Prevalence of Acute Respiratory Tract Infection (ARI) in Paediatric Patient Attending National Hospital Abuja, Nigeria
|
|
|
- Margaret Chambers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences 2018, 8(7): DOI: /j.ajmms Prevalence of Acute Respiratory Tract Infection (ARI) in Paediatric Patient Attending National Hospital Abuja, Nigeria Ajobiewe H. F. 1,*, Ajobiewe J. O. 2, Nehemiah Edet Okon 2 1 Biological Sciences Department, Bingham University, Karu, Nigeria 2 Imo State University Owerri, Nigeria Abstract This study, on the prevalence of Acute Respiratory Tract Infection(ARI), spans the period of six months, from 1 st January to the 30 th of June,2017, at the National Hospital Abuja, located at the central business district of the Federal Capital City of Nigeria. The data were retrospectively collected from patient s folders and attendance register from the medical records department at the general Paediatric Outpatient department, National Hospital over the period of six months, 713(59.3%) males and 490(40.7%) females. Over the six-month period, out of The result showed that among paediatric unisex patients seen, 279 were diagnosed with ARI which is 23.19%. The overall ARI mean, µ, was 25; Standard Deviation, SD, was while the Standard Error, S.E. was, 6.2 with t 4.7 tab t cal. 4.0 at (P 0.05). From the study carried out, there were diseases found to be casually and confoundly associated with ARI which includes sepsis, malaria, dehydration, diarrhoeal disease, febrile convulsion, pneumonia, sickle cell anaemia, and meningitis. Our observation showed that ARI among children between the ages 0-5 years was not significantly high (P 0.05) in agreement with popular opinion from literature search [1, 18]. Despite the devastating and fatal nature of ARI, as it starves the body of oxygen-it is suggested that the non -significance could be favoured due to the clemency of the environment/ weather which these patients were exposed to, when this research was conducted. Keywords Acute Respiratory Tract Infection (ARI), Environment, Paediatrics, Fatal, Clemency 1. Introduction Acute respiratory tract infections (ARIs) are heterogeneous and complex group of diseases caused by a wide range of pathogens in which the possible anatomic site(s) extend from the pharynx to the alveoli. In conjunction with diarrheal diseases and malnutrition, ARIs constitute the major causes of mortality and morbidity among under-five children of the developing world. The percentage of deaths due to all causes for ARI is between 2 times and 6 times higher in less developed countries than in developed countries. ARI constitute one-third of the deaths in children under-five in developing countries. ARIs are not confined to the respiratory tract and have systemic effects because of possible extension of infection or microbial toxins, inflammation, and reduced lung function [2]. Diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), and measles are * Corresponding author: helenajo2000@yahoo.com (Ajobiewe H. F.) Published online at Copyright 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY). vaccine-preventable diseases that may have a respiratory tract component but also affect other systems. Except during the neonatal period, ARIs are the most common causes of both illness and mortality in children under five, who average three to six episodes of ARIs annually regardless of where they live or what their economic situation is Childhood acute respiratory infection (ARI) which is a significant public health problem especially in developing countries [3, 4]. ARI is an acute infection of any part of respiratory tract and related structures including paranasal sinuses, middle ear, and pleural cavity. ARIs include a diverse group of diseases ranging from self-limiting illnesses to bronchiolitis and pneumonia that may require medical care. It includes all infections of less than 30 days duration except those of the middle ear where the duration of an acute episode is less than 14 days. World Health Organization estimates ARI causing 3.9 million deaths throughout the world every year. It is one of the important priority areas for the concerned stakeholders in the health sector especially in developing countries. The occurrence of ARI is determined by the exposure to various risk factors. Air pollution is a risk factor for both acute and chronic respiratory disease. One half of the world's population is exposed to high concentrations of solid fuel
2 American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences 2018, 8(7): smoke that are produced by inefficient open fires, mainly in the rural areas of developing countries. Solid fuel smoke possesses the majority of the toxins found in tobacco smoke and has also been associated with a variety of diseases including ARI in children. Globally, indoor air pollution from solid fuel use is responsible for 1.6 million deaths due to pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and lung cancer. The highest exposures to second-hand smoke are found in Eastern Europe, the Western Pacific and South-East Asia, with more than 50% of some population groups exposed. Environmental factors such as overcrowding coupled with poor ventilation at homes and work places may make the health effects of indoor air pollution more pronounced. Exposure is particularly high among women and children, who spend most time near the domestic health [5]. 2. Literature Review Acute respiratory tract infection (ARI) is a serious infection that prevents normal breathing function. It usually begins as a viral infection in the nose, trachea (windpipe), or lungs. If the infection is not treated, it can spread to the entire respiratory system. Acute respiratory infection prevents the body from getting oxygen and can result in death. According to the World health organization [6] acute respiratory infections kill an estimated 3.9 million children annually worldwide. Identification and early treatment can reduce the burden of ARI among children. Acute respiratory infection (ARI) is a major public health problem worldwide [7]. It is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality and main reason for utilization of health services among children. Identification and intervention of major risk factors can reduce the burden of ARI among children [8]. However, in developing countries, mortality rates are up to 30 times higher (or more). The high morbidity rate makes ARI the main cause for the utilization of health services, representing in the entire world 20-40% of the appointments at paediatric services and 12-35% of the hospitalizations. According to data provided by OPAS/OMS5, pneumonias are responsible for 20-40% of the admissions of children under the age of 5 in developing countries [9]. Studies have shown the importance of social factors for ARI mortality, such as family size, education level, and density of dwellers in the residence. We should emphasize the degree of maternal education as a social factor related to the infant s survival, since the reports point out that the lower the education level is, the higher are the ARI rates and seriousness. It is known that the lack of essential nutrients interferes with the development of humoral and cellular organic defence systems. Thus, though the incidence of ARI is globally similar, the difference is that infections of the inferior airways, especially pneumonia, are more frequent and severe in developing countries due to several factors, especially malnutrition. Smoking is still a serious public health problem, being particularly significant in childhood, since respiratory problems in children (mainly infants) who are passive smokers are more severe and often require hospitalization [10]. The study of ARI in public services is justified by the difficulty in optimizing the structure of public health services for this kind of medical assistance. This difficulty in solving health problems ends up with an unsatisfactory involvement between health service agents and relatives. This leads to the negligence of basic orientations, since