In steady state, new production = carbon export
|
|
|
- Joleen Beasley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 In steady state, new production = carbon export
2 Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing
3 What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority of organic material in the ocean is in the dissolved phase (operationally defined as <0.7 µm or 0.2 µm)
4
5 Contribution of different sources Sources of DOM to ocean ecosystems 1. Direct algal excretion 2. Zooplankton (sloppy feeding, excretion) 3. Viral lysis 4. Bacterial release 5. Solubilization of POM to marine DOM % carbon released Exudation Zooplankton Viral Solubilization Bacterial 20 0 Exudation % 14 C primary production, zooplankton % carbon ingested, solubilization % C released from aggregates, bacterial % release from 14 C labeled organic substrate. Sources: Nagata (2001), Carlson (2002).
6 Why dissolved organics matter Dissolved organic matter constitutes the largest global reservoir of fixed carbon ~700 x g C. Oxidation of even 1% of the seawater DOC pool in a 1 year period would exceed annual anthropogenic CO 2 emissions. DOC can also serve as an important component of new production.
7 Amino acids Identified DOM compound classes Peptides Nucleotides and nucleic acids Lipids Vitamins Monosaccharides Polysaccharides
8 The vast majority of organic matter in the sea remains chemically uncharacterized Carbohydrates, neutral sugars, amino acids, and amino sugars make up ~20% of the bulk DOC pool in the upper ocean
9 Reactivity of DOM Labile: simple sugar monomers, amino acids)-typically nanomolar concentrations Semi-labile: amino sugars (ex. N-acetyl glucosamine)-typically ~1-10 of micromolar Refractory: largely unknown composition, rich in C relative to other nutrients (N, P); 10s of micromolar DOM compound DCAA DFAA Carbohydrates Glucose Bulk DOP Bulk DON Bulk DOC Compound Concentration (µmo L -1 )
10 Typical DOC profile : elevated in near surface water, decreasing through the thermocline, stable at depth. Labile pools cycle over time scales of hours to days. Semi-labile pools persist for weeks to months. Refractory material cycles over on time scales ranging from decadal to multidecadal perhaps longer
11 Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Late winter (January March) deep mixing Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson, UCSB
12 Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson, UCSB
13 Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson, UCSB TOC Profiles at BATS
14 Prebomb organic matter production: 14 C < -50 Post bomb organic matter production: 14 C > ~-50 and <200
15 DIC isotopes indicate bomb carbon has begun to penetrate into the thermocline; moreover DIC appears to turnover ~ years. DOC isotopes indicate prebomb carbon throughout the ocean, with deep waters showing very old, prebomb origin. Some fraction of DOC appears to resist degradation for >6000 years. Prebomb organic matter production: 14 C < -50 Post bomb organic matter production: 14 C > ~-50 and <200 Sargasso Sea deep ocean DOC produced 3970 years ago Southern Ocean DOCproduced 5570 years ago Central N. Pacific DOCproduced 5980 years ago
16 Basin-scale gradients in deep ocean DOC concentrations: slow degradation and transport of organic carbon DOC during circulation ~14 µm
17 Redfield stoichiometry of organic matter remineralization This equation describes photosynthetic nitrate assimilation THE RATIO 106C: 16N : 1P : 138 O 2 mole : mole : mole : mole Aerobic remineralization of organic matter: (CH 2 O) 106 (NH 3 )16H 3 PO O 2 106CO H 2 O +16HNO 3 + H 3 PO 4 Consumes O 2 Produces CO 2 Produces nutrients O 2 during ocean circulation ~200 µm. Thus DOC : O 2 = 14 µm C / 200 µm O 2 = 0.07 C: O 2 compare this to 106C/138O 2 = 0.78 C/O 2 **In the deep ocean, DOC appears to support a small fraction of respiratory O 2 consumed during ocean circulation**
18 Typical DOC profile : elevated in near surface water, decreasing through the thermocline, stable at depth. Almost ½ of the recently produced material is removed by ~1000m where does it go?
19 The Microbial Loop Classic Food web Phytoplankton Inorganic Nutrients A simplified depiction of the microbial loop Heterotrophic bacteria Herbivores Dissolved organic matter Higher trophic levels (zooplankton, fish, etc.) Protozoa
20 Bacterial growth on organic matter requires relatively small (<500 Daltons, ~0.5 nm) molecules that can be readily transported into the cells. Thus, bacteria often utilize cell-surface enzymes to breakdown polymeric organic matter for subsequent uptake nm µm mm Small molecules Dissolved Colloids Viruses Macromolecules Membrane filters Bacteria Clay Particulate Zooplankton Phytoplankton Pollen Silt Sand Screens Molecular sieves Filter papers Small molecular weight DOM Colloids Enzymatic hydrolysis Particulate organic matter Bacteria do not use particulate organic matter for growth--- it must first be converted to dissolved organic matter; this requires energy
Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea
 Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea DOC distributions in the Atlantic Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 Matthew Church Figures from Dennis Hansell DOC distributions in the Pacific Basin scale
Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea DOC distributions in the Atlantic Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 Matthew Church Figures from Dennis Hansell DOC distributions in the Pacific Basin scale
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC.
