What is myotonic dystrophy?
|
|
|
- Rodger Pierce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 What is myotonic dystrophy? Myotonic dystrophy is a muscle condition that falls under the umbrella term muscular dystrophy. The muscular dystrophies all have three features in common; they are hereditary, they are progressive; and each causes a characteristic, selective pattern of muscle wasting and weakness. Myotonic dystrophy is the most common adult form of muscular dystrophy - thought to affect at least 1 in 8,000 people worldwide. Unlike the other muscular dystrophies, the muscle weakness is accompanied by myotonia (delayed relaxation of muscles after contraction) and by a variety of symptoms that affect parts of the body other than the muscles. Myotonic dystrophy can affect both males and females. Myotonic dystrophy is often abbreviated as DM after its Latin name dystrophia myotonica and is also known as Steinert's disease. There are two forms of myotonic dystrophy, usually referred to as type 1 or DM1 and the rarer type 2 or DM2. Both conditions are genetic disorders but each affects a different gene. In this factsheet: What are the symptoms of myotonic dystrophy? What is the age of onset? How is myotonic dystrophy diagnosed? What causes myotonic dystrophy? How does a person get myotonic dystrophy? Do people with myotonic dystrophy become disabled? What is congenital myotonic dystrophy? What is type 2 myotonic dystrophy (DM2)? Is there any specific treatment? What research is being done? Further information What are the symptoms of myotonic dystrophy? There is a wide range of severity of myotonic dystrophy and symptoms may appear at any time from birth to old age. Some people may only start to show some mild signs as adults and the rate of deterioration is usually slow, with little change over a long period; some people never have significant muscle disability and many live a normal life span. At the other end of the spectrum some babies are born with a severe form of the condition called congenital myotonic dystrophy.
2 One of the first signs of myotonic dystrophy is often muscle stiffness - delayed relaxation of voluntary muscles after contraction (myotonia). This is often noticed when trying to release the hand from a grip when shaking hands with somebody for example. However, this is generally less noticeable after the early stages of myotonic dystrophy. The first muscles to be affected by weakness are those of the face, neck, hands, forearms, and feet. The large, weight-bearing muscles of the legs and thighs are much less affected. Myotonic dystrophy can affect the tissues and organs of many body systems in addition to the muscles. The list includes heart problems, cataracts, trouble breathing, adverse reactions to anaesthesia, difficulty swallowing, digestive problems, excessive daytime sleepiness and, in children, learning difficulties. Hormonal problems may also occur including reproductive abnormalities, thyroid dysfunction and diabetes. Consequently myotonic dystrophy may present itself in what one expert has called a "bewildering variety of ways". Note that not everybody with myotonic dystrophy has all of these problems. What is the age of onset? About half of those with the disorder show visible signs by about twenty years of age, but a significant number do not develop clear-cut symptoms until after age fifty. However, when myotonic dystrophy is suspected (because it is present in other members of the family) careful examination may reveal typical abnormalities before obvious symptoms appear. There are also less common forms of myotonic dystrophy with onset in infancy or childhood. The condition tends to be more severe and have an earlier age of onset with each generation in a family. So a grandparent might experience their first mild symptoms at age 60, while their children notice symptoms at 30, and grandchildren may be born with severe symptoms congenital myotonic dystrophy. How is myotonic dystrophy diagnosed? A physical examination will usually reveal the typical pattern of muscle weakness and wasting and the presence of muscle stiffness (myotonia). In addition, early in the disease process, weakness and wasting of facial, jaw, and neck muscles, and frontal balding of men often give the face a characteristic look. However, as many doctors are unfamiliar with myotonic dystrophy, getting the correct diagnosis can take some time. Complicating the immediate recognition of myotonic dystrophy is the fact that patients frequently first seek medical attention for one of the conditions accompanying muscle involvement. In particular eye problems are what may bring a patient to the doctor's office. Tests that may be done to confirm the diagnosis include a blood test, a muscle biopsy, and an electromyogram (EMG). The most precise diagnosis is made by analysing the DNA in a blood sample as it will look for the specific genetic error that causes DM1 or DM2.
3 What causes myotonic dystrophy? Myotonic dystrophy type 1, the most common type of myotonic dystrophy, is caused by the inheritance of extra DNA code at the end of a gene called DMPK. A three letter DNA code is repeated many hundreds of times instead of the usual number which is less than 38. A molecule called RNA is key to causing myotonic dystrophy. RNA is the carbon copy of DNA that carries genetic messages from the centre of the cell (the nucleus) to the rest of the cell in order to build proteins. In myotonic dystrophy the extra repeats in the RNA copy of the DMPK gene cause it to fold in half into a hairpin shape and get stuck inside the nucleus. This toxic RNA then hooks onto certain proteins inside the nucleus, trapping them in clumps. The proteins held in these clumps are then unable to perform their normal functions. For example, the protein known as MBNL1, which has a crucial role in ensuring that the genetic information in certain genes is properly assembled, is trapped by the toxic RNA. Determining which proteins are held and what effect this has on the body is very complex and has taken many years to unravel. This complex mechanism explains how a single genetic change can affect many different processes in the body. Generally the more repeats a person has, the younger they are when symptoms are noticed and the more severe their condition is. Although individuals with a similar repeat count may be quite differently affected. Severely affected children born with symptoms may have several thousands of repeats. The number of repeats tends to increase in each generation of a family, resulting in the increasing severity that was mentioned above. This phenomenon is known by geneticists as anticipation. Please read below to find out what causes myotonic dystrophy type 2 (DM2). How does a person get myotonic dystrophy? Myotonic dystrophy is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. This means that only one myotonic dystrophy gene inherited from either the father or mother, is required to cause the condition. On average half of the children of a person with myotonic dystrophy will have the condition. Both men and women are equally likely to be affected and to pass on the disorder, but affected women are more likely to have a severely affected child. Very few cases of myotonic dystrophy occur 'out of the blue'. Almost always, one parent proves to be affected, often very mildly. Some parents (or grandparents) prove to carry a very slight genetic change that will never give them symptoms. Relatives of people with myotonic dystrophy can have genetic testing on a blood sample to find out whether they have the condition and the risk of passing it on to their children, but this should always be done as part of genetic counselling. Genetic testing of healthy young children is not recommended.
