Sound and hearing 2 The outside of the ear. Sound and hearing 1 How sounds get to our ears
|
|
|
- Dustin Melton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sound and hearing 1 How sounds get to our ears 1. What are some of the sounds you would hear if you were camping on a quiet night? 2. How would you feel if you couldn t hear anything? When you listen to something the sound comes through the ear and it hits the eardrum, then it goes to your brain. Your brain quickly thinks about it and then you will know what to do. Sound is made by something that vibrates. Vibrate means to move quickly backwards and forwards. Science experiment: If you stretch a rubber band between your hands and pluck it, the rubber band will move back and forth and make a humming sound. The hum you hear comes from the vibrations of the rubber band. If you touch the rubber band while it is still humming the hum will stop. This is because you have stopped the vibrations. Place your finger on your throat and hum. You will feel the vibrations. Sound vibrations travel to your ears through the air around us. Sound vibrations traveling through the air are called sound waves. Sound and hearing 2 The outside of the ear On the outside, we see the ear flaps. They are the sound collectors. They are called the pinnae. Why do we have two ears? The sound from one direction reaches one ear a tiny bit sooner than the other. Our brain tells us which direction the sound has come from. Then we can turn in that direction. Try cupping your hand around your ear while you are listening to something. By doing this you will make a larger sound collector and hear the sound more clearly. Many animals have bigger and better sound collectors than we do. Animals can turn their ear flaps to the direction of the sound. If you clap your hands near your dog or cat when it s having a sleep, it will turn the ear flaps to pick up the sound. 1. What are the ear flaps called? 2. Write and draw two animals that have bigger ear flaps than we do. Show the ears. 3. What are vibrations? 4. How do sound vibrations get to our ears?
2 The sense of hearing 3 Inside the ear There are hairs in our ears that are connected to nerves. The nerves carry the sound to the brain. That s when we hear sound. Never poke anything into your ear because it could get stuck in your ear or you could make a hole in the ear drum. Then it couldn t vibrate properly and you couldn t hear properly. Draw and label this picture of the ear. Sound and hearing 4 Inside the ear The inside of the ear has different rooms and pathways. The pathways take twists and turns. It begins with the ear canal. The ear canal has some hairs and sticky ear wax to trap dirt and stop insects from getting in. It leads to the middle ear. Stretched across the entrance to the middle ear is the ear drum. The ear drum is a thin piece of skin that vibrates (shakes) when sound reaches it. Behind the ear drum is an open space filled with air. Three tiny bones go across this space. These bones make the sound louder. They are called the hammer, the anvil and the stirrup. Together they are known as the ossicles. The stirrup touches another piece of thin skin called the oval window. It covers the entrance to the inner ear. Inside the inner ear is a twisty tube called the cochlea. It is shaped like a snail shell. It is filled with liquid and also has thousands of tiny hairs which move back and forth as sound vibrations make the liquid move. The hairs are connected to nerves which carry sound messages to your brain. That s when you hear. 1. Which two parts are made of thin skin? 2. What do the three little bones do?
3 Sound and hearing 5 Vibrations All sounds are made by something vibrating (shaking back and forth very fast). Sound vibrations are called sound waves. They travel can through the air, through water and through solid things. When the vibrations reach our ears, we hear the sound. When you play a musical instrument, part of the instrument vibrates. That makes the air vibrate. The vibrating air travels to your ear and the inside of your ear vibrates. That s when you hear. Most sounds reach us through the air. We hear voices this way. We make a sound when our vocal cords vibrate. If you put your hand on your throat and make a sound you can feel the vibration. Did you know that your voice sounds different to you compared with the way other people hear it? This is because you hear your own voice not just through air, but through the bones in your head. 1. Draw a picture to show this: a guitar string is vibrating. This makes the air vibrate and it reaches your ear. 2. What can sound travel through? Sound and hearing 6 Types of sounds Sounds can be very high-pitched, like a high singing voice. Sounds can be low-pitched like a low singing voice. Sounds can be loud or soft. Very loud noises make the tiny parts inside your ear vibrate too much. This can cause you to become deaf. Never shout in someone s ear. Keep the volume turned down if you are listening to music through headphones. A loud music concert can make your ears ring for hours afterwards. That s a sign that the loud sound was damaging your ears. Think of all the beautiful sounds we can hear. God gave us the gift of music. Birds make beautiful music. Think of sounds that make us happy. Laughter makes us happy. We need to take good care of our ears. 1. Which animal can make a high-pitched sound? 2. Which animal can make a low-pitched sound? 3. How can we damage out ears? 4. What are some of the beautiful sounds God has given us? 5. What sound makes you happy?
