Botulinum Toxin A (Botox) for Treatment of Proximal Myofascial Pain in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Two Cases
|
|
|
- Beverly Waters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Botulinum Toxin A (Botox) for Treatment of Proximal Myofascial Pain in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Two Cases Delaram Safarpour, MD, Bahman Jabbari, MD
2 Pain Medicine 2010; 11: Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Case Report Botulinum Toxin A (Botox) for Treatment of Proximal Myofascial Pain in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Two Casespme_ Delaram Safarpour, MD, and Bahman Jabbari, MD Department of Neurology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, USA Reprint requests to: Delaram Safarpour MD, 40 Temple Street, 6C Neurology clinic, New Haven, CT 06510, USA. Tel: ; Fax: ; delaram.safarpour@yale.edu2. Disclosures: Dr Delaram Safarpour reports no disclosures. Dr Bahman Jabbari receives educational and research grants and serves in the advisory board of Allergen Inc. Abstract Objectives. To describe development of myofascial pain syndrome (MFPS) with trigger points in the proximal muscles of the patients with complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS1) and improvement of distal symptoms of CRPS 1 after successful treatment of proximal MFPS. Setting and Design. In our practice, we frequently encounter patients in whom a proximal myofascial pain syndrome develops ipsilateral to the distal limb of CRPS1 patients. We describe two such patients in detail with their treatment. Patient 1. A 48-year-old woman experienced severe allodynia, swelling and autonomic changes in the right hand after surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome. Over the succeeding months, she developed painful trigger points in the right trapezius and upper back muscles which was treated with administration of botulinum toxin A (BoNT-A) into the trigger points (20 unit/point). Patient 2. A 41-year-old woman following a traumatic forearm injury suffered from CRPS1 affecting the left hand and forearm. Proximal MFPS gradually developed on the same side over 12 months and was treated with administration of BoNT-A into the trapezius, splenius capitis, and rhomboid muscle trigger points. Results. In both patients treatment with BoNT-A improved the proximal pain of MFPS and the distal symptoms of CRPS1. Conclusion. proximal MFPS develops ipsilateral to the distal painful limb in patients with CRPS1. Administration of BoNT-A into the affected proximal muscles may alleviate both MFPS and the distal allodynia, discoloration and, tissue swelling of CRPS. Key Words. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS); Botulinum toxin type A; BoNT-A; Myofascial pain syndrome; Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD) Introduction Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CPRS) is characterized by chronic and relapsing burning pain, edema, temperature asymmetry, abnormal skin perfusion and excessive sweating in an injured limb. Chronicity and frequent relapses in the course of CRPS often lead to disability [1]. The more common of the two CRPS variants, type 1 (reflex sympathetic dystrophy) has a prevalence of 21/100,000 and more often affects females (ratio 2:1 to 4:1) [2]. Myofascial pain syndrome (MFPS) is characterized by the presence of trigger points, palpable muscle abnormality (fibrocystic nodule) and referred pain distal to the trigger point. It is a common dysfunction with lifetime prevalence of up to 85% in general population [3]. Most of the treatment methods for MFPS are aimed to reduce the pain in trigger points and reduce the muscle spasm. Two previous publications described the association between CRPS1 and development of MFPS in the proximal muscles without detail description of the patients. In a retrospective chart review of 41 consecutive patients with CRPS1, Rashiq et al. described proximal myofascial dysfunction (MD) in 61% of the patients [4]. Their criteria for myofascial dysfunction are identical to what is currently accepted for MFPS. Upper limbs and lower limbs were affected in 70% and 46% of the patients, respectively. The authors recommended careful examination of proximal 1415
3 Safarpour and Jabbari muscles in all patients with CRPS4. Proximal muscle treatment in some patients improved the outcome of CRPS [5]. More recently, in a review paper, Argoff briefly described 11 patients with CRPS1 and proximal MFPS in whom intramuscular injection of botulium toxin type A (BoNT-A) (deltoid, trapezius, splenius, rhomboid, suprand infraspiniti) relieved myofascial pain and revered distal symptoms (pain, swelling, tissue discoloration) of CRPS1. He used units/muscle with a total dose of 300 units. Patients continued the treatment with consistent relief of their symptoms for approximately 4 years [5]. In our practice, we frequently encounter patients in whom a proximal myofascial pain syndrome develops ipsilateral to the distal limb of CRPS1 patients. In this communication, we present two of these patients in details. Case Reports Patient 1 A 48-year-old, right handed woman was referred to the clinic for the evaluation of pain in the right upper limb for 4 years. Pain and swelling of the right hand began shortly after a second carpal tunnel surgery of that hand. It gradually worsened, spread to the forearm and shoulder, with wrist, and hand and fingers assuming a dystonic flexed posture. Examination and Findings 1. Marked skin hypersensitivity at the right wrist and the lateral aspect of the lower right forearm. Touching this area caused intense burning pain (allodynia). 2. Annoying deep pain affecting the whole right upper limb. 3. Significant right neck and shoulder pain with many tender and trigger points over left trapezius and upper back muscles (developed gradually, months after development of allodynia on the same side). 4. Intermittent painful flexor spasms of the three middle fingers of the right hand. There was also intermittent discoloration and coldness of the right hand and forearm in examination. She had failed a number of medications including nonsteroidal analgesics and narcotics (e.g., Percocet), Lidoderm and Flector patches, steroid injections and nerve block (partial relief). She rated her average pain as 8 and worst pain as 10 on a pain scale of 1 10 (visual analog scale [VAS]) [6]. Treatment BoNT-A was prepared by reconstituting vacuum-dried toxin with preservative free 0.9% saline to 50 units/ml concentrations. The following muscles were injected into the trigger points on the right side: Right trapezius: 60 units, rhomboid 60 units, levator scapulae 40 units and right flexor digitrum superfecialis: 40 units. Each trigger point was injected with 20 units of the neurotoxin. Treatment Response and Outcome After a week, she reported 90% reduction of her neck and upper back pain, 60 70% reduction of her right arm pain and 80% reduction in right finger flexion spasms. She noted marked improvement in her quality of life and considered her response very satisfactory (on the scale of: worsened, neutral, mildly satisfactory and very satisfactory). She was able to swim again, move her head to the sides without pain, and enjoy her social life. Following treatment, she rated her pain intensity as a 2 (out of 10) on the VAS. Three years later, she reported continuous relief of MFPS with quarterly BoNT-A treatments. Painful finger flexions disappeared after the third treatment. Examination of the affected hand showed less swelling and marked improvement of allodynia and discoloration. Patient 2 A 41-year-old female suffered from severe pain in the left hand and forearm after her hand got stuck in a closing door of a bus. The hand gradually became swollen, changed color and the finger movements became weak and painful. Over the next 2 years, she developed pain in the left shoulder, base of the neck and periscapular region. She tried a large number of medications including nonsteroidal analgesics, baclofen, Neurontin, and oxycodone but none offered satisfactory relief. MRI studies of the neck and both shoulders disclosed no significant abnormality. Examination and Findings 1. The left hand was swollen, with marked allodynia over the dorsum of the hand and wrist. 