Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience
|
|
|
- Edmund Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gut and Liver, Vol. 9, No. 2, March 2015, pp Review Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience Quan-Lin Li and Ping-Hong Zhou Endoscopy Center and Endoscopy Research Institute, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China Worldwide, peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) has achieved remarkable initial outcomes in the treatment of achalasia. In China, POEM has developed very quickly since the first case was performed in our center in August With experience, we have successfully performed POEM for special cases (such as pediatric patients, patients with sigmoidtype esophagus, and patients with recurrent symptoms after previous surgery) and have altered our technique to achieve long-term symptom remission and simplify the POEM procedure. These changes include posterior wall incision, full-thickness myotomy, a push-and-pull technique for myotomy, and water-jet assisted POEM. In this article, our experiences in POEM are summarized, including changes in technique, applications of the procedure, and the management of possible complications. (Gut Liver, 2015;9: ) Key Words: Peroral endoscopic myotomy; Achalasia INTRODUCTION Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) has been developed as a nonincision, minimally invasive endoscopic treatment becoming the most effective option for achalasia, maybe the primary and permanent one. 1 This procedure incorporates concepts of natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) and achieves endoscopic myotomy by using the submucosal tunnel as an operating space. In 2007, Pasricha et al. 2 used this technique successfully to perform endoscopic myotomy in a porcine model. Later, Inoue et al. 3 made it successful in human patients and got a satisfactory outcome. Then, POEM has been developed very quickly and initial published experience in humans is more than encouraging despite a relatively short follow-up. 1 In China, the first case of POEM was performed in our center in August To date POEM procedures have been performed in over 1,300 patients in our center, which may be over half the total cases of the world. Initial experiences from our center about complication managements and POEM for special cases (such as pediatric patients, patients with sigmoid-type esophagus, and recurrent symptoms after Heller myotomy [HM] or previous POEM) have been reported in several international conferences many times. As becoming more experienced, we also make some technique changes for achieving long-term symptom remission and simplifying the procedure of POEM. In this article, our experiences in the technique changes, applications, and complication managements of POEM are summarized. INDICATIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS All patients with achalasia can be treated by POEM. Although its role and efficacy are not clearly validated, POEM has also been successfully performed in other hypertensive motor disorders associated with dysphagia and chest pain, such as diffuse esophageal spasm, 5 nutcracker esophagus, 6 and hypercontractile (jackhammer) esophagus 7 (Table 1). The obvious dilation of esophagus (sigmoid-type esophagus, megaesophagus), recurrence/persistence of symptoms after HM or previous POEM, as well as other previous endoscopic treatments (including botulinum toxin injection, pneumatic dilation, and self-expanding metallic stents) may make subsequent endoscopic tunneling and myotomy more challenging, but usually does not prevent successful POEM. Contraindications for POEM include severe cardiopulmonary disease or other serious disease leading to unacceptable surgical risk, pseudoachalasia, and failure in creating the submucosal tunnel because of severe fibrosis and adhesion. Despite that mild or moderate esophagitis that does not induce stricture of the esophagus is not excluded, severe esophagitis and/or very large Correspondence to: Ping-Hong Zhou Endoscopy Center and Endoscopy Research Institute, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, 180 FengLin Road, Shanghai , China Tel: , Fax: , zhou.pinghong@zs-hospital.sh.cn Received on June 23, Accepted on October 8, pissn eissn This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Li QL, et al: Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience 153 Table 1. Indications and Contraindications for Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy Indications Absolute indications Idiopathic achalasia Relative indications Other hypertensive motor disorders (diffuse esophageal spasm, nutcracker esophagus, jackhammer esophagus) Contraindications Absolute contraindications Severe cardiopulmonary disease or other serious disease Pseudoachalasia Failure in creating the submucosal tunnel because of severe fibrosis and adhesion Relative contraindications Severe esophagitis and/or very large ulcer in the lower esophagus ulcer in the lower esophagus or esophagogastric junction (EGJ) should be considered as the relative contraindication (Table 1). OPERATORS There is a substantial learning curve in performing POEM, 8 and the best outcomes are likely to be achieved in medical centers with extensive experiences of endoscopic treatment. Experiences are needed for not only the operator, but also the assistant and nurse. The main operator should have received regular endoscopic training, owned the experiences of endoscopic resection (endoscopic mucosal resection [EMR], endoscopic submucosal dissection [ESD], and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography [ERCP], etc.), completed at least 30 cases of esophageal ESD, and been with rich experiences in managing the complications such as bleeding and perforation. The beginner is suggested to perform POEM under the close supervision of an experienced operator at the beginning; after performing a sufficient number of supervised POEM procedures, easy cases, such as patients with shorter course of disease and untreated before, can be performed independently. Difficult and advanced cases, such as patients with sigmoid-type esophagus or recurrent symptoms, should be only performed by very experienced operators. CONVENTIONAL POEM PROCEDURE Conventional POEM procedure majorly includes four steps: 3 (1) Step 1: Mucosal incision. The point of entry usually lies on the anterior wall of the esophagus. A 1.5- to 2-cm longitudinal incision is performed in the 2-o clock position about 10 cm above the EGJ after injection of saline mixed with indigo carmine and epinephrine. (2) Step 2: Submucosal tunnel. The tunnel is created distally by using a technique similar to ESD. The tunnel is passed over the EGJ and 3 to 4 cm down to cardia. (3) Step 3: Endoscopic myotomy. Under the direct endoscopic view, 2 cm below the mucosal entry point, the circular muscular layer is selectively dissected until 2 to 3 cm below the EGJ. We routinely divide muscle fibers over a minimum length of 6 to 8 cm in the esophagus and at least 2 cm onto the cardia according to the surgical standards of HM. Substantial reduction of lower esophageal sphincter (LES) tonus is confirmed by opening the EGJ with gentle insufflation through the endoscope and easily passing an endoscope through the lumen of the esophagus. In patients with chest pain caused by the abnormal contractions of hypertrophied muscle within the esophageal body (often considered as type III achalsia on high resolution manometry), a long myotomy is made and all abnormal contractions (endoscopically visible and measured with manometry) are incorporated into the site of mytomy. (4) Step 4: Closure of mucosal entry. After careful hemostasis, the mucosal incision site is closed with several hemostatic clips. TECHNIQUE CHANGES POEM has achieved remarkable initial outcomes for treating achalasia. Apart from the undoubted need to evaluate the clinical efficacy of POEM in prospective multicenter studies, attempts to simplify the procedure are underway. Technique changes introduced by us include posterior wall incision, fullthickness myotomy, a push-and-pull technique for myotomy, and water-jet assisted POEM. Using these techniques, the mean POEM procedure time was just about 35 minutes in our center, and the age of patients with POEM ranged from 3 to 98 years. An example of the POEM procedure using these technique changes is shown in Fig. 1. POSTERIOR WALL INCISION Posterior wall incision in the 5- to 6-o clock position is the one of important modifications introduced by us. 9 This modification makes the operation more convenient and faster because it is much easier to control your knife to create the tunnel and myotomy on the posterior wall versus the anterior wall. The spine located behind the esophagus does not restrict the appropriate positioning of the endoscope tip during posterior myotomy. According to our experience, posterior myotomy is also safe and has a comparable complication rate as with anterior myotomy (including bleeding and gastroesophageal reflux). Posterior myotomy in the 5- to 6-o clock position also achieves myotomy from the luminal side without disturbing the acute angle of His, which is located at the 8-o clock position; this is important to prevent reflux.