4 Do people with myotonic dystrophy become disabled? The course of myotonic dystrophy varies too widely, even in the same family, to permit a general statement about its effects. On the one hand, there are people with the disorder whose symptoms are so mild they hardly know anything is wrong. Whatever muscle weakness they experience is something they take for granted and adapt to. In some cases, the only symptom may be a cataract. Nevertheless these people do indeed have myotonic dystrophy and can transmit a serious case of the condition to their children. For the most part, weakness and wasting slowly progress to the point of some disability, moving beyond the muscles originally involved to those of the shoulders, hips, and thighs. As a rule, disability rarely becomes severe until fifteen to twenty years after the onset of symptoms. The older a person is when muscle weakness is first noticed, the slower is the progression and the less serious the consequences. What is congenital myotonic dystrophy? Congenital myotonic dystrophy is the early childhood form of myotonic dystrophy. As the name indicates, it is present at birth, almost invariably in infants whose mothers are so mildly affected by myotonic dystrophy that they are unaware of it. Congenital myotonic dystrophy is a rare variant of the disease with striking differences from the form it takes among adults. In the newborn period, an affected infant is profoundly weak and floppy, has difficulty with sucking and swallowing, and may have trouble breathing. Respiratory problems may continue after the birth, and can be very severe and life threatening, especially if the baby is premature. Once the neonatal period (28 days after birth) has passed, the respiratory problems tend to improve. Parents, family and carers should be aware that these children often have facial weakness which makes it difficult to make facial expressions it doesn t mean the child is unresponsive. This may improve with time. Older children tend to have poor motivation and concentration and are easily tired. The motor and intellectual milestones tend to be delayed in a child with congenital myotonic dystrophy. Speech therapy can help with speech difficulties and a stimulating environment can help with learning and development. Feeding difficulties are common and input from a range of professionals will be needed to manage this. Special bottles, food supplements, tube feeding (nasogastric tube) and/or IV drips may be needed at different stages. Some children have a squint, and very occasionally children may have impaired vision. Children commonly have club feet (talipes). This can be helped by physiotherapy but if severe corrective surgery will be required. The development of control over the bladder and bowel are sometimes delayed and problems with constipation may persist. Generally, the condition improves through the early years but deteriorates during late childhood and adolescence, when the 'adult' features of the disease gradually emerge. Congenital myotonic dystrophy can vary considerably in severity from child to child but sadly, congenital myotonic dystrophy can be fatal, especially in the early weeks of life. However, a child who lives beyond his or her first birthday is likely to live to become an adult.
5 What is type 2 myotonic dystrophy (DM2) Type 2 myotonic dystrophy, also sometimes called PROMM (proximal myotonic myopathy), is only found in adults, with an age of onset generally between 30 and 60 years. People with DM2 do not usually have the same kind of facial muscle weakness or swallowing problems that are often seen in DM1. Weakness usually affects the muscles closest to the trunk particularly the thighs, and for many patients this is the most disabling feature later in life. It is quite common for DM2 patients to experience muscle pain. In common with DM1 patients, DM2 patients may experience cataracts, heart problems and diabetes. DM2 is caused by the inheritance of extra pieces of repeated DNA in the CNBP gene (also known as ZNF9 ) - a different gene to that causing DM1. In DM2 a four letter DNA code is repeated many hundreds of times instead of the usual number which is 26 or fewer. Unlike DM1, it appears that anticipation (repeat count increasing with each successive generation) is not a feature of DM2. The extra DNA repeats inherited by DM2 patients are thought to cause the symptoms of the disease in a similar way to those inherited in DM1 (described above). Generally DM2 is thought to be much less prevalent than DM1 but this appears to vary in different populations, for example DM2 is thought to be almost as common as DM1 in Germany. Is there any specific treatment? No specific treatment has yet been found for the muscle weakness and wasting in myotonic dystrophy, although ankle and leg braces can help to support muscles as weakness progresses. There are also medications that can relieve the myotonia. Heart problems, cataracts, and other abnormalities associated with the disease can also be treated. Exercise, including range of motion, strengthening and aerobic exercise, is important for the management of myotonic dystrophy. This helps to maintain strength in the muscles for as long as possible and also keep the cardiovascular system healthy. Range of motion exercises are important in maintaining joint function and may play a role in reducing pain that is caused by muscular imbalance or tightness. Since people with myotonic dystrophy often have heart problems, any exercise programme should be undertaken under the guidance of a physiotherapist or other medical professional. Please see the link at the bottom of the page for more information about physiotherapy for myotonic dystrophy. What research is being done? Ever since scientists started to understand how the DNA change in people with myotonic dystrophy was exerting its effect in the late 1990s, they have been searching for potential treatments that could stop the chain of events that leads to the symptoms of myotonic dystrophy. There are several strategies that are being researched to specifically block the toxic RNA that is present in the cells of people with myotonic dystrophy (please see What causes myotonic dystrophy above). The aim is to either destroy the toxic RNA, or stop it interacting with proteins. One approach is to use small pieces of genetic material called antisense oligonucleotides (AONs) which bind to the toxic RNA and stop it interacting with proteins. Other types of AONs destroy the abnormal RNA. AONs have been shown to reverse some of the symptoms of myotonic dystrophy in a