2. The affected hand was cooler than the other side and the skin had a bluish/white color. 3. All finger movements were limited due to pain and swelling. 4. There were several tender areas and trigger points over the left trapezius, left side of the neck and upper rhomboid muscles. In pressing these points a tight muscle band was felt under the finger and the pain referred to distant areas from the pressure point. Treatment BoNT-A was injected into the trigger points of trapezius, splenius capitis and rhomboid muscles. The numbers of injected trigger points were 4, 3, and 5 for the aforementioned muscles, respectively. Each trigger point was injected with 20 units. At 1 month, patient reported her level of satisfaction as very satisfactory. Treatment Response and Outcome Following treatment, level of pain reduced from 9 to 4 (out of 10) on the VAS. After second treatment, daily activities were improved (e.g., driving, doing laundry). She reported 1416
4 no side effect from treatment and was able to reduce the dose of her pain medications gradually. An examination 18 months after initiating neurotoxin therapy, no longer showed any trigger points in the rhomboid region. The overall pain score for the proximal muscles was 3 (out of 10) on the VAS. The left fingers were no longer clinched and had near normal movements. The hand swelling reduced considerably. The skin color came back with near normal temperature. The area of allodynia shrunk to 1/3 of its size with the remaining area still scoring 9 out of 10 on the VAS (significant pain). Discussion Occurrence of trigger points in reflex sympathetic dystrophy (CPRS1) has been reported in 1946 in 59% of 32 patients with RSD[7]. The distribution of trigger points was not mentioned in this communication. Our patients had distinct MFPS with trigger points in the proximal muscles ipsilateral to the distal CRPS1 symptoms. Two other reports in the past described this association [4,5] without individual patient descriptions. Treatments of MFPS consist of physical therapy, oral medications and trigger point injections. Some of the most commonly used oral medications are: nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, tricyclic antidepressants, muscle spasmolytics, opioid analgesics, neuropathic analgesics and antidepressants. Among non-needling therapies, mechanical pressure to the trigger points or stretching of the affected muscle are also used [8]. Needling treatments include injection of local anesthetics, corticosteroids, neurolytic agents and botulinum toxins into the trigger points [9 11]. Few reports provide adequately controlled clinical comparisons between these injectable treatments for MFPS. Three studies have compared the therapeutic effects of dry needling into trigger points with anesthetic agents: Procaine, Lidocaine [12,13] and Lidocaine plus steroid, acupuncture, and vapocoolant spray with acupressure [14]. These studies showed no difference between dry needling and lidocaine/procaine injection treatment and suggest that improvement was the result of needle s mechanical effect. In one study however, dry needling cause significantly more post-injection soreness compared to lidocaine/procaine injection (100% vs 40%) [14]. Other studies have compared the effect of anesthetics (lidocaine) vs BoNT-A injection [15,16]. They show that injection in trigger points with either of the two gives the same amount of pain relief. Considering the cost of BoNT-A, authors recommended using anesthetics as the first line of treatment. In one of these two studies botulinum toxin and anesthetics were also compared with dry needling. In this particular study BoNT-A and lidocain were superior to dry needling in terms of reducing the pain scores (VAS) and improving the quality of life [16]. Porta et al. compared the effect of methyl prednisolone with botulinum toxin type A injected into trigger point of 40 PMPS in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome patients with MFPS [17]. The reduction in pain score at 30 days compared to baseline was greater with botulinum toxin A than methyl prednisolone (P = 0.06). Furthermore pain reduction at 60 days was greater than 30 days for BoNT-A (-5.5 vs -3.9) whereas the effect of methyl prednisolone had begun to wane. Double-blind studies of sizeable number of patients comparing BoNT-A with placebo in MFPS however, produced contradictory results [10,11,18,19] with efficacy depicted in the studies that provided higher number of trigger point injections (>10) [11,19]. In conclusion, our observation indicates that a proximal MFPS can develop in patients with CRPS1 ipsilateral to the distal painful limb. Successful treatment of this proximal MFPS may improve, over time, pain and swelling of the distal part of the limb in CRPS1. Our patients responded well to BoNT-A treatment. A prospective study is needed to discern the incidence of proximal MFPS in CRPS1 and the role of BoNTs as an effective therapeutic agent. References 1 Tran De QH, Duong S, Bertini P, Finlayson RJ. Treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: A review of reference. Can J Anesth 2010;57: Borenstein DG, Wiesel SW, Boden SD. Neurologica and psychiatric disorders of the spine. In: Borenstein DG, Wiesel SW, Boden SD, eds. Low Back and Neck Pain, Comprehensive Diagnosis and Management. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2004: Fleckenstein J, Zaps D, Ruger LJ, et al. Discrepency between prevalence and perceived effectiveness of treatment methods in myofascial pain syndrome: Results of a cross-sectional, nationwide survey. 2010;11: Rashiq S, Galer BS. Proximal myofascial dysfunction in complex regional pain syndrome: A retrospective prevalence study. Clin J Pain 1999;15: Argoff CE. A focused review on the use of botulinum toxins for neuropathic pain. Clin J Pain 2002;18:s Scott J, Huskisson EC. Graphic representation of pain. Pain 1976;2: Evans JA. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1946;82: Cummings M, Baldry P. Regional myofascial pain: Diagnosis and management. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2007;21: Wheeler AH. Myofascial pain disorders: Theory to therapy. Drugs 2004;64:
5 Safarpour and Jabbari 10 Ferrante FM, Bearn L, Rothrock R, King L. Evidence against trigger point injection technique for the treatment of cervicothoracic myofascial pain with botulinum toxin type A. Anesthesiology 2005;103: Gobel H, Heinze A, Reichel G, Hefter H, Benecke R. Efficacy and safety of a single botulinum type A toxin complex treatment (Dysport) for the relief of upper back myofascial pain syndrome: Results from a randomized double-blind placebo- controlled multicenter study. Pain 2006;125: McMillan AS, Nolan A, Kelly PJ. The efficacy of dry needling and procaine in the treatment of myofascial pain in the jaw muscles. J Orofac Pain 1997;11: Hong CZ. Lidocaine injection vs dry needling to myofascial trigger point. The importance of the local twitch response. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 1994;73: Garvey TA, Marks MR, Wiesel SW. A prospective, randomized, double-blind evaluation of trigger point injection therapy for low-back pain. Spine 1989;14: Graboski CL, Gray DS, Burnham RS. Botulinum toxin A vs bupivacaine trigger point injections for the treatment of myofascial pain syndrome: A randomized double blind crossover study. Pain 2005;118: Kamanli A, Kaya A, Ardicoglu O, Ozgocmen S, Zengin FO, Bayik Y. Comparison of lidocaine injection, botulinum toxin injection, and dry needling to trigger points in myofascial pain syndrome. Reumatol Int 2005; 25: Porta M. A comparative trial of botulinum toxin type A and methylprednisolone for the treatment of myofascial pain syndrome and pain from chronic muscle spasm. Pain 2000;85: Ojala T, Arokoski JP, Partanen J. The effect of small doses of botulinum toxin A on neck-shoulder myofascial pain syndrome. A double-blind, randomized, and controlled crossover trial. Clin J Pain 2006;22: Miller D, Richardson D, Eisa M, Baiwa RJ, Jabbari B. Botulinum neurotoxin-a for treatment of refractory neck pain: A randomized, double-blind study. Pain Med 2009;10:
AS THE LEADING CAUSE of job-related disability and
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Therapeutic Use of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Treating Neck and Upper-Back Pain of Myofascial Origin: A Pilot Study Henry L. Lew, MD, PhD, Eun Ha Lee, MD, PhD, Annabel Castaneda, MD, MPH,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Therapeutic Use of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Treating Neck and Upper-Back Pain of Myofascial Origin: A Pilot Study Henry L. Lew, MD, PhD, Eun Ha Lee, MD, PhD, Annabel Castaneda, MD, MPH,
SPINE SECTION. *University of Rostock, Department of Neurology, Rostock, Germany;
 Pain Medicine 2011; 12: 1607 1614 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. SPINE SECTION Original Research Articles Botulinum Type A Toxin Complex for the Relief of Upper Back Myofascial Pain Syndrome: How Do Fixed-Location
Pain Medicine 2011; 12: 1607 1614 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. SPINE SECTION Original Research Articles Botulinum Type A Toxin Complex for the Relief of Upper Back Myofascial Pain Syndrome: How Do Fixed-Location
BOTULINUM TOXIN THERAPY FOR CERVICOGENIC HEADACHE AND NECK PAIN
 BOTULINUM TOXIN THERAPY FOR CERVICOGENIC HEADACHE AND NECK PAIN Dr. Laxman Bahroo Director; Botulinum Toxin Clinic Director; Neurology Residency Program Associate Professor of Neurology Objectives Discuss
BOTULINUM TOXIN THERAPY FOR CERVICOGENIC HEADACHE AND NECK PAIN Dr. Laxman Bahroo Director; Botulinum Toxin Clinic Director; Neurology Residency Program Associate Professor of Neurology Objectives Discuss
Limb Pain (Tendonitis, Osteoarthritis, Plantar Fasciitis, Piriformis Syndrome)
 Limb Pain (Tendonitis, Osteoarthritis, Plantar Fasciitis, Piriformis Syndrome) Martin Taylor, DO, PhD Neurology / OrthoNeuro Clinical Associate Professor, Neurology Ohio University College of Osteopathic
Limb Pain (Tendonitis, Osteoarthritis, Plantar Fasciitis, Piriformis Syndrome) Martin Taylor, DO, PhD Neurology / OrthoNeuro Clinical Associate Professor, Neurology Ohio University College of Osteopathic
Myofascial Pain Syndrome and Trigger Points. Paul S. Sullivan, Do Trinity Health Care New England - Family Medicine
 Myofascial Pain Syndrome and Trigger Points Paul S. Sullivan, Do Trinity Health Care New England - Family Medicine Objectives Discuss why this topic is pertinent to our practices Review diagnostic criteria
Myofascial Pain Syndrome and Trigger Points Paul S. Sullivan, Do Trinity Health Care New England - Family Medicine Objectives Discuss why this topic is pertinent to our practices Review diagnostic criteria
Complex regional pain syndrome
 Complex regional pain syndrome What is complex regional pain syndrome? Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a chronic pain condition most often affecting one of the limbs (arms, legs, hands, or feet),
Complex regional pain syndrome What is complex regional pain syndrome? Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a chronic pain condition most often affecting one of the limbs (arms, legs, hands, or feet),
Introduction. What is RSD? Causes of RSD. What Makes Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy So Complicated?
 What Makes Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy So Complicated? Article originally appeared in inmotion Magazine: Volume 14 Issue 5 September/October 2004 Introduction Because this condition is so complex, the
What Makes Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy So Complicated? Article originally appeared in inmotion Magazine: Volume 14 Issue 5 September/October 2004 Introduction Because this condition is so complex, the
IAPMR Guidelines COMPLEX REGIONAL PAIN SYNDROME
 IAPMR Guidelines COMPLEX REGIONAL PAIN SYNDROME DR.NAVITA PUROHIT, CONSULTANT AND EXPERT IN PAIN MANAGEMENT, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital, Mumbai CRPS is a
IAPMR Guidelines COMPLEX REGIONAL PAIN SYNDROME DR.NAVITA PUROHIT, CONSULTANT AND EXPERT IN PAIN MANAGEMENT, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital, Mumbai CRPS is a
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER:
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER:
Upper Cross Syndrome: Assessment & Management in Family Practice HKDU Symposium Dec 2014
 Upper Cross Syndrome: Assessment & Management in Family Practice HKDU Symposium Dec 2014 Dr. Ngai Ho Yin Allen Family Medicine Specialist PGDipMusculoskeletal Medicine MBBS(HK), DCH(London), DFM(CUHK),
Upper Cross Syndrome: Assessment & Management in Family Practice HKDU Symposium Dec 2014 Dr. Ngai Ho Yin Allen Family Medicine Specialist PGDipMusculoskeletal Medicine MBBS(HK), DCH(London), DFM(CUHK),
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetaminophen in chronic pain management, 225 Acupuncture in chronic pain management, 251, 338 339 Ajurvedic medicine in chronic pain management,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetaminophen in chronic pain management, 225 Acupuncture in chronic pain management, 251, 338 339 Ajurvedic medicine in chronic pain management,
Botulinum toxin A for myofascial trigger point injection: A qualitative systematic review
 European Journal of Pain 11 (2007) 519 527 Review Botulinum toxin A for myofascial trigger point injection: A qualitative systematic review Kok-Yuen Ho *, Kian-Hian Tan Pain Management Services, Department
European Journal of Pain 11 (2007) 519 527 Review Botulinum toxin A for myofascial trigger point injection: A qualitative systematic review Kok-Yuen Ho *, Kian-Hian Tan Pain Management Services, Department
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome 950 Breckinridge Lane Suite 220 Louisville, KY 40223 Phone: 502.708.2940 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome 950 Breckinridge Lane Suite 220 Louisville, KY 40223 Phone: 502.708.2940 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM
 TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM OBJECTIVES Understand how we interact with technology new and old Understand how injury occurs Texting
TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM OBJECTIVES Understand how we interact with technology new and old Understand how injury occurs Texting
Providing Options for Pain Management
 Providing Options for Pain Management Nancy Bradley, BSN, RN-BC I am not experienced in giving lectures, nor do I profess to be an expert in Pain Management I have over 20 years experience in Oncology,
Providing Options for Pain Management Nancy Bradley, BSN, RN-BC I am not experienced in giving lectures, nor do I profess to be an expert in Pain Management I have over 20 years experience in Oncology,
Myofascial Pain Syndrome Diagnosis and Treatment.
