Comparison of the Learning Curve and Outcomes of Robotic Assisted Pediatric Pyeloplasty
|
|
|
- Prosper Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comparison of the Learning Curve and Outcomes of Robotic Assisted Pediatric Pyeloplasty Mathew D. Sorensen,* Catherine Delostrinos, Michael H. Johnson, Richard W. Grady and Thomas S. Lendvay From the Division of Pediatric Urology, Seattle Children s Hospital (RWG, TSL) and Department of Urology (MDS, RWG, TSL), University of Washington School of Medicine (CD, MHJ), Seattle, Washington Purpose: We compared the learning curve and outcomes in children undergoing robotic assisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty during the initiation of a robotic surgery program compared to the benchmark of open pyeloplasty. Materials and Methods: The records of our first consecutive 33 children undergoing robotic assisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty from 2006 to 2009 were retrospectively reviewed and compared to those of age and gender matched children who underwent open repair done by senior faculty surgeons before the initiation of our robotic surgery program. We compared operative time, complications, postoperative pain, length of stay and surgical success for 2 surgeons who adopted the robotic approach at an academic teaching institution. Results: We found no significant differences in length of stay, pain score or surgical success at a median followup of 16 months. The number of complications was similar and they tended to be early and technical in the robotic assisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty group. Overall average operative time was 90 minutes longer (38%) for robotic assisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty (p 0.004). When evaluated chronologically, there was evidence of a learning curve. After 15 to 20 robotic cases overall operative times for robotic assisted laparoscopic cases was consistently within 1 SD of our average open pyeloplasty time with no significant difference in overall operative time (p 0.23). Of the decrease in overall operative time 70% was due to decreased pyeloplasty time rather than peripheral time. Conclusions: There was similar safety and efficacy with robotic assisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty, although complications tended to be technical and early in our initial experience. Operative time decreased with experience and after 15 to 20 cases it was similar to that of open pyeloplasty with similar outcomes and surgical success. Abbreviations and Acronyms MAG3 mercaptoacetyltriglycine RAL robotic assisted laparoscopic Study received Seattle Children s Hospital institutional review board approval. * Correspondence; University of Washington School of Medicine, 1959 Northeast Pacific St., Box , Seattle, Washington (telephone: ; FAX: ; mathews@u.washington.edu). Financial interest and/or other relationship with Spi Surgical. Key Words: kidney, laparoscopy, robotics, learning, outcome and process assessment (health care) THE learning curve has become an increasingly important focus of evaluating RAL procedures. While the urological literature includes reports of adult procedure learning curves, no studies have adequately described the learning curve for RAL pediatric urological reconstructive procedures. Learning curve is a frequently used and often poorly defined term. On the way to achieving mastery the curve represents the initial challenges in competence, and the change in technical proficiency and efficiency with increasing experience. 1,2 In adults increasing surgeon experience decreases operative time for robotic prostatectomy within the first /11/ /0 Vol. 185, , June 2011 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION EDUCATION AND RESEARCH, INC. DOI: /j.juro
2 2518 LEARNING CURVE AND OUTCOMES OF ROBOTIC ASSISTED PEDIATRIC PYELOPLASTY 50 cases, although the learning curve likely extends beyond 150 to 200 cases in terms of surgical margins. 3 8 For practitioners familiar with robotic procedures RAL radical cystectomy has an estimated learning curve of only 20 cases and reports have reassured us that, although operative time and blood loss were initially higher, these initial cases could be done without observed compromises in oncological parameters. 9 Other procedures, such as RAL partial nephrectomy and RAL hysterectomy, appear to have a learning curve of 15 to 30 cases but the complication rate may be higher in these initial cases As a group at a center where RAL pyeloplasty is now regularly performed, we evaluated the learning curve and outcomes of these initial cases. We defined the learning curve as time needed to achieve similar outcomes of success, operative time and complications for RAL pyeloplasty compared to the outcomes of open pyeloplasty performed by senior faculty. We focused primarily on safety and outcomes as markers of proficiency since prior studies demonstrated inferior outcomes during the initiation and establishment of such a new technology. 6,7,10 12 MATERIALS AND METHODS We systematically evaluated the first 33 children undergoing RAL pyeloplasty at our institution as we initiated our RAL surgery program in April Cases were performed during a 34-month period by 2 pediatric urologists using the da Vinci Standard surgical system. Each surgeon had prior laparoscopic experience (approximately 20 cases yearly) but minimal laparoscopic pyeloplasty experience. Neither surgeon had performed any robotic procedures. The last case in this study represents the 106th RAL case performed at our institution and the 67th performed by these 2 urological surgeons. Children who underwent RAL pyeloplasty were compared to children who underwent open pyeloplasty. Since patient age is associated with differences in operative time, complications and postoperative pain, RAL and open cases were matched based on gender and frequency matched for age (0 to 5, 6 to 9 and 10 years or greater). 13,14 To decrease case selection bias open cases were only eligible for inclusion if they were performed before the time when the attending surgeon was performing RAL surgery. Open cases were done by senior faculty with an average of more than 10 years of experience and are thought to represent surgical competence and likely mastery. The learning curve was defined by comparing surgical success and complications. Also, overall operative time in RAL pyeloplasty cases was evaluated chronologically and compared to the average 1 SD overall operative time for open pyeloplasty. Operative time was further evaluated based on the time from skin incision to dressing to perform the pyeloplasty portion of the procedure as well as peripheral time (in room, anesthesia, initial positioning, cystoscopy, repositioning and out of room time). Secondarily we analyzed postoperative pain, length of stay and blood loss. Postoperative pain scores were regularly assessed by nursing staff using a standard 0 to 10 scale. 15 Complications, and their nature and timing in the robotic experience were assessed. RAL and open cases were required to have had at least 90 days of followup, defined as time from surgery to the most recent clinic visit. Success in the 2 groups was defined postoperatively as improved drainage on MAG3 renography and/or improved hydronephrosis combined with renal parenchymal growth on ultrasound or computerized tomography and resolution of renal colic crisis in patients who presented with pain symptoms. Robotic cases were performed using a 12 mm camera port and 2, 8 mm instrument ports. A 14 gauge angiocatheter was used to assist with antegrade ureteral stent placement, tissue retraction, smoke evacuation and suction. 16 Of the cases 54% were done in transmesenteric fashion, when possible. A urethral catheter was left in place overnight and a ureteral stent was left in place for 6 weeks. Open cases were performed through a subcostal or flank incision. A urethral catheter was typically removed the morning after surgery, followed by removal of a percutaneous Penrose drain in the flank. Ureteral stents were placed in 12 patients (36%) and removed 6 weeks later. In each group pain was managed by regional anesthesia or narcotic boluses, followed by oral analgesia with or without ketorolac. Outcomes were compared using conditional logistic regression with robust SEs with a priori adjustment for all matching factors. Chi-square analysis was done for binary variables and Student s t test was performed for continuous variables with significance considered at p Analysis was performed using Stata, version 10. Approval for this study was obtained from the Seattle Children s Hospital institutional review board. RESULTS Patient age and gender were well matched with similar presentations and imaging (table 1). The intraoperative approach to urinary diversion and postoperative imaging differed between the groups (table 1). In the 2 groups 97% success was achieved, that is in 32 of the 33 patients each. In cases of RAL and open failure endoscopic dilation was done. Followup duration was similar between the groups. As a group at a tertiary referral center, we tend to follow remote patients for approximately 12 to 18 months and then return them to the care of the primary care provider and local urologist. During the study period overall average operative time in RAL cases was 38% longer than in open cases with an absolute difference of 90 minutes (p 0.004, table 2). This longer time was due primarily to longer pyeloplasty time (skin incision to dressing, p 0.002) rather than peripheral time (in room, anesthesia, setup, cystoscopy and out of room time, p 0.12). When analyzed chronologically and compared to the overall operative time for the average open pyeloplasty done by senior surgical faculty, a learning curve was identified for the surgeon with the greatest experience