6 mouse model of myotonic dystrophy. The AONs are similar to those currently being tested in clinical trials for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In this case the AONs act in a different way called exon skipping but the results of the clinical trials are looking promising and importantly the AONs appear to be safe, which bodes well for a clinical trial of this approach for myotonic dystrophy in the future. Before this can happen myotonic dystrophy researchers are testing different types of AONs to find the best one to take forward to clinical trial. Scientists have also been searching for other types of molecules that could disrupt the interaction between the toxic RNA and proteins. In 2011 researchers in Spain showed that small pieces of protein which are called peptides were effective in a mouse model of myotonic dystrophy. More recently, researchers in the US have had success with small molecules. Most of the drugs currently on the market are considered small molecules so this strategy may result in a drug that is cheaper and easier to make (than AONs or peptides), and which may get into targeted tissues more easily. Small molecules can also be modified so that they can be taken as oral drugs rather than being injected. The researchers have screened large collections of potential drugs modified versions of known drugs like antibiotics for example and found those that are effective against the toxic RNA. One new compound, known as 2H-4-CA, is the most potent compound known to date that improves signs of myotonic dystrophy in cells grown in the laboratory. The next step will be to test this compound in an animal model of myotonic dystrophy. A major hurdle for any therapy for myotonic dystrophy will be to deliver the drug as widely throughout the body as possible. This will be necessary to treat the wide range of symptoms that affect many different parts of the body including the muscles, heart, eyes and brain. We don't know yet what approach is most likely to result in an effective, safe treatment, but it is promising that several lines of attack are coming forward. The research is initially focussing on type 1 myotonic dystrophy but it is expected that if any of these potential treatments are successful they could be modified and applied to DM2. NOTE: Research is moving forward at a fast pace, so this research summary may not be up-to-date at the time of reading. Feel free to contact MDA's Scientific Communications Officer for an update on the latest developments - kristina.elvidge@mda.org.au Further information Clinical trials your questions answered Physiotherapy guidelines for myotonic dystrophy You can get regular updates by becoming a friend of the MDA Facebook page ( or follow our Scientific Communications Officer on Twitter (@kelvidge). For further information on any of the areas discussed above, please contact MDA on (03) , info@mda.org.au or visit The Home of MDA Revised 24th September 2013
Myotonic Dystrophy OUTLINE
 OUTLINE Myotonic Dystrophy INTRODUCTION: 1). GENERAL OVERVIEW 2). SYMPTOMS 3). DIAGNOSIS 4). CAUSES and PATHOLOGY 5). GENETICS 6). TREATMENT and MEDICAL MANAGEMENT 7). LIFESTYLE IMPACTS 8). RESEARCH 9).
OUTLINE Myotonic Dystrophy INTRODUCTION: 1). GENERAL OVERVIEW 2). SYMPTOMS 3). DIAGNOSIS 4). CAUSES and PATHOLOGY 5). GENETICS 6). TREATMENT and MEDICAL MANAGEMENT 7). LIFESTYLE IMPACTS 8). RESEARCH 9).
Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS)
 Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) This fact sheet is for children and adults diagnosed with congenital myasthenic syndrome. It s a complex subject, so information has been adapted to suit all audiences.
Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) This fact sheet is for children and adults diagnosed with congenital myasthenic syndrome. It s a complex subject, so information has been adapted to suit all audiences.
Nemaline (rod) myopathies
 Nemaline (rod) myopathies Nemaline, or rod, myopathies are a group of conditions which fall under the umbrella of congenital myopathies. They are characterised by rod-like structures in the muscle cells,
Nemaline (rod) myopathies Nemaline, or rod, myopathies are a group of conditions which fall under the umbrella of congenital myopathies. They are characterised by rod-like structures in the muscle cells,
Myotubular (centronuclear) myopathy
 Myotubular (centronuclear) myopathy Myotubular, or centronuclear, myopathy falls under the umbrella of congenital myopathies. It is characterised by a specific pattern in the muscle tissue when viewed
Myotubular (centronuclear) myopathy Myotubular, or centronuclear, myopathy falls under the umbrella of congenital myopathies. It is characterised by a specific pattern in the muscle tissue when viewed
Hypokalaemic periodic paralysis: In these attacks the blood potassium is low
 Periodic paralyses The ability we have to control and move the muscles in our body depends upon the passage of electrical signals along the nerves and into our muscles. The periodic paralyses are conditions
Periodic paralyses The ability we have to control and move the muscles in our body depends upon the passage of electrical signals along the nerves and into our muscles. The periodic paralyses are conditions
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
Understanding Late-Onset Pompe Disease
 Understanding Late-Onset Pompe Disease What Is a Lysosome? Millions of tiny units called cells make up the human body. Each cell has its own job to keep the body running. Within each cell, there are organelles,
Understanding Late-Onset Pompe Disease What Is a Lysosome? Millions of tiny units called cells make up the human body. Each cell has its own job to keep the body running. Within each cell, there are organelles,
Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of
 Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
1GENERAL INFORMATION
 1 GENERAL INFORMATION General information 11 1.1 Diagnosis Some children will have a diagnosis of their muscle-wasting condition when they begin their school life. Others will still be having investigations
1 GENERAL INFORMATION General information 11 1.1 Diagnosis Some children will have a diagnosis of their muscle-wasting condition when they begin their school life. Others will still be having investigations
Muscular System. Disorders & Conditions
 Muscular System Disorders & Conditions Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia is a disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue, sleep, memory and mood issues. Often is described
Muscular System Disorders & Conditions Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia is a disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue, sleep, memory and mood issues. Often is described
Klinefelter syndrome ( 47, XXY )
 Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Cerebral Palsy. By:Carrie Siders and Kelsey Hampsey. 3rd hour.
 Cerebral Palsy By:Carrie Siders and Kelsey Hampsey 3rd hour. What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy is a physical disability It affects movement and posture It is a permanent life-long condition does not
Cerebral Palsy By:Carrie Siders and Kelsey Hampsey 3rd hour. What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy is a physical disability It affects movement and posture It is a permanent life-long condition does not
SMOKING CAUSES PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE SMOKING CAUSES PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE SMOKING CAUSES PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE
 PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE GANGRENE Smoking damages your blood vessels, which can prevent blood circulation, particularly to your legs or feet. This can result in blood clots,
PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE GANGRENE Smoking damages your blood vessels, which can prevent blood circulation, particularly to your legs or feet. This can result in blood clots,
Health Care Information for Families of Children with Down Syndrome
 American Academy of Pediatrics Introduction Down syndrome is a common condition caused by having extra copies of genes on the 21st chromosome. Those extra genes change development during pregnancy, and
American Academy of Pediatrics Introduction Down syndrome is a common condition caused by having extra copies of genes on the 21st chromosome. Those extra genes change development during pregnancy, and
1/28/2019. OSF HealthCare INI Care Center Team. Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy. OSF HealthCare INI Care Center Team: Who are we?
 Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) and OSF HealthCare Illinois Neurological Institute (INI) Care Center Team The Neuromuscular clinic is a designated MDA Care
Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) and OSF HealthCare Illinois Neurological Institute (INI) Care Center Team The Neuromuscular clinic is a designated MDA Care
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
 PAPER 2006 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Myotonic dystrophy C Longman Department of Clinical Genetics, Guy s Hospital, London, England ABSTRACT Myotonic dystrophy is the most common form of
PAPER 2006 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Myotonic dystrophy C Longman Department of Clinical Genetics, Guy s Hospital, London, England ABSTRACT Myotonic dystrophy is the most common form of
SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE
 SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE 02 Changes in our lives can be stressful and leaving school and moving into the
SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE 02 Changes in our lives can be stressful and leaving school and moving into the
UK Myotonic Dystrophy Registry Newsletter Issue 2 September
 UK Myotonic Dystrophy Registry Newsletter Issue 2 September 2013 www.dm-registry.org/uk REMEMBER TO KEEP YOU DETAILS UP TO DATE LOGIN AND CHECK TODAY IN THIS ISSUE Welcome to the second edition of the
UK Myotonic Dystrophy Registry Newsletter Issue 2 September 2013 www.dm-registry.org/uk REMEMBER TO KEEP YOU DETAILS UP TO DATE LOGIN AND CHECK TODAY IN THIS ISSUE Welcome to the second edition of the
Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study. Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting
 Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting approximately one in 6,000 babies. It is estimated that one in every 40 Americans carries
Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting approximately one in 6,000 babies. It is estimated that one in every 40 Americans carries
Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Acute Services Division Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders Introduction Exercise is an important part of all of our daily lives.
Acute Services Division Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders Introduction Exercise is an important part of all of our daily lives.
This guide describes some of the important facts about Neurobloc that you need to be aware of, however, it does not replace the advice given to you
 This guide describes some of the important facts about Neurobloc that you need to be aware of, however, it does not replace the advice given to you by a healthcare professional. Further very important
This guide describes some of the important facts about Neurobloc that you need to be aware of, however, it does not replace the advice given to you by a healthcare professional. Further very important
What is Alport s Syndrome? Why it is called Alport s Syndrome? What Causes Alport s Syndrome, and differences between men and women?
 ALPORT S SYNDROME What is Alport s Syndrome? Why is it called Alport s Syndrome? What causes Alport s Syndrome? How is Alport s Syndrome diagnosed? Is Alport s Syndrome common? Is there any treatment to
ALPORT S SYNDROME What is Alport s Syndrome? Why is it called Alport s Syndrome? What causes Alport s Syndrome? How is Alport s Syndrome diagnosed? Is Alport s Syndrome common? Is there any treatment to
For carers and relatives of people with frontotemporal dementia and semantic dementia. Newsletter
 For carers and relatives of people with frontotemporal dementia and semantic dementia Newsletter AUGUST 2008 1 Welcome Welcome to the August edition of our CFU Support Group Newsletter. Thanks to all of
For carers and relatives of people with frontotemporal dementia and semantic dementia Newsletter AUGUST 2008 1 Welcome Welcome to the August edition of our CFU Support Group Newsletter. Thanks to all of
GENETICS NOTES. Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16
 GENETICS NOTES Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16 DNA contains the genetic code for the production of PROTEINS. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The
GENETICS NOTES Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16 DNA contains the genetic code for the production of PROTEINS. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report
 Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Advice on Resistance Exercise
 Advice on Resistance Exercise You are aiming to increase your amount of body muscle as well as the endurance and strength of your muscles. For endurance training you need a lighter weight or smaller resistance
Advice on Resistance Exercise You are aiming to increase your amount of body muscle as well as the endurance and strength of your muscles. For endurance training you need a lighter weight or smaller resistance
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
Contents. Introduction. Introduction 03
 Genes and dementia Introduction This information is for anyone who wants to know more about the link between genes and dementia. This includes people living with dementia, their carers, friends and families.
Genes and dementia Introduction This information is for anyone who wants to know more about the link between genes and dementia. This includes people living with dementia, their carers, friends and families.
Puzzling Pedigrees. Essential Question: How can pedigrees be used to study the inheritance of human traits?
 Name: Puzzling Pedigrees Essential Question: How can pedigrees be used to study the inheritance of human traits? Studying inheritance in humans is more difficult than studying inheritance in fruit flies
Name: Puzzling Pedigrees Essential Question: How can pedigrees be used to study the inheritance of human traits? Studying inheritance in humans is more difficult than studying inheritance in fruit flies
Clinical Summaries. CLN1 Disease, infantile onset and others
 Clinical Summaries CLN1 Disease, infantile onset and others The gene called CLN1 lies on chromosome 1. CLN1 disease is inherited as an autosomal recessive disorder, which means that both chromosomes carry
Clinical Summaries CLN1 Disease, infantile onset and others The gene called CLN1 lies on chromosome 1. CLN1 disease is inherited as an autosomal recessive disorder, which means that both chromosomes carry
Muscular Dystrophies. Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018
 Muscular Dystrophies Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018 Definition and classification Clinical guide to recognize muscular
Muscular Dystrophies Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018 Definition and classification Clinical guide to recognize muscular
PHYSIOTHERAPY IN SSPE
 PHYSIOTHERAPY IN SSPE Published by: Physiotherapist RUKIYE KORUCU Istanbul, Turkey Sep 2007 English translation by R.Schoenbohm WHY PHYSIOTHERAPY? Preserve the breathing capacity Strengthen the chewing
PHYSIOTHERAPY IN SSPE Published by: Physiotherapist RUKIYE KORUCU Istanbul, Turkey Sep 2007 English translation by R.Schoenbohm WHY PHYSIOTHERAPY? Preserve the breathing capacity Strengthen the chewing
NOTES: : HUMAN HEREDITY
 NOTES: 14.1-14.2: HUMAN HEREDITY Human Genes: The human genome is the complete set of genetic information -it determines characteristics such as eye color and how proteins function within cells Recessive
NOTES: 14.1-14.2: HUMAN HEREDITY Human Genes: The human genome is the complete set of genetic information -it determines characteristics such as eye color and how proteins function within cells Recessive
Congenital hypothyroidism and your child
 Congenital hypothyroidism and your child Contributed by Sirisha Kusuma. B Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist Rainbow Children s hospital What is Thyroid? The thyroid is a small butterfly shaped endocrine
