Phylogenetic analysis of the rst complete hepatitis E virus (HEV) genome from Africa
|
|
|
- Marian Hutchinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology 39 (2003) 133^139 Phylogenetic analysis of the rst complete hepatitis E virus (HEV) genome from Africa a He le'ne van Cuyck a;, Franc ois Juge b, Pierre Roques c;d Weapons of Mass Destruction Centre (WMD Centre), NATO, AB310, Bd. Leopold III, 1110 Brussels, Belgium b Centre de Recherches du Service de Sante des Arme es (CRSSA), De partement des Agents Transmissibles, 24 Ave des Maquis du Gre sivaudan, BP 87, Grenoble, France c De partement de Virologie, CIRMF, BP769, Franceville, Gabon d Service de Neurovirologie, DSV/DRM CEA, CRSSA, Fontenay aux Roses, France Abstract Received 31 March 2003; received in revised form 23 July 2003; accepted 28 July 2003 First published online 10 September 2003 Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is globally distributed, transmitted enterically and between humans and animals. Phylogenetic analysis has identified five distinct HEV genotypes. The first full-length sequence of an African strain (Chad) is presented and compared to 31 complete HEV genomes available, including the fulminant hepatitis strain from India, swine strains and a strain from Morocco. The two African strains are more closely related to genotype 1 than to any other genotypes and together they possibly form a sub-genotype or sixth genotype. The first evidence for recombination between divergent HEV strains is presented. ß 2003 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. Keywords: Hepatitis E virus; Hepatitis E virus genome sequence; Phylogenetic analysis; Recombination 1. Introduction Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is the major cause of enterically transmitted non-a, non-b, non-c hepatitis and is responsible for signi cant morbidity and mortality in developing countries [1]. Outbreaks of hepatitis E have been described in Asia, Africa and Mexico [2^4] while sporadic cases have been noted in the United States and Europe [5^7]. It has been shown that HEV is a zoonotic disease of swine [8^10]. A HEV-related virus in chickens (avian HEV) has been described [11]. Avian HEV shares 50^60% nucleotide sequence with the human and swine viruses [12]. HEV is endemic in human populations in contact with pigs [13,14] and recently many swine HEV strains have been genetically identi ed [9,15]. HEV has been removed from the Calicivirus family and reclassi ed as a separate HEV-like-virus genus. The virus is non-enveloped and has a single positive RNA strand. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +32 (2) ; Fax: +32 (2) addresses: h.vancuyck@skynet.be (H. van Cuyck), h.vancuyck@hq.nato.int (H. van Cuyck). The genome has three open reading frames (ORFs) and is approximately 7200 nucleotides long. The overall length di erences between strains are due to the variation of the poly(a) tail length, and the sequenced segment of the 5P end of the genome. The largest (ORF1) is 5 kb long and encodes a non-structural polyprotein containing consensus elements of methyl transferase, protease, helicase and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [16]. The 3P part of the genome corresponds to ORF2, which encodes the major capsid antigenic proteins. ORF3 is 1kb long, overlaps the ORF1 and ORF2 junction and encodes a protein of unknown function. Several classi cation schemes have been published, but non-o cially accepted, ve genotypes have been described (roman numbers were proposed by Tsarev et al. [26]; arabic numbering was proposed by Wang et al. [43]): genotype I (1) includes Asian (India, Burma, Nepal, China- Xinjiang, Pakistan) [17^23] and African strains (Chad, Algeria, Tunisia, Morocco, Egypt, Namibia) [24^27], genotype III (2) includes Mexican and African (Nigeria) strains [28,29], genotype II (3) includes US and Japanese strains [33], genotype IV (4) includes Chinese (Shanga «) and Japanese strains [33], and nally genotype V (5) includes European strains [5,7]. These designations are based / 03 / $22.00 ß 2003 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. doi: /s (03)
2 134 H. van Cuyck et al. / FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology 39 (2003) 133^139
3 H. van Cuyck et al. / FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology 39 (2003) 133^ on the analysis of partial genome sequences despite the existence of complete sequences from China [20,30], India [17,31], Pakistan [21,22], Nepal [23], Mexico [28], US [6] and from Japanese patients [32,33]. Until recently, no full sequence from Africa has been characterized. In this study we present the rst comparison of complete African genome sequences of HEV: a strain from Chad and a strain from Morocco, and we analyze their relationship to previously described HEV genotypes, including the swine strains. 2. Materials and methods The Chad T3 feces sampled in 1984 from a patient with hepatitis E was used as the source for extraction of RNA as previously described [22]. The sequencing of the RNA was performed with RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) fragments using primers from the Burma sequence or the sequence previously obtained. A consensus sequence was created using the Sequencer 5.0 program and submitted to the GenBank. The sequence comparison of the newly derived Chad strain to the other HEV strains from India, China, Pakistan, Mexico, US, Burma, Japan, Nepal, and Morocco was performed by comparing complete genome sequences of 31 strains isolated from human and swine. The following sequences were retrieved from the GenBank: M Burma-7194 nucleotides (nt); D10330-Myanmar-7194 nt; M74506-Mexico-7170 nt; M80581-Sar55 Pakistan-7138 nt; D11092-China A Xinjiang-7194 nt; M94177-China B Xinjiang-7194 nt; L25595-China C Xinjiang-7193 nt; D11093-China D Xinjiang-7194 nt; X99441-India Madras-7194 nt; AF Nepal TK nt; AF Abb-2B Pakistan-7143 nt; AF India Hyderabad-7129 nt; X98292-Fulminant India-7193 nt; AF HEV US nt; AF HEV US nt; HEE Genotype 4 China Shanga «-7232 nt; AB JKK-Sap Japan-7223 nt; AB JAK- Sai Japan 7224 nt; AB JMK-Ham Japan 7228 nt; AB JKN-Sap Japan-7244 nt; AY Morocco nt; AF USA-S-7207 nt; AB swJ570 Japan-7225 nt; AB HE-J14 Japan-7171 nt; AB HE-JA10 Japan-7244 nt; AB HE-JA1 Japan-7240 nt; AP JRA1 Japan-7230 nt; AY CanswArkell Canada-7242 nt; AF North India Jameel-7191 nt; L08816-China XingYang nt; AB swJ nt. Sequence alignments were constructed using Clustal W version 1.8. The alignment was altered according to the reading frame using the alignment editor Se-Al version 2.0 (A. Rambaut; evolve.zoo.ox.ac.uk). Ambiguities in the sequences were removed. All gap-containing sites were stripped from the alignment. Xia s test was used to assess saturation using DAMBE ([34], Phylogenetic trees based on distance and maximum likelihood methods were built using PAUP 4.0 (D.L. Swo ord, Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, USA). The exact models were selected by model testing using the AIC criterion (Akaike information criterion) or hlrts (hierarchical likelihood ratio tests) as described in the Modeltest version 3.06 [35]. Similarities between HEV strains were tested with similarity plotting using Simplot version 3.2 (R. Stuart, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, 3. Results 3.1. Chad and Moroccan strains belong to genotype 1, and form a sub-genotype The complete genome of the Chad T3 strain was sequenced and submitted to GenBank with the accession number AY The complete genome was 7163 nucleotides long (7150 nt without the poly(a) tail) and 40 nucleotides from the 5P end compared to the Burmese sequence. The genome included the three ORFs, ORF1, 2 and 3, encoding the full viral proteins and polyprotein. The genome was compared to 31 full-length HEV genomes; excluding gaps and ambiguities there were 6939 nucleotide sites in the alignment. Except in the 3P end of the alignment and in the hypervariable region (from base 1760 to 2330) no gaps had to be inserted. Test of saturation [34] using DAMBE, indicates an index of substitution saturation (ISS) = and a critical value ISSc = , indicating little saturation of the data (ISS 6 ISSc). Therefore, the sequences of HEV are suitable for phylogenetic analysis. The similarity plotting, between the di erent full HEV genomes revealed that the Chad strain is more similar to genotype 1 cluster (Asian genotype), than to the other three genotypes: genotype 2 (Mexico), genotype 4 (China-Shanga «, Japanese), and genotype 3 (US, Japanese) (Fig. 1). Within genotype 1, the Chad strain seems to be divergent from the other genotype 1 strains (Fig. 1A). The RNA polymerase region and ORF2 are very conservative 6 Fig. 1. Test of similarity between the sequences of the di erent full HEV genomes using SIMPLOT. A: The test of similarity was performed using the 84-Chad T3 sequence as query. Genotype 1 includes the Asian (Burmese)-like strains, genotype 2 includes the Mexican-like strains, genotype 3 includes the US-like strains and genotype 4 includes the Shanga «-like strains. The parameters used were the following: window size of 400 nt, increment of 60 nt, gap-strip on, Kimura 2 parameter correction, T/t of 4.0. The region of the genome corresponding to 1760^2330 nt was deleted showing a linear pattern in that zone. B: Bootscan analysis using SIMPLOT and the 84-Chad T3 strain as query.