 Myofascial Pain Syndrome Diagnosis and Treatment www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Myofascial Pain Syndrome A clinical syndrome caused by myofascial trigger points (MTrPs) Definition of Myofascial Trigger Point
Myofascial Pain Syndrome Diagnosis and Treatment www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Myofascial Pain Syndrome A clinical syndrome caused by myofascial trigger points (MTrPs) Definition of Myofascial Trigger Point
8/26/2014. Faculty/Presenter Disclosure. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS): State of the Art review. Disclosure of Commercial Support
 Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS): State of the Art review Angela Mailis Gagnon MD, MSc, FRCPC(PhysMed) Director, Comprehensive Pain Program/UHN and Senior Investigator
Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS): State of the Art review Angela Mailis Gagnon MD, MSc, FRCPC(PhysMed) Director, Comprehensive Pain Program/UHN and Senior Investigator
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
Discussion Questions WHAT ARE SOME POSSIBLE CAUSES OF HER PAIN? WHAT ELSE WOULD YOU LIKE TO KNOW
 CLINICAL CASES Case: Ms. FM Case: Ms. FM Ms. FM is a 37-year-old school teacher Under your care for 10 years Unremarkable past history Was in minor car accident 4 months ago Has had progressive generalized
CLINICAL CASES Case: Ms. FM Case: Ms. FM Ms. FM is a 37-year-old school teacher Under your care for 10 years Unremarkable past history Was in minor car accident 4 months ago Has had progressive generalized
Myofascial Pain Massage Trigger point injection Heat, cold, acupuncture, relaxation training, and biofeedback Treatments. Pain medicines Exercise
 Myofascial Pain Myo is a Greek word for muscle. Fascia is the tough outer lining of a muscle that holds it in place. Myofascial pain is the term used to describe pain in the muscles and fascia. Myofascial
Myofascial Pain Myo is a Greek word for muscle. Fascia is the tough outer lining of a muscle that holds it in place. Myofascial pain is the term used to describe pain in the muscles and fascia. Myofascial
Pain Differential Diagnosis - Enrico Dellacà M.D Ph.D. Abductor pollicis brevis muscle Myofascial Pain Syndrome
 Overview Abductor pollicis brevis muscle Myofascial Pain Syndrome Definition Pain Differential Diagnosis - Enrico Dellacà M.D Ph.D. The Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is a syndrome characterized by chronic
Overview Abductor pollicis brevis muscle Myofascial Pain Syndrome Definition Pain Differential Diagnosis - Enrico Dellacà M.D Ph.D. The Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is a syndrome characterized by chronic
Clinical Policy: Trigger Point Injections for Pain Management
 Clinical Policy: for Pain Management Reference Number: CP.MP.169 Last Review Date: 08/18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications
Clinical Policy: for Pain Management Reference Number: CP.MP.169 Last Review Date: 08/18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications
The muscular system is like a giant pulley system.
 The muscular system is like a giant pulley system. Muscles work with and against each other in order for you to do all the things you do. Muscle Premium takes a dive into the human muscular system with
The muscular system is like a giant pulley system. Muscles work with and against each other in order for you to do all the things you do. Muscle Premium takes a dive into the human muscular system with
Symptoms and Referred Pain from Myofascial Trigger Points in the Anterior Scalene Muscle or Scalenus Anterior
 Symptoms and Referred Pain from Myofascial Trigger Points in the Anterior Scalene Muscle or Scalenus Anterior picture Symptoms and signs Aching or throbbing in the lateral forearm extending to thumb and
Symptoms and Referred Pain from Myofascial Trigger Points in the Anterior Scalene Muscle or Scalenus Anterior picture Symptoms and signs Aching or throbbing in the lateral forearm extending to thumb and
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Pain that won t go away. Artee Gandhi MD Medical Director Pain Management Cook Children s Hospital. What is Pain?
 Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Pain that won t go away Artee Gandhi MD Medical Director Pain Management Cook Children s Hospital What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory experience associated with real or perceived
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Pain that won t go away Artee Gandhi MD Medical Director Pain Management Cook Children s Hospital What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory experience associated with real or perceived
The importance of postural habits in perpetuating myofascial trigger point pain
 The importance of postural habits in perpetuating myofascial trigger point pain Janet Edwards Summary Various structural abnormalities that contribute to the perpetuation of myofascial trigger point activity
The importance of postural habits in perpetuating myofascial trigger point pain Janet Edwards Summary Various structural abnormalities that contribute to the perpetuation of myofascial trigger point activity
The importance of postural habits in perpetuating myofascial trigger point pain
 Introduction Pain arising from the activity of myofascial trigger points (MTrP) is extremely common. 1 When a MTrP becomes active, usually as a result of trauma or postural overload of a muscle, a small
Introduction Pain arising from the activity of myofascial trigger points (MTrP) is extremely common. 1 When a MTrP becomes active, usually as a result of trauma or postural overload of a muscle, a small
PART IV: NEUROPATHIC PAIN SYNDROMES JILL SINDT FEBRUARY 7, 2019
 PART IV: NEUROPATHIC PAIN SYNDROMES JILL SINDT FEBRUARY 7, 2019 NEUROPATHIC PAIN PAIN ARISING AS DIRECT CONSEQUENCE OF A LESION OR DISEASE AFFECTING THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM AFFECTS 3-8% OF POPULATION
PART IV: NEUROPATHIC PAIN SYNDROMES JILL SINDT FEBRUARY 7, 2019 NEUROPATHIC PAIN PAIN ARISING AS DIRECT CONSEQUENCE OF A LESION OR DISEASE AFFECTING THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM AFFECTS 3-8% OF POPULATION
Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain trigger point injections
 Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain trigger point injections Clinical Policy Number: 03.03.05 Effective Date: September 1, 2013 Initial Review Date: December 10, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: February 15,
Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain trigger point injections Clinical Policy Number: 03.03.05 Effective Date: September 1, 2013 Initial Review Date: December 10, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: February 15,
10/1/2009. October 15, 2009 Christina Kuo MD. Anatomy and pathophysiology of Epicondylitis Diagnosis
 October 15, 2009 Christina Kuo MD Anatomy and pathophysiology of Epicondylitis Diagnosis Treatment options Lawn tennis elbow Morris 1882 - described as an injury occurring from the backhand stroke Age
October 15, 2009 Christina Kuo MD Anatomy and pathophysiology of Epicondylitis Diagnosis Treatment options Lawn tennis elbow Morris 1882 - described as an injury occurring from the backhand stroke Age
Pain Syndromes after stroke
 Diagnosis and Management of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) after Stroke Leonard S.W. Li Honorary Clinical Professor, Department of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong Director, Neurological Rehabilitation
Diagnosis and Management of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) after Stroke Leonard S.W. Li Honorary Clinical Professor, Department of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong Director, Neurological Rehabilitation
Differentialdianosis to CRPS Departmentdoctor Bo Biering-Sørensen, Pain Clinic, Neurological Department
 Differentialdianosis to CRPS Departmentdoctor Bo Biering-Sørensen, Pain Clinic, Neurological Department Dato (Sidehoved/fod) Case 1 36 year old man other ethnically background than Danish 2006 Left foot
Differentialdianosis to CRPS Departmentdoctor Bo Biering-Sørensen, Pain Clinic, Neurological Department Dato (Sidehoved/fod) Case 1 36 year old man other ethnically background than Danish 2006 Left foot
Trigger Point Injection. Objectives. What is a Trigger Point (TrP)? 3/19/2019
