Original Article. Distinguishing Crohn s disease from intestinal tuberculosis a prospective study
|
|
|
- Alice Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tropical Gastroenterology 2011;32(3): Original Article Distinguishing Crohn s disease from intestinal tuberculosis a prospective study Amit Kumar Dutta, Manoj Kumar Sahu, Sajith Kattiparambil Gangadharan, Ashok Chacko ABSTRACT Department of Gastrointestinal Sciences, Christian Medical College & Hospital, Vellore , Tamil Nadu, India Correspondence: Dr. Ashok Chacko gastro@cmcvellore.ac.in Background: Distinguishing Crohn s disease (CD) from intestinal tuberculosis (ITB) is clinically challenging but important for prognostication and patient management. Methods: Patients with diagnosis of CD and ITB were prospectively enrolled in the study from January 2006 to October The patients were followed up for further 15 months to ascertain that the diagnosis had not changed. Clinical, laboratory, serological [IgG anti Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibody (ASCA)], endoscopic and histologic features were compared between the ITB and CD patients. The ASCA titers were estimated in 100 healthy controls. Patients were diagnosed as ASCA positive when their ASCA titers were three standard deviations above mean of controls. Results: Thirty patients with CD (age years, 70% males) and thirty with ITB (age years, 53.3% males) were included in the study. Features commoner in CD were longer duration of symptoms (p<0.001), blood mixed stool (p=0.006), presence of longitudinal ulcers (p=0.005) and skip lesions (p=0.008) on colonoscopy and more number of colonic segments involved (p=0.004). Anorexia was commoner in ITB patients (p=0.008). Positive ASCA was commoner in CD (30%) than ITB (10%) but did not reach statistical significance (p=0.1). Conclusions: A combined evaluation of clinical features, endoscopy, histology and response to treatment is the key to differentiate between CD and ITB. KEYWORDS: Crohn s disease, intestinal tuberculosis, differentiating, endoscopy, histology, serology Introduction The last two decades has seen the emergence of Crohn s disease (CD) in developing countries like India where intestinal tuberculosis (ITB) is prevalent as well. 1 Distinguishing CD from ITB is often challenging as both diseases have similar radiological, endoscopic and histologic features. 2 Since treatment and prognosis of the two conditions are different, it is crucial to diagnose them correctly. Tests for evaluation of patients with suspicion of CD or ITB include abdominal imaging, serological tests, endoscopy and histology. Results of individual investigations (except for presence of AFB or caseating granuloma for tuberculosis) are often insufficient for diagnosis. Diagnosis is often made after a combined evaluation of above investigations and response to therapy. 2 In this prospective study we report the role of Tropical Gastroenterology 2011
2 Distinguishing CD from ITB 205 clinical features, serology, endoscopy and histology in distinguishing CD from ITB. Methods Patients diagnosed to have CD and ITB at our institute were prospectively enrolled in the study between January 2006 and October Thirty patients with CD and thirty with ITB were recruited. The diagnosis of Crohn s disease was made based on a combination of clinical, radiological, endoscopic and histological features suggested by European evidence based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn s disease. 3 Intestinal tuberculosis was diagnosed in the presence of any of the following features: (I) Intestinal mucosal biopsy showing - a) AFB positive on histopathology or culture, and/ or b) caseating granulomas, and/or c) large or confluent granulomas (II) Response to treatment. 4 Clinical, investigation and treatment data were systematically recorded on a pre-designed proforma. Colonoscopy and terminal ileoscopy (if possible) (Olympus, CF 150L) was performed on the study subjects and gross findings were recorded. Multiple mucosal biopsy specimens were obtained from different segments of colon and terminal ileum during the scopy. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (Olympus, GIF 150) and biopsy from duodenum (D2) and stomach (antrum and incisura) were obtained in all CD patients irrespective of gross findings to assess extent of disease. Evaluation of anti saccharomyces cerevisae antibody (ASCA) was done using the IgG ASCA ELISA kits (AIDA diagnostics, Germany). ASCA recognizes specific mannan, a component of the outer wall of yeast. 5 Serum samples were incubated in the microplates coated with specific antigen. Patient s antibodies, if present in the specimen, bind to the antigen. The unbound fraction was washed off in subsequent steps. Afterwards, antihuman immunoglobulins conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (conjugate) were incubated and reacted with the antigenantibody complex of the samples in the microplates. Unbound conjugate was washed off. Addition of 3,5,3',5'- tetramethylbenzidine (TMB)-substrate generated an enzymatic colorimetric (blue) reaction and the absorbance was read at 450 nm within 30 minutes. The optical density (OD) of each calibrator (y axis) was plotted against the corresponding concentration values in U/ml (x axis). From this plot the antibody concentration of each sample was calculated by finding out the concentration corresponding to their respective OD values. ASCA levels were assessed in 100 healthy controls. The test was considered positive in patients if OD values were 3 standard deviation above mean value of controls. After the diagnosis of CD or ITB was made, the patients were followed up for a further 15 months to assess response to therapy and to confirm that the diagnosis had not changed. Clinical profile, serology, endoscopy and histopathology were compared between the two groups of patients to assess the ability of the above to differentiate Crohn s disease from intestinal tuberculosis. The study was approved by the institutional review board. Data is presented as mean with standard deviation for normally distributed continuous variables and as median with range for non-normally distributed continuous variables. Categorical data is presented as proportions. For comparing categorical variables (including ASCA) chi square test was used. For comparing continuous variables with normal distribution, t test was used. For continuous variable with nonnormal distribution, Mann-Whitney s U test was used. A p value of <0.05 was considered significant. The statistical analysis was done using SPSS software for windows version Results We selected 67 probable patients for our study of whom 60 (30 CD and 30 ITB) fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Four patients with suspected ITB and 3 with suspected CD were excluded due to insufficient diagnostic criteria. At baseline, 5 patients with CD (included in the study) had history of receiving ATT in past. Demographic and clinical features in patients with CD and ITB are shown in (Table 1). There was no significant difference in age, sex and geographical location in patients with CD and ITB. The median duration of symptoms in patients with ITB was 3 months (range 1 month to 2 years) while it was 2 years (range 6 months to 15 years) in patients with CD, the difference being statistically significant (p <0.001). Dull aching and poorly localized abdominal pain was the commonest symptom in patients with CD (60%) and ITB (70%). Blood mixed with stool was seen more often in patients with CD (p=0.006). Anorexia (p=0.008) and weight loss (p=0.067) were seen more often in ITB. Diarrhoea and fever were similar in both groups. Clinical examination of abdomen showed right iliac fossa mass in two patients with CD. In patients with ITB right iliac fossa mass was revealed in two patients, hepatosplenomegaly in
3 206 Tropical Gastroenterology 2011;32(3): one, hepatomegaly in one and cervical lymphadenopathy in two patients. According to the Vienna classification, the disease location in CD patients was L1 (ileal) in 13.3%, L2 (colonic) in 23.3%, L3 (ileocolonic) in 60% and L4 (upper gastrointestinal) in 3.3%. Although upper gastrointestinal lesion was seen in 5 patients (on endoscopy and/or histology), 4 of them had major lesions in ileum and/or colon and hence were not classified as L4. Two patients with CD had internal fistula (jejunocolic and colovesical), 4 had fistula-in-ano and two had anal fissure. Extraintestinal manifestations were present in 4 patients 3 had arthralgia, 1 had pyoderma gangrenosum and 3 had oral ulcers. Thirteen patients underwent surgery for their disease 5 had small bowel surgery for strictures, 7 had right hemicolectomy for ileocolonic disease and 1 had fistulectomy for perianal fistula. The disease location in ITB patients was ileocolonic in 53.3%, ileal in 3.3%, colonic in 33.3% and upper gastrointestinal in 10%. Among patients with ITB two patients had internal fistula (duodenocolic and jejunocolic) and 1 had fistula-in-ano. Extraintestinal manifestation was present in only 1 patient who had arthralgia. Three patients underwent surgery for their disease 1 had small bowel surgery for strictures and other two had partial colonic resections as treatment of internal fistulas. Patients with CD underwent surgery significantly more often compared to ITB patients (p=0.007). Lab investigations revealed low albumin (<3.5 g/dl in 38 patients), high ESR (>30 Table 1: Demographic, clinical and laboratory profile of patients CD ITB p (n=30) (n=30) value Age (yrs.) Sex (M/F) 21/9 16/ Symptom duration 24months 3 months <0.001 [Median (range)] (6-180months) (1-24months) Abdominal pain 18 (60%) 21 (70%) 0.59 Diarrhea 14 (46.7%) 12 (40%) 0.8 Weight loss 13 (43.3%) 21 (70%) Anorexia 12 (40%) 23 (76.7%) Blood in stool 11 (36.7%) 1 (3.3%) Fever 8 (26.7%) 9 (30%) 1.0 Fistula 6 (20%) 3 (10%) 0.47 Extraintestinal 4 (13.3%) 1 (3.3%) 0.35 manifestations