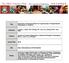
3 LEARNING CURVE AND OUTCOMES OF ROBOTIC ASSISTED PEDIATRIC PYELOPLASTY 2519 Table 1. Demographics and surgical variables in 33 patients with RAL and 33 with open pyeloplasty RAL Open p Value* Age (yrs): No No No. 10 or greater Mean SD No. gender (%): 1.0 M 10 (30) 10 (30) F 23 (70) 23 (70) Mean SD wt (kg) Mean SD body mass index (kg/m 2 ) Mean SD American Society of Anesthesiologists score No. presenting symptoms (%): 0.20 Pain/Dietl s crisis 19 (58) 19 (58) Prenatal hydronephrosis 8 (24) 2 (6) Stones/urinary tract infection 4 (12) 5 (15) Other 2 (6) 7 (21) No. preop imaging: 0.12 MAG Magnetic resonance urogram 4 0 Computerized tomography/ultrasound 5 2 No. complex: Pyelolithotomy 3 2 Repeat pyeloplasty 2 1 Ruptured ureteropelvic junction 1 Horseshoe kidney 1 Stent: Antegrade Retrograde 6 2 Totals 32 (97) 12 (36) Mean duration (wks) No. drain (%): Penrose 30 (91) Closed suction 1 (3) % Postop imaging: 0.05 MAG Ultrasound Computerized tomography 3 3 % Success Followup (mos): Mean SD Median (IQR) 16 (11 23) 12 (5 35) 0.55 * Conditional logistic regression with robust SE adjusted for age category and gender. (see figure). Overall average operative time in the initial 10 RAL pyeloplasty cases was about 6 hours for each surgeon. These initial cases included the 3 longest and most difficult cases, including repeat pyeloplasty in 1 and concurrent large pyelolithotomy in 2. After 15 to 20 cases there was no statistically significant difference in overall operative time for RAL and open pyeloplasty (p 0.23). Overall operative time was also consistently within 1 SD of that of our average open pyeloplasty. Peripheral and the pyeloplasty time decreased with experience but 70% of the decrease was due to pyeloplasty surgical time. The number of complications were similar between the groups (p 0.45). However, complications in the RAL pyeloplasty group tended to be early and technical (see figure). There were 3 complications (9%) in the open group, including a patient who was rehospitalized twice for pyelonephritis and another who was rehospitalized for dehydration, persistent nausea, vomiting and flank pain, which ultimately resolved spontaneously. A third complication was technical in a child in whom asymptomatic stent migration was managed conservatively. There were 5 complications (15%) in the RAL group. One boy had gross hematuria with clot obstruction of the ureteral stent, which was managed conservatively. Another 4 patients in the RAL group had technical complications due to urine extravasation from the anastomotic closure. Two patients were treated conservatively with prolonged urinary drainage, 1 underwent percutaneous nephrostomy tube placement and 1 underwent replacement of a malpositioned stent. After our first year of performing RAL pyeloplasty we began performing intraoperative ultrasound using the S-Nerve ultrasound sys-
4 2520 LEARNING CURVE AND OUTCOMES OF ROBOTIC ASSISTED PEDIATRIC PYELOPLASTY Table 2. Operative and perioperative comparison of patients with RAL vs open pyeloplasty RAL Open Difference p Value* Mean SD time (mins): Peripheral Pyeloplasty Overall operative Mean SD estimated blood loss (ml) Mean SD length of stay (days) No. complications: Intraop Postop (%) 5 (15) 3 (9) 0.45 Technical postop 4 1 Other postop 1 2 * Conditional logistic regression with robust SE adjusted for age category and gender. tem to confirm distal stent position. After this no further episodes of stent malposition occurred. All patients with a postoperative complication ultimately had a successful outcome. Estimated blood loss, length of stay and intraoperative complications were similar in the 2 groups. When analyzed annually, we found a decrease in length of stay with each year of experience, that is a mean of 3.5, 2.0 and 1.2 days for each successive study year, respectively (p 0.01). There were no differences in postoperative pain scores, which may be partly explained by differences in the approach to postoperative pain control. At our institution there were 5 mechanical failures in our initial 100 robotic procedures (5%) during a 12-month period. Three of these failures developed in patients who underwent robotic pyeloplasty. Two cases were completed using conventional laparoscopy and the other was converted to conventional laparoscopy for 1.5 hours while the robot was repaired and then completed robotically. No patient in the RAL cohort required open conversion. Ultimately the 2 robotic arms were replaced. DISCUSSION Our experience demonstrates the realities of the 50% longer overall operative time in our initial robotic cases compared to open operative time in cases done by senior faculty. These RAL cases were performed by surgeons with prior laparoscopic experience and no prior robotic experience except basic pig and dry laboratory experience. Operative time decreased considerably with increasing experience, such that after 15 to Learning curve comparison of overall operative time for RAL vs open pyeloplasty per surgeon. After 15 to 20 cases overall operative times for RAL was consistently within 1 SD of average open pyeloplasty time with no significant difference (p 0.23). Five complications (arrows) tended to be technical and early in learning curve. Gray box represents average overall operative time for open pyeloplasty 1 SD.
5 LEARNING CURVE AND OUTCOMES OF ROBOTIC ASSISTED PEDIATRIC PYELOPLASTY RAL pyeloplasty cases overall operative time was not significantly different from that of open pyeloplasty (p 0.23). Of this decrease in RAL cases 70% was due to improved proficiency with the pyeloplasty portion of the procedure (skin incision to dressing) rather than the peripheral time (in room, anesthesia, positioning, cystoscopy, repositioning and out of room time), although each contributed to the decrease in overall operative time. In the early stages of our robotic pyeloplasty experience we observed outcomes similar to those in our open pyeloplasty cohort. The number of technical complications was higher in the robotic group and tended to occur early in our experience (see figure), providing further evidence of the learning curve. After year 1 we began performing intraoperative ultrasound to identify the bladder curl of the ureteral stent and no further episodes of stent malposition occurred. There were no significant differences in overall blood loss, length of stay or pain score, although there was a decrease in length of stay with each year of experience. We expected length of stay to be similar since we applied more conservative postoperative observation in our initial patients. The success rate was 97% in our open and RAL groups with more than a year of average followup. All patients underwent postoperative imaging, although those in the RAL pyeloplasty group were more rigorously imaged by renograms. During year 1 as we conservatively approached this new technique, almost all patients underwent postoperative MAG3 renography except the 2 who underwent concurrent pyelolithotomy. Our initial mechanical failure rate is higher than the 1% to 2% cited in the literature and highlights the importance of maintaining standard laparoscopy skills. 