3 154 Gut and Liver, Vol. 9, No. 2, March 2015 A B C D E F G H Fig. 1. Water-jet assisted peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) using the changes in technique that we introduced. (A) Cardiac stricture. (B) Submucosal injection in the 5- to 6-o clock position using a water jet-assisted hybrid knife. (C) Mucosal incision on the posterior wall. (D) Creation of the submucosal tunnel. (E, F) Full-thickness myotomy. (G) Closure of the mucosal entry point. (H) Substantial reduction of lower esophageal sphincter tone after POEM. FULL-THICKNESS MYOTOMY Although a circular muscle myotomy preserving the longitudinal outer esophageal muscular layer is often recommended, which is different from the usual full-thickness myotomy performed surgically and designed in order to avoid entering the pleural space and decrease morbidity, it is often hard to achieve since the longitudinal muscle fibers of the esophagus are extremely thin which led frequently to an unintentional splitting of the muscle fibers during POEM. Either a minor electrocautery damage, mechanical trauma from maneuvering the endoscope in the tunnel, or air insufflation alone can result in spreading of the longitudinal muscle fibers, and adventitia and transmural openings into the mediastinum. In fact, a clear separation of circular (to be completely dissected) and longitudinal (to be left) muscular layers cannot be found any more at the EGJ and stomach. Moreover, completeness of myotomy is a prerequisite for sufficient and long-term reduction of LES pressure and is the basis for the excellent result. Given the fact that an incomplete myotomy with possible fibrotic healing may be considered as a major reason for postoperative recurrence, a full-thickness myotomy may reduce the incidence of fusion by further spreading of the cut muscular wall and theoretically induce long-term symptom remission. For these considerations, POEM with a fullthickness myotomy including the internal circular and longitudinal muscular layer has been performed in about half of the achalasia patients in our center. On the basis of more than 1,300 cases experiences in our center, short-term symptom relief and manometry outcomes were comparable between patients undergoing full-thickness and circular muscle myotomy. Full-
4 Li QL, et al: Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience 155 thickness myotomy significantly reduced the procedure time but did not increase the procedure-related adverse events or clinical reflux complications. 9 A PUSH-AND-PULL TECHNIQUE FOR MYOTOMY After successfully creating tunnel in the 5- to 6-o clock position on the posterior esophagus, we can use a push-and-pull technique for full-thickness myotomy. After clinging the knife tip to the longitudinal muscle fibers and lifting them up toward the esophageal lumen, the full-thickness muscle bundles can be sectioned. Continuous cutting can be done just by pushing the scope. There is often no need to adjusting the insertion length of the knife. While in the confined area like cardia, pulling the knife and cutting the muscles from internal to external are usually needed in order to avoid mucosal injury. The technique makes the myotomy more convenient and faster. WATER-JET ASSISTED POEM Water-jet assisted HybridKnife is a new knife that combines high-pressure injection with electrical cutting. During POEM, the use of the HybridKnife leads to a significant decrease in POEM procedure time and facilitates reinjection, possibly contributing to a lower rate of minor intraprocedural bleeding. 10,11 POEM FOR SPECIAL CASES POEM can be also performed in surgical failed or re-poem cases. In these cases, the submucosal space may be obliterated and an obvious esophageal diverticulum may occur at the original myotomy site as a result of previous surgery; it may therefore be very difficult to confidently and easily create the submucosal tunnel, as can be accomplished easily in those who have not had prior surgery. The myotomy should therefore be placed in an unscarred area that has not been previously myotomized. Given that it may be difficult to identify the original myotomy site, an initial mucosal incision is often empirically done in the 5- to 6-o clock position on the posterior esophagus because primary HM is often done on the anterior or left lateral esophagus. 12,13 The sigmoid type of achalasia is considered to be difficult to treat, in which the esophageal lumen is significantly dilated and tortured. In patients with such megaesophagus, treatments include interventional ones and surgery ones, both thoracotomy and laparoscopy, are relatively harder. POEM can be also performed in these cases despite it is very difficult and timeconsuming to make the tunnel. 14 Achalasia is an extremely uncommon pediatric disease, with an estimated annual incidence of 0.02 to 0.11 cases per 100,000 children; however, it can lead to complications such as malnutrition, as well as mental and physical stunting. According to our relatively long-term follow-up study, POEM seems to be a promising new treatment for pediatric patients with achalasia resulting in long-term symptom relief in all cases and without serious complications after a mean of 24.6 months. POEM could become a real alternative to laparoscopic HM in pediatric patients once these results are confirmed in muticenter larger studies with a longer follow-up. 15 COMPLICATION MANAGEMENTS Common complications of POEM consist mainly of gasrelated complications, pneumonitis, and mucosal injury. 16 Other rare but severe complications include delayed bleeding and gastrointestinal (GI) tract leakage (Table 2). Table 2. Complications of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy Common complications Mucosal injury Gas-related complications (intraoperative and postoperative) Subcutaneous emphysema Pneumomediastinum Pneumothorax Pneumoperitoneum Pleural effusion Pneumonitis Fever (temperature 38 C) Severe postoperative pain Rare complications Delay bleeding Submucosal infection Gastrointestinal tract leakage MUCOSAL INJURY One refinement of POEM is the application of the ESD technique to create the submucosal tunnel. This precaution is vital to avoid injuring the overlying mucosa while tunneling because the mucosal injury may put the patient at the risk for a potential fistula with mediatsinal sepsis, especially in those patients who have a full thickness myotomy. It is important to create the tunnel as close as possible to the muscular layers not only to avoid injury to the mucosal flap but also due to the lower vascularity adjacent to the muscle. However, as a consequence of tissue adhesions and limited space, the mucosal injury or even perforation sometimes occurs, especially at the cardia. This area can be clipped with metallic clips after myotomy. The endoscope assisted nasogastric tube placement can also be used for decompression when the injury occurred at the EGJ, especially at the stomach. If the mucosal tear area is large or there are multiple ruptures which cannot be clipped, using of a covered
5 156 Gut and Liver, Vol. 9, No. 2, March 2015 retrievable stent or fibrin sealant can be alternative options for sealing the rupture. After mucosal integrity repaired, the mucosal injury often does not induce any clinical complications, even in those patients who have a full thickness myotomy. The use of blunt dissection for submucosal tunnelling, either balloon or a novel gel, may be considered as an alternative to facilitate the procedure and decrease the risk of incidental mucosal injury, especially for operators without sufficient ESD experience. 9,15,16 COMPLICATIONS ON COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY SCAN Early routine chest computed tomography (CT) scan for achalasia patients who received POEM procedure can detect a number of the common sequelae, postoperative gas-related complications, and noninfectious pneumonitis. Gas-related complications of POEM, including subcutaneous emphysema, pneumothorax, and pneumoperitoneum, are often of limited clinical significance, and can be resolved with conservative treatments. Because of the rapid diffusion, CO 2 gas instead of room air should be advocated for insufflation to reduce the incidence of gas-related complications. The radiographic and clinical features of pulmonary inflammation on CT scan were more consistent with pneumonitis rather than a frank infection. We also did not treat any of the patients for an infectious related pneumonia. In our opinion, the pneumonitis is majorly mostly caused by the irritation and inflammation due to operation injury, rather than aspiration and postoperative factors. Thus, routine CT scan after POEM is probably not warranted due to the high rate of minor and clinically irrelevant findings. Adverse event requiring intervention always has clinical correlate, and we want to stress that the most important parameter in the management of POEM adverse events such as pneumothorax is always the patients clinical status. We therefore suggest post- POEM CT should be selectively used in symptomatic post-poem patients. 