4 Sound and hearing 7 Questions and answer about ears Work with a partner. One can ask the questions. The other can guess the answers. Where are the tiniest bones found in our bodies? Answer: in our ears Why do our ears have flaps on the outside? Answer: They are sound collectors. Try cupping your hands around your ear while you are listening to something. You will make a larger sound collector and hear the sound more clearly. Which animals have bigger sound collectors than humans? Answer: many animals, e.g. elephant What is the inside of your ear like? Answer: It is like a set of rooms with entryways which take twists and turns. What is the entry way closest to the outside? Answer: the ear canal What is in the middle of your ear? Answer: an ear drum Sound and hearing 8 Make a drum What you will need: A balloon Scissors A strong elastic band A can with both ends removed Blow up the balloon and leave it for at least 2 hours so that it can stretch. Carefully cut the end off the balloon. Try not to burst it. Let the air out slowly. Cut a large circle out of the balloon with scissors, Stretch the circle over the tin can and secure it with an elastic band. The balloon is like a skin on a drum. It vibrates as you hit it with your fingers. This makes the sound. 1. What other materials are used to make different types of drums? 2. Why does the skin need to be stretched? 3. The vibrations are travelling through the to our ears. How does an ear drum help us to hear? Answer: It has a thin piece of skins stretched across it that vibrates, (shakes) when the sound reaches it.
5 Sound and hearing 9 Make a guitar and a xylophone Guitar: A small carboard box Rubber bands Cut the front out of the box. Stretch the rubber bands across the open part of the box. Watch the rubber bands vibrating to make the sound. The rubber bands vibrate the air and travel to our ears. Xylophone: What you will need: 5 glasses A jug of water Sound and hearing 10 Make some pan pipes 8 straws Tape Cut the straws into different lengths. Place them in order of shortest to longest and tape the together at one end. To play your pan pipes, blow gently across the top of each pipe. You will find that the longer pipes make a lower sound than the shorter pipes. 1. Which musical instruments are played by blowing? 2. What is vibrating? Fill 5 glasses with different amount of water. The first has only a little, the next has a bit more, the next one has a bit more and the last one is full. Use a metal spoon to hit the glasses. 1. Which glass makes the highest sounds? 2. Which makes the lowest? 3. What is vibrating this time?
6 Sound and hearing 11 Make a shaker ` Paper cups Plastic bottles with lids Rice, lentils, dried beans or peas, sand or pebbles To make a paper-cup shaker, put a handful of rice or lentils into one cup. Turn another cup upside down and tape the two cups together rim to rim. To make plastic bottle shakers, pour a handful of dried peas or beans into the bottle and put the lid on tight. Try making shakers with different sized bottles. You will find that the larger bottles which hold more make deeper sounds. Experiment with the different fillings. You will find that paper cup shakers with lentils or rice make a softer sound than the plastic bottles with dried beans or peas. 1. Which shaker made the louder sound? 2. Which shaker made the lower sound? Sound and hearing 12 Make some telephones 2 clean, empty cans A nail A hammer A piece of string about 6 metres long Ask an adult to help you make a hole in the bottom of each can using a hammer and nail. Push one end of the string through the hole through the open end of the can to the outside. Tie a very big knot (or several knots) to stop the string slipping through. Take the other end of the string and thread if through the other can. Tie a knot in the end. Give one can to a friend. Walk apart from each other until the string is pulled tight. The string must be very straight and must not touch anything. Take turns in talking to each other. One person listens by holding the can to the ear and the other person speaks softly into his/her can. 1. What is vibrating? 2. The sound is of your voice is traveling along the
7 Sound and hearing 13 Animal communication Mammals use their sharp sense of hearing to find food, keep out of danger, attract mates and to guard their homes. Bats hunt at night, using sound to find food, and to find their way around. A bat makes lots of high squeaking sounds, which hit objects, such as insects. The sounds then send back echoes, which the bat picks up with its sharp sense of hearing. It can tell from the echoes what and where the object it. This is called radar. Dolphins use a similar method of sending messages through the water. This is called sonar. Whales send messages to each other by singing underwater. They have very loud, but very low voices. Monkeys get together in groups and make loud noises to keep other monkeys away from their trees. Choose three animals and describe the sounds they make. Explain why they make these sounds. Sound and hearingthe ear 14 People who cannot hear Our ears are a special gift from God. But sometimes people are born unable to hear. They are born deaf. This is not how God intended it to be in His perfect creation, but because sickness and suffering came into the world after Adam and Eve sinned, not everything is perfect anymore. Jesus healed many people who were deaf. How wonderful it was for them to hear for the first time! People who are born deaf are unable to speak, because to learn to speak we have to be able to hear and repeat the sounds we hear. These people use a special sign language to communicate. They can also learn to understand what people are saying by lip reading. Some people lose their hearing after sickness, an accident or exposing their ears to very loud noise. They may still have a little bit of hearing, but things sound very soft. These people can use a hearing aid, which is an electronic device placed in the ear to make the sound louder and clearer. If we know that someone cannot hear very well, we should always make sure that we are looking directly at them before speaking. 1. How can people who have hearing problems be helped? 2. How can we communicate with someone who cannot hear, or cannot hear very well?
