CHAPTER 24 - Microbial Diseases of the Respiratory System
|
|
|
- Roxanne McBride
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction CHAPTER 24 - Microbial Diseases of the Respiratory System Infections of the upper respiratory system are the most common type of human infection. Pathogens that enter the respiratory system may infect other parts of the body by hematogenous spread (Ex: septicemia, meningitis, distant focal infection). I. Structure and Function of the Respiratory System A. The upper respiratory system consists of the nose, pharynx, and associated structures, such as the middle ear and auditory tubes. B. Coarse hairs in the nose filter large particles from air entering the respiratory tract. C. The ciliated mucous membranes of the nose and upper respiratory system trap airborne particles and remove them from the body. D. Lymphoid tissue, tonsils, and adenoids provide immunity to certain infections. E. The ciliary escalator of the lower respiratory system helps prevent microorganisms from reaching the lungs. F. The lower respiratory system consists of the larynx, trachea, bronchial tubes, and alveoli. G. Microbes in the lungs can be phagocytized by alveolar macrophages. H. Respiratory mucus contains IgA antibodies. II. Normal Microbiota of the Respiratory System A. The normal microbiota of the nasal cavity and throat can include pathogenic microorganisms in a carrier status. B. Don t cause disease because of competition with predominant microorganisms. C. The lower respiratory system is usually sterile because of the action of the ciliary escalator. III. Microbial Diseases of the Upper Respiratory System Specific areas of the upper respiratory system can become infected to produce pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, and epiglottitis. Pharyngitis sore throat Larnygitis infected larynx Tonsillitis inflammed tonsils Sinusitis infected sinus Chapter24taft 1
2 Epiglotittis inflammation of the flap like structures of cartilage that prevents swallowed material from entering the larynx possible lifethreatening when inflamed and occludes airway. H. influenzae type b can cause epiglottitis. These infections may be caused by several bacteria and viruses, often in combination. Most respiratory tract infections are self-limiting. A. Streptococcal Pharyngitis (Strep Throat) 1. This infection is caused by group A β-hemolytic streptococci, the group that consists of the species Streptococcus pyogenes. 2. Symptoms of this infection are inflammation of the mucous membrane and fever, tonsillitis, and otitis media may also occur. At least half of pharyngitis cases are caused by viruses. 3. Preliminary rapid clinic diagnosis is made by indirect agglutination tests or next day culture in the micro lab. Definitive diagnosis is based on a rise in IgM antibodies. 4. Penicillin is used to treat streptococcal pharyngitis. 5. Immunity to streptococcal infections is type-specific. 6. Strep throat is usually transmitted by droplets but at one time was commonly associated with unpasteurized milk. B. Scarlet Fever 1. Strep throat, caused by an erythrogenic toxin-producing S. pyogenes, results in scarlet fever. 2. S. pyogenes produces erythrogenic toxin(m protein) when lysogenized by a phage. 3. Means Strep A has to have a bacterial phage carrying the toxin gene. 4. Symptoms include a red rash, high fever, and a red, enlarged tongue, peeled skin. Death is a possible outcome. C. Diphtheria - Corynebacterium diphtheriae 1. Diphtheria is caused by exotoxin-producing Corynebacterium diphtheriae. 2. Gram positive non-spore forming pleomorphic rod. Dividing cells often fold into V and Y shapes. 3. Exotoxin is produced when the bacteria are lysogenized by a phage. 4. Many well people are symptomless carriers. 5. A membrane, containing fibrin and dead human and bacterial cells, forms in the throat and can block the passage of air. diphtheria means leather 6. The exotoxin inhibits protein synthesis, and heart, kidney, or nerve damage may result. Chapter24taft 2
3 7. Laboratory diagnosis is based on isolation of the bacteria and the appearance of growth on differential media. 8. Antitoxin must be administered to neutralize the toxin, and antibiotics can stop growth of the bacteria. 9. Routine immunization in the U.S. includes diphtheria toxoid in the DTaP vaccine. Prior to this diphtheria was the leading killer of children. 10. Slow-healing skin ulcerations are characteristic of cutaneous diphtheria. a) Cutaneous diphtheria characterized by skin lesions is fairly common in tropical countries. In US affects mainly lower socio economic groups. b) There is minimal dissemination of the exotoxin in the bloodstream. D. Otitis Media: an uncomfortable infections of the middle ear. 1. Earache, or otitis media, can occur as a complication of nose and throat infections. 2. Pus accumulation causes pressure on the eardrum. 8 million cases/yr. 3. Bacterial causes include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Hemophilus influenzae, Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Staphylococcus aureus. IV. Viral Disease of the Upper Respiratory System A. The Common Cold - rhinoviruses (50%), corona viruses (15-20%) Any one of approximately 200 different viruses can cause the common cold; rhinoviruses cause about 50% of all colds. 1. Symptoms include sneezing, nasal secretions, and congestion. 2. Sinus infections, lower respiratory tract infections, laryngitis, and otitis media can occur as complications of a cold. Usually no fever in uncomplicated cases. 3. Colds are most often transmitted by indirect contact. 4. Rhinoviruses prefer temperatures slightly lower than body temperature. 5. The incidence of colds increases during cold weather, possibly because of increased interpersonal indoor contact or physiological changes. 6. Antibodies are produced against the specific viruses. Microbial Diseases of the Lower Respiratory System V. Anatomy & Collection of Specimen from Lower Respiratory System Chapter24taft 3