17 For pneumothorax with a volume of more than 30%, thoracic drainage should be carried out. A central venous catheter is inserted at the 3rd or 4th intercostal space instead of regular chest tube for drainage. After 2 to 3 days of the drainage, the decompressed lung comes back to normal condition and the drainage tube can be removed. If the CT image or the X-ray film shows a small amount of free gas under the diaphragm, by maintaining the conservative treatments mentioned above, the gas will be absorbed automatically. If abdominal bloating is severe, a 20-gauge needle should be used for drainage of the gas from the abdominal cavity and a stomach tube is inserted simultaneously when necessary. Pleural effusion occurs in about 40% of the patients after POEM. If the patient only has small volume of pleural effusion and is absence of fever, the spontaneous absorption of the effusion is often observed without further intervention. For the patient who suffers from large amounts of pleural effusion or has persistence of the high temperature, ultrasound-guided thoracentesis and drainage should be performed to prevent further infection. 16 DELAYED BLEEDING Postoperative delayed bleeding in the submucosal tunnel is a rare complication after POEM. Despite of the low incidence, delayed bleeding can result in serious conditions, such as massive bleeding and hemorrhagic shock, once it occurs it can be fatal. Thus, early prevention, prompt diagnosis, and effective management are most critical for the patient outcome. In summary, vomiting of fresh blood and progressive serious retrosternal pain are the major early manifestations in patients with delayed bleeding in the submucosal tunnel after POEM. When delayed bleeding is suspected, emergency gastroscopy should be performed immediately for exploration and a hematoma is often found along the mucosa covering the submucosal tunnel. Chest CT scan can also be used to detect early signs of postoperative bleeding. A hematoma can be often observed on CT scan before any clinical manifestation occurs. Emergency endoscopic hemostasis should be performed immediately after symptom emergence. Blood and any blood clots at the wound and in the tunnel should be patiently and meticulously cleared to expose the bleeding site(s). When the active bleeding points are identified, coagulation using hemostatic forceps can be performed as is done for delayed bleeding after ESD. It should be worth mentioning that a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube is particularly effective for providing compressive hemostasis to staunch post- POEM bleeding. 18 Table 3. Tunnel Endoscopic Surgery Novel procedure Peroral endoscopic myotomy Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection Peroral endoscopic submucosal pyloromyotomy Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection Retrograde submucosal tunneling technique Disease Achalasia Gastrointestinal submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer Pyloric stenosis Large esophageal neoplastic lesions Complete esophageal obstruction
6 Li QL, et al: Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience 157 GI TRACT LEAKAGE GI tract leakage post-poem include esophagomediastinal fistula, esophagothoracic fistula, and so forth. The maintenance of mucosal integrity is critical for the prevention of GI tract leakage. The clips on the tunnel entry breaking off early might be an important reason to result in the GI tract leakage as the leakage orifice was detected at the entrance of the tunnel in the patients. Early diagnosis is difficult as the lack of typical symptoms of esophageal leakage before the oral intake. Leakage should be considered if there is any unusual or slow course of recovery. Endoscopy is recommended as a safe and sensitive method to detect small leakage and an effective treatment for the closure of the leakage in the early stage. Patients with esophageal leakage after POEM could achieve complete recovery in a short time by the endoscopic closure of the leakage, sufficient drainage and optimal conservative management without surgical intervention. Adequate nutrition support by enteric feeding tube is another important factor to significantly reduce the morbidity and healing time. OFFSHOOTS OF POEM The emergence of POEM marks the rising of a new branch of therapeutic endoscopy. Our group defines it as tunnel endoscopic surgery which includes several novel procedures utilizing a submucosal tunnel as an operating space (Table 3). 19 In 2010, we innovated a new procedure that takes advantage of the submucosal tunneling technique popularized by POEM in order to achieve complete, full thickness endoscopic resection of GI submucosal tumors (SMTs) originating from the muscularis propria layer. Our group coined the acronym STER (submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection) for this procedure. 20,21 The advantage of STER is maintenance of GI tract mucosal integrity while achieving an en bloc resection of SMTs. This method will possibly reduce the risk of postoperative GI tract leakage and secondary infection. In contrast to conventional endoscopic procedures and NOTES, this technique is unique because it uses the submucosal space between the mucosal and muscular layers. Other reported applications of tunneling technique include peroral endoscopic submucosal pyloromyotomy for pyloric stenosis, endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for large esophageal neoplastic lesions, retrograde submucosal tunneling technique for management of complete esophageal obstruction, and so forth. 22 In the future, other applications may include sampling of the enteric nervous system and muscle, submucosal implantation of devices (such as microstimulators and drug delivery pumps), and bulking agents for reflux and incontinence. In our center, endoscopic sympathectomy using submucosal tunneling technique has been attempted in a porcine model. This procedure may further be considered as a treatment option for palmar hyperhidrosis. CONCLUSIONS POEM seems to be a safe and effective surgical myotomy option for treating achalasia, even for special cases such as pediatric patients, patients with sigmoid-type esophagus, and recurrent symptoms after previous surgery. In order to achieve long-term symptom remission and simplify the procedure, several technique changes of POEM are introduced by us including posterior wall incision, full-thickness myotomy, a push-andpull technique for myotomy, and water-jet assisted technique. Apart from the undoubted need to evaluate the clinical efficacy of POEM in prospective multicenter studies, attempts to simplify the procedure are still underway. CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This study was supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China ( , , , and ), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (13ZR ), Major Project of Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Committee ( and ), and Academic Leader Training Project of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (13B038). REFERENCES 1. NOSCAR POEM White Paper Committee, Stavropoulos SN, Desilets DJ, et al. Per-oral endoscopic myotomy white paper summary. Gastrointest Endosc 2014;80: Pasricha PJ, Hawari R, Ahmed I, et al. Submucosal endoscopic esophageal myotomy: a novel experimental approach for the treatment of achalasia. Endoscopy 2007;39: Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy 2010;42: Zhou PH, Yao LQ, Cai MY, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia. Chin J Dig Endosc 2011;28: Shiwaku H, Inoue H, Beppu R, et al. Successful treatment of diffuse esophageal spasm by peroral endoscopic myotomy. Gastrointest Endosc 2013;77: Sharata A, Kurian AA, Dunst CM, Bhayani NH, Reavis KM, Swanström LL. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is safe and effective in the setting of prior endoscopic intervention. J Gastrointest Surg 2013;17: Khashab MA, Saxena P, Kumbhari V, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy as a platform for the treatment of spastic esophageal