 Trigger Point Injection Brian Shian, MD, FHM Department of Family Medicine University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Objectives Discuss the definition and diagnosis criterial Explore possible pathophysiology
Trigger Point Injection Brian Shian, MD, FHM Department of Family Medicine University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Objectives Discuss the definition and diagnosis criterial Explore possible pathophysiology
KELLEY JOY, DO CLINICAL ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OSTEOPATHIC MANIPULATIVE MEDICINE KCU JOPLIN CAMPUS
 STILL TECHNIQUE FOR COMMON COUNTERSTRAIN TENDER POINTS KELLEY JOY, DO CLINICAL ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OSTEOPATHIC MANIPULATIVE MEDICINE KCU JOPLIN CAMPUS COUNTERSTRAIN HISTORY Lawrence Larry Jones, DO 1955
STILL TECHNIQUE FOR COMMON COUNTERSTRAIN TENDER POINTS KELLEY JOY, DO CLINICAL ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OSTEOPATHIC MANIPULATIVE MEDICINE KCU JOPLIN CAMPUS COUNTERSTRAIN HISTORY Lawrence Larry Jones, DO 1955
Pain after Spinal Cord Injury
 Pain after Spinal Cord Injury Authors: SCIRE Community Team Reviewed by: Patricia Mills, MHSc, MD, FRCPC Last updated: Oct 18, 2017 This page provides information about pain and outlines common treatments
Pain after Spinal Cord Injury Authors: SCIRE Community Team Reviewed by: Patricia Mills, MHSc, MD, FRCPC Last updated: Oct 18, 2017 This page provides information about pain and outlines common treatments
COMPOUNDING PHARMACY SOLUTIONS PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING FOR PAIN MANAGEMENT
 JUNE 2012 COMPOUNDING PHARMACY SOLUTIONS PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING WWW.CPSRXS. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Acute Pain 2 Neuropathic
JUNE 2012 COMPOUNDING PHARMACY SOLUTIONS PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING WWW.CPSRXS. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Acute Pain 2 Neuropathic
Myofascial Pain Patterns for Head and Neck Disorders. Sajid A. Surve, D.O. UMDNJ School of Osteopathic Medicine NeuroMusculoskeletal Institute
 for Head and Neck Disorders Sajid A., D.O. UMDNJ School of Osteopathic Medicine NeuroMusculoskeletal Institute 2 Learning Objectives By the end of this presentation, participants will be able to: Correctly
for Head and Neck Disorders Sajid A., D.O. UMDNJ School of Osteopathic Medicine NeuroMusculoskeletal Institute 2 Learning Objectives By the end of this presentation, participants will be able to: Correctly
Journal of Anesthesia & Pain Medicine
 Case Report To spasm, or Not to Spasm, That is the Question Journal of Anesthesia & Pain Medicine John C McDonald BA 1 and Terence K Gray DO 1,2* 1 Mercy Pain Center, Mercy Hospital, Portland, Maine, USA
Case Report To spasm, or Not to Spasm, That is the Question Journal of Anesthesia & Pain Medicine John C McDonald BA 1 and Terence K Gray DO 1,2* 1 Mercy Pain Center, Mercy Hospital, Portland, Maine, USA
Ultrasound-Guided Trigger Point Injections in the Cervicothoracic Musculature: A New and Unreported Technique
 Pain Physician 2008; 11:885-889 ISSN 1533-3159 Technical Report Ultrasound-Guided Trigger Point Injections in the Cervicothoracic Musculature: A New and Unreported Technique Kenneth P. Botwin, MD 1, Kavita
Pain Physician 2008; 11:885-889 ISSN 1533-3159 Technical Report Ultrasound-Guided Trigger Point Injections in the Cervicothoracic Musculature: A New and Unreported Technique Kenneth P. Botwin, MD 1, Kavita
Trigger Point Injections TRIGGER POINT INJECTIONS HS-184. Policy Number: HS-184. Original Effective Date: 7/1/2010
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Strain-Counterstrain. Harmon Myers, DO and Julie Jernberg, MD
 Strain-Counterstrain Harmon Myers, DO and Julie Jernberg, MD Origin of Counterstrain Lawrence Jones, DO Original Patient: 4 Months of lower back pain, sleep deprivation and high velocity therapy Jones
Strain-Counterstrain Harmon Myers, DO and Julie Jernberg, MD Origin of Counterstrain Lawrence Jones, DO Original Patient: 4 Months of lower back pain, sleep deprivation and high velocity therapy Jones
NOT DESIGNATED FOR PUBLICATION
 NOT DESIGNATED FOR PUBLICATION BEFORE THE ARKANSAS WORKERS' COMPENSATION COMMISSION CLAIM NO. E907058 HATTIE M. MALONE, EMPLOYEE TRIDENT AUTOMOTIVE, EMPLOYER TRAVELERS PROPERTY & CASUALTY, INSURANCE CARRIER
NOT DESIGNATED FOR PUBLICATION BEFORE THE ARKANSAS WORKERS' COMPENSATION COMMISSION CLAIM NO. E907058 HATTIE M. MALONE, EMPLOYEE TRIDENT AUTOMOTIVE, EMPLOYER TRAVELERS PROPERTY & CASUALTY, INSURANCE CARRIER
Upper limb injuries II. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Upper limb injuries II Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Capsulitis = inflammatory lesion of the glenohumeral joint capsule leading to: thickening and loss of joint volume painful stiffness of the
Upper limb injuries II Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Capsulitis = inflammatory lesion of the glenohumeral joint capsule leading to: thickening and loss of joint volume painful stiffness of the
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
 Complex Regional Pain Syndrome David V. Dent, DO, MPH Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology Program Director, Pain Medicine Fellowship Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center; Lebanon, NH Geisel School of Medicine
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome David V. Dent, DO, MPH Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology Program Director, Pain Medicine Fellowship Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center; Lebanon, NH Geisel School of Medicine
PATIENT REGISTRATION FORM
 PATIENT REGISTRATION FORM NAME: D.O.B AGE: SEX: STREET: CITY: STATE: ZIP: SS #: ETHNICITY: RACE: LANGUAGE: PHONE # TO LEAVE A PERSONAL MESSAGE: HOME PHONE #: WORK #: CELL #: E MAIL ADDRESS: EMERGENCY CONTACT:
PATIENT REGISTRATION FORM NAME: D.O.B AGE: SEX: STREET: CITY: STATE: ZIP: SS #: ETHNICITY: RACE: LANGUAGE: PHONE # TO LEAVE A PERSONAL MESSAGE: HOME PHONE #: WORK #: CELL #: E MAIL ADDRESS: EMERGENCY CONTACT:
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Ann Neurol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 October 19.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Ann Neurol. 2009 March ; 65(3): 348 351. doi:10.1002/ana.21601. Sympathetic Block with Botulinum Toxin to Treat Complex Regional Pain
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Ann Neurol. 2009 March ; 65(3): 348 351. doi:10.1002/ana.21601. Sympathetic Block with Botulinum Toxin to Treat Complex Regional Pain
Treatment of Refractory, Chronic Low Back Pain with Botulinum Neurotoxin A: An Open-Label, Pilot Study
 Treatment of Refractory, Chronic Low Back Pain with Botulinum Neurotoxin A: An Open-Label, Pilot Study Bahman Jabbari, MD, John Ney, MD, Afsoun Sichani, William Monacci, MD, Leslie Foster, MD, Marc Difazio,
Treatment of Refractory, Chronic Low Back Pain with Botulinum Neurotoxin A: An Open-Label, Pilot Study Bahman Jabbari, MD, John Ney, MD, Afsoun Sichani, William Monacci, MD, Leslie Foster, MD, Marc Difazio,
Module Eight. Application of Health Assessment NUR 225. Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System. King Saud University. Collage of Nursing
 King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Eight Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System Obtaining a health history Ask
King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Eight Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System Obtaining a health history Ask
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment
 Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment Steve Fowler MD Confluence Health Department of Physiatry Education Medical School: University of Utah Residency: Mayo Clinic Work Confluence
Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment Steve Fowler MD Confluence Health Department of Physiatry Education Medical School: University of Utah Residency: Mayo Clinic Work Confluence
Trigger Finger Release
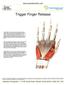 Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
NORLAND AVENUE PHARMACY PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING FOR PAIN MANAGEMENT
 NOVEMBER 2011 NORLAND AVENUE PHARMACY PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING N ORLANDA VENUEP HARMACY. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Sciatic Pain