CRP (%Positive) 71.4% 75% 1.0 Hb(g%) ESR (mm/hr.) 44.1(3-108) 62.8 (6-140) 0.05 Albumin (g/dl) IC Ileocolonic, I- Ileal, C- Colonic, O- Other site M Male, F-Female in 40 patients) and borderline low hemoglobin (<11.0 g% in 32 patients) in most patients. ESR was significantly higher in ITB group compared to CD (p=0.05). All patients with CD and 24 patients with ITB underwent colonoscopy. The other 6 patients with ITB had radiological evidence of intestinal involvement with evidence of tuberculosis at extraintestinal sites. The colonoscopy and mucosal biopsy findings are shown in (Table 2). Colonoscopy showed lesions in twenty five (83%) patients with CD and twenty three patients with ITB (95.8%). Presence of skip lesions (p=0.008), longitudinal ulcers (p=0.005), and multiple colonic segment involvement (p=0.004) were commoner in CD than in ITB. Other colonoscopic findings were not helpful in differentiating CD from ITB. Three patients with CD had UGI involvement on endoscopy (gastric erosions in 2 and duodenal nodularity in 1) and five had noncaseating granulomas on histology (4 in stomach and 1 in duodenum). Histological features suggestive of CD were seen in 90% of CD patients and these included crypt architecture abnormalities, mononuclear infiltration, granulomas, transmural inflammation, segmental distribution of the lesion and patchy and focal inflammation. Remaining three patients had nonspecific histological features and in them, clinical and radiological features along with response to therapy formed the basis of diagnosis. All patients with CD showed response to treatment but 6 of them had a relapse during follow up. Histological features suggestive of ITB were seen in 20 of the Table 2: Colonoscopic and mucosal biopsy findings in patients with ITB and CD Findings CD ITB p (n=30) (n=24) value Aphthous ulcer 11 (36.7%) 4 (16.7%) 0.13 Longitudinal ulcer 10 (33.3%) 1 (4.2%) Transverse ulcer 2 (6.7%) 6 (25%) 0.14 Skip lesions 11 (36.7%) 2 (8.3%) Perianal lesions 6 (20%) 1 (4.2%) 0.1 Mean number of segments involved Cobblestone pattern 3 (10%) 0 (0%) 0.25 Pseudopolyp 9 (30%) 2 (8.3%) 0.09 Stricture 8 (26.7%) 4 (16.7%) 0.51 Narrowed IC valve 3 (10%) 5 (20.8%) 0.44 Patulous IC valve 2 (6.7%) 2 (8.3%) 1.00 Confluent granuloma 0 (0%) 9 (37.5%) NA Microgranuloma 3 (10%) 0 (0%) 0.25 Caseous necrosis 0 (0%) 2 (8.3%) NA AFB positive* 0 (0%) 9 (37.5%) NA AFB Acid Fast Bacilli *Does not include 2 patients with confluent granulomas and AFB together
4 Distinguishing CD from ITB ITB patients undergoing colonoscopy and these included large or confluent granulomas (n=9, 37.5%), caseating granulomas (n=2, 8.3%), and presence of AFB in tissue section or culture of tissue (n=9, 37.5%). The ITB patients with caseation (n=2) or AFB (n=9) had discrete (non-confluent) granulomas seen on histology. Among the 9 patients with confluent granulomas, 2 had AFB. Of the 30 ITB patients, 27 responded to ATT. Among the remaining 3 (all had AFB on histology), 1 expired after 1 month of therapy and 2 had no response to 9 months of ATT. ASCA ELISA was tested on 100 controls to establish the normal cut-off antibody levels in the population. The mean optical density value in controls plus 3 standard deviation was taken as cut-off value and patients with values above this level (equivalent to 7 U/ml) were considered to have a positive ASCA test. 30% of patients with CD had ASCA positive as compared to 10% of patients with ITB (p=0.1) (Table 3). The specificity of ASCA was 90% in differentiating CD from ITB. The occurrence of stricturing and fistulising disease, small bowel disease, history of surgery, marker of disease activity (CRP, ESR, Harvey Bradshaw Score >4) and clinical course were not significantly different between the CD patients who were ASCA positive and those who were ASCA negative. However, the small number of patients makes meaningful comparison difficult. Table 3: ASCA results of CD patients compared with ITB ASCA CD ITB p-value Positive 9 (30%) 3 (10%) 0.10 Negative 21 (70%) 27 (90%) Total Discussion The study was aimed at assessing distinguishing features between CD and ITB in a prospectively recruited cohort. About 35-45% of patients with CD in India are initially diagnosed to have ITB which aptly highlights the difficulty in distinguishing between the two diseases. 6,7 The rising incidence of CD in India further compounds this problem and calls for development of effective tools to differentiate the two conditions. 1 Both the diseases are common in the fourth decade of life and abdominal pain and weight loss are seen in up to two-third of the cases. 4,6 A large case series of ITB (n=173) and another one on CD (n=182) from India suggests that ITB patients have more frequent fever and shorter duration of symptoms (<1 year). 4,6 CD patients are usually symptomatic for years and diarrhea and bleeding per rectum are more common. 6,7 Symptom duration was shorter and anorexia was more common in our ITB patients. Blood in stool was commoner in CD patients while rest of the clinical features were comparable. Amarapurkar et al have reported anemia to be frequent in CD patients and ESR similar in patients with CD and ITB. 7 Our ITB patients had higher ESR than CD patients. In our study, lab features were not helpful in differentiating the two diseases. Serological tests including ASCA and panca are commonly used in western countries to distinguish CD from ulcerative colitis. 8 ASCA is commoner in CD and panca in ulcerative colitis. 8 Since in India we are more often faced with problems of distinguishing CD from ITB, it is logical to study the role of serological tests to differentiate between them. Three studies have been done in India on utility of ASCA but none showed any significant difference in prevalence between CD and ITB patients. 7, 9,10 However, these reports have not commented on establishing local positive cut-offs of ASCA. We analyzed the serum of 100 healthy controls to establish the cut-off value of ASCA in our population. Using this cut-off, 30% of our patients with CD and 10% of patients with ITB were ASCA positive but the difference failed to reach statistical significance. Interestingly, the ASCA prevalence in CD in other Indian studies has ranged from 40-60% as compared to 30% in our series. 7,9,10 The use of cut-off value of ASCA established for our own population in this study may account for this difference. However, ASCA did have a good specificity in distinguishing CD from ITB. Eight of our nine CD patients who had ASCA positive had ileal involvement suggesting that ASCA positivity may point to small bowel involvement in CD. Radiological investigations provide useful clues to diagnosis but their major role is in assessing the extent of the disease. 2 Since we used both barium studies and CT abdomen for this purpose, comparison of any single modality to differentiate the two diseases was not performed due to small number of patients. Studies comparing imaging findings in CD and ITB are few 11,12 and most describe findings in either a group of ITB patients or CD patients. 13,14 Asymmetric thickening of colonic wall, larger lymph nodes (>1cm), necrotic lymph nodes and ascites on CT are suggestive of ITB. 2 Symmetrical bowel wall thickening, smaller (<1cm) lymph nodes and bowel loop displacement by fibrofatty changes are suggestive of CD. 2 Endoscopy plays an important role in diagnosis. 7,15 Apart from visual inspection, mucosal biopsy can be obtained for histopathology, culture and molecular tests. Presence of mucosal ulcers and involvement of ileocecal region are common in both diseases. Colonoscopy studies show that CD patients
5 208 Tropical Gastroenterology 2011;32(3): usually have longitudinal ulcers, cobblestone appearance of mucosa and anorectal involvement. 16 A patulous ileocecal valve, transverse ulcer and involvement of lesser number of colonic segments are commoner in ITB. 7,16 None of these were discriminatory in our patients. Presence of AFB in biopsy samples on histology or on culture is diagnostic of tuberculosis but was present only in a small number of our cases. Granulomas in endoscopic biopsy samples are seen in 20-30% of CD and 50-70% of ITB patients. 6,7,17,18 Previous studies done at our center by Pulimood et al showed that granulomas in ITB and CD have different morphology. 19,20 Granulomas in ITB are multiple (mean number of granulomas per section: 5.35), large (mean widest diameter: 193 micron), confluent and often with caseating necrosis. In CD granulomas were infrequent, small and poorly organized. In addition to microscopic examination, tissue samples can be subjected to PCR tests. Conventional PCR is done after extracting nucleic acids from tissue followed by amplification reactions. In a report on 60 patients with ITB and 20 with CD, PCR was positive in 21.6% of ITB patients vs. 5% CD patients. 21 Another PCR technique called the in-situ PCR does not require nucleic acid extraction from tissues. The targeted DNA sequence is amplified in intact cells. A study done at our center on 20 patients with ITB and CD each showed it to be positive in 30% and 5% patients respectively. 22 What is apparent from these data is that PCR has a good specificity but poor sensitivity. Apart from tissue PCR, fecal sample PCR testing has also been studied at our center in ITB patients and controls and the results are encouraging. 23 In conclusion, differentiating CD from ITB continues to be a challenging problem. Presently, a combination of clinical features, endoscopy, histology, radiology and response to treatment continues to be the key to differentiate these two conditions. We need to continue to develop new tests to help clinicians differentiate between the two conditions. Acknowledgements We thank Dr. Gagandeep Kang, Mrs. Sheela Roy and other staff members in the Microbiology wing of the department of Gastrointestinal sciences who performed the ASCA test on serum of patients and controls. References 1. Desai HG, Gupte PA. Increasing incidence of Crohn s disease in India: is it related to improved sanitation? Indian J Gastroenterol. 