Congenital hypothyroidism and your child Contributed by Sirisha Kusuma. B Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist Rainbow Children s hospital What is Thyroid? The thyroid is a small butterfly shaped endocrine
B1 Question 1 Foundation
 B1 Question 1 Foundation The nucleus controls the activities of a cell. The instructions for how an organism develops i.e. the genes are found in the nuclei of its cells B1 Question 2 Foundation The genes
B1 Question 1 Foundation The nucleus controls the activities of a cell. The instructions for how an organism develops i.e. the genes are found in the nuclei of its cells B1 Question 2 Foundation The genes
Therapy following a neck of femur fracture
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Therapy following a neck of femur fracture Name of patient: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Procedure: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Consultant:
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Therapy following a neck of femur fracture Name of patient: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Procedure: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Consultant:
PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT. Breathing and general exercise for the long term respiratory patient
 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT Breathing and general exercise for the long term respiratory patient This leaflet gives you general advice about managing your breathing. It also describes chest-clearing techniques,
PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT Breathing and general exercise for the long term respiratory patient This leaflet gives you general advice about managing your breathing. It also describes chest-clearing techniques,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Highly Specialised Technology Evaluation
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Highly Specialised Technology Evaluation Drisapersen for treating Duchenne muscular Draft scope (pre-referral) Draft remit/evaluation objective
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Highly Specialised Technology Evaluation Drisapersen for treating Duchenne muscular Draft scope (pre-referral) Draft remit/evaluation objective
Seizures explained. What is a seizure? Triggers for seizures
 Seizures explained What is a seizure? A seizure is a sign of a temporary disruption in the brain s electrical activity. Billions of brain cells pass messages to each other and these affect what we say
Seizures explained What is a seizure? A seizure is a sign of a temporary disruption in the brain s electrical activity. Billions of brain cells pass messages to each other and these affect what we say
Lesson Overview. Human Genetic Disorders. Lesson Overview Human Genetic Disorders
 Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders THINK ABOUT IT Have you ever heard the expression It runs in the family? Relatives or friends might have said that about your smile or the shape of your ears,
Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders THINK ABOUT IT Have you ever heard the expression It runs in the family? Relatives or friends might have said that about your smile or the shape of your ears,
Orofacial function of persons having. Report from questionnaires. Spinal muscular atrophy
 27-2-8 Orofacial function of persons having Spinal muscular atrophy Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Synonyms: SMA I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, SMA II, SMA III (Kugelberg-Welander
27-2-8 Orofacial function of persons having Spinal muscular atrophy Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Synonyms: SMA I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, SMA II, SMA III (Kugelberg-Welander
POSTNATAL EXERCISES. (Early In Patient Postnatal Days Until Six Weeks Post Delivery)
 POSTNATAL EXERCISES (Early In Patient Postnatal Days Until Six Weeks Post Delivery) Exercise Regularly This brochure is intended to educate women about mobility and exercises while as an In Patient and
POSTNATAL EXERCISES (Early In Patient Postnatal Days Until Six Weeks Post Delivery) Exercise Regularly This brochure is intended to educate women about mobility and exercises while as an In Patient and
There are four general types of congenital lung disorders:
 Pediatric Pulmonology Conditions Evaluated and Treated As a parent, watching a child suffer from a respiratory disorder can be frightening and worrisome. Our respiratory specialists provide compassionate
Pediatric Pulmonology Conditions Evaluated and Treated As a parent, watching a child suffer from a respiratory disorder can be frightening and worrisome. Our respiratory specialists provide compassionate
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
 Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency This information is for people in the UK who have been diagnosed with alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, their families, friends and carers. It explains what alpha-1-antitrypsin
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency This information is for people in the UK who have been diagnosed with alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, their families, friends and carers. It explains what alpha-1-antitrypsin
Pompe. Lysosomal Disorders. Introduction
 Introduction disease is an inherited, genetic disorder which results in the lack of an enzyme 'acid alpha-glucosidase. disease is also known as acid maltase deficiency or glycogen storage disease type
Introduction disease is an inherited, genetic disorder which results in the lack of an enzyme 'acid alpha-glucosidase. disease is also known as acid maltase deficiency or glycogen storage disease type
AFL NSW/ACT Exemption & Dispensation Policy
 AFL NSW/ACT Exemption & Dispensation Policy Last reviewed 14 May 2012. AFL NSW/ACT s policy is that age exceptions and/or dispensations will only exist in cases of disability These exemptions require approval
AFL NSW/ACT Exemption & Dispensation Policy Last reviewed 14 May 2012. AFL NSW/ACT s policy is that age exceptions and/or dispensations will only exist in cases of disability These exemptions require approval
The limb girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMDs)
 The limb gird muscular dystrophies (LGMDs) This factsheet is for all peop for whom a diagnosis of limb gird muscular dystrophy (LGMD) has been suggested. This is a complicated subject since there are many
The limb gird muscular dystrophies (LGMDs) This factsheet is for all peop for whom a diagnosis of limb gird muscular dystrophy (LGMD) has been suggested. This is a complicated subject since there are many
THE KING AND THE SCRATCHED DIAMOND
 BIRTH DEFECTS 1 THE KING AND THE SCRATCHED DIAMOND Once there was a king who had a beautiful, large pure diamond. There was no other diamond like it in the world. One day, it became deeply scratched. The
BIRTH DEFECTS 1 THE KING AND THE SCRATCHED DIAMOND Once there was a king who had a beautiful, large pure diamond. There was no other diamond like it in the world. One day, it became deeply scratched. The
Good Posture...just how important is it?
 Good Posture...just how important is it? Posture ranks right up at the top of the list when you are talking about good health. It is as important as eating right, exercising, getting a good night's sleep
Good Posture...just how important is it? Posture ranks right up at the top of the list when you are talking about good health. It is as important as eating right, exercising, getting a good night's sleep
Karyotype = a test to identify and evaluate the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body cells.