the natural evolution of most ARI cases is not complicated [8]. This contributes to the misuse of drugs, and to the same child going to different health service offices, which deviates from the objectives of the ARI Program, commended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. Acute respiratory infection is a serious infection that prevents normal breathing function. It usually begins as a viral infection in the nose, trachea (windpipe), or lungs. If the infection is not treated, it can spread to the entire respiratory system. Acute respiratory infection prevents the body from getting oxygen and can result in death. [11] 2.1. Who is at Risk for Acute Respiratory Infection? While it is almost impossible to avoid viruses and bacteria, certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing acute respiratory infection. The immune systems of children and the elderly are more prone to be affected by viruses and later bacteria. Those most frequently implicated are Adenoviruses, Rhinoviruses Myxoviruses and Paramyxoviruses while the bacterium is the Pneumococcus [11]. Children are especially at risk because of their constant contact with other kids who could be virus carriers. Children often do not wash their hands regularly, rub their eyes, and put their fingers in their mouths, resulting in the spread of viruses. People with heart diseases or other lung problems are more likely to contract an acute respiratory infection. Anyone whose immune system might be weakened by another disease is at risk. Smokers also are at high risk and have more trouble recovering from it [11] Ways to Reduce the Occurrence of Acute Respiratory Infection in Children Most causes of an acute respiratory infection are not treatable. Therefore, prevention is the best method to ward off harmful respiratory infections. Practice good hygiene by doing the following: Wash hands frequently, especially after having been in a public place. Avoid touching one's face, especially eyes and mouth, to prevent introducing germs into one's system. Always sneeze into one's arm of the shirt or in a tissue. Although this may not ease one's symptoms, it will prevent the spreading of infectious diseases Diagnosis of Acute Respiratory Infection In a respiratory exam, the doctor focuses on the patient s breathing. Breath sounds in the lungs are checked for fluid and inflammation. The doctor may peer into the nose and
3 134 Ajobiewe H. F. et al.: Prevalence of Acute Respiratory Tract Infection (ARI) in Paediatric Patient Attending National Hospital Abuja, Nigeria check the throat. If diagnosed early, over-the-counter medications can help alleviate symptoms while the virus runs its course. However, if the infection is advanced, an X-ray or CT scan (computer tomography) may be needed to check the condition of the lungs. Lung function tests have shown to be useful as diagnostic tools and for prognosis purposes. Pulse oximetry, also known as pulse oximeter, may be used to check how much oxygen gets into the lungs. A physician may also need a sputum (material coughed up from the lungs) sample to check for the type of virus causing the disease. Some of potential complications of acute respiratory infection involve; respiratory arrest, respiratory failure and congestive heart failure Types of Acute Respiratory Infection Acute respiratory infections (ARIs) are classified as upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) or lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs). The upper respiratory tract consists of the airways from the nostrils to the vocal cords in the larynx, including the paranasal sinuses and the middle ear. The lower respiratory tract covers the continuation of the airways from the trachea and bronchi to the bronchioles and the alveoli. However, the proportion of mild to severe disease varies between high- and low-income countries, and because of differences in specific etiologies and risk factors, the severity of LRIs in children under five is worse in developing countries, resulting in a higher case-fatality rate. Although medical care can to some extent mitigate both severity and fatality, many severe LRIs do not respond to therapy, largely because of the lack of highly effective antiviral drugs. Some 10.8 million children die each year [12]. Estimates indicate that in the year 2000, 1.9 million of them died because of ARIs, 70 percent of them in Africa and Southeast Asia [13]. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 2 million children under five die of pneumonia each year [14] Treatment Guidelines Current recommendations are for Co-trimoxazole twice a day for five days for pneumonia and intramuscular penicillin or chloramphenicol for children with severe pneumonia. The problems of increasing resistance to co-trimoxazole and unnecessary referrals of children with any chest wall indrawing have led to studies exploring alternatives to the antibiotics currently used in ARI case management. One study indicated that Amoxicillin and Co-trimoxazole are equally effective for nonsevere pneumonia [15] though Amoxicillin costs twice as much as Co-trimoxazole. With respect to the duration of antibiotic treatment, studies in Bangladesh, India, and Indonesia indicate that three days of oral Co-trimoxazole or Amoxicillin are as effective as five days of either drug in children with nonsevere pneumonia [16]. In a multicenter study of intramuscular Penicillin versus oral Amoxicillin in children with severe pneumonia, [17] find similar cure rates. Because patients were treated with oxygen when needed for hypoxemia and were switched to other antibiotics if the treatment failed, this regimen is not appropriate for treating severe pneumonia in an outpatient setting. WHO (1990) [11] recommends administering oxygen, if there is ample supply, to children with signs and symptoms of severe pneumonia and, where supply is limited, to children with any of the following signs: inability to feed and drink, cyanosis, respiratory rate greater than or equal to 70 breaths per minute, or severe chest wall retractions. Oxygen should be administered at a rate of 0.5 liter per minute for children younger than 2 months and 1 liter per minute for older children. Because oxygen is expensive and supply is scarce, especially in remote rural areas in developing countries, WHO (1993) [6] recommends simple clinical signs to detect and treat hypoxemia. Despite those recommendations, a study of 21 first-level facilities and district hospitals in seven developing countries found that more than 50 percent of hospitalized children with LRI were inappropriately treated with antibiotics or oxygen [10] and in several, oxygen was in short supply. Clearly, providing oxygen to hypoxemic babies is lifesaving, though no randomized trials have been done to prove it. 3. Methods 3.1. Population and Sample Size The population consists mainly of patients seen in the Out-patient Paediatric section of National Hospital, Abuja. The researcher was given access to their files to obtain all necessary information needed for the success of this research. The population size and sample size are approximately 1,300 (it could be less). This study was carried out for a period of six months (January to June 2017). The researcher found the observation method of data collection to be useful, as the researcher was able to observe the patients that were brought in for the treatment of ARI. The researcher was also granted access to some of the patients file to gather all necessary information The sources used to gather all necessary information needed in this research work was mainly secondary data; over the period in which the research work began up until its completion. Both null and researcher s /alternative hypotheses were instruments used for the analysis of findings. HYPOTHESES H 0 Prevalence of ARI among children aged 0-5years (in/out patients) attending National Hospital, Abuja is not significantly high. H 1 Prevalence of ARI among children aged 0-5years (in/out patients) attending National Hospital, Abuja is significantly high. Where, H o = Null Hypothesis, and Ha = Alternate or Researcher s Hypothesis. 4. Results There were a total of 1203 cases of ARI seen at National
