Viral Hemorrhagic Fever
|
|
|
- Stella Woods
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Viral Hemorrhagic Fever
2 Overview Organism History Epidemiology Transmission Disease in Humans Disease in Animals Prevention and Control
3 What is Viral Hemorrhagic Fever? Severe multisystem syndrome Diffuse Damage to overall vascular system Symptoms often accompanied by hemorrhage Rarely life threatening in itself Includes conjunctivitis, petechia, echymosis Relatively high mortality
4 Quick Overview: Who are they? VHFs are: Enveloped Lipid-encapsulated Single-strand RNA Zoonotic (animal-borne) Geographically restricted by host Persistent in nature (rodents, bats, mosquitoes, ticks, livestock, monkeys, and primates) Survival dependent on an animal or insect host, for the natural reservoir
5 Quick Overview: Who are they? Arenaviridae Lassa Fever Argentine HF (Junin) Bolivian HF (Machupo) Brazilian HF (Sabia) Venezuelan HF (Guanarito) Bunyaviridae Rift Valley Fever (RVF) Crimean Congo HF (CCHF) Hantavirus (Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS)) Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) Filoviridae Marburg Ebola Flaviviridae Yellow Fever Dengue Fever Omsk HF Kyasanur Forest Disease
6 Quick Overview: How do we get infected? Rodents & Arthropods, both reservoir & vector Bites of infected mosquito or tick Inhalation of rodent excreta Infected animal product exposure Person-to-Person Blood/body fluid exposure Airborne potential for some arenaviridae, filoviridae
7 Arenaviridae Junin virus Machupo virus Guanarito virus Lassa virus Sabia virus
8 Arenaviridae History First isolated in : Junin virus - Argentina First to cause hemorrhagic fever Argentine hemorrhagic fever 1963: Machupo virus Bolivia Bolivian hemorrhagic fever Guanarito (Venezuela) Sabia (Brazil) 1969: Lassa virus Nigeria Lassa fever
9 Arenavirus Structure Single-stranded, bi-segmented RNA genome Large segment (7200nt), small one (3500nt) Lipid envelope with 8-10nm club-shaped projections
10 Arenaviridae Transmission Virus transmission and amplification occurs in rodents Shed virus through urine, feces, and other excreta Human infection Contact with excreta Contaminated materials Aerosol transmission Person-to-person transmission
11 Arenaviridae in Humans Incubation period days Fever and malaise 2 4 days Hemorrhagic stage Hemorrhage, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia Neurologic signs
12 Arenaviridae: Lassa Fever First seen in Lassa, Nigeria in Now in all countries of West Africa 5-14% of all hospitalized febrile illness Rodent-borne (Mastomys natalensis) Interpersonal transmission Direct Contact Sex Breast Feeding
13 Lassa Fever Virus Background Discovered in 1969 when two missionary nurses died in Lassa, Nigeria, W. Africa It expands to Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone 100 to 300 thousand cases per year with approx. 5,000 deaths
14 Lassa Fever Distinguishing Features Gradual onset Retro-sternal pain Exudative pharyngitis Hearing loss in 25% may be persistent Spontaneous abortion Mortality 1-3% overall (up to 50% in epidemics) Therapy: Ribavirin
15 Bunyaviridae Rift Valley Fever virus Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever virus Hantavirus L-segment codes for an L- protein (the RNA dependent RNA polymerase); M segment codes for two surface glycoproteins G1 and G2 which form the envelope spikes; S segment codes for an N- protein (nucleocapsid protein).
16 Rift Valley Fever (RVF) Bunyaviridae Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever (CCHF) Hantavirus Old World: Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) New World: Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) 5 genera with over 350 viruses
17 Bunyaviridae Transmission Arthropod vector Exception Hantaviruses RVF Aedes mosquito CCHF Ixodid tick Hantavirus Rodents Less common Aerosol Exposure to infected animal tissue
18 Bunyaviridae Transmission to humans Arthropod vector (RVF, CCHF) Contact with animal blood or products of infected livestock Rodents (Hantavirus) Laboratory aerosol Person-to-person transmission with CCHF
19 Rift Valley Fever Predominantly a disease of sheep and cattle 1930: First identified in an infected newborn lamb in Egypt In livestock: ~100% abortion 90% mortality in young 5-60% mortality in adults
20 Rift Valley Fever Asymptomatic or mild illness in humans Distinguishing Characteristics Hemorrhagic complications rare (<5%) Vision loss (retinal hemorrhage, vasculitis) in 1-10% Overall mortality 1% Therapy: Ribavirin?
21 Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Distinguishing features Abrupt onset Most humans infected will develop hemorrhagic fever Profuse hemorrhage Mortality 15-40% Therapy: Ribavirin
22 Bunyaviridae: Crimean-Congo HF Transmission to humans: Ixodid, Hyalomma spp. ticks Contact with animal blood/products Person-to-person Laboratory aerosols Extensive geographical distribution
23 Bunyaviridae: Hantaviruses Transmission to humans: Exposure to rodent saliva and excreta Inhalation Bites Ingestion in contaminated food/water (?) Person-to-person (Andes virus in Argentina)
24 Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) Distinguishing Features Insidious onset Intense headaches, Blurred vision kidney failure (causing severe fluid overload) Mortality: 1-15%
25 RVF Bunyaviridae Humans Incubation period 2-5 days 0.5% - Hemorrhagic Fever CCHF Incubation period 3-7 days Hemorrhagic Fever days following clinical signs Hantavirus Incubation period 7 21 days HPS and HFRS
26 Filoviridae Ebola Ebola-Zaire Ebola-Sudan Ebola-Ivory Coast Ebola-Bundibugyo (Ebola-Reston) Marburg Ebola Marburg
27 Filoviridae History 1967: Marburg, Frankfurt, Belgrade European laboratory workers 1976: Ebola virus Ebola Zaire Ebola Sudan 1989 and 1992: Ebola Reston USA and Italy Imported macaques from Philippines 1994: Ebola Côte d'ivoire
28 Filoviridae Transmission Reservoir is UNKNOWN Bats implicated with Marburg Intimate contact Nosicomial transmission Reuse of needles and syringes Exposure to infectious tissues, excretions, and hospital wastes Aerosol transmission Primates
29 Filoviridae: Ebola Rapidly fatal febrile hemorrhagic illness Transmission: bats implicated as reservoir Person-to-person Nosocomial Five subtypes Ebola-Zaire, Ebola-Sudan, Ebola-Ivory Coast, Ebola-Bundibugyo, Ebola-Reston Ebola-Reston imported to US, but only causes illness in non-human primates Human-infectious subtypes found only in Africa
30 Filoviridae: Ebola Distinguishing features: Acute onset Weight loss/protration 25-90% case-fatality
31 Filoviridae: Marburg Transmission: Animal host unknown Person-to-person infected animal blood/fluid exposure Indigenous to Africa Uganda Western Kenya Zimbabwe Democratic Republic of Congo Angola
32 Filoviridae: Marburg Distinguising features Sudden onset Chest pain Maculopapular rash on trunk Pancreatitis Jaundice 21-90% mortality
33 Filoviridae Humans Most severe hemorrhagic fever Incubation period: 4 10 days Abrupt onset Fever, chills, malaise, and myalgia Hemorrhage and DIC Death around day 7 11 Painful recovery
34 Flaviviridae Dengue virus Yellow Fever virus Omsk Hemorrhagic Fever virus Kyassnur Forest Disease virus
35 Flaviviridae History 1648 : Yellow Fever described 17 th 20 th century Yellow Fever and Dengue outbreaks 1927: Yellow Fever virus isolated 1943: Dengue virus isolated 1947 Omsk Hemorrhagic Fever virus isolated 1957: Kyasanur Forest virus isolated
36 Flaviviridae Transmission Arthropod vector Yellow Fever and Dengue viruses Aedes aegypti Sylvatic cycle Urban cycle Kasanur Forest Virus Ixodid tick Omsk Hemorrhagic Fever virus Muskrat urine, feces, or blood