Table of Contents Science Action Labs
 Table of Contents Science Action Labs 1: Vibrating Sound......................................5 2: Sound Fun..........................................8 3: How Sound Travels..................................11
Table of Contents Science Action Labs 1: Vibrating Sound......................................5 2: Sound Fun..........................................8 3: How Sound Travels..................................11
The Human Ear. Grade Level: 4 6
 The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
Draw a cross section of the human ear and label its parts.
 Human Ear 1. Open the Human Ear session and follow the instructions. 2. Complete the Human Ear worksheet as you progress through the session. Draw a cross section of the ear and label its parts. 3. Using
Human Ear 1. Open the Human Ear session and follow the instructions. 2. Complete the Human Ear worksheet as you progress through the session. Draw a cross section of the ear and label its parts. 3. Using
Science - Year 4. Sound Block 4S. Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack
 Science - Year 4 Sound Block 4S Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. We refer you to our
Science - Year 4 Sound Block 4S Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. We refer you to our
Unit 4P.1: Sound. How sounds are made? Loudness and pitch Hearing sound Noise Traveling of sound Echo
 Unit 4P.1: How sounds are made? Loudness and pitch Hearing sound Noise Traveling of sound Echo Science skills: Predicting Observing and classifying UBy the end of this unit you should: Know that sound
Unit 4P.1: How sounds are made? Loudness and pitch Hearing sound Noise Traveling of sound Echo Science skills: Predicting Observing and classifying UBy the end of this unit you should: Know that sound
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours)
 HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093
 Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
AND THE EARS HAVE IT! (1 Hour)
 (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will explore the nature of human hearing by attempting to determine the location at different locations
(1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will explore the nature of human hearing by attempting to determine the location at different locations
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe how vibrating objects make sound waves. Explain how sound waves move through
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe how vibrating objects make sound waves. Explain how sound waves move through
Unit 1.P.2: Sensing Sound
 Unit 1.P.2: Sensing Sound Sensing sound Experiencing sounds Science skills: Predicting Observing Classifying By the end of this unit you should know: We use our senses to detect sound. We hear things with
Unit 1.P.2: Sensing Sound Sensing sound Experiencing sounds Science skills: Predicting Observing Classifying By the end of this unit you should know: We use our senses to detect sound. We hear things with
SENDING SECRET MESSAGES (1 Hour)
 SENDING SECRET MESSAGES (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound
SENDING SECRET MESSAGES (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound
5. Which word refers to making
 Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Wonderlab. Sound. The Statoil Gallery. The science and maths behind the exhibits LIGHT WONDERLAB: THE STATOIL GALLERY LEVEL 3, SCIENCE MUSEUM LONDON
 Wonderlab The Statoil Gallery and maths s Sound Age (s) Topic 7 11 LIGHT INFORMATION 11-14 Location WONDERLAB: THE STATOIL GALLERY LEVEL 3, SCIENCE MUSEUM LONDON 1 What s the science? What more will you
Wonderlab The Statoil Gallery and maths s Sound Age (s) Topic 7 11 LIGHT INFORMATION 11-14 Location WONDERLAB: THE STATOIL GALLERY LEVEL 3, SCIENCE MUSEUM LONDON 1 What s the science? What more will you
Low? High or. v vv \T\ \ C\ [ \(\(\(\(\ PITCH FREQUENCY CHAPTER4
 CHAPTER4 High or Low? PITCH Another quality that an oscilloscope shows is pitch. Pitch is a measurement of how high or low a sound is. If you make your voice high and squeaky, then it has a high pitch.
CHAPTER4 High or Low? PITCH Another quality that an oscilloscope shows is pitch. Pitch is a measurement of how high or low a sound is. If you make your voice high and squeaky, then it has a high pitch.