4 American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences 2018, 8(7): Hospital over the period of six months, 713 (59.3%) males and 490 (40.7%) females. In January, a total number of 202 (16.97%) patients were seen, 17 (11.11%) of them were diagnosed of ARI. In February a total number of 262 (21.77%), 34 patients (22.22%) were diagnosed of ARI. In March a total number of 231 (19.20%), 41 (26.79%) patients were diagnosed of ARI. In April a total of 171 (14.21%), 20 (13.07%) patients were diagnosed of ARI, 10 (13.88%). In May a total of 175 (14.54%), 21 (13.72%) patients were diagnosed of ARI. In June a total of 162 (13.46%), 20 (13.07%) patients were diagnosed of ARI. (P 0.05). From the study carried out, there were diseases found to be associated with ARI which includes sepsis, malaria, dehydration, diarrhoeal disease, febrile convulsion, pneumonia, sickle cell anaemia, and meningitis. Sepsis was the highest with 42 patients (27.45%), followed by malaria with 34 patients (22.22%), dehydration with 20 patients (13.07%), diarrhoeal disease with 15 patients (9.80%), febrile convulsion with 11 patients (7.18%), pneumonia with 7 patients (4.57%), sickle cell anaemia with 6 patients (3.92), and meningitis with 1 patient (0.65%) Table A: Showing Total No of Patients Seen, Admitted and Diagnosed for ARI S/N MONTH SEEN ADMITTED OF PATIENTS DIAGNOSED OF ARI January February March April May June TOTAL 1, Percentage Percentage Seen = Source: Secondary Data, % ( per month) 100% ( per month) Percentage Admitted = of patients diagnosed of AR X 100% per month Percentage of ARI = ( ) 4.3. Table B: Showing Total Percentage of Patients Seen, Admitted, Diagnosed of ARI S/N MONTH TOTAL NUMBER SEEN (%) ADMITTED (%) OF PATIENTS DIAGNOSED OF ARI (%) STUDENT S T TEST RESULT January February MEAN, µ = 25 STANDARD DEVIATION, 3. March SD = April STANDARD May June ERROR, S.E = 6.2 TOTAL t tabulated = t calculated = 4.0 at 95% confidence limits. INFERENCE Since tabulated t. 05 Is greater than the Calculated t. 05 we have no enough evidence to accept the alternative hypothesis, hence the Null hypothesis is retained. N.B the total percentages were approximated to the nearest whole number STANDARD DEVIATION SD, = (x x )2 Where x = x = n = Standard Error = t value = Sample n Sample mean Number Standard Deviation n x 0 Standard Deviation
5 136 Ajobiewe H. F. et al.: Prevalence of Acute Respiratory Tract Infection (ARI) in Paediatric Patient Attending National Hospital Abuja, Nigeria 5. Discussion Subjecting the hypotheses to critical analysis revealed the following; H 0 prevalence of ARI among children aged 0-5years (in/out patients) attending National Hospital, Abuja, Nigeria is not significantly high. (P 0.05). We have no enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis, H o, thus it was retained instead of the alternative/researcher s hypothesis, H a. The research showed that within the stipulated time for the research, the occurrence of ARI among children between the ages of 0-5 years is not significantly high, (P 0.05) and this may be due to the weather conditions in agreement with earlier researches carried out by Lucy Eberechukwu, Tochi Ada (2015) [18] and Cherian et al, (1990) [1] - their researches proved that ARI is more prevalent during the rainy season than the dry season. ARIs have remained a major contributor to morbidity among children, especially children in developing countries. In the study carried out, a total of 1203 cases of ARIs were seen over a 6-month period (during the harmattan). Most cases of ARI seen in this study were upper respiratory tract infections which is consistent with the reports by other authors. The incidence of pneumonia in developing countries is high due to the increased prevalence of malnutrition, low birth weight and indoor air pollution in these countries. 6. Conclusions Despite the devastating and fatal nature of ARI, as it starves the body of oxygen-it is suggested that the non -significance could be favoured due to the clemency of the environment/ weather which these patients were exposed to, when this research was conducted.. REFERENCES [1] Cherian T., Simoes E.A., Steinhoff M.C., Chitra K., John M., Raghupathy P. et al. Bronchiolitis in Tropical South India. American Journal of Diseases of Children; 1990; 144(9): [2] Chatterjee, S. A Study of Epidemiological Factors Related to Acute Respiratory Infection in under Five Children Attending the Immunization Clinic of Calcutta National Medical College and Hospital. The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine; (2): 1-6. [3] Kamath K.R., Feldman R. A., Rao P.S.S., Webb J.K. Infection and Disease in a Group of South Indian Families. American Journal of Epidemiology 1969; 89: [4] Monto A.S., Ullman B.M. Acute Respiratory Illness in an American Community; The Tecumseh Study. Journal of the American Medical Association.1974; 227(2): [5] Zaman, K., Baqui, A. H., Yunus, M., Sack, R. B., Bateman, O. M., Chowdhury, H. R., and Black, R. E. Acute Respiratory Infections in Children: A Community Based Longitudinal Study in Rural Bangladesh. J. Trop. Pediatr (3): [6] WHO 1993 Oxygen Therapy for Acute Respiratory Infections in Young Children in Developing Countries. Geneva, WHO NewPublications/CHILD HEALTH/WHO ARI htm. [7] Wall R.A., Corrah P.T., Mabey D.C., Greenwood B.M. The Aetiology of lobar of lobar pneumonia in the Gambia. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 1986; 64 (4): [8] John, T.J Who Determines National Health Policies In Vaccination and World Health: fourth Annual Public Health Forum of the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, ed. F.T. Cutts and P.G.. Smith, Chichester, U.K John Wiley. [9] Sharma D., Kappusamy K., Bhoorasamy A. Prevalence of acute respiratory infections (ARI) and their determinants in under five children in urban and rural areas of Kancheepuram district, south India. Ann Trop Med Public Health, [10] Nolan T., Angos P., Cunh A. J., Muhe L., Qazi S., Simoes E. A. et al. Quality of Hospital Care for Seriously lll Children in Less-Developed Countries. Lancet.2001; 357(9250): [11] WHO (World Health Organization) Antibiotics in the Treatment of acute Respiratory infections in Young Children. Unpublished document WHO/ARI/90.10, available on request from the division of Child Health and Development, formerly the Division of Diarrhoeal and Acute Respiratory Diseases Control, WHO, Geneva. [12] Black R.E., Morris S.S., Bryce J. Where and Why Are 10 Million Children Dying Every Year? Lancet. 2003; 361(9376): [13] Williams B.G., Gouws E., Boschi-Pinto C., Bryce J., Dye C. Estimates of Worldwide Distribution of Child Deaths from Acute Respiratory Infections. Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2002; 2: [14] Bryce J., Bosch-Pinto C., Shibuya K., Black R.E.WHO Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group. WHO Estimates of the Causes of Death in Children. Lancet 2005; 365: [15] Catchup Study Group. Clinical Efficacy of Co-Trimoxazole versus Amoxicillin Twice Daily for Treatment of Pneumonia: A randomized Controlled Clinical Trial in Pakistan. Archives of Disease in Childhood. 2002; 86: [16] Agarwal G., Awasthi S., Kabra S. K., Kaul A., Singhi S., Walter S. D.ISCAP Study Group. Three- Day versus Five-Day Treatment with Amoxicillin for Non-Severe Pneumonia in Young Children: A Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial. British Medical Journal. 2004; 328: [17] Addo-Yobo E., Chisaka N., Hassan M., Hibberd P., Lozano J.M., Jeena P. et al. Oral Amoxicillin versus Injectable Penicillin for severe pneumonia in children aged three to fifty nine months; A randomized multicentre equivalence study. Lancet, 2004; 364(9440): [18] Yaguo Ide, Lucy Eberechukwu, and Tochi Ada Uchenwa- Onyenegecha. "Burden of Acute Respiratory Tract Infections as Seen in University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital Nigeria." Journal of US-China Medical Science (2015).