37 Flaviviridae Epidemiology Yellow Fever Virus Africa and Americas Case fatality rate varies Dengue Virus Asia, Africa, Australia, and Americas Case fatality rate 1-10% Kyasanur Forest virus India Case fatality rate 3 5% Omsk Hemorrhagic Fever virus Europe Case fatlity rate 0.5 3%
38 Flaviviridae Humans Yellow Fever Incubation period 3 6 days Short remission Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Incubation period 2 5 days Infection with different serotype Kyasanur Forest Disease Omsk Hemorrhagic Fever Lasting sequela
39 Yellow Fever Distinguishing features Biphasic infection Common hepatic involvement & jaundice Mortality: 15-50%
40 Flaviviridae: Dengue Dengue Fever (DF) /Fatality: <1% Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF)/ Fatality: 5-6% Dengue Shock Syndrome (DSS) /Fatality 12-44% Four distinct serotypes DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3, DEN-4 Distinguishing Features Sudden onset Eye pain Rash Complications/sequelae uncommon Illness less severe in younger children
41 Omsk Hemorrhagic Fever Distinguishing Features Acute Onset Biphasic infection Complications Hearing loss Hair loss Psycho-behavioral difficulties Mortality: 0.5 3%
42 Flaviviridae: Kyanasur Forest Distribution: limited to Karnataka State, India Distinguishing Features Acute onset Biphasic Case-fatality: 3-5% ( cases annually)
43 Symptoms/Signs vary with the type of VHF
44 Common Pathophysiology Small vessel involvement Increased vascular permeability Multiple cytokine activation Cellular damage Abnormal vascular regulation: Early -> mild hypotension Severe/Advanced -> Shock Viremia Macrophage involvement Inadequate/delayed immune response
45 Common Pathophysiology Multisystem Involvement Hematopoietic Neurologic Pulmonary Hepatic (Ebola, Marburg, RVF, CCHF, Yellow Fever) Renal (Hantavirus) Hemorrhagic complications Hepatic damage Consumptive coagulopathy Primary marrow injury to megakaryocytes
46 Common Clinical Features: Early/Prodromal Symptoms Fever Myalgia Malaise Fatigue/weakness Headache Dizziness Arthralgia Nausea Non-bloody diarrhea
47 Common Clinical Features: Progressive Signs Conjunctivitis Facial & thoracic flushing Pharyngitis Exanthems Periorbital edema Pulmonary edema Hemorrhage Subconjunctival hemorrhage Ecchymosis Petechiae But the hemorrhage itself is rarely lifethreatening.
48 Symptoms Incubation period of 6-21 days 80% of human infections are asyptomatic Onset is slow: fever, weakness, & malaise Few days: headache, pharyngitis, muscle pain, retrostinal & abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, conjunctivitis, diarrhea, cough, & proteinuria Severe cases: facial swelling, lung cavity fluid, hemorrhaging, hyopotension, Neurological problems: tremors, encephalitis, hair loss, gait disturbance, deafness 95% death rate among pregnant women & spontaneous abortion
49 Common Clinical Features: Severe/End-stage Multisystem compromise Profuse bleeding Consumptive coagulopathy/dic Encephalopathy Shock Death
50 Clinical Symptoms More severe Bleeding under skin Petechiae, echymoses, conjunctivitis Bleeding in internal organs Bleeding from orifices Blood loss rarely cause of death
51 Major antiviral cells in early phrase Plasmcytoid DC2 1.A major IFNα producer after viral infection 2. Toll-like receptor -3 < 2 days after viral infection 1. Cytolysis by perforin-granzyme 2. IFN γ: protect uninfected cells and activate macrophages 3. Mediate ADCC IFNγ 1. Phagocytosis of virus and virus-infected cells 2. Kill virus-infected cells 3. Produce antiviral molecules: TNFα, NO, IFNα
52 Adaptive (specific) immune response to viral infection IFNγ IFNα and IFNβ Neighboring uninfected cells Protection Killing
53 Innate & Adaptive Immunity Timeline Cambridge University Immunology Lectures (www)
54 Complete Blood Count Lab studies Leucopenia, leucocytosis, thrombocytopenia, hemoconcentration, DIC Liver enzymes Alb Proteinuria universal Serological tests Ab not detected acute phase; Direct examination blood/tissues for viral Ag enzyme immunoassay. Immunohistochemical staining liver tissue Virus isolation in cell culture RT-PCR sequencing of virus Electron microscopy specific and sensitive
55 Treatment Supportive care: Fluid and electrolyte management Hemodynamic monitoring Ventilation and/or dialysis support Steroids for adrenal crisis Anticoagulants, IM injections, Treat secondary bacterial infections
56 Treatment Manage severe bleeding complications Cryoprecipitate (concentrated clotting factors) Platelets Fresh Frozen Plasma Heparin for DIC Ribavirin in vitro activity vs. Lassa fever New World Hemorrhagic fevers Rift Valley Fever No evidence to support use in Filovirus or Flavivirus infections
57 Prevention and Control
58 Prevention Nosocomial: Complete equipment sterilization & protective clothing House to house rodent trapping Better food storage & hygiene Cautious handling of rodent if used as food source If human case occurs Decrease person-to-person transmission Isolation of infected individuals
59 Prevention and Control Avoid contact with host species Rodents Control rodent populations Discourage rodents from entering or living in human populations Safe clean up of rodent nests and droppings Insects Use insect repellents Proper clothing and bed nets Window screens and other barriers to insects
60 Vaccination Argentine and Bolivian HF PASSIVE IMMUNIZATION Treat with convalescent serum containing neutralizing antibody or immune globulin Yellow Fever ACTIVE IMMUNIZATION Travelers to Africa and South America Experimental vaccines under study Argentine HF, Rift Valley Fever, Hantavirus and Dengue HF
61 VHF Personal Protective Equipment Airborne and Contact isolation for patients with respiratory symptoms N-95 or PAPR mask Negative pressure isolation Gloves Gown Fitted eye protection and shoe covers if going to be exposed to splash body fluids Droplet and Contact isolation for patients without respiratory symptoms Surgical mask Gloves Gown Fitted eye protection and shoe covers if going to be exposed to splash body fluids Environmental surfaces Cleaned with hospital approved disinfectant Linen incinerated, autoclaved, double-bagged for wash
62 Why do VHFs make good Bioweapons? Disseminate through aerosols Low infectious dose High morbidity and mortality Cause fear and panic in the public No effective vaccine Available and can be produced in large quantity Research on weaponization has been conducted
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) By : Assis. Prof Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) By : Assis. Prof Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Overview Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a group of illnesses caused by four families of viruses. Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae,
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) By : Assis. Prof Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Overview Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a group of illnesses caused by four families of viruses. Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae,
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers CDC, AFIP
 CDC, AFIP Diverse group of illnesses caused by RNA viruses from 4 families: Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Filoviridae, Flaviridae Differ by geographic occurrence and vector/reservoir Share certain clinical