4 VI. Bacterial Diseases of the Lower Respiratory System Many of the same microorganisms that infect the upper respiratory system also infect the lower respiratory system. Diseases of the lower respiratory system include bronchitis and pneumonia. Pneumonia is a term applied to severe complications of bronchitis with the alveoli involved. A. Pertussis (Whooping Cough) -Bordetella pertussis 1. Pertussis is caused by Bordetella pertussis, a Gram itive coccal bacillus 2. The initial stage of pertussis resembles a cold and is called the catarrhal stage. 3. The accumulation of mucus in the trachea and bronchi causes deep coughs characteristic of the paroxysmal (second) stage. 4. Trying to clear mucous leads to violent coughing with gasping (whooping) for breaths. Ciliary action is blocked by accumulation of dense masses of these bacteria in the trachea and bronchi. 5. The convalescence (third) stage can last for months. 6. Laboratory diagnosis is based on isolation of the bacteria on enrichment and selective media (or PCR), followed by serological tests. 7. Have to collect specimen with thin wire with a special swab. See slide below. 8. Regular immunization for children has decreased the incidence of pertussis. The acellular vaccine has minimal side effects vs. the whole cell. B. Tuberculosis -Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 1. Tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a slow growing acid-fast bacillus 2. Large amounts of lipids in the cell wall account for the bacterium' s acid-fast characteristic as well as its resistance to drying and disinfectants. 3. M. tuberculosis may be ingested by alveolar macrophages. If not killed, the bacteria reproduce in the macrophages. Resistant to phagocytosis. 4. Lesions formed by M. tuberculosis are called tubercles; dead macrophages and bacteria form the caseous lesion that might calcify and appear in an X ray as a Ghon complex. Ghon complex means calcified caseous lesions. Caused by hypersensitivity reaction. 5. Liquefaction of the caseous lesion results in a tuberculous cavity in which M. tuberculosis can grow. 6. New foci of infection can develop when a caseous lesion ruptures and releases bacteria into blood or lymph vessels; this is called miliary tuberculosis. 7. Miliary (characterized by lesions resembling millet seeds) tuberculosis is characterized by weight loss, coughing, and loss of vigor. Chapter24taft 4
5 8. Chemotherapy usually involves two drugs taken for 1-2 years; multidrugresistant M. tuberculosis is becoming prevalent. DOT therapy. 9. Drugs are Streptomycin, rifampin, isoniazid (INH) and ethanbutol. 10. Intracellular growth shields TB from antibiotics. 11. Stress and genetic differences contribute to susceptibility. 12. A positive tuberculin skin test can indicate either an active case of TB, or prior infection, or vaccination and immunity to the disease. 13. Sensitized T-cells are present at site of infection or skin test. 14. Laboratory diagnosis is based on the presence of acid-fast bacilli and isolation of the bacteria, which requires incubation of up to 8 weeks. 15. Mycobacterium bovis causes bovine tuberculosis and can be transmitted to humans by unpasteurized milk. a) M. bovis infections usually affect the bones or lymphatic system. b) BCG vaccine for tuberculosis consists of a live, avirulent culture of M. bovis. Useful if given early in childhood. Mainly outside of US> 16. M. avium-intracellulare complex infects patients in the late stages of HIV infection. C. Bacterial Pneumonias- 1. Streptococcus pneumoniae a) Pneumococcal pneumonia is caused by encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae. b) Symptoms are fever, breathing difficulty, chest pain, and rust-colored sputum. c) The bacteria can be identified by the production of alpha-hemolysins, inhibition by optochin, bile solubility, and through serological tests. d) A vaccine consists of purified capsular material from 23 serotypes of S. pneumoniae. 2. Hemophilus influenzae a) Alcoholism, poor nutrition, cancer, and diabetes are predisposing factors for H. influenzae pneumonia. b) H. influenzae is a small gram-negative coccobacillus. 3. Mycoplasmal Pneumonia -Mycoplasma pneumoniae a) Mycoplasmal pneumonia is common in children and young adults; as many as 20% of cases. Lowgrade fever, cough of long 2-3 weeks duration. b) Organism has no cell wall so is difficult to grow so presents like a viral infection. c) Described as atypical or walking pneumonia. d) M. pneumoniae produces small fried-egg colonies after 2 weeks' incubation on enriched media containing horse serum and yeast extract. Chapter24taft 5
6 e) A complement-fixation test, used to diagnose the disease, is based on the rising of antibody titer. f) Treated with tetracyclines. D. Legionellosis -Legionella pneumophila 1. The disease is caused by the aerobic gram-negative rod Legionella pneumophila. 2. Legionnaires Disease due to 1976 outbreak of the American Legion meeting. 3. The bacterium can grow in water, such as air-conditioning cooling towers, slow plumbing, and then be disseminated in the air. 4. This pneumonia does not appear to be transmitted from person to person. High fever, cough, general symptoms of pneumonia. 5. Bacterial culture, FA tests, and DNA probes are used for laboratory diagnosis. 6. Treated with Erythromycin and Rifampin E. Psittacosis (Ornithosis) Chlamydia psittaci 1. Chlamydia psittaci is transmitted by contact with contaminated droppings and exudates of fowl. 2. Psittacine birds such as parakeets and parrots but other birds are infected too. 3. Are obligate intracellular parasites but have an elementary body stage that allows the bacteria to survive outside a host. 4. Commercial bird handlers are most susceptible to this disease. 5. The bacteria are isolated in embryonated eggs, mice, or cell culture; identification is based on FA staining. Treated with tetracycline. F. Other Bacterial Pneumonias 1. Gram-positive bacteria that cause pneumonia include Staph aureus and Strep pyogenes. 2. Gram-negative bacteria that cause pneumonia include Moraxella.(B.) catarrhalis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas species. VII. Viral Diseases of the Lower Respiratory System A. Viral Pneumonia 1. A number of viruses can cause pneumonia as a complication of infections such as influenza. 2. The etiologies are not usually identified in a clinical laboratory because of the difficulty in isolating and identifying viruses. Chapter24taft 6