Burden of Acute Respiratory Tract Infections as Seen in University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital Nigeria
 Journal of US-China Medical Science 12 (2015) 158-162 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2015.04.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Burden of Acute Respiratory Tract Infections as Seen in University of Lucy Eberechukwu Yaguo
Journal of US-China Medical Science 12 (2015) 158-162 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2015.04.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Burden of Acute Respiratory Tract Infections as Seen in University of Lucy Eberechukwu Yaguo
Pneumonia. Trachea , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. id Last reviewed: 11/11/2017 1
 Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
Acute respiratory infections among under five children in a rural area of Kancheepuram district, Tamil Nadu, India: a cross-sectional study
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Savitha AK et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2018 Aug;5(8):3445-3449 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Savitha AK et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2018 Aug;5(8):3445-3449 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
Bronchitis. Anatomy of the Lungs The lungs allow us to fill our blood with oxygen. The oxygen we breathe is absorbed into our blood in the lungs.
 Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Safety, feasibility and efficacy of outpatient management of moderate pneumonia at Port Moresby General Hospital: a prospective study
 Safety, feasibility and efficacy of outpatient management of moderate pneumonia at Port Moresby General Hospital: a prospective study Dr Rose Morre Master of Medicine research project, 2017 Aim To trial
Safety, feasibility and efficacy of outpatient management of moderate pneumonia at Port Moresby General Hospital: a prospective study Dr Rose Morre Master of Medicine research project, 2017 Aim To trial
World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences WJPLS
 wjpls, 2016, Vol. 2, Issue 3, 375-380 Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 Reddy. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 3.347 A STUDY ON PREVALENCE OF PNEUMONIA IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS P. Nishaandhini Reddy*,
wjpls, 2016, Vol. 2, Issue 3, 375-380 Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 Reddy. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 3.347 A STUDY ON PREVALENCE OF PNEUMONIA IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS P. Nishaandhini Reddy*,
Shabir A. Madhi. Progress and Challenges of Immunization Contributing Toward Attaining the MDG Goal to Reduce under-5 Childhood Mortality.
 Shabir A. Madhi Progress and Challenges of Immunization Contributing Toward Attaining the MDG Goal to Reduce under-5 Childhood Mortality. National Institute for Communicable Diseases & University of Witwatersrand,
Shabir A. Madhi Progress and Challenges of Immunization Contributing Toward Attaining the MDG Goal to Reduce under-5 Childhood Mortality. National Institute for Communicable Diseases & University of Witwatersrand,
Global Update. Reducing Mortality From Major Childhood Killer Diseases. infant feeding, including exclusive breastfeeding.
 INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-FEBRUARY 1998 Global Update Reducing Mortality From Major Childhood Killer Diseases Seven out of 10 childhood deaths in developing countries can be attributed to just five main
INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-FEBRUARY 1998 Global Update Reducing Mortality From Major Childhood Killer Diseases Seven out of 10 childhood deaths in developing countries can be attributed to just five main
Childhood Pneumonia & Meningitis: Recent Advances
 Childhood Pneumonia & Meningitis: Recent Advances Karachi, Pakistan January 31, 2009 MEDIA COVERAGE DAWN KARACHI, Pakistan February 1, 2009 Experts pin hopes on pentavalent vaccines A programme to introduce
Childhood Pneumonia & Meningitis: Recent Advances Karachi, Pakistan January 31, 2009 MEDIA COVERAGE DAWN KARACHI, Pakistan February 1, 2009 Experts pin hopes on pentavalent vaccines A programme to introduce
PEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS (RSV) ALL THAT WHEEZES IS NOT ASTHMA
 PEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS (RSV) ALL THAT WHEEZES IS NOT ASTHMA Season changes here in Ohio can send the census numbers in our local P.I.C.U. s, N.I.C.U. s and Emergency Rooms through the roof.
PEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS (RSV) ALL THAT WHEEZES IS NOT ASTHMA Season changes here in Ohio can send the census numbers in our local P.I.C.U. s, N.I.C.U. s and Emergency Rooms through the roof.
The burden of asthma on the US Healthcare system and for the State of Texas is enormous. The causes of asthma are multifactorial and well known.