CDC, AFIP Diverse group of illnesses caused by RNA viruses from 4 families: Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Filoviridae, Flaviridae Differ by geographic occurrence and vector/reservoir Share certain clinical
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers
 Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (VHFs) http://www.ncrr.nih.gov/publications/ncrr_reporter/summer-fall2009/images/essential_2.jpg Definition Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) refer to a group of illnesses that are
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (VHFs) http://www.ncrr.nih.gov/publications/ncrr_reporter/summer-fall2009/images/essential_2.jpg Definition Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) refer to a group of illnesses that are
Marburg and Lassa viruses ศาสตราจารย ดร.พ ไลพ นธ พ ธว ฒนะ
 Marburg and Lassa viruses ศาสตราจารย ดร.พ ไลพ นธ พ ธว ฒนะ ศ นย ความร วมม อการว จ ยไข หว ดใหญ ภาคว ชาจ ลช วว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล มหาว ทยาล ยมห ดล Situation analysis of laboratory based surveillance
Marburg and Lassa viruses ศาสตราจารย ดร.พ ไลพ นธ พ ธว ฒนะ ศ นย ความร วมม อการว จ ยไข หว ดใหญ ภาคว ชาจ ลช วว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล มหาว ทยาล ยมห ดล Situation analysis of laboratory based surveillance
VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC FEVER (VHF)
 VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC FEVER (VHF) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive laboratory result to the local public health department where
VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC FEVER (VHF) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive laboratory result to the local public health department where
UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October EMS TB Ebola Virus Disease (EVD)
 UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October 2014 EMS TB 14-006 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Purpose: 1. To inform & provide management recommendations to UTSW/BioTel EMS System EMS Providers about Ebola Virus
UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October 2014 EMS TB 14-006 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Purpose: 1. To inform & provide management recommendations to UTSW/BioTel EMS System EMS Providers about Ebola Virus
Introduction to Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers
 Introduction to Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers Linus Ndegwa, MPHE, HCS Infection Control, Manager Global Disease Detection-GDD Centers for Disease Control and Prevention-Kenya Session Objectives To explain
Introduction to Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers Linus Ndegwa, MPHE, HCS Infection Control, Manager Global Disease Detection-GDD Centers for Disease Control and Prevention-Kenya Session Objectives To explain
The Ebola Virus. By Emilio Saavedra
 The Ebola Virus By Emilio Saavedra Etiological Agents: Ebolavirus is the etiologic agent. [1] There are four main families of viruses that are agents of Ebola (hemorrhagic fever). [1] These four families
The Ebola Virus By Emilio Saavedra Etiological Agents: Ebolavirus is the etiologic agent. [1] There are four main families of viruses that are agents of Ebola (hemorrhagic fever). [1] These four families
Summary of current outbreak in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone
 ALERT TO HEALTHCARE WORKERS: EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE OUTBREAK IN GUINEA, LIBERIA AND SIERRA LEONE, WEST AFRICA 04 April 2014 Summary of current outbreak in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone In this update and
ALERT TO HEALTHCARE WORKERS: EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE OUTBREAK IN GUINEA, LIBERIA AND SIERRA LEONE, WEST AFRICA 04 April 2014 Summary of current outbreak in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone In this update and
Ebola Virus Patient Advisory
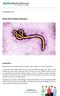 22 September 2014 Ebola Virus Patient Advisory Introduction Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly
22 September 2014 Ebola Virus Patient Advisory Introduction Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly
Media centre Ebola virus disease
 1 of 6 10/15/2014 10:59 AM Media centre Ebola virus disease Fact sheet N 103 Updated September 2014 Key facts Ebola virus disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal
1 of 6 10/15/2014 10:59 AM Media centre Ebola virus disease Fact sheet N 103 Updated September 2014 Key facts Ebola virus disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal
Epidemiology of Lassa Fever
 Epidemiology of Lassa Fever Njideka E. Kanu Department of Community Medicine, University of Medical Sciences, Ondo A lecture delivered at the Academic Seminar of University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, 14
Epidemiology of Lassa Fever Njideka E. Kanu Department of Community Medicine, University of Medical Sciences, Ondo A lecture delivered at the Academic Seminar of University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, 14
Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Essential information
 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Essential information Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Origins The Ebola virus is named after the Ebola River in what was Zaire (now Democratic Republic of Congo) where the first outbreak
Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Essential information Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Origins The Ebola virus is named after the Ebola River in what was Zaire (now Democratic Republic of Congo) where the first outbreak
Biological Terrorist Agents: Part 2 Viral Agents
 Biological Terrorist Agents: Part 2 Viral Agents ROBERT BURKE Published: July 2002 Viruses are the simplest type of microorganisms and the smallest of all living things. They are much smaller than bacteria
Biological Terrorist Agents: Part 2 Viral Agents ROBERT BURKE Published: July 2002 Viruses are the simplest type of microorganisms and the smallest of all living things. They are much smaller than bacteria
Emerging Infectious Diseases
 Emerging Infectious Diseases Dr Arthur Jackson Consultant in Infectious Diseases September 2014 The time has come to close the book on infectious diseases. We have basically wiped out infection in the
Emerging Infectious Diseases Dr Arthur Jackson Consultant in Infectious Diseases September 2014 The time has come to close the book on infectious diseases. We have basically wiped out infection in the
Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers
 Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers Travel Medicine Conference Constanţa, September 2018 Dr Ian Cropley Department of Infectious Diseases High Level Isolation Unit Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust Viral Haemorrhagic
Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers Travel Medicine Conference Constanţa, September 2018 Dr Ian Cropley Department of Infectious Diseases High Level Isolation Unit Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust Viral Haemorrhagic
黃熱病 衞生署疾病管制局中區傳染病防治醫療網王任賢指揮官
 黃熱病 衞生署疾病管制局中區傳染病防治醫療網王任賢指揮官 What is Viral Hemorrhagic Fever? Severe multisystem syndrome Damage to overall vascular system Symptoms often accompanied by hemorrhage Rarely life threatening in itself Includes
黃熱病 衞生署疾病管制局中區傳染病防治醫療網王任賢指揮官 What is Viral Hemorrhagic Fever? Severe multisystem syndrome Damage to overall vascular system Symptoms often accompanied by hemorrhage Rarely life threatening in itself Includes
