Significance of Algal Viruses and Ecology of Phaeocystis Host-Virus Interactions.
|
|
|
- Merry Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Significance of Algal Viruses and Ecology of Phaeocystis Host-Virus Interactions. Bratbak, G. and M. Heldal Department of Microbiology, University of Bergen. Jahnebakken 5, N-5020 Bergen, Norway. ABSTRACT The ecological significance of algal viruses is suggested by the presence of algal cells containing virus like particles, the presence of viruses infecting specific algae and the succession of phytoplankton and virus in natural aquatic ecosystems. The interaction between Phaeocystis pouchetii and the lytic virus PpV01 was investigated in laboratory microcosms. The experiments show that P. pouchetii is susceptible to virus infection in all stages of growth, and that nitrate, phosphate and light limitation of algal growth do not prevent virus reproduction and cell lysis. Inferior growth conditions caused a decrease in burst size of > 50% compared to more copious growth conditions. The length of the lytic cycle and the infectivity of the viruses was apparently not affected by the host s growth conditions. Viral infection did not affect photosynthesis until near the onset of cell lysis. Release of dissolved organic carbon was low in non-infected cultures, while in infected cultures the entire algal biomass was converted to DOC. The DOC released during viral lysis was rapidly and efficiently utilized for bacterial growth. Introduction Little is known about algal viruses in general and it is only during the last decade that we have begun to consider their possible ecological roles. The ecological significance of algal viruses in natural aquatic ecosystems is suggested by three differed types of observations. The first is the presence of algal cells containing virus like particles (VLPs) in natural waters. VLPs have been found in cells from about 50 different algal species representing nearly all major algal classes [16, 21, 25]. Virus infection may thus be as common for microalgae as it is for any other group of organisms. Moreover, blooms of different marine phytoplankton species such as Emiliania huxleyi [1, 5], Aureococcus anophagefferens [11, 17] and Heterosigma akashiwo [13,14] have been found to have a significant fraction of VLP containing cells as the blooms were about to collapse. Methods The second type of observation is the presence of viruses in natural waters infecting specific algae. The two first microalgal viruses (Micromonas pusilla virus and Chlorella virus) were isolated in the 1970 s [10, 22]. At present, less than 10 different microalga host virus systems have been reported to be available in culture, but four of these have been isolated during the last five years (Table 1). With an increasing awareness that algal viruses may be important, more effort has been invested in isolating algal host-virus systems for further investigation in the laboratory and the number of isolated viruses will presumably increase significantly in the next few years. 1
2 Table 1. Microalgae host virus systems currently available in culture Host algae Reference Chlorophyceae Chlorella sp. 22 Chrysophyceae Aureococcus anophagefferens 11 Prasiophyceae Micromonas pusilla 6 Pyramimonas orientalis 12 Prymnesiophyceae Chrysochromulina brevifilum 19 Phaeocystis pouchetii 9 Raphidophyceae Heterosigma akashiwo 15 The third type of observations suggesting that algal viruses may be important in natural waters is case studies where the succession of phytoplankton and free virus like particles suggest a causative relationship [1,4]. A virus (PpV-01) infecting and lysing the marine prymnesiophyte Phaeocystis pouchetii has recently been isolated [9]. We have conducted a series experiments to elucidate how the virus production is affected by host cells growth and nutrition and how the virus infection affects primary production, release of dissolved organic carbon and bacterial secondary production [2,3]. Results The experimental studies show that Phaeocystis was sensitive to virus infection in all phases of growth (exponential-, early stationary- and late stationary - senescence-phase) and that the population was decimated within 3 days after virus infection. Nutrient deficient cultures, i.e. batch cultures entering stationary phase due to phosphorus or nitrogen limitation, showed complete lysis within 3-4 days after virus infection as did control cultures growing in complete medium. Virus infected cultures incubated in the dark lysed more slowly than the control cultures incubated in the light. When comparing total virus counts and counts of infective viral particles (i.e. most probable number) we found no apparent relationship between host cell growth condition and infectivity of the viral particles produced. The fraction of infective particles in fresh algal lysates did however show a larger variation than has been reported for other systems (Table 2). Table 2. Infectivity of algal viruses Host virus system % Infectivity Reference Phaeocystis pouchetii - PpV Chlorella - PBCV Micromonas pusilla - MpV-SP
3 Discussion The conclusions that can be drawn from these experiments are that P. pouchetii was susceptible to virus infection in all stages of growth, and that nutrient (nitrate or phosphate) or light limitation of algal growth did not prevent viral reproduction and cell lysis. The main effect of host cell growth condition on virus production appeared to be on the number of viruses produced per infected host cell. A high burst size (maximum 510) was found in exponentially growing cultures, while low burst size (minimum 15) was found in stationary phase cultures, in nutrient depleted cultures and in light limited cultures. This is qualitatively comparable to what has been found for other algal host-virus systems (Table 3) but P- deficiency does not seem to be as important as has been found for some other systems. Table 3. Virus proliferation as a function of host cell growth condition Host Effect of host growth condition on virus proliferation Reference Phaeocystis pouchetii Burst size decreased by 50-90% at inferior growth 3 conditions. Chlorella Poor replication in stationary-phase cells. 20,21 Emiliania huxleyi Synechococcus No virus production and cell lysis when phosphate was depleted. Length of lytic cycle increased and the burst size decreased by 80% when cell growth was phosphate limited Virus infection in Phaeocystis pouchetii does not seem to affect the cells photosynthetic apparatus and it allowed primary production in the cells to continue throughout most of the lytic cycle which lasts for h [9]. In this respect, the response of Phaeocystis to virus infection resembled virus infection in Synechococcus, but it was apparently different from that of other eucaryotic algae where photosynthesis is shut down immediately or shortly after the infection (Table 4). Accumulation of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and bacterial biomass in cultures of Phaeocystis indicate that excretion amounts to 20-30% of the algae s particulate production (bacterial growth efficiency assumed to be 50%). Viral lysis of the algal cells resulted in a massive release of DOC which in terms of carbon approximated that of the entire algal biomass. Growth of bacteria succeeding cell lysis demonstrated that the DOC released was readily available for bacterial secondary production and the net effect of the virus infection was an efficient conversion of algal biomass into bacterial biomass. For viral lysis of Aureococcus anophagefferens, Gobler et al [8] estimated that bacterial carbon production was 22% of the total algal carbon while 15% was released to the dissolved phase. Compared to our results obtained with Phaeocystis pouchetii this suggests that both the amount and bioavailability of organic material released from algae due to viral lysis, and the bacterial secondary production succeeding such lysis, may vary significantly. 3