 The burden of asthma on the US Healthcare system and for the State of Texas is enormous. The causes of asthma are multifactorial and well known. There are also indications that rural counties have a higher
The burden of asthma on the US Healthcare system and for the State of Texas is enormous. The causes of asthma are multifactorial and well known. There are also indications that rural counties have a higher
Coughs, Colds & Pneumonia
 Coughs, colds and pneumonia affect millions of people worldwide and can kill. Older children can learn how to avoid coughs or colds, stop them spreading and prevent them developing. They can learn about
Coughs, colds and pneumonia affect millions of people worldwide and can kill. Older children can learn how to avoid coughs or colds, stop them spreading and prevent them developing. They can learn about
Risk Factors of Pneumonia in Children A Community Survey
 TAJ December 2007; Volume 20 Number 2 ISSN 1019-8555 The Journal of Teachers Association RMC, Rajshahi Original Article Risk Factors of Pneumonia in Children A Community Survey M I Bari 1, A B Siddiqui
TAJ December 2007; Volume 20 Number 2 ISSN 1019-8555 The Journal of Teachers Association RMC, Rajshahi Original Article Risk Factors of Pneumonia in Children A Community Survey M I Bari 1, A B Siddiqui
Respiratory System. Respiratory System Overview. Component 3/Unit 11. Health IT Workforce Curriculum Version 2.0/Spring 2011
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 11-Respiratory System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health and
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 11-Respiratory System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health and
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
NEW PNEUMONIA CASE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES. By Andolo Miheso,Christine Wambugu, Sophie Ngugi, Warfa Osman (NCAHU MOH) & Ambrose Agweyu (KWT)
 NEW PNEUMONIA CASE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES By Andolo Miheso,Christine Wambugu, Sophie Ngugi, Warfa Osman (NCAHU MOH) & Ambrose Agweyu (KWT) Outline of the presentation: Overview of Child Health situation
NEW PNEUMONIA CASE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES By Andolo Miheso,Christine Wambugu, Sophie Ngugi, Warfa Osman (NCAHU MOH) & Ambrose Agweyu (KWT) Outline of the presentation: Overview of Child Health situation
PNEUMONIA. Your Treatment and Recovery
 PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
Shally Awasthi Professor of Pediatrics Chhatrapati Shahuji Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow
 Shally Awasthi Professor of Pediatrics Chhatrapati Shahuji Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow Magnitude of problem Misclassification of pneumonia Inappropriate use of antibiotics Inadequate Surveillance
Shally Awasthi Professor of Pediatrics Chhatrapati Shahuji Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow Magnitude of problem Misclassification of pneumonia Inappropriate use of antibiotics Inadequate Surveillance
Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women
 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis. Before the introduction
Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis. Before the introduction
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
FLU VACCINE INFORMATION The FLU JAB
 FLU VACCINE INFORMATION 2018 In the UK the flu vaccine is available each year from late September or early October onwards. It is recommended to get the flu vaccine in the autumn, before outbreaks of flu
FLU VACCINE INFORMATION 2018 In the UK the flu vaccine is available each year from late September or early October onwards. It is recommended to get the flu vaccine in the autumn, before outbreaks of flu
Flu is a more severe form of what people generally associate with as Cough, Cold and Fever and symptoms are usually incapacitating.
 SEASONAL HUMAN INFLUENZA (THE FLU) What is Seasonal Human Influenza? Seasonal Influenza is a viral infection that affects millions of people worldwide. It is transmitted from person to person through direct
SEASONAL HUMAN INFLUENZA (THE FLU) What is Seasonal Human Influenza? Seasonal Influenza is a viral infection that affects millions of people worldwide. It is transmitted from person to person through direct
h e a l t h l i n e ISSN X Volume 3 Issue 1 January-June 2012
 Original article A study of risk factors of acute respiratory tract infection (ARI) of under five age group in uban and rural communities of Ahmedabad district, Gujarat Bipin Prajapati 1, Niti Talsania
Original article A study of risk factors of acute respiratory tract infection (ARI) of under five age group in uban and rural communities of Ahmedabad district, Gujarat Bipin Prajapati 1, Niti Talsania
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
TB 2015 burden, challenges, response. Dr Mario RAVIGLIONE Director
 TB 2015 burden, challenges, response Dr Mario RAVIGLIONE Director Addis Ababa, Ethiopia 11-13 November 2015 Overview TB basics TB burden & challenges Response: End TB Strategy DAY 1 What is TB? Definition
TB 2015 burden, challenges, response Dr Mario RAVIGLIONE Director Addis Ababa, Ethiopia 11-13 November 2015 Overview TB basics TB burden & challenges Response: End TB Strategy DAY 1 What is TB? Definition
RSV infection. Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your child developing a severe infection.
 RSV infection Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your child developing a severe infection. What is RSV? RSV is one of the most common respiratory viruses and is spread easily. By
RSV infection Information about RSV and how you can reduce the risk of your child developing a severe infection. What is RSV? RSV is one of the most common respiratory viruses and is spread easily. By
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiratory Problems in Children
 Respiratory Problems in Children A/Prof Alex Tang all that glitters is not gold, all the wheezes is not asthma Objective Describe an overview of respiratory problems in children Define common respiratory
Respiratory Problems in Children A/Prof Alex Tang all that glitters is not gold, all the wheezes is not asthma Objective Describe an overview of respiratory problems in children Define common respiratory
COUNTY OF MORRIS DEPARTMENT OF LAW & PUBLIC SAFETY OFFICE OF HEALTH MANAGEMENT
 1 COUNTY OF MORRIS DEPARTMENT OF LAW & PUBLIC SAFETY OFFICE OF HEALTH MANAGEMENT P.O. Box 900 Morristown, NJ 07963 (973) 631-5485 (973) 631-5490 Fax www.morrishealth.org 2012-2013 Influenza Season FREQUENTLY
1 COUNTY OF MORRIS DEPARTMENT OF LAW & PUBLIC SAFETY OFFICE OF HEALTH MANAGEMENT P.O. Box 900 Morristown, NJ 07963 (973) 631-5485 (973) 631-5490 Fax www.morrishealth.org 2012-2013 Influenza Season FREQUENTLY
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION
 Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
CHILD HEALTH. There is a list of references at the end where you can find more information. FACT SHEETS
 SOME 18,000 CHILDREN STILL DIE EVERY DAY FROM DISEASES THAT ARE MOSTLY PREVENTABLE. This fact sheet outlines some of the basic information related to the health and wellbeing of children under five years