17 No mechanical failure resulted in a significant increase in operative time, estimated blood loss or length of hospitalization. Excluding these mechanical failures did not alter our conclusions for any of the outcomes analyzed and, thus, they were included in all analyses. Our institution has since upgraded to the da Vinci Si system and we have not experienced a mechanical failure in 35 cases using the new robot. Defining the learning curve for reconstructive procedures represents a unique challenge. The factors available for evaluation of proficiency are somewhat limited, especially compared to oncological cases, which have several variables, such as margin status, number of lymph nodes, continence, potency and overall/cancer specific survival, in addition to the variables that we evaluated, such as surgical success, complications, pain and blood loss. We acknowledge that it likely takes 15 to 20 cases to achieve rudimentary proficiency when we evaluated the somewhat crude outcomes of safety, efficacy and operative time. Also, although operative time is likely to continue to decrease with greater experience, achieving true technical mastery of a pediatric reconstructive procedure likely takes far more than the 33 cases that we evaluated. 4,6,7 These findings have important implications for practitioners and institutions electing to perform these types of robotic pediatric reconstructive procedures. Initial operative time is longer and depending on the case volume it may take several years for operative time to approach that of established open procedures. These initial cases were performed at the beginning of establishing our robotic surgery program and, thus, surgical staff and surgeons were acclimating to the new technology. We believe that there is a synergistic effect, in that an experienced robotics surgery staff may accelerate a novice surgeon learning curve and vice versa. We compared an open procedure performed by experienced senior faculty to a newly adopted robotic surgical technique. Although this sets a high standard, we believe that it offers a realistic comparison of the options that would have otherwise been open to families presenting for surgery at our institution. Furthermore, there were differences in surgical and postoperative management between the RAL and open groups with the RAL group favoring a ureteral stent while most cases had a Penrose drain and sometimes a ureteral stent (97% vs 91% and 36%, respectively). Thus, a second anesthesia was required in almost every robotics case, a factor that must be discussed when obtaining consent for this procedure from the families. The RAL group also tended to undergo more imaging, including nuclear renography and ultrasound, while the open group tended to be followed with serial ultrasound only, reflecting practitioner bias. We thought that it was important to match patients with RAL and open surgery by age and gender since age is associated with differences in operative time, complications and pain in children who undergo laparoscopic procedures. 13,14,18 This study has limitations. It is a retrospective study done at a tertiary academic referral center and is subject to the inherent limitations of this study design. The degree of resident and/or fellow participation in either group was not assessed and could have biased surgical time. This study includes data primarily from 1 surgeon. However, we found it reassuring that the second surgeon appeared to have experienced a similar learning curve in the initial 9 cases (p 0.61). This study includes our first 33 RAL pyeloplasty cases, which may have limited our power to detect small differences between the groups. Despite our efforts to minimize case selection bias by selecting controls from a time when the attending surgeons were not performing any RAL procedures, patients were not randomized. In our initial robotic experience we attempted several complex cases, which likely impacted outcomes. We suggest that complex cases should be reserved for after the initial learning curve has been traversed. Comparing outcomes and operative times for our initial experience with a new technology vs a well estab-
6 2522 LEARNING CURVE AND OUTCOMES OF ROBOTIC ASSISTED PEDIATRIC PYELOPLASTY lished open procedure likely influenced our evaluation but we believe that this comparison is honest and real for those considering adoption of this technology. Although prior studies have demonstrated similar outcomes, it was not possible to evaluate traditional laparoscopic pyeloplasty since our institutional experience was too small to allow any meaningful comparisons. 19 CONCLUSIONS The initial learning curve for RAL pyeloplasty appears to be 15 to 20 cases. True mastery of the procedure extends beyond this initial evaluation but it is important to note that during this learning curve we observed similar safety and efficacy outcomes with the caveat of a few early technical complications. This reality should be brought up during preoperative patient counseling. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Dr. Martin Koyle reviewed the manuscript, Jeff Bice assisted with data acquisition and Carrie Wachob assisted with figures. REFERENCES 1. Wright TP: Factors affecting the cost of airplanes. J Aeronaut Sci 1936; 3: Perspectives on Experience. Boston: Boston Consulting Group 1972; p Menon M, Shrivastava A, Tewari A et al: Laparoscopic and robot assisted radical prostatectomy: establishment of a structured program and preliminary analysis of outcomes. J Urol 2002; 168: Patel VR, Tully AS, Holmes R et al: Robotic radical prostatectomy in the community setting the learning curve and beyond: initial 200 cases. J Urol 2005; 174: Ahlering TE, Woo D, Eichel L et al: Robot-assisted versus open radical prostatectomy: a comparison of one surgeon s outcomes. Urology 2004; 63: Doumerc N, Yuen C, Savdie R et al: Should experienced open prostatic surgeons convert to robotic surgery? The real learning curve for one surgeon over 3 years. BJU Int 2010; 106: Herrell SD and Smith JA Jr: Robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy: what is the learning curve? Urology 2005; 66: 105. EDITORIAL COMMENT 8. Ahlering TE, Skarecky D, Lee D et al: Successful transfer of open surgical skills to a laparoscopic environment using a robotic interface: initial experience with laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. J Urol 2003; 170: Pruthi RS, Smith A and Wallen EM: Evaluating the learning curve for robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy. J Endourol 2008; 22: Haseebuddin M, Benway BM, Cabello JM et al: Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: evaluation of learning curve for an experienced renal surgeon. J Endourol 2010; 24: Bell MC, Torgerson JL and Kreaden U: The first 100 da Vinci hysterectomies: an analysis of the learning curve for a single surgeon. S D Med 2009; 62: Seamon LG, Fowler JM, Richardson DL et al: A detailed analysis of the learning curve: robotic hysterectomy and pelvic-aortic lymphadenectomy for endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol 2009; 114: Lee RS, Retik AB, Borer JG et al: Pediatric robot assisted laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty: comparison with a cohort of open surgery. J Urol 2006; 175: Casale P, Patel RP and Kolon TF: Nerve sparing robotic extravesical ureteral reimplantation. J Urol 2008; 179: Wong DL and Baker CM: Pain in children: comparison of assessment scales. Pediatr Nurs 1988; 14: Hotaling JM, Shear S and Lendvay TS: 14-gauge angiocatheter: the assist port. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 2009; 19: Kim WT, Ham WS, Jeong W et al: Failure and malfunction of da Vinci Surgical systems during various robotic surgeries: experience from six departments at a single institute. Urology 2009; 74: Yee DS, Shanberg AM, Duel BP et al: Initial comparison of robotic-assisted laparoscopic versus open pyeloplasty in children. Urology 2006; 67: Mufarrij PW, Woods M, Shah OD et al: Robotic dismembered pyeloplasty: a 6-year, multi-institutional experience. J Urol 2008; 180: While there are several challenges to this study, the effort to quantitate and, thereby, begin to understand surgical learning is admirable. The concept of the learning curve emerged in the early aircraft industry and was described by Wright (reference 1 in article). It was based on the hypothesis that if an operation (not necessarily surgical) were repeated, it would take less time to perform. The learning curve was a representation of the number of repetitions needed to decrease the time spent. To measure this Wright described the learning percent as the difference in time taken after the number of operations is doubled. In this report it was about 67% (100% minus 33%, that is 6 hours for the initial 10 cases and about 4 hours for the second 10 or 2 hours/6 hours 33%). This is good compared to some industries. This value provides an assessment of the learning curve that may be compared among providers and systems. Craig A. Peters Department of Pediatric Surgery Children s National Medical Center Washington, D.C.