2005;24: Almadi MA, Ghosh S, Aljebreen AM. Differentiating intestinal tuberculosis from Crohn s disease: a diagnostic challenge. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104: Stange EF, Travis SP, Vermeire S, Beglinger C, Kupcinkas L, Geboes K, et al. European evidence based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn s disease: definitions and diagnosis. Gut. 2006;55 Suppl 1:i Patel N, Amarapurkar D, Agal S, Baijal R, Kulshrestha P, Pramanik S, et al. Gastrointestinal luminal tuberculosis: establishing the diagnosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;19: Zholudev A, Zurakowski D, Young W, Leichtner A, Bousvaros A. Serologic testing with ANCA, ASCA, and anti-ompc in children and young adults with Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis: diagnostic value and correlation with disease phenotype. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99: Das K, Ghoshal UC, Dhali GK, Benjamin J, Ahuja V, Makharia GK. Crohn s disease in India: a multicenter study from a country where tuberculosis is endemic. Dig Dis Sci. 2009;54: Amarapurkar DN, Patel ND, Rane PS. Diagnosis of Crohn s disease in India where tuberculosis is widely prevalent. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14: Barahona-Garrido J, Sarti HM, Barahona-Garrido MK, Hernández-Calleros J, Coss-Adame E, Garcia-Saenz SM, et al. Serological markers in inflammatory bowel disease: a review of their clinical utility. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2009;74: Makharia GK, Sachdev V, Gupta R, Lal S, Pandey RM. Anti- Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibody does not differentiate between Crohn s disease and intestinal tuberculosis. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52: Ghoshal UC, Ghoshal U, Singh H, Tiwari S. Anti- Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibody is not useful to differentiate between Crohn s disease and intestinal tuberculosis in India. J Postgrad Med. 2007;53: Makanjuola D. Is it Crohn s disease or intestinal tuberculosis? CT analysis. Eur J Radiol. 1998;28: Boudiaf M, Zidi SH, Soyer P, Lavergne-Slove A, Kardache M, Logeay O, et al. Tuberculous colitis mimicking Crohn s disease: utility of computed tomography in the differentiation. Eur Radiol. 1998;8: Balthazar EJ, Gordon R, Hulnick D. Ileocecal tuberculosis: CT and radiologic evaluation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990;154: Sinan T, Sheikh M, Ramadan S, Sahwney S, Behbehani A. CT features in abdominal tuberculosis: 20 years experience. BMC Med Imaging. 2002;2: Shah S, Thomas V, Mathan M, Chacko A, Chandy G, Ramakrishna BS, et al. Colonoscopic study of 50 patients with colonic tuberculosis. Gut. 1992;33: Lee YJ, Yang SK, Byeon JS, Myung SJ, Chang HS, Hong SS, et al. Analysis of colonoscopic findings in the differential diagnosis between intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn s disease. Endoscopy. 2006;38: Kim KM, Lee A, Choi KY, Lee KY, Kwak JJ. Intestinal tuberculosis: clinicopathologic analysis and diagnosis by endoscopic biopsy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93: Alvares JF, Devarbhavi H, Makhija P, Rao S, Kottoor R. Clinical,
6 Distinguishing CD from ITB 209 colonoscopic, and histological profile of colonic tuberculosis in a tertiary hospital. Endoscopy. 2005;37: Pulimood AB, Ramakrishna BS, Kurian G, Peter S, Patra S, Mathan VI, et al. Endoscopic mucosal biopsies are useful in distinguishing granulomatous colitis due to Crohn s disease from tuberculosis. Gut. 1999;45: Pulimood AB, Peter S, Ramakrishna B, Chacko A, Jeyamani R, Jeyaseelan L, et al. Segmental colonoscopic biopsies in the differentiation of ileocolic tuberculosis from Crohn s disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;20: Amarapurkar DN, Patel ND, Amarapurkar AD, Agal S, Baigal R, Gupte P. Tissue polymerase chain reaction in diagnosis of intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn s disease. J Assoc Physicians India 2004;52: Pulimood AB, Peter S, Rook GW, Donoghue HD. In situ PCR for Mycobacterium tuberculosis in endoscopic mucosal biopsy specimens of intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129: Balamurugan R, Venkataraman S, John KR, Ramakrishna BS. PCR amplification of the IS6110 insertion element of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in fecal samples from patients with intestinal tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:
Differentiation Between Ileocecal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease using a Combination of Clinical, Endoscopic and Histological Characteristics
 38 Original Article Differentiation Between Ileocecal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease using a Combination of Clinical, Endoscopic and Histological Characteristics Anuchapreeda S Leelakusolvong S Charatcharoenwitthaya
38 Original Article Differentiation Between Ileocecal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease using a Combination of Clinical, Endoscopic and Histological Characteristics Anuchapreeda S Leelakusolvong S Charatcharoenwitthaya
Endoscopic Diagnosis and Differentiation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 REVIEW Clin Endosc 2016;49:370-375 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.090 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Endoscopic Diagnosis and Differentiation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Ji
REVIEW Clin Endosc 2016;49:370-375 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.090 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Endoscopic Diagnosis and Differentiation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Ji
What do we need for diagnosis of IBD
 What do we need for diagnosis of IBD Kaichun Wu Dept. of Gastroenterology, Xijing Hospital Fourth Military Medical University Xi an an,, China In China UC 11.6/10 5,CD 1.4/10 5 Major cause of chronic diarrhea
What do we need for diagnosis of IBD Kaichun Wu Dept. of Gastroenterology, Xijing Hospital Fourth Military Medical University Xi an an,, China In China UC 11.6/10 5,CD 1.4/10 5 Major cause of chronic diarrhea
Original Article Etiologic and clinical analysis of chronic complex anal and rectal inflammation in children less than 3 years old
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(11):4016-4023 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002461 Original Article Etiologic and clinical analysis of chronic complex anal and rectal inflammation in children less than
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(11):4016-4023 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002461 Original Article Etiologic and clinical analysis of chronic complex anal and rectal inflammation in children less than
STATEMENT INTRODUCTION EPIDEMIOLOGY
 STATEMENT ISSN 1598-9100(Print) ISSN 2288-1956(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5217/ir.2015.13.1.6 Intest Res 2015;13(1):6-10 Seminar Report From the 2014 Taiwan Society of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (TSIBD)
STATEMENT ISSN 1598-9100(Print) ISSN 2288-1956(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5217/ir.2015.13.1.6 Intest Res 2015;13(1):6-10 Seminar Report From the 2014 Taiwan Society of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (TSIBD)
Endoscopic mucosal biopsies are useful in distinguishing granulomatous colitis due to Crohn s disease from tuberculosis
 Gut 1999;45:537 541 537 Wellcome Research Unit, Department of Gastrointestinal Sciences, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore 632 004, Tamilnadu, India A B Pulimood B S Ramakrishna G Kurian
Gut 1999;45:537 541 537 Wellcome Research Unit, Department of Gastrointestinal Sciences, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore 632 004, Tamilnadu, India A B Pulimood B S Ramakrishna G Kurian
Segmental colonoscopic biopsies in the differentiation of ileocolic tuberculosis from Crohn s disease
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKJGHJournal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology0815-93192005 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty LtdMay 2005205688696Original ArticleSegmental biopsies in and Crohn s diseaseab
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKJGHJournal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology0815-93192005 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty LtdMay 2005205688696Original ArticleSegmental biopsies in and Crohn s diseaseab
IBD 101. Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition
 IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
 National University Faculty of Medicine INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Gehan M. Osman, MD. MBBS Pediatrician Jaffar Ibn Auf Specialized Hospital EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES Definitions and spectrum of (IBD) Epidemiology
National University Faculty of Medicine INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Gehan M. Osman, MD. MBBS Pediatrician Jaffar Ibn Auf Specialized Hospital EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES Definitions and spectrum of (IBD) Epidemiology
children Crohn s disease in MR enterography for GI Complications Microscopy Characterization Primary sclerosing cholangitis Anorectal fistulae
 MR enterography for Crohn s disease in children BOAZ KARMAZYN, MD PEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Characterization Crohn disease Idiopathic chronic transmural IBD Increasing incidence Age 7/100,000
MR enterography for Crohn s disease in children BOAZ KARMAZYN, MD PEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Characterization Crohn disease Idiopathic chronic transmural IBD Increasing incidence Age 7/100,000
Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University.
 Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University. Chronic transmural inflammatory process of the bowel & affects any part of the gastro -intestinal tract from the mouth to the
Mohamed EL-hemaly Gastro- intestinal surgical center, Mansoura University. Chronic transmural inflammatory process of the bowel & affects any part of the gastro -intestinal tract from the mouth to the
IBD 101. Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition
 IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
Surgical Management of IBD. Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003
 Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
IBD. Crohn s. Outline. Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? UC vs. Crohn s? Is it easy? Biopsy settings 21/07/2017 IBD
 Outline Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? Roger Feakins Colorectal biopsies Ileal and upper GI biopsies Special situations New techniques Summary Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Outline Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn s disease: is biopsy useful? Roger Feakins Colorectal biopsies Ileal and upper GI biopsies Special situations New techniques Summary Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Implementation of disease and safety predictors during disease management in UC
 Implementation of disease and safety predictors during disease management in UC DR ARIELLA SHITRIT DIGESTIVE DISEASES INSTITUTE SHAARE ZEDEK MEDICAL CENTER JERUSALEM Case presentation A 52 year old male
Implementation of disease and safety predictors during disease management in UC DR ARIELLA SHITRIT DIGESTIVE DISEASES INSTITUTE SHAARE ZEDEK MEDICAL CENTER JERUSALEM Case presentation A 52 year old male
Tissue Polymerase Chain Reaction in Diagnosis of Intestinal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease
 Original Article Tissue Polymerase Chain Reaction in Diagnosis of Intestinal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease DN Amarapurkar*, ND Patel*, AD Amarapurkar**, S Agal*, R Baigal*, P Gupte* Abstract Aims and
Original Article Tissue Polymerase Chain Reaction in Diagnosis of Intestinal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease DN Amarapurkar*, ND Patel*, AD Amarapurkar**, S Agal*, R Baigal*, P Gupte* Abstract Aims and
The Morphologic Profile of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and the Diagnostic Problem of Crohn s Disease versus TB Colitis A Case Series
 OPEN ACCESS CASE REPORT The Morphologic Profile of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and the Diagnostic Problem of Crohn s Disease versus TB Colitis A Case Series Maria Lourdes Tilbe, Francia Victoria De Los
OPEN ACCESS CASE REPORT The Morphologic Profile of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and the Diagnostic Problem of Crohn s Disease versus TB Colitis A Case Series Maria Lourdes Tilbe, Francia Victoria De Los
Original Research Article
 CLINICAL AND COLONOSCOPIC PROFILE OF ISOLATED COLONIC TUBERCULOSIS AT A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN NORTH INDIA Vijant Singh Chandail 1, Vinu Jamwal 2 1Lecturer, PG Department of Medicine, Government Medical
CLINICAL AND COLONOSCOPIC PROFILE OF ISOLATED COLONIC TUBERCULOSIS AT A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN NORTH INDIA Vijant Singh Chandail 1, Vinu Jamwal 2 1Lecturer, PG Department of Medicine, Government Medical
The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Dr. Richard A. Beable Consultant Gastrointestinal Radiologist Queen Alexandra Hospital Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Topics for Discussion
The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Dr. Richard A. Beable Consultant Gastrointestinal Radiologist Queen Alexandra Hospital Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Topics for Discussion
Inflammatory Bowel Disease When is diarrhea not just diarrhea?
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease When is diarrhea not just diarrhea? Jackie Kazik, MA, PA C CME Resources CAPA Annual Conference, 2011 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives Discuss what is known about the pathophysiology
Inflammatory Bowel Disease When is diarrhea not just diarrhea? Jackie Kazik, MA, PA C CME Resources CAPA Annual Conference, 2011 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives Discuss what is known about the pathophysiology
A Case of Gastric Tuberculosis Mimicking Advanced Gastric Cancer
 The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine: 21:62-67, 2006 A Case of Gastric Tuberculosis Mimicking Advanced Gastric Cancer Seong-Eun Kim, M.D., Ki-Nam Shim, M.D., Su Jin Yoon, M.D., Sung-Ae Jung, M.D., Tae
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine: 21:62-67, 2006 A Case of Gastric Tuberculosis Mimicking Advanced Gastric Cancer Seong-Eun Kim, M.D., Ki-Nam Shim, M.D., Su Jin Yoon, M.D., Sung-Ae Jung, M.D., Tae
IBD Tools to Aid in the Accurate Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 IBD Tools to Aid in the Accurate Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Inflammatory Bowel Disease Experts in Autoimmunity Inova Diagnostics offers a complete array of methods to aid in the diagnosis
IBD Tools to Aid in the Accurate Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Inflammatory Bowel Disease Experts in Autoimmunity Inova Diagnostics offers a complete array of methods to aid in the diagnosis
NON INVASIVE MONITORING OF MUCOSAL HEALING IN IBD. THE ROLE OF BOWEL ULTRASOUND. Fabrizio Parente
 NON INVASIVE MONITORING OF MUCOSAL HEALING IN IBD. THE ROLE OF BOWEL ULTRASOUND Fabrizio Parente Gastrointestinal Unit, A.Manzoni Hospital, Lecco & L.Sacco School of Medicine,University of Milan - Italy
NON INVASIVE MONITORING OF MUCOSAL HEALING IN IBD. THE ROLE OF BOWEL ULTRASOUND Fabrizio Parente Gastrointestinal Unit, A.Manzoni Hospital, Lecco & L.Sacco School of Medicine,University of Milan - Italy
Endoscopy in IBD. F.Hartmann K.Kasper-Kliniken (St.Marienkrankenhaus) Frankfurt/M.