4 Table 4. Effect of virus infection on photosynthesis in different algal host virus systems Host-virus system Observed effect of virus infection on photosynthesis Reference Phaeocystis pouchetii - Photosynthesis is active during most of the lytic 2 PpV01 cycle. Micromonas pusilla - Significantly reduced within 2h after infection. 23 MpV Chlorella - PBCV-1 CO 2 fixation inhibited almost immediately. 20 Synechococcus (BCC1) - S-BBS1 Photosynthetic rates in infected cultures were similar to those in non-infected control cultures until near the onset of cell lysis. 18 Acknowledgements This work was supported by funding from The European Commission to the MAST-III Project MEDEA, contract number MAS3-CT and by funding from The Research Council of Norway, project number /120 and /420. We thank Evy Foss Skjoldal, Jorunn Viken and Gunhild Bødtker for their excellent technical assistance. The EM work was done at the Laboratory for Electron Microscopy University of Bergen. References 1. Bratbak G, Egge JK, Heldal M (1993) Viral mortality of the marine alga Emiliania huxleyi (Haptophyceae) and termination of algal blooms. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 93: Bratbak G, Jacobsen A, Heldal M (1998a) Viral lysis of Phaeocystis pouchetii and bacterial secondary production. Aquat Microb Ecol 16: Bratbak G, Jacobsen A, Heldal M, Nagasaki K, Thingstad F (1998b) Virus production in Phaeocystis pouchetii and its relation to host cell growth and nutrition. Aquat Microb Ecol 16: Bratbak G, Levasseur, M, Michaud, S, Cantin, G, Fernández, E, Heimdal, BR, Heldal M (1995) Viral activity in relation to Emiliania huxleyi blooms: a possible mechanism of DMSP release? Mar Ecol Prog Ser 128: Brussaard C P D, Kempers, R S, Kop, A J, Riegman, R, Heldal, M (1996) Virus like particles in a summer bloom of Emiliania huxleyi in the North Sea. Aquatic Microb Ecol 10: Cottrell MT, Suttle CA (1991) Wide-spread occurrence and clonal variation in viruses which cause lysis of a cosmopolitan eucaryotic marine phytoplankter, Micromonas pusilla. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 78: Cottrell MT, Suttle, CA (1995) Dynamics of a lytic virus infecting the photosynthetic marine picoflagellate Micromonas pusilla. Limnol Oceanogr 40:
5 8. Gobler CJ, Hutchins, DA, Fisher, NS, Cosper, EM, Sañudo-Wilhewlmy SA (1997) Release and bioavailability of C,N,P, Se and Fe following viral lysis of a marine chrysophyte. Limnol Oceanogr 42: Jacobsen A, Bratbak G and Heldal M (1996) Isolation and characterisation of a virus infecting Phaeocystis pouchetii (Prymnesiophyceae). J Phycol 32: Mayer JA, Taylor FJR (1979) A virus which lyses the marine nanoflagellate Micromonas pusilla. Nature (London) 281: Milligan KLD, Cosper EM (1994) Isolation of a virus capable of lysing the brown tide microalga, Aureococcus anophagefferens. Science 266: Mortimer E, Patching J W (1998) Characterisation of a microalgal virus isolated from Irish waters and initial genome studies. Algal Virus Workshop. Abstract. Bergen, Norway. June 14-18, Nagasaki K, Ando M, Imai I, Itakura S, Ishida Y (1994a) Virus-like particles in Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae): a possible red tide disintegration mechanism. Mar Biol 119: Nagasaki K, Ando M, Itakura S, Imai I, Ishida Y (1994b) Viral mortality in the final stage of Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae) red tide. J Plankton Res 16: Nagasaki K, Yamaguchi M (1997) Isolation of a virus infectious to the harmful bloom causing microalga Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae). Aquat Microb Ecol 13: Reisser W (1993) Viruses and virus-like particles of freshwaterand marine eucaryotic algae - a review. Arch Protistenkd 143: Sieburth JMcN, Johnson PW, Hargraves PE (1988) Ultrastructure and ecology of Aureococcus anophagefferens gen. et sp. nov. (Chrysophyceae): The dominant picoplankter during a bloom in Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island, summer J Phycol 24: Suttle CA, Chan AM (1993) Marine cyanophages infecting oceanic and coastal strains of Synechococcus: abundance, morphology, cross-infectivity and growth characteristics. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 92: Suttle CA, Chan AM (1995) Viruses infecting the marine Prymnesiophyte Chrysochromulina spp: isolation preliminary characterization and natural abundance. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 118: van Etten JL, Burbank DE, Xia Y, Meints RH (1983) Growth cycle of a virus, PBCV-1, that infects Chlorella-like algae. Virology 126: van Etten JL, Lane LC, Meints RH (1991) Viruses and virus-like particles of eucaryotic algae. Microbiol Rev 55: van Etten JL, Meints RH, Burbank DE, Kuczmarski D, Cuppels DA, Lane LC (1981) Isolation and characterisation of a virus from the intracellular green algae symbiotic with Hydra viridis. Virology 113: Waters RE, Chan AT (1982) Micromonas pusilla virus: The virus growth cycle and associated physiological events within the host cells; host range mutation. J gen Virol 63: Wilson WH, Carr NG, Mann NH (1996) The effect of phosphate status on the kinetics of cyanophage infection in the oceanic cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp WH7803. J Phycol 32: Zingone A (1995) The role of viruses in the dynamics of phytoplankton blooms. Giornale Botanico Italiano 129:
Stable coexistence in marine algal host-virus systems
 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 254: 27 35, 2003 Published June 4 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Stable coexistence in marine algal host-virus systems Runar Thyrhaug 1, 2, *, Aud Larsen 1, T. Frede Thingstad 1,
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 254: 27 35, 2003 Published June 4 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Stable coexistence in marine algal host-virus systems Runar Thyrhaug 1, 2, *, Aud Larsen 1, T. Frede Thingstad 1,
Quantitative and qualitative impacts of viral infection on a Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae) bloom in Hiroshima Bay, Japan
 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 34: 227 238, 2004 Published March 9 Aquat Microb Ecol Quantitative and qualitative impacts of viral infection on a Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae) bloom in Hiroshima
AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 34: 227 238, 2004 Published March 9 Aquat Microb Ecol Quantitative and qualitative impacts of viral infection on a Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae) bloom in Hiroshima
Seasonal dynamics in the abundance of Micromonas pusilla (Prasinophyceae) and its viruses in the Gulf of Naples (Mediterranean Sea)
 Journal of Plankton Research Vol.21 no.11 pp.2143 2159, 1999 Seasonal dynamics in the abundance of Micromonas pusilla (Prasinophyceae) and its viruses in the Gulf of Naples (Mediterranean Sea) Adriana
Journal of Plankton Research Vol.21 no.11 pp.2143 2159, 1999 Seasonal dynamics in the abundance of Micromonas pusilla (Prasinophyceae) and its viruses in the Gulf of Naples (Mediterranean Sea) Adriana
Isolation of a virus infecting the novel shellfishkilling dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama
 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 23: 103 111, 2001 Published January 31 Aquat Microb Ecol Isolation of a virus infecting the novel shellfishkilling dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama Kenji Tarutani,
AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 23: 103 111, 2001 Published January 31 Aquat Microb Ecol Isolation of a virus infecting the novel shellfishkilling dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama Kenji Tarutani,
Large double-stranded DNA viruses which cause the lysis of a marine heterotrophic nanoflagellate (Bodo sp.) occur in natural marine viral communities
 Vol. 9: 203-210, 1995 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Aquat microb Ecol Published December 21 Large double-stranded DNA viruses which cause the lysis of a marine heterotrophic nanoflagellate (Bodo sp.) occur
Vol. 9: 203-210, 1995 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Aquat microb Ecol Published December 21 Large double-stranded DNA viruses which cause the lysis of a marine heterotrophic nanoflagellate (Bodo sp.) occur
Direct estimates of the contribution of viral lysis and microzooplankton grazing to the decline of a Micromonas spp. population
 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 30: 207 219, 2003 Published January 23 Aquat Microb Ecol Direct estimates of the contribution of viral lysis and microzooplankton grazing to the decline of a Micromonas spp.
AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 30: 207 219, 2003 Published January 23 Aquat Microb Ecol Direct estimates of the contribution of viral lysis and microzooplankton grazing to the decline of a Micromonas spp.
Virally induced mortality of Phaeocystis globosa during two spring blooms in temperate coastal waters
 AQUATIC MICROIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 44: 27 217, 26 Published October 1 Aquat Microb Ecol Virally induced mortality of Phaeocystis globosa during two spring blooms in temperate coastal waters Anne-Claire audoux,
AQUATIC MICROIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 44: 27 217, 26 Published October 1 Aquat Microb Ecol Virally induced mortality of Phaeocystis globosa during two spring blooms in temperate coastal waters Anne-Claire audoux,
Effects of temperature and salinity on diatom cell lysis by DNA and RNA viruses
 The following supplement accompanies the article Effects of temperature and salinity on diatom cell lysis by DNA and RNA viruses Kei Kimura, Yuji Tomaru* *Corresponding author: tomaruy@affrc.go.jp Aquatic
The following supplement accompanies the article Effects of temperature and salinity on diatom cell lysis by DNA and RNA viruses Kei Kimura, Yuji Tomaru* *Corresponding author: tomaruy@affrc.go.jp Aquatic
Viruses in the sea Curtis A. Suttle 1
 INSIGHT REVIEW NATURE Vol 437 15 September 2005 doi:10.1038/nature04160 Viruses in the sea Curtis A. Suttle 1 Viruses exist wherever life is found. They are a major cause of mortality, a driver of global
INSIGHT REVIEW NATURE Vol 437 15 September 2005 doi:10.1038/nature04160 Viruses in the sea Curtis A. Suttle 1 Viruses exist wherever life is found. They are a major cause of mortality, a driver of global
Growth responses of Ulva prolifera to inorganic and organic. nutrients: Implications for macroalgal blooms in the
 1 2 3 Growth responses of Ulva prolifera to inorganic and organic nutrients: Implications for macroalgal blooms in the southern Yellow Sea, China 4 5 Hongmei Li a, Yongyu Zhang a *, Xiurong Han b, Xiaoyong
1 2 3 Growth responses of Ulva prolifera to inorganic and organic nutrients: Implications for macroalgal blooms in the southern Yellow Sea, China 4 5 Hongmei Li a, Yongyu Zhang a *, Xiurong Han b, Xiaoyong
Co-occurrence of DNA- and RNA-viruses infecting the bloom-forming dinoflagellate, Heterocapsa circularisquama, on the Japan coast
 Plankton Benthos Res 4(4): 129 134, 2009 Plankton & Benthos Research The Plankton Society of Japan Co-occurrence of DNA- and RNA-viruses infecting the bloom-forming dinoflagellate, Heterocapsa circularisquama,
Plankton Benthos Res 4(4): 129 134, 2009 Plankton & Benthos Research The Plankton Society of Japan Co-occurrence of DNA- and RNA-viruses infecting the bloom-forming dinoflagellate, Heterocapsa circularisquama,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Quantity of phosphorus spared via phospholipid substitutions by picocyanobacteria. (1 6 P atoms cell -1 )* (% of P in DNA) Synechococcus WH812.7 ±.1 15 ± 2 Synechococcus WH783 2.7
Supplementary Table 1. Quantity of phosphorus spared via phospholipid substitutions by picocyanobacteria. (1 6 P atoms cell -1 )* (% of P in DNA) Synechococcus WH812.7 ±.1 15 ± 2 Synechococcus WH783 2.7
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis!
 Factors Affecting Photosynthesis! Temperature Eppley (1972) Light Sverdrup s Critical Depth Model Nutrients Limitations Uptake Kinetics Temperature! The oceans vary much less than the land does, both seasonally
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis! Temperature Eppley (1972) Light Sverdrup s Critical Depth Model Nutrients Limitations Uptake Kinetics Temperature! The oceans vary much less than the land does, both seasonally
Received 3 August 1994/Accepted 14 December 1994
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1995, p. 1033 1038 Vol. 61, No. 3 0099-2240/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Regeneration of Phosphorus and Nitrogen by Four Species
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1995, p. 1033 1038 Vol. 61, No. 3 0099-2240/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Regeneration of Phosphorus and Nitrogen by Four Species
Temperature is a key factor in Micromonas virus interactions
 (217) 11, 61 612 217 International Society for Microbial Ecology All rights reserved 1751-7362/17 www.nature.com/ismej ORIGINAL ARTICLE Temperature is a key factor in Micromonas virus interactions David
(217) 11, 61 612 217 International Society for Microbial Ecology All rights reserved 1751-7362/17 www.nature.com/ismej ORIGINAL ARTICLE Temperature is a key factor in Micromonas virus interactions David
In steady state, new production = carbon export
 In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
Link NIOZ Repository:
 This is a postprint of: Martínez Martínez, J., Boere, A., Gilg, I., Lent, J.W.M. van, Witte, H., Bleijswijk, J.D.L. van & Brussaard, C.P.D., (2015) New lipid envelope-containing dsdna virus isolates infecting
This is a postprint of: Martínez Martínez, J., Boere, A., Gilg, I., Lent, J.W.M. van, Witte, H., Bleijswijk, J.D.L. van & Brussaard, C.P.D., (2015) New lipid envelope-containing dsdna virus isolates infecting
Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea
 The following supplement accompanies the article Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea Eva Sintes 1, 2, *, Karen Stoderegger 1, Veronica Parada 1,
The following supplement accompanies the article Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea Eva Sintes 1, 2, *, Karen Stoderegger 1, Veronica Parada 1,
The Influence of Iron on the Cellular Quota of Prochlorococcus
 The Influence of Iron on the Cellular Quota of Prochlorococcus Mak Saito Department of Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2393 fax:
The Influence of Iron on the Cellular Quota of Prochlorococcus Mak Saito Department of Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2393 fax:
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC.
