stopher, A/CNS Vascular Surgery ...it is best to think of a wound not as a disease, but rather as a manifestation of disease. Joe McCulloch In order
VASCULAR WOUNDS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT Lucy Stopher, A/CNS Vascular Surgery ...it is best to think of a wound not as a disease, but rather as a manifestation of disease. Joe McCulloch In order
Peripheral arterial disease for primary care Ed Aboian, MD
 Peripheral arterial disease for primary care Ed Aboian, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Palo Alto Medical Foundation, Burlingame Ca Disclosures Nothing to disclose Clinical presentation
Peripheral arterial disease for primary care Ed Aboian, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Palo Alto Medical Foundation, Burlingame Ca Disclosures Nothing to disclose Clinical presentation
Peripheral Vascular Examination. Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Peripheral Vascular Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Competencies 1. Inspection of upper extremity for: size symmetry swelling venous pattern color Texture nail beds Competencies
Peripheral Vascular Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Competencies 1. Inspection of upper extremity for: size symmetry swelling venous pattern color Texture nail beds Competencies
LIMB SALVAGE IN THE DIABETIC PATIENT
 LIMB SALVAGE IN THE DIABETIC PATIENT WHO? HOW? BEST? DISCLOSURES Educational grant from Cook Inc OBJECTIVES Review risk stratification and staging schemes for the threatened limb Discuss current concepts
LIMB SALVAGE IN THE DIABETIC PATIENT WHO? HOW? BEST? DISCLOSURES Educational grant from Cook Inc OBJECTIVES Review risk stratification and staging schemes for the threatened limb Discuss current concepts
National Vascular Registry
 National Vascular Registry Angioplasty Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or
National Vascular Registry Angioplasty Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or
Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI?
 Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI? Peter F. Lawrence, M.D. Gonda Vascular Center Division of Vascular Surgery
Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI? Peter F. Lawrence, M.D. Gonda Vascular Center Division of Vascular Surgery
Popliteal Artery Aneurysms: Diagnosis and Repair Options
 Deepak N. Deshmukh DO April 27, 2018 Popliteal Artery Aneurysms: Diagnosis and Repair Options No Disclosures Popliteal Artery Aneurysms (PAAs) Male Predominanace Most common peripheral Aneurysm (70%) 30-50%
Deepak N. Deshmukh DO April 27, 2018 Popliteal Artery Aneurysms: Diagnosis and Repair Options No Disclosures Popliteal Artery Aneurysms (PAAs) Male Predominanace Most common peripheral Aneurysm (70%) 30-50%
Surgery for lower limb ischaemia
 Surgery for lower limb ischaemia Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us what is important
Surgery for lower limb ischaemia Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us what is important
Intended Learning Outcomes
 2011 Acute Limb Ischemia Definition, Etiology & Pathophysiology Clinical Evaluation Management Ali SABBOUR Prof. of Vascular Surgery, Ain Shams University Acute Limb Ischemia Intended Learning Outcomes
2011 Acute Limb Ischemia Definition, Etiology & Pathophysiology Clinical Evaluation Management Ali SABBOUR Prof. of Vascular Surgery, Ain Shams University Acute Limb Ischemia Intended Learning Outcomes
Intermittent Claudication
 Intermittent Claudication Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us what is important to
Intermittent Claudication Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us what is important to
The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care
 The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care Anita Murray - Senior Podiatrist Diabetes, SCH Learning Outcomes Knowledge of the Model of Care For The Diabetic Foot
The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care Anita Murray - Senior Podiatrist Diabetes, SCH Learning Outcomes Knowledge of the Model of Care For The Diabetic Foot
The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography
 Research imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2572-5483.100036 Journal of Preventive Medicine The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography Andrew
Research imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2572-5483.100036 Journal of Preventive Medicine The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography Andrew
Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease: Less is Sometimes More. Spence M Taylor, M.D.
 Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease: Less is Sometimes More Spence M Taylor, M.D. President, Greenville Health System Clinical University Senior Associate Dean for Academic Affairs and Diversity
Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease: Less is Sometimes More Spence M Taylor, M.D. President, Greenville Health System Clinical University Senior Associate Dean for Academic Affairs and Diversity
ASSESSING THE VASCULAR STATUS OF THE FEET FOR PATIENTS WITH DIABETES
 ASSESSING THE VASCULAR STATUS OF THE FEET FOR PATIENTS WITH DIABETES Caroline McIntosh is Senior Lecturer in Podiatry, University of Huddersfield, Yorkshire A reduced blood supply to the lower limb, due
ASSESSING THE VASCULAR STATUS OF THE FEET FOR PATIENTS WITH DIABETES Caroline McIntosh is Senior Lecturer in Podiatry, University of Huddersfield, Yorkshire A reduced blood supply to the lower limb, due
Appendix D: Leg Ulcer Assessment Form
 Nursing Best Practice Guideline Appendix D: Ulcer Assessment Form Person Completing Assessment: Date: Client Name: Caf # CM# VON ID #: District CCAC ID # Address Telephone Home: Work: Date of Birth Y/M/D:
Nursing Best Practice Guideline Appendix D: Ulcer Assessment Form Person Completing Assessment: Date: Client Name: Caf # CM# VON ID #: District CCAC ID # Address Telephone Home: Work: Date of Birth Y/M/D:
Bilateral Persistent Sciatic Arteries with Failed Iliofemoral Grafts
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 34, No. 4, December 2012 Bilateral Persistent Sciatic Arteries with Failed Iliofemoral Grafts Hani Al Fadhel, MD, FRCR* Faisal Rafeea, MD, SBEM** Abeer Moustafa Abdul Latif,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 34, No. 4, December 2012 Bilateral Persistent Sciatic Arteries with Failed Iliofemoral Grafts Hani Al Fadhel, MD, FRCR* Faisal Rafeea, MD, SBEM** Abeer Moustafa Abdul Latif,
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital
 Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital Deep Venous Thrombosis Varicose Veins Venous insufficiency Phlebitis Lymphedema Elephantiasis nostras
Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital Deep Venous Thrombosis Varicose Veins Venous insufficiency Phlebitis Lymphedema Elephantiasis nostras
USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential
 USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential MEASURE STEWARD: The US Wound Registry [Note: This measure
USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential MEASURE STEWARD: The US Wound Registry [Note: This measure
Steal Syndrome: The Role of the Vascular Lab
 Steal Syndrome: The Role of the Vascular Lab Eighth Overlook Noninvasive Vascular Lab Symposium Larry A. Scher, M.D. Professor of Surgery Division of Vascular Surgery Montefiore Medical Center Albert Einstein
Steal Syndrome: The Role of the Vascular Lab Eighth Overlook Noninvasive Vascular Lab Symposium Larry A. Scher, M.D. Professor of Surgery Division of Vascular Surgery Montefiore Medical Center Albert Einstein
Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes
 Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes Ashok Handa Reader in Surgery and Consultant Surgeon Nuffield Department of Surgery University of Oxford Introduction Vascular
Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes Ashok Handa Reader in Surgery and Consultant Surgeon Nuffield Department of Surgery University of Oxford Introduction Vascular
Arterial Bypass Grafts to the Legs and Femoral Endarterectomy
 Patient Information Arterial Bypass Grafts to the Legs and Femoral Endarterectomy We expect you to make a rapid recovery after your operation and to experience no serious problems. However, it is important
Patient Information Arterial Bypass Grafts to the Legs and Femoral Endarterectomy We expect you to make a rapid recovery after your operation and to experience no serious problems. However, it is important
Accepted Manuscript. External iliac artery injury secondary to indirect pressure wave effect from gun shot wound. Eugene Ng, Andrew MTL.
 Accepted Manuscript External iliac artery injury secondary to indirect pressure wave effect from gun shot wound Eugene Ng, Andrew MTL. Choong PII: S1008-1275(16)00034-1 DOI: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2016.01.013
Accepted Manuscript External iliac artery injury secondary to indirect pressure wave effect from gun shot wound Eugene Ng, Andrew MTL. Choong PII: S1008-1275(16)00034-1 DOI: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2016.01.013