 F.Hartmann K.Kasper-Kliniken (St.Marienkrankenhaus) Frankfurt/M. F.Hartmann@em.uni-frankfurt.de Indications for endoscopy Diagnosis Management Surveillance Diagnosis Single most valuable tool: ileocolonoscopy
F.Hartmann K.Kasper-Kliniken (St.Marienkrankenhaus) Frankfurt/M. F.Hartmann@em.uni-frankfurt.de Indications for endoscopy Diagnosis Management Surveillance Diagnosis Single most valuable tool: ileocolonoscopy
2015 복영증례 51/M C.C. Past Hx: DM, HTN (1998), Lab: WBC (11500/ μl ), CRP (0.71 mg/dl) 순천향서울병원황지영, 홍성숙 APCT (HAD #1) APCT (HAD#1) APCT (HAD #15)
 Case 1 2015 복영증례 순천향서울병원황지영, 홍성숙 51/M C.C Abdominal pain and chilling (1 week ago) Diarrhea (a month ago) Past Hx: DM, HTN (1998), Alcoholic liver disease (2008) Lab: WBC (11500/ μl ), CRP (0.71 mg/dl)
Case 1 2015 복영증례 순천향서울병원황지영, 홍성숙 51/M C.C Abdominal pain and chilling (1 week ago) Diarrhea (a month ago) Past Hx: DM, HTN (1998), Alcoholic liver disease (2008) Lab: WBC (11500/ μl ), CRP (0.71 mg/dl)
Crohn s Disease. Resident Lecture 1/17/19
 Crohn s Disease Resident Lecture 1/17/19 Objectives Features/Classification of Crohn s Disease Medical Treatment Surgical Indications Surgical Considerations 2 Case 25 yo F presents to your office with
Crohn s Disease Resident Lecture 1/17/19 Objectives Features/Classification of Crohn s Disease Medical Treatment Surgical Indications Surgical Considerations 2 Case 25 yo F presents to your office with
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE. Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic
 INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic WHAT IS INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD)? Chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract Two related
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic WHAT IS INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD)? Chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract Two related
Accuracy of computed tomographic features in differentiating intestinal tuberculosis from Crohn s disease: a systematic review with meta-analysis
 SYSTEMATIC REVIEW pissn 1598-9100 eissn 88-56 https://doi.org/10.57/ir.17.15.2.149 Intest Res 17;15(2):149-159 Accuracy of computed tomographic features in differentiating intestinal tuberculosis from
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW pissn 1598-9100 eissn 88-56 https://doi.org/10.57/ir.17.15.2.149 Intest Res 17;15(2):149-159 Accuracy of computed tomographic features in differentiating intestinal tuberculosis from
METASTASES FROM GASTRIC CARCINOMA TO COLON LESIONS: A CASE REPORT IN THE FORM OF MULTIPLE FLAT ELEVATED CASE PRESENTATION
 H.C. Lee, M.T. Yang, K.Y. Lin, et al METASTASES FROM GASTRIC CARCINOMA TO COLON IN THE FORM OF MULTIPLE FLAT ELEVATED LESIONS: A CASE REPORT Hsi-Chang Lee, Min-Ta Yang, 1 Kuang-Yang Lin, 1 Hsing-Yang Tu,
H.C. Lee, M.T. Yang, K.Y. Lin, et al METASTASES FROM GASTRIC CARCINOMA TO COLON IN THE FORM OF MULTIPLE FLAT ELEVATED LESIONS: A CASE REPORT Hsi-Chang Lee, Min-Ta Yang, 1 Kuang-Yang Lin, 1 Hsing-Yang Tu,
Terumitsu; Nagayasu, Takeshi
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation A rare case of segmental ulcerative Tominaga, Tetsuro; Nonaka, Takashi; Shuichi; Kunizaki, Masaki; Sumida, Terumitsu; Nagayasu, Takeshi Acta medica
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation A rare case of segmental ulcerative Tominaga, Tetsuro; Nonaka, Takashi; Shuichi; Kunizaki, Masaki; Sumida, Terumitsu; Nagayasu, Takeshi Acta medica
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 6, Issue 5 2016 Article 4 Isolated Jejunal Crohn s Disease, A Diagnostic Dilemma Elise Biesboer BS Lacey Stelle MD Michelle M. Olson MD, MACM Paul Tender MD University
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 6, Issue 5 2016 Article 4 Isolated Jejunal Crohn s Disease, A Diagnostic Dilemma Elise Biesboer BS Lacey Stelle MD Michelle M. Olson MD, MACM Paul Tender MD University
A Case of Crohn s Disease with Mesalazine Allergy that was Difficult to Differentiate from Comorbid Ulcerative Colitis
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1607-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT A Case of Crohn s Disease with Mesalazine Allergy that was Difficult to Differentiate from Comorbid Ulcerative Colitis Rumiko Tsuboi,
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1607-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT A Case of Crohn s Disease with Mesalazine Allergy that was Difficult to Differentiate from Comorbid Ulcerative Colitis Rumiko Tsuboi,
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: NOT FOUND. Team Members: Shrouq alsomali + Basel almeflh + Alaa alaqeel + Raneem alghamdi Team Leader: Haneen Alsubki Revised By: Maha AlGhamdi Resources: 435 team
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: NOT FOUND. Team Members: Shrouq alsomali + Basel almeflh + Alaa alaqeel + Raneem alghamdi Team Leader: Haneen Alsubki Revised By: Maha AlGhamdi Resources: 435 team
Visceral Fat as a Useful Parameter in the Differential Diagnosis of Crohn s Disease and Intestinal Tuberculosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1598-9100(Print) ISSN 2288-1956(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5217/ir.2014.12.1.42 Intest Res 2014;12(1):42-47 Visceral Fat as a Useful Parameter in the Differential Diagnosis of Crohn
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1598-9100(Print) ISSN 2288-1956(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5217/ir.2014.12.1.42 Intest Res 2014;12(1):42-47 Visceral Fat as a Useful Parameter in the Differential Diagnosis of Crohn
Histomorphological Spectrum of Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 26, No. 1, March 2004 Histomorphological Spectrum of Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis Ashok Kumar Malik,MD, MNAMS, FRCPath* Lily Pal, MD** Wig JD, MS, FRCS*** Objective:To study
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 26, No. 1, March 2004 Histomorphological Spectrum of Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis Ashok Kumar Malik,MD, MNAMS, FRCPath* Lily Pal, MD** Wig JD, MS, FRCS*** Objective:To study
GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 1071-1076, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM JAMES A. NELSON,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 1071-1076, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM JAMES A. NELSON,
Disease behavior in adult patients- are there predictors for stricture or fistula formation?
 Disease behavior in adult patients- are there predictors for stricture or fistula formation? Falk Symposium 168, Madrid, Spain Iris Dotan, M.D., Head, IBD Center, Department of Gastroenterology and Liver
Disease behavior in adult patients- are there predictors for stricture or fistula formation? Falk Symposium 168, Madrid, Spain Iris Dotan, M.D., Head, IBD Center, Department of Gastroenterology and Liver
Tuberculosis and Crohn's Disease Revisited
 REVIEW ARTICLE Tuberculosis and Crohn's Disease Revisited Ibrahim Koral Onal 1, Murat Kekilli 2, Alpaslan Tanoglu 3, Harun Erdal 1, Mehmet Ibis 1 and Mehmet Arhan 1 ABSTRACT Crohn's Disease (CD) and Intestinal
REVIEW ARTICLE Tuberculosis and Crohn's Disease Revisited Ibrahim Koral Onal 1, Murat Kekilli 2, Alpaslan Tanoglu 3, Harun Erdal 1, Mehmet Ibis 1 and Mehmet Arhan 1 ABSTRACT Crohn's Disease (CD) and Intestinal
Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Michael Weiss MD, FACG
 Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Michael Weiss MD, FACG What is IBD? IBD is an immune-mediated chronic intestinal disorder, characterized by chronic or relapsing inflammation within the GI tract.
Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Michael Weiss MD, FACG What is IBD? IBD is an immune-mediated chronic intestinal disorder, characterized by chronic or relapsing inflammation within the GI tract.
What is the most accurate method for the diagnosis of intestinal tuberculosis?