12 June The average EVD case fatality rate has been around 50 per cent.
 12 June 2015 Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. EVD is
12 June 2015 Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. EVD is
Diseases Related to Bioterrorism
 Newfoundland and Labrador Disease Control Manual Section 8 Diseases Related to Bioterrorism Bioterrorism Agents...8.1-1 Small Pox, List A...8.2-1 Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers, List A...8.3-1 8.1 Bioterrorism
Newfoundland and Labrador Disease Control Manual Section 8 Diseases Related to Bioterrorism Bioterrorism Agents...8.1-1 Small Pox, List A...8.2-1 Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers, List A...8.3-1 8.1 Bioterrorism
Ebola. Wessex CPD Event 14/11/14. Dr Ishani Kar-Purkayastha, CCDC, Wessex PHE Centre Tel:
 Ebola Wessex CPD Event 14/11/14 Dr Ishani Kar-Purkayastha, CCDC, Wessex PHE Centre wessex@phe.gov.uk Tel: 0345 055 2022 Outline Background About the current outbreak Situation in the UK Clinical management
Ebola Wessex CPD Event 14/11/14 Dr Ishani Kar-Purkayastha, CCDC, Wessex PHE Centre wessex@phe.gov.uk Tel: 0345 055 2022 Outline Background About the current outbreak Situation in the UK Clinical management
CE Unit. Viruses and Vaccines
 CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES WITH GLOBAL IMPACT
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education on
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education on
Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases
 Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: Hemorrhagic fevers caused by: i) Ebola virus and ii) Marburg virus and iii) Other viral causes including
Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: Hemorrhagic fevers caused by: i) Ebola virus and ii) Marburg virus and iii) Other viral causes including
EBOLA VIRUS AWARENESS
 EBOLA VIRUS AWARENESS Yvonne S. Butler, MD Assistant Professor; Obstetrics and Gynecology Global Women s Health Program Liberia Chevron-Liberia / BIPAI Partnership Baylor College of Medicine Texas Children
EBOLA VIRUS AWARENESS Yvonne S. Butler, MD Assistant Professor; Obstetrics and Gynecology Global Women s Health Program Liberia Chevron-Liberia / BIPAI Partnership Baylor College of Medicine Texas Children
*NCCT is approved as a provider of continuing education programs in the clinical laboratory sciences by the ASCLS P.A.C.E. Program, provider #122.
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Viral hemorrhagic fevers are serious infections with a high case fatality rate and the propensity to spread to caretakers of infected persons, either family members or healthcare workers,
COURSE DESCRIPTION Viral hemorrhagic fevers are serious infections with a high case fatality rate and the propensity to spread to caretakers of infected persons, either family members or healthcare workers,
This also applies to all travellers transiting through countries with risk of transmission of yellow fever.
 JAMAICA YELLOW FEVER ENTRY REQUIREMENTS 29 MAY 2016 Vaccination against yellow fever is required to prevent the importation of yellow fever virus into Jamaica where the disease does not occur but where
JAMAICA YELLOW FEVER ENTRY REQUIREMENTS 29 MAY 2016 Vaccination against yellow fever is required to prevent the importation of yellow fever virus into Jamaica where the disease does not occur but where
West Nile Fever. F. Karup Pedersen 2012
 F. Karup Pedersen 2012 West Nile virus first isolated 1937 in West Nile district, Uganda Japanese encephalitis reconvalescens serum could neutralize West Nile virus Virus antigenically related to Japanese
F. Karup Pedersen 2012 West Nile virus first isolated 1937 in West Nile district, Uganda Japanese encephalitis reconvalescens serum could neutralize West Nile virus Virus antigenically related to Japanese
Marburg virus disease
 Marburg virus disease Fact sheet available at http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs_marburg/en/ Updated 20 October 2017 Key facts Marburg virus disease (MVD), formerly known as Marburg haemorrhagic
Marburg virus disease Fact sheet available at http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs_marburg/en/ Updated 20 October 2017 Key facts Marburg virus disease (MVD), formerly known as Marburg haemorrhagic
Genus Ebolavirus is 1 of 3 members of the Filoviridae family (filovirus), along with genus Marburgvirus and genus Cuevavirus.
 EBOLA VIRUS Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a severe, often fatal illness, with a case fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most virulent diseases.the infection is transmitted by direct contact
EBOLA VIRUS Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a severe, often fatal illness, with a case fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most virulent diseases.the infection is transmitted by direct contact
ZIKA VIRUS. Epic and aspects of management
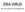 ZIKA VIRUS Epic and aspects of management Classification - Belong to the family Flaviviridae which are mosquitoes borne viruses such as Dengue virus ( DEN V ), West Nile virus ( WN V ), Yellow fever Virus
ZIKA VIRUS Epic and aspects of management Classification - Belong to the family Flaviviridae which are mosquitoes borne viruses such as Dengue virus ( DEN V ), West Nile virus ( WN V ), Yellow fever Virus
Surveillance Protocol Dengue Fever (Breakbone fever, Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever)
 Surveillance Protocol Dengue Fever (Breakbone fever, Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever) Provider Responsibilities 1. Report suspect or confirmed cases of Dengue Fever (DF) or Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF).to your
Surveillance Protocol Dengue Fever (Breakbone fever, Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever) Provider Responsibilities 1. Report suspect or confirmed cases of Dengue Fever (DF) or Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF).to your
Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive)
 Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) July 2012 May 2018 December 2005 Case Definition Confirmed Case Clinical
Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) July 2012 May 2018 December 2005 Case Definition Confirmed Case Clinical
OUR COMMUNITY: OUR WORLD: ONE HEALTH. Ebola : Geomedicine Conference
 OUR COMMUNITY: OUR WORLD: ONE HEALTH Ebola 2013-14: Geomedicine Conference Early Geomedicine East Africa, El Nino 1997 RVF: A One Health Response Ecological prediction models Animal vaccination Human
OUR COMMUNITY: OUR WORLD: ONE HEALTH Ebola 2013-14: Geomedicine Conference Early Geomedicine East Africa, El Nino 1997 RVF: A One Health Response Ecological prediction models Animal vaccination Human
ZIKA VIRUS. John J. Russell MD May 27, 2016
 John J. Russell MD May 27, 2016 HISTORY Discovered 1947 Zika Forest of Uganda in rhesus monkeys, thus the name Found in humans in Africa in 1952 Not considered a public health threat until outbreak in
John J. Russell MD May 27, 2016 HISTORY Discovered 1947 Zika Forest of Uganda in rhesus monkeys, thus the name Found in humans in Africa in 1952 Not considered a public health threat until outbreak in
LECTURE topics: 1. Immunology. 2. Emerging Pathogens
 LECTURE 23 2 topics: 1. Immunology 2. Emerging Pathogens Benefits of the Normal Flora: 1. Protect us from colonization by other bacteria and fungi (competitive exclusion). 2. Many synthesize vitamins,
LECTURE 23 2 topics: 1. Immunology 2. Emerging Pathogens Benefits of the Normal Flora: 1. Protect us from colonization by other bacteria and fungi (competitive exclusion). 2. Many synthesize vitamins,
Ebola Virus Transmission
 Ebola Virus Zoonotic virus bats the most likely reservoir, although species unknown Spillover event from infected wild animals (e.g., fruit bats, monkey, duiker) to humans, followed by human-human transmission
Ebola Virus Zoonotic virus bats the most likely reservoir, although species unknown Spillover event from infected wild animals (e.g., fruit bats, monkey, duiker) to humans, followed by human-human transmission
saipem Ebola virus diseases EVD August 2014
 Ebola virus diseases EVD August 2014 Why Ebola generates such fear? Ebola is one of the world's most deadly diseases. It can kill up to 90% of people who developed Ebola virus disease. There is not treatment
Ebola virus diseases EVD August 2014 Why Ebola generates such fear? Ebola is one of the world's most deadly diseases. It can kill up to 90% of people who developed Ebola virus disease. There is not treatment
WHO SOUTHERN SUDAN HEALTH UPDATE May 2004
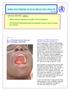 WHO SOUTHERN SUDAN HEALTH UPDATE SPECIAL EDITION: EBOLA Ebola outbreak confirmed in Yambio, Western Equatoria World Health Organization leads international response team to contain the outbreak Photo by:
WHO SOUTHERN SUDAN HEALTH UPDATE SPECIAL EDITION: EBOLA Ebola outbreak confirmed in Yambio, Western Equatoria World Health Organization leads international response team to contain the outbreak Photo by:
Where is Yellow Fever found?