4 136 H. van Cuyck et al. / FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology 39 (2003) 133^139 Fig. 2. Comparison of 31 HEV genomes (6939 nt) using distance HKJ to obtain the neighbor-joining tree, with 100 bootstrap replicates. Only bootstrap values higher than 70 were considered as signi cant. and represent the stable part among all strains as previously stated [26]. Di erences in relative identity between strains from di erent genotypes remain the same across the genome. For example, the identity increases in the polymerase region (4000^5000) and in the ORF2 part of the genome (5000^7000) for all strains and genotypes (Fig. 1B). The same approximate relationships were found whatever sequence was used as the query. Phylogenetic tree, constructed using PAUP, con rmed that African strains, Chad T3 and Moroccan strains are closest to genotype 1, and form an independent lineage distinct from the Chinese and Burma/India cluster, and they could be clustered within a new genotype (Fig. 2) Recombination between HEV strains Bootscan analysis of Chad T 3 sequence against the other sequences was then performed to re ne the relationships within the genotype. The breakpoint locations delimited (61^1000, 1000^3000, 3000^3500, 3500^4000, 3500^5000 and 5000^7000) were used to construct neighbor-joining trees (Fig. 3). For all regions the Chad sequence clusters basal to genotype 1. Several strains cluster di erently in the phylogenetic trees from the di erent genomic regions. In particular China D and Indian-fulminant strains cluster di erently depending on the part of the genome studied, as well as the Nepalese strain TK15^92 within the Indian cluster. The changes in the phylogenetic position of other strains within the Asian genotype 1 seem to be a consequence of this. These results indicate a possible recombination between divergent HEV viruses. The change in the phylogenetic position of the genotype 4-like cluster of strains (Japanese JKK Sap and JAK Sai) based on the ORF1 part of the genome (61^3500) could also be related to a recombination event. Repeating the bootscan analysis and reconstructing phylogenetic analysis excluding the putative HEV recombinants indicate that the Chad sequence is not an obvious recombinant. Further analysis has revealed, for the rst time, very strong evidence for recombination between divergent HEV strains (data not shown).
5 H. van Cuyck et al. / FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology 39 (2003) 133^ Fig. 3. Comparison of HEV genome fragments (61^1000; 1000^3000; 3000^3500; 3500^3500; 3500^5000; 5000^7000 length) using distance HKJ to obtain the neighbor-joining tree, with 100 bootstrap replicates. When two strains were 100% similar (India 90 and Hyderabad; HE North India and Jameel N. India; China 1986 and China B 1993), one sequence from both was included in the analysis (India 90; Jameel N. India; China B 1993). Only bootstrap values higher than 70 were considered as signi cant.
6 138 H. van Cuyck et al. / FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology 39 (2003) 133^ Discussion The Chad strain of HEV was fully sequenced and compared to 31 other complete HEV genomes available in the GenBank, including another African strain from Morocco. No special editing signal seems to be involved for translation of ORF2 and 3 [36]. Clustering with genotype 1 of the Chad strain based on the phylogenetic analysis of its complete genome sequence con rmed previous analysis using a partial sequence in more conservative regions of the genome [24]. Phylogenetic analysis with the Chad strain con rmed that HEV strains cluster in four genotypes: genotype 1 (Chad/African; Chinese from Xinjiang; India; Burma; Nepal; Pakistan), genotype 2 (Mexico), genotype 3 (US and Japan) and genotype 4 (Chinese from Shanga «; Japan). However, the comparison using the two complete sequences from Africa reveals that African strains are clustered together, possibly forming a new sub-genotype of genotype I, or a genotype VI (or 6, depending on the numbering of future classi cation). Interestingly, this new partition is supported by phylogenetic analysis of partial sequences in conservative regions proposed previously, which thus remains useful for clustering in order to perform identi cation and epidemiological surveillance of HEV [24,26]. The distribution of strains within these genotypes is not geographically restricted but might be related to migration of populations within and between continents. Thus, relationships are observed between Chinese and Pakistanis or Japanese strains [22,30,37], or Nigerian and Mexican strains [29], or Japanese and US strains [33]. Inter-genotype recombination was suspected within genotype 1; strain China D, isolated in the Xinjiang Province in the Northwest of China appeared to be a recombinant. Moreover, co-infection in the same patient has been described recently [33]. Two di erent genotypes of HEV were involved, implying that recombination between genotypes is possible. Such recombination events have been described for other plus-strand RNA viruses such as the poliovirus, alphaviruses and more recently, the Dengue virus [38^42]. In conclusion, for the rst time a strain from Africa, the 84-Chad T3 strain, was fully sequenced and shown to belong to the Asian genotype. The comparison with another African full-length genome indicated the possibility of new genotyping of HEV. The genotype VI, or 6, is proposed to cluster the African-Asian-related strains in two sub-genotype. Acknowledgements This work was supported by the French Army Health Service. We are grateful to Dr. Jacques Viret and Dr. Dominique Dormont for promoting this work, and to David Robertson and Philippe Lemey for valuable comments on the results. We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Annemie Vandamme for organizing the Eighth European Workshop on Virus Evolution and Molecular Epidemiology. References [1] Harrison, T.J. (1999) Hepatitis E virus - an update. Liver 19, 171^ 176. [2] Arankalle, V.A., Chadha, M.S., Chitambar, S.D., Walimbe, A.M., Chobe, L.P. and Gandhe, S.S. (2001) Changing epidemiology of hepatitis A and hepatitis E in urban and rural India (1982^98). J. Viral Hepat. 8, 293^303. [3] van Cuyck-Gandre, H., Caudill, J.D., Zhang, H.Y., Longer, C.F., Molinie, C., Roue, R., Deloince, R., Coursaget, P., Mamouth, N.N. and Buisson, Y. (1996) Short report: polymerase chain reaction detection of hepatitis E virus in North African fecal samples. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 54, 134^135. [4] Purcell, R.H. and Emerson, S.U. (2001) In: Fields Virology, 4th edn. (D.M. Knipe, P.M. Howley, D.E. Gri n, M.A. Martin, R.A. Lamb, B. Roizman and S.E. Strauss, Eds.). Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA. [5] Schlauder, G.G., Desai, S.M., Zanetti, A.R., Tassopoulos, N.C. and Mushahwar, I.K. (1999) Novel hepatitis E virus (HEV) isolates from Europe: evidence for additional genotypes of HEV. J. Med. Virol. 57, 243^251. [6] Schlauder, G.G., Dawson, G.J., Erker, J.C., Kwo, P.Y., Knigge, M.F., Smalley, D.L., Rosenblatt, J.E., Desai, S.M. and Mushahwar, I.K. (1998) The sequence and phylogenetic analysis of a novel hepatitis E virus isolated from a patient with acute hepatitis reported in the United States. J. Gen. Virol. 79, 447^456. [7] Zanetti, A.R., Schlauder, G.G., Romano, L., Tanzi, E., Fabris, P., Dawson, G.J. and Mushahwar, I.K. (1999) Identi cation of a novel variant of hepatitis E virus in Italy. J. Med. Virol. 