 Turk J Gastroenterol 2010; 21 (1): 91-96 TURKISH INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE SOCIETY RECOMMENDATIONS ON SELECTED TOPICS OF CROHN S DISEASE TÜRK NFLAMATUVAR BARSAK HASTALIKLARI DERNE N N CROHN HASTALI I
Turk J Gastroenterol 2010; 21 (1): 91-96 TURKISH INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE SOCIETY RECOMMENDATIONS ON SELECTED TOPICS OF CROHN S DISEASE TÜRK NFLAMATUVAR BARSAK HASTALIKLARI DERNE N N CROHN HASTALI I
Study of biochemical, pathological & radiological correlation of various types of abdominal tuberculosis
 Original article: Study of biochemical, pathological & radiological correlation of various types of abdominal tuberculosis 1 Dr. J.S Dhadwad*, 2 Dr. Akshay Shewale 1Associate Professor in Medicine, Pad.Dr.DY
Original article: Study of biochemical, pathological & radiological correlation of various types of abdominal tuberculosis 1 Dr. J.S Dhadwad*, 2 Dr. Akshay Shewale 1Associate Professor in Medicine, Pad.Dr.DY
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: fecal_calprotectin_test 8/2009 11/2017 11/2018 11/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Fecal calprotectin
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: fecal_calprotectin_test 8/2009 11/2017 11/2018 11/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Fecal calprotectin
Deep Enteroscopy Methods to Diagnose Small Bowel IBD
 Deep Enteroscopy Methods to Diagnose Small Bowel IBD Name: Institution: Peter Draganov University of Florida, Gainesville, FL Overview Types of enteroscopy Enteroscopy equipment Enetoscopy do and don'ts
Deep Enteroscopy Methods to Diagnose Small Bowel IBD Name: Institution: Peter Draganov University of Florida, Gainesville, FL Overview Types of enteroscopy Enteroscopy equipment Enetoscopy do and don'ts
Original Article. Evaluation of Small Intestinal Biopsies in Malabsorption Syndromes
 Original Article Evaluation of Small Intestinal Biopsies in Malabsorption Syndromes Ashmeet Kaur 1 *, Poojaba Jadeja 2, Neha Garg 2, SML Rai 2 and N. Mogra 2 1 Department Of Pathology, Santokba Durlabhji
Original Article Evaluation of Small Intestinal Biopsies in Malabsorption Syndromes Ashmeet Kaur 1 *, Poojaba Jadeja 2, Neha Garg 2, SML Rai 2 and N. Mogra 2 1 Department Of Pathology, Santokba Durlabhji
Normal small intestine Variations
 THE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM BIOPSY K. Geboes, MD, PhD, AGAF, dr. H.C. Belgium Normal small intestine Variations Duodenum Ileum 1 Proliferative compartment Normal variations 2
THE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM BIOPSY K. Geboes, MD, PhD, AGAF, dr. H.C. Belgium Normal small intestine Variations Duodenum Ileum 1 Proliferative compartment Normal variations 2
Tubercular versus Crohn s ileal strictures: role of endoscopic balloon dilatation without fluoroscopy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2013) 26, 1-5 Tubercular versus Crohn s ileal strictures: role of endoscopic balloon dilatation without fluoroscopy Surinder Singh Rana, Deepak Kumar Bhasin,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2013) 26, 1-5 Tubercular versus Crohn s ileal strictures: role of endoscopic balloon dilatation without fluoroscopy Surinder Singh Rana, Deepak Kumar Bhasin,
INTERNATIONAL COURSE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM VICTOR BABES NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF PATHOLOGY BUCHAREST 7-8 BUCHAREST 2014
 INTERNATIONAL COURSE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM VICTOR BABES NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF PATHOLOGY BUCHAREST 7-8 BUCHAREST 2014 Endoscopic biopsy samples of naïve colitides patients: Role of basal
INTERNATIONAL COURSE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM VICTOR BABES NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF PATHOLOGY BUCHAREST 7-8 BUCHAREST 2014 Endoscopic biopsy samples of naïve colitides patients: Role of basal
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS Cary B. Aarons, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon & Rectal Surgery University of Pennsylvania AGENDA Background Diagnosis/Work-up Medical Management
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS Cary B. Aarons, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon & Rectal Surgery University of Pennsylvania AGENDA Background Diagnosis/Work-up Medical Management
The Spectrum of IBD. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Symptoms. Epidemiology. Tests for IBD. CD or UC? Inflamatory Bowel Disease. Fernando Vega, M.D.
 The Spectrum of IBD Inflammatory Bowel Disease Fernando Vega, M.D. Epidemiology CD and UC together 1:400 UC Prevalence 1:500 UC Incidence 6-12K/annum CD Prevalence 1:1000 CD Incidence 3-6K/annum Symptoms
The Spectrum of IBD Inflammatory Bowel Disease Fernando Vega, M.D. Epidemiology CD and UC together 1:400 UC Prevalence 1:500 UC Incidence 6-12K/annum CD Prevalence 1:1000 CD Incidence 3-6K/annum Symptoms
The aim of this study was to find the diagnostic yield of ileoscopy in patients undergoing colonoscopy.
 The Professional Medical Journal ORIGINAL PROF-2673 1. FCPS (Internal Medicine), FCPS (Gastroenterology) Associate Professor Department of Gastroenterology, Liaquat National Hospital & Medical College
The Professional Medical Journal ORIGINAL PROF-2673 1. FCPS (Internal Medicine), FCPS (Gastroenterology) Associate Professor Department of Gastroenterology, Liaquat National Hospital & Medical College
Crohn s Disease: Should We Treat Based on Symptoms or Based on Objective Markers of Inflammation?
 Crohn s Disease: Should We Treat Based on Symptoms or Based on Objective Markers of Inflammation? Edward V. Loftus, Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic
Crohn s Disease: Should We Treat Based on Symptoms or Based on Objective Markers of Inflammation? Edward V. Loftus, Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
ד"ר דוד ירדני המכון לגסטרואנטרולוגיה ומחלות כבד מרכז רפואי סורוקה
 ד"ר דוד ירדני המכון לגסטרואנטרולוגיה ומחלות כבד מרכז רפואי סורוקה Presentaion: S.A is 38 years old. Referred for rectal bleeding investigation. Describes several occasions of bleeding and abdominal pain.
ד"ר דוד ירדני המכון לגסטרואנטרולוגיה ומחלות כבד מרכז רפואי סורוקה Presentaion: S.A is 38 years old. Referred for rectal bleeding investigation. Describes several occasions of bleeding and abdominal pain.
The Challenge of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Diagnosis in Asia
 Review Received: May 29, 2016 Accepted: July 13, 2016 Published online: August 19, 2016 The Challenge of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Diagnosis in Asia Yue Li Jia-ming Qian Division of Gastroenterology,
Review Received: May 29, 2016 Accepted: July 13, 2016 Published online: August 19, 2016 The Challenge of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Diagnosis in Asia Yue Li Jia-ming Qian Division of Gastroenterology,
In Situ PCR for Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Endoscopic Mucosal Biopsy Specimens of Intestinal Tuberculosis and Crohn Disease
 Microbiology and Infectious Disease / In Situ PCR for Intestinal Tuberculosis In Situ PCR for Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Endoscopic Mucosal Biopsy Specimens of Intestinal Tuberculosis and Crohn Disease
Microbiology and Infectious Disease / In Situ PCR for Intestinal Tuberculosis In Situ PCR for Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Endoscopic Mucosal Biopsy Specimens of Intestinal Tuberculosis and Crohn Disease
PROFILE OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS IN SOUTH INDIAN REGION: KARAIKAL D.BADMAPRIYA*, V.SATHISH KUMAR 1
 Page47 Available Online through IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 PROFILE OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS IN SOUTH INDIAN REGION: KARAIKAL D.BADMAPRIYA*, V.SATHISH KUMAR 1 * PHARMACIST, GOVERNMENT GENERAL
Page47 Available Online through IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 PROFILE OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS IN SOUTH INDIAN REGION: KARAIKAL D.BADMAPRIYA*, V.SATHISH KUMAR 1 * PHARMACIST, GOVERNMENT GENERAL
GASTROENTEROLOGY. Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association. CoPYRIGHT 1975 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS Co.