7 B. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) 1. RSV is the most common cause of pneumonia in infants with 110K hospitalizations and 4500 deaths in US. Epidemics in winter/early spring. Fever and wheezing. 2. Rapid testing using serology. 3. Ribavirin may be given in aerosol to diminish symptoms. C. Influenza (Flu) Influenza virus 1. Influenza is caused by influenza virus and is characterized by chills, fever, headache, and general muscular aches. 2. Hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N) spikes project from the outer lipid bilayer of the virus. 3. Viral strains are identified by antigenic differences in the H and N spikes; they are also divided by antigenic differences in their protein coats (A, B, and C). 4. Viral isolates are identified by hemagglutination-inhibition tests and immunofluorescence testing with monoclonal antibodies. 5. Antigenic shifts that alter the antigenic nature of the H and N spikes make natural immunity and vaccination of questionable value and may lead to pandemics. Minor antigenic changes are caused by antigenic drift and are covered by vaccines. 6. Deaths during an influenza epidemic are usually from secondary bacterial infections. 7. Multivalent vaccines are available for the elderly and other high-risk groups that are 70-90% effective for no more than 3 years for that strain. 8. Amantadine and rimantadine given early, reduce symptoms against A-type Influenzavirus. Also zanamivir Relenza) and oseltamivir (Tamiflu). VIII. Fungal Diseases of the Lower Respiratory System 1. Fungal spores are easily inhaled; they may germinate in the lower respiratory tract. 2. The incidence of fungal diseases has been increasing in recent years. 3. The mycoses below can be treated with amphotericin B. A. Coccidioidomycosis: San Joaquin Valley Fever 1. Inhalation of the airborne arthrospores of Coccidioides immitis can result in coccidioidomycosis, typically limited minor a lung infection. Found dry soils of SW US. 2. Most cases are subclinical with about 1% of cases progressing to a TB like course of illness. Predisposing factors such as fatigue and poor nutrition, older age, HIV may lead to disseminated disease. Chapter24taft 7
8 3. See dimorphic froms in tissue: spherules with endospores. 4. Same treatment as Histo using fluconazole (diflucan), ketoconazole, and itraconazole. Sometimes use Amphotericin B to treat serious cases but it is very toxic. B. Pneumocystis Pneumonia - Pneumocystis jiroveci (carinii) 1. Pneumocystis jiroveci, currently classified as a fungus, is found in healthy human lungs. Taxonomy in question but probably related to yeasts. 2. Pneumocytis carinii causes disease in immunosuppressed patients. Transmitted by direct contact. Causes alveoli to become filled with a frothy exudate. 3. Common in AIDS patients or other immunosuppressed conditions (cancer, transplant pts). Untreated infections maybe lethal in these cases. 4. Pneumocytis pneumonia is currently being treated with trimethoprim or pentamidine. Chapter24taft 8
Ch 19. Infectious Diseases Affecting the Respiratory System
 Ch 19 Infectious Diseases Affecting the Respiratory System Student Learning Outcomes Describe how microorganisms are prevented from entering the respiratory system and the natural defenses present in the
Ch 19 Infectious Diseases Affecting the Respiratory System Student Learning Outcomes Describe how microorganisms are prevented from entering the respiratory system and the natural defenses present in the
INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Return to Syllabus INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES General Goal: To know the major mechanisms of defense in the URT, the major mechanisms invaders use
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Return to Syllabus INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES General Goal: To know the major mechanisms of defense in the URT, the major mechanisms invaders use
Pathogens of the Respiratory System
 Pathogens of the Respiratory System Chapter 21, Pages 531-567 1. Respiratory System Introduction A. Anatomy (Pages 532-534) i. Upper Respiratory Track a. Nasal Hairs b. Paranasal Sinuses c. Nasal Chonchae
Pathogens of the Respiratory System Chapter 21, Pages 531-567 1. Respiratory System Introduction A. Anatomy (Pages 532-534) i. Upper Respiratory Track a. Nasal Hairs b. Paranasal Sinuses c. Nasal Chonchae
Topic: Respiratory and Systemic Disease. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of Upper Respiratory System, Sinuses, and Ears
 Topic: Respiratory and Systemic Disease 1 Structures of the Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the blood Respiratory system divided into
Topic: Respiratory and Systemic Disease 1 Structures of the Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the blood Respiratory system divided into
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani
 RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Anatomy of the Respiratory System Respiratory Infections Respiratory tract can be divided into: Upper Respiratory Tract (URT): Sinuses Nasopharynx,.