7 158 Gut and Liver, Vol. 9, No. 2, March 2015 disorders refractory to medical therapy (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2014;79: Kurian AA, Dunst CM, Sharata A, Bhayani NH, Reavis KM, Swanström LL. Peroral endoscopic esophageal myotomy: defining the learning curve. Gastrointest Endosc 2013;77: Li QL, Chen WF, Zhou PH, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia: a clinical comparative study of endoscopic full-thickness and circular muscle myotomy. J Am Coll Surg 2013;217: Cai MY, Zhou PH, Yao LQ, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for idiopathic achalasia: randomized comparison of water-jet assisted versus conventional dissection technique. Surg Endosc 2014;28: Zhou PH, Cai MY, Yao LQ, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for esophageal achalasia by HybridKnife: a case report. Case Rep Gastrointest Med 2012;2012: Zhou PH, Li QL, Yao LQ, et al Peroral endoscopic remyotomy for failed Heller myotomy: a prospective single-center study. Endoscopy 2013;45: Li QL, Zhou PH, Yao LQ, Xu MD. Peroral endoscopic remyotomy (Re-POEM) for recurrence/persistence of symptoms after previous POEM. Gastrointest Endosc 2014;79(5 Suppl):AB Hu JW, Li QL, Yao LQ, Zhong YS, Zhang YQ, Chen WF. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia of sigmoid type: a prospective single center study. Endoscopy 2012;44(Suppl 1):A Chen WF, Li QL, Zhou PH, et al. Long-term outcomes of peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia in pediatric patients: a prospective, single-center study. Gastrointest Endosc 2015;81: Ren Z, Zhong Y, Zhou P, et al. Perioperative management and treatment for complications during and after peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia (EA) (data from 119 cases). Surg Endosc 2012;26: Cai MY, Zhou PH, Yao LQ, Zhu BQ, Liang L, Li QL. Thoracic CT after peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc 2014;80: Li QL, Zhou PH, Yao LQ, et al. Early diagnosis and management of delayed bleeding in the submucosal tunnel after peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2013;78: Cai M, Chen J, Zhou P, Yao L. The rise of tunnel endoscopic surgery: a case report and literature review. Case Rep Gastrointest Med 2012;2012: Xu MD, Cai MY, Zhou PH, et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection: a new technique for treating upper GI submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 2012;75: Wang XY, Xu MD, Yao LQ, et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for submucosal tumors of the esophagogastric junction originating from the muscularis propria layer: a feasibility study (with videos). Surg Endosc 2014;28: Li QL, Zhou PH, Xu MD, Cai MY, Yao LQ. Offshoots of peroral endo scopic myotomy: submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection, pyloromyotomy, and beyond. Tech Gastrointest Endosc 2013;15:
How I Do It? Per-oral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) Ping-hong ZHOU, MD. Endoscopy Center, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai, China
 How I Do It? Per-oral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) Ping-hong ZHOU, MD Endoscopy Center, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai, China The 2 nd World Congress on CONTROVERSIES IN GASTROENTEROLOGY Prof.
How I Do It? Per-oral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) Ping-hong ZHOU, MD Endoscopy Center, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai, China The 2 nd World Congress on CONTROVERSIES IN GASTROENTEROLOGY Prof.
Duke Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando, FL. September 17, Session VI: Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery: Miscellaneous
 Duke Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando, FL September 17, 2016 Session VI: Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery: Miscellaneous NOTES and POEM James D. Luketich MD, FACS Henry T. Bahnson
Duke Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando, FL September 17, 2016 Session VI: Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery: Miscellaneous NOTES and POEM James D. Luketich MD, FACS Henry T. Bahnson
POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY
 Original Issue Date (Created): November 26, 2013 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): November 26, 2013 Effective Date: April 1, 2014 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS
Original Issue Date (Created): November 26, 2013 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): November 26, 2013 Effective Date: April 1, 2014 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS
Case Report The Rise of Tunnel Endoscopic Surgery: A Case Report and Literature Review
 Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 847640, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/847640 Case Report The Rise of Tunnel Endoscopic Surgery: A Case Report and Literature Review Mingyan
Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 847640, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/847640 Case Report The Rise of Tunnel Endoscopic Surgery: A Case Report and Literature Review Mingyan
Description. Section: Medicine Effective Date: January 15, 2015 Subsection: Original Policy Date: December 6, 2013 Subject: Page: 1 of 7
 Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 7 Description Esophageal achalasia is characterized by prolonged occlusion of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and reduced peristaltic activity, making
Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 7 Description Esophageal achalasia is characterized by prolonged occlusion of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and reduced peristaltic activity, making
Esophageal Perforation
 Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection of upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria
 REVIEW ARTICLE Annals Gastroenterology (2017) 30, 1-11 Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria Deepanshu Jain a, Aakash Desai b, Ejaz
REVIEW ARTICLE Annals Gastroenterology (2017) 30, 1-11 Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria Deepanshu Jain a, Aakash Desai b, Ejaz
Clinical analysis of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection in treating esophageal submucosal tumors.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9231-9235 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Clinical analysis of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection in treating esophageal submucosal tumors. Fu Xinjuan 1,2, Shi
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9231-9235 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Clinical analysis of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection in treating esophageal submucosal tumors. Fu Xinjuan 1,2, Shi
B Barrett neoplasia, early, endoscopic mucosal resection of, in Europe, 297
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, treatment of, history of, 258 259 Achalasia myotomy, 270 Adenocarcinomas, endoscopic management of, in Asia, 289 290 B Barrett neoplasia,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, treatment of, history of, 258 259 Achalasia myotomy, 270 Adenocarcinomas, endoscopic management of, in Asia, 289 290 B Barrett neoplasia,
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Esophageal Achalasia
 Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Esophageal Achalasia Policy Number: 2.01.91 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 3/2018 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Esophageal Achalasia Policy Number: 2.01.91 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 3/2018 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks
 Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks Ali A. Siddiqui, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Interventional Endoscopy Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia, PA When Do You Suspect a Luminal
Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks Ali A. Siddiqui, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Interventional Endoscopy Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia, PA When Do You Suspect a Luminal
Management of the Difficult Patient with Type 3 Achalasia. Steven R. DeMeester Professor and Clinical Scholar Department of Surgery
 Management of the Difficult Patient with Type 3 Achalasia Steven R. DeMeester Professor and Clinical Scholar Department of Surgery Achalasia Treatment Concepts Disease leads to non-relaxing LES and loss
Management of the Difficult Patient with Type 3 Achalasia Steven R. DeMeester Professor and Clinical Scholar Department of Surgery Achalasia Treatment Concepts Disease leads to non-relaxing LES and loss
잭해머식도를경구내시경근절개술로치료한 1 예
 Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 64 No. 6, 370-374 http://dx.doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.64.6.370 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 CASE REPORT 잭해머식도를경구내시경근절개술로치료한 1 예 고원진, 이병무, 박원영, 김진녕, 조준형, 이태희, 홍수진 1, 조주영 순천향대학교서울병원소화기병센터,
Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 64 No. 6, 370-374 http://dx.doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.64.6.370 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 CASE REPORT 잭해머식도를경구내시경근절개술로치료한 1 예 고원진, 이병무, 박원영, 김진녕, 조준형, 이태희, 홍수진 1, 조주영 순천향대학교서울병원소화기병센터,
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Comparison of the Outcomes of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia According to Manometric Subtype
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 5, September 2017, pp. 642-647 ORiginal Article Comparison of the Outcomes of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia According to Manometric Subtype Won Hee Kim 1, Joo Young
Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 5, September 2017, pp. 642-647 ORiginal Article Comparison of the Outcomes of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia According to Manometric Subtype Won Hee Kim 1, Joo Young
Achalasia: Classic View
 Achalasia: Dilate, Botox, Knife or POEM Prateek Sharma, MD Kansas University School of Medicine Achalasia: Classic View 1 Diagnosis of Achalasia Endoscopy may be normal in as many as 44% Upper GI series
Achalasia: Dilate, Botox, Knife or POEM Prateek Sharma, MD Kansas University School of Medicine Achalasia: Classic View 1 Diagnosis of Achalasia Endoscopy may be normal in as many as 44% Upper GI series
A Novel Endoscopic Treatment for Achalasia Is the POEM mightier than the sword?