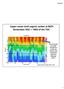 Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Total organic carbon at BATS Remember that DOC = ~98% of the TOC.
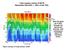 Total organic carbon at BATS Remember that DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Total organic carbon at BATS Remember that DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Southern Ocean MBL CCN Budget: Contribution from Primary Sea Spray Aerosol Organics. Trish Quinn NOAA PMEL
 Southern Ocean MBL CCN Budget: Contribution from Primary Sea Spray Aerosol Organics Trish Quinn NOAA PMEL patricia.k.quinn@noaa.gov Marine Biota Climate Feedback Loop Charlson et al., Nature, 1987. Aerosol
Southern Ocean MBL CCN Budget: Contribution from Primary Sea Spray Aerosol Organics Trish Quinn NOAA PMEL patricia.k.quinn@noaa.gov Marine Biota Climate Feedback Loop Charlson et al., Nature, 1987. Aerosol
Zackary Johnson Department of Oceanography
 Zackary Johnson Department of Oceanography http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621 Application of Bioenergetics to Biological Oceanography Biochemical parameters indicative of stock
Zackary Johnson Department of Oceanography http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621 Application of Bioenergetics to Biological Oceanography Biochemical parameters indicative of stock
Biogeochemical cycling of dissolved organic C and nutrients. Figure by MIT OCW.
 Biogeochemical cycling of dissolved organic C and nutrients Figure by MIT OCW. The profile of [DOC] With depth in the ocean 1. Measured by HTCO or wet chemical oxidation 2. Surface values are 60-80µM C
Biogeochemical cycling of dissolved organic C and nutrients Figure by MIT OCW. The profile of [DOC] With depth in the ocean 1. Measured by HTCO or wet chemical oxidation 2. Surface values are 60-80µM C
Zooplankton. Fall 2006
 Zooplankton Fall 2006 Plankton Classification Plankton Holoplankton Meroplankton Plankton Classification Picoplankton (0.2 2 µm) Plankton Nanoplankton (2-20 µm) Microplankton (20-200 µm) Mesoplankton (200-2000
Zooplankton Fall 2006 Plankton Classification Plankton Holoplankton Meroplankton Plankton Classification Picoplankton (0.2 2 µm) Plankton Nanoplankton (2-20 µm) Microplankton (20-200 µm) Mesoplankton (200-2000
Prokaryotic Metabolism *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44606 1 Prokaryotic Metabolism * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m44606 1 Prokaryotic Metabolism * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
I. ROLE OF CARBON IN ORGANISMS: Organic compounds = compounds that contain carbon Ex: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins
 I. ROLE OF CARBON IN ORGANISMS: Organic compounds = compounds that contain carbon Ex: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins Inorganic compounds = compounds that DO NOT contain carbon Ex: Vitamins, minerals,
I. ROLE OF CARBON IN ORGANISMS: Organic compounds = compounds that contain carbon Ex: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins Inorganic compounds = compounds that DO NOT contain carbon Ex: Vitamins, minerals,
Derived copy of Bis2A 08.0 Metabolism from a microbes perspective *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56799 1 Derived copy of Bis2A 08.0 Metabolism from a microbes perspective * Erin Easlon Based on Bis2A 08.0 Metabolism from a microbes perspective by OpenStax Mitch Singer This work
OpenStax-CNX module: m56799 1 Derived copy of Bis2A 08.0 Metabolism from a microbes perspective * Erin Easlon Based on Bis2A 08.0 Metabolism from a microbes perspective by OpenStax Mitch Singer This work
Soil Organic Matter. Unit 2. Forms of Soil Organic Matter: OM OC x (assumes 30% C) (1.72 typically used as a conversion factor)
 Unit 2 Soil Organic Matter OM OC x 1.7-2.0 (assumes 30% C) (1.72 typically used as a conversion factor) Histosol Alfisol Spodosol Forms of Soil Organic Matter: - dissolved (soil solution): DOM Nonliving
Unit 2 Soil Organic Matter OM OC x 1.7-2.0 (assumes 30% C) (1.72 typically used as a conversion factor) Histosol Alfisol Spodosol Forms of Soil Organic Matter: - dissolved (soil solution): DOM Nonliving
Biochemistry Name: Practice Questions
 Name: Practice Questions 1. Carbohydrate molecules A and B come in contact with the cell membrane of the same cell. Molecule A passes through the membrane readily, but molecule B does not. It is most likely
Name: Practice Questions 1. Carbohydrate molecules A and B come in contact with the cell membrane of the same cell. Molecule A passes through the membrane readily, but molecule B does not. It is most likely
Macronutrients in the ocean
 Macronutrients in the ocean Philip Boyd NIWA/OTAGO, New Zealand September 2011 OUTLINE What is a macronutrient? Trends in nutrients & limitation The N cycle sources, sinks and recycling Silicate the body
Macronutrients in the ocean Philip Boyd NIWA/OTAGO, New Zealand September 2011 OUTLINE What is a macronutrient? Trends in nutrients & limitation The N cycle sources, sinks and recycling Silicate the body
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-III
 OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-III Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621/ dc 1 /dt = growth Standing Stock C 1 Overview
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-III Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621/ dc 1 /dt = growth Standing Stock C 1 Overview
Bacterial Mortality: A Pathway for the Formation of Refractory DOM?
