LECTURE OUTLINE. The genus Vibrio Vibrio cholerae Epidemiology of cholera Pathogenesis. Vaccine development Ecology of V. cholerae
|
|
|
- Crystal Shields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LECTURE OUTLINE The genus Vibrio Vibrio cholerae Epidemiology of cholera Pathogenesis Disease Virulence factors Vaccine development Ecology of V. cholerae Environmental survival and persistence Phase variation Biofilm formation
2 The genus Vibrio Vibrios are aquatic organisms They occur in both marine and fresh water habitats Have relatively simple growth factor requirements grow in synthetic media with glucose as a carbon and energy source require salt or sea-water based medium for optimal growth tolerate alkaline media and sensitive to acid Growth temperature varies 10-37C
3 Vary in metabolic versatility The genus Vibrio Some species can grow on more than 150 different organic compounds as a carbon and energy source Capable of both respiratory and fermentative metabolism Some species can grow very fast (double in 10 minutes) Gram negative straight or curved rods Motile In liquid media by means of single polar flagellum On solid media they may synthesize lateral flagella Free living or in association with aquatic animals Live in mutualistic association with fish and other marine life Pathogenic to fish, vertebrates and invertebrates
4 Clinically important Vibrio species V. vulnificus and V. parahaemolyticus Halophiles (require salt water environment) Normal residents of coastal waters Temperature and salinity of water influences their abundance (cell number increases during the summer) In the US they are the most common vibrios associated with seafood borne illness Oyster beds in Texas closed in the summer of 1998 (416 people in 13 states fell ill after eating oysters harvested from this location) In the summer of 1997, V. paraheamlyticus caused large outbreak in the Pacific NorthWest (209 cases, 1 death)
5 Clinically Significant Vibrio species V. parahemolyticus Diarrhea Consumption of contaminated sea food Infective dose is one million cells Most people develop symptoms (12-24 hours) will recover in 2-3 days Can cause large outbreaks Common pathogen in Asia (Taiwan, Japan) Strains endemic to Asia introduced to US by ballast water discharged from ships which traveled to Asia Is microbial traffic important in emergence of pathogens?
6 Clinically Significant Vibrio species V. vulnificus Diarrhea/Sepsis (microorganism in blood stream) Consumption of contaminated sea food Exposure to brackish or salt water containing the pathogen if the skin is broken Infective dose is 100 cells Healthy people with intact immune system develop gastroenteritis People with liver disease, cancer,aids, diabetes are at high risk Symptoms develop from 7 hours to several days after exposure Does not cause large outbreaks but cause severe and often fatal infections
7 Vibrio cholerae Isolated in pure culture by Robert Koch in 1883 Gram negative, facultative anaerobe Curved rod shaped Motile, single polar flagellum Over 200 serotype is identified based on LPS O-antige Disease cholera is caused by O1 and O139 Inhabitants of brackish and estuarine waters Can grow in fresh and salt water Facultative human pathogen M. Waldor
8 DEFINITIONS FROM (Bacterial Pathogenesis of Salyers and Whitt) Epidemiology study of incidence, transmission and prevention of disease Endemic--disease continually present at low levels in the community Epidemic--disease that appears sporadically and affects many individuals in a community Pandemic epidemic involving different countries
9 Epidemiology of Cholera Cholera is endemic to India, Bangladesh, regions of South America, Africa, Australia and Gulf coast of the US There has been seven pandemics since 1817 First six started in Indian subcontinent (Ganges delta) and caused by Classical strains The last one started in Indonesia and caused by El Tor strains Since 1992, a new serotype has emerged, O139 which may represent the eight pandemic strain
10 Epidemiology of Cholera High degree of clustering of cases by location and season Highest rate of infection in children 1-5 years of age Protection against the disease is improved by sanitation and preexisting immunity Cholerae has been categorized as an emerging and re-emerging infections
11 WHO REPORT The seventh pandemic is still ongoing and the number of affected countries continues to increase especially in Africa. We do not know whether epidemic strain V. cholerae O139 Bengal will continue to be restricted to its present geographical area, or spread further. The threat of a new pandemic caused by V. cholerae O139 Bengal cannot be ruled out. An increasing number of geographic areas are becoming endemic for cholera reflecting a failure of effective epidemic control. Case fatality rates in Africa remain unacceptably high.