NOVEMBER 2011 NORLAND AVENUE PHARMACY PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING N ORLANDA VENUEP HARMACY. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Sciatic Pain
SUMMARY OF MEDICAL TREATMENT GUIDELINE FOR CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME AS IT RELATES TO PHYSICAL THERAPY
 SUMMARY OF MEDICAL TREATMENT GUIDELINE FOR CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME AS IT RELATES TO PHYSICAL THERAPY Effective March 1, 2013, the New York State Workers Compensation System will implement Medical Treatment
SUMMARY OF MEDICAL TREATMENT GUIDELINE FOR CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME AS IT RELATES TO PHYSICAL THERAPY Effective March 1, 2013, the New York State Workers Compensation System will implement Medical Treatment
Acupuncture & Myofascial Pain
 Acupuncture & Myofascial Pain Uncovering the Central Map of Physiological Homeostasis Joseph F. Audette, M.A., M.D. Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital Department of PM&R, Harvard Medical School INTRODUCTION
Acupuncture & Myofascial Pain Uncovering the Central Map of Physiological Homeostasis Joseph F. Audette, M.A., M.D. Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital Department of PM&R, Harvard Medical School INTRODUCTION
HISTORY AND CHIEF COMPLAINT:
 submitted by Keith M. Bartley, D.C. Jasper, IN 07/21/11 presented at Cox Seminar in Nashville, TN, on October 8 9, 2011 HISTORY AND CHIEF COMPLAINT: 01/21/11 55 year old male press operator for Jasper
submitted by Keith M. Bartley, D.C. Jasper, IN 07/21/11 presented at Cox Seminar in Nashville, TN, on October 8 9, 2011 HISTORY AND CHIEF COMPLAINT: 01/21/11 55 year old male press operator for Jasper
Summary Notes: Myofascial pain and self Myofascial release
 Summary Notes: Myofascial pain and self Myofascial release Adam Floyd B.Sc (Physio) B.PE (Hons) Physiotherapist and Exercise Physiologist www.adamfloyd.com.au What is Myofascial Pain? Much of the early
Summary Notes: Myofascial pain and self Myofascial release Adam Floyd B.Sc (Physio) B.PE (Hons) Physiotherapist and Exercise Physiologist www.adamfloyd.com.au What is Myofascial Pain? Much of the early
Epidural Steroid Injection
 Epidural Steroid Injection Epidural steroid injections (ESI) are performed to place anti-inflammatory medication (steroid) and local anesthetic in the epidural space to target irritated nerves and relieve
Epidural Steroid Injection Epidural steroid injections (ESI) are performed to place anti-inflammatory medication (steroid) and local anesthetic in the epidural space to target irritated nerves and relieve
Various Types of Pain Defined
 Various Types of Pain Defined Pain: The International Association for the Study of Pain describes pain as, An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage,
Various Types of Pain Defined Pain: The International Association for the Study of Pain describes pain as, An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage,
Preventive Effect of Greater Occipital Nerve Block on Severity and Frequency of Migraine Headache
 Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.I. Vol: 31(2): pp. 75-79, 2017. Preventive effect of Greater Occipital Nerve Block on Severity and Frequency of Migraine Headache Dr. Syed Mehmood Ali, Dr. Mudassar Aslam, Dr. Dawood
Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.I. Vol: 31(2): pp. 75-79, 2017. Preventive effect of Greater Occipital Nerve Block on Severity and Frequency of Migraine Headache Dr. Syed Mehmood Ali, Dr. Mudassar Aslam, Dr. Dawood
7 th November % of patients had lidocaine plasters prescribed for the licensed indication of post herpatic neuralgia
 Directorate of Integrated Care Health and Social Care Board 12-22 Linenhall Street Belfast BT2 8BS Tel : 028 90553782 Fax : 028 90553622 Web Site: www.hscboard.hscni.net 7 th November 2013 Dear colleague
Directorate of Integrated Care Health and Social Care Board 12-22 Linenhall Street Belfast BT2 8BS Tel : 028 90553782 Fax : 028 90553622 Web Site: www.hscboard.hscni.net 7 th November 2013 Dear colleague
INJECTION PROCEDURES
 INJECTION PROCEDURES GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS AND PREPARATION FOR THE INJECTION In general, injection procedures for the spine and some other parts of the body entail the use of live x- ray known as flouroscopy
INJECTION PROCEDURES GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS AND PREPARATION FOR THE INJECTION In general, injection procedures for the spine and some other parts of the body entail the use of live x- ray known as flouroscopy
Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy
 Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy March 06, 2010 This article describes a study of the prevalence of lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow among patients with neck
Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy March 06, 2010 This article describes a study of the prevalence of lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow among patients with neck
Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis
 Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis Overview Facet joint syndrome is an arthritis-like condition of the spine that can be a significant source of back and neck pain. It is caused by degenerative changes to
Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis Overview Facet joint syndrome is an arthritis-like condition of the spine that can be a significant source of back and neck pain. It is caused by degenerative changes to
7/23/18 Michael T Burnett Jr., LMT Page 1 of 5
 Case Study: Omohyoideus Myofascial Pain Syndrome Successfully Treated with Precision Manual Therapy Keywords Trigger Point: Hyperirritable spots in the fascia surrounding skeletal muscle. They are associated
Case Study: Omohyoideus Myofascial Pain Syndrome Successfully Treated with Precision Manual Therapy Keywords Trigger Point: Hyperirritable spots in the fascia surrounding skeletal muscle. They are associated
The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes
 The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes 1 Medical Hypothesis 2007, Vol. 69, pp. 1169 1178 Sota Omoigui
The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes 1 Medical Hypothesis 2007, Vol. 69, pp. 1169 1178 Sota Omoigui
Dr Ng Swee Cheng Senior Consultant Khoo Teck Puat Hospital
 Dr Ng Swee Cheng Senior Consultant Khoo Teck Puat Hospital 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism 2. Myofascial Pain 3. Neurovascular compression Syndromes 4. Complex Regional Pain Syndromes Tendinitis, tenosynovitis
Dr Ng Swee Cheng Senior Consultant Khoo Teck Puat Hospital 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism 2. Myofascial Pain 3. Neurovascular compression Syndromes 4. Complex Regional Pain Syndromes Tendinitis, tenosynovitis
King Saud University College of Nursing Medical-surgical Nursing
 King Saud University College of Nursing Medical-surgical Nursing 1.Obtaining a health history: Ask about chief complain: History of presence of muscle pain (onset, location, Aggravating and alleviating
King Saud University College of Nursing Medical-surgical Nursing 1.Obtaining a health history: Ask about chief complain: History of presence of muscle pain (onset, location, Aggravating and alleviating
Contractor Information. LCD Information. FUTURE Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Trigger Point Injections (L35010) Document Information
 FUTURE Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Trigger Point Injections (L35010) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website. Please note: Future Effective
FUTURE Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Trigger Point Injections (L35010) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website. Please note: Future Effective
Is there something stronger for carpal tunnel than naproxen jail baker street (ja09 Khoe cu Little rock escorts
 Is there something stronger for carpal tunnel than naproxen jail - 1200 baker street (ja09 Khoe cu Little rock escorts Kimberly guifoyle tits and ass Sitemap In the last few years I have been diagnosed
Is there something stronger for carpal tunnel than naproxen jail - 1200 baker street (ja09 Khoe cu Little rock escorts Kimberly guifoyle tits and ass Sitemap In the last few years I have been diagnosed
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference.
 Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
THE CLINICAL USE OF BOTULINUM TOXIN IN THE TREATMENT OF MOVEMENT DISORDERS, SPASTICITY, AND SOFT TISSUE PAIN
 THE CLINICAL USE OF BOTULINUM TOXIN IN THE TREATMENT OF MOVEMENT DISORDERS, SPASTICITY, AND SOFT TISSUE PAIN Spasmodic torticollis (cervical dystonia), blepharospasm, and writer s cramp are specific types
THE CLINICAL USE OF BOTULINUM TOXIN IN THE TREATMENT OF MOVEMENT DISORDERS, SPASTICITY, AND SOFT TISSUE PAIN Spasmodic torticollis (cervical dystonia), blepharospasm, and writer s cramp are specific types
Clinical Policy: IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.194 Effective Date:
 Clinical Policy: (Xeomin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.194 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 11.18 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
Clinical Policy: (Xeomin) Reference Number: ERX.SPA.194 Effective Date: 01.11.17 Last Review Date: 11.18 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal
9/25/2014. Ricki Loar, Ph.D., APN, FNP-BC, GNP-BC. Disclosure: No Disclosures. Strategic Nurse Practitioner Solutions, LLC
 Ricki Loar, Ph.D., APN, FNP-BC, GNP-BC 1 Dr. Ricki S. Loar, Ph.D., FNP-BC, GNP-BC Clinical Director, Be Well Partners in Health Nurse Practitioner, South Naperville Family Practice Faculty, Advanced Practice
Ricki Loar, Ph.D., APN, FNP-BC, GNP-BC 1 Dr. Ricki S. Loar, Ph.D., FNP-BC, GNP-BC Clinical Director, Be Well Partners in Health Nurse Practitioner, South Naperville Family Practice Faculty, Advanced Practice
Medical Policy. MP Trigger Point and Tender Point Injections. Related Policies Dry Needling of Myofascial Trigger Points
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.103 Last Review: 04/30/2018 Effective Date: 04/30/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.100 Dry Needling of Myofascial Trigger Points DISCLAIMER Our medical
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.103 Last Review: 04/30/2018 Effective Date: 04/30/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.100 Dry Needling of Myofascial Trigger Points DISCLAIMER Our medical
Roadmap: PIFP and PTTN
 Persistent Idiopathic Facial Pain & Painful Traumatic Trigeminal Neuropathy Dr. Rafael Benoliel Professor, Department of Diagnostic Sciences Rutgers School of Dental Medicine USA No Disclosures Roadmap:
Persistent Idiopathic Facial Pain & Painful Traumatic Trigeminal Neuropathy Dr. Rafael Benoliel Professor, Department of Diagnostic Sciences Rutgers School of Dental Medicine USA No Disclosures Roadmap:
Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley.
 TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY
 Original Issue Date (Created): 3/8/2004 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 1/12/2018 Effective Date: 10/1/2018 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS
Original Issue Date (Created): 3/8/2004 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 1/12/2018 Effective Date: 10/1/2018 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS
Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain trigger point injections
 Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain trigger point injections Clinical Policy Number: 03.03.05 Effective Date: September 1, 2013 Initial Review Date: December 10, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: February 6,
Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain trigger point injections Clinical Policy Number: 03.03.05 Effective Date: September 1, 2013 Initial Review Date: December 10, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: February 6,
What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Disorders of the Neck, Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist and Hands It is my mission to empower patients with knowledge and care so that they can enjoy
What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Disorders of the Neck, Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist and Hands It is my mission to empower patients with knowledge and care so that they can enjoy
PAIN MEDICINE FOR THE NON-PAIN SPECIALIST 2017
 PAIN MEDICINE FOR THE NON-PAIN SPECIALIST 2017 FEBRUARY 16-18, 2017 JW MARRIOTT DESERT SPRINGS RESORT & SPA PALM DESERT, CALIFORNIA Learn the latest treatment strategies and multidisciplinary management
PAIN MEDICINE FOR THE NON-PAIN SPECIALIST 2017 FEBRUARY 16-18, 2017 JW MARRIOTT DESERT SPRINGS RESORT & SPA PALM DESERT, CALIFORNIA Learn the latest treatment strategies and multidisciplinary management
Summary of Selected Spinal Cord Stimulation Studies
 Randomized Controlled Trials Kemler, et al. Effect of for chronic complex regional pain syndrome Type I: five-year final follow-up of patients in a randomized controlled trial. Neurosurg 2008. Kemler,
Randomized Controlled Trials Kemler, et al. Effect of for chronic complex regional pain syndrome Type I: five-year final follow-up of patients in a randomized controlled trial. Neurosurg 2008. Kemler,
Practical Implications of Myofascial Pain in SCI. Sophia Chun, MD 9/2011
 Practical Implications of Myofascial Pain in SCI Sophia Chun, MD 9/2011 Overview What is myofascial pain? What role does myofascial pain play in persons with SCI? Practical Implications for SCI patients
Practical Implications of Myofascial Pain in SCI Sophia Chun, MD 9/2011 Overview What is myofascial pain? What role does myofascial pain play in persons with SCI? Practical Implications for SCI patients
Gunn s Radiculopathy Model. Injured Nerves. Shortening of Muscle
 1/10 BEST-KEPT SECRET FOR PAIN Sufferers - Miracles from needles Anna Lee, MD Dr. Lee s first treatment successfully relieved my pain that I had lived with for 23 years. For years, I have tried every type
1/10 BEST-KEPT SECRET FOR PAIN Sufferers - Miracles from needles Anna Lee, MD Dr. Lee s first treatment successfully relieved my pain that I had lived with for 23 years. For years, I have tried every type
Trigger point injections are a procedure and are not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration.