 A Novel Endoscopic Treatment for Achalasia Is the POEM mightier than the sword? Pavlos Kaimakliotis, MD Department of Gastroenterology Lahey Hospital and Medical Center Assistant Professor of Medicine
A Novel Endoscopic Treatment for Achalasia Is the POEM mightier than the sword? Pavlos Kaimakliotis, MD Department of Gastroenterology Lahey Hospital and Medical Center Assistant Professor of Medicine
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia in a 10-Year-Old Male Patient
 18 Case Report THIEME Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia in a 10-Year-Old Male Patient Jörg Filser 1 Anke Dick 2 Thomas Meyer 1 Christoph-Thomas Germer 1 Burkard H.A. von Rahden
18 Case Report THIEME Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia in a 10-Year-Old Male Patient Jörg Filser 1 Anke Dick 2 Thomas Meyer 1 Christoph-Thomas Germer 1 Burkard H.A. von Rahden
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings. M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid
 Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara
 SSS EESOPHAGEAL HPOSAGEAL DISORDERS IN SURGICAL PERSPECTIVE Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara CONTENT 1. Esophageal Atresia 2. Achalasia 3. Esophageal Rupture 4. Tumor
SSS EESOPHAGEAL HPOSAGEAL DISORDERS IN SURGICAL PERSPECTIVE Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara CONTENT 1. Esophageal Atresia 2. Achalasia 3. Esophageal Rupture 4. Tumor
Treating Achalasia. When to consider surgery and New options for therapy
 Treating Achalasia When to consider surgery and New options for therapy James B. Wooldridge,Jr., MD Ochsner Medical Center Senior Staff Surgeon General, Laparoscopic, and Bariatric Surgery Disclosures
Treating Achalasia When to consider surgery and New options for therapy James B. Wooldridge,Jr., MD Ochsner Medical Center Senior Staff Surgeon General, Laparoscopic, and Bariatric Surgery Disclosures
Per-oral Endoscopic Myotomy
 POEM With the Flexible Scope as a Treatment for Achalasia and Zenker's Diverticulum Abraham Mathew, MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Penn State College of Medicine Penn State Hershey Medical Center Per-oral
POEM With the Flexible Scope as a Treatment for Achalasia and Zenker's Diverticulum Abraham Mathew, MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Penn State College of Medicine Penn State Hershey Medical Center Per-oral
Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Early Gastric Cancer
 CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2015;48:251-255 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.251 Open Access Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2015;48:251-255 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.251 Open Access Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Paraesophageal Hernias &
 530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
Submucosal tunneling and endoscopic resection of submucosal tumors at the esophagogastric junction
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.578 World J Gastroenterol 2015 January 14; 21(2): 578-583 ISSN 1007-9327 (print)
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.578 World J Gastroenterol 2015 January 14; 21(2): 578-583 ISSN 1007-9327 (print)
Endoscopic Resection of Subepithelial Tumors
 REVIEW Clin Endosc ;45:240-244 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce..45.3.240 Open Access Endoscopic Resection of Subepithelial Tumors Gwang Ha Kim Department of Internal
REVIEW Clin Endosc ;45:240-244 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce..45.3.240 Open Access Endoscopic Resection of Subepithelial Tumors Gwang Ha Kim Department of Internal
Primary Achalasia : POEM Vs Heller's Myotomy AMOL BAPAYE MD (MS ), FAS GE
 Primary Achalasia : POEM Vs Heller's Myotomy AMOL BAPAYE MD (MS ), FAS GE SHIVANAND DESAI CENTER FOR DIG EST IVE DISOR DERS DEENANAT H MANGESHKAR HOSPITAL & R ESEAR C H C ENTER, PUNE, INDIA What is Achalasia
Primary Achalasia : POEM Vs Heller's Myotomy AMOL BAPAYE MD (MS ), FAS GE SHIVANAND DESAI CENTER FOR DIG EST IVE DISOR DERS DEENANAT H MANGESHKAR HOSPITAL & R ESEAR C H C ENTER, PUNE, INDIA What is Achalasia
MP Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Esophageal Achalasia
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.91 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.38 Transesophageal Endoscopic Therapies for Gastroesophageal Reflux
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.91 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.38 Transesophageal Endoscopic Therapies for Gastroesophageal Reflux
Achalasia: Inject, Dilate, or Surgery?
 Achalasia: Inject, Dilate, or Surgery? John E. Pandolfino, MD, MSCI, FACG Professor of Medicine Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Northwestern
Achalasia: Inject, Dilate, or Surgery? John E. Pandolfino, MD, MSCI, FACG Professor of Medicine Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Northwestern
Review Article Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia: An Analysis
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2013, Article ID 389596, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/389596 Review Article Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia: An Analysis
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2013, Article ID 389596, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/389596 Review Article Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia: An Analysis
Abstract CASE REPORT. Sha Shi, Kuangi Fu, Xin-Qian Dong, Yu-Jing Hao, Sen-Lin Li
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i2.99 World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017 February 16; 9(2): 99-104 ISSN 1948-5190 (online) CASE REPORT Combination of concurrent endoscopic
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i2.99 World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017 February 16; 9(2): 99-104 ISSN 1948-5190 (online) CASE REPORT Combination of concurrent endoscopic
34th Annual Toronto Thoracic Surgery Refresher Course
 34th Annual Toronto Thoracic Surgery Refresher Course TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ACHALASIA Dr. Carmine Simone Director, Intensive Care Unit Head, Division of Critical Care Departments of Medicine and Surgery
34th Annual Toronto Thoracic Surgery Refresher Course TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ACHALASIA Dr. Carmine Simone Director, Intensive Care Unit Head, Division of Critical Care Departments of Medicine and Surgery
Diagnosis and Management of Achalasia: Past, Present, & Future
 Diagnosis and Management of Achalasia: Past, Present, & Future Kyle A. Perry, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Division of General & Gastrointestinal Surgery The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Diagnosis and Management of Achalasia: Past, Present, & Future Kyle A. Perry, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Division of General & Gastrointestinal Surgery The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City
 Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City Peptic stricture Shtki Schatzki s ring Esophageal cancer Radiation therapy
Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City Peptic stricture Shtki Schatzki s ring Esophageal cancer Radiation therapy
An innovative ex-vivo porcine upper gastrointestinal model for submucosal tunnelling endoscopic resection (STER)
 THIEME E1101 An innovative ex-vivo porcine upper gastrointestinal model for submucosal tunnelling endoscopic resection (STER) Authors Baldwin Yeung 1, Philip Chiu 1, 2, Anthony Teoh 1, Linfu Zheng 2, Shannon
THIEME E1101 An innovative ex-vivo porcine upper gastrointestinal model for submucosal tunnelling endoscopic resection (STER) Authors Baldwin Yeung 1, Philip Chiu 1, 2, Anthony Teoh 1, Linfu Zheng 2, Shannon
Endoscopic Management of Perforations
 Endoscopic Management of Perforations Gregory G. Ginsberg, MD Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine Gastroenterology Division Executive Director of Endoscopic Services
Endoscopic Management of Perforations Gregory G. Ginsberg, MD Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine Gastroenterology Division Executive Director of Endoscopic Services
Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for treating esophageal motility disorders. Citation Annals of Translational Medicine, 2017, v. 5 n. 8, p.