57, 356^360. [8] Clayson, E.T., Innis, B.L., Myint, K.S., Narupiti, S., Vaughn, D.W., Giri, S., Ranabhat, P. and Shrestha, M.P. (1995) Detection of hepatitis E virus infections among domestic swine in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 53, 228^232. [9] Meng, X.J., Purcell, R.H., Halbur, P.G., Lehman, J.R., Webb, D.M., Tsareva, T.S., Haynes, J.S., Thacker, B.J. and Emerson, S.U. (1997) A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 9860^9865. [10] van der Poel, W.H., Verschoor, F., van der Heide, R., Herrera, M.I., Vivo, A., Kooreman, M. and de Roda Husman, A.M. (2001) Hepatitis E virus sequences in swine related to sequences in humans, The Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 7, 970^976. [11] Haqshenas, G., Shivaprasad, H.L., Woolcock, P.R., Read, D.H. and Meng, X.J. (2001) Genetic identi cation and characterization of a novel virus related to human hepatitis E virus from chickens with hepatitis-splenomegaly syndrome in the United States. J. Gen. Virol. 82, 2449^2462. [12] Haqshenas, G., Huang, F.F., Fenaux, M., Guenette, D.K., Pierson, F.W., Larsen, C.T., Shivaprasad, H.L., Toth, T.E. and Meng, X.J. (2002) The putative capsid protein of the newly identi ed avian hepatitis E virus shares antigenic epitopes with that of swine and human hepatitis E viruses and chicken big liver and spleen disease virus. J. Gen. Virol. 83, 2201^2209. [13] Withers, M.R., Correa, M.T., Morrow, M., Stebbins, M.E., Seriwatana, J., Webster, W.D., Boak, M.B. and Vaughn, D.W. (2002) Antibody levels to hepatitis E virus in North Carolina swine workers, non-swine workers, swine, and murids. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 66, 384^388. [14] Meng, X.J., Wiseman, B., Elvinger, F., Guenette, D.K., Toth, T.E., Engle, R.E., Emerson, S.U. and Purcell, R.H. (2002) Prevalence of
7 H. van Cuyck et al. / FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology 39 (2003) 133^ antibodies to hepatitis E virus in veterinarians working with swine and in normal blood donors in the United States and other countries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40, 117^122. [15] Arankalle, V.A., Chobe, L.P., Joshi, M.V., Chadha, M.S., Kundu, B. and Walimbe, A.M. (2002) Human and swine hepatitis E viruses from Western India belong to di erent genotypes. J. Hepatol. 36, 417^425. [16] Koonin, E.V., Gorbalenya, A.E., Purdy, M.A., Rozanov, M.N., Reyes, G.R. and Bradley, D.W. (1992) Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 8259^8263. [17] Panda, S.K., Nanda, S.K., Zafrullah, M., Ansari, I.H., Ozdener, M.H. and Jameel, S. (1995) An Indian strain of hepatitis E virus (HEV): cloning, sequence, and expression of structural region and antibody responses in sera from individuals from an area of highlevel HEV endemicity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33, 2653^2659. [18] Tam, A.W., Smith, M.M., Guerra, M.E., Huang, C.C., Bradley, D.W., Fry, K.E. and Reyes, G.R. (1991) Hepatitis E virus (HEV): molecular cloning and sequencing of the full-length viral genome. Virology 185, 120^131. [19] Aye, T.T., Uchida, T., Ma, X., Iida, F., Shikata, T., Zhuang, H. and Win, K.M. (1992) Sequence comparison of the capsid region of hepatitis E viruses isolated from Myanmar and China. Microbiol. Immunol. 36, 615^621. [20] Bi, S.L., Purdy, M.A., McCaustland, K.A., Margolis, H.S. and Bradley, D.W. (1993) The sequence of hepatitis E virus isolated directly from a single source during an outbreak in China. Virus Res. 28, 233^247. [21] Tsarev, S.A., Emerson, S.U., Reyes, G.R., Tsareva, T.S., Legters, L.J., Malik, I.A., Iqbal, M. and Purcell, R.H. (1992) Characterization of a prototype strain of hepatitis E virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 559^563. [22] van Cuyck-Gandre, H., Zhang, H.Y., Tsarev, S.A., Warren, R.L., Caudill, J.D., Snellings, N.J., Begot, L., Innis, B.L. and Longer, C.F. (2000) Short report: phylogenetically distinct hepatitis E viruses in Pakistan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 62, 187^189. [23] Gouvea, V., Snellings, N., Popek, M.J., Longer, C.F. and Innis, B.L. (1998) Hepatitis E virus: complete genome sequence and phylogenetic analysis of a Nepali isolate. Virus Res. 57, 21^26. [24] van Cuyck-Gandre, H., Zhang, H.Y., Tsarev, S.A., Clements, N.J., Cohen, S.J., Caudill, J.D., Buisson, Y., Coursaget, P., Warren, R.L. and Longer, C.F. (1997) Characterization of hepatitis E virus (HEV) from Algeria and Chad by partial genome sequence. J. Med. Virol. 53, 340^347. [25] Chatterjee, R., Tsarev, S., Pillot, J., Coursaget, P., Emerson, S.U. and Purcell, R.H. (1997) African strains of hepatitis E virus that are distinct from Asian strains. J. Med. Virol. 53, 139^144. [26] Tsarev, S.A., Binn, L.N., Gomatos, P.J., Arthur, R.R., Monier, M.K., van Cuyck-Gandre, H., Longer, C.F. and Innis, B.L. (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis E virus isolates from Egypt. J. Med. Virol. 57, 68^74. [27] He, J., Binn, L.N., Tsarev, S.A., Hayes, C.G., Frean, J.A., Isaacson, M. and Innis, B.L. (2000) Molecular characterization of a hepatitis E virus isolate from Namibia. J. Biomed. Sci. 7, 334^338. [28] Huang, C.C., Nguyen, D., Fernandez, J., Yun, K.Y., Fry, K.E., Bradley, D.W., Tam, A.W. and Reyes, G.R. (1992) Molecular cloning and sequencing of the Mexico isolate of hepatitis E virus (HEV). Virology 191, 550^558. [29] Buisson, Y., Grandadam, M., Nicand, E., Cheval, P., van Cuyck- Gandre, H., Innis, B., Rehel, P., Coursaget, P., Teyssou, R. and Tsarev, S. (2000) Identi cation of a novel hepatitis E virus in Nigeria. J. Gen. Virol. 81, 903^909. [30] Yin, S., Purcell, R.H. and Emerson, S.U. (1994) A new Chinese isolate of hepatitis E virus: comparison with strains recovered from di erent geographical regions. Virus Genes 9, 23^32. [31] Jameel, S., Zafrullah, M., Chawla, Y.K. and Dilawari, J.B. (2002) Reevaluation of a North India isolate of hepatitis E virus based on the full-length genomic sequence obtained following long RT-PCR. Virus Res. 86, 53^58. [32] Takahashi, K., Kang, J.H., Ohnishi, S., Hino, K. and Mishiro, S. (2002) Genetic heterogeneity of hepatitis E virus recovered from Japanese patients with acute sporadic hepatitis. J. Infect. Dis. 185, 1342^ [33] Takahashi, M., Nishizawa, T., Yoshikawa, A., Sato, S., Isoda, N., Ido, K., Sugano, K. and Okamoto, H. (2002) Identi cation of two distinct genotypes of hepatitis E virus in a Japanese patient with acute hepatitis who had not travelled abroad. J. Gen. Virol. 83, 1931^1940. [34] Xia, X. and Xie, Z. (2001) DAMBE: software package for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. J. Hered. 92, 371^373. [35] Posada, D. and Crandall, K.A. (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14, 817^818. [36] Wang, Y., Zhang, H., Ling, R., Li, H. and Harrison, T.J. (2000) The complete sequence of hepatitis E virus genotype 4 reveals an alternative strategy for translation of open reading frames 2 and 3. J. Gen. Virol. 81, 1675^1686. [37] Takahashi, K., Iwata, K., Watanabe, N., Hatahara, T., Ohta, Y., Baba, K. and Mishiro, S. (2001) Full-genome nucleotide sequence of a hepatitis E virus strain that may be indigenous to Japan. Virology 287, 9^12. [38] Rico-Hesse, R., Pallansch, M.A., Nottay, B.K. and Kew, O.M. (1987) Geographic distribution of wild poliovirus type 1 genotypes. Virology 160, 311^322. [39] Copper, P.D., Steiner-Pryor, A., Scotti, P.D. and Delong, D. (1974) On the nature of poliovirus genetic recombinants. J. Gen. Virol. 23, 41^49. [40] Hahn, C.S., Lustig, S., Strauss, E.G. and Strauss, J.H. (1988) Western equine encephalitis virus is a recombinant virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 5997^6001. [41] Tolou, H.J., Couissinier-Paris, P., Durand, J.P., Mercier, V., de Pina, J.J., de Micco, P., Billoir, F., Charrel, R.N. and de Lamballerie, X. (2001) Evidence for recombination in natural populations of dengue virus type 1 based on the analysis of complete genome sequences. J. Gen. Virol. 82, 1283^1290. [42] Uzcategui, N.Y., Camacho, D., Comach, G., Cuello de Uzcategui, R., Holmes, E.C. and Gould, E.A. (2001) Molecular epidemiology of dengue type 2 virus in Venezuela: evidence for in situ virus evolution and recombination. J. Gen. Virol. 82, 2945^2953. [43] Wang et al. (1999) J. Gen. Virol. 80, 169^177.