 Bacterial Mortality: A Pathway for the Formation of Refractory DOM? T. Nagata 1, D. L. Kirchman 2 1 Ocean Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Minami-dai, Nakano, Tokyo 164-8639 Japan 2 College of
Bacterial Mortality: A Pathway for the Formation of Refractory DOM? T. Nagata 1, D. L. Kirchman 2 1 Ocean Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Minami-dai, Nakano, Tokyo 164-8639 Japan 2 College of
Lecture 19: Soil Organic Matter
 Lecture 19: Soil Organic Matter Effects of OM Properties on Soil Property Dark color Excellent water retention Binds to clay minerals Metal chelation Low water solubility ph buffering High CEC Nutrient
Lecture 19: Soil Organic Matter Effects of OM Properties on Soil Property Dark color Excellent water retention Binds to clay minerals Metal chelation Low water solubility ph buffering High CEC Nutrient
The importance of trace metal nutrients for marine phytoplankton and bacteria along Line-P. Jay T. Cullen, Maite Maldonado (UBC), Erin Lane (UBC)
 The importance of trace metal nutrients for marine phytoplankton and bacteria along Line-P Jay T. Cullen, Maite Maldonado (UBC), Erin Lane (UBC) Outline Trace Metals and Marine Biogeochemical Cycles Iron
The importance of trace metal nutrients for marine phytoplankton and bacteria along Line-P Jay T. Cullen, Maite Maldonado (UBC), Erin Lane (UBC) Outline Trace Metals and Marine Biogeochemical Cycles Iron
Soil organic matter composition, decomposition, mineralization and immobilization
 Soil organic matter composition, decomposition, mineralization and immobilization SOIL ORGANIC MATTER Substances containing carbon are organic matter. Soil organic matter consists of decomposing plant
Soil organic matter composition, decomposition, mineralization and immobilization SOIL ORGANIC MATTER Substances containing carbon are organic matter. Soil organic matter consists of decomposing plant
Nutrients. Classification of Elements or Nutrients (Wally Broecker):
 Nutrients Nutrients are generally considered to be elements or compounds (e.g. N is a nutrient, NO3 and NH4 are types of N compound that are also nutrients) that are needed for biological growth. Classification
Nutrients Nutrients are generally considered to be elements or compounds (e.g. N is a nutrient, NO3 and NH4 are types of N compound that are also nutrients) that are needed for biological growth. Classification
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-II
 OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-II Zackary Johnson MSB614 zij@hawaii.edu Chemosynthesis (Chemolithotrophy) Use of small inorganic
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-II Zackary Johnson MSB614 zij@hawaii.edu Chemosynthesis (Chemolithotrophy) Use of small inorganic
Introduction to Biochemistry
 Life is Organized in Increasing Levels of Complexity Introduction to Biochemistry atom simple molecule What is the chemical makeup of living things? macromolecule organ organ system organism organelle
Life is Organized in Increasing Levels of Complexity Introduction to Biochemistry atom simple molecule What is the chemical makeup of living things? macromolecule organ organ system organism organelle
Guangyi Wang. Chemosynthesis (Chemolithotrophy)
 OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-II Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621/ Chemosynthesis (Chemolithotrophy) Use of small
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-II Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621/ Chemosynthesis (Chemolithotrophy) Use of small
By: Mochamad Nurcholis Food Science Department Brawijaya University 2013
 PHYSIOLOGY & METABOLISMS of Microorganisms By: Mochamad Nurcholis Food Science Department Brawijaya University 2013 What is metabolisms? Can you explain it? Overall biochemical reaction within cells of
PHYSIOLOGY & METABOLISMS of Microorganisms By: Mochamad Nurcholis Food Science Department Brawijaya University 2013 What is metabolisms? Can you explain it? Overall biochemical reaction within cells of
Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1
 Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Chapter 8. An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism
 Chapter 8 An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism The metabolism of microbes Metabolism sum of all chemical reactions that help cells function Two types of chemical reactions: Catabolism -degradative;
Chapter 8 An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism The metabolism of microbes Metabolism sum of all chemical reactions that help cells function Two types of chemical reactions: Catabolism -degradative;
Standard B-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the flow of energy within and between living systems.