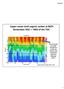 Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Carbon versus iron limitation of bacterial growth in the California upwelling regime
 December 2000 Volume 45 Number 8 Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(8), 2000, 1681 1688 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Carbon versus iron limitation of bacterial growth in the California
December 2000 Volume 45 Number 8 Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(8), 2000, 1681 1688 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Carbon versus iron limitation of bacterial growth in the California
In situ gross growth rates of Emiliania huxleyi in enclosures with different phosphate loadings revealed by die1 changes in DNA content
 Vol. 121: 271-277,1995 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Mar Ecol Prog Ser i Published May 25 In situ gross growth rates of Emiliania huxleyi in enclosures with different phosphate loadings revealed by die1
Vol. 121: 271-277,1995 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Mar Ecol Prog Ser i Published May 25 In situ gross growth rates of Emiliania huxleyi in enclosures with different phosphate loadings revealed by die1
Abundance and Distribution of Synechococcus spp. and Cyanophages in the Chesapeake Bay
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2011, p. 7459 7468 Vol. 77, No. 21 0099-2240/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aem.00267-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Abundance
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2011, p. 7459 7468 Vol. 77, No. 21 0099-2240/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aem.00267-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Abundance
Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling
 Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling Monika Winder Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences Stockholm University What does a more acidic
Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling Monika Winder Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences Stockholm University What does a more acidic
Ammonium uptake and growth limitation in marine phytoplankton
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 52(6), 2007, 2496 2506 E 2007, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Ammonium uptake and growth limitation in marine phytoplankton William G. Sunda and D. Ransom
Limnol. Oceanogr., 52(6), 2007, 2496 2506 E 2007, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Ammonium uptake and growth limitation in marine phytoplankton William G. Sunda and D. Ransom
Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea
 Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea DOC distributions in the Atlantic Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 Matthew Church Figures from Dennis Hansell DOC distributions in the Pacific Basin scale
Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea DOC distributions in the Atlantic Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 Matthew Church Figures from Dennis Hansell DOC distributions in the Pacific Basin scale
Dynamics of the decline of a phytoplankton bloom after an upwelling event
 Vol. 16: 121-126, 1984 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Published February 29 Dynamics of the decline of a phytoplankton bloom after an upwelling event R. G. Barlow Sea Fisheries
Vol. 16: 121-126, 1984 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Published February 29 Dynamics of the decline of a phytoplankton bloom after an upwelling event R. G. Barlow Sea Fisheries
Influence of Groundwater Constituents on Initiation of the Brown Tide in the Peconics Bay System
 Final Report to Suffolk County Department of Health Services Office of Ecology Influence of Groundwater Constituents on Initiation of the Brown Tide in the Peconics Bay System Contract No.: 525822801130000001
Final Report to Suffolk County Department of Health Services Office of Ecology Influence of Groundwater Constituents on Initiation of the Brown Tide in the Peconics Bay System Contract No.: 525822801130000001
High acrylate concentrations in the mucus of Phaeocystis globosa colonies
 Vol. 16: 45-52.1998 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Aquat Microb Ecol Published October 15 High acrylate concentrations in the mucus of Phaeocystis globosa colonies Diana J. B. Noordkamplr*, Michiel Schotten2,
Vol. 16: 45-52.1998 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Aquat Microb Ecol Published October 15 High acrylate concentrations in the mucus of Phaeocystis globosa colonies Diana J. B. Noordkamplr*, Michiel Schotten2,
Sverdrup s Critical Depth Revisited
 Sverdrup s Critical Depth Revisited For Homework 2, question 4, you need some additional information. Sverdrup assumed that the Compensation Depth (Ec) includes respiration from both phytoplankton and
Sverdrup s Critical Depth Revisited For Homework 2, question 4, you need some additional information. Sverdrup assumed that the Compensation Depth (Ec) includes respiration from both phytoplankton and
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 209: 19 34, 2001 Published January 5 Mar Ecol Prog Ser
 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 209: 19 34, 2001 Published January 5 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Effects of organic carbon, organic nitrogen, inorganic nutrients, and iron additions on the growth of phytoplankton
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 209: 19 34, 2001 Published January 5 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Effects of organic carbon, organic nitrogen, inorganic nutrients, and iron additions on the growth of phytoplankton
Effects of colloidal organic matter on the growth of bacteria and protists in lake water
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 39(6), 1994, 1276-1285 0 1994, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, 1nc. Effects of colloidal organic matter on the growth of bacteria and protists in lake water Lars
Limnol. Oceanogr., 39(6), 1994, 1276-1285 0 1994, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, 1nc. Effects of colloidal organic matter on the growth of bacteria and protists in lake water Lars
Three-year survey of abundance, prevalence and genetic diversity of chlorovirus populations in a small urban lake
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln James Van Etten Publications Plant Pathology Department 4-2016 Three-year survey of abundance, prevalence and genetic diversity
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln James Van Etten Publications Plant Pathology Department 4-2016 Three-year survey of abundance, prevalence and genetic diversity
The exopolymer secretions (EPS) layer surrounding Aureoumbra lagunensis cells affects growth, grazing, and behavior of protozoa
 1187 Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(5), 2000, 1187 1191 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. The exopolymer secretions (EPS) layer surrounding Aureoumbra lagunensis cells affects growth,
1187 Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(5), 2000, 1187 1191 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. The exopolymer secretions (EPS) layer surrounding Aureoumbra lagunensis cells affects growth,
Utilization of various nitrogen, phosphorus, and selenium compounds by Cochlodinium polykrikoides
 Journal of Environmental Biology September 2008, 29(5) 799-804 (2008) Triveni Enterprises, Lucknow (India) For personal use only Free paper downloaded from: www. jeb.co.in Commercial distribution of this
Journal of Environmental Biology September 2008, 29(5) 799-804 (2008) Triveni Enterprises, Lucknow (India) For personal use only Free paper downloaded from: www. jeb.co.in Commercial distribution of this
Interactions between algae and the microbial loop in experimental microcosms
 OIKOS 95: 231 238. Copenhagen 2001 Interactions between algae and the microbial loop in experimental microcosms Florence D. Hulot, Peter J. Morin and Michel Loreau Hulot, F. D., Morin, P. J. and Loreau,
OIKOS 95: 231 238. Copenhagen 2001 Interactions between algae and the microbial loop in experimental microcosms Florence D. Hulot, Peter J. Morin and Michel Loreau Hulot, F. D., Morin, P. J. and Loreau,
Differences in growth and alkaline phosphatase activity between Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella pyrenoidosa
 J. Limnol., 70(1): 21-25, 2011 DOI: 10.3274/JL11-70-1-04 Differences in growth and alkaline phosphatase activity between Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella pyrenoidosa in response to media with different
J. Limnol., 70(1): 21-25, 2011 DOI: 10.3274/JL11-70-1-04 Differences in growth and alkaline phosphatase activity between Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella pyrenoidosa in response to media with different
Infect Chlorella Cells
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1991, p. 3433-3437 0099-2240/91/123433-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1991, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 57, No. 12 Screening of Natural Waters for Viruses
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1991, p. 3433-3437 0099-2240/91/123433-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1991, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 57, No. 12 Screening of Natural Waters for Viruses
N itrogen fixation is a critical process to provide new bioavailable nitrogen to phytoplankton in the ocean1 5,
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: MICROBIAL BIOOCEANOGRAPHY BIOGEOCHEMISTRY Received 19 December 2013 Accepted 7 March 2014 Published 24 March 2014 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to T.-Y.H.