Perception of Sound. To hear sound, your ear has to do three basic things:
 Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
SOUNDS LIKE FUN SCIENCE GRADE 4 STELLA BIZZIO. TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class.
 SOUNDS LIKE FUN TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class. OVERVIEW: Using hands-on activities and demonstrations the lesson will focus on the production of sound as energy that can make matter vibrate. Students
SOUNDS LIKE FUN TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class. OVERVIEW: Using hands-on activities and demonstrations the lesson will focus on the production of sound as energy that can make matter vibrate. Students
Norwood Science Center
 Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Sound All Around. Visit for thousands of books and materials.
 Sound All Around A Reading A Z Level M Leveled Reader Word Count: 432 LEVELED READER M Written by Penny Atcheson Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Sound
Sound All Around A Reading A Z Level M Leveled Reader Word Count: 432 LEVELED READER M Written by Penny Atcheson Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Sound
Producing and Detecting Sound
 Sound Producing and Detecting Sound What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Sound Producing and Detecting Sound What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
GRADE 4: Physical processes 1. UNIT 4P.1 11 hours. Sound. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 4: Physical processes 1 Sound UNIT 4P.1 11 hours About this unit This unit is the first of two units on physical processes for Grade 4. The unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
GRADE 4: Physical processes 1 Sound UNIT 4P.1 11 hours About this unit This unit is the first of two units on physical processes for Grade 4. The unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears.
 Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2
 IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound transmission
IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound transmission
Hearing and Sound Study Guide
 Hearing and Sound Study Guide I made the following website as a study tool to help you prepare for Thursday with videos and sample questions hearingandsound.weebly.com 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations
Hearing and Sound Study Guide I made the following website as a study tool to help you prepare for Thursday with videos and sample questions hearingandsound.weebly.com 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations
Science5 (SoundMulberry4th)
 Science5 (SoundMulberry4th) Name: Date: 1. The figure below shows a glass partly filled with water. Grace tapped the glass with a metal spoon and heard a sound. Which action would raise the pitch when
Science5 (SoundMulberry4th) Name: Date: 1. The figure below shows a glass partly filled with water. Grace tapped the glass with a metal spoon and heard a sound. Which action would raise the pitch when
Sound Unit Teacher Masters: Table of Contents
 Sound Unit Teacher Masters: Table of Contents Introductory Letter to Families Welcome to the Sound Unit................................................................ 1 Teacher Masters Ear Labels (Lesson
Sound Unit Teacher Masters: Table of Contents Introductory Letter to Families Welcome to the Sound Unit................................................................ 1 Teacher Masters Ear Labels (Lesson
Please visit the website hearingandsound.weebly.com to help you study, as well as viewing the videos and booklet posted.
 Hearing and Sound Study Guide Please visit the website hearingandsound.weebly.com to help you study, as well as viewing the videos and booklet posted. 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations move in all
Hearing and Sound Study Guide Please visit the website hearingandsound.weebly.com to help you study, as well as viewing the videos and booklet posted. 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations move in all
Sound Waves. Making Sound Waves
 Benchmarks SC.B.1.3.6 Annually Assessed (pp. 195, 197): The student knows the properties of waves; that each wave consists of a number of crests and troughs; and the effects of different media on waves;
Benchmarks SC.B.1.3.6 Annually Assessed (pp. 195, 197): The student knows the properties of waves; that each wave consists of a number of crests and troughs; and the effects of different media on waves;
FUNNELS OF SOUND. Activity Pack. Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears. Neurosciences and Mental Health
 FUNNELS OF SOUND Activity Pack Description: Duration of Activity: Age: Topic: Key words: Resources: Related Activities: Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears No
FUNNELS OF SOUND Activity Pack Description: Duration of Activity: Age: Topic: Key words: Resources: Related Activities: Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears No
17.4 Sound and Hearing
 You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations
 secondary science 2013 16 Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations Content 16.1 Sound production by vibrating sources 16.2 Sound travel in medium 16.3 Loudness, pitch and frequency 16.4 Worked examples
secondary science 2013 16 Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations Content 16.1 Sound production by vibrating sources 16.2 Sound travel in medium 16.3 Loudness, pitch and frequency 16.4 Worked examples
Fact cards. Sounds can be high or low in pitch. Sounds can be loud or quiet. Many animals, including humans, use sound to communicate.