 Title Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for treating esophageal motility disorders Author(s) Wong, YHI; Law, SYK Citation Annals of Translational Medicine, 2017, v. 5 n. 8, p. 192:1-8 Issued Date 2017
Title Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for treating esophageal motility disorders Author(s) Wong, YHI; Law, SYK Citation Annals of Translational Medicine, 2017, v. 5 n. 8, p. 192:1-8 Issued Date 2017
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation. See specific types, e.g., Thermal ablation Achalasia, 53 75 described, 53 features of, 53 management of past options, 54 POEM
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation. See specific types, e.g., Thermal ablation Achalasia, 53 75 described, 53 features of, 53 management of past options, 54 POEM
Advanced techniques for resection of large polyps. John G. Lee, MD February 2, 2018
 Advanced techniques for resection of large polyps John G. Lee, MD February 2, 2018 Background 1cm - large polyp on screening 2cm - large for polypectomy 3cm giant polyp 10-15% of polyps can t be removed
Advanced techniques for resection of large polyps John G. Lee, MD February 2, 2018 Background 1cm - large polyp on screening 2cm - large for polypectomy 3cm giant polyp 10-15% of polyps can t be removed
Title: A comparison of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection and endoscopic fullthickness resection for gastric fundus submucosal tumors
 Title: A comparison of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection and endoscopic fullthickness resection for gastric fundus submucosal tumors Authors: Tian-Ying Duan, Yu-Yong Tan, Xue-Hong Wang, Liang Lv,
Title: A comparison of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection and endoscopic fullthickness resection for gastric fundus submucosal tumors Authors: Tian-Ying Duan, Yu-Yong Tan, Xue-Hong Wang, Liang Lv,
Combined Experience of Two European Centers
 Minimally Invasive Surgery for Achalasia: Combined Experience of Two European Centers Garzi A, Valla JS*, Molinaro F, Amato G, Messina M. Unit of Pediatric Surgery, University of Siena (Italy) *Lenval
Minimally Invasive Surgery for Achalasia: Combined Experience of Two European Centers Garzi A, Valla JS*, Molinaro F, Amato G, Messina M. Unit of Pediatric Surgery, University of Siena (Italy) *Lenval
Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
Per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM): a new endoscopic treatment for achalasia
 1130-0108/2017/109/10/719-726 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2017. SEPD y ARÁN EDICIONES, S.L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2017, Vol. 109, N.º 10, pp. 719-726 REVIEW Per-oral endoscopic myotomy
1130-0108/2017/109/10/719-726 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2017. SEPD y ARÁN EDICIONES, S.L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2017, Vol. 109, N.º 10, pp. 719-726 REVIEW Per-oral endoscopic myotomy
Achalasia and Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy
 1 Monterey County Surgical Associates 2 Upper Ragsdale Drive, Bldg B, Suite 230 Monterey, CA 93940 Phone: (831) 649-0808 Fax: (831) 649-8795 Mark Vierra, MD Achalasia and Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy Introduction
1 Monterey County Surgical Associates 2 Upper Ragsdale Drive, Bldg B, Suite 230 Monterey, CA 93940 Phone: (831) 649-0808 Fax: (831) 649-8795 Mark Vierra, MD Achalasia and Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy Introduction
Per-oral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia cardia: outcomes in over 400 consecutive patients
 Per-oral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia cardia: outcomes in over 400 consecutive patients Authors Zaheer Nabi 1, Mohan Ramchandani 1, Radhika Chavan 1, Rakesh Kalapala 1,SantoshDarisetty 2, Guduru Venkat
Per-oral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia cardia: outcomes in over 400 consecutive patients Authors Zaheer Nabi 1, Mohan Ramchandani 1, Radhika Chavan 1, Rakesh Kalapala 1,SantoshDarisetty 2, Guduru Venkat
The current state of per oral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia
 Review Article on Aerodigestive Endoscopy The current state of per oral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia Shane P. Smith, Brian E. Louie Swedish Medical Center and Cancer Institute, Seattle, WA, USA Contributions:
Review Article on Aerodigestive Endoscopy The current state of per oral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia Shane P. Smith, Brian E. Louie Swedish Medical Center and Cancer Institute, Seattle, WA, USA Contributions:
Peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia
 Neurogastroenterology & Motility Neurogastroenterol Motil (2014) 26, 3 12 doi: 10.1111/nmo.12257 REVIEW ARTICLE Peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia A. J. BREDENOORD,* T. R OSCH & P. FOCKENS* *Department
Neurogastroenterology & Motility Neurogastroenterol Motil (2014) 26, 3 12 doi: 10.1111/nmo.12257 REVIEW ARTICLE Peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia A. J. BREDENOORD,* T. R OSCH & P. FOCKENS* *Department
Marc F. Catalano, MD, FACG, FACP, AGAF, FASGE Professor of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology The
 Marc F. Catalano, MD, FACG, FACP, AGAF, FASGE Professor of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology The University of Texas, McGovern Medical School Review the
Marc F. Catalano, MD, FACG, FACP, AGAF, FASGE Professor of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology The University of Texas, McGovern Medical School Review the
Information Technology Solutions
 2016 2014 CPT Esophagoscopy Changes - Gastroenterology CPT Changes Information Technology Solutions ASGE LOGO AND INFO Esophagogastroduodenoscopy CPT Codes 43235-43270 The American Society for Gastrointestinal
2016 2014 CPT Esophagoscopy Changes - Gastroenterology CPT Changes Information Technology Solutions ASGE LOGO AND INFO Esophagogastroduodenoscopy CPT Codes 43235-43270 The American Society for Gastrointestinal
LAPAROSCOPIC HELLER MYOTOMY WITH FUNDOPLICATION FOR ACHALASIA
 LAPAROSCOPIC HELLER MYOTOMY WITH FUNDOPLICATION FOR ACHALASIA I-Rue Lai, 1 Wei-Jei Lee, 1,2 and Ming-Te Huang 2 Background and Purpose: Laparoscopic Heller cardiomyotomy for the treatment of achalasia
LAPAROSCOPIC HELLER MYOTOMY WITH FUNDOPLICATION FOR ACHALASIA I-Rue Lai, 1 Wei-Jei Lee, 1,2 and Ming-Te Huang 2 Background and Purpose: Laparoscopic Heller cardiomyotomy for the treatment of achalasia
Title: endoscopic myotomy (POEM): a new. new endoscopic treatment for achalasia
 Title: Per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM): a new endoscopic treatment for achalasia Authors: Pablo Miranda García, Fernando Casals Seoane, Jean-Michel Gonzalez, Marc Barthet, Cecilio Santander Vaquero
Title: Per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM): a new endoscopic treatment for achalasia Authors: Pablo Miranda García, Fernando Casals Seoane, Jean-Michel Gonzalez, Marc Barthet, Cecilio Santander Vaquero
Surgical Treatment for Achalasia
 Surgical Treatment for Achalasia Date of Origin: 08/2015 Last Review Date: 08/23/2017 Effective Date: 08/23/2017 Dates Reviewed: 08/2016, 08/2017 Developed By: Medical Necessity Criteria Committee I. For
Surgical Treatment for Achalasia Date of Origin: 08/2015 Last Review Date: 08/23/2017 Effective Date: 08/23/2017 Dates Reviewed: 08/2016, 08/2017 Developed By: Medical Necessity Criteria Committee I. For
Quiz Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been increasing in the last 20 years. a. True b. False
 Quiz 1 1. Which of the following are risk factors for esophagus cancer. a. Obesity b. Gastroesophageal reflux c. Smoking and Alcohol d. All of the above 2. Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been
Quiz 1 1. Which of the following are risk factors for esophagus cancer. a. Obesity b. Gastroesophageal reflux c. Smoking and Alcohol d. All of the above 2. Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been