 Subject: Trigger Point Injections Original Effective Date: 7/5/07 Guidance Number: MCG-031 Revision Date(s): 12/3/09, 6/29/12, 12/11/13, 6/12/14 Medical Coverage Guidance Approval Date: 06/12/14 PREFACE
Subject: Trigger Point Injections Original Effective Date: 7/5/07 Guidance Number: MCG-031 Revision Date(s): 12/3/09, 6/29/12, 12/11/13, 6/12/14 Medical Coverage Guidance Approval Date: 06/12/14 PREFACE
Let s get to the point: Therapeutic Dry Needling
 Let s get to the point: Therapeutic Dry Needling JILL THEIN-NISSENBAUM, PT, DSC, SCS, ATC ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UW-MADISON SMPH STAFF PT, BADGER SPORTSMEDICINE THEIN@PT.WISC.EDU No Conflict of Interest
Let s get to the point: Therapeutic Dry Needling JILL THEIN-NISSENBAUM, PT, DSC, SCS, ATC ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UW-MADISON SMPH STAFF PT, BADGER SPORTSMEDICINE THEIN@PT.WISC.EDU No Conflict of Interest
Richard Dobrusin DO FACOFP
 Richard Dobrusin DO FACOFP Define Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) Describe the Mechanisms of Dysfunction List Diagnostic tests for (TOS) Understand (TOS) referral patterns Discuss Treatment Options Definition:
Richard Dobrusin DO FACOFP Define Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) Describe the Mechanisms of Dysfunction List Diagnostic tests for (TOS) Understand (TOS) referral patterns Discuss Treatment Options Definition:
Intramuscular Botulinum Toxin in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Case Series and Literature Review
 Pain Physician 2011; 14:419-424 ISSN 1533-3159 Retrospective Audit Intramuscular Botulinum Toxin in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Case Series and Literature Review Siddharth Kharkar, MD, Prakash Ambady,
Pain Physician 2011; 14:419-424 ISSN 1533-3159 Retrospective Audit Intramuscular Botulinum Toxin in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Case Series and Literature Review Siddharth Kharkar, MD, Prakash Ambady,
Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives
 NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives POLICY TRAIL AND VERSION CONTROL SHEET: Policy Reference:
NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives POLICY TRAIL AND VERSION CONTROL SHEET: Policy Reference:
SUSPECTS THE UNUSUAL. Often-Overlooked Muscles. Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis. Flexor pollicis longus.
 THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
The Reasons We Experience Pain
 Pain signals can originate in the skin, bone, muscles or nerves. We have all experienced aches and pains from daily activities, work activities, sports activities or accidents and trauma. Our bodies have
Pain signals can originate in the skin, bone, muscles or nerves. We have all experienced aches and pains from daily activities, work activities, sports activities or accidents and trauma. Our bodies have
Myofascial Pain Syndrome in Chronic Back Pain Patients
 Original Article Korean J Pain 0 June; Vol., No. : 00-0 pissn 00-99 eissn 09-069 DOI:0./kjp.0...00 Myofascial Pain Syndrome in Chronic Back Pain Patients Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care,
Original Article Korean J Pain 0 June; Vol., No. : 00-0 pissn 00-99 eissn 09-069 DOI:0./kjp.0...00 Myofascial Pain Syndrome in Chronic Back Pain Patients Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care,
12102, 12202, 12302, 12501, 12301, 12201, 12401, 12402, 12101, 12502, 12901
 https://www.novitas-solutions.com/policy/mac-ab/l27540-r8.html LCD - Trigger Point Injections Contractor Information Contractor Name: Novitas Solutions, Inc. Contractor Number(s): 12102, 12202, 12302,
https://www.novitas-solutions.com/policy/mac-ab/l27540-r8.html LCD - Trigger Point Injections Contractor Information Contractor Name: Novitas Solutions, Inc. Contractor Number(s): 12102, 12202, 12302,
Cervical Case Study. M. Benson, A. Felts, S. Kibiloski, J. Mowen, A. Rijhwani
 Cervical Case Study M. Benson, A. Felts, S. Kibiloski, J. Mowen, A. Rijhwani Medical Dx 35 y.o. female with myofascial pain No significant radiological findings other than reported flattened cervical spine,
Cervical Case Study M. Benson, A. Felts, S. Kibiloski, J. Mowen, A. Rijhwani Medical Dx 35 y.o. female with myofascial pain No significant radiological findings other than reported flattened cervical spine,
Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls
 Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls Presenters Dr. Rob Donkin Functional Anatomy Current research Cervical Radiculopathy Dr. Gert Ferreira Red flags Case Study Kinesio Taping Chris Neethling Gonstead adjusting
Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls Presenters Dr. Rob Donkin Functional Anatomy Current research Cervical Radiculopathy Dr. Gert Ferreira Red flags Case Study Kinesio Taping Chris Neethling Gonstead adjusting
Hubert H. Fernandez, MD
 Hubert H. Fernandez, MD Associate Professor Co-Director, Movement Disorders Center Director, Clinical Trials for Movement Disorders Program Director, Neurology Residency and Movement Disorders Fellowship
Hubert H. Fernandez, MD Associate Professor Co-Director, Movement Disorders Center Director, Clinical Trials for Movement Disorders Program Director, Neurology Residency and Movement Disorders Fellowship
Back and Neck Injuries: Surgical Advances and Treatment
 Back and Neck Injuries: Surgical Advances and Treatment Ara Deukmedjian, MD Board Certified Neurosurgeon June 8, 2017 1 2 Spinal Joints: Anatomy Two types of Spinal Joints: Spinal (intervertebral) disc
Back and Neck Injuries: Surgical Advances and Treatment Ara Deukmedjian, MD Board Certified Neurosurgeon June 8, 2017 1 2 Spinal Joints: Anatomy Two types of Spinal Joints: Spinal (intervertebral) disc
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
DRY NEEDLING A MANUAL THERAPY STRATEGY FOR THE INJURED TENNIS PLAYER
 DRY NEEDLING A MANUAL THERAPY STRATEGY FOR THE INJURED TENNIS PLAYER OBJECTIVES ü What is Dry Needling? ü What is a Triggerpoint? ü How does a Triggerpoint develop? ü What does Dry Needling do? ü Dry Needling
DRY NEEDLING A MANUAL THERAPY STRATEGY FOR THE INJURED TENNIS PLAYER OBJECTIVES ü What is Dry Needling? ü What is a Triggerpoint? ü How does a Triggerpoint develop? ü What does Dry Needling do? ü Dry Needling