 Fact cards Sounds can be loud or quiet. Sounds can be high or low in pitch. Many animals, including humans, use sound to communicate. Noise is usually unwanted sound. Illustrations Chris Saunderson PHOTOCOPIABLE
Fact cards Sounds can be loud or quiet. Sounds can be high or low in pitch. Many animals, including humans, use sound to communicate. Noise is usually unwanted sound. Illustrations Chris Saunderson PHOTOCOPIABLE
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities SAMPLE
 COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
Sound Waves. Sound waves can only travel through matter. The energy carried by a sound wave is transferred by the collisions between the
 Sound Waves Making Sound Waves How does the motion of a drummer s drumsticks produce sound waves? The impact of the sticks on the head of a drum causes the drum head to vibrate. These vibrations transfer
Sound Waves Making Sound Waves How does the motion of a drummer s drumsticks produce sound waves? The impact of the sticks on the head of a drum causes the drum head to vibrate. These vibrations transfer
Hearing Loss. How does the hearing sense work? Test your hearing
 Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz
 The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
This nonfiction book
 This nonfiction book presents basic facts about ears and hearing in both people and animals. Diagrams help simplify challenging concepts. Interesting details about animals ears are supported by photos
This nonfiction book presents basic facts about ears and hearing in both people and animals. Diagrams help simplify challenging concepts. Interesting details about animals ears are supported by photos
Sound and Music. Acoustical Society of America 2
 Sound and Music Acoustical Society of America 2 What is Sound? Sit quietly and listen to the sounds around you. Today you will be Sound Detectives 3 What is Sound? Strike the tuning fork with a rubber
Sound and Music Acoustical Society of America 2 What is Sound? Sit quietly and listen to the sounds around you. Today you will be Sound Detectives 3 What is Sound? Strike the tuning fork with a rubber
X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary
 X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary Introduction Tinnitus causes a person to hear a persistent sound in the ear when no sound exists. According to the American Tinnitus Association, at least 12 million
X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary Introduction Tinnitus causes a person to hear a persistent sound in the ear when no sound exists. According to the American Tinnitus Association, at least 12 million
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1
 SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
Formatting notes: Bold black text are questions to ask your students to answer Blue bold: learning goals write these on the board.
 These slides could be used in the classroom but are designed with the intent of describing the lesson. When we tested this material with students, we did not project these slides. The teacher used them
These slides could be used in the classroom but are designed with the intent of describing the lesson. When we tested this material with students, we did not project these slides. The teacher used them
A community of VALUED individuals. Versatile Aspirational Learning Understanding Engaged Determined. Year 7 Physics Sound Name. Red, amber or Green?
 A community of VALUED individuals Versatile Aspirational Learning Understanding Engaged Determined Year 7 Physics Sound Name Part 1 What are Waves? I was present for this lesson (tick) Red, amber or Green?
A community of VALUED individuals Versatile Aspirational Learning Understanding Engaged Determined Year 7 Physics Sound Name Part 1 What are Waves? I was present for this lesson (tick) Red, amber or Green?
9.3 Sound The frequency of sound Frequency and pitch pitch Most sound has more than one frequency The frequency spectrum
 9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
Talking Whales. By listening to these a lot, you kind of develop a sense of the vocabulary of killer whales, Viers says of his audio recordings.
 Talking Whales Talking Whales Val Viers loves listening to killer whales talk. Viers, a retired professor, spends a lot of his time recording and listening to the sounds made by killer whales swimming
Talking Whales Talking Whales Val Viers loves listening to killer whales talk. Viers, a retired professor, spends a lot of his time recording and listening to the sounds made by killer whales swimming
Hearing Loss. Understanding hearing loss, its effects and available solutions.
 Hearing Loss Understanding hearing loss, its effects and available solutions. Hearing loss is a very common health condition in adults but it is often unrecognised and untreated. Introduction Hearing loss
Hearing Loss Understanding hearing loss, its effects and available solutions. Hearing loss is a very common health condition in adults but it is often unrecognised and untreated. Introduction Hearing loss
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AE Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AE Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Vision How do our brains make 3-D images out of 2-D inputs? We live in a 3-dimensional world, but each of our eyes is only capable
Biological Psychology Unit Two AE Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Vision How do our brains make 3-D images out of 2-D inputs? We live in a 3-dimensional world, but each of our eyes is only capable
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
The Nature of Sound. Section 1: What Is Sound? (p. 534)
 CHAPTER 21 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET The Nature of Sound As you read Chapter 21, which begins on page 532 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Would You Believe...? (p. 532) 1. What did Marco
CHAPTER 21 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET The Nature of Sound As you read Chapter 21, which begins on page 532 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Would You Believe...? (p. 532) 1. What did Marco
Converting Sound Waves into Neural Signals, Part 1. What happens to initiate neural signals for sound?
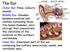 The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
A Kazoo For You. Science Activity.
 A Kazoo For You Science Activity www.apologia.com A Kazoo For You Science Activity Published by Apologia Educational Ministries, Inc. 1106 Meridian Street, Suite 340 Anderson, IN 46016 www.apologia.com
A Kazoo For You Science Activity www.apologia.com A Kazoo For You Science Activity Published by Apologia Educational Ministries, Inc. 1106 Meridian Street, Suite 340 Anderson, IN 46016 www.apologia.com
Sounds Good to Me. Engagement. Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
 Sounds Good to Me Students make a mental model of how frequencies are detected by the cochlear membrane. Using this model, students examine how cochlear implants can be used to help treat deafness. Next
Sounds Good to Me Students make a mental model of how frequencies are detected by the cochlear membrane. Using this model, students examine how cochlear implants can be used to help treat deafness. Next
Sound Workshop. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum
 Sound Workshop a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum Echoes Ultrasound Loudspeakers
Sound Workshop a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum Echoes Ultrasound Loudspeakers
Chapter 17 Sound Sound and Hearing. Properties of Sound Waves 1/20/2017. Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action
 Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action Chapter 17 Sound Standing Waves in Music When the string of a violin is played with a bow, it vibrates and creates standing waves. Some instruments,
Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action Chapter 17 Sound Standing Waves in Music When the string of a violin is played with a bow, it vibrates and creates standing waves. Some instruments,
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide
 E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
Learning Targets. Module 20. Hearing Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages.
 Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing
 SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages
 PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
9.3 Sound. The frequency of sound. pitch - the perception of high or low that you hear at different frequencies of sound.
 9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE
 2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE INTRODUCTION What Students Do in this Activity Students learn more about the form that sound waves take and how humans hear sound. They build a model of a human eardrum
2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE INTRODUCTION What Students Do in this Activity Students learn more about the form that sound waves take and how humans hear sound. They build a model of a human eardrum
Hearing for life Facts about hearing. How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing
 Hearing for life Facts about hearing How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing 3 Our hearing develops fully while we are still in the womb Our hearing is the only one of our senses
Hearing for life Facts about hearing How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing 3 Our hearing develops fully while we are still in the womb Our hearing is the only one of our senses
E3586. What?! Protect Your Hearing. Leader s Guide
 E3586 What?! Protect Your Hearing Leader s Guide 1 What?! Protect Your Hearing This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION:
E3586 What?! Protect Your Hearing Leader s Guide 1 What?! Protect Your Hearing This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION:
1.34 Intensity and Loudness of Sound
 1.34. Intensity and Loudness of Sound www.ck12.org 1.34 Intensity and Loudness of Sound Define intensity of sound and relate it to loudness. Compare decibel levels of different sounds. Identify factors
1.34. Intensity and Loudness of Sound www.ck12.org 1.34 Intensity and Loudness of Sound Define intensity of sound and relate it to loudness. Compare decibel levels of different sounds. Identify factors
Related KidsHealth Links
 K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
Sound. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. 1 Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
 _ Sound Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. _ 1. Sound is a disturbance that travels through a medium as a a. longitudinal wave. b. surface wave.
_ Sound Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. _ 1. Sound is a disturbance that travels through a medium as a a. longitudinal wave. b. surface wave.
Good Vibrations: The Science of Sound
 Science and Technology Good Vibrations: The Science of Sound OBJECTIVES: Understand that sounds are made by vibrations. Understand how sounds travel and are heard. Develop science skills of observing,
Science and Technology Good Vibrations: The Science of Sound OBJECTIVES: Understand that sounds are made by vibrations. Understand how sounds travel and are heard. Develop science skills of observing,
Directions: Review the sound vocabulary words. In the pre column place a 2, 1, or 0 2 = expert 1 = heard of it 0 = do not know it
 Directions: Review the sound vocabulary words. In the pre column place a 2, 1, or 0 2 = expert 1 = heard of it 0 = do not know it pre Sound Vocabulary Absorption Amplitude Compression Crest Decibels Echo
Directions: Review the sound vocabulary words. In the pre column place a 2, 1, or 0 2 = expert 1 = heard of it 0 = do not know it pre Sound Vocabulary Absorption Amplitude Compression Crest Decibels Echo
Hearing The ice show was in its final moments and the music was louder than ever. There was a final chord that echoed across the arena.
 Hearing Hearing The ice show was in its final moments and the music was louder than ever. There was a final chord that echoed across the arena. The audience rose to its feet to applaud. Wow, that was really
Hearing Hearing The ice show was in its final moments and the music was louder than ever. There was a final chord that echoed across the arena. The audience rose to its feet to applaud. Wow, that was really
To learn more, visit the website and see the Find Out More section at the end of this booklet.
 Loving Your Child, Learning How to Help Congratulations! As a parent of a precious baby or young child, you have a wonderful journey ahead. The fact that your child has a hearing loss is only one part
Loving Your Child, Learning How to Help Congratulations! As a parent of a precious baby or young child, you have a wonderful journey ahead. The fact that your child has a hearing loss is only one part
Sound and Music Adams, W. K.
 Acoustical Society of America Lesson Plan acousticalsociety.org exploresound.org Sound and Music Adams, W. K. Students explore the physics of sound, how the ear hears and how musical instruments work through
Acoustical Society of America Lesson Plan acousticalsociety.org exploresound.org Sound and Music Adams, W. K. Students explore the physics of sound, how the ear hears and how musical instruments work through
Loud or Soft? BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN. SC.B The student recognizes systems of matter and energy.
 activity 30 Loud or Soft? BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 1 Quarter 3 Activity 30 SC.B.2.1.1 The student recognizes systems of matter and energy. SC.C.1.1.2 The student knows that
activity 30 Loud or Soft? BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 1 Quarter 3 Activity 30 SC.B.2.1.1 The student recognizes systems of matter and energy. SC.C.1.1.2 The student knows that
Audiology - Hearing Care Torbay and South Devon. Before you receive your hearing aid
 Audiology - Hearing Care Torbay and South Devon Before you receive your hearing aid How our ears work Our ears are divided into three sections, the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear (see diagram opposite).
Audiology - Hearing Care Torbay and South Devon Before you receive your hearing aid How our ears work Our ears are divided into three sections, the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear (see diagram opposite).
Sound (11-16) Click here to buy the clear version of Sound (11-16). This pdf file can be downloaded and used on your PC or tablet.
 Sound (11-16) Click here to buy clear version of Sound (11-16). This pdf file can be downloaded and used on your PC or tablet. NOT AVAILABLE YET TEST PAGES ONLY Contents Topic Page Contents Page Sound
Sound (11-16) Click here to buy clear version of Sound (11-16). This pdf file can be downloaded and used on your PC or tablet. NOT AVAILABLE YET TEST PAGES ONLY Contents Topic Page Contents Page Sound
You ve got to be kidding Dad. You wouldn t be able to hear anything with ear plugs. Sure I could, his father said. Your mother and I wore them when
 Hearing Hearing The ice show was ending. The music was louder than ever. One last chord echoed across the arena. The audience stood and clapped. Wow, that was really something! Jake said. They really put
Hearing Hearing The ice show was ending. The music was louder than ever. One last chord echoed across the arena. The audience stood and clapped. Wow, that was really something! Jake said. They really put
The bloom guide to better hearing. Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide
 The bloom guide to better hearing Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide Let us help you find the best solution for your hearing Coming to terms with
The bloom guide to better hearing Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide Let us help you find the best solution for your hearing Coming to terms with
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Sensation and Perception. 8.2 The Senses
 Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
LISTEN! You might be going deaf DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE
 LISTEN! You might be going deaf OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE 1 DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI GET THE ANSWERS ABOUT HOW NOISE AFFECTS YOU. Issued by the Occupational Safety & Health Service,
LISTEN! You might be going deaf OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE 1 DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI GET THE ANSWERS ABOUT HOW NOISE AFFECTS YOU. Issued by the Occupational Safety & Health Service,
M-Team. In Search of Hearing
 M-Team In Search of Hearing Medelina Smarty Marty Prof. Opusonix The M-Team Lea Cochlea Art by Burkard Schulz Story by Justyna Konczalska When our M-Team friends arrived in Le Dem, they met with Doctor
M-Team In Search of Hearing Medelina Smarty Marty Prof. Opusonix The M-Team Lea Cochlea Art by Burkard Schulz Story by Justyna Konczalska When our M-Team friends arrived in Le Dem, they met with Doctor
How Sound Works. Visit for thousands of books and materials.