E E Hepatitis E SARS 29, Lancet. E A B Enterically-Transmitted Non-A, Hepatitis E. Virus HEV nm. 1.35g/cm s ALT AST HEV HEV
 7850 2004 Hepatitis E Tian-Cheng LI Naokazu TAKEDA Tatsuo MIYAMURA SARS 8 Lancet E E E Hepatitis E VirusHEV E E HEV HEV E 1955 29,000 E E A A B Enterically-Transmitted Non-A, Non-B Hepatitis 1983 Balayan
7850 2004 Hepatitis E Tian-Cheng LI Naokazu TAKEDA Tatsuo MIYAMURA SARS 8 Lancet E E E Hepatitis E VirusHEV E E HEV HEV E 1955 29,000 E E A A B Enterically-Transmitted Non-A, Non-B Hepatitis 1983 Balayan
Detection of IgA-class anti-hev antibody
 Detection of IgA-class anti-hev antibody Hiroaki OKAMOTO E IgA-HE IgA HEV E HEV E E E 10 E 1997 E E 1, 2 2001 E 3 HEV 4 1979 HEV 5 A B C A B C E 6, 7 E HEV E 8 11 2003 8 19 http:www.mhlw. go.jphoudou200308h0819-2.html
Detection of IgA-class anti-hev antibody Hiroaki OKAMOTO E IgA-HE IgA HEV E HEV E E E 10 E 1997 E E 1, 2 2001 E 3 HEV 4 1979 HEV 5 A B C A B C E 6, 7 E HEV E 8 11 2003 8 19 http:www.mhlw. go.jphoudou200308h0819-2.html
Received 27 September 2001/Returned for modification 19 December 2001/Accepted 29 January 2002
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2002, p. 1326 1332 Vol. 40, No. 4 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.4.1326 1332.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2002, p. 1326 1332 Vol. 40, No. 4 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.4.1326 1332.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 9860 9865, September 1997 Medical Sciences A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus XIANG-JIN MENG*, ROBERT H. PURCELL*, PATRICK
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 9860 9865, September 1997 Medical Sciences A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus XIANG-JIN MENG*, ROBERT H. PURCELL*, PATRICK
Short Communication. P. Billam, Z. F. Sun and X.-J. Meng
 Journal of General Virology (2007), 88, 1538 1544 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.82754-0 Short Communication Analysis of the complete genomic sequence of an apparently avirulent strain of avian hepatitis E virus (avian
Journal of General Virology (2007), 88, 1538 1544 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.82754-0 Short Communication Analysis of the complete genomic sequence of an apparently avirulent strain of avian hepatitis E virus (avian
Z. F. Sun, C. T. Larsen, F. F. Huang, P. Billam, F. W. Pierson, T. E. Toth, and X. J. Meng*
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 2004, p. 2658 2662 Vol. 42, No. 6 0095-1137/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.6.2658 2662.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 2004, p. 2658 2662 Vol. 42, No. 6 0095-1137/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.6.2658 2662.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Detection of swine hepatitis E virus in the porcine hepatic lesion in Jeju Island
 J. Vet. Sci. (2007),G8(1), 51 55 J O U R N A L O F Veterinar y Science Detection of swine hepatitis E virus in the porcine hepatic lesion in Jeju Island Song-Hak Lee 1, Sang-Chul Kang 1, Dae-Yong Kim 2,
J. Vet. Sci. (2007),G8(1), 51 55 J O U R N A L O F Veterinar y Science Detection of swine hepatitis E virus in the porcine hepatic lesion in Jeju Island Song-Hak Lee 1, Sang-Chul Kang 1, Dae-Yong Kim 2,
Epidemiological profiles of viral hepatitis in Italy Effects of migration
 Epidemiological profiles of viral hepatitis in Italy Effects of migration Hepatitis A and E T. Santantonio UOC di Malattie Infettive Università degli Studi di Foggia Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Ospedali
Epidemiological profiles of viral hepatitis in Italy Effects of migration Hepatitis A and E T. Santantonio UOC di Malattie Infettive Università degli Studi di Foggia Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Ospedali
To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank
 Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
A Patient with Clinical Features of Acute Hepatitis E Viral Infection and Autoimmune Hepatitis
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2005, 206, 173-179 Acute HEV Infection and AIH 173 A Patient with Clinical Features of Acute Hepatitis E Viral Infection and Autoimmune Hepatitis Case Report FUTOSHI NAGASAKI, YOSHIYUKI
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2005, 206, 173-179 Acute HEV Infection and AIH 173 A Patient with Clinical Features of Acute Hepatitis E Viral Infection and Autoimmune Hepatitis Case Report FUTOSHI NAGASAKI, YOSHIYUKI
Existence of reassortant A (H1N2) swine influenza viruses in Saitama Prefecture, Japan
 International Congress Series 1263 (2004) 749 753 Existence of reassortant A (H1N2) swine influenza viruses in Saitama Prefecture, Japan Shin ichi Shimada a, *, Takayasu Ohtsuka b, Masayuki Tanaka b, Munehito
International Congress Series 1263 (2004) 749 753 Existence of reassortant A (H1N2) swine influenza viruses in Saitama Prefecture, Japan Shin ichi Shimada a, *, Takayasu Ohtsuka b, Masayuki Tanaka b, Munehito
Detection of Hepatitis E Virus-Specific Immunoglobulin A in Patients Infected with Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 1 or 3
 CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Mar. 2007, p. 276 280 Vol. 14, No. 3 1556-6811/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.00312-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Detection of
CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Mar. 2007, p. 276 280 Vol. 14, No. 3 1556-6811/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.00312-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Detection of
Cell Culture of Sporadic Hepatitis E Virus in China
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 1999, p. 729 733 Vol. 6, No. 5 1071-412X/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cell Culture of Sporadic
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 1999, p. 729 733 Vol. 6, No. 5 1071-412X/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cell Culture of Sporadic
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is an unclassified nonenveloped
 Recombinant hepatitis E virus genomes infectious for primates: Importance of capping and discovery of a cis-reactive element S. U. Emerson*, M. Zhang*, X.-J. Meng*, H. Nguyen*, M. St. Claire, S. Govindarajan,
Recombinant hepatitis E virus genomes infectious for primates: Importance of capping and discovery of a cis-reactive element S. U. Emerson*, M. Zhang*, X.-J. Meng*, H. Nguyen*, M. St. Claire, S. Govindarajan,
Sequence analysis for VP4 of enterovirus 71 isolated in Beijing during 2007 to 2008
 16 2009 3 4 1 Journal of Microbes and Infection, March 2009, Vol. 4, No. 1 2007 2008 71 VP4 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2 1., 100730; 2., 100020 : 2007 2008 71 ( EV71), 2007 3 EV71( 1, 2 ) 2008 5 EV71(
16 2009 3 4 1 Journal of Microbes and Infection, March 2009, Vol. 4, No. 1 2007 2008 71 VP4 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2 1., 100730; 2., 100020 : 2007 2008 71 ( EV71), 2007 3 EV71( 1, 2 ) 2008 5 EV71(
Use of Serological Assays for Diagnosis of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 1 and 3 Infections in a Setting of Low Endemicity
 CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, May 2007, p. 562 568 Vol. 14, No. 5 1556-6811/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.00231-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Use of Serological
CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, May 2007, p. 562 568 Vol. 14, No. 5 1556-6811/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.00231-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Use of Serological
Molecular and Serological Epidemiology of Swine Hepatitis E Virus from Pigs in Two Countries
 Molecular and Serological Epidemiology of Swine Hepatitis E Virus from Pigs in Two Countries by Kerri Lee Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
Molecular and Serological Epidemiology of Swine Hepatitis E Virus from Pigs in Two Countries by Kerri Lee Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Cross-species infection of specific-pathogen-free pigs by a genotype 4 strain of human hepatitis E virus Citation for published version: Feagins, AR, Huang, YW, Meng, XJ, Opriessnig,
Edinburgh Research Explorer Cross-species infection of specific-pathogen-free pigs by a genotype 4 strain of human hepatitis E virus Citation for published version: Feagins, AR, Huang, YW, Meng, XJ, Opriessnig,
a-hV. Code assigned:
 This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
Routes of Transmission of Swine Hepatitis E Virus in Pigs
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2004, p. 5047 5052 Vol. 42, No. 11 0095-1137/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.5047 5052.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2004, p. 5047 5052 Vol. 42, No. 11 0095-1137/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.5047 5052.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Hepatitis E Virus Infection. Disclosures
 Hepatitis E Virus Infection Simona Rossi, MD Associate Chair, Division of Hepatology Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia Consultant for BMS Speaker for Gilead Disclosures I have no conflicts to report
Hepatitis E Virus Infection Simona Rossi, MD Associate Chair, Division of Hepatology Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia Consultant for BMS Speaker for Gilead Disclosures I have no conflicts to report
Erratum to: A systematic review of the epidemiology of hepatitis E virus in Africa
 Kim et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2017) 17:187 DOI 10.1186/s12879-017-2274-3 ERRATUM Erratum to: A systematic review of the epidemiology of hepatitis E virus in Africa Open Access Jong-Hoon Kim 1*, Kenrad
Kim et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2017) 17:187 DOI 10.1186/s12879-017-2274-3 ERRATUM Erratum to: A systematic review of the epidemiology of hepatitis E virus in Africa Open Access Jong-Hoon Kim 1*, Kenrad
Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus among Blood Donors in Omdurman Locality, Sudan
 Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus among Blood Donors in Omdurman Locality, Sudan Alaaeldeen Balal Ahmed a and Yousif Fadlalla Hamedelnil b a Omdurman Islamic University, Faculty of Medical laboratory
Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus among Blood Donors in Omdurman Locality, Sudan Alaaeldeen Balal Ahmed a and Yousif Fadlalla Hamedelnil b a Omdurman Islamic University, Faculty of Medical laboratory
Transmission of HEV by plasmapheresis. Vincent Mallet, MD, PhD CHU Cochin, Université Paris Descartes, APHP, Inserm
 Transmission of HEV by plasmapheresis Vincent Mallet, MD, PhD CHU Cochin, Université Paris Descartes, APHP, Inserm Transmission of HEV by secured plasma Transmission of HEV by plasma IA Transmission of
Transmission of HEV by plasmapheresis Vincent Mallet, MD, PhD CHU Cochin, Université Paris Descartes, APHP, Inserm Transmission of HEV by secured plasma Transmission of HEV by plasma IA Transmission of
Epidemiology of hepatitis E: Current status
 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05933.x EPIDEMIOLOGY MINISERIES jgh_5933 1484..1493 Epidemiology of hepatitis E: Current status Rakesh Aggarwal and Sita Naik Departments of Gastroenterology and Immunology,
doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05933.x EPIDEMIOLOGY MINISERIES jgh_5933 1484..1493 Epidemiology of hepatitis E: Current status Rakesh Aggarwal and Sita Naik Departments of Gastroenterology and Immunology,
Evolution of influenza
 Evolution of influenza Today: 1. Global health impact of flu - why should we care? 2. - what are the components of the virus and how do they change? 3. Where does influenza come from? - are there animal
Evolution of influenza Today: 1. Global health impact of flu - why should we care? 2. - what are the components of the virus and how do they change? 3. Where does influenza come from? - are there animal
The Development of Chronic Hepatitis in Rabbits Experimentally Infected. with HEV Isolate from Rabbit
 The Development of Chronic Hepatitis in Rabbits Experimentally Infected with HEV Isolate from Rabbit Peking University, Beijing, China Ling Wang October 7 2014 Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Characteristics Faecal-oral
The Development of Chronic Hepatitis in Rabbits Experimentally Infected with HEV Isolate from Rabbit Peking University, Beijing, China Ling Wang October 7 2014 Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Characteristics Faecal-oral
Complete Nucleotide Sequence of RNA1 of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Y Strain and Evolutionary Relationships among Genome RNAs of the Virus Strains
 Complete Nucleotide Sequence of RNA1 of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Y Strain and Evolutionary Relationships among Genome RNAs of the Virus Strains Jiro KATAOKA*, Chikara MASUTA* and Yoichi TAKANAMI* Abstract
Complete Nucleotide Sequence of RNA1 of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Y Strain and Evolutionary Relationships among Genome RNAs of the Virus Strains Jiro KATAOKA*, Chikara MASUTA* and Yoichi TAKANAMI* Abstract
From Mosquitos to Humans: Genetic evolution of Zika Virus
 Article: From Mosquitos to Humans: Genetic evolution of Zika Virus Renata Pellegrino, PhD Director, Sequencing lab Center for Applied Genomics The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Journal Club Clinical
Article: From Mosquitos to Humans: Genetic evolution of Zika Virus Renata Pellegrino, PhD Director, Sequencing lab Center for Applied Genomics The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Journal Club Clinical
Antigenic epitope composition and protectivity of avian hepatitis E virus (avian HEV) ORF2 protein and vertical transmission of avian HEV
 Retrospective Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 2006 Antigenic epitope composition and protectivity of avian hepatitis E virus (avian HEV) ORF2 protein
Retrospective Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 2006 Antigenic epitope composition and protectivity of avian hepatitis E virus (avian HEV) ORF2 protein
Evolution of hepatitis C virus in blood donors and their respective recipients
 Journal of General Virology (2003), 84, 441 446 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.18642-0 Short Communication Correspondence Jean-François Cantaloube jfc-ets-ap@gulliver.fr Evolution of hepatitis C virus in blood donors
Journal of General Virology (2003), 84, 441 446 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.18642-0 Short Communication Correspondence Jean-François Cantaloube jfc-ets-ap@gulliver.fr Evolution of hepatitis C virus in blood donors
Avian Influenza Virus H7N9. Dr. Di Liu Network Information Center Institute of Microbiology Chinese Academy of Sciences
 Avian Influenza Virus H7N9 Dr. Di Liu Network Information Center Institute of Microbiology Chinese Academy of Sciences Avian Influenza Virus RNA virus, Orthomyxoviruses Influenza A virus Eight Gene segments
Avian Influenza Virus H7N9 Dr. Di Liu Network Information Center Institute of Microbiology Chinese Academy of Sciences Avian Influenza Virus RNA virus, Orthomyxoviruses Influenza A virus Eight Gene segments
West Nile Disease. World situation and impact on public health
 West Nile Disease World situation and impact on public health Contents Global view on WNV The Public Health consequences: the case of USA WNV circulation in Europe and Mediterranean Basin West Nile Disease
West Nile Disease World situation and impact on public health Contents Global view on WNV The Public Health consequences: the case of USA WNV circulation in Europe and Mediterranean Basin West Nile Disease
Detection of negative sense RNA in packaged hepatitis E virions using improved strand specific RT-PCR method
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 28 11 December January 2012 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06717-11 Copyright 2011, 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 28 11 December January 2012 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06717-11 Copyright 2011, 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
aV (modules 1 and 9 are required)
 This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
This form should be used for all taxonomic proposals. Please complete all those modules that are applicable (and then delete the unwanted sections). For guidance, see the notes written in blue and the
Epidemiology of hepatitis E infection in Hong Kong
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epidemiology of hepatitis E infection in Hong Kong DPC Chan *, KCK Lee, SS Lee K e y M e s s a g e s 1. The overall anti hepatitis E virus (HEV) seropositivity
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epidemiology of hepatitis E infection in Hong Kong DPC Chan *, KCK Lee, SS Lee K e y M e s s a g e s 1. The overall anti hepatitis E virus (HEV) seropositivity
Hepatitis E Virus Update December 2014
 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 Tel 604.707.2400 Fax 604.707.2516 www.bccdc.ca Hepatitis E Virus Update December 2014 What is hepatitis E Virus? Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) was first identified
655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 Tel 604.707.2400 Fax 604.707.2516 www.bccdc.ca Hepatitis E Virus Update December 2014 What is hepatitis E Virus? Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) was first identified
Hepatitis E Vaccine Pipeline
 Hepatitis E Vaccine Pipeline A document prepared for Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) by the Hepatitis E Vaccine Working Group Contents Executive summary... 3 Introduction...
Hepatitis E Vaccine Pipeline A document prepared for Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) by the Hepatitis E Vaccine Working Group Contents Executive summary... 3 Introduction...
Rama Nada. - Malik
 - 2 - Rama Nada - - Malik 1 P a g e We talked about HAV in the previous lecture, now we ll continue the remaining types.. Hepatitis E It s similar to virus that infect swine, so its most likely infect
- 2 - Rama Nada - - Malik 1 P a g e We talked about HAV in the previous lecture, now we ll continue the remaining types.. Hepatitis E It s similar to virus that infect swine, so its most likely infect
Recent outbreaks of chikungunya in Sri Lanka and the role of Asian Tigers
 Recent outbreaks of chikungunya in Sri Lanka and the role of Asian Tigers Introduction CHIK Virus Classification: An ARBOVIRUS Family - Togaviridae Genus Alphavirus ** Enveloped, positive- strand RNA virus.
Recent outbreaks of chikungunya in Sri Lanka and the role of Asian Tigers Introduction CHIK Virus Classification: An ARBOVIRUS Family - Togaviridae Genus Alphavirus ** Enveloped, positive- strand RNA virus.
HEV Assay Development Update
 HEV Assay Development Update Jeffrey M. Linnen, Ph.D. Senior Director, Research & Development Hologic Gen-Probe, San Diego, California USA IPFA/PEI 20th International Workshop on Surveillance and Screening
HEV Assay Development Update Jeffrey M. Linnen, Ph.D. Senior Director, Research & Development Hologic Gen-Probe, San Diego, California USA IPFA/PEI 20th International Workshop on Surveillance and Screening
Transfusion-transmitted hepatitis E in a misleading context of autoimmunity and drug-induced toxicity
 Transfusion-transmitted hepatitis E in a misleading context of autoimmunity and drug-induced toxicity Stéphanie Haïm-Boukobza 1,2,3, Marie-Pierre Ferey 1, Anne-Laure Vétillard 4, Asma Jeblaoui 1, Elisabeth
Transfusion-transmitted hepatitis E in a misleading context of autoimmunity and drug-induced toxicity Stéphanie Haïm-Boukobza 1,2,3, Marie-Pierre Ferey 1, Anne-Laure Vétillard 4, Asma Jeblaoui 1, Elisabeth
Hepatitis E in South Africa. Tongai Maponga
 Hepatitis E in South Africa Tongai Maponga 7th FIDSSA CONGRESS 2017 This is what usually comes to mind History of hepatitis E virus An ET-NANB hepatitis virus later named HEV was first suspected in 1980.
Hepatitis E in South Africa Tongai Maponga 7th FIDSSA CONGRESS 2017 This is what usually comes to mind History of hepatitis E virus An ET-NANB hepatitis virus later named HEV was first suspected in 1980.