 B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
Competitive Inhibitor
 is a substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by entering the active site in place of the substrate whose structure it mimics. Competitive Inhibitor Identify the following molecule: Polysaccharide
is a substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by entering the active site in place of the substrate whose structure it mimics. Competitive Inhibitor Identify the following molecule: Polysaccharide
Learning Target: Describe characteristics and functions of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Compare and contrast the classes of organic
 Learning Target: Describe characteristics and functions of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Compare and contrast the classes of organic compounds. What are inorganic molecules? Molecules that CANNOT
Learning Target: Describe characteristics and functions of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Compare and contrast the classes of organic compounds. What are inorganic molecules? Molecules that CANNOT
Biomolecules. Unit 3
 Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Microbial Metabolism. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM
 CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM I. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions A. Metabolism - The sum of all chemical reactions within a living cell either releasing or requiring energy. (Overhead) Fig 5.1 1. Catabolism
CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM I. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions A. Metabolism - The sum of all chemical reactions within a living cell either releasing or requiring energy. (Overhead) Fig 5.1 1. Catabolism
Carbon & Energy Utilization OCN 621
 Carbon & Energy Utilization OCN 621 Lecture Outline 1) Materials Balance Approach defined 2) Sloppy Feeding 3) Egestion: as relates to Assimilation efficiency 4) Metabolism: Allometric Equation 1) Temperature
Carbon & Energy Utilization OCN 621 Lecture Outline 1) Materials Balance Approach defined 2) Sloppy Feeding 3) Egestion: as relates to Assimilation efficiency 4) Metabolism: Allometric Equation 1) Temperature
2 3 Carbon Compounds Slide 1 of 37
 1 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with
1 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 2 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. 3 of 37 Macromolecules Macromolecules Macromolecules
Biology 1 of 37 2 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. 3 of 37 Macromolecules Macromolecules Macromolecules
Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea
 The following supplement accompanies the article Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea Eva Sintes 1, 2, *, Karen Stoderegger 1, Veronica Parada 1,
The following supplement accompanies the article Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea Eva Sintes 1, 2, *, Karen Stoderegger 1, Veronica Parada 1,
Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate
 Introduction Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate Compounds of nitrogen and phosphorus are major cellular components of organisms. Since the availability of these elements may
Introduction Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate Compounds of nitrogen and phosphorus are major cellular components of organisms. Since the availability of these elements may
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis!
 Factors Affecting Photosynthesis! Temperature Eppley (1972) Light Sverdrup s Critical Depth Model Nutrients Limitations Uptake Kinetics Temperature! The oceans vary much less than the land does, both seasonally
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis! Temperature Eppley (1972) Light Sverdrup s Critical Depth Model Nutrients Limitations Uptake Kinetics Temperature! The oceans vary much less than the land does, both seasonally
Organic Compounds. B-3.5 Students will be able to summarize the functions of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats in the human body.
 Organic Compounds B-3.4 tudents will be able to summarize how the structures of organic molecules (including proteins, carbohydrates, and fats) are related to their relative caloric values. B-3.5 tudents
Organic Compounds B-3.4 tudents will be able to summarize how the structures of organic molecules (including proteins, carbohydrates, and fats) are related to their relative caloric values. B-3.5 tudents
Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis Reactions. ne_content/animations/reaction_types.ht ml
 Glucose Molecule Macromolecules Carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are polymers Polymers long molecules made from building blocks linked by covalent bonds Monomers the building blocks to polymers
Glucose Molecule Macromolecules Carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are polymers Polymers long molecules made from building blocks linked by covalent bonds Monomers the building blocks to polymers
Feeding Measurements
 Feeding Measurements Measures of Feeding Rates (or specific mortality rate) Clearance Rate Concept Clearance Rate (F) = Volume cleared of prey pred -1 time -1 predator prey A consumer may have different
Feeding Measurements Measures of Feeding Rates (or specific mortality rate) Clearance Rate Concept Clearance Rate (F) = Volume cleared of prey pred -1 time -1 predator prey A consumer may have different
Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
The. Crash Course. Basically, almost all living things are made up of these 4 Elements: - Carbon (C) - Nitrogen (N) - Hydrogen (H) - Oxygen (O)
 The Biochemistry Crash Course Basically, almost all living things are made up of these 4 Elements: - Carbon (C) - Nitrogen (N) - Hydrogen (H) - Oxygen (O) This exercise is designed to familiarize you with
The Biochemistry Crash Course Basically, almost all living things are made up of these 4 Elements: - Carbon (C) - Nitrogen (N) - Hydrogen (H) - Oxygen (O) This exercise is designed to familiarize you with
Group 1: Macromolecules Make sure each slide at least covers the points below.