 Karyotype = a test to identify and evaluate the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body cells. Homologous chromosomes are arranged by size, banding patterns, and centromere placement.
Karyotype = a test to identify and evaluate the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body cells. Homologous chromosomes are arranged by size, banding patterns, and centromere placement.
Genetics. the of an organism. The traits of that organism can then be passed on to, on
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Leg Posture in Children
 Leg Posture in Children Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Leg Posture in Children A guide for parents This leaflet has been produced to provide information on the normal postural variation of
Leg Posture in Children Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Leg Posture in Children A guide for parents This leaflet has been produced to provide information on the normal postural variation of
Posture. In this article
 Posture Posture is the way we hold our bodies against gravity and maintaining a good posture involves training yourself to become aware of how you hold yourself in all activities as your posture is constantly
Posture Posture is the way we hold our bodies against gravity and maintaining a good posture involves training yourself to become aware of how you hold yourself in all activities as your posture is constantly
Orofacial function of persons having. Spinal muscular atrophy
 Orofacial function of persons having Report from questionnaires 31 questionnaires Synonym SMA I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, SMA II, SMA III (Kugelberg-Welander disease). ICD-10 G12.0 Estimated occurance
Orofacial function of persons having Report from questionnaires 31 questionnaires Synonym SMA I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, SMA II, SMA III (Kugelberg-Welander disease). ICD-10 G12.0 Estimated occurance
ICHTHYOSIS. What are the aims of this leaflet?
 ICHTHYOSIS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about ichthyosis. It will tell you what it is, the types of ichthyosis, what can be done about it,
ICHTHYOSIS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about ichthyosis. It will tell you what it is, the types of ichthyosis, what can be done about it,
STAYING FIT WITH KIDNEY DISEASE
 STAYING FIT WITH KIDNEY DISEASE www.kidney.org Introduction Regular exercise is important for everyone and that includes people with kidney disease. Regular exercise will help you feel better, stronger,
STAYING FIT WITH KIDNEY DISEASE www.kidney.org Introduction Regular exercise is important for everyone and that includes people with kidney disease. Regular exercise will help you feel better, stronger,
Genetics. by their offspring. The study of the inheritance of traits is called.
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Returning to fitness after birth
 Returning to fitness after birth This leaflet is designed for all women, whether you have given birth vaginally or by Caesarean section. During pregnancy your body undergoes many changes to adapt to your
Returning to fitness after birth This leaflet is designed for all women, whether you have given birth vaginally or by Caesarean section. During pregnancy your body undergoes many changes to adapt to your
The Muscular System. The Muscular System: Moving your Body
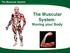 The Muscular System: Moving your Body The Muscular System So, which systems have Which systems will we learned about sowe far? learn about next? Can you sit totally still without moving a muscle? Ø Try
The Muscular System: Moving your Body The Muscular System So, which systems have Which systems will we learned about sowe far? learn about next? Can you sit totally still without moving a muscle? Ø Try
Look Good Feel Good. after pregnancy. Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums
 Look Good Feel Good after pregnancy Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums How to exercise after pregnancy with physiotherapy Bowel Tail Bone Uterus Bladder Pubic Bone Pelvic Floor Muscles Urethra
Look Good Feel Good after pregnancy Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums How to exercise after pregnancy with physiotherapy Bowel Tail Bone Uterus Bladder Pubic Bone Pelvic Floor Muscles Urethra
Retinopathy Of Prematurity (or) Retrolental Fibroplasia )
 Medical Information Document On Retinopathy Of Prematurity (or) Retrolental Fibroplasia ) What we see is made in the brain from signals given to it by the eyes. What we see is in fact made in the brain.
Medical Information Document On Retinopathy Of Prematurity (or) Retrolental Fibroplasia ) What we see is made in the brain from signals given to it by the eyes. What we see is in fact made in the brain.
Anaemia. The symptoms of anaemia are tiredness, shortness of breath and being pale. The anaemia in CDA is very variable.
 Anaemia The symptoms of anaemia are tiredness, shortness of breath and being pale. The anaemia in CDA is very variable. In some patients, it is very mild and does not cause them significant symptoms. In
Anaemia The symptoms of anaemia are tiredness, shortness of breath and being pale. The anaemia in CDA is very variable. In some patients, it is very mild and does not cause them significant symptoms. In
IBMPFD Educational Information For Patients and Families
 Page 1 of 5 CLIA # 05D1034314 CA State License: CLF 332383 IBMPFD Educational Information For What is IBMPFD? IBMPFD stands for Inclusion Body Myopathy associated with Paget s disease of bone and/or Frontotemporal
Page 1 of 5 CLIA # 05D1034314 CA State License: CLF 332383 IBMPFD Educational Information For What is IBMPFD? IBMPFD stands for Inclusion Body Myopathy associated with Paget s disease of bone and/or Frontotemporal
KAT6A Syndrome. rarechromo.org
 KAT6A Syndrome rarechromo.org This leaflet is designed to help families and healthcare professionals looking after people affected by KAT6A syndrome. It contains information about the cause of KAT6A syndrome,
KAT6A Syndrome rarechromo.org This leaflet is designed to help families and healthcare professionals looking after people affected by KAT6A syndrome. It contains information about the cause of KAT6A syndrome,
A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health
 2 Does it Run in the Family? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health National Council of La Raza Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes me unique? 2 Tell me more about
2 Does it Run in the Family? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health National Council of La Raza Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes me unique? 2 Tell me more about
Down s Syndrome What is the most common genetic condition? Down syndrome, the chromosomal
 Erin Thompson Miss. Brant Biology Genetic project December 3, 2013 Down s Syndrome What is the most common genetic condition? Down syndrome, the chromosomal disorder, is the most common. This genetic condition
Erin Thompson Miss. Brant Biology Genetic project December 3, 2013 Down s Syndrome What is the most common genetic condition? Down syndrome, the chromosomal disorder, is the most common. This genetic condition
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
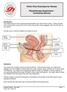 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Gene Expression and Mutation
 Gene Expression and Mutation GENE EXPRESSION: There are hormonal and environmental factors that may cause the expression of some genetic information. Some examples are: 1. The two- colour pattern of some
Gene Expression and Mutation GENE EXPRESSION: There are hormonal and environmental factors that may cause the expression of some genetic information. Some examples are: 1. The two- colour pattern of some
Diastasis of the Rectus Abdominus Muscle (DRAM) Cork University Maternity Hospital
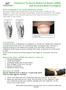 Diastasis of the Rectus Abdominus Muscle (DRAM) Cork University Maternity Hospital What is diastasis of the rectus abdominus muscle? The rectus abdominus muscle sits on top of all the other muscles of
Diastasis of the Rectus Abdominus Muscle (DRAM) Cork University Maternity Hospital What is diastasis of the rectus abdominus muscle? The rectus abdominus muscle sits on top of all the other muscles of
Health Care Information for Families of Children with Down Syndrome
 Health Care Information for Families of Children with Down Syndrome American Academy of Pediatrics Introduction Down syndrome is a common condition caused by having extra copies of genes on the 21st chromosome.