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: MICROBIAL BIOOCEANOGRAPHY BIOGEOCHEMISTRY Received 19 December 2013 Accepted 7 March 2014 Published 24 March 2014 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to T.-Y.H.
Microbial herbivory on the brown tide alga, Aureococcus anophagefferens: results from natural ecosystems, mesocosms and laboratory experiments
 Harmful Algae 3 (2004) 439 457 Microbial herbivory on the brown tide alga, Aureococcus anophagefferens: results from natural ecosystems, mesocosms and laboratory experiments David A. Caron a,, Christopher
Harmful Algae 3 (2004) 439 457 Microbial herbivory on the brown tide alga, Aureococcus anophagefferens: results from natural ecosystems, mesocosms and laboratory experiments David A. Caron a,, Christopher
4.1 Cycling of Matter Date: Cycling of Organic and Inorganic Matter. Build your Own Notes:
 4.1 Cycling of Matter Date: Build your Own Notes: Use these topics as guidelines to create your own notes for 4.1 from pages 83 84 Study Notes/Questions Cycling of Organic and Inorganic Matter Matter is
4.1 Cycling of Matter Date: Build your Own Notes: Use these topics as guidelines to create your own notes for 4.1 from pages 83 84 Study Notes/Questions Cycling of Organic and Inorganic Matter Matter is
Bacterial community structures in the Arctic Ocean: the effect of increased carbon load on nutrient competition and bacterial diversity Birte Töpper
 Bacterial community structures in the Arctic Ocean: the effect of increased carbon load on nutrient competition and bacterial diversity Birte Töpper Dissertation for the degree philosophiae doctor (PhD)
Bacterial community structures in the Arctic Ocean: the effect of increased carbon load on nutrient competition and bacterial diversity Birte Töpper Dissertation for the degree philosophiae doctor (PhD)
Discovery of. 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes. 1931: first images of viruses obtained using
 Discovery of (1884: invention of the Chamberland filter with pores smaller than bacteria) 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes a paper in which shows that extracts from diseased tobacco plants
Discovery of (1884: invention of the Chamberland filter with pores smaller than bacteria) 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes a paper in which shows that extracts from diseased tobacco plants
Utilization of Organic Nitrogen Sources by Two Phytoplankton Species and a Bacterial Isolate in Pure and Mixed Cultures
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 1994, p. 1554-156 Vol. 6, No. 5 99-224/94/$4.+ Copyright C) 1994, American Society for Microbiology Utilization of Organic Nitrogen Sources by Two Phytoplankton
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 1994, p. 1554-156 Vol. 6, No. 5 99-224/94/$4.+ Copyright C) 1994, American Society for Microbiology Utilization of Organic Nitrogen Sources by Two Phytoplankton
Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos
 Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos Jonathan Herzog University of Washington School of Oceanography 1 NON-TECHNICAL SUMMARY The goal of this experiment
Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos Jonathan Herzog University of Washington School of Oceanography 1 NON-TECHNICAL SUMMARY The goal of this experiment
Primary Productivity and Lake Health: Examination of Phytoplankton Growth Rate Regulations in Keuka Lake via Short-term Microcosm Experiments
 Primary Productivity and Lake Health: Examination of Phytoplankton Growth Rate Regulations in Keuka Lake via Short-term Microcosm Experiments Extended Abstract Rochester Academy of Sciences Student Scientific
Primary Productivity and Lake Health: Examination of Phytoplankton Growth Rate Regulations in Keuka Lake via Short-term Microcosm Experiments Extended Abstract Rochester Academy of Sciences Student Scientific
The Biochemical Composition of Some Micro-Algal Species Isolated From the Shatt al-arab River
 Marina Mesopotamica Volume 18, Number 1, pp. 1 8 (2003) The Biochemical Composition of Some Micro-Algal Species Isolated From the Shatt al-arab River Marine Science Centre, University of Basrah, Basrah,
Marina Mesopotamica Volume 18, Number 1, pp. 1 8 (2003) The Biochemical Composition of Some Micro-Algal Species Isolated From the Shatt al-arab River Marine Science Centre, University of Basrah, Basrah,
elucidate the role of trace metals in the ecology of the oceans and the
 CHAPTER I I. INTRODUCTION Microalgae acquire nutrients from their environment in order to sustain their growth and division. The classification of nutrients is made on the basis of their quantitative requirements
CHAPTER I I. INTRODUCTION Microalgae acquire nutrients from their environment in order to sustain their growth and division. The classification of nutrients is made on the basis of their quantitative requirements
Chlorovirus: A Genus of Phycodnaviridae that Infects Certain Chlorella-Like Green Algae
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Papers in Plant Pathology Plant Pathology Department 1-1-2005 Chlorovirus: A Genus of Phycodnaviridae that Infects Certain
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Papers in Plant Pathology Plant Pathology Department 1-1-2005 Chlorovirus: A Genus of Phycodnaviridae that Infects Certain
Cell volume to cell carbon conversion factors for a bacterivorous Monas sp. enriched from seawater
 Vol. 36: 171-175, 1987 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1 Published March I Cell volume to cell carbon conversion factors for a bacterivorous Monas sp. enriched from seawater Knut
Vol. 36: 171-175, 1987 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1 Published March I Cell volume to cell carbon conversion factors for a bacterivorous Monas sp. enriched from seawater Knut
Intraspecies Host Specificity of a Single-Stranded RNA Virus Infecting a Marine. Photosynthetic Protist Is Determined at the Early Steps of Infection
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 15 November 2006 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01082-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 15 November 2006 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01082-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Responses of bacterioplankton and phytoplankton to organic carbon and inorganic nutrient additions in contrasting oceanic ecosystems
 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 22: 175 184, 2000 Published September 8 Aquat Microb Ecol Responses of bacterioplankton and phytoplankton to organic carbon and inorganic nutrient additions in contrasting
AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 22: 175 184, 2000 Published September 8 Aquat Microb Ecol Responses of bacterioplankton and phytoplankton to organic carbon and inorganic nutrient additions in contrasting
VERIFICATION OF THE PREDICTED SHIFT FROM DIATOMS TO FLAGELLATES IN COASTAL SEAS USING LARGE SCALE MESOCOSM DATA
 International Journal of Latest Research in Science and Technology Volume, Issue 1: Page No.11-1, January-February 15 http://www.mnkjournals.com/ijlrst.htm ISSN (Online):7-599 VERIFICATION OF THE PREDICTED
International Journal of Latest Research in Science and Technology Volume, Issue 1: Page No.11-1, January-February 15 http://www.mnkjournals.com/ijlrst.htm ISSN (Online):7-599 VERIFICATION OF THE PREDICTED
Predicting excretion rates of microzooplankton from carbon metabolism and elemental ratios
 468 Comment Limnol. Oceanogr., 38(2), 1993,468-472 0 1993, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Predicting excretion rates of microzooplankton from carbon metabolism and elemental
468 Comment Limnol. Oceanogr., 38(2), 1993,468-472 0 1993, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Predicting excretion rates of microzooplankton from carbon metabolism and elemental
Bacterial Mortality: A Pathway for the Formation of Refractory DOM?