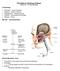
12 Water-borne illness Disease CHOLERA Transmitted by ingestion of food or water contaminated with V. cholerae The Infectious Dose- ID 50 varies depending on the ph of the stomach. In healthy volunteers bacteria produces infection, after neutralization of stomach acid 10 4 bacteria can cause disease The small intestine is the primary site of infection Clinical symptoms are voluminous diarrhea and dehydration
13 Infection Cycle of Vibrio cholerae Reidl and Klose, FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 26:125-
14 Motility and chemotaxis Virulence Factors Non-motile mutants are reduced for virulence Little is known about chemotaxis and signals that lead to colonization of intestine Adherence Long filamentous pili termed the toxin-coregulated pilus (TCP) that form bundles on bacterial surface is essential for colonization Mutants lacking TCP are avirulent in human volunteers and in animal models Genes necessary for production of TCP are organized in an operon that contains 15 genes which is part of Vibrio pathogenicity island (VPI) Major pilin subunit Assembly Secretion
15 Cholera toxin(ctx) Virulence Factors The most critical virulence factor, all the disease symptoms are caused by the action of cholerae toxin Structure It is composed of two polypeptides, A subunit and B subunit The ratio of B:A is 5:1 Mode of Action Catalyzes an ADP-ribosylation reaction CTX binds to surface sugar on the intestinal cells via B subunits After binding A subunit which has ADP-ribosylating enzymatic activity is transported into host cell Inside the cell, the A subunit ADP ribosylates (attaches an ADP-ribose) a G protein (largest family of mammalian cell-surface receptors, they mediate cellular response to signaling molecules)
16 Virulence Factors G protein regulates activity of adenylate cyclase ADP ribosylation leads to increased adenylate cyclase activity Increased camp levels Increased camp within intestinal epitelial cells leads to increased Cl - secretion Osmotic imbalance causes water flow into the intestinal lumen---diarrhea CTX genetic element Cholera toxin genes are encoded on a lysogenic filamentous bacteriophage The phage can infect strains of V. cholerae missing toxin genes The receptor for the phage is TCP Transfer can occur in the gastrointestinal tract Transfer can occur in the aquatic environment Is evolution/generation of pathogens important for re-emergence of pathogens?
17 Vaccine Development A single clinical exposure to V. cholerae O1 confers protective immunity Live attenuated strain of V. cholerae as a vaccine Ctx deletion strains still caused mild diarrhea TCP mutants failed to induce significant protection Vaccine trials have been unsuccessful in clinical trials Rehydration therapy remains essential in cholera treatment
18 Environmental Factors and Survival of Vibrio cholerae Physical and Chemical Properties of Aquatic Habitat Temperature ph Salinity Nutrients Climate Rainfall Sunlight Temperature Vibrio cholerae Biological Properties of Aquatic Habitat Phytoplankton bloom Zooplankton bloom
19 Environmental Survival Entry into viable but non culturable (VBNC) state Phase variation (turning on/off selected genes via genetic re-arrangements) Biofilm formation
20 What Is a Biofilm? Biofilms are surface attached microbial communites formed when bacteria adhere to surfaces in aqueous environments and begin to excrete a slimy, glue-like substance that can anchor them to all kinds of material such as metals, plastics, soil particles, medical implant materials, and tissue. A biofilm can be formed by a single bacterial species, but more often biofilms consist of many species of bacteria, as well as fungi, algae, protozoa.
21 Advantageous of Biofilm Growth Mode Surfaces adsorb and concentrate nutrients Attached bacteria can degrade biotic surfaces (i.e chitin) In mixed species biofilms bacteria engage in metabolic interactions with other members Protection from toxic compounds
Cholera. By Cate Turner. Name Common Name: Cholera Etiologic agent: V ibrio cholerae (1)
 Cholera By Cate Turner Name Common Name: Cholera Etiologic agent: V ibrio cholerae (1) Transmission Vibrio cholerae i s transmitted by the fecal-oral route by infection of epithelial cells in the small
Cholera By Cate Turner Name Common Name: Cholera Etiologic agent: V ibrio cholerae (1) Transmission Vibrio cholerae i s transmitted by the fecal-oral route by infection of epithelial cells in the small
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
 Vibrio parahaemolyticus Frequently Asked Questions What is Vibrio parahaemolyticus? What type of illness is caused by V. parahaemolyticus? How does infection with V. parahaemolyticus occur? How common
Vibrio parahaemolyticus Frequently Asked Questions What is Vibrio parahaemolyticus? What type of illness is caused by V. parahaemolyticus? How does infection with V. parahaemolyticus occur? How common
General Characteristics of Vibrio, Aeromonas and Plesiomonas
 THE GENUS VIBRIO, CAMPYLOBACTER AND ASSOCIATED BACTERIA (AEROMONAS, HELICOBACTER, PLESIOMONAS) General Characteristics of Vibrio, Aeromonas and Plesiomonas Gram-negative Facultative anaerobes Fermentative
THE GENUS VIBRIO, CAMPYLOBACTER AND ASSOCIATED BACTERIA (AEROMONAS, HELICOBACTER, PLESIOMONAS) General Characteristics of Vibrio, Aeromonas and Plesiomonas Gram-negative Facultative anaerobes Fermentative
Bacteria Affect Seafood Quality and Safety (part 3)