 Yellow Fever Introduction Yellow Fever is an acute viral hemorrhagic disease transmitted by a female mosquito of the Aedes family (Aedes aegypti). Man and monkeys are the only reservoir for this virus.
Yellow Fever Introduction Yellow Fever is an acute viral hemorrhagic disease transmitted by a female mosquito of the Aedes family (Aedes aegypti). Man and monkeys are the only reservoir for this virus.
A BSL-1 lab houses activities that require only standard microbial practices. These include:
 BSL-1 A BSL-1 lab houses activities that require only standard microbial practices. These include: Work should be performed on an open lab bench or table Spills must be decontaminated immediately Infectious
BSL-1 A BSL-1 lab houses activities that require only standard microbial practices. These include: Work should be performed on an open lab bench or table Spills must be decontaminated immediately Infectious
HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority
 HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority Introduction Definition Symptom Transmission Global situation Local situation Control Content Introduction Yellow fever (YF) is a mosquito-borne
HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority Introduction Definition Symptom Transmission Global situation Local situation Control Content Introduction Yellow fever (YF) is a mosquito-borne
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever
 Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Onder Ergonul, MD, MPH Koç University, School of Medicine, Istanbul 30 March 2018 Content Epidemiology Diagnosis Clinical course Therapy Post-exposure prophylaxis Crimean-Congo
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Onder Ergonul, MD, MPH Koç University, School of Medicine, Istanbul 30 March 2018 Content Epidemiology Diagnosis Clinical course Therapy Post-exposure prophylaxis Crimean-Congo
USING ADVANCED GENOMIC ANALYSIS FOR POTENTIAL HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER CAUSATIVE AGENTS. J H Kofi Bonney, PhD
 USING ADVANCED GENOMIC ANALYSIS FOR POTENTIAL HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER CAUSATIVE AGENTS J H Kofi Bonney, PhD Noguchi Memorial Institute Medical Research Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research University
USING ADVANCED GENOMIC ANALYSIS FOR POTENTIAL HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER CAUSATIVE AGENTS J H Kofi Bonney, PhD Noguchi Memorial Institute Medical Research Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research University
Biological Warfare Agents
 Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
VOLUME - XIII ISSUE - LXXIV MAR/APR 2016
 VOLUME - XIII ISSUE - LXXIV MAR/APR 2016 1 2 7 10 11 13 Editorial Disease Diagnosis Interpretation Bouquet Trouble Shooting Tulip News VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC FEVERS WITH THE ONSET OF KAYSANUR FOREST DISEASE
VOLUME - XIII ISSUE - LXXIV MAR/APR 2016 1 2 7 10 11 13 Editorial Disease Diagnosis Interpretation Bouquet Trouble Shooting Tulip News VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC FEVERS WITH THE ONSET OF KAYSANUR FOREST DISEASE
CE Unit 7. Viruses and Vaccines
 CE Unit 7 Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
CE Unit 7 Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
Viral hemorrhagic fever
 Page 1 of 5 Viral hemorrhagic fever From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a diverse group of animal and human illnesses in which fever and hemorrhage are caused by a
Page 1 of 5 Viral hemorrhagic fever From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a diverse group of animal and human illnesses in which fever and hemorrhage are caused by a
When infections go viral Zika Virus
 When infections go viral Zika Virus John Fangman, MD Associate Professor of Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Senior Medical Director of Ambulatory, Medical College Physicians Medical College of Wisconsin
When infections go viral Zika Virus John Fangman, MD Associate Professor of Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Senior Medical Director of Ambulatory, Medical College Physicians Medical College of Wisconsin
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences A STUDY OF CLINCAL PROFILE IN DENGUE CASES ABSTRACT
 Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A STUDY OF CLINCAL PROFILE IN DENGUE CASES DHANDAPANI E.* 1 AND SUDHA M 2 1 Formerly Professor of Medicine,
Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A STUDY OF CLINCAL PROFILE IN DENGUE CASES DHANDAPANI E.* 1 AND SUDHA M 2 1 Formerly Professor of Medicine,
What s Lurking out there??????
 What s Lurking out there?????? Dave Warshauer, PhD, D(ABMM) Deputy Director, Communicable Diseases Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene david.warshauer@slh.wisc.edu WISCONSIN STATE LABORATORY OF HYGIENE
What s Lurking out there?????? Dave Warshauer, PhD, D(ABMM) Deputy Director, Communicable Diseases Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene david.warshauer@slh.wisc.edu WISCONSIN STATE LABORATORY OF HYGIENE
Fact sheet. Yellow fever
 Fact sheet Key facts is an acute viral haemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected mosquitoes. The yellow in the name refers to the jaundice that affects some patients. Up to 50% of severely affected
Fact sheet Key facts is an acute viral haemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected mosquitoes. The yellow in the name refers to the jaundice that affects some patients. Up to 50% of severely affected
Ebola Virus Introduction
 Ebola Ebola Virus Introduction First appeared in Africa 1976 African Hemorrhagic Fever acute, mostly fatal disease causes blood vessel bursting systemic (all organs/tissues) humans and nonhuman primates
Ebola Ebola Virus Introduction First appeared in Africa 1976 African Hemorrhagic Fever acute, mostly fatal disease causes blood vessel bursting systemic (all organs/tissues) humans and nonhuman primates
The Struggle with Infectious Disease. Lecture 5
 The Struggle with Infectious Disease Lecture 5 Tropical Diseases Life and infectious disease began in the rift valley/rain forest of Eastern Africa Peoples migrated North to temperate regions Tropical
The Struggle with Infectious Disease Lecture 5 Tropical Diseases Life and infectious disease began in the rift valley/rain forest of Eastern Africa Peoples migrated North to temperate regions Tropical
Yellow fever. Key facts
 From: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/yellow-fever WHO/E. Soteras Jalil Yellow fever 14 March 2018 Key facts Yellow fever is an acute viral haemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected
From: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/yellow-fever WHO/E. Soteras Jalil Yellow fever 14 March 2018 Key facts Yellow fever is an acute viral haemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected
Rift Valley Fever RVF. Enhancing Safe Inter-Regional Livestock Trade Dubai, United Arab Emirates June 13-16, 2011
 Rift Valley Fever RVF Enhancing Safe Inter-Regional Livestock Trade Dubai, United Arab Emirates June 13-16, 2011 Definition Rift valley fever (RVF) is an acute febrile arthropod-borne zoonotic disease.