 Bacterial Mortality: A Pathway for the Formation of Refractory DOM? T. Nagata 1, D. L. Kirchman 2 1 Ocean Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Minami-dai, Nakano, Tokyo 164-8639 Japan 2 College of
Bacterial Mortality: A Pathway for the Formation of Refractory DOM? T. Nagata 1, D. L. Kirchman 2 1 Ocean Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Minami-dai, Nakano, Tokyo 164-8639 Japan 2 College of
Competition for inorganic and organic forms of nitrogen and phosphorous between phytoplankton and bacteria during an Emiliania huxleyi spring bloom
 Biogeosciences, 5, 371 383, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Competition for inorganic and organic forms of nitrogen and
Biogeosciences, 5, 371 383, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Competition for inorganic and organic forms of nitrogen and
The role of water in the maintenance of life
 Inorganic compounds The role of water in the maintenance of life As mentioned in Table (Reference), up to 65% of our bodies are made up of water. Water is an inorganic compound made up of two hydrogen
Inorganic compounds The role of water in the maintenance of life As mentioned in Table (Reference), up to 65% of our bodies are made up of water. Water is an inorganic compound made up of two hydrogen
Macronutrients in the ocean
 Macronutrients in the ocean Philip Boyd NIWA/OTAGO, New Zealand September 2011 OUTLINE What is a macronutrient? Trends in nutrients & limitation The N cycle sources, sinks and recycling Silicate the body
Macronutrients in the ocean Philip Boyd NIWA/OTAGO, New Zealand September 2011 OUTLINE What is a macronutrient? Trends in nutrients & limitation The N cycle sources, sinks and recycling Silicate the body
Seasonal and vertical difference in negative and positive effects of grazers on heterotrophic bacteria in Lake Biwa
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(8), 2000, 1689 1696 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Seasonal and vertical difference in negative and positive effects of grazers on heterotrophic
Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(8), 2000, 1689 1696 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Seasonal and vertical difference in negative and positive effects of grazers on heterotrophic
The influence of nitrogen and phosphorus on the growth of a diatom Skeletonema costatum (Greville) Cleve
 Bangladesh}. Fish. Res., 2(1 ), 1998 : 23-29 The influence of nitrogen and phosphorus on the growth of a diatom Skeletonema costatum (Greville) Cleve 1 * 1 S. Khan ', M.M. Haque, 0. Arakawa and Y. Onoue
Bangladesh}. Fish. Res., 2(1 ), 1998 : 23-29 The influence of nitrogen and phosphorus on the growth of a diatom Skeletonema costatum (Greville) Cleve 1 * 1 S. Khan ', M.M. Haque, 0. Arakawa and Y. Onoue
Phaeocystis colony mucus components and the importance of calcium ions for colony stability
 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Published October 19 NOTE Phaeocystis colony mucus components and the importance of calcium ions for colony stability W. H. M. van Boekel Department
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Published October 19 NOTE Phaeocystis colony mucus components and the importance of calcium ions for colony stability W. H. M. van Boekel Department
Journal of Marine Systems
 Journal of Marine Systems 85 (2011) 71 85 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Marine Systems journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jmarsys Carbon and nitrogen flows during a bloom
Journal of Marine Systems 85 (2011) 71 85 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Marine Systems journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jmarsys Carbon and nitrogen flows during a bloom
Influence of UV-B radiation on bacterial activity in coastal waters
 Journal of Plankton Research Vol.22 no.8 pp.1501 1511, 2000 Influence of UV-B radiation on bacterial activity in coastal waters Kim Gustavson 1,4, Kristine Garde 1, Sten-Åke Wängberg 2 and Johanne-Sophie
Journal of Plankton Research Vol.22 no.8 pp.1501 1511, 2000 Influence of UV-B radiation on bacterial activity in coastal waters Kim Gustavson 1,4, Kristine Garde 1, Sten-Åke Wängberg 2 and Johanne-Sophie
Influence of different concentrations of sodium bicarbonate on growth rate and chlorophyll content of Chlorella salina
 7 J. Mar. Biol. Ass. India, 5 (1) : 7-78, January - June Reeta 8 Jayasankar and K.K. Valsala Influence of different concentrations of sodium bicarbonate on growth rate and chlorophyll content of Chlorella
7 J. Mar. Biol. Ass. India, 5 (1) : 7-78, January - June Reeta 8 Jayasankar and K.K. Valsala Influence of different concentrations of sodium bicarbonate on growth rate and chlorophyll content of Chlorella
Nutrients & iclicker Question Which is not a major ion? A) Sodium (Na + ) B) Potassium (K + ) C) Chloride (Cl - ) D) Silicon (Si) E) Sulfate (SO 4
 Nutrients & Tracers Non-conservative element: short residence time removed efficiently by biological or chemical processes Nutrients: used by living organisms Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorous, Iron, silicate,
Nutrients & Tracers Non-conservative element: short residence time removed efficiently by biological or chemical processes Nutrients: used by living organisms Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorous, Iron, silicate,
Temperature effects on phytoplankton growth in continuous culture1
 932 Notes lation of marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17 : 37 l-382. MACISAAC, J. J., AND R. C. DUGDALE. 1972. Interactions of light and inorganic nitrogen in controlling nitrogen uptake in the sea.
932 Notes lation of marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17 : 37 l-382. MACISAAC, J. J., AND R. C. DUGDALE. 1972. Interactions of light and inorganic nitrogen in controlling nitrogen uptake in the sea.