 Bacteria Affect Seafood Quality and Safety (part 3) Brian Himelbloom, PhD University of Alaska Fairbanks School of Fisheries and Ocean Sciences Kodiak Seafood and Marine Science Center Kodiak, AK 99615
Bacteria Affect Seafood Quality and Safety (part 3) Brian Himelbloom, PhD University of Alaska Fairbanks School of Fisheries and Ocean Sciences Kodiak Seafood and Marine Science Center Kodiak, AK 99615
PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS
 PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS Some microorganisms are : 1- Harmless microorganism, as normal flora 2- Harmfull microorganism, as pathogenic. A pathogenic microorganism is defined as one that causes or
PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS Some microorganisms are : 1- Harmless microorganism, as normal flora 2- Harmfull microorganism, as pathogenic. A pathogenic microorganism is defined as one that causes or
Vibrio cholerae Serogroup O1
 U.S. Food & Drug Administration Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Handbook Vibrio cholerae Serogroup O1 1. Name of the Organism: Vibrio cholerae
U.S. Food & Drug Administration Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Handbook Vibrio cholerae Serogroup O1 1. Name of the Organism: Vibrio cholerae
2013 Disease Detectives
 2013 Disease Detectives Since the catastrophic earthquake that hit Haiti in January of 2010, there have been an alarming number of cases of Cholera, spread by the Vibrio cholera bacterium, reported within
2013 Disease Detectives Since the catastrophic earthquake that hit Haiti in January of 2010, there have been an alarming number of cases of Cholera, spread by the Vibrio cholera bacterium, reported within
CLIMATE CHANGE, HARMFUL ALGAL BLOOMS AND HEALTH RISKS IN ONE HEALTH CONTEXT
 CLIMATE CHANGE, HARMFUL ALGAL BLOOMS AND HEALTH RISKS IN ONE HEALTH CONTEXT Iddya Karunasagar Nitte University Mangalore-575018, India Iddya.Karunasagar@nitte.edu.in Climate change and human health During
CLIMATE CHANGE, HARMFUL ALGAL BLOOMS AND HEALTH RISKS IN ONE HEALTH CONTEXT Iddya Karunasagar Nitte University Mangalore-575018, India Iddya.Karunasagar@nitte.edu.in Climate change and human health During
Cholera Clinical Guidelines. OAHPP Rounds January 11, 2011 Vanessa G. Allen MD FRCPC Medical Microbiologist
 Cholera Clinical Guidelines OAHPP Rounds January 11, 2011 Vanessa G. Allen MD FRCPC Medical Microbiologist Overview Cholera clinical guidelines Development and review process Content Reference for diagnosis,
Cholera Clinical Guidelines OAHPP Rounds January 11, 2011 Vanessa G. Allen MD FRCPC Medical Microbiologist Overview Cholera clinical guidelines Development and review process Content Reference for diagnosis,
Communicable diseases. Gastrointestinal track infection. Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology
 Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
True Pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae: Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia Salmonella
 Lec. 6 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin True Pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae: Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia Salmonella General Characteristics of Salmonella جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Coliform bacilli
Lec. 6 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin True Pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae: Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia Salmonella General Characteristics of Salmonella جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Coliform bacilli
What is Cholera? V. cholerae. Profile of vibrio cholerae. Gram-negative Highly motile; polar flagellum Brackish rivers, coastal waters
 What is Cholera? Intestinal infection Severe diarrhea Caused by Cholera Toxin of bacterium, Vibrio cholera Grows in salt and fresh water Can survive and multiply in brackish water by infecting copepods
What is Cholera? Intestinal infection Severe diarrhea Caused by Cholera Toxin of bacterium, Vibrio cholera Grows in salt and fresh water Can survive and multiply in brackish water by infecting copepods
Vibrios, short curved rods
 Vibrios, short curved rods We are accustomed to characterizing bacteria as cocci (spheres), bacilli (rod-shaped), or spirillum (corkscrew shaped). However, we have noted spirochetes as curved with special
Vibrios, short curved rods We are accustomed to characterizing bacteria as cocci (spheres), bacilli (rod-shaped), or spirillum (corkscrew shaped). However, we have noted spirochetes as curved with special
Disease Report: Cholera Cassidy Smith May 6, 2014
 Disease Report: Cholera Cassidy Smith May 6, 2014 Disease Cholera is an acute diarrheal infection caused by ingestion of food or water contaminated with the bacterium Vibrio cholerae (01 and 0139). It
Disease Report: Cholera Cassidy Smith May 6, 2014 Disease Cholera is an acute diarrheal infection caused by ingestion of food or water contaminated with the bacterium Vibrio cholerae (01 and 0139). It
Vibrio parahaemolyticus in the United States,
 Vibrio parahaemolyticus in the United States, 2007-2012 Anna Newton, MPH Surveillance Epidemiologist ISSC webinar January 8, 2013 National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases Division
Vibrio parahaemolyticus in the United States, 2007-2012 Anna Newton, MPH Surveillance Epidemiologist ISSC webinar January 8, 2013 National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases Division
PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether each of the following statements are true or false.
 MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
Foundations in Microbiology
 Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Vibrio Cholerae (non-o1, non-o139)
 August 2011 Vibrio Cholerae (non-o1, non-o139) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011
August 2011 Vibrio Cholerae (non-o1, non-o139) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011
Gram-Negative rods Introduction to
 Lec 5 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Gram-Negative rods Introduction to Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics: جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Small gram-negative rods (2-5 by 0.5 microns) Most motile with peritrichous
Lec 5 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Gram-Negative rods Introduction to Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics: جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Small gram-negative rods (2-5 by 0.5 microns) Most motile with peritrichous
BIOTECHNOLOGY Vol. IX - Molecular Tools for Improving Seafood Safety - Karunasagar, Iddya MOLECULAR TOOLS FOR IMPROVING SEAFOOD SAFETY
 MOLECULAR TOOLS FOR IMPROVING SEAFOOD SAFETY Karunasagar, Iddya University of Agricultural Sciences, College of Fisheries, Mangalore, India Keywords: Seafood, aquaculture, pathogens, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio
MOLECULAR TOOLS FOR IMPROVING SEAFOOD SAFETY Karunasagar, Iddya University of Agricultural Sciences, College of Fisheries, Mangalore, India Keywords: Seafood, aquaculture, pathogens, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio
Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus reveals distinct differences in strains from the Pacific Northwest of the U.S.
 Western Washington University Western CEDAR Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference 2014 Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference (Seattle) May 2nd, 8:30 AM - 10:00 AM Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Western Washington University Western CEDAR Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference 2014 Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference (Seattle) May 2nd, 8:30 AM - 10:00 AM Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Al-Mustansiriyah University
 Al-Mustansiriyah University Monday 27/2/2017 College of Medicine Small Group Learning Committee/ Department of Microbiology Year 3/ Semester 2 / Case#2 An 18-year-old lady living in a rural area outside
Al-Mustansiriyah University Monday 27/2/2017 College of Medicine Small Group Learning Committee/ Department of Microbiology Year 3/ Semester 2 / Case#2 An 18-year-old lady living in a rural area outside
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS
 BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
Cholera Table of Contents
 Subsection: Cholera Page 1 of 11 Cholera Table of Contents Cholera Fact Sheet Cholera and Other Vibrio Illness Surveillance Report (CDC 52.79) Subsection: Cholera Page 2 of 11 Cholera Overview (1,2) Although
Subsection: Cholera Page 1 of 11 Cholera Table of Contents Cholera Fact Sheet Cholera and Other Vibrio Illness Surveillance Report (CDC 52.79) Subsection: Cholera Page 2 of 11 Cholera Overview (1,2) Although
Bacterial Emerging Risks to Seafood Safety WORKSHOP "SEAFOOD AND EMERGING FOOD SAFETY ISSUES"
 Bacterial Emerging Risks to Seafood Safety WORKSHOP "SEAFOOD AND EMERGING FOOD SAFETY ISSUES" Populations dynamics and diseases Two Models: Salmonella Vibrio V. cholerae V. parahaemolyticus Foodborne pathogen
Bacterial Emerging Risks to Seafood Safety WORKSHOP "SEAFOOD AND EMERGING FOOD SAFETY ISSUES" Populations dynamics and diseases Two Models: Salmonella Vibrio V. cholerae V. parahaemolyticus Foodborne pathogen
LECTURE topics: 1. Immunology. 2. Emerging Pathogens
 LECTURE 23 2 topics: 1. Immunology 2. Emerging Pathogens Benefits of the Normal Flora: 1. Protect us from colonization by other bacteria and fungi (competitive exclusion). 2. Many synthesize vitamins,
LECTURE 23 2 topics: 1. Immunology 2. Emerging Pathogens Benefits of the Normal Flora: 1. Protect us from colonization by other bacteria and fungi (competitive exclusion). 2. Many synthesize vitamins,
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
Principles of Disease and Epidemiology
 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Symbiosis living together An association between two or more species and one species is typically dependent on the other Mutualism - Commensalism - Parasitism - Infection
Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Symbiosis living together An association between two or more species and one species is typically dependent on the other Mutualism - Commensalism - Parasitism - Infection
Shigella and salmonella
 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
Microbial Pathogenesis. How do bacteria cause disease? How do E.coli become pathogens? Commensal flora
 Microbial Pathogenesis How do E.coli become pathogens? Commensal flora Acquire genes that cause disease How do bacteria cause disease? 1- Direct toxic effects proteases flesh eating bacteria 2- Activation
Microbial Pathogenesis How do E.coli become pathogens? Commensal flora Acquire genes that cause disease How do bacteria cause disease? 1- Direct toxic effects proteases flesh eating bacteria 2- Activation
Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease
 Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease Normal Flora Virulence and Pathogenicity Toxicity vs. Invasiveness WE ARE NOT ALONE! We are outnumbered. The average human contains about 10 trillion cells. On
Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease Normal Flora Virulence and Pathogenicity Toxicity vs. Invasiveness WE ARE NOT ALONE! We are outnumbered. The average human contains about 10 trillion cells. On
Microbiology - Problem Drill 21: Microbial Diseases of the Digestive System
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 21: Microbial Diseases of the Digestive System No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following organs is not part of the gastrointestinal tract (GI)? (A) Esophagus (B) Small intestine
Microbiology - Problem Drill 21: Microbial Diseases of the Digestive System No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following organs is not part of the gastrointestinal tract (GI)? (A) Esophagus (B) Small intestine
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
Chapter 13. Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology
 Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
Cholera. Communicable Disease Management Protocol. Case Definition. Reporting Requirements. Clinical Presentation/Natural History.