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association CoPYRIGHT 1975 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS Co. Vol68 April 1975 Number 4 ALIMENTARY TRACT CLINICAL PATTERNS IN CROHN'S DISEASE:
GASTROENTEROLOGY Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association CoPYRIGHT 1975 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS Co. Vol68 April 1975 Number 4 ALIMENTARY TRACT CLINICAL PATTERNS IN CROHN'S DISEASE:
Recurrent Intestinal Obstruction in a Patient with Selective IgA Deficiency
 Case Report Recurrent Intestinal Obstruction in a Patient with Selective IgA Deficiency Chee-Kin Hui 1,2 Submitted: 27 May 2015 Accepted: 27 Mar 2016 Online: 7 Dec 2016 1 Centre for Alimentary Studies,
Case Report Recurrent Intestinal Obstruction in a Patient with Selective IgA Deficiency Chee-Kin Hui 1,2 Submitted: 27 May 2015 Accepted: 27 Mar 2016 Online: 7 Dec 2016 1 Centre for Alimentary Studies,
Case History B Female patient 1970 Clinical History : crampy abdominal pain and episodes of bloody diarrhea Surgical treatment
 Case History B-1325945 Female patient 1970 Clinical History : crampy abdominal pain and episodes of bloody diarrhea Surgical treatment Case History B-1325945 Pathology Submucosa & Muscularis Endometriosis
Case History B-1325945 Female patient 1970 Clinical History : crampy abdominal pain and episodes of bloody diarrhea Surgical treatment Case History B-1325945 Pathology Submucosa & Muscularis Endometriosis
Characteristics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Serology in Patients With Indeterminate Colitis
 Characteristics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Serology in Patients With Indeterminate Colitis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Characteristics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Serology in Patients With Indeterminate Colitis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
EDITOR S PICK RECENT ADVANCES IN THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF ABDOMINAL TUBERCULOSIS
 EDITOR S PICK Mandavdhare et al. give an excellent overview of extrapulmonary tuberculosis, with a special focus on abdominal involvement. Unfortunately, this topic requires the attention of all, due to
EDITOR S PICK Mandavdhare et al. give an excellent overview of extrapulmonary tuberculosis, with a special focus on abdominal involvement. Unfortunately, this topic requires the attention of all, due to
Guided by Dr. Michal Amitai Head of Abdominal Imaging Department of Diagnostic Imaging Sheba Medical Center Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv
 Guided by Dr. Michal Amitai Head of Abdominal Imaging Department of Diagnostic Imaging Sheba Medical Center Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University 1 SHARE study My year Collaboration between gastroenterology
Guided by Dr. Michal Amitai Head of Abdominal Imaging Department of Diagnostic Imaging Sheba Medical Center Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University 1 SHARE study My year Collaboration between gastroenterology
NEW CONCEPTS IN CROHN S DISEASE GLENDON BURRESS, MD PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY ROCKFORD, IL
 NEW CONCEPTS IN CROHN S DISEASE GLENDON BURRESS, MD PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY ROCKFORD, IL CROHN S DISEASE Chronic disease of uncertain etiology Etiology- genetic, environmental, and infectious Transmural
NEW CONCEPTS IN CROHN S DISEASE GLENDON BURRESS, MD PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY ROCKFORD, IL CROHN S DISEASE Chronic disease of uncertain etiology Etiology- genetic, environmental, and infectious Transmural
Treating Crohn s and Colitis in the ASC
 Treating Crohn s and Colitis in the ASC Kimberly M Persley, MD Texas Digestive Disease consultants TASC Meeting Outline IBD 101 Diagnosis Treatment Burden of Disease Role of ASC Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Treating Crohn s and Colitis in the ASC Kimberly M Persley, MD Texas Digestive Disease consultants TASC Meeting Outline IBD 101 Diagnosis Treatment Burden of Disease Role of ASC Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Intestinal tuberculosis and tuberculous peritonitis
 Intestinal tuberculosis and tuberculous peritonitis GAO Hong Department of Gastroenterology, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University Objectives 1. To master the clinical manifestations, complications, diagnosis
Intestinal tuberculosis and tuberculous peritonitis GAO Hong Department of Gastroenterology, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University Objectives 1. To master the clinical manifestations, complications, diagnosis
Beyond Anti TNFs: positioning of other biologics for Crohn s disease. Christina Ha, MD Cedars Sinai Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center
 Beyond Anti TNFs: positioning of other biologics for Crohn s disease Christina Ha, MD Cedars Sinai Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Objectives: To define high and low risk patient and disease features
Beyond Anti TNFs: positioning of other biologics for Crohn s disease Christina Ha, MD Cedars Sinai Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Objectives: To define high and low risk patient and disease features
Patho Basic Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Jürg Vosbeck Pathology
 Patho Basic Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Jürg Vosbeck Pathology General Group of chronic relapsing diseases with chronic bloody or watery diarrhea Usually ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn s disease
Patho Basic Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Jürg Vosbeck Pathology General Group of chronic relapsing diseases with chronic bloody or watery diarrhea Usually ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn s disease
Page 1. Is the Risk This High? Dysplasia in the IBD Patient. Dysplasia in the Non IBD Patient. Increased Risk of CRC in Ulcerative Colitis
 Screening for Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Francis A. Farraye MD, MSc Clinical Director, Section of Gastroenterology Co-Director, Center for Digestive Disorders Boston Medical Center
Screening for Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Francis A. Farraye MD, MSc Clinical Director, Section of Gastroenterology Co-Director, Center for Digestive Disorders Boston Medical Center
How to differentiate Segmental Colitis Associated with Diverticulosis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases?
 How to differentiate Segmental Colitis Associated with Diverticulosis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases? Alessandro Armuzzi Lead IBD Unit Complesso Integrato Columbus Fondazione Policlinico Gemelli Università
How to differentiate Segmental Colitis Associated with Diverticulosis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases? Alessandro Armuzzi Lead IBD Unit Complesso Integrato Columbus Fondazione Policlinico Gemelli Università
The revised Porto criteria for diagnosing
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Long-term Outcome of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Unclassified in Children SIBA PROSAD PAUL AND BHUPINDER KAUR SANDHU From Bristol Royal Hospital for Children, Upper Maudlin Street,
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Long-term Outcome of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Unclassified in Children SIBA PROSAD PAUL AND BHUPINDER KAUR SANDHU From Bristol Royal Hospital for Children, Upper Maudlin Street,
Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 7 (2013) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans V.Subbukesavaraja
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 7 (2013) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans V.Subbukesavaraja
Grand round on a case of ileocecal tuberculosis. Presenters Alula (R3) Getahun (R1) Berhanu (Intern) Department of internal medicine April 2014
 Grand round on a case of ileocecal tuberculosis Presenters Alula (R3) Getahun (R1) Berhanu (Intern) Department of internal medicine April 2014 Introduction: Extrapulmonary tuberculosis prevalence: Seropositive:
Grand round on a case of ileocecal tuberculosis Presenters Alula (R3) Getahun (R1) Berhanu (Intern) Department of internal medicine April 2014 Introduction: Extrapulmonary tuberculosis prevalence: Seropositive:
Research Article Comparison between Intestinal Behçet s Disease and Crohn s Disease in Characteristics of Symptom, Endoscopy, and Radiology
 Hindawi Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 3918746, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3918746 Research Article Comparison between Intestinal Behçet s Disease and Crohn s
Hindawi Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 3918746, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3918746 Research Article Comparison between Intestinal Behçet s Disease and Crohn s
Mucosal healing: does it really matter?
 Oxford Inflammatory Bowel Disease MasterClass Mucosal healing: does it really matter? Professor Jean-Frédéric Colombel, New York, USA Oxford Inflammatory Bowel Disease MasterClass Mucosal healing: does
Oxford Inflammatory Bowel Disease MasterClass Mucosal healing: does it really matter? Professor Jean-Frédéric Colombel, New York, USA Oxford Inflammatory Bowel Disease MasterClass Mucosal healing: does
GUIDANCE ON THE INDICATIONS FOR DIAGNOSTIC UPPER GI ENDOSCOPY, FLEXIBLE SIGMOIDOSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY
 Position Statement produced by BSG, AUGIS and ACPGBI GUIDANCE ON THE INDICATIONS FOR DIAGNOSTIC UPPER GI ENDOSCOPY, FLEXIBLE SIGMOIDOSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY Introduction In 2011 the Independent Practice
Position Statement produced by BSG, AUGIS and ACPGBI GUIDANCE ON THE INDICATIONS FOR DIAGNOSTIC UPPER GI ENDOSCOPY, FLEXIBLE SIGMOIDOSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY Introduction In 2011 the Independent Practice
Filiform polyposis of ulcerative colitis
 Filiform polyposis of ulcerative colitis Authors: Keisuke Yamada, Hironori Samura, Tatsuya Kinjo, Tetsu Kinjo, Akira Hokama, Jiro Fujita Article type: Clinical image Received: December 7, 2018. Accepted:
Filiform polyposis of ulcerative colitis Authors: Keisuke Yamada, Hironori Samura, Tatsuya Kinjo, Tetsu Kinjo, Akira Hokama, Jiro Fujita Article type: Clinical image Received: December 7, 2018. Accepted:
... Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment.