Marine Life. Plankton and Primary Production
 Marine Life Plankton and Primary Production Marine Plankton Key Ideas Drifting, floating and weakly swimming plants and animals - mainly in sunlit portion of ocean Phytoplankton Plankton make up more well
Marine Life Plankton and Primary Production Marine Plankton Key Ideas Drifting, floating and weakly swimming plants and animals - mainly in sunlit portion of ocean Phytoplankton Plankton make up more well
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
 Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Enrichment experiments for determining nutrient limitation: Four methods compared1
 Notes 649 Enrichment experiments for determining nutrient limitation: Four methods compared1 Abstract-Four nutrient bioassay techniques were compared in studies of an oligotrophic, soft-water lake in New
Notes 649 Enrichment experiments for determining nutrient limitation: Four methods compared1 Abstract-Four nutrient bioassay techniques were compared in studies of an oligotrophic, soft-water lake in New
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Acquisition of intact polar lipids from the prymnesiophyte Phaeocystis globosa by its lytic virus PgV-07T Maat, D.S.; Bale, N.J.; Hopmans, E.C.; Baudoux, A.C.; Sinninghe
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Acquisition of intact polar lipids from the prymnesiophyte Phaeocystis globosa by its lytic virus PgV-07T Maat, D.S.; Bale, N.J.; Hopmans, E.C.; Baudoux, A.C.; Sinninghe
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VIRUS AS POPULATIONS COMPOSITION COMPLEXITY DYNAMICS AND BIOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : VIRUS AS POPULATIONS COMPOSITION COMPLEXITY DYNAMICS AND BIOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 virus as populations composition pdf virus as populations composition
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VIRUS AS POPULATIONS COMPOSITION COMPLEXITY DYNAMICS AND BIOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 virus as populations composition pdf virus as populations composition
Eelgrass Wasting Disease: an Overview
 Western Washington University Western CEDAR Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference 2014 Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference (Seattle, Wash.) Apr 30th, 10:30 AM - 12:00 PM Eelgrass Wasting Disease: an Overview Fred
Western Washington University Western CEDAR Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference 2014 Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference (Seattle, Wash.) Apr 30th, 10:30 AM - 12:00 PM Eelgrass Wasting Disease: an Overview Fred
Microbial nutrition. Nutrients. Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth. Chapter 7
 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth Chapter 7 Microbial nutrition Macronutrients required in large quantities; play principal roles in cell structure & metabolism proteins, carbohydrates
Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth Chapter 7 Microbial nutrition Macronutrients required in large quantities; play principal roles in cell structure & metabolism proteins, carbohydrates
Isolation, Characterization of algal Chlorophyll and Hydrocarbon content in algae found in National Capital Region
 Isolation, Characterization of algal Chlorophyll and Hydrocarbon content in algae found in National Capital Region Bhatnagar Tripti, Awasthi Shashank, Kumar Sanjeev Codon Biotech Pvt. Ltd., C-23, Sector
Isolation, Characterization of algal Chlorophyll and Hydrocarbon content in algae found in National Capital Region Bhatnagar Tripti, Awasthi Shashank, Kumar Sanjeev Codon Biotech Pvt. Ltd., C-23, Sector
Title. Author(s)KURASAWA, Hideo. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title The Phytoplankton Zooplankton Relationships in Two P Author(s)KURASAWA, Hideo 北海道大學理學部紀要 = JOURNAL OF THE FACULTY OF SCIENCE HOKKA CitationZOOLOGY, 13(1-4): 180-186 Issue Date 1957-08 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/27223
Title The Phytoplankton Zooplankton Relationships in Two P Author(s)KURASAWA, Hideo 北海道大學理學部紀要 = JOURNAL OF THE FACULTY OF SCIENCE HOKKA CitationZOOLOGY, 13(1-4): 180-186 Issue Date 1957-08 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/27223
Replication Defective Enterovirus Infections: Implications for Type I Diabetes
 Replication Defective Enterovirus Infections: Implications for Type I Diabetes N. M. Chapman Department of Pathology & Microbiology University of Nebraska Medical Center Enterovirus Genome and 2 Capsid
Replication Defective Enterovirus Infections: Implications for Type I Diabetes N. M. Chapman Department of Pathology & Microbiology University of Nebraska Medical Center Enterovirus Genome and 2 Capsid
Nutrient uptake in the reef-building coral Acropora palmata at natural environmental concentrations
 Vol. 68: 65-69, 1990 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Published December 15 Nutrient uptake in the reef-building coral Acropora palmata at natural environmental concentrations John
Vol. 68: 65-69, 1990 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Published December 15 Nutrient uptake in the reef-building coral Acropora palmata at natural environmental concentrations John
RECENT BROWN TIDE ACTIVITY
 New York Report #7 September 2002 RECENT BROWN TIDE ACTIVITY Following are the current results of the Suffolk County Department of Health Services monitoring for the year 2002 on Long Island. The Peconic
New York Report #7 September 2002 RECENT BROWN TIDE ACTIVITY Following are the current results of the Suffolk County Department of Health Services monitoring for the year 2002 on Long Island. The Peconic
Effect of B-vitamins (B 1, B 12 ) and inorganic nutrients on algal bloom dynamics in a coastal ecosystem
 Vol. 49: 181 194, 27 doi: 1.3354/ame1132 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Aquat Microb Ecol Published November 15 Effect of B-vitamins (B 1, B 12 ) and inorganic nutrients on algal bloom dynamics in a coastal
Vol. 49: 181 194, 27 doi: 1.3354/ame1132 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Aquat Microb Ecol Published November 15 Effect of B-vitamins (B 1, B 12 ) and inorganic nutrients on algal bloom dynamics in a coastal
Bacterial-algal interactions in polysaccharide production
 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Aquat Microb Ecol / Published August 31 Bacterial-algal interactions in polysaccharide production Franca Guerrini, Annalisa Mazzotti, Laurita Boni, Rossella Pistocchi* Scienze
AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Aquat Microb Ecol / Published August 31 Bacterial-algal interactions in polysaccharide production Franca Guerrini, Annalisa Mazzotti, Laurita Boni, Rossella Pistocchi* Scienze
Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific
 PICES 2014 Annual Meeting Yeosu, Korea Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific T. Fujiki 1, K. Matsumoto 1, Y.
PICES 2014 Annual Meeting Yeosu, Korea Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific T. Fujiki 1, K. Matsumoto 1, Y.