 Cholera Manitoba Health Public Health Communicable Disease Control Unit Case Definition Confirmed Case: Isolation of cholera-toxinproducing Vibrio cholerae serotype 01 or serotype 0139 from a person with
Cholera Manitoba Health Public Health Communicable Disease Control Unit Case Definition Confirmed Case: Isolation of cholera-toxinproducing Vibrio cholerae serotype 01 or serotype 0139 from a person with
Marine vibrio s summary of food safety concerns regarding trade of bivalve molluscs from USA to EU
 Marine vibrio s summary of food safety concerns regarding trade of bivalve molluscs from USA to EU 1. Objective. This paper is tabled for discussion at the electronic working group on vibrios established
Marine vibrio s summary of food safety concerns regarding trade of bivalve molluscs from USA to EU 1. Objective. This paper is tabled for discussion at the electronic working group on vibrios established
Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Chapter 14. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Chapter 14 Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Introduction Pathology, Infection and Disease Terms: Pathogen: disease causing organism Pathology: scientific
Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Chapter 14 Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Introduction Pathology, Infection and Disease Terms: Pathogen: disease causing organism Pathology: scientific
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION
 M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 14 Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 14 Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville
Dinophysis acuminata in Delaware s Inland Bays and coastal waters
 Dinophysis acuminata in Delaware s Inland Bays and coastal waters 2001-2015 Ed Whereat, Program Coordinator, University of Delaware Citizen Monitoring Program Delaware Sea Grant Marine Advisory Service
Dinophysis acuminata in Delaware s Inland Bays and coastal waters 2001-2015 Ed Whereat, Program Coordinator, University of Delaware Citizen Monitoring Program Delaware Sea Grant Marine Advisory Service
Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases
 Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases HOST DISEASE TRIAD PATHOGEN ENVIRONMENT OTHER MICROBES Microbial Interactions KOCH'S POSTULATES Four criteria that were established
Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases HOST DISEASE TRIAD PATHOGEN ENVIRONMENT OTHER MICROBES Microbial Interactions KOCH'S POSTULATES Four criteria that were established
Objective 3 Viruses & Bacteria genetic material capsule Pili DNA
 Objective 3 Viruses & Bacteria 1. Compare the structure and functions of viruses to cells and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases and conditions such as acquired immune deficiency syndrome,
Objective 3 Viruses & Bacteria 1. Compare the structure and functions of viruses to cells and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases and conditions such as acquired immune deficiency syndrome,
Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease
 Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease Normal Flora Virulence and Pathogenicity Toxicity vs. Invasiveness WE ARE NOT ALONE! We are outnumbered. The average human contains about 10 trillion cells. On
Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease Normal Flora Virulence and Pathogenicity Toxicity vs. Invasiveness WE ARE NOT ALONE! We are outnumbered. The average human contains about 10 trillion cells. On
LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK. How can we prove infection causes disease?
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Correlation a connection between two factors. Causation when a change in one factor results in a change in another. Vector an organism that transmits a pathogen from reservoir to host.
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Correlation a connection between two factors. Causation when a change in one factor results in a change in another. Vector an organism that transmits a pathogen from reservoir to host.
Lecture 2: Virology. I. Background
 Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Seminar 4. Bugs on the Move. Carleton Learning in Retirement What s Bugging You? Daniel Burnside
 Seminar 4 Bugs on the Move Carleton Learning in Retirement What s Bugging You? Daniel Burnside Epidemiology Epidemiology and Public Health Epidemiology is the study of the distribution and cause of disease
Seminar 4 Bugs on the Move Carleton Learning in Retirement What s Bugging You? Daniel Burnside Epidemiology Epidemiology and Public Health Epidemiology is the study of the distribution and cause of disease
Epidemiology, Genetics, and Ecology of Toxigenic Vibrio cholerae
 MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Dec. 1998, p. 1301 1314 Vol. 62, No. 4 1092-2172/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Epidemiology, Genetics,
MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Dec. 1998, p. 1301 1314 Vol. 62, No. 4 1092-2172/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Epidemiology, Genetics,
AOHS Global Health. Unit 1, Lesson 3. Communicable Disease
 AOHS Global Health Unit 1, Lesson 3 Communicable Disease Copyright 2012 2016 NAF. All rights reserved. A communicable disease is passed from one infected person to another The range of communicable diseases
AOHS Global Health Unit 1, Lesson 3 Communicable Disease Copyright 2012 2016 NAF. All rights reserved. A communicable disease is passed from one infected person to another The range of communicable diseases
Massachusetts 2014 Vibrio parahaemolyticus Presentation
 Massachusetts 2014 Vibrio parahaemolyticus Presentation Johanna Vostok, MPH Massachusetts Department of Public Health Scott Troppy, MPH, PMP Massachusetts Department of Public Health What is Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Massachusetts 2014 Vibrio parahaemolyticus Presentation Johanna Vostok, MPH Massachusetts Department of Public Health Scott Troppy, MPH, PMP Massachusetts Department of Public Health What is Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Microbiology With Diseases by Taxonomy
 Microbiology With Diseases by Taxonomy Second Edition PowerPoint Lecture Slides 14 Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology SARS: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome 2003 Chapter opener 14 Chapter
Microbiology With Diseases by Taxonomy Second Edition PowerPoint Lecture Slides 14 Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology SARS: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome 2003 Chapter opener 14 Chapter
Vibrio Infections in Louisiana: Twenty-Five Years of Surveillance
 Vibrio Infections in Louisiana: Twenty-Five of Surveillance 198-25 Annu Thomas, MPH; Susanne Straif-Bourgeois, PhD, MPH; Theresa M. Sokol, MPH; and Raoult C. Ratard, MD, MPH&TM A total of 1,7 Vibrio infections
Vibrio Infections in Louisiana: Twenty-Five of Surveillance 198-25 Annu Thomas, MPH; Susanne Straif-Bourgeois, PhD, MPH; Theresa M. Sokol, MPH; and Raoult C. Ratard, MD, MPH&TM A total of 1,7 Vibrio infections
What location in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract has tight, or impermeable, junctions between the epithelial cells?