Facing Surgery. for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing Surgery for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Urinary Tract Obstruction Your urinary system produces, stores, and eliminates urine. It includes
Facing Surgery for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Urinary Tract Obstruction Your urinary system produces, stores, and eliminates urine. It includes
Facing Surgery. for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing Surgery for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condit ion: Urinary Tract Obstruction Your urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters and the
Facing Surgery for a Urinary Tract Condition? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condit ion: Urinary Tract Obstruction Your urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters and the
Facing Surgery. for Urinary Tract Conditions? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option
 Facing Surgery for Urinary Tract Conditions? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option The Condition: Urinary Tract Obstruction The urinary system is the group of organs that produces,
Facing Surgery for Urinary Tract Conditions? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option The Condition: Urinary Tract Obstruction The urinary system is the group of organs that produces,
The Management of Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction Presenting with Prenatal Hydronephrosis
 Review Special Issue: Pre- and Postnatal Management of Hydronephrosis TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 400 403 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.51 The Management of Ureteropelvic Junction
Review Special Issue: Pre- and Postnatal Management of Hydronephrosis TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 400 403 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.51 The Management of Ureteropelvic Junction
Laparoscopic Surgery. The Da Vinci Robot. Limits of Laparoscopy. What Robotics Offers. Robotic Urologic Surgery: A New Era in Patient Care
 Laparoscopic Surgery Robotic Urologic Surgery: A New Era in Patient Care Laparoscopic technique was introduced in urologic surgery in the 1990s Benefits: Improved recovery time, decreased morbidity Matthew
Laparoscopic Surgery Robotic Urologic Surgery: A New Era in Patient Care Laparoscopic technique was introduced in urologic surgery in the 1990s Benefits: Improved recovery time, decreased morbidity Matthew
Simplified Open Approach to Surgical Treatment of Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction in Young Children and Infants
 Hydronephrosis Simplified Open Approach to Surgical Treatment of Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction in Young Children and Infants Eduardo Ruiz, Ricardo Soria, Edurne Ormaechea, Mauricio Marcelo Urquizo
Hydronephrosis Simplified Open Approach to Surgical Treatment of Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction in Young Children and Infants Eduardo Ruiz, Ricardo Soria, Edurne Ormaechea, Mauricio Marcelo Urquizo
Pathologic Outcomes during the Learning Curve for Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
 Clinical Urology Pathologic Outcomes While Learning RALP International Braz J Urol Vol. 34 (2): 159-163, March - April, 2008 Pathologic Outcomes during the Learning Curve for Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic
Clinical Urology Pathologic Outcomes While Learning RALP International Braz J Urol Vol. 34 (2): 159-163, March - April, 2008 Pathologic Outcomes during the Learning Curve for Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic
Outcomes of Infants Undergoing Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty Compared to Open Repair
 Outcomes of Infants Undergoing Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty Compared to Open Repair Pankaj P. Dangle, James Kearns, Blake Anderson and Mohan S. Gundeti* From the Department of Surgery, Division
Outcomes of Infants Undergoing Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty Compared to Open Repair Pankaj P. Dangle, James Kearns, Blake Anderson and Mohan S. Gundeti* From the Department of Surgery, Division
The Minimally Invasive Management of Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction in Horseshoe Kidneys
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Urology Faculty Papers Department of Urology 1-25-2011 The Minimally Invasive Management of Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction in Horseshoe
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Urology Faculty Papers Department of Urology 1-25-2011 The Minimally Invasive Management of Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction in Horseshoe
Kaiser Oakland Urology
 Kaiser Oakland Urology What is Laparoscopy? Minimally invasive surgical alternative to standard surgery How is Laparoscopy Performed? A laparoscope and video camera are used to visualize internal organs
Kaiser Oakland Urology What is Laparoscopy? Minimally invasive surgical alternative to standard surgery How is Laparoscopy Performed? A laparoscope and video camera are used to visualize internal organs
da Vinci Prostatectomy My Greek personal experience
 da Vinci Prostatectomy My Greek personal experience Vassilis Poulakis MD, PhD, FEBU Ass. Prof. of Urology Director of Urologic Clinic Doctors Hospital Athens Laparoscopy - golden standard in Urology -
da Vinci Prostatectomy My Greek personal experience Vassilis Poulakis MD, PhD, FEBU Ass. Prof. of Urology Director of Urologic Clinic Doctors Hospital Athens Laparoscopy - golden standard in Urology -
Transperitoneal Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy After Prosthetic Mesh Herniorrhaphy
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Transperitoneal Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy After Prosthetic Mesh Herniorrhaphy Costas D. Lallas, MD, Mark L. Pe, MD, Jitesh V. Patel, MD, Pranav Sharma, Leonard G. Gomella,
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Transperitoneal Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy After Prosthetic Mesh Herniorrhaphy Costas D. Lallas, MD, Mark L. Pe, MD, Jitesh V. Patel, MD, Pranav Sharma, Leonard G. Gomella,
Goals & Objectives by Year in Training: U-1
 Goals & Objectives by Year in Training: U-1 U-1 (PGY-2, 3) Resident Responsibilities, Goals and Objectives In addition to the goals listed for PGY-1, the U-1 resident will add to his/her knowledge base
Goals & Objectives by Year in Training: U-1 U-1 (PGY-2, 3) Resident Responsibilities, Goals and Objectives In addition to the goals listed for PGY-1, the U-1 resident will add to his/her knowledge base
Laparoscopic Diverticulocystoplasty for Low Compliance Bladder in a Child
 CASE REPORT Laparoscopic Diverticulocystoplasty for Low Compliance Bladder in a Child Manickam Ramalingam, MCh, Kallappan Senthil, MCh, Anandan Murugesan, MCh, Mizar Ganapathy Pai, MCh ABSTRACT Low compliance
CASE REPORT Laparoscopic Diverticulocystoplasty for Low Compliance Bladder in a Child Manickam Ramalingam, MCh, Kallappan Senthil, MCh, Anandan Murugesan, MCh, Mizar Ganapathy Pai, MCh ABSTRACT Low compliance
Laparo-endoscopic single site surgery in pediatrics: Feasibility and surgical outcomes from a preliminary prospective Canadian experience
 Original research Laparo-endoscopic single site surgery in pediatrics: Feasibility and surgical outcomes from a preliminary prospective Canadian experience Aziz Khambati, MD; Elias Wehbi, MD; Walid A.
Original research Laparo-endoscopic single site surgery in pediatrics: Feasibility and surgical outcomes from a preliminary prospective Canadian experience Aziz Khambati, MD; Elias Wehbi, MD; Walid A.
Transition from open to robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy: 7 years experience at Hackensack University Medical Center
 J Robotic Surg (27) 1:155 159 DOI 1.7/s1171-7-23- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transition from open to robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy: 7 years experience at Hackensack University Medical Center Ravi Munver
J Robotic Surg (27) 1:155 159 DOI 1.7/s1171-7-23- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transition from open to robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy: 7 years experience at Hackensack University Medical Center Ravi Munver
Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom. Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium
 Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium Editors : Anthony Caldamone, USA Pierre Mouriquand, France Newborn boy History of prenatally diagnosed
Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium Editors : Anthony Caldamone, USA Pierre Mouriquand, France Newborn boy History of prenatally diagnosed
da Vinci Prostatectomy
 da Vinci Prostatectomy Justin T. Lee MD Director of Robotic Surgery Urology Associates of North Texas (UANT) USMD Prostate Cancer Center (www.usmdpcc.com) Prostate Cancer Facts Prostate cancer Leading
da Vinci Prostatectomy Justin T. Lee MD Director of Robotic Surgery Urology Associates of North Texas (UANT) USMD Prostate Cancer Center (www.usmdpcc.com) Prostate Cancer Facts Prostate cancer Leading
Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: Evaluation of learning curve for an experienced renal surgeon
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2010 Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: Evaluation of learning curve for an experienced renal surgeon Mohammed
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2010 Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: Evaluation of learning curve for an experienced renal surgeon Mohammed
Content and Construct Validation of a Robotic Surgery Curriculum Using an Electromagnetic Instrument Tracker
 Content and Construct Validation of a Robotic Surgery Curriculum Using an Electromagnetic Instrument Tracker Timothy J. Tausch,* Timothy M. Kowalewski, Lee W. White, Patrick S. McDonough, Timothy C. Brand
Content and Construct Validation of a Robotic Surgery Curriculum Using an Electromagnetic Instrument Tracker Timothy J. Tausch,* Timothy M. Kowalewski, Lee W. White, Patrick S. McDonough, Timothy C. Brand