Health Care Information for Families of Children with Down Syndrome American Academy of Pediatrics Introduction Down syndrome is a common condition caused by having extra copies of genes on the 21st chromosome.
Human Genetic Disorders. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Human Genetic Disorders
 Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders THINK ABOUT IT Have you ever heard the expression It runs in the family? Relatives or friends might have said that about your smile or the shape of your ears,
Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders THINK ABOUT IT Have you ever heard the expression It runs in the family? Relatives or friends might have said that about your smile or the shape of your ears,
Patient Adult Information History
 Patient Adult Information History Patient name: Age: Date: What is the main reason for today s evaluation? Infant History Birth delivery: Normal C-section Delayed Epidural Premature: No Yes If yes, how
Patient Adult Information History Patient name: Age: Date: What is the main reason for today s evaluation? Infant History Birth delivery: Normal C-section Delayed Epidural Premature: No Yes If yes, how
Lesson Overview. Human Genetic Disorders. Lesson Overview Human Genetic Disorders
 Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders From Molecule to Phenotype There is a direct connection between molecule and trait, and between genotype and phenotype. In other words, there is a molecular
Lesson Overview 14.2 Human Genetic Disorders From Molecule to Phenotype There is a direct connection between molecule and trait, and between genotype and phenotype. In other words, there is a molecular
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
Rehabilitation programme after cannulated hip screw surgery
 Rehabilitation programme after cannulated hip screw surgery Information for patients at Princess Royal University Hospital This leaflet gives you advice about the things you can do after your operation
Rehabilitation programme after cannulated hip screw surgery Information for patients at Princess Royal University Hospital This leaflet gives you advice about the things you can do after your operation
CHRONIC CONDITIONS FYI
 CHRONIC CONDITIONS FYI AIDS More than 2,500 cases of HIV/AIDS have been identified in Nebraska. ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) Approximately 95 people in Nebraska have ALS. As many as 800 Nebraskans
CHRONIC CONDITIONS FYI AIDS More than 2,500 cases of HIV/AIDS have been identified in Nebraska. ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) Approximately 95 people in Nebraska have ALS. As many as 800 Nebraskans
Each person has a unique set of characteristics, such as eye colour, height and blood group.
 1 of 51 2 of 51 What is inheritance? 3 of 51 Each person has a unique set of characteristics, such as eye colour, height and blood group. A person s characteristics are determined by a combination of the
1 of 51 2 of 51 What is inheritance? 3 of 51 Each person has a unique set of characteristics, such as eye colour, height and blood group. A person s characteristics are determined by a combination of the
Medical Advisory Council: Verified
 What is White Sutton Syndrome? White Sutton Syndrome (WHSUS) is a condition characterized by autism and developmental delay and/or intellectual disability, as well as a characteristic facial profile. Children
What is White Sutton Syndrome? White Sutton Syndrome (WHSUS) is a condition characterized by autism and developmental delay and/or intellectual disability, as well as a characteristic facial profile. Children
Controlling Weight With Exercise
 Controlling Weight With Exercise Session 4 consists of information regarding your metabolism during and after smoking, tips to boost your metabolism without smoking and tips for exercise while kicking
Controlling Weight With Exercise Session 4 consists of information regarding your metabolism during and after smoking, tips to boost your metabolism without smoking and tips for exercise while kicking
GA-1. Glutaric Aciduria Type 1. TEMPLE Tools Enabling Metabolic Parents LEarning. Information for families after a positive newborn screening
 Glutaric Aciduria Type 1 GA-1 Information for families after a positive newborn screening Adapted by the Dietitians Group BIMDG British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group BASED ON THE ORIGINAL TEMPLE WRITTEN
Glutaric Aciduria Type 1 GA-1 Information for families after a positive newborn screening Adapted by the Dietitians Group BIMDG British Inherited Metabolic Diseases Group BASED ON THE ORIGINAL TEMPLE WRITTEN
FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT
 THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
5 Exercises You Can Do While Pregnant
 5 Exercises You Can Do While Pregnant Dr Paul Staerker 1st Edition Introduction... 3 Warm-up with the Cat/Cow... 4 1. Quadruped Single-Leg Raise... 6 2. Plié Squats... 8 3. Outer Thigh and Hip Abductors...
5 Exercises You Can Do While Pregnant Dr Paul Staerker 1st Edition Introduction... 3 Warm-up with the Cat/Cow... 4 1. Quadruped Single-Leg Raise... 6 2. Plié Squats... 8 3. Outer Thigh and Hip Abductors...
Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders
 Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders These guidelines were drawn following a workshop held in Newcastle 2002. Several experts from different disciplines including
Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders These guidelines were drawn following a workshop held in Newcastle 2002. Several experts from different disciplines including
Neurodevelopmental Disorders
 Neurodevelopmental Disorders Intellectual Disability Disorder Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADD/ADHD) Motor Disorders/Tourette s Disorder Intellectual Disability
Neurodevelopmental Disorders Intellectual Disability Disorder Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADD/ADHD) Motor Disorders/Tourette s Disorder Intellectual Disability
Below are photos from a 6 month old child with Werdnig-Hoffman s disease.