Prevalence of hepatitis E virus infection in West Bengal, India: a hospital-based study
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2014), 63, 975 980 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.072249-0 Prevalence of hepatitis E virus infection in West Bengal, India: a hospital-based study Nidhi S. Chandra, 1 Durbadal Ojha,
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2014), 63, 975 980 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.072249-0 Prevalence of hepatitis E virus infection in West Bengal, India: a hospital-based study Nidhi S. Chandra, 1 Durbadal Ojha,
Hepatitis E Virus. Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is the causative agent of hepatitis E 1 and the. History. Virus DAVID A. ANDERSON
 177 Hepatitis E Virus DAVID A. ANDERSON Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is the causative agent of hepatitis E 1 and the type member of a distinct virus family. HEV is enterically transmitted and causes an acute
177 Hepatitis E Virus DAVID A. ANDERSON Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is the causative agent of hepatitis E 1 and the type member of a distinct virus family. HEV is enterically transmitted and causes an acute
Hepatitis E virus in Israel
 Hepatitis E virus in Israel Daniela Ram 1, Yossi Manor 1, Yael Gozlan 1, Rachel Shirazi 1, Eli Schwartz 2,3, Ziv Ben-Ari 3,4, Ella Mendelson 1,5, Pozzi Shaul 6, Orna Mor 1 1 Central Virology Laboratory,
Hepatitis E virus in Israel Daniela Ram 1, Yossi Manor 1, Yael Gozlan 1, Rachel Shirazi 1, Eli Schwartz 2,3, Ziv Ben-Ari 3,4, Ella Mendelson 1,5, Pozzi Shaul 6, Orna Mor 1 1 Central Virology Laboratory,
Noronet report, April 2014
 Noronet report, April 2014 Janko van Beek, Annelies Kroneman, Harry Vennema, Marion Koopmans A. van Leeuwenhoeklaan 9 3721 MA Bilthoven Postbus 1 3720 BA Bilthoven www.rivm.nl T 030 274 91 11 F 030 274
Noronet report, April 2014 Janko van Beek, Annelies Kroneman, Harry Vennema, Marion Koopmans A. van Leeuwenhoeklaan 9 3721 MA Bilthoven Postbus 1 3720 BA Bilthoven www.rivm.nl T 030 274 91 11 F 030 274
Characterization of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Among Liver Patients in Kenya
 Characterization of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Among Liver Patients in Kenya By MISSIANI OCHWOTO (Medical Research officer, KEMRI) Julius Oyugi 2, Dufton Mwaengo 2, James Kimotho 1 Carla Osiowy 3 and Elijah
Characterization of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Among Liver Patients in Kenya By MISSIANI OCHWOTO (Medical Research officer, KEMRI) Julius Oyugi 2, Dufton Mwaengo 2, James Kimotho 1 Carla Osiowy 3 and Elijah
Enterovirus 71 Outbreak in P. R. China, 2008
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 13 May 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00563-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 13 May 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00563-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Report concerning identification of the Northern European isolate of BTV (26 th August 2006)
 Report concerning identification of the Northern European isolate of BTV (26 th August 2006) Peter Mertens, Carrie Batten, Simon Anthony, Lydia Kgosana, Karin Darpel, Kasia Bankowska, Eva Veronesi, Abid
Report concerning identification of the Northern European isolate of BTV (26 th August 2006) Peter Mertens, Carrie Batten, Simon Anthony, Lydia Kgosana, Karin Darpel, Kasia Bankowska, Eva Veronesi, Abid
Regional Overview of the implementation of National Control Strategies for Avian Influenza. Summary review of questionnaire OIE RRAP
 Regional Overview of the implementation of National Control Strategies for Avian Influenza Summary review of questionnaire OIE RRAP The OIE Questionnaire on Influenza A surveillance in animals in the Asia
Regional Overview of the implementation of National Control Strategies for Avian Influenza Summary review of questionnaire OIE RRAP The OIE Questionnaire on Influenza A surveillance in animals in the Asia
OIE Situation Report for Avian Influenza
 OIE Situation Report for Avian Influenza Latest update: 24/04/2017 This report presents an overview of current disease events reported to the OIE by its Members. The objective is to describe what is happening
OIE Situation Report for Avian Influenza Latest update: 24/04/2017 This report presents an overview of current disease events reported to the OIE by its Members. The objective is to describe what is happening
Avian Influenza/Newcastle Disease Virus Subcommittee
 Avian Influenza/Newcastle Disease Virus Subcommittee David L. Suarez D.V.M., Ph.D. Patti Miller D.V.M., Ph.D. Claudio Afonso Ph.D. Southeast Poultry Research Laboratory United States National Poultry Research
Avian Influenza/Newcastle Disease Virus Subcommittee David L. Suarez D.V.M., Ph.D. Patti Miller D.V.M., Ph.D. Claudio Afonso Ph.D. Southeast Poultry Research Laboratory United States National Poultry Research
OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza
 OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Latest update: 31/05/2018 The epidemiology of avian influenza (AI) is complex. The AI virus constantly evolves by mutation and re-assortment with
OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Latest update: 31/05/2018 The epidemiology of avian influenza (AI) is complex. The AI virus constantly evolves by mutation and re-assortment with
Keywords: PRRSV, wild boar, seroprevalence, phylogenetic analyses
 54 EUROPRRS2011, Novi Sad, Serbia PORCINE REPRODUCTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYNDROME VIRUS (PRRSV) INFECTION IN LITHUANIAN WILD BORS (SUS SCROFA) POPULATION Arunas Stankevicius 1, Jurate Buitkuviene 1, Jurgita
54 EUROPRRS2011, Novi Sad, Serbia PORCINE REPRODUCTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYNDROME VIRUS (PRRSV) INFECTION IN LITHUANIAN WILD BORS (SUS SCROFA) POPULATION Arunas Stankevicius 1, Jurate Buitkuviene 1, Jurgita
ISSN International Journal of Innovative and Applied Research (2017) Journal home page: RESEARCH ARTICLE
 Journal home page: http://www.journalijiar.com RESEARCH ARTICLE PROTEIN ORGANIZATION AND PLEOMORPHICITY OF ARENAVIRUS. Dr. Abdullah Sethar 1, Dr. Benjamin W. Neuman 2, Dr. Gul Hassan Sethar 3 and Dr. Nargis
Journal home page: http://www.journalijiar.com RESEARCH ARTICLE PROTEIN ORGANIZATION AND PLEOMORPHICITY OF ARENAVIRUS. Dr. Abdullah Sethar 1, Dr. Benjamin W. Neuman 2, Dr. Gul Hassan Sethar 3 and Dr. Nargis
OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza
 OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Latest update: 30/06/2018 The epidemiology of avian influenza (AI) is complex. The AI virus constantly evolves by mutation and re-assortment with
OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Latest update: 30/06/2018 The epidemiology of avian influenza (AI) is complex. The AI virus constantly evolves by mutation and re-assortment with
Outbreak evaluation of highly pathogenic avian influenza in Bangladesh. Mymensingh *Corresponding author:
 Outbreak evaluation of highly pathogenic avian influenza in Bangladesh M. Giasuddin 1*, M.E.Haque 2, A.H.M.Kamal 2, M.R. Islam 2, A. Jahangir 1, E.H. Chowdhury 2 M.J.F.A.Taimur 1 and M. Hafizur Rahman
Outbreak evaluation of highly pathogenic avian influenza in Bangladesh M. Giasuddin 1*, M.E.Haque 2, A.H.M.Kamal 2, M.R. Islam 2, A. Jahangir 1, E.H. Chowdhury 2 M.J.F.A.Taimur 1 and M. Hafizur Rahman
OIE Situation Report for Avian Influenza
 OIE Situation Report for Avian Influenza Latest update: 08/05/2017 This report presents an overview of current disease events reported to the OIE by its Members. The objective is to describe what is happening
OIE Situation Report for Avian Influenza Latest update: 08/05/2017 This report presents an overview of current disease events reported to the OIE by its Members. The objective is to describe what is happening
Detection of HEV in Estonia. Anna Ivanova, Irina Golovljova, Valentina Tefanova
 Detection of HEV in Estonia Anna Ivanova, Irina Golovljova, Valentina Tefanova National Institute for Health Development Department of Virology Zoonotic pathogens Tick-borne pathogens: TBEV, Borrelia sp.,
Detection of HEV in Estonia Anna Ivanova, Irina Golovljova, Valentina Tefanova National Institute for Health Development Department of Virology Zoonotic pathogens Tick-borne pathogens: TBEV, Borrelia sp.,
The use of nonhuman primates in biomedical research has led to the isolation of many