SOME 18,000 CHILDREN STILL DIE EVERY DAY FROM DISEASES THAT ARE MOSTLY PREVENTABLE. This fact sheet outlines some of the basic information related to the health and wellbeing of children under five years
Malik Sallam. Ola AL-juneidi. Ammar Ramadan. 0 P a g e
 1 Malik Sallam Ola AL-juneidi Ammar Ramadan 0 P a g e Today's lecture will be about viral upper respiratory tract infections. Those include: common cold, sinusitis, otitis, etc. Infections in the upper
1 Malik Sallam Ola AL-juneidi Ammar Ramadan 0 P a g e Today's lecture will be about viral upper respiratory tract infections. Those include: common cold, sinusitis, otitis, etc. Infections in the upper
PAA NEWS TO USE FALL/WINTER Please visit our website at
 PAA NEWS TO USE FALL/WINTER 2009-2010 Please visit our website at www.paalex.com THANKS TO EVERYONE WHO PARTICIPATED IN OUR 50 TH ANNIVERSARY ART CONTEST! CONGRATULATIONS TO OUR WINNERS! PAA MASCOT WINNER:
PAA NEWS TO USE FALL/WINTER 2009-2010 Please visit our website at www.paalex.com THANKS TO EVERYONE WHO PARTICIPATED IN OUR 50 TH ANNIVERSARY ART CONTEST! CONGRATULATIONS TO OUR WINNERS! PAA MASCOT WINNER:
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
GraspIT AQA GCSE Infection and Response
 A. Infection and Response part 1 Communicable diseases (viral, bacterial, fungal and protist) 1. Tuberculosis (TB) is a communicable disease caused by a bacterium. TB is spread by droplets in the air when
A. Infection and Response part 1 Communicable diseases (viral, bacterial, fungal and protist) 1. Tuberculosis (TB) is a communicable disease caused by a bacterium. TB is spread by droplets in the air when
Guidelines for management of suspected sepsis in young infants where referral is not possible
 Guidelines for management of suspected sepsis in young infants where referral is not possible Kenya Paediatrics Association Conference, 26-29 April 2016, Eldoret Kenya 1 Kenya Paediatrics Association Conference,
Guidelines for management of suspected sepsis in young infants where referral is not possible Kenya Paediatrics Association Conference, 26-29 April 2016, Eldoret Kenya 1 Kenya Paediatrics Association Conference,
Self-study course. Pneumonia
 Self-study course Pneumonia This brochure is available in alternate formats. Call 1-800-282-8096 (V/TTY) 2 Course objectives: At the end of this course you will be able to: 1) Identify a series of steps
Self-study course Pneumonia This brochure is available in alternate formats. Call 1-800-282-8096 (V/TTY) 2 Course objectives: At the end of this course you will be able to: 1) Identify a series of steps
Respiratory System Virology
 Respiratory System Virology Common Cold: Rhinitis. A benign self limited syndrome caused by several families of viruses. The most frequent acute illness in industrialized world. Mild URT illness involving:
Respiratory System Virology Common Cold: Rhinitis. A benign self limited syndrome caused by several families of viruses. The most frequent acute illness in industrialized world. Mild URT illness involving:
COUNSELING CARDS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS
 www.calcuttakids.org info@calcuttakids.org COUNSELING CARDS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS For Community Health Workers Created by Calcutta Kids, May 2012 COUNSELING POINTS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS Sheet 1 Tuberculosis Sheet
www.calcuttakids.org info@calcuttakids.org COUNSELING CARDS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS For Community Health Workers Created by Calcutta Kids, May 2012 COUNSELING POINTS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS Sheet 1 Tuberculosis Sheet
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
 RESPIRATORY DISORDERS INTRODUCTION Respiratory disorders refers to the medical term that include different pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues of respiratory system which make gas
RESPIRATORY DISORDERS INTRODUCTION Respiratory disorders refers to the medical term that include different pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues of respiratory system which make gas
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Human infection with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus: updated interim WHO guidance on global surveillance
 Human infection with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus: updated interim WHO guidance on global surveillance 10 July 2009 Background This document updates the interim WHO guidance on global surveillance of pandemic
Human infection with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus: updated interim WHO guidance on global surveillance 10 July 2009 Background This document updates the interim WHO guidance on global surveillance of pandemic
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB)
 Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB) TB infection vs. TB disease Information about TB TB skin testing Active TB disease TB risk factors Role of Peel Public Health in TB prevention and control Environmental and
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB) TB infection vs. TB disease Information about TB TB skin testing Active TB disease TB risk factors Role of Peel Public Health in TB prevention and control Environmental and
Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations.
 Vaccinations Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations. DTP - Diphtheria Tetanus Polio Yellow fever Hepatitis A Typhoid fever Cerebrospinal meningitis
Vaccinations Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations. DTP - Diphtheria Tetanus Polio Yellow fever Hepatitis A Typhoid fever Cerebrospinal meningitis
Community Acquired Pneumonia
 April 2014 References: 1. Bradley JS, Byington CL, Shah SS, Alverson B, Carter ER, Harrison C, Kaplan SL Mace SE, McCracken Jr. GH, Moor MR, St. Peter SD, Stockwell JA, and Swanson JT. The Management of
April 2014 References: 1. Bradley JS, Byington CL, Shah SS, Alverson B, Carter ER, Harrison C, Kaplan SL Mace SE, McCracken Jr. GH, Moor MR, St. Peter SD, Stockwell JA, and Swanson JT. The Management of
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Influenza Backgrounder
 Influenza Backgrounder Influenza Overview Influenza causes an average of 36,000 deaths and 200,000 hospitalizations in the U.S. every year. 1,2 Combined with pneumonia, influenza is the seventh leading
Influenza Backgrounder Influenza Overview Influenza causes an average of 36,000 deaths and 200,000 hospitalizations in the U.S. every year. 1,2 Combined with pneumonia, influenza is the seventh leading
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Bronchiolitis: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis in children. 1.1 Short title Bronchiolitis in children 2 The remit The
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Bronchiolitis: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis in children. 1.1 Short title Bronchiolitis in children 2 The remit The
Setting The setting was outpatient departments of referral hospitals. The economic analysis was conducted in India.