 PBL 4 Sadie s story Sadie s Story Objectives of PBL: 1) Review and be able to answer questions about normal skeletal muscle organization and structure. 2) Review and be able to answer questions about spinal
PBL 4 Sadie s story Sadie s Story Objectives of PBL: 1) Review and be able to answer questions about normal skeletal muscle organization and structure. 2) Review and be able to answer questions about spinal
Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders
 Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders These guidelines were drawn following a workshop held in Newcastle 2002. Several experts from different disciplines including
Guidelines for exercise and orthoses in children with neuromuscular disorders These guidelines were drawn following a workshop held in Newcastle 2002. Several experts from different disciplines including
Newborn Bloodspot Screening Information for parents
 Newborn Bloodspot Screening Information for parents You will be offered a bloodspot screening test for your newborn baby for several rare but serious conditions. The sample for this test is usually taken
Newborn Bloodspot Screening Information for parents You will be offered a bloodspot screening test for your newborn baby for several rare but serious conditions. The sample for this test is usually taken
Adult Asthma My Days of Living in Tension with Asthma are Over!
 Published on: 9 Jul 2014 Adult Asthma My Days of Living in Tension with Asthma are Over! Introduction This is a recent picture, taken when we went on a family picnic. We climbed up this big hill and I
Published on: 9 Jul 2014 Adult Asthma My Days of Living in Tension with Asthma are Over! Introduction This is a recent picture, taken when we went on a family picnic. We climbed up this big hill and I
This fact sheet describes the condition Fragile X and includes a discussion of the symptoms, causes and available testing.
 11111 Fact Sheet 54 FRAGILE X SYNDROME This fact sheet describes the condition Fragile X and includes a discussion of the symptoms, causes and available testing. In summary Fragile X is a condition caused
11111 Fact Sheet 54 FRAGILE X SYNDROME This fact sheet describes the condition Fragile X and includes a discussion of the symptoms, causes and available testing. In summary Fragile X is a condition caused
ARTHRITIS ACTION FACTSHEETS
 LAST REVIEW: MARCH 2017 COPYRIGHT OF ARTHRITIS ACTION PAIN MANAGEMENT Sometimes the cause of pain such as a broken bone is obvious. Other times the cause is less clear, especially if pain is in areas that
LAST REVIEW: MARCH 2017 COPYRIGHT OF ARTHRITIS ACTION PAIN MANAGEMENT Sometimes the cause of pain such as a broken bone is obvious. Other times the cause is less clear, especially if pain is in areas that
Newborn Bloodspot Screening Information for parents
 Newborn Bloodspot Screening Information for parents You will be offered a bloodspot screening test for your newborn baby for several rare but serious conditions. The sample for this test is usually taken
Newborn Bloodspot Screening Information for parents You will be offered a bloodspot screening test for your newborn baby for several rare but serious conditions. The sample for this test is usually taken
Genetic Conditions and Services: An Introduction
 Genetic Conditions and Services: An Introduction Jennifer Roberts, MC, MS, CGC Laboratory Genetics Counselor The Children s Mercy Hospital, 2017 Goals Determine which children/families may benefit from
Genetic Conditions and Services: An Introduction Jennifer Roberts, MC, MS, CGC Laboratory Genetics Counselor The Children s Mercy Hospital, 2017 Goals Determine which children/families may benefit from
First aid for seizures
 First aid for seizures What is epilepsy? Epilepsy is a tendency to have repeated seizures that begin in the brain. For most people with epilepsy their seizures will be controlled by medication. Around
First aid for seizures What is epilepsy? Epilepsy is a tendency to have repeated seizures that begin in the brain. For most people with epilepsy their seizures will be controlled by medication. Around
Chapter 21 NECK AND HEAD Upper vertebrae (mid back and neck) viewed from back
 Chapter 21 NECK AND HEAD INJURIES 319 Chapter 21 NECK AND HEAD The neck (cervical vertebrae) is the upper end of the back s vertebral column, on top of the mobile thoracic, and lumbar, and fused sacral
Chapter 21 NECK AND HEAD INJURIES 319 Chapter 21 NECK AND HEAD The neck (cervical vertebrae) is the upper end of the back s vertebral column, on top of the mobile thoracic, and lumbar, and fused sacral
CHRONIC CONDITIONS FYI
 CHRONIC CONDITIONS FYI AIDS More than 2,500 cases of HIV/AIDS have been identified in Nebraska. Nationwide, this number is more than 1.2 million. ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) There are 87 people
CHRONIC CONDITIONS FYI AIDS More than 2,500 cases of HIV/AIDS have been identified in Nebraska. Nationwide, this number is more than 1.2 million. ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) There are 87 people
What is Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (acgh)?
 i If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
i If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
Advice and exercises during pregnancy
 Advice and exercises during pregnancy During pregnancy, your body goes through many changes. This leaflet is designed to help you reduce the strain on your body and make you more comfortable. If you need
Advice and exercises during pregnancy During pregnancy, your body goes through many changes. This leaflet is designed to help you reduce the strain on your body and make you more comfortable. If you need
Learning Area 3 The Impact of Stroke on Swallowing. Stroke Helpline stroke.org.uk
 Learning Area 3 The Impact of Stroke on Swallowing The hidden aspect of stroke Hidden: Concealed, obscured, covert Something that can not be seen Not often associated with stroke Can be hidden from: Professionals
Learning Area 3 The Impact of Stroke on Swallowing The hidden aspect of stroke Hidden: Concealed, obscured, covert Something that can not be seen Not often associated with stroke Can be hidden from: Professionals
THE HUMAN BODY. study of the structure of living organisms. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: studying the structure of the heart.
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
Facts about Scoliosis
 Facts about Scoliosis Have you or someone in your family recently been diagnosed with scoliosis? Or do you suspect somebody you know has the condition? That is when we usually start googling to learn all
Facts about Scoliosis Have you or someone in your family recently been diagnosed with scoliosis? Or do you suspect somebody you know has the condition? That is when we usually start googling to learn all