 CASE 32 A 17-year-old boy presents to his primary care physician with complaints of diarrhea for the last 2 days. The patient states that he just returned to the United States after visiting relatives
CASE 32 A 17-year-old boy presents to his primary care physician with complaints of diarrhea for the last 2 days. The patient states that he just returned to the United States after visiting relatives
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7. Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods. Bacillus
 Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10. Mycobacterium. Actinomycetes. Nocardia
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
Cholera. Cholera prevention and control. Mode of Transmission. Ganges River Delta. Public health significance
 * This presentation is prepared by the author in one s personal capacity for the purpose of academic exchange and does not represent the views of his/her organisations on the topic discussed. Cholera prevention
* This presentation is prepared by the author in one s personal capacity for the purpose of academic exchange and does not represent the views of his/her organisations on the topic discussed. Cholera prevention
Vibrio outbreak and surveillance: Maryland's collaborative approach
 Vibrio outbreak and surveillance: Maryland's collaborative approach Catey Dominguez, Ph.D Developmental Scientist Maryland Department of Health Core Sequencing James Pettengill PhD Biostatistics and Bioinformatics
Vibrio outbreak and surveillance: Maryland's collaborative approach Catey Dominguez, Ph.D Developmental Scientist Maryland Department of Health Core Sequencing James Pettengill PhD Biostatistics and Bioinformatics
Hepatitis E FAQs for Health Professionals
 Hepatitis E FAQs for Health Professionals Index of Questions ± Overview and Statistics What is Hepatitis E? How common is Hepatitis E in the United States? Where is Hepatitis E most common? Are there different
Hepatitis E FAQs for Health Professionals Index of Questions ± Overview and Statistics What is Hepatitis E? How common is Hepatitis E in the United States? Where is Hepatitis E most common? Are there different
Key words: imported infectious diseases, travelers' health care, quarantine, health consultation, health information. Abstract
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemiological Approach to the Prevention of Imported Infectious Diseases in the Age of Globalization Michiya OHTAKA, M.D., Ph.D. Narita Airport Quarantine Station, Ministry of Health
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemiological Approach to the Prevention of Imported Infectious Diseases in the Age of Globalization Michiya OHTAKA, M.D., Ph.D. Narita Airport Quarantine Station, Ministry of Health
Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease:
 Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences
 Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 11. Epidemiology and Public Health Chapter 11 Outline Epidemiology Interactions Among Pathogens, Hosts and the Environment Chain of Infection Reservoirs
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 11. Epidemiology and Public Health Chapter 11 Outline Epidemiology Interactions Among Pathogens, Hosts and the Environment Chain of Infection Reservoirs
Enteric bacteria(pseudomonas+salmonella) Dr.Asem shihabi. Jumanah Nayef Abu Asbeh
 15 Microbiology sheet #15 1. Gram-negative facultative anaerobic rapidly growing bacteria are divided into 2 major Lactose fermenter group which is represented by the Coliforms. 2. Lactose non-fermenter
15 Microbiology sheet #15 1. Gram-negative facultative anaerobic rapidly growing bacteria are divided into 2 major Lactose fermenter group which is represented by the Coliforms. 2. Lactose non-fermenter
Public Health Microbiology. CE421/521 Lecture Prof. Tim Ellis
 Public Health Microbiology CE421/521 Lecture 10-03-06 Prof. Tim Ellis Pathogens and parasites Epidemiology Definitions epidemiology = study of spread of d in populations infectious disease = disease that
Public Health Microbiology CE421/521 Lecture 10-03-06 Prof. Tim Ellis Pathogens and parasites Epidemiology Definitions epidemiology = study of spread of d in populations infectious disease = disease that
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses
 Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13. Mycobacterium Actinomycetes
 Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN. Chapter 14. Pathogenicity
 MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 14 Pathogenicity Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Pathogenicity -The ability to cause disease Virulence - The extent of pathogenicity Virulence Factors Adhesion
MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 14 Pathogenicity Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Pathogenicity -The ability to cause disease Virulence - The extent of pathogenicity Virulence Factors Adhesion
Infection, Detection, Prevention...
 Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Ch 15. Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Ch 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Student Learning Outcomes Identify the principal portals of entry and exit. Using examples, explain how microbes adhere to host cells. Explain how capsules and
Ch 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Student Learning Outcomes Identify the principal portals of entry and exit. Using examples, explain how microbes adhere to host cells. Explain how capsules and
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
May 14, Review for final exam (May 21, 2011, 8 AM)
 May 14, 2011 Review for final exam (May 21, 2011, 8 AM) The final exam is comprehensive. Two thirds of the test will cover material from the last one third of the class. The remaining one third of the
May 14, 2011 Review for final exam (May 21, 2011, 8 AM) The final exam is comprehensive. Two thirds of the test will cover material from the last one third of the class. The remaining one third of the
Unit 1: Asepsis and Infection Control
 Unit 1: Asepsis and Infection Control Outlines - Type of microorganism causing infection. - Types of infection. - Nosocomial infection. - Chain of infection. - Body defenses against infection. - Factors
Unit 1: Asepsis and Infection Control Outlines - Type of microorganism causing infection. - Types of infection. - Nosocomial infection. - Chain of infection. - Body defenses against infection. - Factors
Microbiology The study of Microbes are organisms to be seen with the
 Module 1 Chapter 1 The microbial world and you Microbes in our lives Overall theme of this course is to discuss microbes and how they are involved in the lives of humans. Microbes make the biggest news
Module 1 Chapter 1 The microbial world and you Microbes in our lives Overall theme of this course is to discuss microbes and how they are involved in the lives of humans. Microbes make the biggest news
All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction
 Infectious Diseases All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction *Organisms must take nutrients essential for growth and proliferation from the environment. *In many conditions
Infectious Diseases All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction *Organisms must take nutrients essential for growth and proliferation from the environment. *In many conditions
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 7 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology, and Growth Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 7 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology, and Growth Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Epidemiology of Diarrheal Diseases. Robert Black, MD, MPH Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Classification of Diseases
 Classification of Diseases Disease Any condition that causes the systems of a plant or animal to not function properly. How diseases occur Sporadic: isolated incident in a single animal Enzootic: disease
Classification of Diseases Disease Any condition that causes the systems of a plant or animal to not function properly. How diseases occur Sporadic: isolated incident in a single animal Enzootic: disease
Standard B-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the flow of energy within and between living systems.
 B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
Pathogenicity and Infection. Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 35 Pathogenicity and Infection Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 35.1 Pathogenicity and Infectious Disease 1. Compare and contrast
35 Pathogenicity and Infection Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 35.1 Pathogenicity and Infectious Disease 1. Compare and contrast
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Portals of Entry Mucous membranes Conjunctiva Respiratory tract: Droplet inhalation of moisture and dust particles. Most common portal of entry. GI tract: food, water,
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Portals of Entry Mucous membranes Conjunctiva Respiratory tract: Droplet inhalation of moisture and dust particles. Most common portal of entry. GI tract: food, water,
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
 Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Paper No.: 03. Paper Title: FOOD MICROBIOLOGY. Module 30: Fungal agents for food borne diseases
 Paper No.: 03 Paper Title: FOOD MICROBIOLOGY Module 30: Fungal agents for food borne diseases INTRODUCTION Food, a vital necessity for all organisms present on this earth, is huge repertoire of microorganisms.
Paper No.: 03 Paper Title: FOOD MICROBIOLOGY Module 30: Fungal agents for food borne diseases INTRODUCTION Food, a vital necessity for all organisms present on this earth, is huge repertoire of microorganisms.
FOOD BORNE DISEASES Lectures
 FOOD BORNE DISEASES Lectures Nur Hidayat Jur TIP FTP UB http://nurhidayat.lecture.ub.ac.id/mikrobiolologi-bioproses/ FOOD BORNE INTOXICATIONS These are diseases caused by consumption of food containing:
FOOD BORNE DISEASES Lectures Nur Hidayat Jur TIP FTP UB http://nurhidayat.lecture.ub.ac.id/mikrobiolologi-bioproses/ FOOD BORNE INTOXICATIONS These are diseases caused by consumption of food containing:
Gastroenteritis and viral infections
 Gastroenteritis and viral infections A Large number of viruses are found in the human gut; these include some that are associated with gastroenteritis Rotaviruses Adenoviruses 40/41 Caliciviruses Norwalk-like
Gastroenteritis and viral infections A Large number of viruses are found in the human gut; these include some that are associated with gastroenteritis Rotaviruses Adenoviruses 40/41 Caliciviruses Norwalk-like
Chapter 29 Lecture Notes: Parasitism, pathogenicity and resistance
 Chapter 29 Lecture Notes: Parasitism, pathogenicity and resistance I. Symbiosis relationship in which 2 organisms spend a portion or all of their lifecycles associated with one another A. Commensalism
Chapter 29 Lecture Notes: Parasitism, pathogenicity and resistance I. Symbiosis relationship in which 2 organisms spend a portion or all of their lifecycles associated with one another A. Commensalism
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3)
 Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Outline. Introduction to Epidemiology. Epidemiology. Epidemiology. History of epidemiology
 Outline Introduction to Epidemiology Joshua Vest Epidemiologist Austin/Travis County Health & Human Services Department Define History Basis of epidemiology Objectives of epidemiology Causal inference
Outline Introduction to Epidemiology Joshua Vest Epidemiologist Austin/Travis County Health & Human Services Department Define History Basis of epidemiology Objectives of epidemiology Causal inference
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2012-2013 MICROBIOLOGY BIO-2B28 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2012-2013 MICROBIOLOGY BIO-2B28 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in
Transmission (How Germs Spread) Module 1
 Transmission (How Germs Spread) Module 1 Learner outcomes By the end of this module you will be able to: State the goal of infection prevention and control. List the links in the chain of transmission.