 Three day versus five day treatment with amoxicillin for non-severe pneumonia in young children: a multicentre randomised controlled trial ISCAP study group Record Status This is a critical abstract of
Three day versus five day treatment with amoxicillin for non-severe pneumonia in young children: a multicentre randomised controlled trial ISCAP study group Record Status This is a critical abstract of
Swine flu - information prescription
 Swine flu - information prescription Introduction Swine flu is a relatively new strain of influenza (flu) that was responsible for a flu pandemic during 2009-2010. It is sometimes known as H1N1 influenza
Swine flu - information prescription Introduction Swine flu is a relatively new strain of influenza (flu) that was responsible for a flu pandemic during 2009-2010. It is sometimes known as H1N1 influenza
The Unfinished Agenda in Global Health. Richard Skolnik
 The Unfinished Agenda in Global Health Richard Skolnik Objectives Objectives: What do poor people in poor countries get sick and die from? What are the risk factors for this burden of disease? What can
The Unfinished Agenda in Global Health Richard Skolnik Objectives Objectives: What do poor people in poor countries get sick and die from? What are the risk factors for this burden of disease? What can
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Downloaded from
 Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
Data on burden of pneumonia in the country is limited
 Data on burden of pneumonia in the country is limited Top Killer of Children: Pneumonia Maria Rosario Z. Capeding, M.D. Research Institute for Tropical Medicine Pneumonia remains to be a major cause of
Data on burden of pneumonia in the country is limited Top Killer of Children: Pneumonia Maria Rosario Z. Capeding, M.D. Research Institute for Tropical Medicine Pneumonia remains to be a major cause of
Lecture Notes. Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia
 Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Respiration.notebook March 07, Unit 3. Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Hodgkin s Disease STSE
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN. IAP UG Teaching slides
 PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN 1 INTRODUCTION 156 million new episodes / yr. worldwide 151 million episodes developing world 95% in developing countries 19% of all deaths in children
PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN 1 INTRODUCTION 156 million new episodes / yr. worldwide 151 million episodes developing world 95% in developing countries 19% of all deaths in children
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 - 1 - - - 1 P a g e بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم This sheet was made from record section 1 all information are included - Introduction Our respiratory tract is divided anatomically to upper (URT),middle and
- 1 - - - 1 P a g e بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم This sheet was made from record section 1 all information are included - Introduction Our respiratory tract is divided anatomically to upper (URT),middle and
Tiredness/Fatigue Mild Moderate to severe, especially at onset of symptoms Head and Body Aches and Pains
 What is the difference between a cold COLD FLU and the flu? How it starts Symptoms It s Cold and Flu Season in Snohomish County! Colds and Flu are respiratory illnesses caused by viruses. Our Immune Systems
What is the difference between a cold COLD FLU and the flu? How it starts Symptoms It s Cold and Flu Season in Snohomish County! Colds and Flu are respiratory illnesses caused by viruses. Our Immune Systems
CHILDREN S SERVICES. Patient information Leaflet BRONCHIOLITIS
 CHILDREN S SERVICES Patient information Leaflet BRONCHIOLITIS Sept 2014 INTRODUCTION This leaflet aims to help you understand bronchiolitis, how to make your child comfortable and when to contact for emergency
CHILDREN S SERVICES Patient information Leaflet BRONCHIOLITIS Sept 2014 INTRODUCTION This leaflet aims to help you understand bronchiolitis, how to make your child comfortable and when to contact for emergency
Upper Respiratory Infections PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET. Clinical Governance. Dr David Gilliland FY2
 Version: 2.0 Upper Respiratory Infections PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET Authorised by: (Also state if external document) Clinical Governance Date authorised: June 2017 Next review date: June 2020 Document
Version: 2.0 Upper Respiratory Infections PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET Authorised by: (Also state if external document) Clinical Governance Date authorised: June 2017 Next review date: June 2020 Document
Objectives. Case Presentation. Respiratory Emergencies
 Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
IMCI Health Facility Survey
 IMCI Health Facility Survey Sudan March - April 23 World Health Organization Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean Federal Ministry of Health Republic of Sudan OBJECTIVES 1 To assess the quality
IMCI Health Facility Survey Sudan March - April 23 World Health Organization Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean Federal Ministry of Health Republic of Sudan OBJECTIVES 1 To assess the quality
A STUDY ON PREVALENCE OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS(ARI) IN UNDER FIVE CHILDREN IN URBAN AND RURAL COMMUNITIES OF AHMEDABAD DISTRICT, GUJARAT
 Original Article.. A STUDY ON PREVALENCE OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS(ARI) IN UNDER FIVE CHILDREN IN URBAN AND RURAL COMMUNITIES OF AHMEDABAD DISTRICT, GUJARAT Bipin Prajapati 1, Nitiben Talsania
Original Article.. A STUDY ON PREVALENCE OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS(ARI) IN UNDER FIVE CHILDREN IN URBAN AND RURAL COMMUNITIES OF AHMEDABAD DISTRICT, GUJARAT Bipin Prajapati 1, Nitiben Talsania
BMJ Open. Secondary Subject Heading: Infectious diseases, Paediatrics, Respiratory medicine
 Follow up of severe pneumonia children at day-care clinic/hospital after an observational and randomized controlled study in Bangladesh Journal: BMJ Open Manuscript ID: bmjopen-0-000 Article Type: Research
Follow up of severe pneumonia children at day-care clinic/hospital after an observational and randomized controlled study in Bangladesh Journal: BMJ Open Manuscript ID: bmjopen-0-000 Article Type: Research
Study of risk factors of acute respiratory infections in children admitted in a tertiary care hospital of Southern Maharashtra
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Kaware AC et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Sep;4(9):3129-3134 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Kaware AC et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Sep;4(9):3129-3134 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu
 INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
Improving the prevention, diagnosis and clinical management of sepsis
 SEVENTIETH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A70/13 Provisional agenda item 12.2 13 April 2017 Improving the prevention, diagnosis and clinical management of sepsis Report by the Secretariat 1. The Executive Board
SEVENTIETH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A70/13 Provisional agenda item 12.2 13 April 2017 Improving the prevention, diagnosis and clinical management of sepsis Report by the Secretariat 1. The Executive Board
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple)
 Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Peterborough County-City Health Unit Pandemic Influenza Plan Section 1: Introduction
 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction...1-2 1.1 Background...1-2 1.2 Why Does Peterborough County and City Need a Plan for Influenza Pandemic?...1-2 1.3 About Influenza...1-3 1.4 When Does Influenza Become
TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction...1-2 1.1 Background...1-2 1.2 Why Does Peterborough County and City Need a Plan for Influenza Pandemic?...1-2 1.3 About Influenza...1-3 1.4 When Does Influenza Become
Update /Le point. Integrated management of the sick child* World Health Organization, Division of Diarrhoeal and Acute Respiratory Disease Control1
 Update /Le point Integrated management of the sick child* World Health Organization, Division of Diarrhoeal and Acute Respiratory Disease Control1 Diarrhoea, pneumonia, measles, malaria and malnutrition
Update /Le point Integrated management of the sick child* World Health Organization, Division of Diarrhoeal and Acute Respiratory Disease Control1 Diarrhoea, pneumonia, measles, malaria and malnutrition
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum
 The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
County of Santa Cruz. General Questions About Measles HEALTH SERVICES AGENCY. Public Health Division. What is measles?
 County of Santa Cruz Public Health Division HEALTH SERVICES AGENCY POST OFFICE BOX 962, 1080 EMELINE AVE., SANTA CRUZ, CA 95060 TELEPHONE: (831) 454-4000 FAX: (831) 454-4770 General Questions About Measles
County of Santa Cruz Public Health Division HEALTH SERVICES AGENCY POST OFFICE BOX 962, 1080 EMELINE AVE., SANTA CRUZ, CA 95060 TELEPHONE: (831) 454-4000 FAX: (831) 454-4770 General Questions About Measles
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
 Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Invasive Pneumococcal Disease) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic
Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Invasive Pneumococcal Disease) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic
Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics)
 Page 1 of 8 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2014 UpToDate Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics) Authors Thomas J Marrie, MD Thomas M File, Jr, MD Section Editor John
Page 1 of 8 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2014 UpToDate Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics) Authors Thomas J Marrie, MD Thomas M File, Jr, MD Section Editor John
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Nursing care for children with respiratory dysfunction
 Nursing care for children with respiratory dysfunction 1 Lung Development Specific Immunity to Respiratory Infection Secretory IgA in mucosal immunity IgG in systemic immunity Risk Factors Associated with
Nursing care for children with respiratory dysfunction 1 Lung Development Specific Immunity to Respiratory Infection Secretory IgA in mucosal immunity IgG in systemic immunity Risk Factors Associated with
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
A Guide for Parents. Protect your child. What parents should know. Flu Information The Flu:
 Flu Information The Flu: A Guide for Parents Influenza (also known as flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. Flu is different from
Flu Information The Flu: A Guide for Parents Influenza (also known as flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. Flu is different from
In the United States, flu season runs from October to May, with most cases occurring between late December and early March.