Minimally invasive surgery for giant esophageal leiomyoma: a case report & review of the literatures
 Case Report Minimally invasive surgery for giant esophageal leiomyoma: a case report & review of the literatures Xiaosang Chen, Yong Xi, Hao Wang, Lijie Tan Department of Thoracic Surgery, Zhongshan Hospital
Case Report Minimally invasive surgery for giant esophageal leiomyoma: a case report & review of the literatures Xiaosang Chen, Yong Xi, Hao Wang, Lijie Tan Department of Thoracic Surgery, Zhongshan Hospital
SAGES guidelines for the surgical treatment of esophageal achalasia
 Surg Endosc (2012) 26:296 311 DOI 10.1007/s00464-011-2017-2 and Other Interventional Techniques GUIDELINES SAGES guidelines for the surgical treatment of esophageal achalasia Dimitrios Stefanidis William
Surg Endosc (2012) 26:296 311 DOI 10.1007/s00464-011-2017-2 and Other Interventional Techniques GUIDELINES SAGES guidelines for the surgical treatment of esophageal achalasia Dimitrios Stefanidis William
Pneumothorax. Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms
 Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
This information is intended as an overview only
 This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
Correspondence should be addressed to Justin Cochrane;
 Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 794282, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/794282 Case Report Acute on Chronic Pancreatitis Causing a Highway to the Colon with Subsequent
Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 794282, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/794282 Case Report Acute on Chronic Pancreatitis Causing a Highway to the Colon with Subsequent
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Achalasia: Initial Results of a Korean Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2013;46:161-167 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2013.46.2.161 Open Access Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Achalasia:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2013;46:161-167 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2013.46.2.161 Open Access Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Achalasia:
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD
 Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
SETTING Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. RESPONSIBLE PARTY Haiquan Chen MD.
 OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
A video demonstration of the Li s anastomosis the key part of the non-tube no fasting fast track program for resectable esophageal carcinoma
 Surgical Technique A video demonstration of the the key part of the non-tube no fasting fast track program for resectable esophageal carcinoma Yan Zheng*, Yin Li*, Zongfei Wang, Haibo Sun, Ruixiang Zhang
Surgical Technique A video demonstration of the the key part of the non-tube no fasting fast track program for resectable esophageal carcinoma Yan Zheng*, Yin Li*, Zongfei Wang, Haibo Sun, Ruixiang Zhang
Historical perspective
 Raj Santharam, MD GI Associates, LLC Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical College of Wisconsin Historical perspective FFS first widespread use in the early 1970 s Expansion of therapeutic techniques
Raj Santharam, MD GI Associates, LLC Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical College of Wisconsin Historical perspective FFS first widespread use in the early 1970 s Expansion of therapeutic techniques
01/26/2010 GENERAL SURGERY ABSITE ANATOMY ANATOMY. Yvonne M. Carter, MD Georgetown University Medical Center. Layers. mucosa. squamous epithelium
 GENERAL SURGERY ABSITE REVIEW: ESOPHAGUS Yvonne M. Carter, MD Georgetown University Medical Center ANATOMY Layers mucosa muscle squamous epithelium columnar epithelium (distal 2cm) inner = circular outer
GENERAL SURGERY ABSITE REVIEW: ESOPHAGUS Yvonne M. Carter, MD Georgetown University Medical Center ANATOMY Layers mucosa muscle squamous epithelium columnar epithelium (distal 2cm) inner = circular outer
Difficult Polypectomy 2015 Tool of the Trade
 Difficult Polypectomy 2015 Tool of the Trade Jonathan Cohen, MD FACG FASGE Clinical Professor of Medicine NYU Langone School of Medicine Improving Therapeutics in the Colon Improved detection of polyp
Difficult Polypectomy 2015 Tool of the Trade Jonathan Cohen, MD FACG FASGE Clinical Professor of Medicine NYU Langone School of Medicine Improving Therapeutics in the Colon Improved detection of polyp
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
 Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
Chapter 14: Training in Radiology. DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12
 DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
Barrett s Esophagus. lining of the lower esophagus that bears his name (i.e., Barrett's esophagus). We now
 Shamika Johnson Anatomy & Physiology 206 April 20, 2010 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s Esophagus? Norman Barrett was a pathologist. In 1950, he described an abnormality in the lining of the lower
Shamika Johnson Anatomy & Physiology 206 April 20, 2010 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s Esophagus? Norman Barrett was a pathologist. In 1950, he described an abnormality in the lining of the lower
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code
 Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
The scope of flexible endoscopy has increased with the introduction
 Recent Advances in Third-Space Endoscopy Zaheer Nabi, MD, DNB, D. Nageshwar Reddy, MD, DM, and Mohan Ramchandani, MD, DM Dr Nabi and Dr Ramchandani are consultant gastroenterologists and Dr Reddy is chairman
Recent Advances in Third-Space Endoscopy Zaheer Nabi, MD, DNB, D. Nageshwar Reddy, MD, DM, and Mohan Ramchandani, MD, DM Dr Nabi and Dr Ramchandani are consultant gastroenterologists and Dr Reddy is chairman
Managing Foreign Objects in the GI Tract Tips & Tricks
 Managing Foreign Objects in the GI Tract Tips & Tricks STEPHEN LANDRENEAU, MD Take home o Perform emergent endoscopy in cases of: Esophageal obstruction due to food bolus impaction or foreign object. Disk
Managing Foreign Objects in the GI Tract Tips & Tricks STEPHEN LANDRENEAU, MD Take home o Perform emergent endoscopy in cases of: Esophageal obstruction due to food bolus impaction or foreign object. Disk
Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion
 Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Esophageal injuries. 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119
 Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic Pre-test 2 Which contrast agent
Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic Pre-test 2 Which contrast agent
Management of pharynx fistula after upper digestive tract instrumentation
 RESEARCH ROJSP 2017, Vol. 2 (issue 1): E 35-40. Management of pharynx fistula after upper digestive tract instrumentation Popescu Bogdan 1,2, Voiculescu Ștefan 1, Scăunașu Răzvan 1, Alexandra Oana Păun
RESEARCH ROJSP 2017, Vol. 2 (issue 1): E 35-40. Management of pharynx fistula after upper digestive tract instrumentation Popescu Bogdan 1,2, Voiculescu Ștefan 1, Scăunașu Răzvan 1, Alexandra Oana Păun
Surgical Evaluation for Benign Esophageal Disease. Kimberly Howard, PA-C, MHS Duke University Medical Center April 7, 2018
 Surgical Evaluation for Benign Esophageal Disease Kimberly Howard, PA-C, MHS Duke University Medical Center April 7, 2018 Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this presentation. Objectives (for CME purposes)
Surgical Evaluation for Benign Esophageal Disease Kimberly Howard, PA-C, MHS Duke University Medical Center April 7, 2018 Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this presentation. Objectives (for CME purposes)
Shou Jiang Tang, MD, FASGE. Director of Endoscopic Research Professor in Medicine
 Shou Jiang Tang, MD, FASGE Director of Endoscopic Research Professor in Medicine Through-the-scope clipping devices Over-the-scope clipping devices First reported clipping device Hayshi T, Yonezawa M,