Rift Valley Fever RVF Enhancing Safe Inter-Regional Livestock Trade Dubai, United Arab Emirates June 13-16, 2011 Definition Rift valley fever (RVF) is an acute febrile arthropod-borne zoonotic disease.
INFECTION PREVENTION NEWS & UPDATES
 CONTACT + DROPLET EBOLA INFECTION While the Ebola outbreak from the Democratic Republic of the Congo from earlier this year is over, a new outbreak of Ebola has been identified that has infected at least
CONTACT + DROPLET EBOLA INFECTION While the Ebola outbreak from the Democratic Republic of the Congo from earlier this year is over, a new outbreak of Ebola has been identified that has infected at least
Biological Warfare Agents
 Chapter 29 The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID). Medical Management of
Chapter 29 The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID). Medical Management of
West Nile Virus. By Frank Riusech
 West Nile Virus By Frank Riusech Disease Etiology: West Nile virus(wnv), genus, flavivirus is positive- stranded RNA arbovirus (arthropod- borne), belonging to the Flaviviridae family. Included in this
West Nile Virus By Frank Riusech Disease Etiology: West Nile virus(wnv), genus, flavivirus is positive- stranded RNA arbovirus (arthropod- borne), belonging to the Flaviviridae family. Included in this
EBOLA OUTBREAK IN WEST AFRICA
 Mil. Med. Sci. Lett. (Voj. Zdrav. Listy) 2015, vol. 84(4), p. 177-181 ISSN 0372-7025 REVIEW ARTICLE EBOLA OUTBREAK IN WEST AFRICA Vanda Bostik 1, Miloslav Salavec 2, Radek Sleha 1, Petr Prasil 3, Jan Marek
Mil. Med. Sci. Lett. (Voj. Zdrav. Listy) 2015, vol. 84(4), p. 177-181 ISSN 0372-7025 REVIEW ARTICLE EBOLA OUTBREAK IN WEST AFRICA Vanda Bostik 1, Miloslav Salavec 2, Radek Sleha 1, Petr Prasil 3, Jan Marek
General Description. Significance
 General Description The Zika virus is a member of the Flavivirus family, and is a small, enveloped virus (easy to kill with a hospital disinfectant). Zika virus is an emerging mosquito-borne virus that
General Description The Zika virus is a member of the Flavivirus family, and is a small, enveloped virus (easy to kill with a hospital disinfectant). Zika virus is an emerging mosquito-borne virus that
Questions and Answers on Ebola
 Updated: August 26, 2014 The 2014 Ebola outbreak is the largest Ebola outbreak in history and the first in West Africa. The current outbreak is affecting four countries in West Africa: Guinea, Liberia,
Updated: August 26, 2014 The 2014 Ebola outbreak is the largest Ebola outbreak in history and the first in West Africa. The current outbreak is affecting four countries in West Africa: Guinea, Liberia,
EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES EMERGING NONE
 EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES NONE EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES New, re-emerging, or drug-resistant infections whose incidence: threatens to increase in humans has increased within the past
EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES NONE EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES New, re-emerging, or drug-resistant infections whose incidence: threatens to increase in humans has increased within the past
BICHAT GUIDELINES* FOR THE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER VIRUSES AND BIOTERRORISM-RELATED HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER VIRUSES
 BICHAT GUIDELINES* FOR THE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER VIRUSES AND BIOTERRORISM-RELATED HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER VIRUSES P Bossi, A Tegnell, A Baka, F Van Loock, J Hendriks, A Werner, H Maidhof,
BICHAT GUIDELINES* FOR THE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER VIRUSES AND BIOTERRORISM-RELATED HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER VIRUSES P Bossi, A Tegnell, A Baka, F Van Loock, J Hendriks, A Werner, H Maidhof,
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers
 Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers WRAIR Tropical Medicine, February 2014 Tim Burgess, MD, MPH CAPT, MC, USN Chief, Infectious Diseases Service, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Acknowledgement: Mark
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers WRAIR Tropical Medicine, February 2014 Tim Burgess, MD, MPH CAPT, MC, USN Chief, Infectious Diseases Service, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Acknowledgement: Mark
PUBLIC HEALTH SIGNIFICANCE SEASONAL INFLUENZA AVIAN INFLUENZA SWINE INFLUENZA
 INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC FEVER JULY 2008
 VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC FEVER JULY 2008 Outline Introduction Epidemiology Clinical Features Differential Diagnosis Laboratory Diagnosis Treatment and Prophylaxis Complications Infection Control Pearls and Pitfalls
VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC FEVER JULY 2008 Outline Introduction Epidemiology Clinical Features Differential Diagnosis Laboratory Diagnosis Treatment and Prophylaxis Complications Infection Control Pearls and Pitfalls
Everything you ever wanted to know about Zika Virus Disease
 Everything you ever wanted to know about Zika Virus Disease (in 14 slides) Jon Temte, MD/PhD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health 28 January 2016 Zika Virus mosquito-borne flavivirus
Everything you ever wanted to know about Zika Virus Disease (in 14 slides) Jon Temte, MD/PhD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health 28 January 2016 Zika Virus mosquito-borne flavivirus
Ebola Virus Disease. What the physician needs to know. (Overview, Transmission and Clinical Features)
 Ebola Virus Disease What the physician needs to know (Overview, Transmission and Clinical Features) Sources: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines (www.cdc.gov) and WHO guidelines
Ebola Virus Disease What the physician needs to know (Overview, Transmission and Clinical Features) Sources: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines (www.cdc.gov) and WHO guidelines
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Zika virus disease
 European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Zika virus disease Stockholm, 19 February 2016 Background information Zika virus is a member of the Flaviviridae family and transmitted by mosquitoes
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Zika virus disease Stockholm, 19 February 2016 Background information Zika virus is a member of the Flaviviridae family and transmitted by mosquitoes
An Outbreak of Hemorrhagic Fever in Africa
 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Case Studies in Applied Epidemiology No. 812-N10 An Outbreak of Hemorrhagic Fever in Africa Student s Guide Learning Objectives After completing this case study,
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Case Studies in Applied Epidemiology No. 812-N10 An Outbreak of Hemorrhagic Fever in Africa Student s Guide Learning Objectives After completing this case study,
EBOLA. Harford County Health Department October 22, 2014
 EBOLA Harford County Health Department October 22, 2014 Zaire ebolvirus The 2014 Ebola outbreak concerns the most deadly of the five Ebola viruses, Zaire ebolvirus, which has killed 79 percent of the people
EBOLA Harford County Health Department October 22, 2014 Zaire ebolvirus The 2014 Ebola outbreak concerns the most deadly of the five Ebola viruses, Zaire ebolvirus, which has killed 79 percent of the people
Emerging Infectious Diseases & Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers
 Emerging Infectious Diseases & Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers Samuel R. Dominguez, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases & Microbiology IDPT 8013: Tropical Medicine & Global Health November
Emerging Infectious Diseases & Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers Samuel R. Dominguez, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases & Microbiology IDPT 8013: Tropical Medicine & Global Health November
Confirmed (Laboratory Tests) Serum positive for IgM anti-hbc or, hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg).
 Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
Dr. Johnmark Opondo MB. ChB. (Nairobi UON), MPH ( Emory) Deputy Medical Health Officer Saskatoon Health Region
 Dr. Johnmark Opondo MB. ChB. (Nairobi UON), MPH ( Emory) Deputy Medical Health Officer Saskatoon Health Region OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the basic science behind EVD 2. To review the issues behind the
Dr. Johnmark Opondo MB. ChB. (Nairobi UON), MPH ( Emory) Deputy Medical Health Officer Saskatoon Health Region OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the basic science behind EVD 2. To review the issues behind the
Ebola: 22,000 cases, 8700 deaths. Enterovirus D68: 1100 cases, 14 deaths. Chikungunya virus: almost a million cases in the Western Hemisphere
 Sally Williams MD Ebola: 22,000 cases, 8700 deaths Enterovirus D68: 1100 cases, 14 deaths Chikungunya virus: almost a million cases in the Western Hemisphere } A nonpolio enterovirus identified in 1962,
Sally Williams MD Ebola: 22,000 cases, 8700 deaths Enterovirus D68: 1100 cases, 14 deaths Chikungunya virus: almost a million cases in the Western Hemisphere } A nonpolio enterovirus identified in 1962,
An Introduction to Dengue, Zika and Chikungunya Viruses
 An Introduction to Dengue, Zika and Chikungunya Viruses Natalie Marzec, MD, MPH Zoonoses Epidemiologist 2017 Global Health and Disasters Course Objectives Arbovirus Overview Public Health Activities Clinical
An Introduction to Dengue, Zika and Chikungunya Viruses Natalie Marzec, MD, MPH Zoonoses Epidemiologist 2017 Global Health and Disasters Course Objectives Arbovirus Overview Public Health Activities Clinical
Following the bite of a mosquito infected with CHIKV, most individuals will
 3. CLINICAL 3A. Clinical Presentation of Acute Disease Following the bite of a mosquito infected with CHIKV, most individuals will present with symptomatic disease after an incubation period of 3-7 days
3. CLINICAL 3A. Clinical Presentation of Acute Disease Following the bite of a mosquito infected with CHIKV, most individuals will present with symptomatic disease after an incubation period of 3-7 days
Ebola Virus Disease. Global Epidemiology and Surveillance in Hong Kong. as of 13 August 2014
 Ebola Virus Disease Global Epidemiology and Surveillance in Hong Kong as of 13 August 2014 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Ebola virus disease (EVD), (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe,
Ebola Virus Disease Global Epidemiology and Surveillance in Hong Kong as of 13 August 2014 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Ebola virus disease (EVD), (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe,
WHAT WILL WE LEARN FROM ESEI RESEARCH?
 WHAT WILL WE LEARN FROM ESEI RESEARCH? Mark Woolhouse University of Edinburgh WHAT WILL WE LEARN FROM ESEI RESEARCH? Dealing with diverse disease ecologies Diversity and generalisation Endemic diseases
WHAT WILL WE LEARN FROM ESEI RESEARCH? Mark Woolhouse University of Edinburgh WHAT WILL WE LEARN FROM ESEI RESEARCH? Dealing with diverse disease ecologies Diversity and generalisation Endemic diseases
Grace Kubin, Ph.D. 10 th Annual Alabama Laboratory Meeting 2015
 Grace Kubin, Ph.D. 10 th Annual Alabama Laboratory Meeting 2015 Viral hemorrhagic fever Member of Filoviridae family Ebolavirus genera: Zaire 50-90% fatality rate Sudan 50% fatality rate Bundibugyo 30%
Grace Kubin, Ph.D. 10 th Annual Alabama Laboratory Meeting 2015 Viral hemorrhagic fever Member of Filoviridae family Ebolavirus genera: Zaire 50-90% fatality rate Sudan 50% fatality rate Bundibugyo 30%
Palliative Care in Ebola
 Palliative Care in Ebola CHALLENGES IN DELIVERY AND EXPERIENCES FROM THE CURRENT OUTBREAK Background Ebola: filovirus from the family filoviridae Named after the Ebola River in DRC (then Zaire) where first
Palliative Care in Ebola CHALLENGES IN DELIVERY AND EXPERIENCES FROM THE CURRENT OUTBREAK Background Ebola: filovirus from the family filoviridae Named after the Ebola River in DRC (then Zaire) where first
CDC Ebola Response Team
 Ebola Preparations from the Healthcare Epidemiologists Perspective August 25th, 2014 CDC Ebola Response Team Barbara Knust, DVM, MPH Epidemiology Team Lead Tim Uyeki, MD Clinical Team Lead Nancy Cornish,
Ebola Preparations from the Healthcare Epidemiologists Perspective August 25th, 2014 CDC Ebola Response Team Barbara Knust, DVM, MPH Epidemiology Team Lead Tim Uyeki, MD Clinical Team Lead Nancy Cornish,
Public Health Image Library. CDC/ Cynthia Goldsmith. Image #
 Zika Virus Fredrick M. Abrahamian, D.O., FACEP, FIDSA Clinical Professor of Medicine UCLA School of Medicine Director of Education Department of Emergency Medicine Olive View-UCLA Medical Center Sylmar,
Zika Virus Fredrick M. Abrahamian, D.O., FACEP, FIDSA Clinical Professor of Medicine UCLA School of Medicine Director of Education Department of Emergency Medicine Olive View-UCLA Medical Center Sylmar,
Virology and clinical aspects of EVD. ID and PH Forum 13 Aug 2014
 Virology and clinical aspects of EVD ID and PH Forum 13 Aug 2014 Virology Filoviruses First recognized in 1967 Non-segmented, negative-sense, singlestranded RNA viruses 5 different species (the Zaire,
Virology and clinical aspects of EVD ID and PH Forum 13 Aug 2014 Virology Filoviruses First recognized in 1967 Non-segmented, negative-sense, singlestranded RNA viruses 5 different species (the Zaire,
KILLER BITES: Mosquito-Borne Viruses Jon Mark Hirshon, MD, MPH, PhD
 KILLER BITES: Mosquito-Borne Viruses Jon Mark Hirshon, MD, MPH, PhD Professor, Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of Medicine Disclosures Conflicts of Interest: Pfizer consultant
KILLER BITES: Mosquito-Borne Viruses Jon Mark Hirshon, MD, MPH, PhD Professor, Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of Medicine Disclosures Conflicts of Interest: Pfizer consultant
Hepatitis A and Hepatitis E
 Hepatitis A and Hepatitis E Luis S. Marsano, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition University of Louisville and Louisville VAMC 2011 Viruses that cause Hepatitis
Hepatitis A and Hepatitis E Luis S. Marsano, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition University of Louisville and Louisville VAMC 2011 Viruses that cause Hepatitis
EBOLA & OTHER VIRUSES IN THE NEWS EBOLA VIRUS, CHIKUNGUNYA VIRUS, & ENTEROVIRUS D68
 EBOLA & OTHER VIRUSES IN THE NEWS EBOLA VIRUS, CHIKUNGUNYA VIRUS, & ENTEROVIRUS D68 PRESENTERS Patricia Quinlisk, MD, MPH, Medical Director /State Epidemiologist Samir Koirala, MBBS, MSc Epidemic Intelligence