 Partners in Pediatrics, PC 7110 Forest Ave Suite 105 Richmond, VA 23226 804-377-7100 Influenza (Flu) Influenza, commonly known as "the flu," is a highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory tract.
Partners in Pediatrics, PC 7110 Forest Ave Suite 105 Richmond, VA 23226 804-377-7100 Influenza (Flu) Influenza, commonly known as "the flu," is a highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory tract.
Part 3- Biology Paper 1 Infection and Response Application Questions Triple Science
 Part 3- Biology Paper 1 Infection and Response Application Questions Triple Science 1 AQA Biology (8461) from 2016 Topic B4.3 Infection and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Explain what a pathogen
Part 3- Biology Paper 1 Infection and Response Application Questions Triple Science 1 AQA Biology (8461) from 2016 Topic B4.3 Infection and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Explain what a pathogen
AOHS Global Health. Unit 1, Lesson 3. Communicable Disease
 AOHS Global Health Unit 1, Lesson 3 Communicable Disease Copyright 2012 2016 NAF. All rights reserved. A communicable disease is passed from one infected person to another The range of communicable diseases
AOHS Global Health Unit 1, Lesson 3 Communicable Disease Copyright 2012 2016 NAF. All rights reserved. A communicable disease is passed from one infected person to another The range of communicable diseases
How It Spreads Symptoms Can Include Complications
 OUR BEST SHOT: The Importance of Vaccines for Older Adults VACCINES QUICK GUIDE TO VACCINATION FOR ADULTS AGES 60+ Vaccines are an important step in protecting your health and the health of your family.
OUR BEST SHOT: The Importance of Vaccines for Older Adults VACCINES QUICK GUIDE TO VACCINATION FOR ADULTS AGES 60+ Vaccines are an important step in protecting your health and the health of your family.
Rotavirus Factsheet What you need to know about Rotavirus
 THE REPUBLIC OF UGANDA MINISTRY OF HEALTH Introduction Rotavirus Factsheet What you need to know about Rotavirus Rotavirus infection is the leading cause of diarrhoea in children under 5 years of age worldwide.
THE REPUBLIC OF UGANDA MINISTRY OF HEALTH Introduction Rotavirus Factsheet What you need to know about Rotavirus Rotavirus infection is the leading cause of diarrhoea in children under 5 years of age worldwide.
DIARRHEAL DISEASE MESSAGING
 DEFEATDD.ORG DIARRHEAL DISEASE MESSAGING PATH developed these messages for use by anyone interested in communicating the impact of diarrhea on the health and development of children and families around
DEFEATDD.ORG DIARRHEAL DISEASE MESSAGING PATH developed these messages for use by anyone interested in communicating the impact of diarrhea on the health and development of children and families around
Training Your Caregiver: Flu Prevention and Treatment for Disabled and the Elderly
 Training Your Caregiver: Flu Prevention and Treatment for Disabled and the Elderly Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a contagious illness that can be severe and life threatening, especially for
Training Your Caregiver: Flu Prevention and Treatment for Disabled and the Elderly Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a contagious illness that can be severe and life threatening, especially for
Seasonal Influenza in Pregnancy and Puerperium Guideline (GL1086)
 Seasonal Influenza in Pregnancy and Puerperium Guideline (GL1086) Approval Approval Group Job Title, Chair of Committee Date Maternity & Children s Services Clinical Governance Committee Chair, Maternity
Seasonal Influenza in Pregnancy and Puerperium Guideline (GL1086) Approval Approval Group Job Title, Chair of Committee Date Maternity & Children s Services Clinical Governance Committee Chair, Maternity
Cough Associated with Bronchitis
 Cough Associated with Bronchitis Bronchitis (bron-ki-tis) is a condition in which the bronchial tubes, the tubes that carry air to your lungs, become inflamed. People who have bronchitis often have a cough
Cough Associated with Bronchitis Bronchitis (bron-ki-tis) is a condition in which the bronchial tubes, the tubes that carry air to your lungs, become inflamed. People who have bronchitis often have a cough
Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from?
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
Viruses, bacteria, fungus, parasites (in rare cases) or other organisms can cause pneumonia.
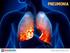 1 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection which inflames the air sacs either in one or both of the lungs. The air sacs are generally filled with fluid or pus, causing cough along with phlegm or pus, fever,
1 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection which inflames the air sacs either in one or both of the lungs. The air sacs are generally filled with fluid or pus, causing cough along with phlegm or pus, fever,
Impact of Immunization on Under 5 Mortality
 Annals of Community Health (AoCH) pissn 2347-5455 eissn 2347-5714 An Indexed (Index Medicus, DOAJ and More), Peer Reviewed, Quarterly, International Journal focusing exclusively on Community Medicine and
Annals of Community Health (AoCH) pissn 2347-5455 eissn 2347-5714 An Indexed (Index Medicus, DOAJ and More), Peer Reviewed, Quarterly, International Journal focusing exclusively on Community Medicine and
Original Article Zinc supplementation for the treatment of severe pneumonia in hospitalized children: A randomized controlled trial
 Original Article Zinc supplementation for the treatment of severe pneumonia in hospitalized children: A randomized controlled trial Nazia Shehzad (1), Muhammd Irfan Anwar (2), Tahira Muqaddas (1) (1) Lahore
Original Article Zinc supplementation for the treatment of severe pneumonia in hospitalized children: A randomized controlled trial Nazia Shehzad (1), Muhammd Irfan Anwar (2), Tahira Muqaddas (1) (1) Lahore
Vaccines for Children
 Vaccines for Children 0-9 old Our goal is to offer your family the best care possible, which includes making sure your child is up to date on all vaccines. DTaP (Diptheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) Vaccine
Vaccines for Children 0-9 old Our goal is to offer your family the best care possible, which includes making sure your child is up to date on all vaccines. DTaP (Diptheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) Vaccine