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 29 September 2010 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01928-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 29 September 2010 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01928-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Sequencing-Based Identification of a Novel Coronavirus in Ferrets with Epizootic Catarrhal Enteritis and Development of Molecular Diagnostic Tests
 Sequencing-Based Identification of a Novel Coronavirus in Ferrets with Epizootic Catarrhal Enteritis and Development of Molecular Diagnostic Tests A. Wise, Matti Kiupel,, C. Isenhour, R. Maes Coronaviruses
Sequencing-Based Identification of a Novel Coronavirus in Ferrets with Epizootic Catarrhal Enteritis and Development of Molecular Diagnostic Tests A. Wise, Matti Kiupel,, C. Isenhour, R. Maes Coronaviruses
Update of hepa++s E in Hong Kong. Dr Chow Chi Wing Department of Medicine Tseung Kwan O Hospital
 Update of hepa++s E in Hong Kong Dr Chow Chi Wing Department of Medicine Tseung Kwan O Hospital HEV: The History Probably causing human disease for centuries Iden+fied on EM by Dr Balayan in 1983 Viral
Update of hepa++s E in Hong Kong Dr Chow Chi Wing Department of Medicine Tseung Kwan O Hospital HEV: The History Probably causing human disease for centuries Iden+fied on EM by Dr Balayan in 1983 Viral
Evidence for Other Non-Poliovirus Enteroviruses Multiplies in L20B Cells. ACCEPTED LUIS SARMIENTO*, PEDRO MÁS, ROSA PALOMERA, LUIS MORIER, MAGILÉ
 CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 14 March 2007 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:10.1128/cvi.00017-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 14 March 2007 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:10.1128/cvi.00017-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
Molecular Evolution of the SARS Coronavirus During the Course of the SARS Epidemic in China
 Molecular Evolution of the SARS Coronavirus During the Course of the SARS Epidemic in China The Chinese SARS Molecular Epidemiology Consortium* *The complete list of authors and their affiliated institutions
Molecular Evolution of the SARS Coronavirus During the Course of the SARS Epidemic in China The Chinese SARS Molecular Epidemiology Consortium* *The complete list of authors and their affiliated institutions
SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF A HEPATITIS E VIRUS VACCINE CONDUCTED IN NEPAL
 SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF A HEPATITIS E VIRUS VACCINE CONDUCTED IN NEPAL Shrestha M.P., Scott R.M., and Shrestha S.K. Walter Reed/AFRIMS Research Unit Nepal (WARUN) Kathmandu, Nepal Myint K.S.A.*, and Mammen
SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF A HEPATITIS E VIRUS VACCINE CONDUCTED IN NEPAL Shrestha M.P., Scott R.M., and Shrestha S.K. Walter Reed/AFRIMS Research Unit Nepal (WARUN) Kathmandu, Nepal Myint K.S.A.*, and Mammen
A SEROLOGICAL SURVEY OF ARBOVIRAL DISEASES AMONG THE HUMAN POPULATION OF THE ANDAMAN AND NICOBAR ISLANDS, INDIA
 A SEROLOGICAL SURVEY OF ARBOVIRAL DISEASES AMONG THE HUMAN POPULATION OF THE ANDAMAN AND NICOBAR ISLANDS, INDIA VS Padbidri 1, NS Wairagkar 1, GD Joshi 1, UB Umarani 1, AR Risbud 2, DL Gaikwad 1, SS Bedekar
A SEROLOGICAL SURVEY OF ARBOVIRAL DISEASES AMONG THE HUMAN POPULATION OF THE ANDAMAN AND NICOBAR ISLANDS, INDIA VS Padbidri 1, NS Wairagkar 1, GD Joshi 1, UB Umarani 1, AR Risbud 2, DL Gaikwad 1, SS Bedekar
A. Study Purpose and Rationale
 IRB Proposal/CRC Rotation Sabrina J Gard, MD MPH Internal Medicine, PGY 1 5 May 2014 A. Study Purpose and Rationale Dengue is the most prevalent arthropod-transmitted virus, with conservative estimates
IRB Proposal/CRC Rotation Sabrina J Gard, MD MPH Internal Medicine, PGY 1 5 May 2014 A. Study Purpose and Rationale Dengue is the most prevalent arthropod-transmitted virus, with conservative estimates
Rajesh Kannangai Phone: ; Fax: ; *Corresponding author
 Amino acid sequence divergence of Tat protein (exon1) of subtype B and C HIV-1 strains: Does it have implications for vaccine development? Abraham Joseph Kandathil 1, Rajesh Kannangai 1, *, Oriapadickal
Amino acid sequence divergence of Tat protein (exon1) of subtype B and C HIV-1 strains: Does it have implications for vaccine development? Abraham Joseph Kandathil 1, Rajesh Kannangai 1, *, Oriapadickal
Development of a novel enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti-igg against swine hepatitis E virus
 pissn 1229-845X, eissn 1976-555X J. Vet. Sci. (2013), 14(4), 467-472 http://dx.doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2013.14.4.467 Received: 7 Dec. 2012, Revised: 16 Feb. 2013, Accepted: 19 Feb. 2013 Original Article JOURNAL
pissn 1229-845X, eissn 1976-555X J. Vet. Sci. (2013), 14(4), 467-472 http://dx.doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2013.14.4.467 Received: 7 Dec. 2012, Revised: 16 Feb. 2013, Accepted: 19 Feb. 2013 Original Article JOURNAL
Epidemiology of HAV, HDV and HEV in Belgium
 Epidemiology of HAV, HDV and HEV in Belgium Prof. Dr. Steven Van Gucht National Reference Centre of Hepatitis Viruses B, C, D and E Viral Diseases Scientific Institute of Public Health (WIV-ISP) Brussels
Epidemiology of HAV, HDV and HEV in Belgium Prof. Dr. Steven Van Gucht National Reference Centre of Hepatitis Viruses B, C, D and E Viral Diseases Scientific Institute of Public Health (WIV-ISP) Brussels
Bioinformation by Biomedical Informatics Publishing Group
 Predicted RNA secondary structures for the conserved regions in dengue virus Pallavi Somvanshi*, Prahlad Kishore Seth Bioinformatics Centre, Biotech Park, Sector G, Jankipuram, Lucknow 226021, Uttar Pradesh,
Predicted RNA secondary structures for the conserved regions in dengue virus Pallavi Somvanshi*, Prahlad Kishore Seth Bioinformatics Centre, Biotech Park, Sector G, Jankipuram, Lucknow 226021, Uttar Pradesh,
Reassortment of influenza A virus genes linked to PB1 polymerase gene
 International Congress Series 1263 (2004) 714 718 Reassortment of influenza A virus genes linked to PB1 polymerase gene Jean C. Downie* www.ics-elsevier.com Centre for Infectious Diseases and Microbiology,
International Congress Series 1263 (2004) 714 718 Reassortment of influenza A virus genes linked to PB1 polymerase gene Jean C. Downie* www.ics-elsevier.com Centre for Infectious Diseases and Microbiology,
Hepatitis E virus infections in humans and animals
 Review article CLINICAL EXPERIMENTAL VACCINE RESEARCH Hepatitis E virus infections in humans and animals Clin Exp Vaccine Res 2014;3:29-36 http://dx.doi.org/10.7774/cevr.2014.3.1.29 pissn 2287-3651 eissn
Review article CLINICAL EXPERIMENTAL VACCINE RESEARCH Hepatitis E virus infections in humans and animals Clin Exp Vaccine Res 2014;3:29-36 http://dx.doi.org/10.7774/cevr.2014.3.1.29 pissn 2287-3651 eissn
Immune pressure analysis of protease and reverse transcriptase genes of primary HIV-1 subtype C isolates from South Africa
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 10(24), pp. 4784-4793, 6 June, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB10.560 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Academic Journals Full Length
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 10(24), pp. 4784-4793, 6 June, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB10.560 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Academic Journals Full Length
Envelope e_ :------, Envelope glycoproteins e_ ~ Single-stranded RNA ----, Nucleocapsid
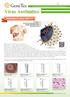 Virus Antib(tdies Your Expertise, Our Antibodies, Accelerated Discovery. Envelope e_---------:------, Envelope glycoproteins e_-------1~ Single-stranded RNA ----, Nucleocapsid First identified in 1989,
Virus Antib(tdies Your Expertise, Our Antibodies, Accelerated Discovery. Envelope e_---------:------, Envelope glycoproteins e_-------1~ Single-stranded RNA ----, Nucleocapsid First identified in 1989,
ETIOLOGY OF ENTERICALLY-TRANSMITTED HEPATITIS AMONG FOREIGNERS IN NEPAL
 ETIOLOGY OF ENTERICALLY-TRANSMITTED HEPATITIS AMONG FOREIGNERS IN NEPAL Robert McN Scott, Prativa Pandey 2, David R Shlim 2 and Khin-Saw-Aye-Myint Walter Reed/AFRIMS Research Unit Nepal (WARUN), Kathmandu;
ETIOLOGY OF ENTERICALLY-TRANSMITTED HEPATITIS AMONG FOREIGNERS IN NEPAL Robert McN Scott, Prativa Pandey 2, David R Shlim 2 and Khin-Saw-Aye-Myint Walter Reed/AFRIMS Research Unit Nepal (WARUN), Kathmandu;
Is it the time to start blood screening for Hepatitis-E?