ROBOTIC ASSISTED LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY (RALP) Does The Patients Weight Effect The Surgical Results? Boris Chertin MD
 ROBOTIC ASSISTED LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY (RALP) Does The Patients Weight Effect The Surgical Results? Boris Chertin MD Chairman, The Departments of Urology & Pediatric Urology, Shaare Zedek Medical Center
ROBOTIC ASSISTED LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY (RALP) Does The Patients Weight Effect The Surgical Results? Boris Chertin MD Chairman, The Departments of Urology & Pediatric Urology, Shaare Zedek Medical Center
Current Status of Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Surgery in Pediatric Urology
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.8.499 Review Article http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.8.499&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-08-16 Current Status of Robot-Assisted
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.8.499 Review Article http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.8.499&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-08-16 Current Status of Robot-Assisted
Robotic distal ureterectomy with psoas hitch and ureteroneocystostomy: Surgical technique and outcomes
 Asian Journal of Urology (2015) 2, 123e127 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ajur CASE REPORT Robotic distal with psoas hitch and
Asian Journal of Urology (2015) 2, 123e127 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ajur CASE REPORT Robotic distal with psoas hitch and
Ureteral Stenting after Flexible Ureterorenoscopy with Ureteral Access Sheath; Is It Really Needed?: A Prospective Randomized Study
 Ureteral Stenting after Flexible Ureterorenoscopy with Ureteral Access Sheath; Is It Really Needed?: A Prospective Randomized Study J Med Assoc Thai 2017; 100 (Suppl. 3): S174-S178 Full text. e-journal:
Ureteral Stenting after Flexible Ureterorenoscopy with Ureteral Access Sheath; Is It Really Needed?: A Prospective Randomized Study J Med Assoc Thai 2017; 100 (Suppl. 3): S174-S178 Full text. e-journal:
Procedure related complications and how to prevent them
 Procedure related complications and how to prevent them Rama Jayanthi, M.D. Section of Urology Nationwide Children s Hospital The Ohio State University Retroperitoneoscopic surgery Inadvertent peritoneal
Procedure related complications and how to prevent them Rama Jayanthi, M.D. Section of Urology Nationwide Children s Hospital The Ohio State University Retroperitoneoscopic surgery Inadvertent peritoneal
GENERAL GOALS & OBJECTIVES U-1. U-1 (PGY-2, 3) GENERAL GOALS and OBJECTIVES
 GENERAL GOALS & OBJECTIVES U-1 U-1 (PGY-2, 3) GENERAL GOALS and OBJECTIVES In addition to the goals listed for PGY-1, the U-1 resident will add to his/her knowledge base by participating actively in conferences,
GENERAL GOALS & OBJECTIVES U-1 U-1 (PGY-2, 3) GENERAL GOALS and OBJECTIVES In addition to the goals listed for PGY-1, the U-1 resident will add to his/her knowledge base by participating actively in conferences,
Prenatal Hydronephrosis
 Prenatal Hydronephrosis What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis is dilation of the kidney, specifically the renal pelvis (place where urine is stored after its production). This can be the result of an
Prenatal Hydronephrosis What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis is dilation of the kidney, specifically the renal pelvis (place where urine is stored after its production). This can be the result of an
Robotic Surgery for Prostate Cancer: A Realistic Approach to Getting Started The Evolution of a Robotic Surgeon
 Robotic Surgery for Prostate Cancer: A Realistic Approach to Getting Started The Evolution of a Robotic Surgeon Douglas S. Scherr, M.D. Clinical Director, Urologic Oncology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Robotic Surgery for Prostate Cancer: A Realistic Approach to Getting Started The Evolution of a Robotic Surgeon Douglas S. Scherr, M.D. Clinical Director, Urologic Oncology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Forgotten JJ stent: A rare case report
 Ped Urol Case Rep 2015; 2(2):6-10 DOI: 10.14534/PUCR.201529390 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Forgotten
Ped Urol Case Rep 2015; 2(2):6-10 DOI: 10.14534/PUCR.201529390 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Forgotten
Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux
 Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux Suzi DEMIRBAG, MD Department of Pediatric Surgery, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, TURKEY Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux Suzi DEMIRBAG, MD Department of Pediatric Surgery, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, TURKEY Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
Over the years, several surgical modifications have been incorporated into radical
 Focused Issue of This Month Radical Prostatectomy: Respective Roles and Comparisons of Robotic and Open Surgeries Young Deuk Choi, MDJae Seung Chung, MD Department of Urology, Yonsei University College
Focused Issue of This Month Radical Prostatectomy: Respective Roles and Comparisons of Robotic and Open Surgeries Young Deuk Choi, MDJae Seung Chung, MD Department of Urology, Yonsei University College
Facing Prostate Cancer?
 The Enabling Technology: The da Vinci Surgical System Your doctor is one of the growing number of surgeons worldwide offering da Vinci Surgery for a range of complex conditions. The da Vinci Surgical System
The Enabling Technology: The da Vinci Surgical System Your doctor is one of the growing number of surgeons worldwide offering da Vinci Surgery for a range of complex conditions. The da Vinci Surgical System
LOGBOOK EBU ORAL EXAM 2015
 LOGBOOK EBU ORAL EXAM 2015 Surname First Name Date of Birth (daymonthyear) MEDICAL DEGREE (MD) UROLOGIST TRAINING: - Training in urology - Training in surgery (as part of the urology training) - Other
LOGBOOK EBU ORAL EXAM 2015 Surname First Name Date of Birth (daymonthyear) MEDICAL DEGREE (MD) UROLOGIST TRAINING: - Training in urology - Training in surgery (as part of the urology training) - Other
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic ductal, laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for, 61 Adrenal cortical carcinoma, laparoscopic adrenalectomy for, 114
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic ductal, laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for, 61 Adrenal cortical carcinoma, laparoscopic adrenalectomy for, 114
Minimally invasive surgery in urology oncology. Dr. Tongchai Nakamont 23 Jan 2014
 Minimally invasive surgery in urology oncology Dr. Tongchai Nakamont 23 Jan 2014 Urology oncology Renal cell carcinoma ( RCC) Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) Kidney Ureter Bladder Prostate cancer Urological
Minimally invasive surgery in urology oncology Dr. Tongchai Nakamont 23 Jan 2014 Urology oncology Renal cell carcinoma ( RCC) Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) Kidney Ureter Bladder Prostate cancer Urological
DISMEMBERED LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY WITH ANTEGRADE PLACEMENT OF URETERAL STENT: SIMPLIFICATION OF THE TECHNIQUE
 Surgical Technique International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 28 (5): 439-445, September - October, 2002 DISMEMBERED LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY WITH ANTEGRADE PLACEMENT
Surgical Technique International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 28 (5): 439-445, September - October, 2002 DISMEMBERED LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY WITH ANTEGRADE PLACEMENT
Although open surgery has stood the test of time for
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 23, Number 3, March 2009 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 463 467 DOI: 10.1089=end.2008.0208 Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty: Our New Gold Standard Stephanie J. Symons, M.D., Parag S.
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 23, Number 3, March 2009 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 463 467 DOI: 10.1089=end.2008.0208 Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty: Our New Gold Standard Stephanie J. Symons, M.D., Parag S.
Index. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 14 (2005) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Surg Oncol Clin N Am 14 (2005) 433 439 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominosacral resection, of recurrent rectal cancer, 202 215 Ablative techniques, image-guided,
Surg Oncol Clin N Am 14 (2005) 433 439 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominosacral resection, of recurrent rectal cancer, 202 215 Ablative techniques, image-guided,
Current Outcome of Patients With Ureteral Stents for the Management of Malignant Ureteral Obstruction
 Current Outcome of Patients With Ureteral Stents for the Management of Malignant Ureteral Obstruction Kouji Izumi,* Atsushi Mizokami, Yuji Maeda, Eitetsu Koh and Mikio Namiki From the Department of Integrative
Current Outcome of Patients With Ureteral Stents for the Management of Malignant Ureteral Obstruction Kouji Izumi,* Atsushi Mizokami, Yuji Maeda, Eitetsu Koh and Mikio Namiki From the Department of Integrative
RADICAL CYSTECTOMY. Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery
 RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery The da Vinci Surgical System High-definition 3D vision EndoWrist instrumentation Intuitive motion RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Maintains the oncologic
RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery The da Vinci Surgical System High-definition 3D vision EndoWrist instrumentation Intuitive motion RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Maintains the oncologic
Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Surgery: Hysterectomy If you have gynecologic cancer - such as cancer of the
Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Surgery: Hysterectomy If you have gynecologic cancer - such as cancer of the
PERIOPERATIVE BLOOD LOSS IN OPEN RETROPUBIC RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY IS IT SAFE TO GET OPERATED AT AN EDUCATIONAL HOSPITAL?