Isolation of Microalgae Strains from Pond Water and their Medium Standardization for Lipid Production
 Research Article Isolation of Microalgae Strains from Pond Water and their Medium Standardization for Lipid Production Vidyadharani Gopalakrishnan, Dhandapani Ramamurthy * Department of Microbiology, Periyar
Research Article Isolation of Microalgae Strains from Pond Water and their Medium Standardization for Lipid Production Vidyadharani Gopalakrishnan, Dhandapani Ramamurthy * Department of Microbiology, Periyar
Detection of Karenia mikimotoi by spectral absorption signatures
 Detection of Karenia mikimotoi by spectral absorption signatures P. A. STÆHR* 2 AND J. J. CULLEN 1 NATIONAL ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE, DEPARTMENT OF MARINE ECOLOGY, FREDERIKSBORGVEJ 399, PO BOX
Detection of Karenia mikimotoi by spectral absorption signatures P. A. STÆHR* 2 AND J. J. CULLEN 1 NATIONAL ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE, DEPARTMENT OF MARINE ECOLOGY, FREDERIKSBORGVEJ 399, PO BOX
Michael J. Behrenfeld Oregon State University
 Michael J. Behrenfeld Oregon State University global > 15 o C Tidbits Based on Vertically Generalized Production Model (VGPM) Initial increase = 1,930 TgC/yr Subsequent decrease = 190 TgC/yr Global trends
Michael J. Behrenfeld Oregon State University global > 15 o C Tidbits Based on Vertically Generalized Production Model (VGPM) Initial increase = 1,930 TgC/yr Subsequent decrease = 190 TgC/yr Global trends
Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate
 Introduction Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate Compounds of nitrogen and phosphorus are major cellular components of organisms. Since the availability of these elements may
Introduction Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate Compounds of nitrogen and phosphorus are major cellular components of organisms. Since the availability of these elements may
Utilization of N, P and organic C by heterotrophic bacteria. 11. Comparison of experiments and a mathematical model
 Vol. 37: 285-293, 1987 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. l Published May 5 Utilization of N, P and organic C by heterotrophic bacteria. 11. Comparison of experiments and a mathematical
Vol. 37: 285-293, 1987 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. l Published May 5 Utilization of N, P and organic C by heterotrophic bacteria. 11. Comparison of experiments and a mathematical
Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean
 Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean Michael Landry Integrative Oceanography Division Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego SIBER Workshop
Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean Michael Landry Integrative Oceanography Division Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego SIBER Workshop
Phytoplankton Climate Regulation in Positive and Negative Feedback Systems: The CLAW and anti-claw hypotheses
 Phytoplankton Climate Regulation in Positive and Negative Feedback Systems: The CLAW and anti-claw hypotheses Adam Stoer, Undergraduate Student, Dalhousie University Abstract The global climate crisis
Phytoplankton Climate Regulation in Positive and Negative Feedback Systems: The CLAW and anti-claw hypotheses Adam Stoer, Undergraduate Student, Dalhousie University Abstract The global climate crisis
Prasinovirus Attack of Ostreococcus Is Furtive by Day but Savage by Night
 JVI Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 29 November 2017 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01703-17 Copyright 2017 Derelle et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons
JVI Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 29 November 2017 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01703-17 Copyright 2017 Derelle et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons
J. Theo M. Elzenga 1 and Hidde B. A. Prins Department of Plant Biology, University of Groningen, P.O. Box 14, 9750AA Haren, The Netherlands
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(2), 2000, 372 380 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. The role of extracellular carbonic anhydrase activity in inorganic carbon utilization of Phaeocystis
Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(2), 2000, 372 380 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. The role of extracellular carbonic anhydrase activity in inorganic carbon utilization of Phaeocystis
High control of bacterial production by viruses in a eutrophic oxbow lake
 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 27: 1 12, 2002 Published February 18 Aquat Microb Ecol High control of bacterial production by viruses in a eutrophic oxbow lake Ulrike R. Fischer, Branko Velimirov* Institut
AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Vol. 27: 1 12, 2002 Published February 18 Aquat Microb Ecol High control of bacterial production by viruses in a eutrophic oxbow lake Ulrike R. Fischer, Branko Velimirov* Institut
Biomass Production and Assimilation of Dissolved Organic Matter by SAR11 Bacteria in the Northwest Atlantic Ocean
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 2005, p. 2979 2986 Vol. 71, No. 6 0099-2240/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aem.71.6.2979 2986.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 2005, p. 2979 2986 Vol. 71, No. 6 0099-2240/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aem.71.6.2979 2986.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Dinophysis acuminata in Delaware s Inland Bays and coastal waters
 Dinophysis acuminata in Delaware s Inland Bays and coastal waters 2001-2015 Ed Whereat, Program Coordinator, University of Delaware Citizen Monitoring Program Delaware Sea Grant Marine Advisory Service
Dinophysis acuminata in Delaware s Inland Bays and coastal waters 2001-2015 Ed Whereat, Program Coordinator, University of Delaware Citizen Monitoring Program Delaware Sea Grant Marine Advisory Service
Mechanisms and Rates of Decay of Marine Viruses in Seawatert
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1992, P. 3721-3729 0099-2240/92/113721-09$02.00/0 Copyright 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 58, No. 11 Mechanisms and Rates of Decay of Marine
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1992, P. 3721-3729 0099-2240/92/113721-09$02.00/0 Copyright 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 58, No. 11 Mechanisms and Rates of Decay of Marine
Diel periodicity in Synechococcus populations and grazing by heterotrophic nanoflagellates: Analysis of food vacuole contents
 Notes 1565 Limnol. Oceanogr., 44(6), 1999, 1565 1570 1999, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Diel periodicity in Synechococcus populations and grazing by heterotrophic nanoflagellates:
Notes 1565 Limnol. Oceanogr., 44(6), 1999, 1565 1570 1999, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Diel periodicity in Synechococcus populations and grazing by heterotrophic nanoflagellates:
Lecture 2: Virology. I. Background
 Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
BACTERIAL GROWTH. FYBSc.
 BACTERIAL GROWTH FYBSc. Bacterial growth Binary fission Generation time Phases of growth 4-2 Binary fission 1. Prokaryote cells grow by increasing in cell number (as opposed to increasing in size). 2.
BACTERIAL GROWTH FYBSc. Bacterial growth Binary fission Generation time Phases of growth 4-2 Binary fission 1. Prokaryote cells grow by increasing in cell number (as opposed to increasing in size). 2.
Effect of Temperature on Growth, Respiration, and Nutrient Regeneration by an Omnivorous Microflagellatet
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1986, p. 1340-1347 Vol. 52, No. 6 0099-2240/86/121340-08$02.00/0 Copyright 1986, American Society for Microbiology Effect of Temperature on Growth, Respiration,
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1986, p. 1340-1347 Vol. 52, No. 6 0099-2240/86/121340-08$02.00/0 Copyright 1986, American Society for Microbiology Effect of Temperature on Growth, Respiration,
Nutrient- vs. Energy-Limitation in the Sea:
 Nutrient- vs. Energy-Limitation in the Sea: The Red Sea and the Antarctic Ocean as Extreme Case Studies Max M. Tilzer University of Constance, Germany ISEEQS-Meeting, 29 May 1 June 2005 Katsushika Hokusai:
Nutrient- vs. Energy-Limitation in the Sea: The Red Sea and the Antarctic Ocean as Extreme Case Studies Max M. Tilzer University of Constance, Germany ISEEQS-Meeting, 29 May 1 June 2005 Katsushika Hokusai:
