Can you hear Me Now? Created by Staff Scientist Joanna Correa Connecticut Science Center
|
|
|
- Winifred Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. Can you hear Me Now? Created by Staff Scientist Joanna Correa Connecticut Science Center April 2011
2 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. Table of Contents Section Page SCIENCE STATE FRAMEWORKS... 3 HEALTH STATE STANDARDS... 3 Core Science Curriculum Frameworks... 4 UNDERLYING CONCEPTS: STUDENTS SHOULD UNDERSTAND THAT:... 4 GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS: STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO:... 4 CMT EXPECTED PERFORMANCES... 4 AGE APPROPRIATENESS... 4 Type of Program... 5 Duration of Program... 5 Attendance Capacity and Space Accommodations... 5 Languages... 5 Disclaimer... 6 Can You Hear Me Now?... 6 General Description... 6 PROGRAM OBJECTIVES... 7 KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS DELIVERY OF THE PROGRAM SAFETY CONNECTICUT SCIENCE CENTER CONNECTIONS GOING FURTHER Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
3 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. Can You Hear Me Now? 5.2. Science: Sense organs: The Sense of Hearing Science Enrichment: Physiology Health Standard # 1: Core Concepts of Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Health Standard # 3: Self Management of Healthy Behaviors This program is part of the CHEFA grant initiatives on Science and Health Education for the 5 th grade. Science State Frameworks Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. Enrichment Content Standard for High School Science in Physiology: Organisms have a variety of mechanisms to combat disease: The skin provides nonspecific defenses against infection. Health State Standards P.1.3. Identify and describe functions of body parts (e.g. ears) P.1.9. Discuss germs and their connection to illness H.1.1. Analyze how behaviors can affect health maintenance and disease prevention P.3.3. Identify personal health and cleaning behaviors that might need to be discussed with a healthcare professional and may need to be changed. E.3.5. Develop and practice safety techniques to avoid and reduce injury and disease 250 Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
4 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. Core Science Curriculum Frameworks 5.2.a. The sense organs perceive stimuli from the environment and send signals to the brain through the nervous system. Underlying Concepts: Students should understand that: 1. Animals have sense organs that are structured to gather information about their environment. Information perceived by the senses allows animals to find food, water, mates and protection. 2. Each sense organ perceives specific kinds of stimuli. Some human senses are more or less developed than the senses of other animals. 4. The human ear is structured to collect sound vibrations from the environment and pass them through the middle ear (eardrum and small bones) and inner ear (hair lined tubes) to the auditory nerve where they are transformed into electrical signals that are sent to different parts of the brain. SCIENTIFIC LITERACY TERMINOLOGY: sense organ, vibration. Grade Level Expectations: Students should be able to: 1. Explain the role of the sensory organs the ears, in perceiving stimuli (e.g., sound) and sending signals to the brain. 5. Identify the major structures of the human ear, and explain their functions. CMT Expected Performances B21. Science Curriculum: Describe the structure and function of the human sense of hearing and the signals it perceives. Age Appropriateness Age Appropriateness: 6 and Up School grades: This program can be presented to 1 st graders and up. Student interest has been observed from 1 st grade, and up to 9 th grade. 250 Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
5 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. IMPORTANT NOTE TO THE TEACHER: This program presents science and medical content, on the subject matter of the sense of hearing and the human ear. Students of different ages are more or less familiarized with the human body and its many parts, such as the ears. To maximize their learning experience and the enjoyment of your students, the program will be adapted delivered to the grade level or average age of the group. Please be sure to communicate in advance, to the presenting Staff Scientist the approximate age level and school grade of your group(s) of students. It is advisable to do this during the making of arrangements to attend the program. Type of Program Gallery Floor hands-on presenter guided activity. Duration of Program Each presentation of the program will last up to 30 minutes, depending on the size of the group. The size of the attending group should be mentioned during the making of arrangements to the program. The program can be arranged to be presented multiple times by prior request, to meet the requirements for larger groups. For multiple presentations, there will be a reset and clean up time between presentations to prepare for the next group. Please make sure to discuss scheduling details with the presenting Staff Scientist at the time of arranging your group s attendance to this Gallery Program. Attendance Capacity and Space Accommodations The physical setting can accommodate approximately up to 20 people. There will be active participants and passive audience, and /or those waiting for their turn. Maximum group size of participating students per session of presentation: 16 students. They will not all be active at the same time but will take turns. Setting accommodations: Some parts of the activity are to be done while standing and others will be done sitting. The activity is accessible for students on wheel chairs. Languages The program is delivered in English, but currently the option of having the program delivered in Spanish, or bilingually, depending on your group s needs is available. 250 Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
6 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. Languages other than English, in which the program can be delivered is subject to the availability of presenters with the skill. For inquiries about particular language requests, please contact the Staff Scientists in advance prior to your visit. Disclaimer The information provided by this program and contained in this written program package is for informational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice and is not intended to supplement or replace medical care or information provided by a qualified health care professional. The Connecticut Science Center and the creators, authors and presenters of this program assume no responsibility, and shall not be liable, for any damages or injury resulting from your reliance on any information provided by this program or contained in the written program package. Can You Hear Me Now? General Description Learn the structure and function of the sense of hearing organs: The Ears. Explore the form and function of the outer ear s canal and discover how the ear canal is involved in our hearing, much more than we had given thought to! Students will go through a hands-on guided activity using otoscopes to look inside ear canals of life size simulated human ears. Students will get a comprehensive look at the outer ear parts: the ear canal, the eardrum and the earwax that are present in a normal and healthy ear. 250 Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
7 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. Students will explore some normal and abnormal conditions of the ear canal and tympanic membrane, like the presence of ear wax, infections and foreign bodies. Proper ear care practices will also be discussed. The program will give a special emphasis on ear wax: its production, function, and its importance as part of the immune system to keep germs out and off. Program Objectives After completing this program, attending students should have gained some understanding on: 1. The sense of Hearing organ: the Ear What is the Ear? 1.2. What are the ears for? 1.3. What else do they do? THE HUMAN EAR: The ears are the sense organs of hearing. They allow us to hear and to have body balance when we walk or are standing up. 2. The Parts of the Ear: 2.3. inner ear 2.1. Outer ear 2.2. middle ear PARTS OF THE EAR: The part of the ear that we can see and touch is called outer ear. Our ears have more parts. These parts we don t see, because they are inside our heads. The parts inside our head are called middle ear and inner ear. When the doctor looks inside the ear with an otoscope, he sees the ear canal and the eardrum. He also sees Earwax and sometimes, other things. Healthy ears have earwax. A Healthy Eardrum is of a uniform pinkish gray color. An infected eardrum looks red and swollen. 3. A Healthy ear canal and eardrum: 3.1. Earwax 250 Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
8 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms The Eardrum or Tympanic membrane EAR WAX: Ear wax is a soft, natural oily and sticky substance that is excreted by the skin inside the ear canal. Its function is to act as a water repellent and to keep the ear canal and ear drum protected. Any foreign object, be it dust, bacteria or small insects, get trapped in the ear wax before getting inside to damage the ear. The ear wax then dries out and falls out, keeping the ear clean. The Eardrum or Tympanic membrane is the membrane that separates the outer ear from the internal ear (middle ear and inner ear). The eardrum vibrates to sound, so that we can hear. 4. Unhealthy ears can be painful Am I cleaning too much? Is this dangerous for my ears? 4.2. What is an ear infection? 4.3. What is a pierced eardrum? 4.4. Strange things that can get inside the ears What do we do?? Even though earwax seems yucky, it serves an important purpose. Therefore, it should not be removed. Too much cleaning can leave the ear unprotected and more susceptible to ear infections. An ear infection is an inflammation of the ear, caused by a bacterium, virus or fungus proliferating in there. Some people suffer ear injuries in which the eardrum membrane gets ruptured. This is a pierced eardrum. Sometimes eardrums can be pierced by placing foreign objects inside the ear: like cotton swabs, pencils, other objects, or sometimes foreign objects can get inside the ear accidentally, like flying or crawling small insects. All this situations are solved by the Ear Doctor. 5. Proper Ear Care: 5.1. Just clean the opening of your Ears Don t put anything smaller than your elbows in your ears. Wash your ears with soap and water during your shower, or just clean the opening of your ear gently with a washcloth. There's an old saying that you shouldn't put anything smaller than your elbow in your ear. Not all old sayings are true, but this one is! You can hurt your ear by 250 Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
9 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. poking around in there. It's not even a good idea to use a cotton swab. This can push wax deeper in your ear, where it can get stuck. Irritating the ear canal with a cotton swab can even lead to an ear canal infection. And definitely don't put anything sharp in your ear because it can cause bleeding or serious damage. If you think you have dirt or too much earwax in your ear, ask your mom or dad to help you clean it out. 250 Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
10 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. Key Terms and Concepts Physiology Science that studies the how does the body and the individual body parts (like the organs), of living things work. Physiologists are Biology scientists. Ear Canal The ear canal is the tunnel, or ear hole through which sound travels to the inside of the ear, The Ear Canal stops at the Eardrum. The Eardrum (or Tympanic Membrane) Is a thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves reach it. It separates the ear canal and outer ear from the inner ear and middle ear. The Eustachian tube Is another tube-like part of the ear, but this one is located close to the nose and throat, that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose; it is lined with mucus just like the nose and throat. The Eustachian tubes equalize the pressure between the inside of the ears and the air outside. When you "pop" your ears as you change altitude (going up a mountain or in an airplane), you are equalizing the air pressure in your middle. You do this passing air through your Eustachian tubes. Not only air passes through them, also fluid from your middle ear to your nasal passages. Cold, flu, and allergies can irritate the Eustachian tube and cause the lining of this passageway to become swollen. Nervous System /Auditory nerve The Auditory nerve carries sound in the form of electrochemical signals to your brain. Your brain notices the sound. The auditory nerve begins in your inner ear (at the cochlea) and is connected to your brain. Earwax Also called Cerumen by health care professionals, Ear wax is an oily soft, substance produced by your ears. It is excreted by skin glands in the linning of the ear canal. People of all ages are constantly producing ear wax. And just as we produce it, we shed it off! Yes, earwax dries and flakes and comes out on its own, without us even noticing it. Ear wax acts as a water repellent and also keeps the ear canal and ear drum protected. Any foreign object, be it dust, bacteria or gnats or small insects, get trapped in the ear wax before getting inside to 250 Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
11 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. damage the ear. As the old dry ear wax falls out with all the things it trapped, keeps he ears clean. Infection Ear Infections are called Otitis by scientists. Oti means ear and itis means inflammation. Therefore to have an ear infection means that our ears are tender, probably swollen, most likely in pain, and inflammation reaction is going on. The reaction is against agents that caused the inflammation process or infection. These ear infection causing agents are bacterium, viruses or even fungus. When the infection was caused by a fungus it s called Otomycosis. Ruptured Eardrum When too much fluid builds up in the middle ear, it can put pressure on the eardrum until it ruptures. Signs of a ruptured eardrum include yellow, brown, or white fluid draining from the ear. Pain may disappear suddenly because the pressure of the fluid on the eardrum is gone. Although a ruptured eardrum sounds frightening, it usually heals itself in a couple of weeks. Cotton Swabs Cotton swabs are not a good idea. Cotton threads often stay in, harboring bacteria. The cotton swabs can also be lodged too deep or the child can suddenly move and the swab can puncture the ear drum. Ear Tubes Ear tubes are little plastic tube devices placed by doctors to let fluid drain out of the middle ear and prevent fluid from building back up. This can decrease pressure and pain, while restoring hearing. The tubes are usually left in for 8 to 18 months until they fall out on their own. Swimmer s Ear Swimmer's ear is an infection that occurs when water is trapped in the external ear canal. Bacteria breed in the water and cause pain, swelling, and itching of the outer ear. Although it's often associated with swimming, anyone can get swimmer's ear. The condition is usually treated with ear drops and is not a cause of middle ear infections. 250 Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
12 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. Delivery of the Program Activity 1: Introduction to the Ears as the Organs of the Sense of Hearing and Body Balance. Sounds will be played as we explore the ears as sense of hearing organs and a balance test will be done which aims at understanding the part that ears play at maintaining body balance when standing up and walking. Activity 2: Introduction to the Ear Canal. What do you think we would find inside our ears if we could look inside?? Notice and Wonder Activity 3: Ear Exam: The students will examine the ears of ear simulators and other sets of ears, using the medical tool for that purpose: The Otoscope. The will be shown first 1) normal healthy ear canals with Ear Wax. They will be shown isolated earwax (simulated) in Petri dishes and earwax will be discussed. Then they will be shown other sets of ears with pathological or injured conditions: 2) Ear Infections, 3) Ruptured Eardrums and 4) Foreign object inside ear canal. The foreign object will be removed following the appropriate technique usually performed at healthcare institutions. Activity 4: Proper Ear care practices will be shown and discussed. Cotton swabs in? or Cotton Swabs out? Safety Prior to coming to this gallery program review with your students expectations for appropriate behavior, handling of materials, and cooperative group procedures to be sure the activities are accessible and above all, safe for all. Once at the site, supervise your group. Students will be expected to behave according to common practices in laboratory settings: wear safety protective barriers (like gloves, aprons and goggles) if they are instructed to do so, do not strike objects or handle them roughly, listen to instructions carefully, and make sure materials are handled appropriately. Latex gloves are not used in the science center; however please check in advance for the presence of allergies to nitrile or vinyl, since safety materials made of these compounds might be present. Although rare, some skin reactions to nitrile have been observed. 250 Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
13 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. For more comprehensive information on science safety, consult the guidelines from the Council of State Science Supervisors; Connecticut Department of Education: Connecticut Science Center Connections Sight and Sound Experience Exhibits 4 North Sight and Sound Gallery Rube Goldberg Machines Exhibit 5 North Invention Dimension Gallery Discovery Center 5.1 Sound Program: Ride the Wave Discovery Labs. Discovery Center 5.2 Senses Program: Making Sense of Your Senses Discovery Labs. Connecticut Science Center Outreach Program Sound. Going Further 1. American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) Tomahawk Creek Parkway Leawood, KS , (913) ; (800) : 2. American Academy of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery One Prince St. Alexandria, VA (703) : 3. Your Gross and Cool Body 4. Kids Health: 5. Family Doctor: Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version
14 CT Perceiving and responding to information about the environment is critical to the survival of organisms. Gallery Science 5.2 Can You Hear Me Now? * Find the Staff Scientist in the Body LAB! 5 th Floor south Draw a diagram of an ear with the ear canal and the position of the eardrum Draw a healthy Eardrum What substance should be there? Draw an injured or unhealthy Eardrum What is wrong with it? How did that happen? How can you keep your ears healthy? *If you wish for your students to take advantage of this Gallery Science program, you must make arrangements with a Gallery Scientist 30 days prior to your visit. For more information please contact Joanna Correa at jcorrea@ctsciencecenter.org 250 Columbus Blvd. Hartford, CT Version Page 14
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Otitis Media. Anatomy & Hearing Our ears are very specialized organs that allow us to hear and keep our balance.
 Otitis Media Introduction Otitis media is a middle ear infection. 75% of all children experience at least one episode of otitis media before they turn 3 years old. If otitis media is left untreated, it
Otitis Media Introduction Otitis media is a middle ear infection. 75% of all children experience at least one episode of otitis media before they turn 3 years old. If otitis media is left untreated, it
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1
 SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
What causes swimmer s ear?
 Swimmer s Ear Affecting the outer ear, swimmer s ear is a painful condition resulting from inflammation, irritation, or infection. These symptoms often occur after water gets trapped in your ear, with
Swimmer s Ear Affecting the outer ear, swimmer s ear is a painful condition resulting from inflammation, irritation, or infection. These symptoms often occur after water gets trapped in your ear, with
The Human Ear. Grade Level: 4 6
 The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
Gangguan Telinga. Ruptur Gendang Telinga. Mula Tarigan, S.Kp
 Gangguan Telinga Ruptur Gendang Telinga Mula Tarigan, S.Kp Ruptured eardrum Introduction A ruptured (perforated) eardrum is a tear or a hole in eardrum (tympanic membrane), the thin membrane that separates
Gangguan Telinga Ruptur Gendang Telinga Mula Tarigan, S.Kp Ruptured eardrum Introduction A ruptured (perforated) eardrum is a tear or a hole in eardrum (tympanic membrane), the thin membrane that separates
MIDDLE EAR INFECTIONS
 MIDDLE EAR INFECTIONS A Guide to Treatment and Prevention A Common Problem Middle ear infections are due to a buildup of fluid in the middle ear. This is a common problem in younger children, whose ears
MIDDLE EAR INFECTIONS A Guide to Treatment and Prevention A Common Problem Middle ear infections are due to a buildup of fluid in the middle ear. This is a common problem in younger children, whose ears
Norwood Science Center
 Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Special Senses Lecture Notes
 Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Special Senses Lecture Notes 4.04 Describe the Special Senses A. Smell Smell occurs when specialized cells in the nose (chemoreceptors) detect certain chemicals resulting in
Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Special Senses Lecture Notes 4.04 Describe the Special Senses A. Smell Smell occurs when specialized cells in the nose (chemoreceptors) detect certain chemicals resulting in
Ear Exam and Hearing Tests
 Ear Exam and Hearing Tests Test Overview A thorough evaluation of a person's hearing requires an ear exam and hearing tests. In children, normal hearing is important for language to develop correctly.
Ear Exam and Hearing Tests Test Overview A thorough evaluation of a person's hearing requires an ear exam and hearing tests. In children, normal hearing is important for language to develop correctly.
Assisting in Otolaryngology
 Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Glue ear/grommets Child health
 Glue ear/grommets Child health Patient information How to contact us Watford General Hospital West Hertfordshire Hospitals NHS Trust Watford Hertfordshire WD18 0HB If you need this leaflet in another language,
Glue ear/grommets Child health Patient information How to contact us Watford General Hospital West Hertfordshire Hospitals NHS Trust Watford Hertfordshire WD18 0HB If you need this leaflet in another language,
Scrub In. What is the function of cerumen? Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into the auditory canal?
 Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Middle Ear Fluid in Young Children: Parent Guide
 Vinod K. Anand, MD, FACS Nose and Sinus Clinic Middle Ear Fluid in Young Children: Parent Guide Purpose of This Booklet This booklet is about middle ear fluid in children ages 1 through 3 who have no other
Vinod K. Anand, MD, FACS Nose and Sinus Clinic Middle Ear Fluid in Young Children: Parent Guide Purpose of This Booklet This booklet is about middle ear fluid in children ages 1 through 3 who have no other
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY. For Better Health and Hearing
 MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears.
 Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
X-Plain Tympanoplasty Reference Summary
 X-Plain Tympanoplasty Reference Summary Introduction Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure to repair a perforated eardrum. The eardrum is a thin membrane inside the ear at the end of the ear canal. Eardrum
X-Plain Tympanoplasty Reference Summary Introduction Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure to repair a perforated eardrum. The eardrum is a thin membrane inside the ear at the end of the ear canal. Eardrum
NATURAL SCIENCES 3 UNIT 3 OUR SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION INTERACTION REPRODUCTION. ü Excretory system
 NATURAL SCIENCES 3 UNIT 3 OUR SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION INTERACTION REPRODUCTION ü Digestive system ü Circulatory system ü The senses ü Nervous system ü Reproductive system
NATURAL SCIENCES 3 UNIT 3 OUR SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION INTERACTION REPRODUCTION ü Digestive system ü Circulatory system ü The senses ü Nervous system ü Reproductive system
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH
 College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION OPTIMYXIN Gramicidin and Polymyxin B Sulfate Oto-Ophthalmic Solution sterile Eye/Ear Drops Antibiotic Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Revision: November 25, 2015 145 Jules-Léger Boucherville,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION OPTIMYXIN Gramicidin and Polymyxin B Sulfate Oto-Ophthalmic Solution sterile Eye/Ear Drops Antibiotic Sandoz Canada Inc. Date of Revision: November 25, 2015 145 Jules-Léger Boucherville,
Treatment of glue ear with grommets
 Treatment of glue ear with grommets Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust This leaflet explains about glue ear, how it can be treated using grommets and
Treatment of glue ear with grommets Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust This leaflet explains about glue ear, how it can be treated using grommets and
Unit 3 Lesson 3 How Do Cells Work Together? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 How Cells Are Organized Cells are organized to work together so the body functions smoothly. How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 1 How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 2 Organ
How Cells Are Organized Cells are organized to work together so the body functions smoothly. How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 1 How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 2 Organ
LESSON ASSIGNMENT , Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-9. TASK TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-833-0059, Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-9. TASK TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-833-0059, Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson,
Chapter 2. The Senses
 Chapter 2. The Senses 2.1 Sensory Receptors (p.25-27) sensory receptors - specialized nerve cells whose function is to collect information about changes in the surrounding environment. sensory organs -
Chapter 2. The Senses 2.1 Sensory Receptors (p.25-27) sensory receptors - specialized nerve cells whose function is to collect information about changes in the surrounding environment. sensory organs -
Assistive Technology Project. Presented By: Rose Aldan
 Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary
 X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary Introduction Tinnitus causes a person to hear a persistent sound in the ear when no sound exists. According to the American Tinnitus Association, at least 12 million
X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary Introduction Tinnitus causes a person to hear a persistent sound in the ear when no sound exists. According to the American Tinnitus Association, at least 12 million
Nervous System. Made of two parts. Central Peripheral
 Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY
 NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours)
 HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
Our Sense Organs Ears
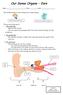 Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
2 Sensing the Environment
 CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
AND THE EARS HAVE IT! (1 Hour)
 (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will explore the nature of human hearing by attempting to determine the location at different locations
(1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will explore the nature of human hearing by attempting to determine the location at different locations
1 ahmadanizahscienceteacher14
 CHAPTER 1: THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES 1.1 THE SENSOR ORGAN AND THEIR FUNCTION 8. The diagram below shows a girl watching a television show 1. Which of the following A,B,C or D is a sensory organ 2. Diagram
CHAPTER 1: THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES 1.1 THE SENSOR ORGAN AND THEIR FUNCTION 8. The diagram below shows a girl watching a television show 1. Which of the following A,B,C or D is a sensory organ 2. Diagram
Myringotomy and Grommets Children s Ward Patient information Leaflet
 Myringotomy and Grommets Children s Ward Patient information Leaflet Page 1 Myringotomy and Grommets Your child is coming into hospital for insertion of grommet(s). The operation is a day case procedure
Myringotomy and Grommets Children s Ward Patient information Leaflet Page 1 Myringotomy and Grommets Your child is coming into hospital for insertion of grommet(s). The operation is a day case procedure
Senses and Sense Organs
 Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
CHAPTER ONE LEARNING AREA: The World Through Our Senses LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
 CHAPTER ONE LEARNING AREA: The World Through Our Senses LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1.1 Sensory Organs and Their Functions 1.2 Our Sense of Touch 1.3 Our Sense of Smell 1.4 Our Sense of Taste 1.5 Our Sense of
CHAPTER ONE LEARNING AREA: The World Through Our Senses LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1.1 Sensory Organs and Their Functions 1.2 Our Sense of Touch 1.3 Our Sense of Smell 1.4 Our Sense of Taste 1.5 Our Sense of
Organs of the Nervous System: brain, spinal cord, and nerves
 Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
Senses. hear. smell. see. taste. touch. Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things.
 Human Body Senses 1 Senses Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things. They also help you to detect pain, pressure, and temperature. All
Human Body Senses 1 Senses Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things. They also help you to detect pain, pressure, and temperature. All
Main Idea and Details Sort
 Main Idea and Details Sort Students are given 4 different main ideas and 12 details. Students must match up the details to the correct main idea. Print the main ideas (page 25) in one color and the details
Main Idea and Details Sort Students are given 4 different main ideas and 12 details. Students must match up the details to the correct main idea. Print the main ideas (page 25) in one color and the details
5. Which word refers to making
 Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
PNEUMONIA. Your Treatment and Recovery
 PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS
 Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS
 Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide
 E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
Follow us on Find us on Facebook at Visit our website:
 Audiology Service Ear wax Information for you Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other formats
Audiology Service Ear wax Information for you Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other formats
Sound and hearing 2 The outside of the ear. Sound and hearing 1 How sounds get to our ears
 Sound and hearing 1 How sounds get to our ears 1. What are some of the sounds you would hear if you were camping on a quiet night? 2. How would you feel if you couldn t hear anything? When you listen to
Sound and hearing 1 How sounds get to our ears 1. What are some of the sounds you would hear if you were camping on a quiet night? 2. How would you feel if you couldn t hear anything? When you listen to
UNIT 5. INTERACTION AND HEALTH. PRIMARY 4 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 5. INTERACTION AND HEALTH PRIMARY 4 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández INTERACTION It is a vital function of living things. Human beings have five senses: sight, hearing, smell, taste
UNIT 5. INTERACTION AND HEALTH PRIMARY 4 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández INTERACTION It is a vital function of living things. Human beings have five senses: sight, hearing, smell, taste
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Special Senses. Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition)
 Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
The bloom guide to better hearing. Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide
 The bloom guide to better hearing Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide Let us help you find the best solution for your hearing Coming to terms with
The bloom guide to better hearing Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide Let us help you find the best solution for your hearing Coming to terms with
Cochlear Implant The only hope for severely Deaf
 Cochlear Implant The only hope for severely Deaf By: Dr. M. Sohail Awan, FCPS (ENT) Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi - Pakistan For centuries, people believed that only a miracle could restore hearing
Cochlear Implant The only hope for severely Deaf By: Dr. M. Sohail Awan, FCPS (ENT) Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi - Pakistan For centuries, people believed that only a miracle could restore hearing
Biology. Slide 1 of 49. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Protect Your Hearing!
 Protect Your Hearing! What is noise? Loud sounds if they are over 85 db can be damaging. How do I know if I am listening to levels above 85dB? It is invisible, tasteless, odorless, and IGNORED as a form
Protect Your Hearing! What is noise? Loud sounds if they are over 85 db can be damaging. How do I know if I am listening to levels above 85dB? It is invisible, tasteless, odorless, and IGNORED as a form
TASTE: Taste buds are the sense organs that respond to gustatory stimuli. Chemoreceptors that respond to chemicals broken down from food in the saliva
 UNIT 5: Nervous System- Senses Somatic Senses Somatic senses are associated with receptors in the skin, muscles, joints, and viscera (organs of the body) Include senses of touch, pressure, temperature,
UNIT 5: Nervous System- Senses Somatic Senses Somatic senses are associated with receptors in the skin, muscles, joints, and viscera (organs of the body) Include senses of touch, pressure, temperature,
Pneumonia. Trachea , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. id Last reviewed: 11/11/2017 1
 Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
taste hearing smell sight Our sense of touch is in the skin that covers our body, especially in our hands.the skin is very sensitive.
 2. Now listen and complete the text: 2 a. Our sense of touch is in our skin. We use our skin to feel. b. Our sense of sight is in our eyes. We use our eyes to see. c. Our sense of hearing is in our ears.
2. Now listen and complete the text: 2 a. Our sense of touch is in our skin. We use our skin to feel. b. Our sense of sight is in our eyes. We use our eyes to see. c. Our sense of hearing is in our ears.
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing Loss. How does the hearing sense work? Test your hearing
 Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
MASTOID EXPLORATION (MASTOID SURGERY) AND MASTOIDECTOMY
 MASTOID EXPLORATION (MASTOID SURGERY) AND MASTOIDECTOMY This information leaflet is to support your decision with your Specialist. This leaflet will explain about the ear are and what surgery can be offered
MASTOID EXPLORATION (MASTOID SURGERY) AND MASTOIDECTOMY This information leaflet is to support your decision with your Specialist. This leaflet will explain about the ear are and what surgery can be offered
Revised 12/10. Copyright 2003 St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Page 1 of 5
 Some treatments, such as starting an IV or putting a needle in a port, are painful. Whenever possible, your child should have the option of reducing this pain as much as possible. One way to not feel the
Some treatments, such as starting an IV or putting a needle in a port, are painful. Whenever possible, your child should have the option of reducing this pain as much as possible. One way to not feel the
CAST CARE. Helping Broken Bones Heal
 CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
Guess: Correct or Incorrect. Trial (perform in random order)
 AP Biology Senses Lab Names Per. Our senses are constantly bombarded with various stimuli from the environment, which are relayed to the central nervous system where the information is interpreted. In
AP Biology Senses Lab Names Per. Our senses are constantly bombarded with various stimuli from the environment, which are relayed to the central nervous system where the information is interpreted. In
Children s hearing. A guide for parents
 Children s hearing A guide for parents Creating the future Children are our future. By giving them access to a world full of sounds, we can help them to develop the hearing skills they need to build their
Children s hearing A guide for parents Creating the future Children are our future. By giving them access to a world full of sounds, we can help them to develop the hearing skills they need to build their
Converting Sound Waves into Neural Signals, Part 1. What happens to initiate neural signals for sound?
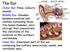 The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
17.4 Sound and Hearing
 You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
Draw a cross section of the human ear and label its parts.
 Human Ear 1. Open the Human Ear session and follow the instructions. 2. Complete the Human Ear worksheet as you progress through the session. Draw a cross section of the ear and label its parts. 3. Using
Human Ear 1. Open the Human Ear session and follow the instructions. 2. Complete the Human Ear worksheet as you progress through the session. Draw a cross section of the ear and label its parts. 3. Using
Surgery to the middle ear to improve hearing (stapedectomy)
 Surgery to the middle ear to improve hearing (stapedectomy) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to
Surgery to the middle ear to improve hearing (stapedectomy) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to
Low? High or. v vv \T\ \ C\ [ \(\(\(\(\ PITCH FREQUENCY CHAPTER4
 CHAPTER4 High or Low? PITCH Another quality that an oscilloscope shows is pitch. Pitch is a measurement of how high or low a sound is. If you make your voice high and squeaky, then it has a high pitch.
CHAPTER4 High or Low? PITCH Another quality that an oscilloscope shows is pitch. Pitch is a measurement of how high or low a sound is. If you make your voice high and squeaky, then it has a high pitch.
Effective Date: August 31, To provide guidelines for the proper administration of ear irrigation
 SUBJECT: EAR IRRIGATION 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 406 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 To provide guidelines for the proper
SUBJECT: EAR IRRIGATION 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 406 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 To provide guidelines for the proper
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093
 Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
Nasolacrimal Duct Blockage
 The eyelids play a key role in protecting the eyes. They help spread moisture (tears) over the surface of the eyes when they close (for example, while blinking); thus, they help prevent the eyes from becoming
The eyelids play a key role in protecting the eyes. They help spread moisture (tears) over the surface of the eyes when they close (for example, while blinking); thus, they help prevent the eyes from becoming
A Patient s Guide to Cervical Foraminotomy
 A Patient s Guide to Cervical Foraminotomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Cervical Foraminotomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Patient & Family Guide. Using TENS for Pain.
 Patient & Family Guide 2017 Using TENS for Pain www.nshealth.ca Using TENS for Pain TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) provides stimulation that your body responds to by making natural
Patient & Family Guide 2017 Using TENS for Pain www.nshealth.ca Using TENS for Pain TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) provides stimulation that your body responds to by making natural
When does ear wax need to be removed? Who is at risk of an ear-wax blockage? What s the link between ear wax and tinnitus?...
 FACTSHEET Hearing health Ear wax Ear wax keeps our ears clean and healthy. It usually works its way out of the ears by itself, but sometimes too much wax can build up and block the ears. This factsheet
FACTSHEET Hearing health Ear wax Ear wax keeps our ears clean and healthy. It usually works its way out of the ears by itself, but sometimes too much wax can build up and block the ears. This factsheet
Aural Care, West Wing Welcome to the Aural Care Service
 Aural Care, West Wing Welcome to the Aural Care Service Who are we and what do we do? We are nurses within the Ear, Nose and Throat department who have undergone specific training to allow us to specialise
Aural Care, West Wing Welcome to the Aural Care Service Who are we and what do we do? We are nurses within the Ear, Nose and Throat department who have undergone specific training to allow us to specialise
Patient/Carer instructions for the administration of Subcutaneous Cytarabine
 Patient/Carer instructions for the administration of Subcutaneous Cytarabine This document covers the following information: What cytarabine is What subcutaneous means What happens if you decide to inject
Patient/Carer instructions for the administration of Subcutaneous Cytarabine This document covers the following information: What cytarabine is What subcutaneous means What happens if you decide to inject
Sound from Left or Right?
 Sound from Left or Right? Pre-Activity Quiz 1. How does our sense of hearing work? 2. Why do we have two ears? 3. How does a stethoscope work? (A device used by doctors to listen to the sound of your heart.)
Sound from Left or Right? Pre-Activity Quiz 1. How does our sense of hearing work? 2. Why do we have two ears? 3. How does a stethoscope work? (A device used by doctors to listen to the sound of your heart.)
2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE
 2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE INTRODUCTION What Students Do in this Activity Students learn more about the form that sound waves take and how humans hear sound. They build a model of a human eardrum
2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE INTRODUCTION What Students Do in this Activity Students learn more about the form that sound waves take and how humans hear sound. They build a model of a human eardrum
Repair of the middle ear
 Repair of the middle ear Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust This leaflet explains repair of the middle ear and what to expect when your child comes
Repair of the middle ear Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust This leaflet explains repair of the middle ear and what to expect when your child comes
Teacher Lesson Plan Let s Get Allergy Aware! Primary (Grades 1-3)
 Teacher Lesson Plan Let s Get Allergy Aware! Primary (Grades 1-3) Respecting Differences Common Allergens Inclusion Hand Washing Healthy Food Choices Signs & Symptoms Epinephrine Topic 1: Respecting Differences
Teacher Lesson Plan Let s Get Allergy Aware! Primary (Grades 1-3) Respecting Differences Common Allergens Inclusion Hand Washing Healthy Food Choices Signs & Symptoms Epinephrine Topic 1: Respecting Differences
SPECIAL SENSES. Anatomy & Physiology
 SPECIAL SENSES Anatomy & Physiology BELL WORK: DEFINE LACRIMAL ACHROMATIC OTOSCOPE TENNITIS VERTIGO STANDARD 25) Define key terms associated with vision disorders, ear disorders, nose disorders, and mouth
SPECIAL SENSES Anatomy & Physiology BELL WORK: DEFINE LACRIMAL ACHROMATIC OTOSCOPE TENNITIS VERTIGO STANDARD 25) Define key terms associated with vision disorders, ear disorders, nose disorders, and mouth
Table of Contents. Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings
 Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Hemodialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY
 Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY WHO KNOWS WHAT HEARING IS? Hearing, auditory perception, or audition is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations, changes in the
Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY WHO KNOWS WHAT HEARING IS? Hearing, auditory perception, or audition is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations, changes in the
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Where kids come first. Your Child and Ear Infections
 17 Where kids come first Your Child and Ear Infections How common are ear infections? Infection of the middle ear, or otitis media, is the most common affliction requiring medical therapy for children
17 Where kids come first Your Child and Ear Infections How common are ear infections? Infection of the middle ear, or otitis media, is the most common affliction requiring medical therapy for children
FUNNELS OF SOUND. Activity Pack. Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears. Neurosciences and Mental Health
 FUNNELS OF SOUND Activity Pack Description: Duration of Activity: Age: Topic: Key words: Resources: Related Activities: Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears No
FUNNELS OF SOUND Activity Pack Description: Duration of Activity: Age: Topic: Key words: Resources: Related Activities: Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears No
Reflecting on Reflexes
 Reflecting on Reflexes Pre-Lesson Quiz 1. What happens when you accidentally touch a hot plate? 2. Name two human reflexes and state how they work. 2 Pre-Lesson Quiz Answers 1. What happens when you accidentally
Reflecting on Reflexes Pre-Lesson Quiz 1. What happens when you accidentally touch a hot plate? 2. Name two human reflexes and state how they work. 2 Pre-Lesson Quiz Answers 1. What happens when you accidentally
3 Ear. Ear is a very important organ of human body which has two important roles comprising our organ of hearing and organ of balance.
 3 Ear Ear is a very important organ of human body which has two important roles comprising our organ of hearing and organ of balance. Common diseases of the ear In this chapter we will cover different
3 Ear Ear is a very important organ of human body which has two important roles comprising our organ of hearing and organ of balance. Common diseases of the ear In this chapter we will cover different
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities SAMPLE
 COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
ENT SURGICAL CONSULTANTS
 ENT SURGICAL CONSULTANTS Thomas K. Kron, MD, FACS Michael G. Gartlan, MD, FAAP, FACS Rajeev H. Mehta, MD, FACS Scott W. DiVenere, MD Sung J. Chung, MD Ankit M. Patel, MD 2201 Glenwood Ave., Joliet, IL
ENT SURGICAL CONSULTANTS Thomas K. Kron, MD, FACS Michael G. Gartlan, MD, FAAP, FACS Rajeev H. Mehta, MD, FACS Scott W. DiVenere, MD Sung J. Chung, MD Ankit M. Patel, MD 2201 Glenwood Ave., Joliet, IL
LEARNING NATIONAL CURRICULUM. Influenza Virus
 This section aims to teach students how poor respiratory hygiene can lead to the spread of microbes and disease. In 2.2, students observe on a large scale how far microbes are carried when they sneeze
This section aims to teach students how poor respiratory hygiene can lead to the spread of microbes and disease. In 2.2, students observe on a large scale how far microbes are carried when they sneeze
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Having a modified radical mastoidectomy. Information for patients Ear Nose and Throat
 Having a modified radical mastoidectomy Information for patients Ear Nose and Throat page 2 of 12 How does the ear work? The ear consists of the ear canal, the middle ear and the inner ear. The ear canal
Having a modified radical mastoidectomy Information for patients Ear Nose and Throat page 2 of 12 How does the ear work? The ear consists of the ear canal, the middle ear and the inner ear. The ear canal
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss
 THE NEW YORK OTOLARYNGOLOGY GROUP, P.C. The Ear, Nose and Throat Specialists Neil M. Sperling, M.D. Otology/Neuro-Otology Diseases of the Ear Facial Nerve Balance Disorders Surgery for Conductive Hearing
THE NEW YORK OTOLARYNGOLOGY GROUP, P.C. The Ear, Nose and Throat Specialists Neil M. Sperling, M.D. Otology/Neuro-Otology Diseases of the Ear Facial Nerve Balance Disorders Surgery for Conductive Hearing
Audiology - Hearing Care Torbay and South Devon. Before you receive your hearing aid
 Audiology - Hearing Care Torbay and South Devon Before you receive your hearing aid How our ears work Our ears are divided into three sections, the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear (see diagram opposite).
Audiology - Hearing Care Torbay and South Devon Before you receive your hearing aid How our ears work Our ears are divided into three sections, the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear (see diagram opposite).
Surgery to the jaw joint (TMJ surgery) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Surgery to the jaw joint (TMJ surgery) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
Surgery to the jaw joint (TMJ surgery) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
What is Otolaryngology? (pronounced oh/toe/lair/in/goll/oh/jee) is the oldest medical specialty in the United States.
 What is Otolaryngology? (pronounced oh/toe/lair/in/goll/oh/jee) is the oldest medical specialty in the United States. Otolaryngologists are physicians trained in the medical and surgical management and
What is Otolaryngology? (pronounced oh/toe/lair/in/goll/oh/jee) is the oldest medical specialty in the United States. Otolaryngologists are physicians trained in the medical and surgical management and