Shou Jiang Tang, MD, FASGE Director of Endoscopic Research Professor in Medicine Through-the-scope clipping devices Over-the-scope clipping devices First reported clipping device Hayshi T, Yonezawa M,
Foreign Body Management
 Foreign Body Management NYSGE Fellows Summer Course Susana Gonzalez, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine 1 Objectives Timing of endoscopy When? Anatomic location Where? High risk objects What? Choosing
Foreign Body Management NYSGE Fellows Summer Course Susana Gonzalez, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine 1 Objectives Timing of endoscopy When? Anatomic location Where? High risk objects What? Choosing
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of an Inverted Early Gastric Cancer-Forming False Gastric Diverticulum
 CSE REPORT Clin Endosc 2016;49:86-90 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.49.1.86 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open ccess Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of an Inverted Early Gastric Cancer-Forming
CSE REPORT Clin Endosc 2016;49:86-90 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.49.1.86 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open ccess Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of an Inverted Early Gastric Cancer-Forming
9/18/2015. Disclosures. Objectives. Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C. I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest
 Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C Disclosures I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest Objectives Define what dysphagia is Define types of dysphagia Define studies
Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C Disclosures I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest Objectives Define what dysphagia is Define types of dysphagia Define studies
Achalasia is a primary esophageal motility disorder of unknown
 Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy for Achalasia Andrew Pierre, MD, MSc Achalasia is a primary esophageal motility disorder of unknown etiology. Pathologically, it is characterized by loss of ganglion cells in
Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy for Achalasia Andrew Pierre, MD, MSc Achalasia is a primary esophageal motility disorder of unknown etiology. Pathologically, it is characterized by loss of ganglion cells in
A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES. Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus
 A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus CASE DESCRIPTION 63yo, F, single, attending nurse. PMH includes T2DM (Sitagliptin/Metformin), Hyperlipidemia
A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus CASE DESCRIPTION 63yo, F, single, attending nurse. PMH includes T2DM (Sitagliptin/Metformin), Hyperlipidemia
Case Report Thoracic Imaging. Eun Kyung Khil, MD 1, Heon Lee, MD, PhD 1, Keun Her, MD 2 INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.173 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):173-177 Spontaneous Intramural Full-Length Dissection of Esophagus Treated
Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.173 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):173-177 Spontaneous Intramural Full-Length Dissection of Esophagus Treated
SAGES Guidelines for the Surgical Treatment of Esophageal Achalasia
 Practice/Clinical Guidelines published on: 05/2011 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) SAGES Guidelines for the Surgical Treatment of Esophageal Achalasia Dimitrios
Practice/Clinical Guidelines published on: 05/2011 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) SAGES Guidelines for the Surgical Treatment of Esophageal Achalasia Dimitrios
(a) (b) Plate 16.1 Esophageal tear after passage of the echoendoscope.
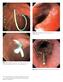 Plate 16.1 Esophageal tear after passage of the echoendoscope. Plate 11.1 Prophylactic pancreatic duct stents. 3-Fr, 4-cm long single-pigtail stent. 5-Fr, 3-cm long flanged stent. Plate 16.2 Esophageal
Plate 16.1 Esophageal tear after passage of the echoendoscope. Plate 11.1 Prophylactic pancreatic duct stents. 3-Fr, 4-cm long single-pigtail stent. 5-Fr, 3-cm long flanged stent. Plate 16.2 Esophageal
SAGES 2017 Flexible Endoscopy Course for Fellows
 Goals and Objectives: At the end of the course, the MIS fellow will be familiar with GI endoscopes, towers, and the instruments used for endoscopy and endoscopic surgery. The fellow will also be able to
Goals and Objectives: At the end of the course, the MIS fellow will be familiar with GI endoscopes, towers, and the instruments used for endoscopy and endoscopic surgery. The fellow will also be able to
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia. Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone. Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital
 THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
Pancreatic Benign April 27, 2016
 Department of Surgery Pancreatic Benign April 27, 2016 James Choi Dr. Hernandez Objectives Medical Expert: 1. Anatomy and congenital anomalies of the pancreas and pancreatic duct (divisum, annular pancreas
Department of Surgery Pancreatic Benign April 27, 2016 James Choi Dr. Hernandez Objectives Medical Expert: 1. Anatomy and congenital anomalies of the pancreas and pancreatic duct (divisum, annular pancreas
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy)
 Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540
 Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
CASE REPORTS. Giant Esophagus. An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy
 CASE REPORTS An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy and Dilatation of the Esophagus and Proximal Stomach Mark H. Wall, M.D., Epifanio E. Espinas, M.D., Arthur W. Silver, M.D., and Francis X.
CASE REPORTS An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy and Dilatation of the Esophagus and Proximal Stomach Mark H. Wall, M.D., Epifanio E. Espinas, M.D., Arthur W. Silver, M.D., and Francis X.
Hong Kong Society of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons CLINICAL MEETING 29 NOV 2012
 Hong Kong Society of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons CLINICAL MEETING 29 NOV 2012 Esophageal Leiomyoma Introduction Case presentation Operative video Discussion Esophageal Leiomyoma Benign tumors of the
Hong Kong Society of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons CLINICAL MEETING 29 NOV 2012 Esophageal Leiomyoma Introduction Case presentation Operative video Discussion Esophageal Leiomyoma Benign tumors of the
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 15: , 2018
 4356 Therapeutic application of purse-string sutures with nylon loops and metal clips under single-channel endoscopy for repair of gastrointestinal wall defects ZHENGUO QIAO 1*, XIN LING 1*, JIANHONG ZHU
4356 Therapeutic application of purse-string sutures with nylon loops and metal clips under single-channel endoscopy for repair of gastrointestinal wall defects ZHENGUO QIAO 1*, XIN LING 1*, JIANHONG ZHU
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS
 INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
Danis Procedure Pack - BASIC
 Danis Procedure Pack - BASIC Manufactured by: ELLA CS, s.r.o. Milady Horákové 504 500 06 Hradec Králové 6 Czech Republic Phone: +420 49 527 91 11 Fax: +420 49 526 56 55 E-mail: volenec@ellacs.eu Danis
Danis Procedure Pack - BASIC Manufactured by: ELLA CS, s.r.o. Milady Horákové 504 500 06 Hradec Králové 6 Czech Republic Phone: +420 49 527 91 11 Fax: +420 49 526 56 55 E-mail: volenec@ellacs.eu Danis
Perforated peptic ulcer
 Perforated peptic ulcer - Despite the widespread use of gastric anti-secretory agents and eradication therapy, the incidence of perforated peptic ulcer has changed little, age limits increase NSAIDs elderly
Perforated peptic ulcer - Despite the widespread use of gastric anti-secretory agents and eradication therapy, the incidence of perforated peptic ulcer has changed little, age limits increase NSAIDs elderly