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Anatomy of the Respiratory System Respiratory Infections Respiratory tract can be divided into: Upper Respiratory Tract (URT): Sinuses Nasopharynx,.
Infectious Diseases Affecting the Respiratory System
 Infectious Diseases Affecting the Respiratory System Respiratory tract system Most common entry point for infections Upper tract Mouth, nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, throat, epiglottis, and larynx Lower
Infectious Diseases Affecting the Respiratory System Respiratory tract system Most common entry point for infections Upper tract Mouth, nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, throat, epiglottis, and larynx Lower
Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia. Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali
 Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali Pneumonia P n e u m o n i a i s a n infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Atypical! Pneumonia Symptoms. X-ray
Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali Pneumonia P n e u m o n i a i s a n infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Atypical! Pneumonia Symptoms. X-ray
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
1. Selected Viral Pathogens
 Chapters 19-24: Selected Pathogens 1. Selected Viral Pathogens 2. Selected Bacterial Pathogens 1. Selected Viral Pathogens Influenza (flu) (pp. 678-682) Caused by various strains of Influenzavirus (RNA,
Chapters 19-24: Selected Pathogens 1. Selected Viral Pathogens 2. Selected Bacterial Pathogens 1. Selected Viral Pathogens Influenza (flu) (pp. 678-682) Caused by various strains of Influenzavirus (RNA,
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella 1 Haemophilus "loves heme" Small gram-negative coccobacilli Non-spore forming Non-motile Growth is enhanced in CO2 Present
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella 1 Haemophilus "loves heme" Small gram-negative coccobacilli Non-spore forming Non-motile Growth is enhanced in CO2 Present
Orthomyxoviridae and Paramyxoviridae. Lecture in Microbiology for medical and dental medical students
 Orthomyxoviridae and Paramyxoviridae Lecture in Microbiology for medical and dental medical students Orthomyxoviridae and Paramyxoviridae are ss RNA containng viruses Insert Table 25.1 RNA viruses 2 SIZE
Orthomyxoviridae and Paramyxoviridae Lecture in Microbiology for medical and dental medical students Orthomyxoviridae and Paramyxoviridae are ss RNA containng viruses Insert Table 25.1 RNA viruses 2 SIZE
Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders
 F.A. Davis: Advantage Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders (11.16.15) Page 1 Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders The respiratory system is an interconnected network of organs, tissues, and
F.A. Davis: Advantage Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders (11.16.15) Page 1 Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders The respiratory system is an interconnected network of organs, tissues, and
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
Characteristics of Mycobacterium
 Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
NFECTIONS THROUGH THE RESPIRATORY TRACT
 NFECTIONS THROUGH THE RESPIRATORY TRACT **Infective agent s **Transmission **Host * viral infections * Bacterial infections *Fungal infections **Control of air-borne infections **INFECTIVE AGENTS The infective
NFECTIONS THROUGH THE RESPIRATORY TRACT **Infective agent s **Transmission **Host * viral infections * Bacterial infections *Fungal infections **Control of air-borne infections **INFECTIVE AGENTS The infective
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13. Mycobacterium Actinomycetes
 Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Chapter 38. Human Diseases Caused by Bacteria 1
 Chapter 38 Human Diseases Caused by Bacteria 1 1 공기매개질병 클라미디아폐렴 디프테리아 재향군인병 수막염 마이코박테리아감염 마이코플라즈마성폐렴 백일해 연쇄상구균질병 2 클라미디아폐렴 Chlamydial pneumonia Chlamydia pneumoniae Obligate intracellular parasite ( 세포내절대기생세균
Chapter 38 Human Diseases Caused by Bacteria 1 1 공기매개질병 클라미디아폐렴 디프테리아 재향군인병 수막염 마이코박테리아감염 마이코플라즈마성폐렴 백일해 연쇄상구균질병 2 클라미디아폐렴 Chlamydial pneumonia Chlamydia pneumoniae Obligate intracellular parasite ( 세포내절대기생세균
Acute respiratory illness This is a disease that typically affects the airways in the nose and throat (the upper respiratory tract).
 Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10. Mycobacterium. Actinomycetes. Nocardia
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23 Chapter 21 I. MICROBIAL DISEASES OF THE SKIN A. Defense 1. Keratin 2. Sweat ducts 3. Oil glands
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science BIO 140 Lecture Outline Chapters 21, 22 and 23 Chapter 21 I. MICROBIAL DISEASES OF THE SKIN A. Defense 1. Keratin 2. Sweat ducts 3. Oil glands
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Medical Bacteriology Lecture 15
 Medical Bacteriology Lecture 15 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella pertussis Haemophilus "loves heme" small gram-negative coccobacilli, non-spore forming, non-motile, require enriched media
Medical Bacteriology Lecture 15 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella pertussis Haemophilus "loves heme" small gram-negative coccobacilli, non-spore forming, non-motile, require enriched media
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology
 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
 Corynebacterium diphtheriae Aerobic gram-positive bacillus Toxin production occurs only when C. diphtheriae infected by virus (phage) carrying tox gene If isolated, must be distinguished from normal diphtheroid
Corynebacterium diphtheriae Aerobic gram-positive bacillus Toxin production occurs only when C. diphtheriae infected by virus (phage) carrying tox gene If isolated, must be distinguished from normal diphtheroid
PNEUMONIA. I. Background 6 th most common cause of death in U.S. Most common cause of infection related mortality
 Page 1 of 8 September 4, 2001 Donald P. Levine, M.D. University Health Center Suite 5C Office: 577-0348 dlevine@intmed.wayne.edu Assigned reading: pages 153-160; 553-563 PNEUMONIA the most widespread and
Page 1 of 8 September 4, 2001 Donald P. Levine, M.D. University Health Center Suite 5C Office: 577-0348 dlevine@intmed.wayne.edu Assigned reading: pages 153-160; 553-563 PNEUMONIA the most widespread and
Chapter 17. Infectious Diseases
 Chapter 17 Infectious Diseases Lesson 1 What is an infectious disease? Infectious disease Is any disease that is caused by an agent that can be passed from one living thing to another. Disease causing
Chapter 17 Infectious Diseases Lesson 1 What is an infectious disease? Infectious disease Is any disease that is caused by an agent that can be passed from one living thing to another. Disease causing
Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever. Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University Gram negative: Diplococci Bacilli Coccobacilli Gram Positive: Diplococci Chains
Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University Gram negative: Diplococci Bacilli Coccobacilli Gram Positive: Diplococci Chains
Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever. Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University Gram negative: Diplococci Bacilli Coccobacilli Gram Positive: Diplococci Chains
Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University Gram negative: Diplococci Bacilli Coccobacilli Gram Positive: Diplococci Chains
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS 1 INTRODUCTION Most common problem in children below 5 years. In this age group they get about 6 8 episodes per year. It includes infections of nasal cavity, throat,
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS 1 INTRODUCTION Most common problem in children below 5 years. In this age group they get about 6 8 episodes per year. It includes infections of nasal cavity, throat,
Viral Infections of the Respiratory System. Dr. MONA BADR Assistant Professor College of Medicine & KKUH
 Viral Infections of the Respiratory System Dr. MONA BADR Assistant Professor College of Medicine & KKUH Objectives Introduction to respiratory viral infections Characteristics of respiratory viruses (Orthomyxoviridae,
Viral Infections of the Respiratory System Dr. MONA BADR Assistant Professor College of Medicine & KKUH Objectives Introduction to respiratory viral infections Characteristics of respiratory viruses (Orthomyxoviridae,
Respiratory tract infections. Krzysztof Buczkowski
 Respiratory tract infections Krzysztof Buczkowski Etiology Viruses Rhinoviruses Adenoviruses Coronaviruses Influenza and Parainfluenza Viruses Respiratory Syncitial Viruses Enteroviruses Etiology Bacteria
Respiratory tract infections Krzysztof Buczkowski Etiology Viruses Rhinoviruses Adenoviruses Coronaviruses Influenza and Parainfluenza Viruses Respiratory Syncitial Viruses Enteroviruses Etiology Bacteria
1/9/ :00:00AM 1/9/ :40:15AM 6/9/2017 9:19:16AM A/c Status. Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval. Nasal Swab
 LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091523 Age 36 Years Gender Female 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 114015AM 6/9/2017 91916AM Ref By Final RESIRATORY COMREHENSIVE ANEL (33 ATHOGENS) RESIRATORY ANEL 1 #
LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091523 Age 36 Years Gender Female 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 114015AM 6/9/2017 91916AM Ref By Final RESIRATORY COMREHENSIVE ANEL (33 ATHOGENS) RESIRATORY ANEL 1 #
INFLUENZA VIRUS. INFLUENZA VIRUS CDC WEBSITE
 INFLUENZA VIRUS INFLUENZA VIRUS CDC WEBSITE http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/diseases/flu/fluinfo.htm 1 THE IMPACT OF INFLUENZA Deaths: PANDEMICS 1918-19 S p a n is h flu 5 0 0,0 0 0 U S 2 0,0 0 0,0 0 0 w o rld
INFLUENZA VIRUS INFLUENZA VIRUS CDC WEBSITE http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/diseases/flu/fluinfo.htm 1 THE IMPACT OF INFLUENZA Deaths: PANDEMICS 1918-19 S p a n is h flu 5 0 0,0 0 0 U S 2 0,0 0 0,0 0 0 w o rld
Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
 Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Robin Jump, MD, PhD Cleveland Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center Case Western Reserve University
Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Robin Jump, MD, PhD Cleveland Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center Case Western Reserve University
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTION
 UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTION OVERVIEW To learn the epidemiology and various clinical presentation of URT To identify the common etiological agents causing these syndromes To study the laboratory diagnosis
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTION OVERVIEW To learn the epidemiology and various clinical presentation of URT To identify the common etiological agents causing these syndromes To study the laboratory diagnosis
Respiratory System. Respiratory System Overview. Component 3/Unit 11. Health IT Workforce Curriculum Version 2.0/Spring 2011
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 11-Respiratory System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health and
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 11-Respiratory System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health and
Rapid and progressive necrosis of the tissue underlying epidermis (cellulitis)
 Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System
 Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System Histoplasmosis(cave disease) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Histoplasma capsulatum, is usually
Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System Histoplasmosis(cave disease) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Histoplasma capsulatum, is usually
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
Streptococci facultative anaerobe
 THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
Pneumonia Aetiology Why is it so difficult to distinguish pathogens from innocent bystanders?