 292 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF MEDICAL RESEARCH July 22, 2009 Eur J Med Res (2009) 14: 292-296 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2009 PERIOPERATIVE BLOOD LOSS IN OPEN RETROPUBIC RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY IS IT SAFE TO GET
292 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF MEDICAL RESEARCH July 22, 2009 Eur J Med Res (2009) 14: 292-296 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2009 PERIOPERATIVE BLOOD LOSS IN OPEN RETROPUBIC RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY IS IT SAFE TO GET
Jaspreet S. Sandhu,*,, Geoffrey T. Gotto,*, Luis A. Herran, Peter T. Scardino, James A. Eastham and Farhang Rabbani
 Age, Obesity, Medical Comorbidities and Surgical Technique are Predictive of Symptomatic Anastomotic Strictures After Contemporary Radical Prostatectomy Jaspreet S. Sandhu,*,, Geoffrey T. Gotto,*, Luis
Age, Obesity, Medical Comorbidities and Surgical Technique are Predictive of Symptomatic Anastomotic Strictures After Contemporary Radical Prostatectomy Jaspreet S. Sandhu,*,, Geoffrey T. Gotto,*, Luis
PYELOPLASTY (LAPAROSCOPIC AND OPEN PROCEDURE)
 PYELOPLASTY (LAPAROSCOPIC AND OPEN PROCEDURE) AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k Tameside: 0161 922
PYELOPLASTY (LAPAROSCOPIC AND OPEN PROCEDURE) AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k Tameside: 0161 922
M E M O R A N D U M. RE: Resident Surgical Index Case List Redefined For 2009: Recommended Minimum Numbers and Core Domains Emphasized
 M E M O R A N D U M TO: FROM: Urology Program Directors Louise King Executive Director, Residency Review Committee for Urology 312.755.5498 lking@acgme.org Members, Review Committee for Urology DATE: February
M E M O R A N D U M TO: FROM: Urology Program Directors Louise King Executive Director, Residency Review Committee for Urology 312.755.5498 lking@acgme.org Members, Review Committee for Urology DATE: February
Research Article Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty for Ureteropelvic Junctions Obstruction in Adults: 6 Years Experience in One Center
 Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 6743512, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6743512 Research Article Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty for Ureteropelvic Junctions Obstruction in
Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 6743512, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6743512 Research Article Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty for Ureteropelvic Junctions Obstruction in
Robotic Surgery for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma. Li-Ming Su, MD
 Robotic Surgery for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Li-Ming Su, MD David A. Cofrin Professor of Urology, Associate Chairman of Clinical Affairs, Chief, Division of Robotic and Minimally Invasive Urologic
Robotic Surgery for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Li-Ming Su, MD David A. Cofrin Professor of Urology, Associate Chairman of Clinical Affairs, Chief, Division of Robotic and Minimally Invasive Urologic
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Endourology
 Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 1, No. 3, 165-169 Summer 2004 Printed in IRAN ORIGINAL ARTICLES Endourology A Comparison between Laparoscopic and Open Pyeloplasty in Patients with Ureteropelvic Junction
Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 1, No. 3, 165-169 Summer 2004 Printed in IRAN ORIGINAL ARTICLES Endourology A Comparison between Laparoscopic and Open Pyeloplasty in Patients with Ureteropelvic Junction
Department of Urology, Cochin hospital Paris Descartes University
 Technical advances in the treatment of localized prostate cancer Pr Michaël Peyromaure Department of Urology, Cochin hospital Paris Descartes University Introduction Curative treatments of localized prostate
Technical advances in the treatment of localized prostate cancer Pr Michaël Peyromaure Department of Urology, Cochin hospital Paris Descartes University Introduction Curative treatments of localized prostate
Monday. Morning. Afternoon
 Monday l 8.30 am Welcome to participants ANESTHESIA Principles and specificities of anesthesia for laparoscopy EQUIPMENT Operating theatre - choice of equipment - the laparoscopic unit Conventional laparoscopic
Monday l 8.30 am Welcome to participants ANESTHESIA Principles and specificities of anesthesia for laparoscopy EQUIPMENT Operating theatre - choice of equipment - the laparoscopic unit Conventional laparoscopic
TECHNIQUE OF ENDOPYELOTOMY WITH THE ACUCISE CUTTING BALLOON
 Surgical Technique Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 26 (1): 71-75, January - February, 2000 TECHNIQUE OF ENDOPYELOTOMY WITH THE ACUCISE CUTTING BALLOON
Surgical Technique Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 26 (1): 71-75, January - February, 2000 TECHNIQUE OF ENDOPYELOTOMY WITH THE ACUCISE CUTTING BALLOON
Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy- the current gold standard
 Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy- the current gold standard Anoop M. Meraney, M.D Director, Urologic Oncology, Helen and Harry Gray Cancer Center, Hartford Hospital and Connecticut Surgical Group. Is it
Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy- the current gold standard Anoop M. Meraney, M.D Director, Urologic Oncology, Helen and Harry Gray Cancer Center, Hartford Hospital and Connecticut Surgical Group. Is it
Downloaded from Medico Research Chronicles Pelvi-ureteric junction obstruction - A ten year single center review in north central Nigeria.
 PELVI-URETERIC JUNCTION OBSTRUCTION - A TEN YEAR SINGLE CENTER REVIEW IN NORTH CENTRAL NIGERIA. 1,2 1,2 1 1 Atim T, Aisuodionoe-Shadrach O, Ajibola O. H, Magnus F. E Division of Urology, Departments of
PELVI-URETERIC JUNCTION OBSTRUCTION - A TEN YEAR SINGLE CENTER REVIEW IN NORTH CENTRAL NIGERIA. 1,2 1,2 1 1 Atim T, Aisuodionoe-Shadrach O, Ajibola O. H, Magnus F. E Division of Urology, Departments of
Radical Cystectomy A Patient s Guide
 Radical Cystectomy A Patient s Guide Introduction The urinary system, which includes the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys, helps maintain stable chemical conditions in the body, stores, and eliminates
Radical Cystectomy A Patient s Guide Introduction The urinary system, which includes the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys, helps maintain stable chemical conditions in the body, stores, and eliminates
Robotic Technology at the Service of Surgery
 Robotic Technology at the Service of Surgery -The Challenge of Robotic Urology - Vassilis Poulakis MD, PhD, FEBU Ass. Professor of Urology, University of Frankfurt, Germany Director of Urologic Clinic
Robotic Technology at the Service of Surgery -The Challenge of Robotic Urology - Vassilis Poulakis MD, PhD, FEBU Ass. Professor of Urology, University of Frankfurt, Germany Director of Urologic Clinic
Ureteroscopy Is Indicated in every patient with suspected Upper Tract Urothelial Tumor
 Ureteroscopy Is Indicated in every patient with suspected Upper Tract Urothelial Tumor Scott G. Hubosky, MD The Demetrius H. Bagley Jr., MD Associate Professor of Urology Director of Endourology Vice Chair
Ureteroscopy Is Indicated in every patient with suspected Upper Tract Urothelial Tumor Scott G. Hubosky, MD The Demetrius H. Bagley Jr., MD Associate Professor of Urology Director of Endourology Vice Chair
Urethral catheter removal 3 days after radical retropubic prostatectomy is feasible and desirable
 Urethral catheter 3 days after radical retropubic prostatectomy is feasible and desirable (2002) 5, 291 295 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1365 7852/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/pcan JM
Urethral catheter 3 days after radical retropubic prostatectomy is feasible and desirable (2002) 5, 291 295 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1365 7852/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/pcan JM
SciFed Journal of Public Health. Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature
 SciFed Journal of Public Health Case Report Open Access Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature * Yasin Idweini * Chairperson of Urology Department