 Is it the time to start blood screening for Hepatitis-E? Dr. Somnath Mukherjee MD, MAMS Assistant Professor All India Institute of Medical Sciences Bhubaneswar During last 25 years the safety of blood
Is it the time to start blood screening for Hepatitis-E? Dr. Somnath Mukherjee MD, MAMS Assistant Professor All India Institute of Medical Sciences Bhubaneswar During last 25 years the safety of blood
Detection of Immunoglobulin M Antibodies to Hepatitis E Virus by Class Capture Enzyme Immunoassay
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, July 2003, p. 579 586 Vol. 10, No. 4 1071-412X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.10.4.579 586.2003 Detection of Immunoglobulin M Antibodies to Hepatitis E Virus
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, July 2003, p. 579 586 Vol. 10, No. 4 1071-412X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.10.4.579 586.2003 Detection of Immunoglobulin M Antibodies to Hepatitis E Virus
Research article Acute viral hepatitis morbidity and mortality associated with hepatitis E virus infection: Uzbekistan surveillance data
 Acute Hepatitis E Infection In A Visitor To Louisiana.(Case Report): An Article From: Southern Medical Journal [HTML] [Digital] By James Edward, Jr. Walker;Todd Martin Brown;Thomas Lanier Hagood;William
Acute Hepatitis E Infection In A Visitor To Louisiana.(Case Report): An Article From: Southern Medical Journal [HTML] [Digital] By James Edward, Jr. Walker;Todd Martin Brown;Thomas Lanier Hagood;William
Multi-clonal origin of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolates. determined by multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Ashraf
 number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
Influenza Viruses A Review
 Influenza Viruses A Review AVIAN INFLUENZA: INTERSECTORAL COLLABORATION Larnaca, Cyprus 20 22 July 2009 Kate Glynn Scientific and Technical Department, OIE Influenza Viruses C. Goldsmith,1981 Influenza
Influenza Viruses A Review AVIAN INFLUENZA: INTERSECTORAL COLLABORATION Larnaca, Cyprus 20 22 July 2009 Kate Glynn Scientific and Technical Department, OIE Influenza Viruses C. Goldsmith,1981 Influenza
TITLE: Influenza A (H7N9) virus evolution: Which genetic mutations are antigenically important?
 TITLE: Influenza A (H7N9) virus evolution: Which genetic mutations are antigenically important? AUTHORS: Joshua G. Petrie 1, Adam S. Lauring 2,3 AFFILIATIONS: 1 Department of Epidemiology, University of
TITLE: Influenza A (H7N9) virus evolution: Which genetic mutations are antigenically important? AUTHORS: Joshua G. Petrie 1, Adam S. Lauring 2,3 AFFILIATIONS: 1 Department of Epidemiology, University of
HEPATITIS C VIRUS GENOTYPING IN CHRONIC HEPATITIS C PATIENTS
 HEPATITIS C VIRUS GENOTYPING IN CHRONIC HEPATITIS C PATIENTS I. Qattan Centres for Hepatology, Royal Free & University College Medical School, London V. Emery Department of Virology, Royal Free & University
HEPATITIS C VIRUS GENOTYPING IN CHRONIC HEPATITIS C PATIENTS I. Qattan Centres for Hepatology, Royal Free & University College Medical School, London V. Emery Department of Virology, Royal Free & University
Community-Based Seroepidemiological Survey of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Catalonia, Spain
 CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Dec. 2006, p. 1328 1332 Vol. 13, No. 12 1556-6811/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.00255-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Community-Based
CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Dec. 2006, p. 1328 1332 Vol. 13, No. 12 1556-6811/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.00255-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Community-Based
OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza
 OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Latest update: 28/02/2018 The epidemiology of avian influenza is complex. The virus constantly evolves and the behavior of each new subtype (and
OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Latest update: 28/02/2018 The epidemiology of avian influenza is complex. The virus constantly evolves and the behavior of each new subtype (and
Donors in Northern Thailand. Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical medicine 42(2). p135-
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Seroprevalence of Antibody to Hepat Donors in Northern Thailand Jutavijittum, Prapan; Jiviriyawat, Amnat; Hayashi, Shigeki; Itakura, H Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Seroprevalence of Antibody to Hepat Donors in Northern Thailand Jutavijittum, Prapan; Jiviriyawat, Amnat; Hayashi, Shigeki; Itakura, H Citation 熱帯医学 Tropical
OIE Situation Report for Avian Influenza
 OIE Situation Report for Avian Influenza Latest update: 10/07/2017 This report presents an overview of current disease events reported to the OIE by its Members. The objective is to describe what is happening
OIE Situation Report for Avian Influenza Latest update: 10/07/2017 This report presents an overview of current disease events reported to the OIE by its Members. The objective is to describe what is happening
A study of NS1 antigen and platelet count for early diagnosis of dengue infection
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 12 (2013) pp. 40-44 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article A study of NS1 antigen and platelet count for early diagnosis of dengue infection Santosh Shivajirao
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 12 (2013) pp. 40-44 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article A study of NS1 antigen and platelet count for early diagnosis of dengue infection Santosh Shivajirao
Seroepidemiological Evidence of Avian Influenza A Virus Transmission to Pigs in Southern China
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 November 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02625-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Seroepidemiological
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 November 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02625-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Seroepidemiological
Origins and evolutionary genomics of the novel avian-origin H7N9 influenza A virus in China: Early findings
 Origins and evolutionary genomics of the novel 2013 avian-origin H7N9 influenza A virus in : Early findings Jiankui He*, Luwen Ning, Yin Tong Department of Biology, South University of Science and Technology
Origins and evolutionary genomics of the novel 2013 avian-origin H7N9 influenza A virus in : Early findings Jiankui He*, Luwen Ning, Yin Tong Department of Biology, South University of Science and Technology
The In Vitro-Synthesized RNA from a cdna Clone of Hepatitis E Virus Is Infectious
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 2000, p. 2430 2437 Vol. 74, No. 5 0022-538X/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The In Vitro-Synthesized RNA from a cdna Clone
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 2000, p. 2430 2437 Vol. 74, No. 5 0022-538X/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The In Vitro-Synthesized RNA from a cdna Clone
BRIEF COMMUNICATION ANTIGENIC ANALYSIS OF JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS ISOLATED IN HOKKAIDO WITH MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
 Title ANTIGENIC ANALYSIS OF JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS IS MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES Author(s)OCHIAI, Kenichi; TAKASHIMA, Ikuo; HASHIMOTO, Nobuo CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 37(1): 21-2
Title ANTIGENIC ANALYSIS OF JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS IS MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES Author(s)OCHIAI, Kenichi; TAKASHIMA, Ikuo; HASHIMOTO, Nobuo CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 37(1): 21-2
H5N1 avian influenza: timeline
 H5N1 avian influenza: timeline 28 October 2005 Previous events in Asia 1996 Highly pathogenic H5N1 virus is isolated from a farmed goose in Guangdong Province, China. 1997 Outbreaks of highly pathogenic
H5N1 avian influenza: timeline 28 October 2005 Previous events in Asia 1996 Highly pathogenic H5N1 virus is isolated from a farmed goose in Guangdong Province, China. 1997 Outbreaks of highly pathogenic
SEA/CD/154 Distribution : General. Avian Influenza in South-East Asia Region: Priority Areas for Research
 SEA/CD/154 Distribution : General Avian Influenza in South-East Asia Region: Priority Areas for Research World Health Organization Publications of the World Health Organization enjoy copyright protection
SEA/CD/154 Distribution : General Avian Influenza in South-East Asia Region: Priority Areas for Research World Health Organization Publications of the World Health Organization enjoy copyright protection
It is well known that some pathogenic microbes undergo
 Colloquium Effects of passage history and sampling bias on phylogenetic reconstruction of human influenza A evolution Robin M. Bush, Catherine B. Smith, Nancy J. Cox, and Walter M. Fitch Department of
Colloquium Effects of passage history and sampling bias on phylogenetic reconstruction of human influenza A evolution Robin M. Bush, Catherine B. Smith, Nancy J. Cox, and Walter M. Fitch Department of
Investigation of the genetic differences between bovine herpesvirus type 1 variants and vaccine strains
 Investigation of the genetic differences between bovine herpesvirus type 1 variants and vaccine strains Name: Claire Ostertag-Hill Mentor: Dr. Ling Jin Bovine herpesvirus Bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) Pathogen
Investigation of the genetic differences between bovine herpesvirus type 1 variants and vaccine strains Name: Claire Ostertag-Hill Mentor: Dr. Ling Jin Bovine herpesvirus Bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) Pathogen