 Pneumonia Aetiology Why is it so difficult to distinguish pathogens from innocent bystanders? David Murdoch Department of Pathology University of Otago, Christchurch Outline Background Diagnostic challenges
Pneumonia Aetiology Why is it so difficult to distinguish pathogens from innocent bystanders? David Murdoch Department of Pathology University of Otago, Christchurch Outline Background Diagnostic challenges
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 - 1 - - - 1 P a g e بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم This sheet was made from record section 1 all information are included - Introduction Our respiratory tract is divided anatomically to upper (URT),middle and
- 1 - - - 1 P a g e بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم This sheet was made from record section 1 all information are included - Introduction Our respiratory tract is divided anatomically to upper (URT),middle and
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections / 42
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections 1 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Acute tonsillitispharyngitis Acute otitis media Acute sinusitis Common cold Acute laryngitis Otitis externa Mastoiditis Acute apiglottis
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections 1 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Acute tonsillitispharyngitis Acute otitis media Acute sinusitis Common cold Acute laryngitis Otitis externa Mastoiditis Acute apiglottis
Welcome to Pathogen Group 4
 Welcome to Pathogen Group 4 Chlamydia trachomatis Trachoma Genital chlamydia Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) psittaci Bacillus anthracis Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae, type B Helicobacter pylori
Welcome to Pathogen Group 4 Chlamydia trachomatis Trachoma Genital chlamydia Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) psittaci Bacillus anthracis Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae, type B Helicobacter pylori
Babak Valizadeh, DCLS
 Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections of the Respiratory Tract Babak Valizadeh, DCLS 1391. 02. 05 2012. 04. 25 Babak_Valizadeh@hotmail.com Biological Safety Cabinet Process specimens in biological
Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections of the Respiratory Tract Babak Valizadeh, DCLS 1391. 02. 05 2012. 04. 25 Babak_Valizadeh@hotmail.com Biological Safety Cabinet Process specimens in biological
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences
 Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Section VII. Pathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanisms Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 14. Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases 1 Chapter
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Section VII. Pathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanisms Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 14. Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases 1 Chapter
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Immune System. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: Immune System Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the bacteria is the cause of pneumonia? a. staphylococci c. Treponema
Class: Date: Immune System Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the bacteria is the cause of pneumonia? a. staphylococci c. Treponema
Diphtheria. Vaccine Preventable Childhood Diseases. General information
 Diphtheria General information Caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheria. Transmission is most often person-to-person spread via respiratorydroplets. The word diphtheria comes from Greek and means
Diphtheria General information Caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheria. Transmission is most often person-to-person spread via respiratorydroplets. The word diphtheria comes from Greek and means
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Bacteria causing respiratory tract infections
 Editing file Bacteria causing respiratory tract infections Objectives : Recognize signs & symptoms of different bacterial respiratory tract infections Be able to come up with a short differential to relevant
Editing file Bacteria causing respiratory tract infections Objectives : Recognize signs & symptoms of different bacterial respiratory tract infections Be able to come up with a short differential to relevant
Upper Respiratory Infections. Mehreen Arshad, MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases Duke University
 Upper Respiratory Infections Mehreen Arshad, MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases Duke University Disclosures None Objectives Know the common age- and season-specific causes of pharyngitis
Upper Respiratory Infections Mehreen Arshad, MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases Duke University Disclosures None Objectives Know the common age- and season-specific causes of pharyngitis
FINAL. Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know. Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Page No. Know term "diphtheroids"...
 10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS
 CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
Influenza Infection In Human. Dr. Zuhaida A. Jalil Surveillance Sector Disease Control Division, MOH Malaysia 3 May 2018
 Influenza Infection In Human Dr. Zuhaida A. Jalil Surveillance Sector Disease Control Division, MOH Malaysia 3 May 2018 Objective of the session: After completing this session, you will be able to: Understand
Influenza Infection In Human Dr. Zuhaida A. Jalil Surveillance Sector Disease Control Division, MOH Malaysia 3 May 2018 Objective of the session: After completing this session, you will be able to: Understand
INFLUENZA AND OTHER RESPIRATORY VIRUSES
 INFLUENZA AND OTHER RESPIRATORY VIRUSES Lung Foundation Australia Patient Seminar 21 st October 2017 Lynette Reid Respiratory Clinical Nurse Specialist, RHH What is influenza (the flu )? Influenza (flu)
INFLUENZA AND OTHER RESPIRATORY VIRUSES Lung Foundation Australia Patient Seminar 21 st October 2017 Lynette Reid Respiratory Clinical Nurse Specialist, RHH What is influenza (the flu )? Influenza (flu)
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
INTRODUCTION. Diphtheria is a widespread severe infectious disease that has the potential for causing epidemics.