 How Sound Works A Reading A Z Level U Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,637 LEVELED READER U Written by Penny Atcheson Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com How Sound
How Sound Works A Reading A Z Level U Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,637 LEVELED READER U Written by Penny Atcheson Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com How Sound
HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT
 HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT (50 MINUTES) PRE/POST- ASSESSMENT SHEET HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? 1. What sensors or senses do we humans
HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT (50 MINUTES) PRE/POST- ASSESSMENT SHEET HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? 1. What sensors or senses do we humans
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Nervous System. Made of two parts. Central Peripheral
 Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HEARING.HEALTH.MIL. HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1
 HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
Overview. Meeting Length 90 minutes. Senses [Meeting 1]
![Overview. Meeting Length 90 minutes. Senses [Meeting 1] Overview. Meeting Length 90 minutes. Senses [Meeting 1]](/thumbs/89/98894094.jpg) Overview Girls have fun exploring their five senses and how they use them in everyday life. They also learn about what life would be like without one of their senses. Note to Volunteers A few agenda activities
Overview Girls have fun exploring their five senses and how they use them in everyday life. They also learn about what life would be like without one of their senses. Note to Volunteers A few agenda activities
McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TAKS Practice Test. Grade 5, Chapter 5 Sound. Name. Date
 McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TKS Practice Test Grade 5, hapter 5 Sound Name ate Use the illustration and your knowledge of science to answer Questions 1 to 3. 1 Why does the rubber band make
McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TKS Practice Test Grade 5, hapter 5 Sound Name ate Use the illustration and your knowledge of science to answer Questions 1 to 3. 1 Why does the rubber band make
Middle Ear Fluid in Young Children: Parent Guide
 Vinod K. Anand, MD, FACS Nose and Sinus Clinic Middle Ear Fluid in Young Children: Parent Guide Purpose of This Booklet This booklet is about middle ear fluid in children ages 1 through 3 who have no other
Vinod K. Anand, MD, FACS Nose and Sinus Clinic Middle Ear Fluid in Young Children: Parent Guide Purpose of This Booklet This booklet is about middle ear fluid in children ages 1 through 3 who have no other
Meet the Science Expert
 Meet the Science Expert DESCUBRA! CREATE-IT POCKET SCIENCE HANDOUTS Let s have a Whale of Time! 1. Overview: This activity offers children a wonderful opportunity to learn about sound and to think about
Meet the Science Expert DESCUBRA! CREATE-IT POCKET SCIENCE HANDOUTS Let s have a Whale of Time! 1. Overview: This activity offers children a wonderful opportunity to learn about sound and to think about
Protect Your Hearing!
 Protect Your Hearing! What is noise? Loud sounds if they are over 85 db can be damaging. How do I know if I am listening to levels above 85dB? It is invisible, tasteless, odorless, and IGNORED as a form
Protect Your Hearing! What is noise? Loud sounds if they are over 85 db can be damaging. How do I know if I am listening to levels above 85dB? It is invisible, tasteless, odorless, and IGNORED as a form
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997
 ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
When hearing is painful. Can we damage our ears?
 When hearing is painful Can we damage our ears? What is the link? What is the link? Have you ever wondered what we learned from dolphins and use in submarines today? Objectives: To describe what noise
When hearing is painful Can we damage our ears? What is the link? What is the link? Have you ever wondered what we learned from dolphins and use in submarines today? Objectives: To describe what noise
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY. For Better Health and Hearing
 MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
Lecture 9: Sound Localization
 Lecture 9: Sound Localization Localization refers to the process of using the information about a sound which you get from your ears, to work out where the sound came from (above, below, in front, behind,
Lecture 9: Sound Localization Localization refers to the process of using the information about a sound which you get from your ears, to work out where the sound came from (above, below, in front, behind,
ì<(sk$m)=bdegcf< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Life Science Genre Expository nonfiction Comprehension Skills and Strategy
Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Life Science Genre Expository nonfiction Comprehension Skills and Strategy
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Animal Senses 9/2/16
 Animal Senses 9/2/16 Animal Senses 9/4/15 Fly Hair Cells Animal hearing Elephants can hear lower frequencies than humans 10 Hz (humans 20 Hz) But not as high 12,000 Hz (humans 20,000 Hz) Elephant Ears
Animal Senses 9/2/16 Animal Senses 9/4/15 Fly Hair Cells Animal hearing Elephants can hear lower frequencies than humans 10 Hz (humans 20 Hz) But not as high 12,000 Hz (humans 20,000 Hz) Elephant Ears
Otitis Media. Anatomy & Hearing Our ears are very specialized organs that allow us to hear and keep our balance.
 Otitis Media Introduction Otitis media is a middle ear infection. 75% of all children experience at least one episode of otitis media before they turn 3 years old. If otitis media is left untreated, it
Otitis Media Introduction Otitis media is a middle ear infection. 75% of all children experience at least one episode of otitis media before they turn 3 years old. If otitis media is left untreated, it
UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS
 Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS
 Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