EBOLA & OTHER VIRUSES IN THE NEWS EBOLA VIRUS, CHIKUNGUNYA VIRUS, & ENTEROVIRUS D68 PRESENTERS Patricia Quinlisk, MD, MPH, Medical Director /State Epidemiologist Samir Koirala, MBBS, MSc Epidemic Intelligence
TM6 Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHF), Oncocerciasis and Leprosy. Viral Hemorrhagic fevers (VHF), Onchocerciasis and Leprosy
 TM6 Viral Hemorrhagic fevers (VHF), Onchocerciasis and Leprosy General Objective To familiarize participants with the epidemiological and clinical characteristics of viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHF), Oncocerciasis
TM6 Viral Hemorrhagic fevers (VHF), Onchocerciasis and Leprosy General Objective To familiarize participants with the epidemiological and clinical characteristics of viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHF), Oncocerciasis
Zika Virus Basics. Flaviviridae Flavivirus Disease Vector Vaccine *Dengue (serotypes 1-4) Zika Virus Basics. Zika Virus Transmission Cycle
 Zika: Infection,, and Protection Roxanne P. Liles, Ph.D., MLS(ASCP) CM Assistant Professor of Biology Louisiana State University at Alexandria 318-473-6518 rliles@lsua.edu Zika Virus Basics Virion: Enveloped
Zika: Infection,, and Protection Roxanne P. Liles, Ph.D., MLS(ASCP) CM Assistant Professor of Biology Louisiana State University at Alexandria 318-473-6518 rliles@lsua.edu Zika Virus Basics Virion: Enveloped
Provider Health & Safety Alert Ebola Virus Disease September 30, 2014
 Provider Health & Safety Alert Ebola Virus Disease September 30, 2014 With the announcement of the first confirmed case of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) in Dallas Texas, there could be interactions with individuals
Provider Health & Safety Alert Ebola Virus Disease September 30, 2014 With the announcement of the first confirmed case of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) in Dallas Texas, there could be interactions with individuals
Ebola Virus Disease(EVD)
 Yemeni International Congress of Infectious Diseases 16-18 December 2014 University of Science & Technology Hospital Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences Ebola Virus Disease(EVD) Presented by: Dr Ahmed
Yemeni International Congress of Infectious Diseases 16-18 December 2014 University of Science & Technology Hospital Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences Ebola Virus Disease(EVD) Presented by: Dr Ahmed
Disease Transmission Methods
 Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Endemic: rhinovirus, Epidemic: pertussis several years ago Pandemic: H1N1 in was a pandemic just not as severe as originally feared
 1 2 3 Endemic: rhinovirus, Epidemic: pertussis several years ago Pandemic: H1N1 in 2009 10 was a pandemic just not as severe as originally feared 4 5 Endemic, Epidemic 6 Endemic, Epidemic 7 H5N1 H7N9 8
1 2 3 Endemic: rhinovirus, Epidemic: pertussis several years ago Pandemic: H1N1 in 2009 10 was a pandemic just not as severe as originally feared 4 5 Endemic, Epidemic 6 Endemic, Epidemic 7 H5N1 H7N9 8
Zika Virus. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Zika Virus Ingrid Rabe Medical Epidemiologist Arboviral Diseases Branch Centers for Disease Control and Prevention February 1, 2016 Zika Virus Single stranded
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Zika Virus Ingrid Rabe Medical Epidemiologist Arboviral Diseases Branch Centers for Disease Control and Prevention February 1, 2016 Zika Virus Single stranded
Epidemiology and entomology of the Zika virus outbreak
 Epidemiology and entomology of the Zika virus outbreak M A T T H E W B A Y L I S I N S T I T U T E O F I N F E C T I O N A N D G L O B A L H E A L T H U N I V E R S I T Y O F L I V E R P O O L Zika in
Epidemiology and entomology of the Zika virus outbreak M A T T H E W B A Y L I S I N S T I T U T E O F I N F E C T I O N A N D G L O B A L H E A L T H U N I V E R S I T Y O F L I V E R P O O L Zika in
OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES. Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs
 OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs Viral diseases Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C STI HIV Other viral diseases
OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs Viral diseases Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C STI HIV Other viral diseases
AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES)
 AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES) HOUSEKEEPING ITEMS For educational and quality improvement purposes, this ECHO session will be recorded Project ECHO collects participation data
AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES) HOUSEKEEPING ITEMS For educational and quality improvement purposes, this ECHO session will be recorded Project ECHO collects participation data
Ebola Virus Disease: the Facts, Response & the Way Forward. Dr. Abraham Idokoko Ebola Emergency Operations Centre (EEOC), Lagos.
 Ebola Virus Disease: the Facts, Response & the Way Forward. Dr. Abraham Idokoko Ebola Emergency Operations Centre (EEOC), Lagos. 2 Yearly trend of Emergence of New Infectious Diseases Globally, an average
Ebola Virus Disease: the Facts, Response & the Way Forward. Dr. Abraham Idokoko Ebola Emergency Operations Centre (EEOC), Lagos. 2 Yearly trend of Emergence of New Infectious Diseases Globally, an average
EBOLA VIRUS Guidance for Michigan local health departments and healthcare providers
 EBOLA VIRUS Guidance for Michigan local health departments and healthcare providers VERSION 2 Interim Guidelines for Evaluation of US Patients Suspected of Having Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) This is a rapidly
EBOLA VIRUS Guidance for Michigan local health departments and healthcare providers VERSION 2 Interim Guidelines for Evaluation of US Patients Suspected of Having Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) This is a rapidly
EBOLA FACTS. During this outbreak, most of the disease has spread through human-to-human transmission.
 EBOLA FACTS Ebola virus disease (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe and often fatal illness, with a fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most dreaded diseases. However,
EBOLA FACTS Ebola virus disease (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe and often fatal illness, with a fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most dreaded diseases. However,