 DIPHTHERIA 1 INTRODUCTION Diphtheria is a widespread severe infectious disease that has the potential for causing epidemics. Clinical description: An illness characterized by laryngitis or pharyngitis
DIPHTHERIA 1 INTRODUCTION Diphtheria is a widespread severe infectious disease that has the potential for causing epidemics. Clinical description: An illness characterized by laryngitis or pharyngitis
Histoplasmosis. Disease Etiology: Disease Transmission: Reservoirs: Specific Microbial Characteristics: By: Ernest Aguilar
 Histoplasmosis By: Ernest Aguilar Disease Etiology: Histoplasmosis is an infection resulting from the inhalation of spores belonging to the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. [1] This one of three fungi that
Histoplasmosis By: Ernest Aguilar Disease Etiology: Histoplasmosis is an infection resulting from the inhalation of spores belonging to the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. [1] This one of three fungi that
Warm Up. What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease?
 Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview
 MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview Hieucam Phan, MD Pediatrics St. Luke s Hospital San Francisco, CA Microbiology 6/01 1 Introduction Major Achievements of Medical Sciences in the 20th Century Microbiology DNA
MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview Hieucam Phan, MD Pediatrics St. Luke s Hospital San Francisco, CA Microbiology 6/01 1 Introduction Major Achievements of Medical Sciences in the 20th Century Microbiology DNA
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease
 Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Nursing care for children with respiratory dysfunction
 Nursing care for children with respiratory dysfunction 1 Lung Development Specific Immunity to Respiratory Infection Secretory IgA in mucosal immunity IgG in systemic immunity Risk Factors Associated with
Nursing care for children with respiratory dysfunction 1 Lung Development Specific Immunity to Respiratory Infection Secretory IgA in mucosal immunity IgG in systemic immunity Risk Factors Associated with
4. The most common cause of traveller s diarrheoa is a. Rotavirus b. E coli c. Shigella d. Giardia e. Salmonella
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE CHAPTER 13: VIRUSES. 1. Obligate intracellular parasites that multiply in living host cells
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE CHAPTER 13: VIRUSES I. CHARACTERISTICS OF VIRUSES A. General Characteristics 1. Obligate intracellular parasites that multiply in living host cells 2. Contain a single
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE CHAPTER 13: VIRUSES I. CHARACTERISTICS OF VIRUSES A. General Characteristics 1. Obligate intracellular parasites that multiply in living host cells 2. Contain a single
Influenza. Gwen Clutario, Terry Chhour, Karen Lee
 Influenza Gwen Clutario, Terry Chhour, Karen Lee Overview Commonly referred to as the flu Defined as a highly contagious viral infection where it starts at the upper respiratory tract and attacks the nose,
Influenza Gwen Clutario, Terry Chhour, Karen Lee Overview Commonly referred to as the flu Defined as a highly contagious viral infection where it starts at the upper respiratory tract and attacks the nose,
May 14, Review for final exam (May 21, 2011, 8 AM)
 May 14, 2011 Review for final exam (May 21, 2011, 8 AM) The final exam is comprehensive. Two thirds of the test will cover material from the last one third of the class. The remaining one third of the
May 14, 2011 Review for final exam (May 21, 2011, 8 AM) The final exam is comprehensive. Two thirds of the test will cover material from the last one third of the class. The remaining one third of the
1918 Influenza; Influenza A, H1N1. Basic agent information. Section I- Infectious Agent. Section II- Dissemination
 1918 Influenza; Influenza A, H1N1 Basic agent information Section I- Infectious Agent Risk Group: - RG3 Synonym or Cross reference: - Spanish Flu - 1918 Flu - El Grippe Characteristics: - SELECT AGENT
1918 Influenza; Influenza A, H1N1 Basic agent information Section I- Infectious Agent Risk Group: - RG3 Synonym or Cross reference: - Spanish Flu - 1918 Flu - El Grippe Characteristics: - SELECT AGENT
Emerging Respiratory Infections NZ Amanda McNaughton Respiratory Physician CCDHB Wellington
 Emerging Respiratory Infections NZ 2015 Amanda McNaughton Respiratory Physician CCDHB Wellington Respiratory Infection: overview Influenza virus Clinical picture Emerging infection New Zealand Influenza
Emerging Respiratory Infections NZ 2015 Amanda McNaughton Respiratory Physician CCDHB Wellington Respiratory Infection: overview Influenza virus Clinical picture Emerging infection New Zealand Influenza
Fighting Disease. enter body bacteria produce TOXINS which enter bloodstream and travel throughout body
 Pathogen: a disease-causing microorganism ex. parasites How Bacterial Pathogens Work Fighting Disease enter body bacteria produce TOXINS which enter bloodstream and travel throughout body WEBSITES Symptoms:
Pathogen: a disease-causing microorganism ex. parasites How Bacterial Pathogens Work Fighting Disease enter body bacteria produce TOXINS which enter bloodstream and travel throughout body WEBSITES Symptoms:
Shapes and Genera of cocci-shaped organisms:
 BIO230 Microbiology 19: Pathogenic Gram-Positive Cocci and Bacilli 1. Gram-positive pathogens Color reaction Shapes and Genera of cocci-shaped organisms: Genera of bacilli-shaped organisms: 2. Staphylococcus
BIO230 Microbiology 19: Pathogenic Gram-Positive Cocci and Bacilli 1. Gram-positive pathogens Color reaction Shapes and Genera of cocci-shaped organisms: Genera of bacilli-shaped organisms: 2. Staphylococcus
Welcome to Big Sky Country. Pediatrics Infectious disease update. Todd TwogoodMD
 Welcome to Big Sky Country Pediatrics Infectious disease update Todd TwogoodMD My kid is always sick!! We have to deal with parents Snotty nose kids Average number of colds in children from Oct to March
Welcome to Big Sky Country Pediatrics Infectious disease update Todd TwogoodMD My kid is always sick!! We have to deal with parents Snotty nose kids Average number of colds in children from Oct to March
Cases in employees. Cases. Day of onset (July)
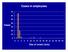 Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases)
 INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases) 1. Agent: Influenza viruses A, B, and C. Only influenza A and B are of public health concern since they are responsible for epidemics. 2. Identification:
INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases) 1. Agent: Influenza viruses A, B, and C. Only influenza A and B are of public health concern since they are responsible for epidemics. 2. Identification:
My kid is always sick!!
 Welcome to Big Sky Country My kid is always sick!! Pediatrics Infectious disease update Todd Twogood MD We have to deal with parents Snotty nose kids Average number of colds in children from Oct to March
Welcome to Big Sky Country My kid is always sick!! Pediatrics Infectious disease update Todd Twogood MD We have to deal with parents Snotty nose kids Average number of colds in children from Oct to March
Malik Sallam. Ola AL-juneidi. Ammar Ramadan. 0 P a g e
 1 Malik Sallam Ola AL-juneidi Ammar Ramadan 0 P a g e Today's lecture will be about viral upper respiratory tract infections. Those include: common cold, sinusitis, otitis, etc. Infections in the upper
1 Malik Sallam Ola AL-juneidi Ammar Ramadan 0 P a g e Today's lecture will be about viral upper respiratory tract infections. Those include: common cold, sinusitis, otitis, etc. Infections in the upper
The Throat. Image source:
 The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
The Chain of Infection
 The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
CE Unit. Viruses and Vaccines
 CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
Novel H1N1 Influenza. It s the flu after all! William Muth M.D. Samaritan Health Services 9 November 2009
 Novel H1N1 Influenza It s the flu after all! William Muth M.D. Samaritan Health Services 9 November 2009 Influenza A Primer.. What is the flu? How do you get it? What s a virus anyhow? Can the flu be prevented,
Novel H1N1 Influenza It s the flu after all! William Muth M.D. Samaritan Health Services 9 November 2009 Influenza A Primer.. What is the flu? How do you get it? What s a virus anyhow? Can the flu be prevented,
Infectious Diseases through Viruses. Obj. 3.c. & 3.g.
 Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Germs. winter is coming
 Game of Germs winter is coming C. difficile What it is: Clostridium difficile, also known as C. difficile or C. diff, is a bacterium that lives in the intestines of a some people (even healthy people).
Game of Germs winter is coming C. difficile What it is: Clostridium difficile, also known as C. difficile or C. diff, is a bacterium that lives in the intestines of a some people (even healthy people).
Study Guide 23, 24 & 47
 Study Guide 23, 24 & 47 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 23-3 Bacteria and Humans Name Period Date 1. One bacterial disease that is transmitted by contaminated drinking water is a. Lyme disease b. gonorrhea c. tuberculosis
Study Guide 23, 24 & 47 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 23-3 Bacteria and Humans Name Period Date 1. One bacterial disease that is transmitted by contaminated drinking water is a. Lyme disease b. gonorrhea c. tuberculosis
TETANUS, DIPHTHERIA, PERTUSSIS (Td/Tdap)
 TETANUS, DIPHTHERIA, PERTUSSIS (Td/Tdap) WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ARE YOU SURE YOU USE THE RIGHT MEASURES TO PROTECT YOURSELF AGAINST TETANUS, DIPHTHERIA OR PERTUSSIS? GET INFORMED! GET VACCINATED! GET PROTECTED!
TETANUS, DIPHTHERIA, PERTUSSIS (Td/Tdap) WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ARE YOU SURE YOU USE THE RIGHT MEASURES TO PROTECT YOURSELF AGAINST TETANUS, DIPHTHERIA OR PERTUSSIS? GET INFORMED! GET VACCINATED! GET PROTECTED!
Chapter 13. Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology
 Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract
 Before you start: You must read the slides! The Dr. did not bother to explain them all Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract - TB is a global problem that the WHO is trying to combat.
Before you start: You must read the slides! The Dr. did not bother to explain them all Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract - TB is a global problem that the WHO is trying to combat.