SciFed Journal of Public Health Case Report Open Access Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature * Yasin Idweini * Chairperson of Urology Department
An analysis of the impact of previous laparoscopic hysterectomy experience on the learning curve for robotic hysterectomy
 J Robotic Surg (2013) 7:295 299 DOI 10.1007/s11701-012-0388-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE An analysis of the impact of previous laparoscopic hysterectomy experience on the learning curve for robotic hysterectomy
J Robotic Surg (2013) 7:295 299 DOI 10.1007/s11701-012-0388-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE An analysis of the impact of previous laparoscopic hysterectomy experience on the learning curve for robotic hysterectomy
Objectives: To analyze various factors predicting success of retrograde ureteric stenting in managing patients with ureteric obstruction.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 14 Number 1 Factors Predicting Success Rate Of Retrograde Ureteric Stenting In Managing Patients With Ureteric Obstruction- Our Experiences In A South Indian
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 14 Number 1 Factors Predicting Success Rate Of Retrograde Ureteric Stenting In Managing Patients With Ureteric Obstruction- Our Experiences In A South Indian
Robotic assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy for bladder carcinoma: early experience and oncologic outcomes
 Formosan Journal of Surgery (2012) 45, 178e182 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-fjs.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Robotic assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy for bladder carcinoma:
Formosan Journal of Surgery (2012) 45, 178e182 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-fjs.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Robotic assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy for bladder carcinoma:
Laparoscopic pyeloplasty with cephalad translocation of the crossing vessel a new approach to the Hellström technique
 Original paper Videosurgery Laparoscopic pyeloplasty with cephalad translocation of the crossing vessel a new approach to the Hellström technique Tomasz Szydelko 1, Wojciech Apoznanski 2, Piotr Koleda
Original paper Videosurgery Laparoscopic pyeloplasty with cephalad translocation of the crossing vessel a new approach to the Hellström technique Tomasz Szydelko 1, Wojciech Apoznanski 2, Piotr Koleda
Oncourology COMPLICATIONS OF PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY AT OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF RENAL CELL CARCINOMA
 1 Oncourology COMPLICATIONS OF PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY AT OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Address: Eduard Oleksandrovych Stakhovsky, 03022, Kyiv, Lomonosova Str., 33/43, National Cancer Institute
1 Oncourology COMPLICATIONS OF PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY AT OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Address: Eduard Oleksandrovych Stakhovsky, 03022, Kyiv, Lomonosova Str., 33/43, National Cancer Institute
Hydronephrosis. Nephrosis. Refers to the kidney
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
RAPN. in T1b Renal Masses? A. Mottrie. G. Denaeyer, P. Schatteman, G. Novara
 RAPN in T1b Renal Masses? A. Mottrie G. Denaeyer, P. Schatteman, G. Novara Department of Urology O.L.V. Clinic Aalst OLV Vattikuti Robotic Surgery Institute Aalst Belgium Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma
RAPN in T1b Renal Masses? A. Mottrie G. Denaeyer, P. Schatteman, G. Novara Department of Urology O.L.V. Clinic Aalst OLV Vattikuti Robotic Surgery Institute Aalst Belgium Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma
Morbidity Audit and Logbook Tool SNOMED Board Reporting Terms for SET and IMG Urology ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT
 ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Cook Europe Shared Service Centre
 www.cookmedical.com Cook Europe Shared Service Centre Country Telephone E-mail Austria (+43) 1-795-67-121 oeorders@cook.ie Belgium ench (+32) 27-00-16-33 beorders@cook.ie Belgium Flemish (+32) 27-00-16-33
www.cookmedical.com Cook Europe Shared Service Centre Country Telephone E-mail Austria (+43) 1-795-67-121 oeorders@cook.ie Belgium ench (+32) 27-00-16-33 beorders@cook.ie Belgium Flemish (+32) 27-00-16-33
G.Manzoni has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve.
 G.Manzoni has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. ANTENATAL HYRONEPHROSIS UROLOGICAL ASPECTS Dr Gianantonio Manzoni, FEAPU FRCS U.O.
G.Manzoni has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. ANTENATAL HYRONEPHROSIS UROLOGICAL ASPECTS Dr Gianantonio Manzoni, FEAPU FRCS U.O.
Robotics, Laparoscopy & Endosurgery
 Robotics, Laparoscopy and Endosurgery Robotics, Laparoscopy & Endosurgery How to preserve bladder neck during robotic radical prostatectomy? Abdullah Erdem Canda* Department of Urology, Yildirim Beyazit
Robotics, Laparoscopy and Endosurgery Robotics, Laparoscopy & Endosurgery How to preserve bladder neck during robotic radical prostatectomy? Abdullah Erdem Canda* Department of Urology, Yildirim Beyazit
Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts
 Title Page Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts Sabrina H Rossi 1, Brendan Koo 2, Antony Riddick 1, Nimish Shah 1, Grant D Stewart 1 1 Urology Department, Addenbrooke's
Title Page Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts Sabrina H Rossi 1, Brendan Koo 2, Antony Riddick 1, Nimish Shah 1, Grant D Stewart 1 1 Urology Department, Addenbrooke's
RESIDENT GOALS AND OBJECTIVES BY ROTATION U-1 U-1 (PGY-2,3) GOALS AND OBJECTIVES BY ROTATION
 RESIDENT GOALS AND OBJECTIVES BY ROTATION U-1 U-1 (PGY-2,3) GOALS AND OBJECTIVES BY ROTATION The following G&O s are representative of the unique experience gained at the individual institutions and represent
RESIDENT GOALS AND OBJECTIVES BY ROTATION U-1 U-1 (PGY-2,3) GOALS AND OBJECTIVES BY ROTATION The following G&O s are representative of the unique experience gained at the individual institutions and represent
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
West Yorkshire Major Trauma Network Clinical Guidelines 2015
 WYMTN: Pelvic fracture with urogenital trauma KEY RECOMMENDATIONS 1. During the initial exploratory survey / secondary survey, a. The external urethral meatus and the transurethral bladder catheter (if
WYMTN: Pelvic fracture with urogenital trauma KEY RECOMMENDATIONS 1. During the initial exploratory survey / secondary survey, a. The external urethral meatus and the transurethral bladder catheter (if
CURRICULUM VITAE. Michael E. Woods, M.D.
 CURRICULUM VITAE Michael E. Woods, M.D. Employment: University of North Carolina Chapel Hill-Associate Professor of Urology/Surgery, 7/2011- present University of North Carolina Chapel Hill-Clinical Research
CURRICULUM VITAE Michael E. Woods, M.D. Employment: University of North Carolina Chapel Hill-Associate Professor of Urology/Surgery, 7/2011- present University of North Carolina Chapel Hill-Clinical Research
Evolution of Robotic Radical Prostatectomy. BACKGROUND. Robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy (RAP) is the dominant
 1951 Evolution of Robotic Radical Prostatectomy Assessment After 2766 Procedures Ketan K. Badani, MD Sanjeev Kaul, MD Mani Menon, MD Vattikuti Urology Institute, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan.
1951 Evolution of Robotic Radical Prostatectomy Assessment After 2766 Procedures Ketan K. Badani, MD Sanjeev Kaul, MD Mani Menon, MD Vattikuti Urology Institute, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan.
Setting Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Cleveland Clinic Foundation (tertiary care academic centre), USA.
 Prospective randomized clinical trial of laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy versus total abdominal hysterectomy Falcone T, Paraiso M F, Mascha E Record Status This is a critical abstract of
Prospective randomized clinical trial of laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy versus total abdominal hysterectomy Falcone T, Paraiso M F, Mascha E Record Status This is a critical abstract of
UNM SRMC UROLOGY CLINICAL PRIVILEGES.