Transmission (How Germs Spread) Module 1 Learner outcomes By the end of this module you will be able to: State the goal of infection prevention and control. List the links in the chain of transmission.
Addressing climate change driven health challenges in Africa
 Addressing climate change driven health challenges in Africa Ednah N Ototo, Parasitologist, Climate Change and Health Kenyatta University, Kenya Kenya Medical Research Institute Outline The impact of climate
Addressing climate change driven health challenges in Africa Ednah N Ototo, Parasitologist, Climate Change and Health Kenyatta University, Kenya Kenya Medical Research Institute Outline The impact of climate
Biostatistics and Computational Sciences. Introduction to mathematical epidemiology. 1. Biomedical context Thomas Smith September 2011
 Biostatistics and Computational Sciences Introduction to mathematical epidemiology 1. Biomedical context Thomas Smith September 2011 Epidemiology The study of the distribution and determinants of healthrelated
Biostatistics and Computational Sciences Introduction to mathematical epidemiology 1. Biomedical context Thomas Smith September 2011 Epidemiology The study of the distribution and determinants of healthrelated
Acute respiratory illness This is a disease that typically affects the airways in the nose and throat (the upper respiratory tract).
 Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Cholera: with a Focus on Haiti
 Cholera: with a Focus on Haiti Andi L. Shane MD, MPH, MSc Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Emory University School of Medicine 22 November 2011 http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=playe embedded&v=6jxkix-f3jy
Cholera: with a Focus on Haiti Andi L. Shane MD, MPH, MSc Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Emory University School of Medicine 22 November 2011 http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=playe embedded&v=6jxkix-f3jy
Many of you asked about this topic
 Many of you asked about this topic Water borne disease: The largest water quality problem in developing countries. CEE 3510 Environmental Quality Engineering According to: Chemical and Engineering News
Many of you asked about this topic Water borne disease: The largest water quality problem in developing countries. CEE 3510 Environmental Quality Engineering According to: Chemical and Engineering News
Phases of the bacterial growth:
 L3: Physiology of Bacteria: Bacterial growth Growth is the orderly increase in the sum of all the components of an organism. Cell multiplication is a consequence of growth, in unicellular organism, growth
L3: Physiology of Bacteria: Bacterial growth Growth is the orderly increase in the sum of all the components of an organism. Cell multiplication is a consequence of growth, in unicellular organism, growth
Epidemiology of Vibrio Infection in Texas,
 Epidemiology of Vibrio Infection in Texas, 2008-2017 Irina Cody, MPH Epidemiologist, Foodborne team Emerging and Acute Infectious Disease Branch Texas Department of State Health Services Vibrio Infection
Epidemiology of Vibrio Infection in Texas, 2008-2017 Irina Cody, MPH Epidemiologist, Foodborne team Emerging and Acute Infectious Disease Branch Texas Department of State Health Services Vibrio Infection
Introduction. Infections acquired by travellers
 Introduction The number of Australians who travel overseas has increased steadily over recent years and now between 3.5 and 4.5 million exits are made annually. Although many of these trips are to countries
Introduction The number of Australians who travel overseas has increased steadily over recent years and now between 3.5 and 4.5 million exits are made annually. Although many of these trips are to countries
Bio 119 PLAGUE 7/21/ Distinguish between sylvatic, bubonic, septicemic, and pneumonic plague.
 PLAGUE Reading in BOM-12: 35.7 Plague p. 1017 Discussion Questions 1. Distinguish between sylvatic, bubonic, septicemic, and pneumonic plague. 2. Describe the Hemin Storage Phenotype (Hms) phenotype and
PLAGUE Reading in BOM-12: 35.7 Plague p. 1017 Discussion Questions 1. Distinguish between sylvatic, bubonic, septicemic, and pneumonic plague. 2. Describe the Hemin Storage Phenotype (Hms) phenotype and
CH 11. Interaction between Microbes and Humans
 CH 11 Interaction between Microbes and Humans SLOs 1. Differentiate among the terms colonization, infection, and disease. 2. Enumerate the sites where normal biota is found in humans. 3. Discuss how the
CH 11 Interaction between Microbes and Humans SLOs 1. Differentiate among the terms colonization, infection, and disease. 2. Enumerate the sites where normal biota is found in humans. 3. Discuss how the
1/29/2013. Viruses and Bacteria. Infectious Disease. Pathogens cause disease by: Chapters 16 and 17
 Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