 Group : Macromolecules Make sure each slide at least covers the points below. Possible Slide : Four types of macromolecules Slide : Distinguish macromolecules from nutrients Slide : Compare organic to
Group : Macromolecules Make sure each slide at least covers the points below. Possible Slide : Four types of macromolecules Slide : Distinguish macromolecules from nutrients Slide : Compare organic to
Marah Bitar. Bayan Abusheikha ... Anas Abu-Humaidan
 5 Marah Bitar Bayan Abusheikha... Anas Abu-Humaidan Bacterial Metabolism -Metabolism has two components, catabolism and anabolism. -Catabolism encompasses processes that harvest energy released from the
5 Marah Bitar Bayan Abusheikha... Anas Abu-Humaidan Bacterial Metabolism -Metabolism has two components, catabolism and anabolism. -Catabolism encompasses processes that harvest energy released from the
Trace metals in the ocean Lecture January 23, 2006
 Trace metals in the ocean 12.097 Lecture January 23, 2006 Metals of interest Required for metabolic functions Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn Deficiency limits production (photosynthetic ability) Excess limits
Trace metals in the ocean 12.097 Lecture January 23, 2006 Metals of interest Required for metabolic functions Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn Deficiency limits production (photosynthetic ability) Excess limits
The Chemistry of Life
 The Chemistry of Life Biomolecules Warm-up List the percentages of each: Total Fats Saturated Fats 25% Carbohydrates 10% Protein 7% 20% What Biomolecule would cholesterol be classified as? Lipids (fats)
The Chemistry of Life Biomolecules Warm-up List the percentages of each: Total Fats Saturated Fats 25% Carbohydrates 10% Protein 7% 20% What Biomolecule would cholesterol be classified as? Lipids (fats)
Respiration: Allometric Relationship
 Metabolism Defined as: all energy transformations, chemical reactions and pathways that make possible the properties of living organisms Measured as: the Respiration Rate, assumes all organism s energy
Metabolism Defined as: all energy transformations, chemical reactions and pathways that make possible the properties of living organisms Measured as: the Respiration Rate, assumes all organism s energy
189,311, , ,561, ,639, ,679, Ch13; , Carbohydrates
 Lecture 31 (12/8/17) Reading: Ch7; 258-267 Ch10; 371-373 Problems: Ch7 (text); 26,27,28 Ch7 (study-guide: applying); 2,5 Ch7 (study-guide: facts); 6 NEXT (LAST!) Reading: Chs4,6,8,10,14,16,17,18; 128-129,
Lecture 31 (12/8/17) Reading: Ch7; 258-267 Ch10; 371-373 Problems: Ch7 (text); 26,27,28 Ch7 (study-guide: applying); 2,5 Ch7 (study-guide: facts); 6 NEXT (LAST!) Reading: Chs4,6,8,10,14,16,17,18; 128-129,
Chapter 8. Metabolism. Topics in lectures 15 and 16. Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis
 Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Microbial nutrition. Nutrients. Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth. Chapter 7
 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth Chapter 7 Microbial nutrition Macronutrients required in large quantities; play principal roles in cell structure & metabolism proteins, carbohydrates
Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth Chapter 7 Microbial nutrition Macronutrients required in large quantities; play principal roles in cell structure & metabolism proteins, carbohydrates
The building blocks for this molecule are A) amino acids B) simple sugars C) fats D) molecular bases
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a portion of a starch molecule. The building blocks for this molecule are A)
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a portion of a starch molecule. The building blocks for this molecule are A)
Chemical Formulas. Chemical Formula CH 3 COCHCHOCHClCHNH Lewis Dot Structure
 Biochemistry . Chemical Formulas A chemical formula represents the chemical makeup of a compound. It shows the numbers and kinds of atoms present in a compound. It is a kind of shorthand that scientists
Biochemistry . Chemical Formulas A chemical formula represents the chemical makeup of a compound. It shows the numbers and kinds of atoms present in a compound. It is a kind of shorthand that scientists
BIOMOLECULES. Ms. Bosse Fall 2015
 BIOMOLECULES Ms. Bosse Fall 2015 Biology Biology is the study of the living world. Bio = life Major Molecules of Life Macromolecules giant molecules found in living cells; made from thousands of smaller
BIOMOLECULES Ms. Bosse Fall 2015 Biology Biology is the study of the living world. Bio = life Major Molecules of Life Macromolecules giant molecules found in living cells; made from thousands of smaller
Biochemistry. Definition-
 Biochemistry Notes Biochemistry Definition- the scientific study of the chemical composition of living matter AND of the chemical processes that go on in living organisms. Biochemistry Facts 1. The human
Biochemistry Notes Biochemistry Definition- the scientific study of the chemical composition of living matter AND of the chemical processes that go on in living organisms. Biochemistry Facts 1. The human
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration 1. To perform cell work, cells require energy. a. A cell does three main kinds of work: i. Mechanical work, such as the beating of cilia, contraction of muscle cells, and movement
Cellular Respiration 1. To perform cell work, cells require energy. a. A cell does three main kinds of work: i. Mechanical work, such as the beating of cilia, contraction of muscle cells, and movement
Enzymes what are they?
 Topic 11 (ch8) Microbial Metabolism Topics Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 1 Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Metabolism 2 Metabolic balancing act Catabolism Enzymes involved in breakdown of complex
Topic 11 (ch8) Microbial Metabolism Topics Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 1 Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Metabolism 2 Metabolic balancing act Catabolism Enzymes involved in breakdown of complex
Lesson Overview. Carbon Compounds. Lesson Overview. 2.3 Carbon Compounds
 Lesson Overview 2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon What elements does carbon bond with to make up life s molecules? Carbon can bond with many elements, including Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen
Lesson Overview 2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon What elements does carbon bond with to make up life s molecules? Carbon can bond with many elements, including Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen
Model building with craft materials Presented to grade 4; appropriate for grades K 12 with age appropriate modifications
 Unit: Lesson 1: Oceans of Energy Plankton Summary: In this lesson, students are introduced to phytoplankton and zooplankton as the oceans primary producers and consumers. Lesson includes two activities:
Unit: Lesson 1: Oceans of Energy Plankton Summary: In this lesson, students are introduced to phytoplankton and zooplankton as the oceans primary producers and consumers. Lesson includes two activities:
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41. Nutritional Requirements pp Essential Amino Acids p.939. Essential Fatty Acids p.
 Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Objectives. Carbon Bonding. Carbon Bonding, continued. Carbon Bonding
 Biochemistry Table of Contents Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of carbon bonding in biological molecules. Identify functional groups in biological
Biochemistry Table of Contents Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of carbon bonding in biological molecules. Identify functional groups in biological
What are you made of????
 What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
3/19/2009. Ch. 5 Microbial metabolism. Metabolism basics (Fig. 5.1) Basic concepts of metabolic processes. Redox reactions (Fig. 5.
 Ch. 5 Microbial metabolism Breakdown of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins to produce cellular energy (catabolism) Redox (reduction/oxidation) reactions capture, store and use energy via electron transfers
Ch. 5 Microbial metabolism Breakdown of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins to produce cellular energy (catabolism) Redox (reduction/oxidation) reactions capture, store and use energy via electron transfers
modelling the role of Essential Fatty Acids in aquatic food webs
 modelling the role of Essential Fatty Acids in aquatic food webs Gurbir Perhar, George B. Arhonditsis University of Toronto Ecology & Evolutionary Biology g.perhar@utoronto.ca AGENDA: Introduction Objectives
modelling the role of Essential Fatty Acids in aquatic food webs Gurbir Perhar, George B. Arhonditsis University of Toronto Ecology & Evolutionary Biology g.perhar@utoronto.ca AGENDA: Introduction Objectives
Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Name: Period: Date: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Name: Period: Date: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
TOPIC 2.1 MOLECULES TO METABOLISM
 TOPIC 2.1 MOLECULES TO METABOLISM 2.1 A Carbon Compounds & Metabolism http://www.bates.edu/williams-lab/files/2013/05/cell-biology.jpg IB BIO 2.1 Understandings U1: Molecular biology explains living processes
TOPIC 2.1 MOLECULES TO METABOLISM 2.1 A Carbon Compounds & Metabolism http://www.bates.edu/williams-lab/files/2013/05/cell-biology.jpg IB BIO 2.1 Understandings U1: Molecular biology explains living processes
If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism . Anabolism
 If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism. Anabolism is about putting things together. Anabolism: The Use of Energy in Biosynthesis Anabolism energy from catabolism is used
If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism. Anabolism is about putting things together. Anabolism: The Use of Energy in Biosynthesis Anabolism energy from catabolism is used
Carbon Compounds (2.3) (Part 1 - Carbohydrates)
 Carbon Compounds (2.3) (Part 1 - Carbohydrates) The Chemistry of Carbon (Organic Chemistry) Organic Chemistry: The study of compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon can bond with many
Carbon Compounds (2.3) (Part 1 - Carbohydrates) The Chemistry of Carbon (Organic Chemistry) Organic Chemistry: The study of compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon can bond with many
9. At about 0 C., most enzymes are (1.) inactive (2.) active (3.) destroyed (4.) replicated
 Study Guide 1. Which of the following enzymes would digest a fat? (1.) sucrase (2.) fatase (3.) protease (4.) lipase 2. At high temperatures, the rate of enzyme action decreases because the increased heat
Study Guide 1. Which of the following enzymes would digest a fat? (1.) sucrase (2.) fatase (3.) protease (4.) lipase 2. At high temperatures, the rate of enzyme action decreases because the increased heat
Chemistry Regents Review A. A B. B C. C D. D
 hemistry Regents Review Name: ate: 1. Nitrogenous wastes result from the metabolism of 4. Which sugar solution was the first to liberate a measurable volume of O 2?. amino acids. glucose molecules. fatty
hemistry Regents Review Name: ate: 1. Nitrogenous wastes result from the metabolism of 4. Which sugar solution was the first to liberate a measurable volume of O 2?. amino acids. glucose molecules. fatty
Isolation of DOM by adsorption onto hydrophobic resins
 Isolation of DOM by adsorption onto hydrophobic resins Seawater (filtered; ph = 2) 0.1N NaOH or 1N NH 4 OH/MeOH (XAD = polystyrene) 5 10% of DOC sample Isola3on is chemically selec3ve based on affinity
Isolation of DOM by adsorption onto hydrophobic resins Seawater (filtered; ph = 2) 0.1N NaOH or 1N NH 4 OH/MeOH (XAD = polystyrene) 5 10% of DOC sample Isola3on is chemically selec3ve based on affinity
Macromolecule stations. 6 stations
 Macromolecule stations 6 stations 1. Sugar and protein paper pieces to build (with waters) 2. Fatty acid and nucleic acid paper pieces to build with (and water) 3. DNA model with several pieces removed
Macromolecule stations 6 stations 1. Sugar and protein paper pieces to build (with waters) 2. Fatty acid and nucleic acid paper pieces to build with (and water) 3. DNA model with several pieces removed
EH1008 Biomolecules. Inorganic & Organic Chemistry. Water. Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry.
 EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
Ocean Colour and the marine carbon cycle
 Ocean Colour and the marine carbon cycle Bob Brewin 1,2 1 Plymouth Marine Laboratory (PML), Prospect Place, The Hoe, Plymouth PL1 3DH, UK 2 National Centre for Earth Observation, PML, Plymouth PL1 3DH,
Ocean Colour and the marine carbon cycle Bob Brewin 1,2 1 Plymouth Marine Laboratory (PML), Prospect Place, The Hoe, Plymouth PL1 3DH, UK 2 National Centre for Earth Observation, PML, Plymouth PL1 3DH,
Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function
 Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function Cells can be divided into two primary types prokaryotes - Almost all prokaryotes are bacteria eukaryotes - Eukaryotes include all cells of multicellular
Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function Cells can be divided into two primary types prokaryotes - Almost all prokaryotes are bacteria eukaryotes - Eukaryotes include all cells of multicellular
Ch 2 Molecules of life
 Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
Chapter Three (Biochemistry)
 Chapter Three (Biochemistry) 1 SECTION ONE: CARBON COMPOUNDS CARBON BONDING All compounds can be classified in two broad categories: organic compounds and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are made
Chapter Three (Biochemistry) 1 SECTION ONE: CARBON COMPOUNDS CARBON BONDING All compounds can be classified in two broad categories: organic compounds and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are made
CP Biology Chapter 2: Molecules of Life Name Amatuzzi #1: Carbohydrates pp Period Homework
 Amatuzzi #1: Carbohydrates pp. 46-47 Period 1. Which elements make up carbohydrates? a. In which ratio? 2. How do living things use most of their carbohydrates? 3. How do cells get energy from carbs? a.
Amatuzzi #1: Carbohydrates pp. 46-47 Period 1. Which elements make up carbohydrates? a. In which ratio? 2. How do living things use most of their carbohydrates? 3. How do cells get energy from carbs? a.
DISSOLVED ORGANIC MATTER (DOM) AS A DIRECT ORGANIC SUBSIDY TO AQUATIC CONSUMERS
 DISSOLVED ORGANIC MATTER (DOM) AS A DIRECT ORGANIC SUBSIDY TO AQUATIC CONSUMERS STEPHEN B. BAINES ECOLOGY AND EVOLUTION STONY BROOK UNIVERSITY Acknowledgements: Hudson Roditi, Nick Fisher, Jon Cole, Cindy
DISSOLVED ORGANIC MATTER (DOM) AS A DIRECT ORGANIC SUBSIDY TO AQUATIC CONSUMERS STEPHEN B. BAINES ECOLOGY AND EVOLUTION STONY BROOK UNIVERSITY Acknowledgements: Hudson Roditi, Nick Fisher, Jon Cole, Cindy
BACTERIAL GROWTH. FYBSc.
 BACTERIAL GROWTH FYBSc. Bacterial growth Binary fission Generation time Phases of growth 4-2 Binary fission 1. Prokaryote cells grow by increasing in cell number (as opposed to increasing in size). 2.
BACTERIAL GROWTH FYBSc. Bacterial growth Binary fission Generation time Phases of growth 4-2 Binary fission 1. Prokaryote cells grow by increasing in cell number (as opposed to increasing in size). 2.
In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic
 Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 05 FEBRUARY 2014
 CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 05 FEBRUARY 2014 In this lesson we will: Lesson Description Discuss inorganic compounds and their importance Discuss organic compounds and their biological importance. Summary Inorganic
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 05 FEBRUARY 2014 In this lesson we will: Lesson Description Discuss inorganic compounds and their importance Discuss organic compounds and their biological importance. Summary Inorganic
2 3 Carbon Compounds (Macromolecules)
 2 3 Carbon Compounds (Macromolecules) Slide 1 of 37 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Slide 2 of 37 Carbon Living organisms are
2 3 Carbon Compounds (Macromolecules) Slide 1 of 37 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Slide 2 of 37 Carbon Living organisms are
Carbon Compounds. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 2.3 Carbon Compounds
 Lesson Overview Carbon Compounds Lesson Overview 2.3 THINK ABOUT IT In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms organic, believing they were fundamentally different from
Lesson Overview Carbon Compounds Lesson Overview 2.3 THINK ABOUT IT In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms organic, believing they were fundamentally different from
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 7 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology, and Growth Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 7 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology, and Growth Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
- Dual Flow Continuous Culture System (Hoover, 1964) - Hohenheim System (Single Flow Continuous Culture. valerate, isobutyrate, isovalerate)
 In vitro Techniques Simulation of the rumen fermentation Alternative to time consuming and expensive in vivo trials Quantification of the end products of fermentation and/or rumen dry matter digestibility
In vitro Techniques Simulation of the rumen fermentation Alternative to time consuming and expensive in vivo trials Quantification of the end products of fermentation and/or rumen dry matter digestibility
6/28/2016. Growth Media and Metabolism. Complex Media. Defined Media. Made from complex and rich ingredients
 Growth Media and Metabolism Complex Media Made from complex and rich ingredients Ex. Soya protein extracts Milk protein extracts Blood products Tomato juice, etc. Exact chemical composition unknown Can
Growth Media and Metabolism Complex Media Made from complex and rich ingredients Ex. Soya protein extracts Milk protein extracts Blood products Tomato juice, etc. Exact chemical composition unknown Can
Refresher: What do we remember about CARBON? What makes it special? Nickname? Where do we find it?