 Definition Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment. " Epidemiology Humans represent the main reservoir of Clostridium difficile, which is not part of the
Definition Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment. " Epidemiology Humans represent the main reservoir of Clostridium difficile, which is not part of the
LYMPHOMA COMPLICATING ULCERATIVE COLITIS
 LYMPHOMA COMPLICATING ULCERATIVE COLITIS Pages with reference to book, From 37 To 39 Syed Hasnain Ali Shah, Abdul Haleem Khan, Ashfaque Ahmed ( Departments of Medicine, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
LYMPHOMA COMPLICATING ULCERATIVE COLITIS Pages with reference to book, From 37 To 39 Syed Hasnain Ali Shah, Abdul Haleem Khan, Ashfaque Ahmed ( Departments of Medicine, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
Ulcerative Colitis after Multidisciplinary Treatment for Colorectal Cancer with Multiple Liver Metastases : A Case Report
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 315 319, September 2017 Case Report Ulcerative Colitis after Multidisciplinary Treatment for Colorectal Cancer with Multiple Liver Metastases : A Case Report Kodai TOMIOKA 1
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 315 319, September 2017 Case Report Ulcerative Colitis after Multidisciplinary Treatment for Colorectal Cancer with Multiple Liver Metastases : A Case Report Kodai TOMIOKA 1
Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah
 Original Article Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the diagnostic
Original Article Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the diagnostic
For the past 40 years, it has been standard practice to obtain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: GASTROENTEROLOGY Good Agreement Between Endoscopic Findings and Biopsy Reports Supports Limited Tissue Sampling During Pediatric Colonoscopy Michael A. Manfredi, Hongyu Jiang, Lawrence
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: GASTROENTEROLOGY Good Agreement Between Endoscopic Findings and Biopsy Reports Supports Limited Tissue Sampling During Pediatric Colonoscopy Michael A. Manfredi, Hongyu Jiang, Lawrence
Year 2002 Paper two: Questions supplied by Jo 1
 Year 2002 Paper two: Questions supplied by Jo 1 29) A 54 year old man with colonic Crohn s disease is in remission following an 8 week course of prednisolone. Which one of the following medications is
Year 2002 Paper two: Questions supplied by Jo 1 29) A 54 year old man with colonic Crohn s disease is in remission following an 8 week course of prednisolone. Which one of the following medications is
Emergence of Celiac Disease and Crohn s Disease in India
 CHAPTER 32 Emergence of Celiac Disease and Crohn s Disease in India G. K. Makharia, R. K. Tandon Introduction With improved economy, living conditions and personal hygiene there has been a distinct decline
CHAPTER 32 Emergence of Celiac Disease and Crohn s Disease in India G. K. Makharia, R. K. Tandon Introduction With improved economy, living conditions and personal hygiene there has been a distinct decline
THE HISTOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIATION OF TUBERCULOSIS FROM CROHN'S DISEASE IN MUCOSAL BIOPSIES FROM THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT WITH GRANULOMATOUS
 THE HISTOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIATION OF TUBERCULOSIS FROM CROHN'S DISEASE IN MUCOSAL BIOPSIES FROM THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT WITH GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION A Dissertation submitted in part fulfilment
THE HISTOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIATION OF TUBERCULOSIS FROM CROHN'S DISEASE IN MUCOSAL BIOPSIES FROM THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT WITH GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION A Dissertation submitted in part fulfilment
Gastric Carcinoma in Patients with Crohn Disease: Report of Four Cases
 311 0361-803X/91/1 572-0311 C American Roentgen Ray Society Seth N. GIick1 Received January 1 7, 1991 ; accepted after re vision March 1 2, 1991. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Hahnemann University
311 0361-803X/91/1 572-0311 C American Roentgen Ray Society Seth N. GIick1 Received January 1 7, 1991 ; accepted after re vision March 1 2, 1991. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Hahnemann University
Pathology and Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathology and Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) JMAJ 45(2): 45 54, 2002 Takashi SHIMOYAMA Director, Department of Gastroenterology, Hyogo College of Medicine Abstract:
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathology and Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) JMAJ 45(2): 45 54, 2002 Takashi SHIMOYAMA Director, Department of Gastroenterology, Hyogo College of Medicine Abstract:
-2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine. -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency
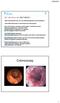 SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v5i6.1 Clinical-Epidemiological Study of Abdominal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v5i6.1 Clinical-Epidemiological Study of Abdominal
Unexpected Findings at Endoscopy
 The Endoscopic Incidentaloma: What to Tell Your Patient t with Unexpected Endoscopic Findings: Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia, Silent Ileitis, Carcinoid David Greenwald, MD Montefiore Medical Center Albert
The Endoscopic Incidentaloma: What to Tell Your Patient t with Unexpected Endoscopic Findings: Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia, Silent Ileitis, Carcinoid David Greenwald, MD Montefiore Medical Center Albert
Fibrotic complications of inflammatory bowel disease
 January 27th 2017, 8th Gastro Foundation Weekend for Fellows; Spier Hotel & Conference Centre, Stellenbosch Fibrotic complications of inflammatory bowel disease Gerhard Rogler, Department of Gastroenterology
January 27th 2017, 8th Gastro Foundation Weekend for Fellows; Spier Hotel & Conference Centre, Stellenbosch Fibrotic complications of inflammatory bowel disease Gerhard Rogler, Department of Gastroenterology
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS
 INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
Pouchitis and Cuffitis A bloody mess. Sze-Lin Peng Colorectal Surgeon Counties Manukau District Health Board
 Pouchitis and Cuffitis A bloody mess Sze-Lin Peng Colorectal Surgeon Counties Manukau District Health Board Ileal-pouch anal anastomosis https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-health-care-professionals/for-physicians/physician-education-and-resources/clinicalbriefings/2018/february/total-proctocolectomy-with-jpouch-reconstruction-for-ulcerative-colitis
Pouchitis and Cuffitis A bloody mess Sze-Lin Peng Colorectal Surgeon Counties Manukau District Health Board Ileal-pouch anal anastomosis https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-health-care-professionals/for-physicians/physician-education-and-resources/clinicalbriefings/2018/february/total-proctocolectomy-with-jpouch-reconstruction-for-ulcerative-colitis
MP Madhu 1, Prachis Ashdhir 1, Garima Sharma 2, Gyan Prakash Rai 1, Rupesh Kumar Pokharna 1, Dilip Ramrakhiani 2 ABSTRACT
 Tropical Gastroenterology 2017;38(2):102-107 Original Article Correlation of serum levels of IgA antitissue transglutaminase (IgA ttg) with the histological severity in celiac disease MP Madhu 1, Prachis
Tropical Gastroenterology 2017;38(2):102-107 Original Article Correlation of serum levels of IgA antitissue transglutaminase (IgA ttg) with the histological severity in celiac disease MP Madhu 1, Prachis
Medical Policy Title: Serum Antibodies for ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/11
 Medical Policy Title: Serum Antibodies for ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/11 Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0314 Revision Date: Code(s): 83516 Immunoassay for
Medical Policy Title: Serum Antibodies for ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/11 Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0314 Revision Date: Code(s): 83516 Immunoassay for
Original Article. Atypical histological features of ulcerative colitis. Siddharth N Shah, 1 Anjali D Amarapurkar, 1 N Shrinivas, 2 Rathi PM 2 ABSTRACT
 Tropical Gastroenterology 2011;32(2):107 111 Original Article Atypical histological features of ulcerative colitis Siddharth N Shah, 1 Anjali D Amarapurkar, 1 N Shrinivas, 2 Rathi PM 2 ABSTRACT Department
Tropical Gastroenterology 2011;32(2):107 111 Original Article Atypical histological features of ulcerative colitis Siddharth N Shah, 1 Anjali D Amarapurkar, 1 N Shrinivas, 2 Rathi PM 2 ABSTRACT Department
Small bowel carcinoma mimicking a relapse of Crohn's disease: A case series
 Journal of Crohn's and Colitis (2011) 5, 152 156 available at www.sciencedirect.com SHORT REPORT Small bowel carcinoma mimicking a relapse of Crohn's disease: A case series J.E. Baars a,, J.C. Thijs b,
Journal of Crohn's and Colitis (2011) 5, 152 156 available at www.sciencedirect.com SHORT REPORT Small bowel carcinoma mimicking a relapse of Crohn's disease: A case series J.E. Baars a,, J.C. Thijs b,
Anne Griffiths MD, FRCPC. SickKids Hospital, University of Toronto. Buenos Aires, August 16, 2014
 Management and Medical Therapies for Crohn disease: strategies to enhance mucosal healing Anne Griffiths MD, FRCPC SickKids Hospital, University of Toronto Buenos Aires, August 16, 2014 New onset Crohn
Management and Medical Therapies for Crohn disease: strategies to enhance mucosal healing Anne Griffiths MD, FRCPC SickKids Hospital, University of Toronto Buenos Aires, August 16, 2014 New onset Crohn
European evidence-based consensus on the use of imaging techniques in inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis and management
 European evidence-based consensus on the use of imaging techniques in inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis and management J. Martin-Comin Hospital U. Bellvitge Hospitalet de Llobregat Spain THE EUROPEAN
European evidence-based consensus on the use of imaging techniques in inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis and management J. Martin-Comin Hospital U. Bellvitge Hospitalet de Llobregat Spain THE EUROPEAN