 o o o Initial privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of privileges (reappointment) Expansion of privileges (modification) INSTRUCTIONS All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved
o o o Initial privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of privileges (reappointment) Expansion of privileges (modification) INSTRUCTIONS All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved
Initial Series of Robotic Radical Nephrectomy with Vena Caval Tumor Thrombectomy
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011) 652 656 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Series of the Month Initial Series of Robotic Radical Nephrectomy with Vena Caval Tumor
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011) 652 656 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Series of the Month Initial Series of Robotic Radical Nephrectomy with Vena Caval Tumor
Uroradiology For Medical Students
 Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018
 Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018 Bladder Anatomy Ureter Anatomy Areas of Injury Bladder: Posterior bladder wall above trigone Ureter Crosses beneath uterine vessels At pelvic brim when ligating
Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018 Bladder Anatomy Ureter Anatomy Areas of Injury Bladder: Posterior bladder wall above trigone Ureter Crosses beneath uterine vessels At pelvic brim when ligating
RESIDENCY TRAINING PROGRAMME IN UROLOGY CERTIFICATION APPLICATION FORM PARTICIPATING INSTITUTE(S)
 Date application Name primary institute RESIDENCY TRAINING PROGRAMME IN UROLOGY CERTIFICATION APPLICATION FORM Name affiliated institute(s) Name Programme Director PARTICIPATING INSTITUTE(S) This form
Date application Name primary institute RESIDENCY TRAINING PROGRAMME IN UROLOGY CERTIFICATION APPLICATION FORM Name affiliated institute(s) Name Programme Director PARTICIPATING INSTITUTE(S) This form
Feasibility and Preliminary Clinical Outcomes of Robotic Laparoendoscopic Single-Site (R-LESS) Pyeloplasty Using a New Single-Port Platform
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 62 (2012) 175 179 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Series of the Month Feasibility and Preliminary Clinical Outcomes of Robotic Laparoendoscopic
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 62 (2012) 175 179 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Series of the Month Feasibility and Preliminary Clinical Outcomes of Robotic Laparoendoscopic
RADICAL CYSTECTOMY. Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery
 RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery The da Vinci Surgical System High-definition 3D vision EndoWrist instrumentation 3D HD Vision 3D HD visualization facilitates accurate
RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery The da Vinci Surgical System High-definition 3D vision EndoWrist instrumentation 3D HD Vision 3D HD visualization facilitates accurate
A Giant Hydronephrotic Kidney with Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction with Blunt Renal Trauma in a Boy
 A Giant Hydronephrotic Kidney with Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction with Blunt Renal Trauma in a Boy BY JUNYA TSURUKIRI, HIDEFUMI SANO, YOSUKE TANAKA, TAKAO SATO, HIROKAZU TAGUCHI Abstract An 18-year-old
A Giant Hydronephrotic Kidney with Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction with Blunt Renal Trauma in a Boy BY JUNYA TSURUKIRI, HIDEFUMI SANO, YOSUKE TANAKA, TAKAO SATO, HIROKAZU TAGUCHI Abstract An 18-year-old
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
Is renal cryoablation becoming an effective alternative to partial nephrectomy?
 Is renal cryoablation becoming an effective alternative to partial nephrectomy? J GARNON 1, G TSOUMAKIDOU 1, H LANG 2, A GANGI 1 1 department of interventional radiology 2 department of urology University
Is renal cryoablation becoming an effective alternative to partial nephrectomy? J GARNON 1, G TSOUMAKIDOU 1, H LANG 2, A GANGI 1 1 department of interventional radiology 2 department of urology University
The European Board of Urology
 Page 1 of 15 The European Board of Urology Sub-specialty certification application: Prostate cancer, A - General information A1 - APPLICATION IDENTIFICATION 1a. Application code blank 1b. EBU internal
Page 1 of 15 The European Board of Urology Sub-specialty certification application: Prostate cancer, A - General information A1 - APPLICATION IDENTIFICATION 1a. Application code blank 1b. EBU internal
Complications in robotic surgery!! Review of the literature! RALP, RAPN and RARC!
 Complications in robotic surgery Review of the literature RALP, RAPN and RARC Anna Wallerstedt, MD Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Agenda The importance of reporting surgical complications
Complications in robotic surgery Review of the literature RALP, RAPN and RARC Anna Wallerstedt, MD Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Agenda The importance of reporting surgical complications
Outcomes of Re-Intervention for Laparoscopic Transperitoneal Pyeloplasty in Children. Leung, L; Chan, HYI; Chung, HY; Lan, CLL; Wong, KKY; Tam, PKH
 Title Outcomes of Re-Intervention for Laparoscopic Transperitoneal Pyeloplasty in Children Author(s) Leung, L; Chan, HYI; Chung, HY; Lan, CLL; Wong, KKY; Tam, PKH Citation Journal of Laparoendoscopic &
Title Outcomes of Re-Intervention for Laparoscopic Transperitoneal Pyeloplasty in Children Author(s) Leung, L; Chan, HYI; Chung, HY; Lan, CLL; Wong, KKY; Tam, PKH Citation Journal of Laparoendoscopic &
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY
 RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
Identifying unrecognized collecting system entry and the integrity of repair during open partial nephrectomy: comparison of two techniques
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 40 (5): 637-643, September - October, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.05.08 Identifying unrecognized collecting system entry and the integrity of repair during open partial
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 40 (5): 637-643, September - October, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.05.08 Identifying unrecognized collecting system entry and the integrity of repair during open partial
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet
 Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
Switching from Endoscopic Extraperitoneal Radical Prostatectomy to Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: Comparing Outcomes and Complications
 Urologia Internationalis Original Paper Urol Int 2015;95:380 385 Received: November 24, 2014 Accepted after revision: January 28, 2015 Published online: March 27, 2015 Switching from Endoscopic Extraperitoneal
Urologia Internationalis Original Paper Urol Int 2015;95:380 385 Received: November 24, 2014 Accepted after revision: January 28, 2015 Published online: March 27, 2015 Switching from Endoscopic Extraperitoneal
Long-Term Complications of Conduit Urinary Diversion
 Long-Term Complications of Conduit Urinary Diversion Mark S. Shimko,* Matthew K. Tollefson, Eric C. Umbreit, Sara A. Farmer, Michael L. Blute and Igor Frank From the Department of Urology (MSS, MKT, ECU,
Long-Term Complications of Conduit Urinary Diversion Mark S. Shimko,* Matthew K. Tollefson, Eric C. Umbreit, Sara A. Farmer, Michael L. Blute and Igor Frank From the Department of Urology (MSS, MKT, ECU,
Multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy combined with EMS lithotripsy for bilateral complex renal stones: our experience
 Liang et al. BMC Urology (2017) 17:15 DOI 10.1186/s12894-017-0205-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy combined with EMS lithotripsy for bilateral complex renal stones:
Liang et al. BMC Urology (2017) 17:15 DOI 10.1186/s12894-017-0205-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy combined with EMS lithotripsy for bilateral complex renal stones:
Comparative Analysis Research of Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy
 Comparative Analysis Research of Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy By: Jonathan Barlaan; Huy Nguyen Mentor: Julio Powsang, MD Reader: Richard Wilder, MD May 2, 211 Abstract Introduction: The
Comparative Analysis Research of Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy By: Jonathan Barlaan; Huy Nguyen Mentor: Julio Powsang, MD Reader: Richard Wilder, MD May 2, 211 Abstract Introduction: The
Hydronephrosis after retroperitoneal laparoscopic. dismembered Anderson Hynes pyeloplasty in adult patients with ureteropelvic junction obstruction.
 101 original paper TRAUMA AND RECONSTRUCTIVE UROLOGY Hydronephrosis after retroperitoneal laparoscopic dismembered Anderson Hynes pyeloplasty in adult patients with ureteropelvic junction obstruction:
101 original paper TRAUMA AND RECONSTRUCTIVE UROLOGY Hydronephrosis after retroperitoneal laparoscopic dismembered Anderson Hynes pyeloplasty in adult patients with ureteropelvic junction obstruction:
FIG The inferior and posterior peritoneal reflection is easily
 PSOAS HITCH, BOARI FLAP, AND COMBINATION OF PSOAS 7 HITCH AND BOARI FLAP The psoas hitch procedure, Boari flap, and transureteroureterostomy are useful operative procedures for reestablishing continuity
PSOAS HITCH, BOARI FLAP, AND COMBINATION OF PSOAS 7 HITCH AND BOARI FLAP The psoas hitch procedure, Boari flap, and transureteroureterostomy are useful operative procedures for reestablishing continuity
Salvage Dextranomer-Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer for Persistent Reflux After Ureteral Reimplantation: Early Success Rates
 Vesicoureteral Reflux Salvage Dextranomer-Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer for Persistent Reflux After Ureteral Reimplantation: Early Success Rates Yuval Bar-Yosef,* Miguel Castellan, Devandra Joshi, Andrew Labbie
Vesicoureteral Reflux Salvage Dextranomer-Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer for Persistent Reflux After Ureteral Reimplantation: Early Success Rates Yuval Bar-Yosef,* Miguel Castellan, Devandra Joshi, Andrew Labbie