 2.3: Carbon Based Molecules Situation: You are tasked with making Chicken Parm and ziti for you entire family (aunts, uncles, cousins, etc). There are 92 different ingredients you have access to in the
2.3: Carbon Based Molecules Situation: You are tasked with making Chicken Parm and ziti for you entire family (aunts, uncles, cousins, etc). There are 92 different ingredients you have access to in the
What is a Biomolecule?
 Biology Unit 03 What is a Biomolecule? Organic molecule made by living organisms Consists mostly of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) But wait What is an Organic Molecule? Organic Molecules: Contain
Biology Unit 03 What is a Biomolecule? Organic molecule made by living organisms Consists mostly of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) But wait What is an Organic Molecule? Organic Molecules: Contain
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Lesson Overview. Carbon Compounds. Lesson Overview. 2.3 Carbon Compounds
 Lesson Overview 2.3 THINK ABOUT IT In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms organic, believing they were fundamentally different from compounds in nonliving things. We
Lesson Overview 2.3 THINK ABOUT IT In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms organic, believing they were fundamentally different from compounds in nonliving things. We
I. ROLE OF CARBON IN ORGANISMS:
 Name: Period: Date: I. ROLE OF CARBON IN ORGANISMS: = compounds that contain carbon Ex: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins = compounds that DO NOT contain carbon Ex: Vitamins, minerals, water Carbon forms
Name: Period: Date: I. ROLE OF CARBON IN ORGANISMS: = compounds that contain carbon Ex: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins = compounds that DO NOT contain carbon Ex: Vitamins, minerals, water Carbon forms
Lecture 14. More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils
 Lecture 14 More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils SOIL INORGANIC SOLIDS saprolite development elemental changes that occur during weathering The gain or loss of chemical constituents in saprolite records
Lecture 14 More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils SOIL INORGANIC SOLIDS saprolite development elemental changes that occur during weathering The gain or loss of chemical constituents in saprolite records
I. ROLE OF CARBON IN ORGANISMS:
 Name: Period: Date: I. ROLE OF CARBON IN ORGANISMS: = compounds that contain carbon Ex: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins = compounds that DO NOT contain carbon Ex: Vitamins, minerals, water Carbon forms
Name: Period: Date: I. ROLE OF CARBON IN ORGANISMS: = compounds that contain carbon Ex: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins = compounds that DO NOT contain carbon Ex: Vitamins, minerals, water Carbon forms
Proteins. Biomolecules. Nucleic Acids. The Building Blocks of Life
 Proteins Biomolecules Nucleic Acids The Building Blocks of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Biomolecules are Organic Molecules 1. Organic molecules that are Carbon based (at least 1 Carbon molecule and often
Proteins Biomolecules Nucleic Acids The Building Blocks of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Biomolecules are Organic Molecules 1. Organic molecules that are Carbon based (at least 1 Carbon molecule and often
Proteins. Biomolecules. Nucleic Acids. The Building Blocks of Life
 Proteins Biomolecules Nucleic Acids The Building Blocks of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Biomolecules are 1. Organic molecules that are (at least 1 Carbon molecule and often chains of Carbon) They all contain.
Proteins Biomolecules Nucleic Acids The Building Blocks of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Biomolecules are 1. Organic molecules that are (at least 1 Carbon molecule and often chains of Carbon) They all contain.
Unit 4- Energy & Cell Processes
 Unit 4- Energy & Cell Processes Energy in the ecosystem ATP Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Fermentation By: Mrs. Stahl Biology Background knowledge Unit Layout Energy- where does it all come from?
Unit 4- Energy & Cell Processes Energy in the ecosystem ATP Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Fermentation By: Mrs. Stahl Biology Background knowledge Unit Layout Energy- where does it all come from?
A. Incorrect! No, this is not the description of this type of molecule. B. Incorrect! No, this is not the description of this type of molecule.
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 08: Carbohydrates No. 1 of 10 1. have one aldehyde (-CHO) or one keto (-C=O) group and many hydroxyl (-OH) groups. (A) Amino acids (B) Proteins (C) Nucleic Acids (D) Carbohydrates
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 08: Carbohydrates No. 1 of 10 1. have one aldehyde (-CHO) or one keto (-C=O) group and many hydroxyl (-OH) groups. (A) Amino acids (B) Proteins (C) Nucleic Acids (D) Carbohydrates
